Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8353 results about "Die casting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used.
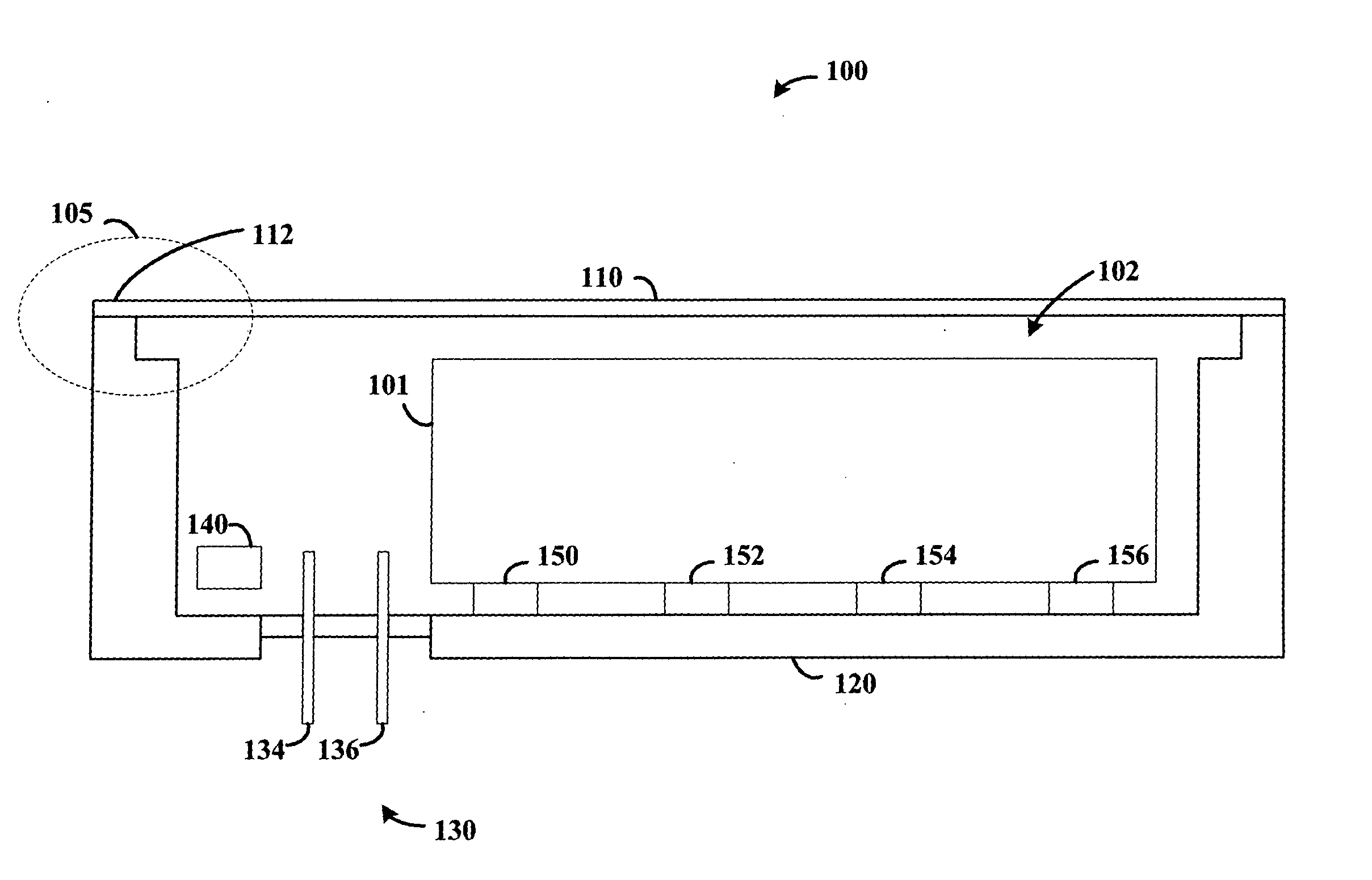
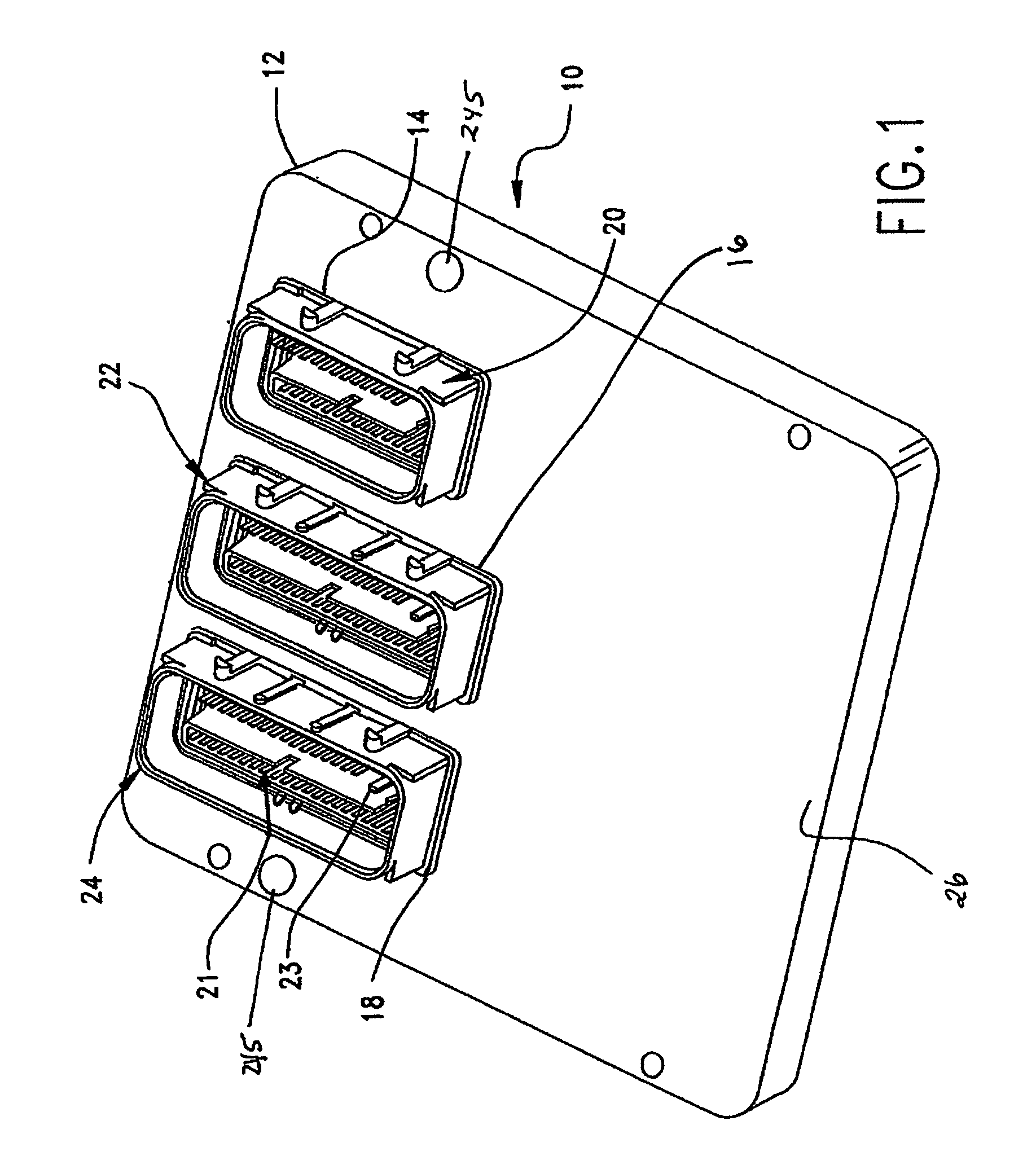
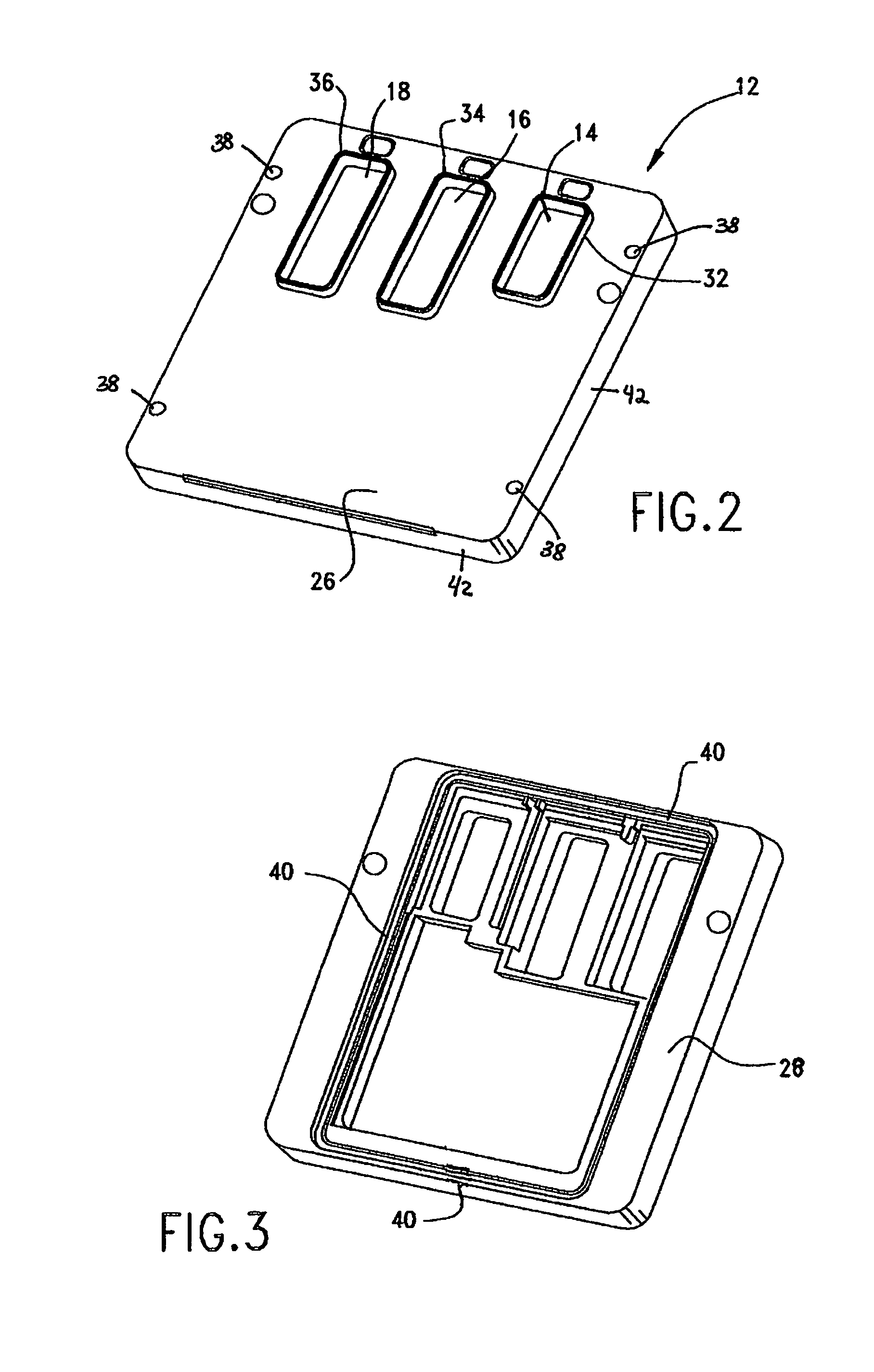
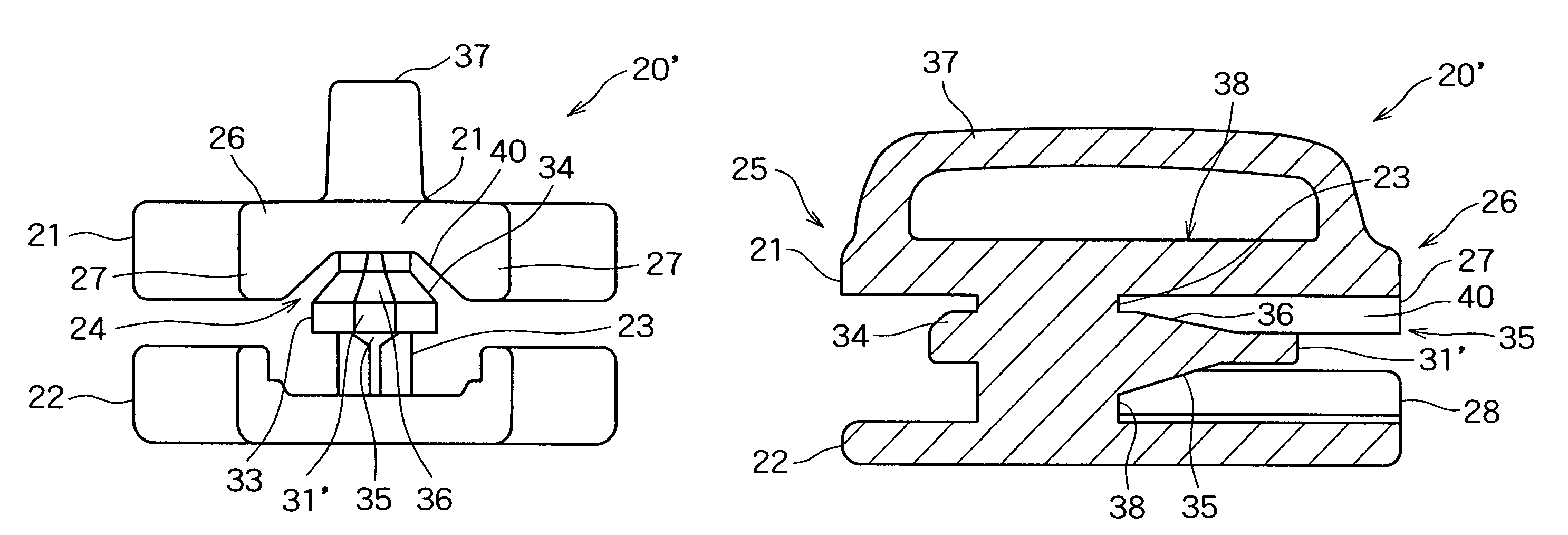
Hermetically sealed electronics arrangement and approach
InactiveUS20050068666A1Reduction of magnetic spacingImprove performanceApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionMetallic enclosureCold formed
A hermetic sealing approach involves welding an Aluminum cover onto a low-cost Aluminum housing. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, a metal housing having a base and sidewalls extending upward therefrom is adapted to receive and couple to an HDD arrangement. The metal housing is formed using material and processing (e.g., cold formed or die cast Aluminum) that are relatively inexpensive. A feedthrough arrangement including a plurality of communication pins extends through an opening in the base and is coupled thereto, with the communication pins adapted to pass signals between the inside and the outside of the metal housing. A metal cover is welded to an upper portion of the sidewalls and, with the feedthrough arrangement, hermetically seals the metal housing.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
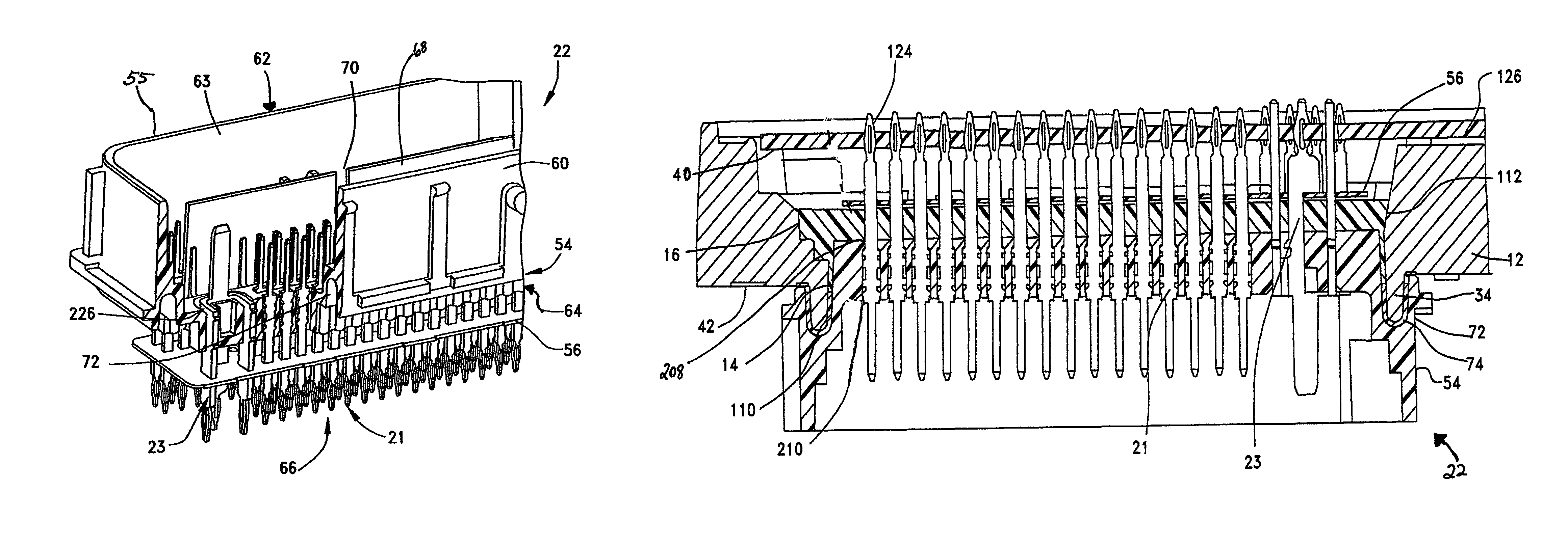
Compliant pin control module and method for making the same
Owner:MOLEX INC
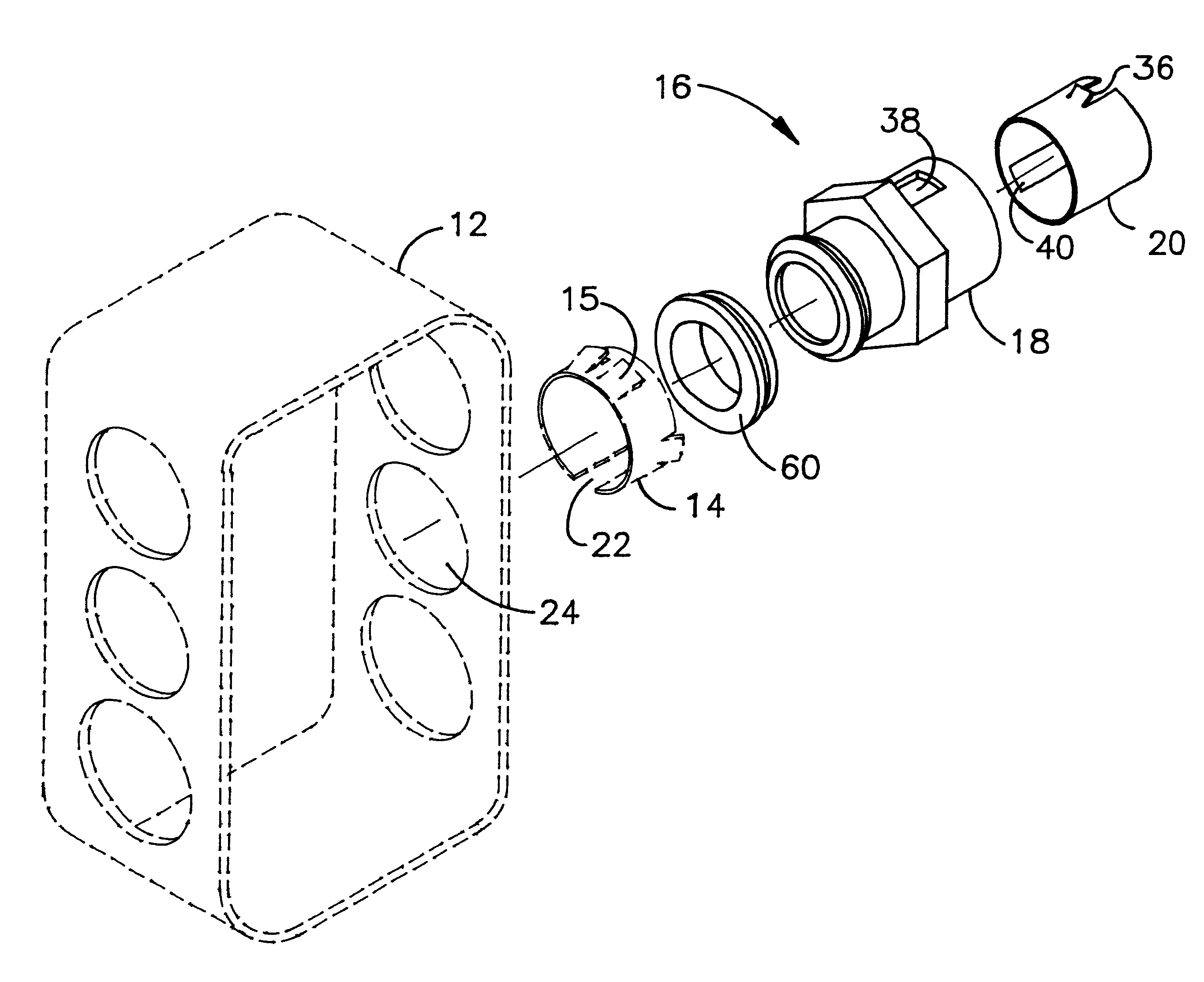
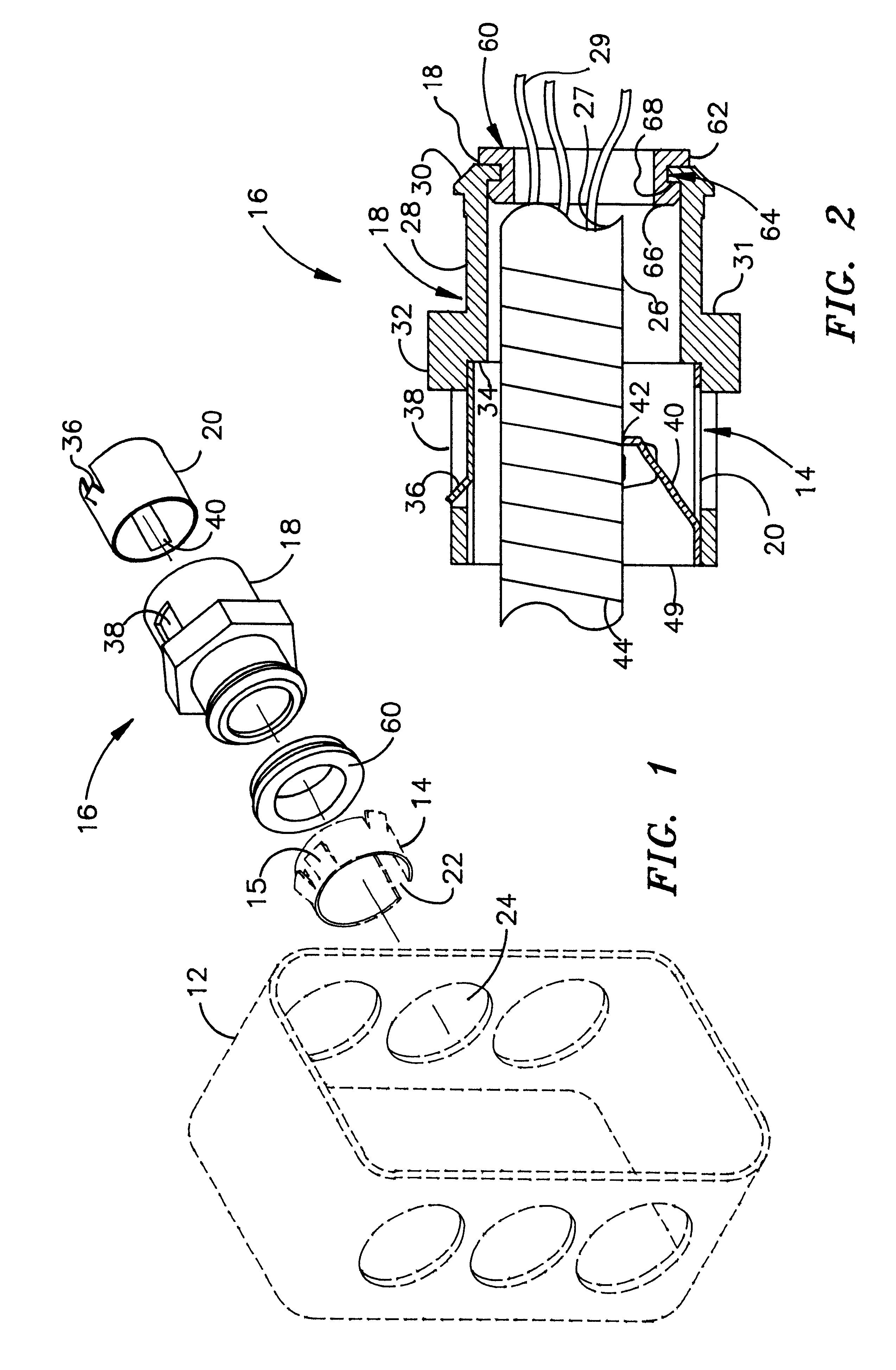
Snap in cable connector
InactiveUS6335488B1Easy to insertElectrically conductive connectionsPipesElectrical junctionDie casting
A snap in locking cable connector is composed of two mating pieces that snap together and provide a connector for armored or metal clad electrical conducts. One piece includes a die cast member including a smooth outer cylindrical section having an inner diameter that may accommodate a spring steel adaptor with flanges to hold the spring steel adaptor in place. The spring steel adaptor is used in conjunction with an electrical junction box to fix the location of the locking cable connector with respect to the junction box. Another piece includes a spring steel locking ring provided to receive an armored cable and lock into the die cast member. The spring steel locking ring has tangs allowing unidirectional insertion into the die cast member and restricting withdrawal motion from the die cast member. The spring steel locking ring also includes oppositely directed tangs to permit reception of the armored cable in one direction and restrict its movement in the reverse direction.
Owner:ARLINGTON INDS
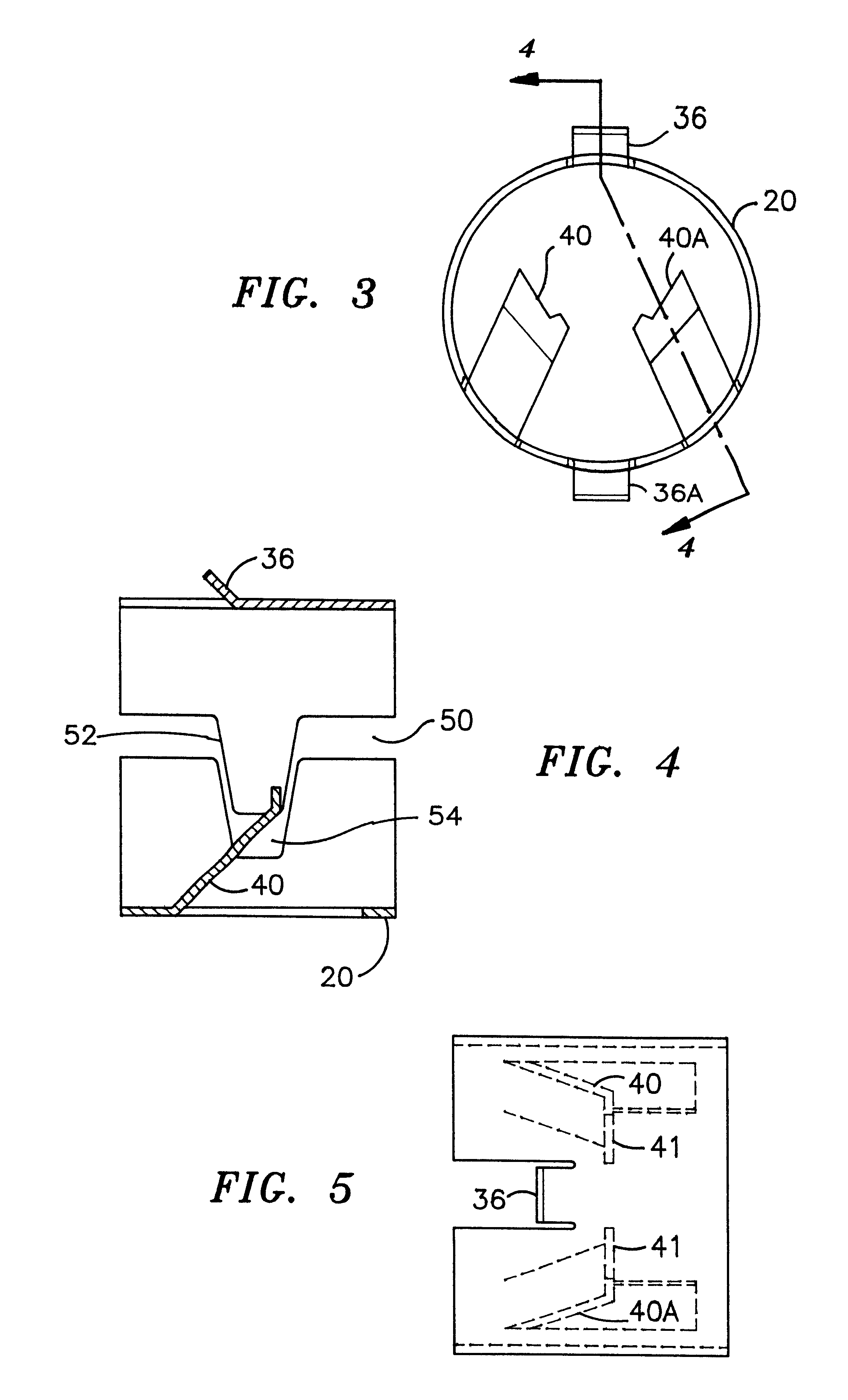
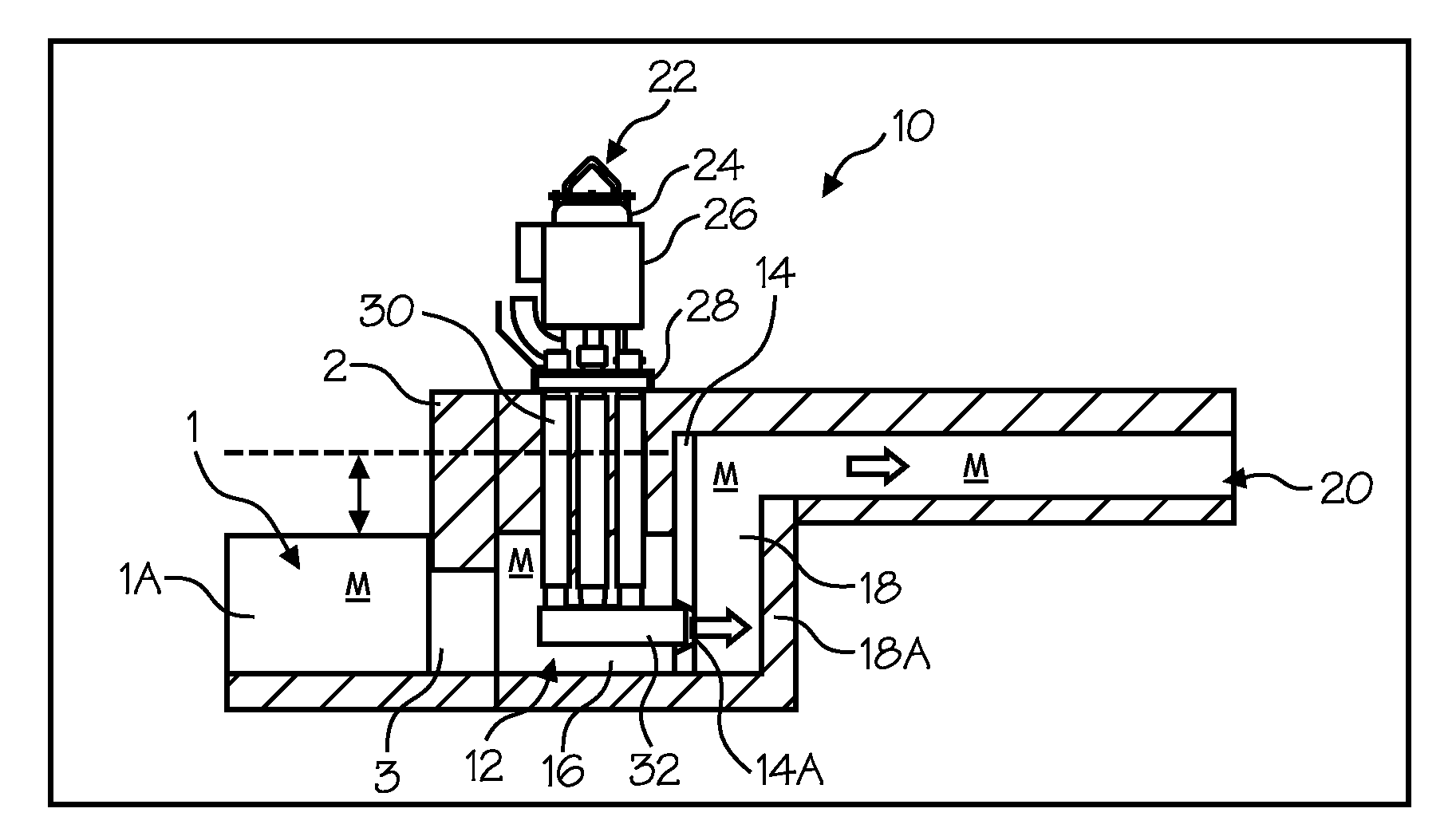
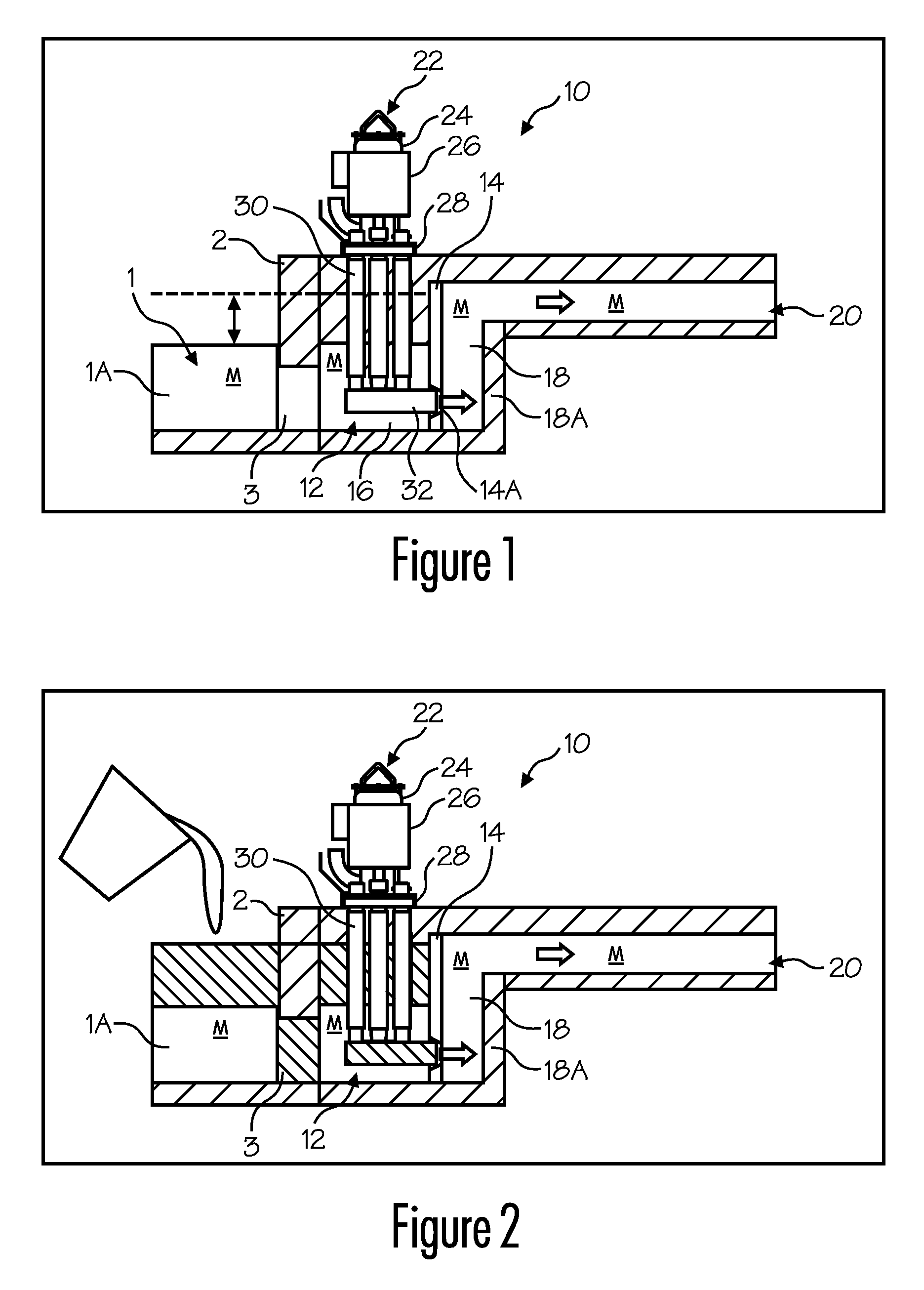
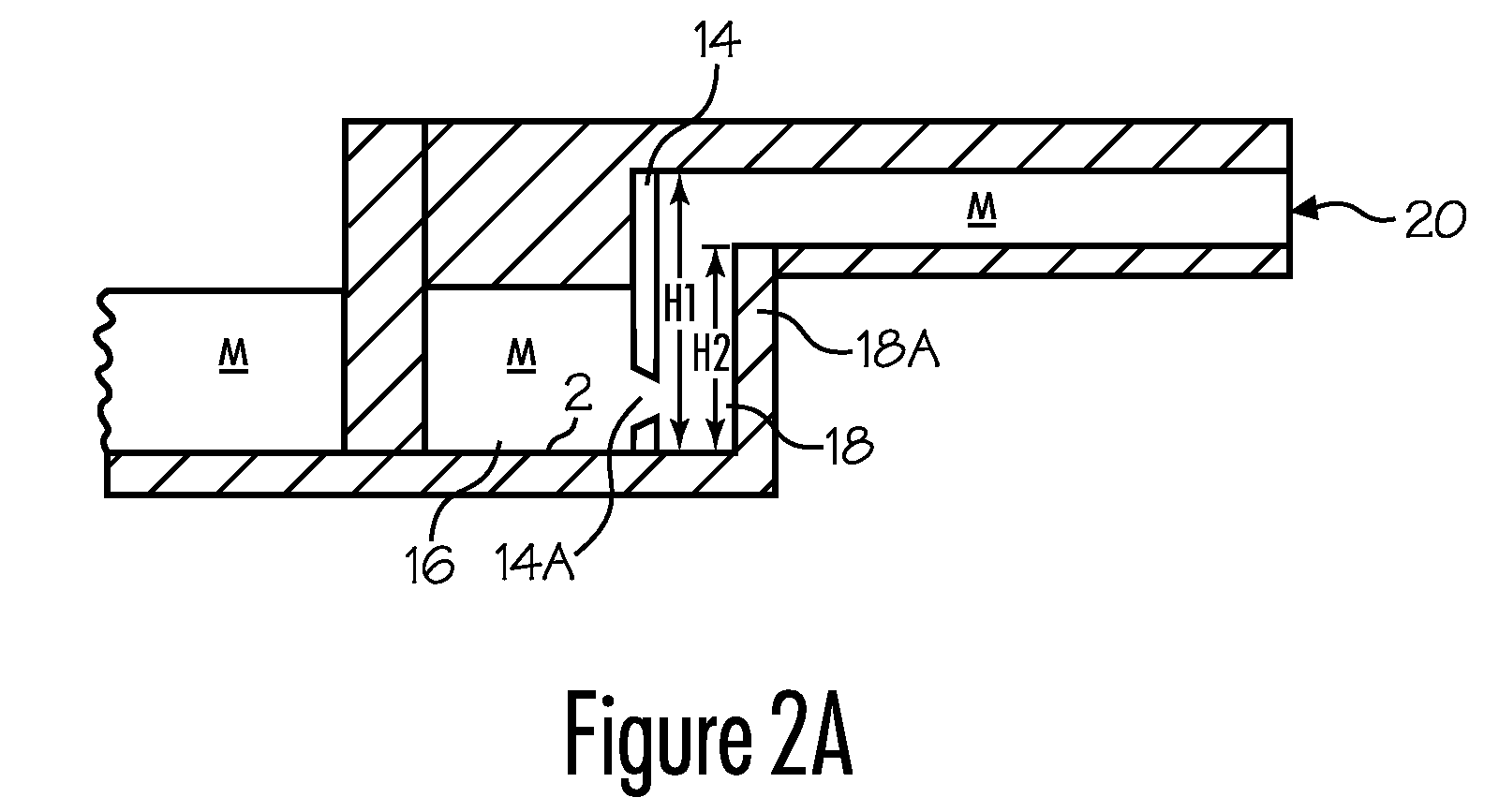
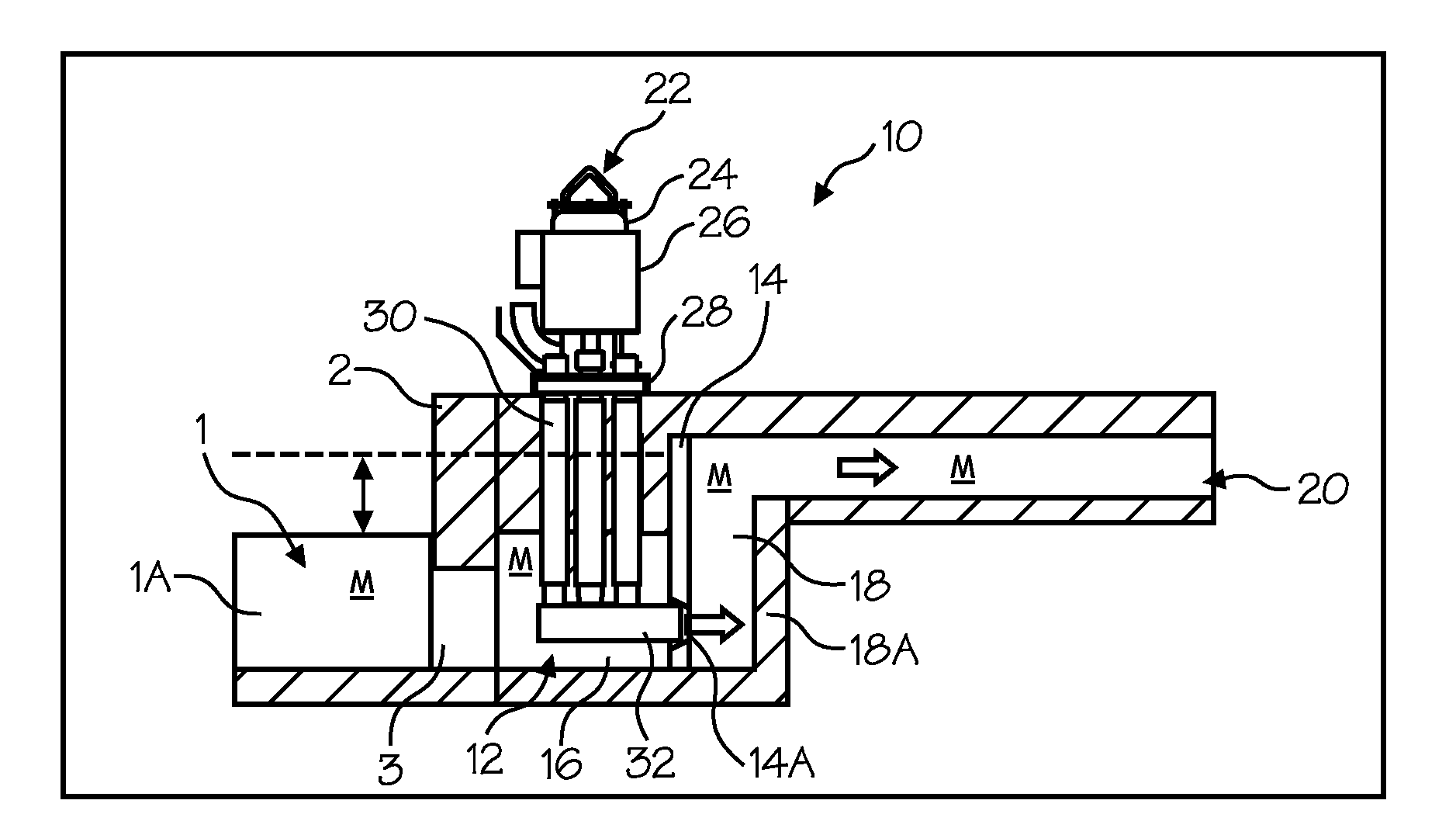
Transferring molten metal from one structure to another
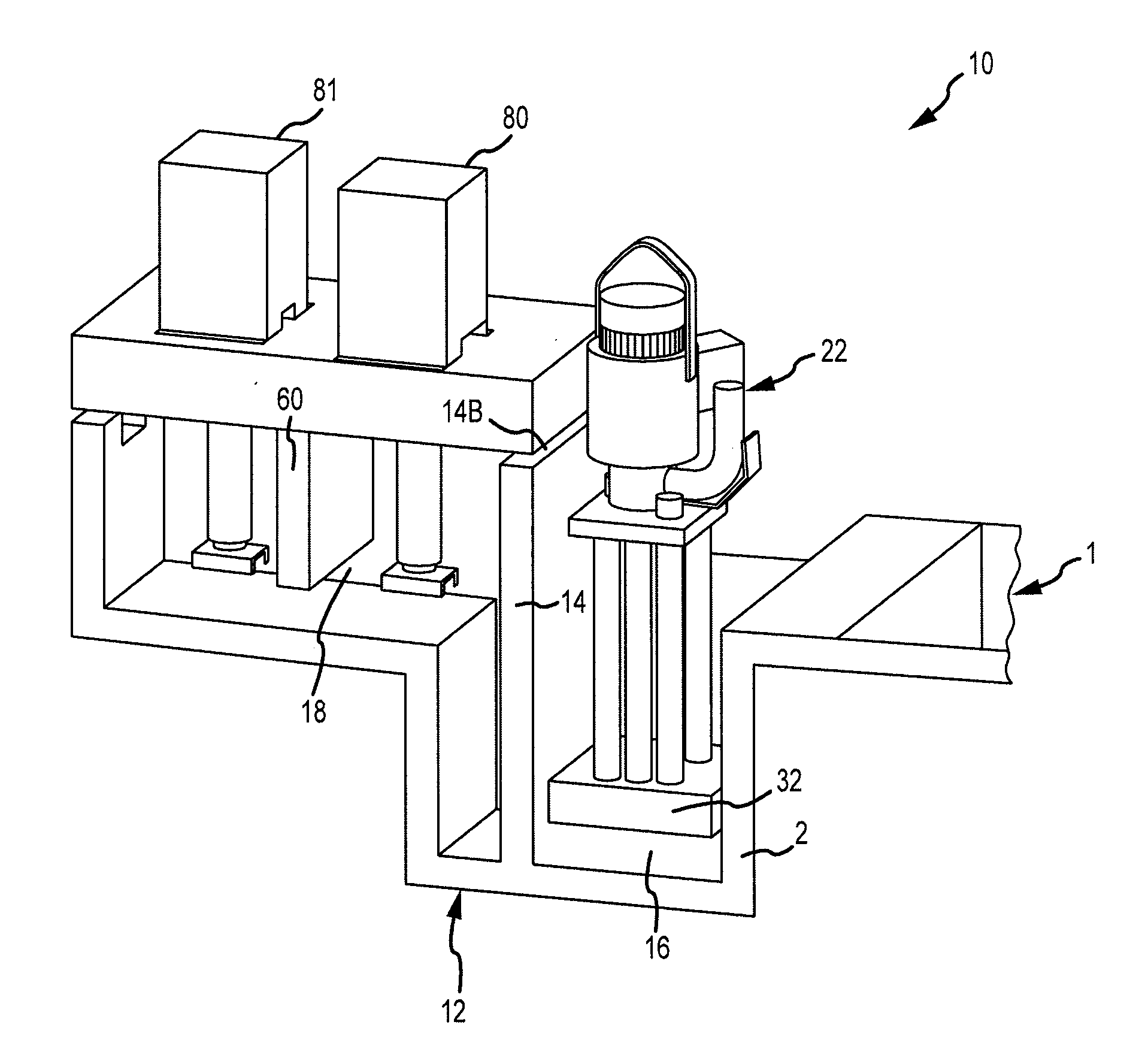
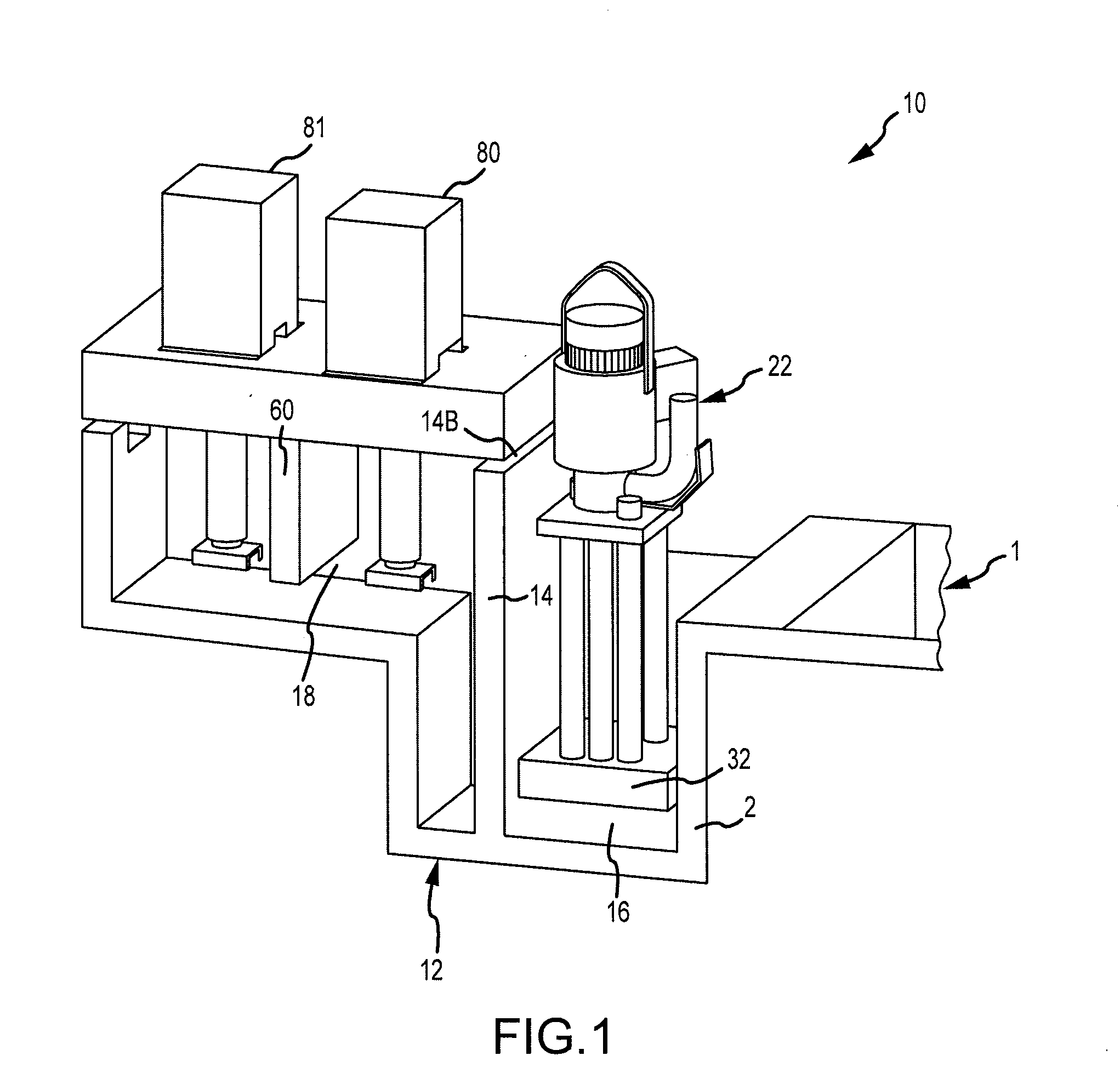
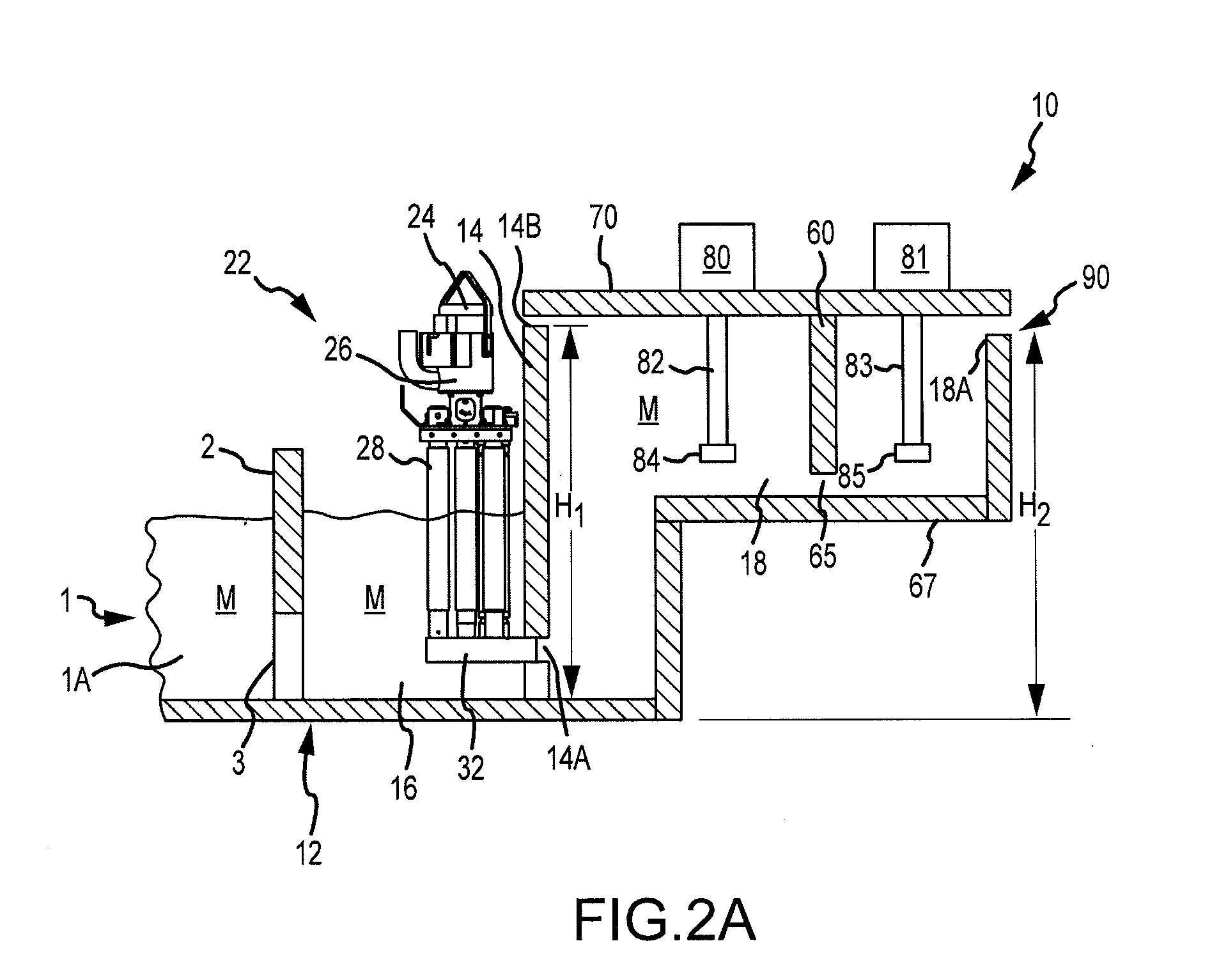
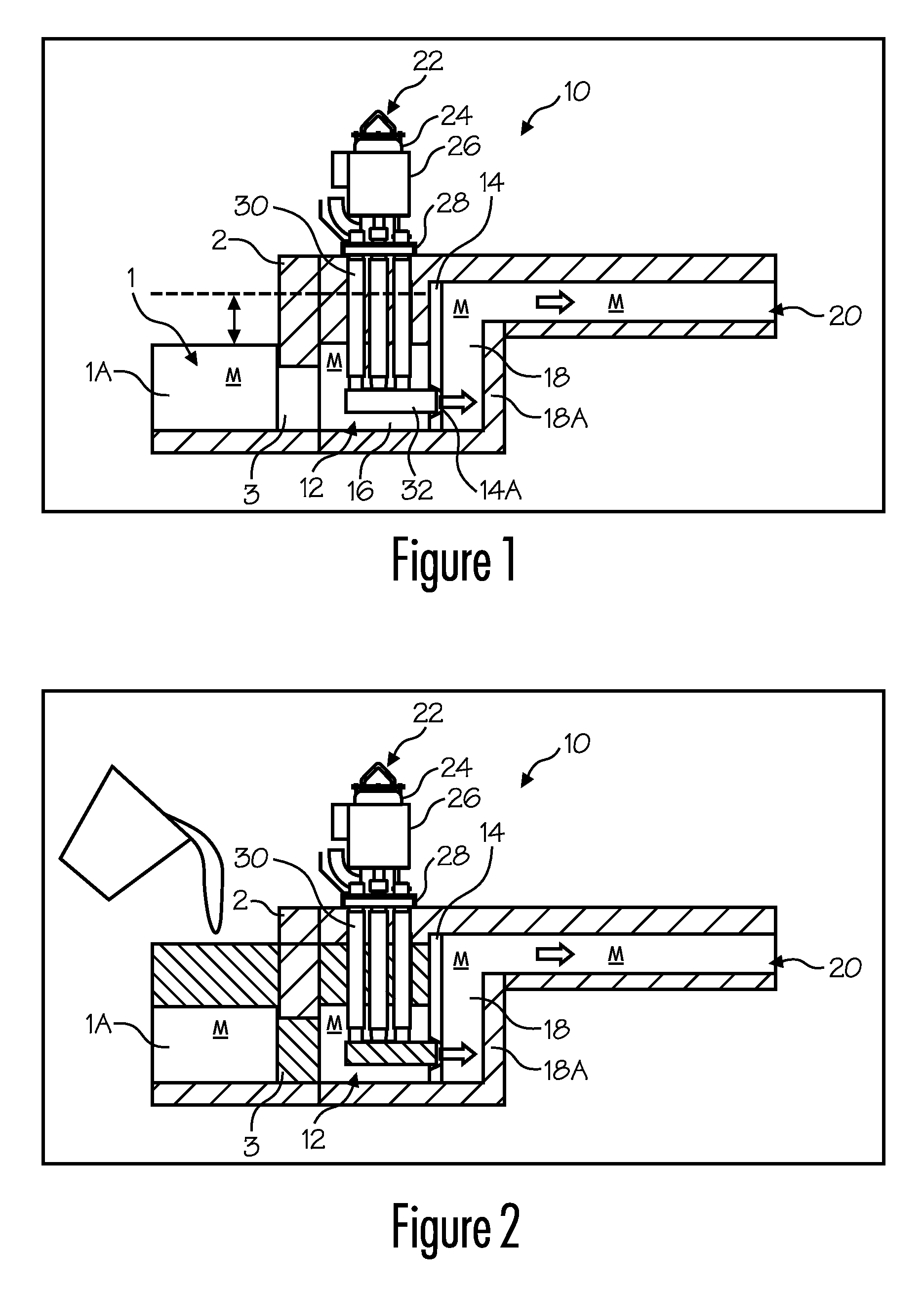
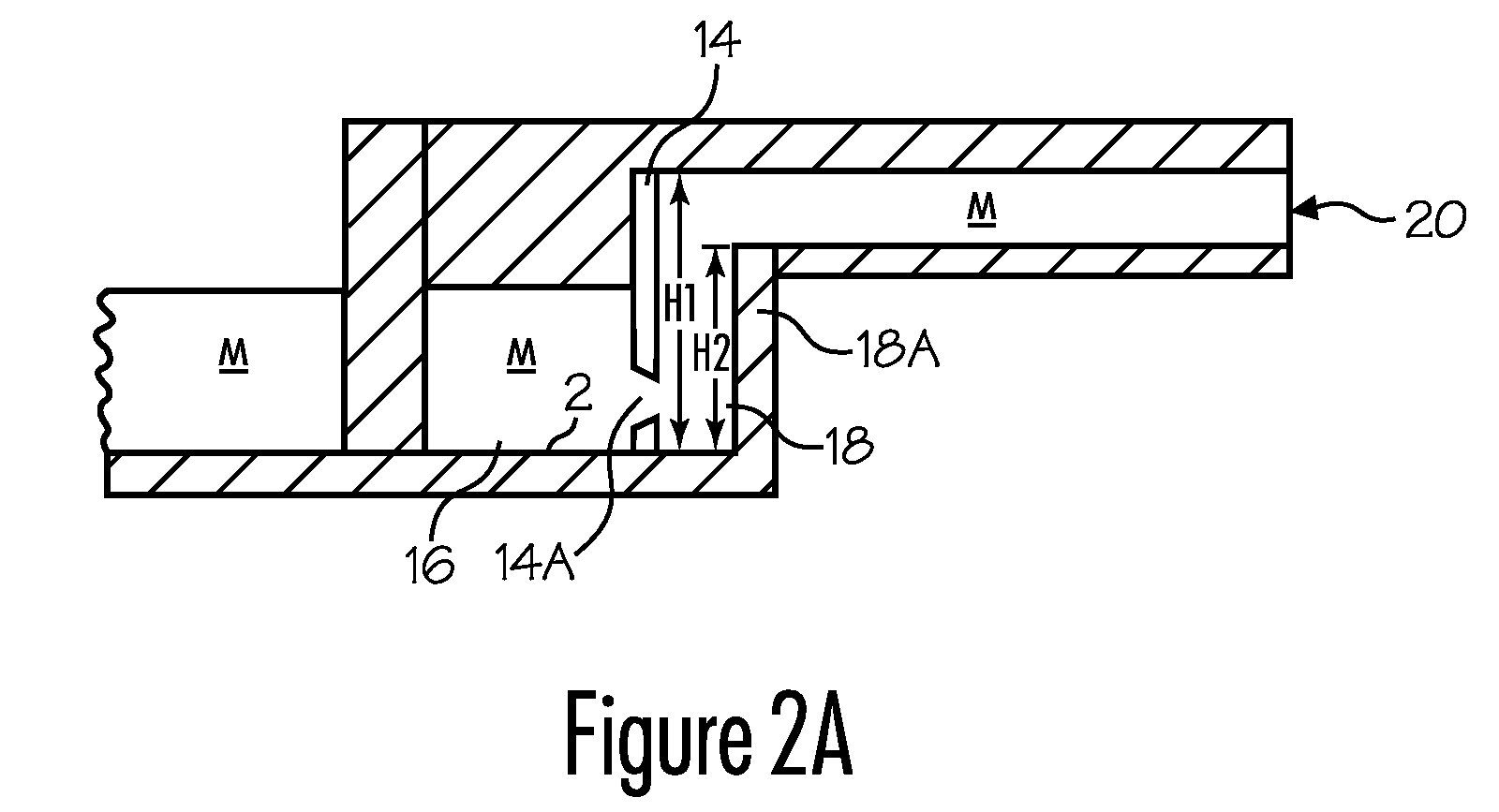
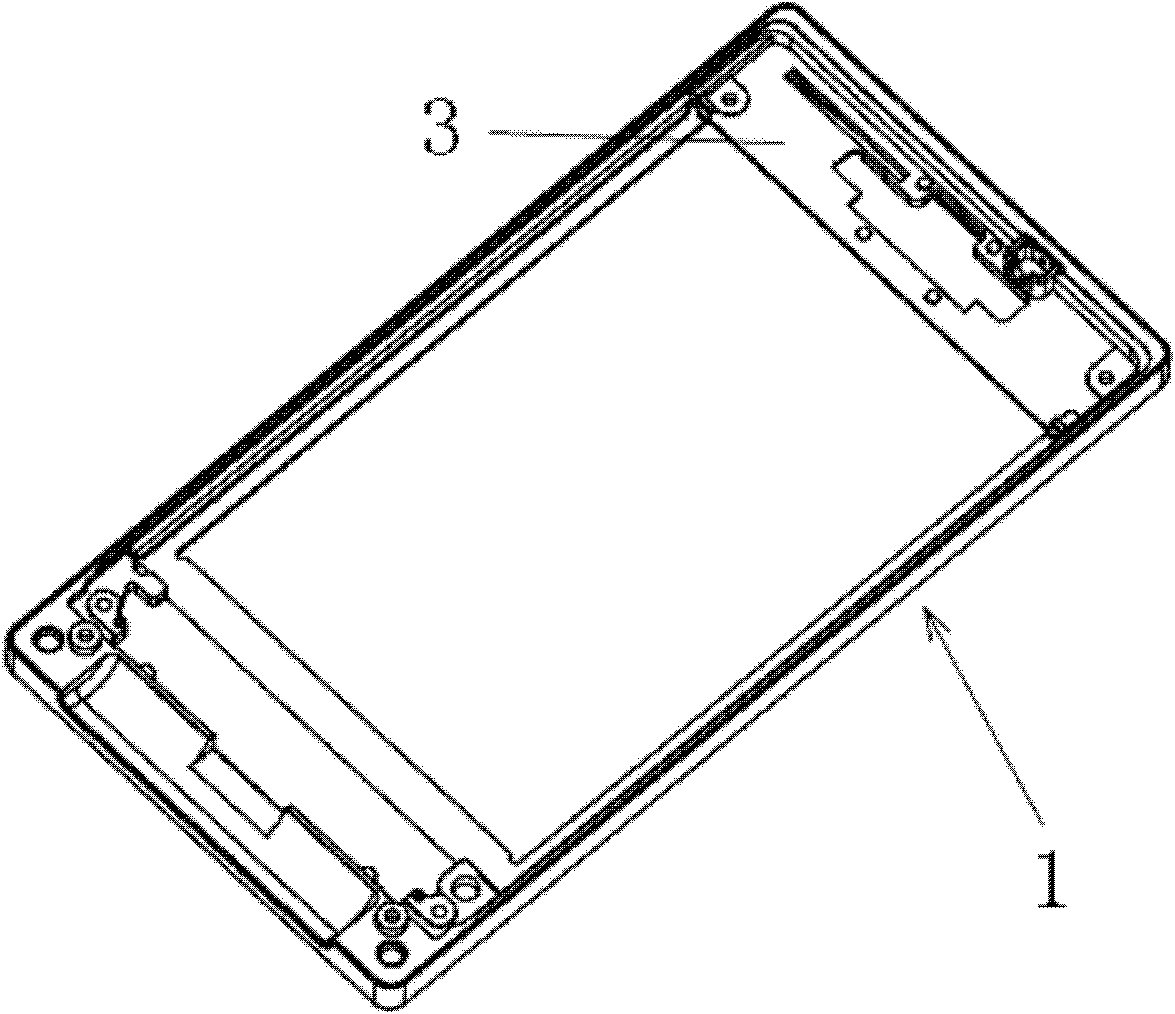
ActiveUS20080314548A1Formation of dross in the ladle or launder are greatly reduced or eliminatedEliminate useMolten metal pouring equipmentsMolten metal supplying equipmentsDie castingMolten metal
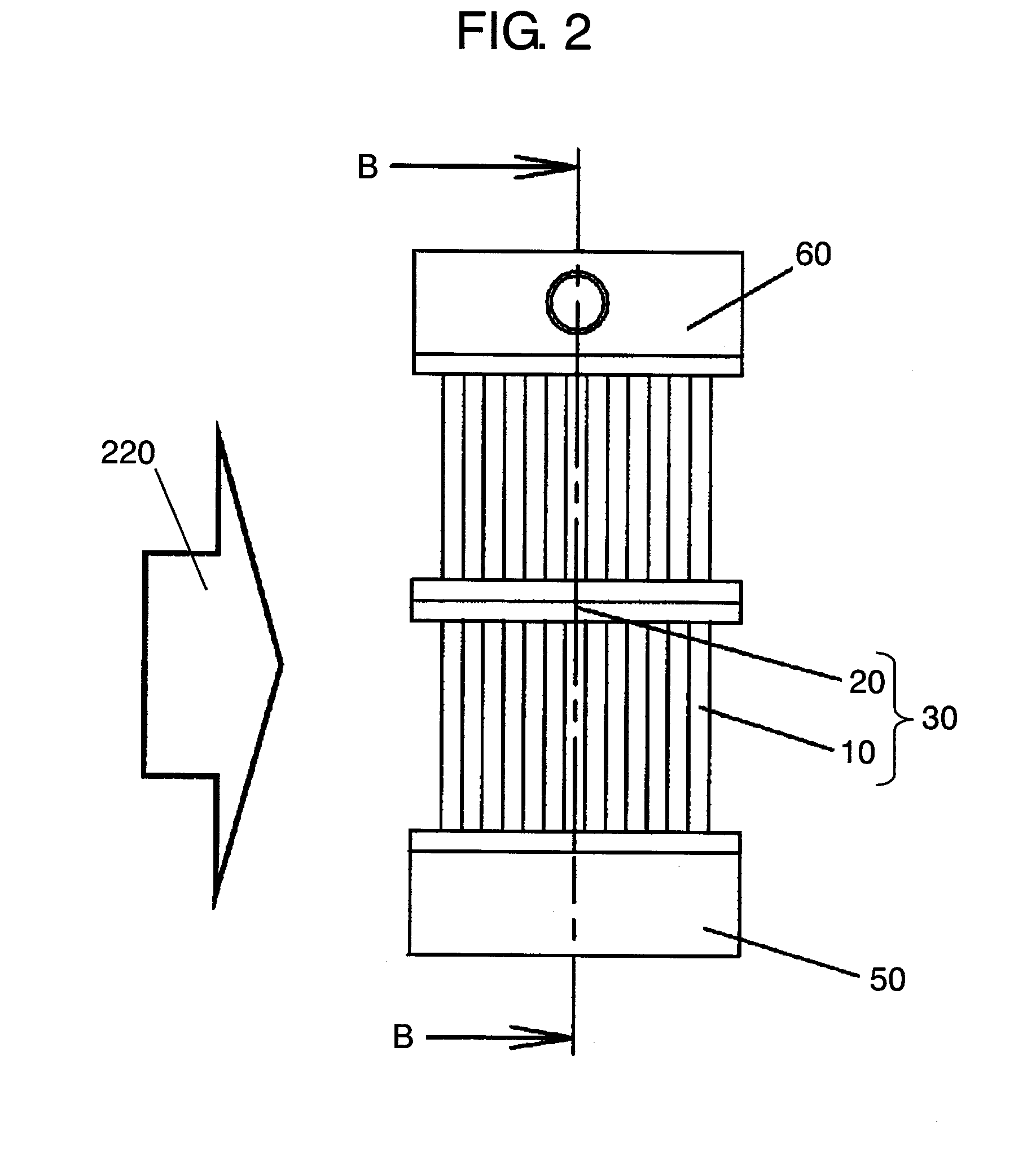
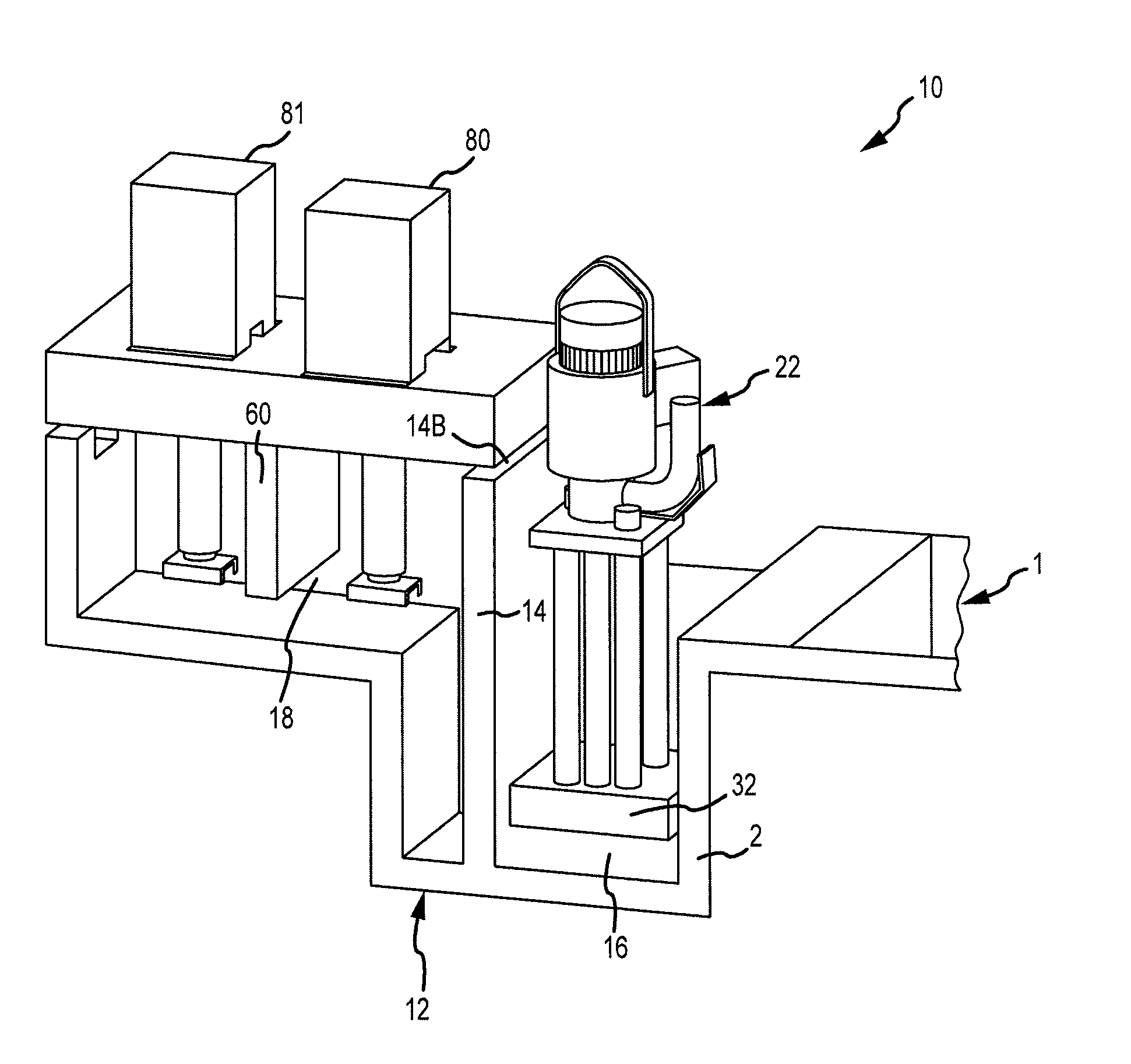
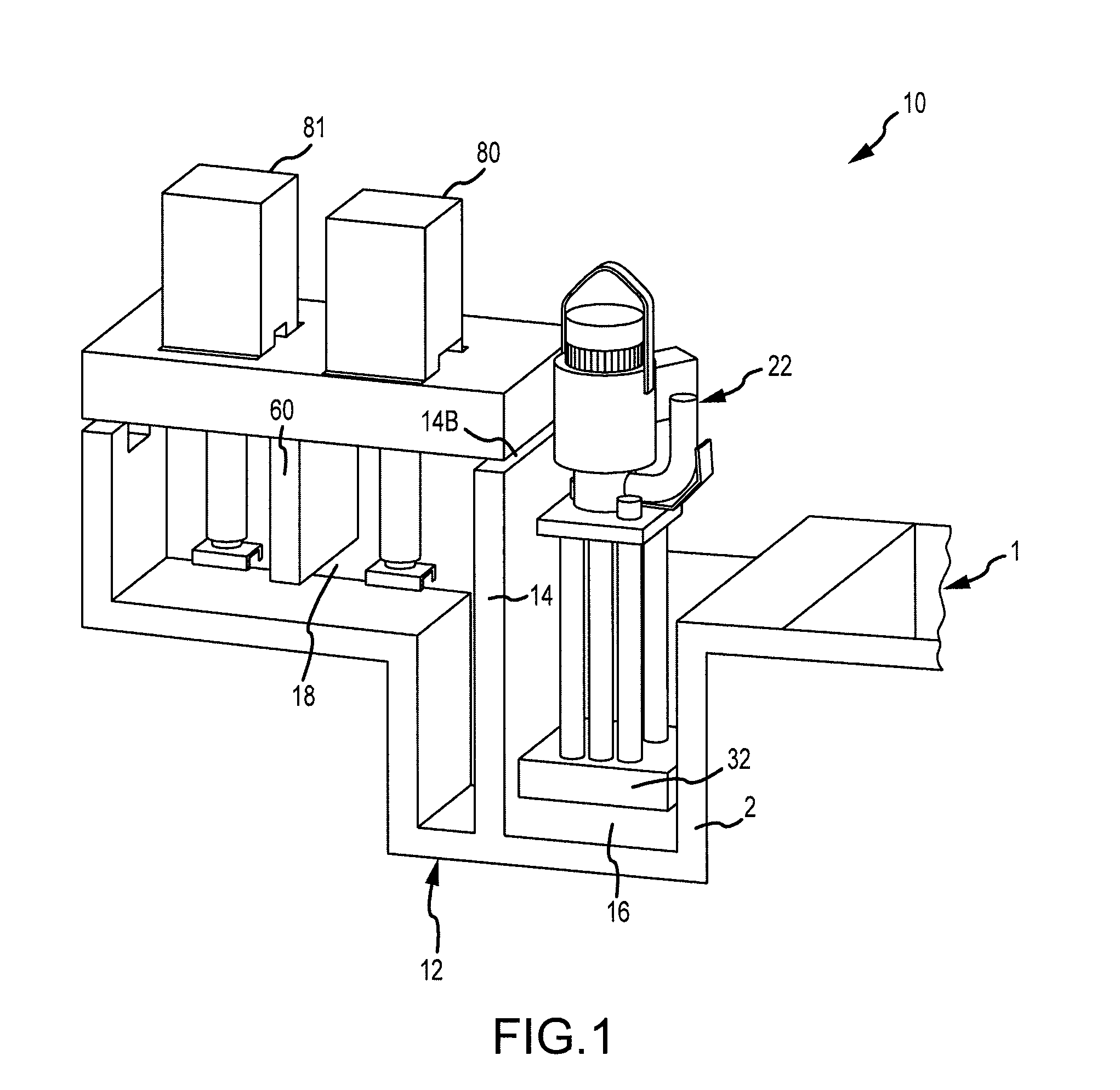
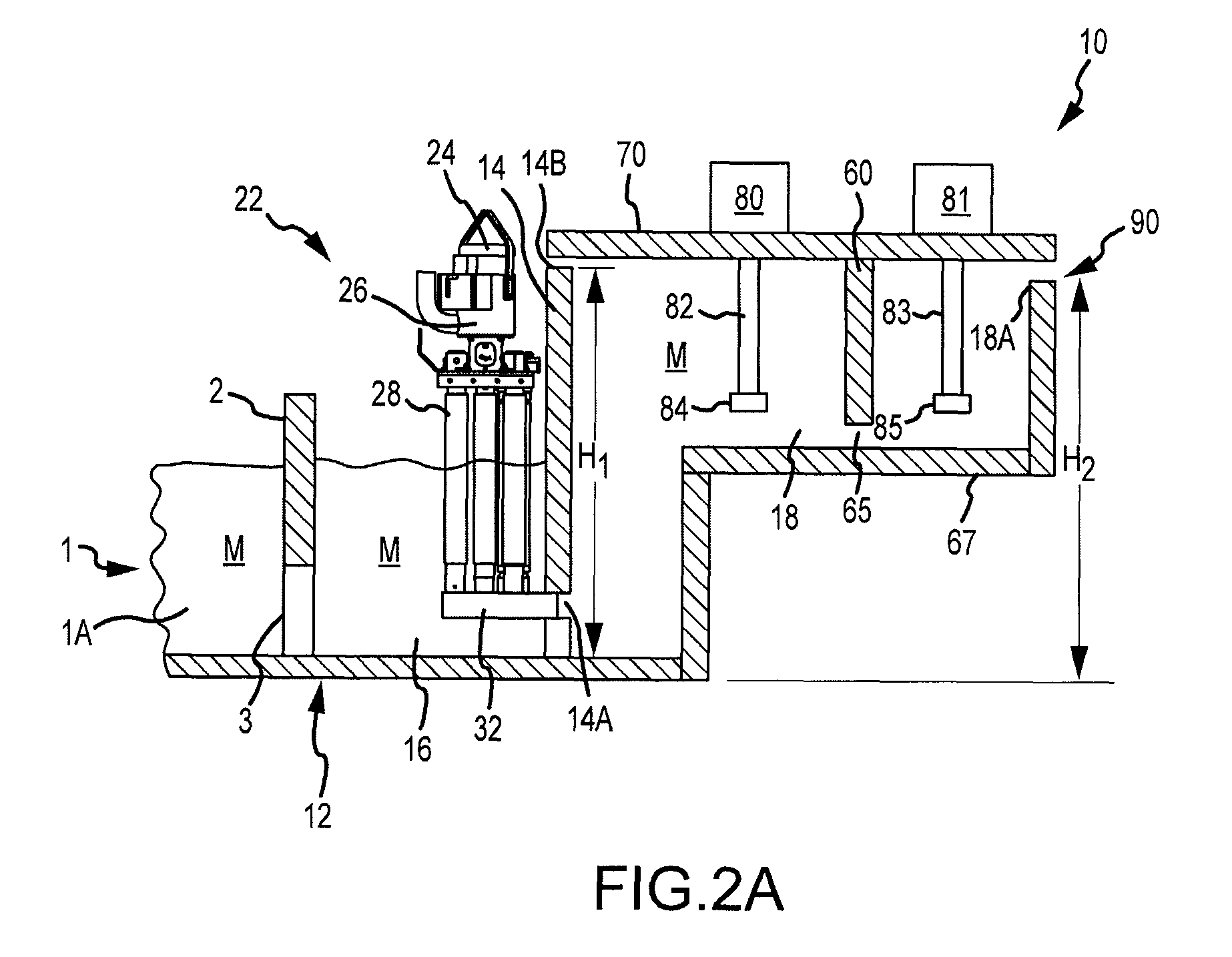
A system for transferring molten metal from a vessel and into one or more of a ladle, ingot mold, launder, feed die cast machine or other structure is disclosed. The system includes at least a vessel for containing molten metal, an overflow (or dividing) wall, and a device or structure, such as a molten metal pump, for generating a stream of molten metal. The dividing wall divides the vessel into a first chamber and a second chamber, wherein part of the second chamber has a height H2. The device for generating a stream of molten metal, which is preferably a molten metal pump, is preferably positioned in the first chamber. When the device operates, it generates a stream of molten metal from the first chamber and into the second chamber. When the level of molten metal in the second chamber exceeds H2, molten metal flows out of the vessel and into another structure, such as into one or more ladles and / or one or more launders.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
Processing method of high-toughness Al-Si system die-casting aluminum alloy
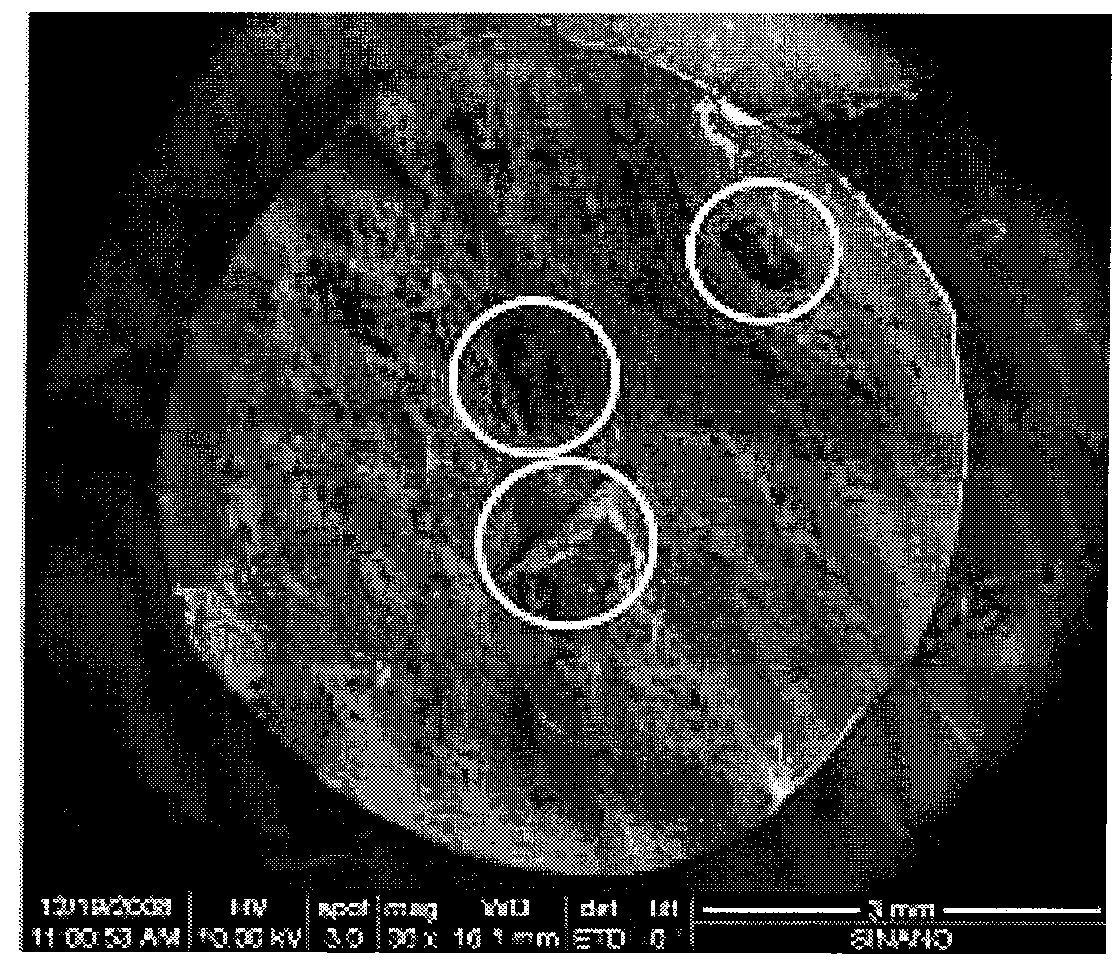
The invention provides a processing method of a high-toughness Al-Si system die-casting aluminum alloy. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out die-casting molding of an Al-Si system aluminum alloy melt, wherein the die casting die temperature is 350-400DEG C and the pressure maintaining time is 1-60s; carrying out die opening, rapidly taking out the obtained object, putting the object in circulating cooling water for quenching, taking out the object from the circulating cooling water after complete cooling, and burring, wherein the time for transferring the object to the circulating cooling water from the die is less than 5s, the quenching temperature is 350-550DEG C and the temperature of the cooling water is less than 30DEG C; and carrying out annealing heat-insulation at 50-250DEG C for 2-3h. The method enables Al-Si system alloy die castings to have the advantages of substantially improved strength and toughness, uniform workpiece structure, excellent mechanical performances, and good safety and reliability, and the application range of the Al-Si system alloy die castings to the enlarged.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
System and method for degassing molten metal
A system for adding gas to and transferring molten metal from a vessel and into one or more of a ladle, ingot mold, launder, feed die cast machine or other structure is disclosed. The system includes at least a vessel for containing molten metal, an overflow (or dividing) wall, a device or structure, such as a molten metal pump, for generating a stream of molten metal, and one or more gas-release devices.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
Slider for a fluid tight slide fastener
ActiveUS8112848B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove product qualitySnap fastenersSlide fastenersDie castingEngineering
Owner:YKK CORP
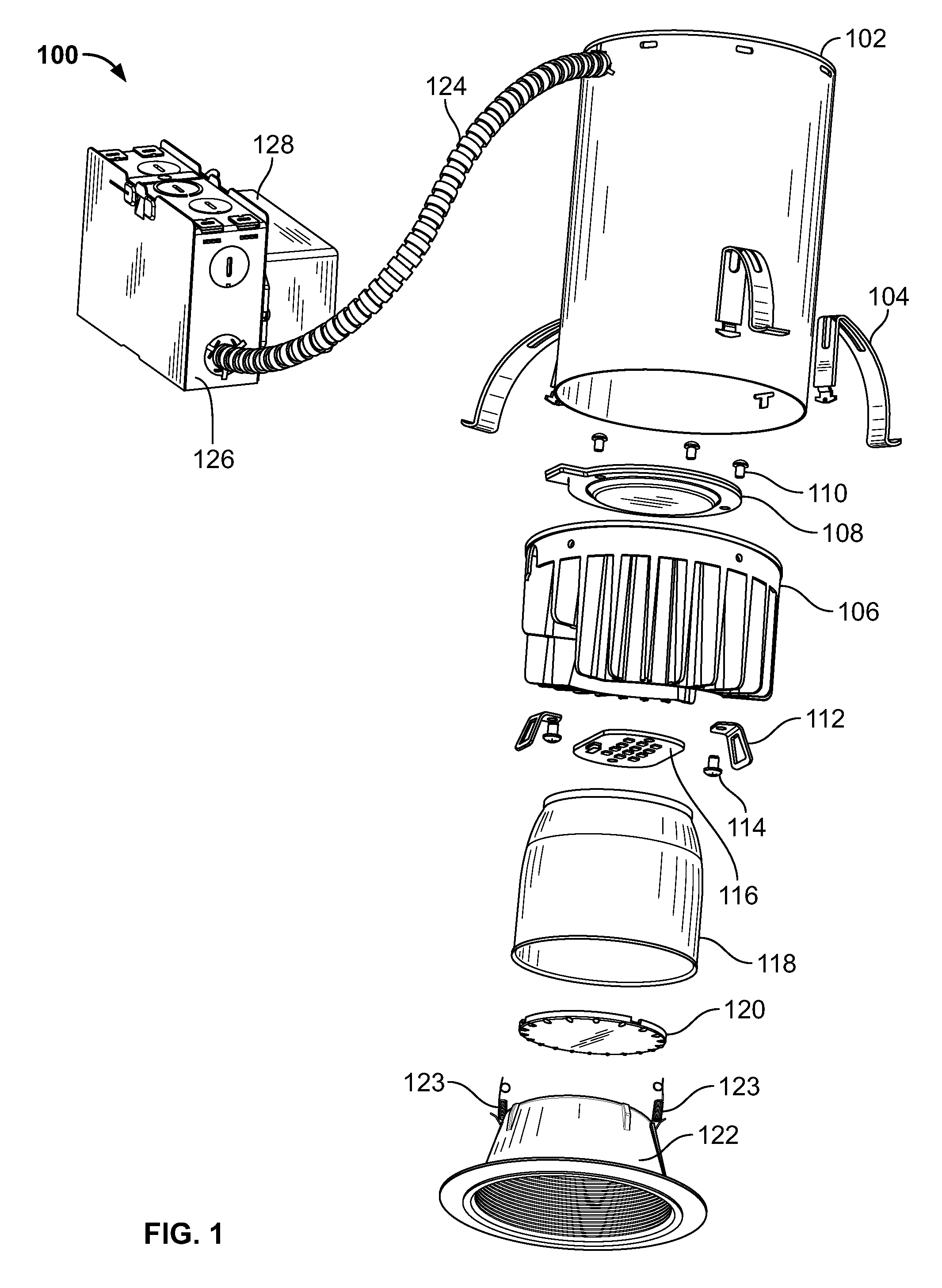
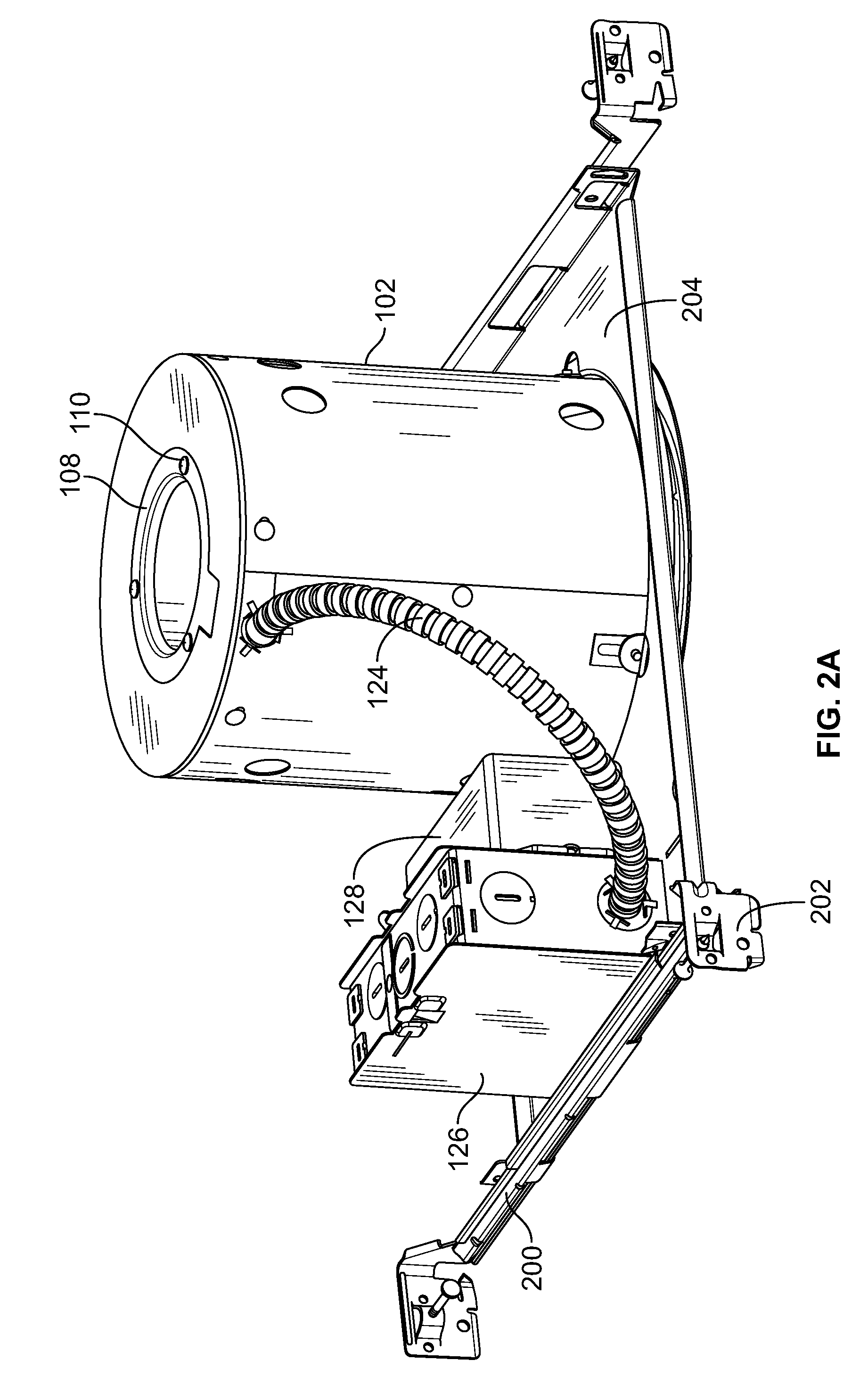
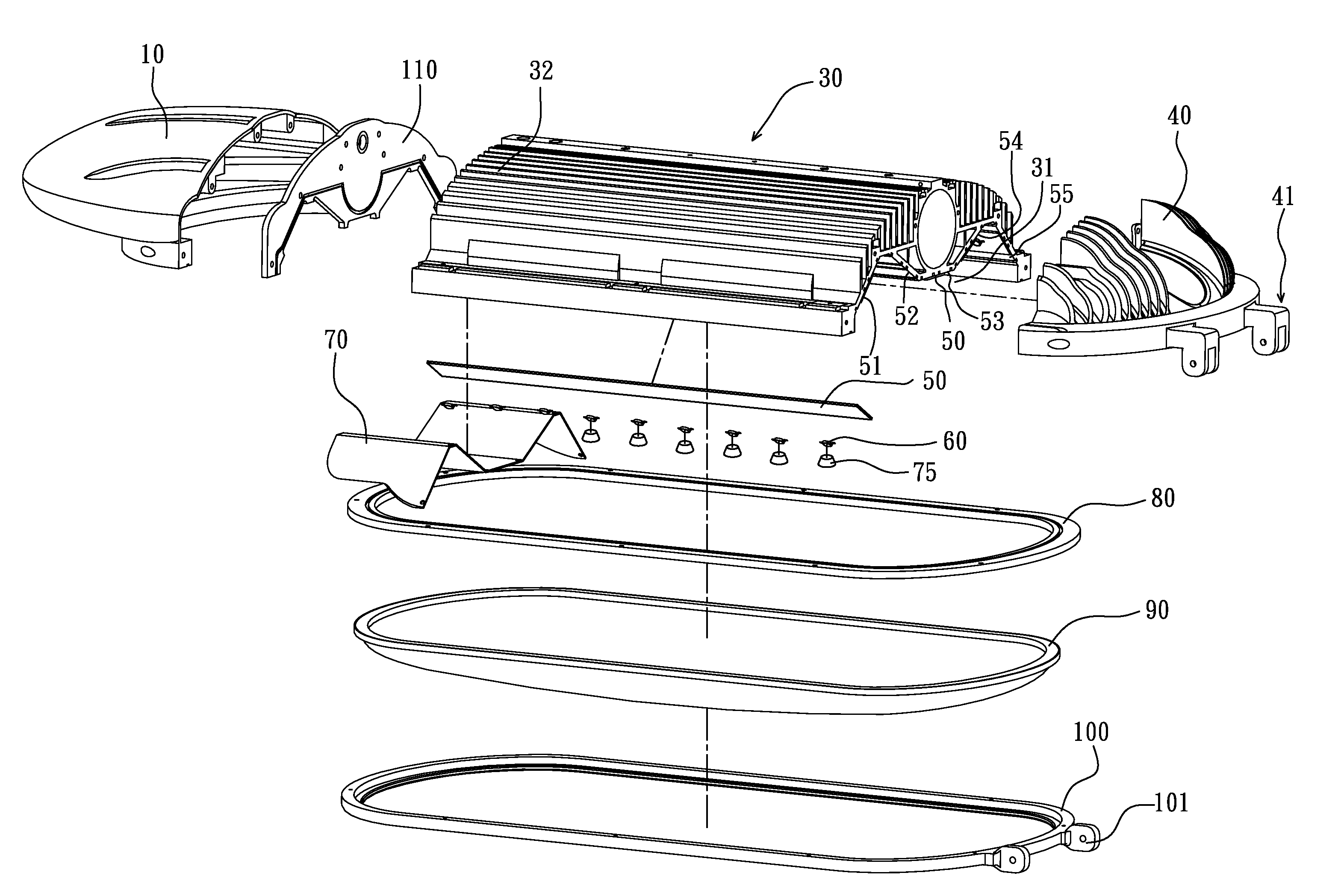
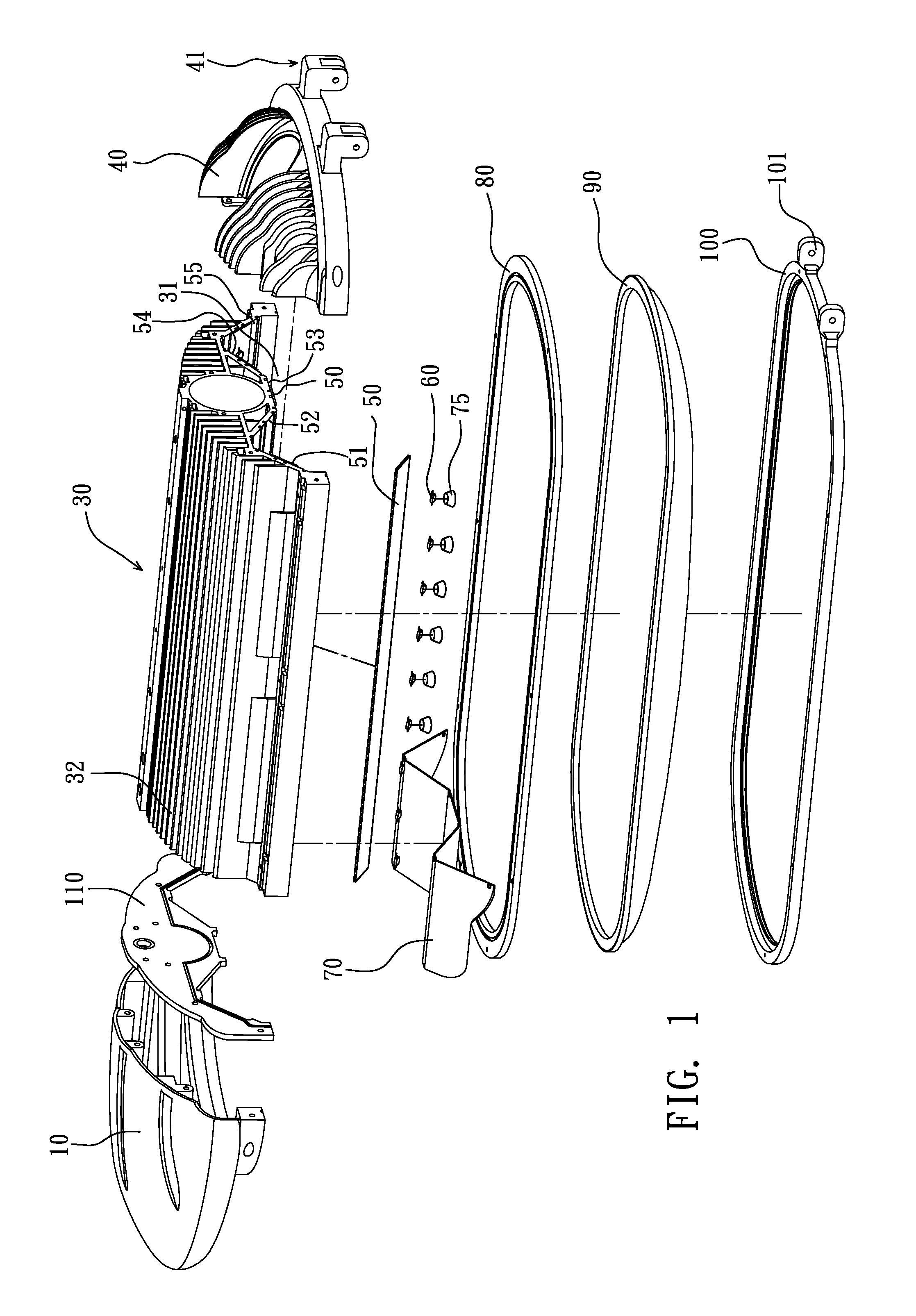
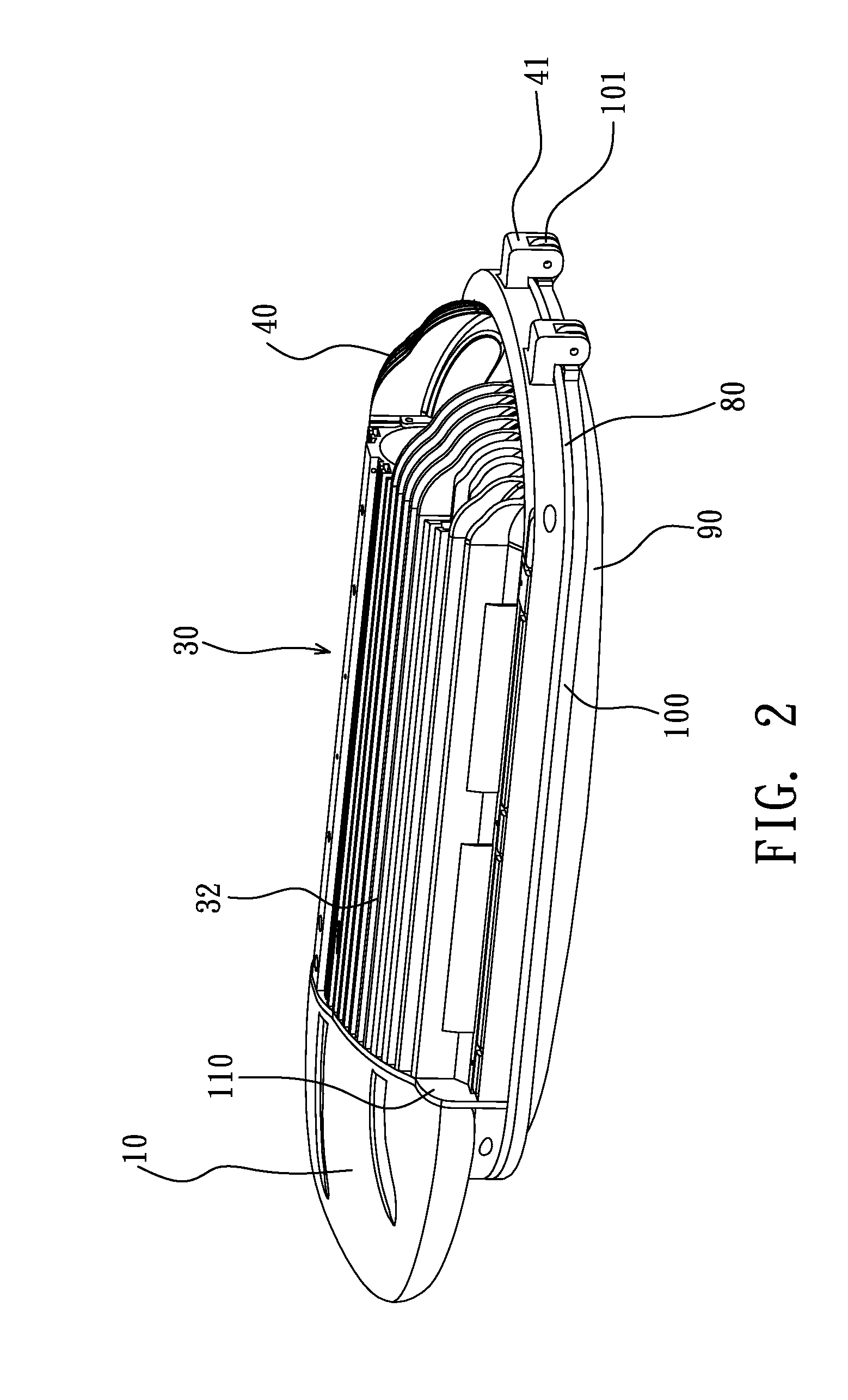
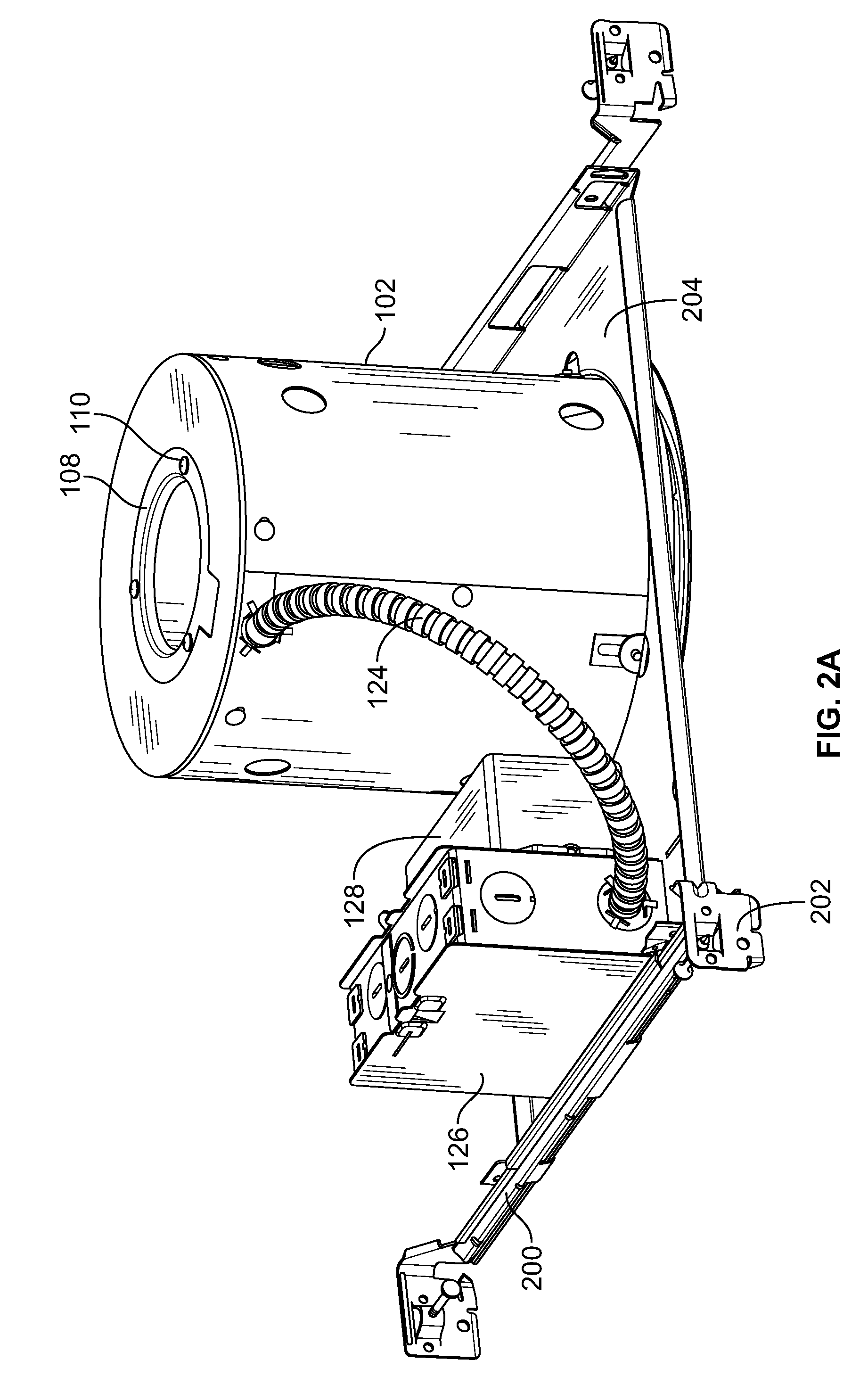
Recessed LED downlight
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Heat Exchanger and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080121387A1Control areaLow costMetal-working apparatusStationary conduit assembliesDie castingEngineering
A heat exchanger is formed by connecting tube-group blocks along a tube axis, where each one of tube-group blocks includes a plurality of substrates having a large number of through holes, which communicate with insides of a plurality of tubes placed between the substrates. A length of the tubes can be shortened so that the tube-group block can be formed within a predetermined size. The substrates and the tubes can be formed by injection molding or die-casting simultaneously with ease, so that the manufacturing steps of inserting the tubes and bonding the substrates can be eliminated. The heat exchanger can be available at a lower cost while it maintains excellent heat exchanging performance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for degassing molten metal
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
Technological process for producing super-thick plate
InactiveCN101439348AQuality improvementLow costTemperature control deviceElectron beam welding apparatusElectro-slag remeltingVacuum chamber
The invention relates to a process for producing an ultra-thick plate and belongs to the field of rolling and producing an ultra-thick steel plate in the metallurgical industry. The invention mainly overcome the defect of producing the ultra-thick steel plate by a traditional model casting manufacturing blank and an electro-slag remelting manufacturing blank. The method comprises the following steps: cutting and fixing lengths of the blanks, mechanically conditioning the blanks (eliminating, leveling and cleaning a single-surface oxide layer of a casting blank with a milling machine, a planer or a shot blast); clamping an assembly (relatively superposing the cleaning surfaces of the two blanks after processing, placing the two blanks oppositely and clamping the blanks); mounting the blanks in a vacuum chamber of an electronic beam welding machine for purpose of vacuuming; sewing the assembly on the electronic beam welding seal edge, heating the assembly in a furnace and rolling the assembly through temperature control; and then producing the ultra-thick steel plate. Compared with the traditional electro-slag remelting production process, the process has the advantages of high production efficiency, reduced electric power consumption, less investment of production devices and low production cost. Compared with the traditional die casting production process, the process solves the problem of segregation and looseness of a large-scale die casting ingot center part; the finished product ratio is high; and the finished product ratio of blank assembly is over 90 %.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
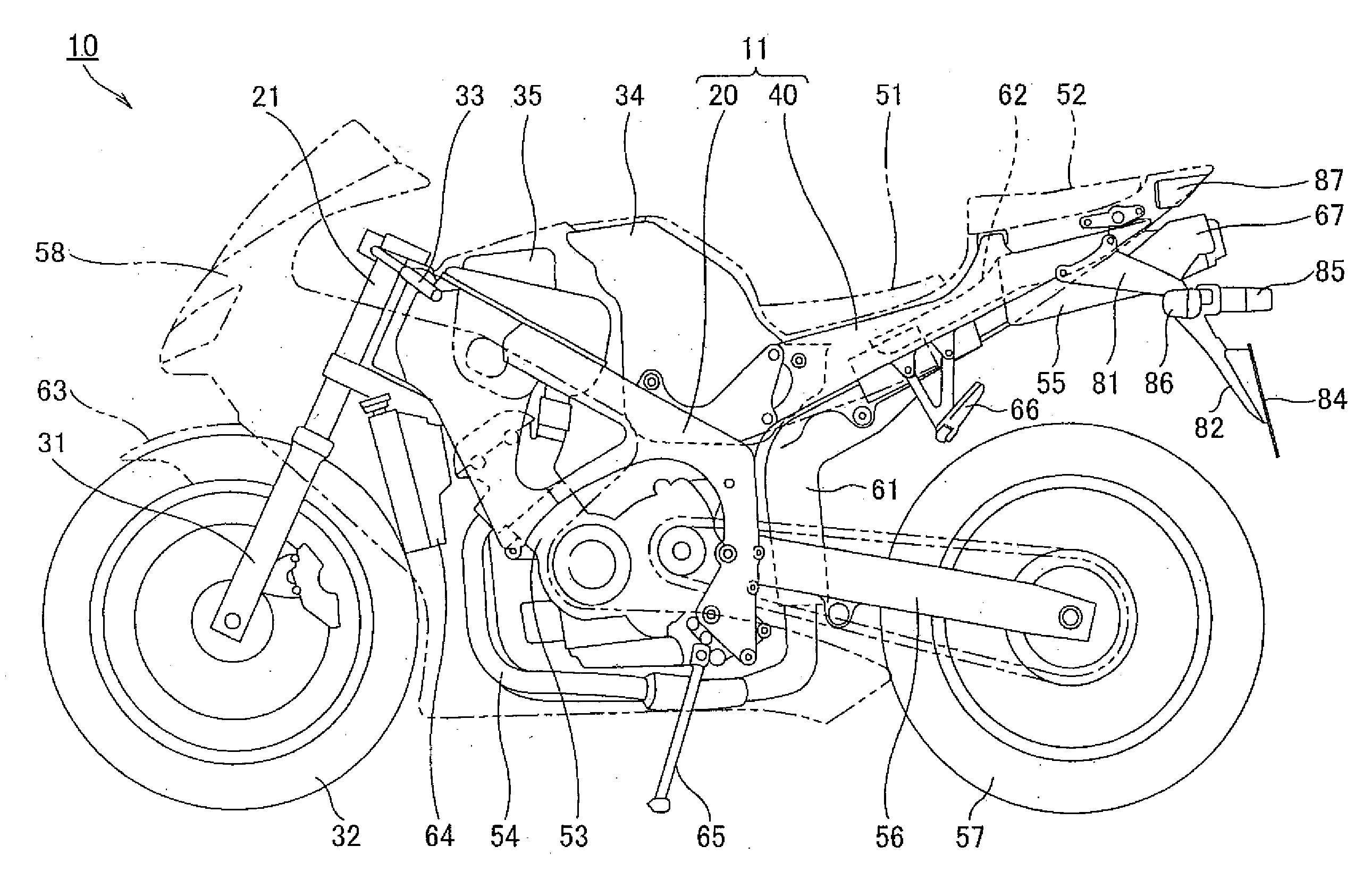
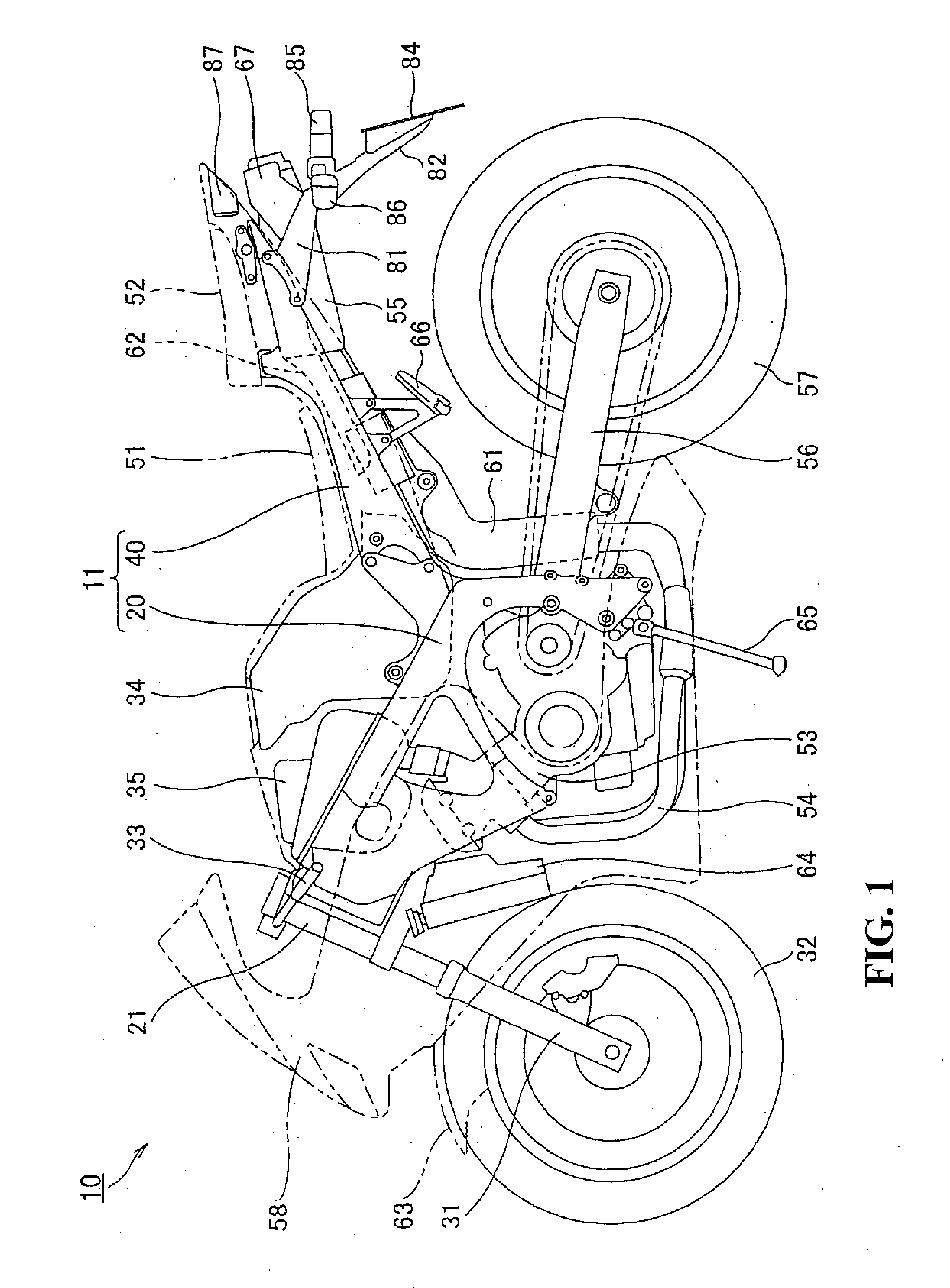
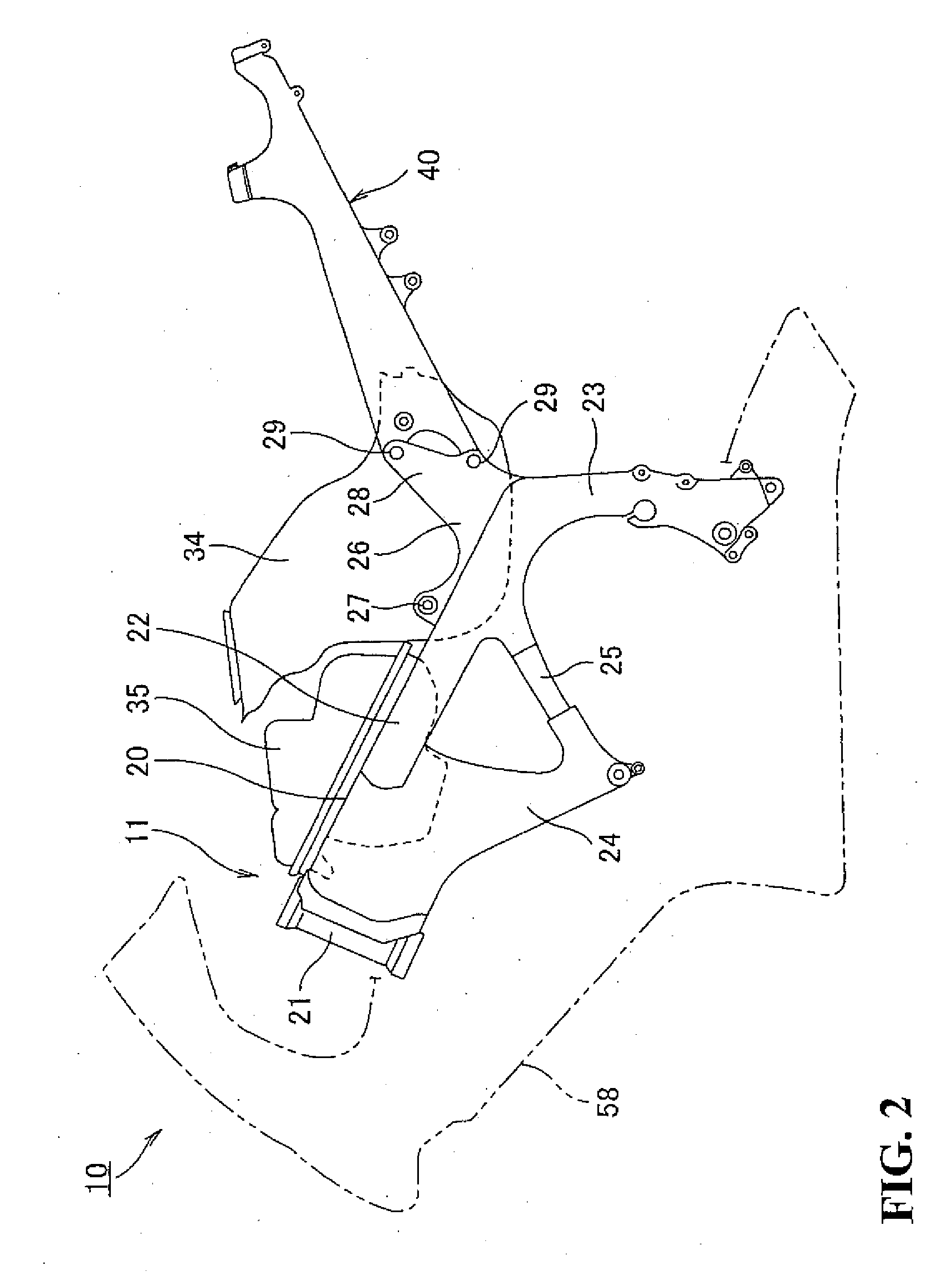
Seat rail structure of motorcycle
InactiveUS20080277980A1Improve productivityHigh strengthMotorcyclesCycle saddlesDie castingEngineering
A seat rail structure for a motorcycle having sufficient strength and rigidity while achieving a weight reduction of a vehicle body. A seat rail structure of a motorcycle includes a main frame and a seat rail formed of magnesium alloy to be secured to the main frame. The seat rail includes a pair of left and right side wall portions extending rearwardly from the main frame, and a plurality of connecting portions formed into a substantially angular C-shape in cross section or into a substantially H-shape in cross section for connecting the left and right side wall portions. At least part of the connecting portions are connected at a level flush with or above the upper surface of the side wall portions. The side wall portions and the connecting portions are integrally formed by die casting.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Transferring molten metal from one structure to another
ActiveUS8337746B2Formation of dross in the ladle or launder are greatly reduced or eliminatedEliminate useMolten metal pouring equipmentsStirring devicesDie castingMolten metal
A system for transferring molten metal from a vessel and into one or more of a ladle, ingot mold, launder, feed die cast machine or other structure is disclosed. The system includes at least a vessel for containing molten metal, an overflow (or dividing) wall, and a device or structure, such as a molten metal pump, for generating a stream of molten metal. The dividing wall divides the vessel into a first chamber and a second chamber, wherein part of the second chamber has a height H2. The device for generating a stream of molten metal, which is preferably a molten metal pump, is preferably positioned in the first chamber. When the device operates, it generates a stream of molten metal from the first chamber and into the second chamber. When the level of molten metal in the second chamber exceeds H2, molten metal flows out of the vessel and into another structure, such as into one or more ladles and / or one or more launders.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
Mobile phone shell and machining method thereof
InactiveCN102811264AGuaranteed Appearance RequirementsLow costTelephone set constructionsMetal layered productsDie castingEngineering
Owner:李树忠 +1
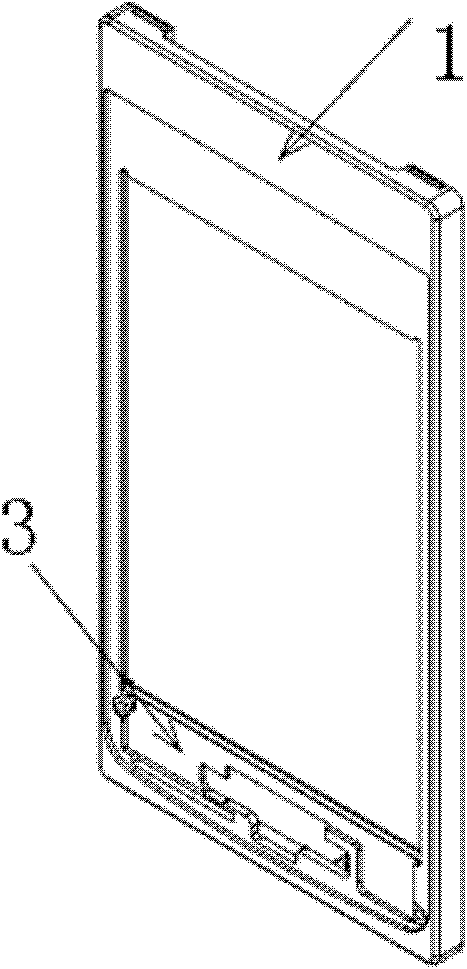
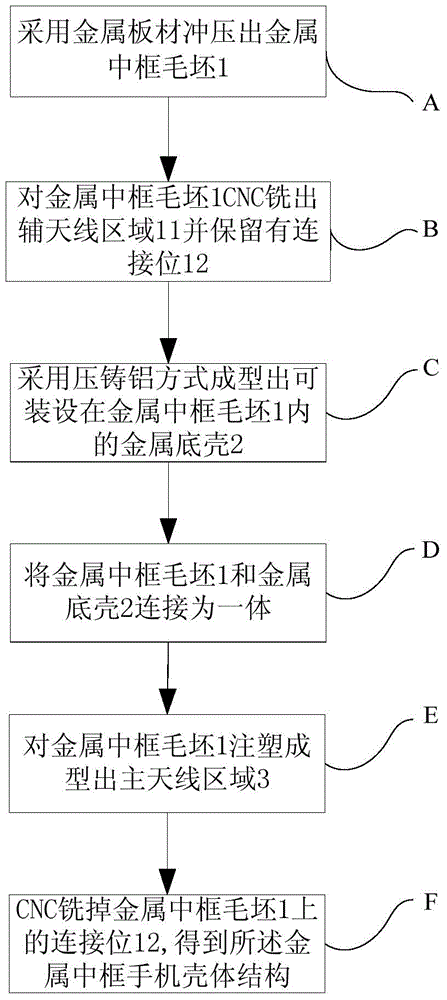
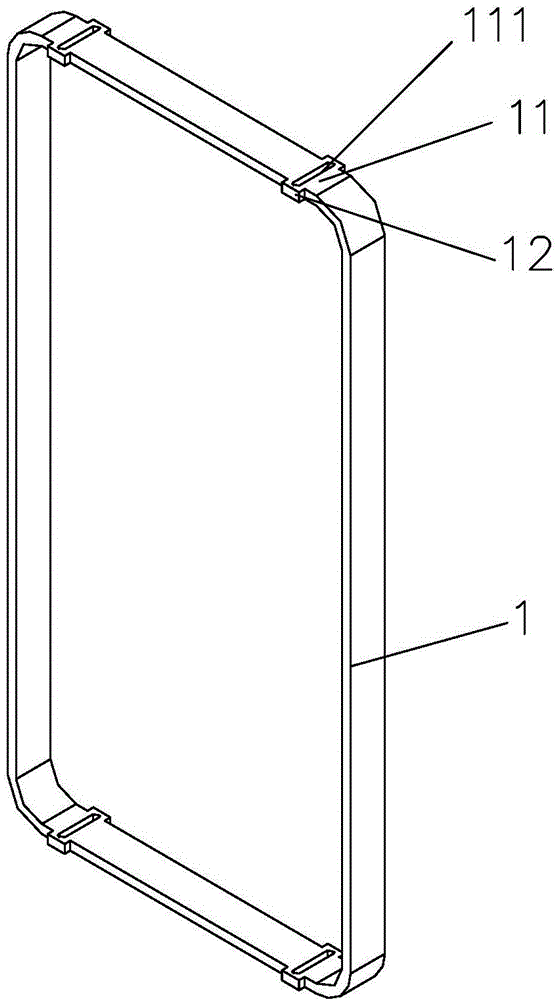
Processing method of metal middle frame mobile phone shell structure
ActiveCN104551562ASolve processabilitySolve the costTelephone set constructionsWhole bodyDie casting
The invention discloses a processing method of a metal middle frame mobile phone shell structure and relates to the technical field of processing of mobile phones. The processing method comprises the following steps: A, stamping a blank of the metal middle frame by using a metal plate; B, milling an auxiliary antenna area on the blank of the metal middle frame in a CNC manner and retaining a connection position; C, forming a metal bottom shell by using an aluminum die casting manner; D, connecting the blank of the metal middle frame with the metal bottom shell to be a whole body; E, forming a main antenna area on the blank of the metal middle frame by using an injection molding manner; and F, milling off the connection position on the blank of the metal middle frame in the CNC manner to obtain the metal middle frame mobile phone shell structure. By combining processes of stamping molding, injection molding and CNC processing, the metal middle frame mobile phone shell structure is processed; the metal middle frame mobile phone shell structure is stable in process, high in production efficiency, short in processing time and low in production cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Even luminance, high heat dissipation efficiency, high power LED lamp structure
InactiveUS20100027269A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyImprove cooling efficiencyPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesDie castingEngineering
An even luminance, high heat dissipation efficiency, high power LED lamp structure includes an aluminum extrusion body, an aluminum die cast front casing and an aluminum die cast rear casing respectively provided at two distal ends of the aluminum extrusion body, a PC board mounted inside the aluminum extrusion body, LEDs mounted in different LED mounting faces of the PC board at different angles, an inner cover plate decorating the inside of the aluminum die cast front casing, a transparent outer cover covering the bottom side of the aluminum extrusion body and sealed with a water seal, and a retaining device fastened to the aluminum extrusion body to secure the transparent outer cover in place.
Owner:LO WEI HUNG
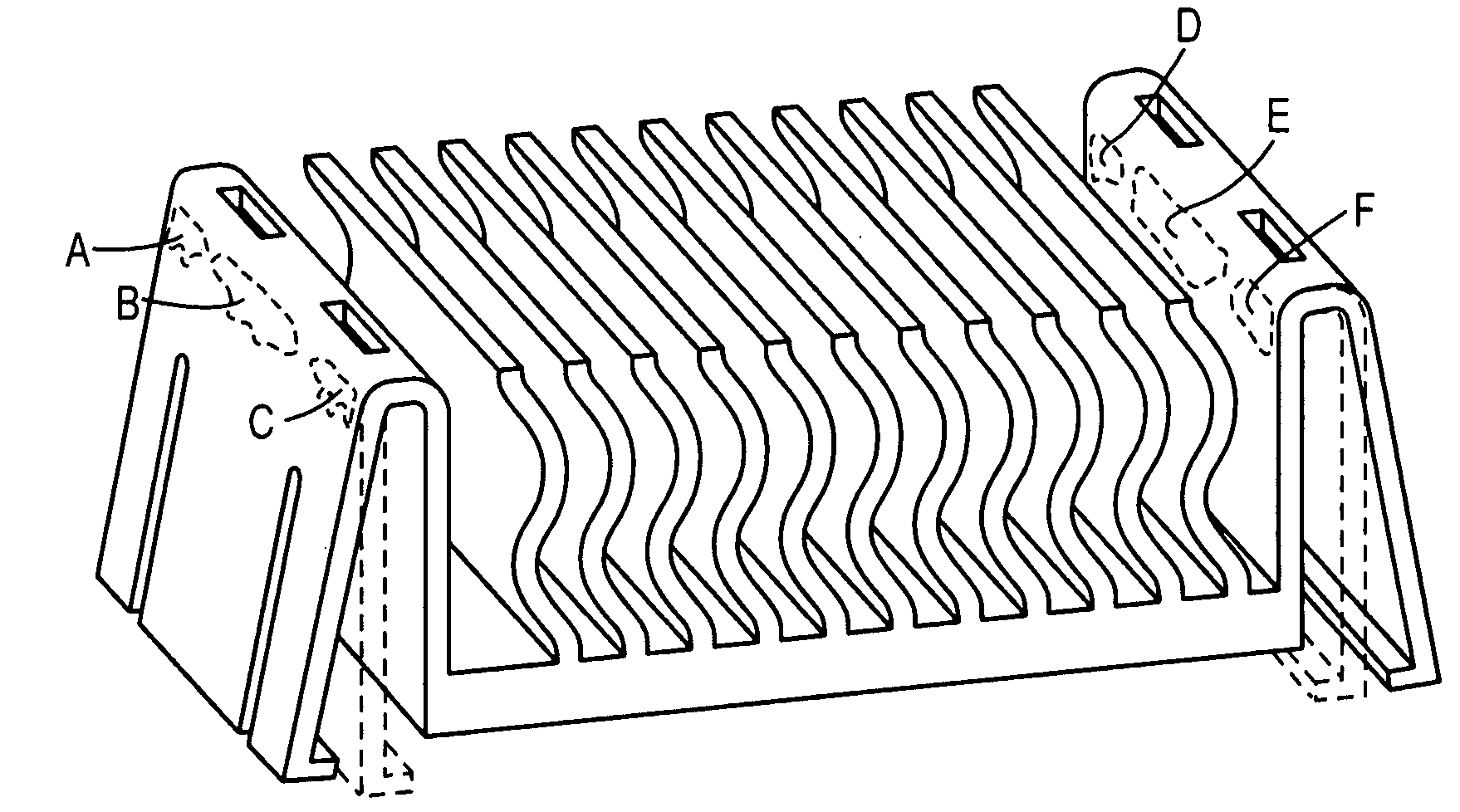
Clip on heat sink
InactiveUS20080310119A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDie castingSolder ball
A heat sink according to an embodiment of the present invention can be attached to any device without printed circuit board (PCB) modification. The heat sink may clamp on device edges, which does not stress solder balls between the device and heat sink. The heat sink may be configured to be installed to or removed from the device without special tools. The heat sink may be extruded, machined, or die cast aluminum or other material to reduce part and tooling cost, and may be black anodized to be electrically non-conductive. A single-piece embodiment eliminates a need for a separate clip, thereby increasing heat transfer by as much as twenty-five percent or more over heat sinks employing clips. Further, wavy fins or other heat dissipation configurations may increase heat transfer by at least eleven percent, for a total heat transfer improvement of at least thirty-six percent over a two-part heat sink.
Owner:TELLABS BEDFORD
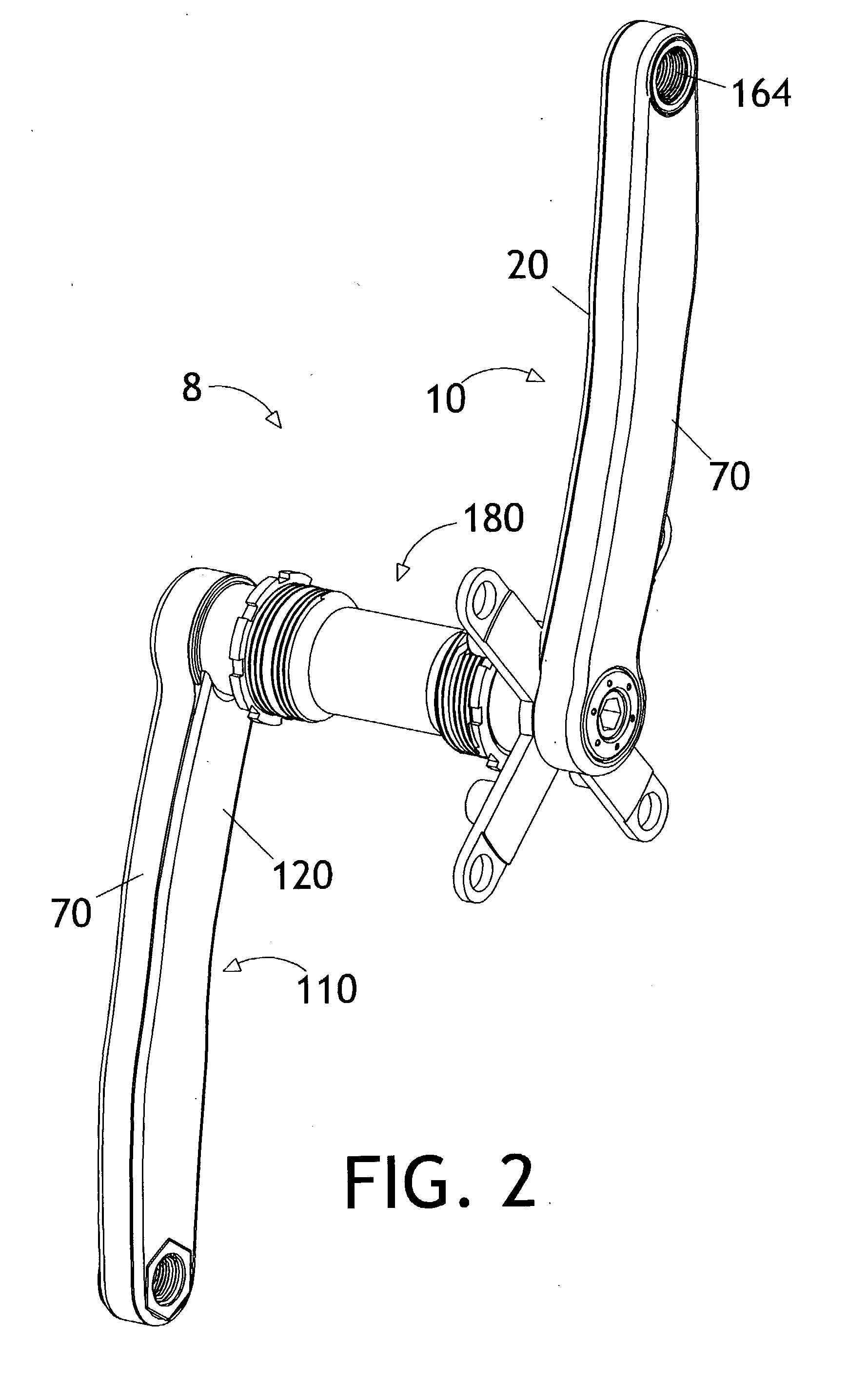
Bicycle crank arm
InactiveUS20040200314A1High strength to weight ratioSimple and inexpensiveControlling membersMechanical apparatusDie castingEngineering
A hollow bicycle crank arm has a central tubular portion to reduce weight and two mounting-boss portions for mounting a crank spindle and pedal during use. A crank arm base is forged or cast with a relatively thin back and sides, preferably out of aluminum or magnesium. The crank arm base has a generally C-shaped cross section. An arm cover has a top and sides and is made from stamped steel or titanium. The cover is placed over the open crank arm base to enclose a significant hollow section. The stamped arm cover does not require any threading or welding. It can be made using a very inexpensive stamping process. The crank arm can be made using relatively inexpensive traditional manufacturing processes such as die casting or forging.
Owner:CRANK BROS INC
Q345q-series super-thick bridge steel plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN101880824AHigh standardRoll force/gap control deviceTemperature control deviceProduction lineChemical composition
The invention discloses a Q345q-series super-thick guaranteed performance and flaw detection bridge steel plate comprising the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.08-0.16 percent of C, 0.20-0.50 percent of Si, 1.15-1.60 percent of Mn, not more than 0.020 percent of P, not more than 0.010 percent of S, not more than 0.12 percent of microalloyed element (V+Nb+Ti+Ni), 0.010-0.050 percent of AlS and the balance of Fe and residual elements; and carbon equivalent is not more than 0.43. The invention also discloses a production method of the steel plate, comprising the steps of rolling, cooling, straightening, cooling in pile and thermal treatment. In the rolling, the cooling and the straightening, the 130 mm super-thick Q345qD(E) steel plate is successfully developed in the production line of a converter, die casting, mill rolling and normalization thermal treatment through carrying out reasonable composition design, die casting, TMCP (Thermal Mechanical Control Process) rolling and thermal treatment; the secondary flaw detection qualification rate reaches 90 percent, the performance initial test qualification rate reaches 100 percent, and the Z-direction performance of the entity of the steel plate can reach Z15 level. The development of the super-thick steel plate satisfies the higher requirements on bridge industry.
Owner:NANYANG HANYE SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
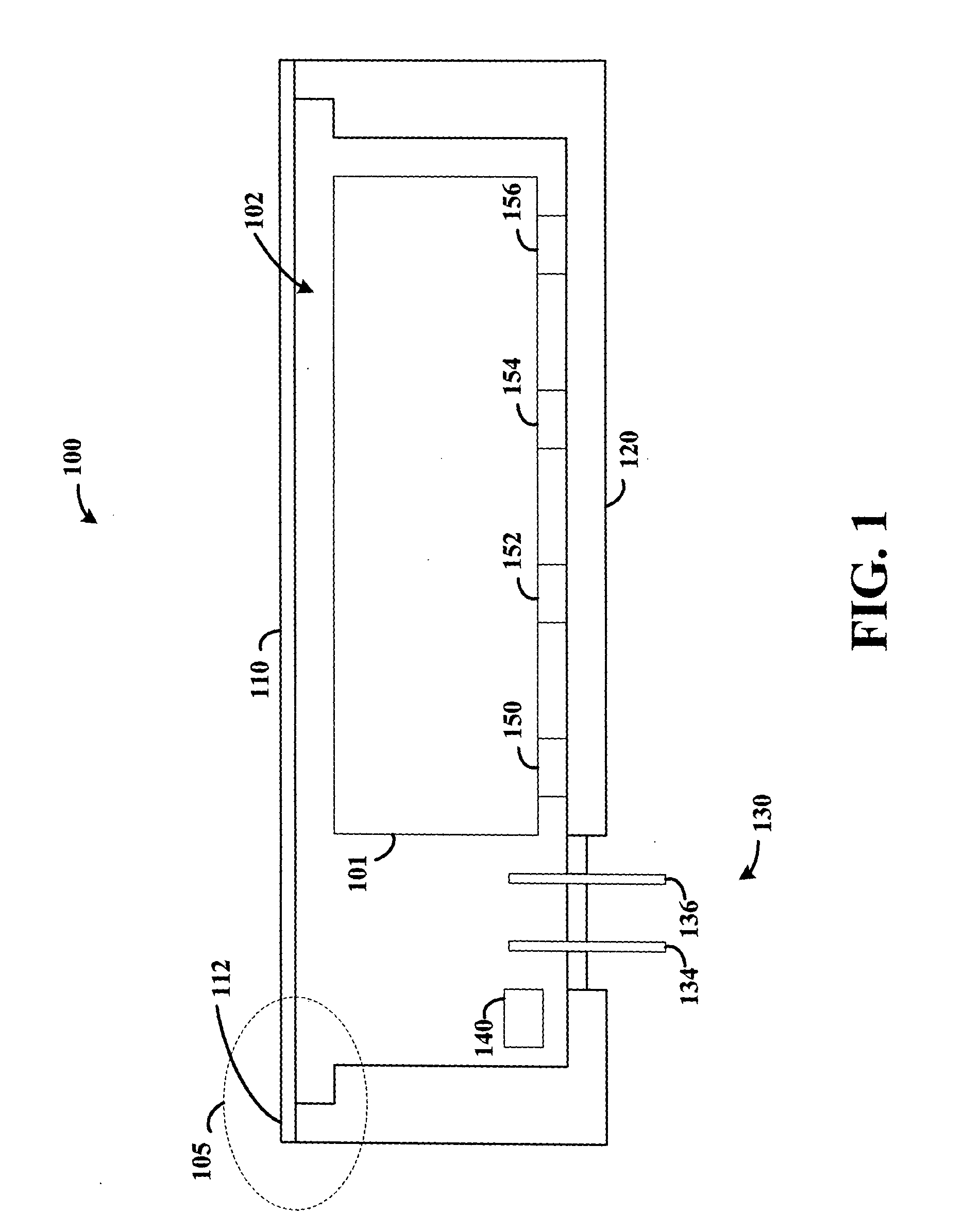
Hermetically sealed electronics arrangement and approach
InactiveUS7123440B2Preventing moisture from reaching portionsCorrosion of heads and disks can be reduced and/or eliminatedApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionCold formedHermetic seal
A hermetic sealing approach involves welding an Aluminum cover onto a low-cost Aluminum housing. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, a metal housing having a base and sidewalls extending upward therefrom is adapted to receive and couple to an HDD arrangement. The metal housing is formed using material and processing (e.g., cold formed or die cast Aluminum) that are relatively inexpensive. A feedthrough arrangement including a plurality of communication pins extends through an opening in the base and is coupled thereto, with the communication pins adapted to pass signals between the inside and the outside of the metal housing. A metal cover is welded to an upper portion of the sidewalls and, with the feedthrough arrangement, hermetically seals the metal housing.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Patterned Implant and Method
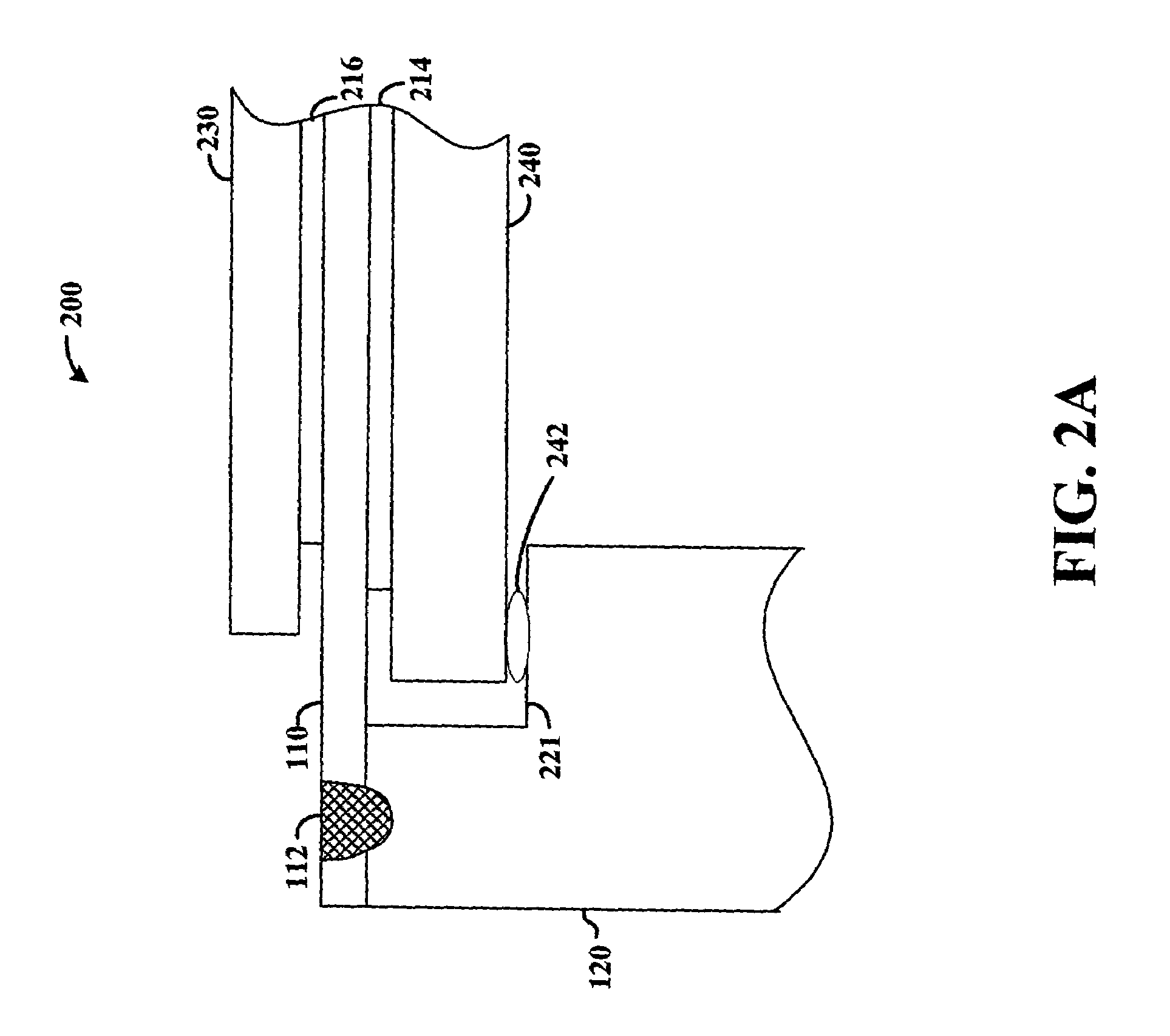
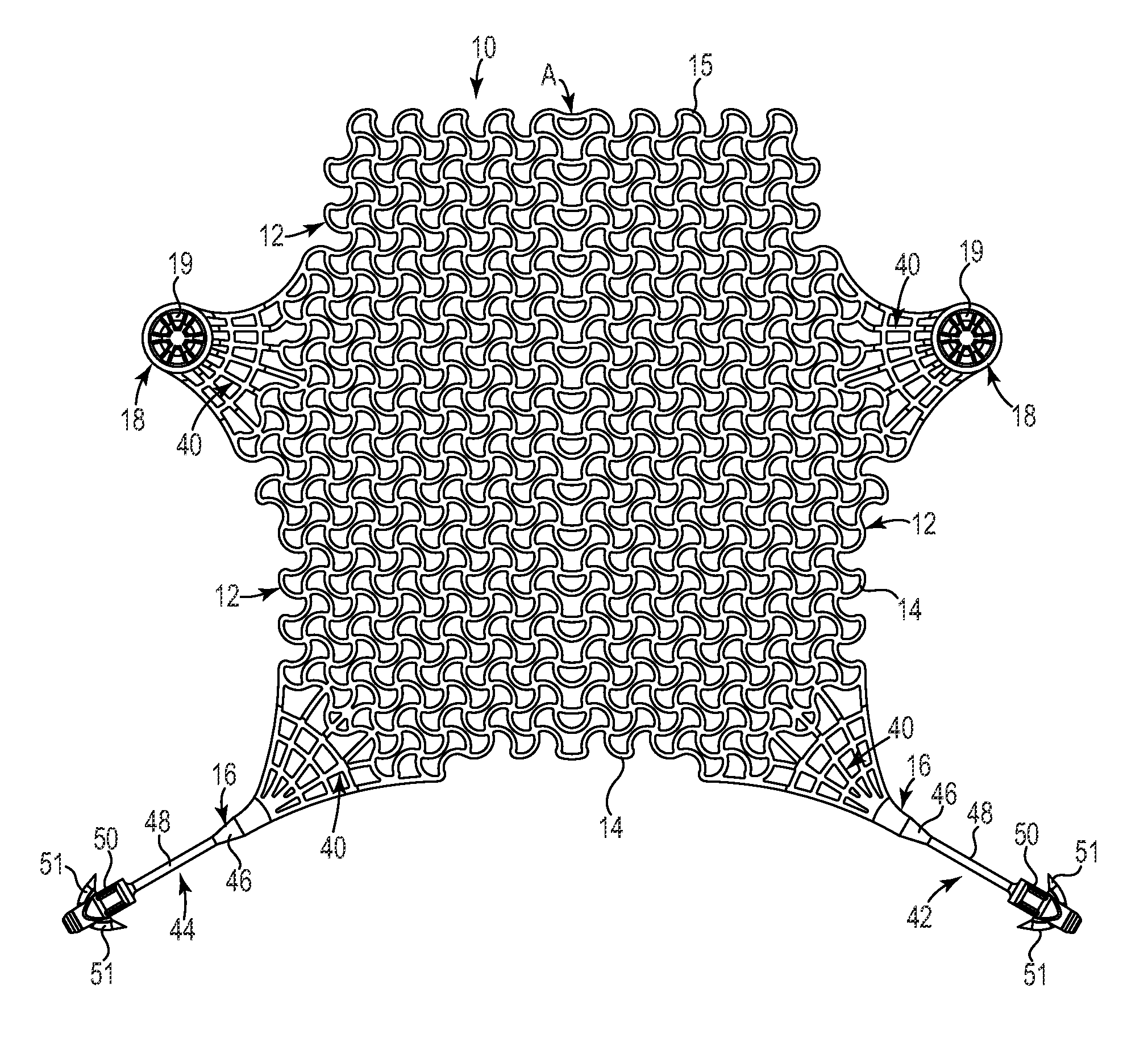
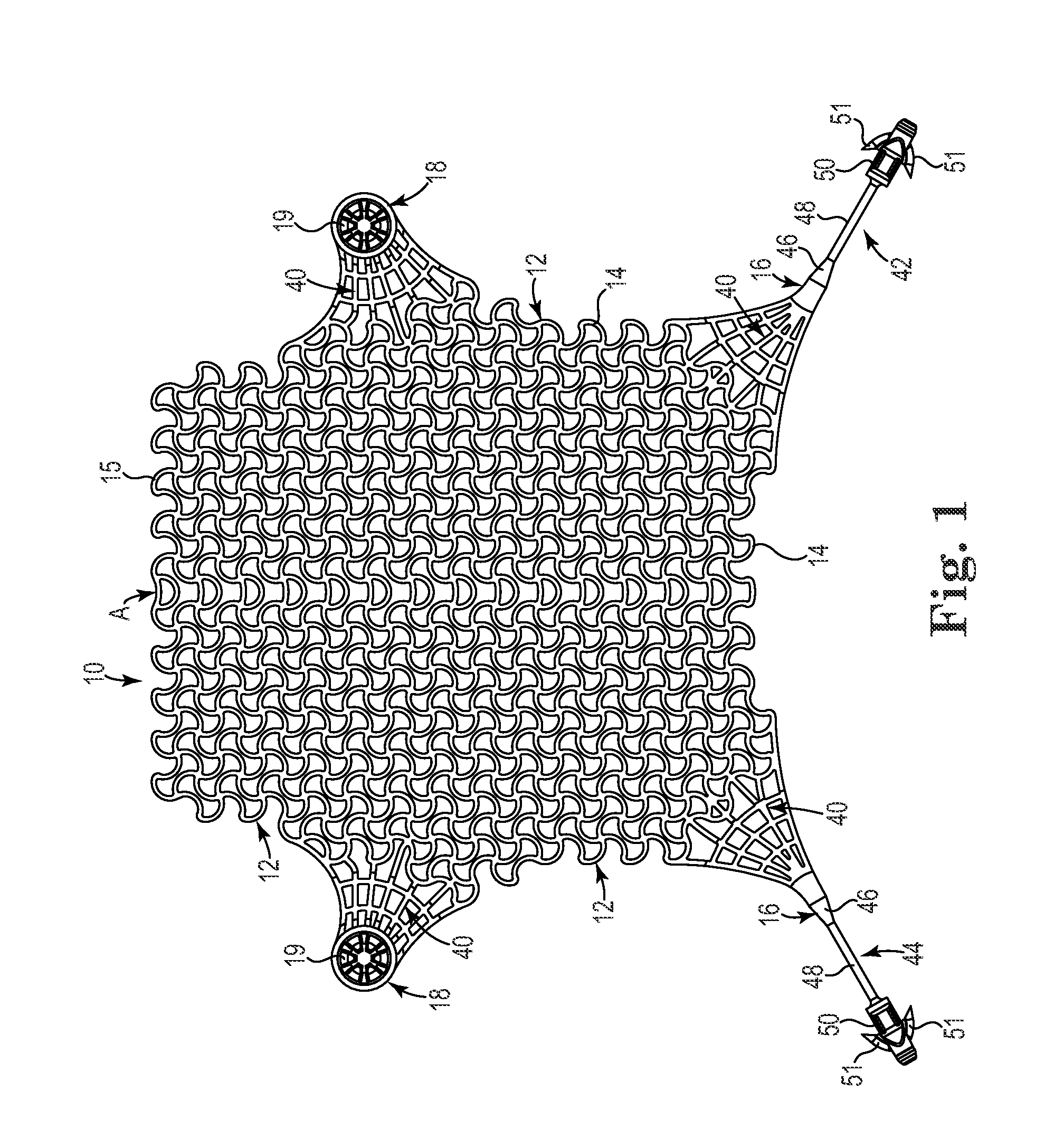
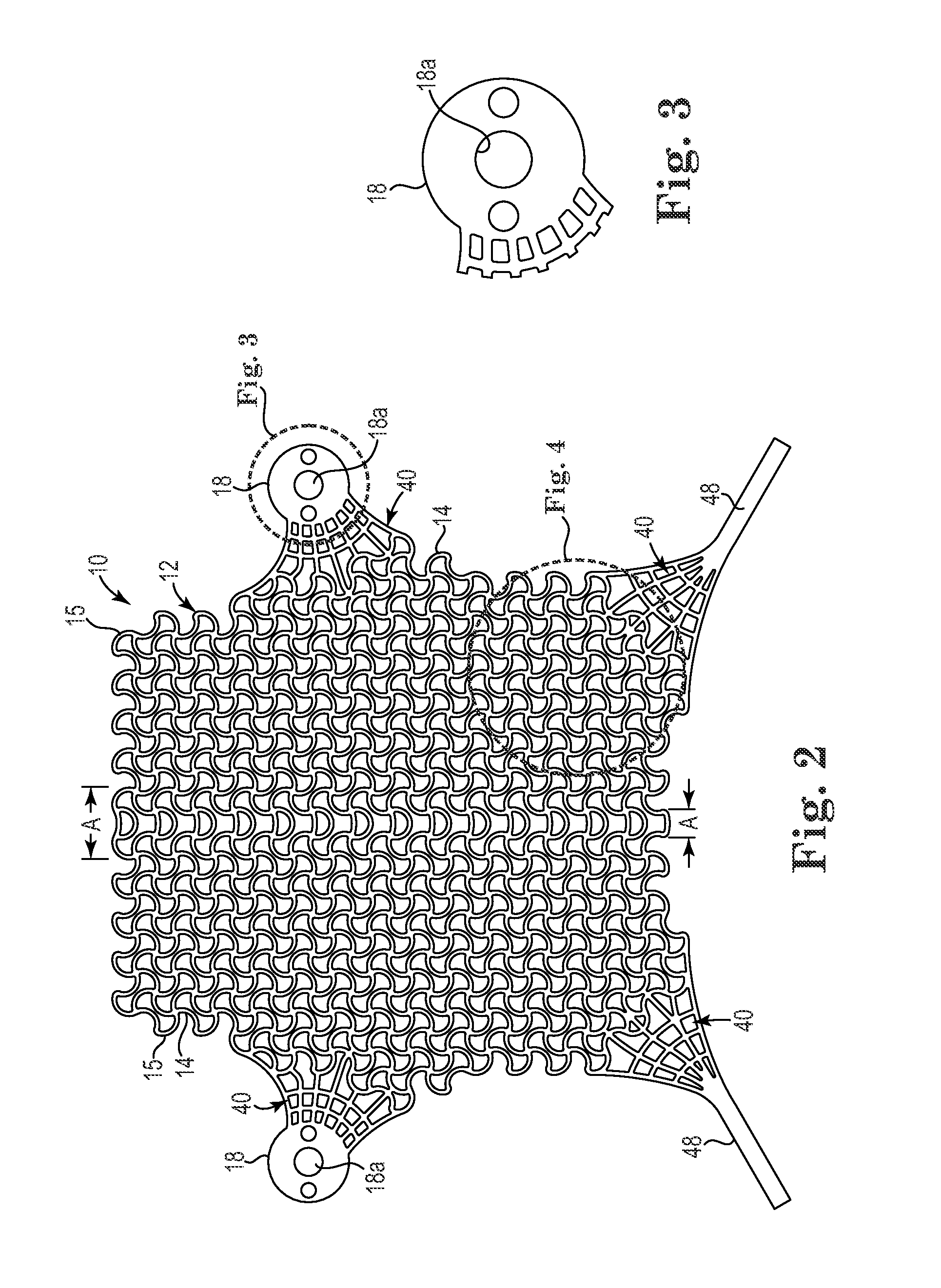
InactiveUS20110144417A1Optimize and increase tissue in-growthIncreased load-bearing capacityAnti-incontinence devicesLigamentsLaser etchingDie casting
A unitary or homogeneous patterned implant is provided. The implant is constructed of patterned cells formed by way of a molding, die casting, laser etching, laser cutting, extruding, and the like. Portions of the implant can be formed into sinusoid or other waveform strut members to control and promote elongation, expansion or contraction along single or multiple axes. As such, controlled and designated stress, tension and compression distribution is promoted across specific or localized areas of the implant.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
High silicon gradient composite aluminum alloy cylinder sleeve material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101709414AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove tribological propertiesDie castingMechanical property
The invention discloses a high silicon gradient composite aluminum alloy cylinder sleeve material and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 13.0-27.0 percent of Si, 0.3-2.0 percent of Fe, 0.5-5 percent of Ni, 1.5-4.0 percent of Cu, 0.3-0.8 percent of Mg, 0.3-0.8 percent of Mn, 0.1-0.5 percent of V, 0.05-0.1 percent of Sr, 0.04-0.1 percent of RE, 0.01-0.1 percent of P and the balance of Al. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out composition design and accurate batching on the materials with preliminary alloys; fusing, covering, refining and inoculation treating; centrifugal casting for forming; thermal treating; and machining and hone machining. The invention is characterized in that a gradient tribology function composite material is obtained by adopting a Sr-P-RE ternary composite modification treatment technology and a centrifugal casting technology controlled by a variable frequency motor, the preparation cost is lower than that of spray deposition technology and a powder metallurgic technology, and the mechanical property and the tribology property of a product is more advantageous than that of the product prepared by a die casting technology; moreover, the prepared cylinder sleeve has more advantageous processing quality and usage effect, and has the advantage of good compatibility with a piston aluminum alloy auxiliary cylinder.
Owner:NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP CORP
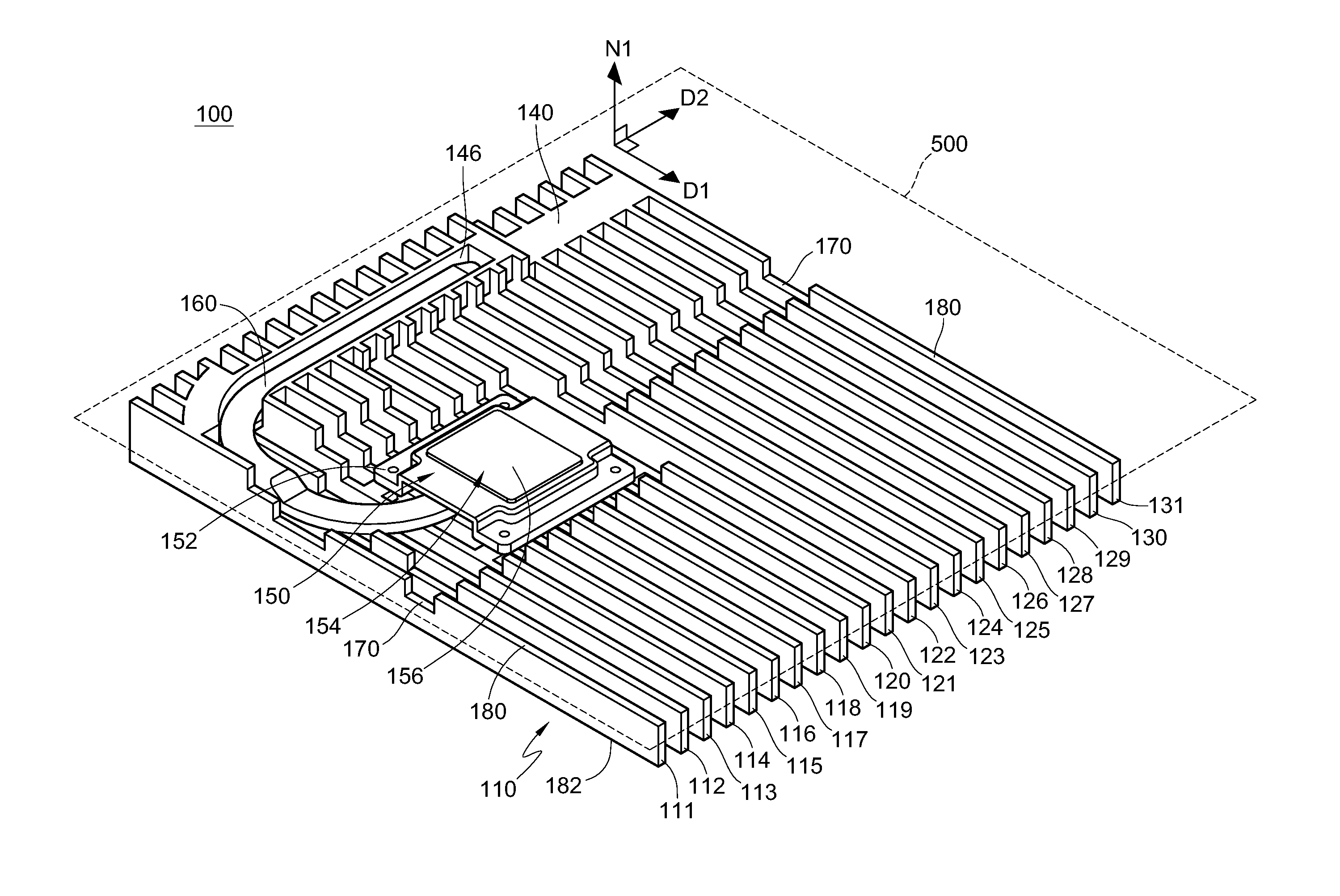
Electronic device and heat dissipation module thereof
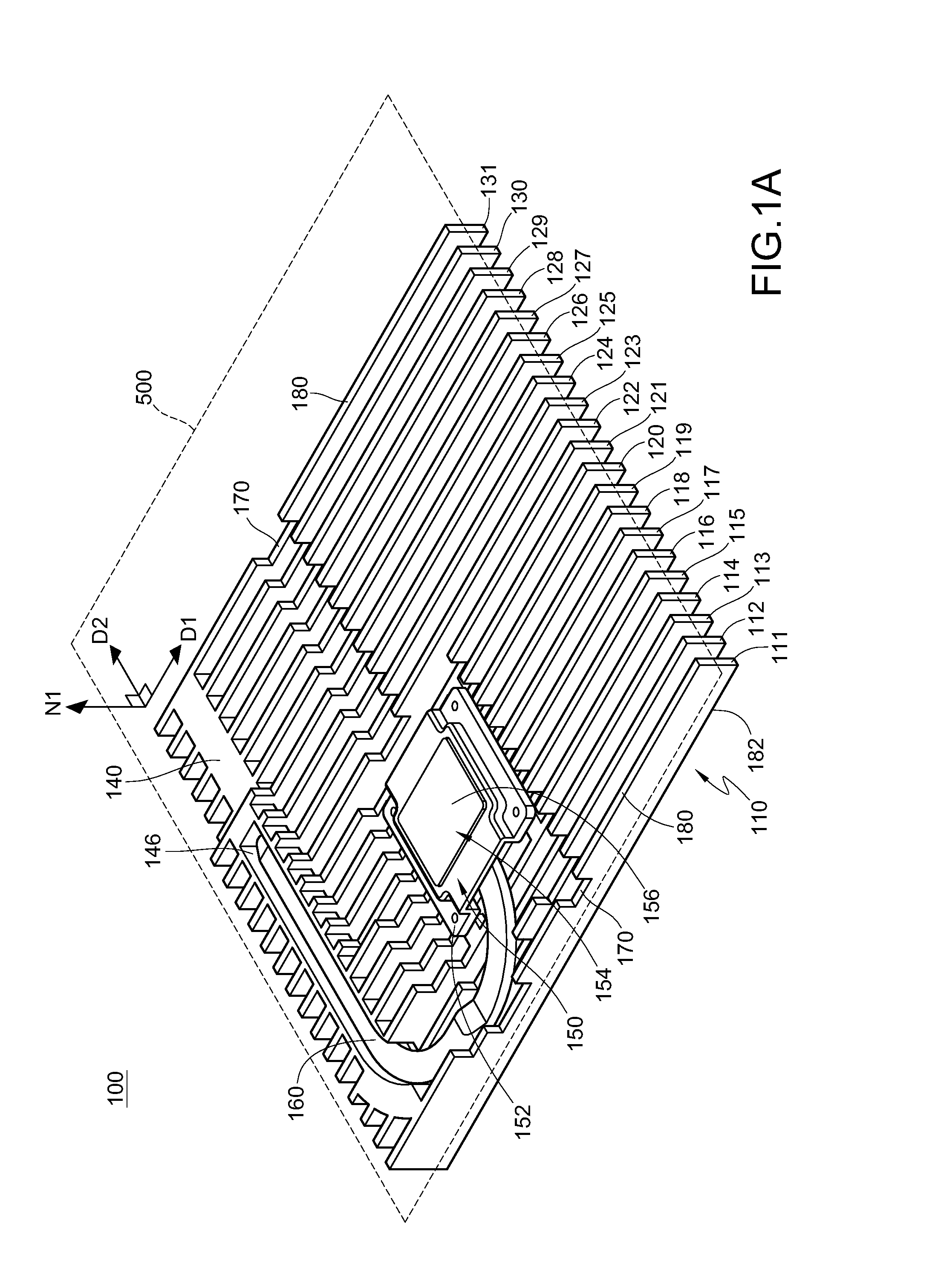
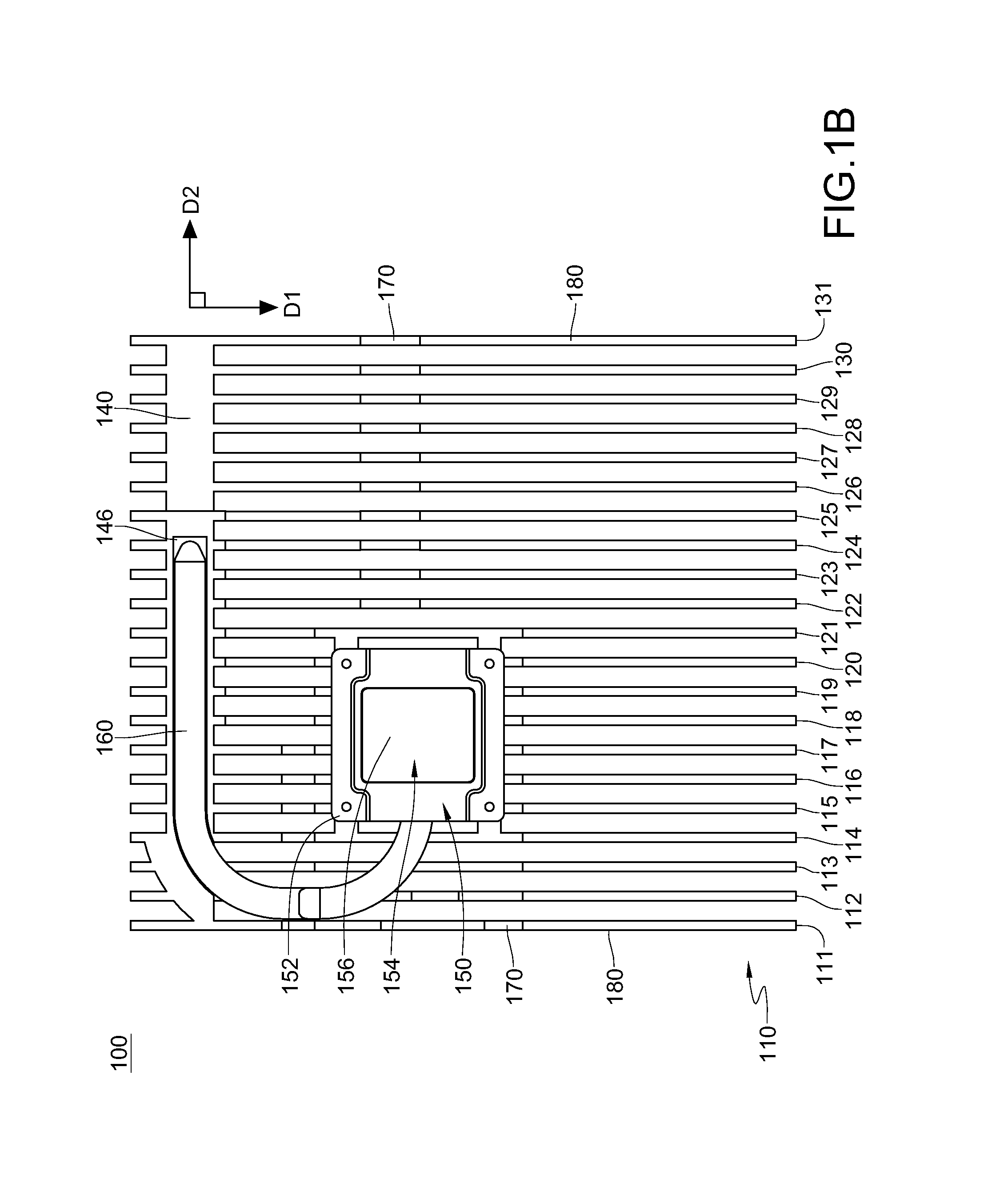
ActiveUS20130294030A1Digital data processing detailsIndirect heat exchangersDie castingComputer module
The disclosure provides an electronic device and a heat dissipation module having an imaginary structural plane. The heat dissipation module includes a fin assembly, a connecting part and a heat pipe. The fin assembly is disposed on the structural plane and includes a plurality of fin elements extending along a first direction. The connecting part is connected to the fin elements. The fin elements are connected to each other via the connecting part. At least one portion of the connecting part is connected to at least one portion of the heat pipe, and the connecting part and the heat pipe both extend along a second direction. The fin assembly and the connecting part are integrated and formed into one piece by die casting. The first direction and the second direction form a first included angle greater than 0 degree.
Owner:INVENTEC PUDONG TECH CORPOARTION +1
Production method for reducing and fining the high-carbon chromium bearing steel D-type impurity
ActiveCN1621538AGood workmanshipMeet production needsProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceAlkalinityHigh carbon
The production process with reduced and fined type-D inclusion in high-carbon chromium bearing steel features the four-step metallurgical process including initial smelting of steel liquid in electric furnace, refining in bottom blowing Ar LF ladle furnace, deairing in VD vacuum furnace, and die casting or continuous casting. By means of the comprehensive deoxidation process including pre-deoxidation of aluminum deposition of the steel from electric furnace, deoxidation with Fe-Si powder diffusion slag in LF site and vacuum carbon deoxidation in VD site; and the new refining process including high alkalinity slag desulfurization in LF site, adoption of low alkalinity slag in the VD site and reducing free CaO inside slag, the present invention reaches the aims of reducing and fining type-D inclusion.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
Pressing roller holder for stretching structure
The invention relates to a pressure roller support for fixing double pressure rollers in a drafting mechanism, which comprises a spring for pressing the double pressure rollers and a fixing frame for the double pressure roller shafts. The holder is a die-cast or injection-molded part, wherein the holder is cast onto the spring. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for producing the pressure roller support, in which the spring is inserted into the mold at least in a partial region so that the holder is connected to the spring during the casting process.
Owner:MASCHINENFABRIK RIETER AG
Diphase stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a diphase stainless steel, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.05 percent of C, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of Si, 0 to 2.0 percent of Mn, 22 to 27 percent of Cr, 0 to 2.0 percent of W, less than or equal to 0.1 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of P, 0 to 0.003 percent of B, more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.2 percent rare earth of which the Ce content is more than 50 percent, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein a casting blank of the diphase stainless steel comprises over 60 percent of isometric crystal. A method for manufacturing the diphase stainless steel comprises the following steps of: performing smelting, die casting or continuous casting to form the casting blank, wherein the thickness of a steel die is more than 30 mm during the die casting to ensure that the cooling velocity of the steel is more than 10 DEG C per minute, and in the process of the continuous casting, the degree of superheating of the casting is between 30 and 100 DEG C, and the casting speed is over 1.2 meters per minute; putting the casting blank into a heating furnace, heating the casting blank to the temperature of between 1,100 and 1,250 DEG C, performing heat preservation on the casting blank, and then forging or hot-rolling the casting blank to a required thickness; and annealing and pickling a steel plate or a plate coil after forging or hot-rolling, and controlling the annealing temperature to be between 1,000 and 1,100 DEG C. The diphase stainless steel has high corrosion resistance and high hot-working performance, and can be widely applied in the fields of petroleum, chemical industry, papermaking, marine engineering and the like in rigorous corrosion environments.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD +1
Recessed LED Downlight
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Short-flow preparation method of micro-sized spherical titanium powder
ActiveCN101716686AReduce dehydrogenation processShort processTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusDehydrogenationDie casting
Owner:江苏金物新材料有限公司
Aluminum-silicon alloy having reduced microporosity
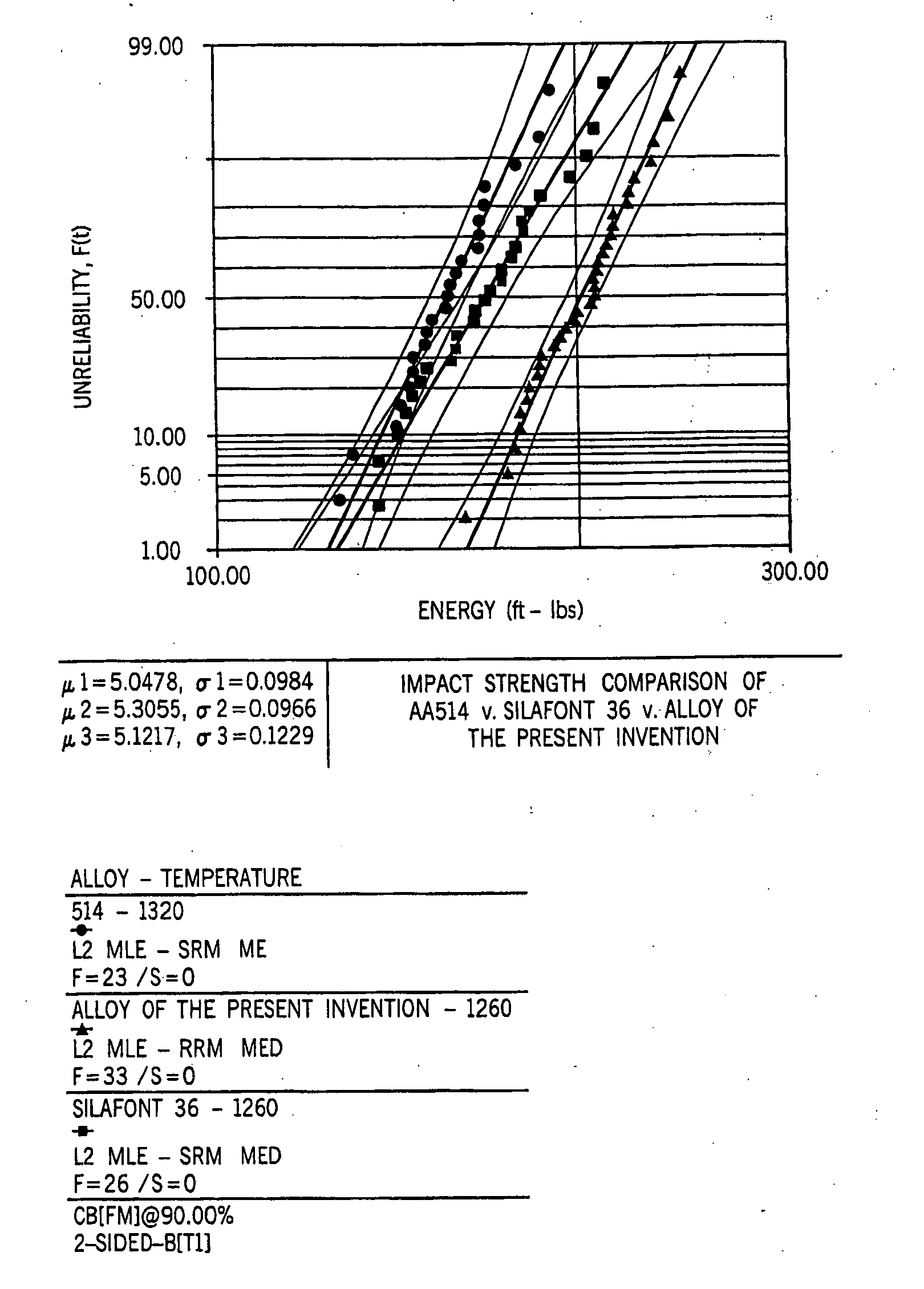
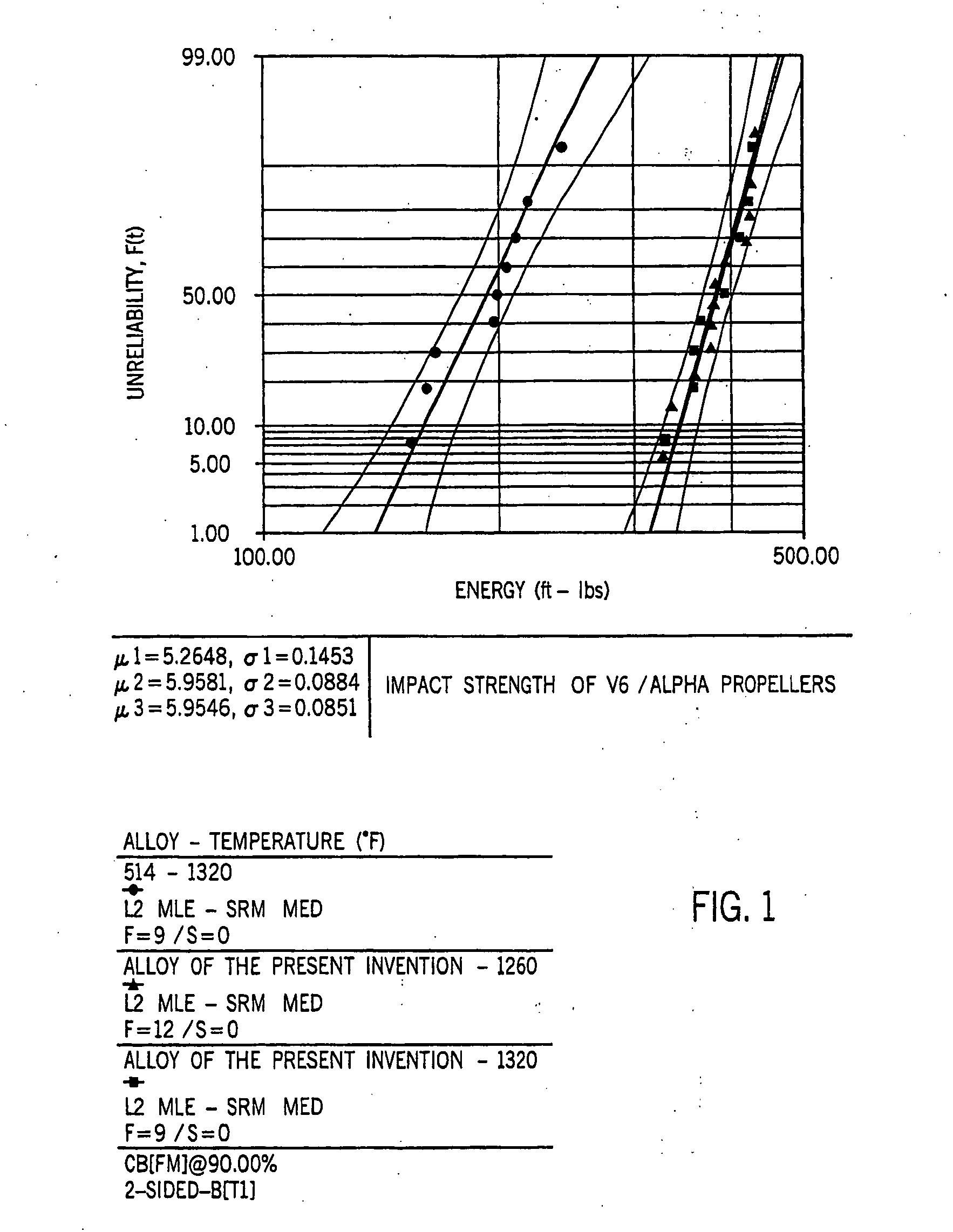
An aluminum silicon die cast alloy having a very low iron content and relatively high strontium content that prevents soldering to dies into die casting process. The alloys of the present invention also have a modified eutectic silicon and modified iron morphology, when iron is present, resulting in low microporosity and high impact properties. The alloy comprises 6-22% by weight silicon, 0.05 to 0.20% by weight strontium and the balance aluminum. Preferably, the alloy of the present invention contains in weight percent: 6-20% silicon, 0.05-0.10% strontium, 0.40% maximum iron and most preferably 0.20% maximum iron, 4.5% maximum copper, 0.50% maximum manganese, 0.60% maximum magnesium, 3.0% maximum zinc, balance aluminum. On cooling from the solution temperature, the strontium serves to modify the eutectic silicon structure as well as create an iron phase morphology change if iron is present, facilitating feeding through the aluminum interdendritic matrix. This, in turn, creates a finished die cast product with extremely low levels of microporosity defects. The strontium content also appears to create a non-wetting monolayer of strontium atoms on the surface of a molten casting, preventing die soldering, even at very low iron contents. The alloy may be used to cast any type of object and is particularly suited for casting outboard marine propellers, driveshaft housings, gear case housings, Gimbel rings and engine blocks.
Owner:BRUNSWICK CORPORATION
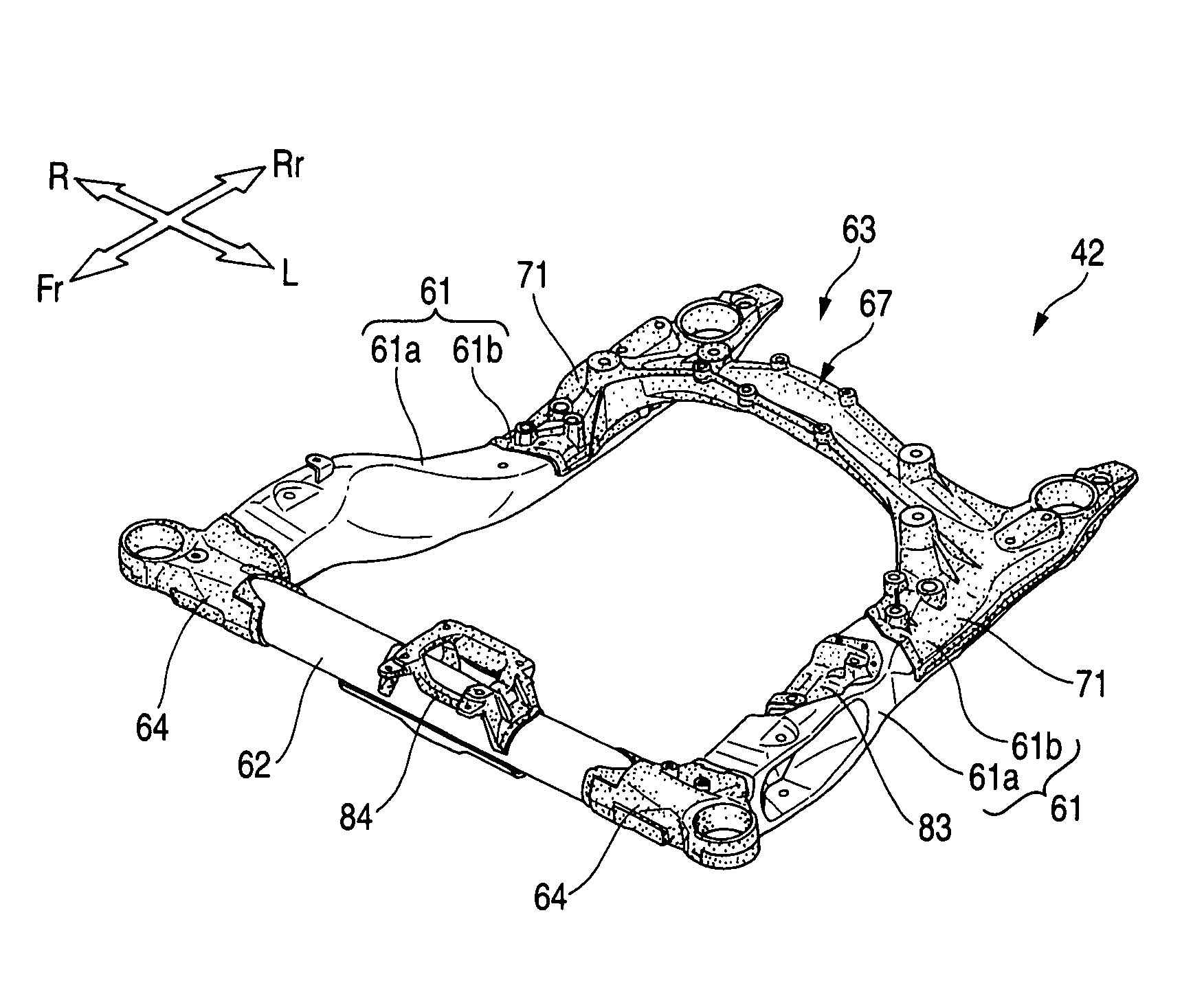
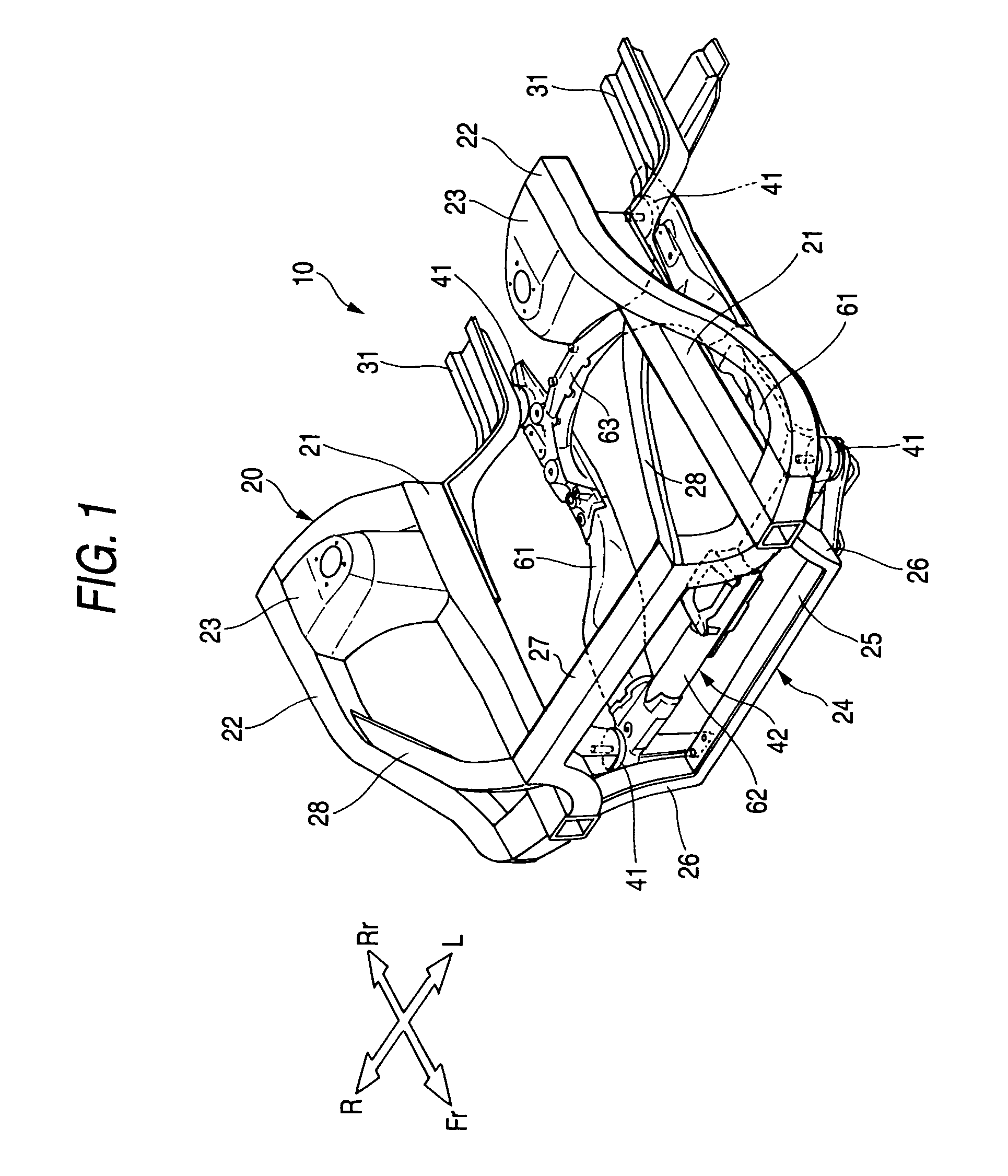
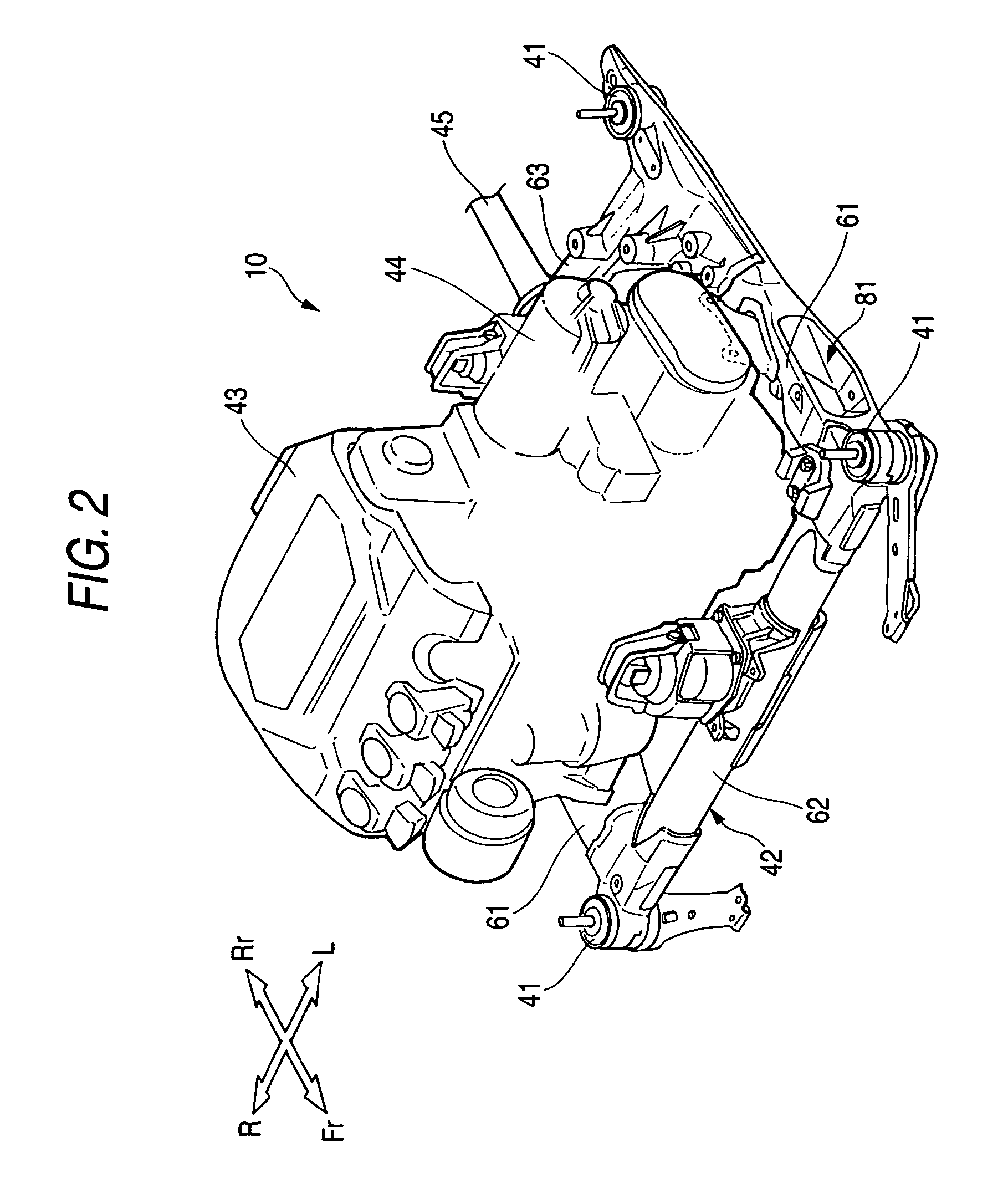
Body frame structure
InactiveUS7520514B2Improve transmission performanceMaintain performanceUnderstructuresSuperstructure subunitsVehicle frameCamber angle
A front subframe 42 is formed of an aluminum alloy into a frame that is formed substantially into a shape of parallel crosses or into a rectangular shape and is made up of left and right front joint portions 64, 64 and left and right rear joint portions 71, 71 which are disposed at corners of the frame that is formed substantially into the shape of parallel crosses or the rectangular shape, and left and right longitudinal members 61, 61, and front and rear cross members 62, 67 which connect the joint portions 64, 64, 71, 71 together. The left and right front joint portions 64, 64 and the left and right rear joint portions 71, 71 are formed of an aluminum alloy die-cast product, whereas the left and right longitudinal members 61, 61 are formed of an aluminum alloy wrought product. In addition, connecting locations 76 . . . of a camber angle adjusting mechanism 157 are formed of an aluminum alloy die-cast product. Additionally, a rear cross member compound 63 is formed of an aluminum alloy die-cast product.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com