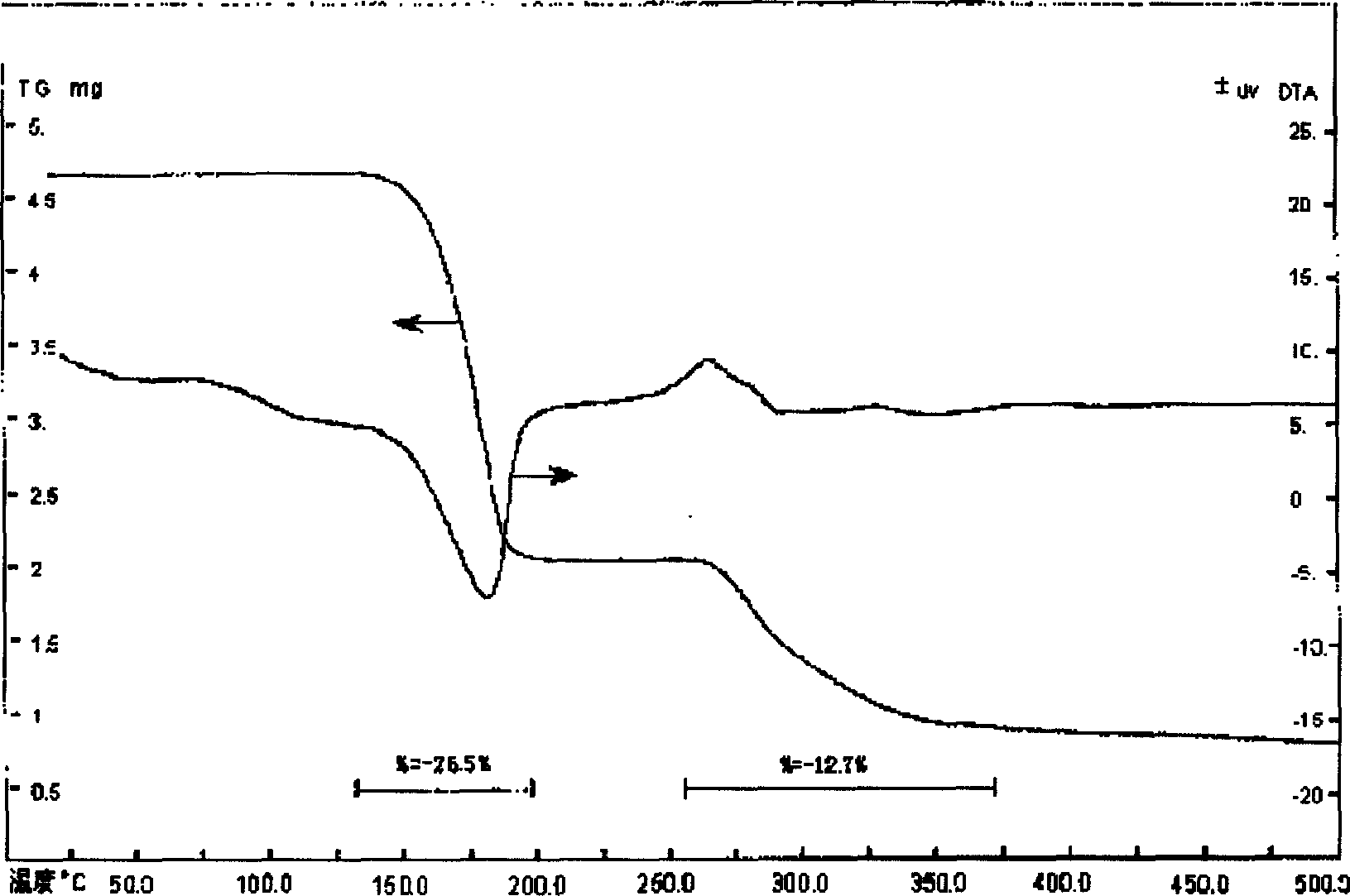
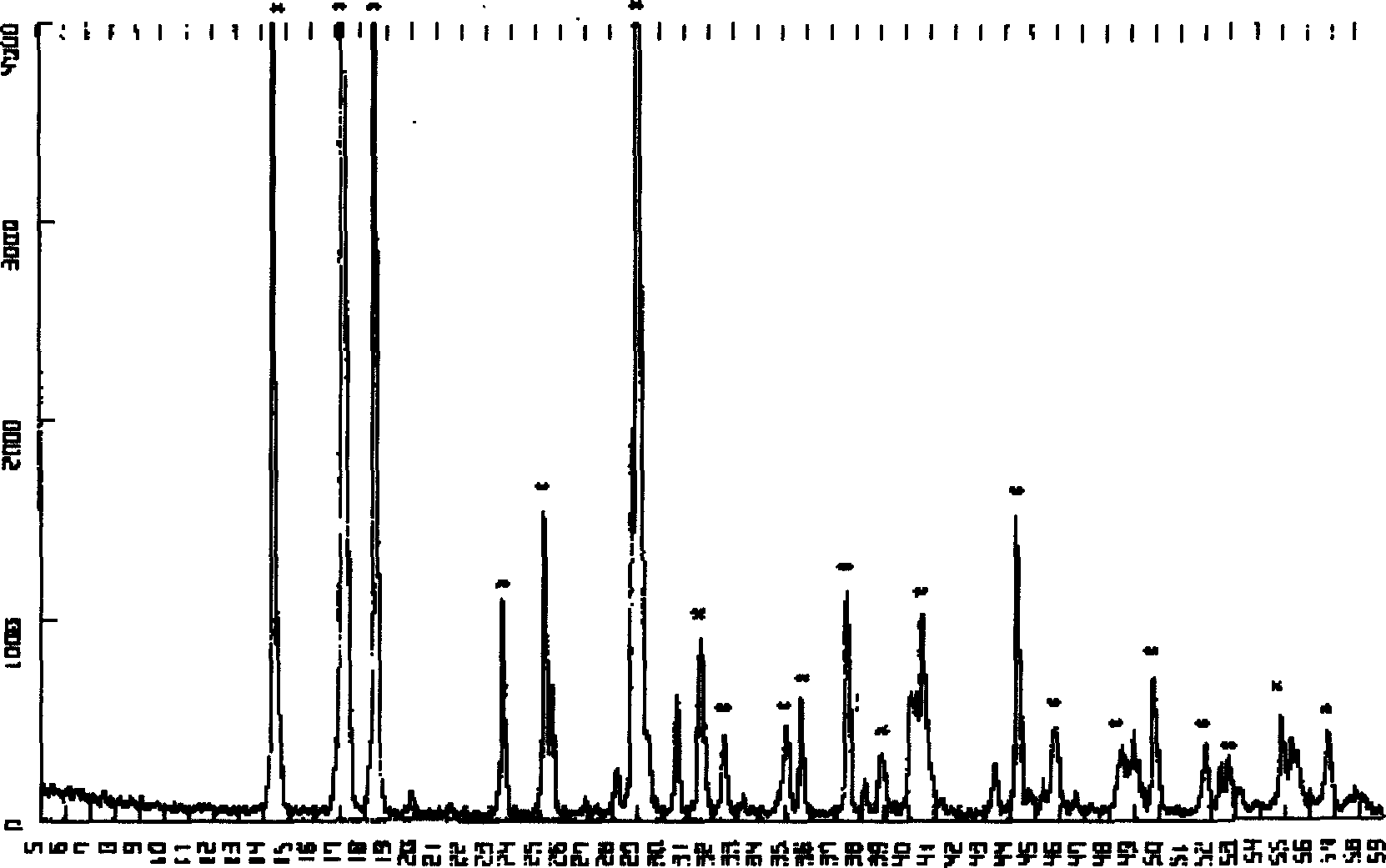
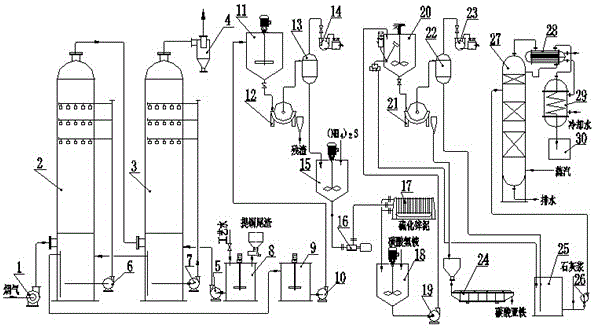
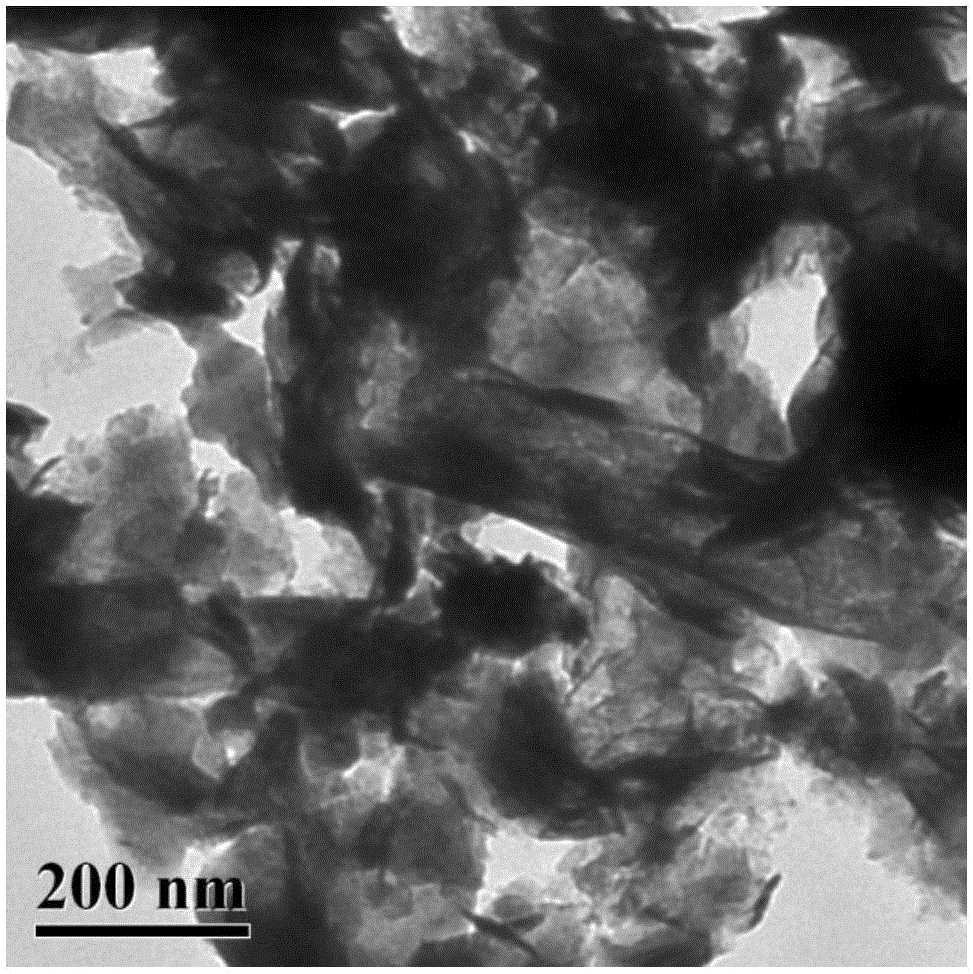
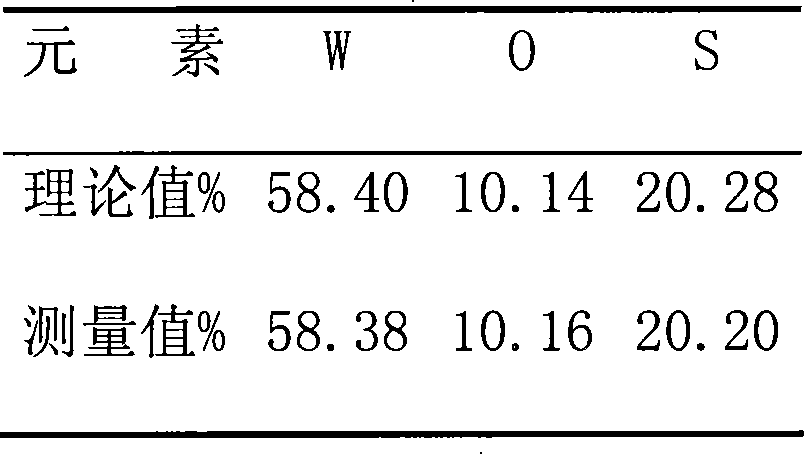
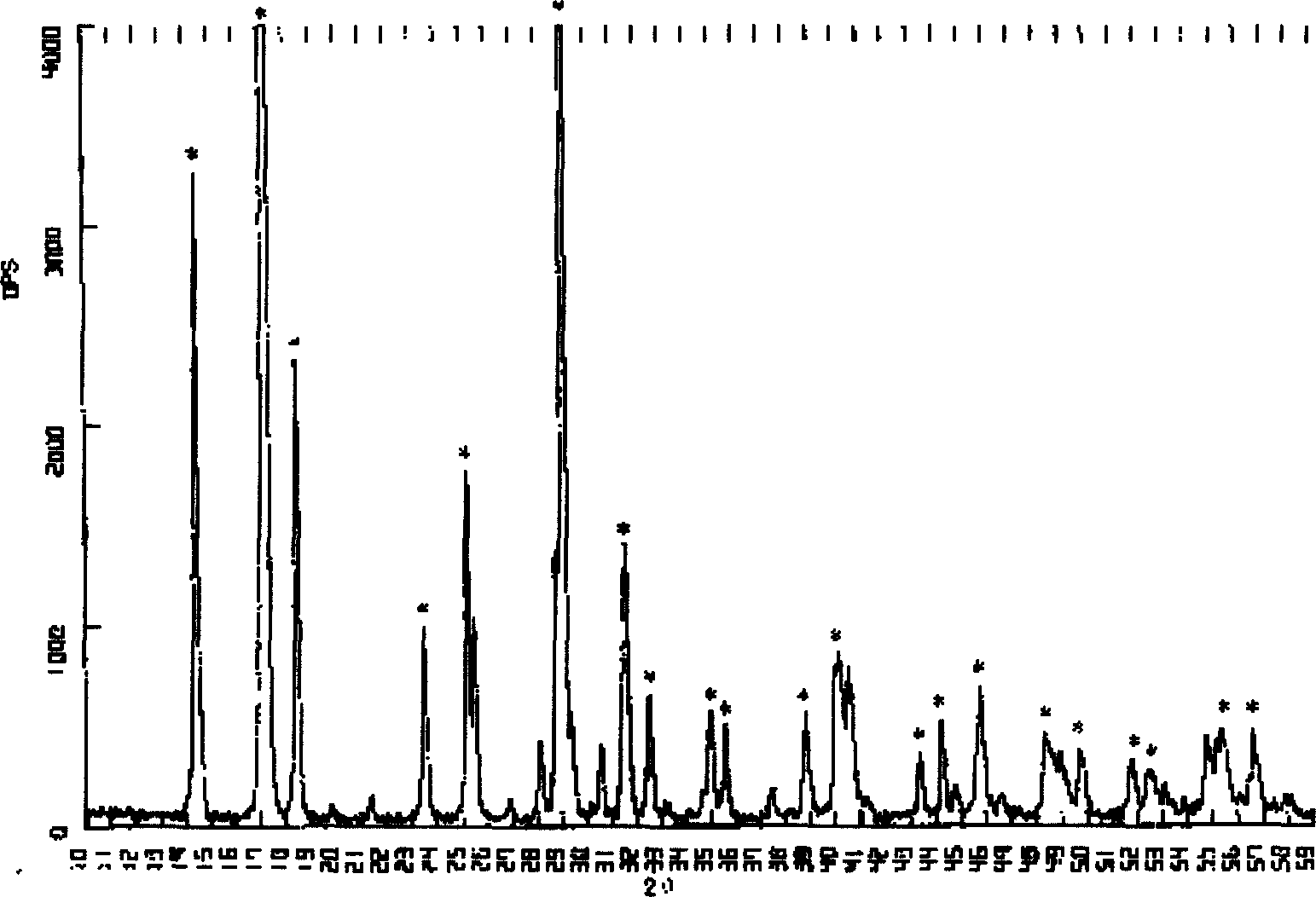
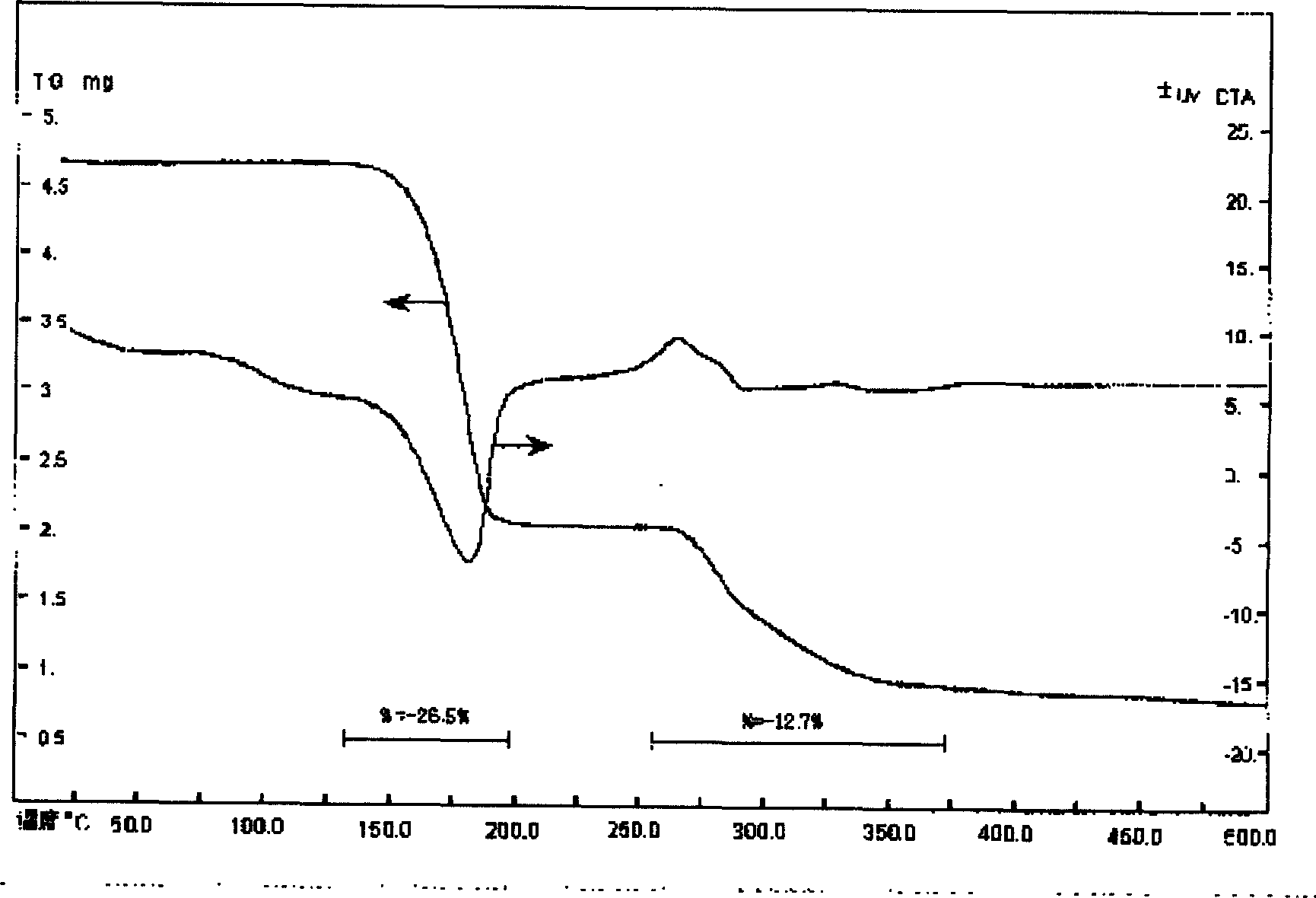
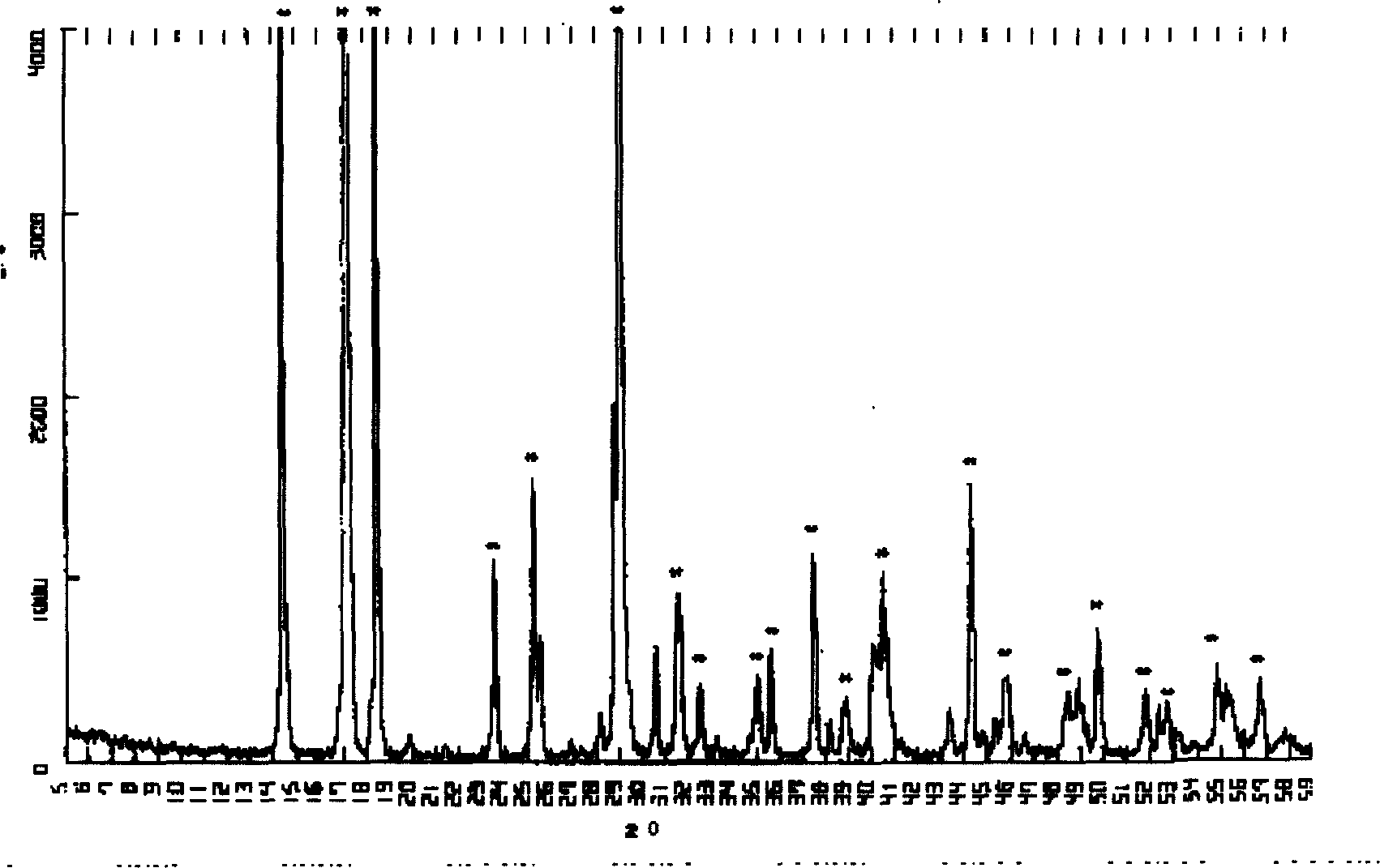
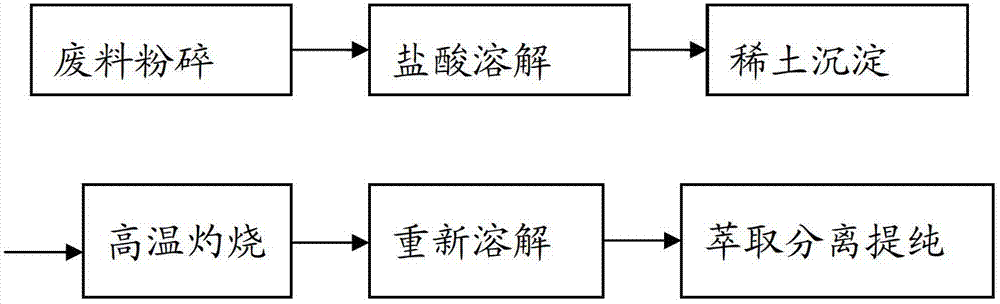
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
157 results about "Ammonium sulphide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ammonium sulfide, also known as diammonium sulfide, is an unstable salt with the formula (NH4)2S. Aqueous solutions purporting to contain this salt are commercially available. With a pKa exceeding 15, the hydrosulfide ion cannot be deprotonated to an appreciable amount by ammonia.
Compositions for improving the organoleptic qualities of cooked foodstuffs
Compositions for generating a cooked flavor in a foodstuff, comprising specified flavor precursors that react on heating to generate the flavor and maintain a reactive association after inclusion in the foodstuff. The compositions may include combination of a sulphur source, e.g. hydrogen sulphide, methane thiol, a sulfur-containing amino acid, thiamine, cystine, sodium sulphide, ammonium sulphide, ammonium polysulphide, onions, garlic, shallots, eggs, methionine, and mixtures thereof, and at least one reductone, e.g. a furanone, a ketone, a pyrone, an aldehyde, a carbonyl compound, isomaltol, maltol, pyruvaldehyde, hydroxyacetone, 3-deoxyglucosone, 5-hydroxy-5,6-dihydromaltol, 2,3-butanedione, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, a process flavor, cooked vegetable concentrates, soy sauce, and mixtures thereof.
Owner:KERRY INGREDIENTS UK
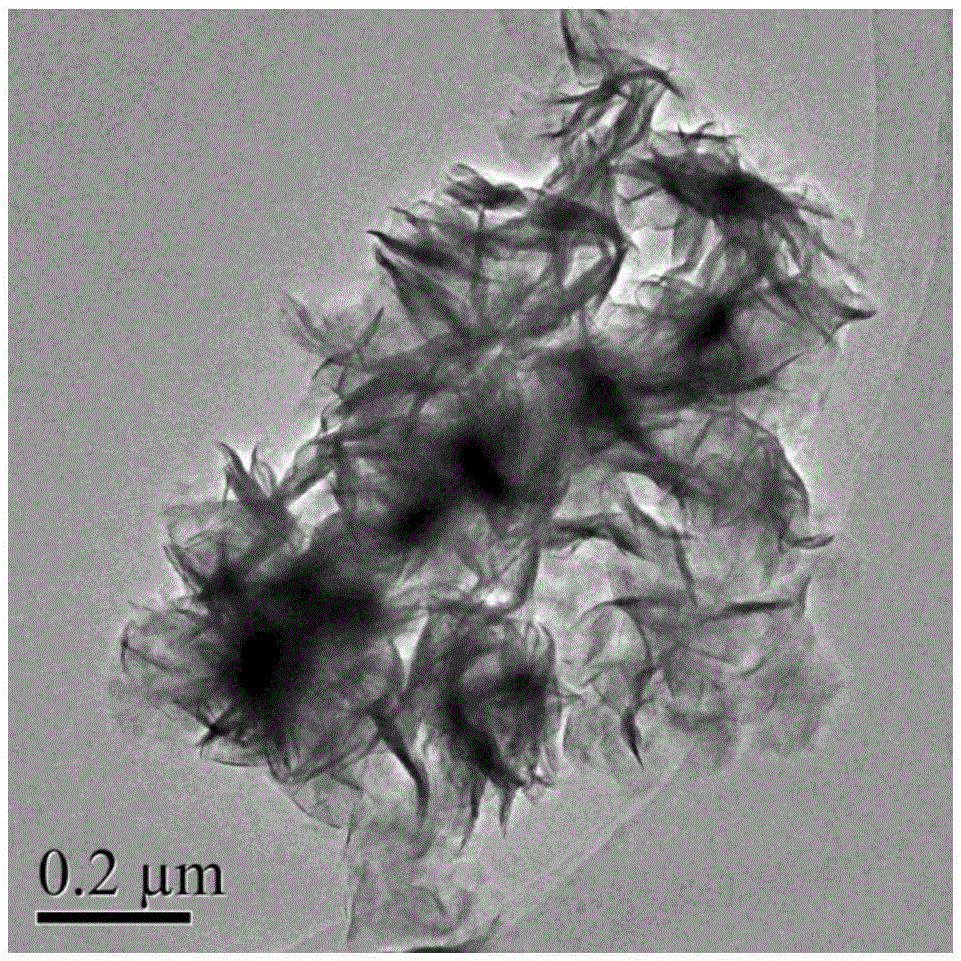
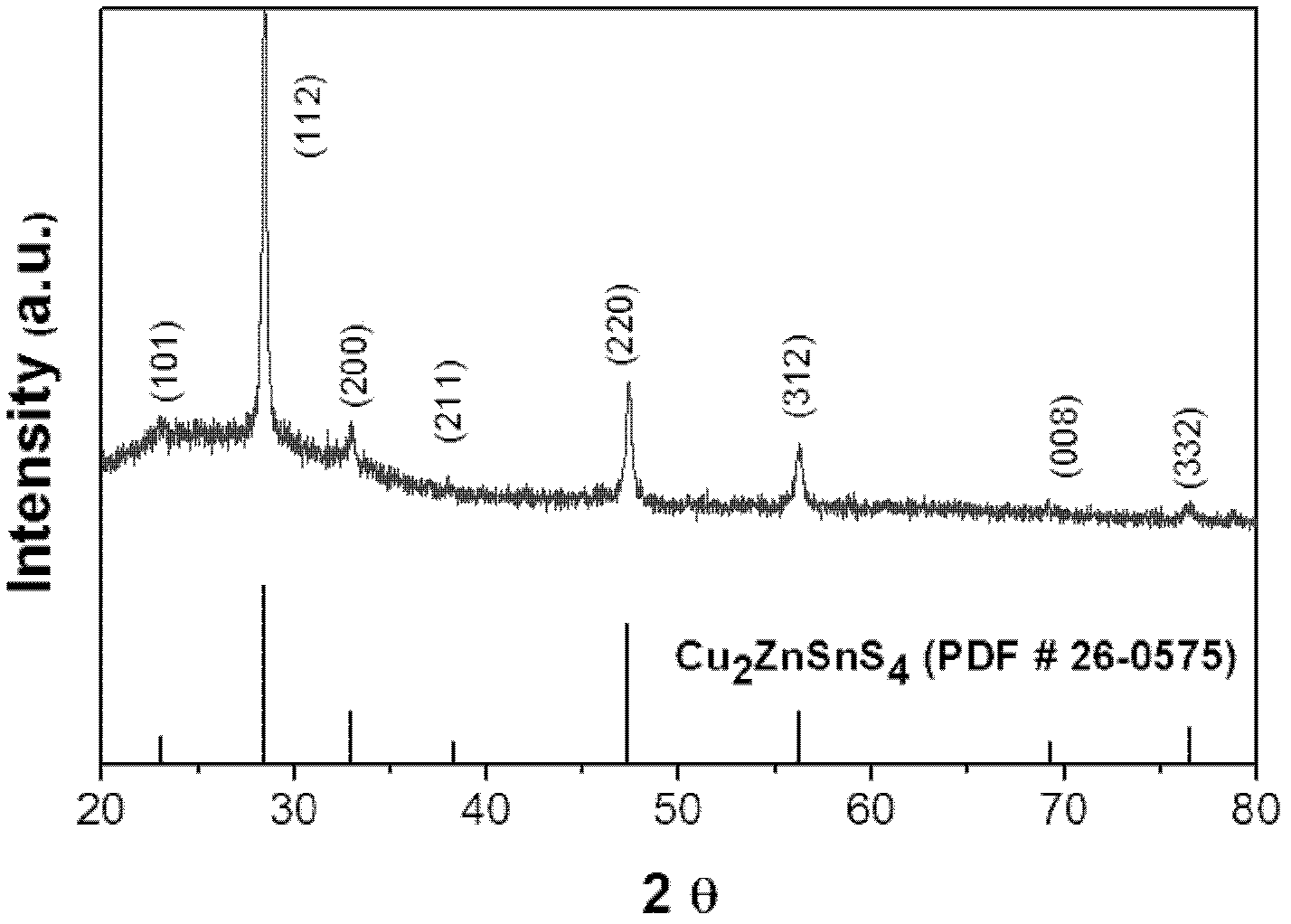
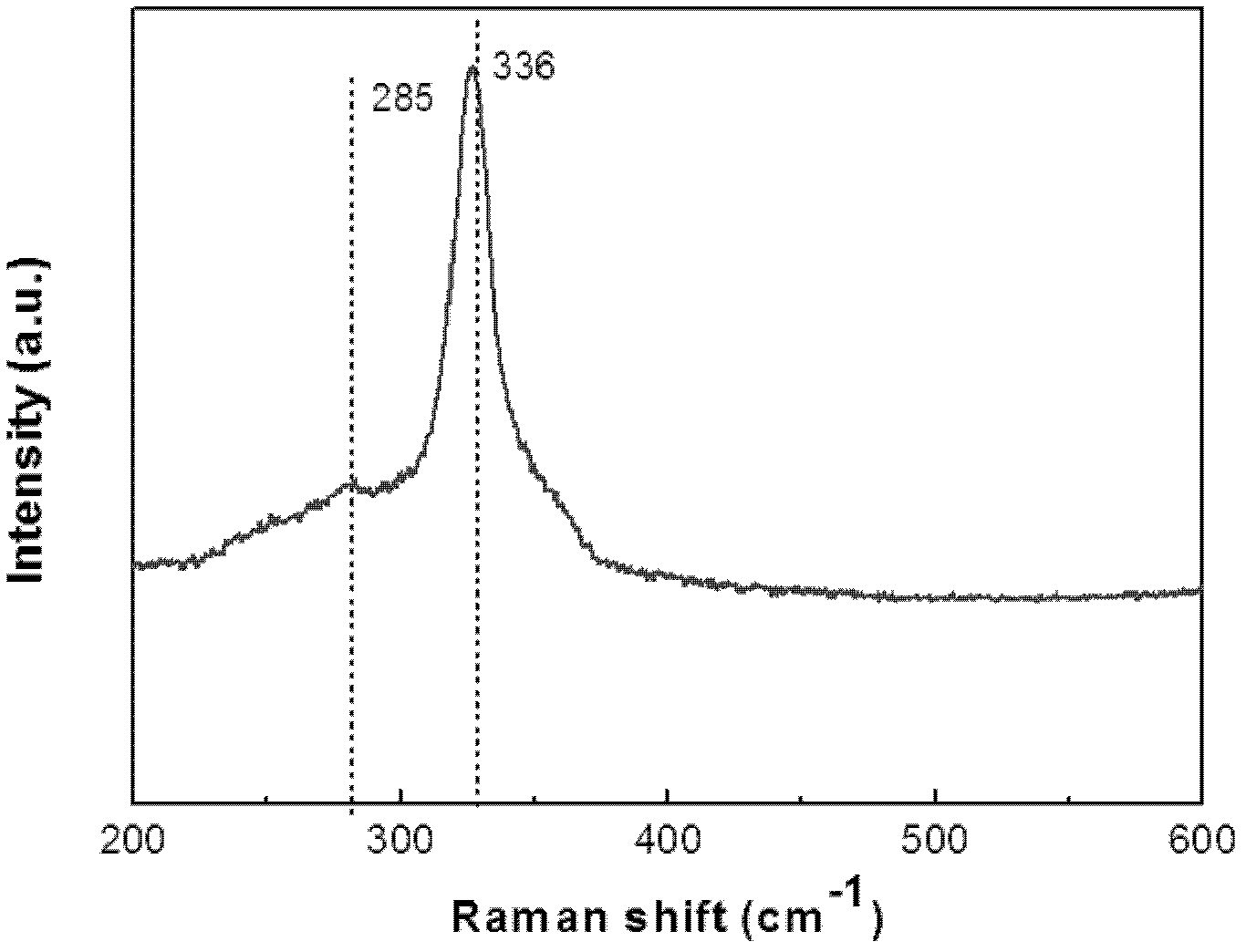
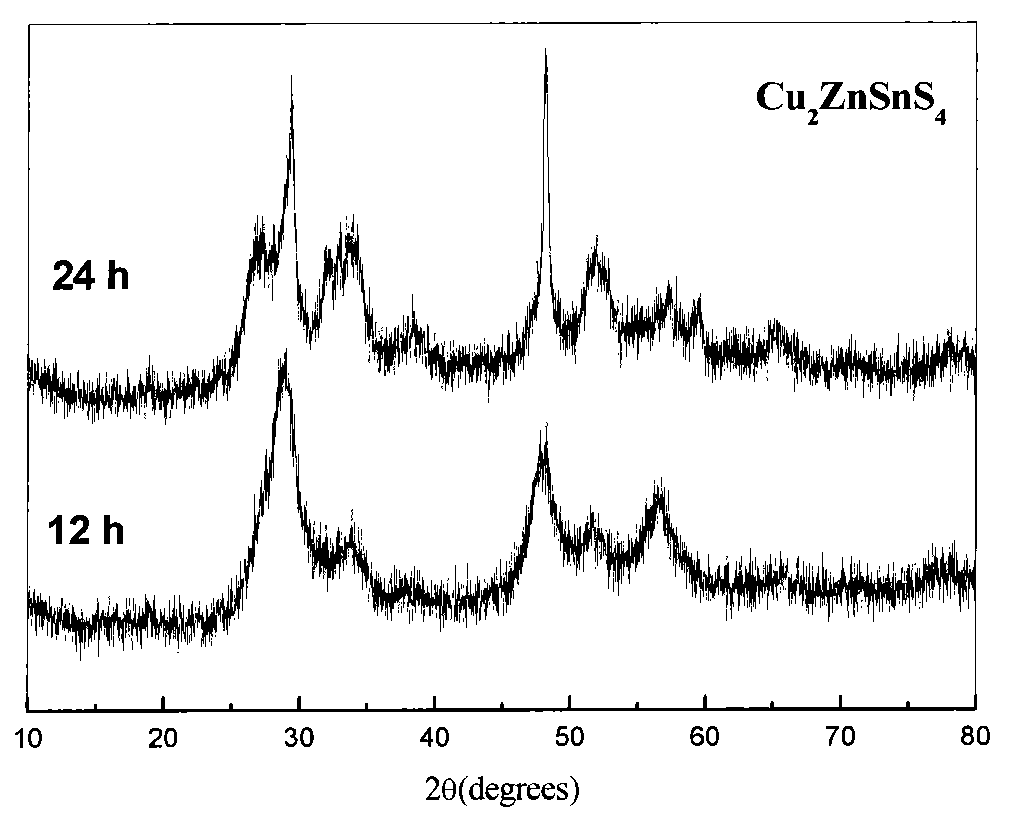
Preparation method of Cu-Zn-Sn-S thin film
InactiveCN102251235AReduce usageSolve unmanageable problemsFinal product manufactureSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingAmmonium sulphidePotassium sulfide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Cu-Zn-Sn-S thin film, comprising the steps of: by adopting a successive ionic layer adsorption reaction method, sequentially or alternatively soaking one substrate in a cation precursor solution and an anion precursor solution to prepare a Cu2SnSx film and ZnS film laminated precast layer structure or a Cu2S film and ZnSnSx film laminated precast layer structure, and then performing heat treatment to obtain the Cu-Zn-Sn-S thin film; the cation precursor solution comprises at least one of copper ions, stannum ions and zinc ions, and the anion precursor solution is selected from at least one of a sodium sulfide solution, a potassium sulfide solution and an ammonium sulfide solution; the substrate is selected from one of glass, PI (polyimide), a stainless steel plate, a molybdenum plate and a titanium plate. The preparation method of Cu-Zn-Sn-S thin film not only solves the problem that the metal components are difficult to control, but also prevents the copper ions from moving to the surface of the film to form a sulfur copper phase. The preparation method is simple and applicable, low in cost and suitable for industrialization production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
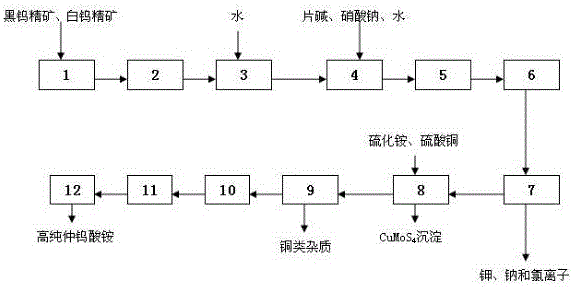
Preparation method of low-potassium low-sodium low-chloride high-purity ammonium paratungstate
A preparation method of low-potassium low-sodium low-chloride high-purity ammonium paratungstate is characterized in that wolframite concentrate and scheelite concentrate are taken as raw materials, the content of impurities in such auxiliary materials as deionized water, ammonium sulfide, copper sulfate and a strippant is controlled, and high-purity ammonium paratungstate is prepared by the procedures of ore blending and ball milling, soda boiling for decomposition, ion exchange, molybdenum removal, crystallization, drying and the like. During conversion between a prepeak solution and a high peak solution in the desorption process, the concentration of WO3 is larger than 100 g / l; during conversion between the prepeak solution and a rear section solution, the concentration of WO3 is larger than 150 g / l; the concentration of WO3 in the taken high peak solution is larger than 220 g / l, wherein K<=5 mg / l, Na<=15 mg / l and Cl<=15 g / l. The content of total impurities in high-purity ammonium paratungstate prepared by the method can be controlled within 70 ppm, which is far lower than the demand for the content (smaller than 177 ppm) of total impurities in zero grade products of the 'paratungstate' national standard (GB / T10116-2007), particularly, Na<=2 ppm, K<=3 ppm and Cl<=10 ppm.
Owner:JIANGXI RARE EARTH & RARE METALS TUNGSTEN GRP
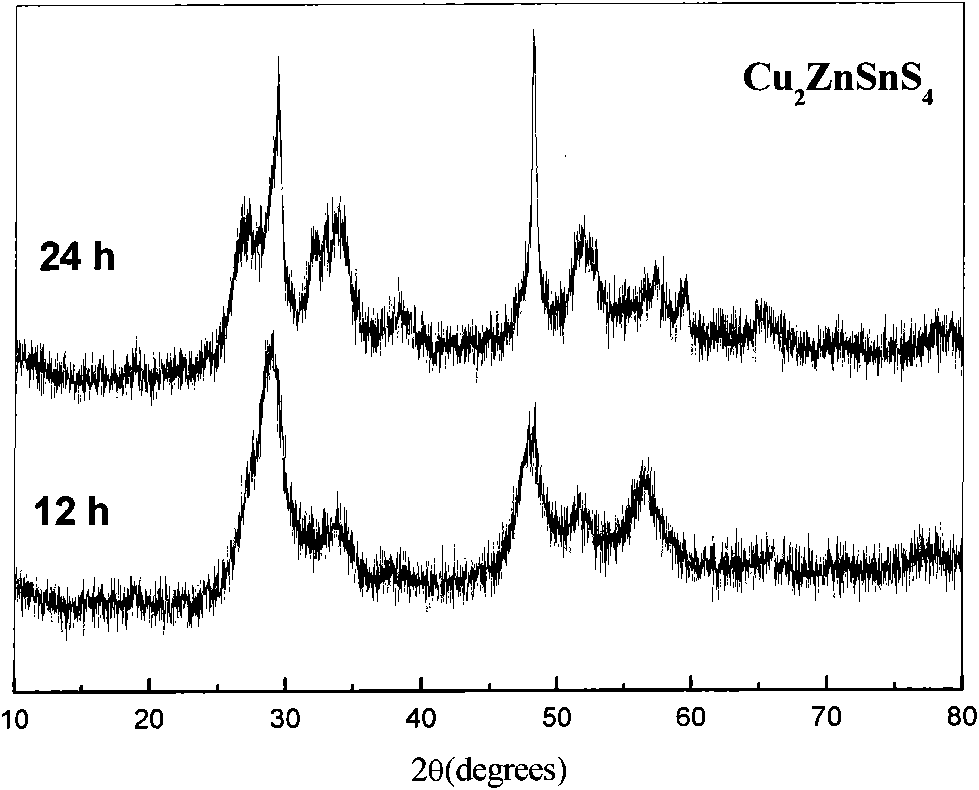
Preparation method of Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material
InactiveCN101780974AAdjustable controlSimple preparation processTin compoundsFinal product manufactureAmmonium sulphideSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a preparation method of Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material and the method uses a mixed solution of stannous chloride, zinc chloride and copper chloride and ammonium sulfide solution as raw materials. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing solution co-precipitation by using the raw materials according to a ratio, secondly performing high pressure hydrothermal treatment, and separating to obtain the Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material. The methods of solution co-precipitation and high pressure hydrothermal treatment are adopted to prepare the Cu2ZnSnS4 semiconductor material and the method has the advantages that the stoichiometric ratio of the product is easy to control and can be adjusted, the preparation technology is simple, the cost is low, the method is environmentally friendly, etc. the obtained material can be used as absorbing layer to be used in thin film solar cells.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Process for conversion of waste fluid streams from chemical processing plants to beneficiary agriculture products
The present invention is directed to the conversion of gas streams comprising ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and water in the form of liquids or gases that are generated by petroleum refineries and coke ovens to beneficiary agriculture products, by forming ammonium sulfide and then converting the ammonium sulfide, using sulfuric acid, to pure ammonium sulfate.
Owner:TESSENDERLO KERLEY INC
Method for preparing (NH4)2WS4
The present invention relates to improved preparation process of high purity chemical. High purity ammonium tetrathiotungstate is prepared through the reaction between ammonium metatungstate or tungsten trioxide and ammonium sulfate solution. Preparing high purity ammonium tetrathiotungstate in the said process of the present invention has ammonium sulfate amount near the required stoichiometric amount, mild reaction condition, short reaction period, less waste exhaust, high product yield, high product purity, and no need of treating virulent and effluvial hydrogen sulfide gas.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Method and device for removing SO2 in flue gas with copper extracting tailings and recycling copper extracting tailings
ActiveCN106422716AWith spray densityIncrease contact areaGas treatmentDispersed particle separationMetasilicateAmmonium sulfide
The invention relates to a method and device for removing SO2 in flue gas with copper extracting tailings and recycling the copper extracting tailings, and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection. Ferrous metasilicate (Fe2SiO4), magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4), hedenbergite (CaFeSi2O6) and other sulfur removal active substances in the copper extracting tailings are used for reacting with SO2 in the flue gas in an aqueous solution to generate sulfite, then sulfate is generated under the action of oxygen in the flue gas, the SO2-containing flue gas makes contact with copper extracting tailing slurry, SO2 is absorbed, and thus the flue gas is purified; by adding ammonium sulfide, ammonium bicarbonate and lime milk step by step, iron ions, zinc ions, copper ions, ammonium ions and other ions in the sulfur removal slurry can be resourcelized to be reused.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Metal cation doped molybdenum disulfide material, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN106608652AImprove thermal stabilityAcid resistantPhysical/chemical process catalystsMolybdenum sulfidesAmmonium sulfideStrong acids
The present invention relates to a metal cation doped molybdenum disulfide material, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method comprises: dispersing and dissolving a molybdenum precursor in an ammonium sulfide solution, adjusting the pH value of the solution to more than or equal to 10 and less than or equal to 14 with ammonia water, carrying out a reaction at a temperature of 50-100 DEG C, adding a coordination reagent protected metal coordination compound solution to the solution after the reaction, stirring until achieving a dried state, carrying out vacuum drying, grinding the obtained solid powder, placing in an inert atmosphere (nitrogen or argon) gas flow, treating for 0.5-8 h at a temperature of 380-500 DEG C, and cooling to a room temperature to prepare the metal cation doped molybdenum disulfide material. According to the present invention, the metal cations are uniformly dispersed between each layer of molybdenum disulfide through the doping; the crystal structure of the metal cation doped molybdenum disulfide material maintains the two-dimensional layered structure of molybdenum disulfide; the material interlayer spacing fluctuates between 6.15-10.0 angstrom according to different types and different contents of the doped metals; and the metal cation doped molybdenum disulfide material has advantages of good thermal stability, strong-acid resistance and large specific surface area, and has potential applications in the fields of catalysis, electrode materials, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing dithio-metal acid ammonium
ActiveCN101624207AHarm reductionEasy to operateMolybdeum compoundsSulfur compoundsAmmonium sulphideSulfur
The invention discloses a method for preparing dithio-metal acid ammonium, which comprises the following steps: adding ammonium sulfide water solution into metal acid ammonium and / or metal oxide, reacting the mixture, standing the mixture and filtering, washing and drying the mixture to obtain a product, wherein the metal is selected from one or more metals from group VIB, and the molar ratio of the sulfur to the metal is 2-2.1. The provided method has the characteristics of simple operation, high product yield and purity, little harm to environments and operators, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing (NH4)2MoS4
The present invention relates to improved preparation process of high purity chemical. High purity ammonium tetrathiomolybdate is prepared through the reaction between ammonium para-molybdate or molybdenum trioxide and ammonium sulfate solution. Preparing high purity ammonium tetrathiomolybdate in the said process of the present invention has ammonium sulfate amount near the required stoichiometric amount, mild reaction condition, short reaction period, less waste exhaust, high product yield, high product purity, and no need of treating virulent and effluvial hydrogen sulfide gas.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Elemental analysis determination method and device
InactiveCN103792223AReduce distractionsSlow heating ratePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationSodium hydrosulfideElemental analysis
The invention discloses an elemental analysis determination method and device. The elemental analysis determination method comprises the following steps: adding an inorganic compound capable of releasing hydrogen in pyrolysis into a to-be-detected sample and mixing the inorganic compound with the sample uniformly; carrying out pyrolysis on the mixture at a certain temperature, enabling an element to form a volatile matter, and determining the volatile matter by an atom spectrogram, wherein the inorganic compound for releasing hydrogen in pyrolysis is sodium bisulfide, potassium hydrogen sulfide, ammonium sulfide, ammonia hydrogen sulfide, ammonium iodide, hydrogen sulfide or hydrogen iodide, and the weight of the added inorganic compound is 0.2-100 times the weight of the sample. According to the invention, an inorganic hydrogen release reagent and a curie point pyrolyser are used, and the advantages of low analysis cost, less interference, high element volatile matter formation speed, high sampling efficiency of to-be-detected elements and the like are realized, and the method is a rapid and accurate analysis method.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing micron-grade zinc oxide with high fluorine and chlorine crude zinc oxide as raw material
InactiveCN105129839ALong runLoose process conditionsZinc oxides/hydroxidesZinc hydroxideAmmonium sulphide
The invention relates to a method for producing micron-grade zinc oxide with high fluorine and chlorine crude zinc oxide as a raw material. The method comprises the process: carrying out wet-metallurgy ammonium salt-ammonia water leaching, oxidizing to remove iron, adding a zinc powder and ammonium sulfide and removing impurities, and neutralizing to prepare zinc hydroxide; and then carrying out 1200 DEG C high-temperature calcination in a dry calcining furnace, and thus preparing the micron-grade zinc oxide with the purity of 99.95%. The process conditions are loose, the operations are simple and convenient, and impurity removal is efficient, controllable and reliable.
Owner:HUNAN HUAXIN RAREANDPRECIOUS METALS TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing manganous carbonate by using waste slag and waste water containing manganese as raw materials
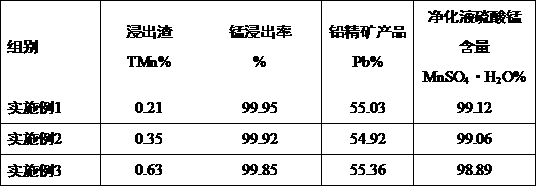
The invention discloses a method for preparing manganous carbonate by using waste slag and waste water containing manganese as raw materials, which is carried out as follows: reducing manganese dioxide by oxalic acid; oxidizing the ferrous iron therein into ferric iron by peroxide to form hydroxid deposit; neutralizing sulphuric acid therein by ammonia; depositing and removing heavy metal ions by ammonium sulfide; condensing to obtain ammonium manganous sulfate crystallization; reacting the ammonium manganous sulphate with ammonium hydrogen carbonate to prepare the manganous carbonate and obtain ammonium sulphate; the invention makes full use of reaction waste material and transforms water materials into useful elements; meanwhile, the invention can reduce emission and environmental pollution, which provides an efficient method for disposing waste slag and waste water containing manganese.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
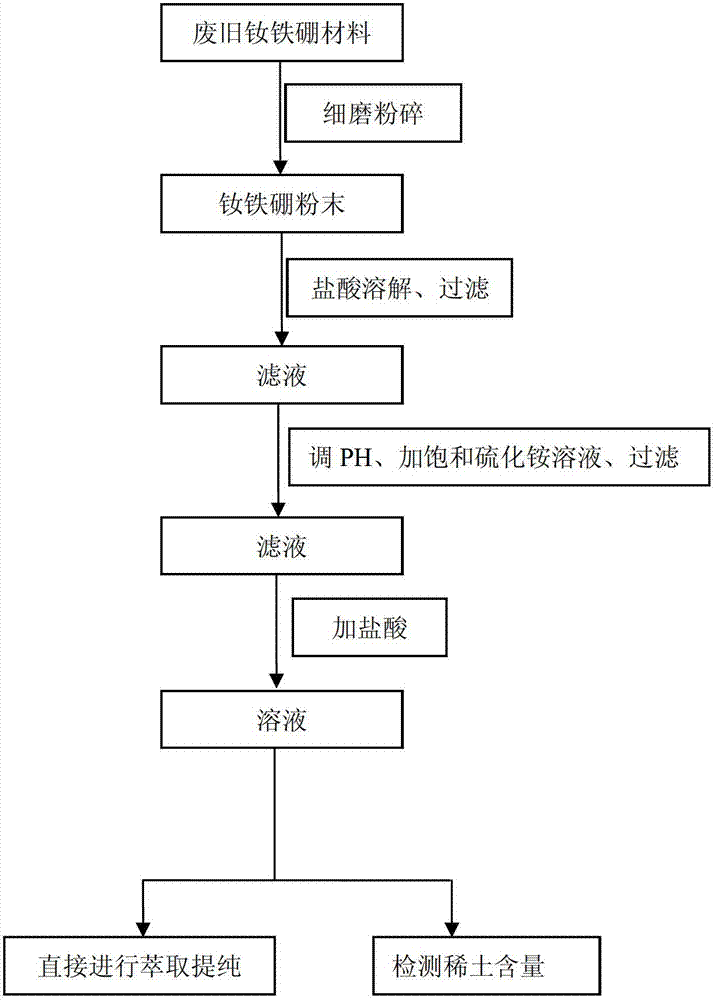
Method for recycling rare earths from waste neodymium-iron-boron material
InactiveCN102776375AHigh recovery rateEasy to produceProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium sulphidePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for recycling rare earths from a waste neodymium-iron-boron material, belonging to the technical field of recycling of neodymium-iron-boron materials. The method comprises the following steps: finely grinding a waste neodymium-iron-boron material, and separating out undissolved B element by a hydrochloric acid selective dissolution process; regulating the pH value of the obtained liquid to 2.0-3.0 with ammonia water; adding an ammonium sulfide solution into a 50-70 DEG C water bath, and reacting for more than 2.0 hours to sufficiently precipitate metal cation impurities under the action of ammonium sulfide; carrying out centrifugal filtration, wherein the filtrate mainly contains rare earth ions and chloride ions; and dropwisely adding hydrochloric acid into the filtrate until no bubbles are generated, heating for more than 10 minutes. The invention saves the trouble of intermediate ignition and secondary dissolution in order to perform extraction and purification in the past technique, and can be directly used for extraction and purification, thereby enhancing the recycling rate, simplifying the production process and lowering the production cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Ammonium sulfide passivation of semiconductors
InactiveUS20120264309A1Speed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAmmonium sulphideSurface layer
The present invention includes methods directed to improved processes for producing a monolayer of sulfur on the surface of a semiconductor. As a surface layer, it functions to passivate the surface; if annealed, it provides a doping element.
Owner:SEMATECH
Preparation method of sulfurization type hydro-cracking catalyst
ActiveCN103769197AIncreased degree of vulcanizationImprove hydrogenation performanceMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingNickel saltPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sulfurization type hydro-cracking catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting a hydro-cracking catalyst carrier component, wherein the carrier component at least comprises a molecular sieve and an amorphous acidic component; adding water into the carrier component powder, pulping so as to obtain slurry (d), then adding an ammonium molybdate and / or ammonium tungstate solution (a), an ammonium sulphide solution (b), and a nickel salt and / or cobalt solution (c) into the slurry (d) to carry out reactions, adding a surfactant at the same time, evenly stirring, filtering, washing, and drying the reaction product in the protection of inert gas, adding an adhesive, kneading, forming, and finally drying and burning in the protection of inert gas so as to obtain the sulfurization type hydro-cracking catalyst. The preparation method makes the active metal be evenly distributed on the carrier so as to generate more II type Ni(Co)Mo(W)S active phases with a higher activity; thus the catalyst has a high sulfurization degree and a high utilization rate of active metal, the hydrogenation activity of the catalyst matches the acidity more reasonably, so the hydrogenation activity and selectivity of the catalyst are both improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Prepn of nano cadmium sulfide/polystyrene core-shell microsphere
During the preparation of nano cadmium sulfide / polystyrene core-shell microsphere, polystyrene microsphere is first prepared through emulsion polymerization, which includes mixing decompress distilled styrene, lauryl sodium sufate, potassium persulfate and twice deionized water in certain proportion, leading in nitrogen while fast raising the temperature to 80 deg.c for reaction, demulsification with sodium chloride solution, filtering, washing and drying; the polystyrene microsphere is then mixed with sulfur source and cadmium source in some solvent and the mixture is heated to prepare the nano cadmium sulfide / polystyrene core-shell microsphere. The cadmium source is cadmium chloride with crystal water, cadmium caetate with crystal water, cadmium sulfate or cadmium nitrate; the sulfur source is thiacetamide, sulfourea, carbon disulfide or ammonium sulfide; and the solvent is ethanol, water or ammonia water. The microsphere is homogeneous in size and has compact shell.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for separating electrolytic manganese anode mud to produce electrolytic manganese metal and recovering lead
ActiveCN108118156AAchieve reuseReduce manufacturing costPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a method for separating electrolytic manganese anode mud to produce electrolytic manganese metal and recovering lead. The method comprises the following steps of S1, mixing andagitating the electrolytic manganese anode mud, a sulfuric acid solution and a waste molasses aqueous solution, then adding iron powder, and separating leachate and a leach residue after a reaction is completed; S2, adding H2O2 into the leachate, so as to obtain COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removed leachate; S3, adding ammonium sulfide or sodium dimethyl dithiocarbamate into the COD removed leachate, adding ammonia water, so as to obtain manganese sulfate purifying liquor, and electrolyzing the manganese sulfate purifying liquor, so as to obtain a manganese metal product. While producing theelectrolytic manganese metal product, the method can be also used for recovering lead concentrate with the lead content of 50 percent or above, and thus, the clean and efficient utilization of the electrolytic manganese anode mud is realized.
Owner:DAXIN MANGANESE MINE BRANCH OF CITIC DAMENG MINING IND
Method for cleaning surface of passivated GaAs substrate
InactiveCN102671894AImprove interface qualityImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsMOSFETAmmonium sulphide
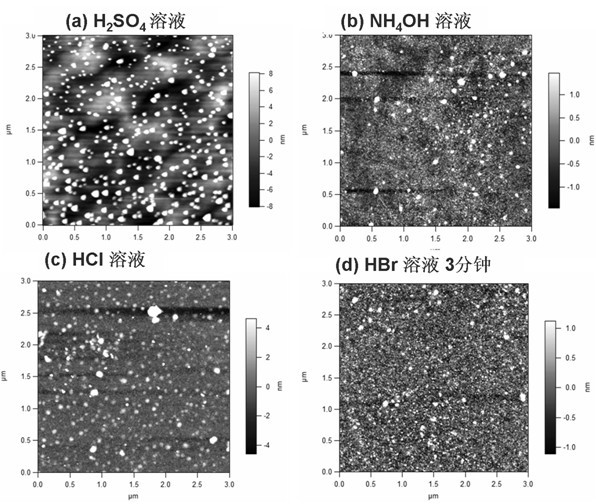
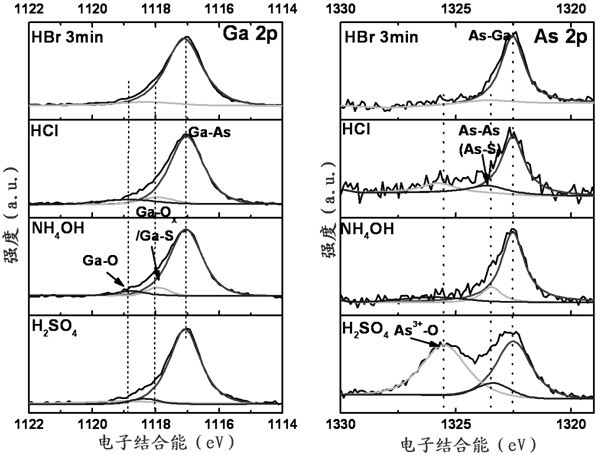
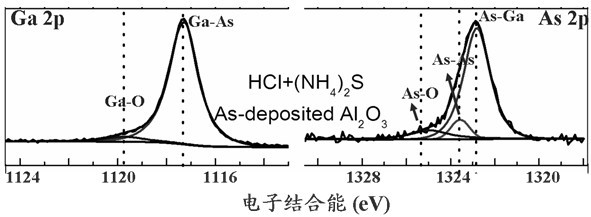
The invention discloses a method for cleaning the surface of a passivated GaAs substrate. The method comprises the following steps of: treating a GaAs substrate by organic solution to remove oil stain on the surface at first; then soaking the GaAs substrate by hydrobromic acid solution to remove an oxide layer on the surface; then placing the GaAs substrate in (NH4)2S solution which is heated to 50 DEG C and soaking the GaAs substrate for 20-30 minutes to passivate; and finally washing the surface of the passivated GaAs substrate by deionized water and blow-drying the surface by high-purity nitrogen. According to the invention, the green and environment-friendly hydrobromic acid solution is used for cleaning and removing oxides on the surface of the GaAs substrate, and then ammonium sulphide solution is used for passivating the surface of the substrate to effectively enhance the smoothness of the surface and greatly improve the interface quality between a gate dielectric film and the GaAs substrate, thus obviously improving the electric performances of a GaAs-based MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) apparatus. The method is simple in process, and has an important application prospect in preparation for a GaAs-based MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) apparatus.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Aerial fog disinfectant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101912409AEasy to disperse and sprayEasy to operateAntibacterial agentsBiocideAmmonium sulphideDisinfectant
The invention discloses an aerial fog disinfectant and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method mainly comprises the steps of preparing poly(hexamethylene biguanide) hydrochloride as a disinfection factor, dimethyl didecyl ammonium sulfide, propylene glycol as a solvent, ethanol, and the like into liquid disinfectant through a certain process and sealing the liquid disinfectant in a pressure-proof vessel and then filling a certain amount of propellant to ensure that the disinfectant is dispersed on the surface of an object in the form of fog. The invention is mainly used for spraying and disinfecting surfaces of hands, skin and ordinary objects to achieve convenient and rapid disinfection effect.
Owner:JIANGSU AITEFU 84
Desulphurization denitration method for ammonium sulfide solution
ActiveCN105233647AEmission complianceImprove removal efficiencyAmmonium nitratesUsing liquid separation agentEvaporationNitric oxide
The invention discloses a desulphurization denitration method for ammonium sulfide solution, and belongs to the technical field of flue gas purification. The method comprises employing an ammonium sulfide solution as an absorbent to absorb sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx); performing dust removal and water-washing pretreatment on industrial kiln and furnace flue gas, and blowing proper amount of air into a flue gas pipe, so as to oxidize nitrogen monoxide in the nitrogen oxides into nitrogen dioxide under a slight hot condition, performing two-stage absorption on the flue gas by ammonium sulfide, so as to enable sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides in the gas to be absorbed and converted into salts and left in the solution; after the absorption reaction is finished, filtering and recovering sulfur, and performing neutralization, oxidation, evaporation crystallization and drying processing on the filtrate, so as to obtain a solid mixture of ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate, wherein the solid mixture can be sold directly as a fertilizer. The method is simple in technology, easy to operate, high in desulphurization denitration efficiency, low in cost and suitable for industrialized application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
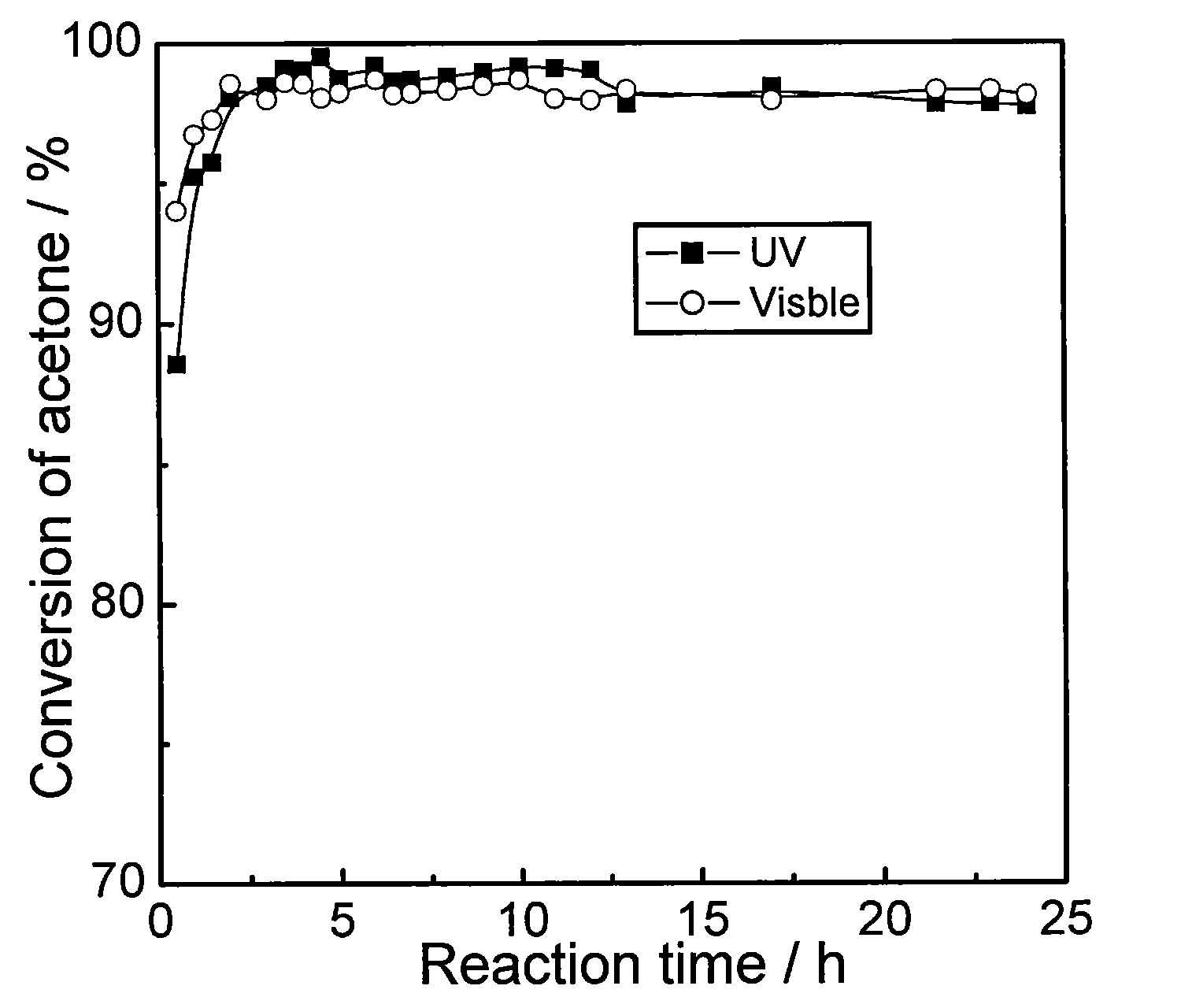
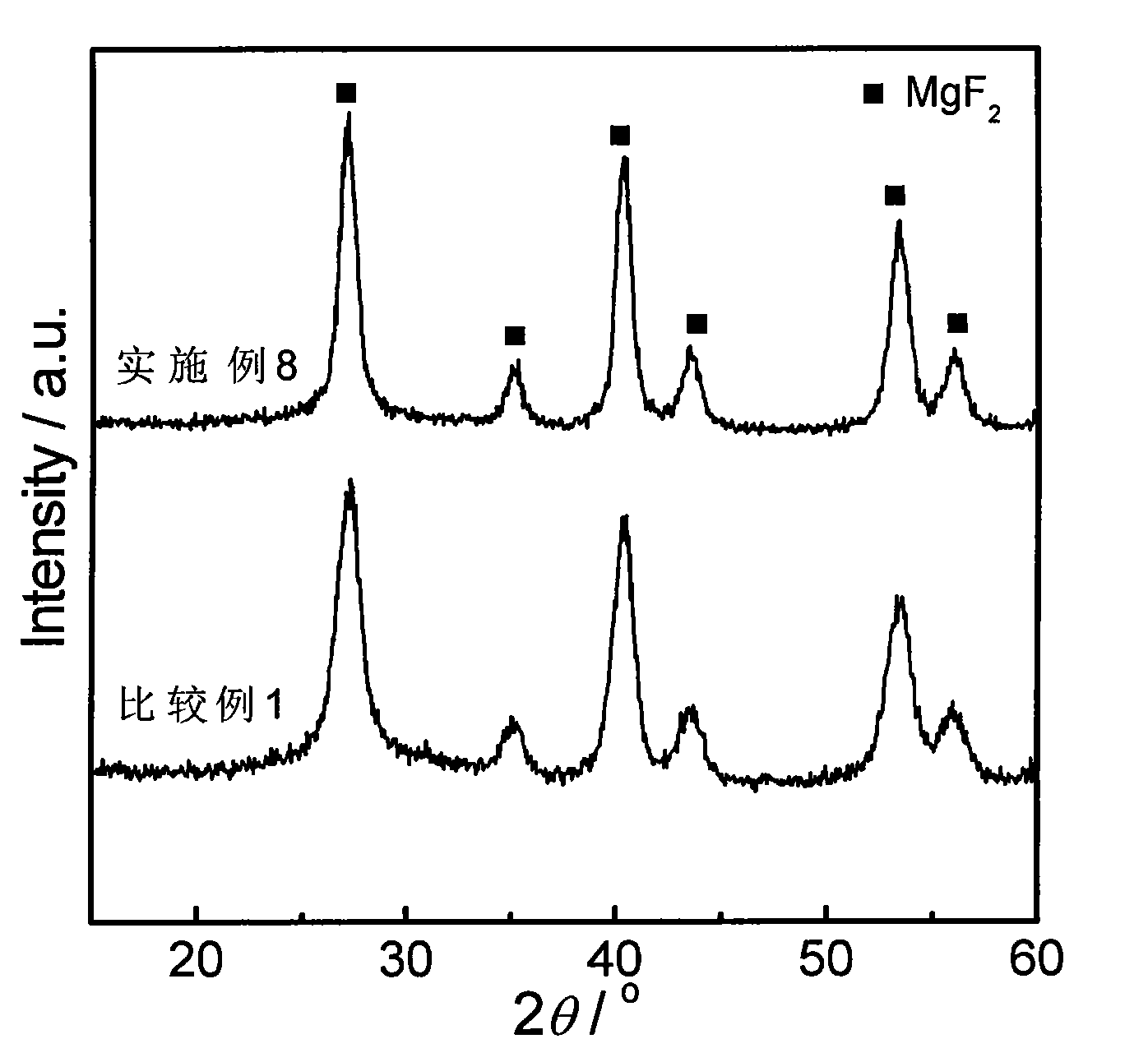
Visible light response catalyst and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101632936AEasy to prepareLow costPhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle separationEvaporationNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a novel catalyst with high visible light catalytic activity, which has a chemical composition general formula of S-x%MoOx / MgF2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) according to the stoichiometric proportion of MgF2, weighing magnesium nitrate and ammonium fluoride which are dissolved in deionized water respectively and then are mixed together to obtain colloidal solution I; (2) weighing ammonium molybdate, dissolving the same in the deionized water, adding the stoichiometric proportion of ammonium sulfide solution (n(S) / n(Mo)=4) to obtain solution II; and (3) mixing the solution I and the solution II, removing the moisture through rotary evaporation, drying the obtained solid, and calcinating the solid at a temperature of between 300 and 450 DEG C in a nitrogen atmosphere for 1 to 4 hours to obtain the catalyst. The catalyst has the advantages of simple preparation process, no need of adding noble metals and low cost; besides, the prepared photocatalyst has excellent activity of performing visible light catalytic degradation on organic pollutants.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cuprite vulcanizing strengthening method in mixed copper ore floatation
ActiveCN103191833AReduce the free energy change valuePlay the role of strengthening vulcanizationFlotationCopper oxideXanthate
The invention relates to a cuprite vulcanizing strengthening method in mixed copper ore floatation. The method includes: aiming at mixed copper ore which is high in calcium and magnesium and high in oxidation rate and mainly contains cuprite, directly using xanthate for floating the copper ore, adding diiron trisulfate, hydrogen peroxide and ammonium persulfate to ore pulp containing cuprite after floatation, stirring for a long time to pre-oxidize the surface of the cuprite; adding ammonium sulfide and sodium sulphide for strengthening vulcanizing the surface of the cuprite; and adding xanthate collectors to cuprite ore pulp after strengthening vulcanizing for floatation so as to recycle copper oxide ore. Cuprous oxide of the surface of the cuprite is converted into copper oxide, vulcanizing activity is increased in terms of thermodynamics, and vulcanizing is strengthened. Ammonium sulfide and sodium sulphide combines to vulcanize the surface of the cuprite after pre-oxidation, utilization efficiency of drugs is improved. The problem that the cuprite is difficult to vulcanize is solved by surface pre-oxidation.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
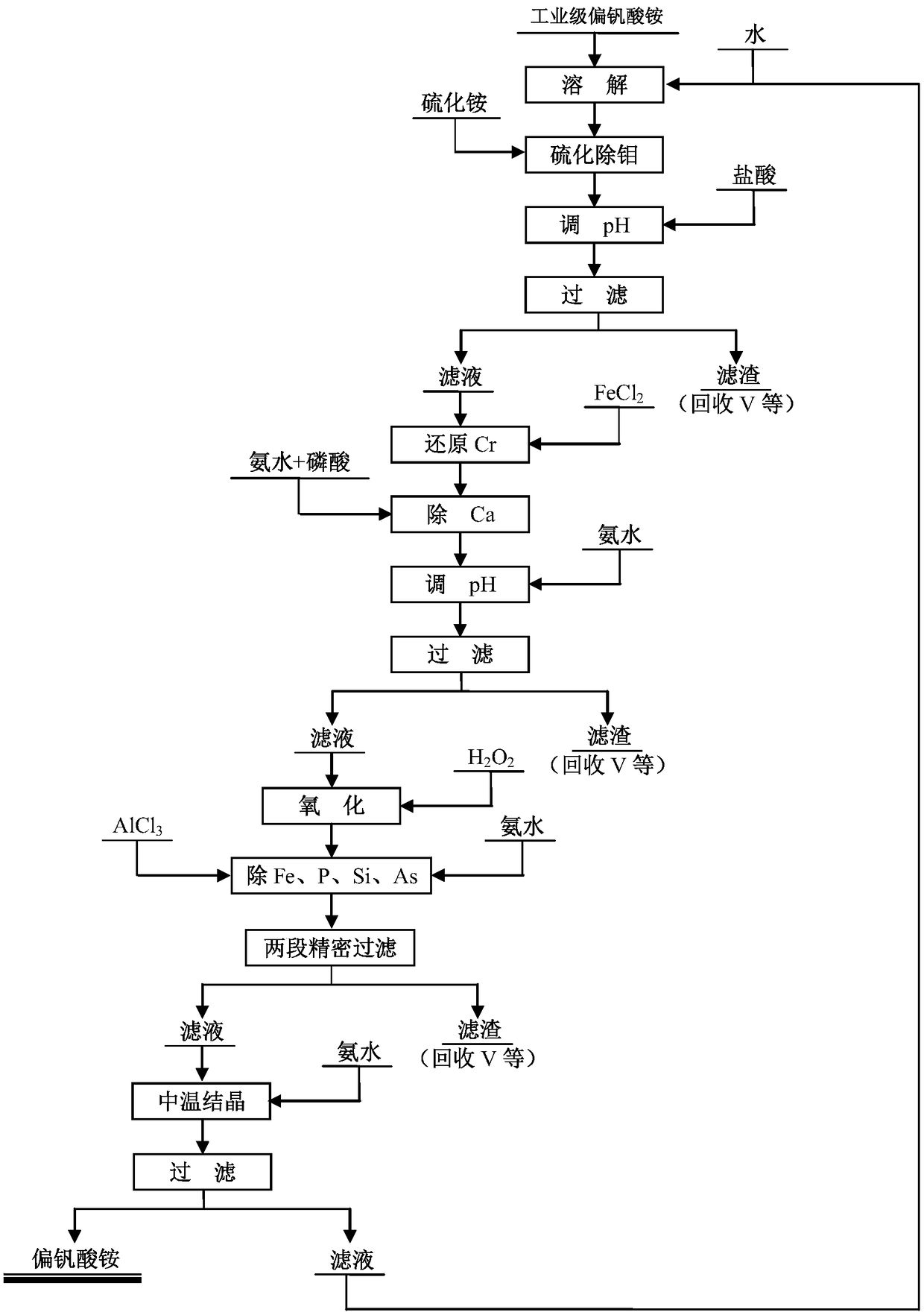
Purification method of industrial grade ammonium metavanadate
ActiveCN109437299AImprove qualitySolve unmanageable problemsVanadium compoundsPurification methodsVulcanization
The invention discloses an extraction method of industrial grade ammonium metavanadate, and belongs to the technical field of wet metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: adding hot waterto solve the industrial grade ammonium metavanadate, adding ammonium sulfide to perform vulcanization for a certain time, adjusting the pH value of a solution to be 3.0 to 3.5, performing reaction for 20 to 50min, and filtering, so as to obtain a filtrate number 1; heating the filtrate number 1, adding a certain amount of ferrite reduced high valence state chromium, performing reaction for 20 to120min, adding phosphate, then adjusting the pH value of the solution to be 7.5 to 8.0, performing reaction for 20 to 40min, and filtering, so as to obtain a filtrate number 2; heating the filtrate number 2, adding hydrogen peroxide and oxygen residual Fe2+, performing reaction for 20 to 40min, then adding a certain amount of aluminum salt, adjusting the pH value of the solution to be 7.5 to 8.0,performing reaction for 40 to 150min, and filtering, so as to obtain a filtrate number 3; performing medium-temperature crystallizing, washing and drying on the number 3 filtrate, so as to obtain a high-purity ammonium metavanadate product. The method overcomes the disadvantage in the prior art that anionic and cationic impurities cannot be removed at the same time in one technology, and has the advantages that the technical process is simple and easy to operate, waste liquor cyclic utilization is achieved, and the method is applicable to industrial promotion.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Process for preparing hydrogen sulfide
The invention discloses a process for preparing hydrogen sulfide through the reaction between sulfuric-acid-containing exhausted liquid (by product of the production process for preparing chemical product and intermediate product by means of chemical reactions) and barium sulphide water soluble liquid phase (prepared from barium sulphide calcined member through water leaching), the produced hydrogen sulfide can be further used in preparing other chemical products, such as sodium hydroxide, sodium hydrogen sulfide, ammonium sulfide, ammonium hydrosulfide, sulfourea, methyl hydrosulfide, ethyl mercaptan and dimethyl sulfur ether.
Owner:唐培堃
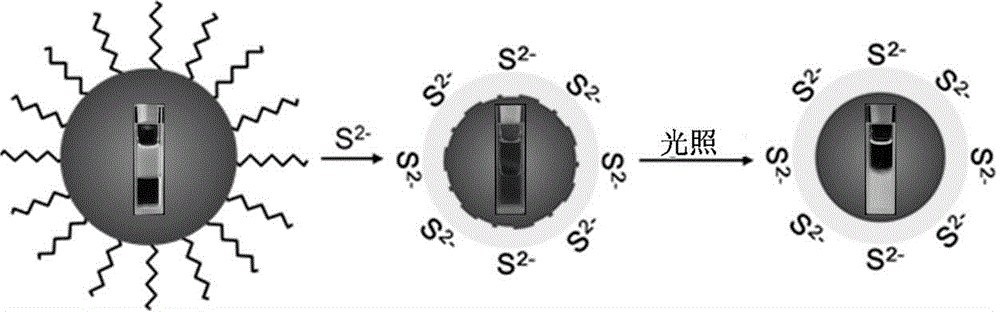
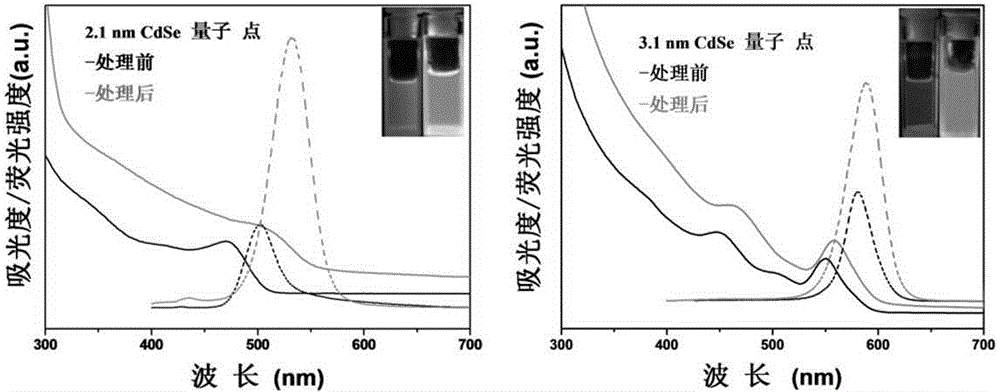
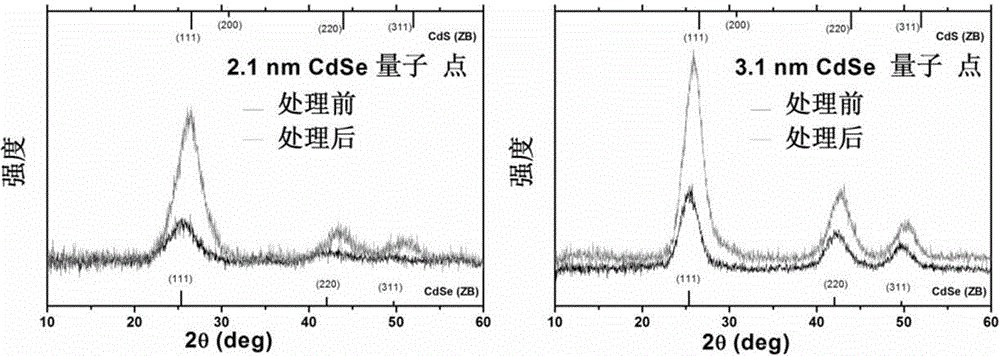
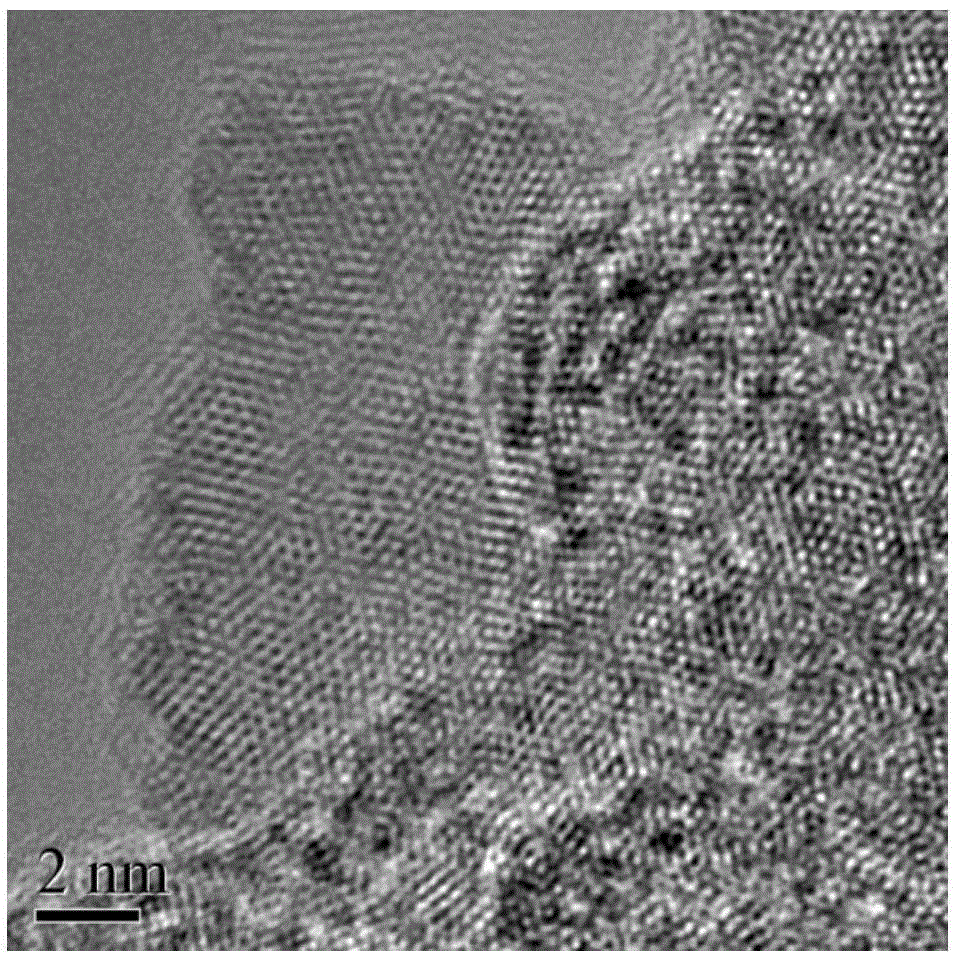
Method for preparing CdSe/CdS nuclear shell semiconductor quantum dots at normal temperature
InactiveCN105154086ASimple processMild reaction conditionsLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldCarbon chain
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic materials, and particularly relates to a method for preparing CdSe / CdS nuclear shell semiconductor quantum dots at a normal temperature. According to the method, a formamide solution of ammonium sulfide or potassium sulphide is used for treating CdSe nano particles at the normal temperature, and CdSe / CdS nuclear shell semiconductor nano particles are obtained; meanwhile, S2- replaces organic long carbon chain ligands on the surfaces of the CdSe nano particles, and the nano particles are dissolved in formamide polar solvent; afterwards, illumination is conducted for two days under the air condition, and fluorescence of the semiconductor nano particles is enhanced; (NH4)2S is used for treating CdSe nano particles of 2 nm so that the quantum yield can be increased to 39.8%, and the quantum yield of CdSe nano particles of 3 nm can be increased to 9.4%; K2S is used for treating the CdSe nano particles of 2 nm so that the quantum yield can be increased to 26.1%, and the quantum yield of the CdSe nano particles of 3 nm can be increased to 3.3%. The method is simple, the reaction condition is moderate, the prepared CdSe / CdS nuclear shell semiconductor quantum dots can be dissolved in the polar solvent, and the quantum yield is high. Broad application prospects can be achieved in the fields of photodiodes, fluorescent marks and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Oxygen-doped molybdenum disulfide material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106607062AControl the amount of incorporationLarge specific surface areaCatalyst activation/preparationStrong acidsHeat stability
The invention relates to an oxygen-doped molybdenum disulfide material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dispersing and dissolving a precursor of molybdenum in an ammonium sulphide solution; adjusting the pH value of the solution to a range of no less than 10 and no more than 14 by using ammonia water; carrying out a reaction at 50 to 100 DEG C for 0.5 to 6 h; after completion of the reaction, transferring the solution to a hydro-thermal synthesis kettle and introducing nitrogen for protection; adding hydrazine hydrate into the solution and enclosing the hydro-thermal synthesis kettle; carrying out hydro-thermal treatment at 140 to 220 DEG C for 0.5 to 24 h; and then successively carrying out cooling to room temperature, filtering, washing with deionized water and vacuum drying so as to prepare the oxygen-doped molybdenum disulfide material. The material has the advantages of good heat stability, strong acid resistance and a large specific surface area, and has potential application value in fields like catalysis and electrode materials.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
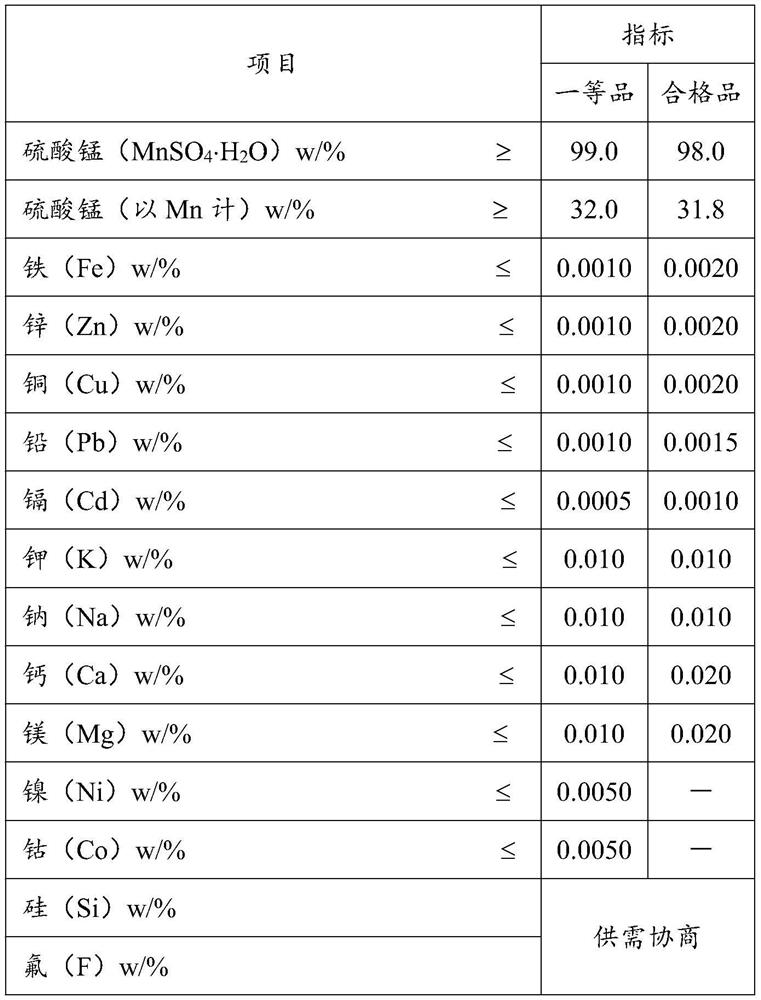
Preparation method of high-purity manganese sulfate
PendingCN113716613AImprove solubilityReduce the chance of sedimentationManganese sulfatesNew energyMagnesium ion
The invention relates to the technical field of new energy ternary lithium battery positive electrode materials, and provides a preparation method of high-purity manganese sulfate, the preparation method comprises the following steps: controlling the pH value to 5-6 and the temperature to 100 DEG C or above in a manganese carbonate precipitation process, and removing calcium and magnesium ions in a crude manganese salt solution by using an ammonium bicarbonate solution under the conditions, then dissolving the obtained manganese carbonate precipitate in electronic-grade sulfuric acid, adding ammonium sulfide to remove heavy metal impurity ions, filtering, and evaporating the obtained filtrate to obtain the high-purity manganese sulfate. In addition, according to the method, heavy metal impurity ions can be removed firstly, and then calcium and magnesium ions are removed through ammonium bicarbonate precipitation. According to the method provided by the invention, calcium and magnesium ions can be conveniently removed by controlling precipitation conditions, the obtained high-purity manganese sulfate meets the requirements of electronic-grade manganese sulfate, and the method is low in operation cost, simple in steps and easy to industrialize.
Owner:四川沃林山水环保科技有限公司
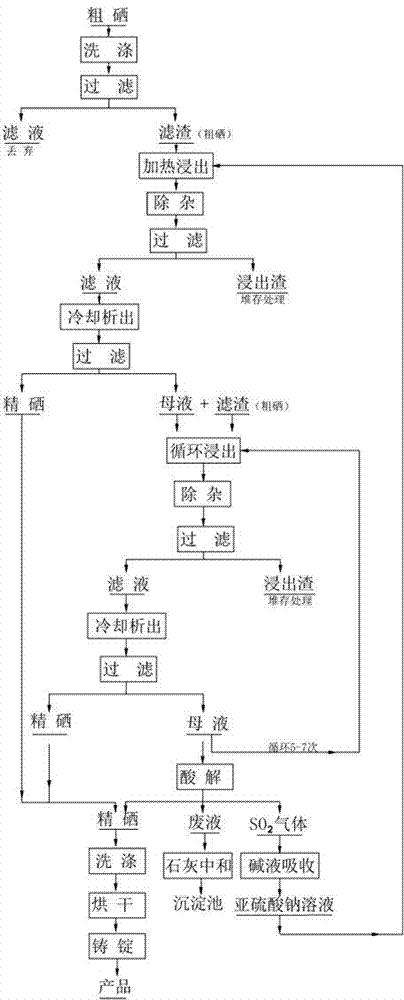
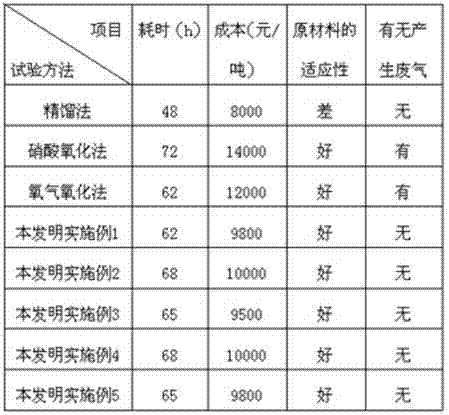
Refining process of crude selenium
The invention relates to the technical field of extracting and refining of rare precious metals and especially discloses a refining process of crude selenium. The refining process of crude selenium comprises the following steps: washing the crude selenium raw material by water for 2-3 times, wherein the ratio between the crude selenium raw material and the water is 1:1; adding 3-8m<3> sodium sulfite solution into per ton of the filtered filter residue, wherein the concentration of the sodium sulfite solution is 150-300g / L; heating the solution to 95-100 DEG C and reacting for 2-3 hours; then adding ammonium sulfide into the solution until no sediment emerges; filtering the solution and removing the filter residue; cooling the filtrate at normal temperature for 48 hour, so that the refined selenium is separated from the sodium sulfite solution; adding 15-20Kg of washed filter residue into per cubic meter of the solution after the separation out of the refined selenium, so that circulating leaching is continued; washing the separated refined selenium until the pH of the eluate is 7.0-7.5; drying the refined selenium and casting the refined selenium into selenium ingot whose grade is 99.99%; and adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the sodium sulfite solution after 5-7 times of recycling use in the technological process to perform acid hydrolysis, so that the sodium sulfite solution can be recycled after acid hydrolysis and cyclically used. The refining process of crude selenium is simple in technical process, small in raw material consumption, low in production cost, friendly to the environment, high in raw material applicability and very good in economic and social benefits.
Owner:DAYE NONFERROUS METALS
Method for recovering iridium from waste materials and residues
InactiveCN111961865AHigh purityShorten the timeProcess efficiency improvementIridiumAmmonium sulphide
The invention discloses a method for recovering iridium from waste materials and residues. The method specifically comprises the following steps of S1, pretreating the waste materials; S2, zinc crushing; S3, carrying out oxidation leaching treatment on the iridium-containing active ash obtained in the step 2 to obtain iridium-containing filtrate; S4, carrying out oxidation iridium precipitation treatment on the iridium-containing filtrate obtained in the step 3 to obtain (NH4) IrCL6 precipitate; S5, reducing and dissolving hydrazine hydrate; S6, purifying ammonium sulfide; S7, carrying out secondary oxidation iridium precipitation to obtain (NH4) IrCl6 crystals; and S8, carrying out calcination-hydrogen reduction treatment on the (NH4) IrCl6 crystal obtained in the step 7 to obtain iridiumpowder. Compared with a method generally adopted in the precious metal industry, the method is short in required time and low in energy consumption, and the obtained iridium powder is high in purity.
Owner:陕西瑞科新材料股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com