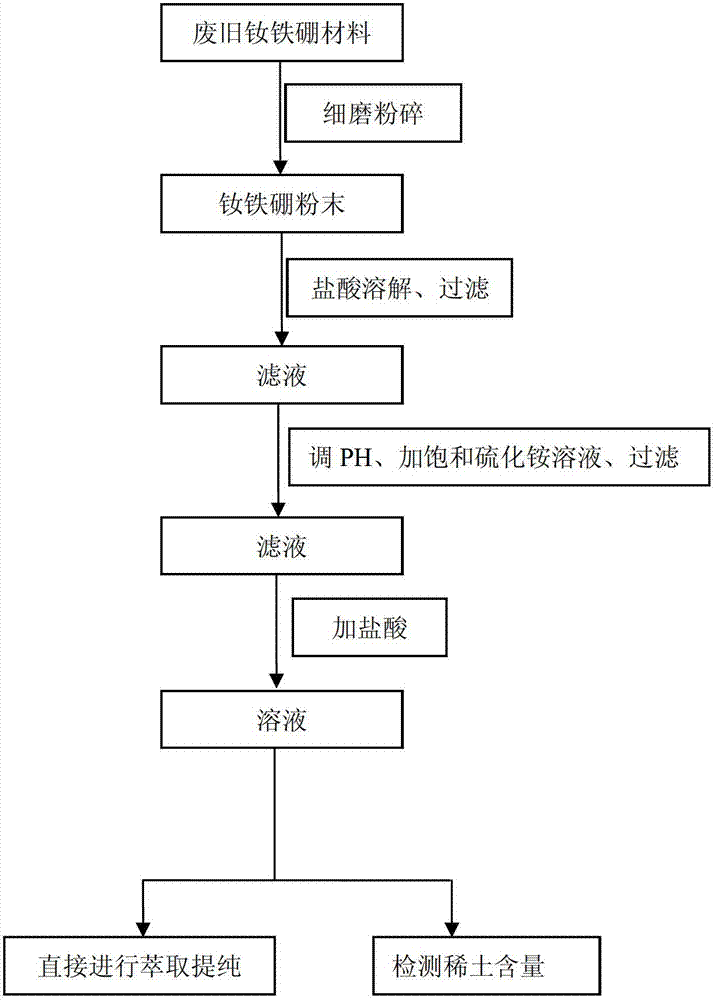
Method for recycling rare earths from waste neodymium-iron-boron material
A kind of neodymium iron boron and waste technology, which is applied in the field of recycling neodymium iron boron materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0022] [Example 1] After crushing 10.0g of NdFeB waste (containing 2.92g of rare earth) to more than 100 mesh, dissolve it with 120mL, 4mol / L hydrochloric acid, and then adjust it with concentrated ammonia water: water with a volume ratio of 1:2. When the pH value reaches 2.0, add a saturated ammonium sulfide solution of 1.1 times the theoretical requirement in a water bath at 60°C, filter, add hydrochloric acid to acidify until no bubbles are generated, and after heating for 10 minutes, the ICP method detects that the content of rare earth elements accounts for all metals 94.563wt.% of ions.
example 2
[0023] [Example 2] After crushing 10.0g of NdFeB waste (containing 2.92g of rare earth) to more than 100 mesh, dissolve it with 80mL, 6mol / L hydrochloric acid, and then adjust it with concentrated ammonia water: water with a volume ratio of 1:2 When the pH value reaches 3.0, add a saturated ammonium sulfide solution of 1.2 times the theoretical requirement in a water bath at 60°C, filter, add hydrochloric acid to acidify until no bubbles are generated, and after heating for 10 minutes, it is detected that the content of rare earth elements accounts for the proportion of all metal ions 98.197wt.%.
example 3
[0024] [Example 3] After crushing 10.0g of NdFeB waste (containing 2.92g of rare earth) to more than 100 mesh, it was dissolved with 96mL, 5mol / L hydrochloric acid, and then adjusted with concentrated ammonia water: water with a volume ratio of 1:2. When the pH value reaches 2.5, add a saturated solution of ammonium sulfide 1.15 times the theoretical requirement in a water bath at 60°C, filter, add hydrochloric acid to acidify until no bubbles are generated, and after heating for 10 minutes, it is detected that the content of rare earth elements accounts for the proportion of all metal ions 98.032wt.%.
[0025] To further obtain high-purity rare earth compounds, the solution obtained in the final step of the above example can be directly extracted, separated and purified.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com