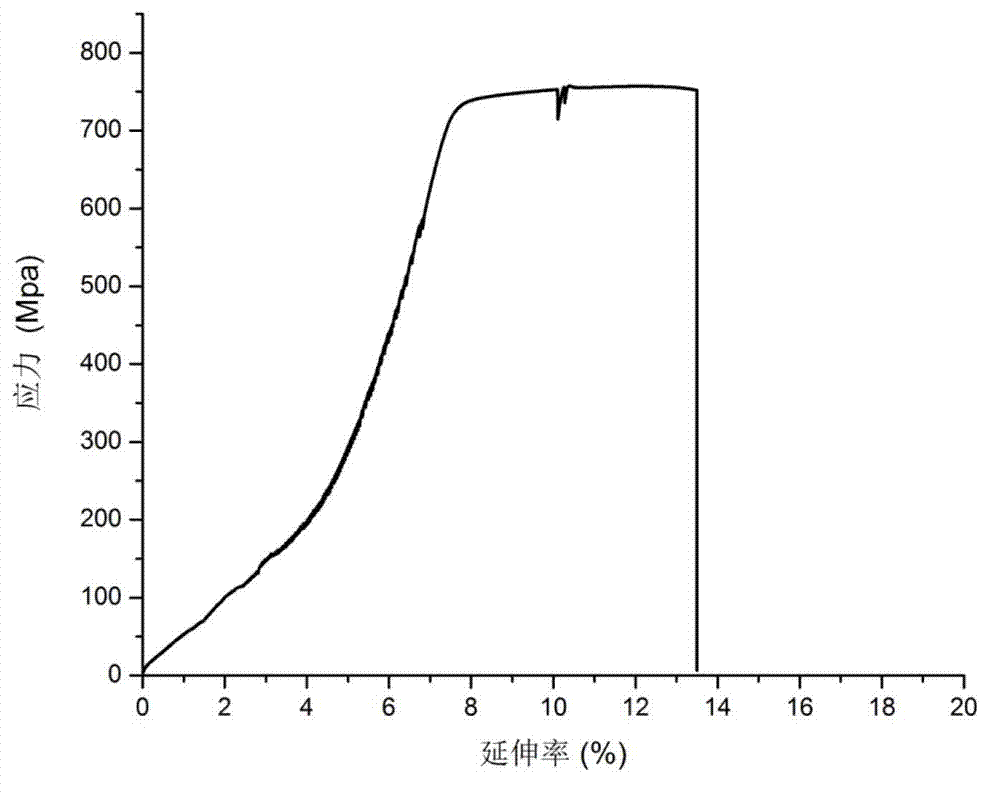
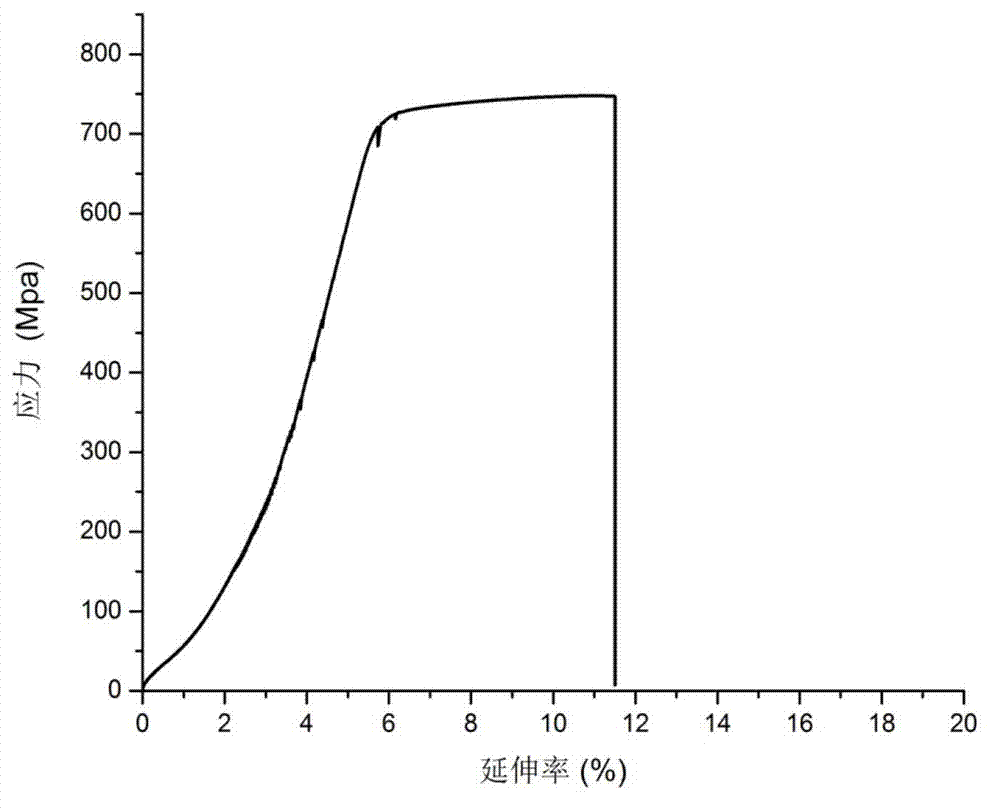
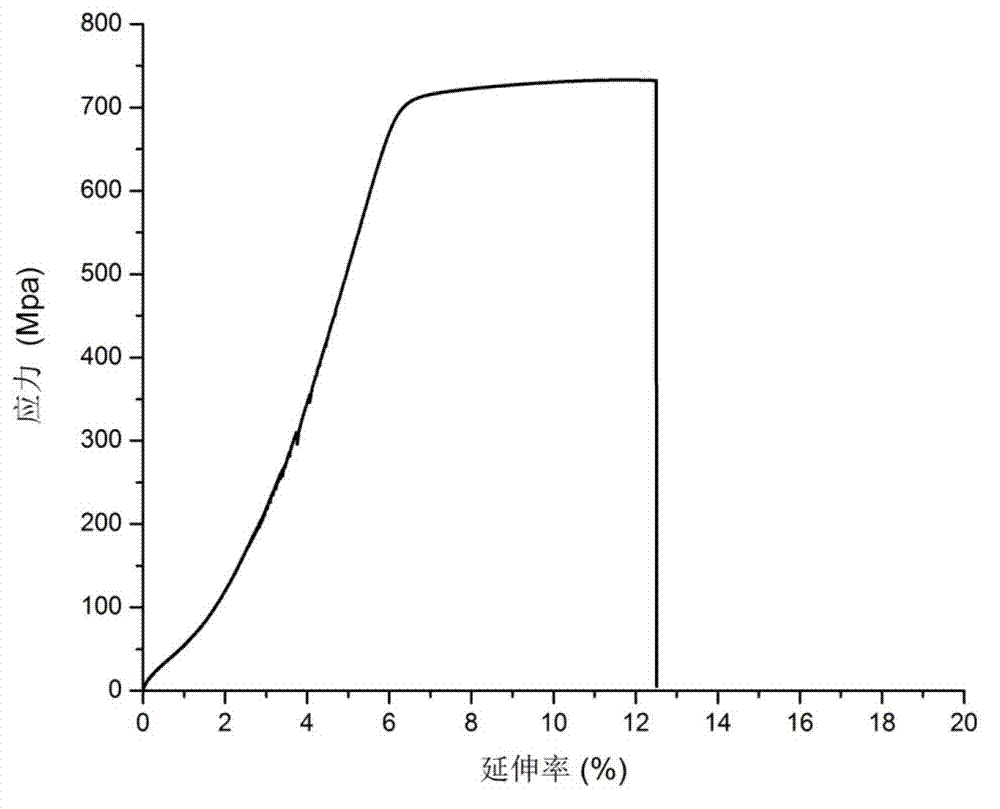
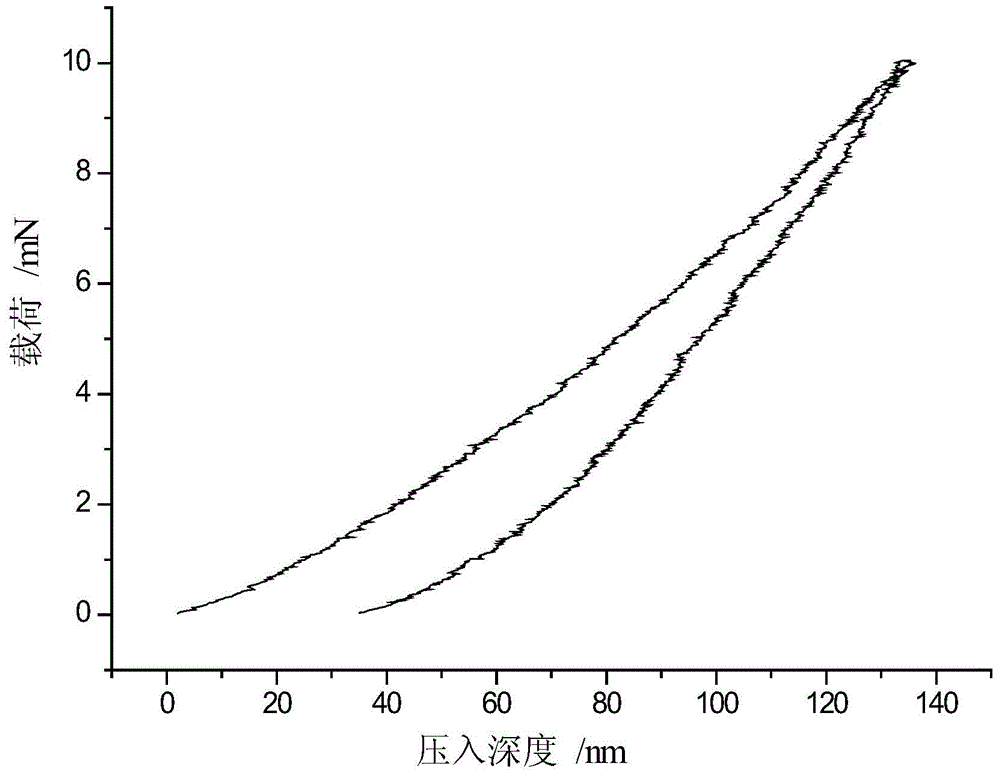
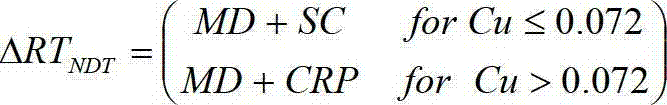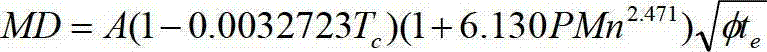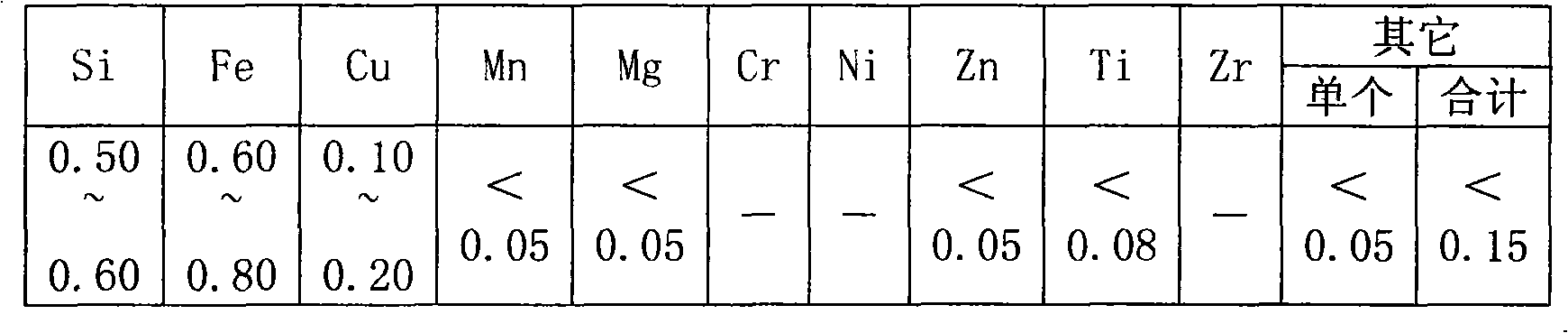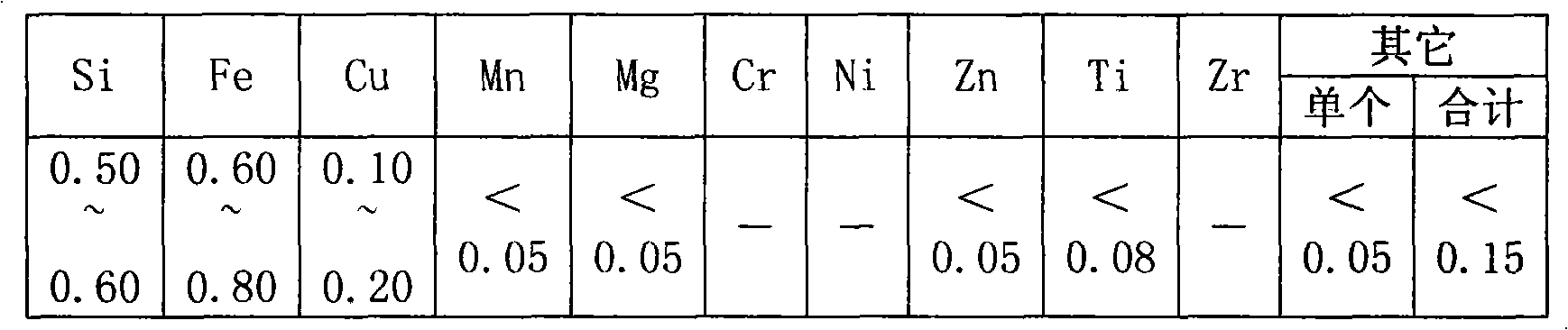Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
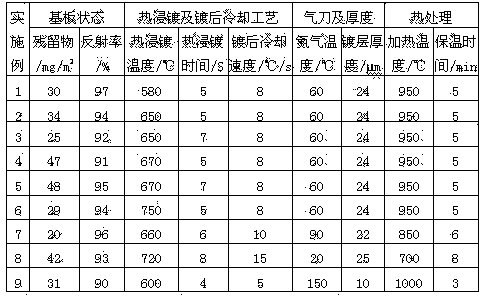
306 results about "Cu element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
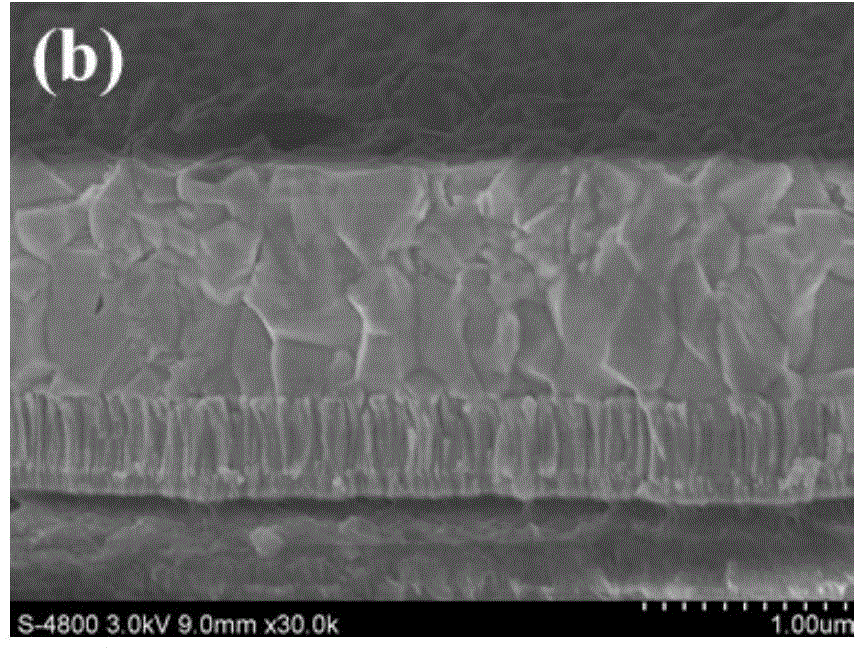
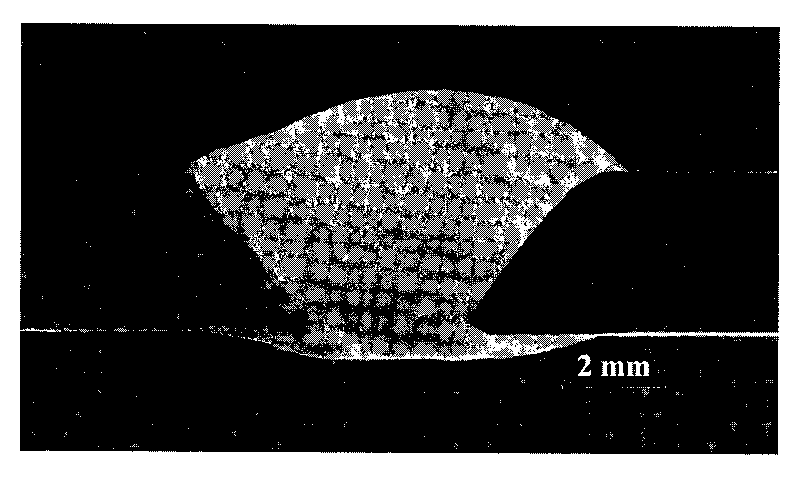
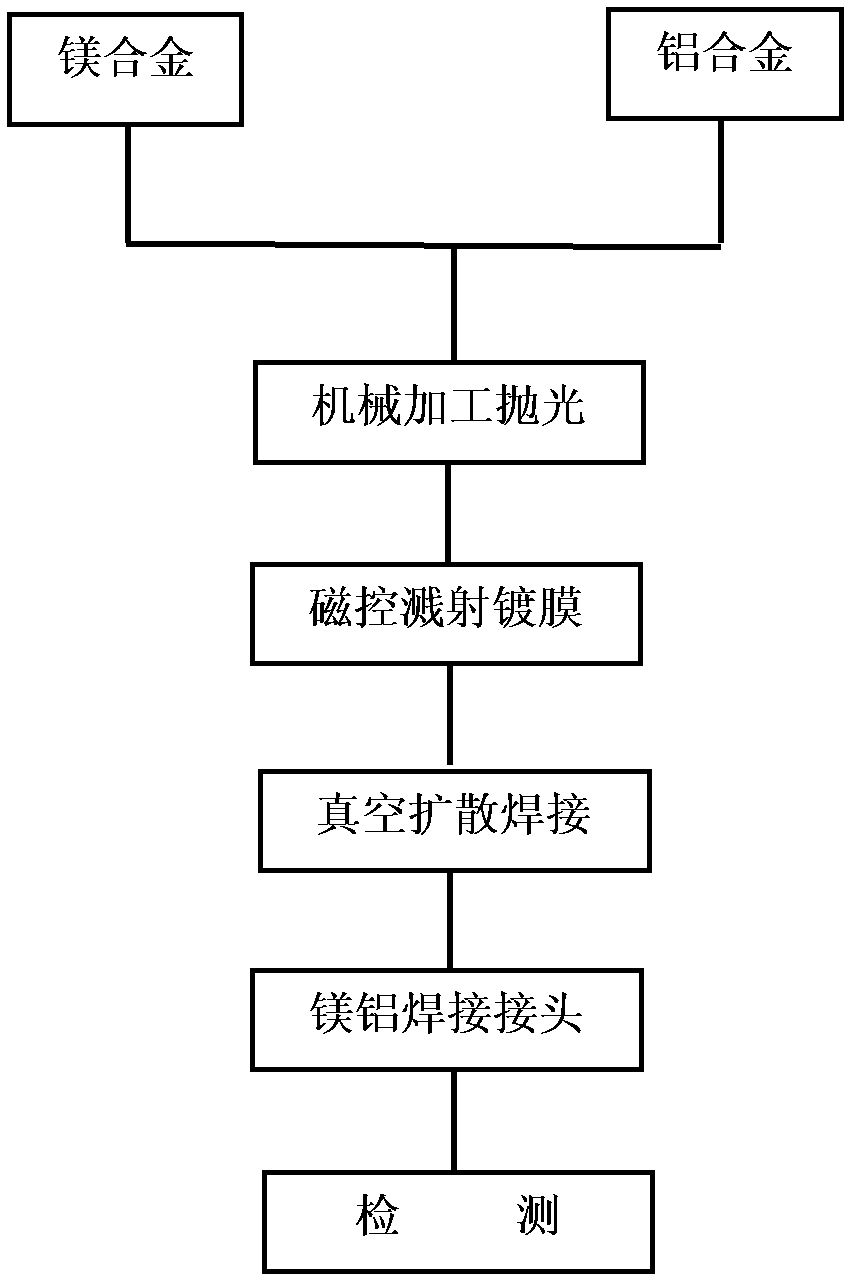
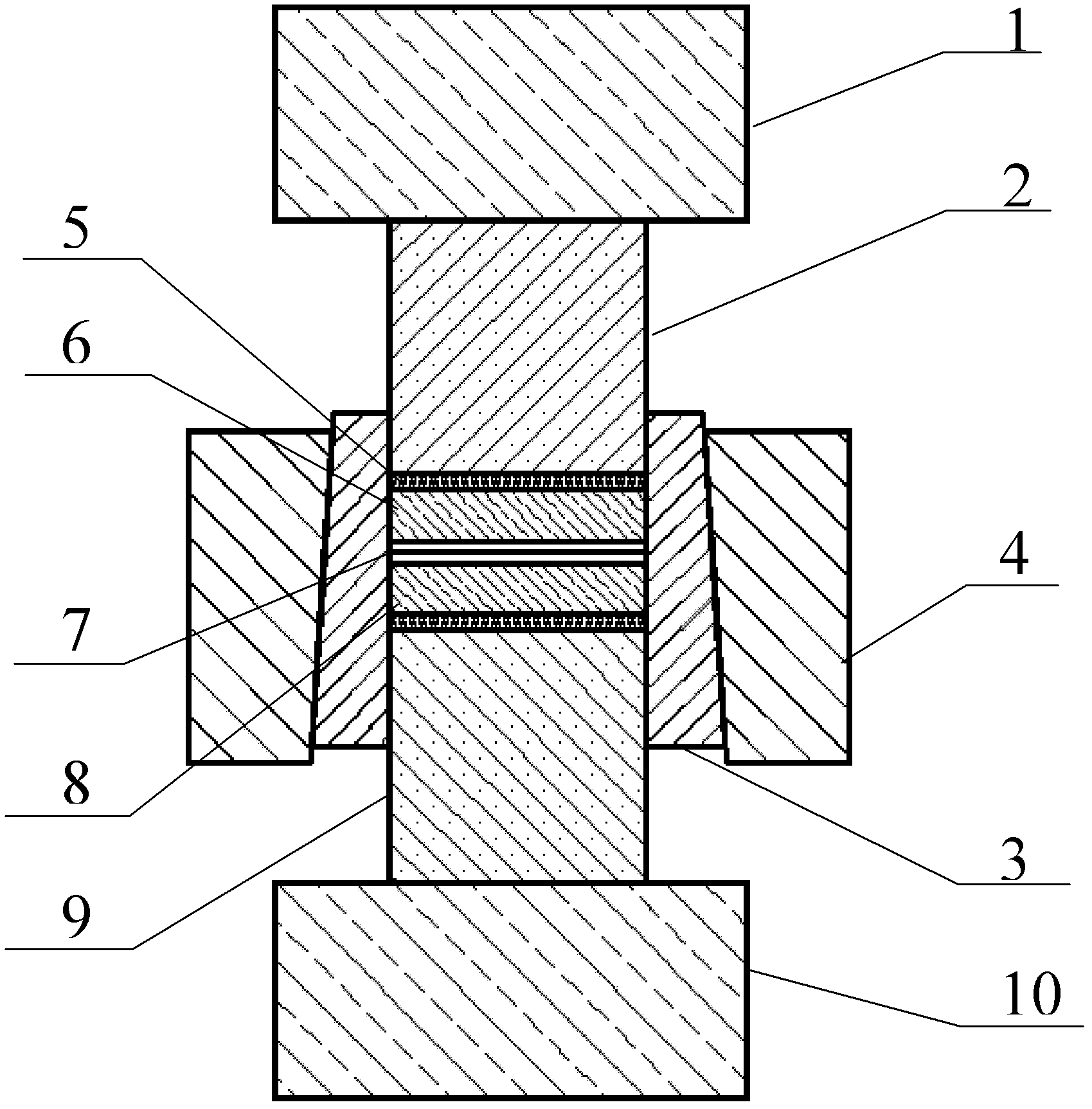
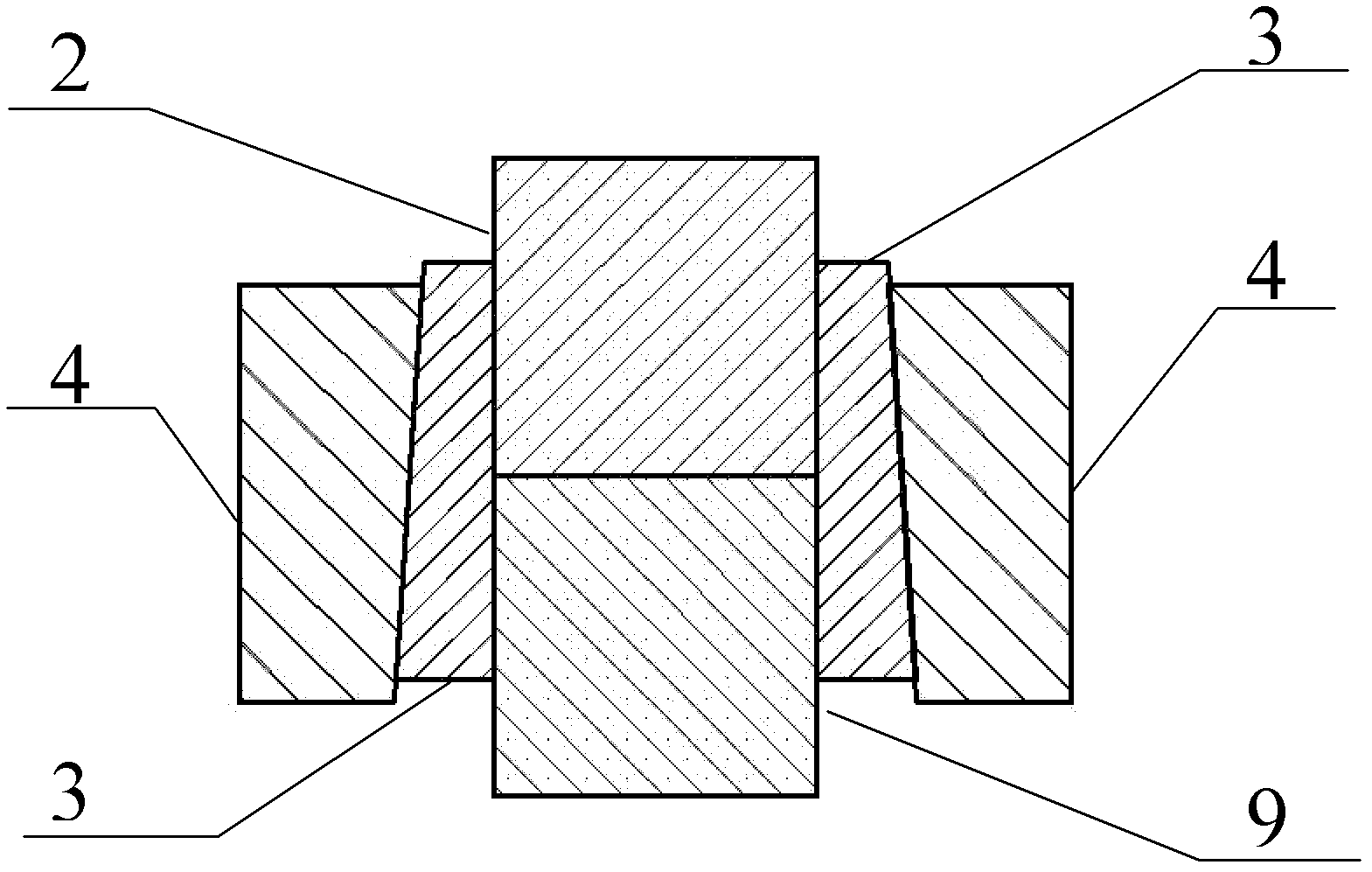
Magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy interlayer diffusion welding method
InactiveCN102248278AClosely connectedImprove parallelismVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCu elementMaterials science
The invention relates to a magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy interlayer diffusion welding method. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) machining a welding metal base, namely processing, abrading, polishing and ultrasonically washing magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy; (2) depositing Cu films on the magnesium alloy and the aluminum alloy by controlling process parameters by using magnetron sputtering coating equipment; and (3) assembling the coated metal base by using a die, placing the die into a vacuum hot-pressing furnace, and controlling welding temperature, heat-preserving time and pressure to obtain a welding joint. The method has the advantages that: (1) the Cu film can protect the surface of the welding metal base better and reduce generation of inert metal oxide layers; (2) the Cu element improves phase constitution and the microstructure of a welding interface and inhibits generation of brittle intermetallic compounds in the midlayer of the welding joint; and (3) the welding joint has high strength, the tensile strength can reach 10 to 20 MPa, small deformation occurs in the welding joint, and the residual stress is small.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
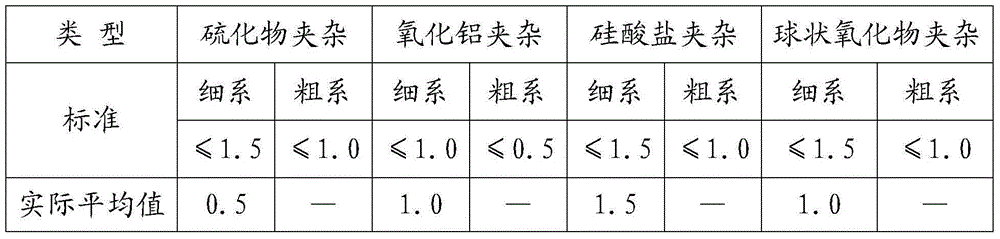
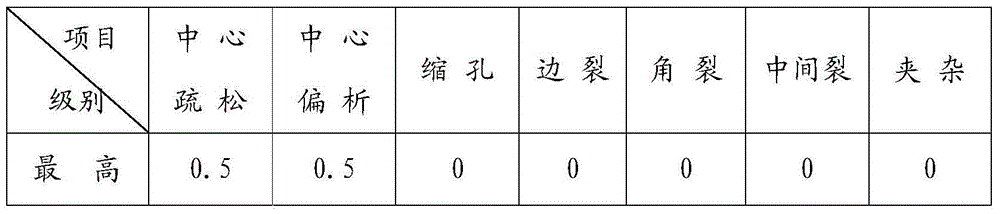
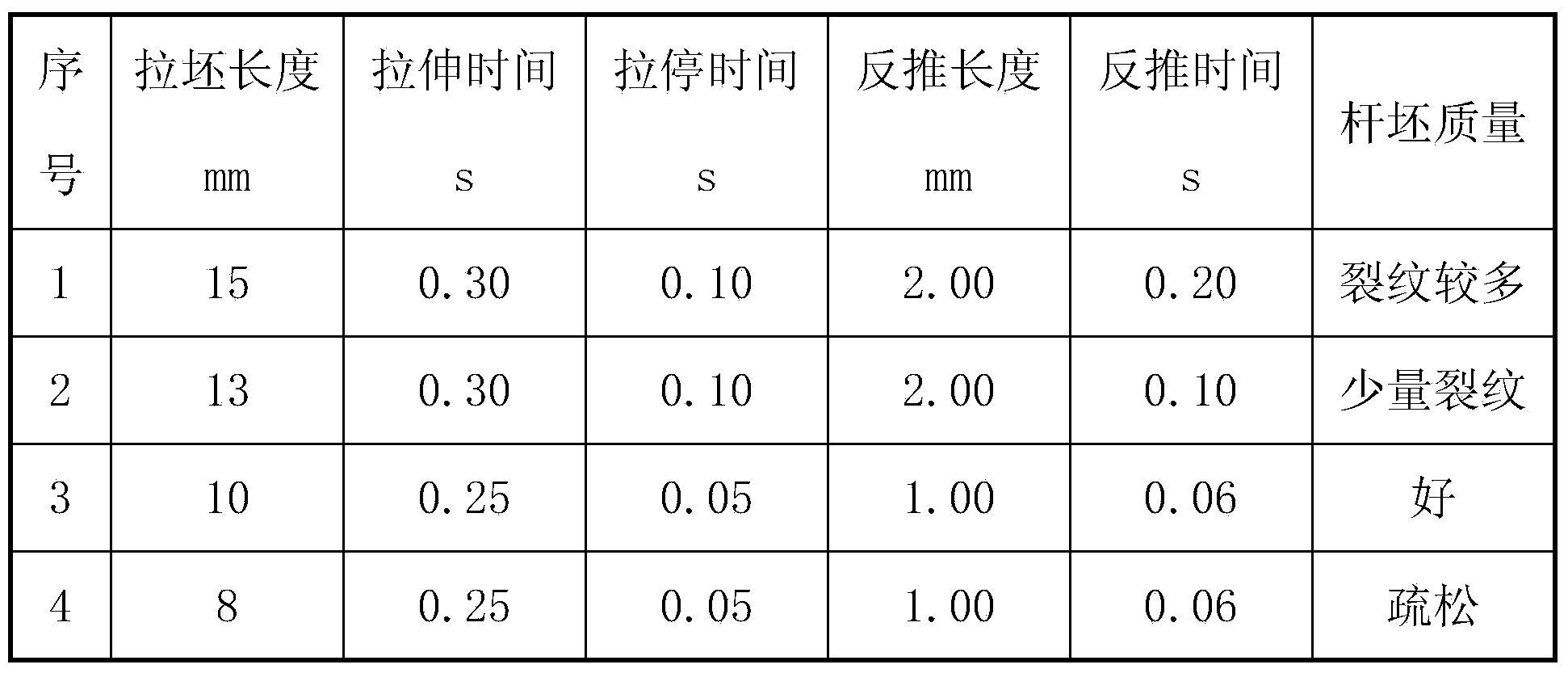
Method for producing sulfuric acid dew-point corrosion-resistant round steel 09CrCuSb
InactiveCN105200349AImprove corrosion resistanceReduce hardnessManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementChemical compositionSmelting process
The invention discloses a method for producing sulfuric acid dew-point corrosion-resistant round steel 09CrCuSb, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1) reasonably determining the chemical composition and the inclusion control level of round steel 09CrCuSb; 2) determining the revolving furnace smelting process and N, H and O gas contents; 3) formulating an appropriate continuous casting secondary cooling schedule to make a casting blank keep away from a cracking temperature in a straightening zone, reasonably adopting crystallizer cooling water parameters and vibration negative slip parameters, and controlling casting blank surface cracks; and 4) determining a reasonable heating schedule and a rolling process, choosing low temperature for fast sintering, and reasonably distributing materials, so as to reduce enrichment of Cu elements on the steel surface and avoid the round steel from generating star-shaped cracks; and by controlling the rhythm of steel rolling, avoiding scratches of the round steel surface. By adding alloy elements such as Cr, Cu and Sb, a passivation film is formed on the steel surface; by formulating reasonable smelting, continuous casting and steel rolling processes, the round steel composition is effectively ensured, corrosion resistance can conform to relevant standards and requirements; and through the process, generation of the cracks of the copper-containing steel is avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN IRON & STEEL GRP
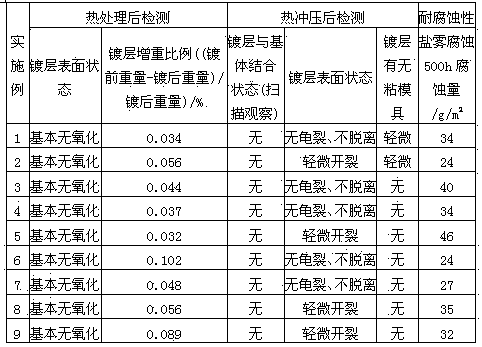
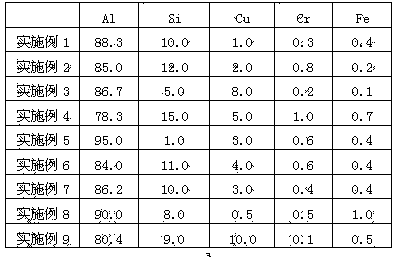
High-temperature oxidation resistant plating layer material and hot dipping method for hot stamping formed steel
ActiveCN104233149AImprove high temperature oxidation resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesHot stampingSheet steel
The invention discloses a high-temperature oxidation resistant plating layer material and a hot dipping method for hot stamping formed steel. A hot stamping formed steel plate enters a plating solution for hot dipping and then is subjected to cooling and heat treatment so that a hot dipping steel plate can be obtained, wherein the plating solution comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 1.0%-15.0% of Si, 0.5%-10.0% of Cu, 0.1%-1.0% of Cr, less than or equal to 1.0% of Fe and the balance of Al and inevitable impurities. According to the method, the Cu element and Al element which are contained in a plating layer form a high-melting point intermetallic compound in a cooling process after the hot dipping, and Cr is gathered on the surface of the plating layer to form a compact oxidation film, so that the high-temperature oxidation resistant property of the plating layer is greatly enhanced; the Cu element is enriched on the surface of the plating layer, so that the corrosion-resisting property of the plating layer is greatly enhanced. The high-temperature oxidation resistance and the high-temperature corrosion resistance of the plating layer are enhanced by utilizing the intermetallic compounds formed among Al, Si, Cr, Cu and Fe; and the obtained plating layer has the advantages of reasonability in structure, tight combination with a substrate and good high-temperature oxidation resistance and corrosion-resisting property.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Austenitic antibiotic stainless steel and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN101230438ASimple smelting processImprove mechanical propertiesChemical compositionCu element
The invention discloses an austenitic antimicrobial stainless steel and the manufacturing method thereof. The stainless steel contains an Ag-Cu binary master alloy with a weight percentage of 0.10 to 4.0 percent and the weight percentage (wt %) for the rest chemical components are as follows: C less than or equal to 0.08 percent, Si less than or equal to 1.0 percent, Mn less than or equal to 2.0 percent, P less than or equal to 0.04 percent, S less than or equal to 0.03 percent, Ni 7.0 to 15.0 percent, Cr 17.0 to 20.0 percent, Mo less than or equal to 4.0 percent, N less than or equal to 0.15 percent and the rest are Fe and unavoidable impurities. The method of manufacturing the antimicrobial stainless steel is as follows: the Ag element and the Cu element, of which Ag takes up 1.0 to 40 percent, are smelted to be a master alloy and then added to the antimicrobial stainless steel material to be smelted. The steel has the advantages of simple and effective smelting technique, excellent mechanical property, excellent corrosion resistance and excellent antibacterial property, can be made into shapes of various types applicable to kitchens, household appliances, medical apparatuses and so on.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
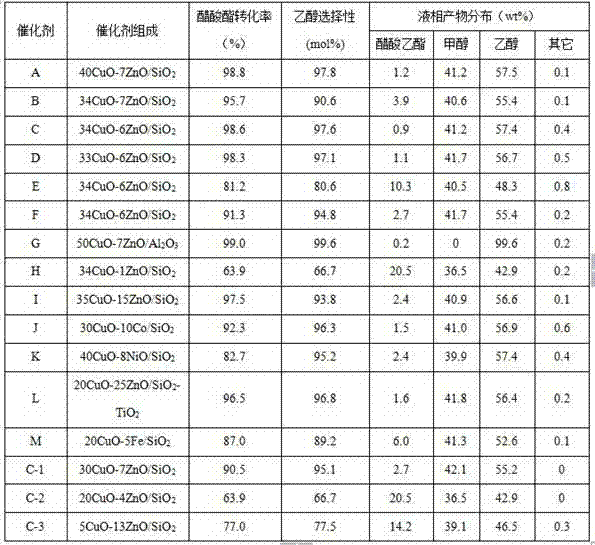
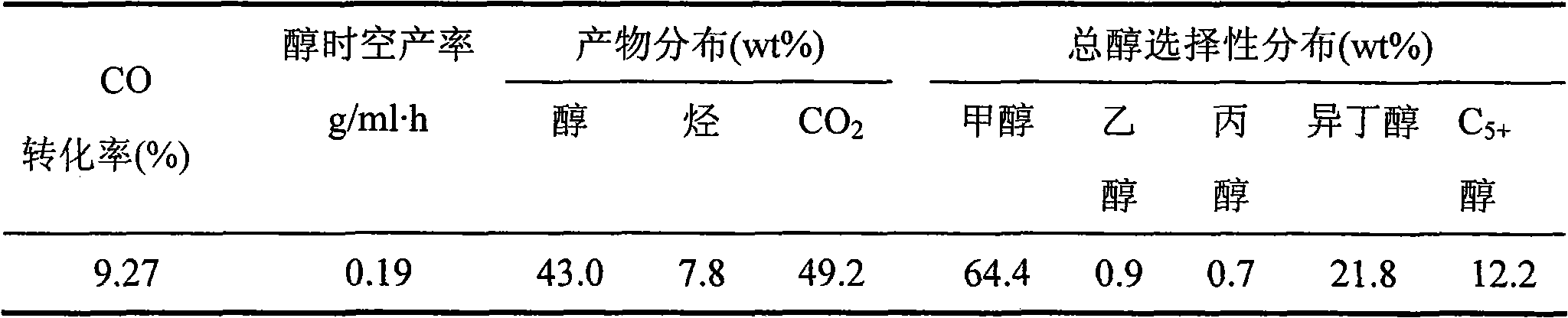
Catalyst for preparing alcohol from acetate through hydrogenation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102962071AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPtru catalystAlcohol ethyl
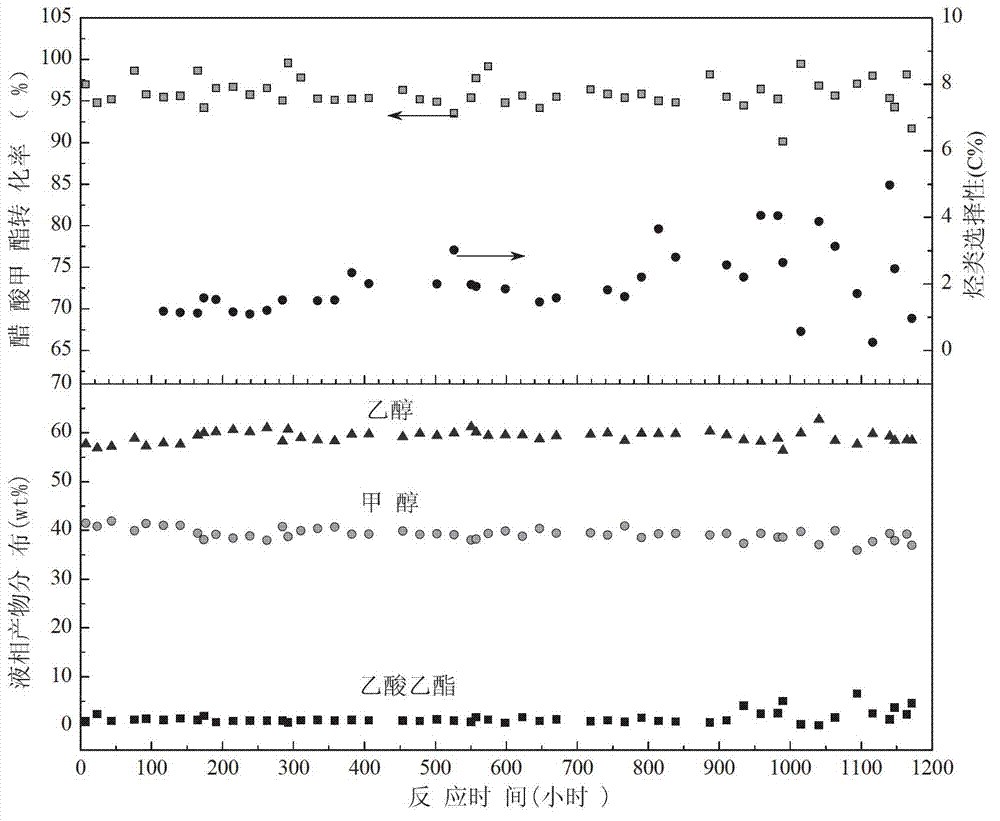
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing alcohol from acetate through hydrogenation as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The active component of the catalyst is Cu element; the assistant is selected from one or the mixture of several of Zn, Co, Ni and Fe; the carrier is silicon oxide, aluminum oxide or SiO2-TiO2 composite oxide; and the content of Cu element is 5-50wt% based on CuO, and the content of the assistant is 1-25wt%. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: weighing the precursor of each component and adding water to prepare a solution, and stirring for 1-10 hours at a temperature from the room temperature to 60 DEG C; hermetically standing at the room temperature or standing in the air at a temperature from the room temperature to 100 DEG C to form gel; and drying the gel and then roasting the gel for 1-10 hours at a temperature of 200-700 DEG C to obtain the catalyst. The prepared catalyst has the advantages of excellent performance, high activity, good selectivity and no reduction of the performance after the catalyst is used for 1200 hours and has very good industrial application prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU SOPO GRP +1
Method for producing wide-amplitude double-zero aluminum foil blank by adopting cast-rolled compact
InactiveCN102492900ASolve the problem of soft tensile propertiesImprove rolling effectMetallurgyCu element
The invention belongs to the technical field of aluminum alloy sheet strip foil material processing, and in particular relates to a method for producing a wide-amplitude double-zero aluminum foil blank by adopting a cast-rolled compact. By adjusting 8079, 1235 and other alloying components and adopting twice intermediate annealing processes, the non-uniform compound scale and distribution, caused by roll cooling intensity difference, of the wide-amplitude cast-rolled compact along the same board plane are eliminated, thus the pinhole degree and performances of the blank foil after rolling are superior to those of 1235; at the same time, through addition of Cu element, the problem of soft tensile property when the wide-amplitude blank is rolled to the double-zero foil after twice annealing is solved; and the rolling performance and foil rolling efficiency of the wide-amplitude blank are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU DINGSHENG NEW MATERIAL JOINT STOCK CO LTD +1
Ultrahigh-intensity, low-quenching sensitivity and weldable aluminum alloy, production technology and section bar processing method
The invention discloses an ultrahigh-intensity, low-quenching sensitivity and weldable aluminum alloy, a production technology and a section bar processing method, wherein the aluminum alloy contains the following elements by weight: 0.15-0.22% of Ce, 0.9-1.4% of Mg, 2.5-3.0% of Zn, 0.35-0.8% of Cu, 0.8-1.2% of Si, 0.15-0.30% of Mn, 0.13-0.20% of Zr, 0.08-0.12% of Ti, and the balance being Al, wherein a sum of contents of Ti and Zr is not less than 0.25%, and a content of Fe is not more than 0.5%. Ce rare earth element introduced in order to optimize casting crystallization structure of the alloy, and generates a CeCu compound with Cu in order to supercool and refining an alloy crystallisation process and enhance crystal boundary, thereby preventing increase of welding crack sensitivity of aluminum because of Cu in a solid solution. Because of containing Si and Cu elements and optimization combination of a plurality of strengthening phase, the tensile strength of the alloy can reach more than 400MPa, and because of low Cu and Mn content and no Cr, the alloy quenching sensitivity is low, thereby making sure small dimension tolerance deformation of the section bar after extruding and quenching.
Owner:GUANGDONG YONGLIJIAN ALUMINUM
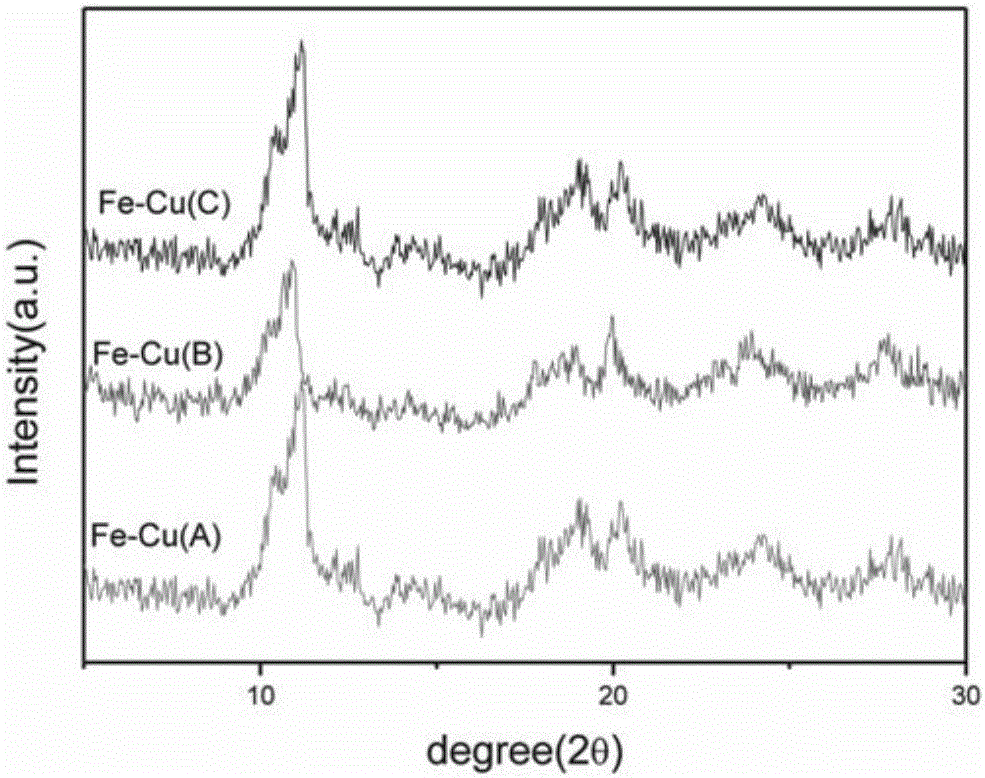
Method for preparing supported bimetal organic framework material MIL-100(Fe-Cu) and denitration application
InactiveCN106268952ACheap sourceUniform crystal formOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDispersed particle separationDispersityMaterial Design
The invention provides a method for preparing a supported bimetal organic framework material MIL-100(Fe-Cu) and denitration application, and belongs to the field of novel material design and preparation. By means of the post-synthesis modification method, the Cu element is successfully introduced into an original MOFs framework, and a novel MOFs material with bimetal active sites is constructed. The method is characterized in that the hydrothermal technology is used, a metal precursor solution is prepared by means of stabilizer to be effectively combined with Fe-MOFs, and the material MIL-100(Fe-Cu) is prepared and used for denitration reaction. Compared with an original monometal catalyst, a catalyst prepared through the method has unsaturated active sites of Fe3+ and Cu+, denitration activity is improved by about 15%, and the material is good in dispersity, high in yield and good in catalytic activity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Non-copper and nickel acid resistant pipeline steel X52MS and production method of hot-rolled plate coil thereof
The invention relates to non-copper and nickel acid resistant pipeline steel X52MS. The non-copper and nickel acid resistant pipeline steel X52MS comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.02-0.06 wt% of C, 0.05-0.35 wt% of Si, 1.0-1.4 wt% of Mn, P not greater than 0.018 wt%, S not greater than 0.003 wt%, 0.10-0.50 wt% of Cr, 0.05-0.10 wt% of Ti, 0.005-0.10 wt% of Nb, 0-0.05 wt% of V, and the balance of Fe and inevitable trace impurities. The invention further provides a preparation method of a hot-rolled plate coil of the non-copper and nickel acid resistant pipeline steel X52MS. Part of all Cr is used for replacing original Ni / Cu elements, so that the material cost is largely reduced under the precondition of guaranteeing the material HIC resistance.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
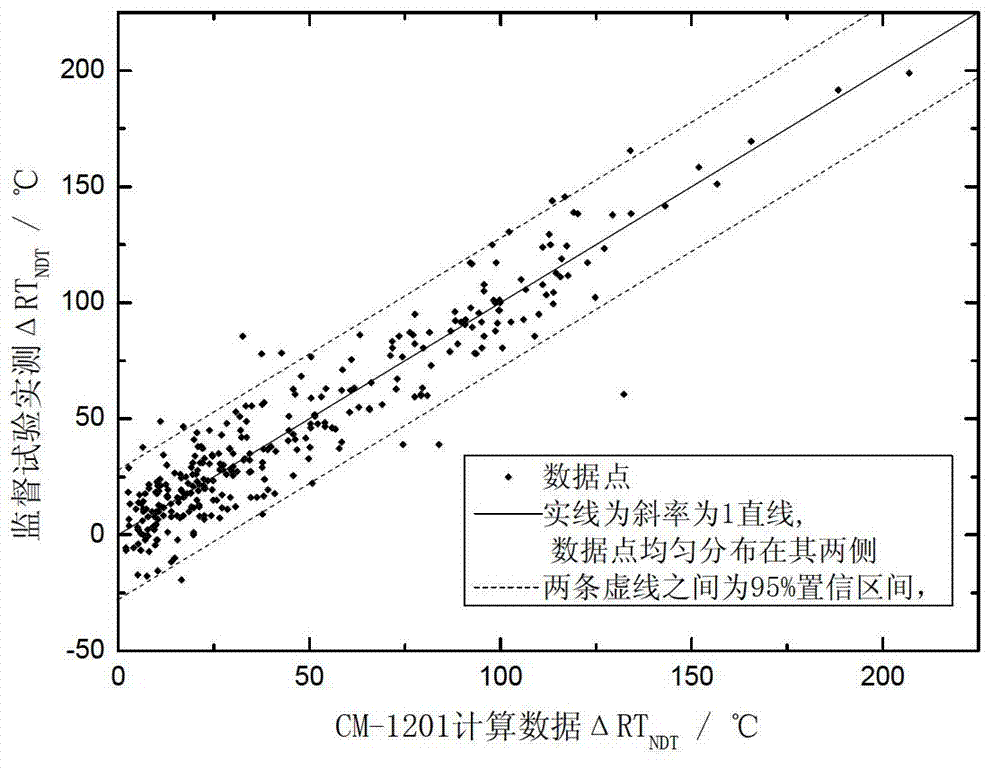
Forecast evaluation method of radiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel
ActiveCN102930167AHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsContribution functionReactor pressure vessel
The invention belongs to the technical field of security evaluation of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) of a nuclear power plant and specifically relates to a forecast evaluation method of radiation embrittlement of an RPV. According to the method, on the basis that RPV bombardment damage mechanisms are understood, experience of international correlation models is obtained; and further, due to the fact that contents of copper (Cu) in domestic RPV materials are low, contribution functions of non Cu element precipitated phase (Solute-Atom Cluster) on irradiation hardening are introduced into a calculation formula, the contribution functions are ignored by each forecast module all the time, and finally a calculation model containing a non Cu element precipitated phase mechanism is formed.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Manufacturing method of steel
The invention provides a manufacturing method of steel, comprising the following steps: smelting the molten steel to ensure that the content of P in the molten steel is less than or equal to 0.035%, the content of S is less than or equal to 0.015% and the content of V is less than or equal to 0.15%; then adding Cu element and Ni element to the molten steel to ensure that the content of Cu in the molten steel is 0.20-0.60% and the content of Ni is 0.15-0.55%; tapping to a steel ladle when the content of C in the molten steel is below 0.05%; adding physical mixture of lime and fluorite and predeoxidizing agent to the steel ladle in the tapping process to ensure that the content of S in the molten steel is less than or equal to 0.012%; adding Cr element, Si element and Mn element to the molten steel to ensure that the content of Si in the molten steel is 0.25-0.60%, the content of Mn is 0.80-1.60% and the content of Cr is 0.20-0.80%; feeding Al simple substance to the molten steel to carry out final deoxidation; heating the molten steel in the condition of argon blowing to lead the steel slag to melt; then adding Al simple substance to the steel ladle to ensure that the content of S in the molten steel is less than or equal to 0.010%; and then adding C element to the molten steel to ensure that the content of C in the molten steel is 0.08-0.16%; feeding Al simple substance and alloy containing Ti, V and N to the molten steel to control that the content of acid-soluble aluminium in the molten steel is 0.025-0.040%, the content of Ti is 0.005-0.015%, the content of V is 0.08-0.15% and the content of N is 0.010-0.020%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +3
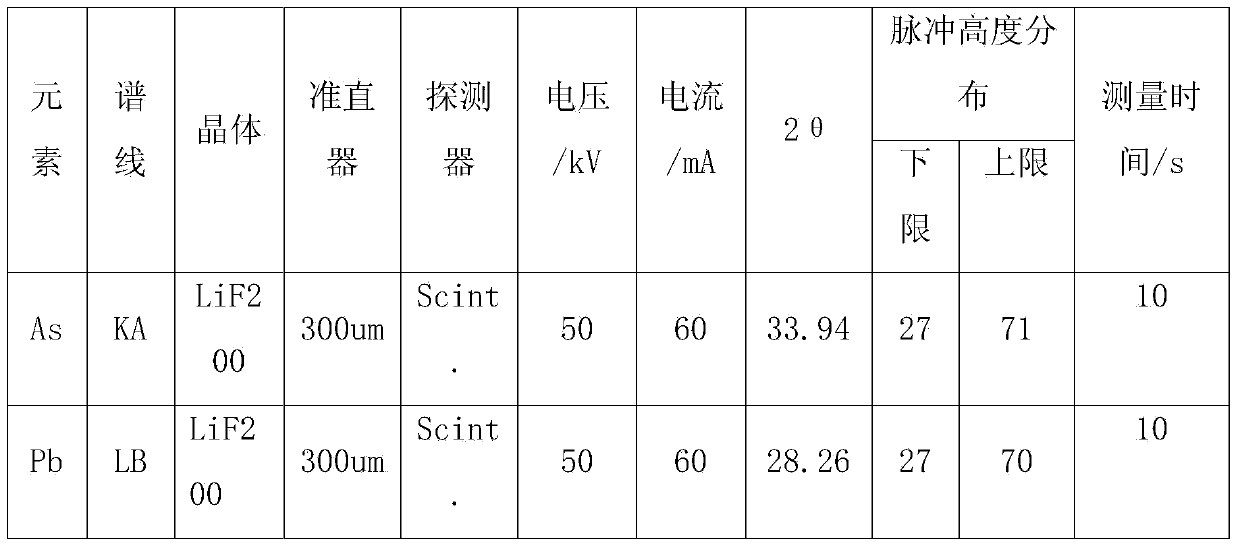
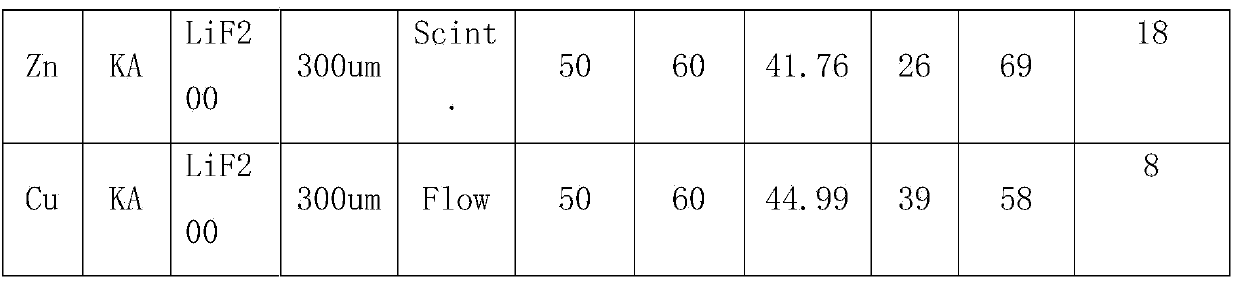
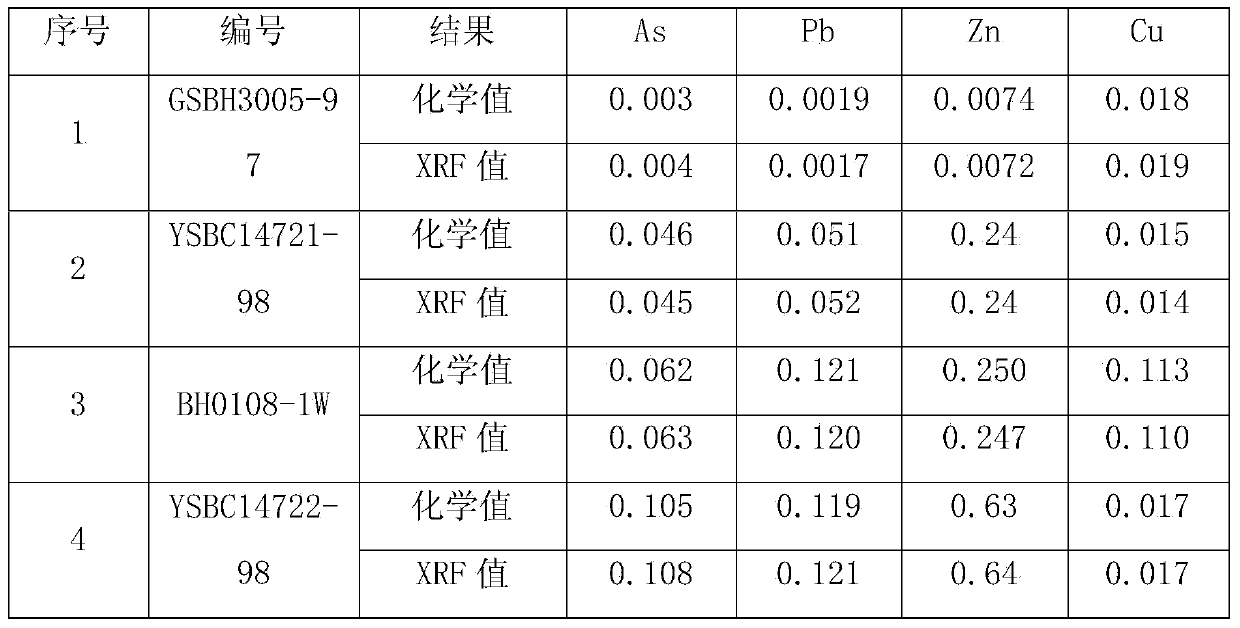
Method for determining the content of harmful elements in iron ore by using X-ray fluorescent spectrometry
InactiveCN103743769AReduce absorption-enhancement effectEvenly distributedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayCu element
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of harmful elements in iron ore by using X-ray fluorescent spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting an iron ore standard sample and a standard substance to prepare a series of standard samples, and then transferring the standard samples, an oxidant and a release agent to a platinum yellow crucible after mixing; preparing a glass sheet after melting at high temperature, so as to obtain a calibration sample; measuring the strength of As, Pb, Zn and Cu elements in the calibration sample by using an X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer, and making a calibration curve; putting a test sample fabricated by the same fabrication method as the calibration sample into the X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer; and making a calibration curve of an X-ray fluorescent spectrometry by using the calibration sample for measuring, so as to obtain the content of As, Pb, Zn and Cu elements in the sample. Thus, the content of main elements of SiO2, CaO, MgO, Al2O3, TiO2, P and the like is measured when the content of As, Pb, Zn and Cu in the iron ore is measured.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Commercial rare earth permanent magnet produced from high-abundance rare earth and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103794323AImprove remanenceHigh energy productPermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrode potentialRemanence
The invention discloses a commercial rare earth permanent magnet produced from high-abundance rare earth and a preparing method of the commercial rare earth permanent magnet. The commercial rare earth permanent magnet comprises a main phase and a grain boundary modification phase, wherein the main phase comprises low H (RE100-aMMa)-Fe-B alloy and high H Nd-Fe-B alloy. According to the commercial rare earth permanent magnet, two kinds of main alloy is adopted, the ingredients of the magnet are controlled, a stable 2:14:1 phase is formed by the high-abundance rare earth, and decomposing will not happen in the sintering process; the Cu element high in electrode potential is added into the grain boundary modification phase, the corrosion resistance of the magnet is improved, and meanwhile the microstructure of the magnet can be optimized by the grain boundary modification phase. According to the method, the two main alloy method is combined with the grain boundary modification technology, the advantages of both the two main alloy method and the grain boundary modification technology are achieved simultaneously, the problems that because of addition of the high-abundance rare earth, the corrosion resistance, the residual magnetism and the magnetic energy product of the magnet are reduced are solved, and the prepared rare earth permanent magnet meets the application requirements of commercial magnets.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Dispersed precipitated phase strengthened austenitic stainless steel with high Cr and high Ni and thermal processing method
InactiveCN103173698AImprove high temperature strengthImproved resistance to radiation swellingThermoformingCu element
The invention relates to dispersed precipitated phase strengthened austenitic stainless steel with high Cr and high Ni and a thermal processing method. The stainless steel component comprises the components in percentage by weight as follows: 0.2-0.8% of Si, not greater than 2% of Mn, 20-28% of Cr, 16-25% of Ni, not greater than 3% of Mo, 0-1% of Ti, 0-1% of W, 0-1% of Zr, 0-1% of V and the balance of Fe. The method comprises the following steps of: weighing according to the component proportion, refining and moulding; thermally forging, wherein the thermal rolling process is that rolling in four gates at 1180-1230 DEG C with the final rolling temperature over 1030 DEG C, wherein deformation is not less than 40% every time, and quenching and cooling; insulating for 20min to 1 hour at 1120-1200 DEG C; immediately quenching; performing high temperature annealing treatment at 950-1050 DEG C, insulating for 1.5-4 hours, then, furnace cooling or air cooling to room temperature, and directly quenching and quickly cooling. According to the invention, MC phase is separated out in the high temperature deformation process by comprehensively adding Ti, W, V, Zr and C elements. After thermal forming, relative materials are separated out through fine dispersion. Dimension of a second precipitated phase is controlled by the cooling rate through controlling subsequent thermal deformation processing parameters and the thermal treatment system.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
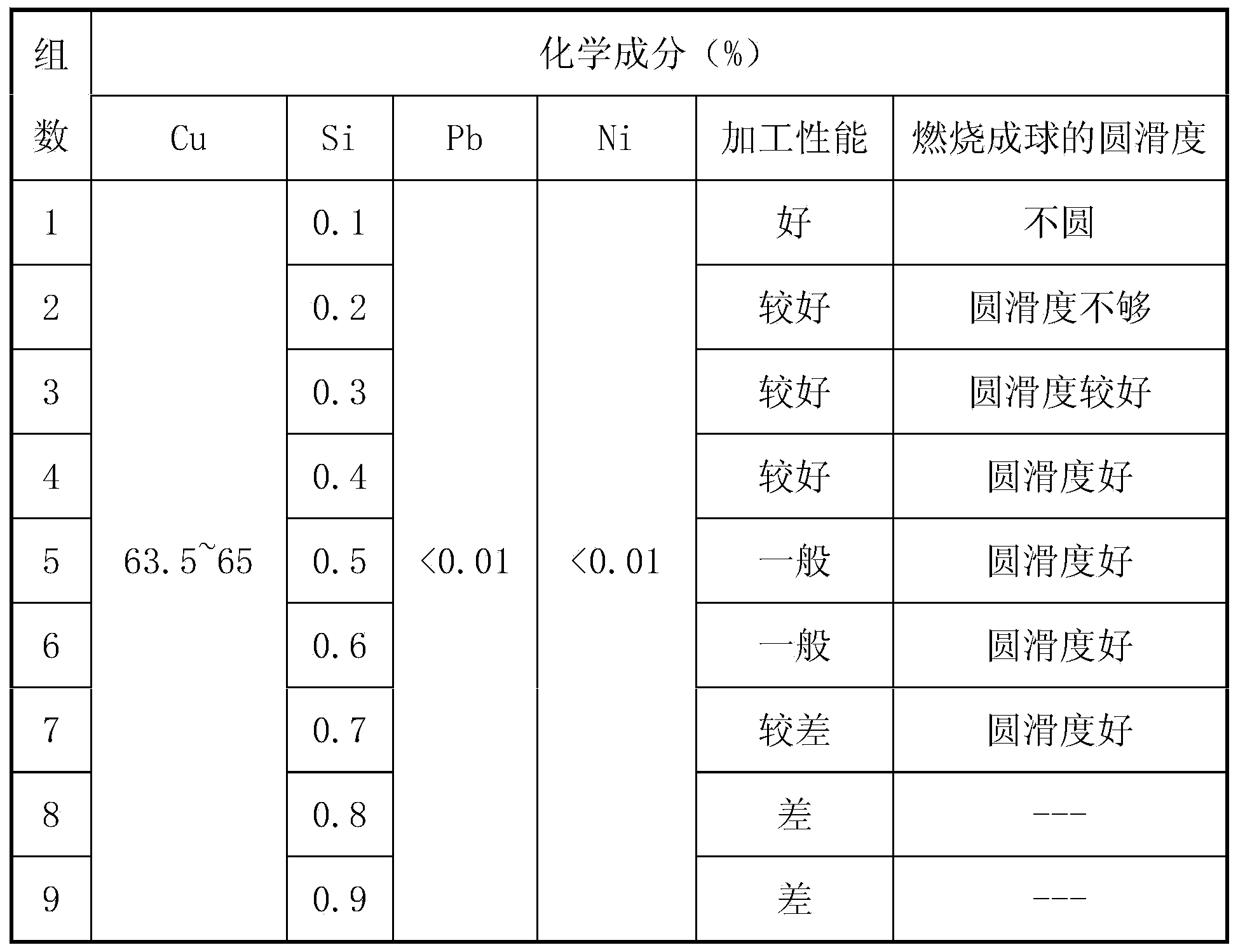
Brass wire and processing method of brass wire
The invention provides a brass wire applied to the technical field of production and processing of wires. The invention simultaneously relates to a processing method of the brass wire. The brass wire comprises the following components: Cu, Sn, Si and Zn, wherein the Cu element accounts for 63.5%-65% by weight, the Sn element accounts for 0.8-1.2% by weight, the Si element accounts for 0.10-0.50% by weight, and the balance is the Zn. In the brass wire and the processing method, provided by the invention, the mechanical performance value of the brass wire is controlled at 650-750MPa, a sphere formed by combustion is smooth and full, the problem of brittle failure caused by over-hard performance can be avoided, and the brass wire can not be processed into a ball needle due to the influence of relatively soft performance. When the brass wire is formed, a rewinding machine is adopted for taking up, and the diameter degree is good; and when the brass wire is machined by a customer, the paying-off is smooth, the wire wrapping phenomenon can be avoided, and the brass wire can completely meet the requirements of jewelry processed from the brass wires in jewelry industry.
Owner:安徽鑫科铜业有限公司
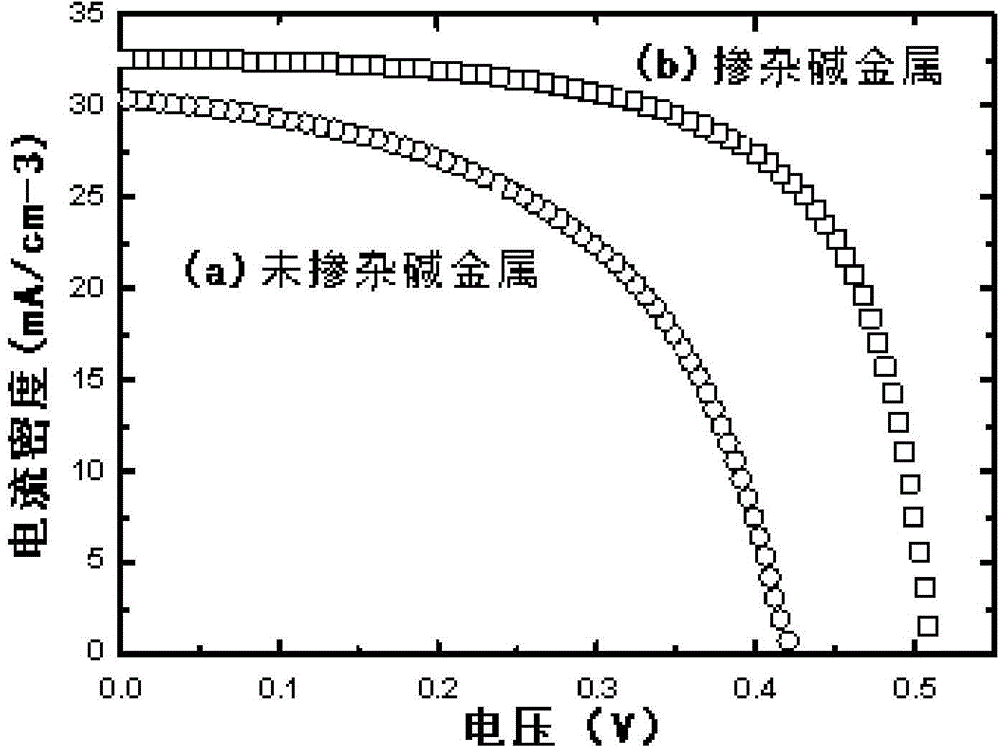
Alkali metal doping method for preparing CIGS absorbing layer on flexible substrate
ActiveCN105720132ASimple processPrevent crystallizationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCu elementEvaporation
The invention relates to an alkali metal doping method for preparing a CIGS absorbing layer on a flexible substrate, and belongs to the technical field of copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin film solar cells. The alkali metal doping method comprises that a CIGS absorbing layer is deposited by using a co-evaporation process; and with the increase of Cu content in the absorbing layer, the thin film growth experiences a copper-poor to copper-rich process, in the copper-rich process, when Cu(In+Ga)>1 in a CIGS thin film, the evaporation of the Cu element is stopped so that the slightly copper-rich CIGS thin film can finally become copper-poor, then the In and Ga atoms are evaporated until the deposition thickness is 1 / 10-3 / 10 of the thickness of the absorbing layer, in this process, an alkali metal compound is co-evaporated, the doping amount is 0.08-0.12% of the atomic ratio with respect to the CIGS thin film, the temperature of the substrate is reduced to the room temperature, and the CIGS thin film having a thickness of 1-3 <mu>m is obtained. The invention has the advantages of having a simplified process, a high production efficiency and thin film crystal high-quality, increasing the carrier concentration of the absorbing layer, lowering the resistivity, improving the electrical properties of the thin film cell, thus improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the CIGS thin film solar cell and the like.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel and production method thereof
ActiveCN101775560AEasy to processGood plasticity at room temperatureProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceCold formedChemical composition
The invention discloses a nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel. The weight percentages of chemical compositions are as follows: less than or equal to 0.1 percent of C, less than or equal to 2.0 percent of Si, 3.0 percent to 4.9 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.04 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.006 percent of S, 16.0 percent to 18.0 percent of Cr, 4.0 percent to 6.0 percent of Ni, 3.0 percent to 5.0 percent of Cu and less than or equal to 0.1 percent of N, 0.04 percent to 0.1 percent of Ce or 0.002 percent to 0.005 percent of B is added as well, and the rest is Fe and inevitable impurities. On the basis of the prior nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel, a moderate amount of Cu element is added, so that excellent plasticity is obtained, and meanwhile, since a Ce or B element is added, the stainless steel with good hot workability is obtained. On the basis of keeping the original low cost, the invention appropriately enhances the cold-forming property and the hot-working property.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Welding wire for connection of aluminum/steel dissimilar alloy and processing process thereof
InactiveCN101745751AHigh affinityGrowth inhibitionWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceCu element
The invention aims to provide a welding wire for connection of aluminum / steel dissimilar alloy and a processing process thereof. The welding wire has a good comprehensive performance, adopts a special element to substitute the Si element, ensures good flow of solder and reduces the brittleness of the compound layer on the joint interface. In the technical scheme, the welding wire is prepared through adding such elements as Ag, Mn, Mg, Ti, Zr and Zn with Al-Cu as a matrix. The processing process of the welding wire comprises stock preparation, melting, component analysis, extrusion, wire drawing and cleaning. The invention has the advantages that: due to the high content of Cu element, the invention can inhibit the growth of the compound layer on the interface, improve the performance of the Al-Fe compound layer, and particularly improves the crack resistance of the compound layer; since the Ag element, the aluminum and the steel all have high affinity, the invention can enhance the flowing property of liquid solder in the steel surface; the Mn and Ti elements can improve the performance of the compound and the flowing property of the solder; the Mg and Zn elements can promote the flowing property of the solder and improve the strength of the welding wire; and the refined grain of Zr can also enhance the strength of the welding wire.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
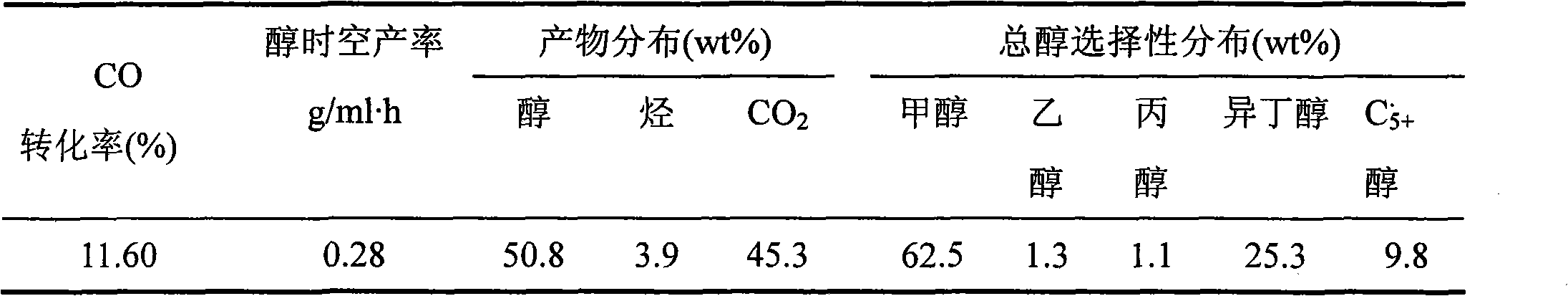
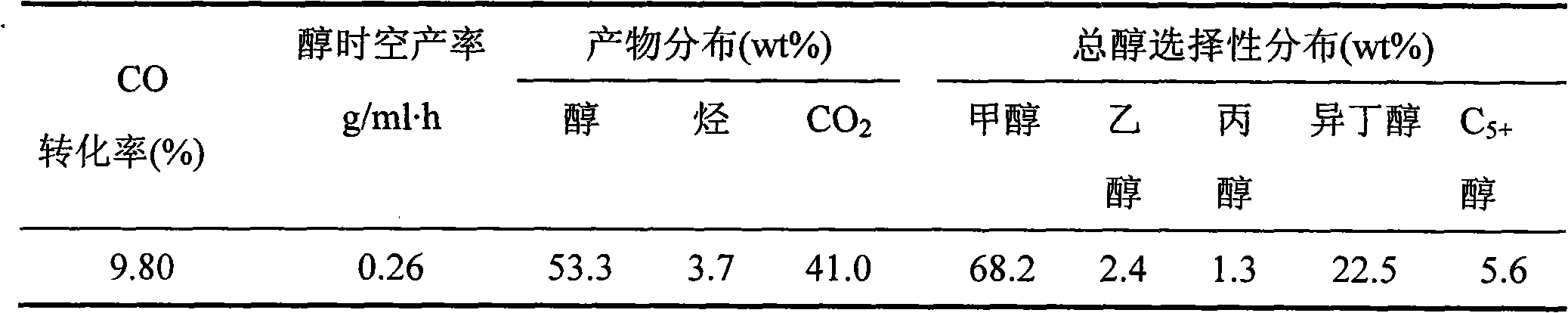
Catalyst for preparing low-carbon mixed alcohol by using synthesis gas and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102029166AHigh selectivityMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationSyngasNitrate
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing low-carbon mixed alcohol by using synthesis gas, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 54 to 75 percent of ZrO, 10 to 20 percent of MnO2, 0.4 to 1.0 percent of RxO, 3 to 5 percent of CuO, 4 to 20 percent of C and 0.5 to 1.5 percent of noble metal. The catalyst is prepared by adopting a co-precipitation method, wherein the precursors of the Zr, Mn and Cu elements are nitrates, and the precursor of the C is starch. The catalyst has mild reaction conditions, the selectivity of C2+ alcohol can be more than 36 weight percent, the selectivity of isobutyl alcohol can be more than 25 weight percent, and the selectivity of hydrocarbon (mainly comprising methane) can be less than 4 weight percent. By adding the starch in the preparation of the catalyst and forming amorphous porous carbon in the drying and roasting processes, the specific surface area of the catalyst can be improved, the dispersion of metal oxides is effectively improved, sintering is prevented, and the stability of the catalyst is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI ENERGY CHEM
Component design and production method of 1500 MPa-grade low-carbon and medium-manganese copper-contained steel
The invention relates to component design and a production method of 1500 MPa-grade low-carbon and medium-manganese copper-contained steel. The 1500 MPa-grade low-carbon and medium-manganese copper-contained steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.20-0.23% of C, 0.5-0.8% of Si, 3.5-4.0% of Mn, 1.2-2.0% of Al, 0.5-1.0% of Cr, 0.6-1.0% of Cu, 0.2-0.5% of Ni, 0.003-0.012% of N, 0.00051-0.003% of B, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. One part of alloy elements are added based on traditional TRIP steel to largely increase the content of manganese to reach the medium-manganese range; when Al is used for replacing the Si elements, a proper amount of Si elements are retained, so that the Al and Si elements are matched for use; and a certain quantity of precipitation-hardened Cu elements are added to match with a proper amount of Ni elements for use to eliminate the hot brittle phenomenon caused by Cu in hot working. In addition, few Cr elements are added; a proper amount of N elements are added to match with the Al elements for use; through matching between hot rolling and hot partition processes, a martensite+residual austenite+separated second-phase particle structure with ultrahigh strength and excellent plasticity is obtained; and the tensile strength exceeds 1500 MPa.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Ultrahigh-strength and high-elongation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy and method for manufacturing same
The invention discloses ultrahigh-strength and high-elongation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy and a method for manufacturing the same, and belongs to the technical field of metal alloy. The alloy mainly comprises, by mass, from 9.7% to 10.3% of Zn, from 1.7% to 2.3% of Mg, from 1% to 1.3% of Cu and from 0.11% to 0.14% of Zr; contents of other impurity elements in the alloy are not higher than 0.1%; and a relation of mass fraction ratios of Zn elements, Mg elements and Cu elements in the alloy meets inequalities of 4.5< / =(Zn+0.8XCu) / Mg< / =6.5, 0.4< / =Cu / Mg< / =0.6 and 8.5< / =[Zn+0.8XCu) / Mg] / (Cu / Mg)< / =10.5. The ultrahigh-strength and high-elongation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy and the method have the advantages that the tensile strength sigma b of the alloy is higher than or equal to 720Mpa, the yield strength sigma 0.2 of the alloy is higher than or equal to 670Mpa, and the elongation delta of the alloy is higher than or equal to 11%; the alloy is manufactured by means of homogenizing annealing, extrusion, solution hardening and T6 artificial ageing treatment in a traditional casting mode; a procedure is simple, the ultrahigh-strength and high-elongation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy is low in cost and excellent in comprehensive performance, and service requirements of the modern aviation industry and the automobile industry on materials are met.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Hard and tough nano composite ZrAlCuN coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104480443AOptimizing Process ParametersHigh hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSingle substanceCu element
The invention discloses a hard and tough nano composite ZrAlCuN coating and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a nano composite coating and a preparation method thereof. A hard and tough coating with thickness of several microns is generated on the surface of a metal matrix to improve the wearing resistance of the matrix under action of impact load, and can be used as a tool and mould surface coating as well as an erosion-resistant protective coating. The coating is a composite coating consisting of a transition layer and a working layer, wherein the transition layer is used for improving bonding strength. The working layer is a nano composite coating consisting of nitrides and metal single substances which are immiscible with one another. The preparation method of the hard and tough nano composite ZrAlCuN coating comprises the following steps: sputtering Zr, Al and Cu elements by adopting a magnetron sputtering technology, and performing co-deposition by taking N2 as a working gas to form the nano composite structure coating. The coating not only has high hardness, but also has high toughness, and can be firmly bonded with the matrix.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Sn-Zn series leadless solder alloy and its preparation method
InactiveCN101058131AImprove wettabilityImprove oxidation resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCu elementRare earth
The invention relates to a Sn-Zn lead free solder alloy. It feeds Cu and RE through Sn-Zn alloy to get Sn-Zn lead free solder alloy, with composition of Zn 8-9%, Cu 1-3%, RE being 0. 025-0. 1%, with the rest being Sn. RE is the surface active element, it can improve the evenness and moisture of the solder tissue, and the Cu element can improve the elasticity of the alloy. On the basis of retaining the low fuse point of the Sn-Zn lead free alloy, it has good moisture and anti oxidization feature. It can be widely used for electronic sealing material.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
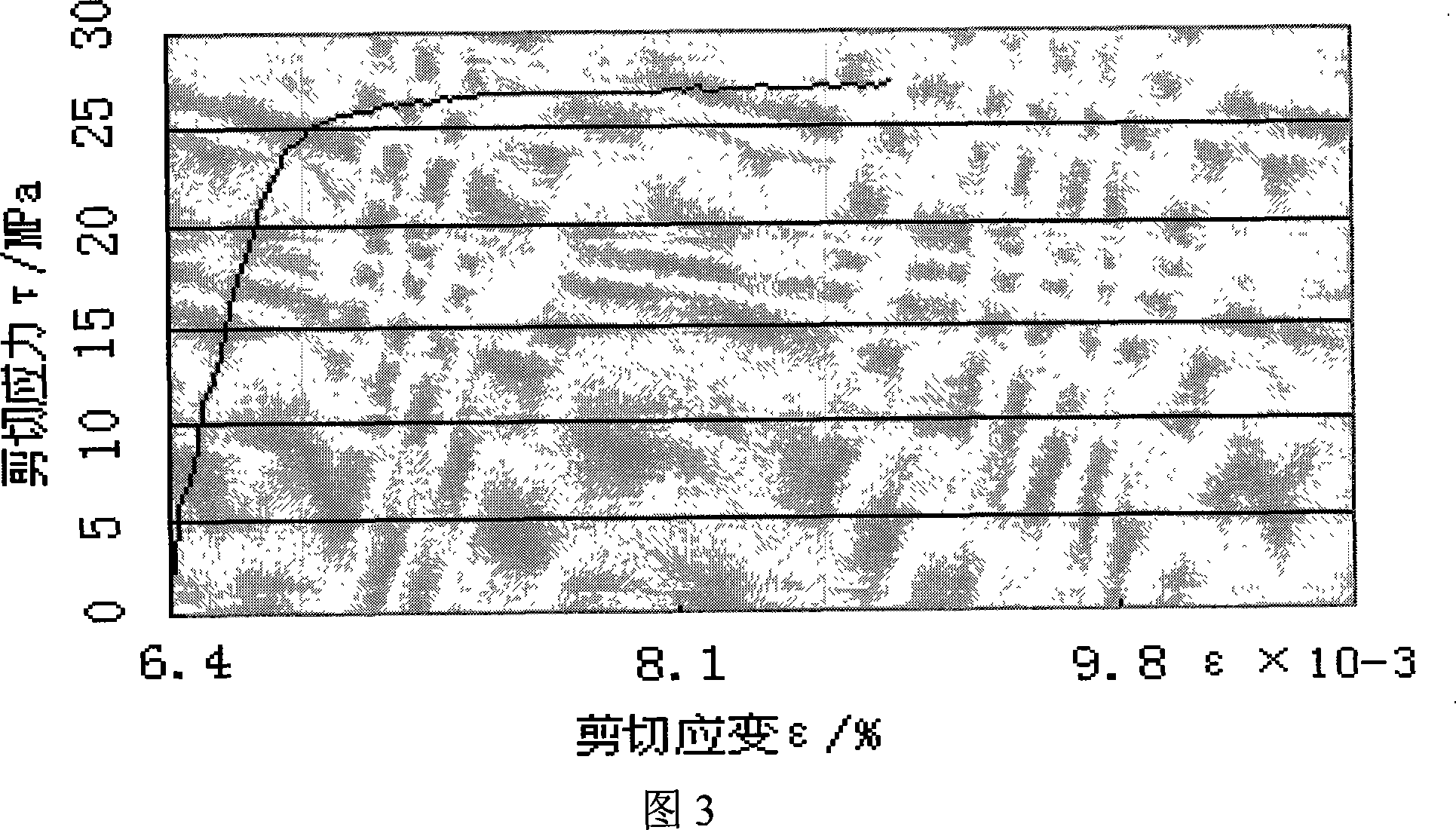
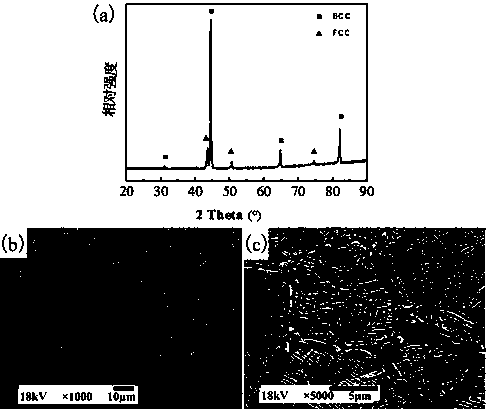
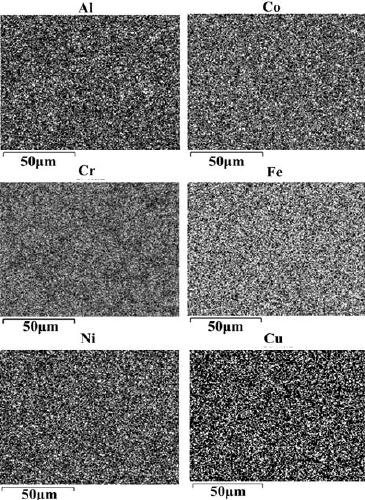
Preparation method of corrosion-resistant high-strength AlCoCrFeNi-Cu high-entropy alloy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a corrosion-resistant high-strength AlCoCrFeNi-Cu high-entropy alloy. The corrosion-resistant high-strength AlCoCrFeNi-Cu high-entropy alloy is preparedby using a high energy ball milling and liquid phase assisted SPS sintering technology. The corrosion-resistant high-strength AlCoCrFeNi-Cu high-entropy alloy prepared by the preparation method of the corrosion-resistant high-strength AlCoCrFeNi-Cu high-entropy alloy has the advantages of the structure is simple; elements are uniformly distributed; the precipitation of a Cu element is avoided, ananometer-sized precipitation / coupling structure is realized; the corrosion resistance is excellent, high strength and high toughness are realized, and wide industrial application prospect is realized.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
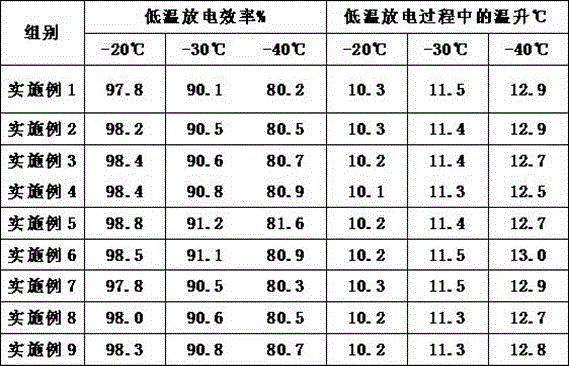
Low-temperature lithium ion secondary battery
ActiveCN106384840AImprove cycle performanceImprove low temperature performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsDischarge efficiencyCu element
The invention discloses a low-temperature lithium ion secondary battery. The low-temperature lithium ion secondary battery comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a diaphragm arranged between the positive electrode and the negative electrode and electrolyte, wherein a positive electrode active material adopted by the positive electrode is prepared by mixing a component A with a component B; a chemical formula of the component A is LiNiCoyMn(1-x-y)O2, wherein x is greater than or equal to 0 and is smaller than or equal to 1, y is greater than or equal to 0 and is smaller than or equal to 1, and the sum of the x and the y is greater than or equal to 0 and is smaller than or equal to 1; the component B is selected from at least one of a lithium-containing compound containing K, Mg, Zr, Zn, Ti, Cr, Al, V or Cu elements; counted by mass percentage, the component B accounts for 10 to 15 percent of the positive electrode active material. Compared with the prior art, the low-temperature lithium ion secondary battery disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the low-temperature discharge ability of a lithium battery is improved while the cycle performance of the lithium battery is guaranteed; 1C discharge is realized under the condition that the temperature is 40DEG C below zero; the discharging efficiency can reach 80 percent or above; in addition, the low-temperature lithium ion secondary battery is low in discharge temperature rise and high in safety coefficient.
Owner:杭州蔚斯博系统科技有限公司
High-strength face-centered cubic structure medium-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
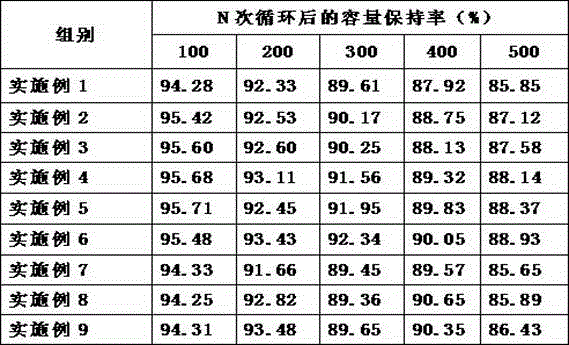
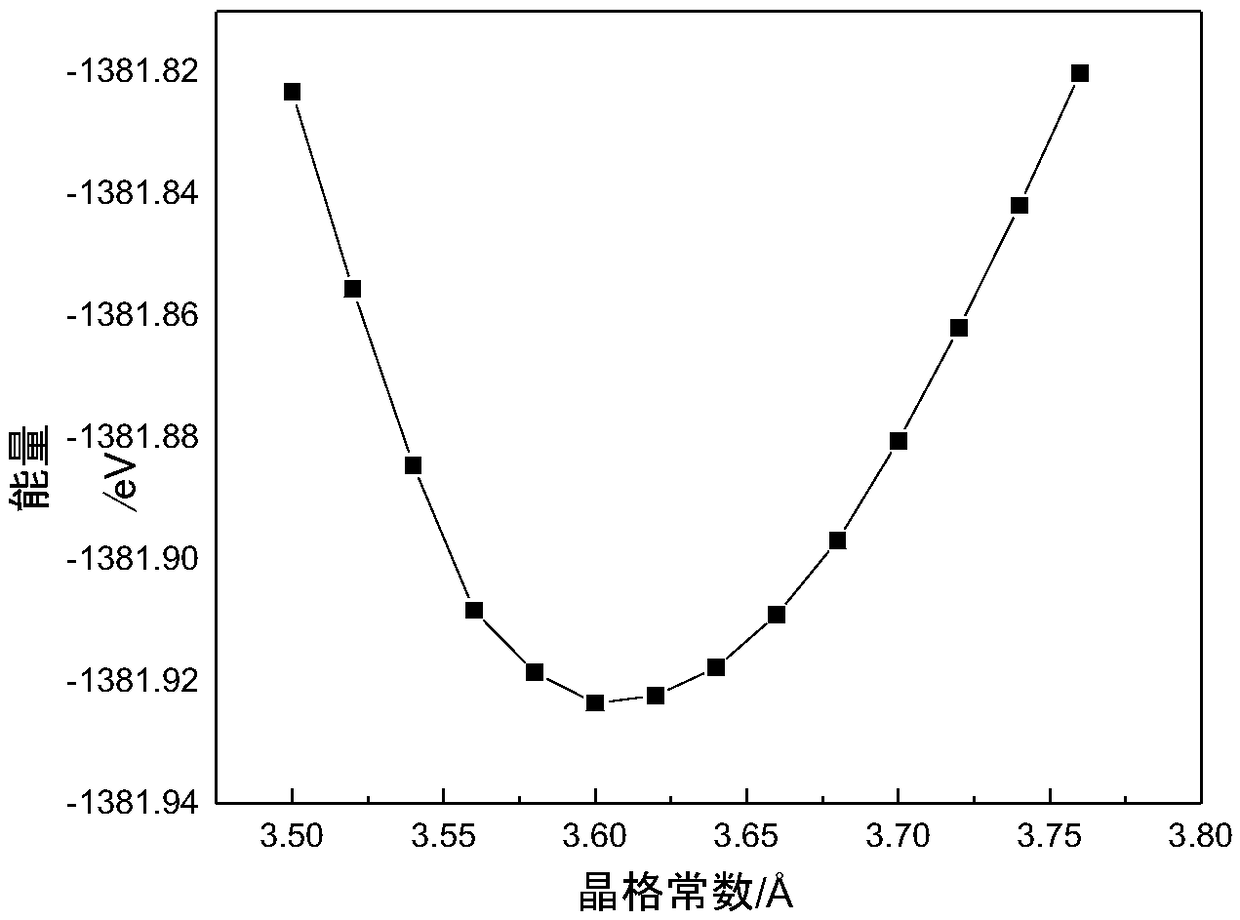
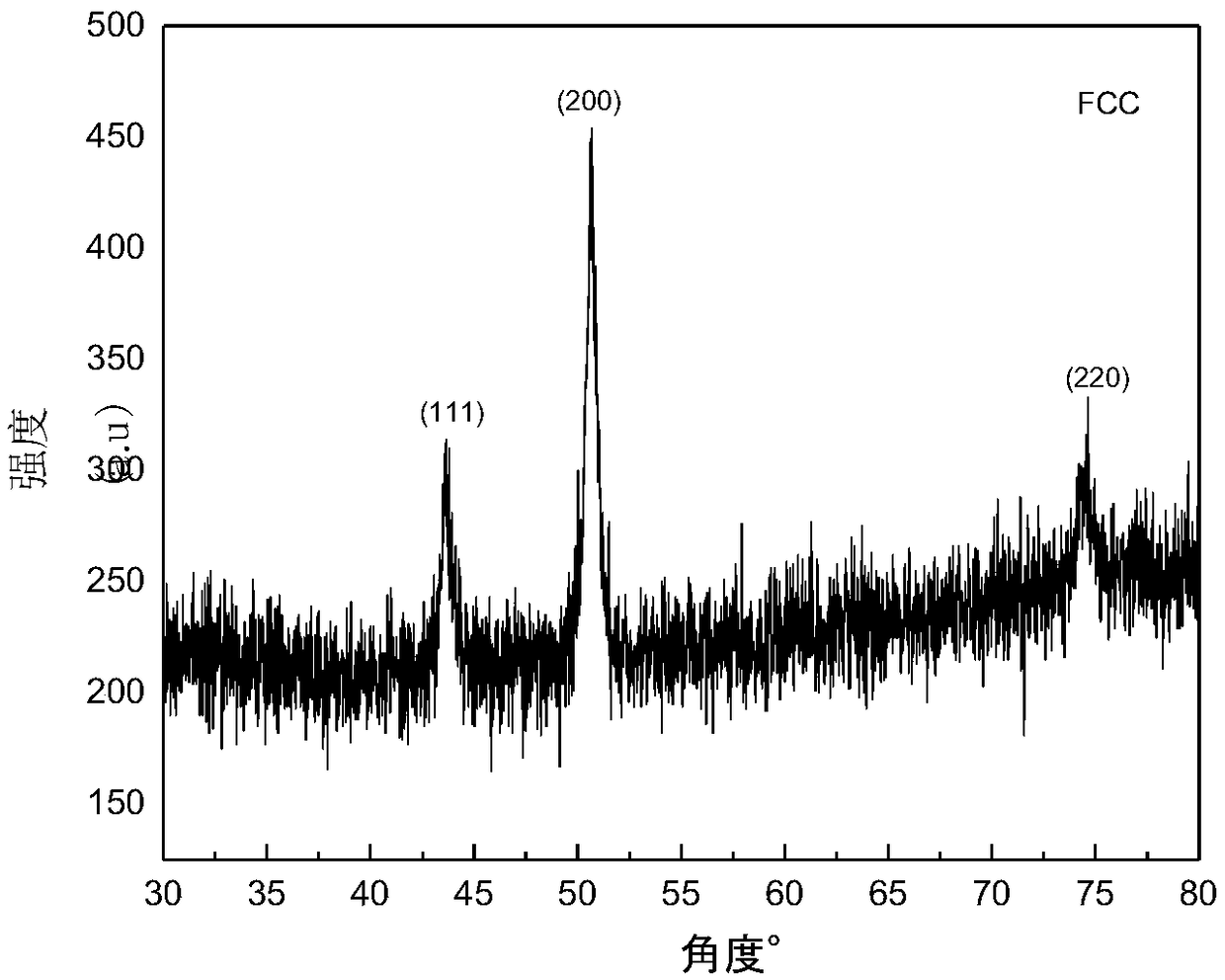
The invention discloses a high-strength face-centered cubic structure medium-entropy alloy and a preparation method thereof. The CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy comprises Co, Ni and Cu elements; a resultof respective comparison of different medium-entropy alloys in electron concentration and mixing enthalpy according to the Gibbs free energy and the phase formation law of the alloy shows that the CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy has the tendency to form a single-phase FCC structure, a CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy model is constructed based on the tendency, and the alloy is predicted to be a ductile material by a first-principles technique. The preparation method of the alloy comprises the following steps: batching, vacuum melting, suction casting, homogenization annealing and solid solution treatment. Co, Cr, and Cu with a purity of 99% or more are selected and are proportioned according to an equimolar ratio or an approximately equimolar ratio, the proportioned raw materials are placed in a vacuum smelting furnace and are multiply smelted, suction casting molding is carried out after the components are uniform, and the obtained casting undergoes homogenization annealing and solid solutiontreatment to obtain the CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy having a single face-centered cubic structure and having a room temperature compressive strength of above 1600 MPa and a compression ratio of above20%.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
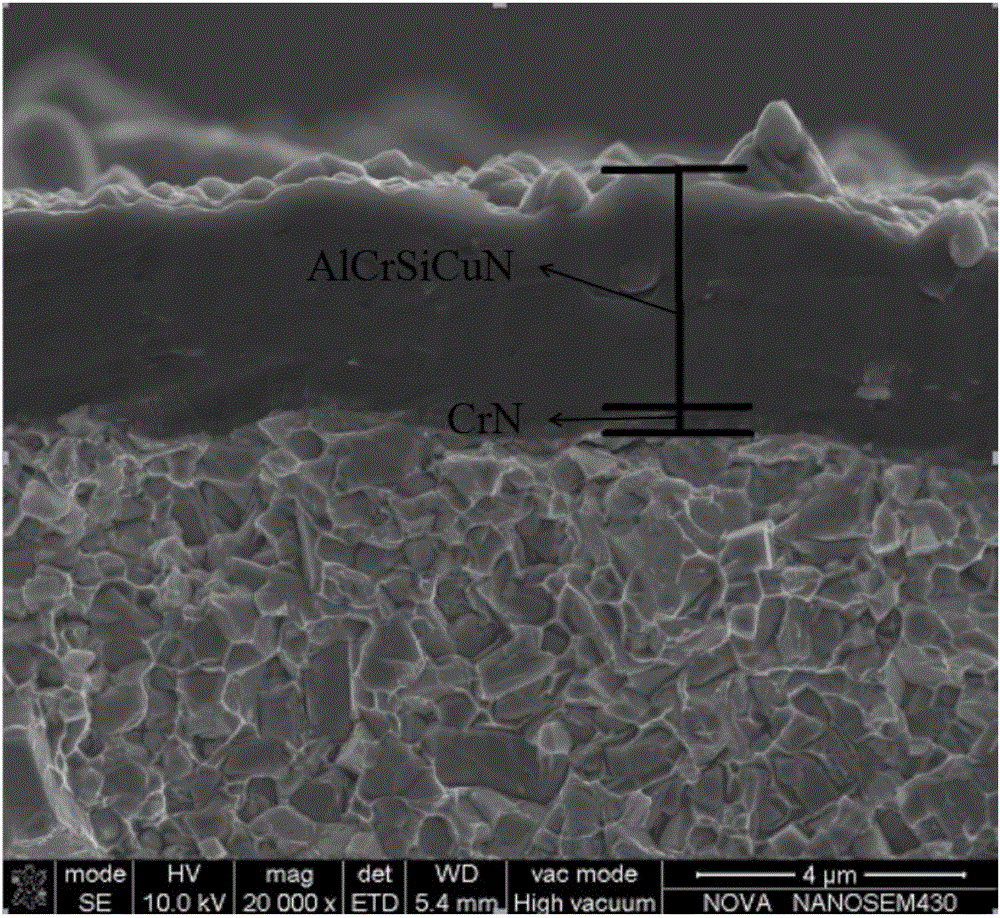
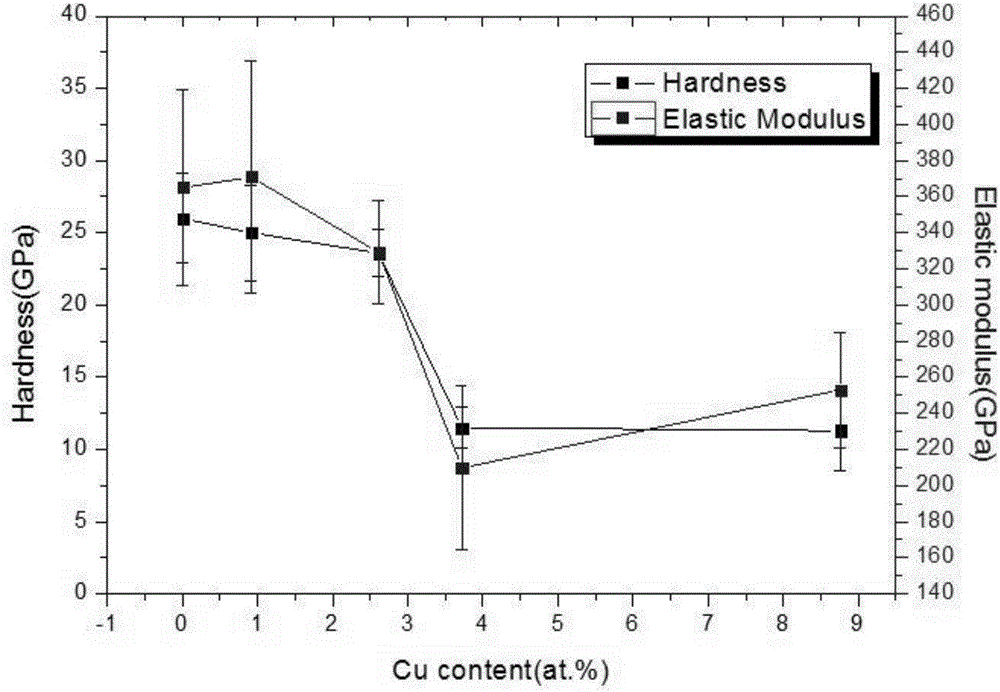
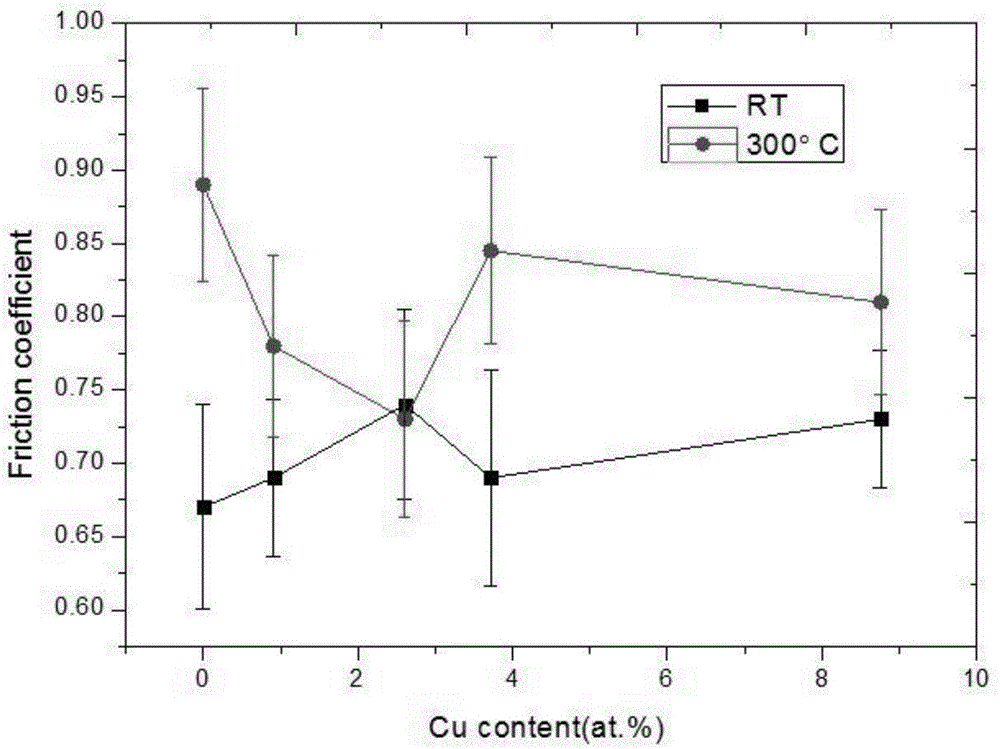
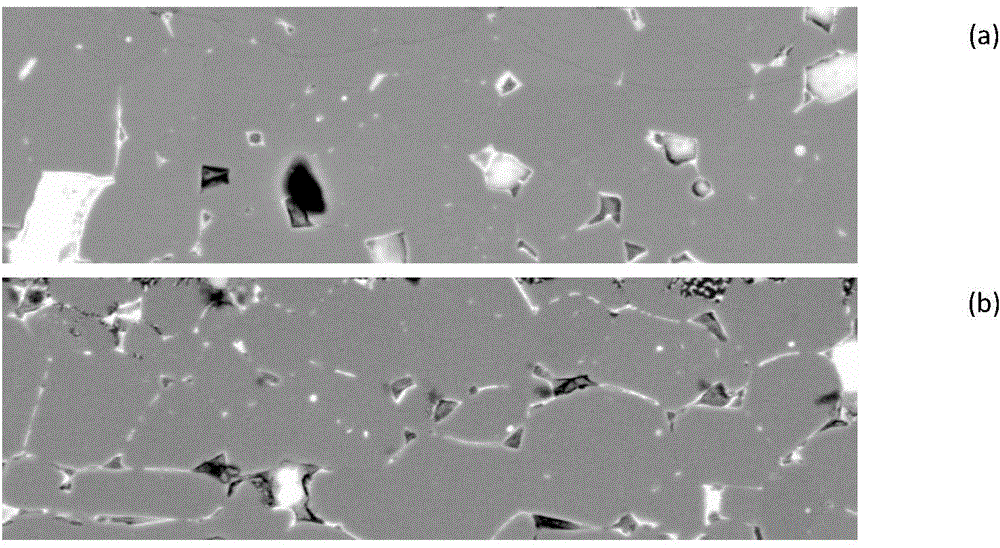
AlCrSiCuN nano multilayer coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107523790AFast cutting speedIncrease feed rateVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringCu element
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
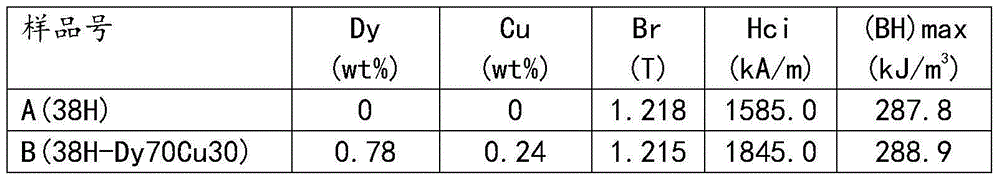
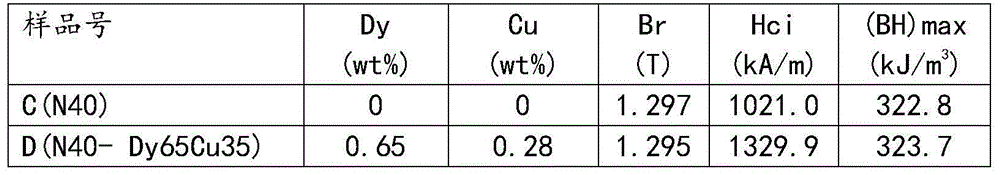
Method for preparing high-performance NdFeB magnet through grain boundary diffusion Dy-Cu alloy
ActiveCN104795228AAdd depthFacilitated DiffusionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAdditive ingredientCu element
Provided is a method for preparing a high-performance NdFeB magnet through grain boundary diffusion Dy-Cu alloy. Dy-Cu alloy rapid-hardening thin straps or common cast ingots are coarsely broken and directly serve as a surface diffusion source of the NdFeB magnet, a Dy-Cu-rich thin layer is formed on the grain boundary of the NdFeB magnet through diffusion thermal treatment, and therefore the high-coercivity NdFeB magnet can be obtained. According to the method, Dy-Cu alloy ingredients are designed as required, after the Dy-Cu alloy rapid-hardening thin straps are made or the traditional cast ingots are coarsely broken, the Dy-Cu alloy rapid-hardening thin straps or the traditional cast ingots are laid around the NdFeB magnet and heated till the temperature is slightly higher than the temperature of the melting point of the Dy-Cu alloy cast ingots so that the Dy-Cu alloy rapid-hardening thin straps or the traditional cast ingots can be molten to be in a liquid state and attached to the surface of the NdFeB magnet, then annealing thermal treatment is performed, and finally, the product is obtained. The diffusion source Dy-Cu alloy will be molten to be in a liquid state within the grain boundary diffusion thermal treatment temperature range, the Dy-Cu alloy rapid-hardening thin straps or the traditional cast ingots can be coarsely broken and serve as the diffusion source, the process that the Dy-Cu alloy rapid-hardening thin straps or the traditional cast ingots are made into fine powder with which the surface of the NdFeB magnet is coated is omitted, diffusion of Dy elements and Cu elements in the grain boundary can be accelerated, the depth of a diffusion layer is increased, and the high-performance NdFeB magnet can be obtained.
Owner:包头品高永磁材料有限公司
Back contact layer structure and CdTe solar battery comprising back contact layer structure
The invention discloses a back contact layer structure and a CdTe solar battery comprising the back contact layer structure. The quantity of Cu elements required by implementation of ohm back contact is greatly decreased by introducing a high-work function transitional metal oxide layer between a CdTe thin film and a metal back electrode; meanwhile, the transitional metal oxide layer achieves an effect of preventing metal atoms in the metal back electrode from being dispersed to a CdTe and CdS / CdTe p-n node; therefore, the stability of the back contact electrode is improved, and high-conversion efficiency of the battery and the long-term stability of the battery in a use process are guaranteed.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
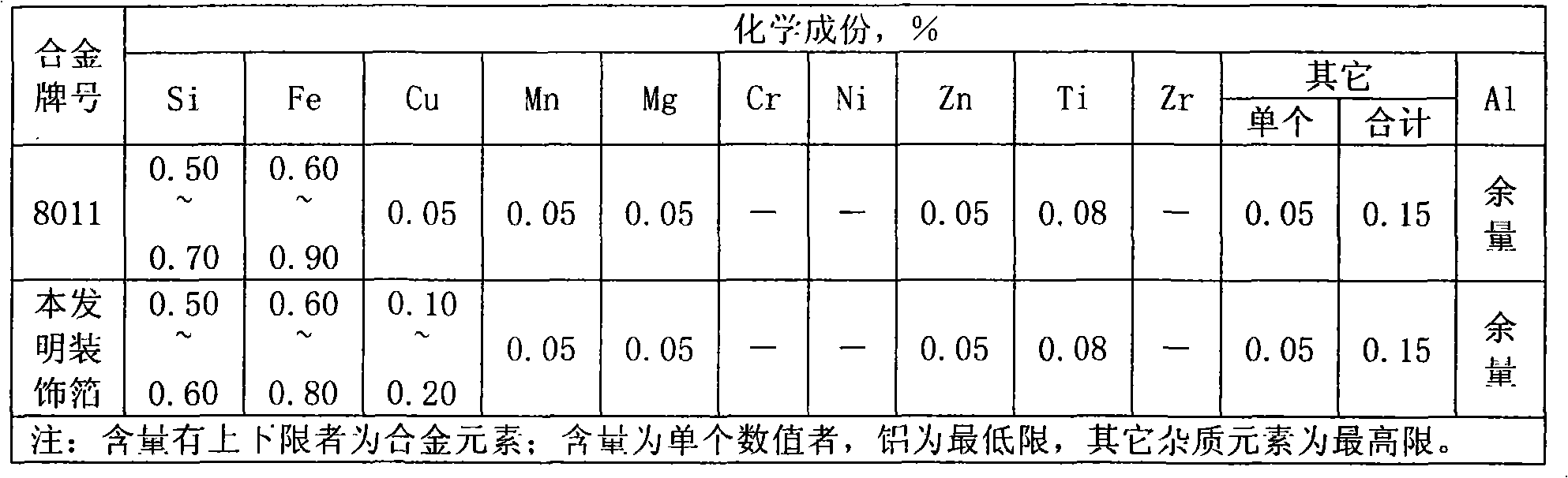
0.022 mm temperature-tolerance decoration foil and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a 0.002 mm temperature-tolerance decoration foil and a preparation method thereof. The decoration foil is characterized by being made by adding 0.10-0.20 percent by weight of Cu element on the basis of 8011 alloy. The preparation method comprises the following process procedures: cold-rolling a cast-rolling plate into 0.44-0.85 mm from 6.0-10.0 mm, adopting an H22 status for interannealing, cold-rolling to 0.28-0.60 mm, foil-rolling to reach a finished thickness of 0.022 mm, and slitting, wherein the H22 status annealing process comprises the following steps: adopting a burner-gas temperature controlling way for annealing, namely, charging below 100 DEG C, heating 1.5 hours till the temperature reaches 350-450 DEG C, and preserving the temperature for 5-15 hours; cooling for 0.5 hour till the temperature reaches 320-380 DEG C, preserving the temperature for 5-15 hours, cooling for 1.5 hours till the temperature reaches 200 DEG C, and discharging; and achieving the total processing ratio being more than 95 percent after interannealing. The invention has good temperature tolerance and stable quality.
Owner:新疆天展新材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com