Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169 results about "Gibbs free energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
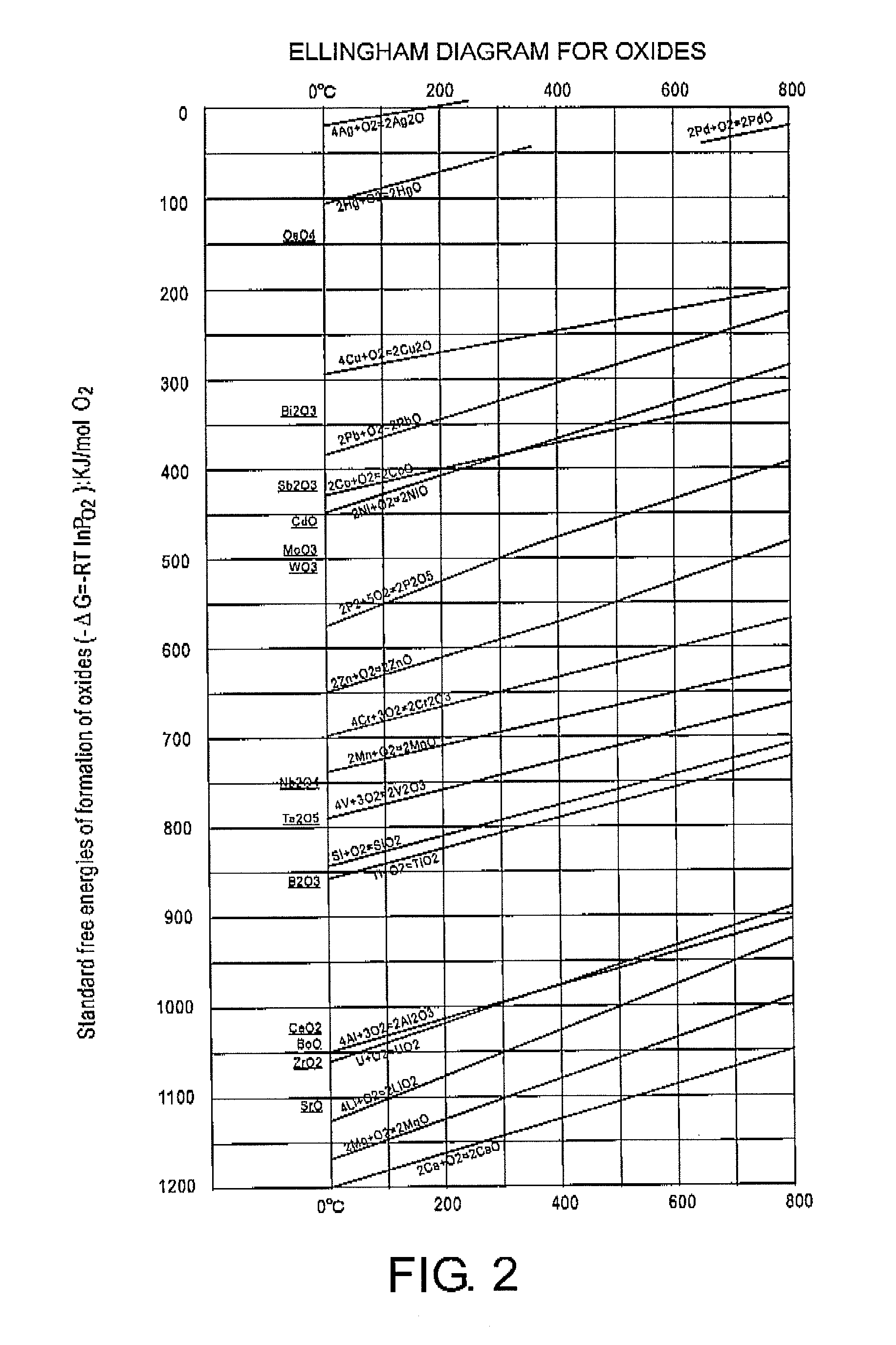
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (IUPAC recommended name: Gibbs energy or Gibbs function; also known as free enthalpy to distinguish it from Helmholtz free energy) is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum of reversible work that may be performed by a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure (isothermal, isobaric). The Gibbs free energy (ΔG∘=ΔH∘-TΔS∘; J in SI units) is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a thermodynamically closed system (one that can exchange heat and work with its surroundings, but not matter); this maximum can be attained only in a completely reversible process.
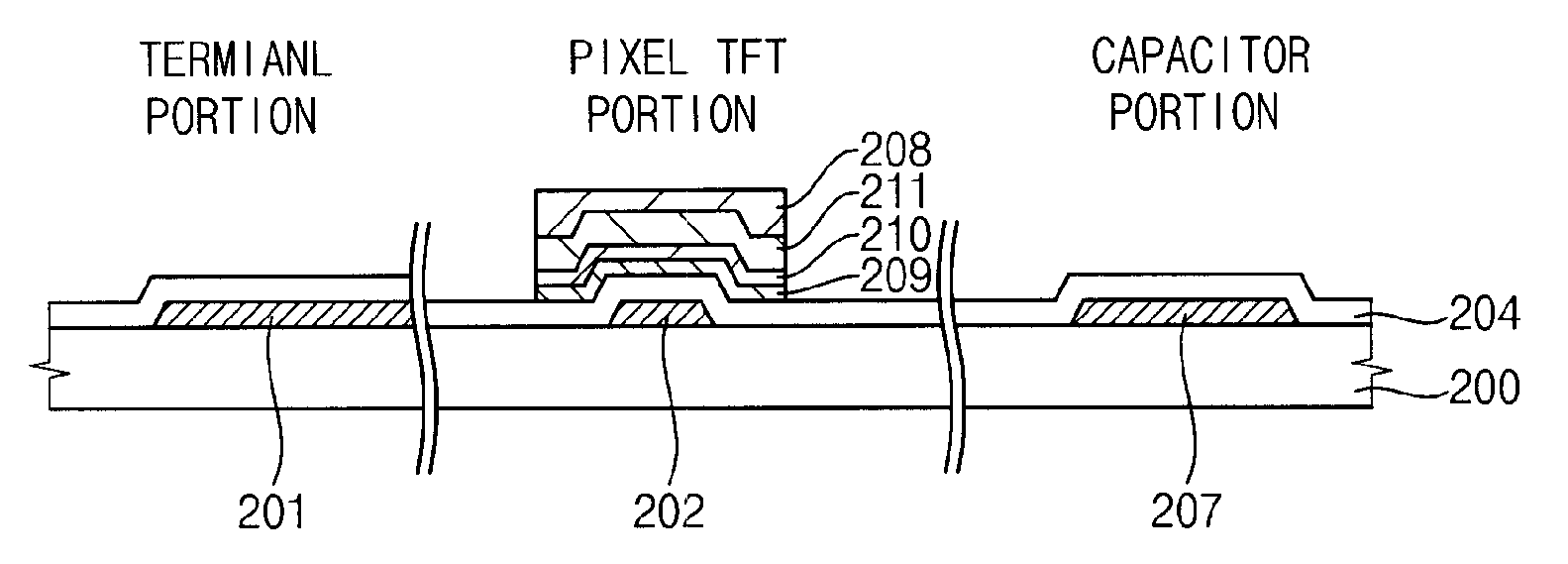
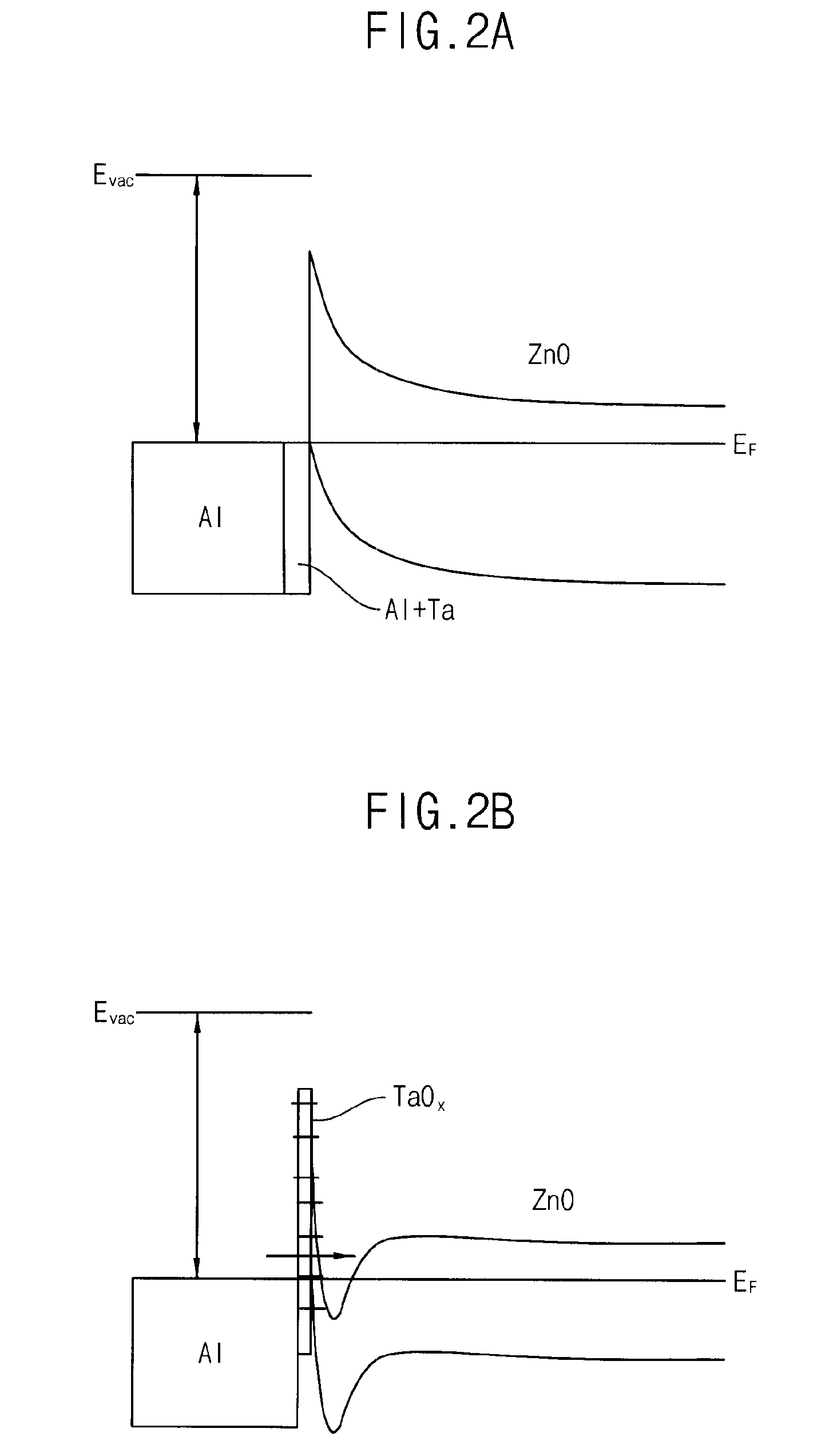
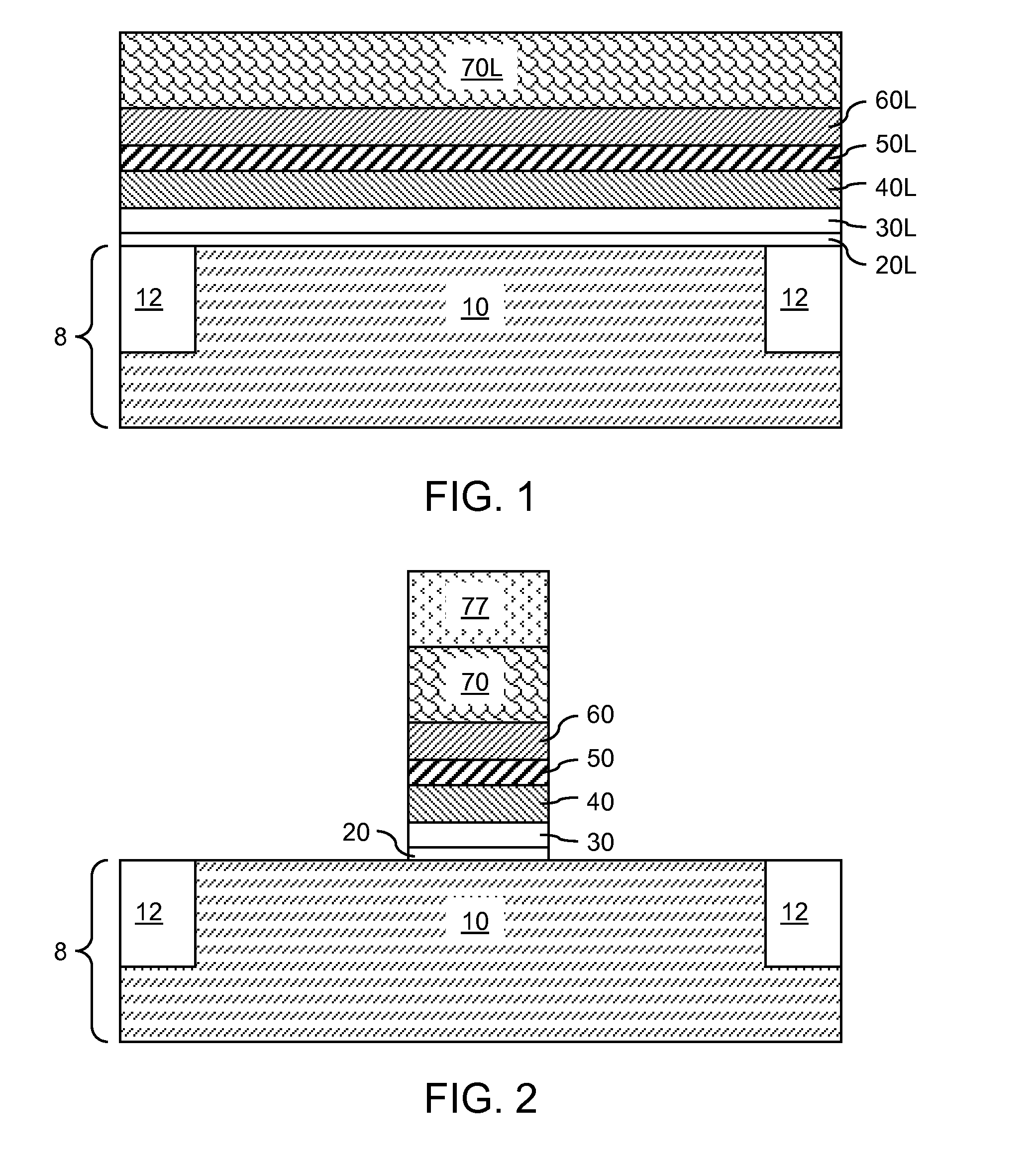
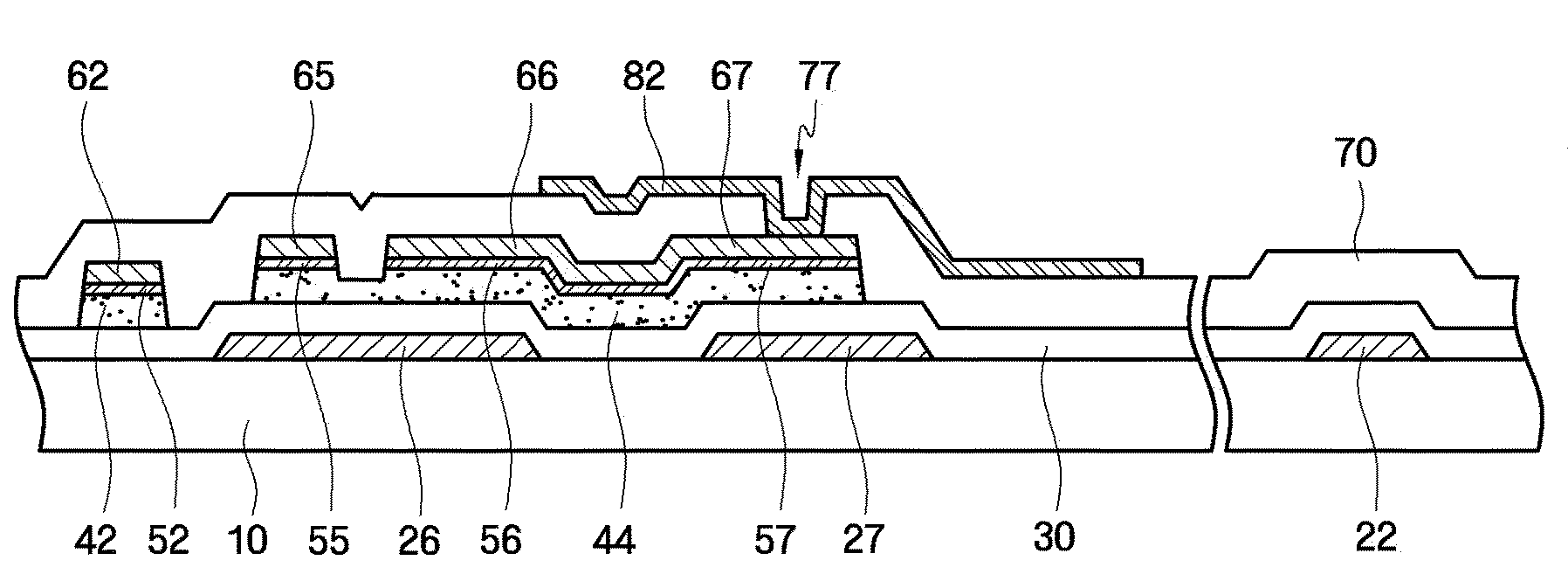
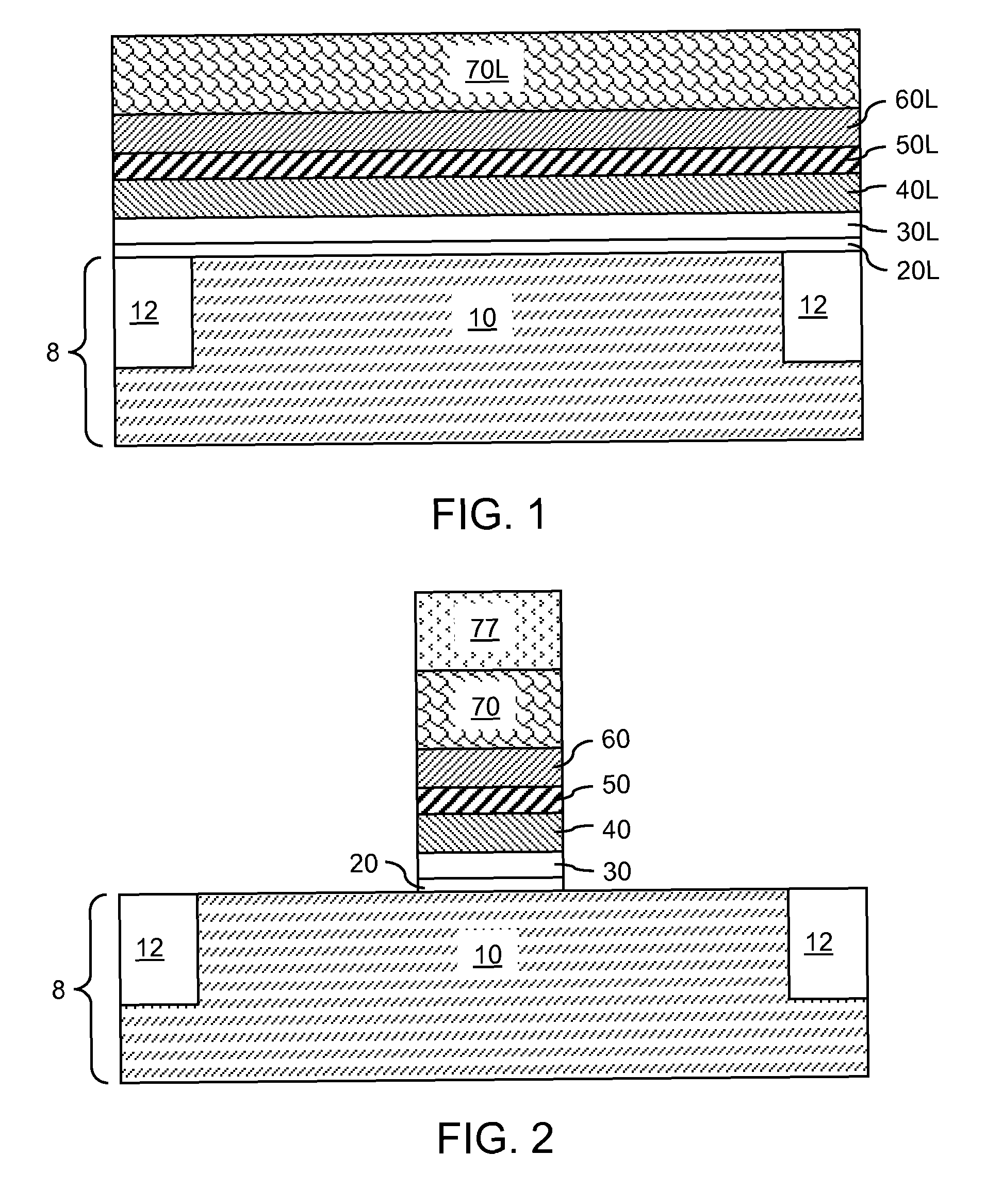
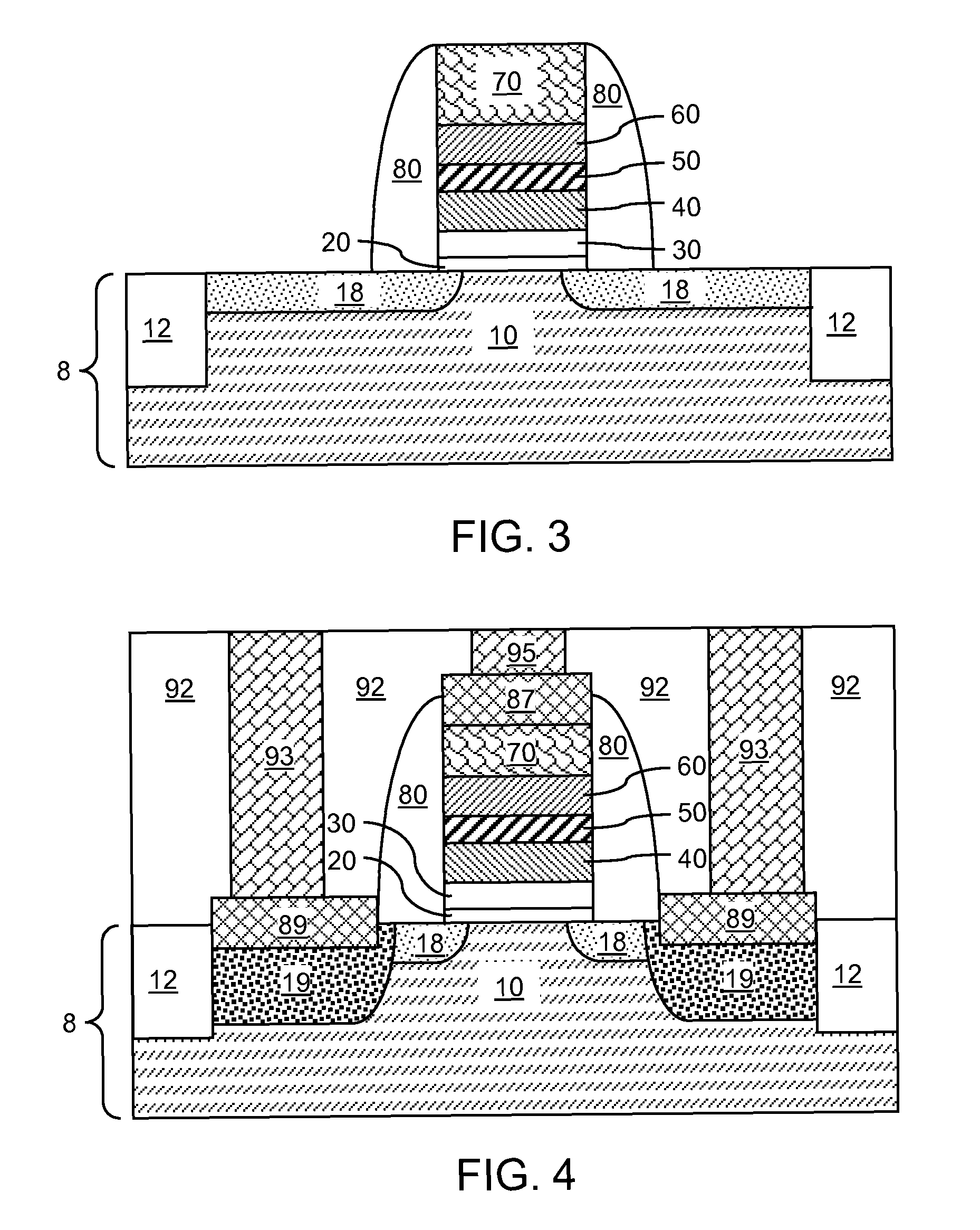
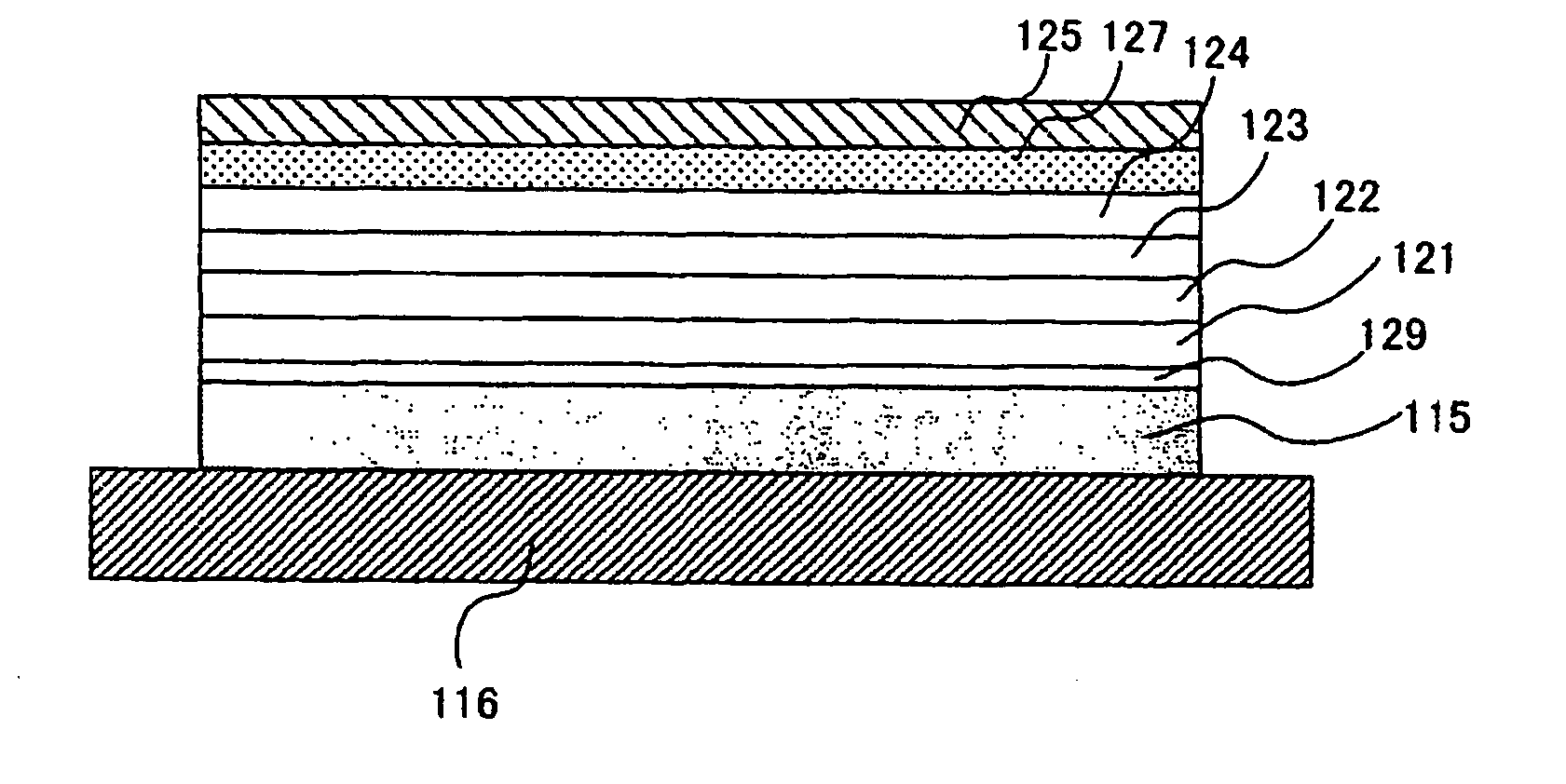
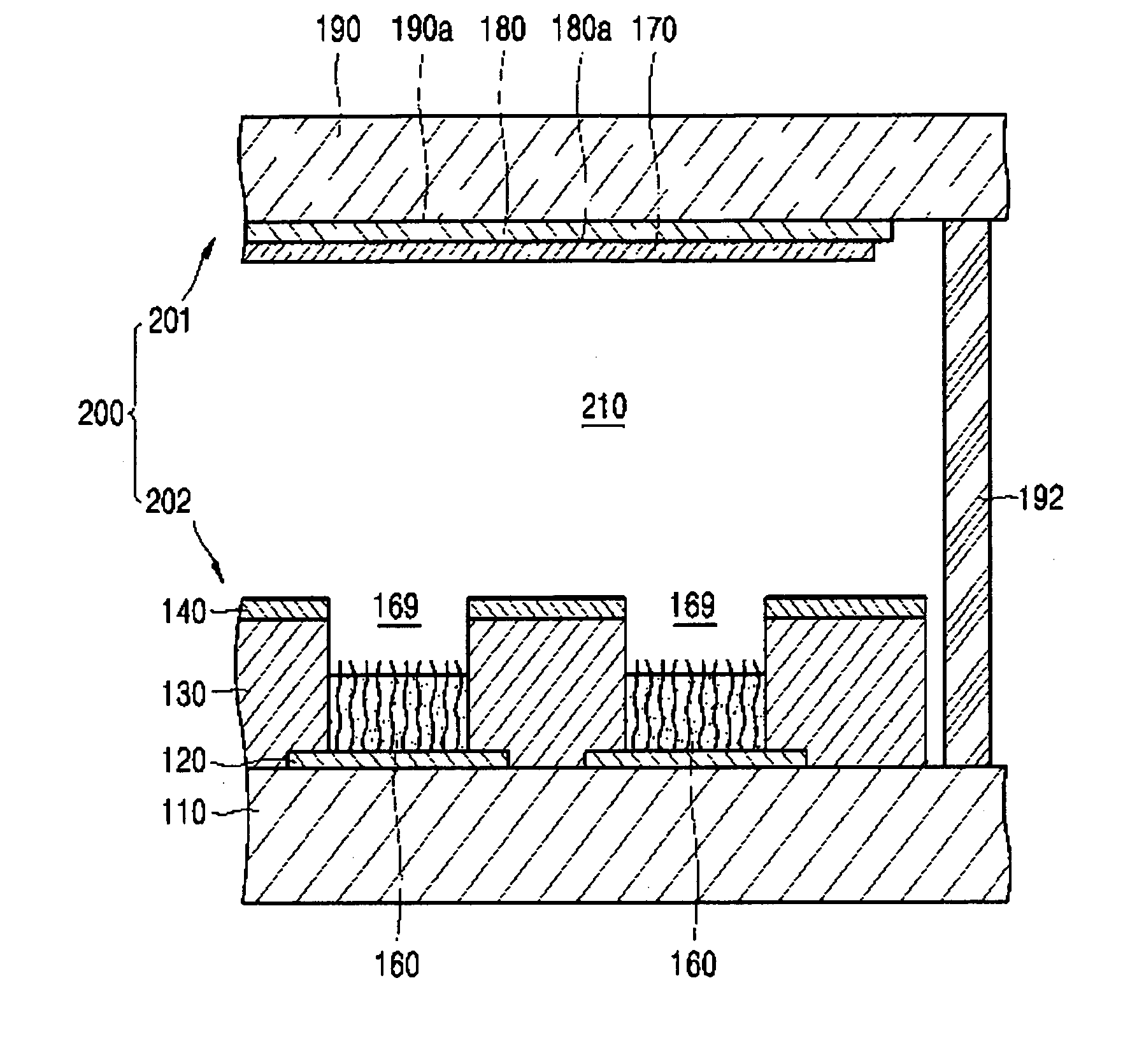
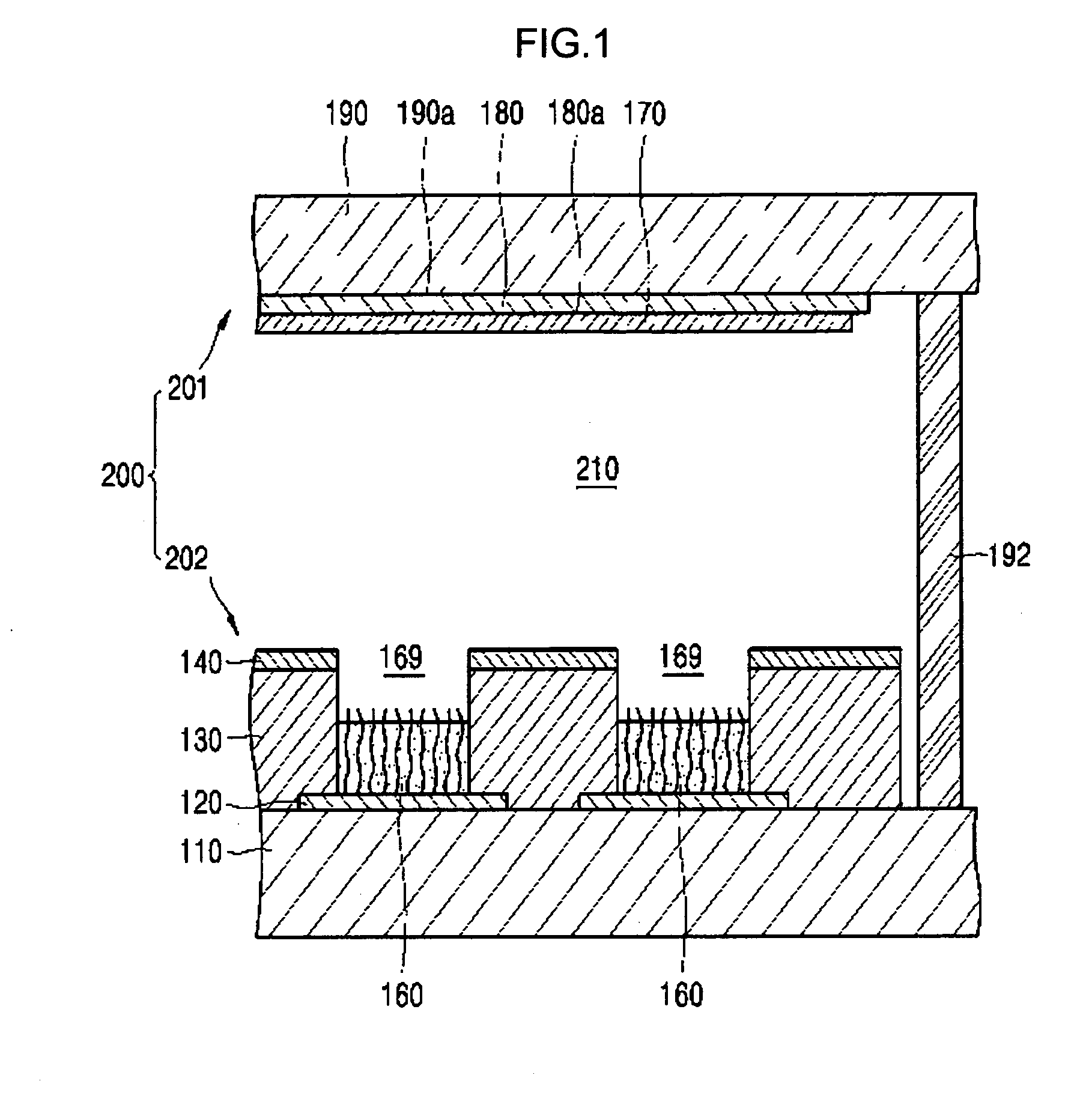
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
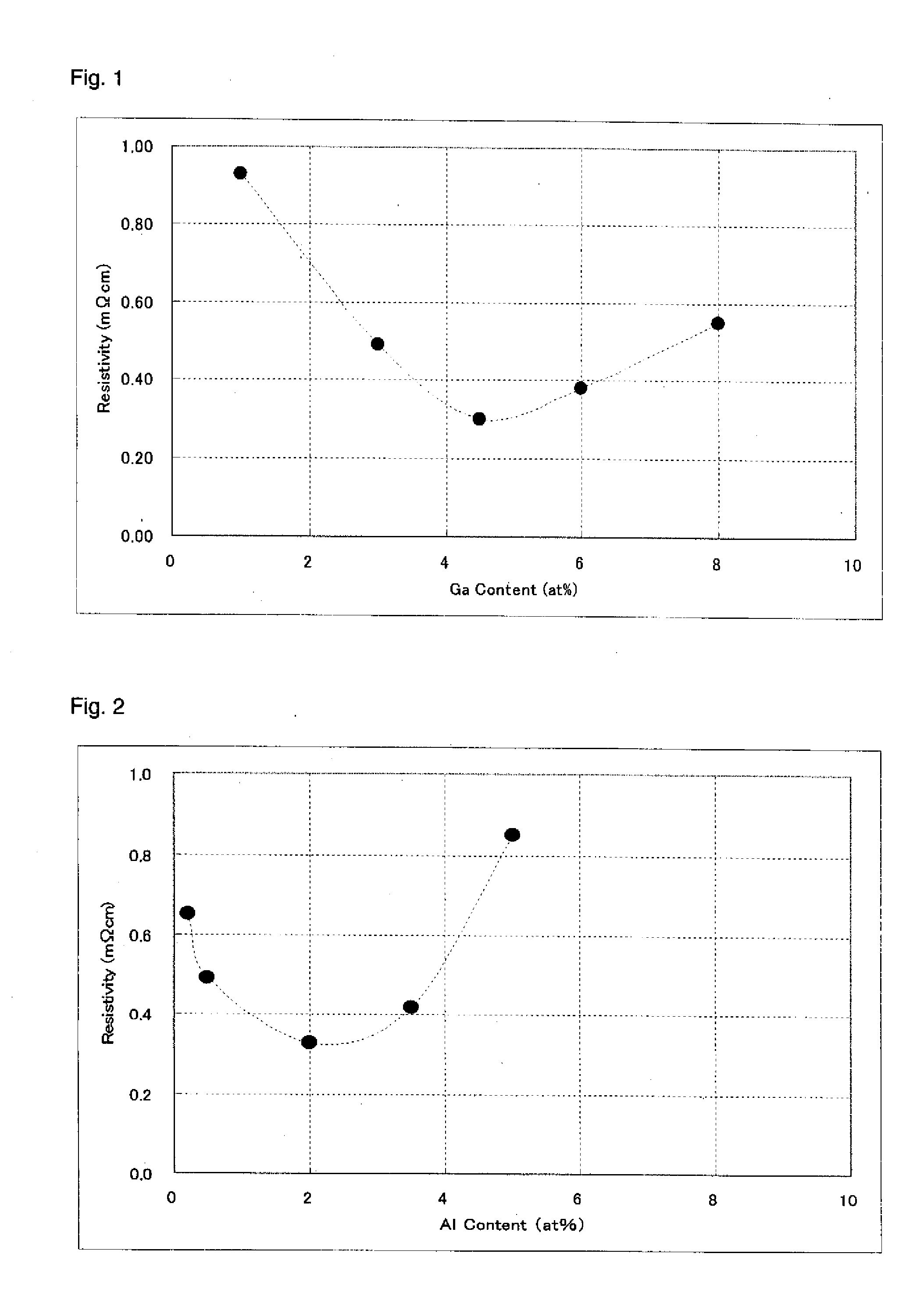
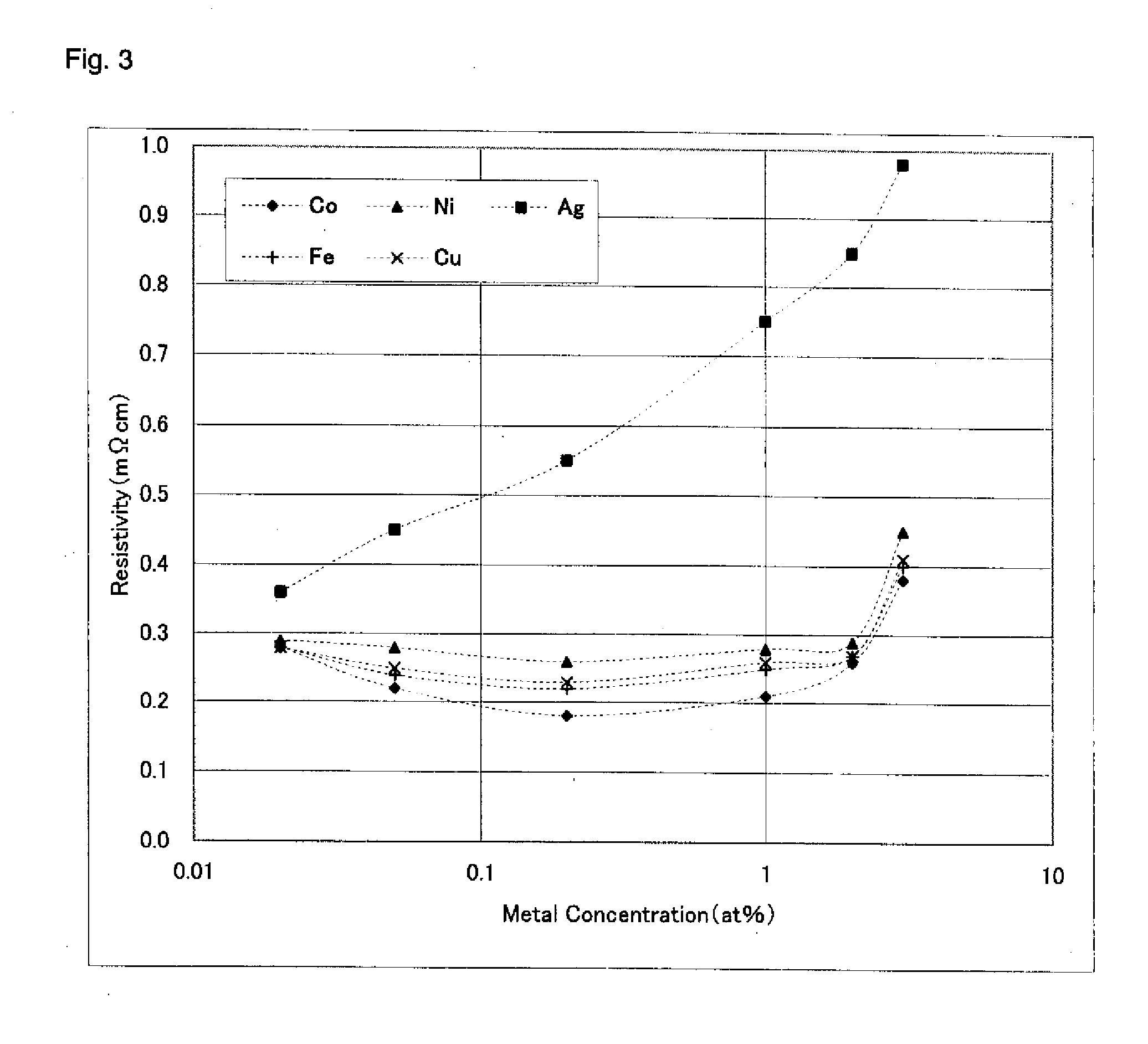
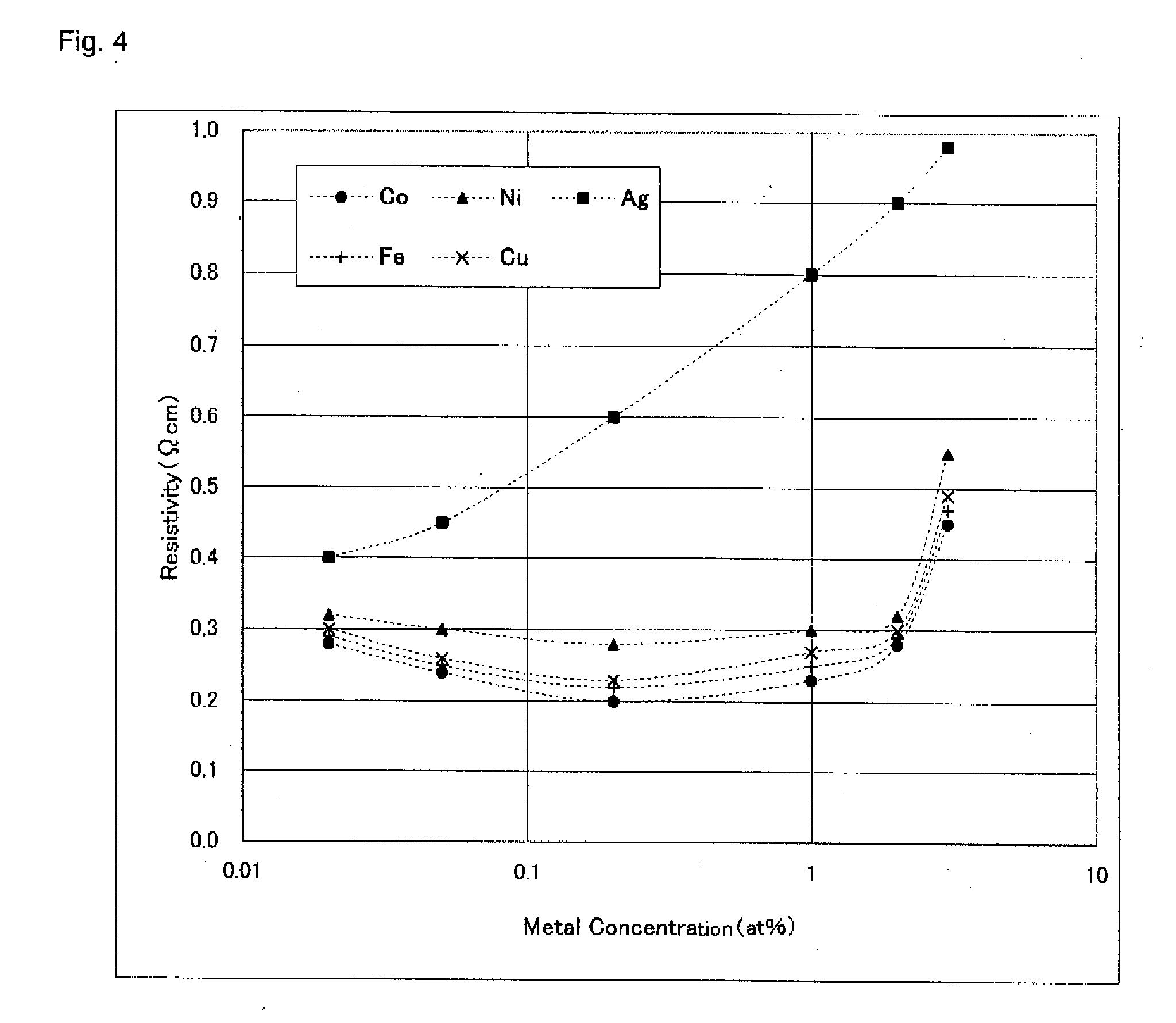
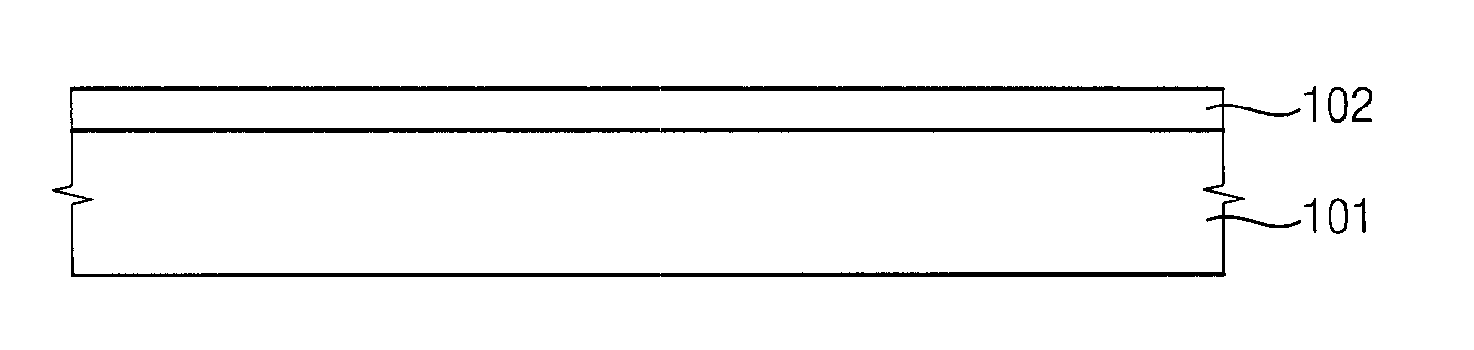
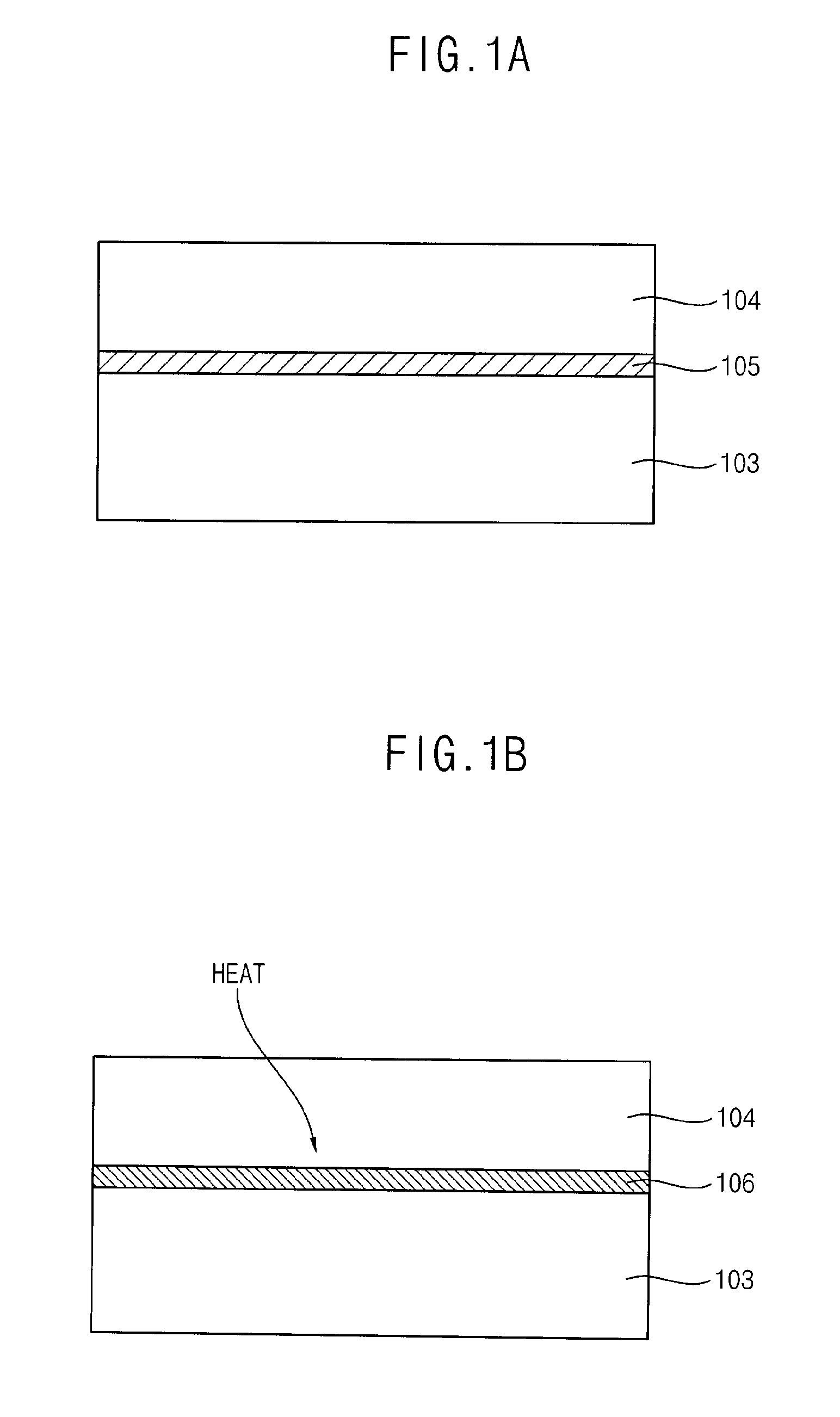
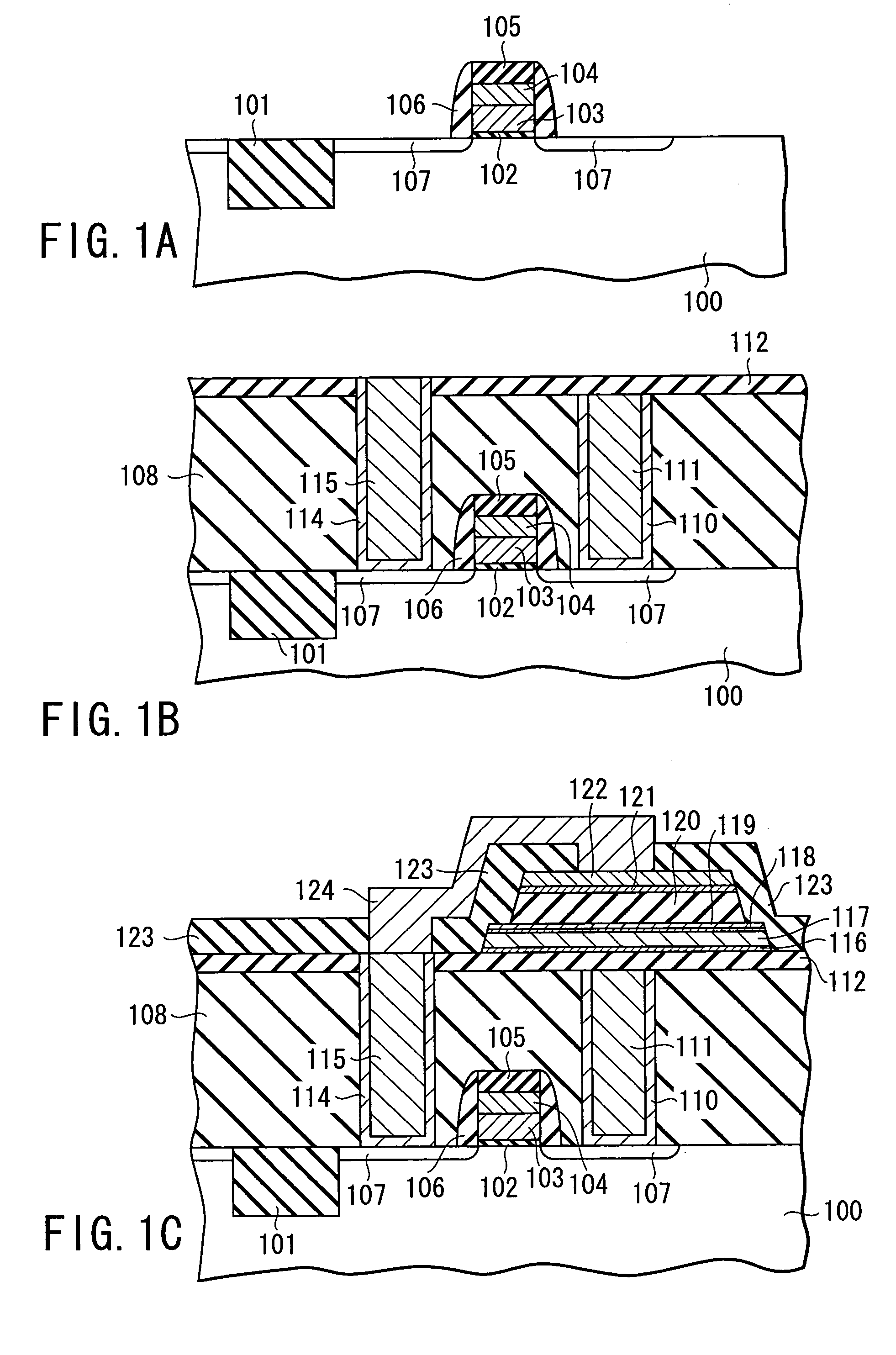
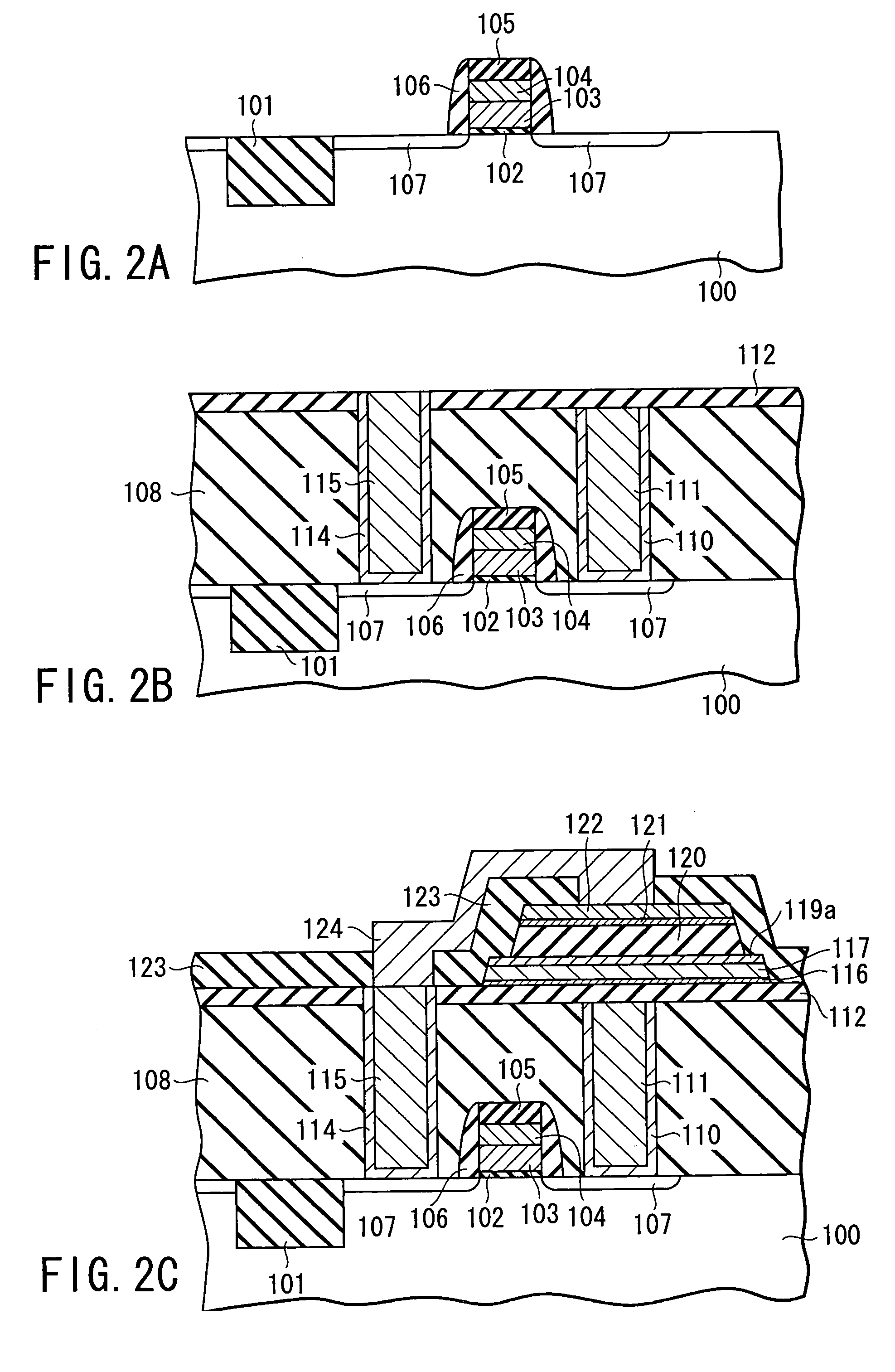
ActiveUS20100123136A1Reduce contact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGibbs free energyDevice material
An oxide or nitride semiconductor layer is formed over a substrate. A first conductive layer including a first element and a second element, and a second conductive layer including the second element are formed over the semiconductor layer. The first element is oxidized or nitrogenized near an interface region between the first conductive layer and the oxide or nitride semiconductor layer by heat treatment or laser irradiation. The Gibbs free energy of oxide formation of the first element is lower than those of the second element or any element in the oxide or nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
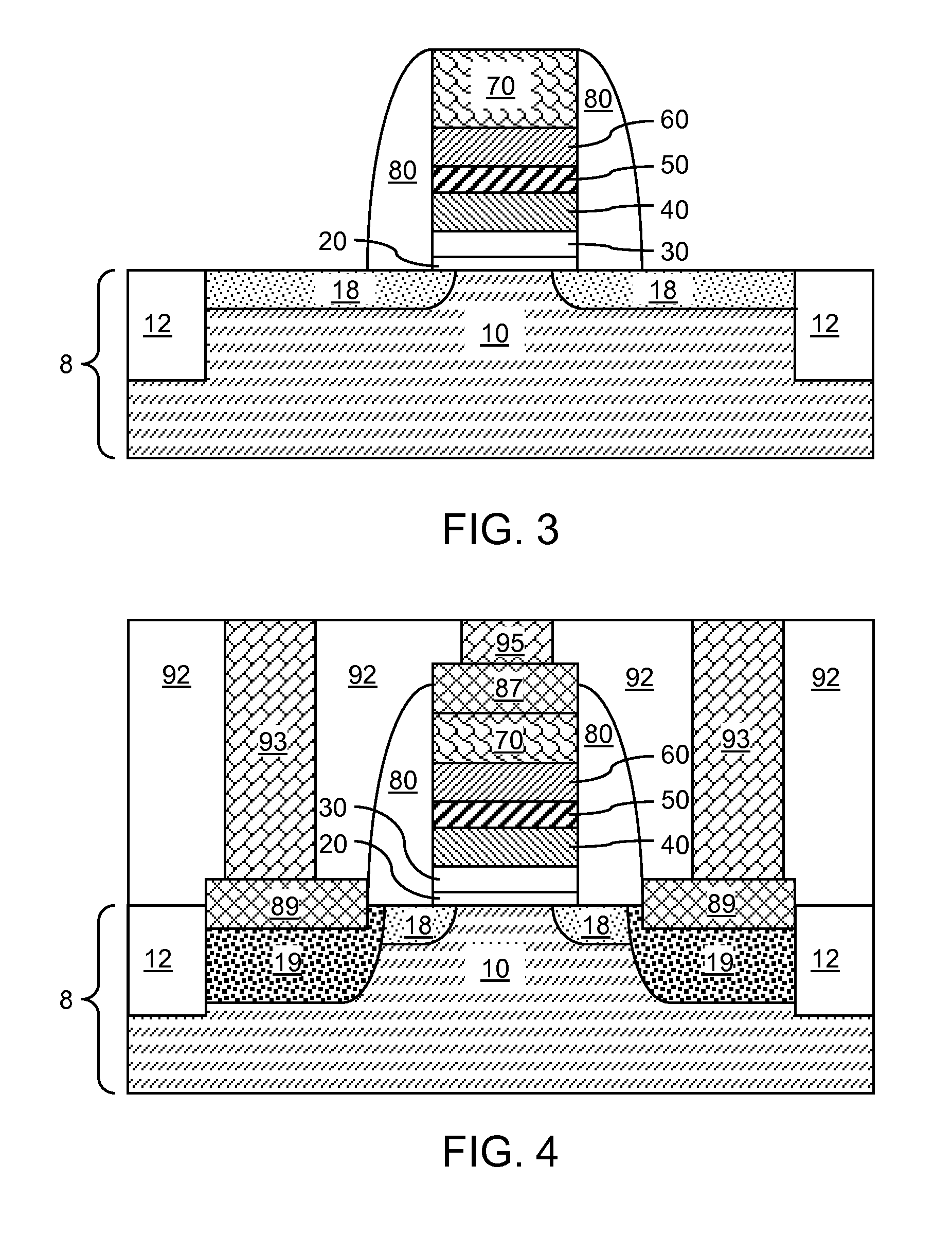
Scavanging metal stack for a high-k gate dielectric
ActiveUS20100320547A1Constant threshold voltageReduce equivalent oxide thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEquivalent oxide thickness
A stack of a high-k gate dielectric and a metal gate structure includes a lower metal layer, a scavenging metal layer, and an upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meets the following two criteria 1) a metal (M) for which the Gibbs free energy change of the reaction Si+2 / y MxOy→2x / y M+SiO2 is positive 2) a metal that has a more negative Gibbs free energy per oxygen atom for formation of oxide than the material of the lower metal layer and the material of the upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meeting these criteria captures oxygen atoms as the oxygen atoms diffuse through the gate electrode toward the high-k gate dielectric. In addition, the scavenging metal layer remotely reduces the thickness of a silicon oxide interfacial layer underneath the high-k dielectric. As a result, the equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) of the total gate dielectric is reduced and the field effect transistor maintains a constant threshold voltage even after high temperature processes during CMOS integration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
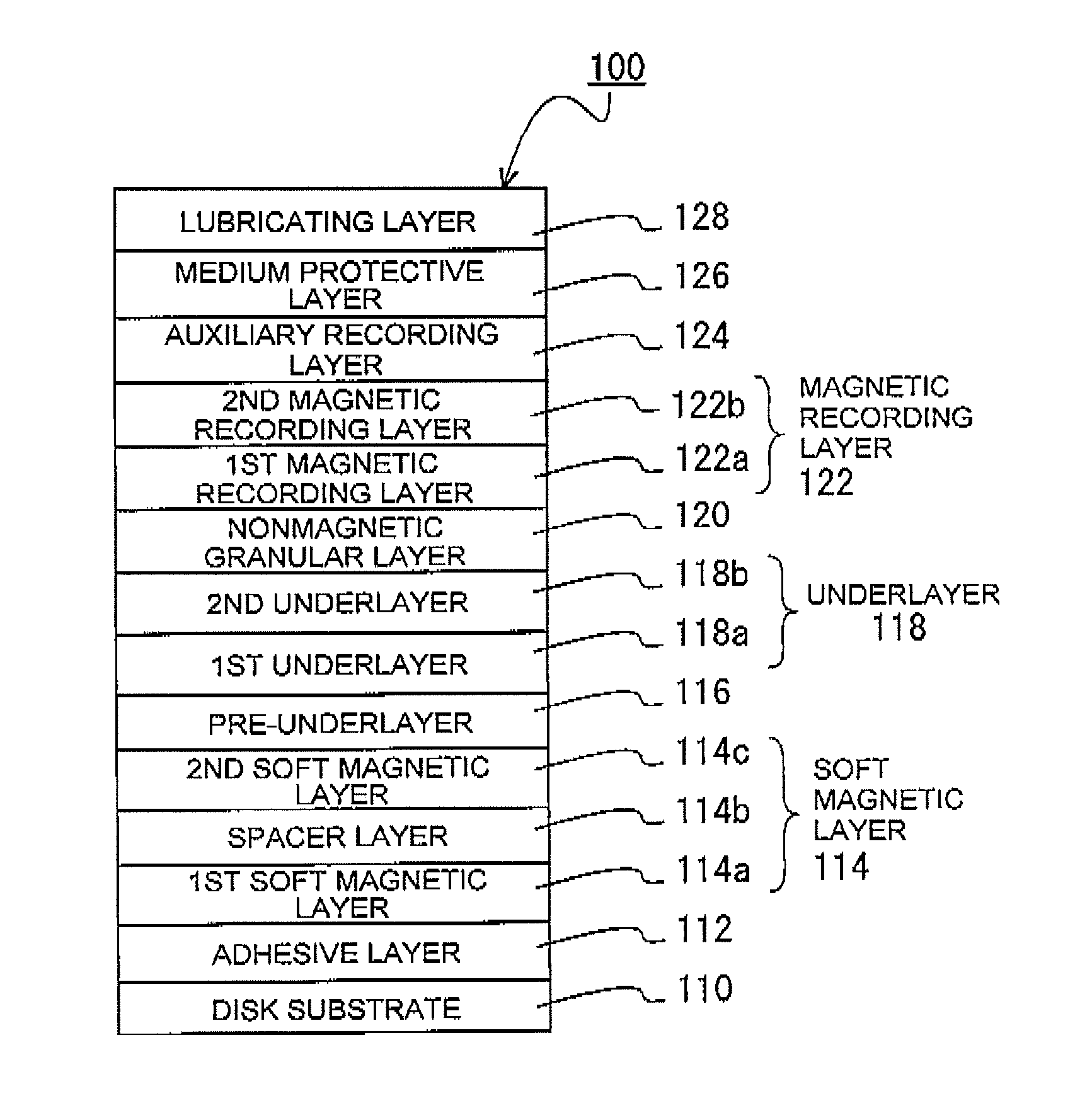
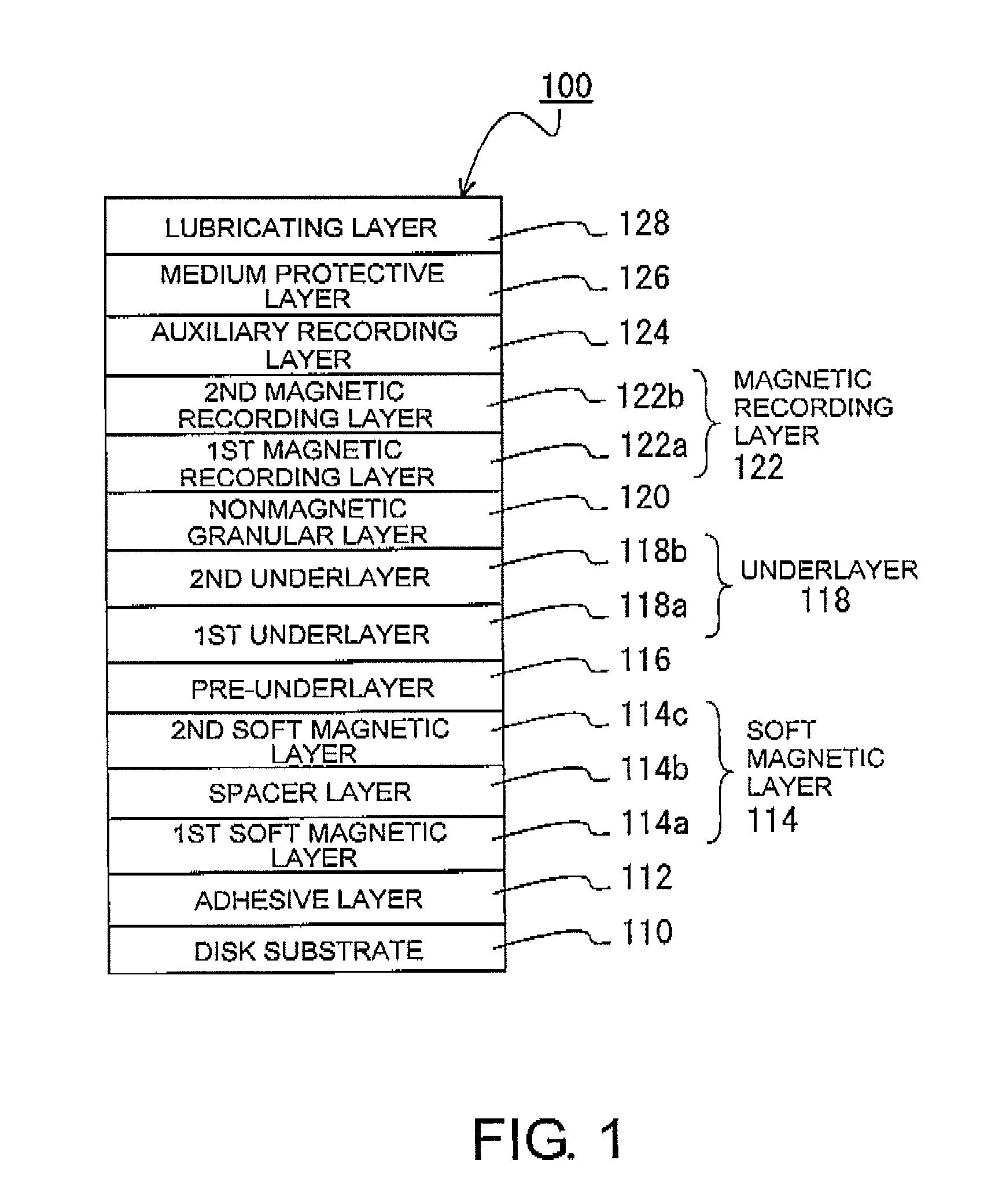
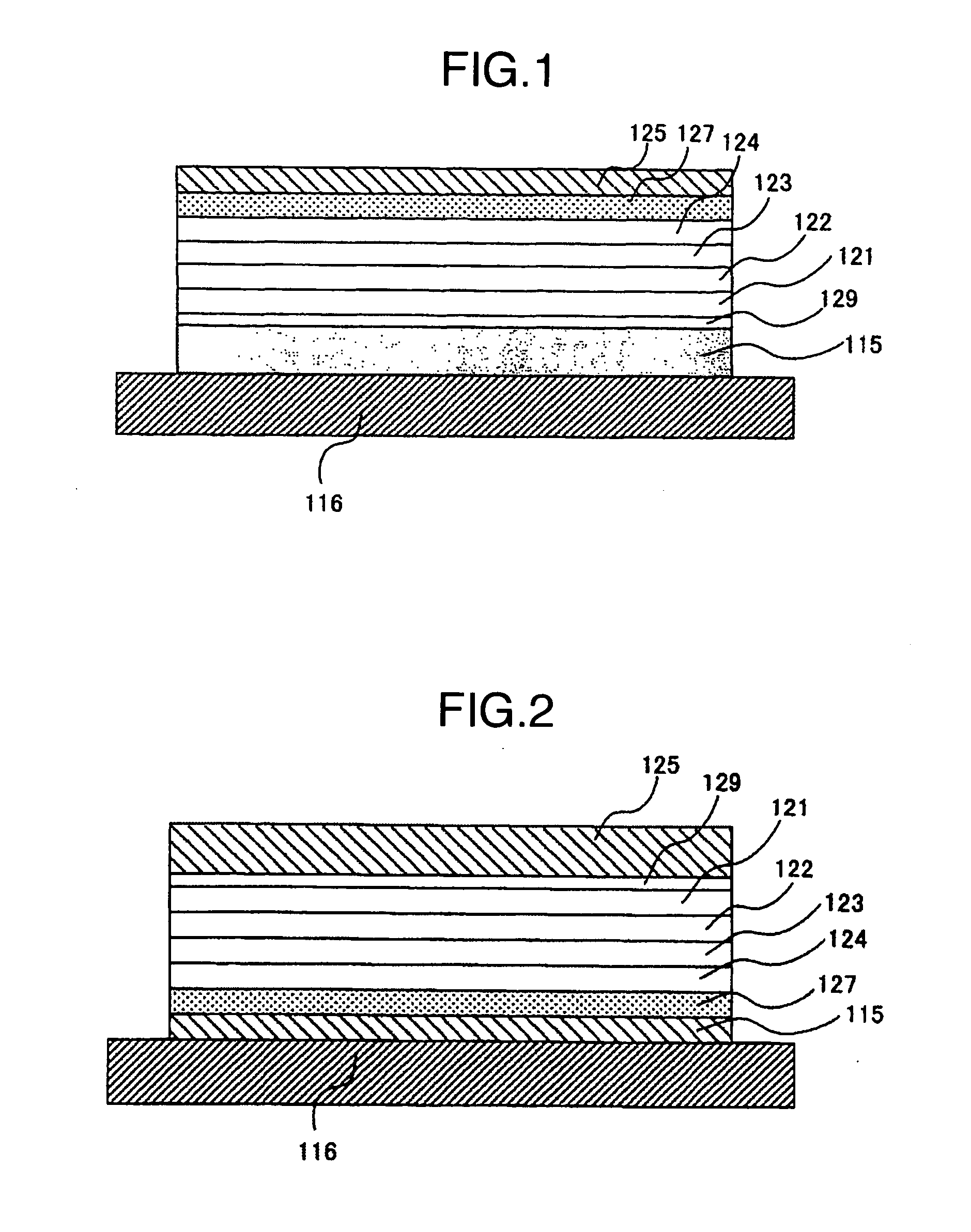
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS8404370B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove recording densityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingGibbs free energyFree energies
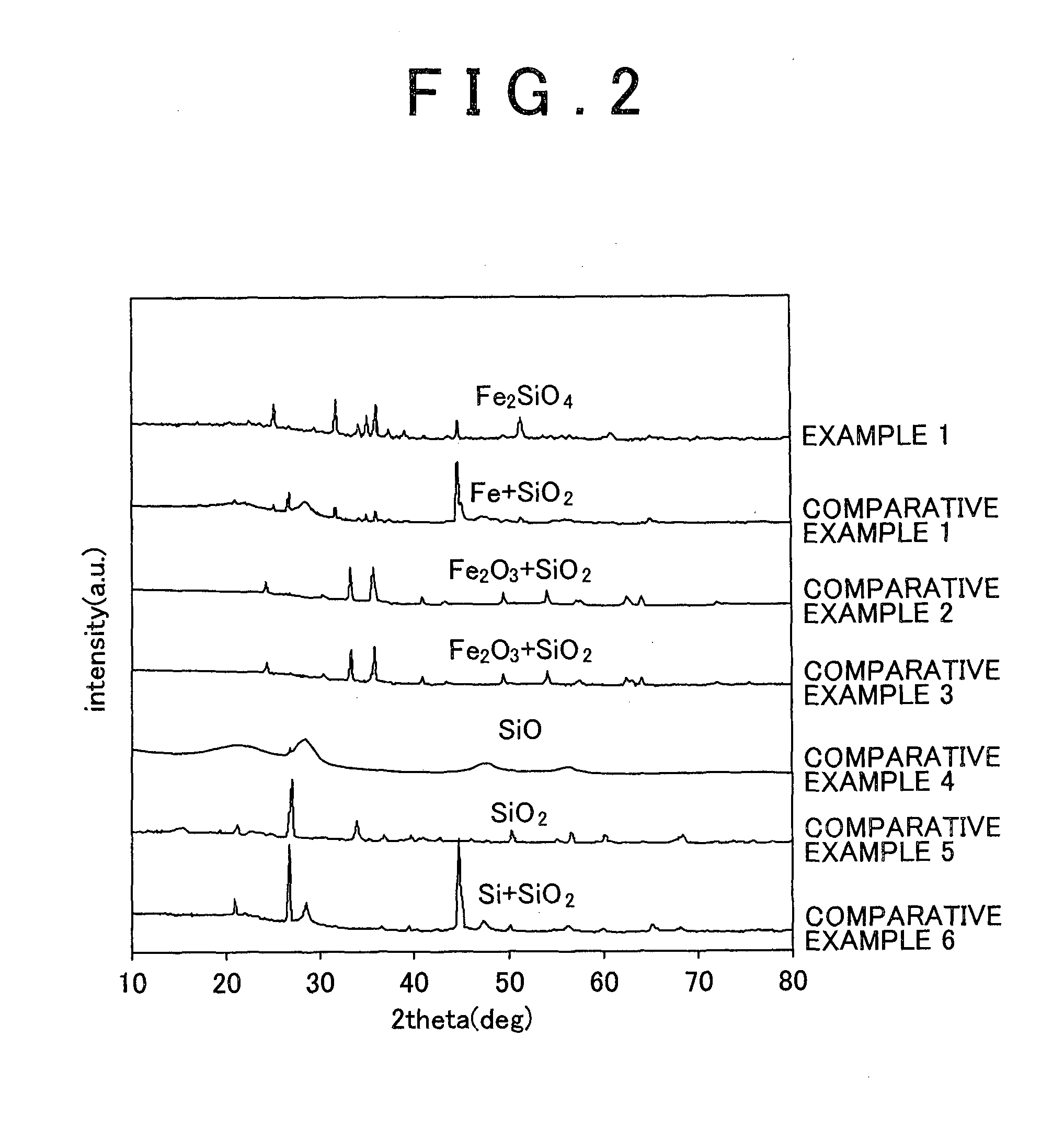
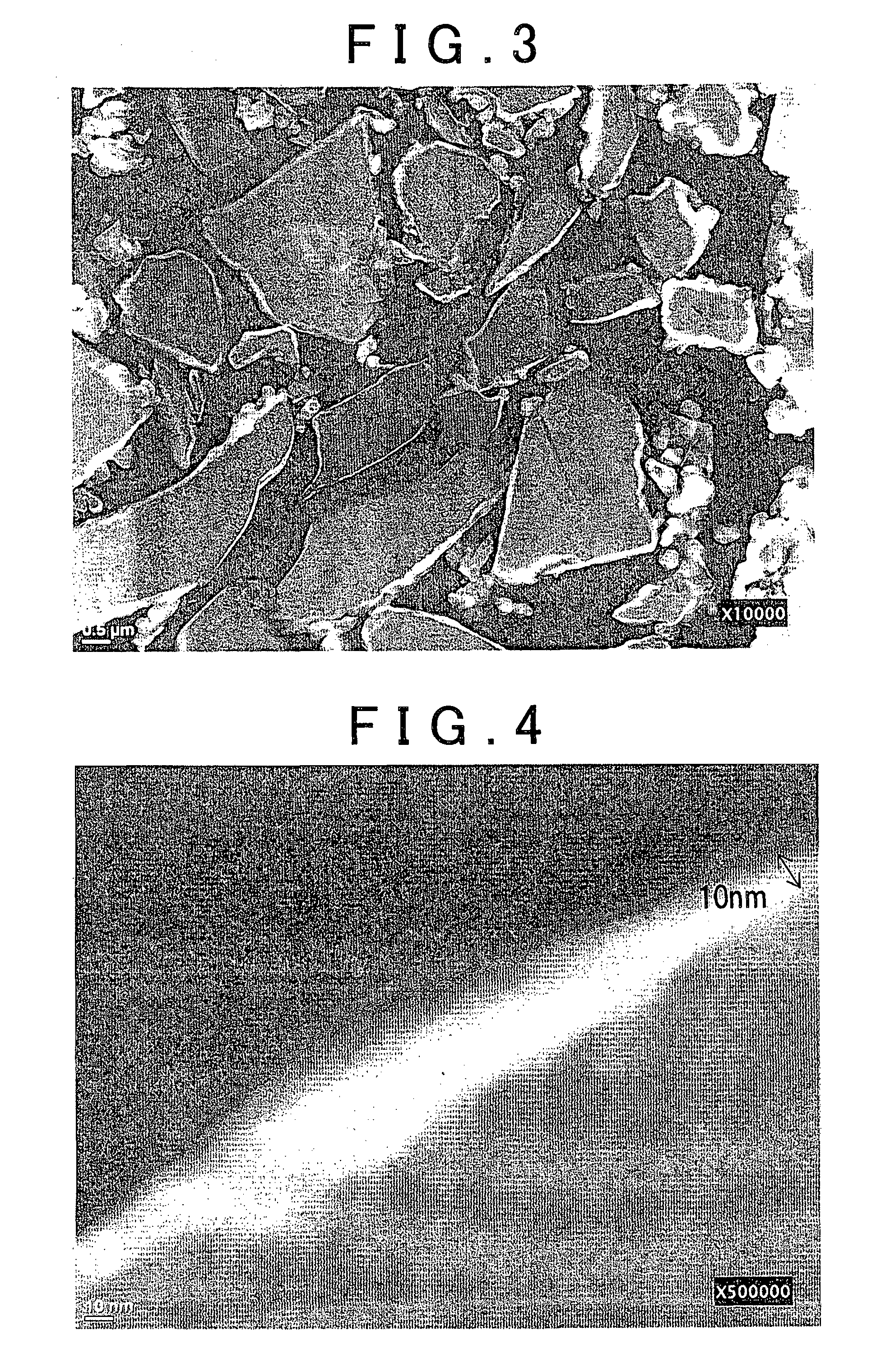
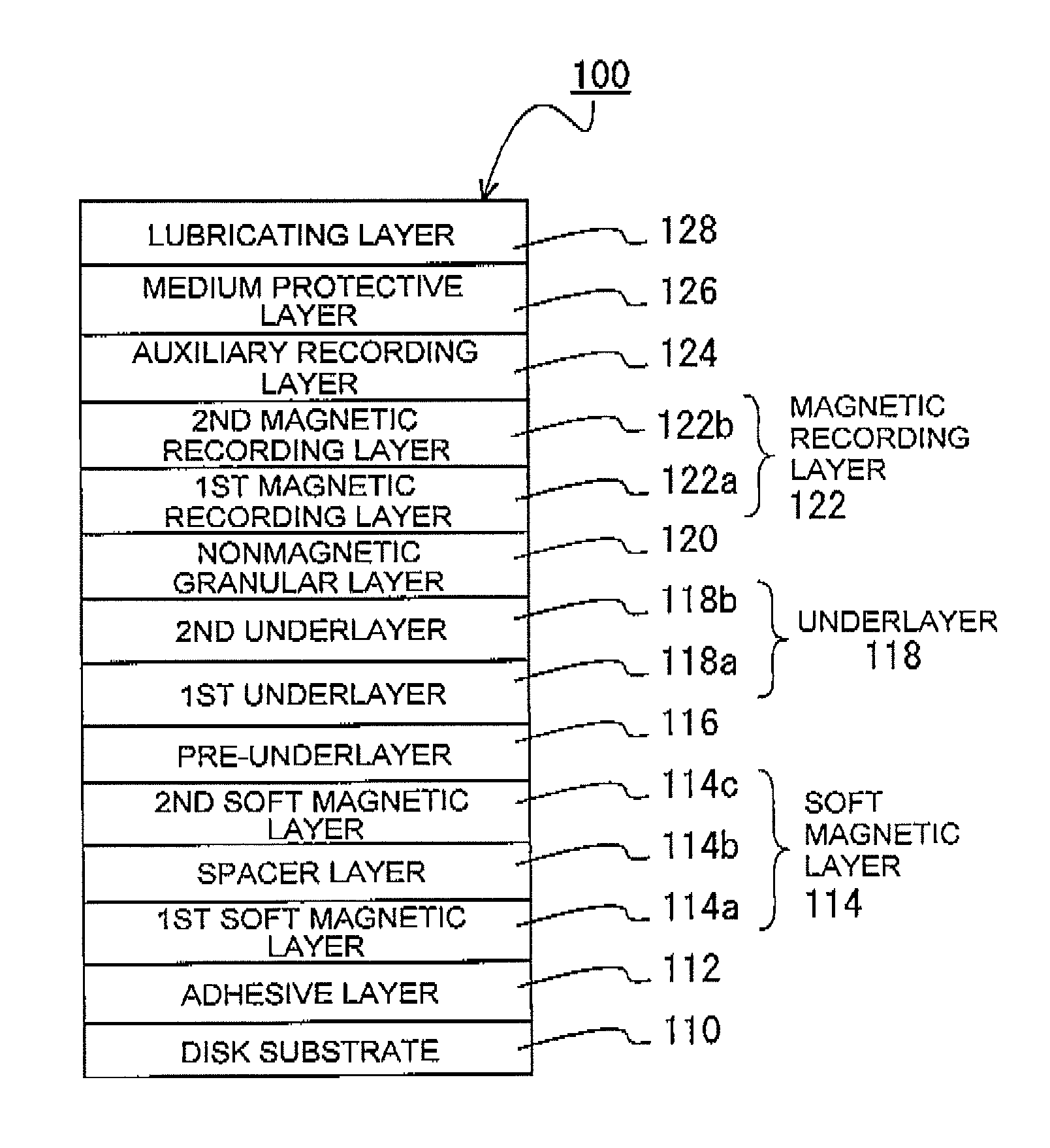
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium 100 has, over a substrate, at least a magnetic recording layer 122 with a granular structure in which nonmagnetic grain boundaries are formed between magnetic grains continuously grown into a columnar shape. The magnetic grains of the magnetic recording layer 122 contain Co, Cr, and Pt. The magnetic recording layer 122 contains at least one oxide selected from a group A including SiO2, TiO2, and Cr2O3, at least one oxide selected from a group B consisting of oxides each having a larger Gibbs free energy ΔG than the group A, and a reducing agent adapted to reduce the oxides of the group B.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Thin-film transistor substrate and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100148169A1Improve electrical performanceReduce bad appearanceTransistorSolid-state devicesFree energiesGibbs free energy
A thin-film transistor (TFT) substrate has improved electrical properties and reduced appearance defects and a method of fabricating the TFT substrate, are provided. The TFT substrate includes: gate wiring which is formed on a surface of an insulating substrate; oxide active layer patterns which are formed on the gate wiring and include an oxide of a first material; buffer layer patterns which are disposed on the oxide active layer patterns to directly contact the oxide active layer patterns and include a second material; and data wiring which is formed on the buffer layer patterns to insulatedly cross the gate wiring, wherein a Gibbs free energy of the oxide of the first material is lower than a Gibbs free energy of an oxide of the second material.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Conductive thickener, electronic device and solar battery comprising electrodes formed by conductive thickener
ActiveCN102376379ANon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialSemiconductor devicesGibbs free energyOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a conductive thickener and an electronic device and a solar battery comprising electrodes formed by the conductive thickener. The conductive thickener comprises conductive powder, a metal glass and an organic carrier, wherein, the metal glass comprises an alloy comprising at least two chemical elements selected from a chemical element having a low resistivity, a chemical element formed a solid solution with the conductive powder or a chemical element having a high oxidation potential, and wherein, the chemical element having the low resistivity has a resistivity about 100 micro-ohmmeter-cm, and the chemical element having the high oxidation potential has a Gibbs free energy absolute value about 100 kilojoule / moore or more.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scavenging metal stack for a high-k gate dielectric
ActiveUS7989902B2Constant voltageReduce thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEquivalent oxide thickness
A stack of a high-k gate dielectric and a metal gate structure includes a lower metal layer, a scavenging metal layer, and an upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meets the following two criteria 1) a metal (M) for which the Gibbs free energy change of the reaction Si+2 / y MxOy→2x / y M+SiO2 is positive 2) a metal that has a more negative Gibbs free energy per oxygen atom for formation of oxide than the material of the lower metal layer and the material of the upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meeting these criteria captures oxygen atoms as the oxygen atoms diffuse through the gate electrode toward the high-k gate dielectric. In addition, the scavenging metal layer remotely reduces the thickness of a silicon oxide interfacial layer underneath the high-k dielectric. As a result, the equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) of the total gate dielectric is reduced and the field effect transistor maintains a constant threshold voltage even after high temperature processes during CMOS integration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Organic light emitting display apparatus
ActiveUS20060261333A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmDopant
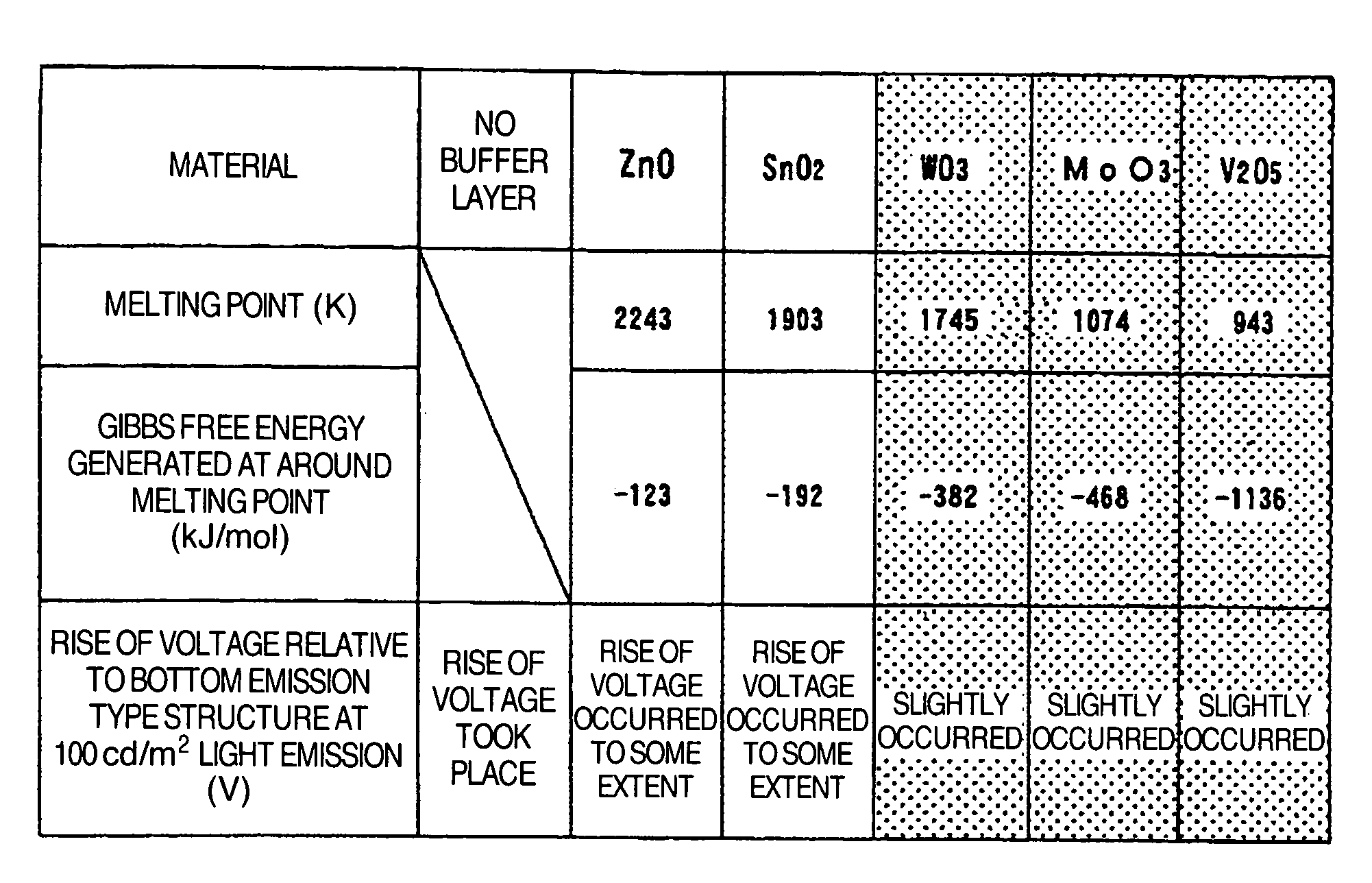
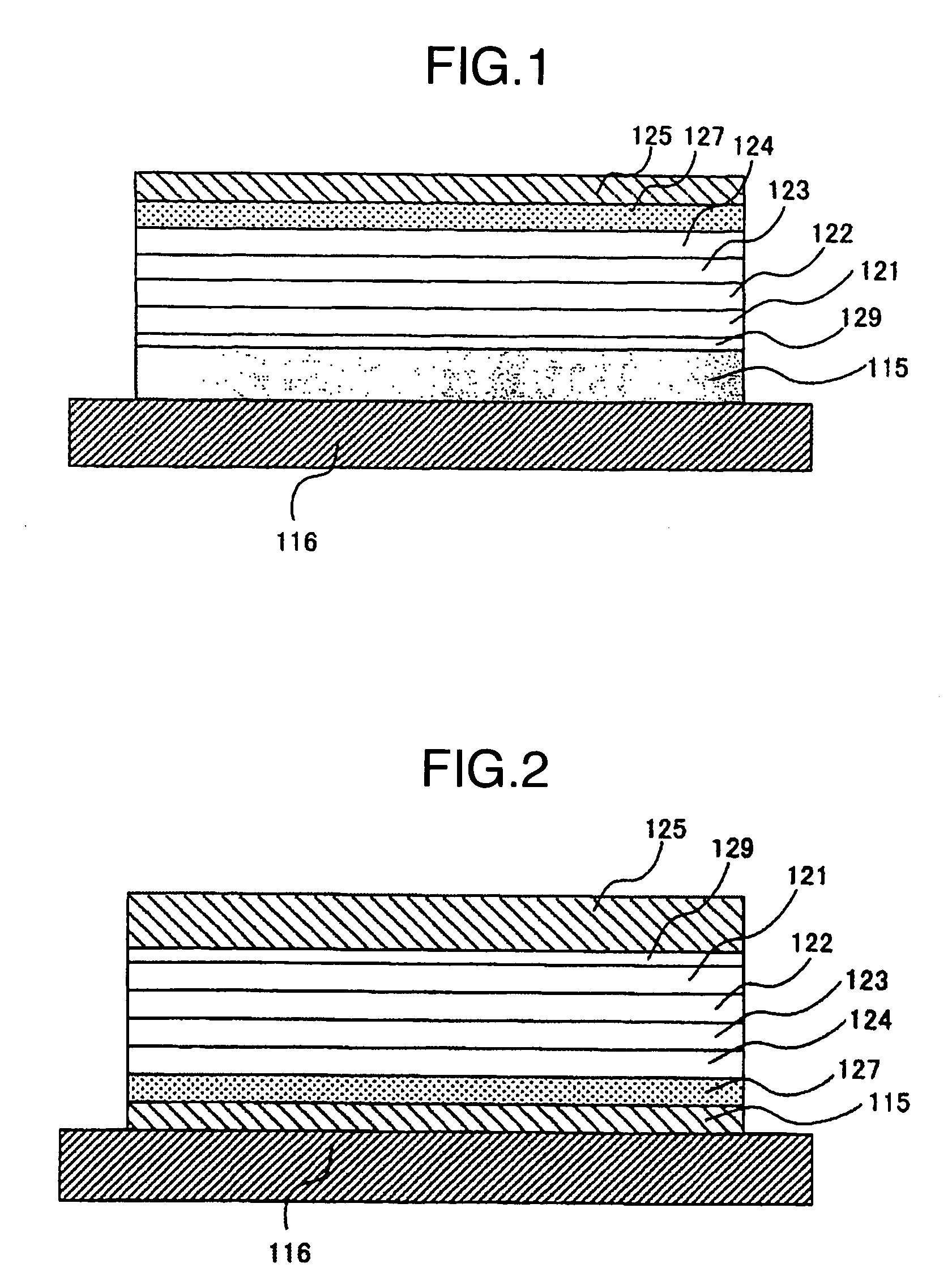
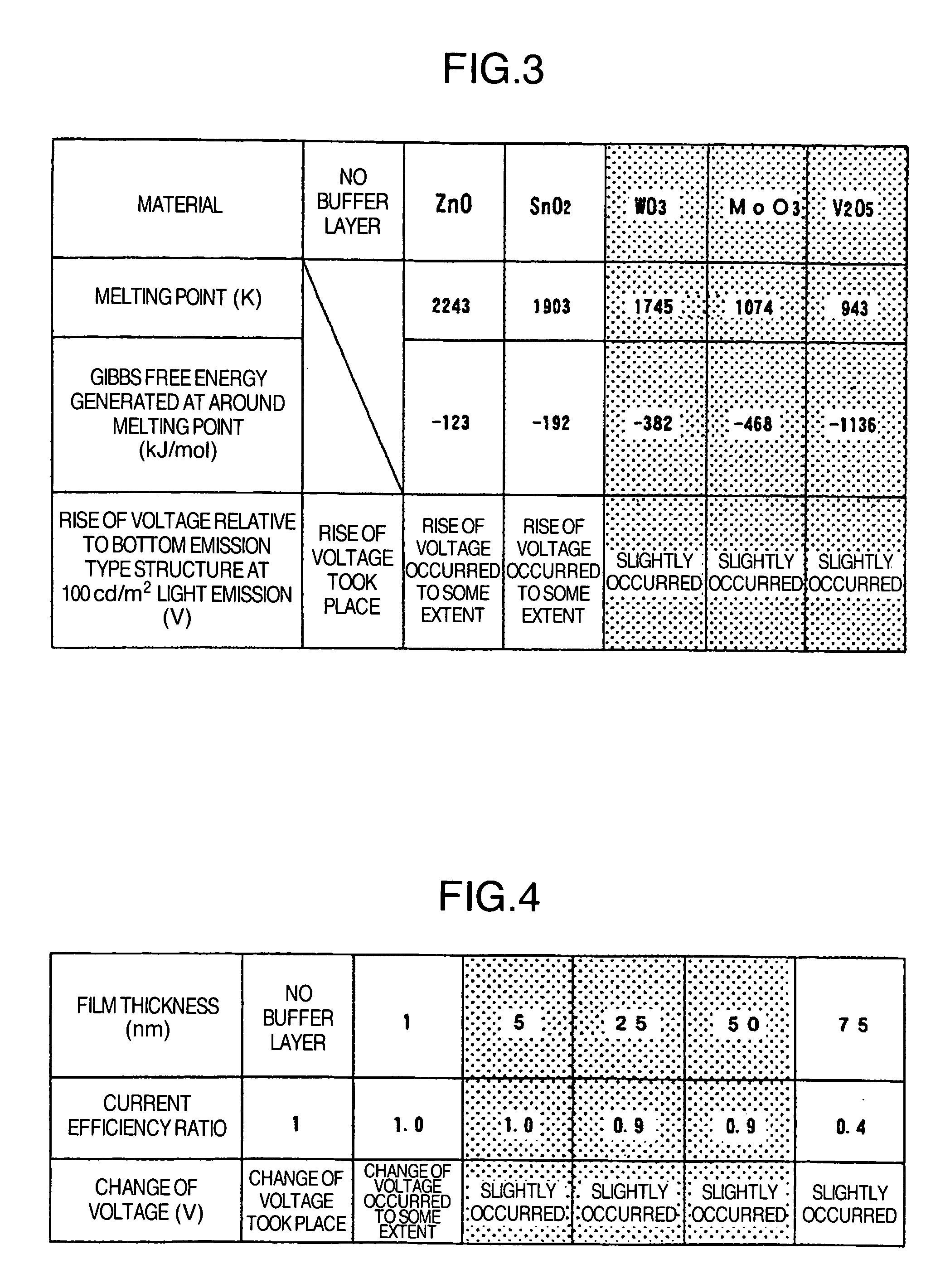
The present invention provides a top emission type organic light emitting display apparatus in which manufacture it is possible to prevent the organic film from being oxidized when the upper transparent electrode is formed, and which is capable of emitting light at a low voltage. This organic light emitting display apparatus includes an organic light emitting layer and an upper electrode and a lower electrode sandwiching the said organic light emitting layer between them, and is of a structure in which the light emitted from the organic light emitting layer is taken out from the upper electrode side, wherein a buffer layer mostly made of an oxide with its Gibbs free energy generated at around the melting point being lower than −300 kJ / mol is provided between the organic light emitting layer and the upper electrode, the side of the organic layer which is in contact with the buffer layer being doped with an electron donative dopant.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Nonvolatile resistive memory element with an oxygen-gettering layer
ActiveUS20140268993A1Increasing the thicknessInhibited DiffusionDigital storageGibbs free energyFree energies
A nonvolatile resistive memory element includes an oxygen-gettering layer. The oxygen-gettering layer is formed as part of an electrode stack, and is more thermodynamically favorable in gettering oxygen than other layers of the electrode stack. The Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔfG°) of an oxide of the oxygen-gettering layer is less (i.e., more negative) than the Gibbs free energy of formation of an oxide of the adjacent layers of the electrode stack. The oxygen-gettering layer reacts with oxygen present in the adjacent layers of the electrode stack, thereby preventing this oxygen from diffusing into nearby silicon layers to undesirably increase an SiO2 interfacial layer thickness in the memory element and may alternately be selected to decrease such thickness during subsequent processing.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
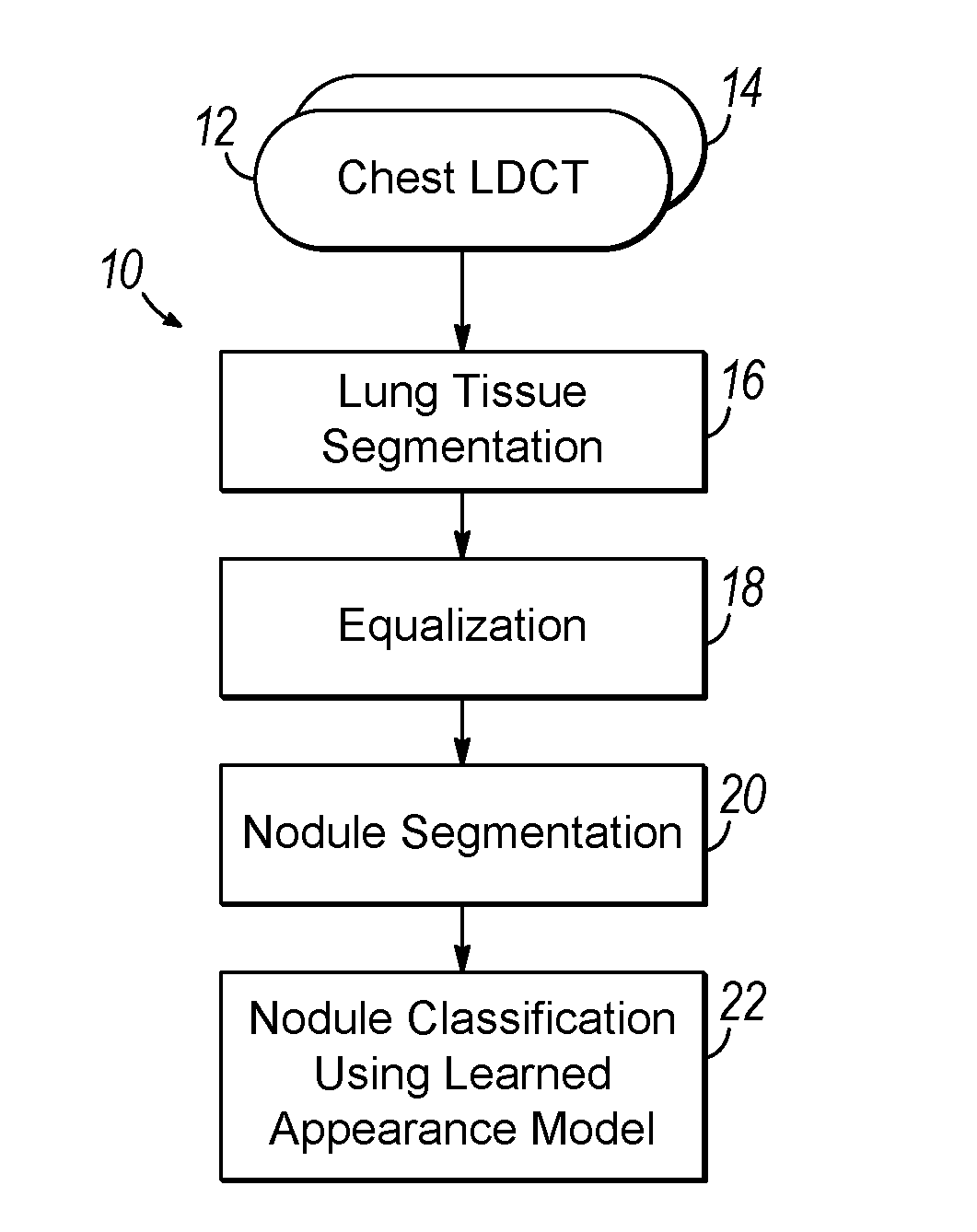
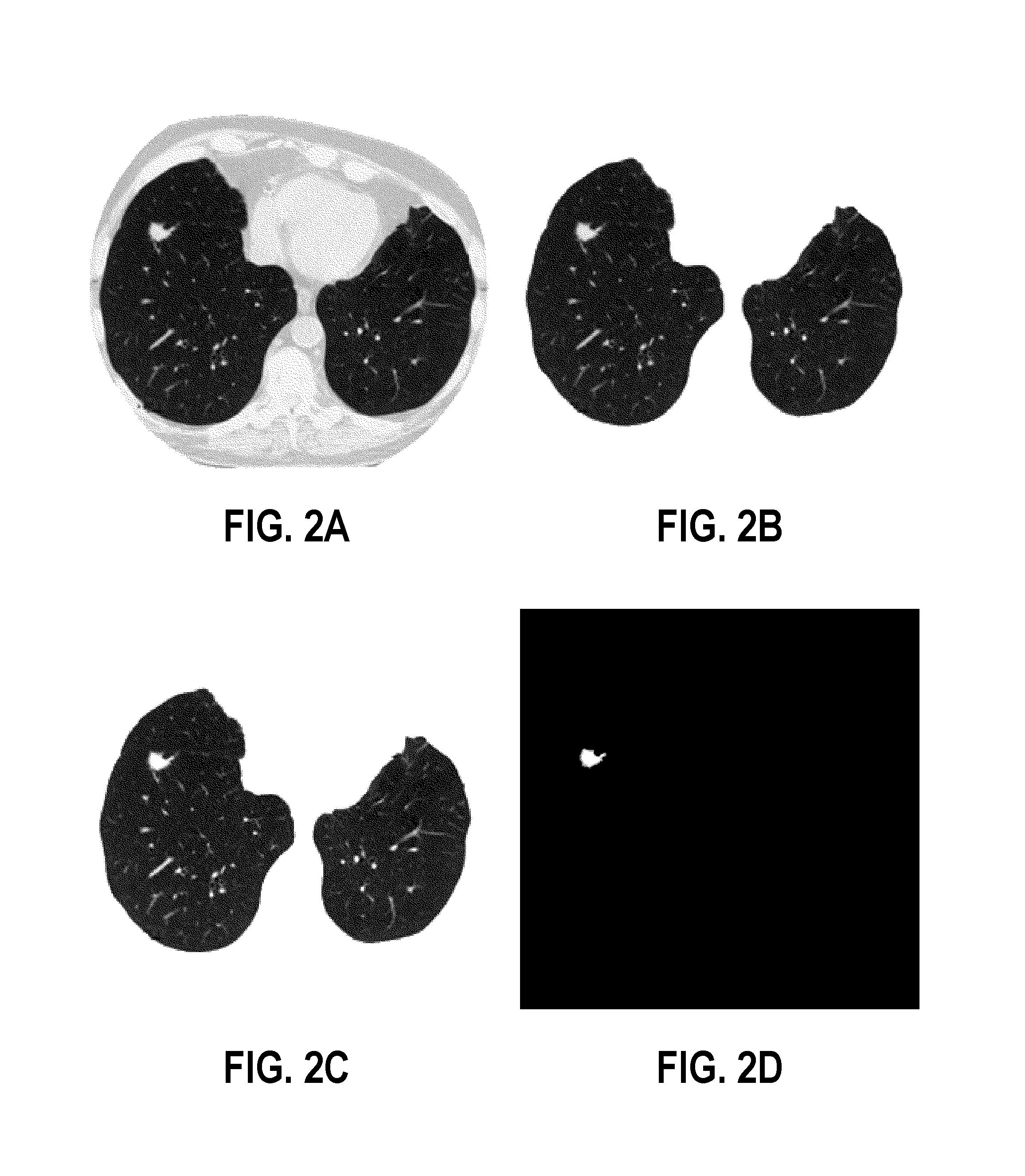
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating appearance analysis for diagnosing malignant lung nodules
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through modeling and analyzing the visual appearance of pulmonary nodules. A learned appearance model used in such analysis describes the appearance of pulmonary nodules in terms of voxel-wise conditional Gibbs energies for a generic rotation and translation invariant second-order Markov-Gibbs random field (MGRF) model of malignant nodules with analytically estimated characteristic voxel neighborhoods and potentials.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
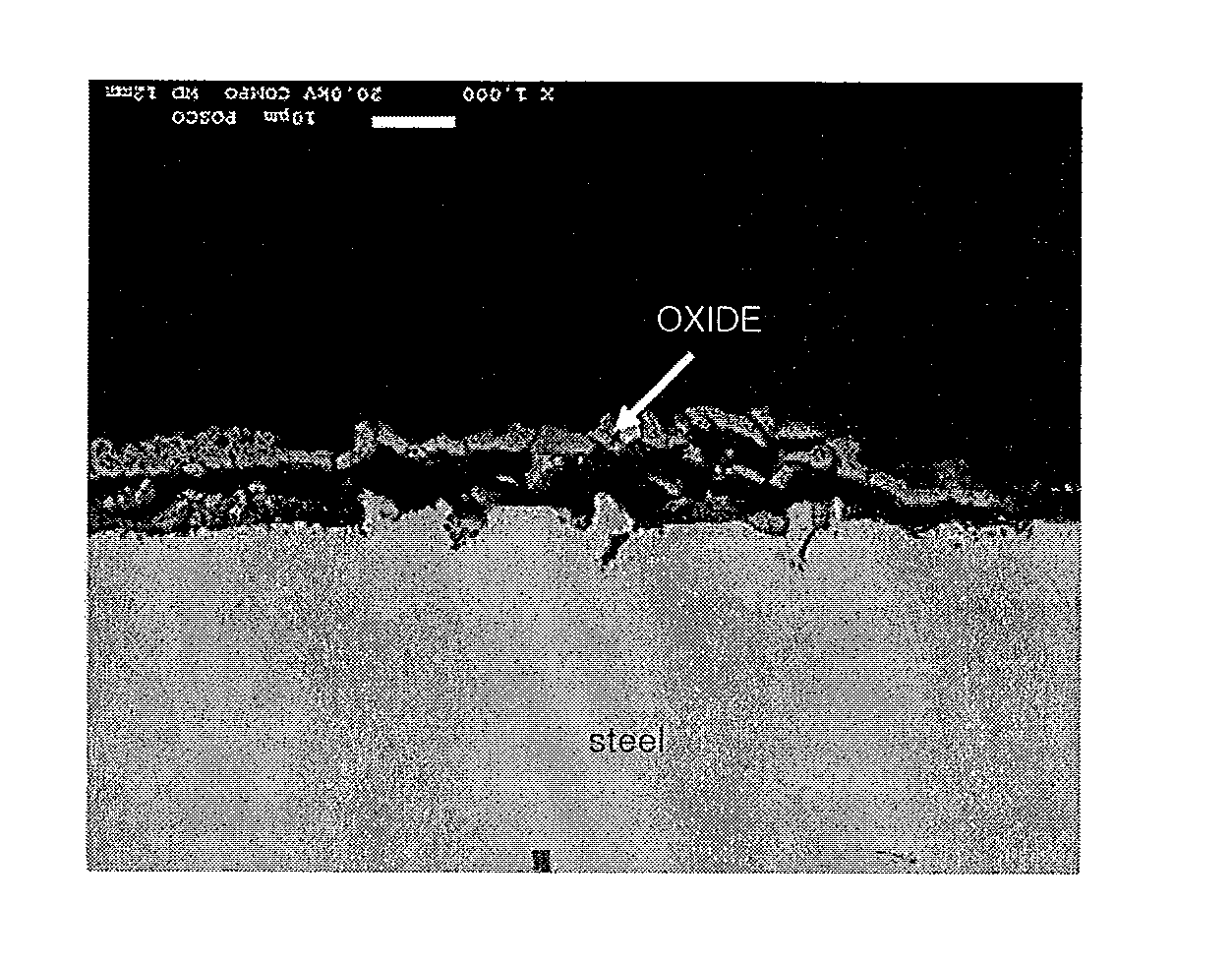
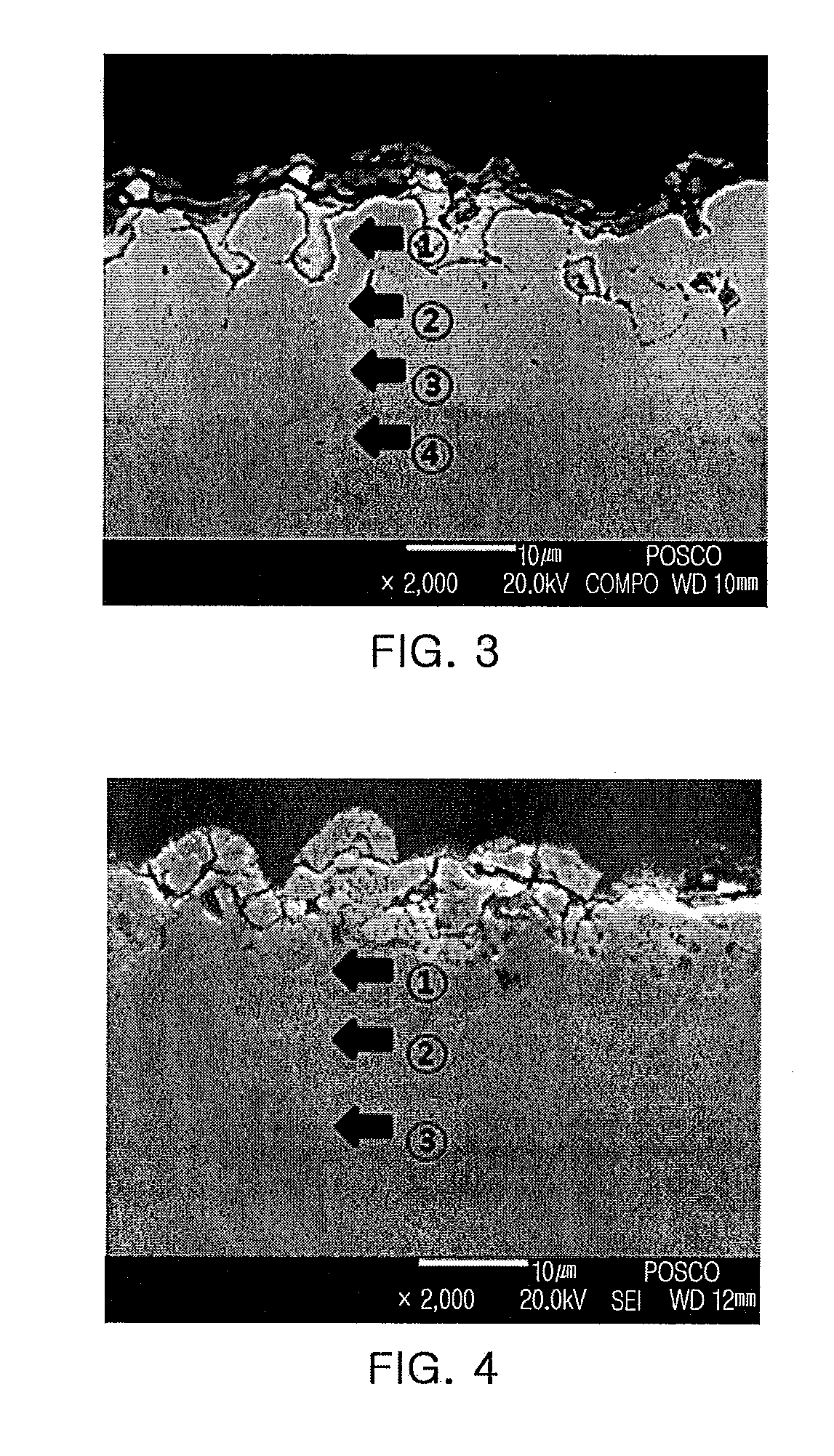
Zinc-plated steel sheet for hot pressing having outstanding surface characteristics, hot-pressed moulded parts obtained using the same, and a production method for the same
ActiveUS20120267012A1High melting temperatureDeterioration of layer be preventedHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingGibbs free energyOxygen
Provided is a zinc-plated steel sheet for hot pressing having outstanding surface characteristics, comprising: a steel foundation plate comprising a metal surface diffusion layer of which the Gibbs free energy reduction per mole of oxygen during oxidation is less than that of Cr; an aluminum-rich layer containing at least 30 wt. % of aluminium formed on the surface diffusion layer, and a zinc plating layer formed on the aluminum-rich layer. In this way, a metal having a low affinity for oxygen is coated to an effective thickness prior to annealing and thus the creation of annealing oxides at the surface of the steel sheet is suppressed and a uniform zinc plating layer is formed, and alloying of the zinc plating layer is promoted during press-processing heat treatment. Cracking in the steel foundation plate during hot press molding is prevented.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Metal precursor powder, method of manufactuirng conductive metal layer or pattern, and device including the same
ActiveUS20140360762A1Avoid reactionChemical stabilityConductive materialInksHydrogenGibbs free energy
A metal precursor powder, a method of manufacturing a conductive metal layer or pattern, and an electronic device including the same, are provided, and in the metal precursor powder, the Gibbs free energy change of hydrogen removal at a temperature range of −25° C. to 25° C. is −100 kJ / mol to 300 kJ / mol.
Owner:ALINK CO LTD
Negative-electrode active material, and method for production of negative-electrode active material
ActiveCN103608952AHigh charge and discharge capacityImprove charge and discharge efficiencyElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureGibbs free energySilicon oxide
A negative-electrode active material characterized by containing a silicon oxide represented by a general formula SiOx (0 aSibOc-m(OH)-n(H20), and a method for the production of a negative-electrode active material which includes a mixing step of mixing a silicon oxide that is represented by a general formula SiOy (0 < y < 2) and a metal oxide, and a heat treatment step of performing a heat treatment on the mixture that is obtained in the mixing step in a non-oxidizing atmosphere and in which the negative absolute value of the standard Gibbs energy of the oxidation reaction of the metal oxide at the heating temperature in the heat treatment step is smaller than the negative absolute value of the standard Gibbs energy of the oxidation reaction of Si at the heating temperature in the heat treatment step.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
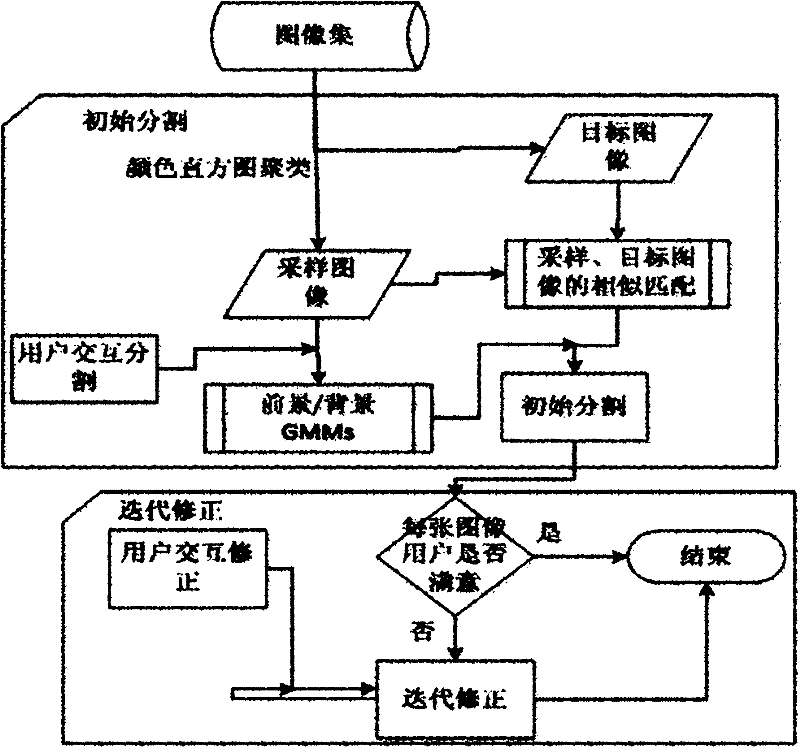
Image set partitioning method based on sampling
The invention discloses an image set partitioning method based on sampling. The method comprises the following steps of: image selection: extracting characteristic vectors of color histograms of all images in an image set and performing characteristic vector clustering; extracting color distributions of the foreground and background of a sampled image; performing similarity matching on the sampled image with a target image; calculating the foreground probability of the target image based on the single sampled image; calculating the foreground probability of the target image; and constructing a Gibbs energy minimizing formula, resolving a result of a foreground or background, which corresponds to each pixel, through image partitioning, and partitioning the image according to the constructed Gibbs energy minimizing formula by using an image partitioning method. The method has the remarkable advantage that a large amount of user interaction required by foreground and background partitioning operation on each image in a large-scale image set can be reduced greatly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
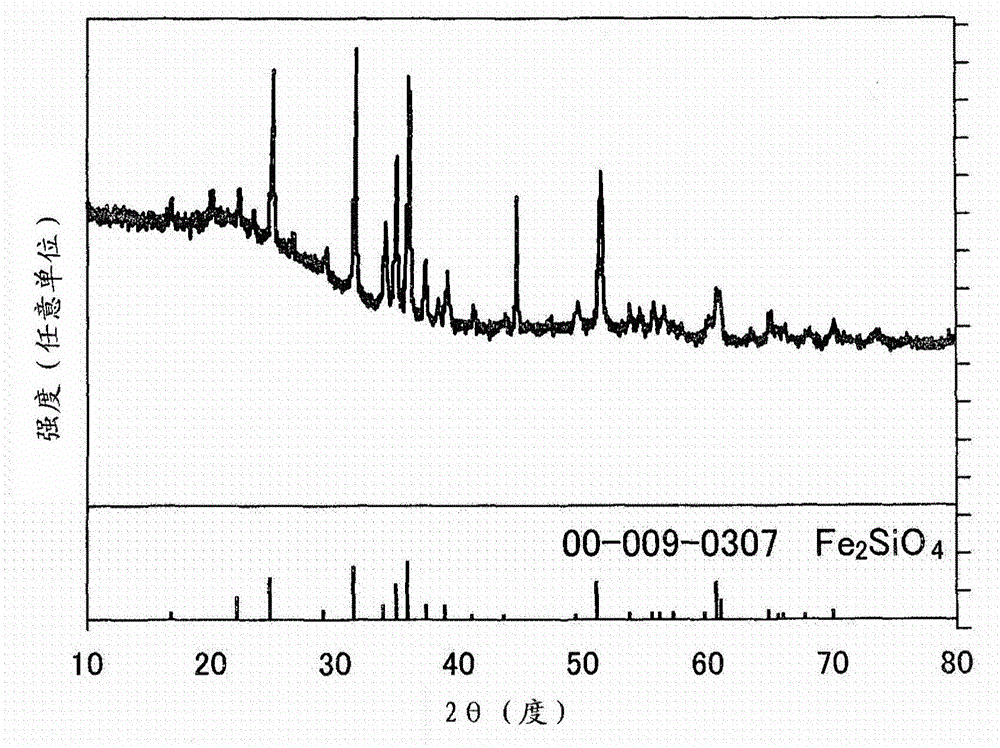
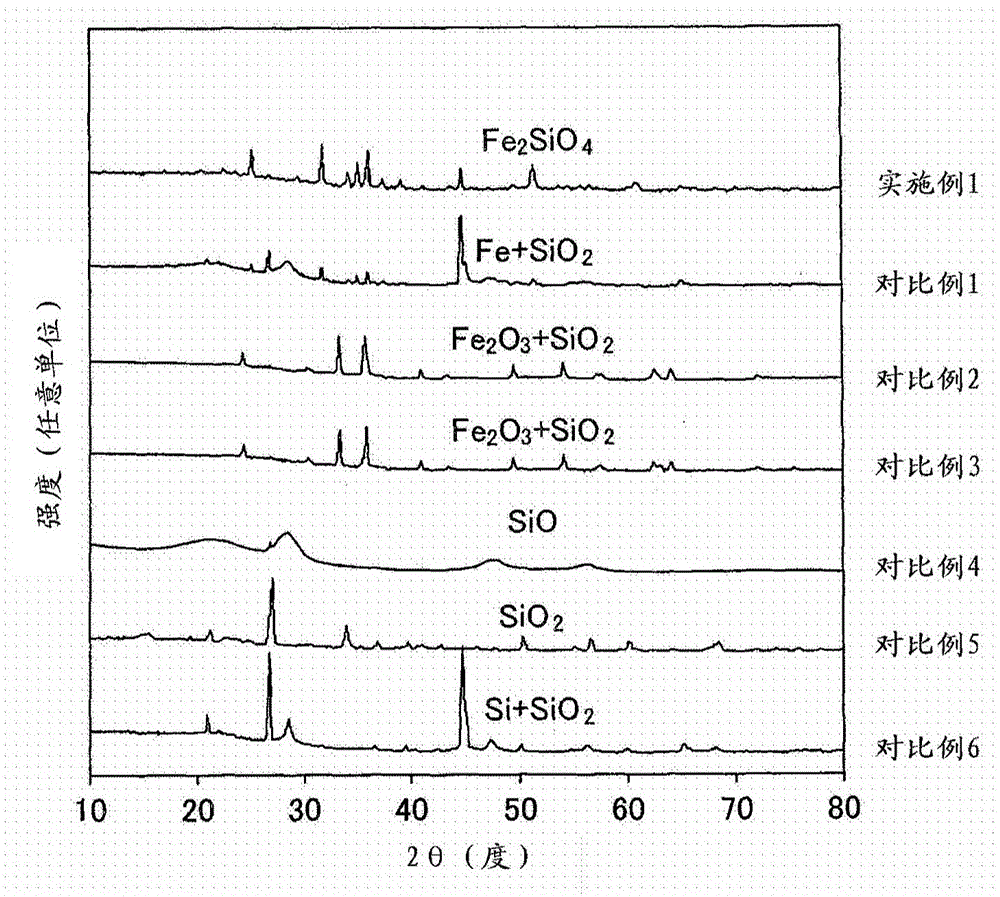
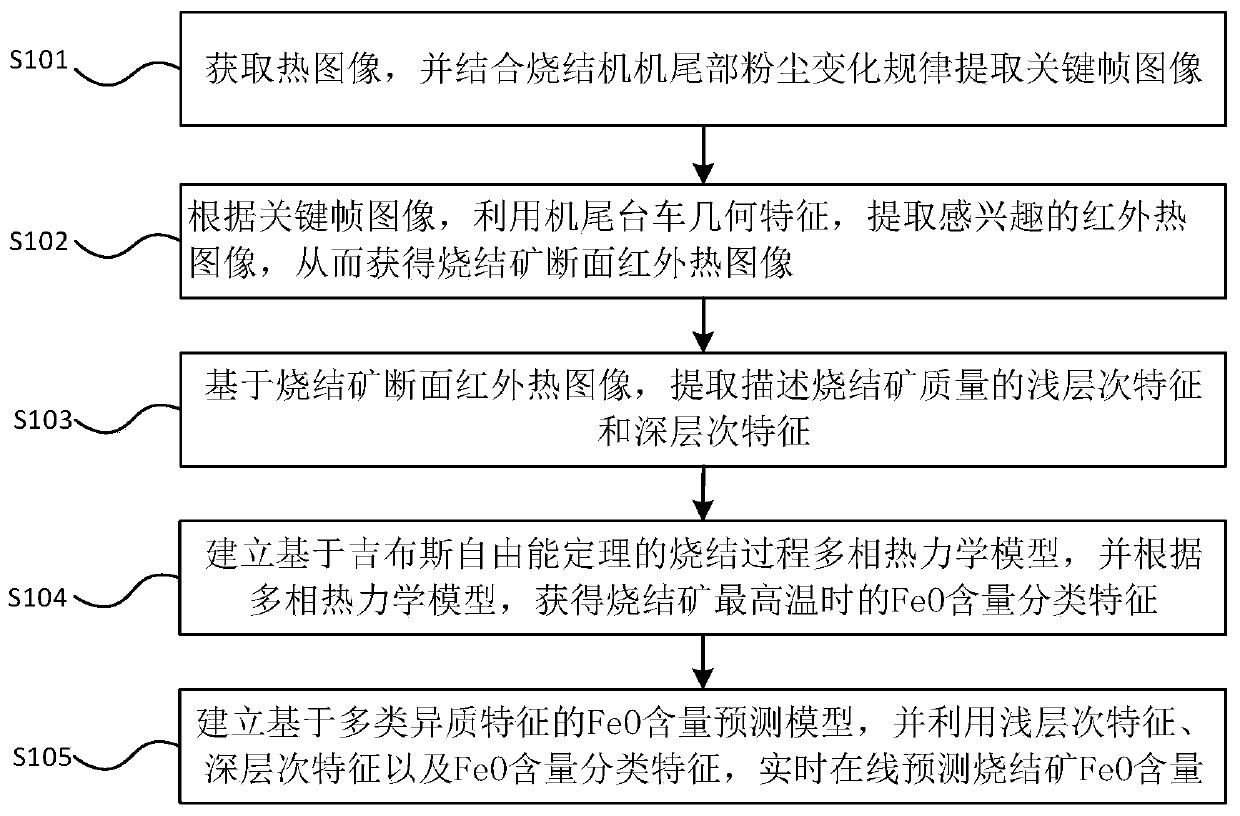
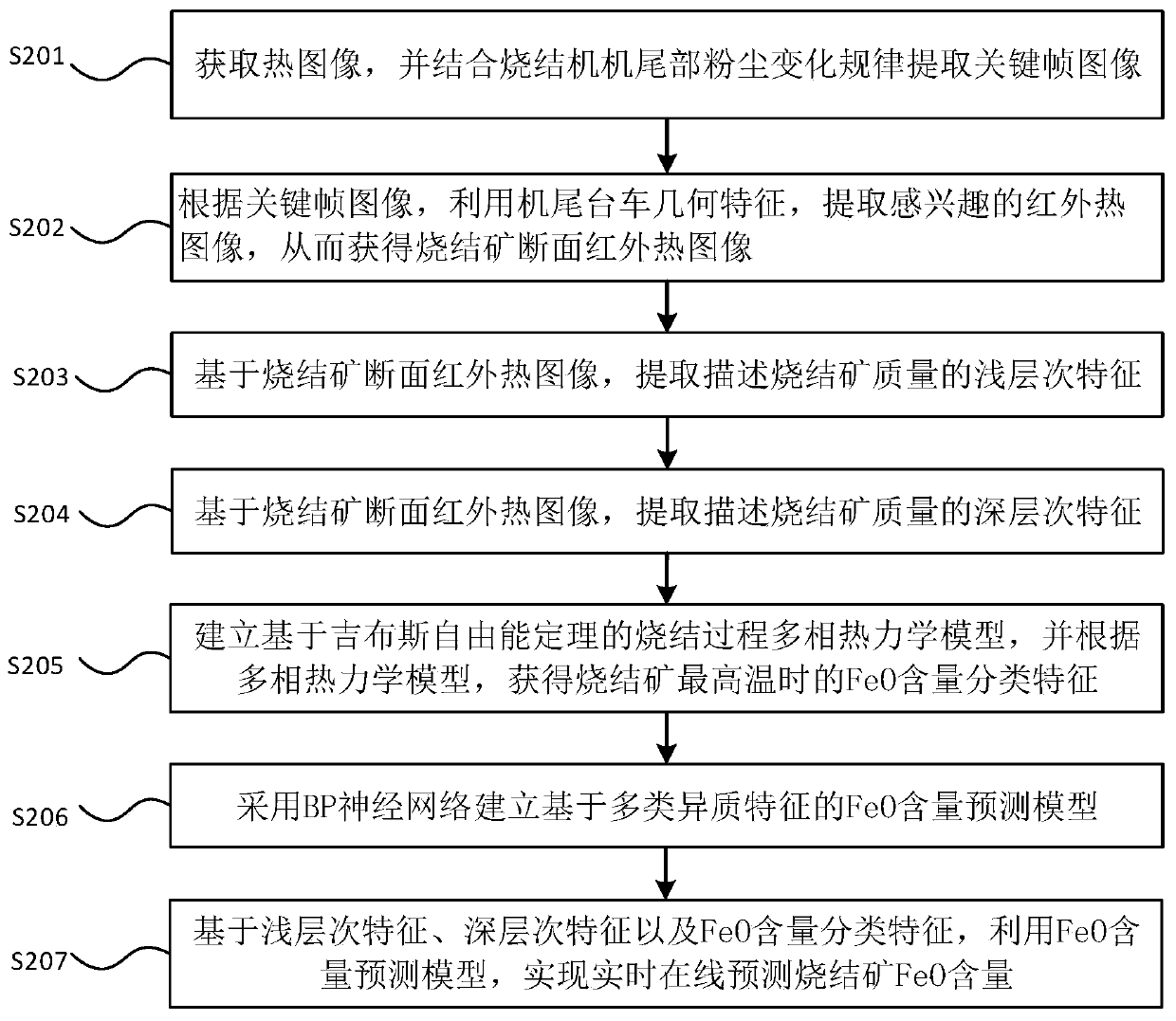
Sintered ore FeO content detection method and sintered ore FeO content detection system
ActiveCN111128313ASolve the technical problem of not being able to accurately detect the FeO content of sintered ore in real timeReal-time online predictionImage enhancementImage analysisGibbs free energyStandard gibbs free energy change
The invention discloses a sintered ore FeO content detection method and a sintered ore FeO content detection system. The method comprises: obtaining a thermal image; extracting a key frame image in combination with a dust change rule at the tail portion of a sintering machine; according to the key frame image, extracting an interested infrared thermal image by utilizing the geometrical characteristics of a trolley at the tail portion of the sintering machine so as to obtain a sintered ore cross section infrared thermal image; based on the sintered ore cross section infrared thermal image, extracting the shallow characteristics and the deep characteristics for describing the quality of the sintered ore; establishing a sintering process multiphase thermodynamic model based on Gibbs free energy theorem; according to the multiphase thermodynamic model, obtaining the FeO content classification characteristics of the sintered ore at the highest temperature, and establishing a FeO content prediction model based on multiple heterogeneous characteristics; and real-timely and onlinely predicting the FeO content of the sintered ore by utilizing the shallow characteristics, the deep characteristics and the FeO content classification characteristics. By adopting the technical scheme, the technical problem that the FeO content of the sintered ore cannot be accurately detected in real time inthe prior art is solved, the FeO content can be accurately detected in real time, and the method has the characteristics of high precision and strong interpretability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of producing lithium ion-storing/releasing material, lithium ion-storing/releasing material, and electrode structure and energy storage device using the material
InactiveUS20120321949A1Reduction in capacity is smallIncrease energy densityMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesGibbs free energySilicon oxide
A method of producing a material capable of electrochemically storing and releasing a large amount of lithium ions is provided. The material is used as an electrode material for a negative electrode, and includes silicon or tin primary particles composed of crystal particles each having a specific diameter and an amorphous surface layer formed of at least a metal oxide, having a specific thickness. Gibbs free energy when the metal oxide is produced by oxidation of a metal is smaller than Gibbs free energy when silicon or tin is oxidized, and the metal oxide has higher thermodynamic stability than silicon oxide or tin oxide. The method of producing the electrode material includes reacting silicon or tin with a metal oxide, reacting a silicon oxide or a tin oxide with a metal, or reacting a silicon compound or a tin compound with a metal compound to react with each other.
Owner:CANON KK
Resistance memory and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102867911ALarge high and low resistance windowErase and write more timesElectrical apparatusGibbs free energyMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of memories, and provides a resistance memory and a preparation method thereof. The resistance memory comprises a top electrode, a bottom electrode and a storage medium layer placed between the top electrode and the bottom electrode, the storage medium layer comprises a metal oxide layer based on a second metal material and a metal nitrogen oxide layer based on a first metal material, the absolute value of Gibbs free energy of the metal nitrogen oxide layer based on the first metal material is higher than that of Gibbs free energy of the metal oxide layer based on the second metal material, and the metal nitrogen oxide layer is partially oxidized at the contacting interface of a metal nitride layer based on the first metal material and the metal oxide layer based on the second metal material. The resistance memory has the advantages of high erasing frequency, high initial resistance and on resistance, large high-low resistance window and fine data retention, the storage performance of the resistance memory can be obviously improved, and the preparation method of the resistance memory is simple.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Zinc Oxide Based Transparent Electric Conductor, Sputtering Target for Forming of the Conductor and Process for Producing the Target
ActiveUS20090200525A1Low resistivityDeteriorates mobilityCellsConductive layers on insulating-supportsResource depletionGibbs free energy
Provided is a zinc oxide transparent electric conductor having zinc oxide (ZnO) as its principal component, containing an element to become an n-type dopant to zinc oxide, containing metal M in which P(P=(G+H mix) / RT, wherein G is the Gibbs free energy at temperature T of the metal, H mix is the mixing enthalpy at temperature T of zinc oxide and the metal, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature) as a parameter showing the wettability with zinc oxide is 6 or less and in which its resistivity is smaller than the resistivity of zinc oxide added with the n-type dopant, and wherein concentration of metal M in relation to the total atomicity of zinc and the n-type dopant and metal M, which are all metal atoms configuring the zinc oxide transparent electric conductor, is 0.05 to 2.0 at %. In the development of a transparent electric conductor that does not contain raw material In which is expensive and with concern of resource depletion, provided is a low resistivity transparent electric conductor by exceeding the limits of the conventional development technique of the single dopant method, presenting guidelines for selecting a secondary additive material effective in achieving low resistivity, and indicating types of specific materials and the appropriate concentration range.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
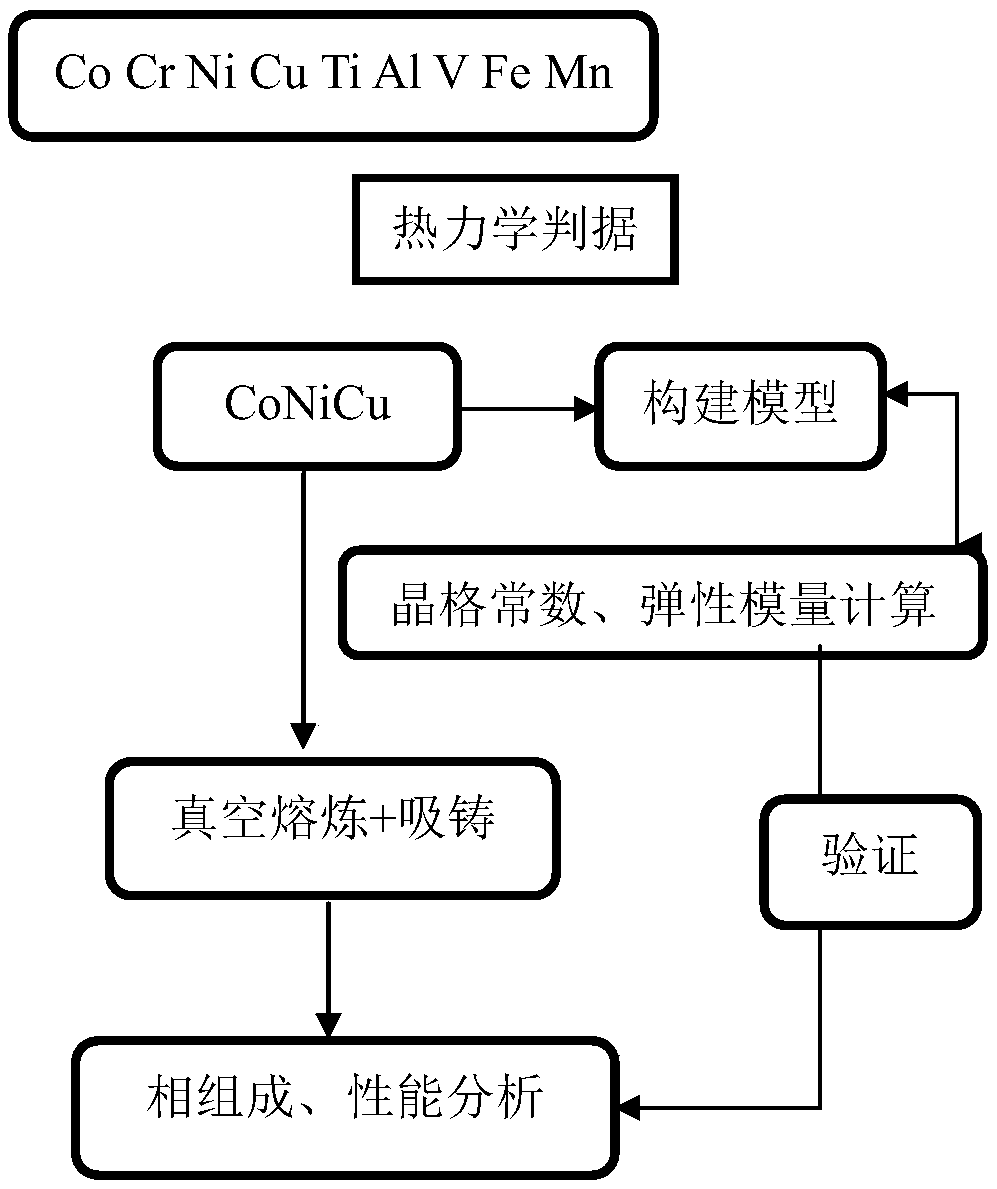
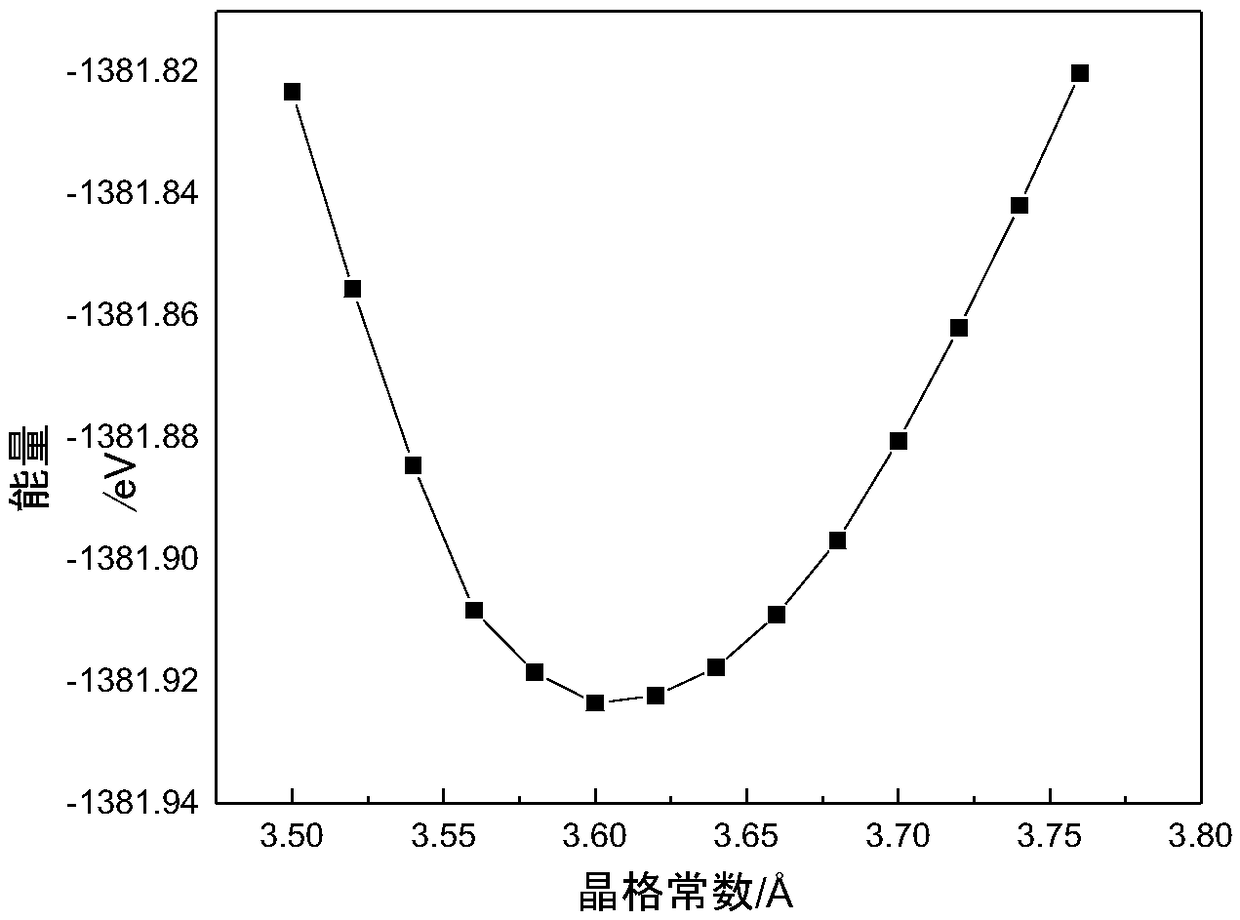
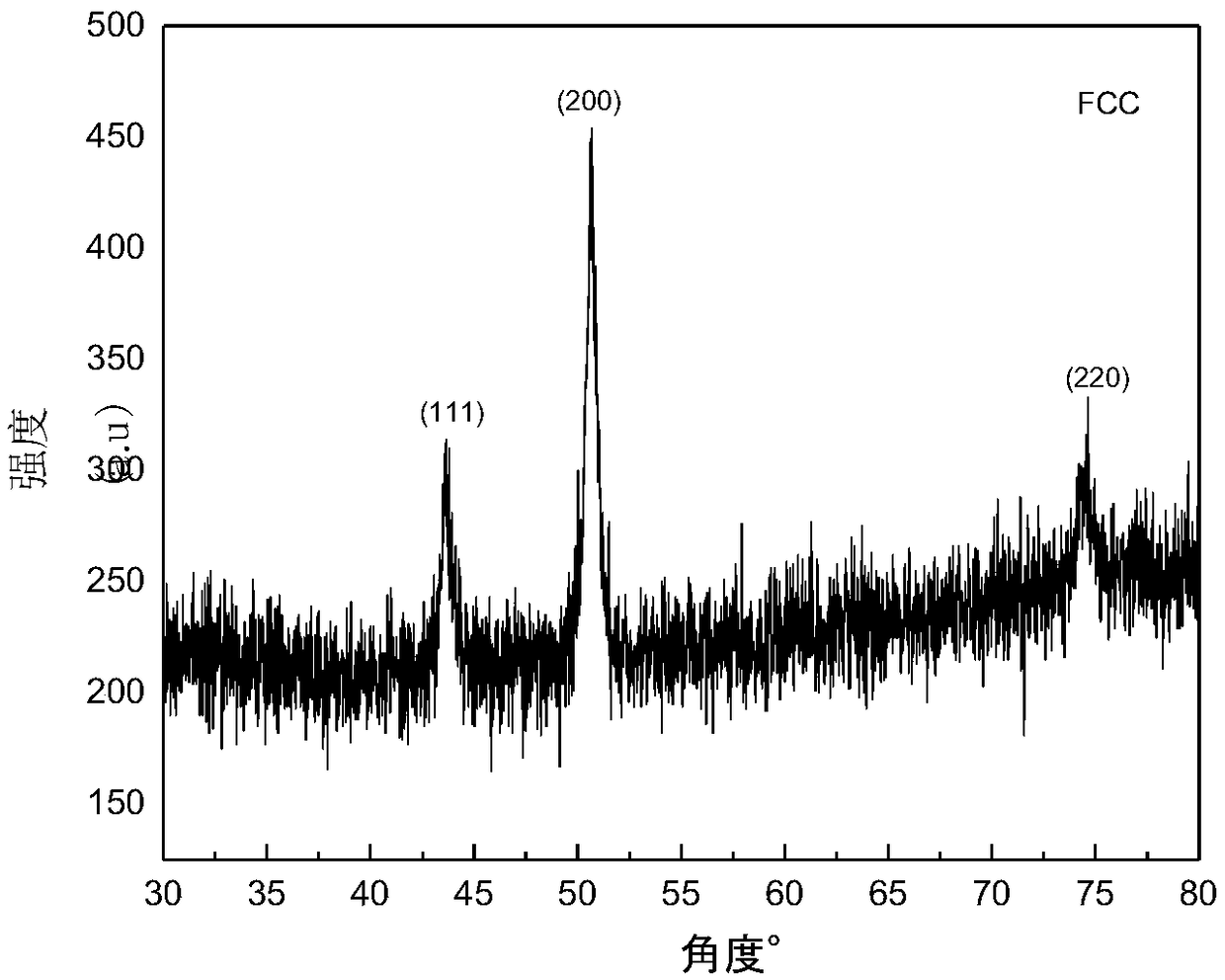
High-strength face-centered cubic structure medium-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength face-centered cubic structure medium-entropy alloy and a preparation method thereof. The CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy comprises Co, Ni and Cu elements; a resultof respective comparison of different medium-entropy alloys in electron concentration and mixing enthalpy according to the Gibbs free energy and the phase formation law of the alloy shows that the CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy has the tendency to form a single-phase FCC structure, a CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy model is constructed based on the tendency, and the alloy is predicted to be a ductile material by a first-principles technique. The preparation method of the alloy comprises the following steps: batching, vacuum melting, suction casting, homogenization annealing and solid solution treatment. Co, Cr, and Cu with a purity of 99% or more are selected and are proportioned according to an equimolar ratio or an approximately equimolar ratio, the proportioned raw materials are placed in a vacuum smelting furnace and are multiply smelted, suction casting molding is carried out after the components are uniform, and the obtained casting undergoes homogenization annealing and solid solutiontreatment to obtain the CoNiCu medium-entropy alloy having a single face-centered cubic structure and having a room temperature compressive strength of above 1600 MPa and a compression ratio of above20%.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Electron emission source, method of preparing the same, and electron emission device employing the electron emission source
InactiveUS20070024177A1Extend your lifeImprove reliabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesMetal coatingGibbs free energy
An electron emission source including a carbon-based material coated with metal carbide in the surface coating layer, of which the metal has a negative Gibbs free energy when forming the metal carbide at 1,500 K or lower, a method of preparing electron emission sources, and an electron emission device including the electron emission source. The electron emission source includes a carbon nanotube coated with metal carbide or a carbon nanotube having a metal carbide layer and a metal coating layer, which are sequentially formed thereon. Thus, the electron emission source has long lifespan without deterioration of electron emitting characteristics. The electron emission source can be used to manufacture electron emission devices with improved reliability.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Negative-electrode active material, and method for production of negative-electrode active material
ActiveUS20140110639A1Efficient synthesisHigh charge and discharge capacityElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureGibbs free energySilicon oxide
A negative-electrode active material characterized by containing a silicon oxide represented by a general formula SiOx (0<x<2) and a silicate compound represented by a composition formula MaSibOc-m(OH)-n(H20), and a method for the production of a negative-electrode active material which includes a mixing step of mixing a silicon oxide that is represented by a general formula SiOy (0<y<2) and a metal oxide, and a heat treatment step of performing a heat treatment on the mixture that is obtained in the mixing step in a non-oxidizing atmosphere and in which the negative absolute value of the standard Gibbs energy of the oxidation reaction of the metal oxide at the heating temperature in the heat treatment step is smaller than the negative absolute value of the standard Gibbs energy of the oxidation reaction of Si at the heating temperature in the heat treatment step.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060170017A1Reduce leakage currentReduce EOTSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGibbs free energySemiconductor materials
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes forming a semiconductor layer containing a semiconductor material having a first oxide-generating Gibbs free energy required to become an oxide; forming a first material for a gate insulator on the semiconductor layer, said first material containing an element having a second oxide-generating Gibbs free energy required to become an oxide and becoming insulative when the element is oxidized or nitrided; and annealing the first material in an atmosphere containing hydrogen atoms, or heavy hydrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms in a temperature range where the first oxide-generating Gibbs free energy is equal to or higher than the second oxide-generating Gibbs free energy.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100255348A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove recording densityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingFree energiesGibbs free energy
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium 100 has, over a substrate, at least a magnetic recording layer 122 with a granular structure in which nonmagnetic grain boundaries are formed between magnetic grains continuously grown into a columnar shape. The magnetic grains of the magnetic recording layer 122 contain Co, Cr, and Pt. The magnetic recording layer 122 contains at least one oxide selected from a group A including SiO2, TiO2, and Cr2O3, at least one oxide selected from a group B consisting of oxides each having a larger Gibbs free energy ΔG than the group A, and a reducing agent adapted to reduce the oxides of the group B.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Natural-energy seawater automatic distilling apparatus
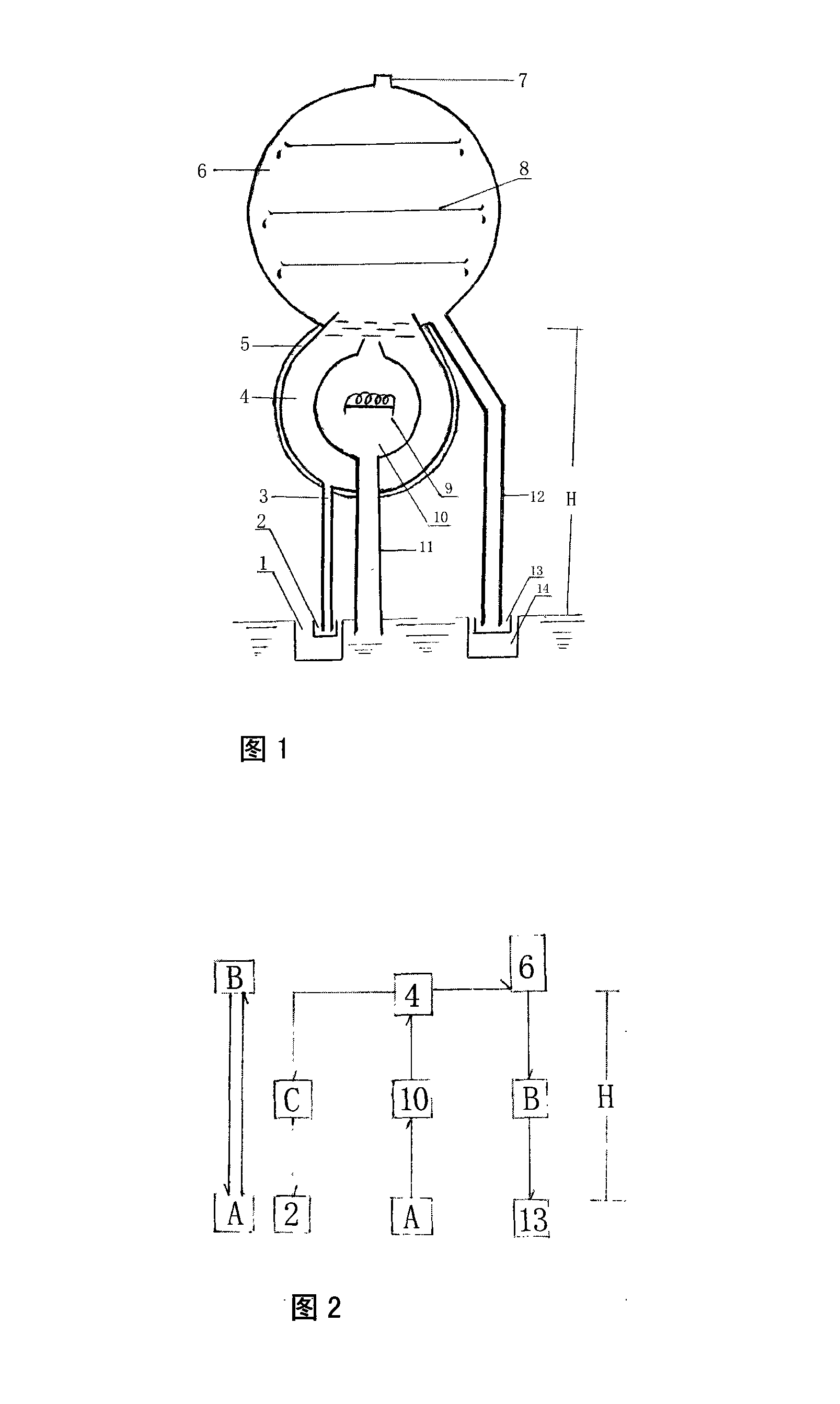
InactiveCN101224913AImprove eco-efficiencySave energyGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentGibbs free energyEngineering
The invention discloses an automatic seawater distilling device, which utilizes natural energy and is characterized in that the natural energy like atmospheric pressure, earth gravity, molecule Gibbs free energy and solar energy and so on is utilized as power, a reverse U-shaped tubular structure with certain height combines two open desalting system and salt-collecting system to form an automatic seawater distilling system at normal temperature and negative pressure and realize the automatic production of fresh water (distilled water) and salt. The invention has the advantages that: 1. the natural energy is utilized as the power to produce fresh water and salt, which does not discharge any pollutant, thus saving fuel energy and protecting environment; 2. ductwork is highly automatic and needs no manual operation, which is safe for production and can improve labor efficiency. In a word, no energy, raw material and labor investment is needed, only equipment investment at a first time is needed, and then profit can be obtained for a long time. The invention is also applied for a bitter water region or be installed on different large ships to produce fresh water by utilizing the afterheat of the power and the water in rivers, lakes and seas on the way; also the invention can be installed on a residential building to produce drinking water with tap water, which has good ecological effect, economic benefit and social benefit and wide market.
Owner:徐祯祥
Organic light emitting display apparatus
ActiveUS7619244B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmDopant
The present invention provides a top emission type organic light emitting display apparatus in which manufacture it is possible to prevent the organic film from being oxidized when the upper transparent electrode is formed, and which is capable of emitting light at a low voltage. This organic light emitting display apparatus includes an organic light emitting layer and an upper electrode and a lower electrode sandwiching the said organic light emitting layer between them, and is of a structure in which the light emitted from the organic light emitting layer is taken out from the upper electrode side, wherein a buffer layer mostly made of an oxide with its Gibbs free energy generated at around the melting point being lower than −300 kJ / mol is provided between the organic light emitting layer and the upper electrode, the side of the organic layer which is in contact with the buffer layer being doped with an electron donative dopant.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
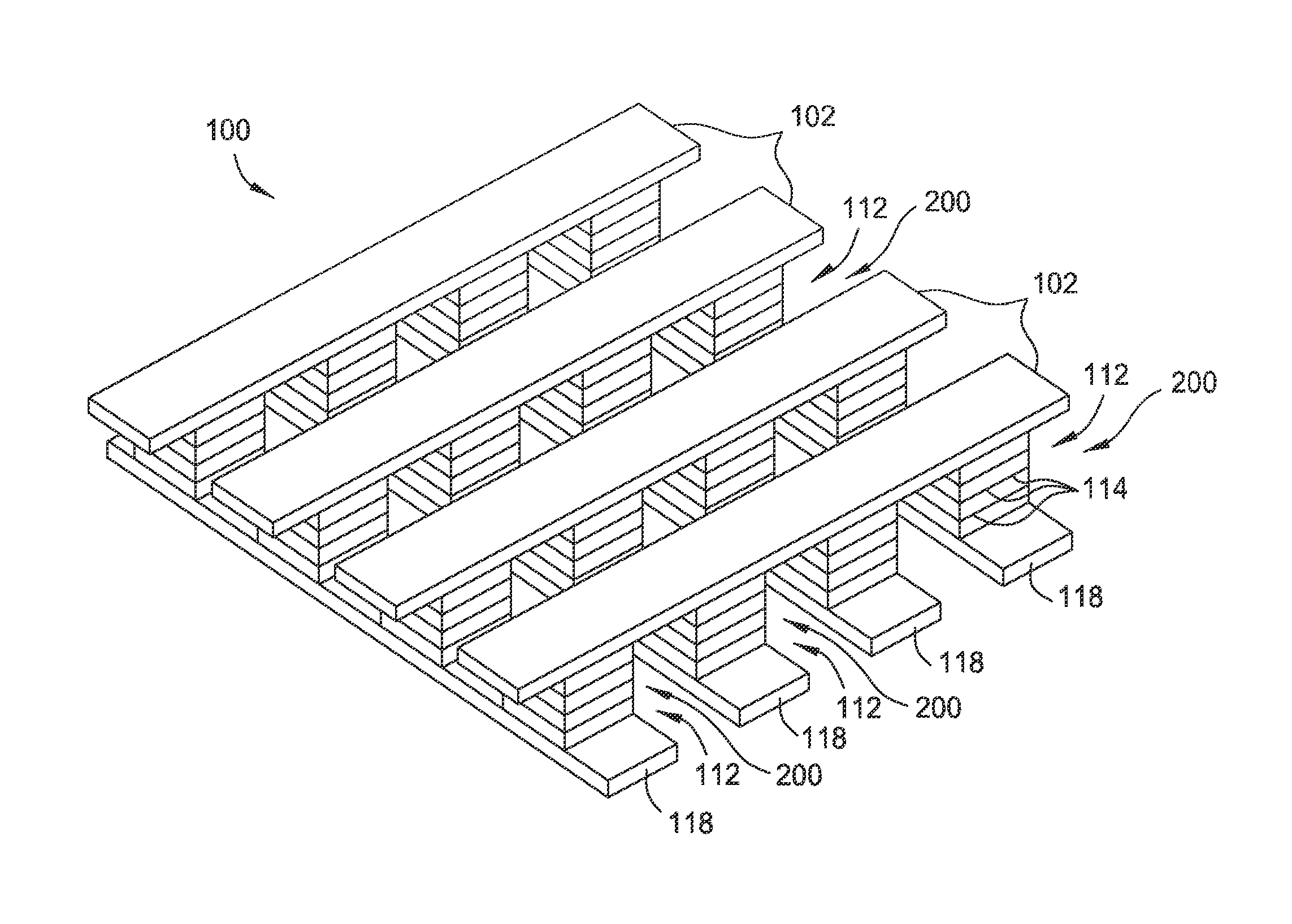
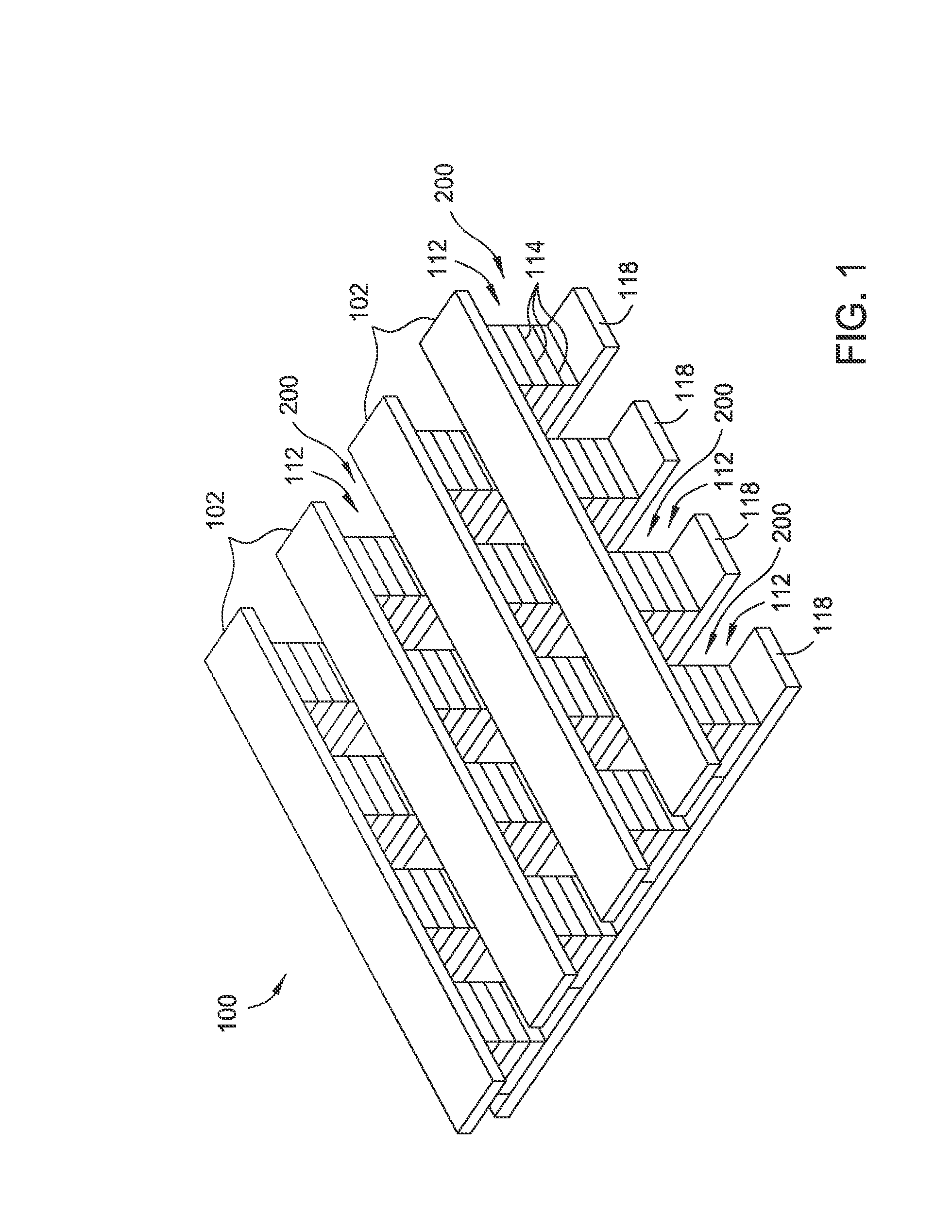
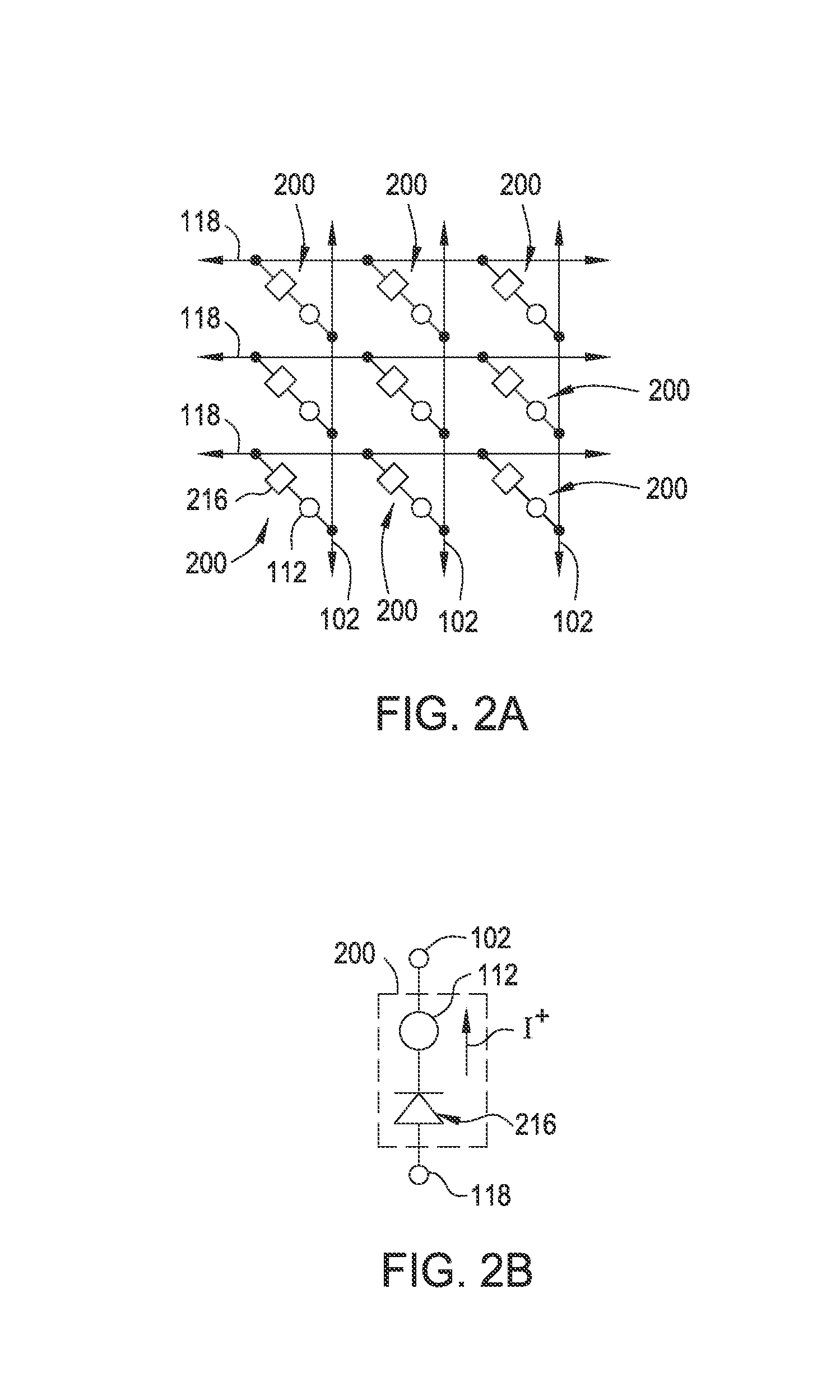
ActiveUS20110266538A1Reduce contact resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGibbs free energyStandard gibbs free energy change
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method for preparing anisotropy heat conduction block material by Gibbs free energy induction
ActiveCN108819400AImprove thermal shock heat transfer efficiencyIncrease the longitudinal thermal shock frequencySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationGibbs free energyMaterials processing
The invention relates to the preparation of heat conduction materials, and belongs to the field of material processing. The method for preparing an anisotropy heat conduction block material by Gibbs free energy induction is characterized in that two-dimensional nanometer materials in a two-dimensional nanometer material dispersion liquid planar liquid film are subjected to directional arrangementand are solidified into an anisotropy film; after overlapping, hot briquetting is carried out to obtain the anisotropy heat conduction block material. Internal two-dimensional nanometer particles havethe advantages of higher heat transfer efficiency and higher speed. Especially when a temperature difference is high, compared with other heat conduction materials of which the internal nanometer particles are in disordered arrangement, the heat conduction block material prepared by the method is characterized in that the lateral ineffective thermal vibration of the two-dimensional nanometer particles on a micro-level can be lowered, the longitudinal thermal vibration frequency of nanometer particles is improved, heat transfer efficiency is improved, and the heat transfer coefficient of the anisotropy heat conduction block material can be 5300W / (m.K).
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Semiconductor device with perovskite capacitor
A semiconductor device comprising a semiconductor substrate, and a capacitor provided above the semiconductor substrate, and including a bottom electrode, a top electrode and a dielectric film between the bottom and top electrodes, the bottom electrode including a conductive film selected from a noble metal film and a noble metal oxide film, a metal oxide film having a perovskite structure, provided between the dielectric film and the conductive film, expressed by ABO3, and containing first metal element as B-site element, and a metal film provided between the conductive film and the metal oxide film, and containing second metal element which is B-site element of a metal oxide having a perovskite structure, a decrease of Gibbs free energy when the second metal element forms oxide being larger than that when the first metal element forms oxide, a thickness of the metal oxide film being 5 nm or less.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
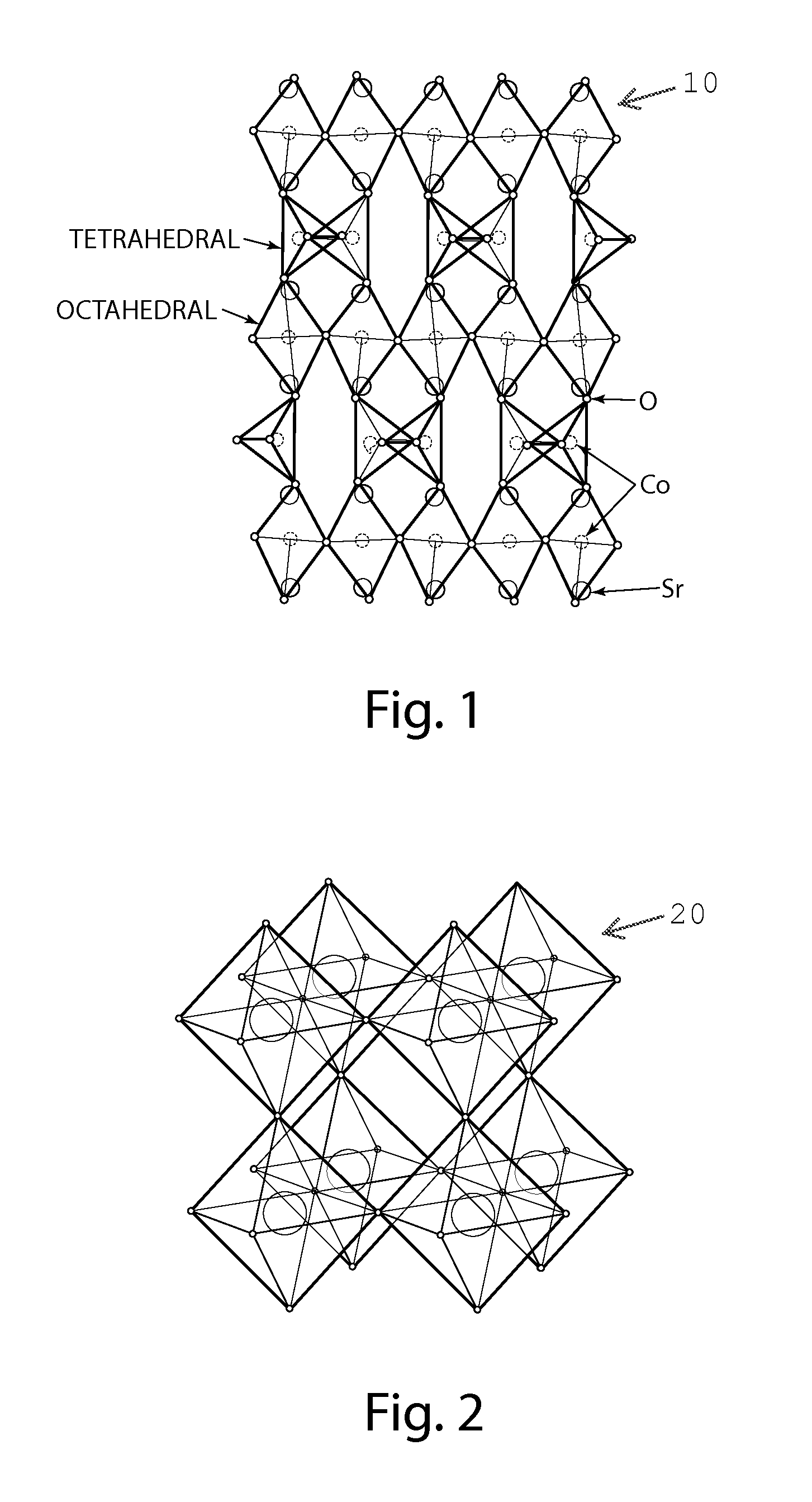
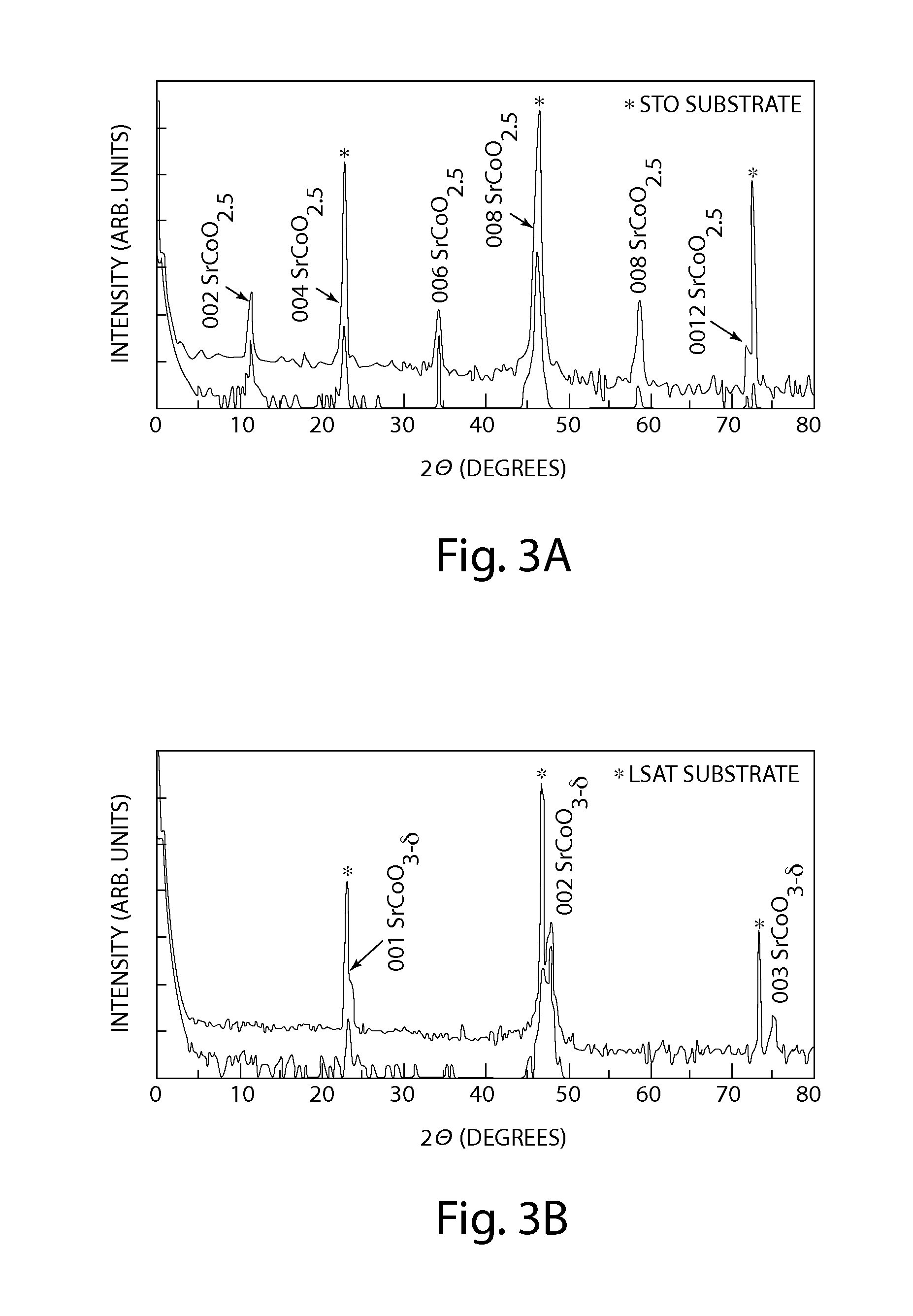
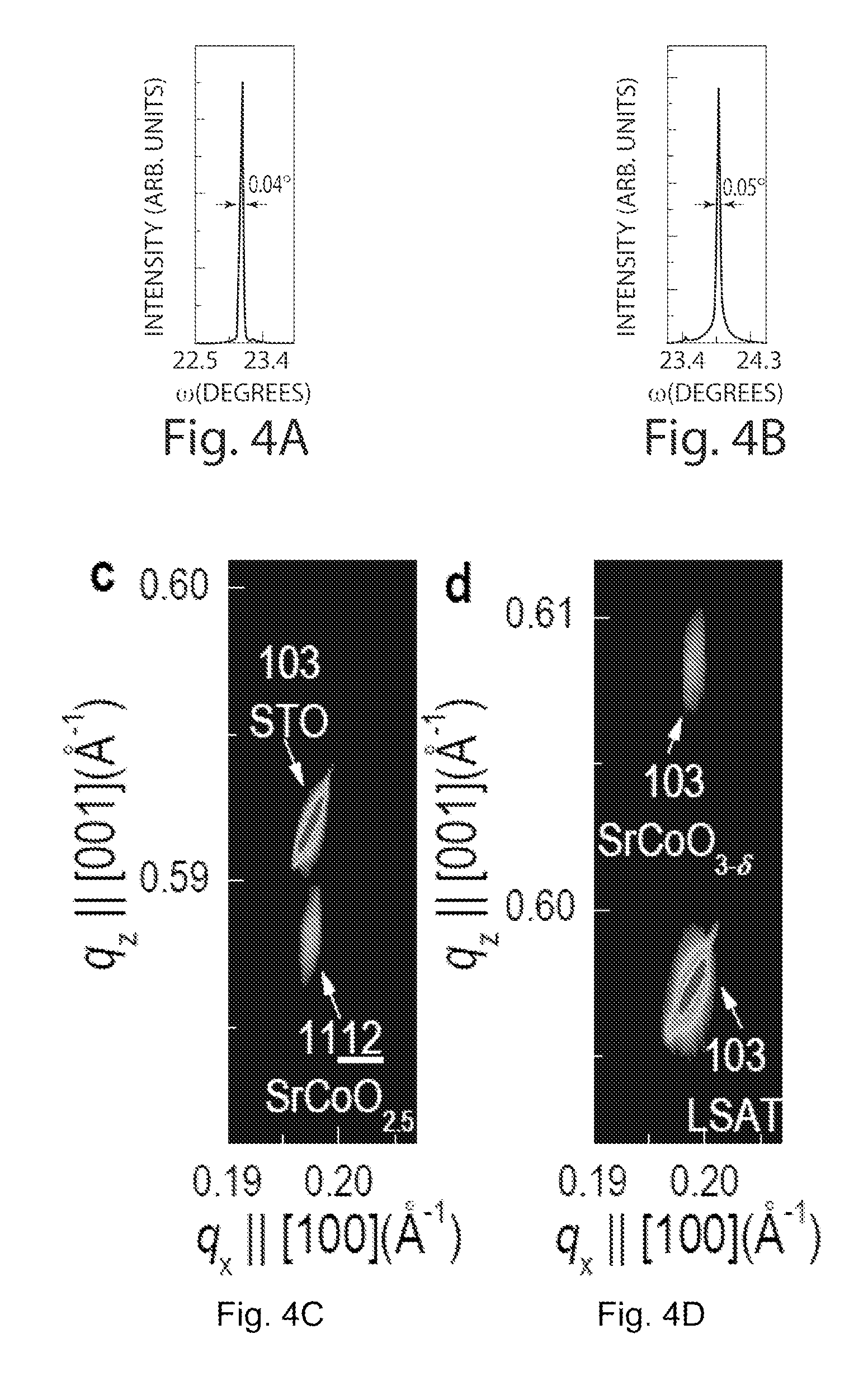
Strontium cobaltite oxygen sponge catalyst and methods of use
ActiveUS20150148218A1Other chemical processesCatalyst activation/preparationGibbs free energyPtru catalyst
Rapid, reversible redox activity may be accomplished at significantly reduced temperatures, as low as about 200° C., from epitaxially stabilized, oxygen vacancy ordered SrCoO2.5 and thermodynamically unfavorable perovskite SrCoO3-δ. The fast, low temperature redox activity in SrCoO3-δ may be attributed to a small Gibbs free energy difference between the two topotactic phases. Epitaxially stabilized thin films of strontium cobaltite provide a catalyst adapted to rapidly transition between oxidation states at substantially low temperatures. Methods of transitioning a strontium cobaltite catalyst from a first oxidation state to a second oxidation state are described.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
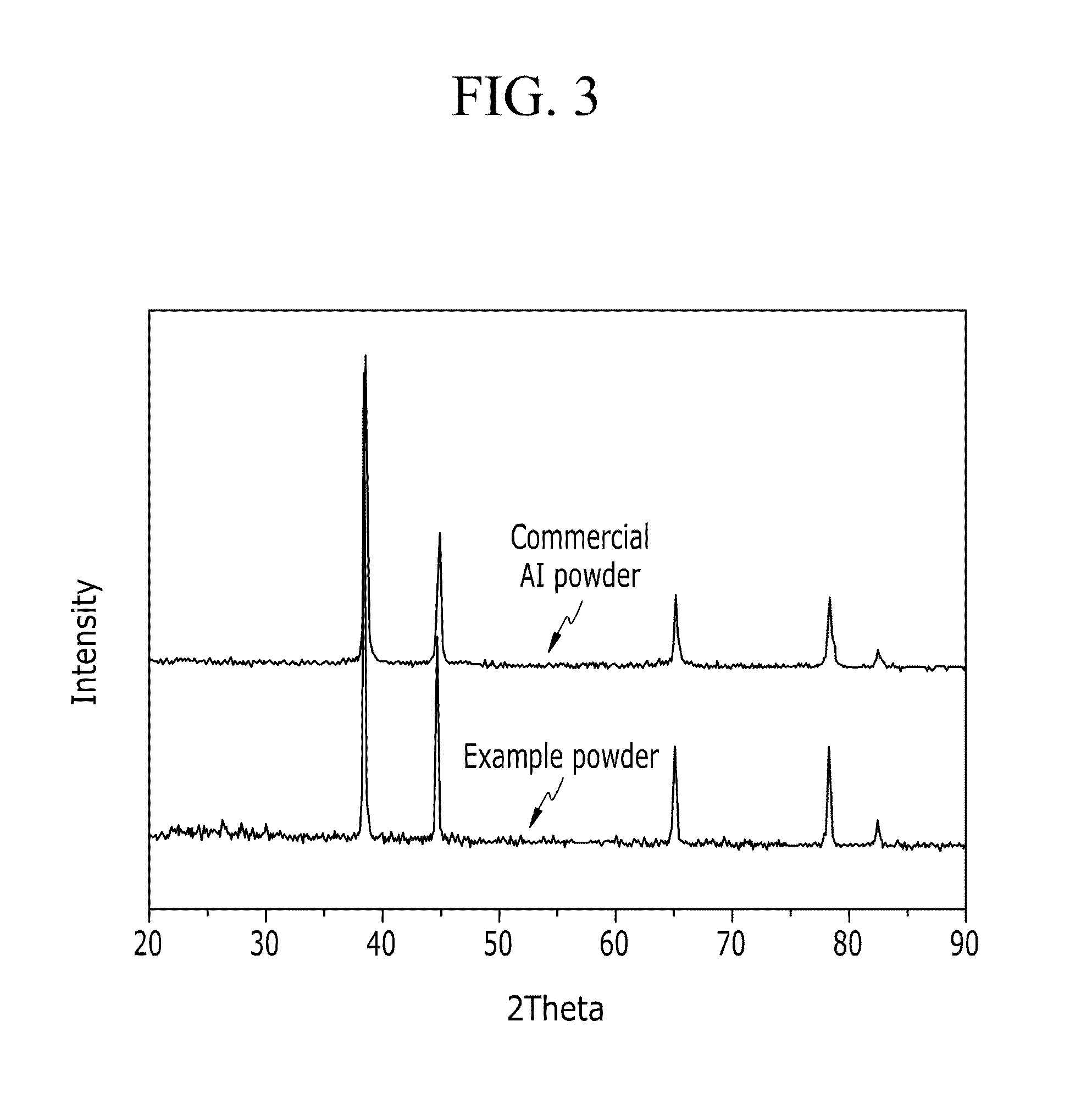
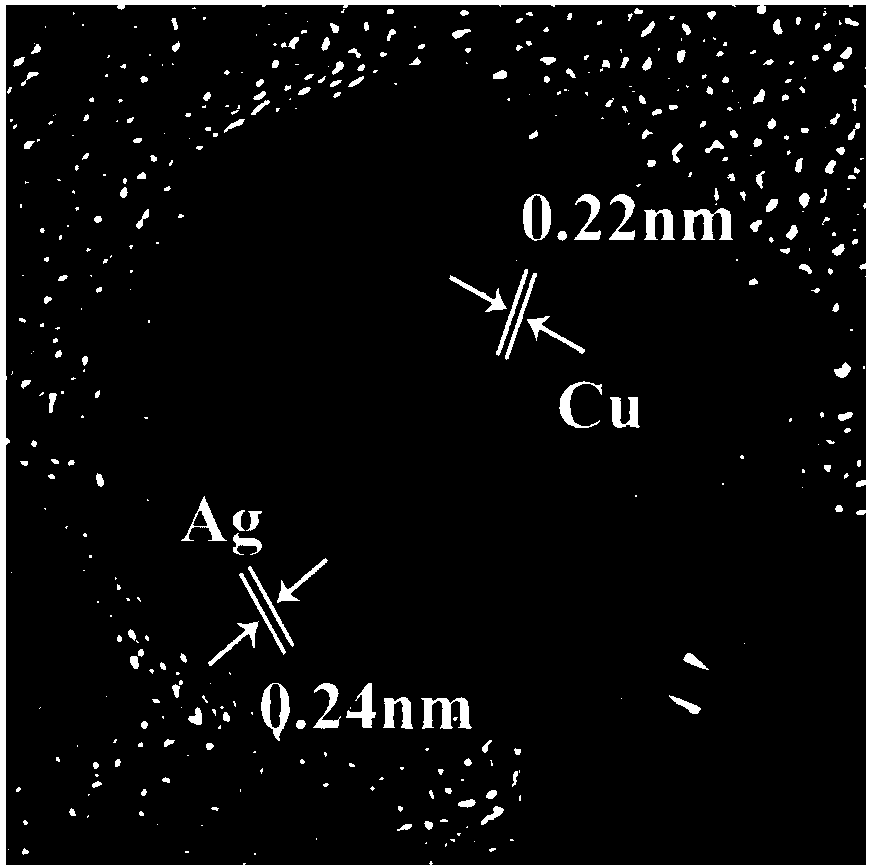
Method for predicting eutectic temperatures of nano Ag-Cu alloy systems in different sizes
ActiveCN108052794AEasy to operateAvoid reunionChemical property predictionTransportation and packagingGibbs free energyFree energies
The invention relates to a method for predicting eutectic temperatures of nano Ag-Cu alloy systems in different sizes. The method includes: preparing Ag-Cu nano alloy particles according to a wet chemical method, coating with SiO2, subjecting the nano alloy particles to representation through TEM, and adopting a DSC (differential scanning calorimeter) for acquiring nano alloy size and melting information. By consideration of related nano particle surface effects, a relationship of corresponding nano particle gibbs free energy changing along with temperature and particle size is extrapolated onblock alloy gibbs free energy according to a CALPHAD method, a correction factor is adjusted according to experimental results, and accordingly a self-consistent related nano particle gibbs free energy describing expression is acquired and used for predicting Ag-Cu nano alloy eutectic temperature, and uniformity of calculative prediction results and experimental results is achieved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
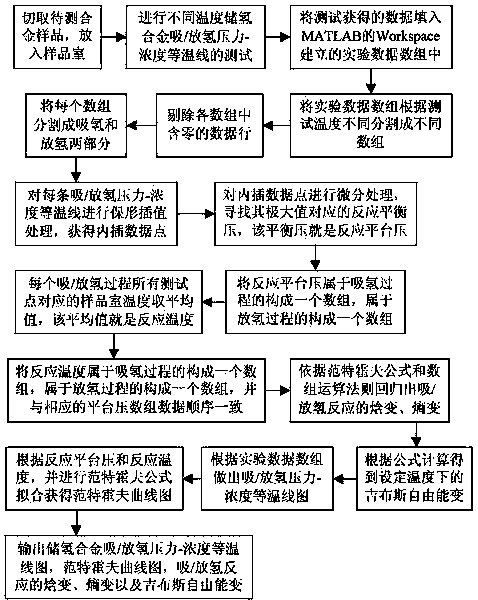
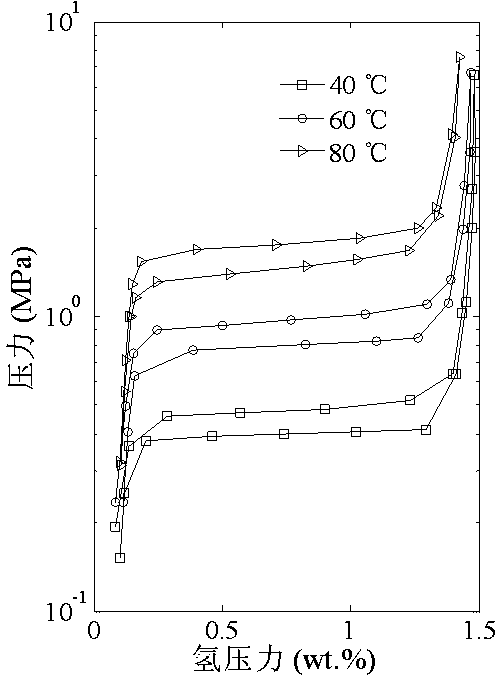
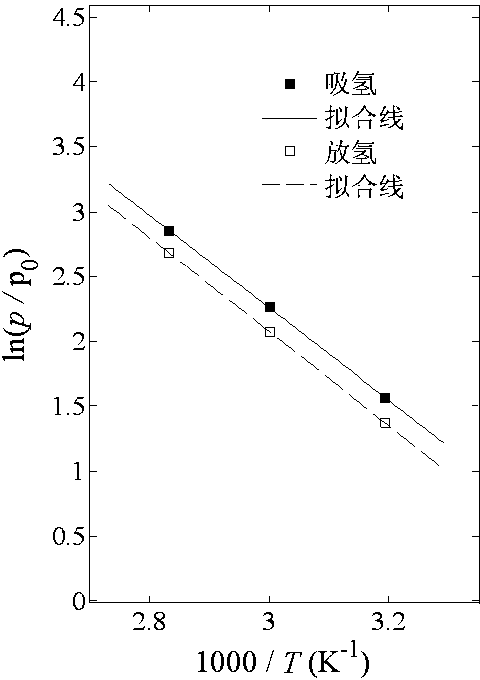
Method for determining hydrogen absorption/desorption thermodynamic parameter of hydrogen storage alloy
InactiveCN103439474AAutomate analysisImprove analysis efficiencyTesting metalsGibbs free energyFree energies
The invention relates to a method for obtaining key performance parameters of an alloy material, particularly to a method for the determining hydrogen absorption / desorption thermodynamic parameter of hydrogen storage alloy. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, a hydrogen storage alloy hydrogen absorption / desorption performance tester is utilized to carry out a dependence test so as to obtain hydrogen absorption / desorption pressure-concentration isotherm data of the hydrogen storage alloy at different temperatures, then, a series of automatic analysis and process are performed on the experimental data, and finally, the hydrogen storage alloy hydrogen absorption / desorption enthalpy change data, hydrogen absorption / desorption entropy change data, and the gibbs free energy change data at the set temperature are output. According to the invention, the hydrogen storage alloy component-performance screening efficiency and the reliability of the analysis conclusion in engineering application are greatly improved, and the problems that the past hydrogen storage alloy hydrogen absorption / desorption thermodynamic parameter data is great in dispersibility, high in mistake occurrence probability, complicated in analytical test process, and not visual enough in data output are solved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com