Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
201 results about "Barium acetate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Barium acetate (Ba(C₂H₃O₂)₂) is the salt of barium(II) and acetic acid.
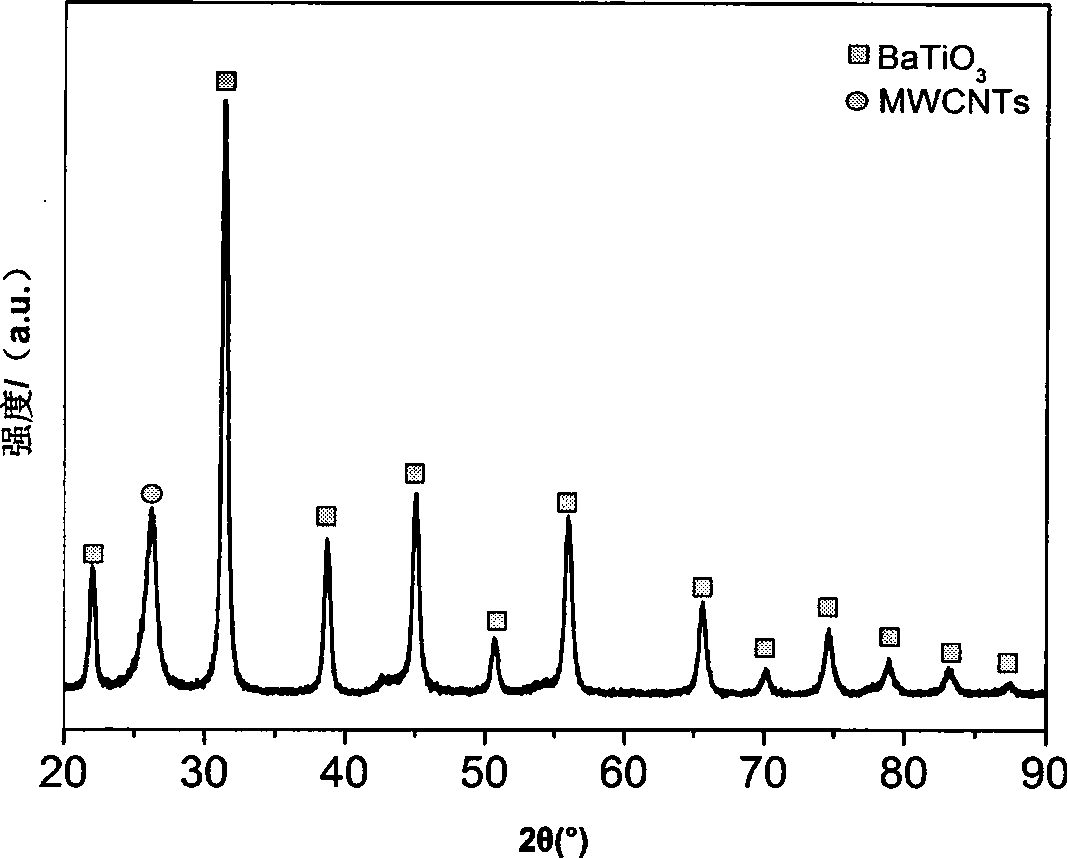
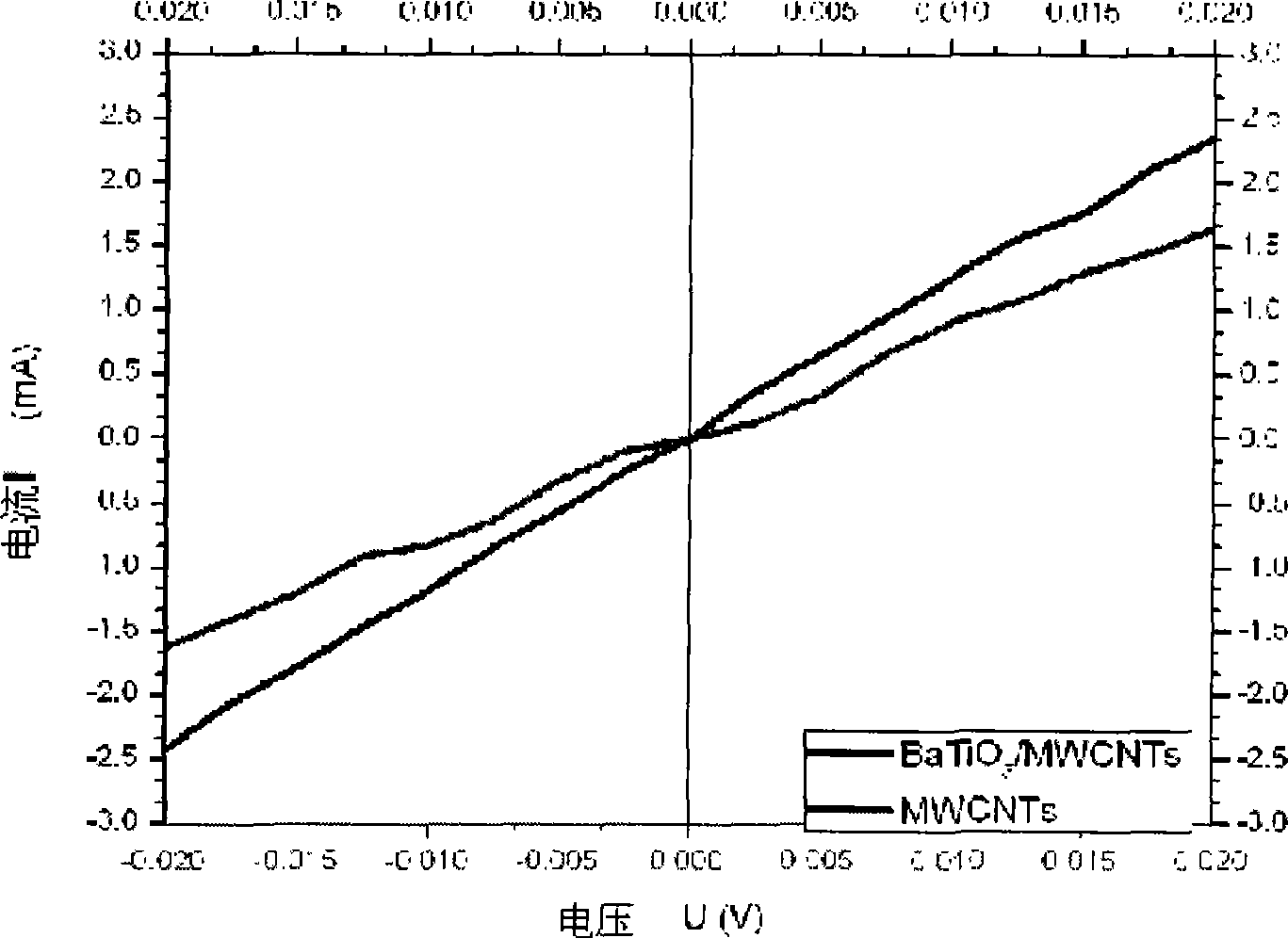
Method for preparing BaTiO3 / multi-wall carbon nano-tube (MWCNTs) nano composite material
InactiveCN101475161AImprove conductivitySmall particlesTitanium compoundsBarium titanatePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a method for preparing a BaTiO3 / MWCNTs nano composite material, which comprises the following steps: using MWCNTs, barium acetate, sodium hydrate and tetrabutyl titanate as initial raw materials, using deionized water, ethylene diamine and ethanolamine as solvents, adopting concentrated nitric acid to modify the surface of the MWCNTs, using a tetrabutyl titanate hydrolysis product as a titanium source, adding a dispersant, namely polyethylene glycol and plasmosan into the mixture, and adopting a solvent hot method to obtain the BaTiO3 / MWCNTs nano composite material. By changing the proportion of the MWCNTs, the barium acetate and the tetrabutyl titanate, the BaTiO3 / MWCNTs nano composite material with different compositions can be obtained. The prepared BaTiO3 / MWCNTs nano composite material has good electric conductivity, the synthesis process and the production equipment are simple, and industrialized production is easy to realize.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing barium titanate nano-powder
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for detecting SO3 content in flue gas
InactiveCN1995956ASampling safetyEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWithdrawing sample devicesAfter treatmentFlue gas
The invention relates to the inspection method and sampling device for the SO3 content of the smoke released by thermal power plant boiler. The sampling device comprises the dust remover, sampling tube, spiral collecting tube and drawing device, with the dust remover at the input end of the sampling tube whose output connected with the input of the spiral collection tube, with the input and output ends of the spiral collection tube on the spiral, and the output connected with the drawing device through hoses. It collects SO3 of the smoke to the spiral collection tube, getting SO42 sample solution after treatment, with arsenazo III as the color developing agent, dropping with barium acetate solution to get the density of SO3. It is accurate, quick, and reliable, with every possible means to avoid heat waste due to improving acid dew point corrosion.
Owner:CPI YUANDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG +1
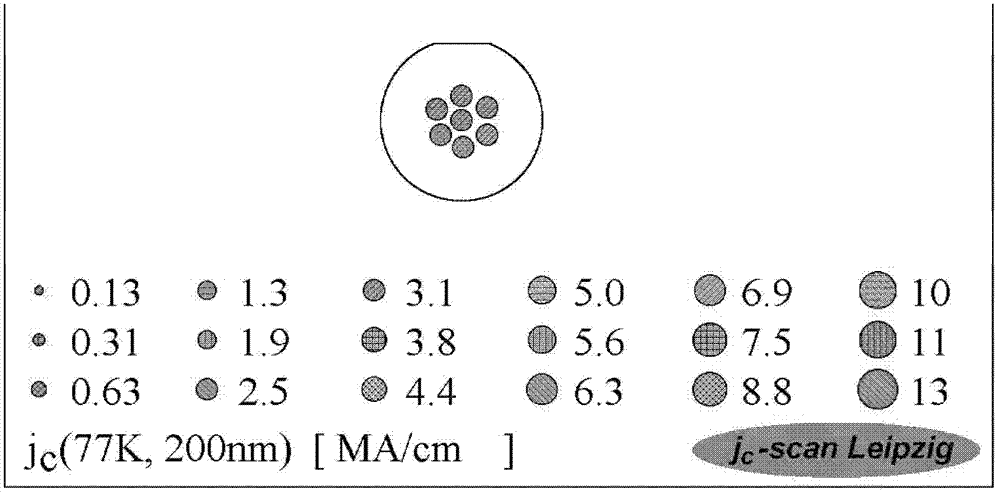
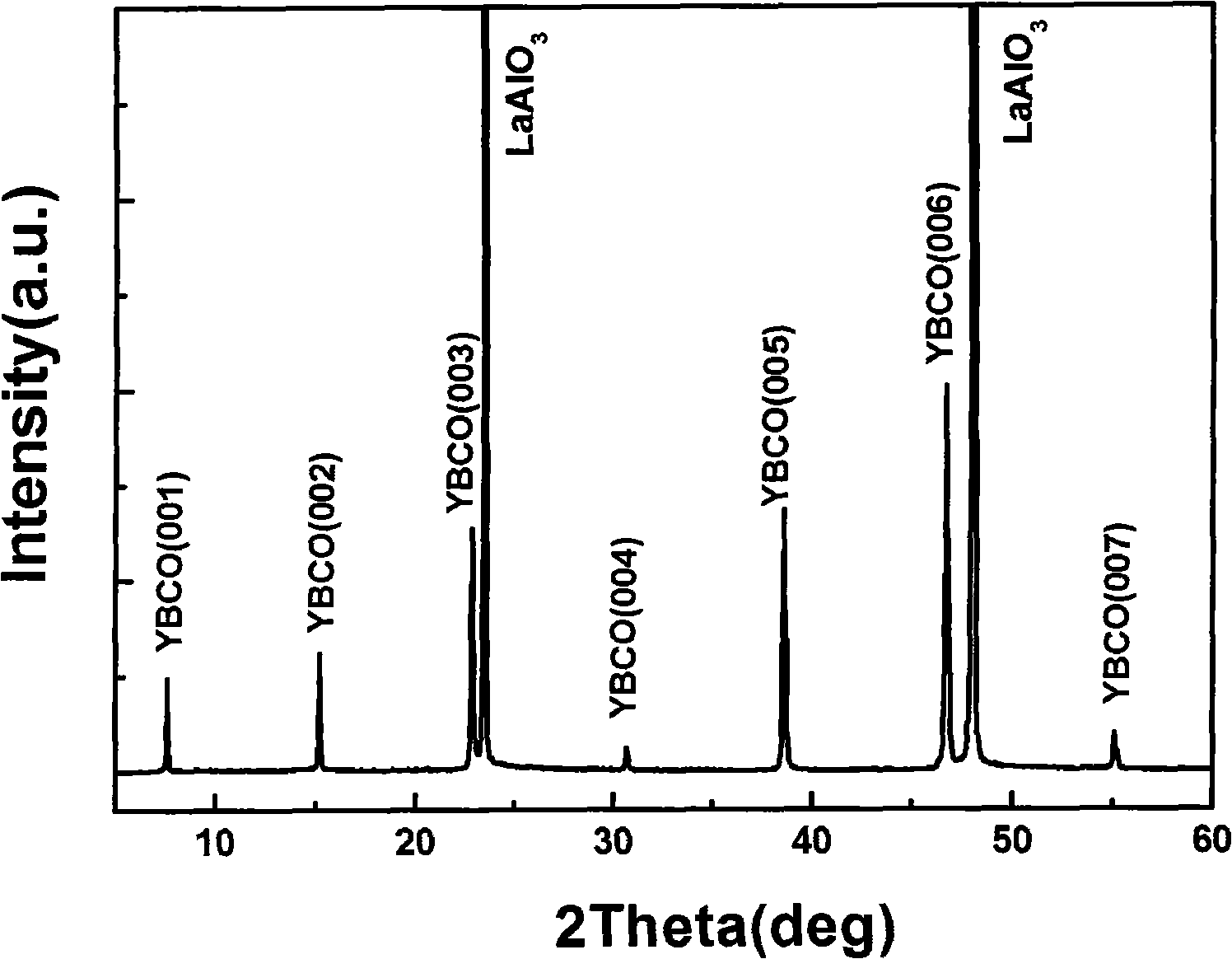
Collosol of yttrium barium cupper oxygen superconducting film and process for preparing high temp. superconducting film thereof
InactiveCN1792806AShorten heat treatment timeEasy to makeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesPolymer scienceOxygen
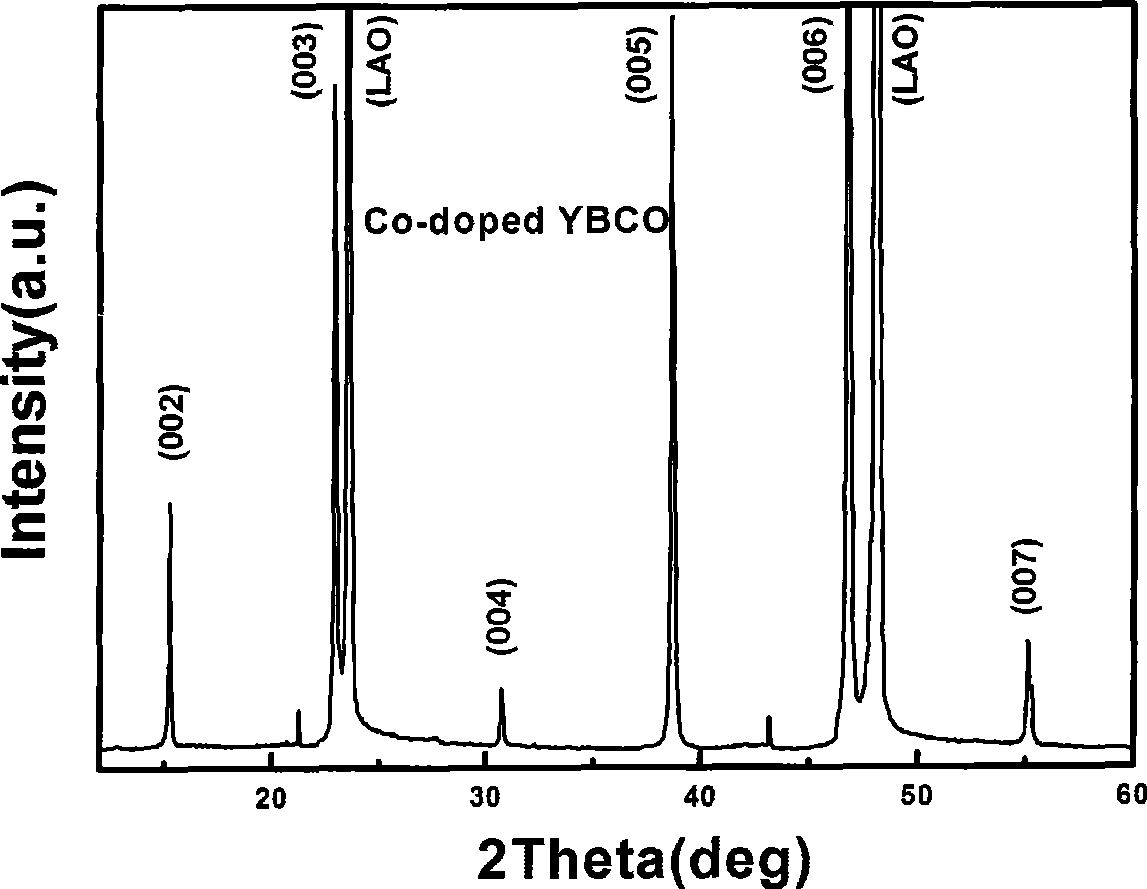
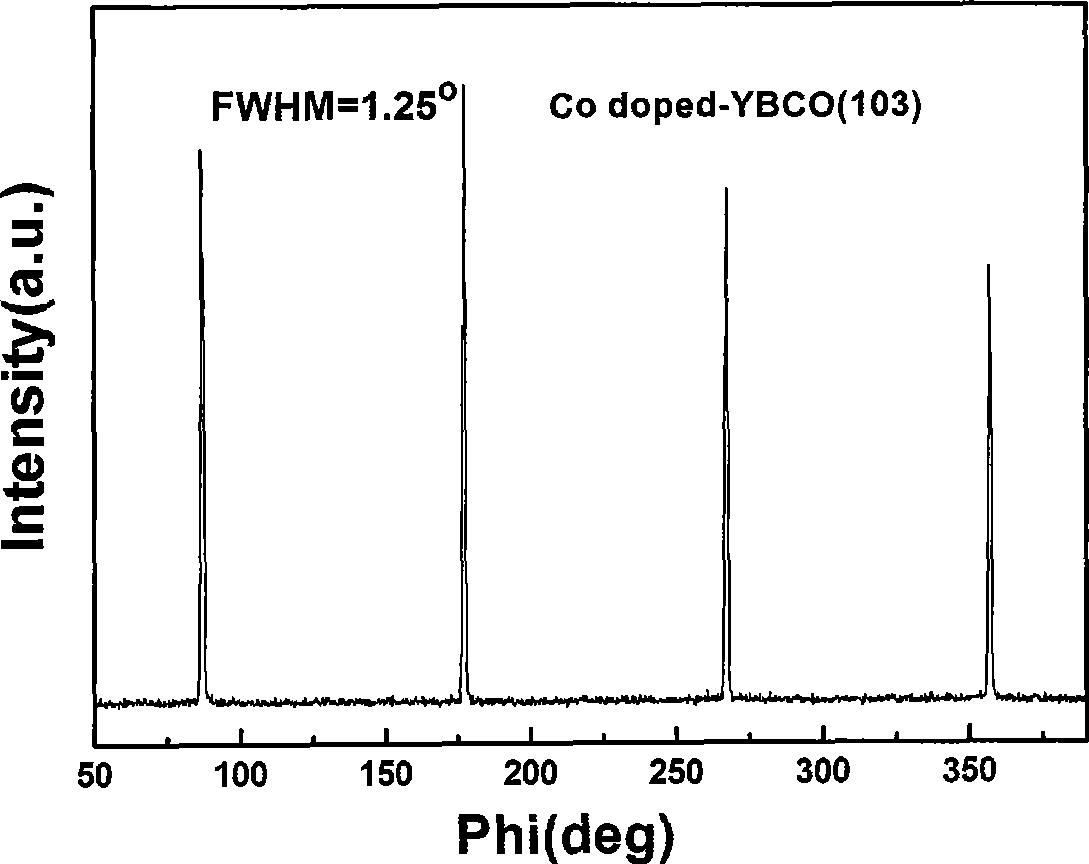
A sol of the Y-Ba-Cu-O (YBCO) superconductor film is proportionally prepared from yttrium acetate, barium acetate, copper acetate, trifluoroacetic acid, water, alpha-methylacrylic acid, divinyltriamine and methanol. A process for preparing the high-temp superconductor film from said sol is also disclosed.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing strontium titanate nanometer powder of one-dimensional structure
InactiveCN101311376AProcess conditions are easy to controlProcess condition controlPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsStrontium titanateNanowire
The invention discloses a method for preparing strontium titanate nanometer powder with one-dimension structure, which consists of procedures of preparing the oxyhydroxide precipitate of titanium and the deionized aqueous solution of barium acetate as reaction materials, adding a feasible quantity of potassium hydroxide to promote crystallization, and appending a suitable viscosity of patterned vertical alignment polymer surfactant to control the feature; under the temperature of 100-150 DEG C, strontium titanate nanowire and a branched crystal structure are obtained after a hydrothermal reaction. The craftwork of the invention is simple; the micro feature of the product is easy to control, the pollution is free; the cost is low; a large-scale production is suitable. The quality of the crystallization of the prepared product is stable; the specific surface is big. A broad application prospect is possessed in fields of micro electronic devices, EO devices, storage devices, oxygen sensors, photocatalyst, and solar battery, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of high temperature superconductive film adopting modified low fluoride solution method
InactiveCN102531567AGood superconducting propertiesReduce manufacturing costElectrical conductorOxygen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high temperature superconductive film adopting a modified low fluoride solution method, which comprises the following steps: dissolving yttrium oxide, barium acetate and copper acetate as raw materials in a solvent using a complexing agent to obtain a low fluoride yttrium barium copper oxygen solution, preparing a gel film and drying, and performing pretreatment and end treatment of the film. The sol has easily adjustable composition, stable performance and good film forming property, the yttrium barium copper oxygen superconductive film can be easily prepared using the sol, and the heat treatment cycle is short and the process repeatability is high. In addition, the solution avoids the introduction of amine group, so as not only to avoid the loss of copper in the heat treatment, but also to avoid the problem that the film is easy to craze. The method of the invention is also used for preparing large-area or long-distance yttrium barium copper oxygen films and coated conductors, the obtained yttrium barium copper oxygen film has good surface smoothness and has good superconductivity.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing high critical current density yttrium barium copper oxide superconducting film
InactiveCN101456726ASimple processShorten the timeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesPolyvinyl butyralPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing a yttrium barium copper oxide superconducting film with high critical current density, which comprises the following concrete steps: a, preparing a precursor solution, which is to dissolve yttrium acetate, barium acetate, copper acetate and acetate of an impurity element into propionic acid according to the proportion that the stoichiometric ratio of yttrium: barium: copper: impurity element is 1: 2: 3-X: X (the X is more than or equal to 0.0002 and less than or equal to 0.008) to obtain the precursor solution, and the impurity element is one of Co, Fe, Zn, Ni, and Li; b, adding a polymer material polyvinyl butyral (PVB) into the precursor solution obtained in a step to obtain a coating colloid; c, coating and drying the coating colloid on a substrate to form a film; and d, performing thermal decomposition treatment on the substrate with the film prepared in c step and then imaging thermal treatment to obtain the YBCO superconducting film. The yttrium barium copper oxide superconducting film prepared by the method has high biaxial texture, smooth and compact surface, high critical current density under a magnetic field, low cost, and simple process, and is suitable for mass industrial production.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing PbO from waste lead-acid battery by using direct wet method
ActiveCN104393364AGuaranteed purityOvercome the problem that desulfurization is not easy to controlLead monoxideWaste accumulators reclaimingAcetic acidLead oxide
The invention provides a method for recovering waste lead-acid batteries to directly produce high-purity lead oxide, wherein the utilized chemical raw materials can be recycled. The preparation method of a high-purity PbO powder comprises the steps of fully charging a waste battery, performing solid-phase mixing on positive / negative lead plaster and waste grid lead powder, and completely converting lead in the lead plaster to lead raw materials consisting of lead oxide PbO and PbSO4 by heating and reduction reaction; leaching by using a mixed liquid of acetic acid and acetate, desulfuring by using byproduct barium sulfate of barium acetate, depositing lead in an alkali liquid to directly obtain the high-purity PbO products, wherein the acetate mother liquid can be used for the next circulation; therefore, the defects that steps of the current lead oxide synthesis process are complex, the purity is low, and a large amount of chemical raw materials is consumed are overcome; the cost is reduced; the technical value-added is high; the energy conservation and environment friendliness are provided; and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:中国人民解放军军事科学院防化研究院
Method for preparing barium titanate monocrystal nano particles of six-pin structural perovskite
InactiveCN102691105AHigh crystal purityGood dispersionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsBarium titanatePotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing barium titanate monocrystal nano particles of six-pin structural perovskite, and a two-step hydrothermal method is adopted. The method comprises the following steps of: depositing tetrabutyl titanate which serves as a precursor by use of oxyhydroxide of titanium prepared from ethylene glycol monomethyl ether; performing hydrothermal reaction by utilizing potassium hydroxide a mineralizer, so as to obtain a K2Ti6O13 nano line; and performing secondary hydrothermal reaction on the prepared K2Ti6O13 nano line which serves as a titanium source, barium acetate which serves as a barium source and KOH which serves as the mineralizer, so as to obtain the barium titanate monocrystal nano particles of the six-pin structural perovskite. The process is simple and easy to control; pollution is avoided; the cost is low; large-scale production is realized; and the barium titanate monocrystal nano particle crystal of the six-pin structural perovskite is high in purity and high in dispersion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of making barium titanate
InactiveUS7001585B2High yieldImprove volumetric efficiencyAlkaline earth titanatesTitanium organic compoundsOxalateBarium titanate
Owner:FERRO CORP
Oxide superconducting film and method of preparing the same
ActiveUS20060153969A1Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperconductor devicesCarboxylic acidLanthanum
The present invention relates to a method of preparing an oxide superconducting film, the method includes reacting a metal acetate containing metal M selected from the group consisting of lanthanum, neodymium and samarium with fluorocarboxylic acid having not less than three carbon atoms, reacting barium acetate with fluorocarboxylic acid having two carbon atoms, reacting copper acetate with fluorocarboxylic acid having not less than two carbon atoms, respectively, followed by refining reaction products, dissolving the reaction products in methanol such that a molar ratio of the metal M, barium and copper is 1:2:3 to prepare a coating solution, and coating a substrate with the coating solution to form a gel film, followed by calcining and firing the gel film to prepare an oxide superconducting film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Yttrium barium copper oxide fluorine-free sol and preparation of high temperature superconducting film
InactiveCN101475370AReduce porosityLow porositySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesDiethylenetriamineOxygen
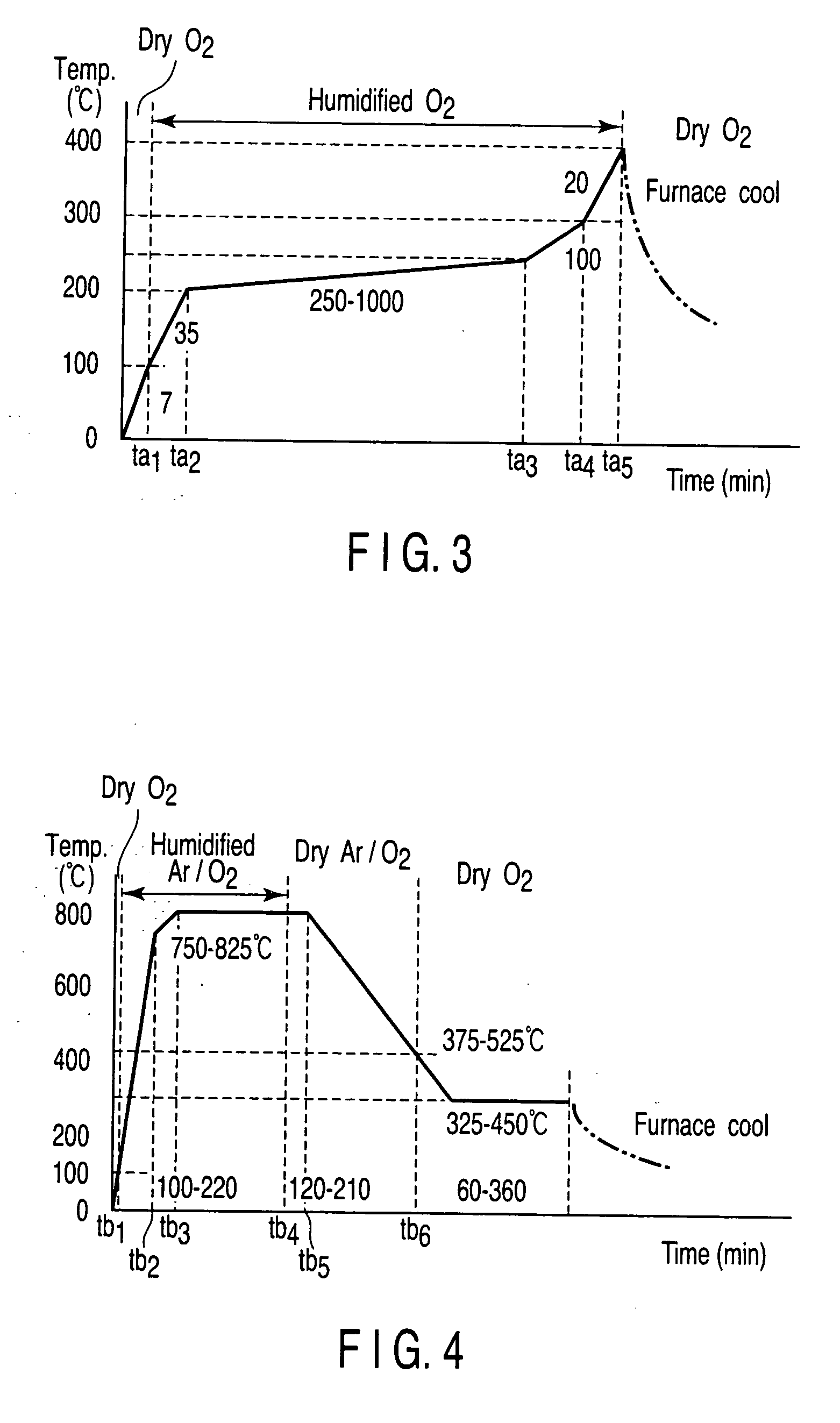
The invention discloses a method for preparing yttrium barium copper oxide fluorine-free sol and a high-temperature superconductive membrane. The mol ratio of the following compositions of the fluorine-free sol, namely yttrium acetate to barium acetate or barium hydroxide to copper acetate to diethylenetriamine or ethanolamine or diethanolamine or trolamine to lactic acid to acrylic acid or alpha-methacrylic acid or metacetonic acid to methanol or ethylene glycol monomethyl ether or ethanol, is 1:2:3-4:1.5-5:6-10:6-40:60-360. The method for preparing the superconductive membrane is to adopt different complexing agents to dissolve acetate in a solvent to prepare the yttrium barium copper oxide fluorine-free sol, adopt a crystal pulling method to prepare the fluorine-free sol into a yttrium barium copper oxide gel membrane, perform heat treatment on the gel membrane, and prepare the yttrium barium copper oxide high-temperature superconductive membrane. During preparation of the membrane from the sol, the pyrolysis process is not required; the whole heat treatment time is shortened by approximately 10 hours compared with the prior fluorine-containing technology; and no corrosive HF gas is generated during preparation of the membrane, so that environmental pollution is low.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing barium plumbate powder by coprecipitation of copper anode mud silver separating residue of circuit board
InactiveCN102660683AAchieve high value recyclingNo secondary pollutionProcess efficiency improvementSodium sulfatePollution
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing one-dimensional core-shell structure BaTiO3@Al2O3 by means of one-step synthesis
InactiveCN106012104AThickness is easy to controlReduce manufacturing costInorganic material artificial filamentsFilament/thread formingElectrospinningEngineering
The invention relates to a method for preparing one-dimensional core-shell structure BaTiO3@Al2O3 by means of one-step synthesis. The method comprises the steps of respectively adding the spinning liquid of a core layer and the spinning liquid of a shell layer into a needle cylinder arranged at the inner layer and a needle cylinder arranged at the outer layer, using two needles heads with different diameters to sleeve each other to form a coaxial two-layer spinneret, and spinning by adopting an electrostatic spinning method, wherein the spinning liquid of the core layer is prepared from barium acetate, tetrabutyl titanate and polypyrrolidone in proportion, and the spinning liquid of the shell layer is prepared from aluminium isopropoxide and polypyrrolidone in proportion. The product prepared by the method has a core-shell structure, organic matters volatilize after the product is sintered at high temperature, and the one-dimensional core-shell structure BaTiO3@Al2O3 is finally formed, wherein the one-dimensional core-shell structure BaTiO3@Al2O3 has the length of about 10-150mu m and the diameter of about 150-400nm (the core layer is about 75-200nm). Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being low in preparation cost, simple in preparation technology and controllable in thicknesses of the core layer and the shell layer, being capable of realizing mass production, etc.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Wet chemical prepn process of leadless functional barium titanate ceramic film
InactiveCN1350071AGood dielectricExcellent ferroelectricPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingBarium titanateSolvent
The method for preparing barium zirconate titanate (BZT) film belongs to the field of functional ceramic film. Its precursor liquor for preparing BZT is made up by using barium acetate, zirconium propylate and butyl titanate as raw material, using glycol methyl ether as solvent and using acetylacetone and glacial acetic acid as stabilizing agent according to the gran molecular concentration mixing ratio of Ba:Zr:Ti=I:X:1-X (X is greater than or equal to O and is less than or equal to 1), and its concentration is 0.2-0.3M. The above-mentioned precursor is undergone the process of filting, film-forming, whirl coating (its speed is 3000-4000 rpm and time is 30 sec.), pretreating, multiple film-forming, pretreating and film-forming to reach to required thickness, and annealing at 650-750 deg.c so as to obtain the invented product. The lead-free BZT functional film prepared by said ivnention possesses good dielectric feeraelectric and piezoelectric properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
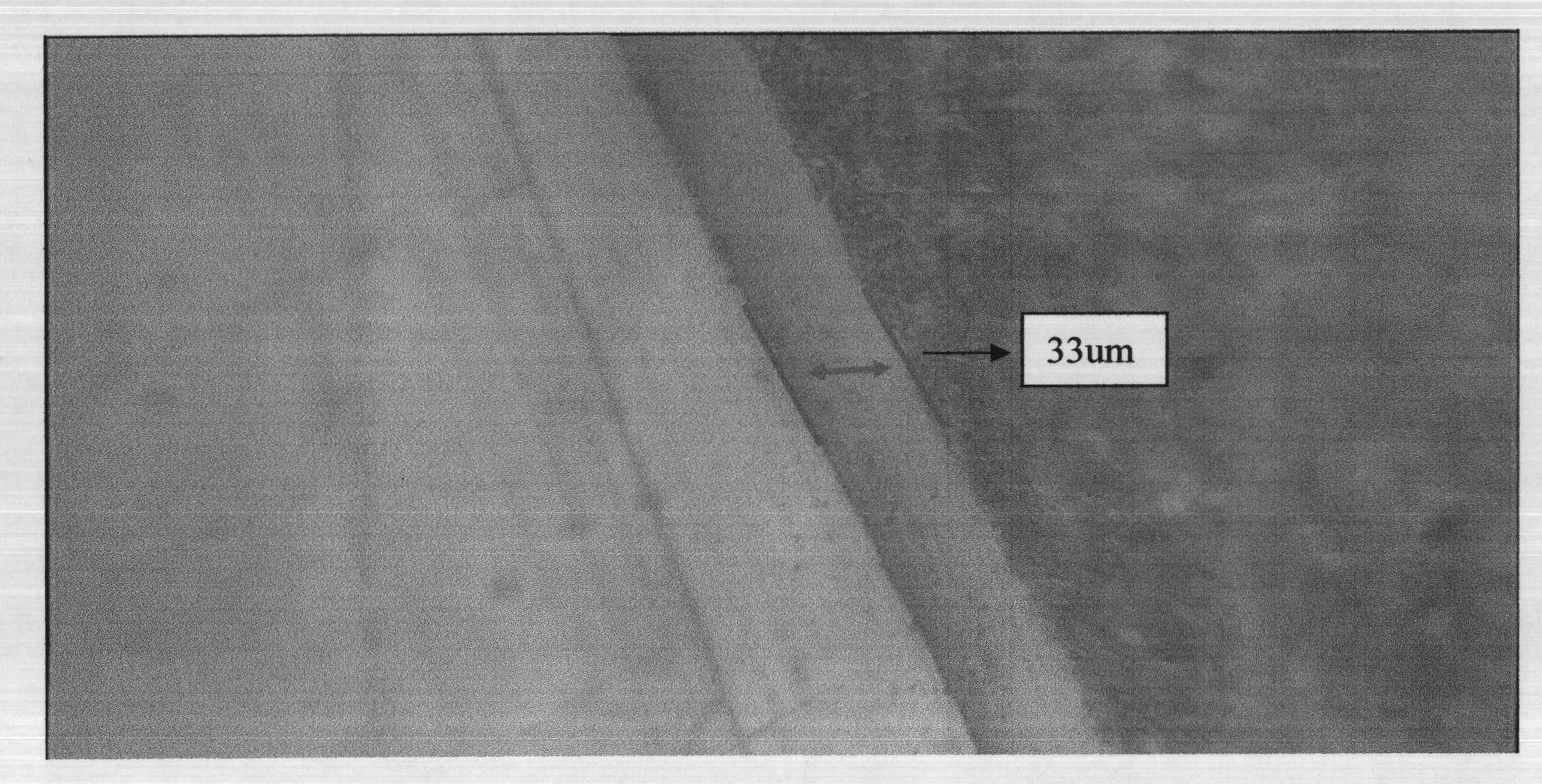
Piston rod and production method thereof as well as carbonitriding agent for piston rod surface treatment
The invention relates to a piston rod and a production method thereof as well as a carbonitriding agent for piston rod surface treatment. The carbonitriding agent comprises the following components by weight percent: 20-24% of urea, 13-15% of thiourea, 10-14% of barium acetate, 24-27% of calcium carbonate, 22-26% of barium carbonate and 4-10% of lithium carbonate. The carbonitriding layer tissue comprises an oxide layer, a tectorium, a compound layer, an Austria layer and a diffusion layer. The carbonitriding agent has the beneficial effects of simple formula and low cost; the piston rod produced by using the carbonitriding agent is smooth in surface, low in roughness and is airproof, the piston rod compound carbonitriding layer is more than 32mu m in thickness and has the characteristics of high corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance, low rejection ratio and long service life; in the piston rod production process, thermal treatment and anti-corrosion treatment are completed once, treatment temperature is between 600 DEG C-700 DEG C, the piston rod production process has the advantage of optimizing the machining process; and nitriding time is shortened to 30-50 minutes, production period is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO ZHANGSHI MACHINERY
Preparation method for barium titanate/graphene composite nanometer material
ActiveCN104402044AHigh purityHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesEthylenediamineChemical reaction
The invention relates to a preparation method for a barium titanate / graphene composite nanometer material, and the method employs a wet chemical reaction process. The preparation steps comprise: taking 2-methoxyethanol as a solvent dissolving a titanium ion, utilizing ammonia water as a precipitating agent to precipitate titanium ion, adding an aqueous solution of graphene oxide, and fully mixing; utilizing a deionized water solution of barium acetate as a barium source, and taking a mixed solution of ethylenediamine and ethanolamine as a solvent; and finally utilizing a mineralization agent potassium hydroxide to promote crystallization, and performing hydro-thermal reaction to obtain the barium titanate / graphene nanometer powder. The preparation method is simple in process, easy to control, free of pollution and low in cost, and the prepared barium titanate / graphene composite nanometer material is high in purity and good in crystallinity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
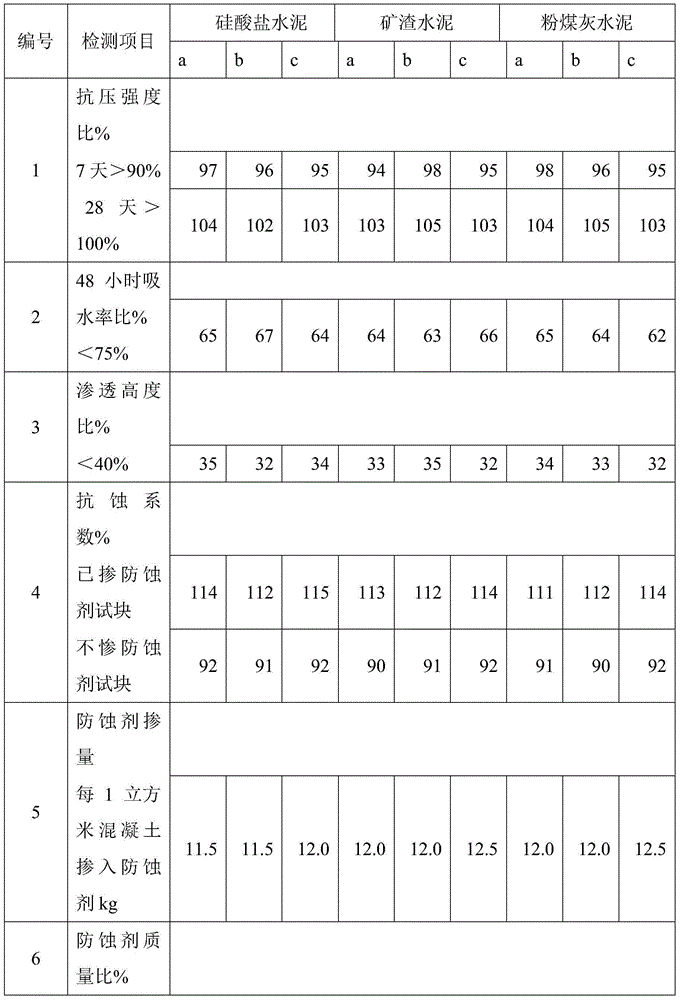
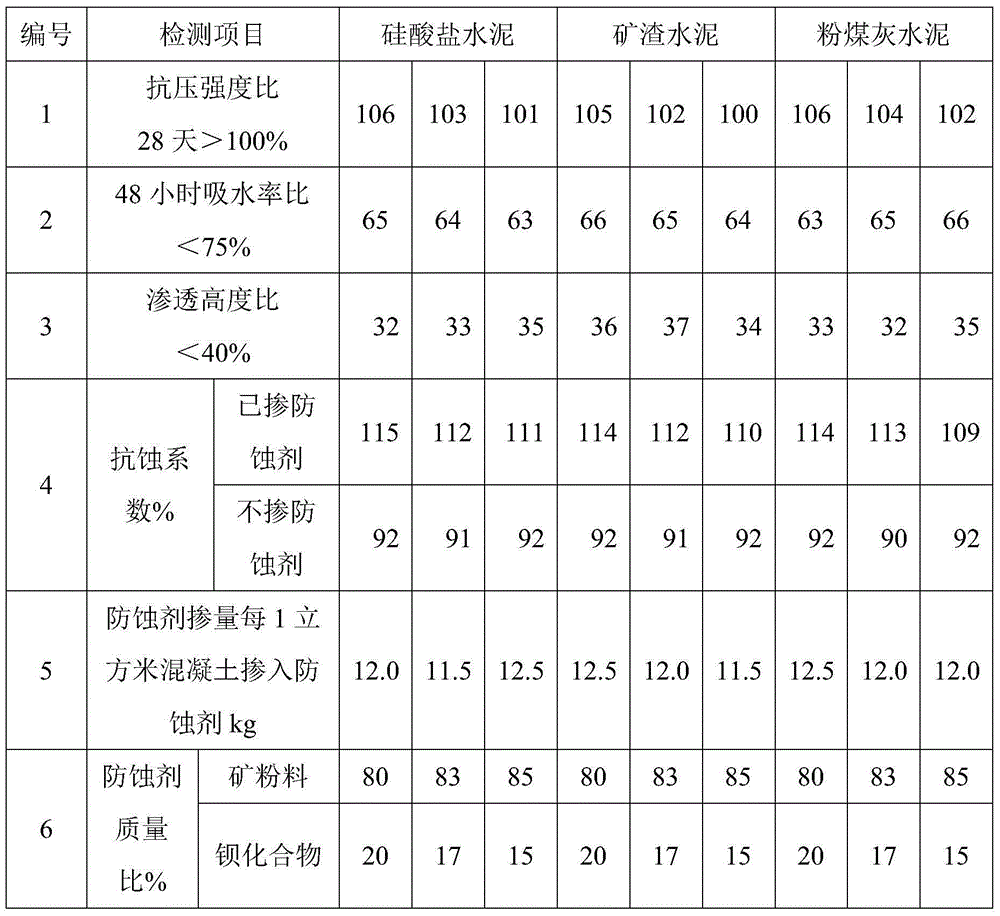
Anticorrosive agent for concrete and anticorrosive concrete
The invention provides an anticorrosive agent for concrete. The anticorrosive agent is a mixture of powder selected from the group consisting of fly ash, blast-furnace water-quenched slag powder, silica fume, light-burnt metakaolin powder, phosphorus slag powder, alum slag powder, natural zeolite powder and the like and a barium compound selected from the group consisting of barium chloride, barium nitrate, barium acetate, barium hydroxide, barium sulfide and the like. The anticorrosive agent for concrete provided by the invention enables Ca(OH)2 by-produced in hydration of cement to bond with SiO2 included in cement so as to produce secondary hydrated calcium silicate, so the strength and impermeability of concrete are improved; barium ions doped into concrete reacts with SO4<2-> from the outside in time to produce inertial and stable secondary barite, so deionization of SO4<2-> is realized and corrosivity of SO4<2-> is eradicated; the secondary barite forms a stable mineral inorganic protection film on the surface layer of concrete, so further invasion of external harmful ions is prevented, the strength, impermeability and corrosion resistance of concrete are further improved, the service life of concrete is substantially prolonged, and economic benefits are increased.
Owner:李亚铃
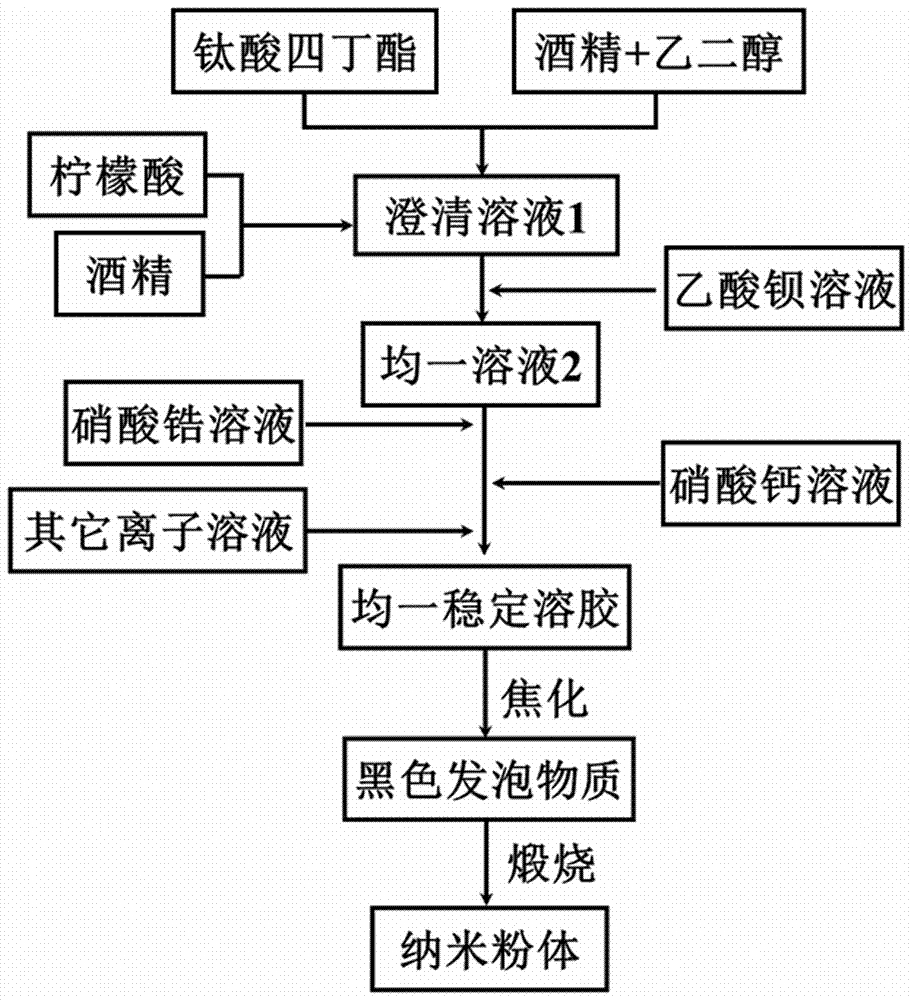
Barium zirconate titanate calcium-based piezoelectric ceramic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106986634AHigh degree of densificationImprove performanceElectronic componentSilver coating
The invention relates to barium zirconate titanate calcium-based piezoelectric ceramic and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of piezoelectric ceramic electronic components and devices. The ceramic has a chemical constitution represented by a general formula as follows: Ba1-xCaxTi1-yZryO3. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing chelate sol from tetrabutyl titanate, citric acid, barium acetate, calcium nitrate, zirconium nitrate, glycol, alcohol and the like in a molar mass / volume ratio, and coking and calcining the sol, so as to obtain nano-powder; and carrying out granulation, dry-pressure formation and glue discharging on the nano-powder, heating to 1250-1290 DEG C, stopping heating, and carrying out furnace cooling until the sintering temperature is 1150-1250 DEG C, so as to obtain the ceramic. After the ceramic is subjected to polishing, silver coating and polarization, measurement shows that the ceramic has excellent electrical properties: the piezoelectric coefficient d33 is equal to 479pC / N-634pC / N, and the maximum relative dielectric constant epsilonr is equal to 12328-13582.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of barium-calcium carbonate and potassium-sodium niobate alternative spin-coating lead-free piezoelectric thick film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a barium-calcium carbonate and potassium-sodium niobate alternative spin-coating lead-free piezoelectric thick film. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: based on a sol-gel process, preparing Bi0.5Ca0.5Ti03(BCT) precursor sol with concentration of 1mol / L by adopting barium acetate (Ba(CH3COO)2), calcium nitrate terahydrate (Ca(NO3)2.4H2O) and tetrabutyl titanate (C16H36O4Ti) as the materials, adopting ethylene glycol monomethyl ether (C3H8O2) and glacial acetic acid (CH3COOH) as solvent, and adopting acetylacetone (C5H8O2) as stabilizing agent; preparing K0.5Na0.5NbO3 (KNN) precursor sol with concentration of 0.6mol / L by adopting ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) as esterifying agent, adopting nitric acid as metal coordination agent and introducing polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as modifying agent; coating the KNN sol on the (Pt / TiO2 / Ti / SiO2 / Si) substrate, and coating the BCT sol after the thermal treatment; repeating the steps by three times, i.e., carrying out spin-coating for six layers alternatively; and obtaining the KNN-BCT film through annealing treatment. The obtained film is uniform in crystalline grain, compact in arrangement, smooth in surface and free of cracks.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
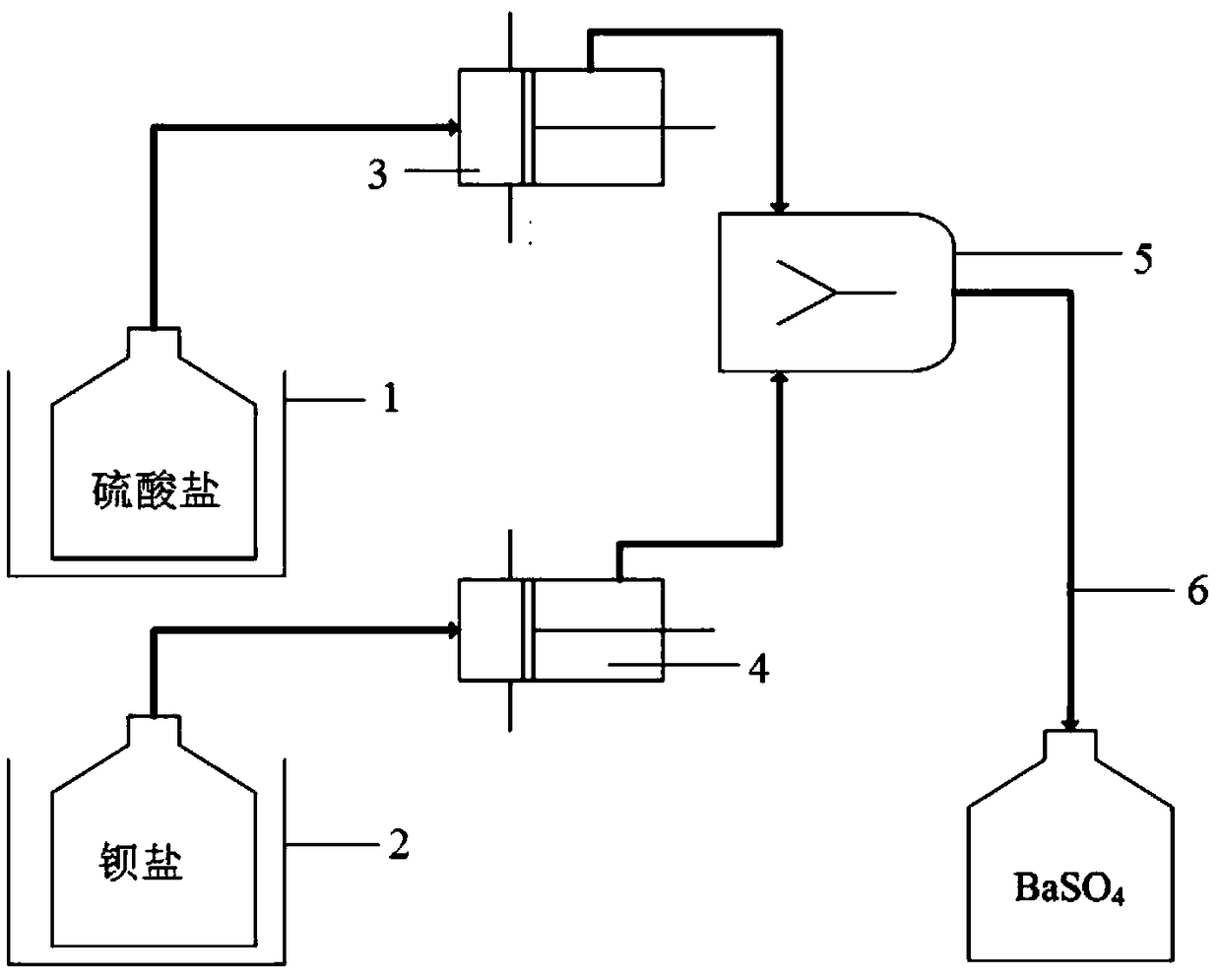
Method for preparing barium sulfate particles through microchannel method
ActiveCN108862355ALarge specific surface areaShort stayMaterial nanotechnologyCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesBarium dichlorideBarium salt
The invention belongs to a method for preparing barium sulfate particles through a microchannel method in the technical field of nanomaterial preparation. The method comprises the following steps: introducing a sulfate water solution and a barium salt water solution into a microchannel reactor for reacting and ageing, and centrifuging, washing and drying an obtained reaction solution, thus obtaining the barium sulfate particles, wherein selected sulfate is sodium sulfate, ammonium sulfate or sodium persulfate, and barium salt is barium chloride, barium acetate or barium nitrate. The morphologyand the particle size distribution of the obtained barium sulfate particles are controllable, and industrial application of medical dry films can be met to a larger extent.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Ruthenium ammonia synthesis catalyst taking ruthenium ammonia complex as precursor
ActiveCN102698749AEasy to manufactureSuitable for mass manufacturingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBulk chemical productionPtru catalystZirconium nitrate
The invention discloses a ruthenium ammonia synthesis catalyst taking a ruthenium ammonia complex as a precursor and a preparation method thereof. The ruthenium ammonia synthesis catalyst comprises the following components: one of RuL+M1+M2 / AC, M1-(RuL+M1+M2) / AC, (RuL+M1+M2)-M1 / AC, and (RuL+M1+M2)-M2-M1 / AC, wherein RuL is a soluble ruthenium complex generated from reaction of potassium ruthenate and ammonia; M1 is one of or a mixture of more of barium nitrate, barium acetate, magnesium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, aluminum nitrate and zirconium nitrate; M2 is one of or a mixture of more of alkali metals such as sodium, potassium, rubidium and caesium, nitrates of rare earth metals, acetates, hydroxides or oxides; and AC is a carrier, namely active carbon or graphitized active carbon. According to the method, the graphitized active carbon is used as the carrier, and the ammonia synthesis catalyst is prepared by the following steps of preparing the potassium ruthenate, preparing the precursor, preparing mixed solution, preparing the catalyst, drying and the like. The preparation method has the advantages of simple equipment and procedure, short preparation period, high efficiency, energy conservation and environmental protection; large-scale production is easy to realize; and the prepared catalyst has high performance price ratio.
Owner:福建三聚福大化肥催化剂国家工程研究中心有限公司 +1
Method for recycling lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide ternary positive electrode material of retired lithium-ion power battery
InactiveCN109704412ASimple processHigh purityCell electrodesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesManganese oxideCobalt
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium battery material recovery, and particularly relates to a method for recycling a lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide ternary positive electrodematerial of a retired lithium-ion power battery. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out discharging, disassembling and sorting on a waste ternary lithium-ion battery, soaking thepositive plate with dilute acid, carrying out cooperative mechanical stirring and ultrasonic cleaning, and separating out a current collector; (2) removing impurities, carrying out filtering, and regulating and controlling the ion proportion of the leachate; (3) carrying out spray drying, and then carrying out stepped high-temperature calcination to obtain the Lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxideternary positive electrode material. According to the invention, the purpose of separating the current collector and the battery material is achieved through a dilute acid leaching-stirring cleaningmethod, and separation efficiency reaches 99% or above; Al and Fe impurity ions are removed by regulating and controlling the pH value through ammonia water; and influence of SO4<2-> ions can be removed by adding barium acetate. The recycling method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, few compounds are introduced in the process, purity of by-products is high, the process is green andpollution-free, and the method is suitable for industrial popularization.
Owner:郑州中科新兴产业技术研究院 +1
Method for preparing yttrium-barium-copper-oxygen high-temperature superconducting film
ActiveCN102731083AReduce manufacturing costEase of industrial productionSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesOxygenSolvent
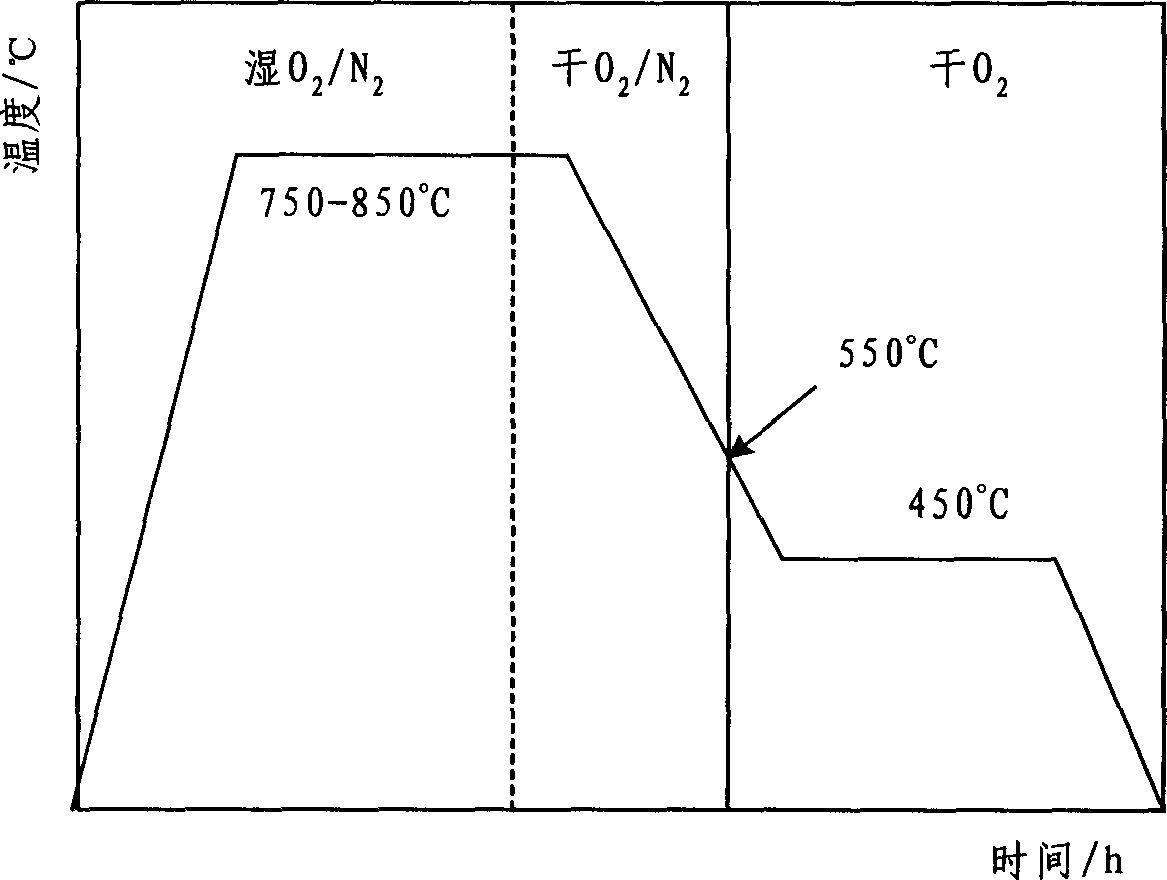
The invention relates to a method for preparing an yttrium-barium-copper-oxygen high-temperature superconducting film. First, a precursor solution is prepared. Yttrium acetate (Y(CH3COO)3), barium acetate (Ba(CH3COO)2), and copper acetate (Cu(CH3COO)2) with a molar ratio that Y:Ba:Cu=1:2:3 are mixed in a water solution of 10-30mol% acetic acid. The mixture is well mixed, and is subjected to vacuum evaporation, such that the solvent is removed, and a gel is obtained; trolamine and terpineol are added to the gel, a proper amount of ammonia water is added, and the pH of the solution is regulated to 5-7, such that a precursor with a total concentration of the Y, Ba and Cu ions being 1.5-3.0mol / L is prepared. The precursor solution is coated on a substrate. The coated film is subjected to a low-temperature heat treatment under a temperature of 300-500 DEG C, and is then subjected to a high-temperature heat treatment under a temperature of 750-850 DEG C and an annealing treatment under a temperature of 450-550 DEG C, such that the YBCO superconducting film is formed.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Modified titanium-silicon molecular sieve, modification method and application thereof in propylene epoxidation reaction
ActiveCN106582807AReduce invalid decompositionImprove effective useOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsDecompositionBarium titanate
The invention discloses a modified titanium-silicon molecular sieve, a modification method, and application thereof in propylene epoxidation reaction. The modified titanium-silicon molecular sieve is obtained by the following steps: dissolving barium salt in water to prepare a barium salt aqueous solution, and then adding a strip-shaped titanium-silicon molecular sieve, wherein the weight ratio of the barium salt to the water to the strip-shaped titanium-silicon molecular sieve is (0.001-0.5):(0.1-5):1; and performing impregnation for 1-72h, performing filtration, drying a solid at 80-120 DEG C for 3-5h, and then performing roasting at 500-550 DEG C for 4-12h to obtain the modified titanium-silicon molecular sieve, wherein the strip-shaped titanium-silicon molecular sieve is obtained by mixing titanium-silicon molecular sieve raw powder with sesbania cannabina powder and silica sol uniformly and then performing strip extrusion forming, and the barium salt is barium nitrate, barium acetate or barium chloride. The modified molecular sieve is a strip-shaped titanium-silicon molecular sieve with an MFI structure; and as a catalyst, the modified molecular sieve is applied to a liquid phase propylene epoxidation process. The modification method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation process, and due to a mutual synergistic effect between the barium salt and the titanium-silicon molecular sieve, the modification method, when applied to the propylene epoxidation reaction, can obviously reduce invalid decomposition of hydrogen peroxide as well as effectively improve the effective utilization of hydrogen peroxide and the selectivity of a product namely propylene epoxide.
Owner:中海亚环保材料有限公司
Process of plating diamond surface with composite film
ActiveCN104479423AImprove wettabilityFully coveredOther chemical processesInorganic pigment treatmentAcetic acidComposite film
The invention discloses a process of plating a diamond surface with a composite film. The process comprises the following steps: 1) performing surface treatment on a diamond grinding material; 2) mixing barium acetate with glacial acetic acid to prepare stable BaO sol, soaking the grinding material with the BaO sol, and drying and roasting the grinding material to obtain the diamond grinding material plated with a BaO film; 3) mixing chromic nitrate with glacial acetic acid to prepare stable Cr2O3 sol, soaking the grinding material with Cr2O3, drying and roasting the grinding materials to obtain the diamond grinding material coated with a BaO / Cr2O3 film. According to the process, the surface of the diamond grinding material can be plated with a layer of compact composite film, so that harmful chemical reaction on the diamond grinding material and ceramic bond in a sintering process can be avoided, the wettability of the diamond grinding material and the ceramic bond can also be improved, the holding force on the diamond grinding material by the ceramic bond is increased, and the service life of a grinding tool is prolonged.
Owner:GUILIN CHAMPION UNION DIAMOND CO LTD
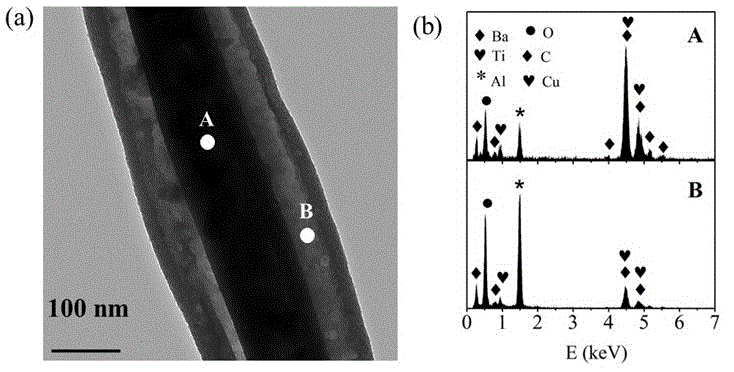
Preparation method of core-shell type highly dielectric filler from barium titanate-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes
The invention provides a preparation method of a core-shell type highly dielectric filler from barium titanate-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes. The filler is prepared through an impregnation sintering method, the surface energy of the acidified multi-walled carbon nanotubes is reduced by the use of an anionic surfactant of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), the adsorption of ions on the acidified multi-walled carbon nanotubes is promoted in the impregnation process, the hydrolysis of a sol-gel impregnation liquid formed from barium acetate and tetrabutyl titanate in an acetic acid and ethanol system is carried out on the surfaces of the acidified multi-walled carbon nanotubes to form a continuous gel layer, and the gel layer is subjected to vacuum drying and high temperature calcination at 800 DEG C under nitrogen atmosphere. The preparation process includes firstly preparing the barium acetate and tetrabutyl titanate sol-gel impregnation liquid, then adding the acidified multi-walled carbon nanotubes, and reacting at room temperature. The core-shell type multi-walled carbon nanotube highly dielectric filler is finally obtained through the regulation of the surfactant. The inventive method is simple in conditions, is an effective way for the preparation of a multifunctional core-shell type multi-walled carbon nanotube composite, and has flexible and wide applicability and industrialized prospects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
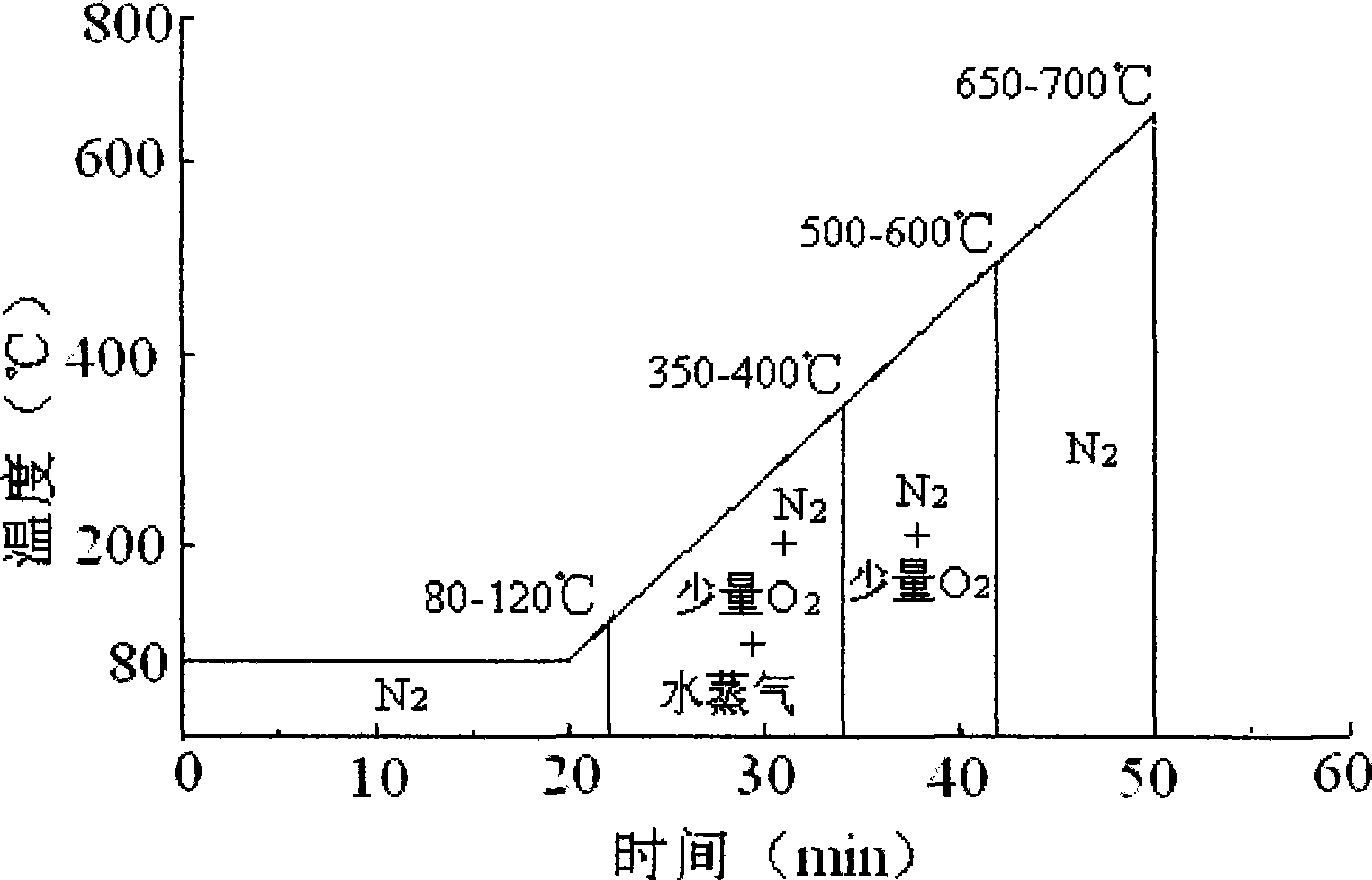
Method for polymer-assistant depositing high temperature superconducting coating conductor superconducting layer
InactiveCN101271956AReduce formationImprove current carrying capacitySuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFurnace temperatureElectrical conductor
A macromolecule-assisted method of deposition for a superconducting layer of a high-temperature superconductivity coating electrical conductor has the preparation method as follows: a. dissolving rare-earth acetate, barium acetate and cupric acetate in monoprop with a stoichiometric proportion that rare-earth: barium: cupric equals to 1:2:3 to acquire a precursor solution; b. adding PVB, PEG or PVP into the precursor solution with the weight ratio of 2-8:100 to acquire a coating colloid; c. coating the coating colloid on a substrate and heating for drying; d. placing the substrate in a tubular furnace to carry out decomposition heat treatment; e. rapidly heating up the furnace temperature to 800-900 DEG C under moist argon atmosphere for 5-15min, then lowering the temperature to 750-780 DEG C for 1-3 hours, and then lowering the temperature to 350-500 DEG C under the argon atmosphere for low temperature oxygen-permeation annealing treatment, and the superconducting layer is acquired by cooling. The method has the advantages of low cost and simple technique, which is applied to industrialized production; the superconducting layer prepared is characterized by high biaxial texture, flat and dense surface and good superconductivity.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing manganese acetate from electrolytic manganese metal leaching residue
ActiveCN102241581AHigh recovery rateReduce pollutionCarboxylic acid salt preparationMANGANESE ACETATEElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing manganese acetate from electrolytic manganese metal leaching residues. The method comprises the following steps: using washing liquid of electrolytic manganese metal leaching residues as a raw material, depositing the washing liquid with carbonate and carrying out separation so as to obtain manganese carbonate deposition and deposition residual liquid; dissolving manganese carbonate deposition with sulfuric acid to obtain a manganese sulfate solution; purifying the manganese sulfate solution to obtain a high purity manganese sulfate solution and depositing the high purity manganese sulfate solution with carbonate to obtain high purity manganese carbonate; acidifying the high purity manganese carbonate with acetic acid to obtain a manganese acetate solution; precipitating SO4<2-> in the manganese acetate solution with barium acetate to obtain a pure manganese acetate solution and carrying out evaporative crystallization and drying to obtain a high purity product of manganese acetate. The method provided in the invention has the advantages of resource conservation, environment-friendliness, good economic benefits, a simple process, low investment cost, etc.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
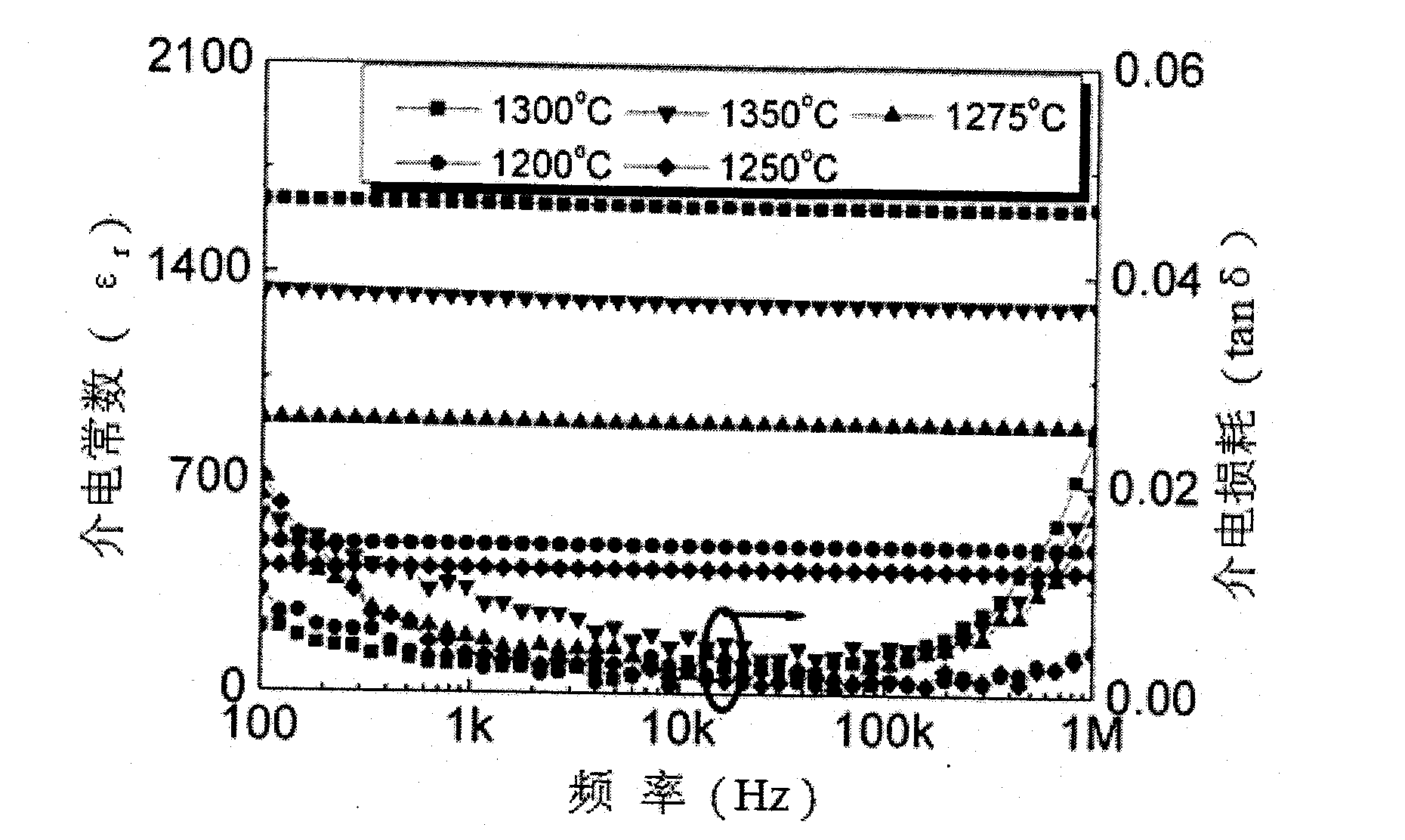
Preparation method for barium strontium titanate (BST) thick film material
InactiveCN101805179ALow dielectric lossImprove electrical performanceBarium strontium titanateStrontium hydroxide octahydrate
The invention discloses a preparation method for a barium strontium titanate thick (BST) film material, which is used for solving the technical problem that the barium strontium titanate (BST) thick film material with a substrate prepared by a conventional preparation method has poor electrical property. The technical scheme comprises the following steps: preparing a BST colloid from barium acetate, strontium hydroxide, tetrabutyl titanate, glacial acetic acid, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetylacetone; and tape-casting the BST colloid and then sintering the colloid at the high temperature so as to obtain the barium strontium titanate thick film material. Because the barium strontium titanate thick film material with substrate is prepared by the tape-casting method, the dielectric loss of the barium strontium titanate thick film material is reduced from about 0.02 to below 0.02 so as to improve the electrical property of the barium strontium titanate thick film material; and the barium strontium titanate thick film material has high compactness and uniform granularity.
Owner:海安远东新材料有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com