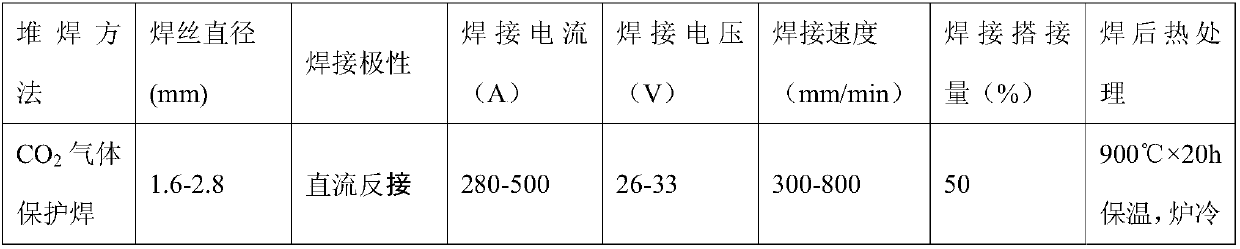
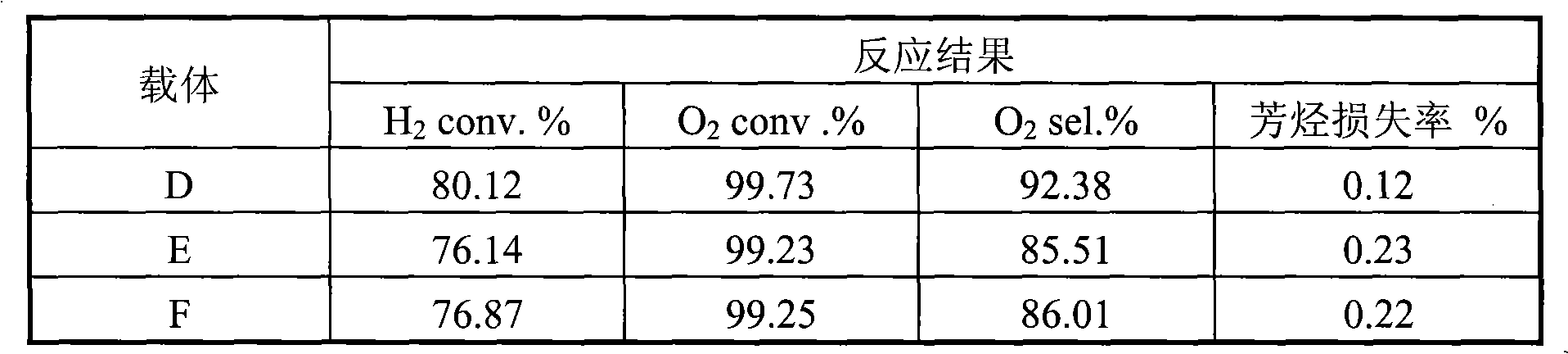
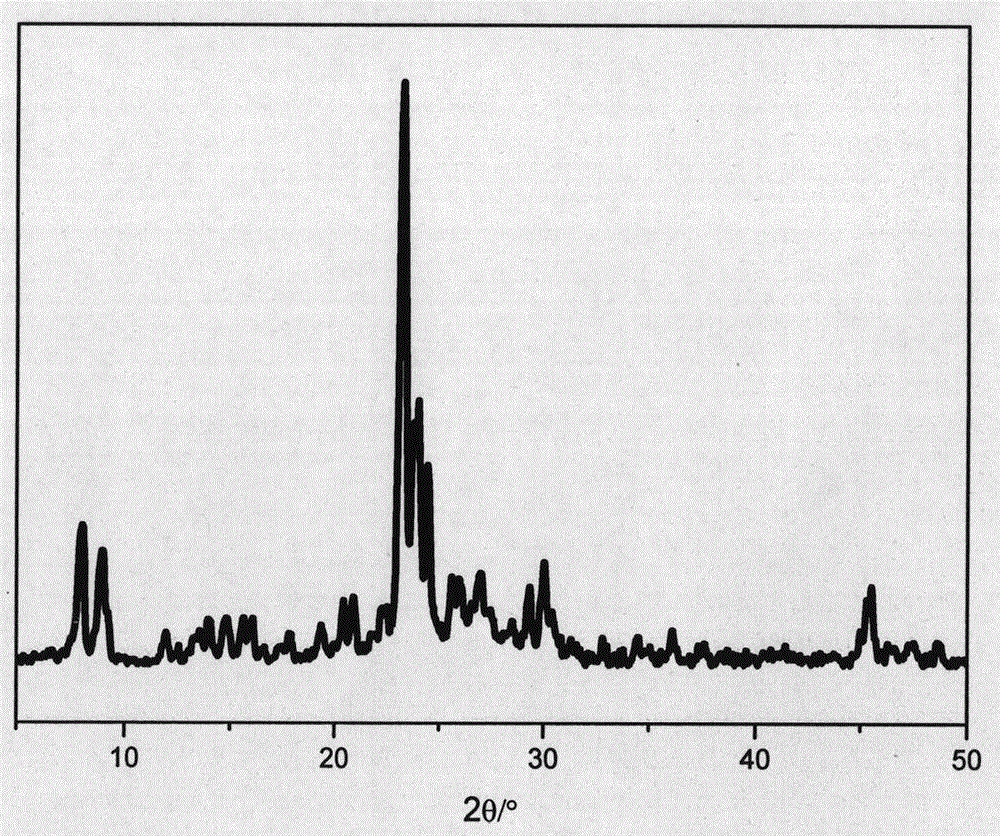
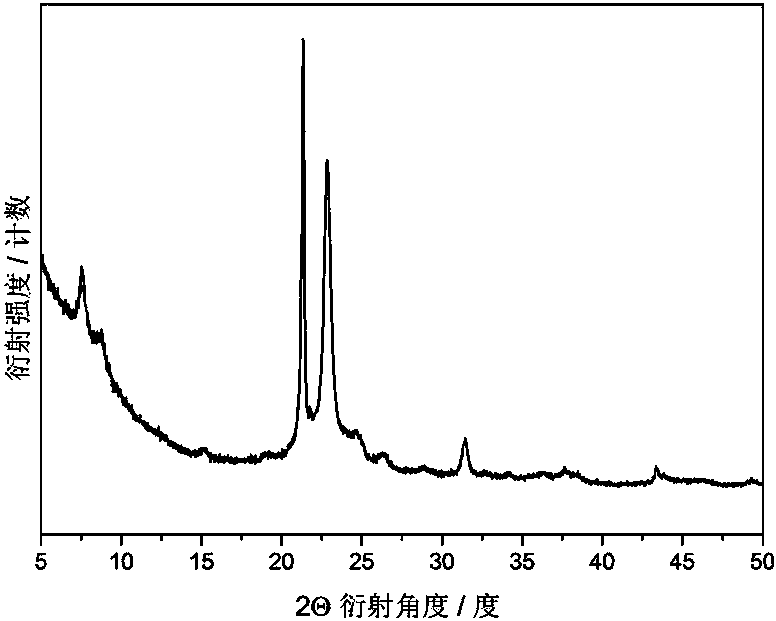
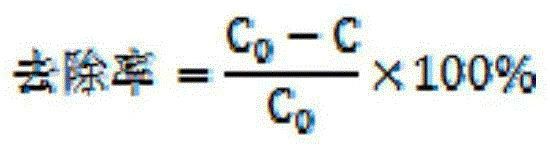Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
198results about How to "Short diffusion path" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
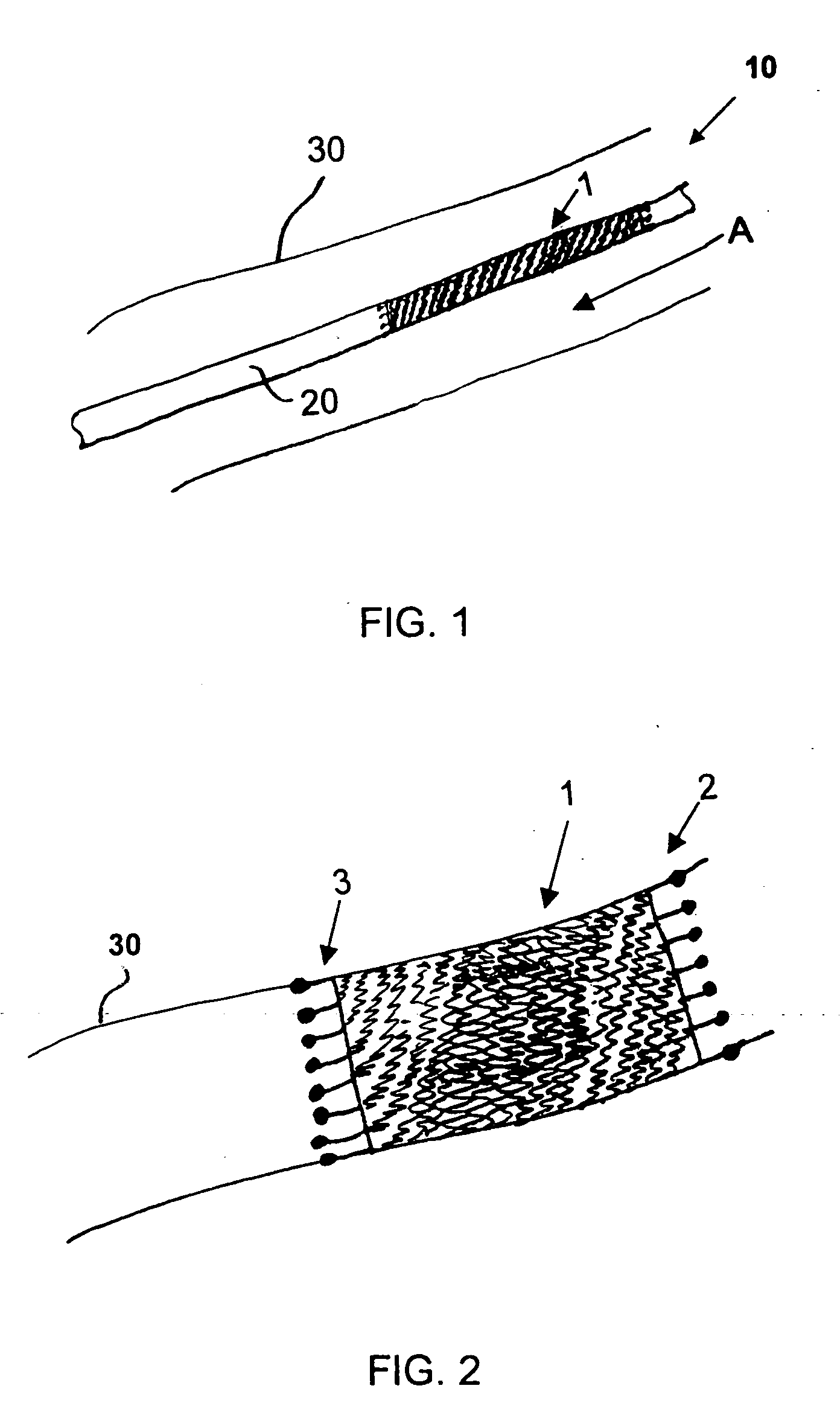
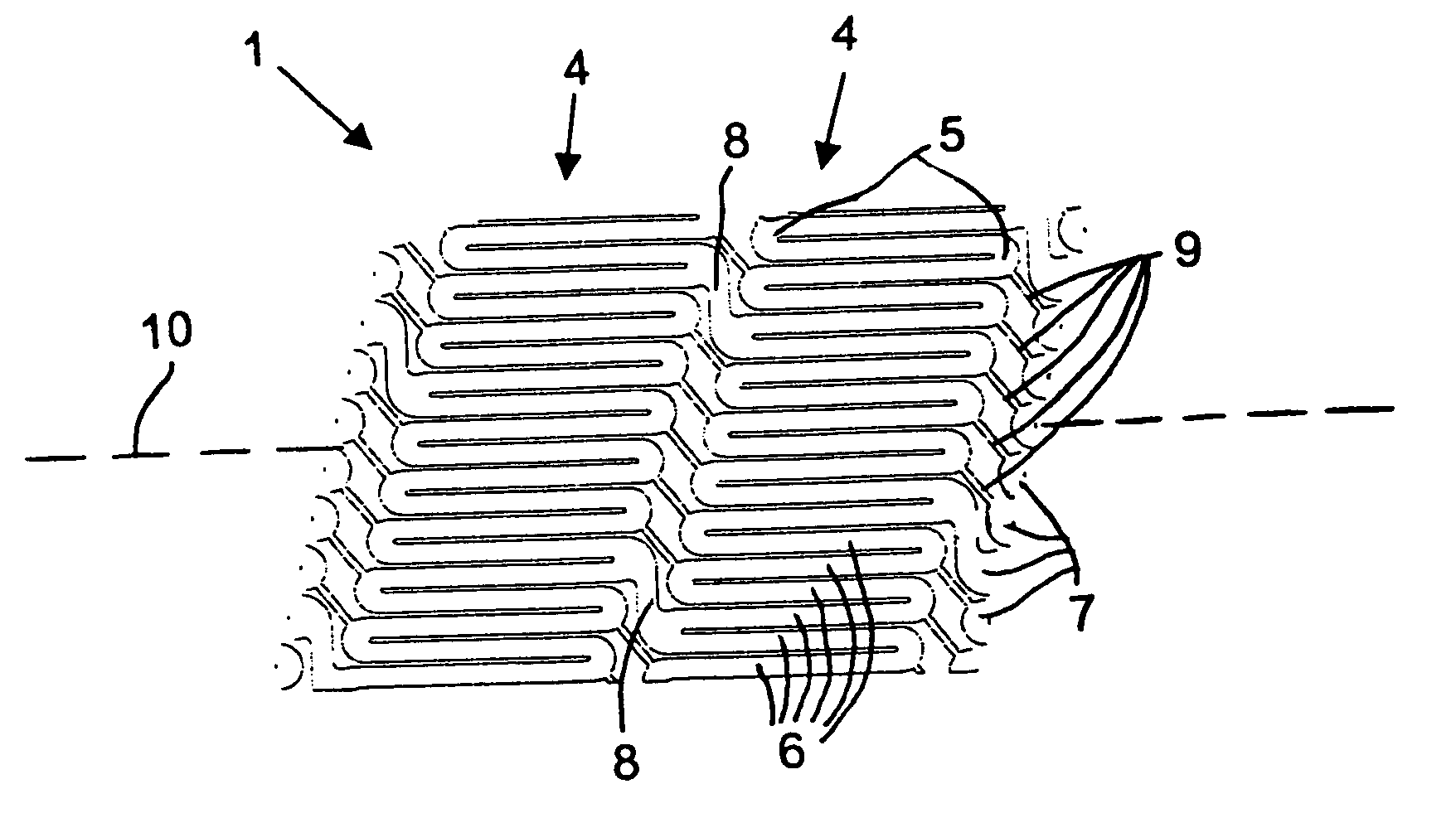
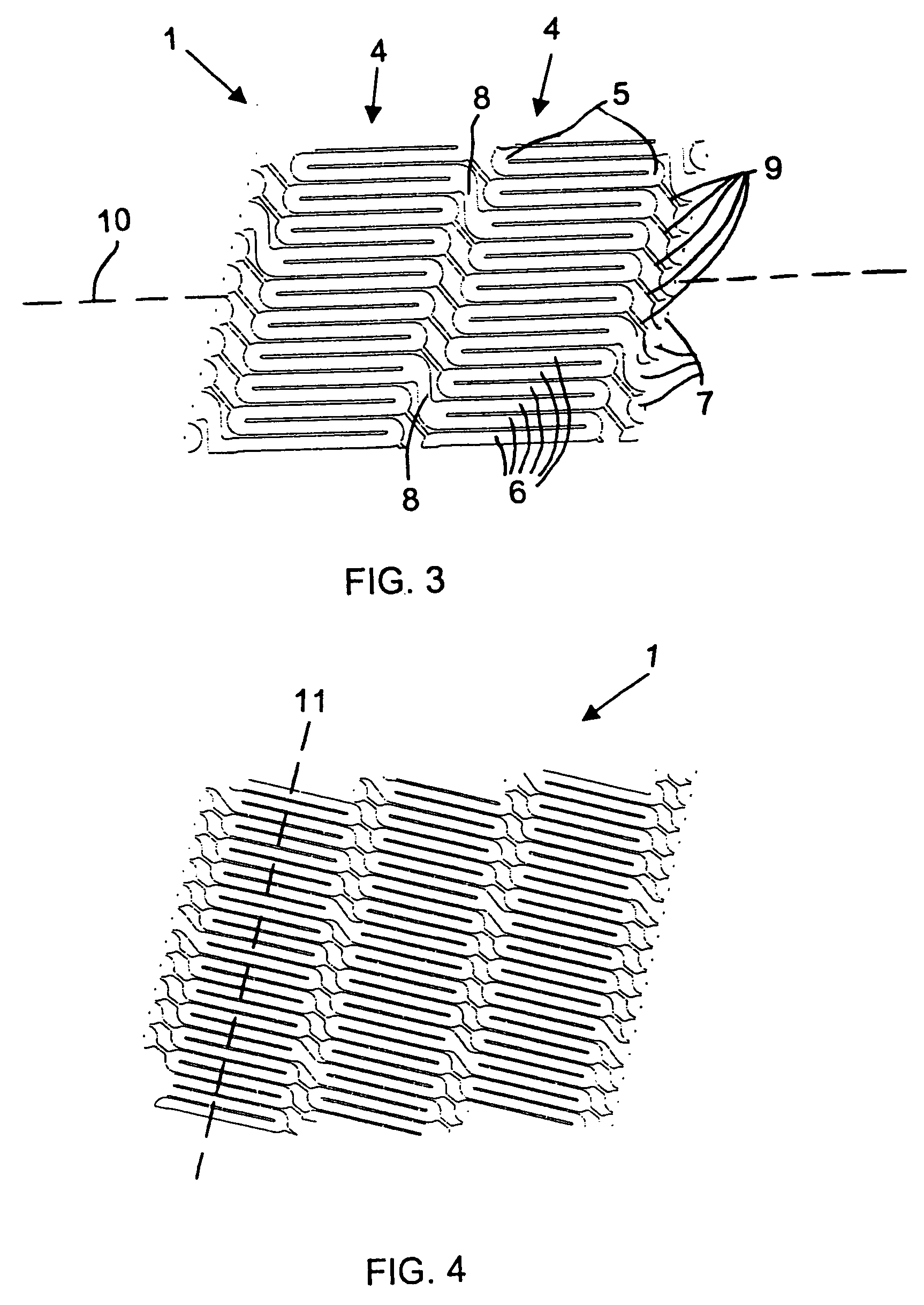
Stent and method for manufacturing the stent
InactiveUS20060074480A1Improves helical machined-tube stentsReduce restenosisStentsLigamentsInsertion stentStent
A stent includes a stent body having a circumference and struts disposed helically about the circumference in turns. At least two of the struts have respective strut ends. At least two paddle-shaped markers extend away from a respective one of the strut ends. The markers have respective marker extreme ends and different overall longitudinal lengths substantially aligning the marker extreme ends approximately along a single circumference of the stent body. A method for manufacturing a helical stent includes the steps of providing a stent body with struts disposed about the circumference thereof in turns and with bridges connecting the struts in adjacent turns. The stent body is expanded and, thereafter, some of the bridges, in particular, sacrificial bridges, are removed.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
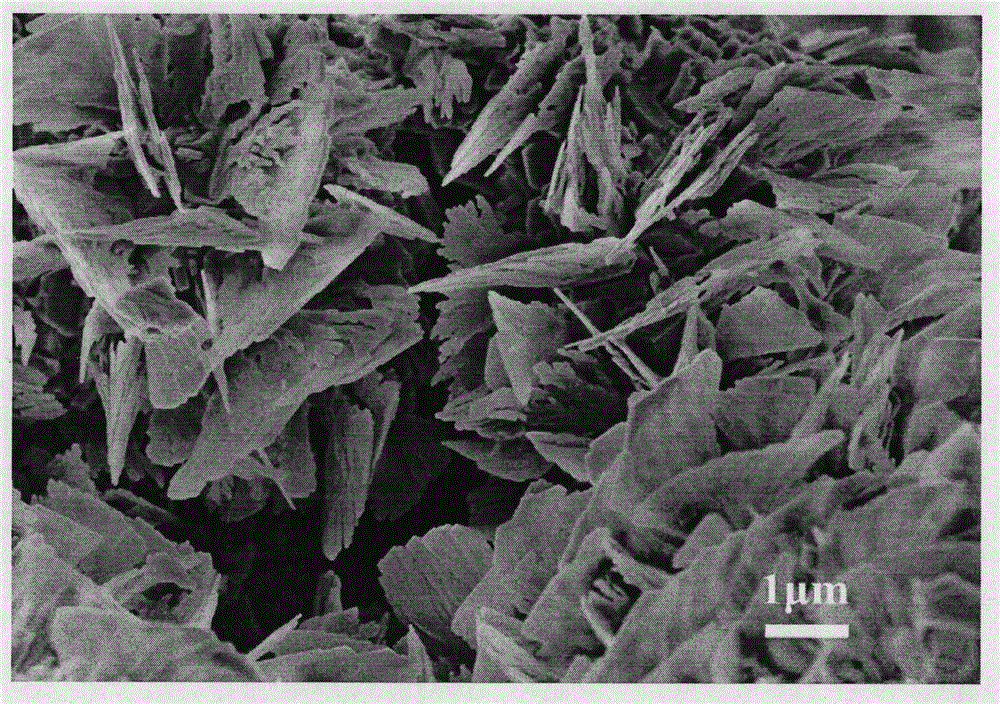
LiFePO4 FLAKES FOR Li-ION BATTERY AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME
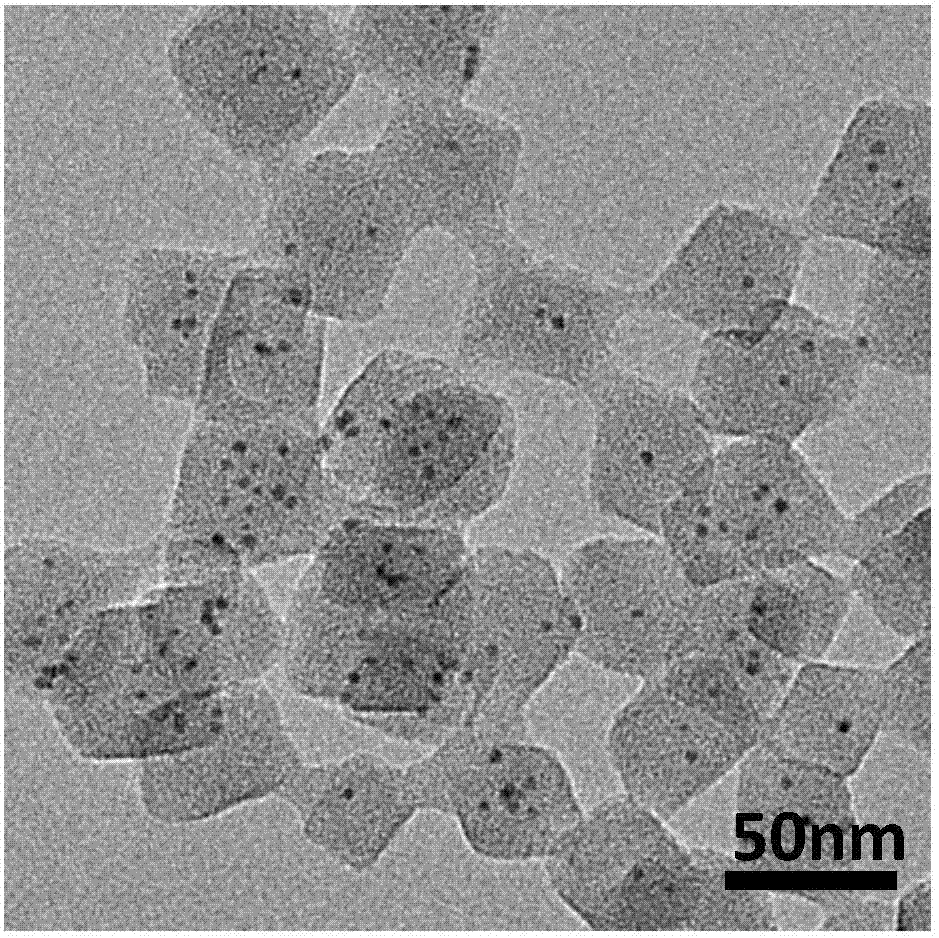
ActiveUS20120328947A1Charge-discharge efficiency can be improvedShort diffusion pathMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphatesCharge dischargeEngineering
LiFePO4 flakes for a Li-ion battery and a method for manufacturing the same are disclosed. The LiFePO4 flakes of the present invention have a thickness of 5 nm-200 nm, and the angle between the flat surface normal of the flake and the Li-ion diffusion channel is 0°-80°. In addition, according to the present invention, the LiFePO4 flakes with short Li ion diffusion path can be prepared through a simple process. Hence, not only the charge-discharge efficiency of the Li-ion battery can be improved by use of the LiFePO4 flakes of the present invention, but also the cost of the Li-ion battery can be further reduced.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method for manufacturing graphene-coated object, negative electrode of secondary battery including graphene-coated object, and secondary battery including the negative electrode
ActiveUS20130045418A1Uniform thicknessEfficient depositionMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsGrapheneMaterials science
To form graphene to a practically even thickness on an object having an uneven surface or a complex surface, in particular, an object having a surface with a three-dimensional structure due to complex unevenness, or an object having a curved surface. The object and an electrode are immersed in a graphene oxide solution, and voltage is applied between the object and the electrode. At this time, the object serves as an anode. Graphene oxide is attracted to the anode because of being negatively charged, and deposited on the surface of the object to have a practically even thickness. A portion where graphene oxide is deposited is unlikely coated with another graphene oxide. Thus, deposited graphene oxide is reduced to graphene, whereby graphene can be formed to have a practically even thickness on an object having surface with complex unevenness.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Preparation method of nano-particle@minisize metal organic frame material
InactiveCN107349964AAvoid reunionShort diffusion pathMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal-organic frameworkBiological imaging
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano-particle@minisize metal organic frame material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, preparing nano-particles modified by polyvinylpyrrolidone; 2, adding the obtained nano-particles into an MOF growth reaction solution, the addition amount of an adjusting agent is controlled, and the nano-particle@minisize metal organic frame material is obtained. The method is simple and easy to implement, mild in condition and high in applicability, and the prepared nano-particle@minisize metal organic frame material can effectively prevent nano-particle aggregation, meanwhile has the advantages of being good in size selectivity, and short in diffusion range between the surface of the metal organic framework and the active center of nano-particles, and has the wide application prospect in the fields of catalysis, biological imaging and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
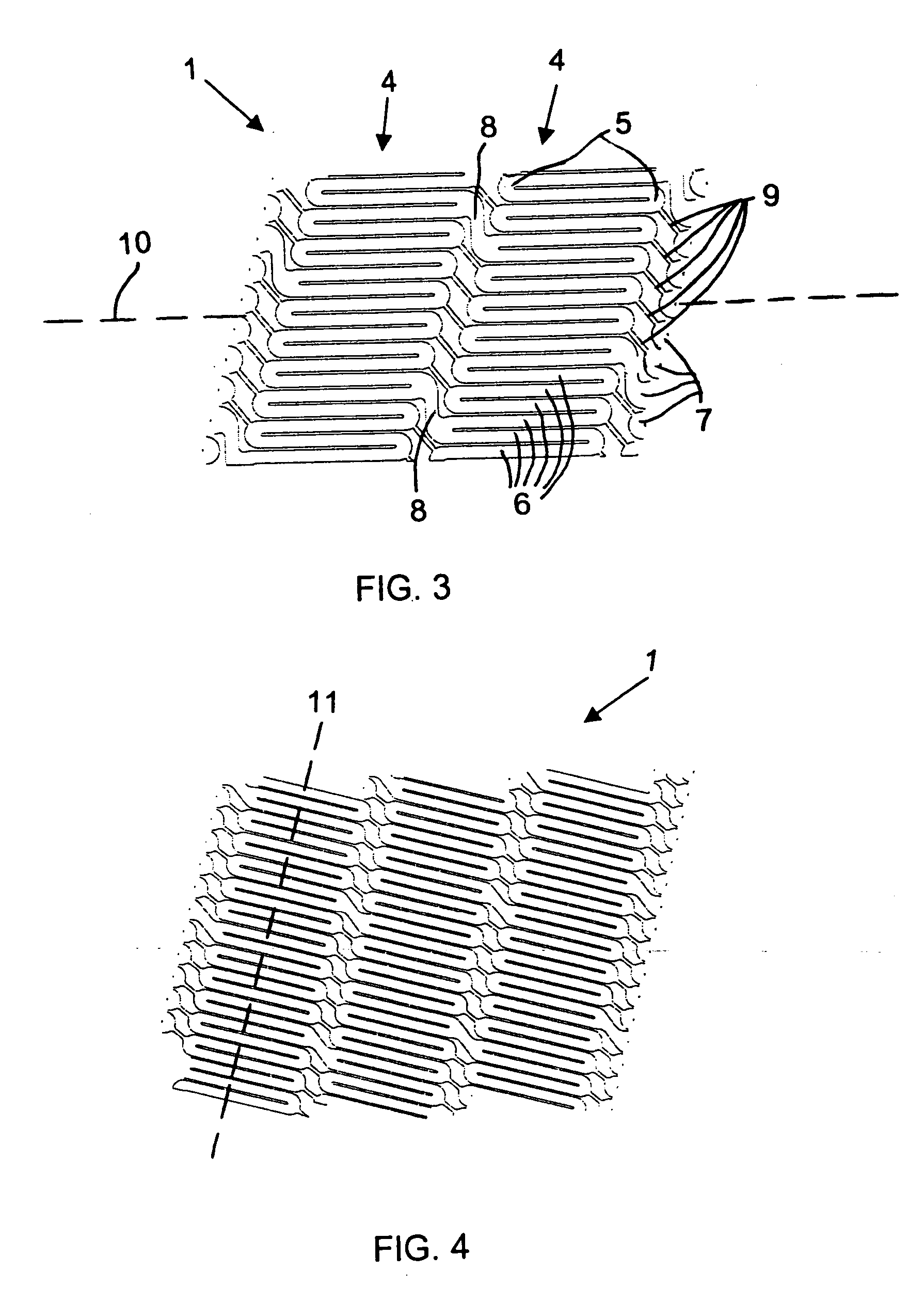
Stent and method for manufacturing the stent
InactiveUS20060060266A1Improves helical machined-tube stentsReduce restenosisStentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesInsertion stentImplantation Site
A method for manufacturing a helical stent includes the steps of providing a stent body with struts disposed about the circumference thereof in turns and with bridges connecting the struts in adjacent turns. The stent body is at least partially expanded and, some time during expansion, some of the bridges, in particular, sacrificial bridges, are removed. A method for implanting this stent includes loading the stent at a stent delivery system, traversing the stent at the delivery system to an implantation site, and implanting the stent at the implantation site.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
Preparation method of polymer porous membrane for removing water pollutants
ActiveCN104548949AHigh porosityLarge surface area of membrane poresSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisCross-linkCyclodextrin
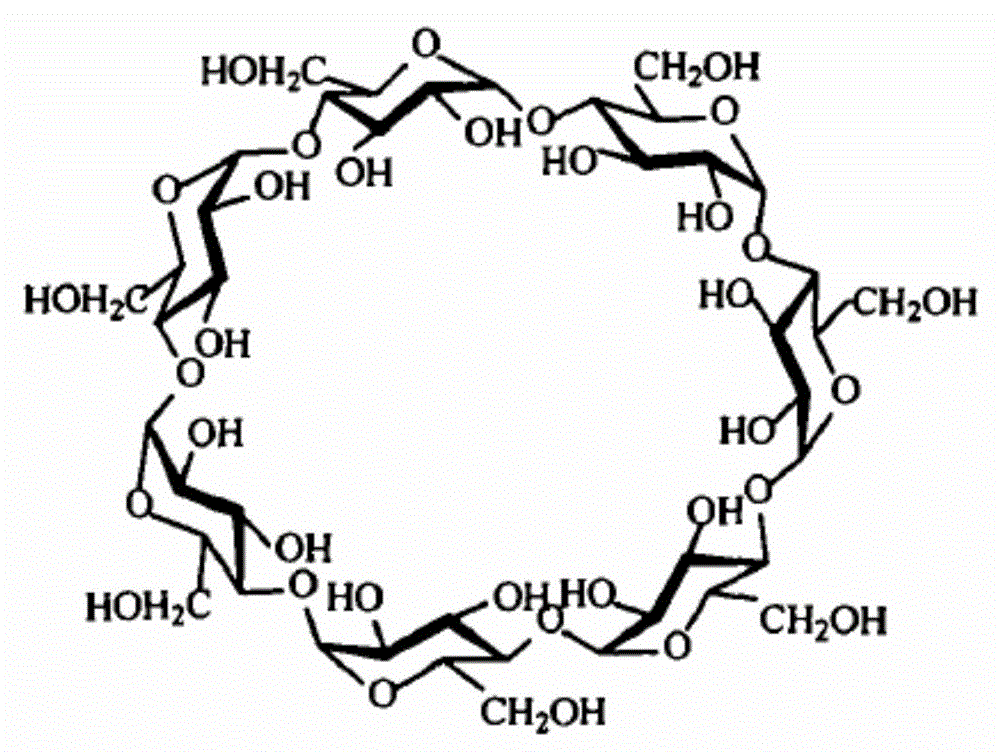
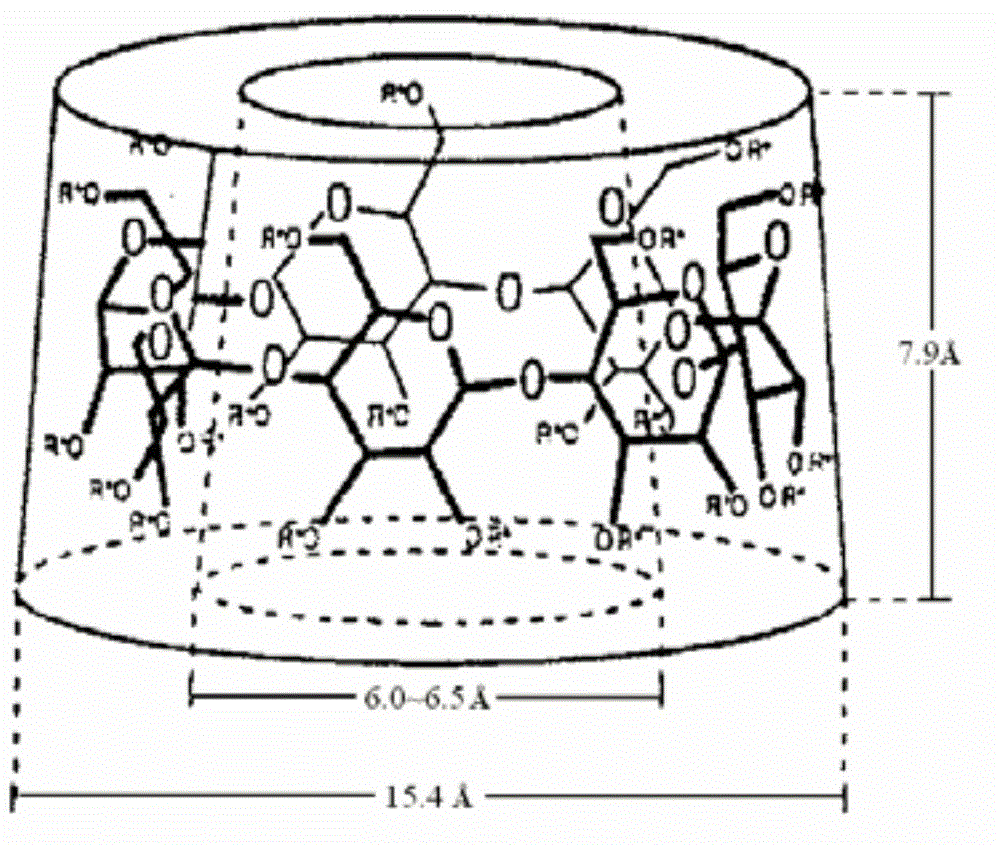
The invention relates to the technical field of separation membranes and discloses a preparation method of a polymer porous membrane for removing water pollutants. The preparation method comprises the following steps of blending cyclodextrin and a membrane preparation material, and adding a cross-linking agent into the mixture to fix the cyclodextrin to the membrane material so that repeated use is avoided, cyclodextrin is lost from the polymer porous membrane, a selective separation function of the polymer porous membrane is lost and polymer porous membrane hydrophility is changed. The polymer porous membrane has a substantial capability of adsorption and removal of organic pollutants such as phenols and aromatic amines (aromatic substances) in water, has good heavy metal ion removal effects, has high separation efficiency and low pressure drop, is convenient for regeneration, can be massively produced and used easily, and can be widely used in an ecological protection water purification treatment system and a water treatment system.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Stent and method for manufacturing the stent
A stent includes a stent body having a circumference and struts disposed helically about the circumference. Each of the struts has a strut length and a ratio of a number of the struts around the circumference to the strut length is greater than 800 per inch, in particular, over 1000 per inch. A method for manufacturing a helical stent includes the steps of providing a stent body with struts disposed about the circumference thereof in turns and with bridges connecting the struts in adjacent turns. The stent body is expanded and, thereafter, some of the bridges, in particular, sacrificial bridges, are removed.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
Hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN103288100AHigh crystallinityHigh yieldPentasil aluminosilicate zeolitePotassium hydroxideSurface-active agents
The invention discloses a hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve and a synthetic method thereof. The hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve is formed by the accumulation of crystalline grains with order nano-layered structures and is integrally structured. The synthetic method comprises the following steps of: with quaternary ammonium salt as a structure-directing agent (SDA), tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) as a silicon source, aluminium isopropoxide (AIP) as an aluminum source, and potassium hydroxide (KOH) as an alkali source, adding a cationic surface active agent (CSF) to prepare a synthetic liquid with the molar ratio of (20-100) SiO2: (1-3) Al2O3: (10-30) SDA: (10-50) KOH: (1,000-3,000) H2O: (1-10) CSF; adding 10 to 20% of Silicalite-1 molecular sieve seed crystal gel; performing hydrothermal crystallization according to the conventional method; processing a product by washing, drying and roasting to obtain the ZSM-5 molecular sieve. The molecular sieve is an agglomeration which is formed by the self-assembly under mutual effect of CSF, seed crystal gel and an inorganic species and is of a lamella and hierarchical zeolite structure; the molecular sieve is relatively high in specific surface area, relatively short in a diffusion path and relatively high in stability. The preparation method also has the advantages of high degree of crystallinity, high yield and simple operation steps, and is easy to separate.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Stent and method for manufacturing the stent
A stent includes a stent body with a diameter of between approximately 4 and 12 mm and a length of between approximately 10 and 250 mm. S-shaped struts are disposed helically about the circumference along helical turns. The struts have straight portions and curved portions connecting respectively adjacent ones of the straight portions. Bridges connect the struts in adjacent ones of the turns. The bridges include connecting bridges and a given number of sacrificial bridges before being expanded, and the connecting bridges and less than the given number of the sacrificial bridges after being at least partially expanded. A method for manufacturing a helical stent includes the steps of providing a stent body with struts disposed about the circumference thereof in turns and with bridges connecting the struts in adjacent turns. The stent body is expanded and, thereafter, some of the bridges, in particular, sacrificial bridges, are removed.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
Preparation method of sodium-ion battery cathode material Na3V2(PO4)3
ActiveCN105098179AShallow embedding depthShort diffusion pathCell electrodesElectrical batteryPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sodium-ion battery cathode material Na3V2(PO4)3. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing a sodium salt, a vandic salt, phosphate, a complexing agent, a high-molecular compound and a solvent to obtain a Na3V2(PO4)3 spinning solution; (2) carrying out electrostatic spinning on the Na3V2(PO4)3 spinning solution to obtain a Na3V2(PO4)3 spinning precursor; and (3) collecting the Na3V2(PO4)3 spinning precursor, carrying out thermal treatment on the Na3V2(PO4)3 spinning precursor in an inert atmosphere and cooling the Na3V2(PO4)3 spinning precursor to obtain the sodium-ion battery cathode material Na3V2(PO4)3. According to the sodium-ion battery cathode material Na3V2(PO4)3 prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, high-capacity charging and discharging of the battery can be realized; and the cycle stability of the battery can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Stent and method for manufacturing the stent
ActiveUS20060064158A1Improves helical machined-tube stentsReduce restenosisStentsLigamentsInsertion stentStent
A stent includes a stent body having a circumference, a diameter of between approximately 4 mm and approximately 12 mm, in particular, 8 mm, and a length of between approximately 10 mm and approximately 250 mm, in particular, 150 mm, and struts disposed helically about the circumference in turns. Substantially circumferentially oriented connecting bridges connect respectively adjacent ones of the turns. A method for manufacturing a helical stent includes the steps of providing a stent body with struts disposed about the circumference thereof in turns and with bridges connecting the struts in adjacent turns. The stent body is expanded and, thereafter, some of the bridges, in particular, sacrificial bridges, are removed.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
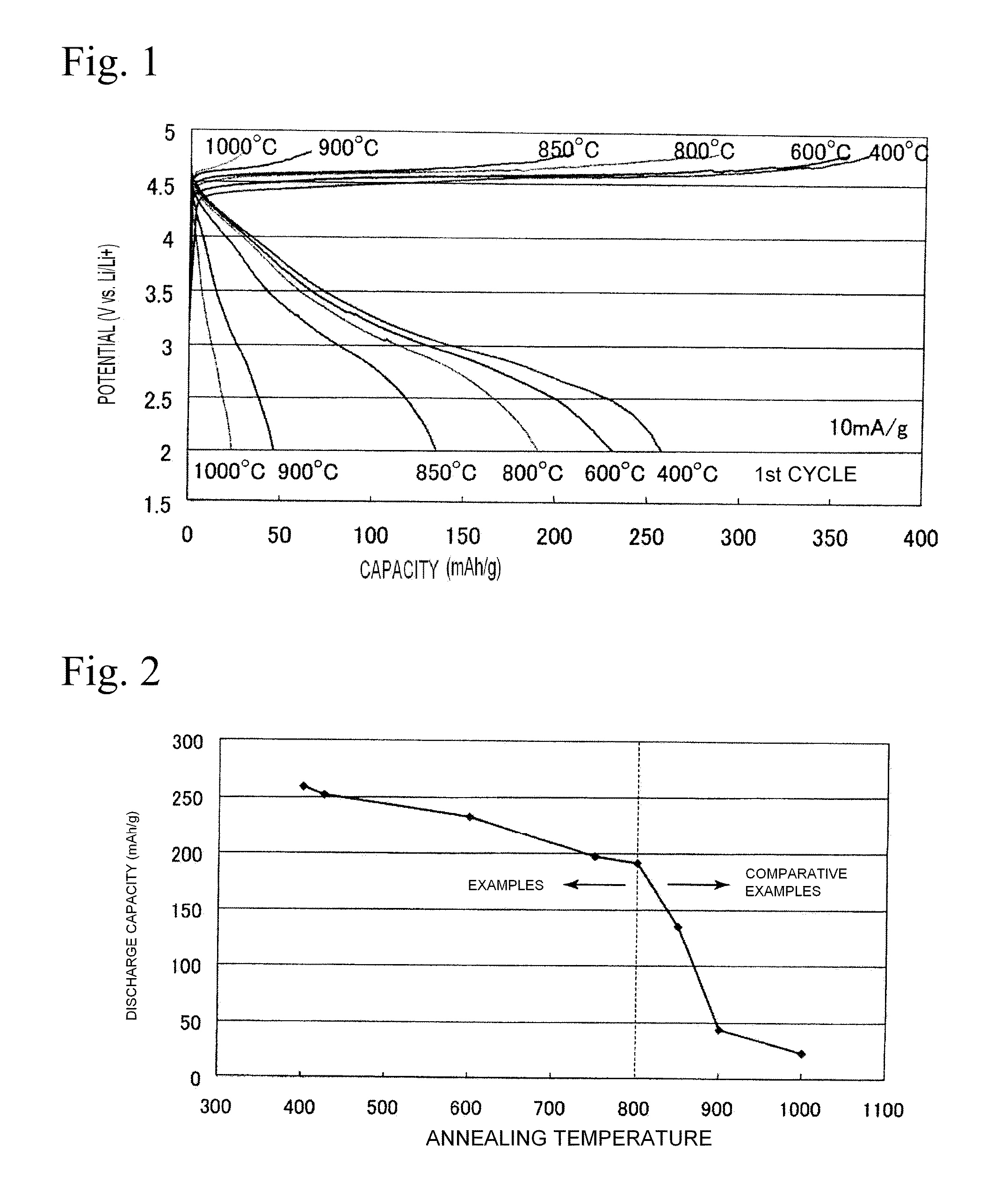
Positive electrode active material for lithium secondary battery and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100112448A1Improve discharge capacityEasy and efficient to manufactureSecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesX-rayCrystal plane
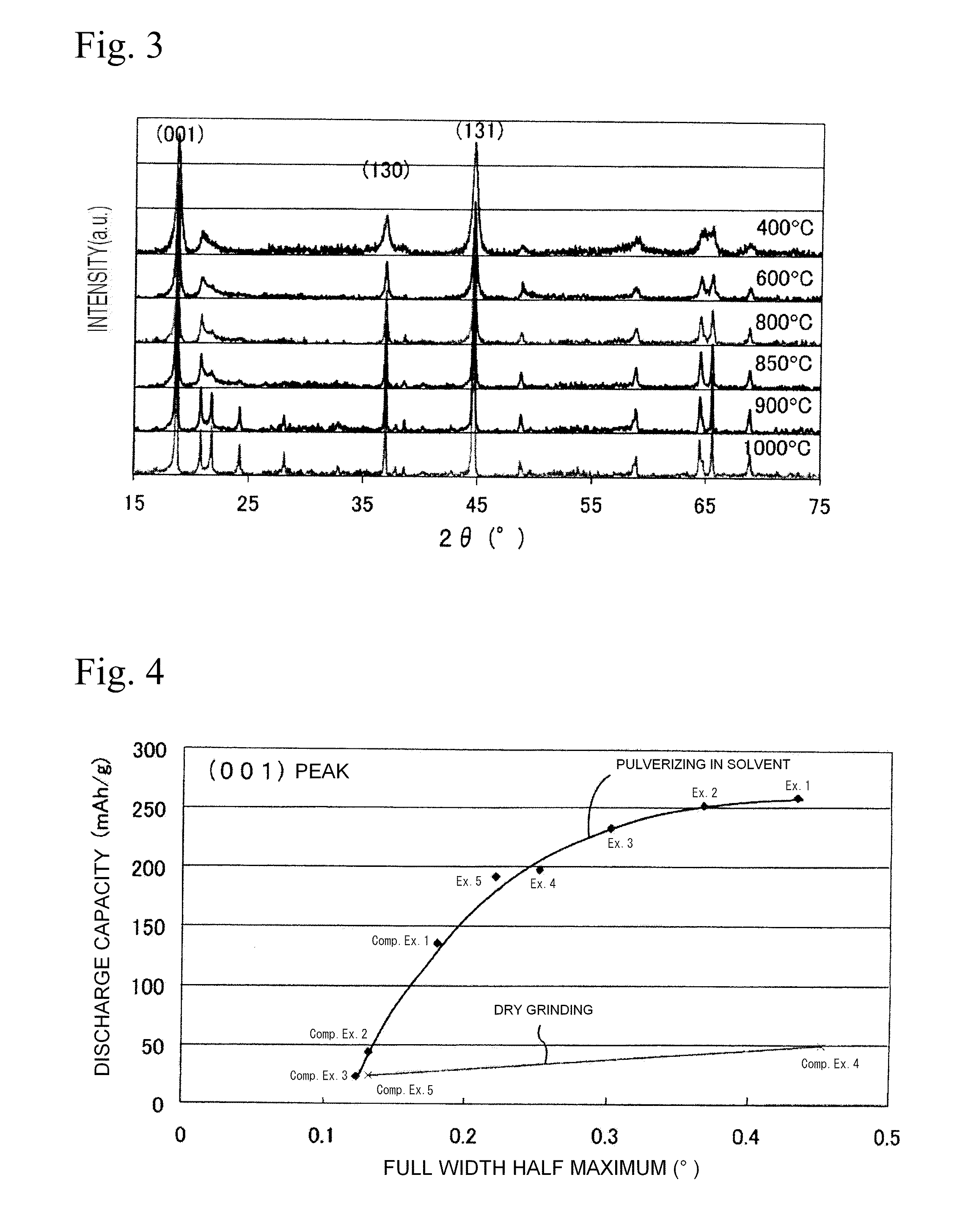
A positive electrode active material includes a layered lithium-manganese oxide represented by the general formula Li2-xMn1-yO3-p, where 0≦x≦2 / 3, 0≦y≦1 / 3, and 0≦p≦1, the lithium-manganese oxide having a full width half maximum of a peak of the (001) crystal plane, as determined by an X-ray diffraction analysis, of 0.22° or greater, and an average particle size of 130 nm or less.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for preparing cerium-activated yttrium aluminium garnet fluorescent powder
The invention relates to a preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet phosphor activated by cerium and a phosphor. The invention provides a generalized preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet phosphor activated by cerium. A chemical formula is Y3-x-y-zRyAl5-mGamO12: Cex, R'z. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparation of metal ions solutions, preparation of precipitant solutions, preparation of metal ions precipitants, addition of flux and solid phase reaction, sintering, grinding powders sintered under high temperature, pickling, alkali washing, water washing and drying, then the target product YAG:Ce phosphor, which has high luminous intensity, low agglomeration degree without ball milling, proper powder size and narrow particle size distribution, is obtained; besides, the phosphor has low agglomeration degree after being treaded under high temperature, and the phosphor can be packed and sealed without ball milling and can maximize the excellent optical property.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
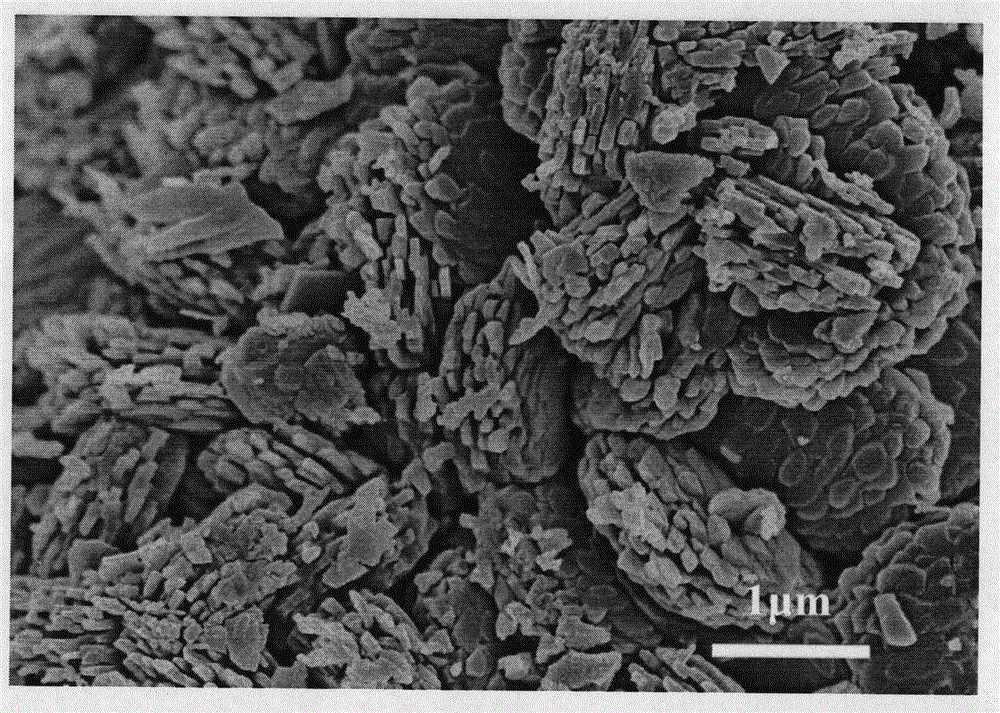
Carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material and preparation method thereof as well application of carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material serving as sodium-ion battery positive electrode material
InactiveCN108123129AIncrease contact areaShort diffusion pathMaterial nanotechnologySecondary cellsCarbon layerHydrocarbon mixtures
The invention discloses a carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material and a preparation method thereof as well application of the carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material serving asa sodium-ion battery positive electrode material. The carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material has an ordered nano-structure and the surface of the material is uniformly cladded with a carbon layer; the preparation method of the carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material comprises the following steps: sequentially carrying out ball milling and mixing on an organic macromolecular surfactant, a phosphorous source, a hydrocarbon type mixture, an iron source and a sodium source to obtain a precursor; putting the precursor into a protective atmosphere and calcining to obtain the carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material. The carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material has the ordered nano-structure and a large contact area with electrolyte; an ion dispersion path is short and an ion dispersion speed in a battery system is effectively improved; an electron transmission speed and the stability of the electrode material are effectively improved through aconductive carbon layer; the carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material is used as the sodium-ion battery positive electrode material and has excellent electrochemical performance, and is anideal sodium-ion battery positive electrode material; a preparation process is simple in technology and low in cost; large-scale production is easy to enlarge and the carbon-cladded sodium ferric pyrophosphate material has a very great application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve with nanosheet layer structure and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN106006666AHigh crystallinityHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsNanotechnologySynthesis methodsPotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve with a nanosheet layer structure and a synthesis method thereof; the hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve with the nanosheet layer structure is formed by cluster stacking of nanosheet layers with the thickness of 30 to 50 nm; an amphiphilic cationic surfactant is used as a structure directing agent, potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide is used as an alkali source, a synthesis solution with the molar ratio of (20-100)SiO2:(0.4-3)Al2O3:(10-50)ROH:(1000-3000)H2O:(1-10)SDA is prepared and then is subjected to hydrothermal crystallization according to a conventional method, and the product is washed, dried and roasted to obtain the ZSM-5 molecular sieve. The molecular sieve is the hierarchical pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve having the nanosheet layer structure and formed by self assembly of the amphiphilic cationic surfactant and an inorganic species through interaction, has the characteristics of large specific surface area, short diffusion path and good stability; and the preparation method has the advantages of high degree of crystallinity and simple operation.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for anode material manganese magnesium silicate of rechargeable magnesium cell
InactiveCN101320806AImprove crystal structureImprove electrochemical activityElectrode manufacturing processesChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesCapacitanceManganese
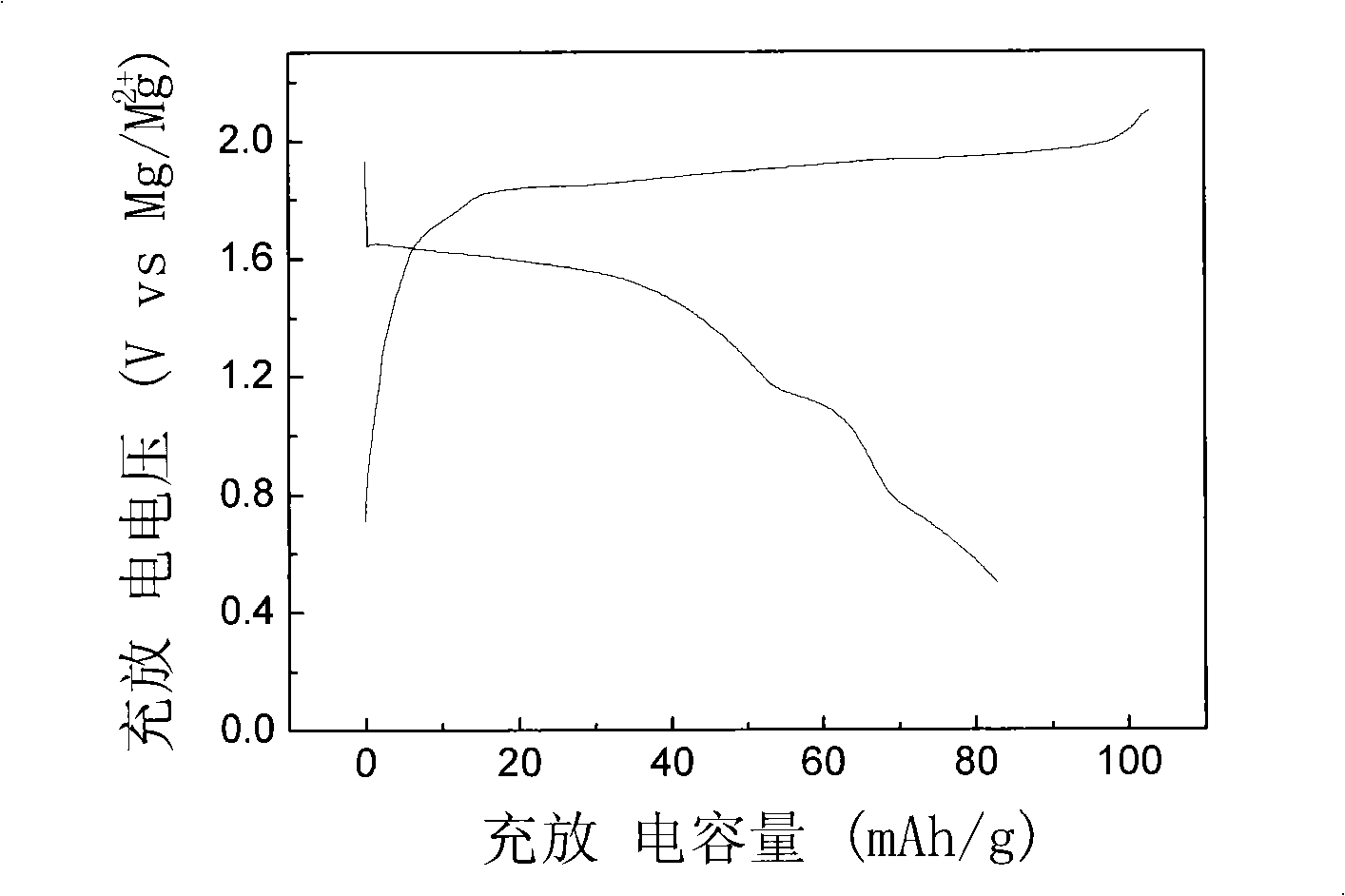
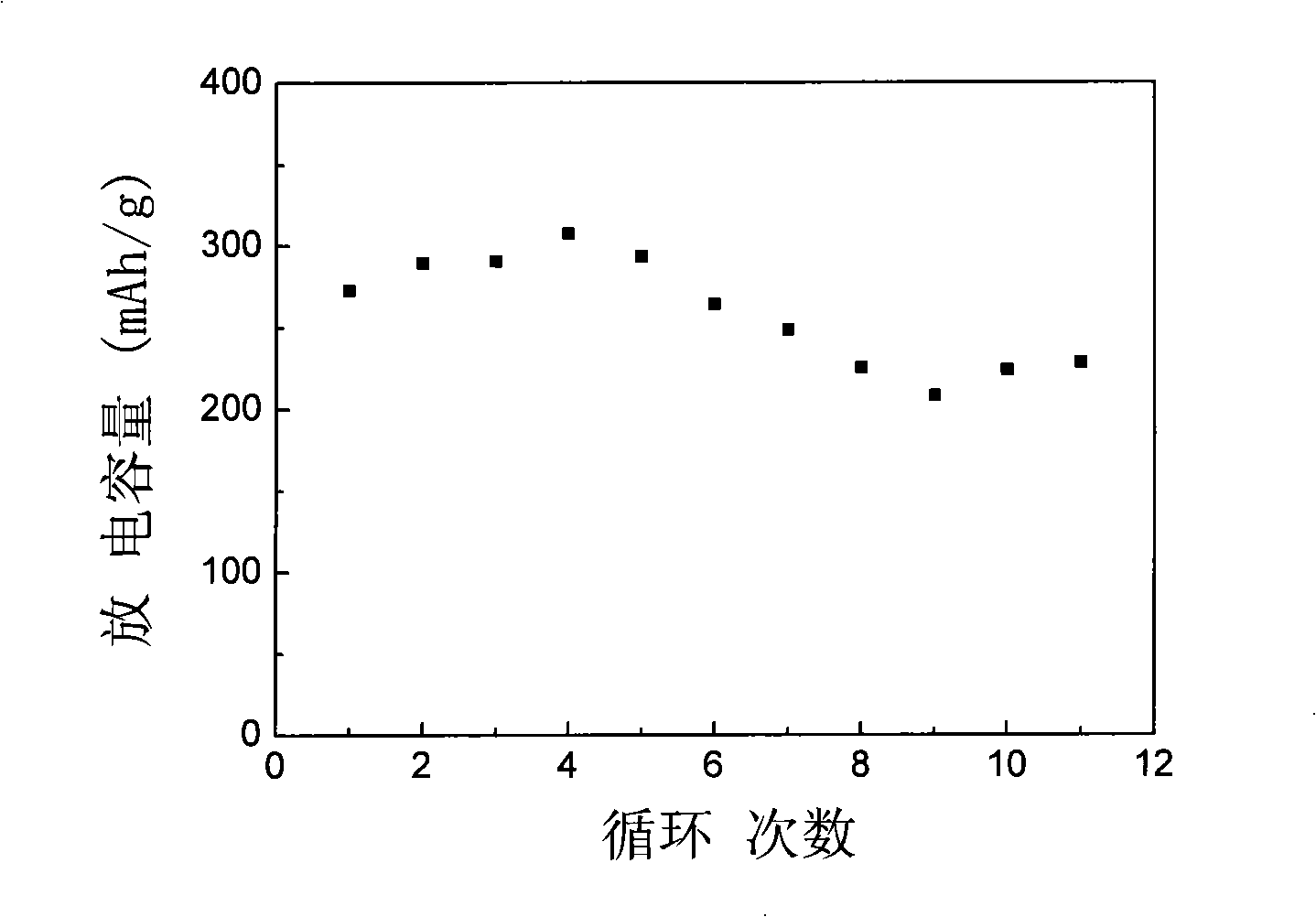
The invention discloses a production method for manganous / magnesium silicate of chargeable magnesium battery positive pole material, which is the manganous / magnesium silicate of chargeable magnesium battery positive pole material using molten salts as reaction medium and having the characteristics of quickening up reaction speed, shortening reaction cycle, simplifying synthesis course, reducing synthesis cost, small synthesis particle size and symmetrical distribution of the particles. The material exhibits remarkable electrochemical charge and discharge effects, the steady discharge platform works up to 1.6V and 1.1V(vs.Mg / Mg<2+>); on the charge and discharge conditions of C / 20 current density, the discharge capacitance can reach 289.3mAh*g<-1>(theoretical capacitance is 92%). In contrast to the relatively ideal positive pole material Mo3S4 of the current chargeable magnesium battery, the manganous / magnesium silicate positive pole material produced by the molten salt process has the advantages of simple production, large capacitance, high discharge voltage platform and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Novel highly porous ceramic and metal aerogels from xerogel powder precursors, and methods for their production and use
ActiveUS20190308912A1Speed up the processReduce lossesTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusConvertersBoride
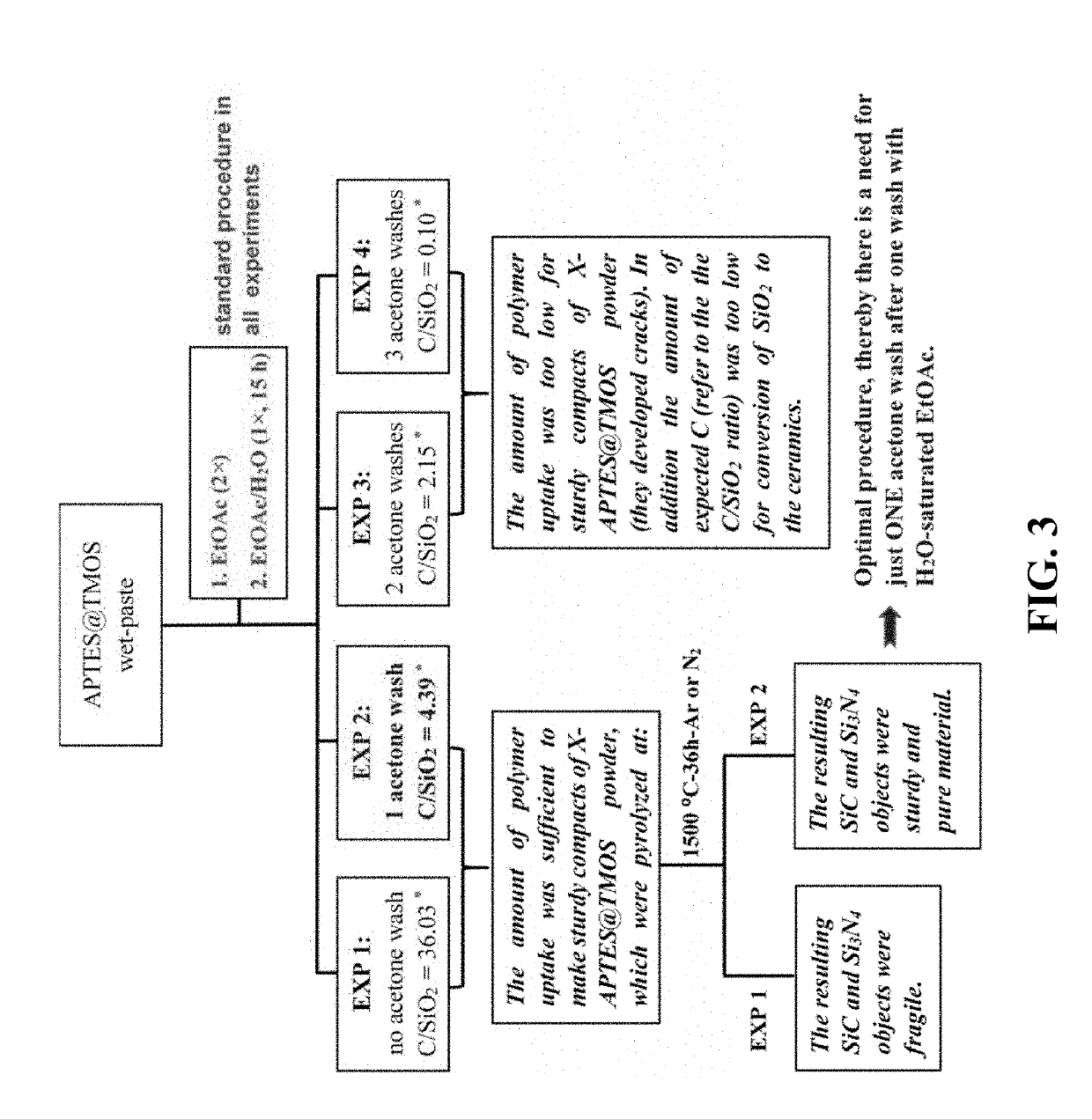
The present invention discloses novel methods for producing highly porous ceramic and / or metal aerogel monolithic objects that are hard, sturdy, and resistant to high temperatures. These methods comprise preparing nanoparticulate oxides of metals and / or metalloids via a step of vigorous stirring to prevent gelation, preparing polymer-modified xerogel powder compositions by reacting said nanoparticulate oxides with one or more polyfunctional monomers, compressing said polymer-modified xerogel powder compositions into shaped compacts, and carbothermal conversion of the shaped xerogel compacts via pyrolysis to provide the highly porous ceramic and / or metal aerogel monolithic objects that have the same shapes as to their corresponding xerogel compact precursors. Representative of the highly porous ceramic and / or metal aerogel monolithic objects of the invention are ceramic and / or metal aerogels of Si, Zr, Hf, Ti, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ru, Au, and the like. Examples include sturdy, shaped, highly porous silicon carbide (SiC), silicon nitride (Si3N4), zirconium carbide (ZrC), hafnium carbide (HfC), chromium carbide (Cr3C2), titanium carbide (TiC), zirconium boride (ZrB2), hafnium boride (HfB2), and metallic aerogels of iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), ruthenium (Ru), gold (Au), and the like. Said aerogel monolithic objects have utility in various applications such as, illustratively, in abrasives, in cutting tools, as catalyst support materials such as in reformers and converters, as filters such as for molten metals and hot gasses, in bio-medical tissue engineering such as bone replacement materials, in applications requiring strong lightweight materials such as in automotive and aircraft structural components, in ultra-high temperature ceramics, and the like.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Magnetic MOFs solid-phase extractant, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104307481AAdjustable thicknessEffectively adjust the thicknessOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCoprecipitationSilica gel
A preparation method for a magnetic MOFs solid-phase extractant comprises the following steps: 1, employing a coprecipitation process to prepare a magnetic Fe3O4 nanosphere with the particle size of 10-20 nm; 2, employing Stober silica gel coupling process to prepare Fe3O4@SiO2 with a shell-core structure; 3, employing an in-situ precipitation process to prepare Fe3O4@SiO2@Cu(OH)2; 4, employing an in-situ conversion manner to synthesize Fe3O4@SiO2@HKUST-1; and 5, performing post-functionalization on Fe3O4@SiO2@HKUST-1 synthesized in the step 4 to synthesize the Bi-I modified magnetic MOFs solid-phase extractant. The advantages comprise that the provided method is simple, convenient, low in cost and friendly to environment. The prepared magnetic MOFs solid-phase extractant has the advantages of rapid adsorption speed, large adsorption capacity, high removal efficiency and the like, and efficient removal of low-concentration Hg<2+> can be realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Heat-resisting and wear-resisting flux-cored wire
ActiveCN105945456ANon-spontaneous nucleationOptimize the reasonable rangeWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare-earth elementNiobium
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal surfacing materials and particularly relates to a heat-resisting and wear-resisting flux-cored wire. The heat-resisting and wear-resisting flux-cored wire is formed by wrapping a low-carbon cold-rolled steel strip on flux core powder. The flux core powder comprises, by weight, 0.25-1.0% of graphene, 40-45% of chromium metal, 5-9% of electrode graphite, 2-4% of marble, 1-3% of chromium carbide, 1-4% of electrolytic manganese metal, 3-6% of silicon iron, 4-6% of molybdenum, 6-10% of nickel, 2-4% of ferro-boron, 0.5-3% of niobium, 0.5-3.0% of tungsten, 0.5-1% of rare earth, and the balance FHY100.25 reduced iron powder. According to the heat-resisting and wear-resisting flux-cored wire, weld metal structures are refined and homogenized by adding components such as graphene, rare earth elements and chromium carbide into the flux core powder and optimizing the reasonable range of components, and the high-temperature tempering stability of surfacing metal is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Preparation method of WC-Co nano powder added with grain growth inhibitor
The invention provides a preparation method of WC-Co nano powder added with a grain growth inhibitor, and belongs to the technical field of powder metallurgy and powder preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: ammonium metatungstate, cobalt nitrate, fuel, ammonium nitrate, metal salt with a needed amount of the added grain growth inhibitor and an organic carbon source are used as raw materials, and oxide / carbon composite powder is prepared by adopting a low-temperature combustion synthesis method; and then carbonization is carried out under atmosphere protection or vacuum to obtain the WC-Co nano powder mixed with the grain growth inhibitor. According to the preparation method, the low-temperature combustion synthesis method belongs to a liquid-phase synthesis method, molecular-level mixing is achieved, so that diffusion range of the carbon in the carbonization process is short, and the requirements for the reaction temperature requirement and the reaction time requirement are low; and in addition, the raw materials are simple to obtain, the equipment is simple, the process is fast, and large-scale production can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Catalyst for H2 selective oxidation in styrene production
ActiveCN101491758AImprove combustion activityImprove anti-carbon performanceCatalyst activation/preparationHydrocarbonsIridiumAlkaline earth metal
The invention relates to a catalyst for hydrogen selective oxidation reaction during phenyl ethylene production, and mainly solves the problems of low using efficiency and short service life of the catalyst, and high raw material loss in the prior art. The catalyst for the hydrogen selective oxidation reaction during the phenyl ethylene production comprises a kernel of an inert carrier and a layered composite carrier which is combined on the kernel and consists of an outer layer of a porous coating material, wherein the outer layer of the layered composite carrier is loaded with at least one platinum series metal selected from ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium and platinum, at least one dressing agent selected from alkali metals and alkaline-earth metals, and an assistant catalyst selected from one of IVA compounds and at least one of lanthanide series compounds. The technical proposal solves the problems well, and the catalyst can be applied in the industrial production of the hydrogen selective oxidation reaction in a process of producing phenyl alkene by ethylbenzene dehydrogenation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation technology for titanium-suboxide conductive ceramic electrode
A preparation technology for a titanium-suboxide conductive ceramic electrode comprises the following steps: (1) according to a reaction equation to respectively weigh a titanium dioxide powder and a titanium hydride powder; (2) fully mixing the weight titanium dioxide powder and titanium hydride powder, so as to obtain a uniform mixture; (3) putting the mixture into a mold and performing precompression, so as to prepare a blocky material; (4) performing vacuum dehydrogenation processing on the blocky material; (5) performing hydrostatic-pressure repressing; and (6) performing high-temperature reaction and sintering, and cooling to obtain the blocky titanium-suboxide conductive ceramic electrode. By employing the in-site dehydrogenation technology, the obtained titanium powder is high in purity, the chemical reaction activity is good, the powder granularity is controllable, and the preparation period of the titanium-suboxide conductive ceramic electrode is substantially shortened.
Owner:CHANGSHA WORUI NEW MATERIAL TECH
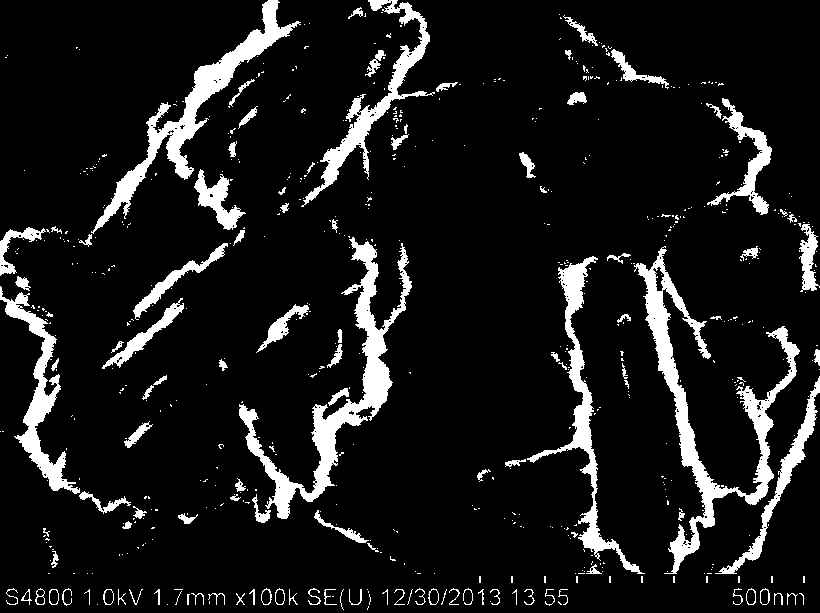
ZSM-5 molecular sieve with nanosheet layer structure and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN106006667AHigh crystallinityHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsNanotechnologySynthesis methodsPotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a ZSM-5 molecular sieve with a nanosheet layer structure and a synthesis method thereof; the ZSM-5 molecular sieve with the nanosheet layer structure is formed by cluster stacking of nanosheet layers with the thickness of 10 to 30 nm; an organic quaternary ammonium salt and an amphiphilic cationic surfactant are used as structure directing agents and template agents, potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide is used as an alkali source, a synthesis solution with the molar ratio of (20-100)SiO2:(0.4-3)Al2O3:(10-30)TPA:(10-50)ROH:(1000-3000)H2O:(1-10)SDA is prepared through a conventional hydrothermal crystallization method, and the product is washed, dried and roasted to obtain the ZSM-5 molecular sieve with the nanosheet layer structure. The molecular sieve is an MFI type molecular sieve having the sheet layers and multi-level pore channel structure and has the characteristics of relatively large specific surface area, relatively short diffusion path and relatively good stability.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of nano-rod-shaped ZSM-48 molecular sieve
InactiveCN104003413ANeat appearanceShort diffusion pathCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveAlkaline earth metal
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic materials, and in particular relates to a preparation method of a nano-rod-shaped ZSM-48 molecular sieve. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a silicon source, an aluminum source, an alkali source, an organic template and a water phase by virtue of adopting a hydro-thermal synthesis method, and stirring into a gel-like mixture used as a raw material for synthesizing the ZSM-48 molecular sieve. The chemical composition of the nano ZSM-48 molecular sieve with high degree of crystallinity is TO2:aY2O3:bM2 / nO, wherein T represents at least one quadrivalent element, Y represents at least one trivalent element, M represents at least one alkaline metal (or) alkaline-earth metal element of which the valence state is n. Prepared ZSM-48 disclosed by the invention not only has neat appearance, relatively short diffusion process, ultra-high degree of crystallinity and relatively rich specific surface area, but also can be used for improving the whole catalytic utilization efficiency of the molecular sieves.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
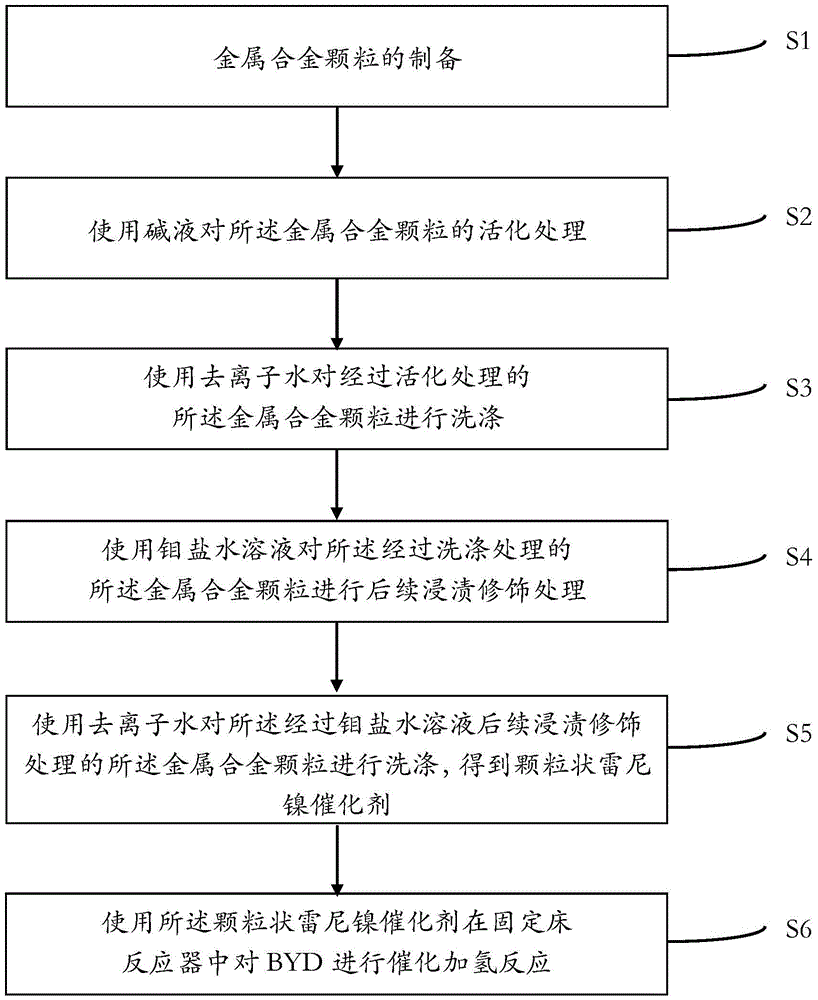
Hydrogenation catalyst using BYD hydrogenation to prepare BDO and method using BYD hydrogenation to prepare BDO
ActiveCN106140196AHigh mechanical strengthShort diffusion pathPreparation by hydrogenationRaney catalystsAqueous solutionMetal alloy
The invention discloses a hydrogenation catalyst using BYD hydrogenation to prepare BDO and a method using BYD hydrogenation to prepare BDO. The method includes: preparing metal alloy particles; using alkali liquor to activate the metal alloy particles; using deionized water to wash the activated metal alloy particles; using a molybdenum salt aqueous solution to perform subsequent impregnation modification on the washed metal alloy particles; using deionized water to wash the impregnated and modified metal alloy particles to obtain the granular Raney nickel catalyst; using the granular Raney nickel catalyst to perform catalytic hydrogenation reaction on BYD in a fixed bed reactor. The method has the advantages that the method is simple in process, promising in application prospect and huge in economic benefit, and the hydrogenation effect is improved evidently.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUNKAI NEW MATERIAL TECH
Emergency medical treatment system
InactiveUS20060207911A1Easy to carrySmall thicknessSmall article dispensingPackage recyclingCredit cardDrug doses
Owner:KILLWORTH RICHARD A
Rechargeable magnesium cell anode material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101439861ABig spaceShort diffusion pathCell electrodesSilicon compoundsMolten saltDischarge rate
The invention discloses a rechargeable magnesium cell anode material and a preparation method thereof. The anode material is magnesium ferrosilite which has the chemical structural formula of MgxFeySiO4, wherein x is higher than and equal to 1 and lower than or equal to 1.2, and y is more than or equal to 0.8 and less than or equal to 1. Nanometer silica dioxide is taken as a silicone source; and the magnesium ferrosilite which is the rechargeable magnesium cell anode material obtained through a molten salt method shows the good electrochemical charge and discharge behavior. In the electrolyte of 0.25mol.L<-1>Mg(AlCl2BuEt) 2 / THF and with the discharge rate of 0.2C, the discharge platform reaches 1.5V(vs.Mg / Mg<2+>) and the discharge capacity reaches 151.7mAhg<-1>. In the electrolyte of 0.4mol.L<-1> [Mg2Cl3] + [AlPh2Cl2] -THF and with the discharge rate of 0.4C, the discharge platform reaches 1.2V(vs. Mg / Mg2+) and the discharge capacity reaches 148.5mAhg-1.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Mn2P2O7 anode material of core-shell structured lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104934599AImprove electrochemical performanceReduce usageMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPhysical chemistryBattery cell
The invention relates to a Mn2P2O7 anode material of a core-shell structured lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The Mn2P2O7 is prepared according to the following steps of: (1) dissolving an organic manganese source and a phosphorus source in deionized water to obtain a mixed solution; (2) adjusting a pH value to be 3 to 8; (3) placing the solution in a water bath at 60 to 90 DEG C, and stirring the solution for 10 to 30 hours to form uniform gel; (4) drying the gel for 4 to 15 hours at 60 to 110 DEG C to obtain a Mn2P2O7 precursor; and (5) placing the Mn2P2O7 precursor in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, sintering the Mn2P2O7 precursor at 350 to 700 DEG C for 4 to 14 hours, and cooling the product to the room temperature, thereby obtaining the Mn2P2O7 anode material of the core-shell structured lithium ion battery. The nanometer rod of the Mn2P2O7 is of a core-shell structure and has high specific area, thereby being favorable for ion transmission and infiltration of an electrolyte to an electrode material; and moreover, the conductivity of the nanometer rod is greatly improved due to uniformly-coated amorphous carbon, and the electrochemical performance of the material is excellent.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Membrane electrode of fuel cell and preparation method and application of membrane electrode
InactiveCN107681163AThin structureSolve the swelling problemCell electrodesFinal product manufactureElectrochemistryElectrical impedance
The invention discloses a preparation method of a membrane electrode of a fuel cell. The method comprises the steps of coating a transfer medium with a substrate layer; carrying out in-situ reduction-deposition of platinum nanoparticles on the substrate layer and then coating the platinum nanoparticles with a layer of proton conducting polymer to form an electrode catalyst layer; and finally transferring the catalyst layer to a proton exchange membrane by adopting a heat transfer process to prepare a membrane electrode. The invention further discloses the membrane electrode of the fuel cell and an application of the membrane electrode on a cathode or an anode of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. The problem of contradiction between reduction time and electrochemical active area in thein-situ deposition process of platinum is relatively well solved and the yield of heat transfer is improved. The membrane electrode has the beneficial effects of high catalyst activity and utilizationrate, large electrochemical active area, low gas transmission impedance in the catalyst layer and the like, and is low in production cost, simple and fast in process and high in yield, and massive production is easy to implement.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Synthesis method of integral hierarchical-pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve
InactiveCN106745055ASimple stepsReduce manufacturing costMolecular sieve catalystsPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteSynthesis methodsSilicon
The invention provides a synthesis method of an integral hierarchical-pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve. The synthesis method comprises the following steps that 1, an aluminum source, sodium hydroxide, an organic template agent and deionized water are added to a beaker (1) to be mixed evenly, then a silicon source is gradually added to the beaker, intense stirring is performed to form homogeneous gel, and the homogeneous gel is poured into a stainless steel reaction kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner and is crystallized at the temperature of 100-220 DEG C for 1-7 days; 2, the product obtained in the step 1 is repeatedly washed with the deionized water till a pH value is approximately neutral, and drying is performed at the temperature of 90-110 DEG C to obtain a ZSM-5 molecular sieve; 3, the ZSM-5 molecular sieve is roasted, and the organic template agent is removed to obtain the integral hierarchical-pore ZSM-5 molecular sieve. The steps of an existing integral hierarchical-pore catalyst preparation technology are simplified, expensive auxiliary materials such as structure guiding agents and special integral carriers are not needed, and the preparation cost is reduced.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com