Stent and method for manufacturing the stent
a stent and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of helical stents, can solve the problems of insufficient coverage of all tissue within the bounds of the stent, use of a stent that is very difficult to manufacture, and insufficient drug elution about these parts, so as to improve the resistance to the passage of emboli, improve flexibility and resistance to buckling, and improve the effect of stent quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
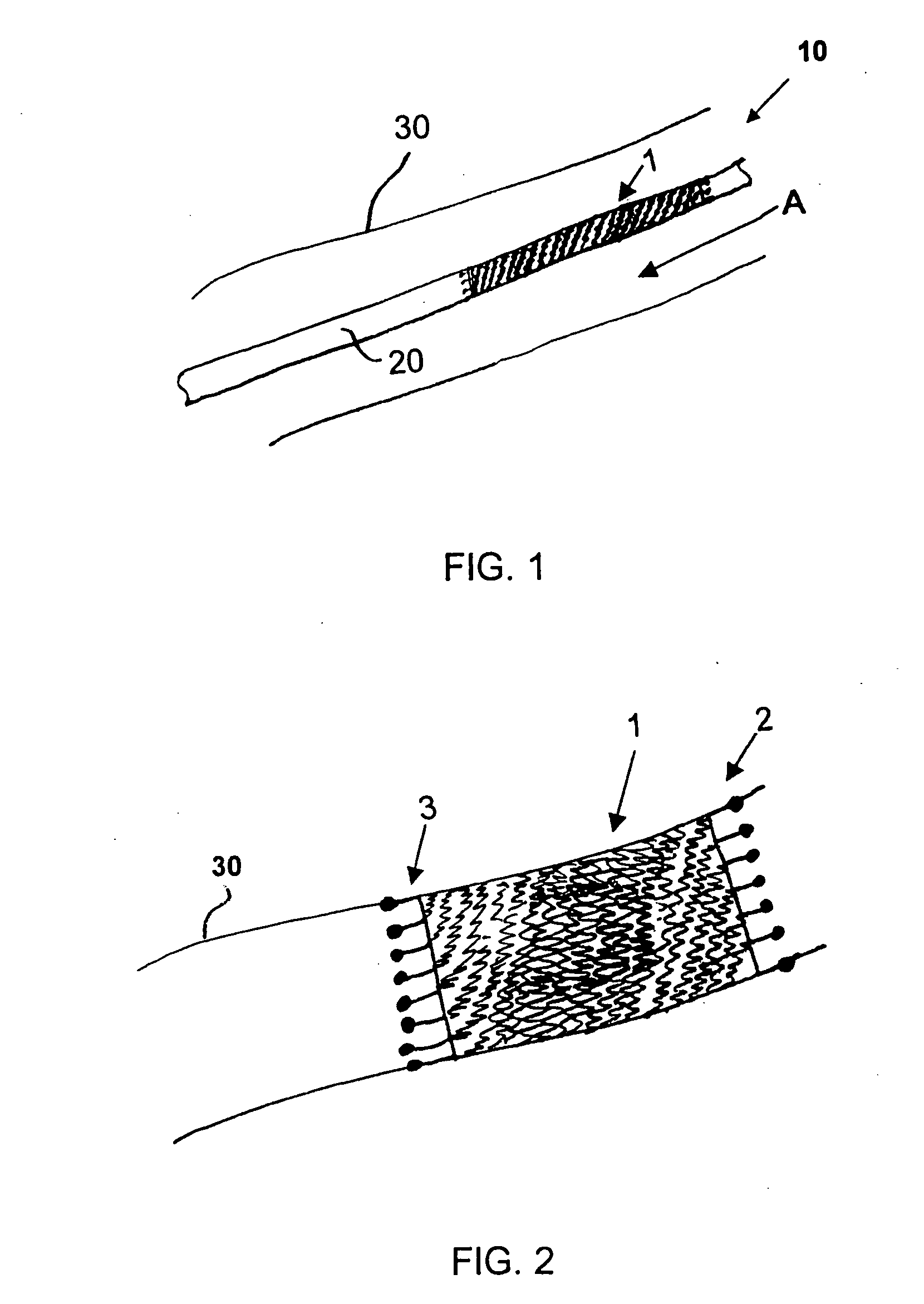
[0067] Referring now to the figures of the drawings in detail and first, particularly to FIG. 1 thereof, there is shown is a helical stent 1 according to the present invention fitted on a delivery catheter 20 of an exemplary delivery system 10. The helical stent 1 is about to be implanted in a vessel 30. The helical stent 1 is in its unexpanded state and loaded into / onto the delivery system 10 that has traveled to an implantation site. FIG. 2 illustrates the helical stent 1 implanted in the vessel 30 after being expanded, whether by a balloon of the catheter 20 or by self-expansion due to a shape memory of the material of the stent 1.
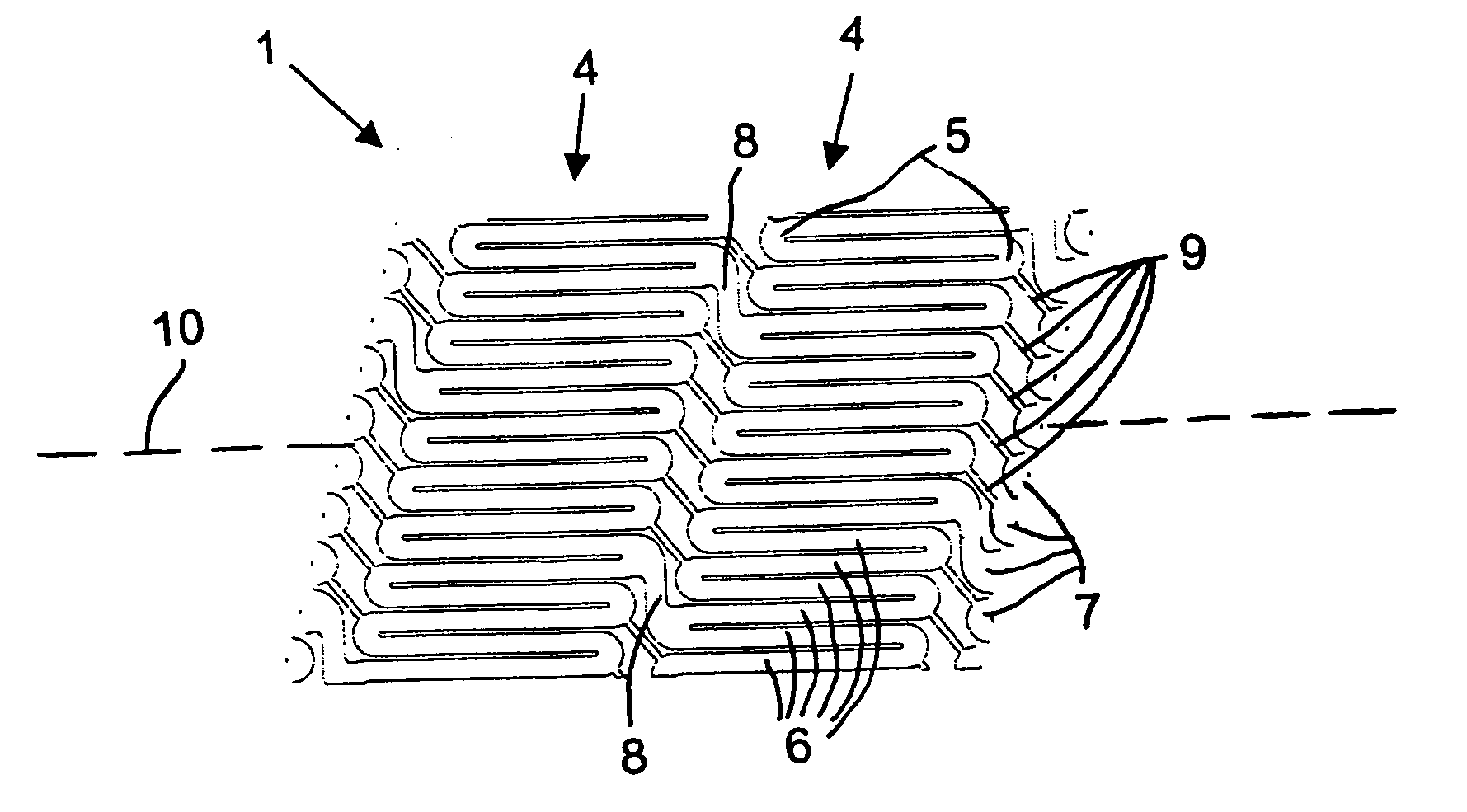
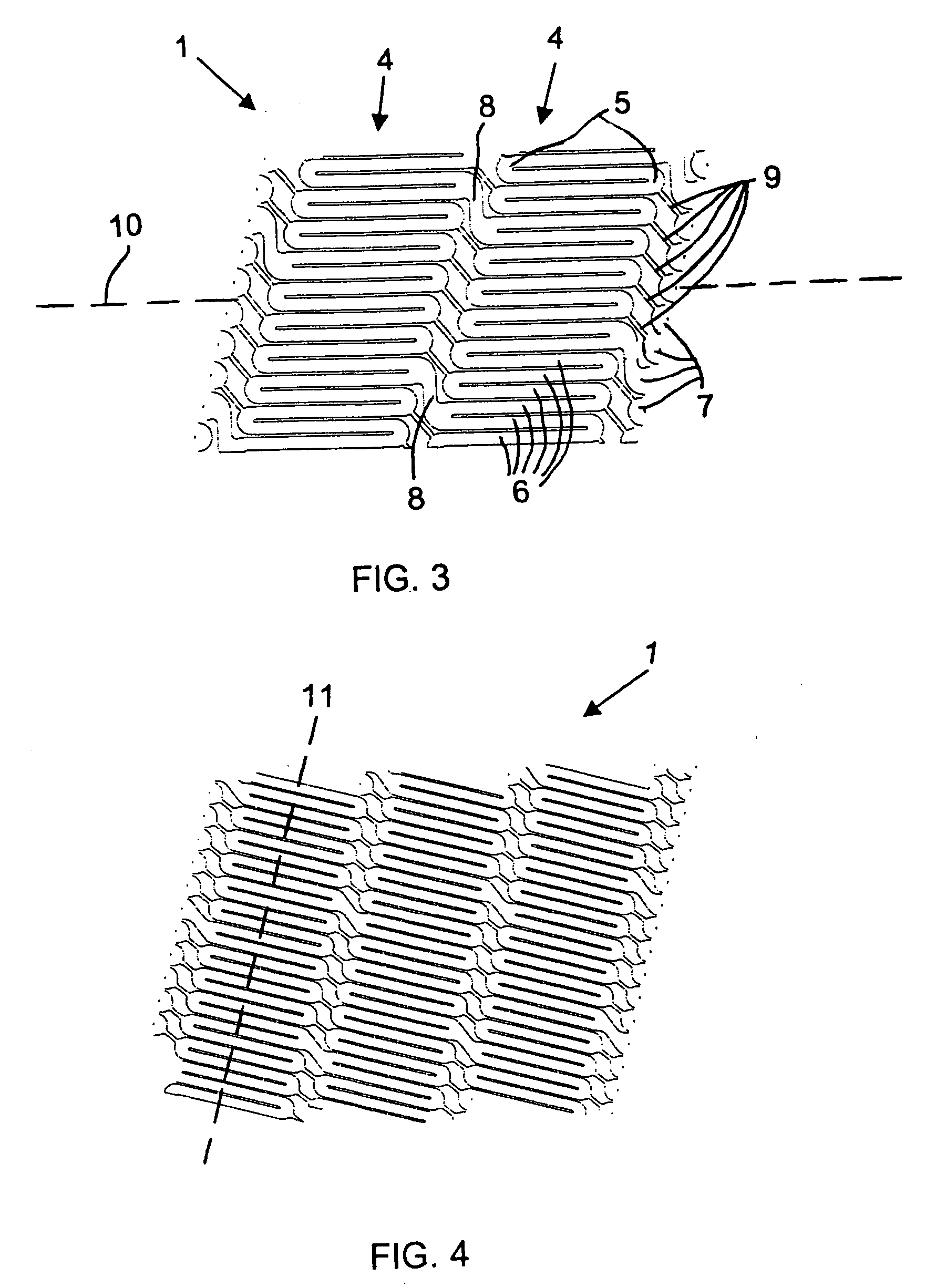
[0068] The helical stent 1 has proximal 2 and distal 3 ends—defined by a blood flow direction A. The helix of the stent 1 can be a single coil with one start at the proximal end that winds all the way to the distal end. Such a configuration is possible with the present invention because the helical stent 1 has very short struts, which will be explained...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com