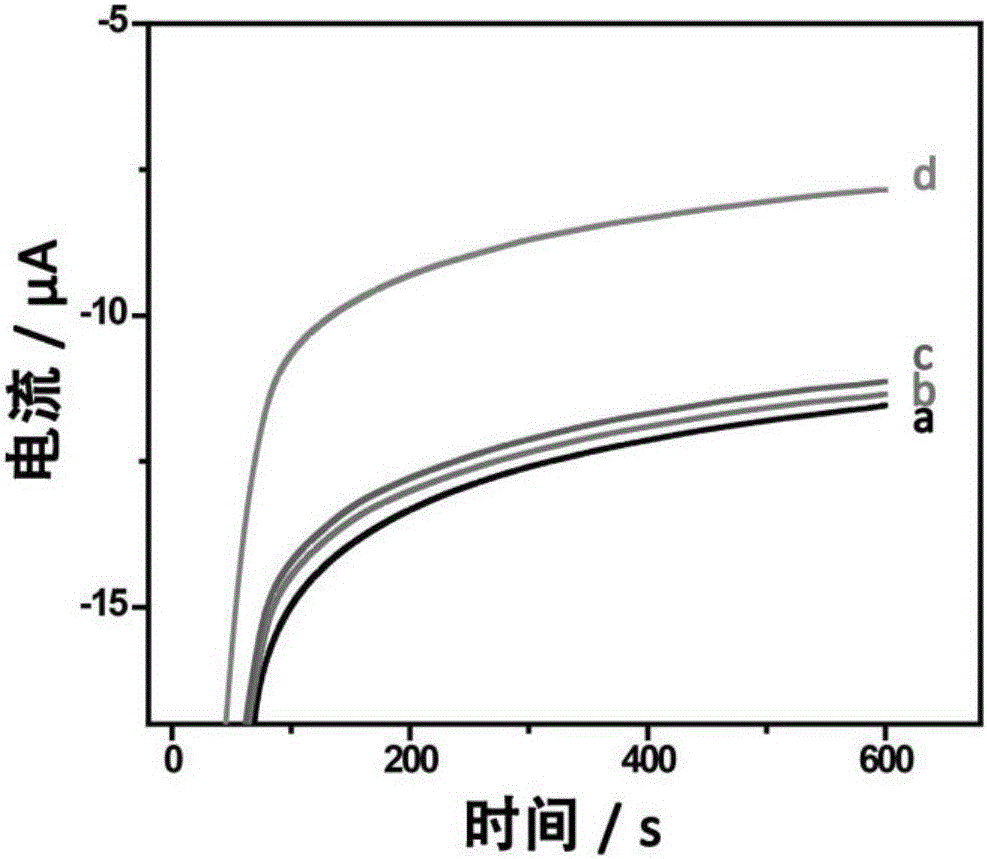
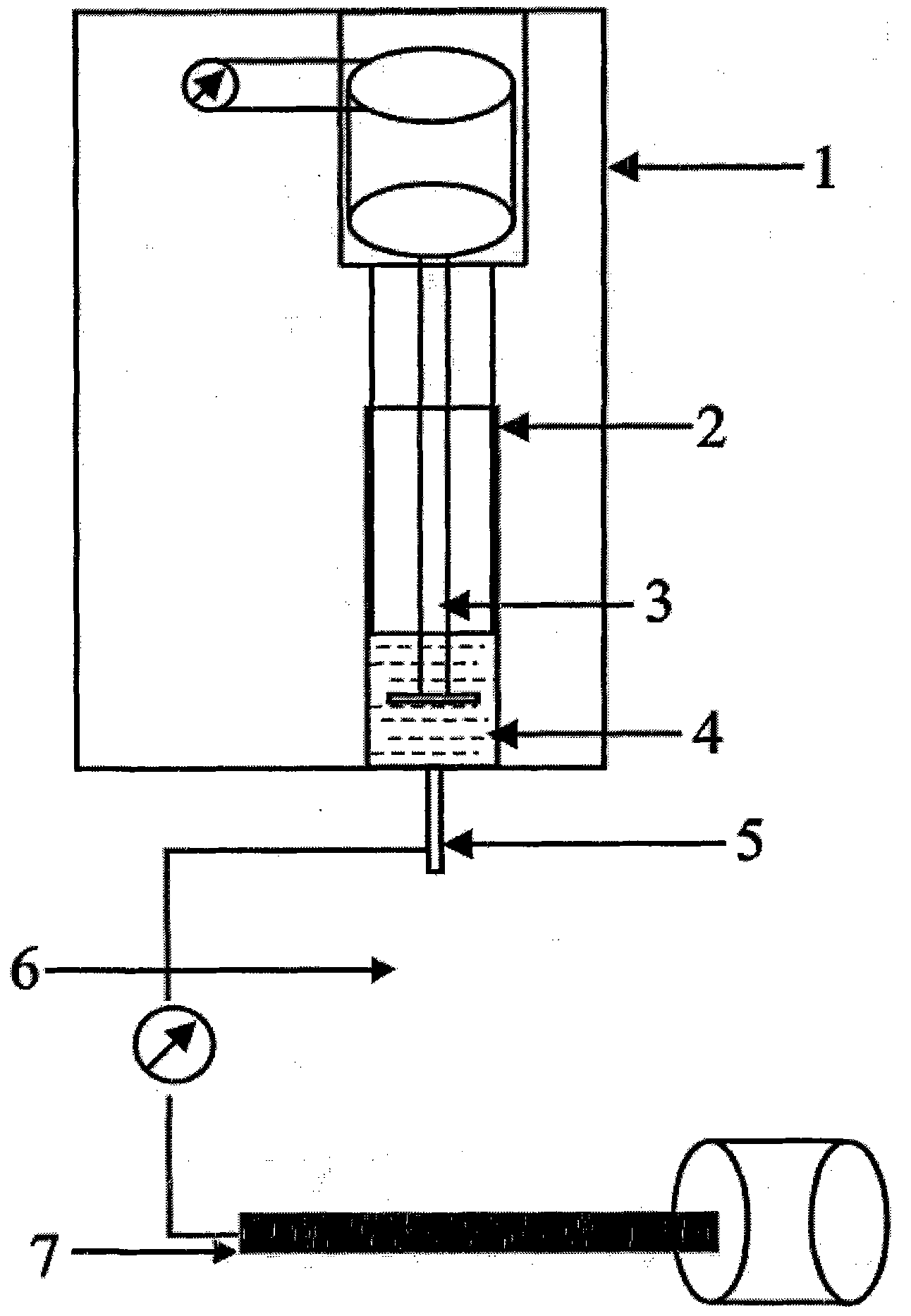
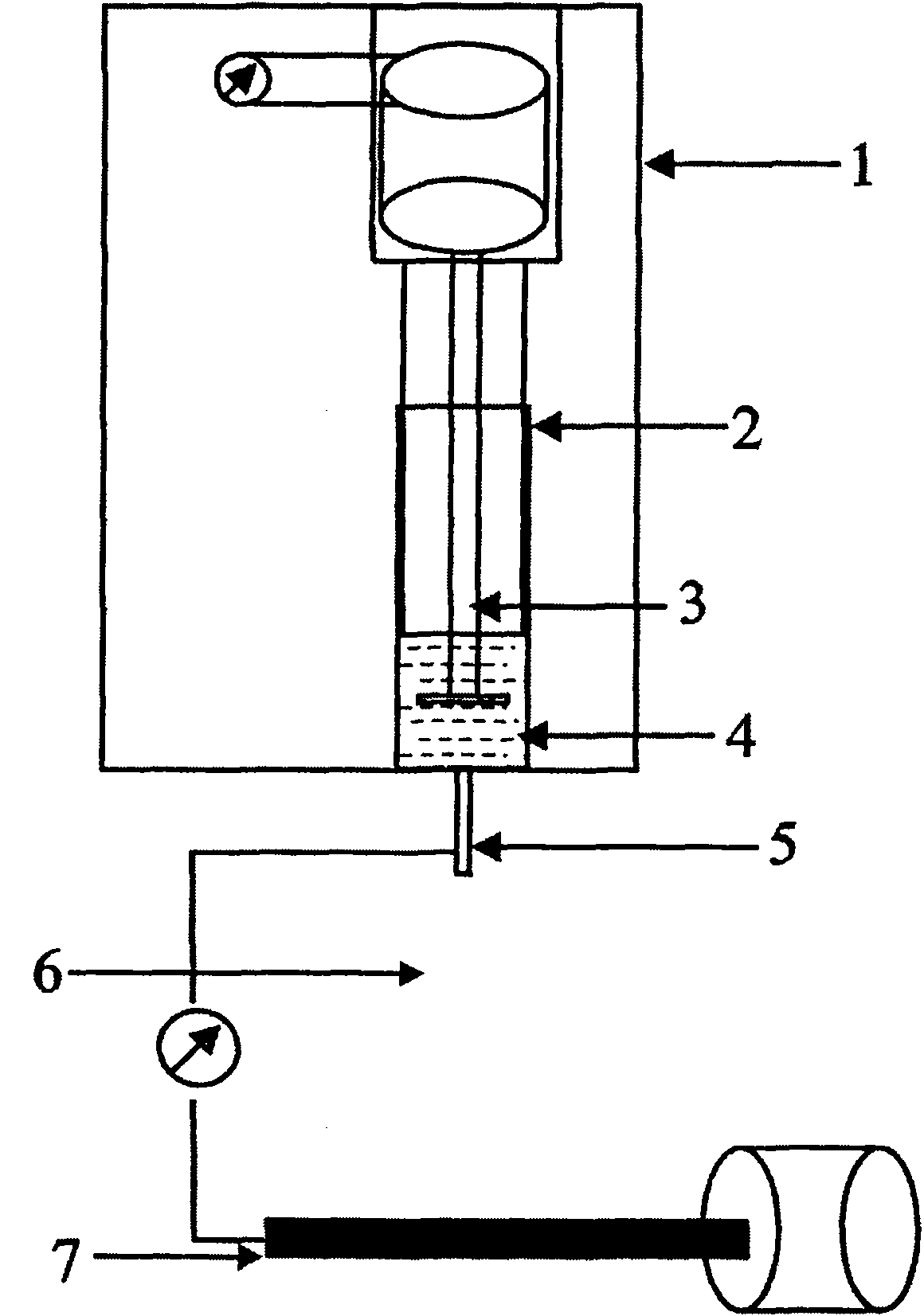
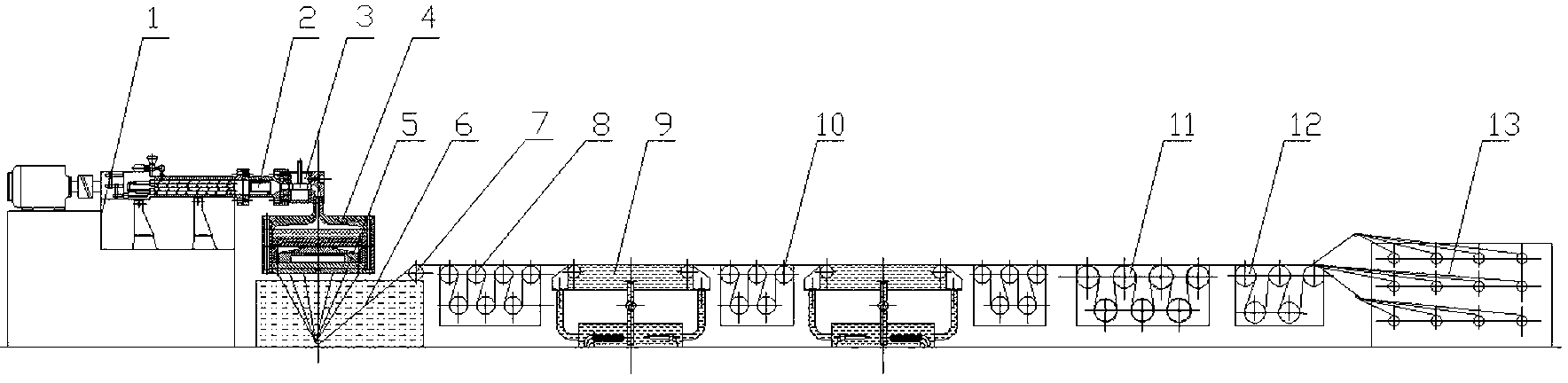
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
136 results about "Polyethylene Terephthalates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyethylene terephthalate is a polyester material that is most often used to make fibers, parts made by injection molding, and containers for food and beverages, pharmaceuticals and make-up. This material may also be recycled to make carpeting or fiber filling.
Elastic polyester fibre and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101126180AIncrease elasticityConvenient careFilament/thread formingMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to a springy polyester fiber and the preparing method. The technical problem of the invention to be solved is that the invention provides a springy fiber and the preparing method to make up the disadvantages of the capability of the spandex and the applying arrange. The springy fiber of the invention adopts the method of the compound filature and uses two screw extrusion machines to respectively melt the two components, and the product is obtained through the extrusion of the compound filature component. The invention is characterized in that the components of the springy fiber comprise two of the following high polymers which have heat shrinking capability difference: the high fasculation PETP, the PET, the PBT, the PTT with the weight proportion of 30-70:50.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGYI GRP CO LTD
Polyesters and articles made therefrom
InactiveUS20140205786A1Excellent gas barrier performanceBottlesDomestic containersPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Disclosed herein are polyesters and articles made therefrom. The article comprising a substrate comprising a first surface and a second surface, the second surface in contact with an outside environment, wherein the substrate comprises a polymer comprising poly(trimethylene furandicarboxylate) (PTF), and wherein the polymer provides an improvement in gas barrier properties of the substrate as compared to a substrate comprising nascent polyethylene terephthalate) (PET).
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Barrier film
InactiveUS7854994B2Improve the level ofImprove homogeneityFibre treatmentBottlesPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene oxide
A barrier composition which is injection mouldable and able to be made into a transparent film or incorporated (by co-extrusion and / or lamination) into multi-layer film products, the composition on dry basis: a) from 45 to 90% by weight of a starch and / or a modified starch selected from starches modified by reaction with a hydroxyl alkyl group, an acetate or a dicarboxylic acid anhydride or a grafting polymer; b) from 4 to 12% by weight of a water soluble polymer selected from polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylacetate, and copolymers of ethylene and vinylalcohol which have a melting point compatible with the molten state of the starch components c) from 5 to 45% by weight of a non-crystallising mixture of sorbitol and at least one other plasticizer selected from glycerol, maltitol, xylitol, mannitol, glycerol trioleate, epoxidised linseed or soybean oil, tributyl citrate, acetyl tri-ethyl citrate, glyceryl triacetate, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate; polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol; d) from 0.3 to 2.5% by weight of a C12-22 fatty acid or salt; e) from 0.25% to 3% of an emulsifier system having a hydrophilic lipophilic balance value between 2 and 10. The barrier film may be co-injection moulded with polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polylactic acid (PLA) for blow moulding into beverage bottles, with polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) or biodegradable polymers for high gas-barrier containers or closures, or may be co-extruded with polyethylene, polypropylene or polylactic acid for thin film packaging applications or for blow-moulded containers.
Owner:PLANTIC TECH
Articles derived from compositions containing modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Compositions of matter including articles derived from (a) from 5 to 99.99 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate and (2) contains a at least one residue derived from polyethylene terephthalate selected from the group consisting of antimony, germanium, diethylene glycol groups, isophthalic acid groups, cis isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, trans isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, sodium benzoate, alkali salts, napthalane dicarboxylic acids, 1,3-propane diols, cobalt, cobalt-containing compounds, and combinations thereof, and (b) from 0.01 to 95 wt. % of a member selected from the group consisting of (1) fillers, (2) a carboxy reactive component, (3) polyethyelene terephthalate, (4) a component including a polycarbonate and an impact modifier. The articles may be derived from various conversion processes, e.g., injection molding processes, extrusion processes, thermoforming processes, melt-blown process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
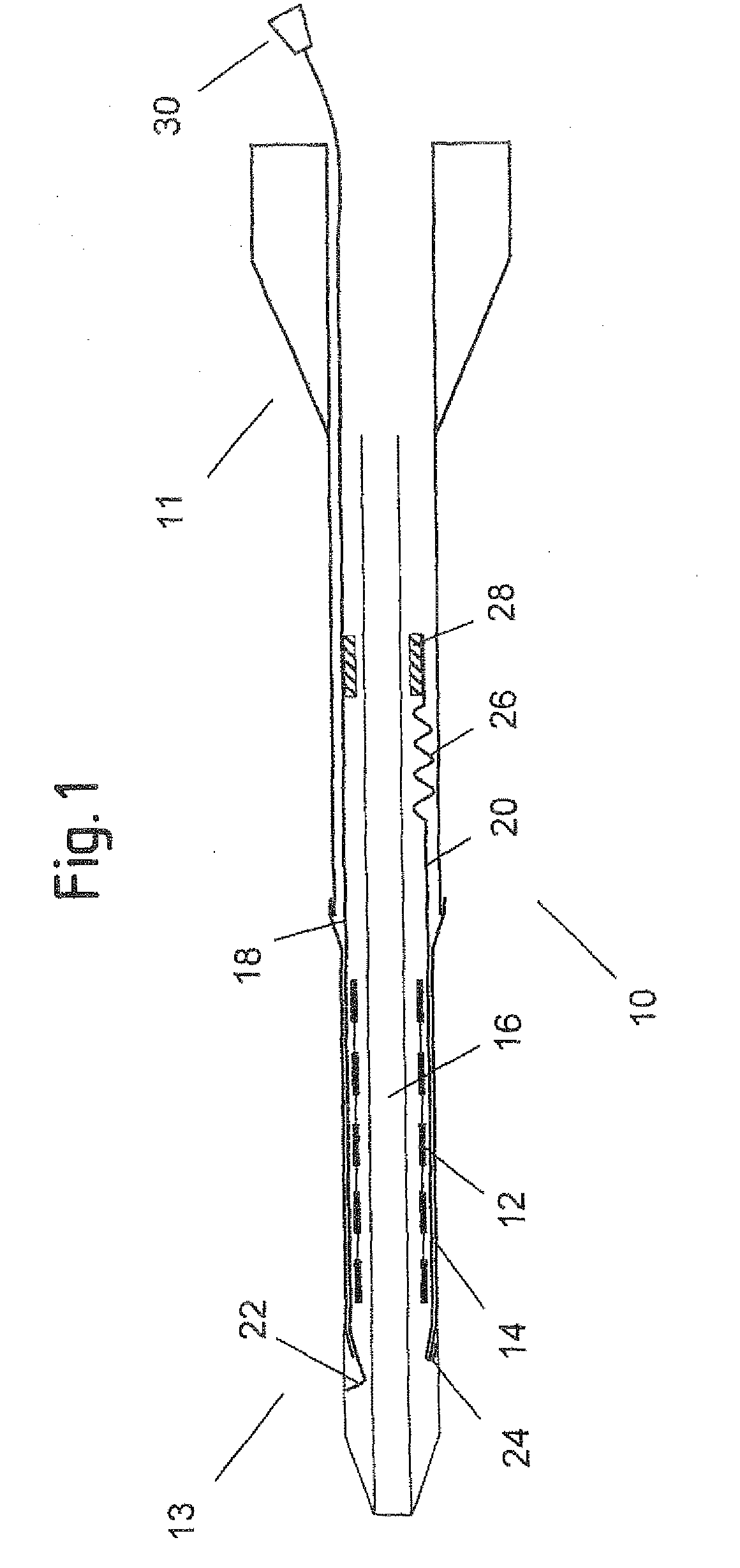
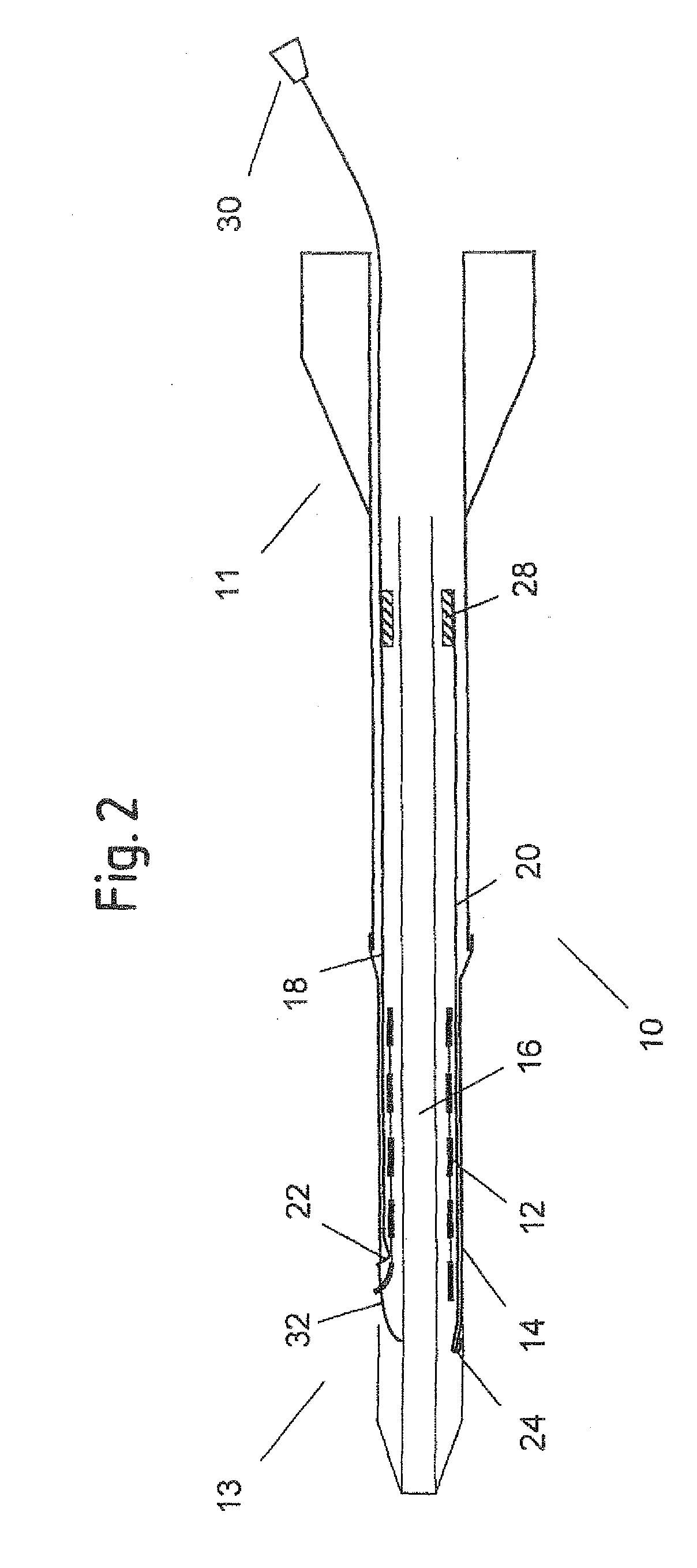
Delivery system for a self-expanding device for placement in a bodily lumen
ActiveUS20100249907A1Easy and reliable removalSimplified splitting mechanismStentsBlood vesselsPolyethylene TerephthalatesLong axis
A delivery system (114) for a self-expanding device (110) for placement in a bodily lumen, the system comprising a sheath (112) that confines the device to a radially compact delivery disposition until the device is to be released into the lumen, the system having an elongate pull element (118) to be pulled proximally from its proximal end, which pull element is arranged radially inside the sheath for pulling preferentially on a pull zone on the circumference of the distal end of the sheath, thereby to tear the sheath progressively along a tear line running the length of the sheath, starting at the distal end of the sheath, to release the device from the confining effect of the sheath, progressively, beginning at the distal end of the device and wherein the sheath is of polyethylene-terephthalate, cold drawn along its long axis, and in that the distal end of the sheath tapers inwardly to provide an inwardly tapered distal end of the system.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Low-melting point and high-crystallization temperature PET copolyester, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN103102646AImprove processing and forming performanceGood flexural modulusCopolyesterPolyethylene terephtalate
The invention discloses a low-melting point and high-crystallization temperature PET (polyethylene terephthalate) copolyester, its preparation method and application. The PET copolyester comprises, by mass: 70%-88% of PET, 5%-10% of a melting point adjusting agent, and 7%-20% of a crystallization accelerating agent. According to the preparation method, in a synthesis process of PET, based on p-phthalic acid (PTA) and ethylene glycol (EG), the melting point adjusting agent and the crystallization accelerating agent are added to undergo a chemical reaction together, thus obtaining the low-melting point and high-crystallization temperature PET copolyester. The PET copolyester provided by the invention has a low melting point and a high crystallization temperature, and has improved processing molding performance, thus being widely applicable in injection molding products.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +2
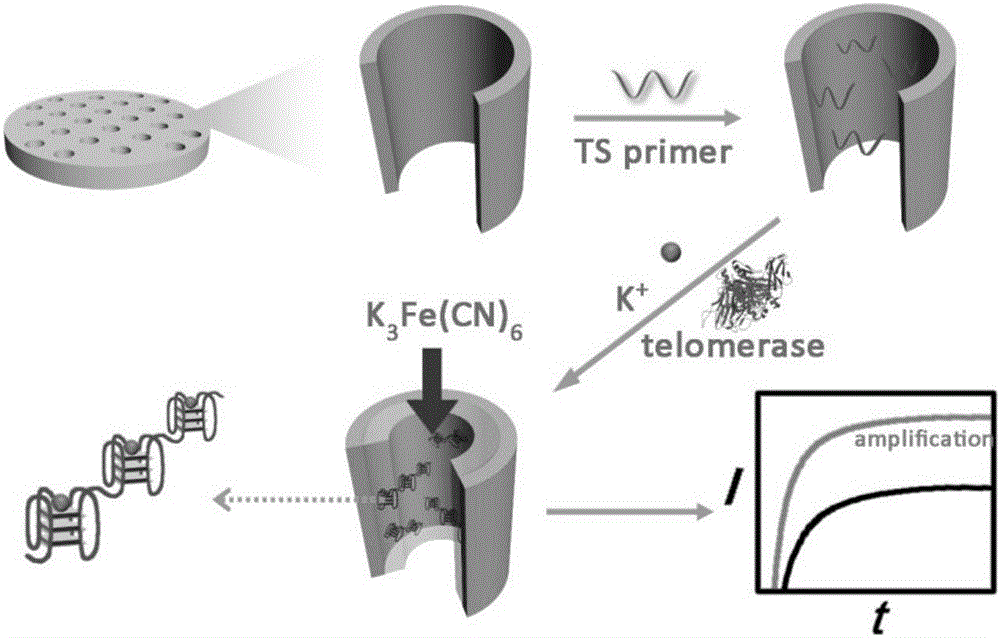
Method for quantitatively detecting telomerase activity based on nano pore channel and electrochemical sensing
ActiveCN105806912AAperture adjustableStable structureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTelomerasePower flow
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting telomerase activity based on a nano pore channel and electrochemical sensing.The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a telomerase recognition sequence is connected to the inner wall of a porous anodic alumina template or a polyethylene terephthalate film to serve as a primer; secondly, telomerase amplifies the primer to form a G-rich sequence; a G-quadruplex is formed in the presence of potassium ions; electrochemical detection is conducted on the current produced through indicating molecules of the nano pore channel by utilizing an electrochemical workstation.The method does not need complex material preparation and DNA probe marking, and can avoid the defects of high detection cost, complicated operation and poor reproducibility caused by the complex material preparation and DNA probe marking and has the advantages of being low in cost, quick, simple, convenient, high in sensitivity and good in accuracy.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Polyethylene terephthalate and polyurethane composite artificial blood vessel and preparation thereof
ActiveCN102008755AIncrease elasticityImprove mechanical propertiesNew-spun product collectionFilament/thread formingCell adhesionPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses a polyethylene terephthalate and polyurethane composite artificial blood vessel and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of biomedical engineering. The artificial blood vessel is prepared from polyethylene terephthalate and polyurethane by means of an electrostatic spinning device with a stirrer. The prepared artificial blood vessel is a tubular object witha microporous structure. The polyurethane added in the artificial blood vessel can improve the elasticity of the blood vessel under the condition of not damaging the strength of the polyethylene terephthalate material, increase the compliance of the artificial blood vessel and achieve the requirements of clinical use. The polyethylene terephthalate and polyurethane composite artificial blood vessel has the advantages of high strength, large elasticity and compliance, good biocompatibility, strong anticoagulant property and large cell adhesion, and can meet the requirements of the clinical useof the artificial blood vessels with large diameter and small diameter. The preparation process is simple and practical, and applicable to preparing the artificial blood vessels with various different requirements on mechanical properties.
Owner:宁波贝昂生物材料有限公司
Process for the production of polyethylene terephthalate copolyester, copolyester obtained thereby and its use and catalyst useful in the process
InactiveCN1961022AImprove productivityMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate
The present invention relates to a process for the production of polyethylene terephthalate copolyester from terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and ethylene glycol, comprising the steps of: a) preparing a catalyst composition comprising a zinc compound being present such that the elemental zinc content is in a range of about 50 to about 500 ppm, preferably about 200 to about 500 ppm, most preferably about 180 to about 260 ppm, based on the copolyester, b) placing the catalyst composition, terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and ethylene glycol in a vessel, and c) reacting the terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and ethylene glycol in an esterification step and a polycondensation step to obtain polyethylene terephthalate copolyester; to the copolyester obtained thereby and its use, as well as to a catalyst composition suitable in the inventive process.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Method for producing ribbon-like filaments through waste PET (polyethylene terephthalate)
InactiveCN103305958AIncrease melt viscosityImprove toughnessMelt spinning methodsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses a method for producing ribbon-like filaments through waste PET (polyethylene terephthalate), belonging to the field of high molecular material processing. The method comprises the steps of: tackifying and toughening the waste PET in a reactive extrusion manner, directly extruding ribbon-like filaments through a special filament dividing mould, cooling the ribbon-like filaments, drafting the cooled ribbon-like filaments through a water bath heating drafting method to orientate the ribbon-like filaments, sizing the oriented ribbon-like filaments through an electrical inductance heating roller, cooling the sized ribbon-like filaments through a cooling roller, and coiling the cooled ribbon-like filaments. The prepared PET ribbon-like filaments have properties of good toughness, drafting and the like, the problem that PET ribbon-like filaments are liable to break when being drafted in the production process is effectively solved, and the breaking strength of the produced PET ribbon-like filaments is higher than 50MPa, so that the PET ribbon-like filaments can be applied to the field of production of high-performance woven bags and container bags.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
PET lytic enzyme mutant, coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a PET (polyethylene terephthalate) lytic enzyme mutant, a coding gene and application thereof. The PET lytic enzyme mutant is represented by an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO.8 or SEQ ID NO.9 obtained by performing point mutation on an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO.7. A lytic enzyme gene of escherichia coli is subjected to directed evolution; by site-specific mutagenesis, the PET lytic enzyme mutant is obtained. According to the amount of decomposition products within the same time, the enzyme activity of the PET lytic enzyme mutant is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing diisooctyl terephthalate through catalyzing alcoholysis of polyethylene terephthalate by choline eutectic ionic liquid
InactiveCN108484392APreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionPolyethylene terephthalate glycolReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing diisooctyl terephthalate (DOTP) through catalyzing the alcoholysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by a novel catalyst. The method is characterizedin that a choline eutectic ionic liquid is used as the alcoholysis catalyst, and choline chloride is used as a hydrogen bond donor and a metal salt is used as a hydrogen bond acceptor during the synthesis of the catalyst. Isooctanol is used as a solvent in the reaction process, and the PET is alcoholyzed under the following conditions: a molar ratio of the above raw material to the solvent of 1:2.5 to 1:8, a reaction temperature of 145-185 DEG C, normal pressure and a catalyst using amount being 0.5-10% of the mass of the raw material, for 30-180 min. The method has the advantages of simple preparation of the catalyst, low cost, mild reaction conditions, short reaction time, high efficiency, high PET conversion rate, high selectivity of the target product, and green and environmentally-friendly reaction process.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-molecular-weight polyethylene terephthalate-lactic acid copolymer
The invention discloses a high-molecular-weight polyethylene terephthalate-lactic acid copolymer, which is formed mainly by copolymerization of terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate and ethylene glycol and lactic acid, wherein the molar ratio of the terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate to the ethylene glycol is 1:0.5-3; the molar ratio of the terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate to the lactic acid is 1:0.1-2; the weight-average molecular weight of the copolymer is 10,000 to 300,000; the intrinsic viscosity of the copolymer 0.3-2.0dl / g; the glass-transition temperature of the copolymer is 50 to 90 DEG C; and the melting point of the copolymer is 110 to 255 DEG C. The copolymer has a high molecular weight and biodegradability, can be used as an environmentally-friendly novel material or a compatibilizer directly and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:TORAY FIBER RES INST(CHINA) CO LTD
Transparent, low-flammability, UV-resistant film made from a crystallizable thermoplastic, its use and process for its production
InactiveUS7138176B2Good orientationMaintain good propertiesGain controlSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplastic2-hydroxybenzophenone
The present invention relates to a transparent, low-flammability, UV-resistant, oriented film made from a crystallizable thermoplastic and having a thickness of from 5 to 300 μm. The film comprises at least one UV stabilizer and at least one flame retardant, and at least the flame retardant, and preferably also the UV stabilizer, is fed directly as a masterbatch to the crystallizable thermoplastic during production of the film. The film may have one or more layers, and the UV stabilizer may have been selected from the group consisting of the 2-hydroxybenzophenones, the 2-hydroxybenzotriazoles, the organonickel compounds, the salicylic esters, the cinnamic ester derivatives, the resorcinol monobenzoates, the oxanilides, the hydroxybenzoic esters, the sterically hindered amines and triazines, and the flame retardant may be an organic phosphorus compound, in particular an organic phosphorus compound soluble in polyethylene terephthalate.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Multilobal profiled polyethylene terephthalate fiber FDY (fully-drawn yarn) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106811821AReduce extrusion swelling effectReduce surface tensionMelt spinning methodsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolyethylene terephthalate glycolBisphenol A
The invention belongs to the field of polyethylene terephthalate spinning and relates to a multilobal profiled polyethylene terephthalate fiber FDY (fully-drawn yarn) and a preparation method thereof. Polyethylene terephthalate refers to modified polyethylene terephthalate, and a molecular chain of the modified polyethylene terephthalate consists of a terephthalic acid chain segment, an ethylene glycol chain segment and a rigid structure chain segment, wherein the rigid structure chain segment is 2,6-naphthalic acid segment, a bisphenol A chain segment, a 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol chain segment, a 2,2-biphenyldicarboxylic acid chain segment, a 4,4-biphenyldicarboxylic acid chain segment or a p-hydroxybenzoic acid chain segment, a molar ratio of the rigid structure chain segment to the terephthalic acid chain segment is 0.02-0.05:1, and a die-swell ratio of a modified polyethylene terephthalate melt is 1.25-1.35. The multilobal profiled polyethylene terephthalate fiber FDY is excellent in shape preserving effect.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGKE ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
BOPP (biaxially-oriented polypropylene) insulating release film
InactiveCN105440450AGood compatibilityImprove insulation performancePolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses a BOPP (biaxially-oriented polypropylene) insulating release film. The BOPP insulating release film comprises BOPP, boron nitride, epoxy resin 6101, phenol-formaldehyde resin 2124, melamine, furfural furfuryl alcohol resin, polyacrylamide, polyamide 66, nano-alumina, mica, talc, poly(vinyl butyral), FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene), PBT (polybutylece terephthalate), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), methoxypolyethylene glycols, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), polymethylmethacrylate, polyphenylene sulfide, organic montmorillonite, paraffin, polyetheretherketone fiber, nano-silica, an antioxidant 1010, a light stabilizer 622, nano-TiO2, PP-g-MAH (maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene), an antifoaming agent, a thickener and a coupling agent. The BOPP insulating release film has excellent insulation, water resistance, corrosion resistance, temperature resistance, weather resistance, adhesiveness as well as heat dissipation and energy storage functions.
Owner:TAICANG CUSTOM NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
PET degradation biocatalyst and application thereof
ActiveCN111100835AAchieve degradationImprove degradation efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Aiming at the problems of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic degradation in the prior art, the invention provides a novel PET degradation biocatalyst and a construction method thereof. The PET degradation whole-bacterium catalyst is obtained by expressing PET enzyme in a heat-resistant strain; the PET enzyme has a sequence of SEQ NO.1 or a sequence with similarity of 99% with the sequence ofSEQ NO.1; and the heat-resistant strain is clostridium thermofibrillae. The construction method of the PET degradation whole-bacterium catalyst comprises the following steps: (1) expressing PET degradation enzyme by a plasmid; (2) expressing PET degradation enzyme by a genome; and (3) expressing PET degradation bodies. The PET degradation whole-bacterium catalyst overcomes the problem of feedbackinhibition, not only has degradation efficiency obviously higher than a known whole-bacterium biodegradation system, but also has a culture condition free of aeration and stirring as an anaerobic microorganism, so that process cost is obviously reduced. In addition, simultaneous degradation of fibers and PET in a blended fabric is realized through a one-pot method; the reaction temperature is low, early-stage separation of fibers is not needed, and an additional carbon source is not needed in a degradation process, so that the PET degradation whole-bacterium catalyst has remarkable economy and efficiency.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of 1,3-butanediol modified PBTPET (Polybutylece Terephthalate Polyethylene Terephthalate) copolymer fiber
InactiveCN101824140ALow melting pointReduce crystallinityFlame-proof filament manufactureMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberP-Toluenesulfonic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of a 1,3-butanediol modified PBTPET (Polybutylece Terephthalate Polyethylene Terephthalate) copolymer fiber. The preparation method is characterized in that raw materials for fiber synthesis comprise terephthalic acid, butanediol, ethylene glycol and 1,3-butanediol; and the combination of p-toluenesulfonic acid and stannous chloride is used as a catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out an esterification reaction on the terephthalic acid and dihydric alcohol to form a prepolymer; and (2) carrying out a condensation polymerization reaction on the prepolymer in the presence of high temperature and high vacuum. Compared with a PBT / PET copolymer fiber, the prepared 1,3-butanediol modified copolymer fiber has higher inherent viscosity and lower terminal carboxyl group number, and the dye-uptake of the modified fiber is also obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGSU YINGXIANG FIBER
Process for separating and drying thermoplastic particles under high pressure
ActiveUS8079158B2Drying using combination processesDrying solid materials without heatLiquid temperatureSlurry
A process for feeding a slurry of thermoplastic synthetic polymer particles such as polyethylene terephthalate homopolymers and copolymers in combination with a liquid such as water at a liquid temperature greater than the normal boiling point of the liquid, under a pressure greater than the vapor pressure of the liquid at the liquid temperature, into a separation zone such as a centrifugal dryer, and within the separation zone:a. separating the liquid from the particles, andb. drying the particles;while under a high pressure equal to or greater than the vapor pressure of the liquid. There is also provided a process for decoupling the dried particles from the separation zone to an atmosphere having a pressure less than the vapor pressure of the liquid while maintaining the vapor pressure of the particles prior to decoupling equal to or above the vapor pressure of the liquid at the liquid temperature.
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
Method for depolymerizing waste polyester bottle
ActiveCN102532591AReduce the possibilityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationPlastic recyclingSodium bicarbonateIce water
The invention provides a method for depolymerizing a waste polyester bottle, comprising the following steps of: adding the waste polyester bottle, ethylene glycol, sodium bicarbonate and distilled water into a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction kettle according to a certain proportion and reacting at a temperature of 170-200 DEG C for 15-40 minutes to depolymerize the waste polyester bottle into sodium terephthalate, ethylene glycol and other byproducts; then, adsorbing by active carbon and de-coloring; acidifying by hydrochloric acid, and cooling and crystallizing by ice water; filtering, washing and drying to obtain terephthalic acid; and carrying out rotary evaporation on a filtering solution to obtain the ethylene glycol to be repeatedly utilized. According to the method for depolymerizing the waste polyester bottle, by utilizing a mixed reaction system, the depolymerization temperature is reduced, the reaction time is shortened, the energy source consumption is reduced, the equipment investment is reduced, the depolymerization rate of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) reaches to be more than 99% and the yield of the target product, namely terephthalic acid, is more than 94%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Polyester polyols with increased clarity
Polyester polyols, processes for making them, and applications for the polyols are disclosed. Some of the polyols comprise recurring units from a digested thermoplastic polyester (e.g., recycled polyethylene terephthalate), a diol, an optional hydrophobe, and a clarifier. The clarifier, which in some cases is a bisphenol, bisphenol alkoxylate, bisphenol polycarbonate, sulfonyl diphenol, or sulfonyl diphenol alkoxylate, helps the polyol remain clear for weeks or months after its preparation. In some aspects, the clarifier is a monophenol, bisphenol, or poly-phenol having two or more phenylene rings wherein at least two of the phenylene rings lack a common molecular axis. The clarifier may also be an alkylated phenol, an epoxy resin, an epoxy novolac resin, a diphenylmethane, or a tris(aryloxy)phosphate. The polyols are valuable for formulating a variety of polyurethanes and related products—including polyurethane dispersions, flexible and rigid foams, coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers—and they provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Preparation method of graphene-modified polyethylene terephthalate (PET) blend fiber
ActiveCN111663199AImprove antistatic performanceGood antibacterialElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMelt spinning methodsFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to the field of chemical fiber. Aiming at the problem of poor dispersibility in the graphene-modified fiber process in the prior art, the invention discloses a preparation methodof a graphene-modified polyethylene terephthalate (PET) blend fiber. The preparation method of the graphene-modified PET blend fiber comprises the following preparation steps of (1) modifying graphene by using a cationic modifier; (2) preparing graphene-modified slices: blending the modified cationic graphene, a modifier and PET slice powder; (3) melting: melting PET slices and the graphene-modified slices; (4) blending: spraying two spinning melts from a composite spinneret so as to form the blend fiber; and (5) carrying out aftertreatment: cooling, oiling, stretching for setting and windingthe blend fiber. Through improving the dispersibility of a graphene slice layer, the uniformity of the graphene in the composite fiber is improved, the graphene-modified PET composite fiber with an excellent performance is obtained, and the fiber has a favorable mechanical property; and through spinning the graphene masterbatch slices and the PET slices through the composite spinneret, the four-leaf clover-shaped composite fiber is prepared.
Owner:浙江双兔新材料有限公司
Novel titanium catalyst for polyester and preparation method of novel titanium catalyst
ActiveCN110643026AExcellent water resistanceGood colorTitanium organic compoundsPolyesterPolymer science
The invention provides a novel titanium catalyst for polyester and a preparation method thereof. The novel titanium catalyst comprises the following components: titanate, complex ligands with different functionality degrees, a stabilizer, a solvent and a catalyst, wherein the mass percentage of titanium element is 0.1-20%, the molar ratio of difunctional ligands to trifunctional ligands to tetrafunctional ligands is (1-10):(0-5):(0-5), and the molar ratio of titanium atoms to the ligands in the solvent is (4:1)-(1:20). The titanium catalyst prepared by the method has excellent water resistance, and the catalyst can be dissolved in ethylene glycol and then can be conveniently added into a reaction system during industrial production. A polyester product polymerized by the titanium catalystprepared by the method has good color and luster, and is suitable for bottle-grade polyethylene terephthalate (PET) production with high requirements on color and luster.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES PACKAGING MATERIALS CO LTD
Method of obtaining terephthalic acid from waste polyethylene terephthalate
PendingUS20210017353A1Low costReduce investmentPreparation from carboxylic acid saltsProductsPolyethylene terephthalate glycolDepolymerization
Method of obtaining terephthalic acid from waste polyethylene terephthalate by depolymerization with microwave heating of the reaction mixture, and its subsequent purification, wherein, after depolymerization, the mixture of products of the depolymerization reaction is mixed with water, a solid phase is separated from the formed mixture, the obtained solution is extracted with water-immiscible organic solvent and, after separation of phases, dissolved impurities are removed from the aqueous phase by its contact with a sorbent that is then separated, wherein, after separation of the sorbent, terephthalic acid is precipitated from the solution by its acidification and subsequently separated from the formed suspension.
Owner:JBPV SRO
Display touch apparatus
ActiveCN105988619AReduce reflectivityNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingPolyethylene TerephthalatesHuman–computer interaction
The invention relates to the field of touch technology, and discloses a display touch device, which includes a display component, a touch component, and an anti-glare film. The anti-glare film is located between the display component and the touch component, wherein the total glare value of the anti-glare film and the display component is between 60 and 80. The above-mentioned anti-glare film may be fogged polyethylene terephthalate, and its thickness is between 100 microns and 300 microns. The invention does not need to greatly change the manufacturing process, and can effectively reduce the reflectivity of the display touch device.
Owner:TPK TOUCH SOLUTIONS (XIAMEN) INC
Composite material capable of slowly releasing antibacterial components, preparation method thereof and antibacterial slow-release bag
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of antibacterial film materials, and particularly discloses a composite material capable of slowly releasing antibacterial components, a preparation method thereof and an antibacterial slow-release bag. The preparation method of the composite material capable of slowly releasing the antibacterial component comprises the following steps: S11, mixing a porous adsorption material with antibacterial essential oil to obtain a porous adsorption material adsorbed with the essential oil; and S12, mixing the porous adsorption material adsorbed with the essential oil with the gelatinized starch to obtain the antibacterial slow-release material. The composite material capable of slowly releasing the antibacterial component prepared by the method can continuously release the essential oil antibacterial component for more than 4 months, and in the best embodiment, the continuous release time of the essential oil antibacterial component reaches 9 months. Furthermore, the composite material capable of slowly releasing the antibacterial components is wrapped in a breathable film bag made of PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PE (polyethylene), PA (polyamide) or PP (polypropylene) to prepare the antibacterial slow-release bag, and the antibacterial slow-release bag can be widely applied to various environments needing antibiosis.
Owner:广州暨明科技有限公司
Application of ionic liquid in polyethylene terephthalate composite fiber
ActiveCN104073910AImprove antibacterial propertiesGood antibacterial effectNon-woven fabricsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses an application of an ionic liquid in polyethylene terephthalate composite fiber. The ionic liquid is taken as an antibiotic additive and applied to the polyethylene terephthalate composite fiber. The polyethylene terephthalate composite fiber with the added ionic liquid shows excellent inhibitory and bactericidal characteristics to staphylococcus aureus of gram-positive bacterium and escherichia coli of Gram-negative bacterium respectively. An antimicrobic polyethylene terephthalate composite fiber thin film provided by the invention can be applied to the fields of medical science, biology, environmental protection, spinning and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JAVA SPECIALTY CHEM CO LTD
Antibacterial chitosan-based hemostatic patch
ActiveCN112791223AAdhesiveStrong water absorption and retention capacitySurgical adhesivesFibre typesPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene Terephthalates
The invention discloses an antibacterial chitosan-based hemostatic patch, which comprises a back lining layer, a hemostatic layer and a protective layer which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top; the back lining layer is a base material prepared from polypropylene or polyethylene terephthalate, and an adhesive is coated on the back lining layer; the hemostatic layer comprises a non-woven fabric on the lower side and a composite hemostatic material on the upper side, and the composite hemostatic material is composite hydrogel prepared from modified chitosan, polyethylene glycol 2000, gelatin, xanthan gum, a tea polysaccharide-nano-selenium compound, dopamine modified nano-silica and oleamide; and the protective layer is a PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) film. The antibacterial chitosan-based hemostatic patch provided by the invention is convenient to store, carry and use, does not stimulate wounds, has good antibacterial and anti-infection effects, can realize rapid blood coagulation through adhesion sealing and activation of a blood coagulation system, and can avoid the occurrence of side effects of vascular embolism.
Owner:HENAN YADU IND
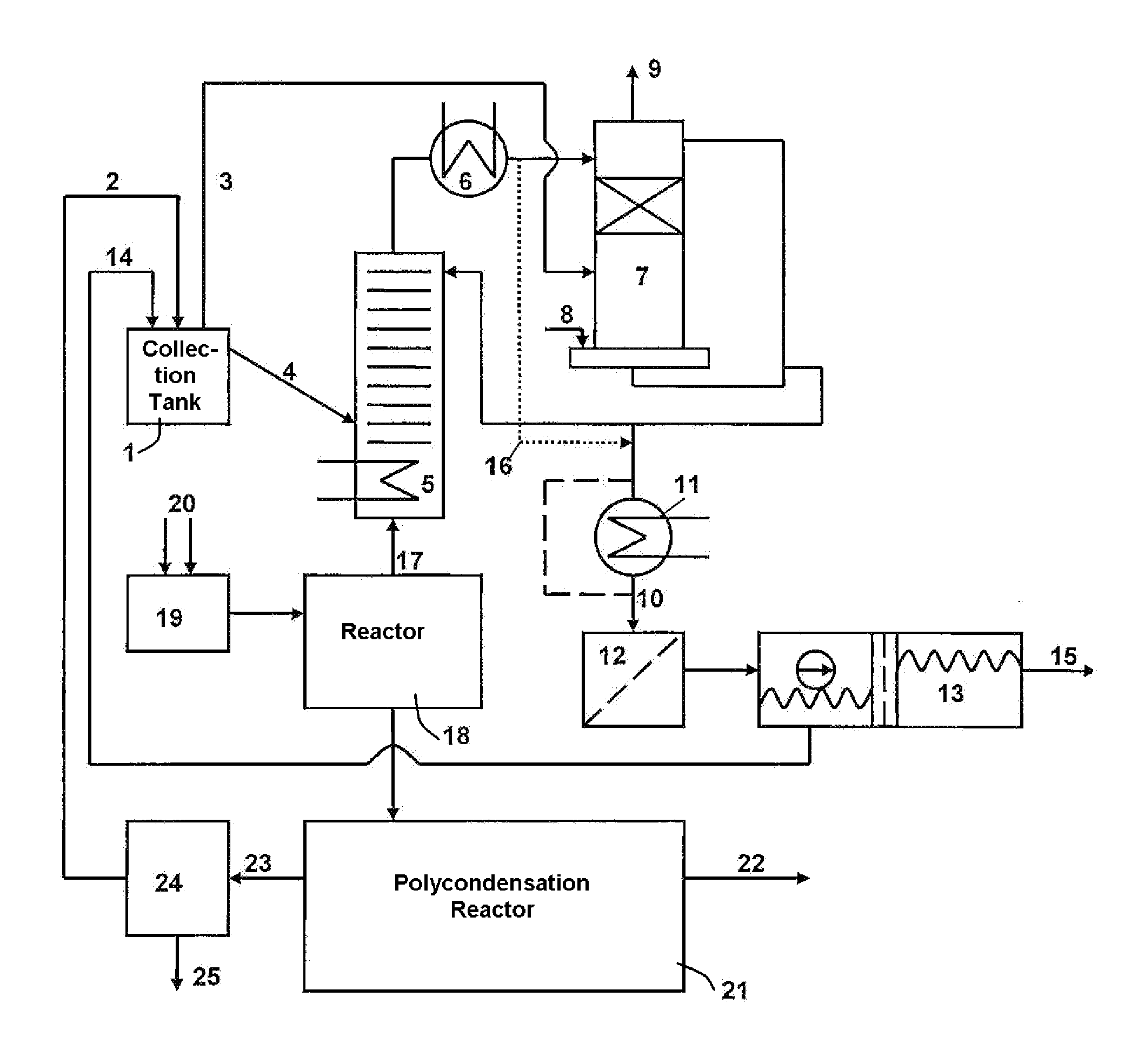
Apparatus for the recovery of ethylene glycol in the production of polyethylene terephthalate
ActiveUS20110097243A1Low costSave investmentOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
In an apparatus for the recovery of ethylene glycol in a polyethylene terephthalate(PET) production process water accumulating in the esterification reaction is mixed with a process fluid containing 2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane (MDO). The mixing is carried out in a tank upstream of a rectification column. Through the increase in the water content in the fluid, a shift in the reaction equilibrium takes place and consequently a cleavage of the 2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane present into ethylene glycol and acetaldehyde takes place. Following the cleavage reaction, the mixture is fed from the tank into a rectification column, whereby the ethylene glycol produced from the cleavage reaction is returned to the PET production process.
Owner:ZIMMER LURGI
68Ga-NODAGA-cyclic polypeptide FG01 targeting EphA2 receptor as well as preparation method and application of 68Ga-NODAGA-cyclic polypeptide FG01
ActiveCN114262362ANo obvious inhibitory effectGood inhibitory effectRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsPolyethylene terephthalate glycolCarboxyl radical
The invention relates to 68Ga-NODAGA-cyclic polypeptide FG01 of a targeted EphA2 receptor as well as a preparation method and application of the 68Ga-NODAGA-cyclic polypeptide FG01. The 68Ga-NODAGA-cyclic polypeptide FG01 forms an amido bond through an amino group of lysine in an amino acid sequence and a carboxyl group of serine, then an amino group at an amino terminal of the cyclic polypeptide FG01 and a coupling agent NODAGA-NHS are subjected to a condensation reaction, a chelating agent NODAGA in the cyclic polypeptide conjugate NODAGA-FG01 is chelated with 68Ga, and the 68Ga-labeled cyclic polypeptide conjugate is constructed. The invention verifies that the annular polypeptide FG01 has no obvious inhibition effect on tumor cells, indicates that the annular polypeptide FG01 has no cytotoxicity, and finds that the 68Ga-NODAGA-annular polypeptide FG01 of a targeted EphA2 receptor can be used for in-vivo imaging of EphA2 high-expression tumors, realizes molecular imaging of the EphA2 high-expression tumors such as non-small cell lung cancer by utilizing PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), and is widely used as a tumor molecular imaging agent.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com