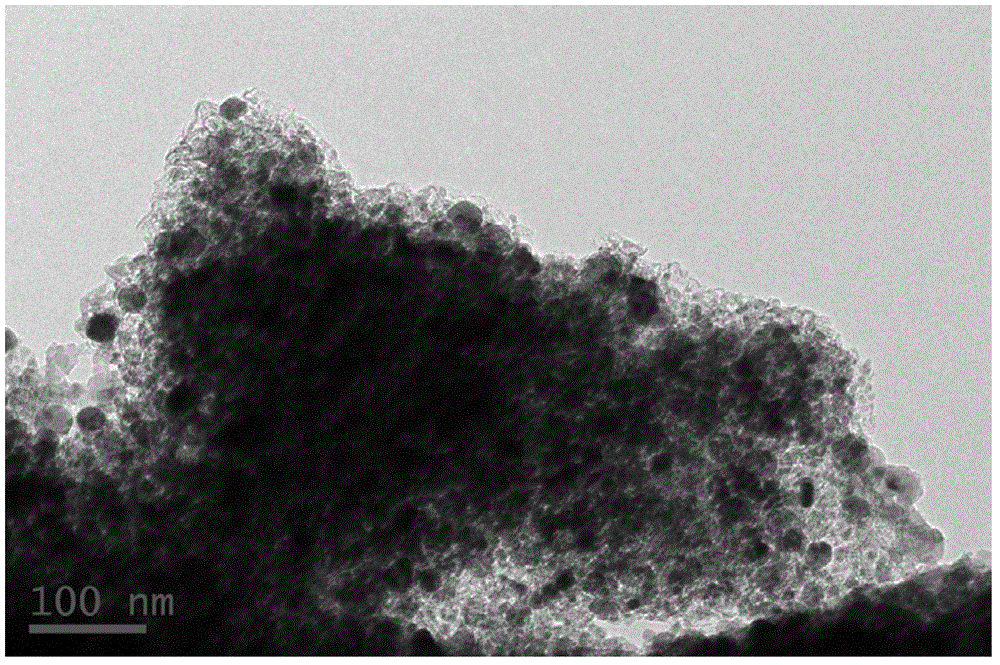
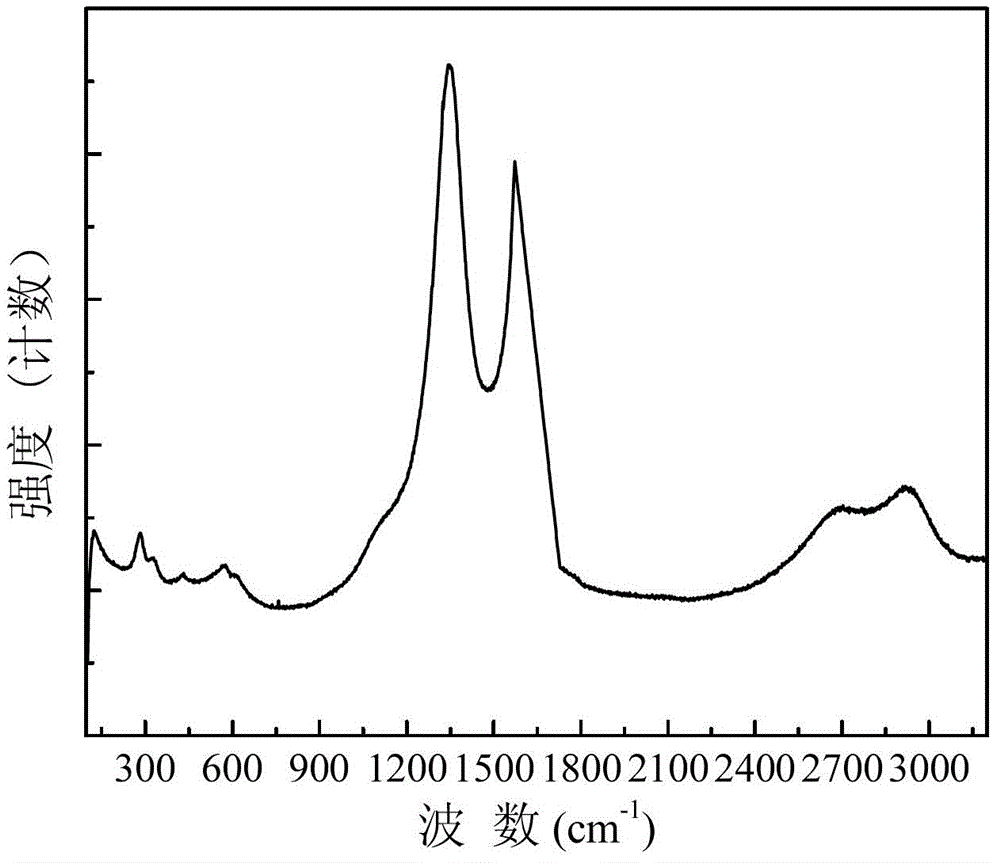
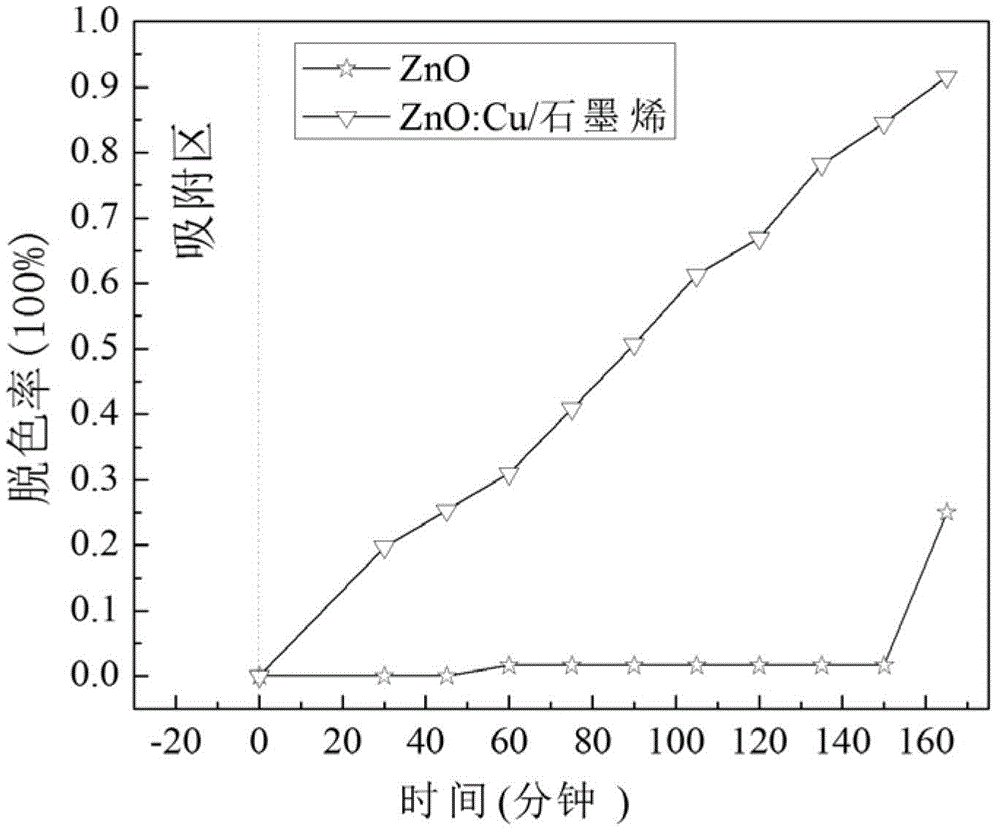
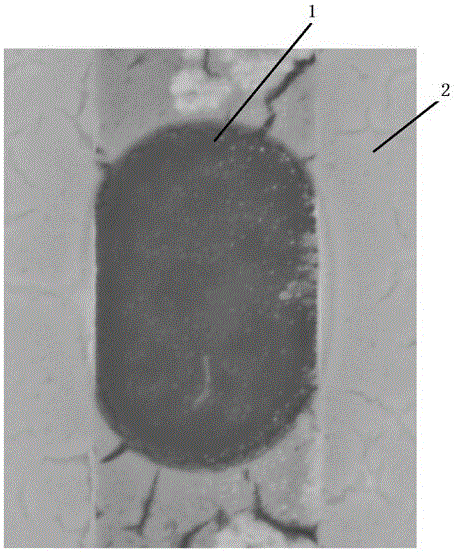
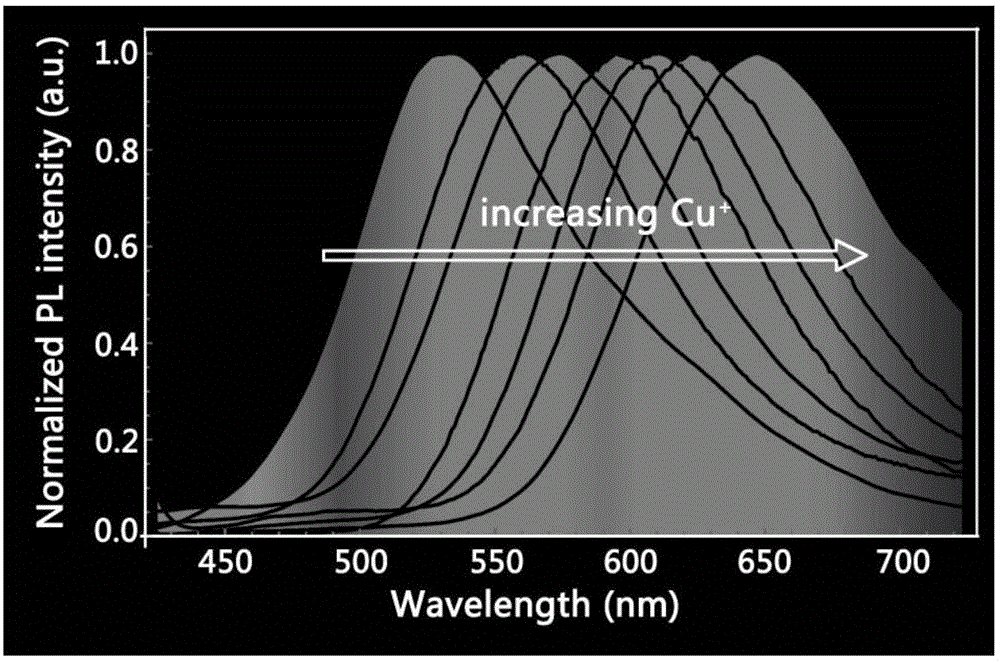
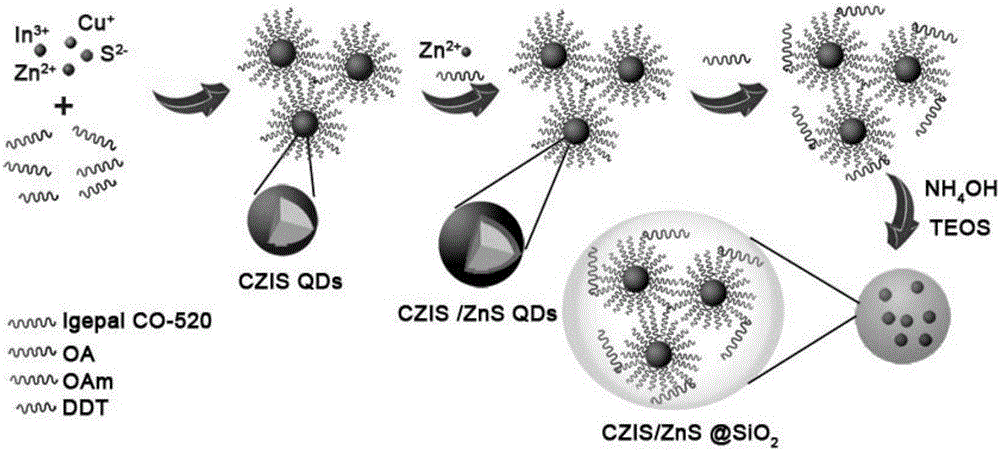
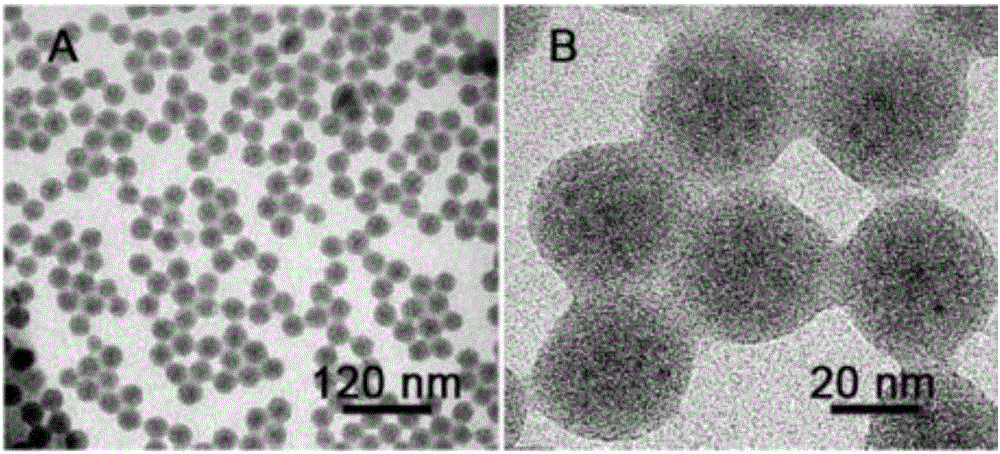
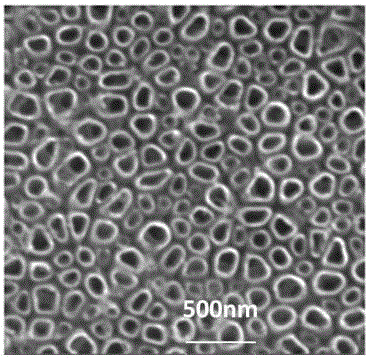
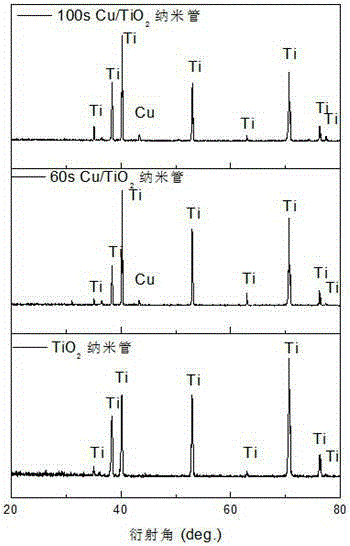
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Cu doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxide sulfide fluorescent powder for white light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof
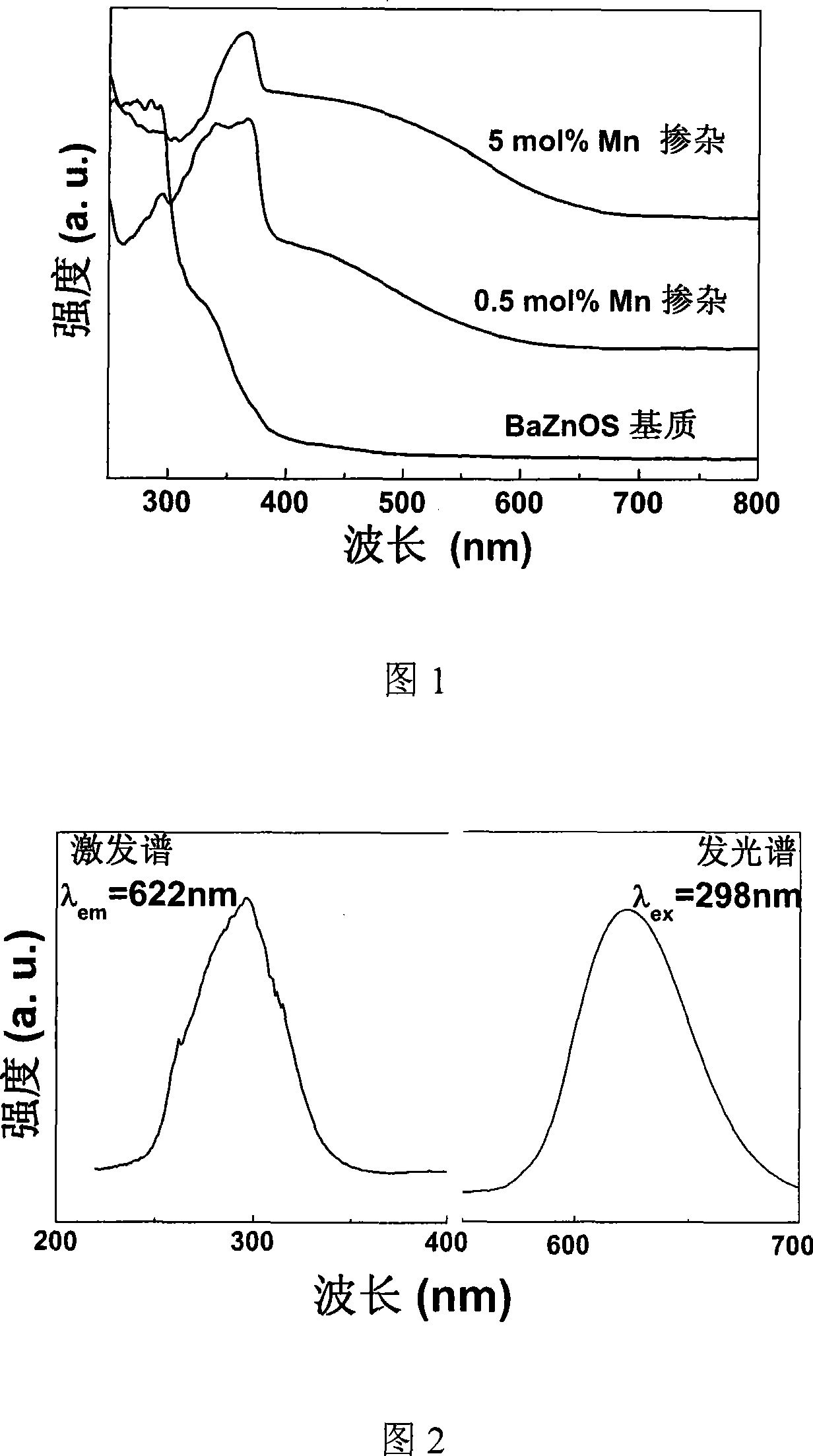
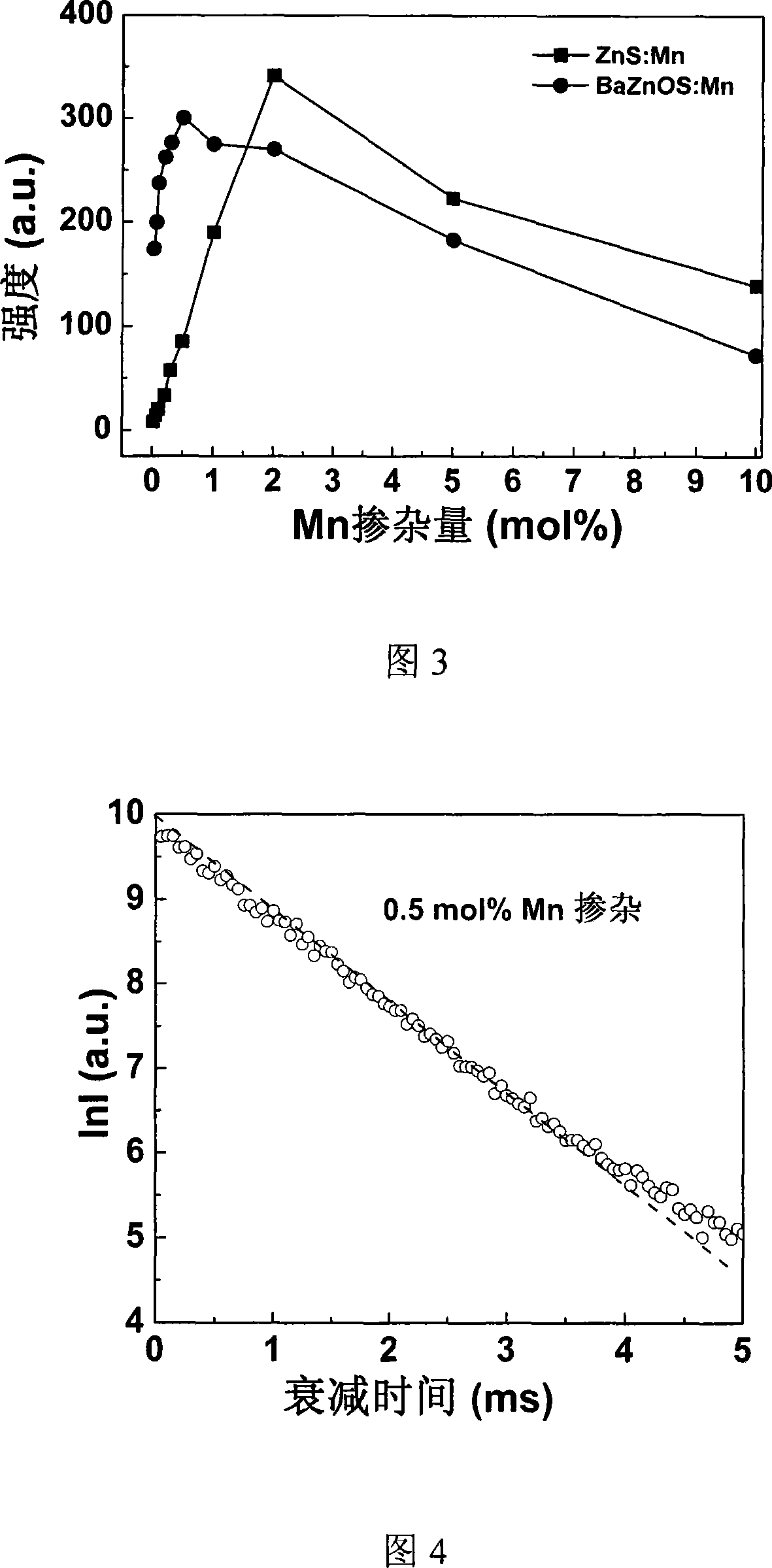
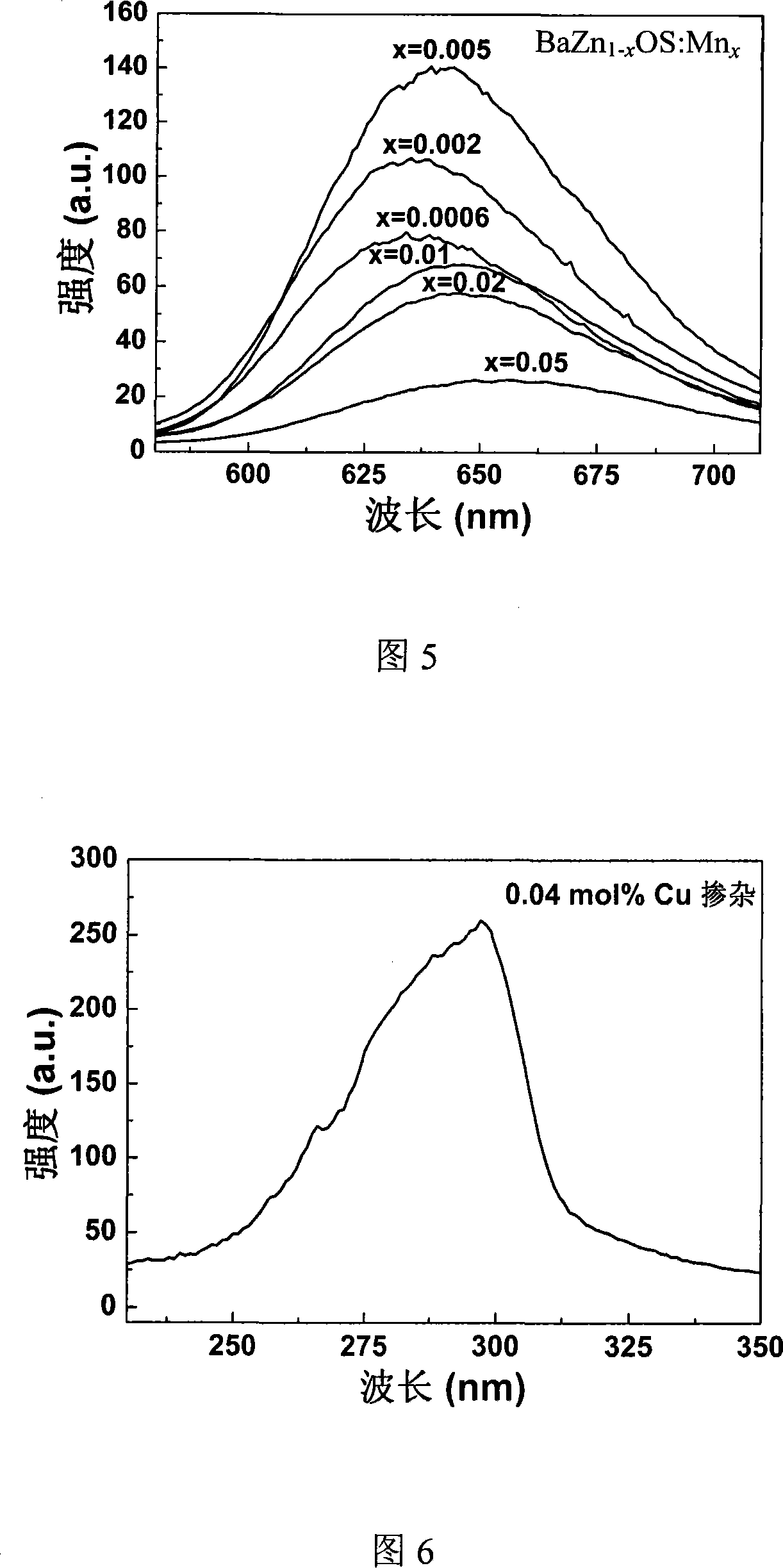
The present invention relates to one kind of doped fluorescent oxysulfide BaZnOS material for white light LED and its preparation process, and features that the fluorescent oxysulfide material Mn or Cu doped BaZnOS in the general expression of BaZn1-xOS:Mnx, where, x=0.0002-0.1, or BaZn1-yOS:Cuy, where, y=0.0002-0.0025. The Mn doped BaZnOS fluorescent material emits red fluorescence with peak at 624 nm, and the Cu doped BaZnOS fluorescent material emits blue fluorescence with peak at 430 nm. The doped BaZnOS fluorescent material is used in white light LED and relevant display and lighting devices. The present invention has unique design, facile materials, simple preparation process, stable chemical property and excellent fluorescence emitting performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Variable-resistance memory doped with ZrO2 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101577308ASimple structureEasy to prepareElectrical apparatusDigital storageHigh resistanceOxygen vacancy
The invention relates to a variable-resistance memory doped with ZrO2 and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of information memory. The memory comprises an upper electrode, a lower electrode and a resistance conversion memory layer that is arranged between the upper electrode and the lower electrode; the lower electrode is made of Al; and the resistance conversion memory layer is made of Cu doped with ZrO2. The variable-resistance memory doped with ZrO2 has simple structure, takes the Al with strong metal activity as the lower electrode, can absorb the oxygen ions in the ZrO2 in the resistance conversion memory layer and can form a large amount of oxygen vacancies in the ZrO2; when the device is firstly converted from high-resistance state to low-resistance state, the device needs not to be activated by a high operation voltage, thus eliminating the Forming process required when the variable-resistance memory is firstly converted from the high-resistance state to the low-resistance state.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermosensitive quantum dot material with core-shell structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103074068AIsolation of electronic processesNo mutual interferenceLuminescent compositionsQuantum dotRoom temperature
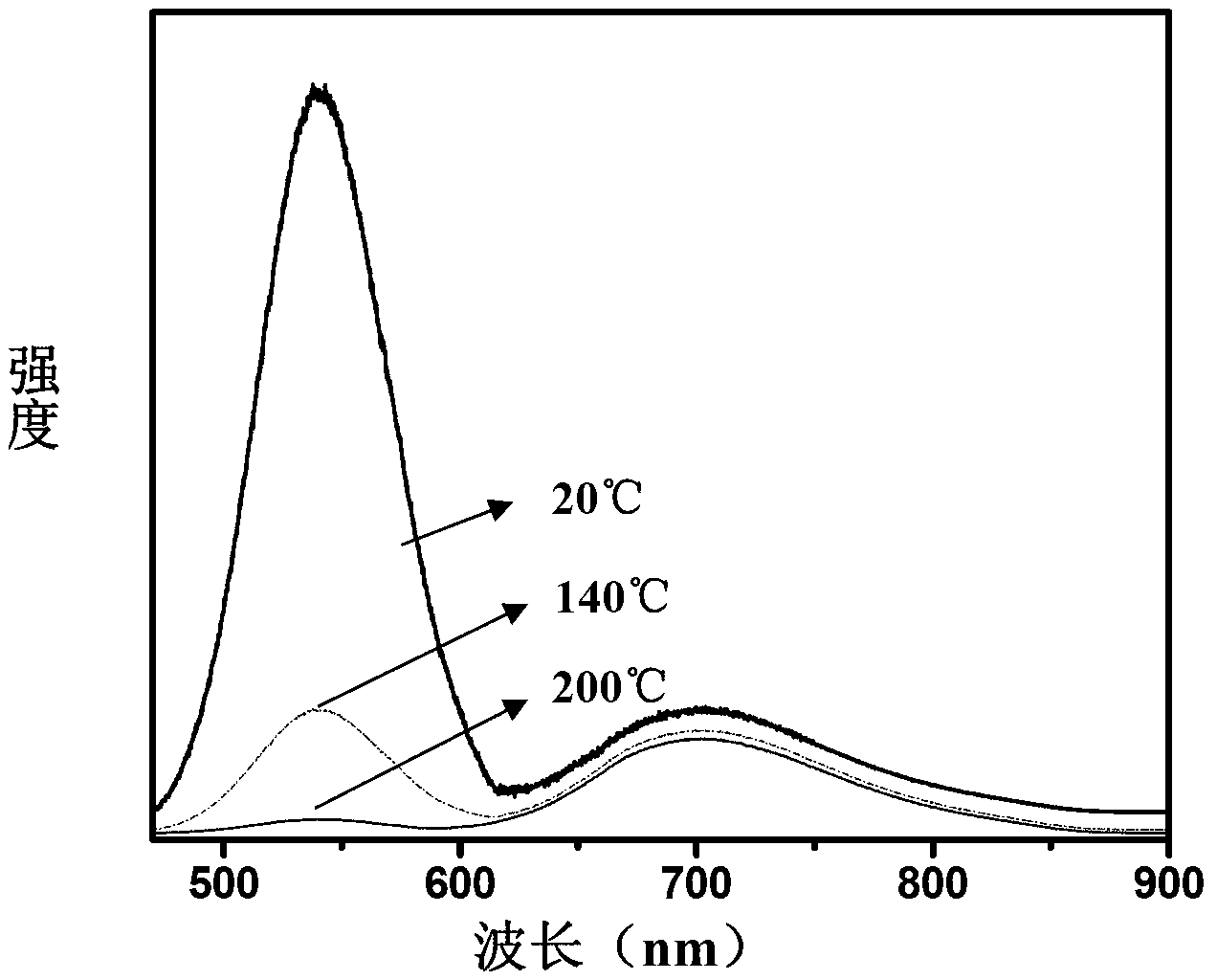
The invention discloses a thermosensitive quantum dot material with a core-shell structure and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of preparation of semiconductor nanomaterials. A core of a quantum dot structure comprises Cu-doped InP quantum dots; on the basis of the core, the quantum dots are coated with an II-VI semiconductor ZnS isolating layer for isolating an inner material from an outer material, then coated with a green light-emitting II-VI semiconductor CdSe nanocrystal shell layer, and finally coated with a ZnS protective layer to enable the CdSe layer to become more stable, thus forming Cu@InP / ZnS / CdSe / ZnS quantum dots ultimately. The quantum dots are highly sensitive to temperature, specifically at different temperatures, the thermosensitive quantum dot material can emit different colors of light: green light is emitted at room temperature, red light is emitted at 200 DEG C, while yellow light at different levels is emitted at an intermediate temperature; the quantum dots are stable in properties, uniform in size and good in dispersion; and after being coated with a shell layer, the quantum dots become perfect spherical particles.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cu-doping modified TiO2 photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103007938AAchieve recyclabilityHigh degree of controllabilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingCatalyst activation/preparationTio2 nanotubeElectrochemical anodization
The invention discloses a Cu-doping modified TiO2 photocatalyst. The Cu-doping modified TiO2 photocatalyst grows on a copper-titanium alloy wire or bar base body and has a two-dimensional structure on the peripheral surface of the copper-titanium alloy wire or bar base body, and the structural unit of the Cu-doping modified TiO2 photocatalyst is a Cu-doping TiO2 nanotube. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the Cu-doping modified TiO2 photocatalyst. The preparation method can be used for directly growing a Cu-doping TiO2 nanotube array which has the two-dimensional structure and higher visible light response property on the copper-titanium alloy wire or bar base body through an electrochemical anode oxidation method. The Cu-doping TiO2 photocatalyst with the two-dimensional structure, which is disclosed by the invention, enlarges the specific area of a TiO2 photocatalyst and effectively extends the forbidden bandwidth of the TiO2 photocatalyst, thereby outstandingly enhancing the adsorptive capacity on a degradation product and obtaining the high-efficiency absorption on a solar spectrum; and the Cu-doping TiO2 photocatalyst is conductive to improving the visible light catalytic activity and has the advantages of good recoverability of the TiO2 photocatalyst, simple process, low cost and high controllable degree.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Composite catalytic material capable of synchronously capturing and recycling carbon dioxide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102211026ACatalyst carriersMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsOrganic fuelCu doping
The invention discloses a composite catalytic material capable of synchronously capturing and recycling carbon dioxide and a preparation method thereof. In the preparation method, transition metal (Ni or Fe) catalytically graphitized or partially graphitized ordered mesoporous carbon is taken as a carrier, a Cu-doped nano semiconductor photocatalyst (TiO2, ZnO and the like) is taken as an active ingredient which is introduced by an immersion method, and the composite catalytic material can be prepared by the steps of drying, heat treatment and the like. The composite material has high CO2 adsorbing and capturing capacity under the environmental condition, and can catalyze (including photocatalysis) the CO2 to react with water to generate organic fuels with high added value, such as hydrocarbon, alcohol and the like.
Owner:李溪
Cu-doped ZnO/graphene composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103182307AUniform grain size distributionImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFiltrationHexamethylenetetramine
The invention discloses a Cu-doped ZnO / graphene composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mixing graphite oxide and a surfactant CTAB (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) in distilled water and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a first precursor reactant; dissolving zinc acetate and cupric acetate in the distilled water and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a second precursor reactant; dissolving hexamethylenetetramine and sodium citrate in the distilled water and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a third precursor reactant; after mixing the first precursor reactant and the second precursor reactant, carrying out ultrasonic treatment, then mixing the obtained product and the third precursor reactant, controlling reaction temperature in the range of 70 DEG C to 120 DEG C and performing reaction; sealing, naturally cooling, standing and carrying out extraction filtration to obtain filter residues; and after drying the filter residues, carrying out annealing treatment. According to the invention, addition of graphene reduces electron-hole compounding possibility; and meanwhile, introduction of Cu ions can be used as an ion trap to temporarily capture a charge carrier and inhibit electron-hole compounding so as to obviously improve photocatalytic efficiency of the product.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
In, Fe and Cu three-doping lithium niobate crystal and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101328612AImprove resistance to photodamageShort response timePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltIndiumReduction treatment
The invention relates to an In, Fe and Cu triple-doped lithium niobate crystal and a preparation method thereof, relating to the lithium niobate crystal and the preparation method thereof. The method solves the problems of slow response time and low light injury resistant ability of a doped lithium tantalite crystal prepared by the prior art. The In, Fe and Cu triple-doped lithium niobate crystal is prepared by Li2CO3, Nb2O5, Fe2O3, CuO and In2O3. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, required compositions are weighed; secondly, sintering is performed; thirdly, the crystal is grown by adoption of the crystal pulling method; fourthly, polarization treatment is performed; and fifthly, oxidation treatment or reduction treatment is performed, and the In, Fe and Cu doped lithium niobate crystal is obtained. The method dopes element indium (In), ferrum (Fe) and Copper (Cu) in the lithium niobate crystal, and obviously improves the light injury resistant ability and the response time of the lithium niobate crystal on the basis of preserving the prior superior performance of the lithium niobate crystal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Ordered Cu-doped nano-porous tin oxide sensing device
InactiveCN105067670AExcellent sensing performanceShort response timeMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCu dopingTin
The invention discloses an ordered Cu-doped nano-porous tin oxide sensing device. The sensing device is produced through the following steps: 1, producing an interdigital electrode-based graphene oxide film through adopting a spin coating method; 2, producing a device coated with a composite sensing film through a spin coating method, drying, and carrying out hot steam treatment; 3, removing a template from the device obtained in step 2; and 4, carrying out a reduction reaction on the device obtained in step 3 under an ultraviolet radiation condition to obtain the nano-porous tin oxide sensing device. The ordered Cu-doped nano-porous tin oxide sensing device has an excellent sensing performance, and the response time and the recovery time to low concentration H2S gas are shorter than 20s respectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Preparation method of Cu:ZnO/N:rGO composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN105521809AEasy to prepareGood repeatabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationUltraviolet lightsP–n junction
The invention discloses a preparation method of a p-n junction type Cu:ZnO / N:rGO composite photocatalyst formed by Cu doped ZnO nanorods and N doped rGO. The Cu:ZnO / N:rGO composite photocatalyst is formed by coating the Cu doped p-type ZnO nanorods with the N doped n-type rGO. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the Cu doped ZnO nanorods are prepared with a hydrothermal method firstly; then the Cu doped ZnO nanorods and GO are assembled with a hydrothermal reduction method to form a Cu:ZnO / rGO composite photocatalyst; finally, Cu:ZnO / rGO is subjected to annealing treatment in NH3 atmosphere for N doping, and the Cu:ZnO / N:rGO composite photocatalyst is obtained. The Cu:ZnO / N:rGO composite photocatalyst prepared with the method has very high photocatalytic activity in ultraviolet light and can inhibit photo-corrosion of ZnO, the stability of the photocatalyst is improved greatly, and the photocatalyst has great potential application values in the field of sewage treatment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Wiring technology of copper doped metal based on A1 material
InactiveCN1414623AImproved resistance to electromigrationGood hole filling abilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopperSilicon
A metal wring process of Cu doping based on Al material mainly uses the physical deposition method to deposit multiple layers of films with Ta, TaN, Ta, Al, TaN within the same equipment continuously, among which Al metal is added with Cu and Si atom to raise antielectromigration ability of Al metal wiring. At the bottom of Al layer, a composite blocking layer is to prevent Al and Cu from diffusing to silicon slice and media. The deposition of Al metal is in two steps of low temperature and high temperature with Al seed crystal layer deposited in low temperature having a good compactness and Al layer deposited in high temperature having a good porefilling ability and a good back-flow result. TaN layer above Al metal layer can be used as a blocking layer as well as top covering layer and antireflective layer of photoetching.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
Flexible CdTe thin film solar cell, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108493296AAchieve optimizationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesNew energyThin layer
The invention belongs to the photovoltaic new energy material and device field, and discloses a flexible CdTe thin film solar cell, and a preparation method and application thereof. The flexible CdTethin film solar cell, and the preparation method and application thereof are characterized in that a mature upper substrate structure CdTe cell preparation technology can be employed on a temporary metal substrate to obtain temporary metal substrate thin layer after completion of cell preparation, thus avoiding technical limitation of back contact preparation, Cu doping, CdS / CdTe heat treatment and the like, caused by the deposition sequence of functional layers, and being conductive to optimization of the cell preparation technology.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of Cu-doped BiVO4 porous nano-tube photocatalyst
InactiveCN107597134ALow costEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationN dimethylformamideAmmonium metavanadate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Cu-doped BiVO4 porous nano-tube photocatalyst, and aims to provide a preparation method of the Cu-doped BiVO4 porous nano-tube photocatalyst which has a simple synthetic process, is low in cost, is easy to control and is high in repeatability. The preparation method of the Cu-doped BiVO4 porous nano-tube photocatalyst disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: bonding macromolecular polyacrylonitrile with a N,N-dimethylformamide solvent by adopting an electrostatic spinning method so as to form electrostatic spinning nano-fibers; by using the electrostatic spinning nano-fibers as a template, using ethylene glycol and ethanol as a mixed solvent and using bismuth nitrate, copper sulfate and ammonium metavanadate as reaction precursors, performing solvent thermal reaction to obtain a mixture; washing and drying the mixture; then performing calcination treatment on the mixture in the air to finally obtain the Cu-doped BiVO4porous nano-tube photocatalyst. The Cu-doped BiVO4 porous nano-tube photocatalyst prepared by the invention has the characteristics of low cost of a product, easiness for control, high uniformity, good repeatability and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing multi-quantum-dot core-silicon dioxide shell composite structure and application of structure to LED
ActiveCN106318374AAvoid reabsorptionRealize white light LEDMaterial nanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsFluorescence1-dodecanethiol
The invention relates to a method for preparing a multi-quantum-dot core-silicon dioxide shell composite structure and application of the structure to an LED. By means of the method modification of chemical reagents such as oleic acid, 1-dodecanethiol and oleylamine, the Cu-doped Zn-In-S quantum dot structure of a multi-surface modifier is synthesized. By controlling and changing the doping amount of Cu, different quantum dot structures emitting fluorescence are synthesized. The quantum dot structures are wrapped in small silicon dioxide spheres with the diameter of tens of nanometers in a liquid-phase environment, the composite structure is placed on the surface of a GaN chip, and the color-adjustable quantum dot LED is successfully obtained. Besides, a quantum dot white light LED is obtained more easily by means of wide emission peaks of doped quantum dots.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
A cu-doped tio2-coupled semiconductor photocatalyst, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102274729AEfficient separationVisible light activeDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLight ActivitySpectral response
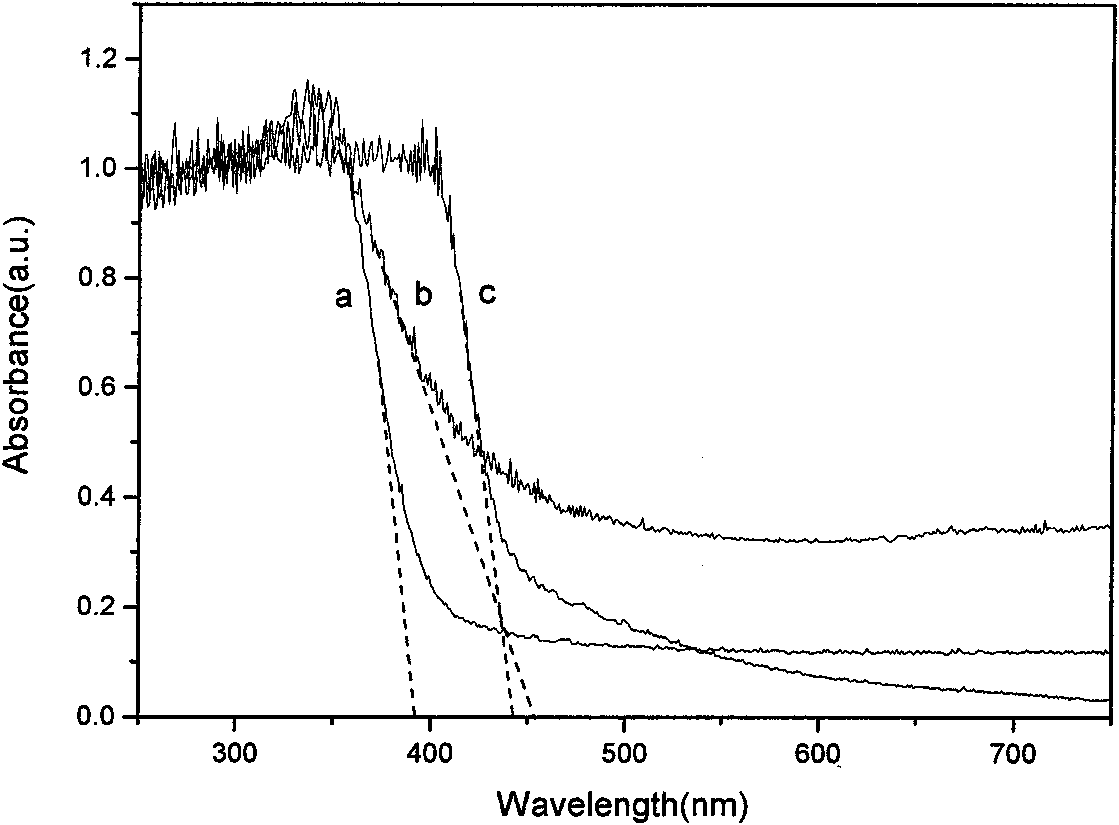
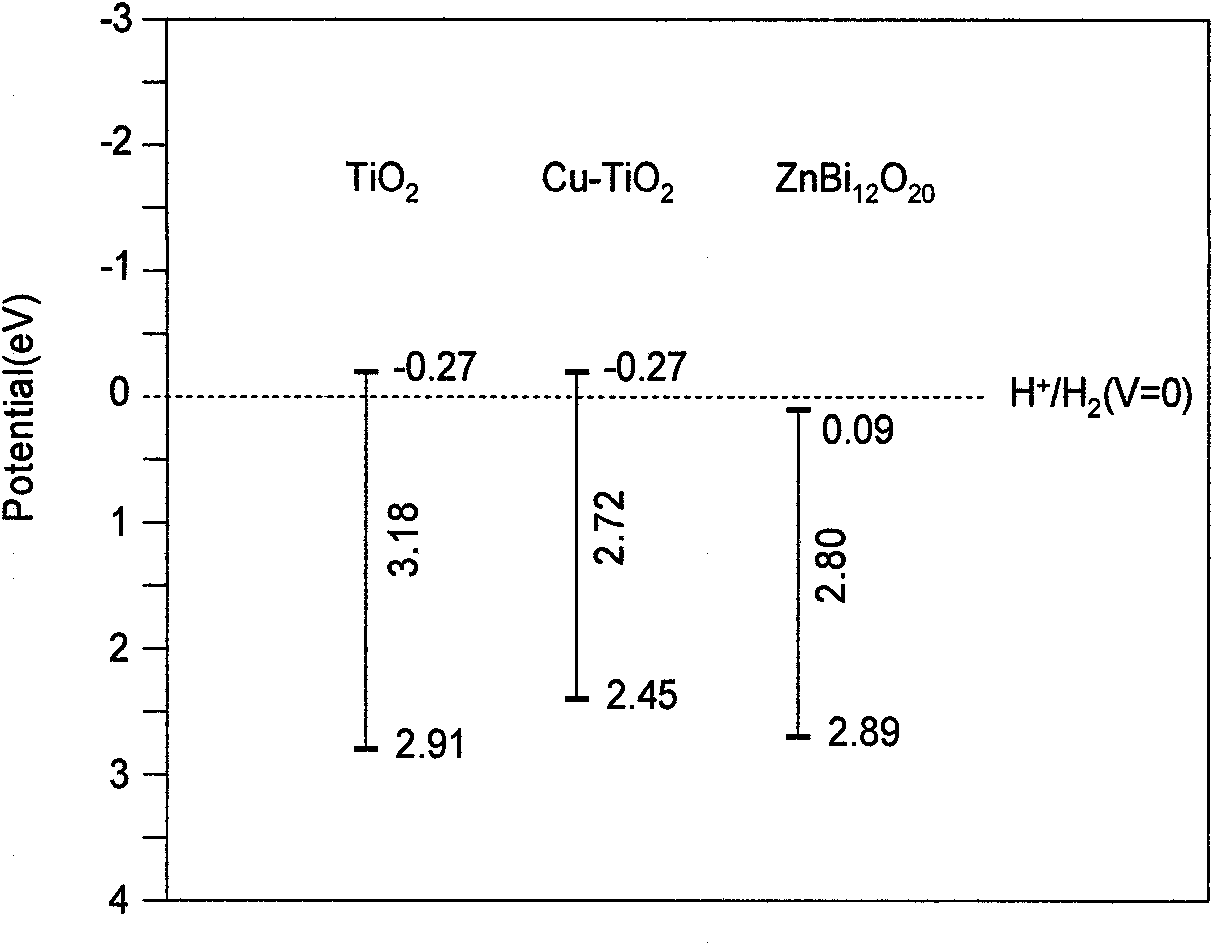
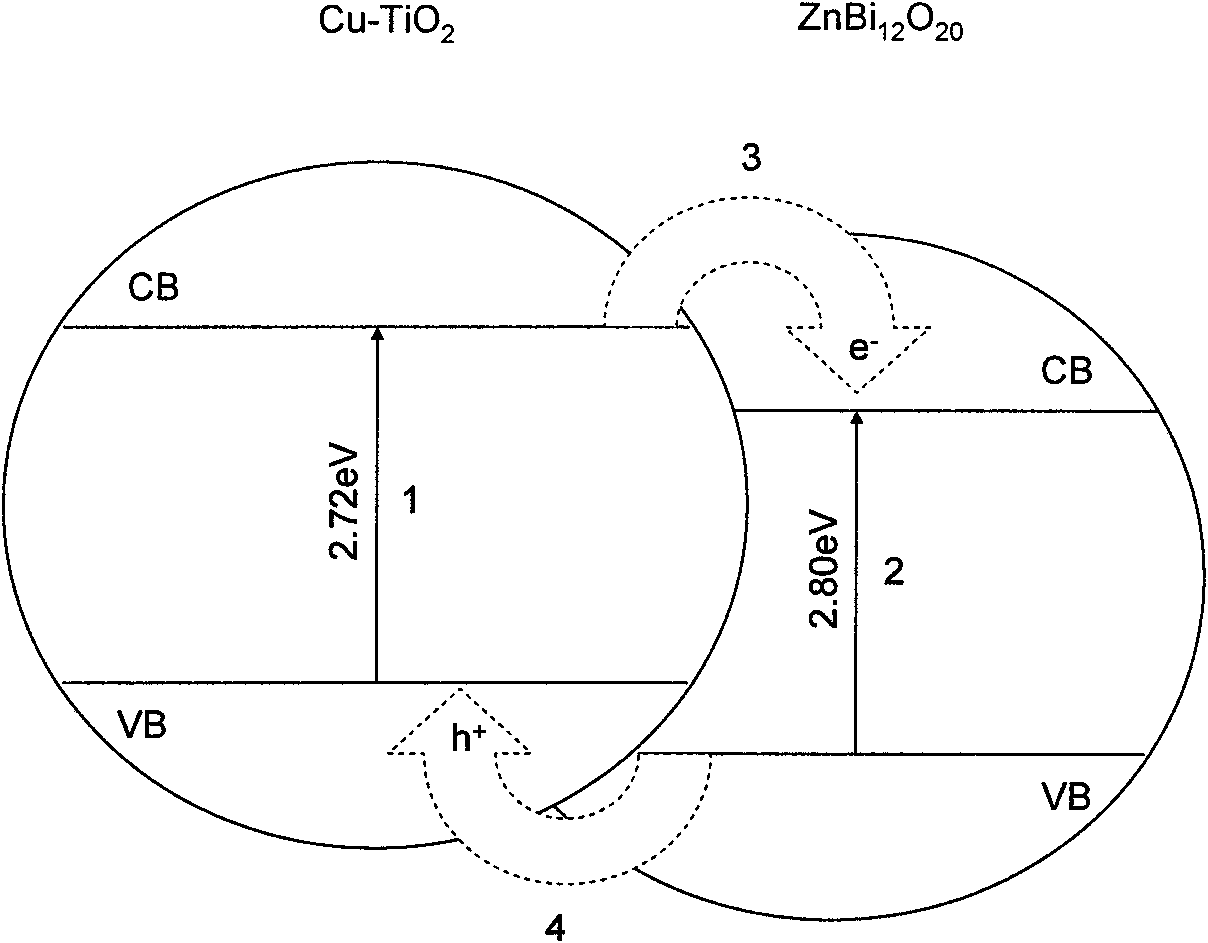
The invention discloses a Cu-doped TiO2 coupled semiconductor photocatalyst Cu-TiO2 / ZnBi12O20 belonging to the category of catalysts, which is used for catalytic conversion of gas phase organic pollutants. Compared with pure TiO2, the catalyst not only extends the spectral response range to the visible light region, but also greatly improves the quantum efficiency and catalytic activity. This is because ZnBi12O20 has a narrow band gap and is active in visible light; and after TiO2 is doped with Cu to form Cu-TiO2, it not only narrows the band gap, makes it have visible light responsiveness, but also modulates the energy level position, coupling with ZnBi12O20 , the energy levels of the two are matched, so that the photogenerated carriers are effectively separated, and the quantum efficiency and catalytic activity are greatly improved.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Method for preparing Cu doped TiN alloy layer on surface of titanium alloy
InactiveCN103243306AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingThermal insulationNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Cu doped TiN alloy layer on the surface of a titanium alloy, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, placing a base material and a target material into a plasma surface alloying furnace, carrying out pre-sputtering processing on the surface of the titanium alloy, and removing surface stains and a passivation layer; then, simultaneously, starting a source electrode and a workpiece voltage, carrying out sputtering on the source electrode through argon ions and carrying out deposition and diffusion on metal ions so as to form a Cu-containing alloy layer on the surface of the titanium alloy; and finally, feeding nitrogen gas into the furnace, and carrying out thermal insulation on the obtained product so as to form a Cu doped TiN alloy layer on the surface of the titanium alloy. A modified layer on the surface of a titanium alloy has a good sterilization effect, the surface hardness is significantly improved, and the wear resistance is significantly improved; and the method is simple in operation, good in repeatability and low in cost, and can be widely used for improving the antibacterial and wear-resisting properties of the surface of the titanium alloy.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Simple and convenient preparation method of Cu-doped Co9S8 nanotube array for supercapacitor
PendingCN109411239AGood repeatabilityEasy to synthesizeHybrid capacitor electrodesNanotechnologyCopper nitrateSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Cu-doped Co9S8 nanotube array for a supercapacitor electrode material. The method for preparing the Cu-doped Co9S8 nanotube array on a foamed nickelsubstrate comprises the steps of adopting cobalt nitrate (Co(NO3)2), copper nitrate (Cu(NO3)2) and urea (CO(NH2)2) as reaction raw materials, taking trimesic acid as a ligand, taking thioacetamide (TAA) as a sulfur source, and preparing the Cu-doped Co9S8 nanotube array through a solvothermal method. The diameter range of the prepared nanotube structure ranges from about 100 nm to 150 nm. The Cu-doped Co9S8 nanotube array preparation method has the advantages of high repeatability, simple synthesis process and low cost; and meanwhile, when the Cu-doped Co9S8 nanotube array is used as the supercapacitor electrode material, relatively specific capacity can be provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE AMOUNT OF Cu DOPING WHEN FORMING A BACK CONTACT OF A PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL
ActiveUS20140065762A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTe elementSolvent
Methods for preparing an exposed surface of a p-type absorber layer of a p-n junction for coupling to a back contact in the manufacture of a thin film photovoltaic device are provided. The method can include: applying a treatment solution onto the exposed surface defined by the p-type absorber layer of cadmium telluride; and annealing the device with the p-type absorber layer in contact with the treatment solution to form a tellurium-enriched region in the p-type absorber layer at the exposed surface. The treatment solution comprises a chlorinated compound component that is substantially free from copper, a copper-containing metal salt, and a solvent.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Cu-doped lithium zinc titanate negative electrode material and preparation method thereof
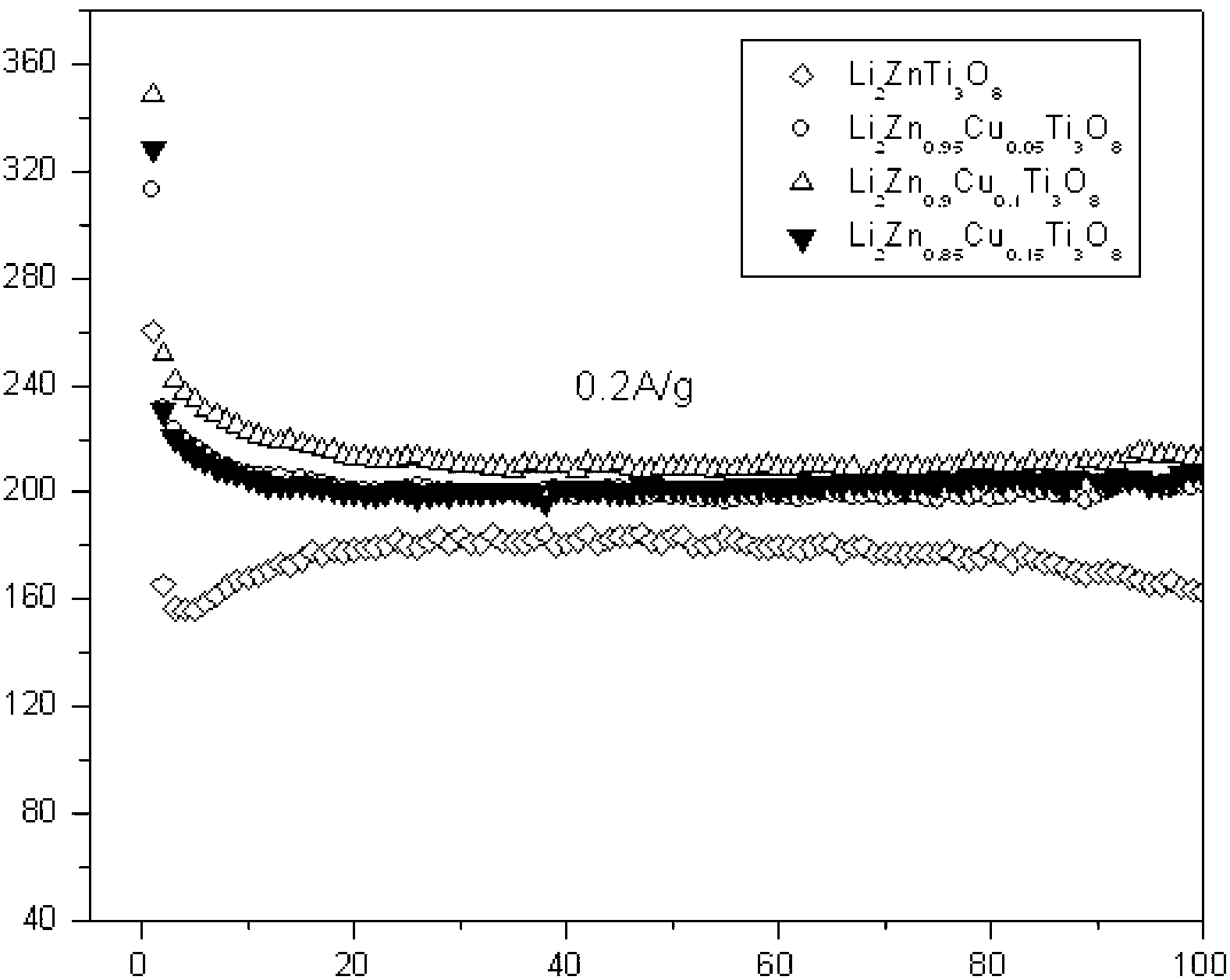
The invention relates to an electrode material and a preparation method thereof, and in particular relates to a Cu-doped lithium zinc titanate negative electrode material and a preparation method thereof. The Cu-doped lithium zinc titanate negative material is characterized by having a molecular formula of Li2Zn1-xCuxTi3O8, wherein x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.15. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: weighing a titanium source, a lithium source, a zinc source and a copper source, uniformly mixing and then drying; and sintering at 750 DEG C for 5 hours, then naturally cooling to the room temperature, and grinding. After Cu is doped, Cu<2+> can be distributed at a tetrahedron position and an octahedron position in a ratio of 3:2, so that the arrangement of ions in the material generates changes slightly, and the stability of a crystal structure of the material during charging and discharging is improved.
Owner:珠海长兴新能源科技有限公司
Light emitting device and electronic device using the same
InactiveUS20100264429A1Efficient emissionsHigh strengthElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPhosphorLength wave
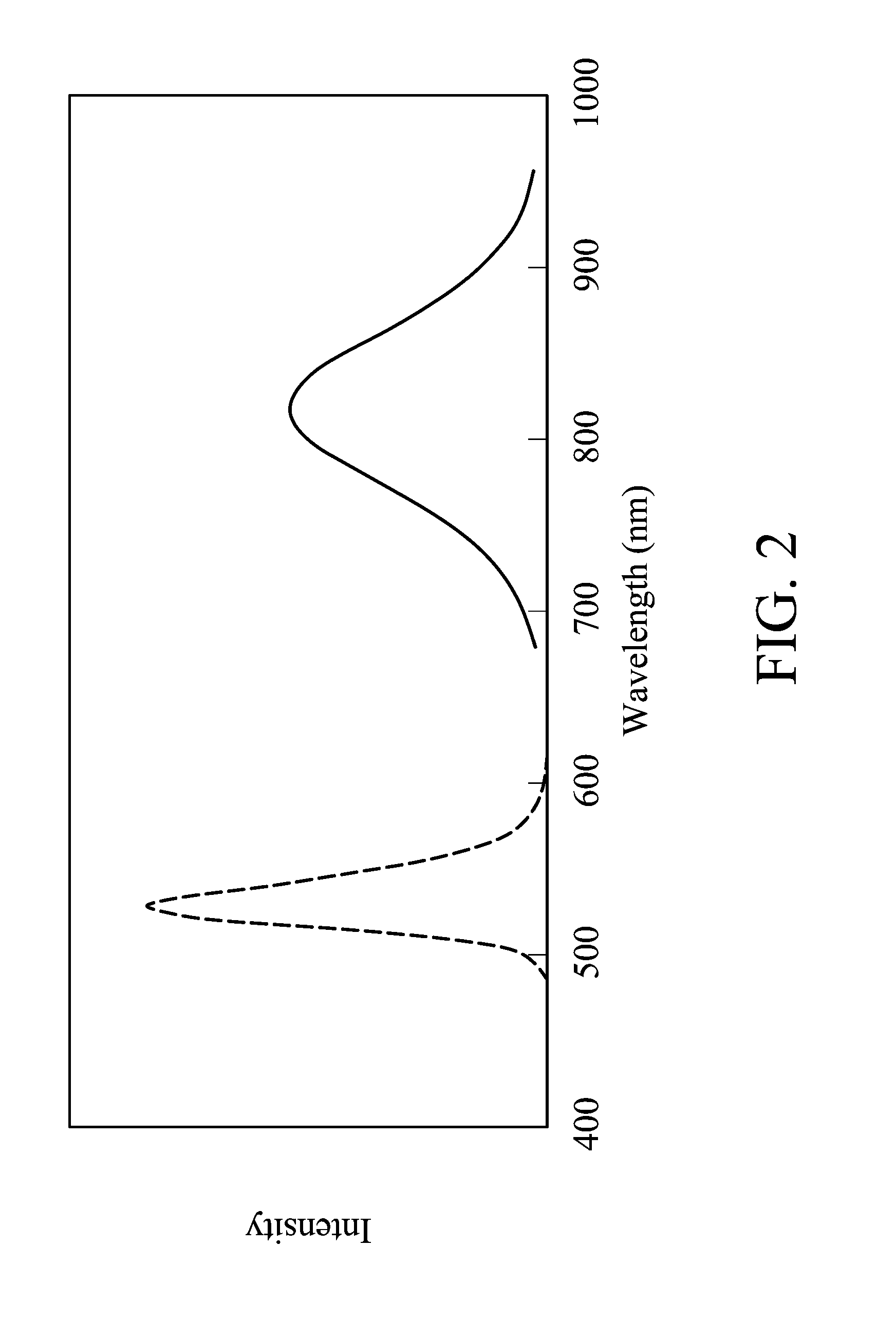
A light emitting device and an electronic device using the same are provided. The light emitting device includes a light emitting chip having a wavelength between 460 nm and 650 nm and phosphor powders, in which the phosphor powders can be stimulated by light emitted from the chip to emit light with a wavelength between 700 nm and 1200 nm. The phosphor powders are selected from the group consisting of Cu-doped CdS, Cu-doped SeS, Cu-doped CdTe and combinations thereof.
Owner:EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS
Method for synthesizing Cu doped CdxCu1-xTe quantum dot by using hydrothermal method
InactiveCN103013521ARaw materials are easy to getLow costLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing Cu doped CdxCu1-xTe quantum dot by using a hydrothermal method; the preparation method comprises the following operation steps of: in the presence of nitrogen, injecting a pre-prepared sodium tellurium hydride NaHTe solution in a pre-prepared mixed solution of cadmium salt, copper salt and water soluble N-acetyl-L-cysteine, to obtain a CdxCu1-xTe precursor solution; then putting the solution in a hydrothermal reaction kettle, reacting to prepare the Cu doped CdxCu1-xTe quantum dot with adjustable fluorescence-emission wavelength and high fluorescence quantum dot yield. The hydrothermal method disclosed by the invention is low in cost, convenient to control, environmentally-friendly, and the like; the obtained Cu doped CdxCu1-xTe quantum dot is high in fluorescence stability, excellent in biocompatibility and low in toxicity, and is expected to be used widely in biochemical analysis and biomedical fields as novel fluorescence nano probe.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Preparation method of Cu-Mn double-doping ZnS quantum dot solution and application
ActiveCN107011892AGood water solubilityOptically stableFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSolubilityFluorescence
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Cu-Mn double-doping ZnS quantum dot solution and application. Firstly, Mn-doped ZnS nanometer crystals are obtained in the nucleation doping process, i.e., Mn precursors and Zn precursors are mixed and are added into S precursors; after the reaction for a period of time, Cu precursors are added; the reaction temperature is controlled, so that the crystals continuously grow; therefore Cu-Mn double-doping ZnS quantum dots are obtained. The prepared double-doping quantum dots simultaneously have Cu and Mn doping fluorescence emission peaks; in addition, the Cu doping fluorescence emission peak is sensitive to the environment and can be used as recognition signals; the Mn doping fluorescence emission peak is used as a reference signal. Therefore the obtained Cu-Mn double-doping ZnS quantum dots can be used as ratio fluorescent probes for analysis and detection. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the preparation method is simple; a green effect is achieved; the repeatability is good; the prepared double-doping ZnS quantum dots have good water solubility; the fluorescence is adjustable.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Preparation method of copper-rich modified defect titanium dioxide and cuprous sulfide heterojunction hydrogen production catalyst
InactiveCN110227495AHigh purityThe synthesis process is simple and advancedPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionHeterojunctionDecomposition
The invention relates to a preparation method of a copper-rich modified defect titanium dioxide and cuprous sulfide heterojunction hydrogen production catalyst. A wide band gap semiconductor TiO2 withgood light absorption capability is doped with Cu, surface detects are artificially introduced to make Cu partially reduced and exposed on the surface of TiO2, and then sulfuration treatment is carried out to form a Cu-doped modified defect TiO2 and Cu2S heterojunction. The doping content of Cu is controlled to make the catalyst have a highest catalytic efficiency, and the catalyst is sulfuratedto form the Cu-doped modified defect TiO2 and Cu2S heterojunction in order to make the heterojunction and doping modification have synergistic effects and obtain a higher photocatalytic efficiency. The method of the invention has the advantages of simplicity, environmental protection and low cost; the catalyst has the advantages of obvious catalytic effect, quickness in reaction, and high repeatability; and the catalyst has potential application values in visible light catalytic water decomposition and hydrogen production.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
Microchannel plate and method for preparing high-resistance thin film with Cu being doped with Al2O3 on inner wall of microchannel plate
InactiveCN109680261AExtended service lifePrecise control of resistivityMutiple dynode arrangementsChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh resistanceWorking environment
The invention relates to a microchannel plate and a method for preparing a high-resistance thin film with Cu being doped with Al2O3 on the inner wall of the microchannel plate. According to preparation of the high-resistance thin film with the Cu being doped with the Al2O3 on the inner wall of the microchannel plate, the high-resistance thin film with the Cu being doped with the Al2O3 is obtainedby the manner that different composition material deposition is performed on the inner wall of the microchannel plate through an atomic layer deposition method, when the deposition is performed, in one large circulation, the Cu doping ratio is controlled by controlling the deposition times of the Al2O3 and the deposition times of the Cu, so that the resistance rate of the thin film can be accurately adjusted and controlled within the range of 10<6>-10<10> omega.cm, the thickness of the thin film is controlled by controlling the circulation times of the large circulation, the resistance rate ofthe prepared thin film basically remains constant under a high-temperature working environment or after high-temperature annealing, and the technical problem of unstable performance of the microchannel plate caused by large change of the resistance rate of an existing microchannel plate surface thin film under the high-temperature condition is solved.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cu-doped cubic phase Ca2Si thermoelectric material
InactiveCN106098922AControl oxidationReduce volatilityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentMetal silicidesAlkaline earth metalMetallurgy
The invention discloses a Cu-doped cubic phase Ca2Si thermoelectric material. A preparation method of the Cu-doped cubic phase Ca2Si thermoelectric material comprises the steps of: uniformly mixing Ca powder, Si powder and Cu powder under a protective atmosphere of Ar gas; then placing the obtained mixture powder and a grinding steel ball in a vacuum stainless steel ball mill jar under the protective atmosphere of Ar gas for sealing; and after a ball-milling reaction, carrying out vacuum sintering and tabletting on the sealed powder in a manner of plasma sintering to obtain a flaky Cu-doped cubic phase Ca2Si thermoelectric material. Because the Cu element has the characters similar with those of an alkaline-earth metal, after the Cu element is added and is used as donor doping, a Ca position is easily substituted, a conduction electron is provided to be used as a current carrier, thus the electric conductivity and the thermoelectric property of the material are improved. The Cu-doped cubic phase Ca2Si thermoelectric material has the advantages of simple process, easy operation, low cost and the like; and the obtained Cu-doped cubic phase Ca2Si thermoelectric material is high in purity, close in bonding and good in industrial prospect.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing copper-doped aluminum nitride base diluted magnetic semiconductor nano rods
InactiveCN101887793ASimple processLow equipment requirementsNanostructure manufactureInorganic material magnetismAluminium chlorideCurie temperature
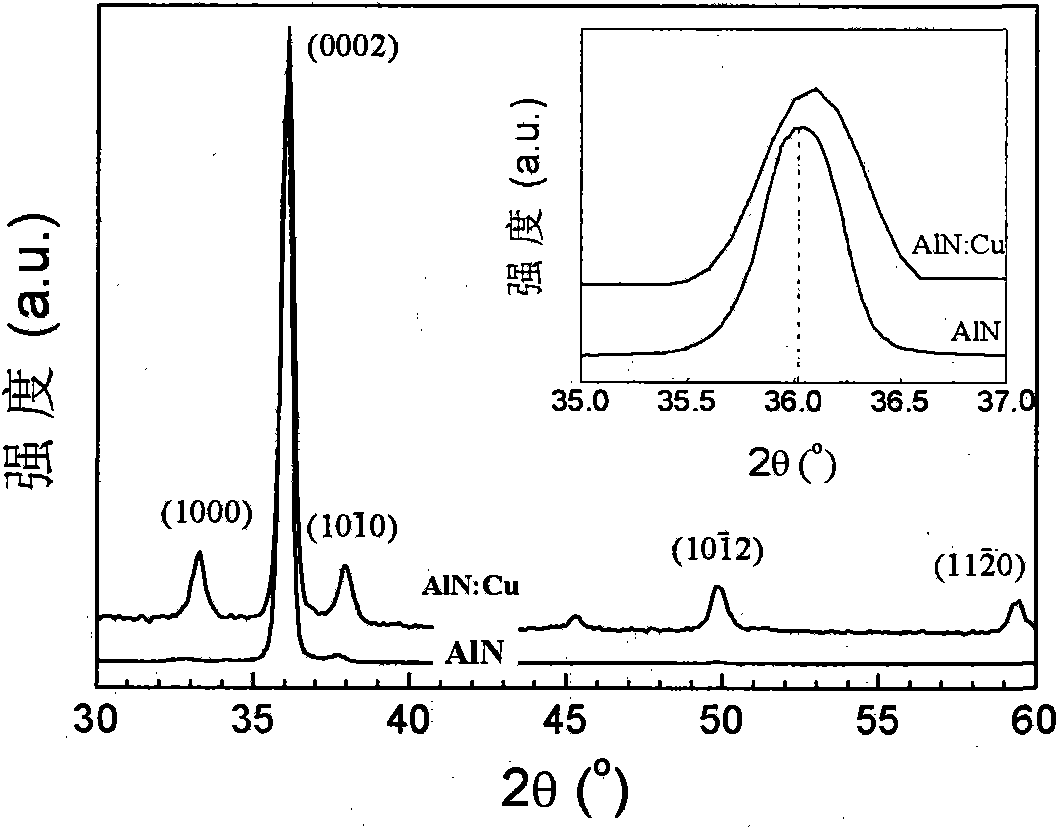
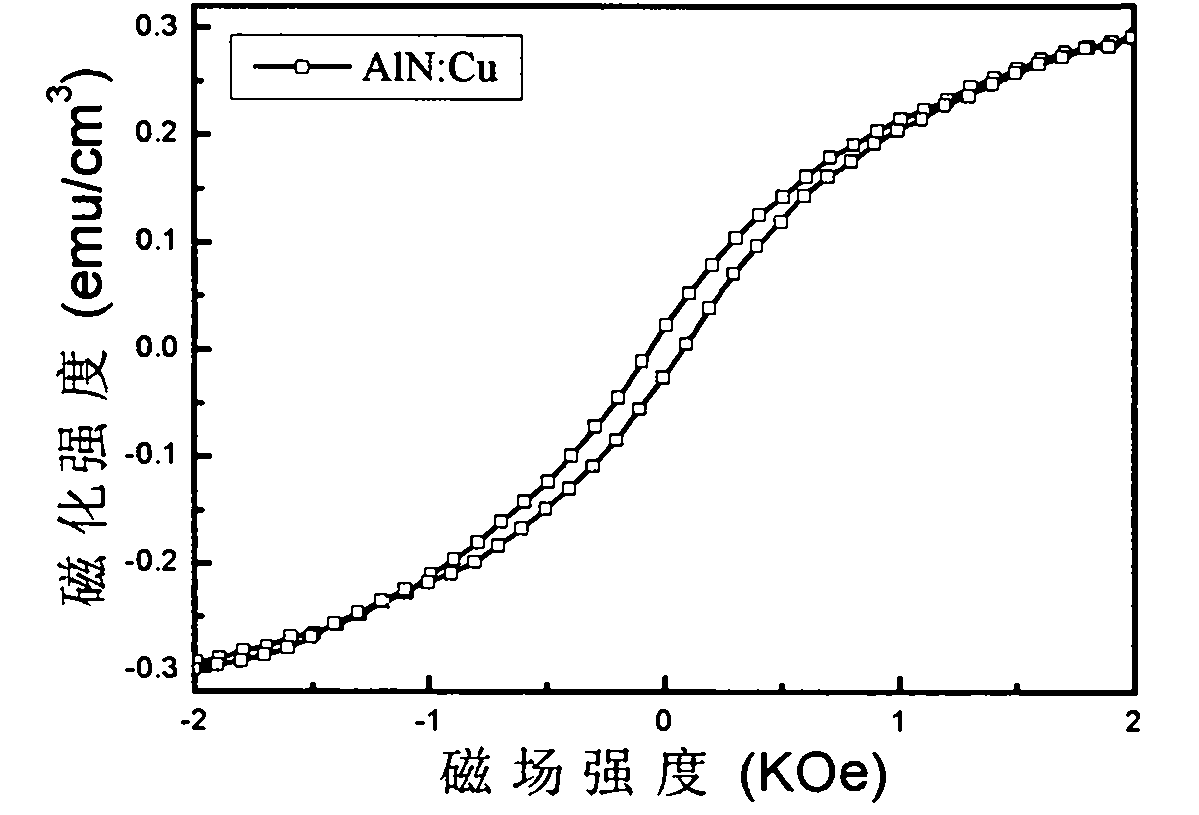
The invention discloses copper-doped aluminum nitride base diluted magnetic semiconductor nano rods and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing aluminum chloride and copper chloride uniformly in a certain molar ratio; and then performing ammoniation on the mixture in an ammonia atmosphere to obtain the Cu-doped aluminum nitride directly. The copper-doped aluminum nitride base diluted magnetic semiconductor nano rod has the advantages of simple method, low equipment requirement, high ferromagnetism of the prepared AIN:Cu, a Curie temperature higher than the room temperature, and good application prospect, and can be applied for nano spintronics devices, such as a spin field effect tube (spin-FET), a spin light-emitting diode (spin-LED) and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Titanium-based positive electrode with high oxygen evolution overpotential and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105502595AIncrease oxygen evolution overpotentialImproved physical and chemical propertiesWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationCu elementTitanium
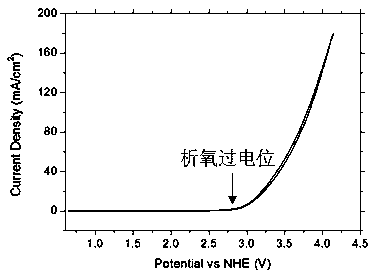
The invention discloses a titanium-based positive electrode with a high oxygen evolution overpotential and a preparing method thereof. A Cu-doped SnO2 film layer and a titanium substrate are arranged in the electrode from outside to inside. According to the preparing method, the titanium substrate which is subjected to decontamination and TiO2 removal treatment and is in any geometrical shape is coated with a precursor solution containing Sn and Cu, and high-temperature annealing is carried out to form the titanium-based Cu-doped SnO2 positive electrode. By means of Cu element doping, physical and chemical properties of a SnO2 film are changed, and the high oxygen evolution potential of the positive electrode exceeds 2.6 V (vs NHE).
Owner:周检
Cu doped Fe-N soft magnetic thin film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105761878ASimple preparation processEasy to control ingredientsInorganic material magnetismCathode sputtering applicationMagnetizationPollution
The invention discloses a Cu doped Fe-N soft magnetic thin film, and belongs to the technical field of soft magnetic thin films.The chemical general formula of the Cu doped Fe-N soft magnetic thin film is (Fe100-yNy)100-xCux, wherein y ranges from 25 to 40, and x ranges from 9 to 18.The invention further discloses a preparation method of the Cu doped Fe-N soft magnetic thin film.The Cu doped Fe-N soft magnetic thin film and the preparation method thereof have the following advantages that a reaction magnetron sputtering method is adopted for preparing the Cu doped Fe-N soft magnetic thin film, the preparation process is simple, ingredient control is easy, and the method is a basic process method for industrially producing the thin film; copper is wide in source and low in cost, and the product is environmentally friendly and free of pollution; the soft magnetic thin film with low coercive force (not larger than 10 Oe) and high saturated magnetization intensity (larger than or equal to 1,200 emu / cc) can be obtained, and magnetism is stable within the temperature range of 0-600 DEG C.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
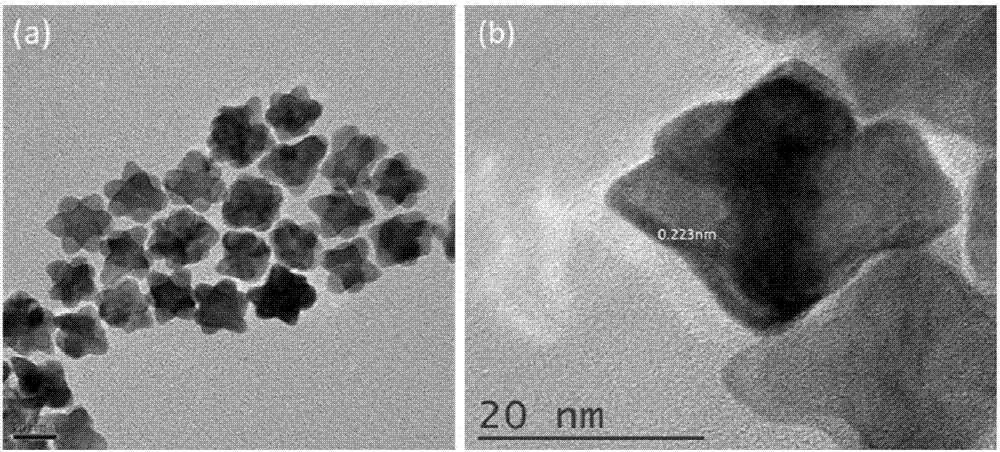
Petal-shaped Cu doped PtRu alloy catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107123818AIncrease surface stressImprove stabilityCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMethanol fuelAlloy catalyst
The invention relates to a petal-shaped Cu doped PtRu alloy catalyst and a preparation method of the catalyst. The petal-shaped Cu doped PtRu alloy catalyst is in a petal-shaped morphology, Pt, Ru and Cu exist in an alloy form, and Pt and Ru atoms are distributed at an active site. The mass activity of the prepared petal-shaped PtRu / Cu catalyst in a methanol oxidation reaction is at least 3.1 times of commercial Pt / C. The preparation method is simple and easy to operate. The catalyst can be widely applied in many fields of methanol fuel cell catalysts and the like due to excellent methanol oxidation performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Application of Cu-doped three-dimensional ordered amorphous titanium dioxide nanotube composite material
ActiveCN105226247AImprove conductivityLower internal resistanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsTio2 nanotubeLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses an application of a Cu-doped three-dimensional ordered amorphous titanium dioxide nanotube composite material, and belongs to the field of development and research of new energy materials. A Cu-doped three-dimensional ordered amorphous TiO2 nanotube array composite material is adopted as a working electrode of a lithium-ion battery. With an amorphous TiO2 nanotube array prepared by an anodic oxidation method as the working electrode, a platinum sheet as a counter electrode, a saturated calomel electrode as a reference electrode, a copper solution as electrolyte, a potentiostatic deposition is carried out for a time period, and then the Cu-doped three-dimensional ordered amorphous TiO2 nanotube composite anode material is prepared. The Cu-doped three-dimensional ordered amorphous titanium dioxide nanotube composite material is simple in preparation technology and friendly to environment; the advantage of high conductivity of metal Cu is fully utilized; and the specific charge / discharge capacity and the cycle stability performance of the electrode are improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing Cu-doped SiO2 nano composite aerogel
InactiveCN108786674ASmall particle sizeLarge specific surface areaNanotechnologyAerogel preparationAlcoholThermal stability
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Cu-doped SiO2 nano composite aerogel. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving Cu(NO3)2.3H2O into absolute ethyl alcohol, adding tetraethylorthosilicate and deionized water, stirring, adding DMF and concentrated nitric acid, continuing to stir for 6.5-7.5 h, pouring a sol into a culture dish, aging for 3-5 d, and thus obtaining a precursor composite alcogel; then continuing to age the obtained alcogel for 23-25 h at the temperature of 25-35 DEG C, soaking in a mixed solution of tetraethyl orthosilicate and absolute ethyl alcohol atthe constant temperature of 34-36 DEG C, soaking for 2-3 d, washing, carrying out constant temperature drying at the temperature of 34-36 DEG C for 14-16 h, and carrying out constant temperature drying at the temperature of 60-65 DEG C for 71-73 h; and finally, putting the sample into an electric furnace, treating for 4-6 h at the temperature of 740-760 DEG C, and then cooling. The composite aerogel prepared by the method has the advantages of small particle size, large specific surface area, perfect microstructure and good thermal stability.
Owner:陈正新
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com