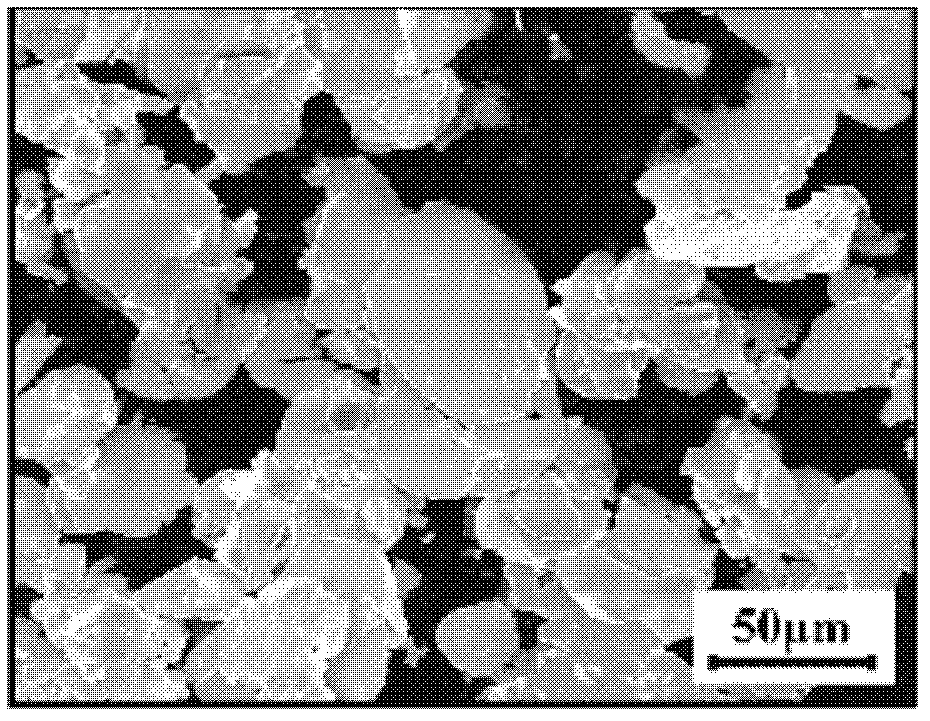
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
221 results about "Ceramic thin films" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
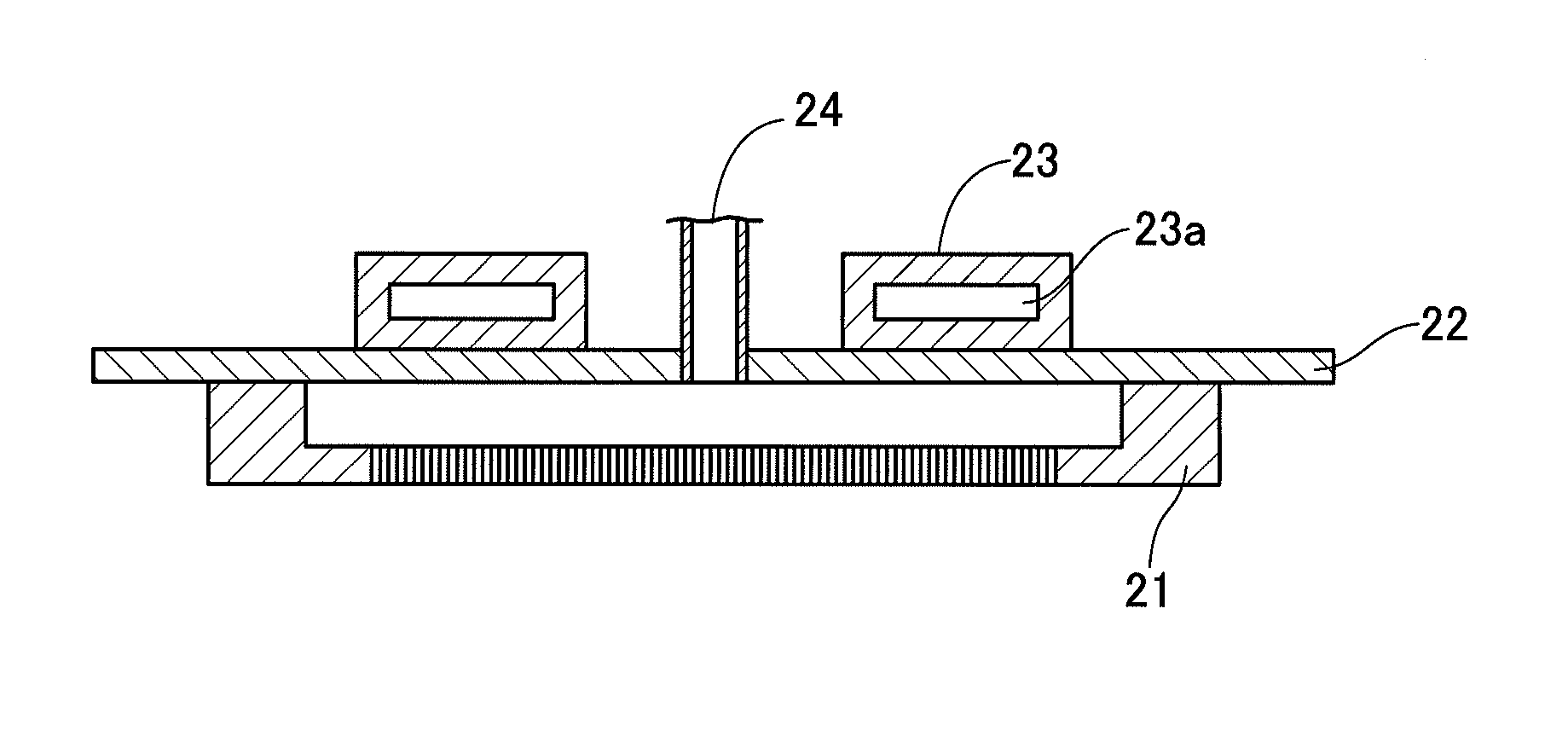
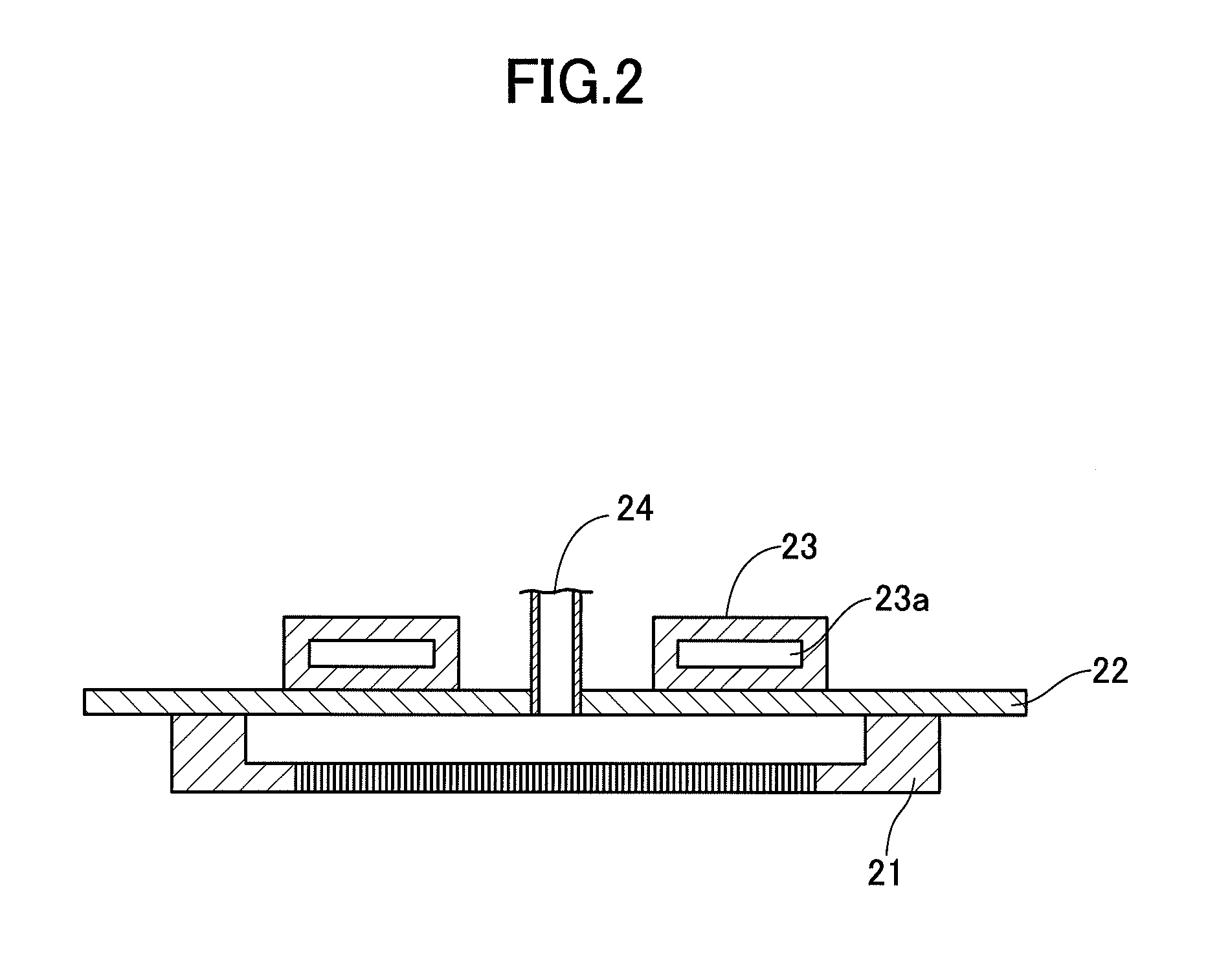
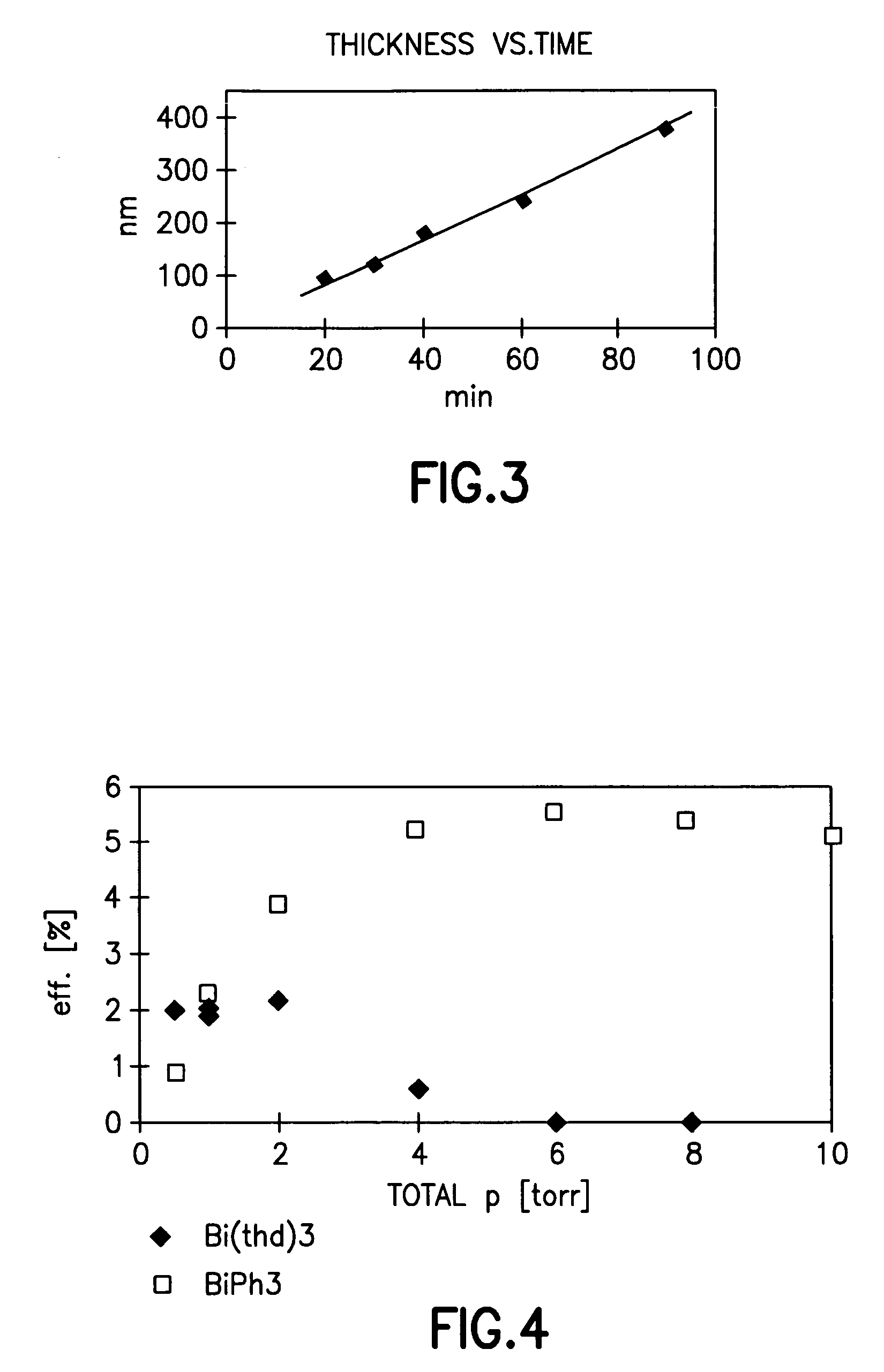
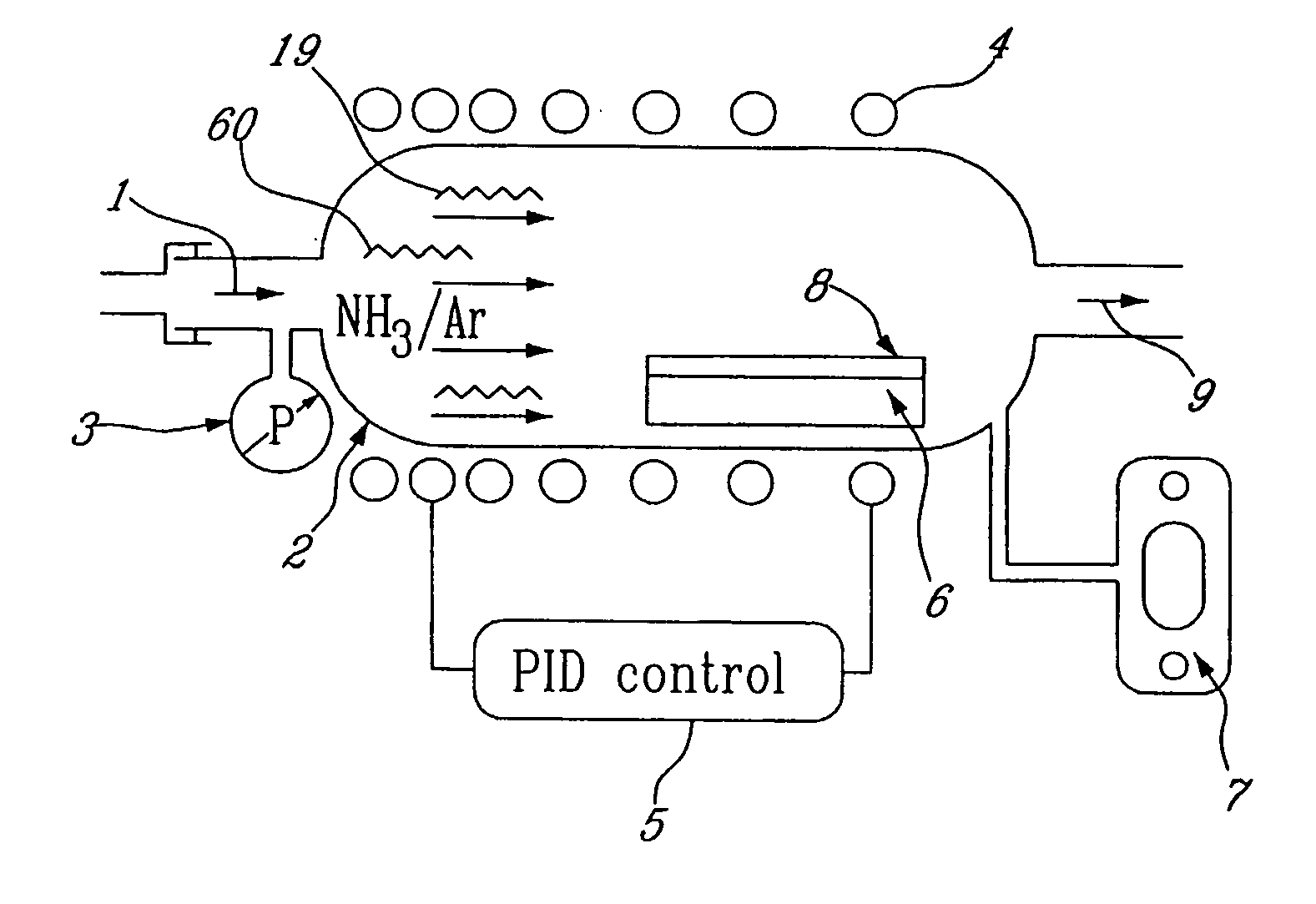
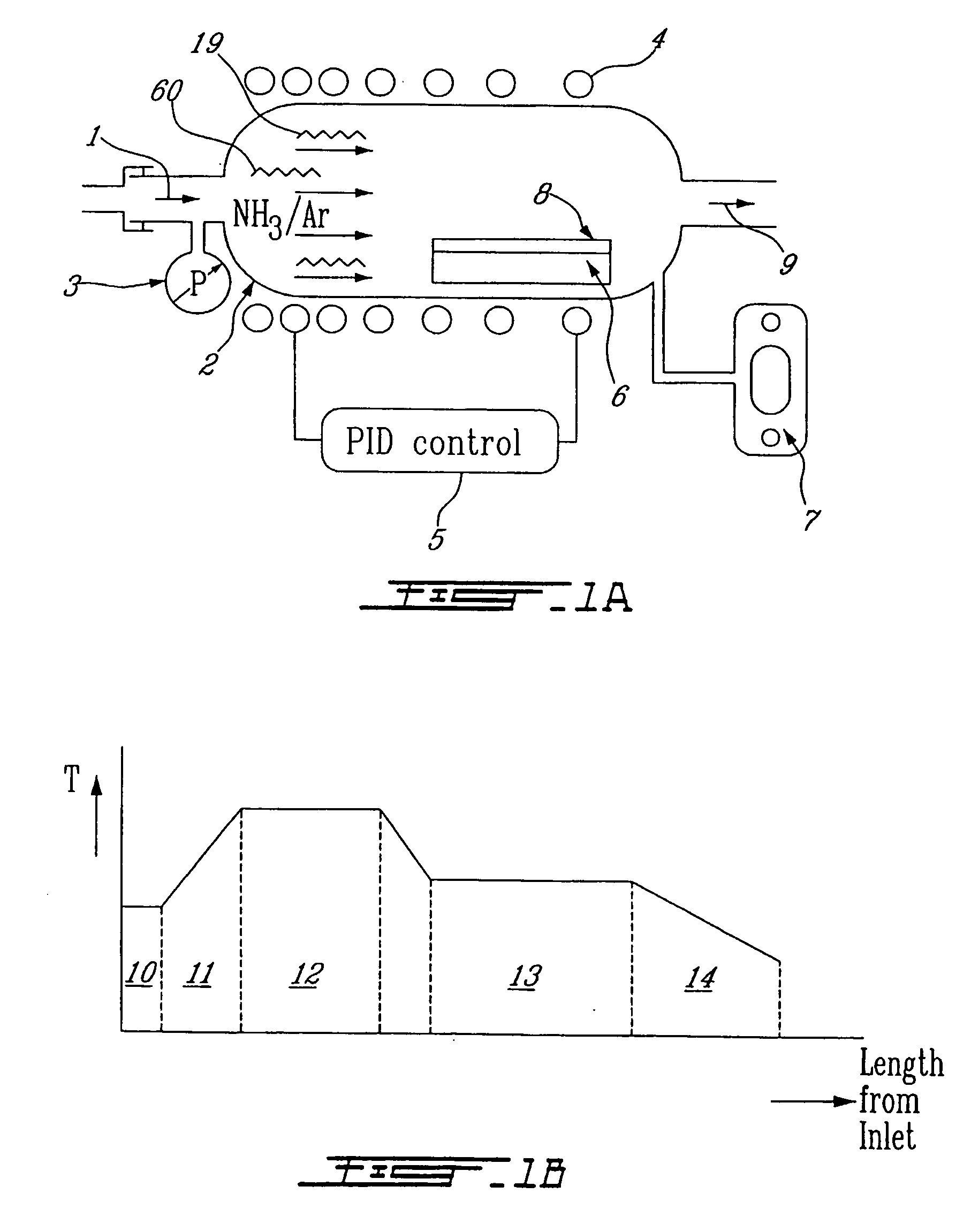
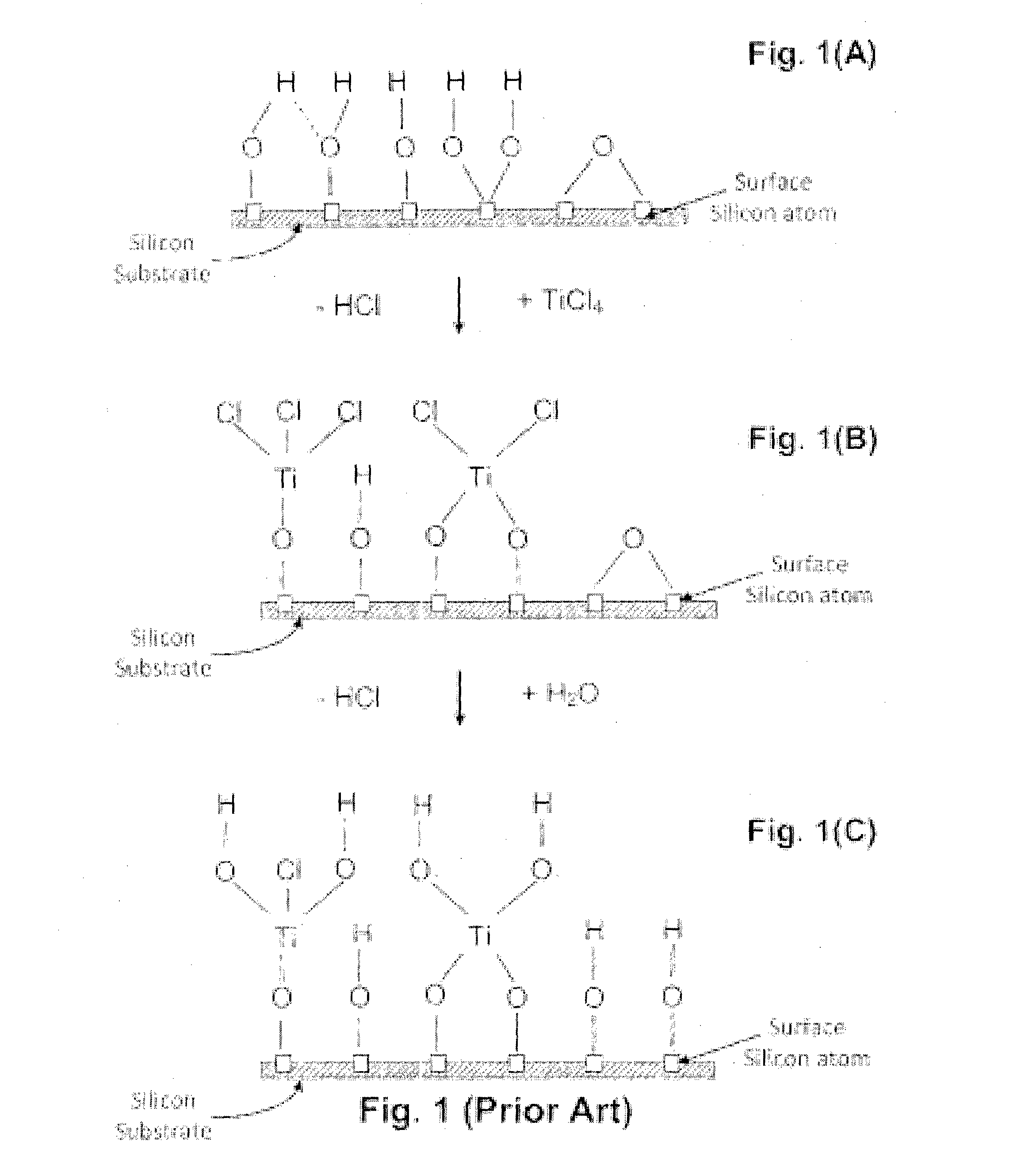
Thin film manufacturing apparatus, thin film manufacturing method and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20130023062A1Easy temperature controlGood effectLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufactured apparatusThermal radiation
In an apparatus for manufacturing a ceramic thin film by employing a thermal CVD method, an internal jig, which is provided with a heat radiation material film on the surface, is provided at a position that faces a substrate (S) on which the film is to be formed. The thin film and a semiconductor device are manufactured using such apparatus.
Owner:ULVAC INC
High frequency and multi frequency band ultrasound transducers based on ceramic films
InactiveUS6761692B2Maximizing electromechanical couplingImprove stabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMulti bandTransceiver
A design and a manufacturing method of ultrasound transducers based on films of ferro-electric ceramic material is presented, the transducers being particularly useful for operating at frequencies above 10 MHz. The designs also involve acoustic load matching layers that provides particularly wide bandwidth of the transducers, and also multiple electric port transducers using multiple piezoelectric layers, for multi-band operation of the transducers over an even wider band of frequencies that covers ~4 harmonics of a fundamental band. A transceiver drive system for the multi-port transducers that provides simple selection of the frequency bands of transmitted pulses as well as transmission of multi-band pulses, and reception of scattered signals in multiple frequency bands, is presented. The basic designs can be used for elements in a transducer array, that provides all the features of the single element transducer for array steering of the focus and possibly also direction of a pulsed ultrasound beam at high frequencies and multi-band frequencies. The manufacturing technique can involve tape-casting of the ceramic films, deposition of the ceramic films onto a substrate with thick film printing, sol-gel, or other deposition techniques, where manufacturing methods for load matching layers and composite ceramic layers are described.
Owner:PREXION
Deposition of perovskite and other compound ceramic films for dielectric applications
InactiveUS20070053139A1Increase capacitanceReduce the temperatureThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricHigh ratePulsed DC
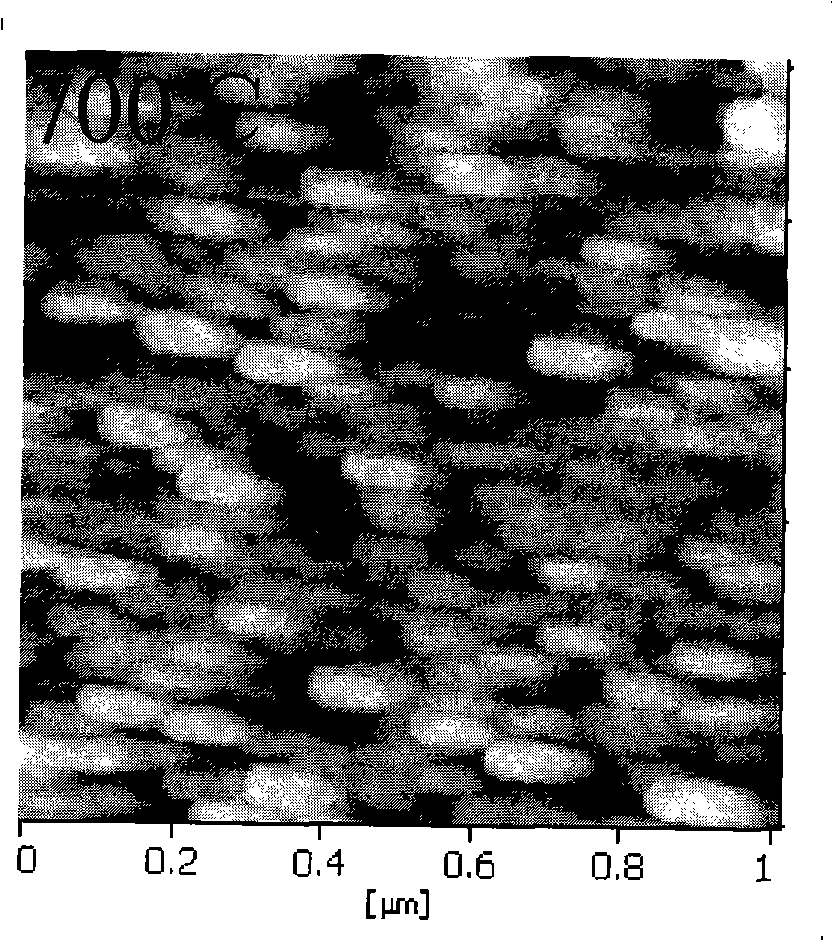
In accordance with the present invention, deposition of perovskite material, for example barium strontium titanite (BST) film, by a pulsed-dc physical vapor deposition process or by an RF sputtering process is presented. Such a deposition can provide a high deposition rate deposition of a layer of perovskite. Some embodiments of the deposition address the need for high rate deposition of perovskite films, which can be utilized as a dielectric layer in capacitors, other energy storing devices and micro-electronic applications. Embodiments of the process according to the present invention can eliminate the high temperature (>700° C.) anneal step that is conventionally needed to crystallize the BST layer.
Owner:DEMARAY
Ceramic thin film on various substrates, and process for producing same
InactiveUS20050139966A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogen concentrationAmorphous silicon
A thin film of an amorphous silicon-based material on a substrate. The thin film has the property of any one of a carrier concentration of 1013 to 1018 cm−3 in a depletion zone next to the substrate, an electron mobility of 5 to 30 cm2V−1s−1, a dangling bond concentration of 1012 to 1019 cm−3, no solvent-related defects, or a residual hydrogen concentration of 0 to 25 atomic %. The thin film may be used to fabricate many devices such as solar cells, light-emitting diodes, transistors, photothyristors, and integrated monolithic devices on a single chip.
Owner:BISHOP'S UNIVERSITY +1
Method for performing electroless nickel plating on surface of aluminum nitride ceramic
ActiveCN101962760AHigh bonding strengthImprove high temperature resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless nickelSodium acetate
The invention provides a method for performing electroless nickel plating on the surface of aluminum nitride ceramic, belonging to the ceramic thin-film metallization field. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1) polishing the surface of aluminum nitride with a machinery; coarsening the aluminum nitride substrate with mixed acid or alkali, completely cleaning away the residual acid or alkali; 3) sensitizing the coarsened substrate in stannous chloride solution, activating in palladium chloride solution or performing activation without palladium; 4) weighting a certain amount of nickel sulphate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium citrate, sodium acetate, lactic acid, thiourea and sodium dodecyl sulfate in sequence to prepare a chemical plating solution; and 5) adjusting the pH value of the solution to 4.0-6.0 with acid or alkali, heating the solution to 70-95 DEG C, and placing the prepared substrate in the solution to perform electroless nickel plating. The invention is characterized in that the electroless nickel plating can be performed on the surface of the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate which is difficult to plate; and a certain amount of surfactant is added so that the plating becomes denser and smoother, the binding force between the plating and the substrate is increased, and the solderability of the plating is better.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
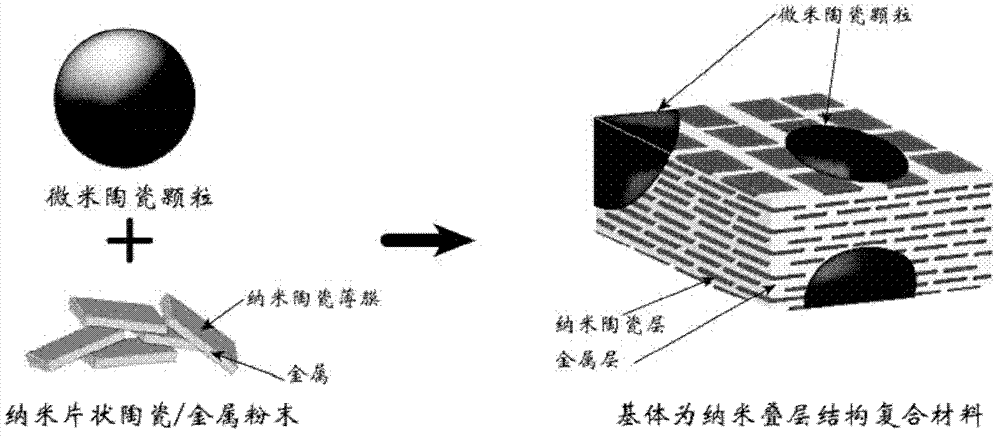
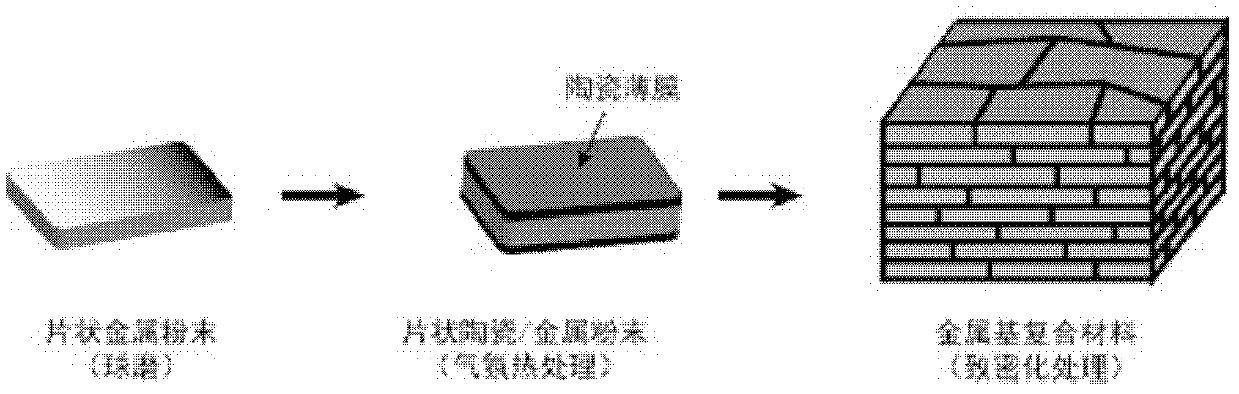
Metal-based composite material with substrate of nano laminated structure and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a metal-based composite material with a substrate of a nano laminated structure and a preparation method of the composite material. The particle-reinforced metal-based composite material is prepared from nano flaky metal powder coated with ceramic thin film on the surface and a micrometer ceramic particle reinforcing body as raw materials. The metal-based composite material prepared by the method has the substrate of a metal / ceramic alternate nano laminated structure, and has high interface volume ratio; the ceramic layer can effectively restrict and keep a deformation micro texture, improve dislocation storage and slippage capability, and cause deflection and passivation of crackles, thereby exerting structure toughening benefit; and finally the metal-based composite material is endowed with mechanical properties of high strength and high toughness. The preparation method is simple and feasible, can realize large-scale preparation of large-size composite material, and is contributed to promoting the engineering application of the metal-based composite material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
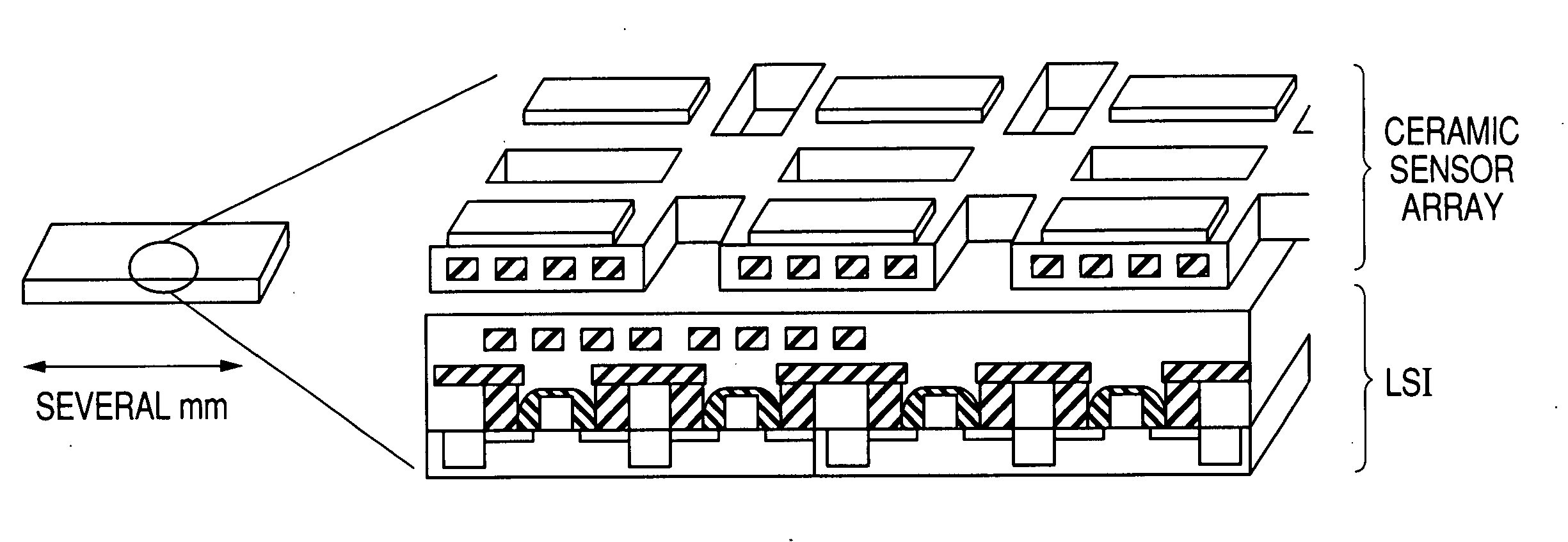
Ceramic sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060185980A1High sensitivityEasy to processMaterial electrochemical variablesMicrocontrollerNano structuring
The compatibility of increased sensitivity with both reliability and durability was difficult, since in a gas sensor composed of polycrystalline grains or ceramic particles, there is a trade-off relationship between increasing sensitivity through particle size reduction and change with time due to grain growth. Moreover, it was difficult to integrate a ceramic sensor with high sensitivity, high durability and high reliability with a Si integrated circuit in the monolith. A gas sensor is composed of an artificial nano-structure ceramic film where a change in the ceramic structure due to grain growth, etc. does not occur because of heat. The ceramic thin film is formed to a pattern shaped template on a nanometer level by using a sol-gel method and cured adequately to form precisely. Moreover, the above-mentioned gas sensor is integrated with an integrated circuit in the monolith.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Metal ceramic composite substrate and manufacturing method for same
InactiveCN103079339AHigh thermal conductivityImprove bindingSolid-state devicesPrinted circuit manufactureComposite substrateBond properties
The invention is applied to the field of substrates, provides a metal ceramic composite substrate and a manufacturing method for the same, and aims to solve the problems of low thermal conductivity of a metal substrate and low bonding properties of a metal ceramic composite substrate in the prior art. The metal ceramic composite substrate comprises a metal substrate, a ceramic layer, a metal line layer and a metal ceramic transition layer, wherein the ceramic layer is arranged on the metal substrate; the metal line layer is arranged on the surface of the ceramic layer; the metal ceramic transition layer is formed on the metal substrate, and is connected with the ceramic layer; the ceramic layer is positioned between the metal ceramic transition layer and the metal line layer; the metal ceramic transition layer consists of metal and metal nitrides; and the ceramic layer consists of a ceramic thin film. The ceramic layer is used for improving the thermal conductivity of the substrate, and the metal ceramic transition layer is arranged to improve the bonding properties between the ceramic layer and the metal substrate to improve bonding reliability.
Owner:SHENZHEN HOYOL OPTO ELECTRONICS
Ceramic thin film thermocouple and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN103900728ALow costWide temperature rangeThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansPlatinumLap joint
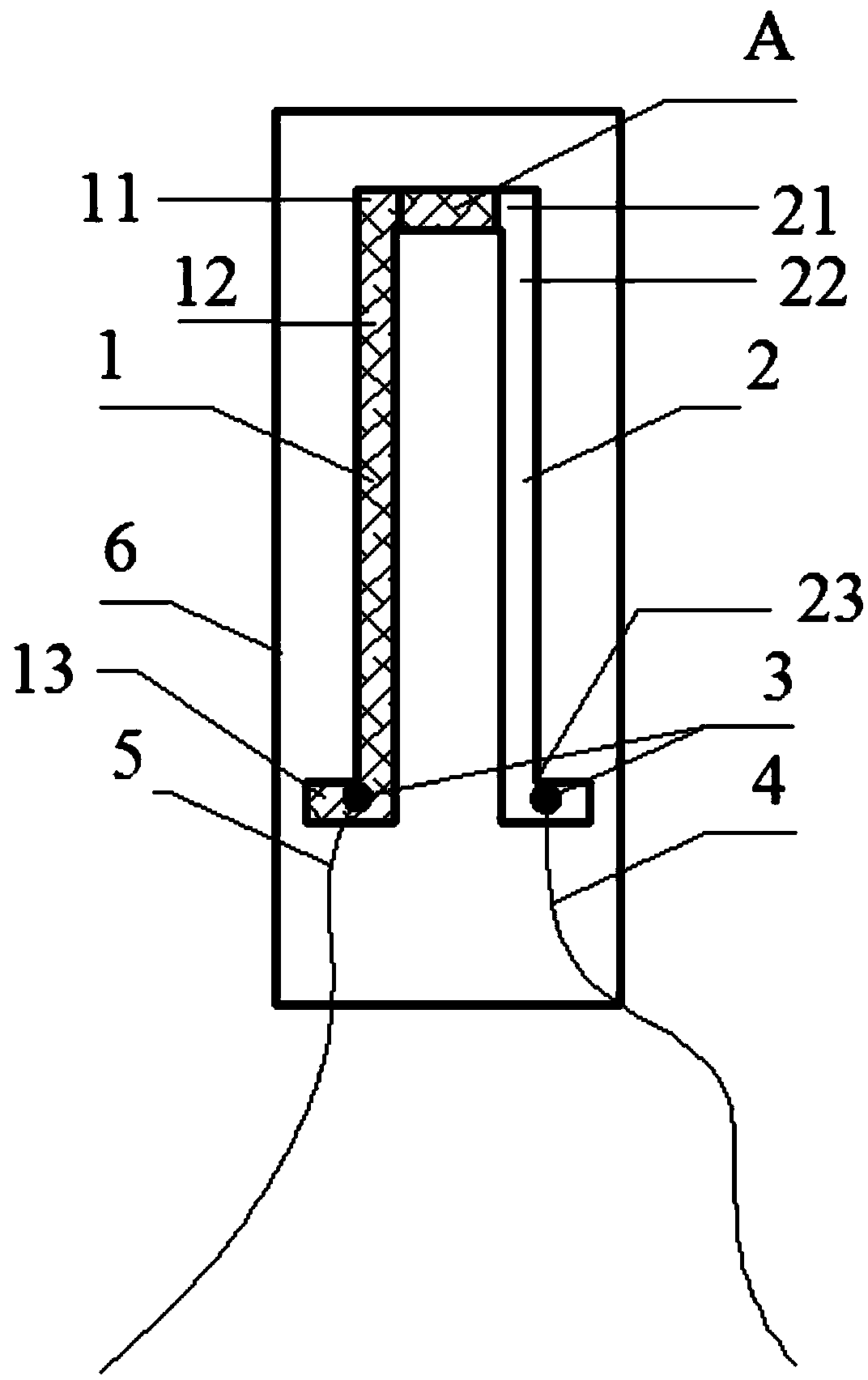
The invention discloses a ceramic thin film thermocouple and a manufacture method thereof. The ceramic thin film thermocouple comprises a thermocouple conductive ceramic thin film comprising a ceramic thermode layer, wherein the ceramic thermode layer comprises a first thermode and a second thermode which are arranged in a mirror symmetry mode along the center line of the thermocouple conductive ceramic thin film. Both the first thermode and the second thermode comprise lap joint transverse ends for performing lap joint of a hot connection point between the thermodes, lead transverse ends connected with leads and transition vertical portions for enabling the lap joint transverse ends to be connected with the lead transverse ends. The lap joint transverse end of the first thermode and the lap joint transverse end of the second thermode are in lap joint partially to form the hot connection point of the thermocouple. Compared with the ordinary K-shaped thermocouple, the ceramic thin film thermocouple has the advantages of being wide in temperature measurement range and adaptive to oxidation and acid-base environments. Compared with other thermocouples made of high temperature resistant materials, such as platinum and rhodium, the ceramic thin film thermocouple is low in cost in the same temperature measurement range, and applicable to temperature measurement of extreme environments in the fields of space flight and aviation and the like.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
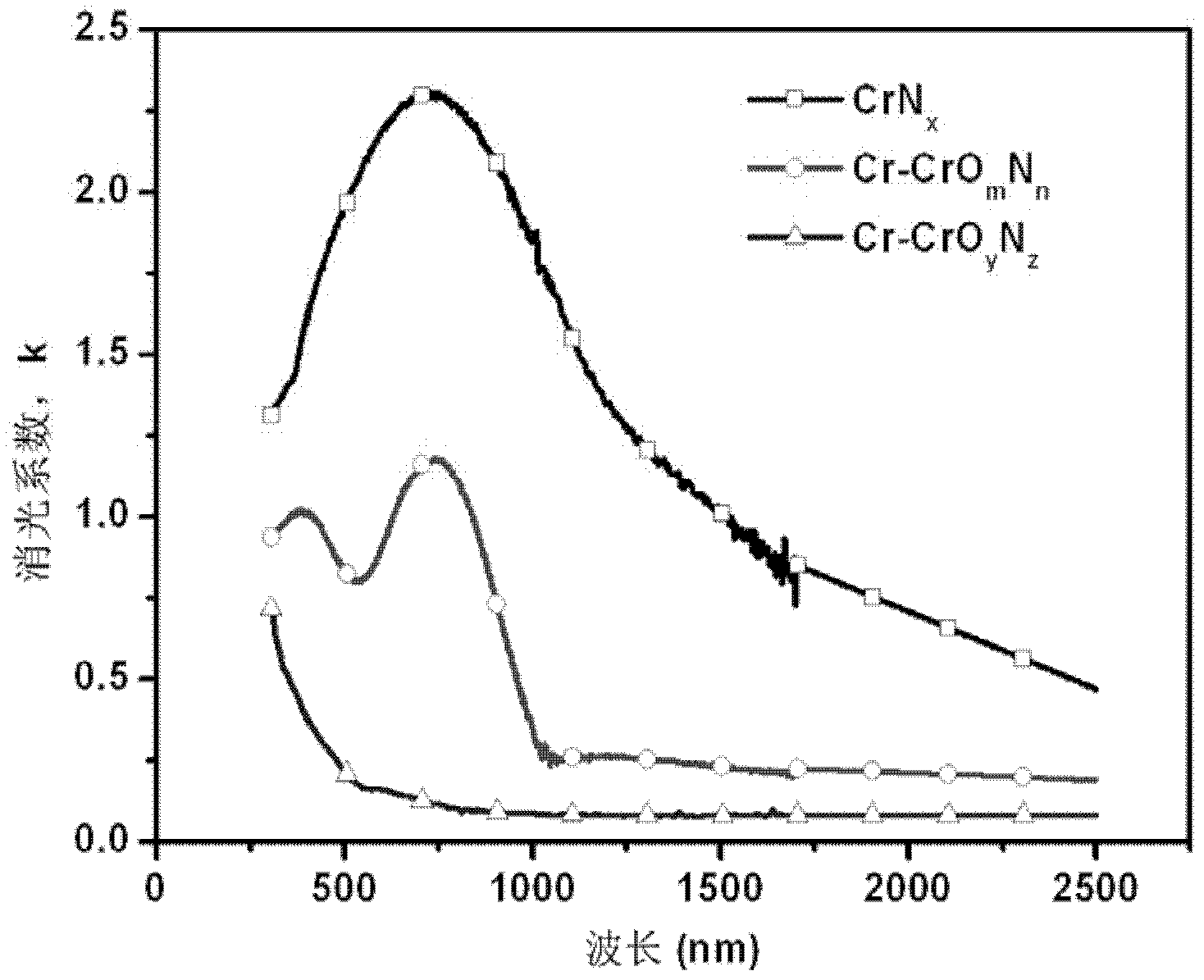
Medium-and-low-temperature solar selective absorption thin film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102620456ALow costSimple preparation processSolar heat devicesVacuum evaporation coatingHeat stabilitySilicon dioxide
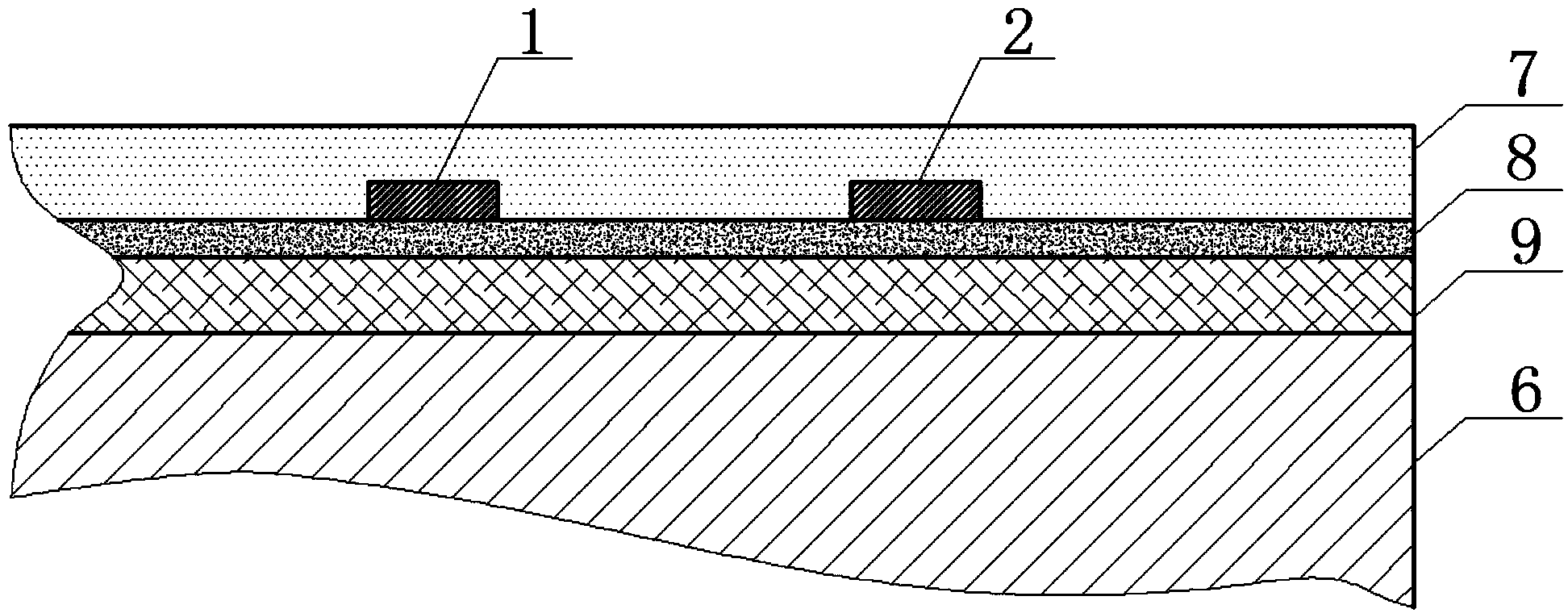
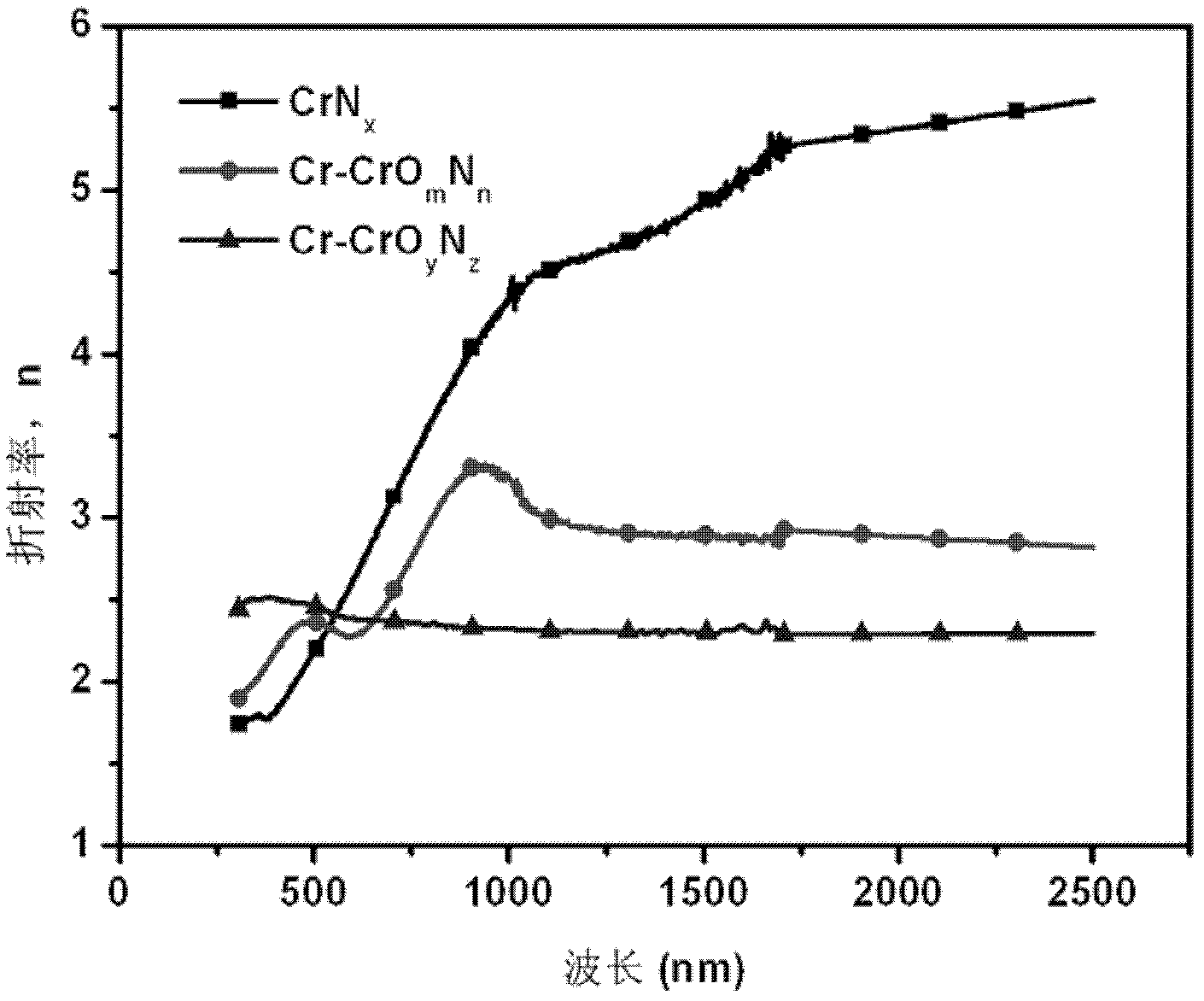
The invention discloses a medium-and-low-temperature solar selective absorption thin film. The medium-and-low-temperature solar selective absorption thin film mainly comprises a diffusion blocking layer, an absorption layer and an anti-reflection layer, which are sequentially deposited on a substrate with an infrared reflection function, or the medium-and-low-temperature solar selective absorption thin film mainly comprises an infrared reflection layer, the diffusion blocking layer, the absorption layer and the anti-reflection layer, which are sequentially deposited on the substrate, wherein the infrared reflection layer comprises the components of copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo) or silver (Ag); the diffusion blocking layer comprises the composite component of chromium and nitrogen; the absorption layer consists of one or two of chromium simple substance / chromium oxide multi-component phase and chromium simple substance / chromium oxynitride multi-component phase; and the anti-reflection layer is a silicon dioxide (SiO2) ceramic thin film. The medium-and-low-temperature solar selective absorption thin film is high in solar spectrum absorption rate, low in infrared emissivity, high in heat stability and high in weather resistance and can be used in medium-and-low-temperature atmospheric environment of below 278 DEG C for a long time. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the medium-and-low-temperature solar selective absorption thin film. The preparation method employs a magnetron sputtering method and is simple in process, low in cost, high in stability and applicable to industrial large-area preparation.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Low temperature chemical vapor deposition process for forming bismuth-containing ceramic thin films useful in ferroelectric memory devices
InactiveUS7005303B2Easy to transportImproved stoichiometry, morphology and ferroelectric characterSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh densityGas phase
A low temperature CVD process for deposition of bismuth-containing ceramic thin films suitable for integration to fabricate ferroelectric memory devices. The bismuth-containing film can be formed using a tris(β-diketonate) bismuth precursor. Films of amorphous SBT can be formed by CVD and then ferroannealed to produce films with Aurivillius phase composition having superior ferroelectric properties suitable for manufacturing high density FRAMs.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Packaging device of light-emitting diode and packaging method thereof
ActiveCN101924175AEasy to passImprove cooling effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMicro arc oxidationCeramic thin films
The invention relates to the field of photoelectron packaging and discloses a packaging device of a light-emitting diode and a packaging method thereof. A packaging structure comprises LED light emitting chips arranged on the front face of a metallic substrate, holes which are formed on the metallic substrate and penetrate the front and back faces of the metallic substrate, and first insulating layers arranged on the back face of the metallic substrate and periphery of the holes. Because the LED light emitting chips are directly arranged on the metallic substrate, heat can be fast transferred and the heat dispersion performance is high. The holes are used as electrodes and independent electric conduction channels are formed between the holes; therefore, the insulating property is reliable; the packaging device can be used for both single-chip packaging and multi-chip packaging. Ceramic thin films formed by a micro-arc oxidation method or a rigid oxidation method are in-situ growth film layers, have high joint strength, thermal expansivity similar to that of the substrate and excellent heat matching property.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
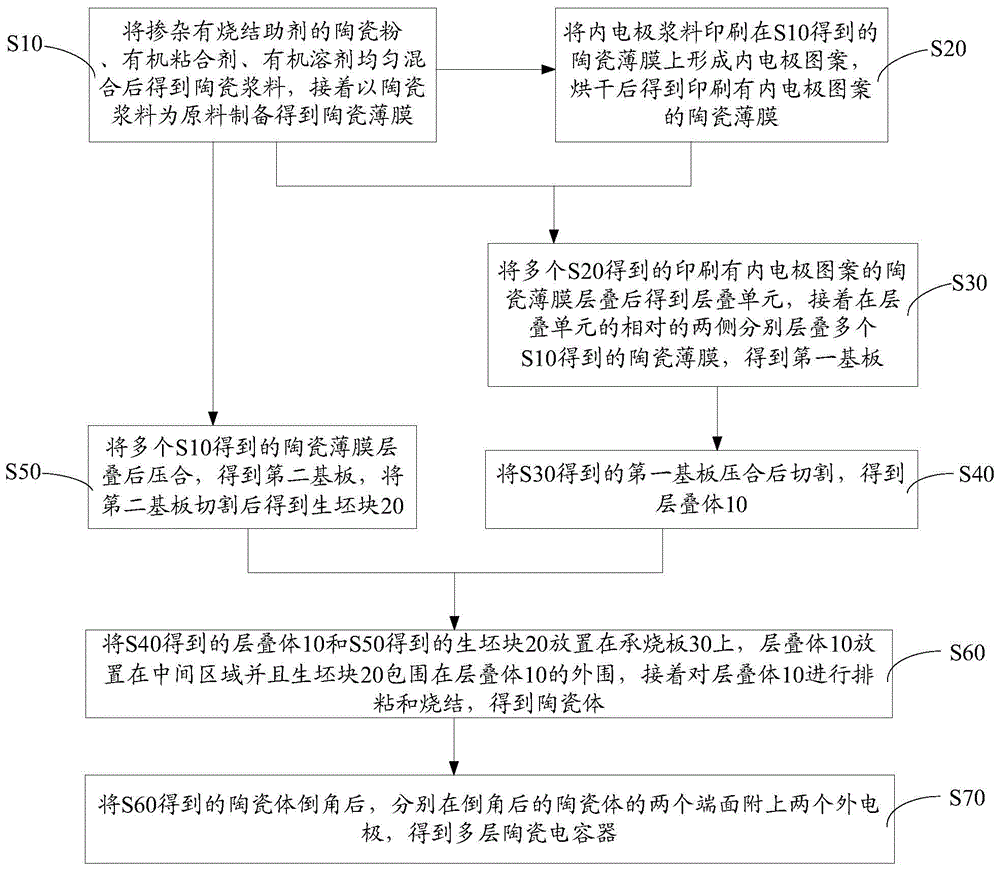
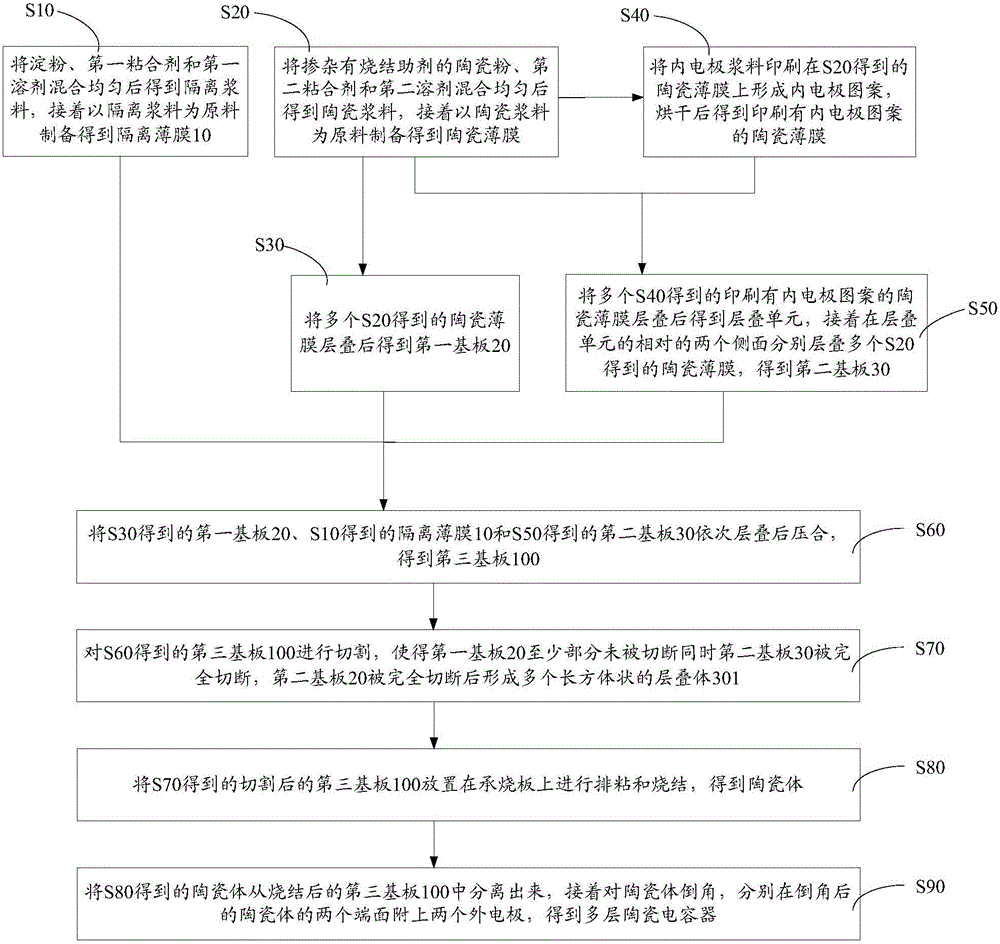
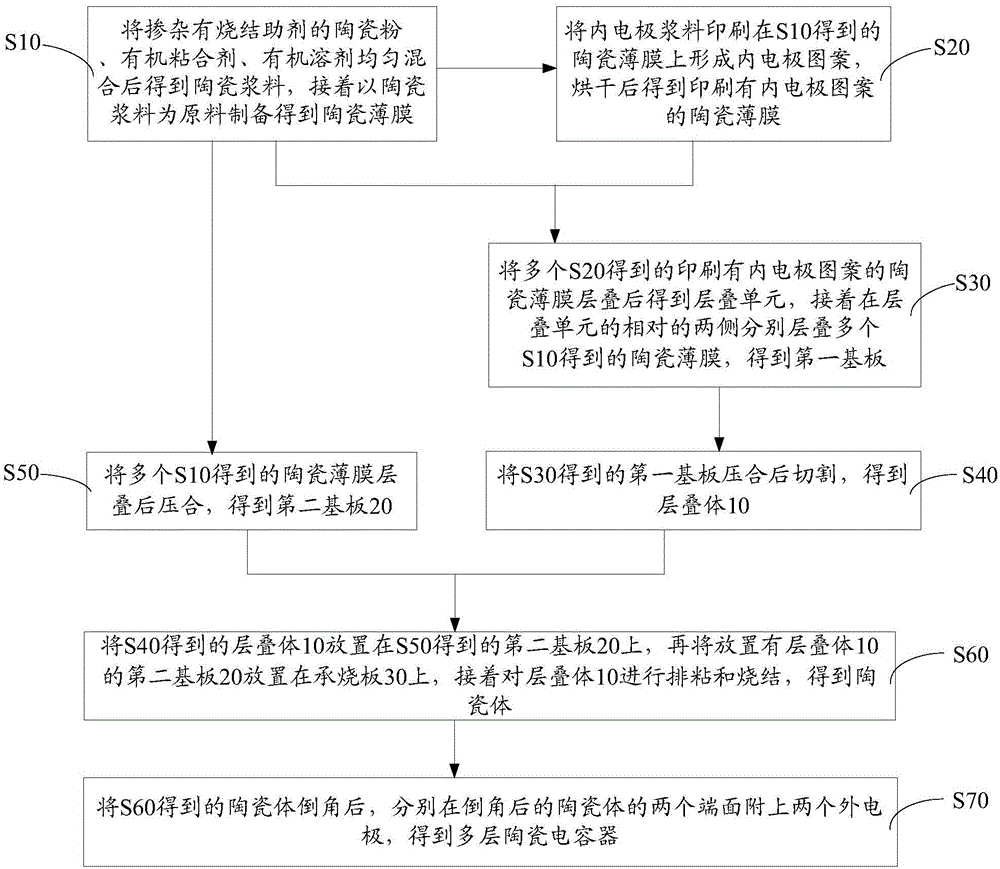
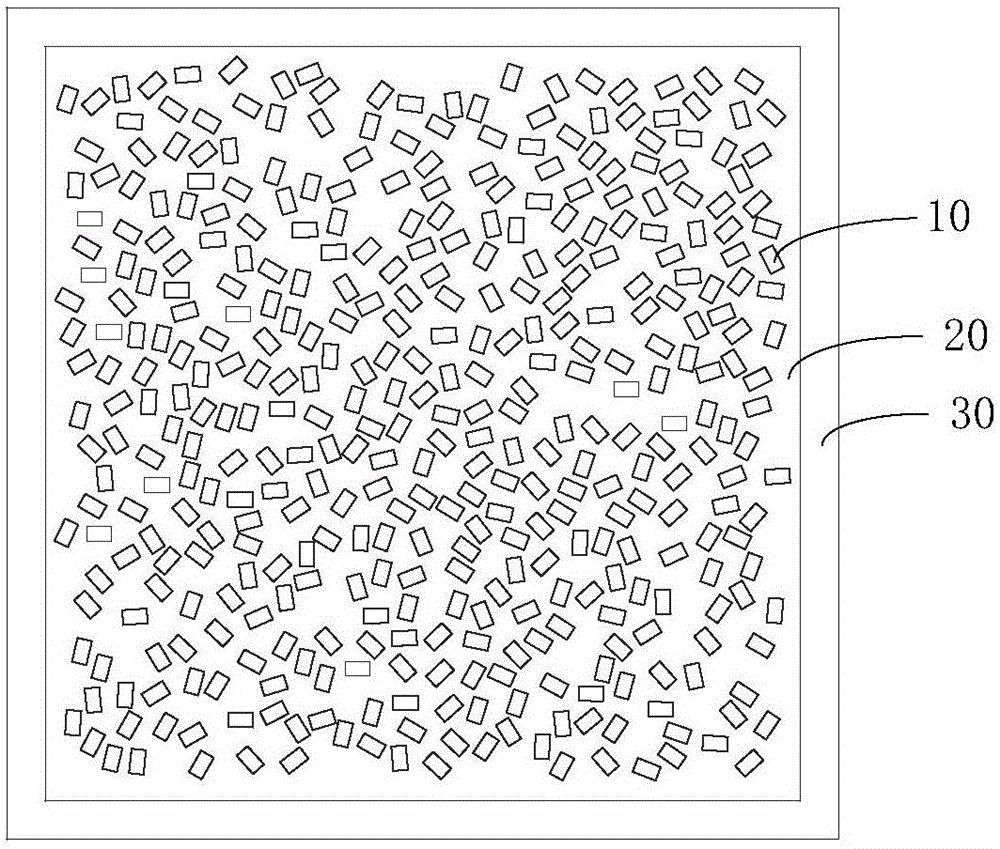
Preparation method for multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveCN104952619APrevent excessive volatilizationImprove consistencyFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsMetallurgyCeramic capacitor
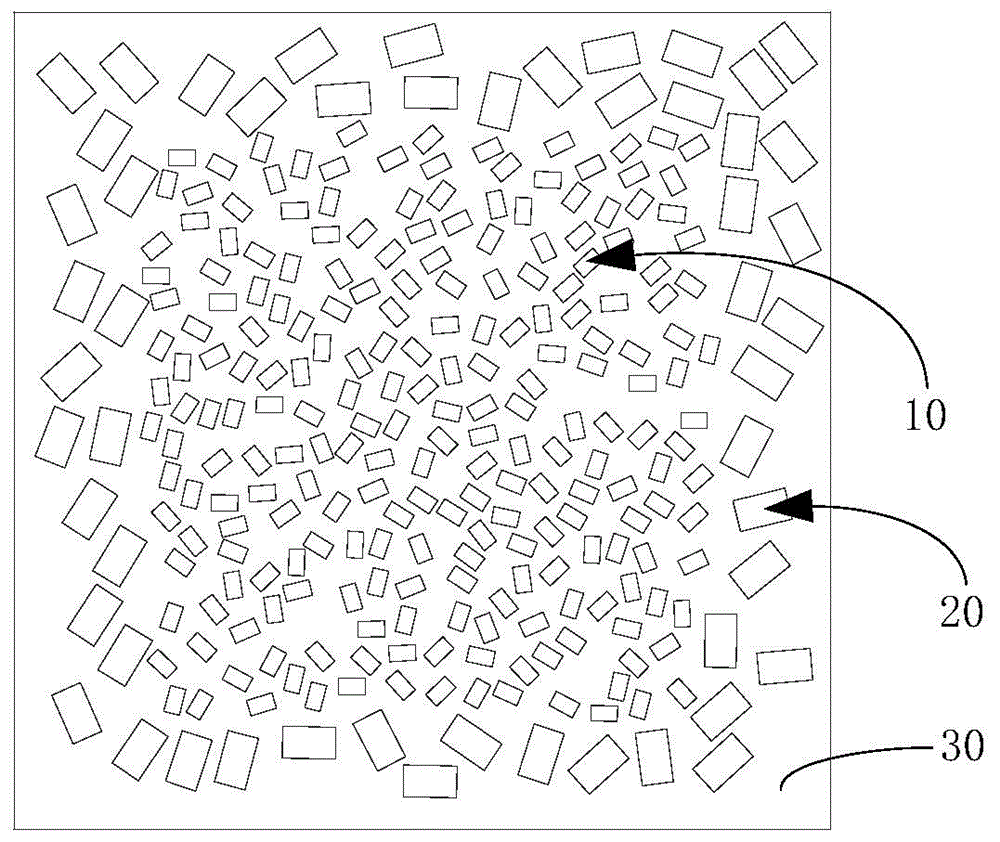
The invention discloses a preparation method for a multilayer ceramic capacitor. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing ceramic thin films and ceramic thin films on which inner electrode patterns are printed, wherein a plurality of ceramic thin films on which the inner electrode patterns are printed are laminated to obtain a laminating unit; respectively laminating a plurality of ceramic thin films on two opposite side faces of the laminating unit, and pressing in and cutting the ceramic thin films to obtain laminating bodies; laminating, pressing in and cutting the plurality of ceramic thin films to obtain green blocks; placing the laminating bodies and the green blocks on a load bearing board, wherein the laminating bodies are placed in a middle area, and the green blocks encircle the peripheries of the laminating bodies, and performing agglomeration discharging and sintering on the laminating bodies to obtain a ceramic body; after chamfering the ceramic body, attaching two outer electrodes at two ends of the ceramic body. According to the preparation method for the multilayer ceramic capacitor, during sintering, sintering-aid components in the green blocks volatilize, so that local atmosphere with higher volatile concentration is formed at the peripheries of the green bodies, and the ceramic body obtained by sintering is uniform, dense and good in consistency.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
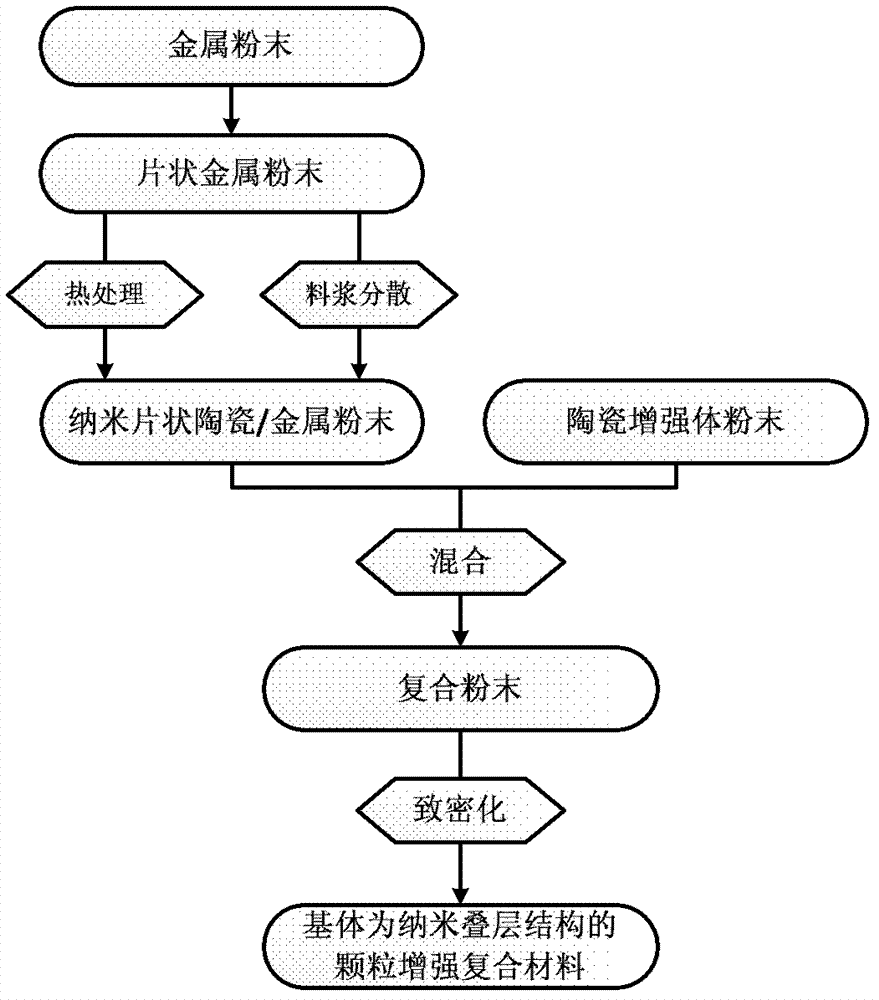
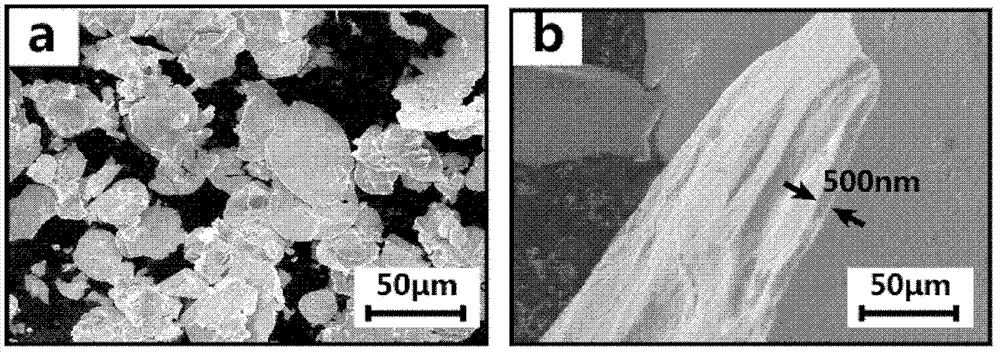
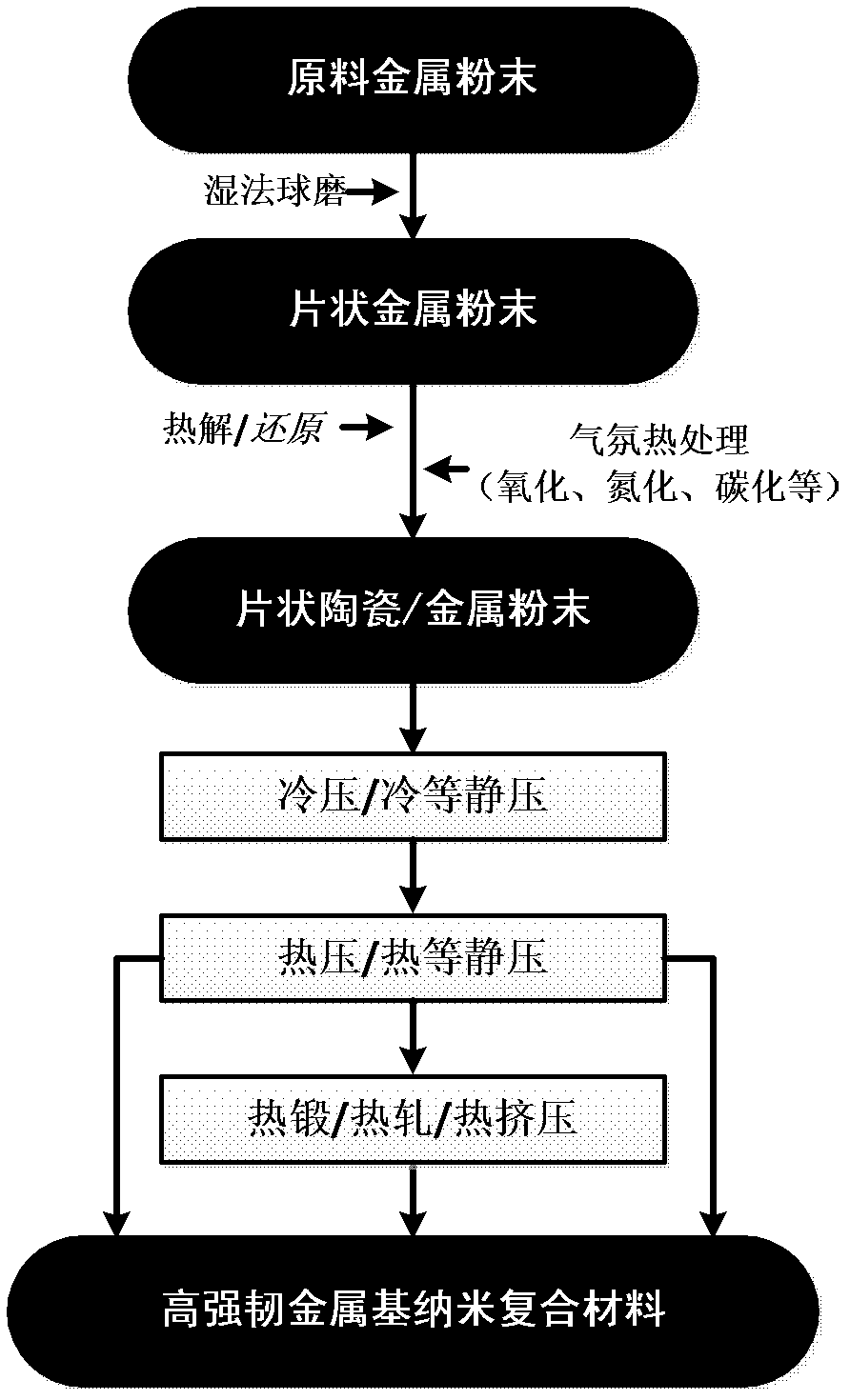
Preparation method of high-toughness metal-based nanometer composite material
The invention provides a preparation method of a high-toughness metal-based nanometer composite material and belongs to the technical field of composite materials. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly, using an atmosphere heat treatment process, generating a layer of a nanometer ceramic thin film on the sheet-shaped metal powder through reaction in-situ; and then carrying out densifying treatment by using a powder metallurgical process, so as to obtain the large compact metal-based composite material. The metal-based composite material prepared by the invention has a metal / ceramic alternative laminated structure, wherein a ceramic layer can be used for effectively restraining the reply of a metal layer and the crystal grain growth, improving the high-position wrong storage capability, keeping a nanometer crystal matrix structure, and causing the rotation and inactivation of fissures, so as to realize mechanical properties matched with the high toughness. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, convenient and practicable, can be used for realizing the macro-quantized preparation of the large-size composite material, and is good for prompting engineering applications of the metal-based nanometer composite material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
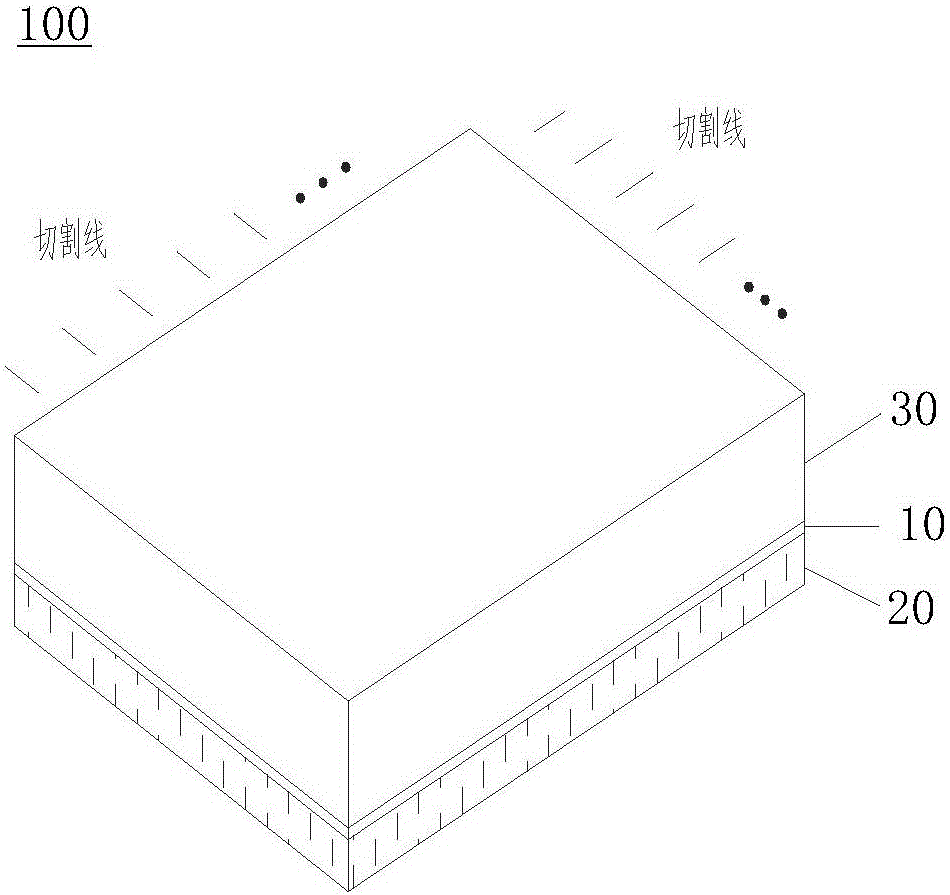
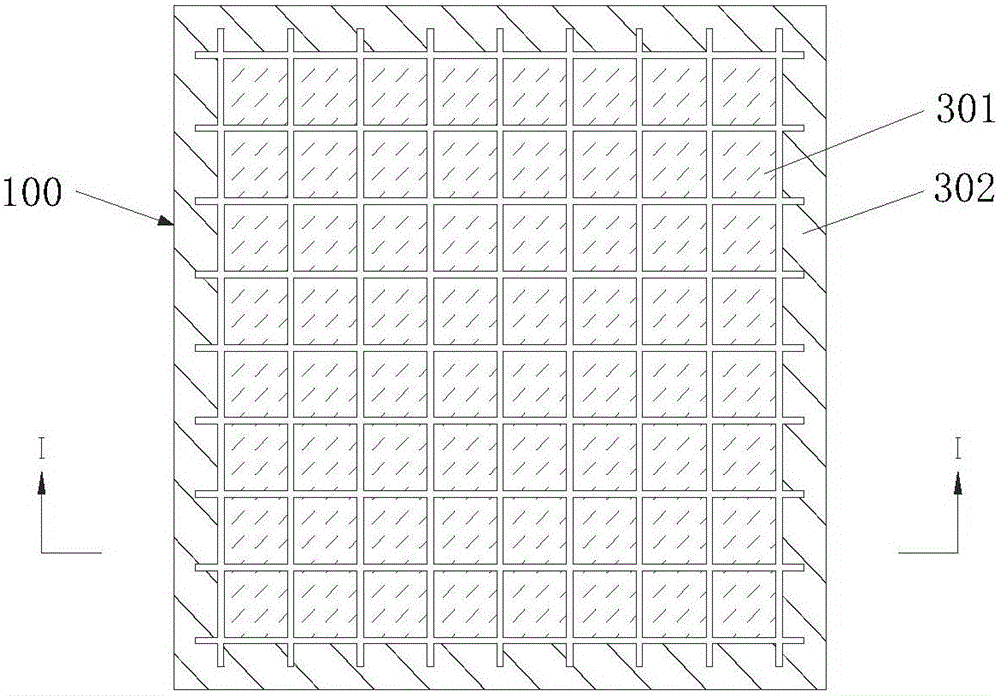
Method for preparing multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveCN104987082AImprove consistencyPrevent excessive volatilizationFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsCeramic capacitorElectrode
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multilayer ceramic capacitor. The method includes the steps that an isolation thin film is prepared; ceramic thin films are prepared; the ceramic thin films are stacked, and a first substrate is obtained; the ceramic thin films on which inner electrode patterns are printed are prepared; the ceramic thin films on which the inner electrode patterns are printed are stacked, a stacking unit is obtained, the ceramic thin films are stacked on the two sides of the stacking unit respectively, and a second substrate is obtained; the first substrate, the isolation thin film and the second substrate are sequentially stacked and then laminated, and a third substrate is obtained; the third substrate is cut, and the second substrate is completely cut off to form multiple stacked bodies; adhesion removal and sintering are conducted on the third substrate, and the stacked bodies are sintered into a ceramic body; the ceramic body is separated and then chamfered, and two outer electrodes are attached to the two ends of the ceramic body. According to the method for preparing the multilayer ceramic capacitor, in the sintering process, sintering additives in the first substrate volatilize, so that the local atmosphere with high volatilization concentration is formed around the stacked bodies, and the sintered ceramic body is uniform, compact and good in uniformity.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
Absorbable suture nail for anastomat
The invention relates to an absorbable suture nail for an anastomat. The absorbable suture nail comprises a suture nail body, a degradable biological ceramic thin film bottom layer and a degradable macromolecule surface layer, wherein the suture nail body is made of medical degradable magnesium alloy wire materials, the degradable biological ceramic thin film bottom layer is attached on the surface of the magnesium alloy wire materials, and the degradable macromolecule surface layer is used for sealing holes. By the aid of surface double-layer protection formed by the degradable ceramic coating layer and the macromolecule thin film and hole sealing effect of an organic coating layer to the surface of an inorganic ceramic coating layer, the absorbable suture nail for the anastomat can be improved effectively, degrading speed of the suture nail is controlled, and the suture nail can be degraded and absorbed completely in in-vivo environment. Meanwhile, at early stage of postoperation, the suture nail has indispensable acid-resisting or alkali-resisting corrosive performance so as to resist early corrosion damage in the strong acid environment of the stomach and is applicable to anastomosis and suture after various operations in vivo, particularly alimentary canal operation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Preparation method of titanium and titanium alloy surface black protective film for surgical implantation
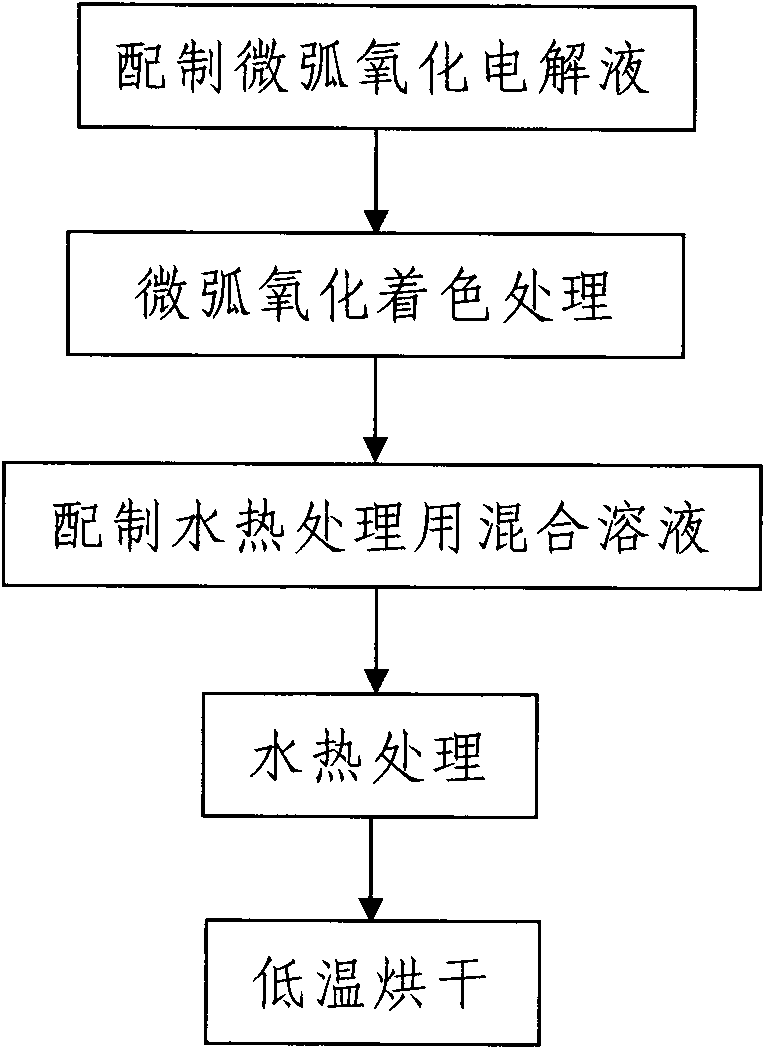
ActiveCN101660190AThe preparation process steps are simpleEasy to operateSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisTectorial membranePlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a titanium and titanium alloy surface black protective film for surgical implantation, comprising the following steps: step 1: carrying out micro-arc oxidation coloring processing on titanium and titanium alloy surface to be processed, in the process, firstly, preparing a micro-arc oxidation electrolysing solution, and then carrying out the micro-arcoxidation coloring processing; and step 2: carrying out subsequent processing on the micro-arc oxidation film, wherein the subsequent processing comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a mixed solution for hydro-thermal processing, completely dipping the titanium and titanium alloy after micro-arc oxidation shading processing in the mixed solution, carrying out the hydro-thermal processing on the surface by adopting a hydro-thermal method, drying the titanium and titanium alloy under the condition of low temperature when the hydro-thermal processing is completed, and generating a layer of pure black micro-arc oxidation film with uniform and plump surface on the titanium and titanium alloy surface. The invention has simple and convenient operation, economy, high production efficiency, and high bonding strength between a generated ceramic film, i.e. the micro-arc oxidation film and a substrate, and the invention can effectively overcome various defects and deficiencies which exist in the prior coating processing techniques.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Photovoltaic cell module and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104716213AImprove performanceReduced Corrosivity RequirementsPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesSlurryEngineering
The invention relates to a photovoltaic cell module and a manufacturing method thereof. An interconnection lead wire of the photovoltaic cell module is connected with a thin grid line and a function ceramic thin film through cured type conducting slurry. According to the manufacturing method of the photovoltaic cell module, the interconnection lead wire coated with the cured type conducting slurry is attached to the surface of a cell piece in a pressing mode, and then curing is carried out; or the cured type conducting slurry is printed on the surface of the cell piece, then the interconnection lead is attached to the cured type conducting slurry in a pressing mode, and connecting of the thin grid line, the function ceramic thin film and the interconnection lead wire is achieved by curing; or a main grid line formed by curing of the cured type conducting slurry is arranged on the surface of the cell piece of the photovoltaic cell module. The photovoltaic cell module and the manufacturing method thereof have the advantages that the interconnection lead wire does not need to be connected with the cell piece through the high-temperature-sintered traditional main grid line, so that the processing step can be well simplified, and the performance of the cell piece is improved; and scaling powder and a protecting thin film are of no need, and the long-time stability of a component is improved.
Owner:常州市异质结管理咨询合伙企业(有限合伙)
Method for preparing multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveCN105047410AImprove consistencyPrevent excessive volatilizationStacked capacitorsHigh concentrationMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC). The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a ceramic film; preparing a ceramic film on which an inner electrode pattern is printed; laminating multiple ceramic films on which inner electrode patterns are printed so as to obtain a lamination unit, laminating multiple ceramic films on the two opposite side surfaces of the lamination unit to obtain a first substrate; press fitting and then cutting the first substrate to obtain a laminate; laminating and then pressing fitting the multiple ceramic films to obtain a second substrate; placing the laminate on the second substrate, placing the second substrate provided with the stacked body on a load bearing board in order to bond and sinter the laminate, thereby obtaining a ceramic body; chamfering the ceramic body and then adhering two outer electrodes so as to obtain the MLCC. According to the method for preparing the MLCC, when sintering is performed, a sintering aid in the second substrate volatilizes so as to form a local atmosphere with high concentration around the stacked body. Thus, the sintered ceramic body is uniform and compact, and good in consistency.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
Environmentally benign bismuth-containing spin-on precursor materials
InactiveUS6303804B1Low toxicityLess capitol intensiveAntimony compoundsFixed capacitorsEngineeringMetallate
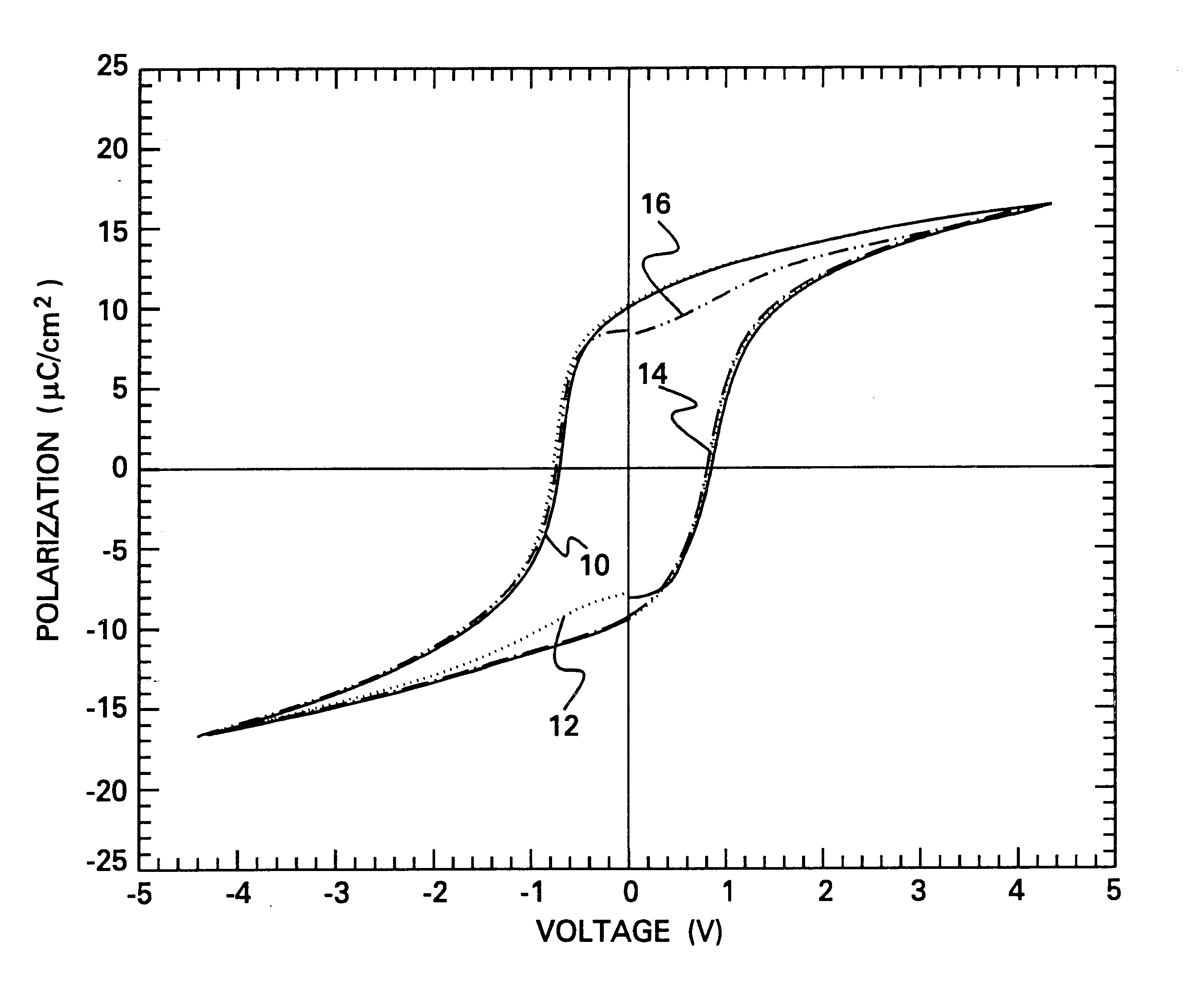
Metal acid salt complexes are provided comprising (1) a first metal ion consisting essentially of bismuth, and optionally, at least one second metal ion selected from the group consisting of barium, calcium, strontium, lead, titanium, tantalum, and niobium, and (2) a polyether acid. The metal acid salt complexes are prepared by combining (1) bismuth ion, and optionally, at least one second metal ion and (2) at least one of a polyether acid and a polyether acid anhydride prepared from the polyether acid. In particular, the use of a mixture of bismuth, strontium, and niobium and / or tantalum salts of the hydrophilic acid 3,6-dioxaheptanoic acid salt is described for production of ceramic thin films, such as for use in ferroelectric devices, using non-toxic solvents. As a consequence, improved electronic devices are formed from less toxic and easier handled precursors and solvents. The present invention provides soluble spin-on precursors which are compatible and soluble in non-toxic and environmentally benign solvents.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
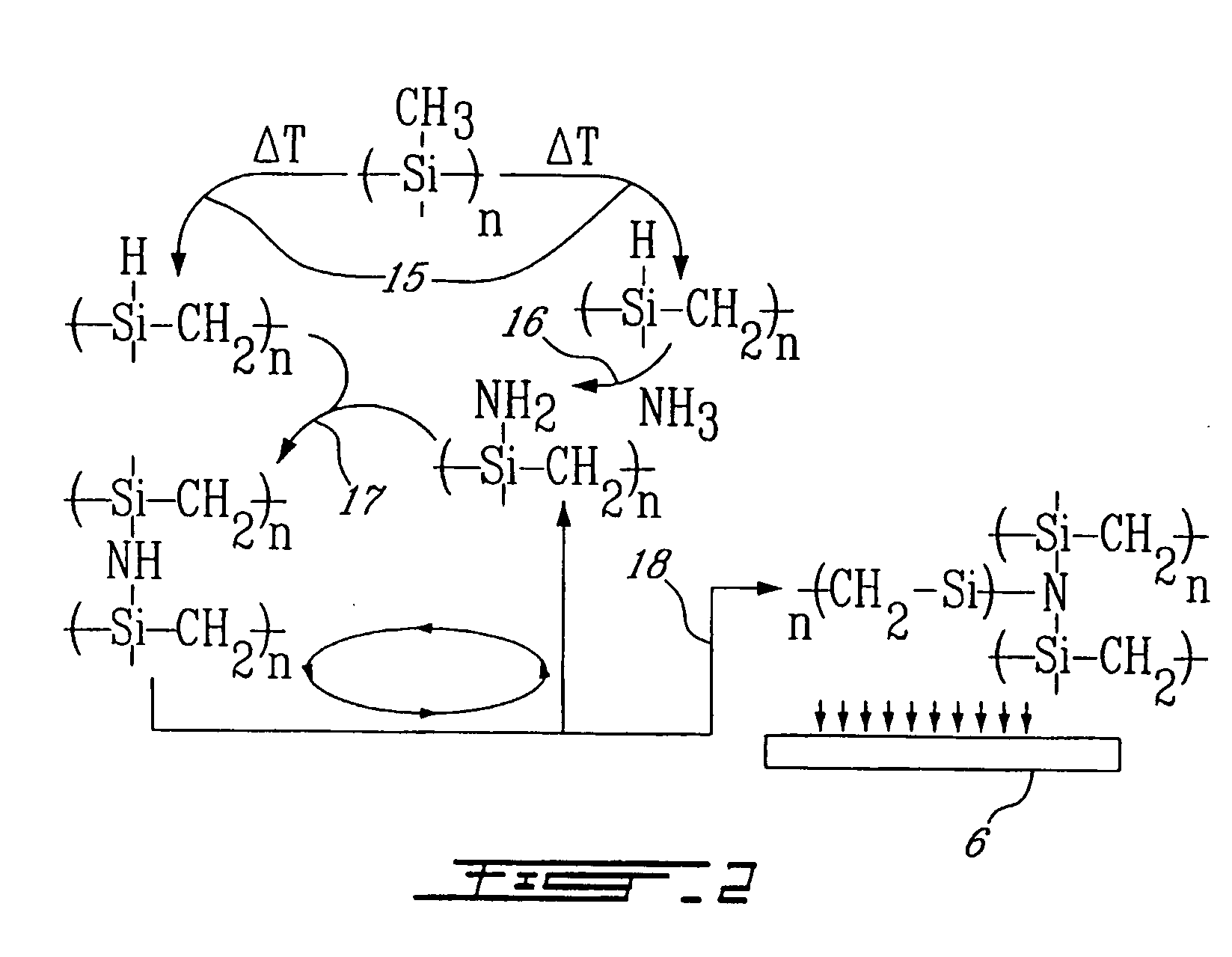
Ceramic thin film on various substrates, and process for producing same
The process of Polymer Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (PACVD) and the semiconductor, dielectric, passivating or protecting thin films produced by the process are described. A semiconductor thin film of amorphous silicon carbide is obtained through vapor deposition following desublimation of pyrolysis products of polymeric precursors in inert or active atmosphere. PA-CVD allows one or multi-layers compositions, microstructures and thicknesses to be deposited on a wide variety of substrates. The deposited thin film from desublimation is an n-type semiconductor with a low donor concentration in the range of 1014-1017 cm−3. Many devices can be fabricated by the PA-CVD method of the invention such as; solar cells; light-emitting diodes; transistors; photothyristors, as well as integrated monolithic devices on a single chip. Using this novel technique, high deposition rates can be obtained from chemically synchronized Si—C bonds redistribution in organo-polysilanes in the temperature range of about 200-450° C.
Owner:SIXTRON ADVANCED MATERIALS
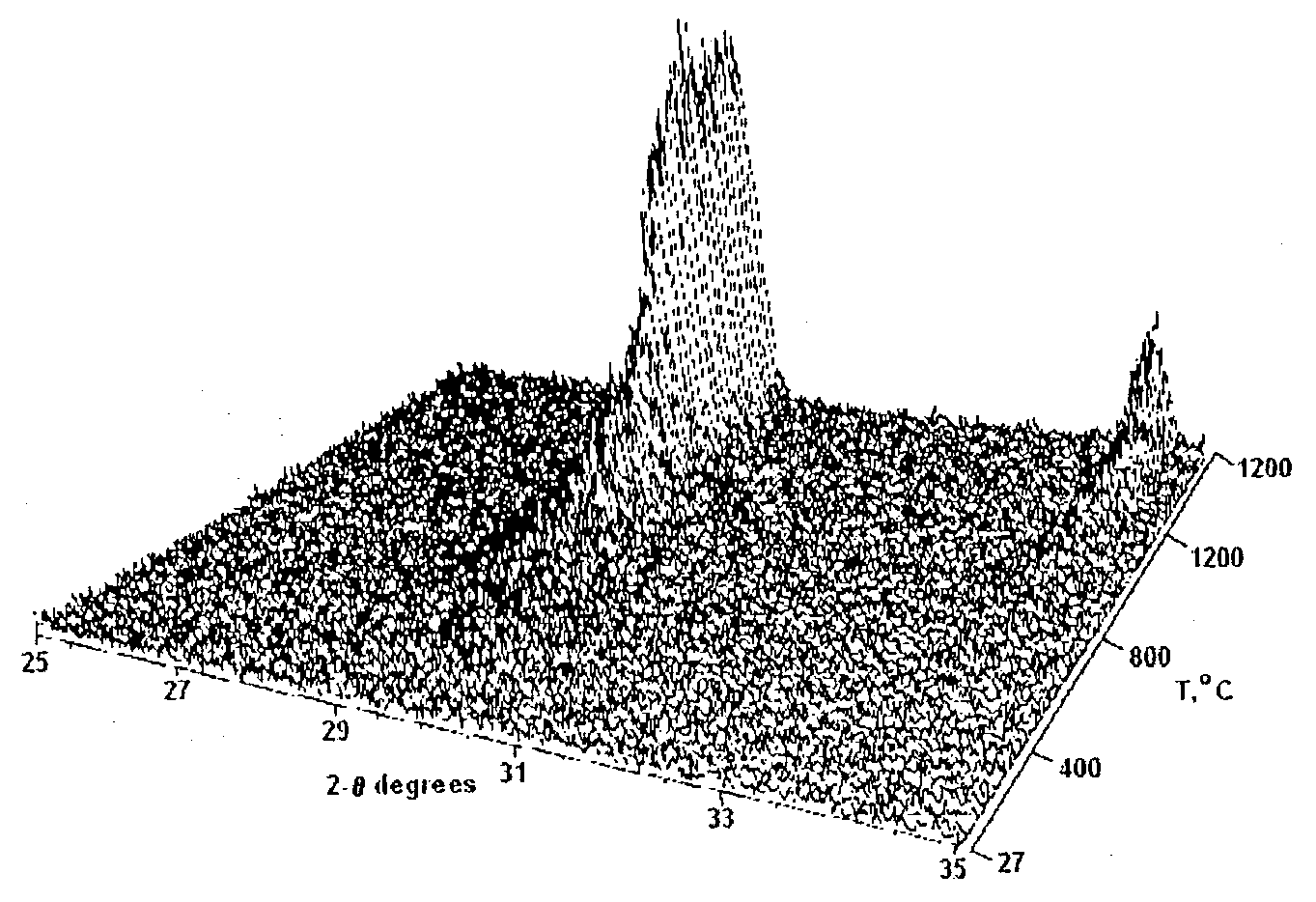
Method for preparing nanocrystalline ceramic thin films
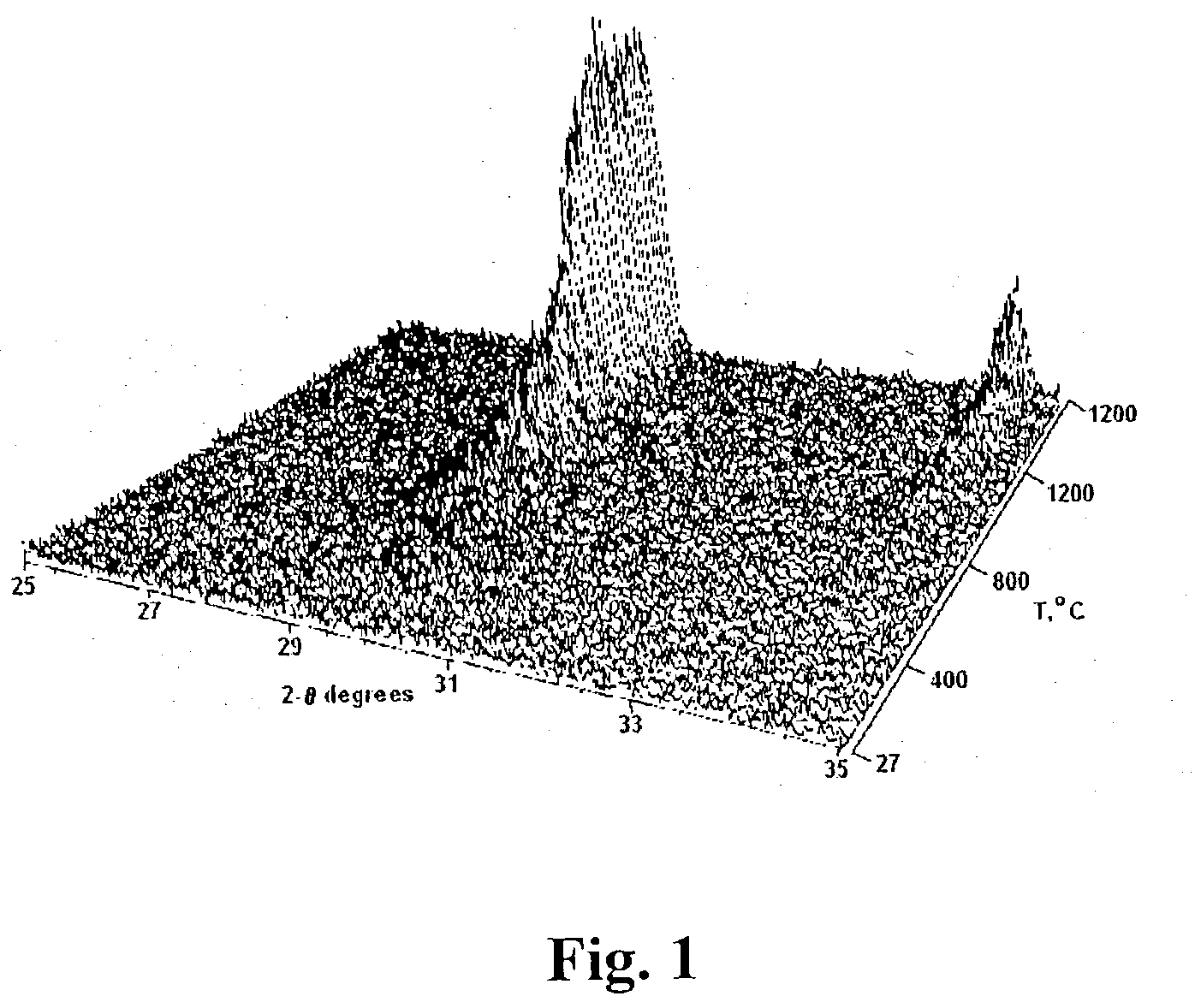
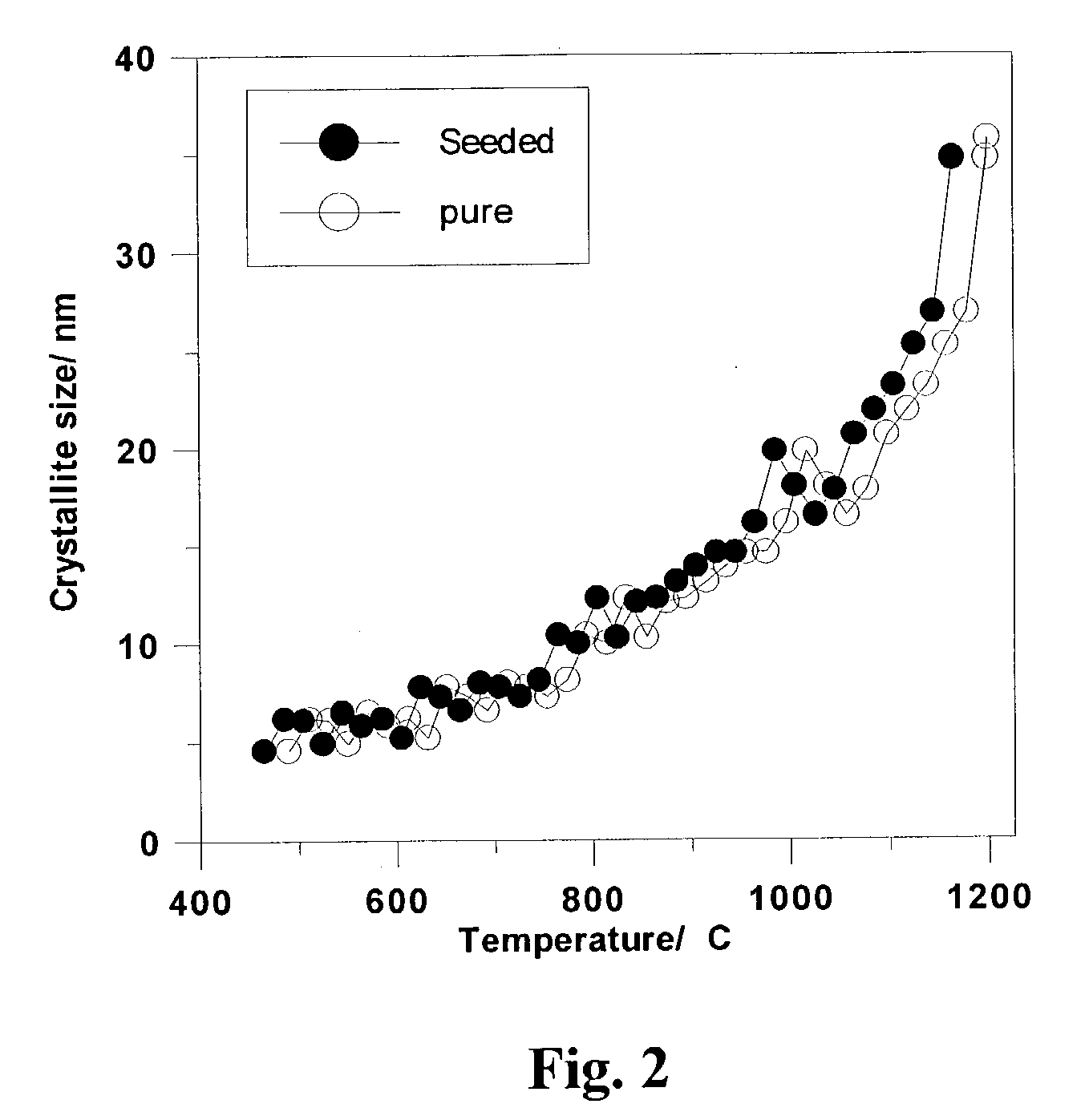
InactiveUS20040247791A1Cost efficientQuality improvementCell electrodesFinal product manufactureOrganic solventThin membrane
A method for preparing nanocrystalline ceramic thin films, particularly at low firing temperatures <1000° C. The method for preparing ceramic thin films comprises preparing a seed gel of metal oxide, dissolving a source compound for cations of the oxide's metal constituents in the solution, then adding a polymerizable organic solvent to the solution and heating to form a polymeric precursor having uniformly dispersed gel seeds within a solid gel structure whereby any voids within the structure are filled with metal cation-containing polymeric precursor. The polymeric precursor is free of precipitates. A surface of a substrate is then coated with at least one layer of the gel-seeded polymeric precursor to form a uniform film of gel-seeded polymeric precursor wherein the film has a thickness of 100 nm to 200 nm per layer. The film is then sintered to convert the film to a nanocrystalline ceramic thin film having a thickness of 100 nm to 1 mum and being substantially free of defects.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Methods of low temperature deposition of ceramic thin films
InactiveUS20150329965A1Affect temperatureIncrease free energyCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsLow temperature depositionOxygen
A method is provided for low temperature deposition of ceramic thin films of carbides, nitrides and mixed phases such as carbo-nitrides by atomic layer deposition (ALD), nano-layer deposition (NLD), and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The deposition chemistries employ combinations of precursors to affect thin film processes at substantially lower temperatures than current deposition processes of thin films of boron (B) carbides, nitrogen (N), nitrides, carbonitrides of silicon (Si), carbon (C), germanium (Ge), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), oxygen (O), sulfur (S), and selenium (S) on substrates. The inventive ALD and corresponding NLD and CVD process methods provide lower temperature deposition of various thin films comprising elements from the group B, C, Si, Ge, N, P, As and O, S and Se. The reactive precursor combinations are selected on the basis of reactivity towards one another as determined by the variation of Gibb's free energy (ΔG) with respect to deposition temperature.
Owner:GADGIL PRASAD NARHAR
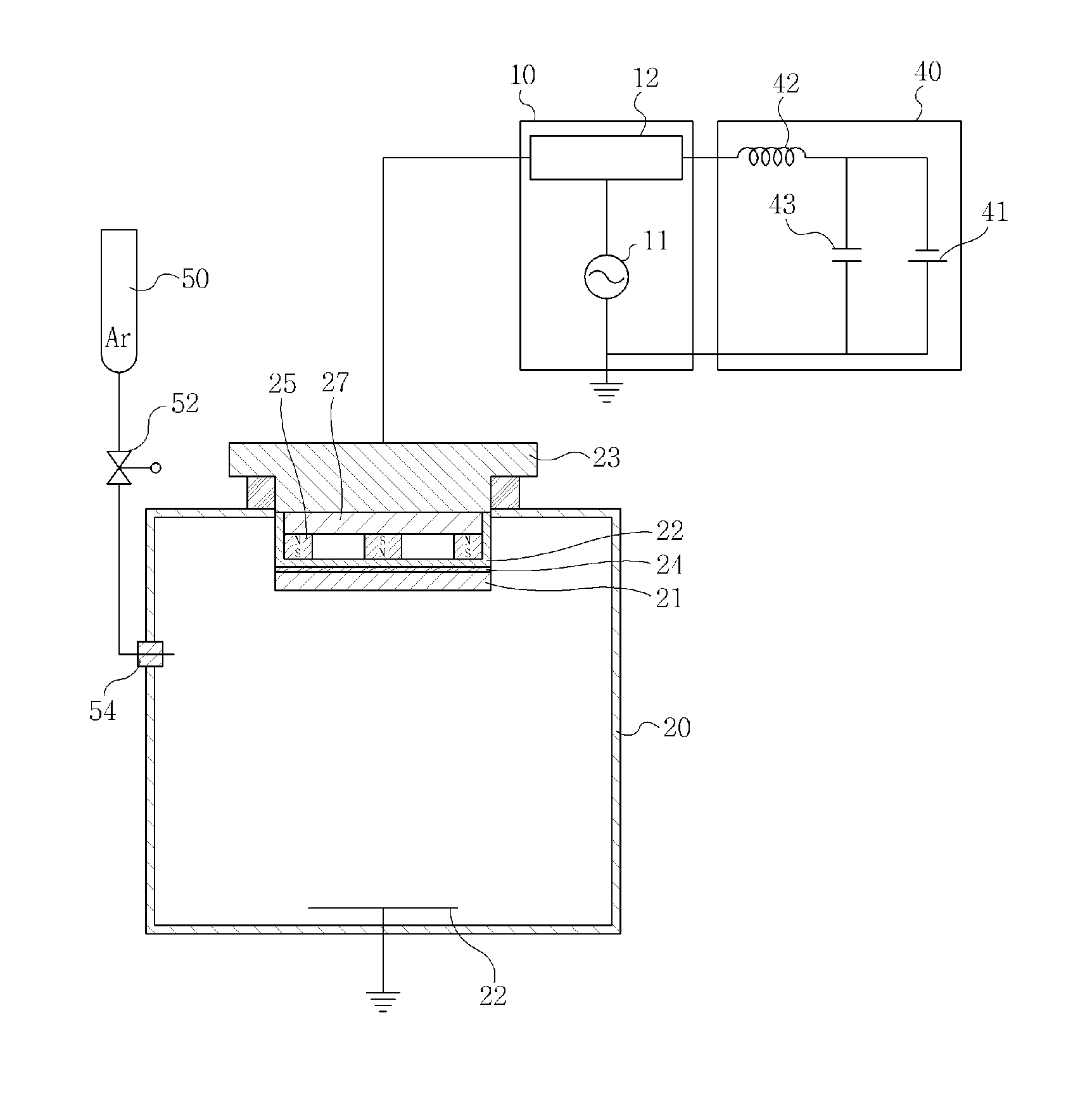
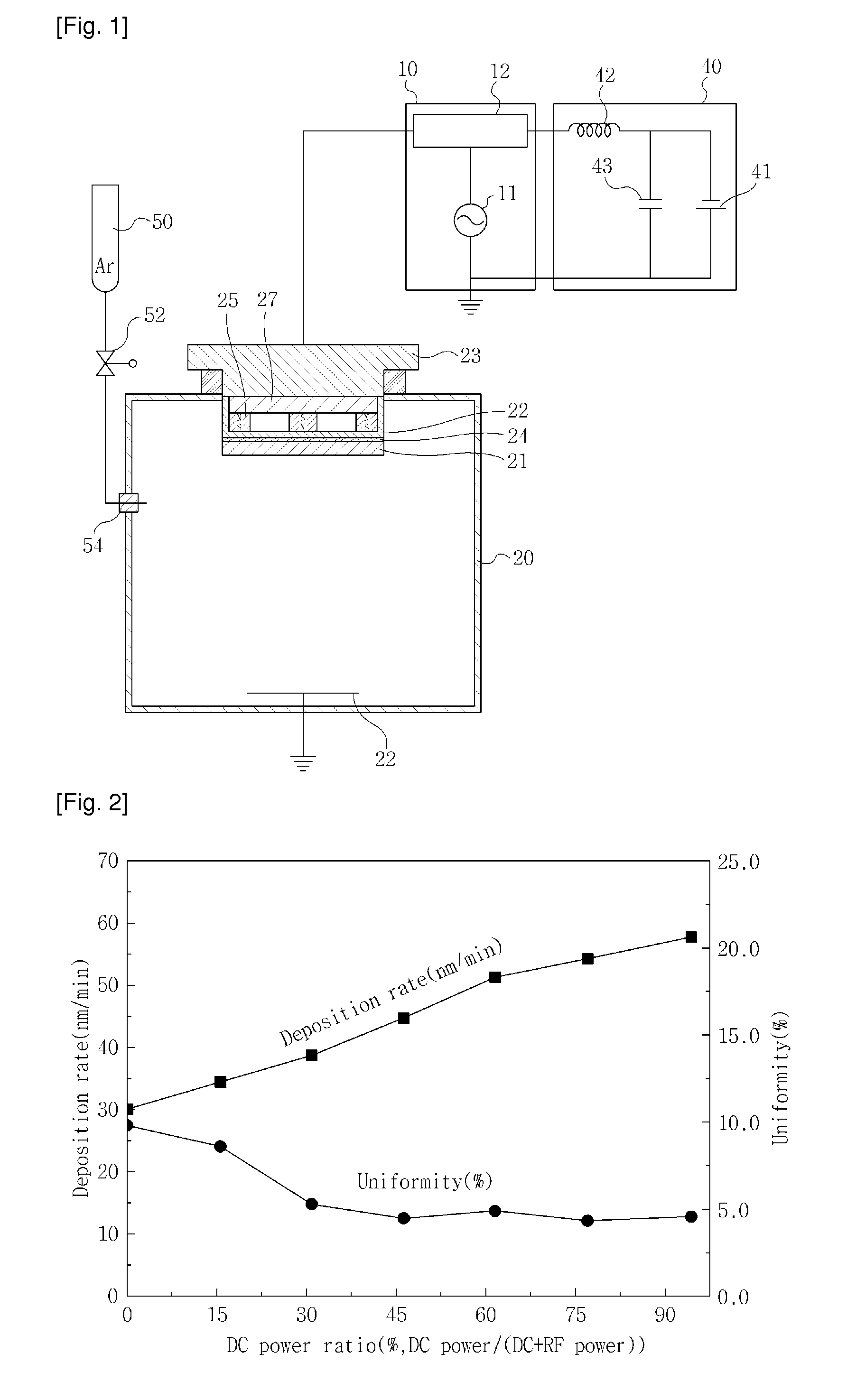
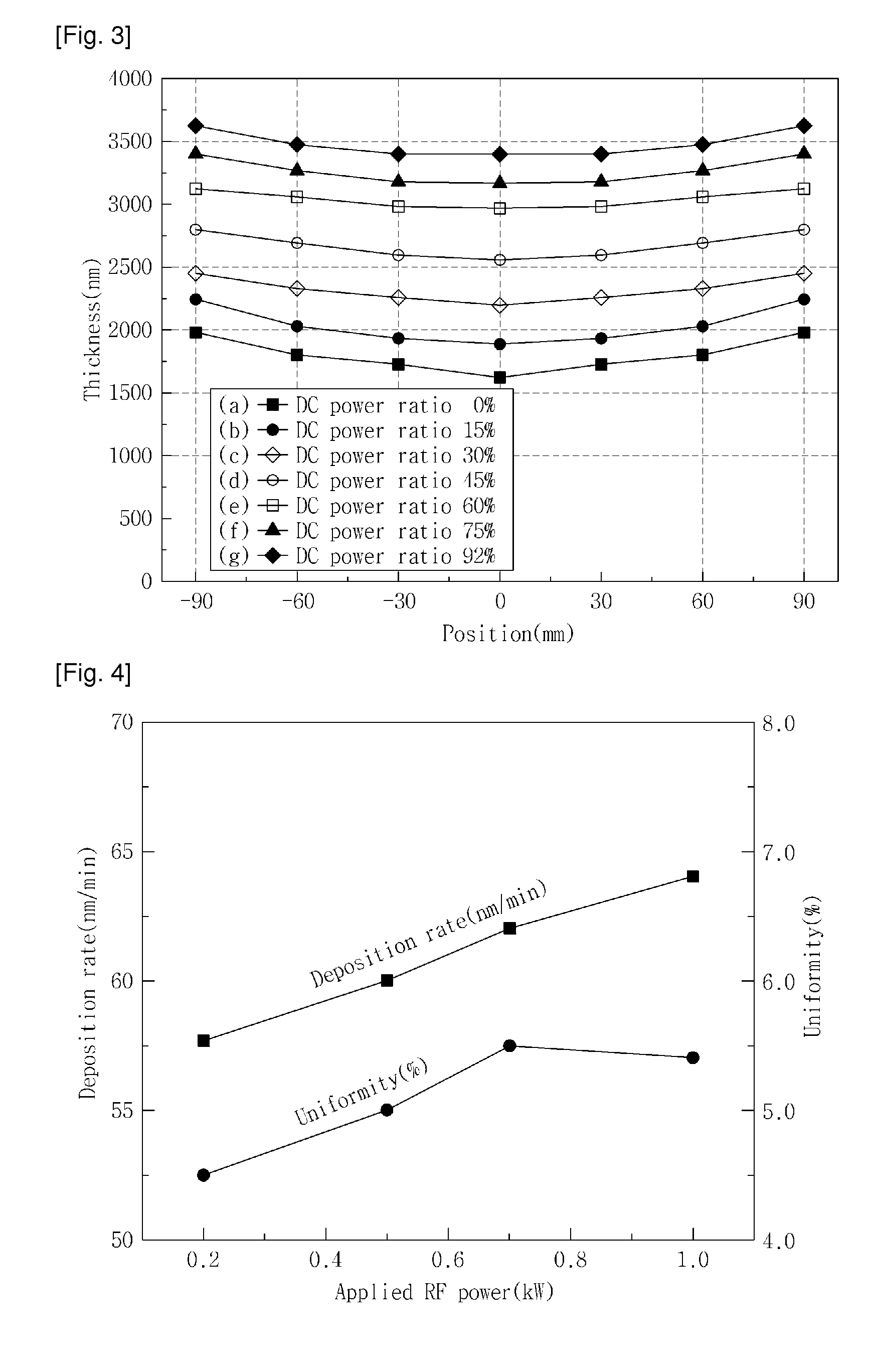
Method for depositing ceramic thin film by sputtering using non-conductive target
InactiveUS20100264017A1Decreasing thin film deposition processing timeImprove uniformityCellsElectric discharge tubesSputter depositionVacuum chamber
A method for depositing a ceramic thin film by sputtering is provided to increase deposition rate of the ceramic thin film and to enhance the uniformity of a deposited thin film, which are accomplished by positioning a nonconductive target within a vacuum chamber, and applying an AC / RF power to the target to produce plasma within the chamber, followed by the application of a hybrid power in combination of an AC / RF power and a DC power to the target to proceed a sputtering process inside the vacuum chamber, such that the ceramic thin film is deposited on a substrate placed in the vacuum chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dielectric ceramic thin film containing Nb composite metal oxide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101293770AEasy to preparePrepare any adjustablePiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesDielectric ceramicsThin membrane
The invention discloses an Nb composite metal oxide-containing dielectric ceramic film and a preparation method thereof. The dielectric ceramic film has a general formula of Ca[Tix(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)(1-x)]O3 (0 is less than or equal to x<1). The preparation method employs a liquid phase spin coating technology. The key precursor solution is obtained by reacting Nb2O5 and hot alkali, and hydrolyzing; reacting the obtained gel and citric acid to obtain an Nb-citric acid solution; polymerizing, and concentrating or esterifying with other metal-citric acid solution. The film is prepared by spin-coating the precursor solution on a clean substrate; drying at 120 DEG C and pretreating at 400-500 DEG C; repeatedly spin-coating and treating; and heat treating at 500-900 DEG C for 0.5-1 hour. With the method, any precursor solution for forming the film can be prepared according to the composition of the dielectric ceramic film; therefore, material cost of Nb element-containing dielectric ceramic film liquid phase forming solution is reduced, and simple and precise control of the film composition is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Thermistor manufactured by ceramic thin films and manufacturing method of thermistor
The invention relates to a ceramic thermistor and a manufacturing method thereof, and particularly relates to a micro NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermistor and a manufacturing method thereof. The thermistor manufactured by ceramic thin films is formed by clamping parallel metal wire leads between two layers of the ceramic thin films, integrally connecting the ceramic thin films with the metal wire leads via a process of 'hot isostatic pressing', then placing the ceramic thin films in a kiln and sintering at a high temperature, wherein the sintering temperature is 900-1200 DEG C, and the sintering time is 3-5 hours; and the used ceramic thin films are prepared from a ceramic slurry via a casting process, and the prescription of the ceramic slurry is decided by the types of thermistors. The manufacturing method of the thermistor comprises the following steps of: cutting the ceramic thin films, hot-pressing and compounding the ceramic thin films with the metal wire leads, parting off the ceramic thin films (with the leads), as well as sintering and packaging a ceramic component.
Owner:东莞市安培龙电子科技有限公司
Metal-ceramic composite substrate and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN101233612AIncrease in sizeReduce thermal resistanceLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsComposite substrateMetal substrate
A metal-ceramic composite substrate having an excellent heat dissipating characteristic and a method for manufacturing such composite substrate at low cost. The metal-ceramic composite substrate (10) is composed of a metal substrate (11), a ceramic layer (12) formed on the metal substrate (11), an electrode layer (13) formed on the ceramic layer (12), and a solder layer (14) formed on the electrode layer (13). The ceramic layer (12) is composed of a ceramic thin film. When the ceramic layer (12) is formed of an aluminum nitride thin film, the metal-ceramic composite substrate (10) having the excellent heat dissipating characteristic is provided for an electronic circuit.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Zinc oxide-based low-voltage pressure-sensitive ceramic film material and preparation method
The invention relates to a zinc oxide pressure-sensitive ceramic, specifically a zinc oxide-based low-voltage pressure-sensitive ceramic film material and a preparation method. The thickness of the film is 1 μm-3 μm, and the ingredients are prepared according to the following molar percentages. ZnO95%-98% is the main material, and Bi2O3, Sb2O3, Co2O3, Cr2O3 and MnO2 are pressure-sensitive functional additives, each of which is 0.1%-1.0%; Drying after ball milling, granulation, pressing into a green body, and sintering into a sputtering target; then using magnetron sputtering to prepare a zinc oxide-based low-voltage varistor ceramic film material: the varistor voltage of the film material is 2.03-4.84V , the nonlinear coefficient is 15.42~19.67, and the leakage current density is 0.24~0.83μA / mm2. The zinc oxide-based low-voltage pressure-sensitive ceramic film material of the invention can be used in integrated circuits to suppress instantaneous high voltage and absorb surge electric energy.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Continuous production and sintering device for self-supported ceramic thin film
ActiveCN105135876AGuaranteed vacuumPlay a thermal insulation effectFurnace typesInsulation layerMetallurgy
The invention discloses a continuous production and sintering device for a self-supported ceramic thin film, and relates to a ceramic thin film. The continuous production and sintering device is provided with a high-temperature furnace system and a sample conveying system. The high-temperature furnace system is provided with a furnace body, a heating device and a vacuum device. The furnace body is provided with a hearth, a heat insulation layer and a vacuum layer. The hearth is divided by the heat insulation layer into a sample introduction chamber, a sintering chamber, a cooling chamber and a sample collection chamber. The heating device is provided with a thermocouple and a temperature controller. The vacuum device is provided with an inner furnace vacuum pump and a vacuum layer vacuum pump. The sample conveying system is provided with a sample introduction chamber sample winding device, a sample conveying device and a sample collection chamber sample winding device. The sample introduction chamber sample winding device is provided with a film winding drum, a fixing rod, a bearing, a motor shaft gear, a bearing gear and a film winding drum motor. The sample conveying device is provided with a sample carrier table, a fixing rod, a bearing, a motor shaft gear, a bearing gear, a big gear wheel, a conveying device motor, a chain and a conveying belt. The sampling chamber sample winding device is provided with a film winding drum, a fixing rod, a bearing, a motor shaft gear, a bearing gear and a film winding drum motor.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Barium titanate and production and process thereof
InactiveUS7431911B2Excellent electrical propertiesSmall particle sizeAlkaline earth titanatesFixed capacitor dielectricBarium titanateProduct gas
The present invention provides a barium titanate having a small particle size, containing small amounts of unwanted impurities, and exhibiting excellent electric characteristics, which can be employed for forming a dielectric ceramic thin film required for a small-sized capacitor which enables production of a small-sized electronic apparatus; and a process for producing the barium titanate. When a titanium oxide sol is reacted with a barium compound in an alkaline solution containing a basic compound, the basic compound is removed in the form of gas after completion of reaction, and the resultant reaction mixture is fired, a barium titanate having a large BET specific surface area and a high tetragonality content is produced.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com