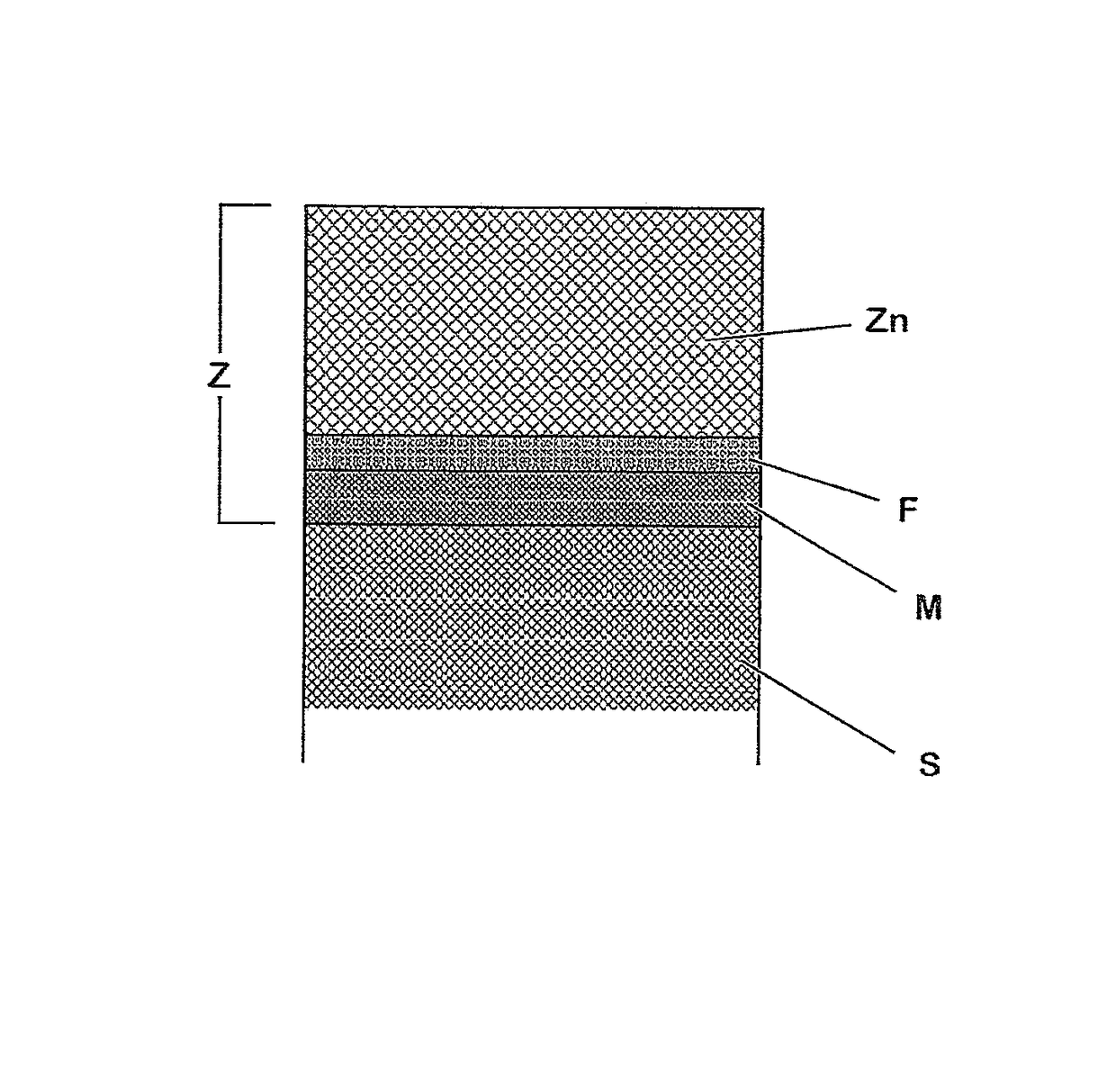
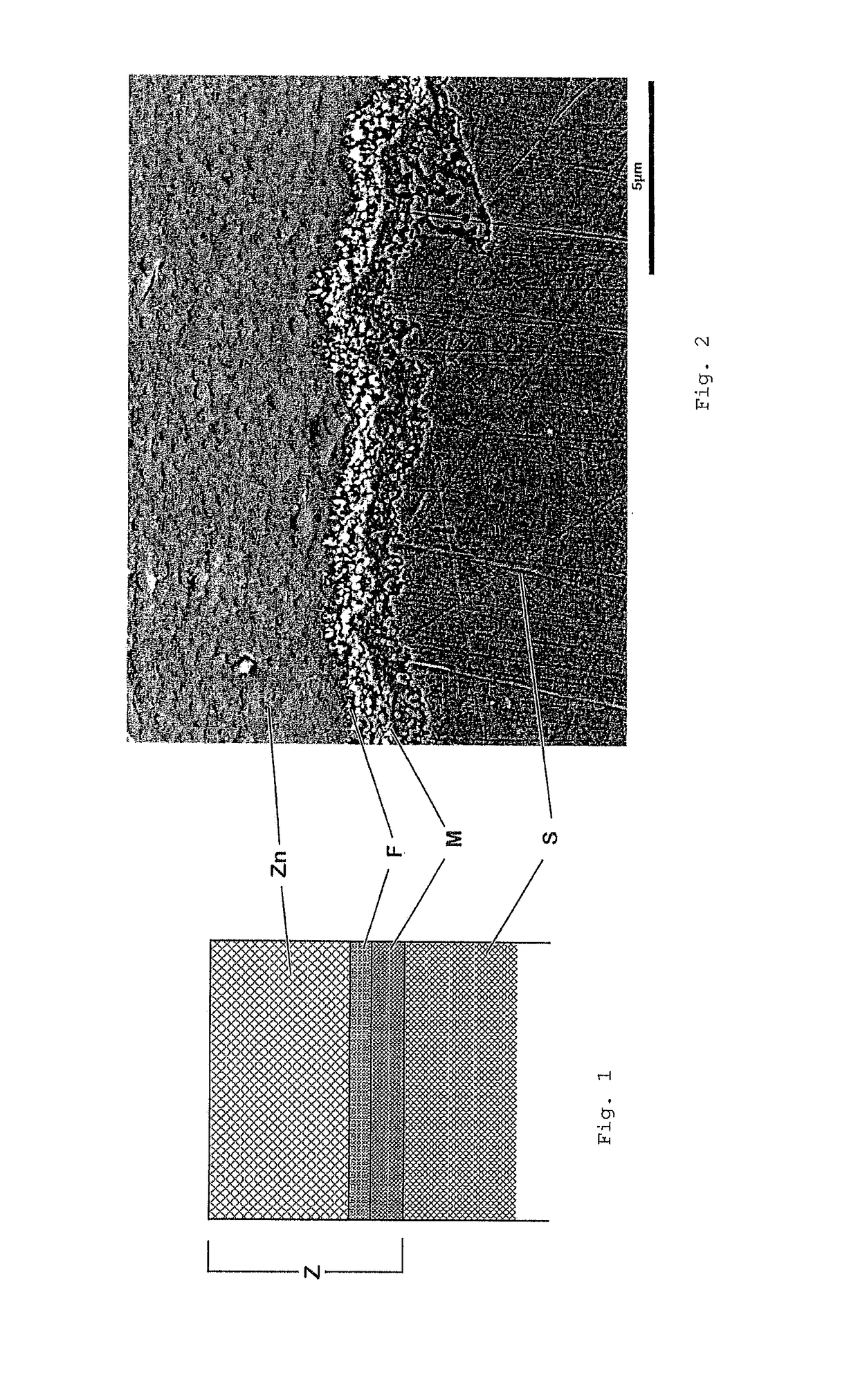
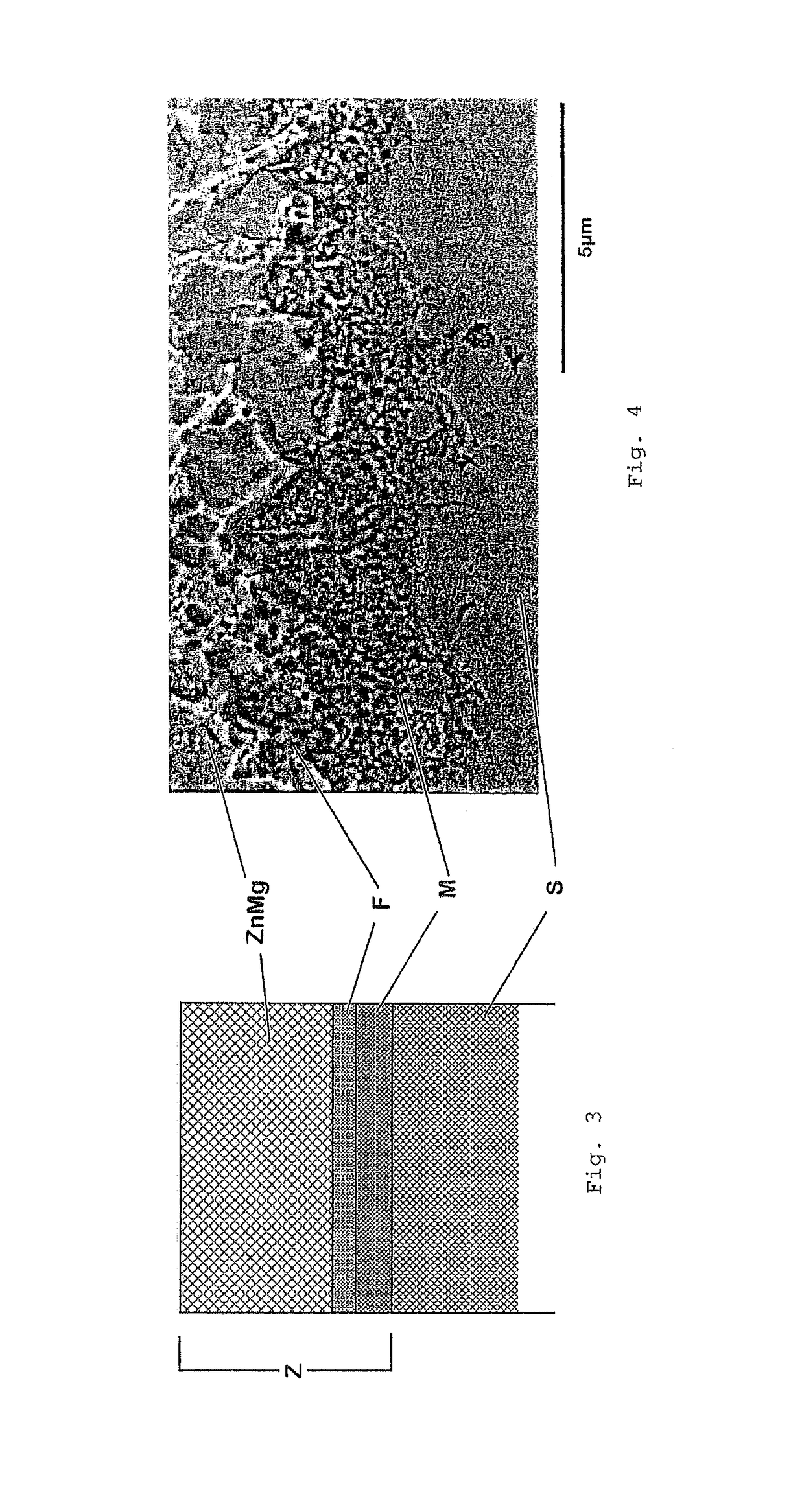
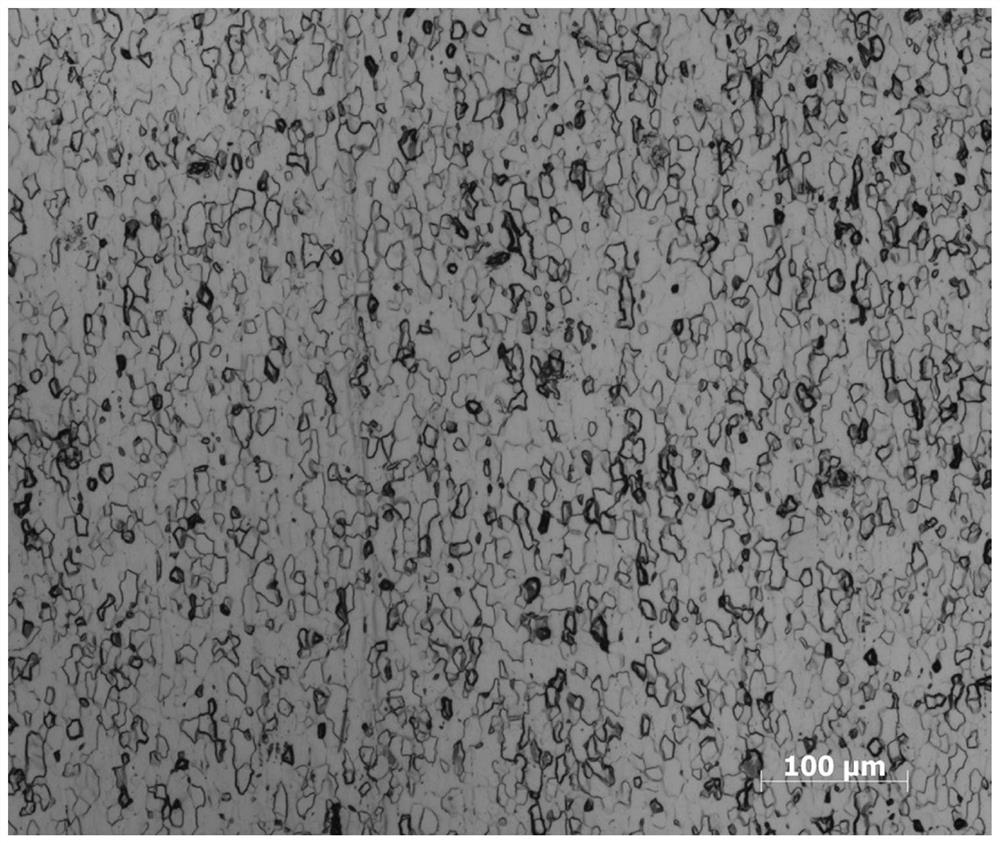
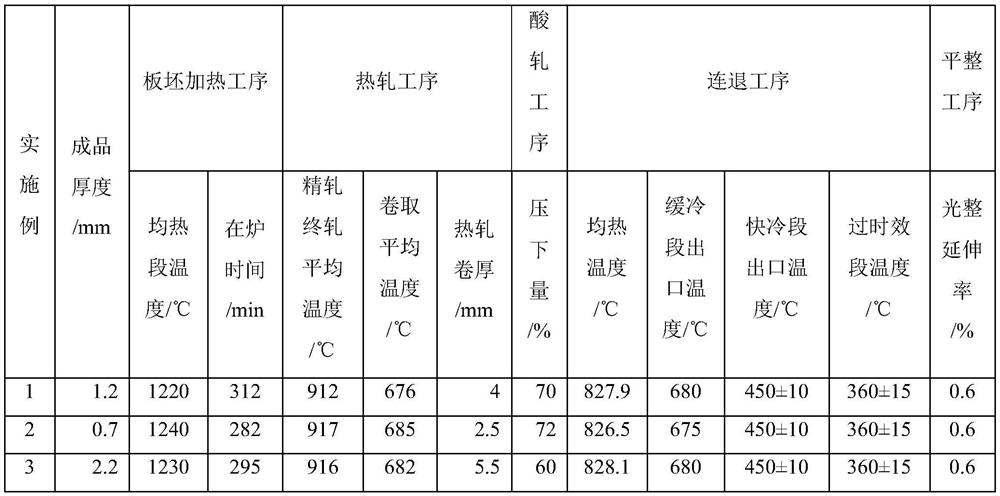
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Annealing atmosphere" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bright annealing in a reducing atmosphere. Annealing is a heat treatment process, where metal parts are heated and cooled in order to give them the desired microstuc- ture and mechanical properties. The time-temperature cycle and atmosphere composition are cri- tical process parameters.
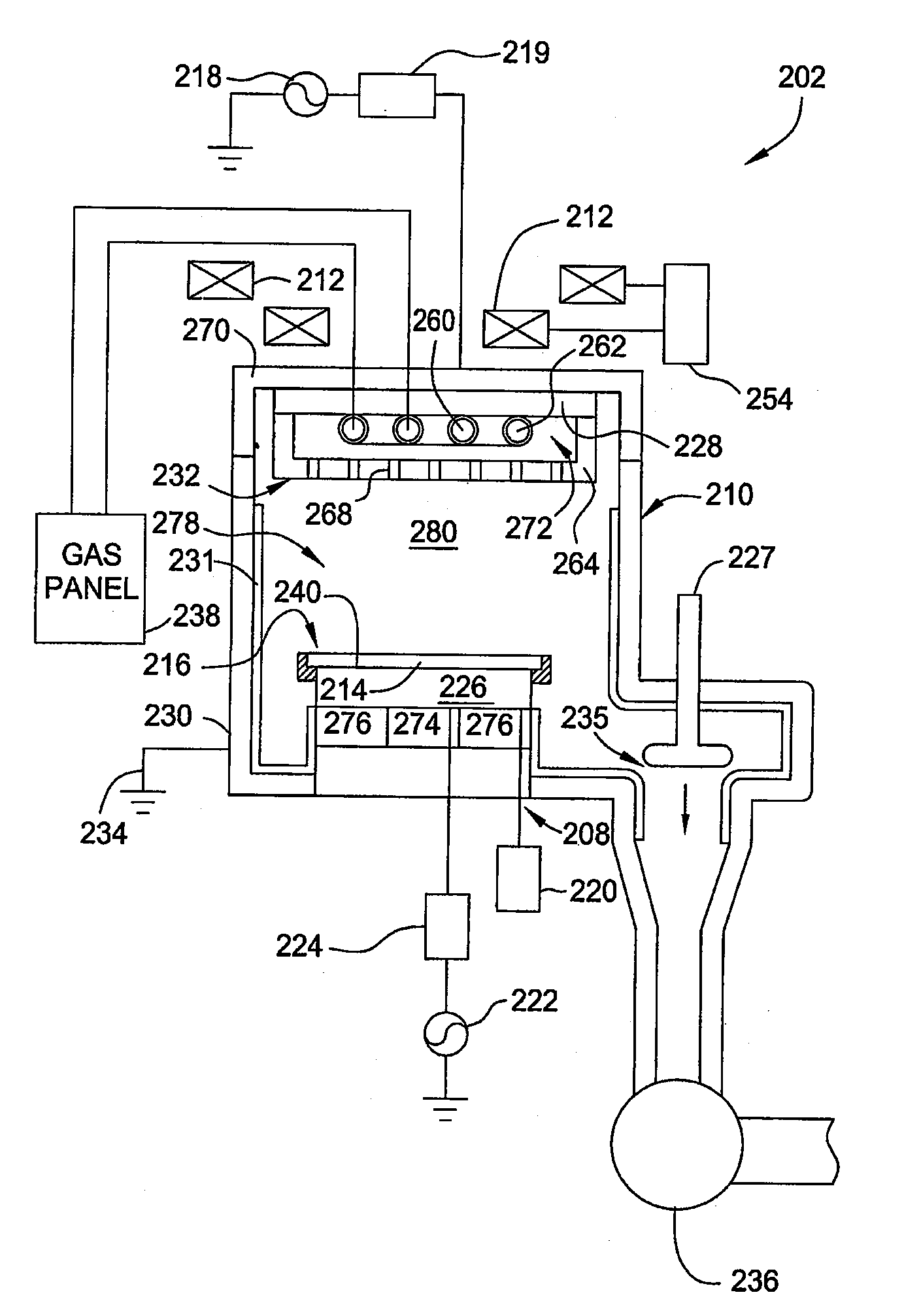
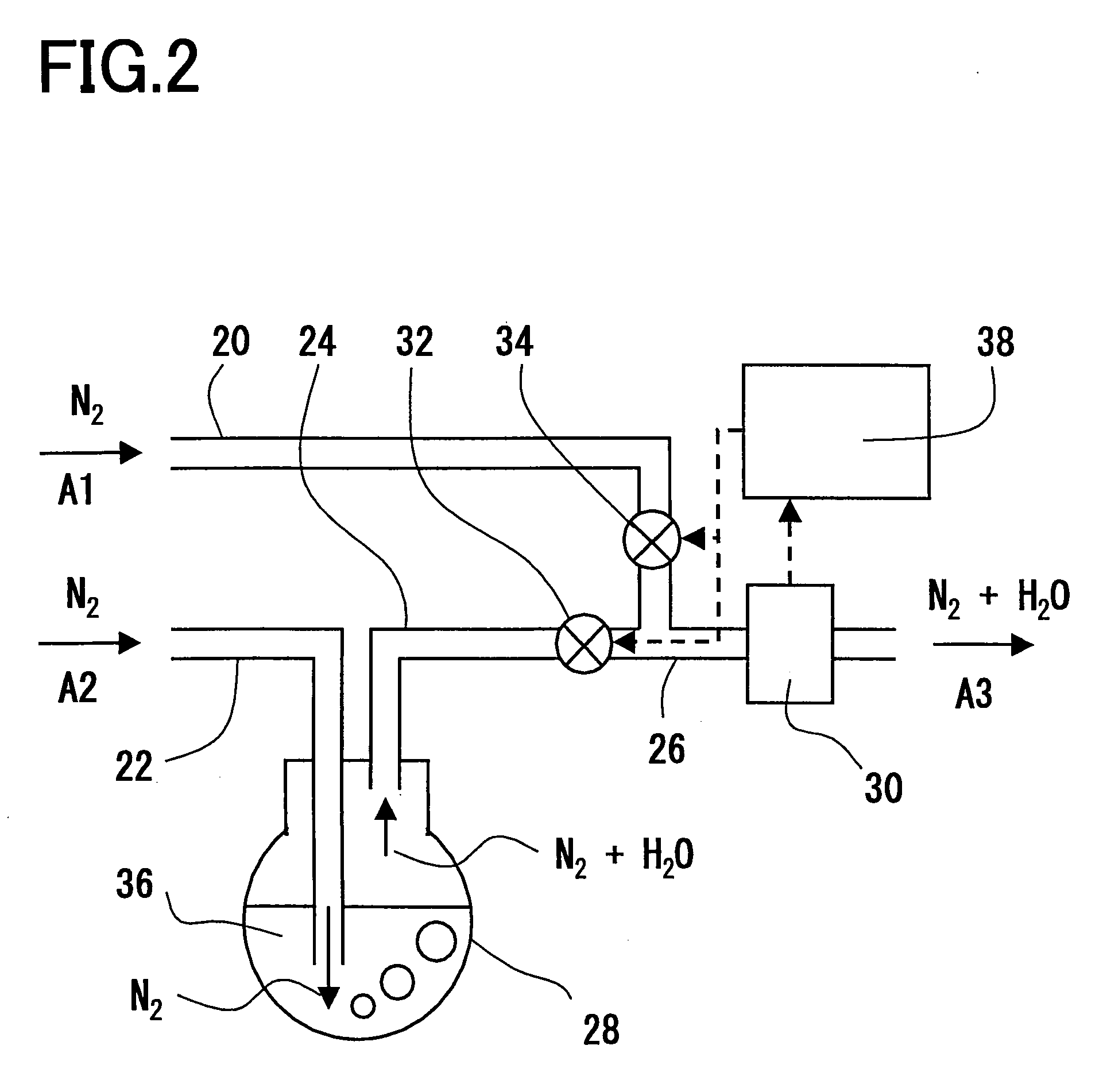
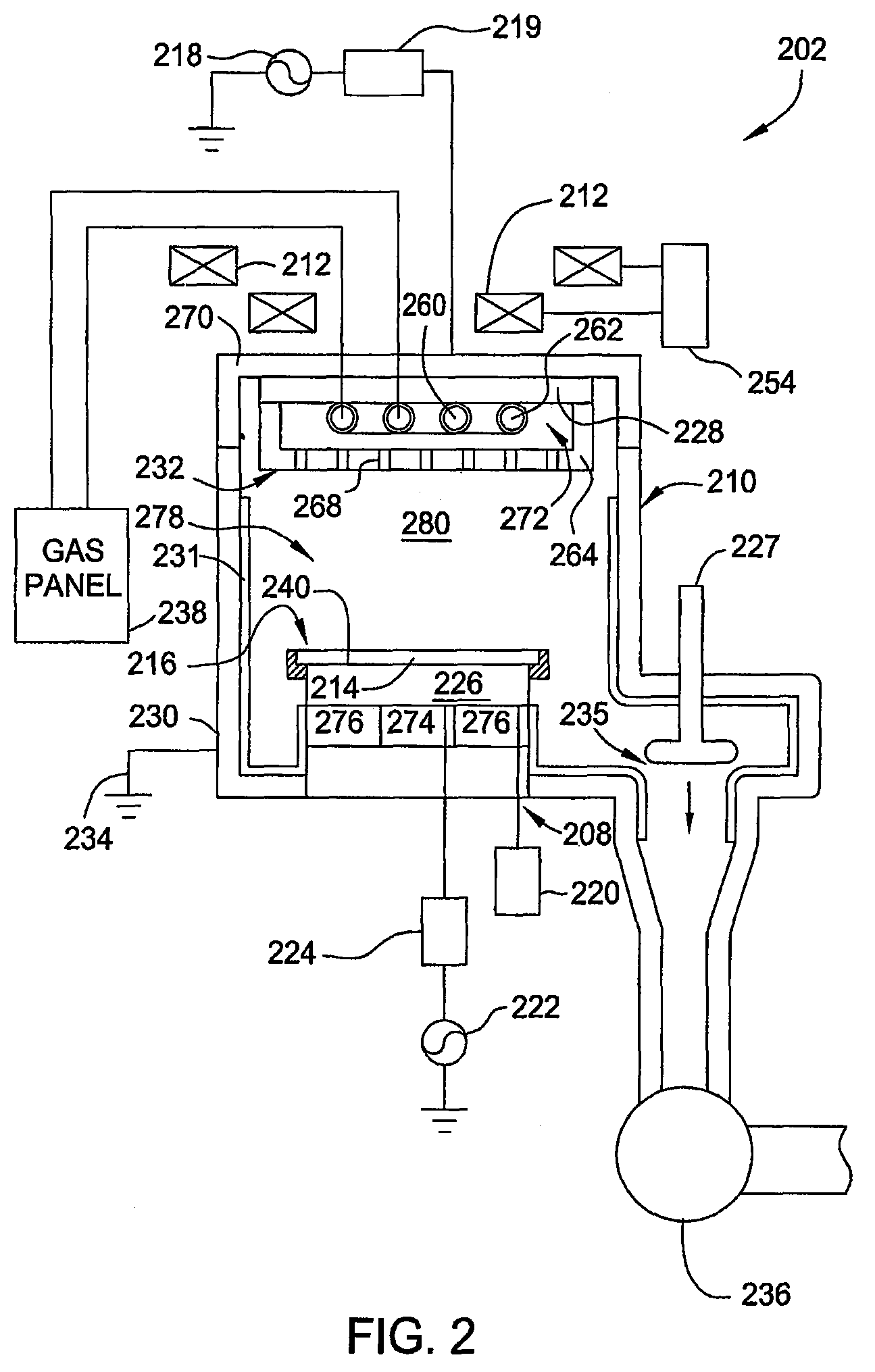
Method for fabricating plasma reactor parts
ActiveUS20080099148A1Wave amplification devicesElectric discharge tubesPlasma reactorAnnealing atmosphere
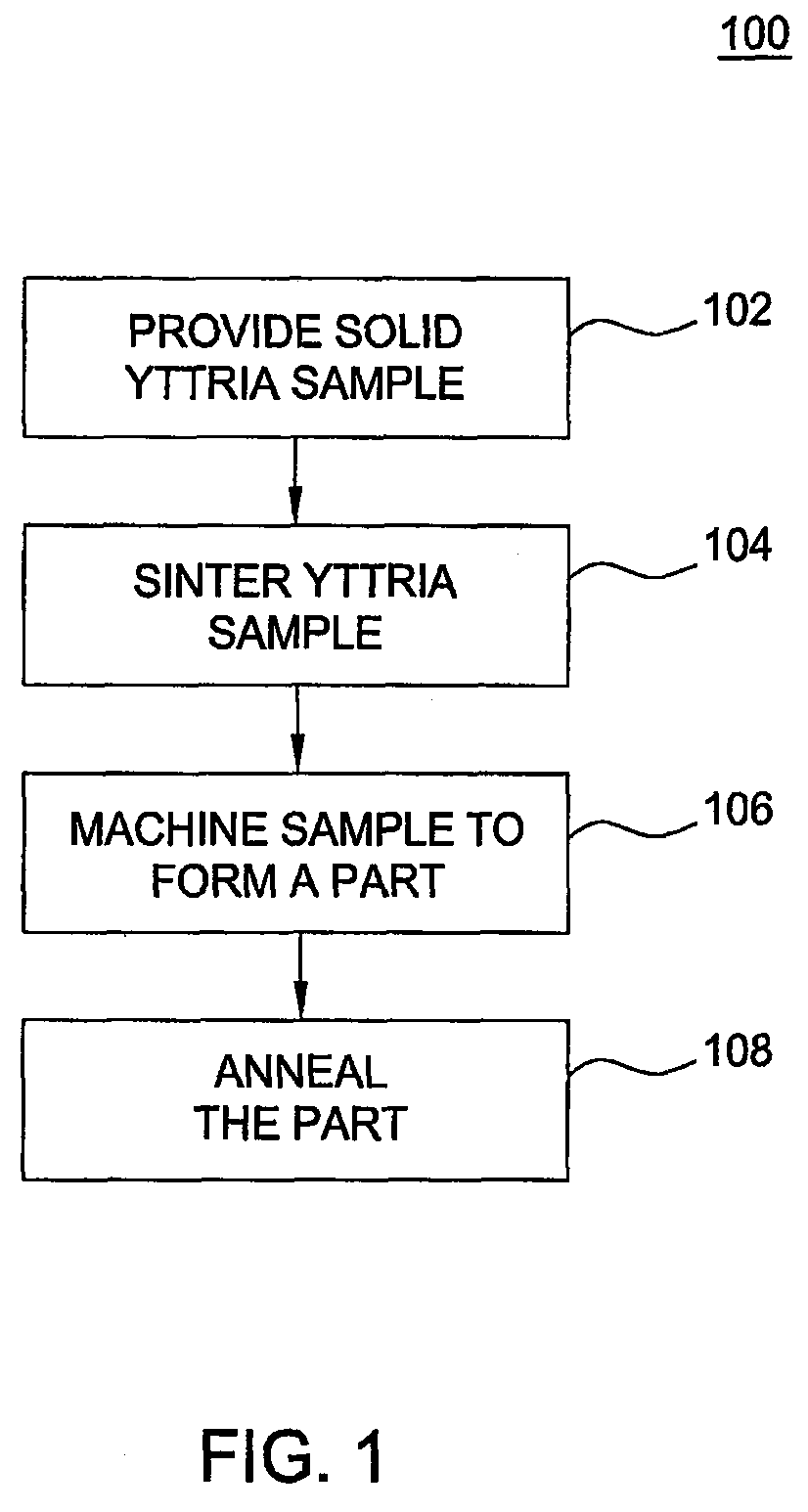
A method of fabricating yttria parts is provided herein. In one embodiment, the method includes sintering a yttria sample, machining the sintered sample to form a part, and annealing the part by heating the part at a predetermined heating rate, maintaining the part at a constant annealing temperature, and cooling the part at a predetermined cooling rate. At least one of the sintering and annealing atmospheres is an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip and grain-oriented electrical steel strip obtained according to said process
InactiveUS20170283903A1Simple stepsReduce oxidationInorganic material magnetismSolid state diffusion coatingThin slabWater vapor
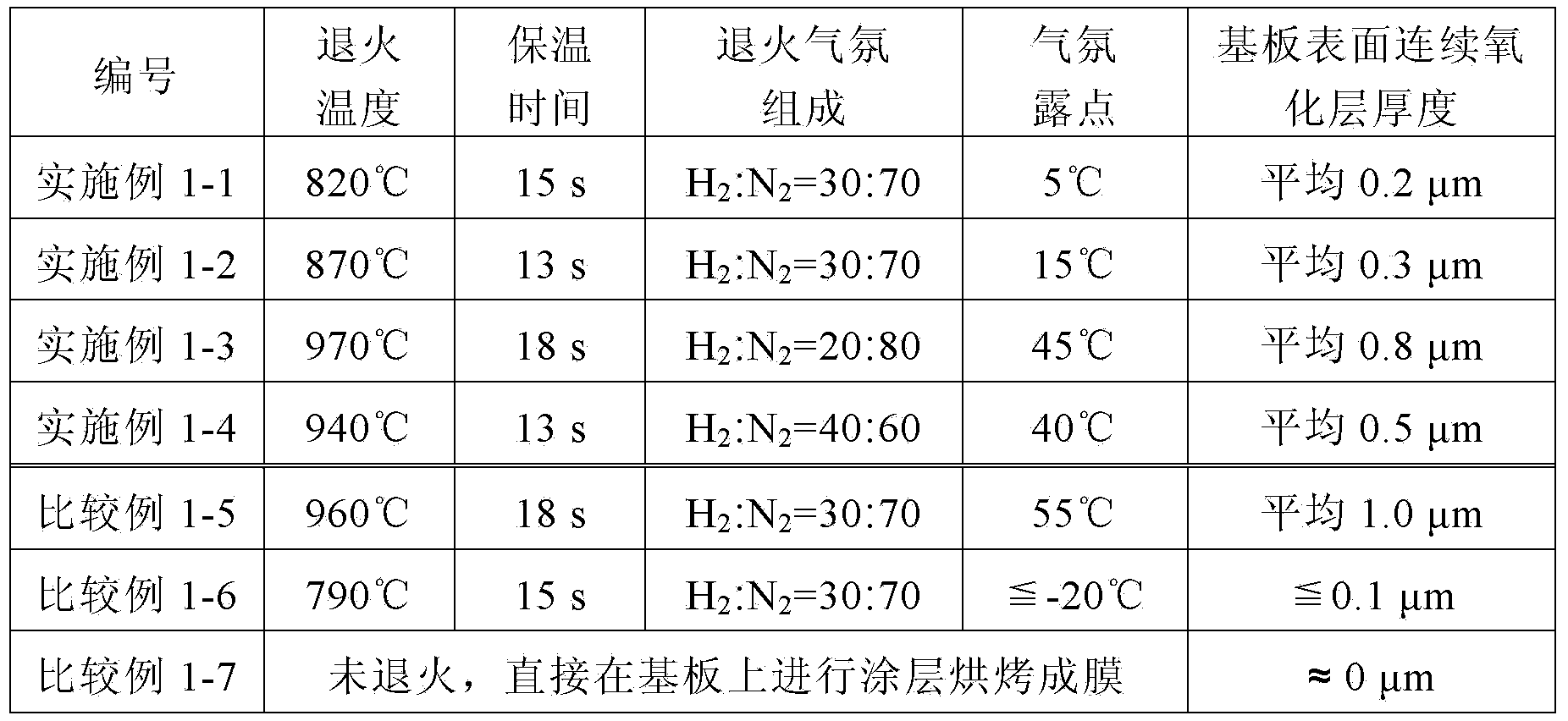
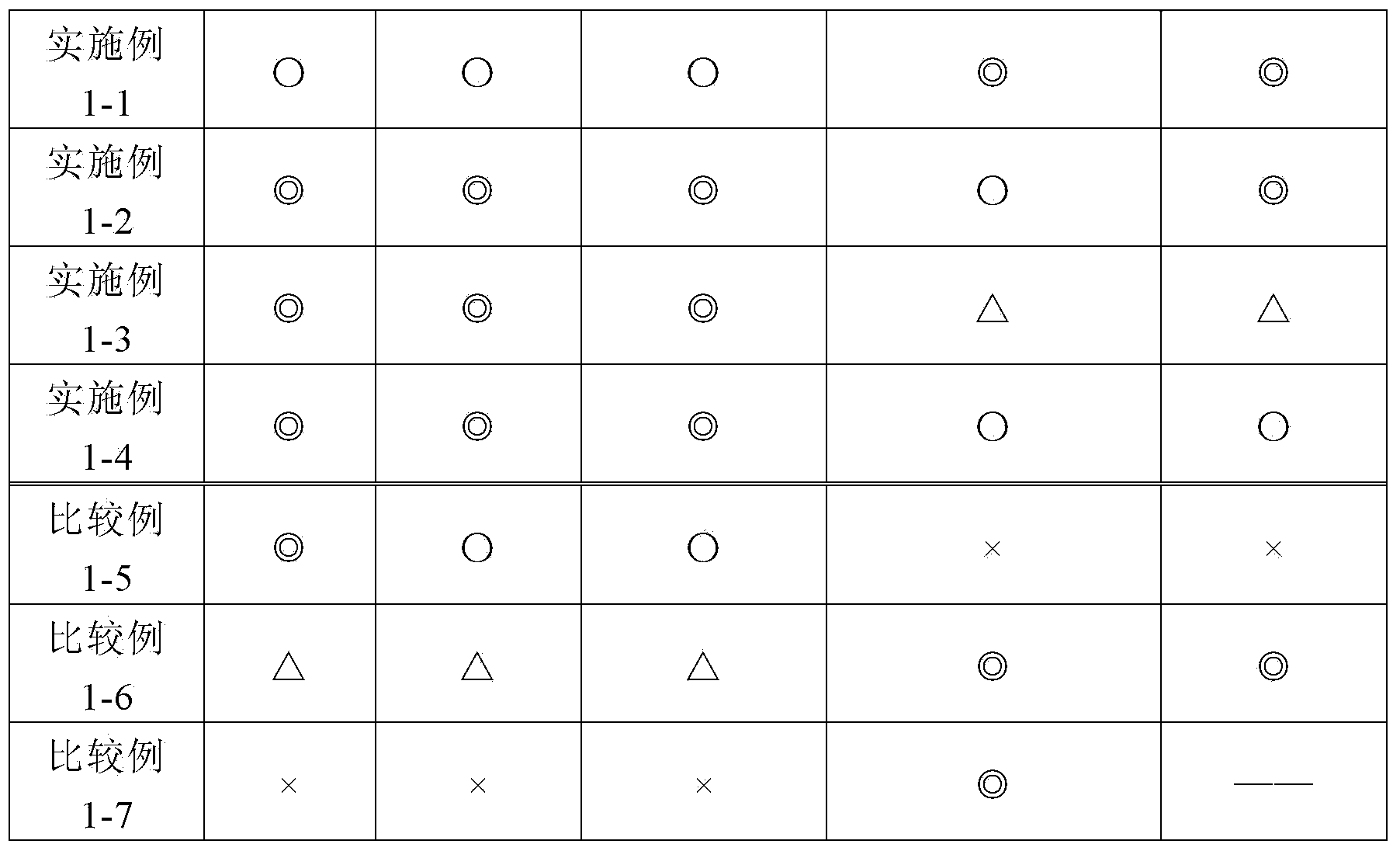
A process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting, comprising the following process steps: a) smelting a steel, b) continuously casting the smelt by thin slab continuous casting, c) heating up the thin slabs and subjecting the slabs to homogenization annealing at a maximum temperature of 1250° C., d) heating to a temperature between 1250° C. and 1350° C., e) continuously hot rolling the thin slabs to form a hot-rolled strip, f) cooling and reeling the hot-rolled strip to form a coil, g) annealing the hot-rolled strip after reeling and prior to a subsequent cold rolling step, h) cold rolling the hot-rolled strip to the nominal usable thickness, i) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing, j) applying an annealing separator (non-stick layer) to the strip surface of the cold-rolled strip, k) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to secondary recrystallization annealing, forming a finished steel strip having a pronounced Goss texture, and l) stress-free annealing the finished steel strip, which has been coated with an insulating layer, provides an improved process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting. This is achieved in that the recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing of the cold-rolled strip in process step h) comprises a decarburization annealing phase and a subsequent nitridation annealing phase, with an intermediate reduction annealing phase being interposed between the decarburization annealing phase and the nitridation annealing phase, and carried out at a temperature ranging from 820° C.-890° C., for a maximum period of 40 seconds, with a dry, gaseous annealing atmosphere, which contains nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) and acts on the cold-rolled strip, and which has a water vapor / hydrogen partial pressure ratio pH2O / pH2 of less than 0.10.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
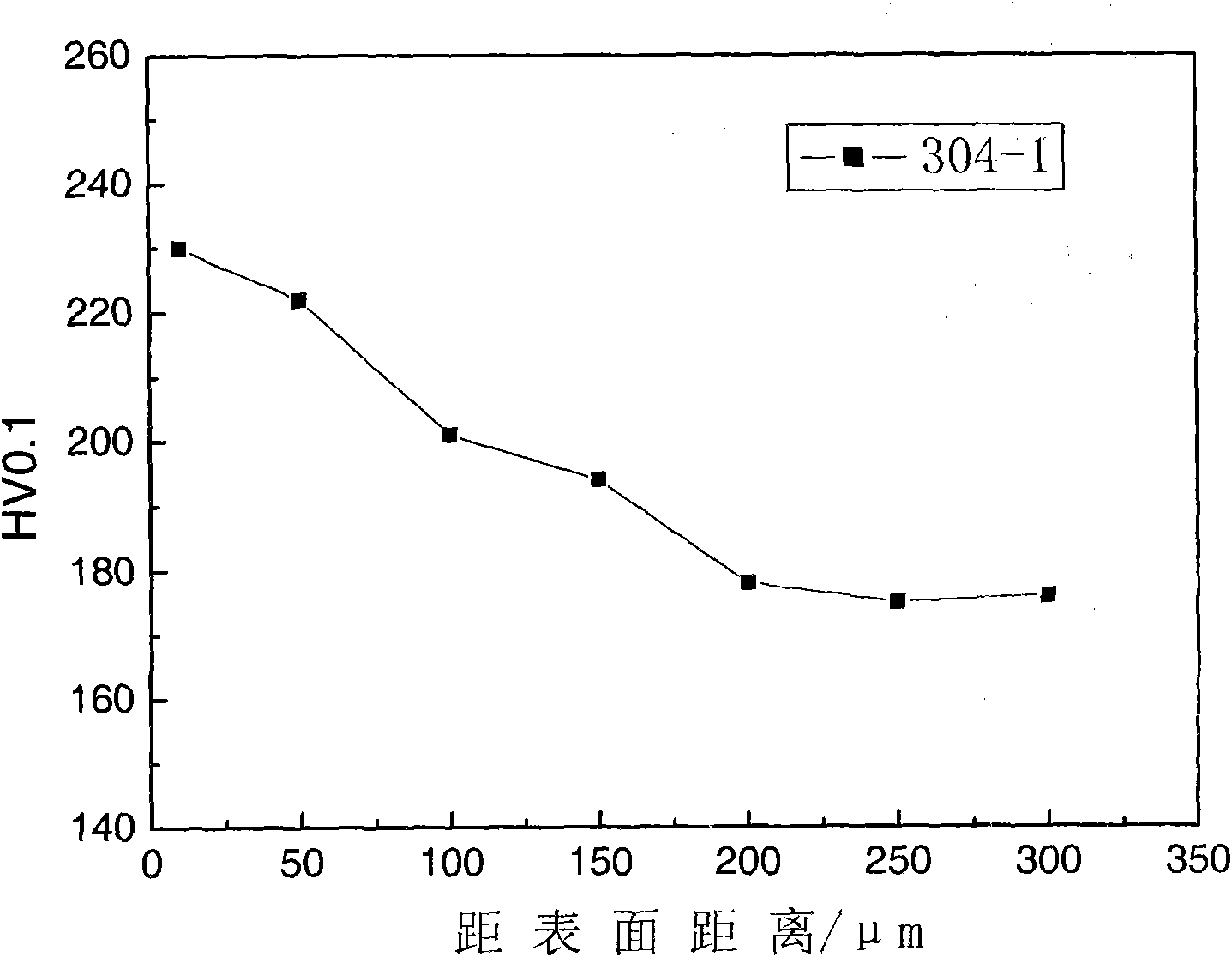
Manufacturing technique of austenitic stainless steel cold-rolled plate with good surface performance
InactiveCN101648334AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceSolid state diffusion coatingGrinding machinesManufacturing technologyPetrochemical
The invention provides a manufacturing technique of an austenitic stainless steel cold-rolled plate with a good surface performance. In the technique, a high-nitrogen surface layer in a solid solutionstate is formed on the austenitic stainless steel cold-rolled plate by improving the subsequent annealing atmosphere and process parameters of the austenitic stainless steel. Due to the solution strengthening function of solid solution nitrogen atoms, the hardness and the abrasive resistance of the surface of the stainless steel plate are greatly improved, and simultaneously the corrosion resistance is also improved; and each performance is improved by 10 to 50 percent, so the service life of components and parts made of the steel plate is prolonged. The austenitic stainless steel cold-rolledplate with the good surface performance is applied in the industries of petrochemical engineering, foods and medicaments and the like, and in the fields of household furniture, building decoration and the like.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
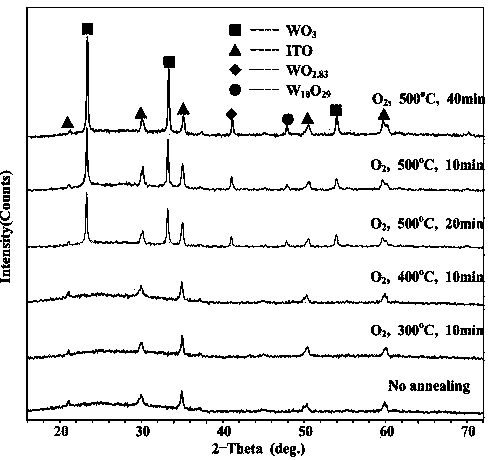
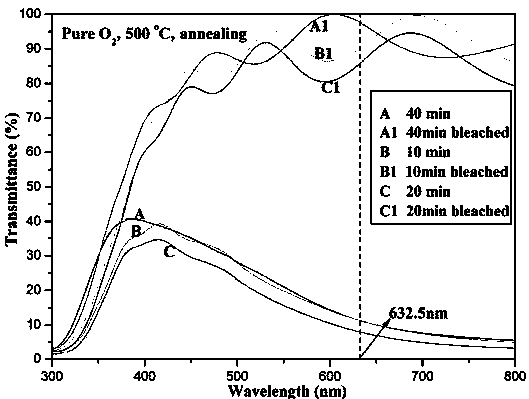
Controllable preparation method of electrochromic WO3 film
ActiveCN104178731ALow integrated transmittance in colored stateLarge optical modulation amplitudeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDisplay deviceElectrochromism
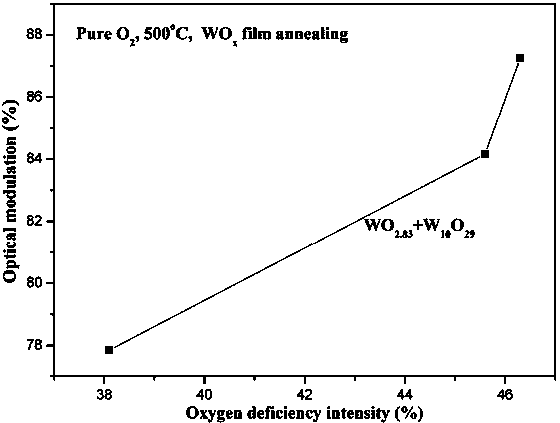
The invention relates to a preparation method of a WO3 film. An ion-beam sputtering deposition technique and a subsequent annealing treatment technique are combined to prepare the electrochromic WO3 film with favorable optical properties, and the strength of the anaerobic phase in the WO3 film is controlled to regulate the optical modulation properties. By using ITO (indium tin oxide) conducting glass as the substrate, the ion-beam sputtering deposition technique is utilized to prepare the WOx film; and by using 99.999% pure O2 as an annealing atmosphere, the WOx film is subjected to annealing treatment at different temperatures for different time periods to prepare the WO3 film containing anaerobic phase. When the WO3 film is subjected to Li<+> electrochemical coloring / discoloring reaction, after the discoloring voltage is applied, the prepared electrochromic WO3 film has the advantages of low coloring-stage integral transmittivity, adjustable anaerobic phase strength, large optical modulation amplitude and favorable controllability. The WO3 film is simple in preparation technique and is hopeful to be applied to the fields of smart windows, electronic information display devices, no-glare reflectors and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110260255A1Effective controlScaled continuouslyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen vacancyActive oxygen
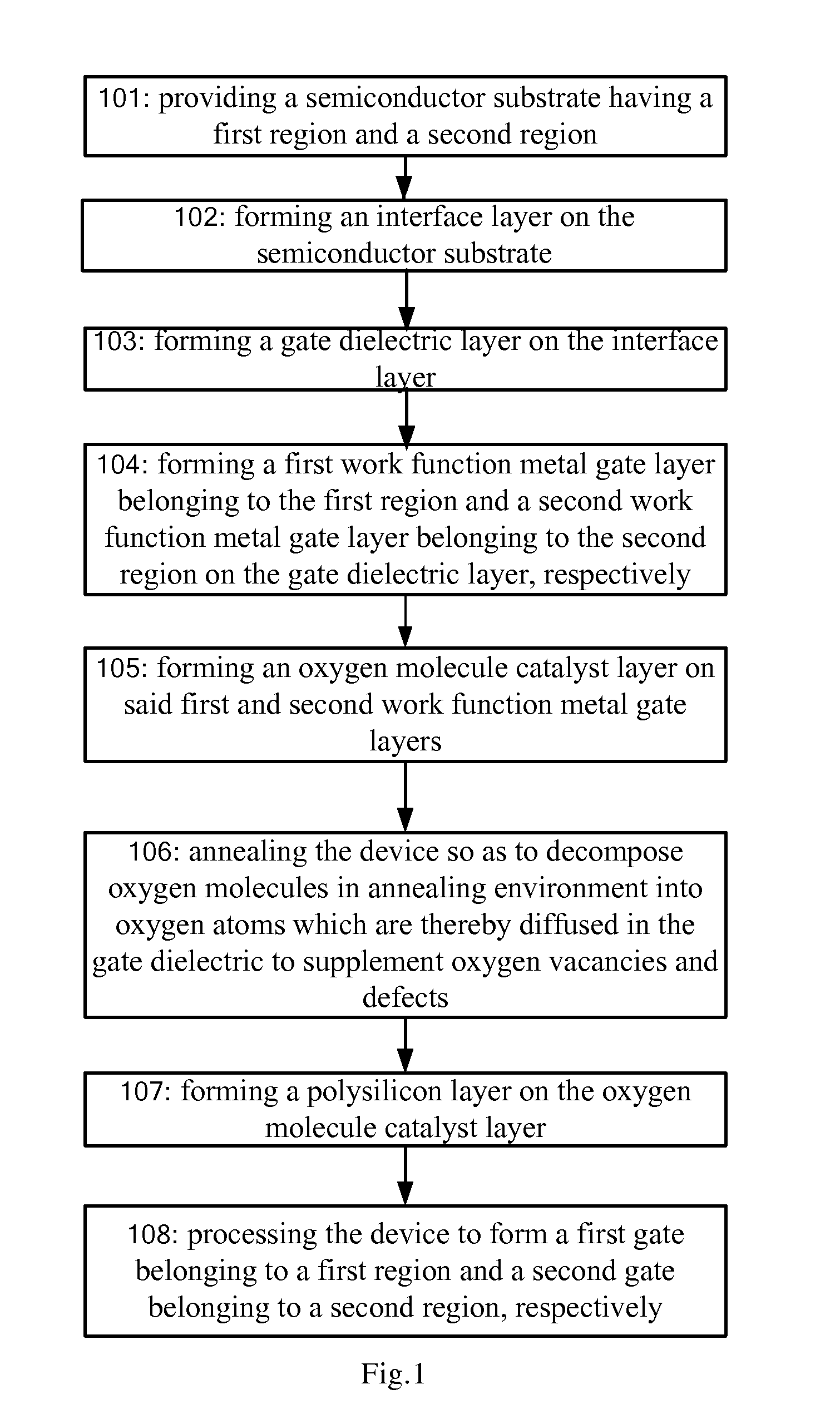
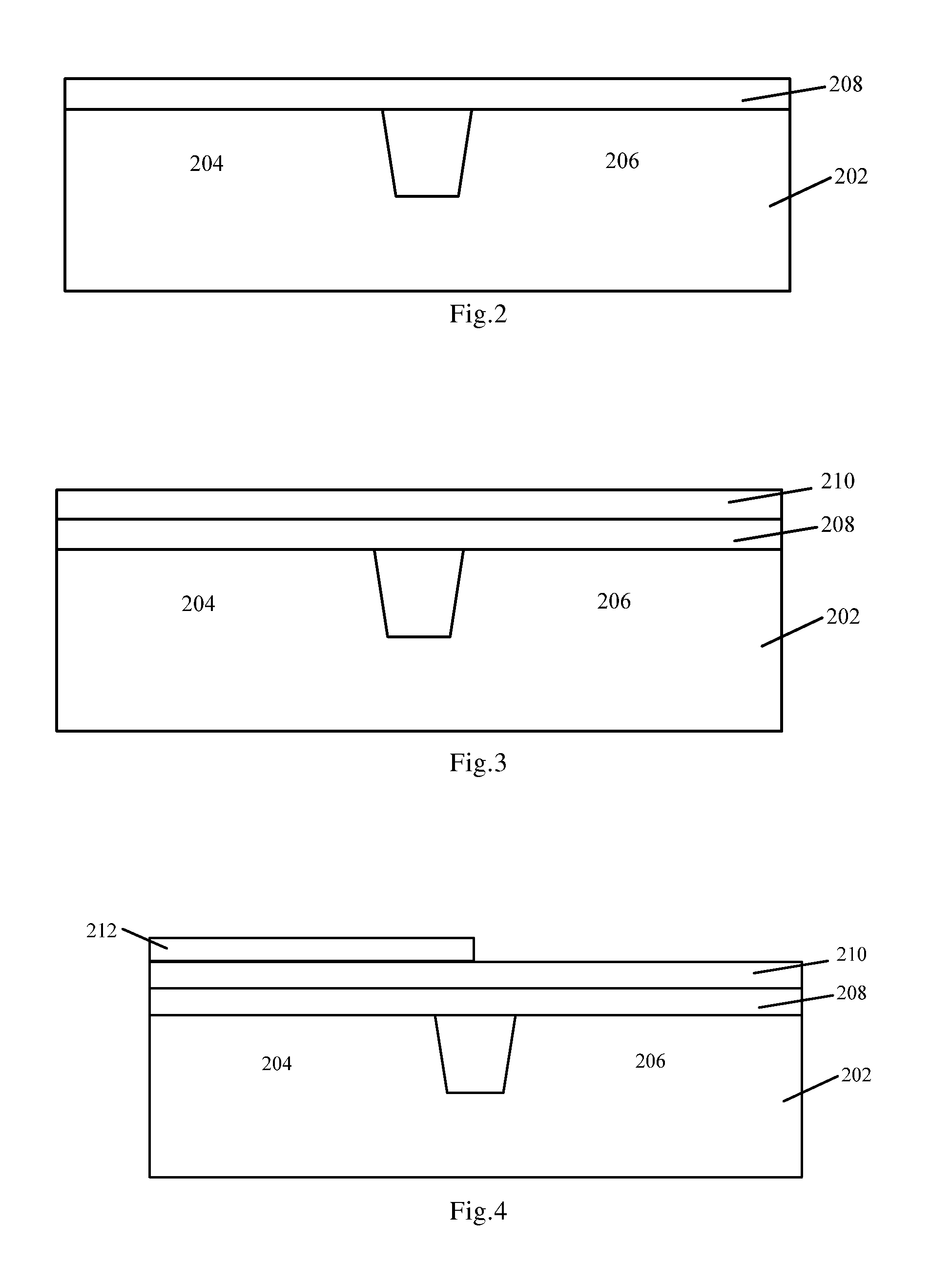
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device. After depositing the metal gate electrode material, a layer of oxygen molecule catalyzing layer having a catalyzing function to the oxygen molecules is deposited, and afterwards, a low-temperature PMA annealing process is used to decompose the oxygen molecules in the annealing atmosphere into more active oxygen atoms. These oxygen atoms are diffused into the high-k gate dielectric film through the metal gate to supplement the oxygen vacancies in the high-k film, in order to alleviate oxygen vacancies in the high-k film and improve the quality of the high-k film. According to the present invention, the oxygen vacancies and defects of high-k gate dielectric film will be alleviated, and further, growth of SiOx interface layer having a low dielectric constant caused by the traditional PDA high temperature process may be prevented. Thereby, the EOT of the entire gate dielectric layer may be effectively controlled, and the MOS device may be continuously scaled. Meanwhile, the present invention further provides a semiconductor device obtained according to the above-mentioned method.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing a hot-formed and heat-treated steel component that is coated with a metal anti-corrosion coating from a sheet steel product
InactiveCN102985570AAvoid brittlenessResist Crack IssuesHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingSheet steelNitride
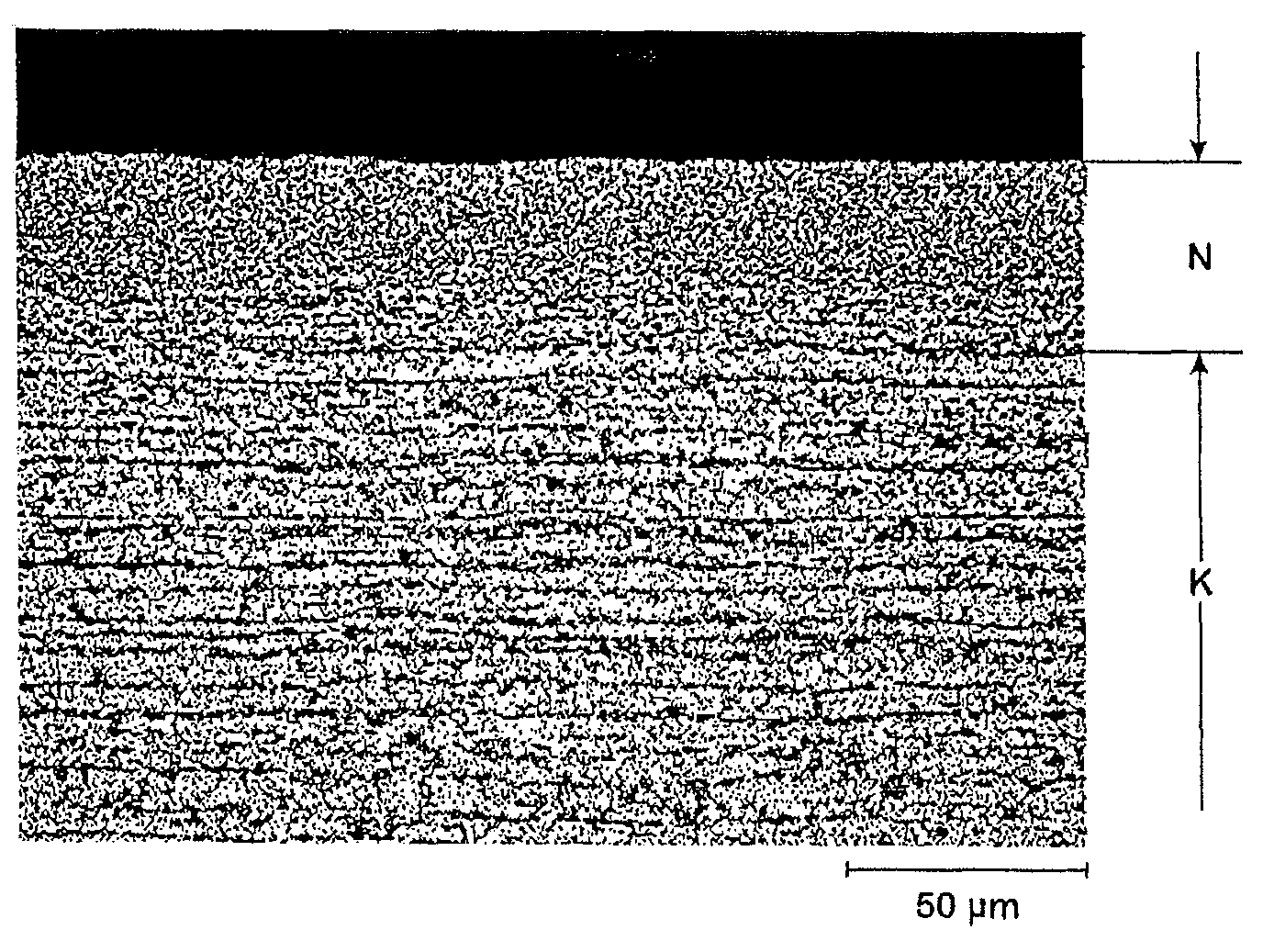
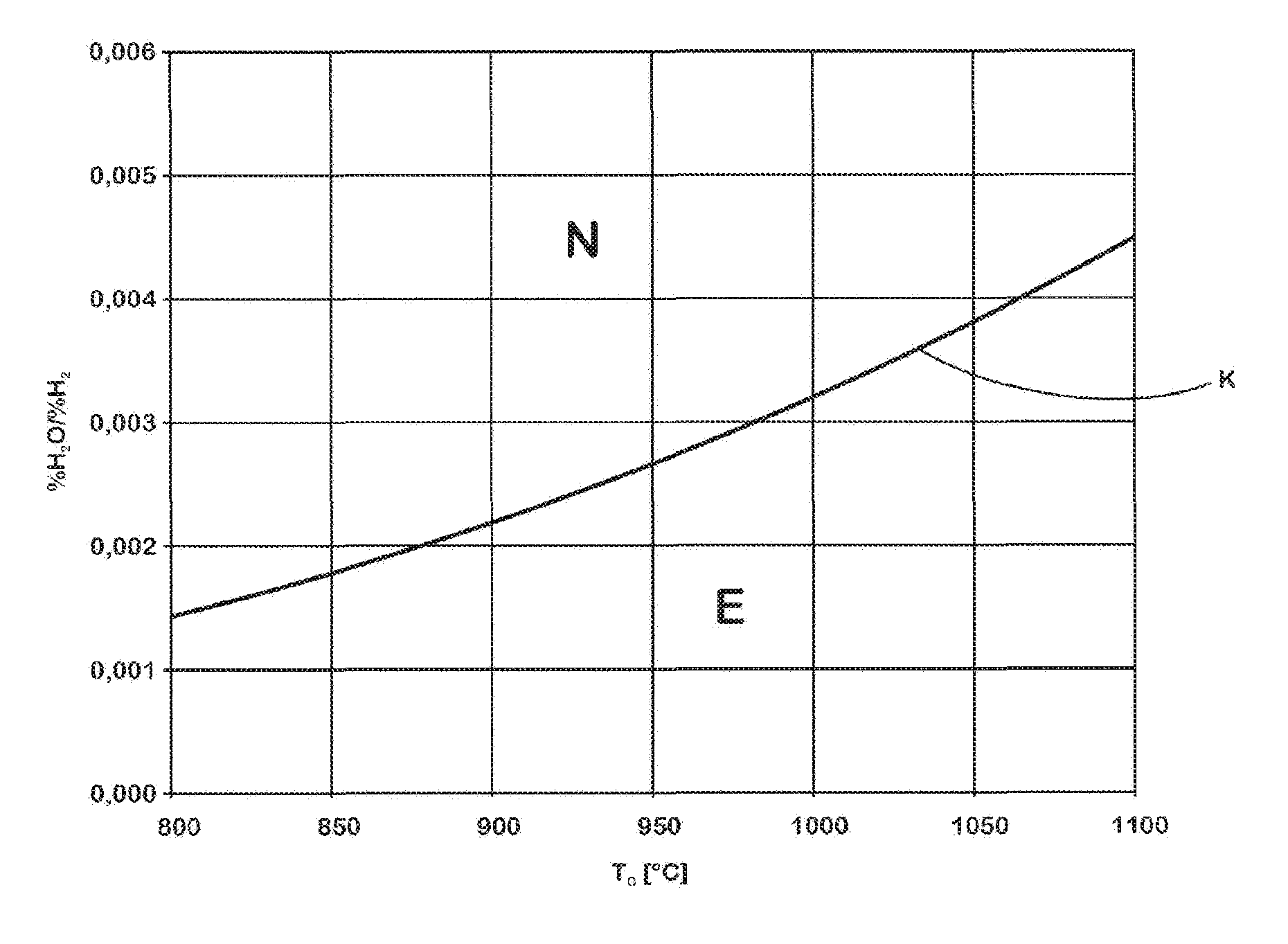
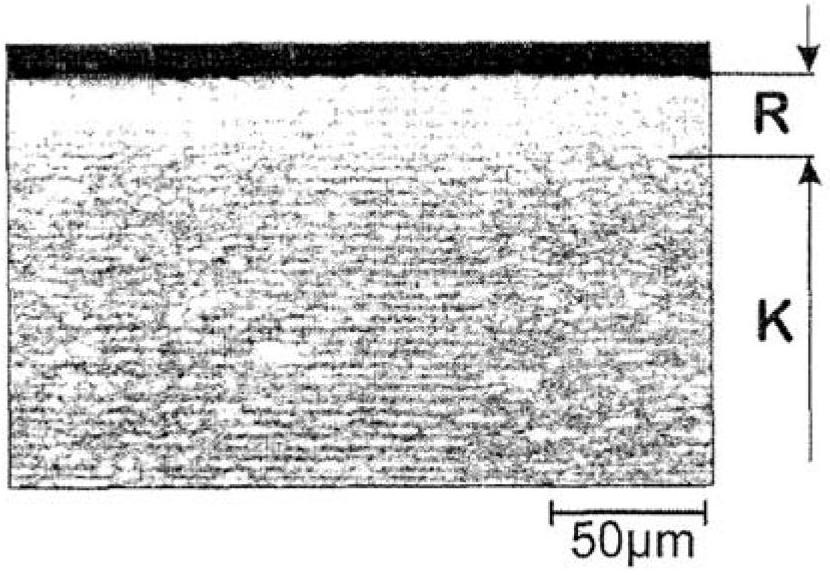
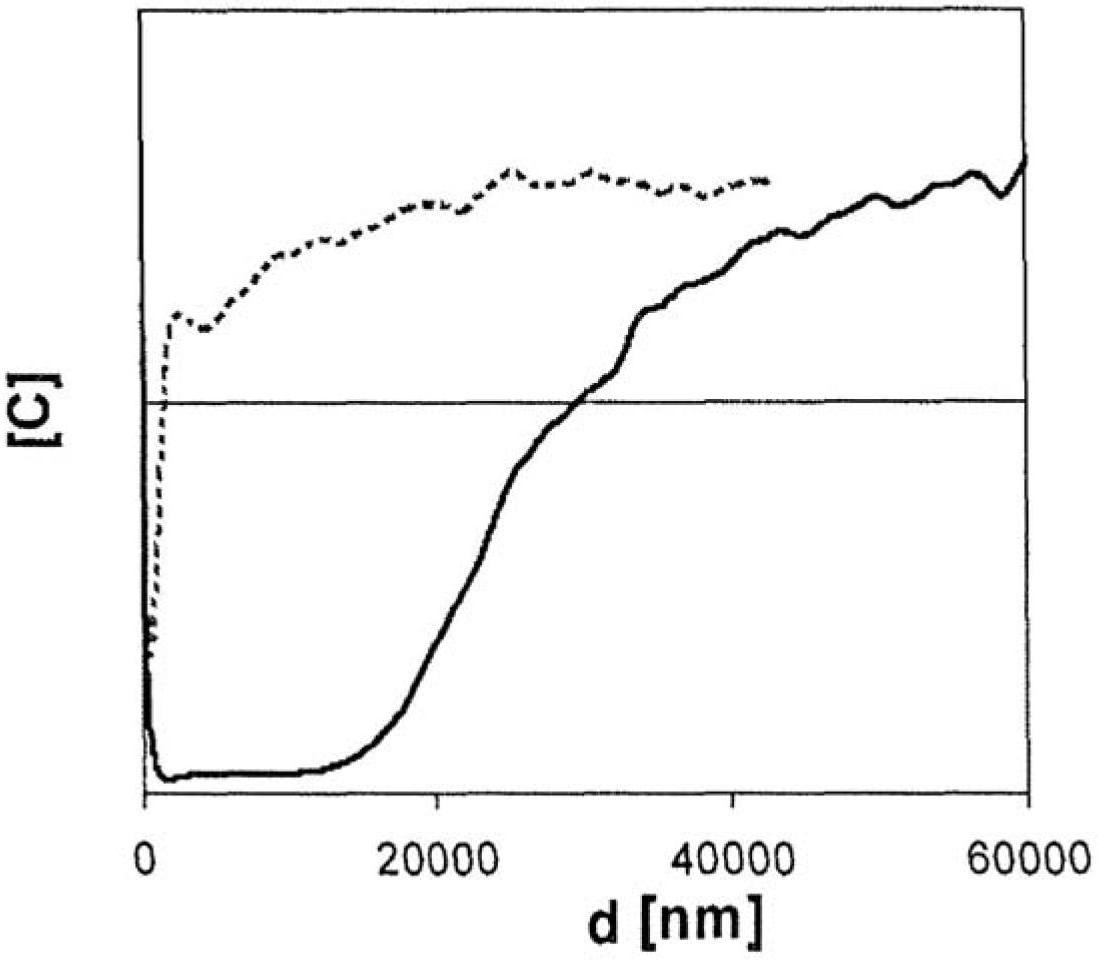
The invention relates to a method for producing a steel component that is coated with a metal protective coating from a sheet steel product comprising at least 0.4 % by weight of Mn. In order to economically generate a high-strength steel component, while minimizing the risk of the development of metal-induced cracks, according to the invention the sheet steel product is annealed in a continuous furnace under an annealing atmosphere containing up to 25% by volume H2, 0.1 - 10% by volume NH3, H2O, the remainder being N2 as well as process-related inevitable impurities, at a dew point ranging between -50 DEG C and -5 DEG C and at a holding temperature of 400 - 1100 DEG C for a holding period of 5 - 600 s. The annealed sheet steel product has a nitride layer (N) 5 - 200 [mu]m thick, the particle size of which is finer than the particle size of the interior core layer (K) of the sheet steel product. After it has been coated with a metal protective layer, a blank is separated from the annealed sheet steel product and is soaked to an austenitizing temperature of 780 - 950 DEG C subsequent to an optional preforming step, is hot-formed to form the steel component and is cooled so quickly that a tempered martensitic structure forms in the sheet steel product.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Multilayer ceramic electronic device and method of production of same
InactiveUS20070230088A1Low costStructural defectFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsReducing atmosphereMethods of production
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of production of a multilayer ceramic electronic device able to prevent the multilayer ceramic electronic device from dropping in mechanical strength and causing structural defects such as cracks at a low cost even if annealing the sintered body for reoxidation, and also such a multilayer ceramic electronic device, i.e., a method of production of a multilayer ceramic electronic device including a step of stacking green sheets and internal electrode layers to obtain a green chip, a step of firing the green chip under a reducing atmosphere to obtain a sintered body, and a reoxidation step of annealing the sintered body in a predetermined annealing atmosphere gas, wherein the annealing atmosphere gas in the reoxidation step has a dew point of −50 to 0° C., and the annealing atmosphere gas in the reoxidation step has a temperature of 900 to 1100° C.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
High-quality gallium oxide wafer preparation method and application
ActiveCN106783944AEasy to achieve mechanical peelingWon't breakSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogenWafering
The present invention relates to a high-quality gallium oxide wafer preparation method and application. The method comprises the steps: (1) cutting gallium oxide single crystal to obtain a body mass single crystal, performing annealing process in a special atmosphere, wherein the annealing temperature is 800-1200 DEG C, the annealing time is 5-100h, and the annealing atmosphere is argon or hydrogen; and (2) scratching the side surface or the side chamfered edge of the body mass single crystal after annealing process, putting the body mass single crystal into water, cutting apart the body mass single crystal from the scratching position by employing a blade, slowly separating the wafer from the body mass single crystal, and obtaining a high-quality gallium oxide wafer. The high-quality gallium oxide wafer preparation method is simple in operation, easily realizes the mechanical exfoliation of a gallium oxide wafer, an obtained gallium oxide wafer cannot be broken, the size of the wafer is large, and the quality of the wafer is high.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for hot-dip coating flat steel products containing 2-35% by weight mn and flat steel products
A method by which a flat steel product containing 2-35 wt. % of Mn can be provided with a coating of Zn which adheres well by annealing at an annealing temperature Ta of 600-1100° C. for an annealing time of 10-240 s under an annealing atmosphere which has a reducing effect on the FeO present on the flat steel product and an oxidising effect on the Mn contained in the steel substrate thereby forming a layer of Mn mixed oxide which covers the flat steel product at least in sections and then cooling the flat steel product to a temperature for bath entry and conveying it through a bath of molten Zn saturated within iron at a temperature of 420-520° C., within a dip time of 0.1-10 s.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Producing method of electrical steel extremely-thick insulating coating with good film-forming property
ActiveCN103934185AImprove film qualityImprove insulation performancePretreated surfacesCoatingsMulti bandAlloy substrate
A producing method of an electrical steel extremely-thick insulating coating with a good film-forming property comprises the following steps that (1) adopted insulating paint is composed of, by weight, 10%-60% of organic resin, 28%-60% of inorganic color filler, 1%-15% of auxiliaries and solvents and the balance pure water; (2) surface treatment is conducted on a substrate, wherein surface modification treatment is conducted on the Fe-Si alloy substrate with the silicon content ranging from 1.5wt% to 3.0wt%, the surface of the substrate is covered with an oxidation film layer, and the surface roughness of the substrate is greater than or equal to 0.4 micron; (3) annealing is conducted, wherein the annealing temperature ranges from 780 DEG C to 1000 DEG C and is kept for 10 seconds-20 seconds, and the annealing atmosphere is a hydrogen and nitrogen gas mixture; (4) baking and curing are conducted, the baking process or the multi-band high infrared heating process or a combination of the baking process and the multi-band high infrared heating process is adopted. The film-forming property of the coating obtained with the method is excellent, and meanwhile the method has the advantages that the solid content required by the electrical steel environment-friendly extremely-thick insulating coating is high, surface insulativity and adhesiveness are excellent, and hot-pressing stability and corrosion resistance are good.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Process for coating a hot- or cold- rolled steel strip containing 6−30% by weight of MN with a metallic protective layer
ActiveUS8394213B2High strengthImprove adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelManganese
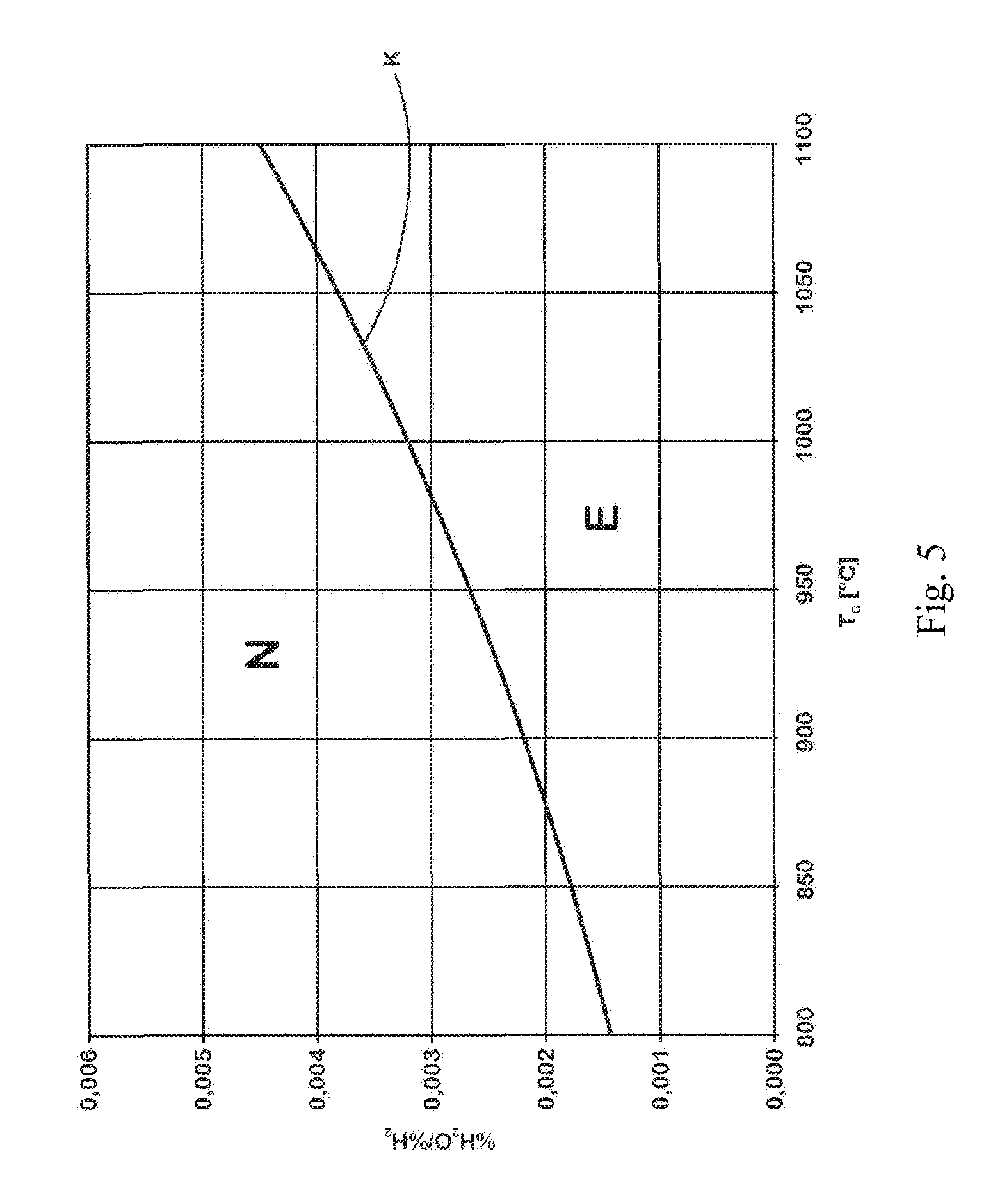
A method for coating hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel strip containing 6-30 wt %. Mn with a metallic protective layer, includes annealing the steel strip at a temperature of 800-1100° C. under an annealing atmosphere containing nitrogen, water and hydrogen and then subjecting the steel strip to hot dip coating. The method provide an economical way of hot dip coating a high manganiferous sheet steel in that, in order to produce a metallic protective layer substantially free from oxidic sub-layers on the steel strip, the % H2O / % H2 ratio of the water content % H2O to the hydrogen content % H2 in the annealing atmosphere is adjusted as a function of the respective annealing temperature TG as follows: % H2O / % H2≦8·10−15·TG3.529.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Manufacturing method of semiconductor laser
InactiveCN102299480AReduce optical power densityDecrease the lasing threshold current densityLaser optical resonator constructionLaser technologySemiconductor package
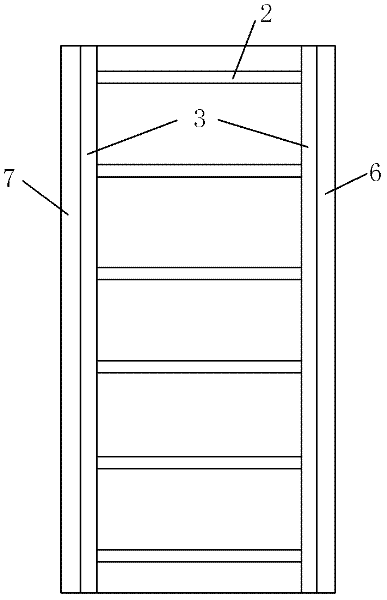
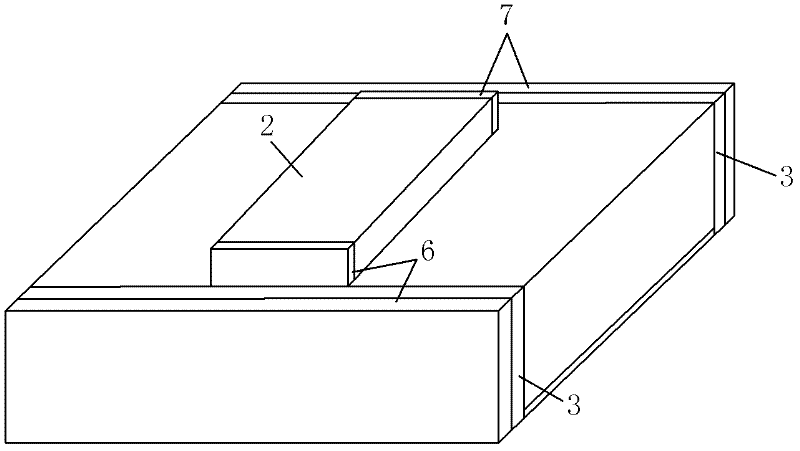
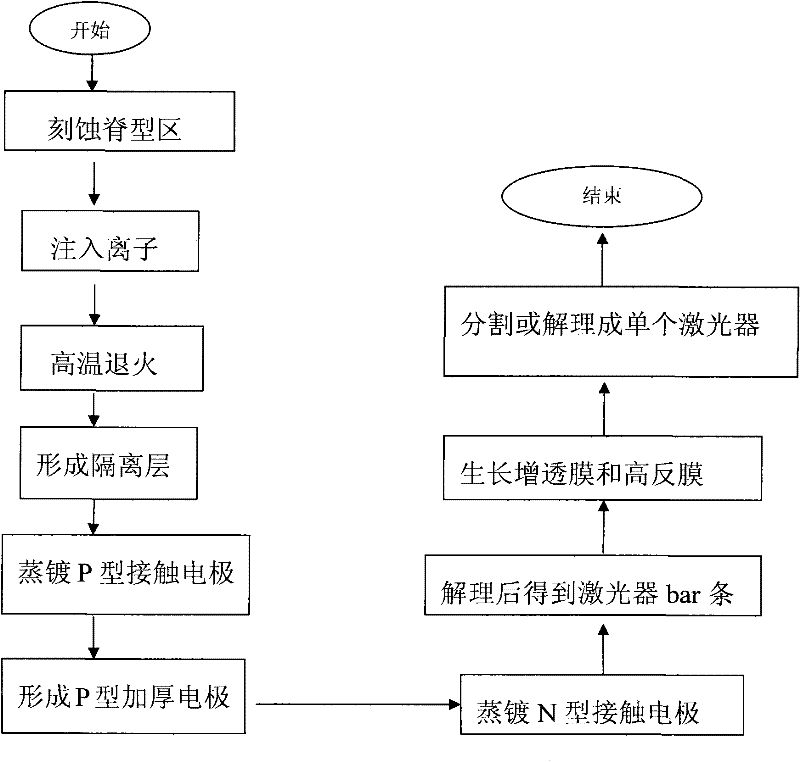
The invention relates to semiconductor laser technology, in particular to a manufacturing method of a semiconductor laser. The steps include: etching a ridge-shaped region (2) on the surface of the laser epitaxial wafer; using photolithography technology, implanting ions near the front and rear cavity surfaces of the laser; Evaporate a P-type contact electrode (5) above the ridge region (2) of the laser; evaporate an N-type contact electrode (8) after thinning the substrate of the laser; obtain a laser bar after cleavage; An anti-reflection film (6) and a high-reflection film (7) are evaporated or deposited on the front cavity surface and the rear cavity surface respectively; finally, the laser bar is divided or cleaved to complete the production of a single laser. The method of the invention can effectively reduce the light absorption at the cavity surface, reduce the optical power density at the cavity surface, and effectively increase the maximum output power of the laser.
Owner:苏州纳睿光电有限公司
Annealing method of cerium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet wafer for white-light LED (Light Emitting Diode)
ActiveCN103590111AEliminate internal defectsEliminate oxygen vacanciesPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsRoom temperatureCe element
The invention discloses an annealing method of a cerium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet wafer for a white-light LED (Light Emitting Diode). The annealing method comprises the following steps: (1) putting the cerium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet wafer in a porcelain boat, feeding the porcelain boat into a tubular annealing furnace, introducing annealing atmosphere and sealing, wherein the annealing atmosphere is a mixed gas A or oxygen, the mixed gas A is iH2+kL, the L stands for an inert protective gas, the i and the k respectively stand for the volume parts of the H2 and the L in the mixed gas A, and i / i+k is greater than or equal to 25% and less than or equal to 75%; (2) heating to 300 DEG C from a room temperature at the rate of 100-150 DEG C / h, and carrying out heat preservation for 3-8 hours; then heating to 900 DEG C at the rate of 150-200 DEG C / h, and carrying out heat preservation for 3-8 hours; heating to 1100-1500 DEG C at the rate of 100-150 DEG C / h, and annealing at a constant temperature for 30-72 hours; after annealing, cooling to 1100 DEG C at the rate of no greater than 50 DEG C / h, then cooling to 900 DEG C at the rate of 100 DEG C / h, finally cooling to a room temperature at the rate of 150-200 DEG C, wherein the time required in the total cooling stage is about 6.5-1.6 hours, and taking out so as to obtain the annealed wafer.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Cold-rolled and recrystallisation annealed flat steel product, and method for production thereof
ActiveCN106795575AImprove ductilityHigh n valueHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesMicro structurePass rate
The invention relates to a cold-rolled and recrystallisation annealed flat steel product with a ferritic micro-structure, having an optimised formability and suitability for painting. In addition, the flat steel product is formed by a steel having C: 0.0001-0.003 wt.%, Si: 0.001-0.025 wt.%, Mn: 0.05-0.20 wt.%, P: 0.001-0.015 wt.%, Al: 0.02-0.055 wt.%, Ti: 0.01-0.1 wt.%, as well as respectively optionally Cr: 0.001-0.05 wt.%, V: up to 0.005 wt.%, Mo: up to 0.015 wt.%, N: 0.001-0.004 wt.%. In addition, the flat steel product has the following mechanical characteristics: Rp0.2 < / = 180 MPa, Rm < / = 340 MPa, A80 < / = 40%, n-value < / = 0.23. Furthermore, on at least one of the surfaces thereof, the flat steel product has an arithmetic roughness average Ra of 0.8-1.6 [mu]m and a peak value RPc of 75 / cm. The production of the flat steel product involves, in a continuous process in a N2-H2- annealing atmosphere, the recrystallisation annealing thereof, and an overaging process. Subsequently, the flat steel product undergoes a skin-pass rolling by means of a working roller and with a skin-pass rate D of 0.4-0.7%, the circumferential surface of which working roller has a roughness average Ra of 1.0-2.5 [mu]m and a peak value RPc > / = 100 / cm, wherein the peaks and depressions shaped into the surface of the skin-pass working roller are provided in a stochastically distributed manner.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG +1
Industrial preparation method of smart glass capable of automatically regulating infrared transmittance
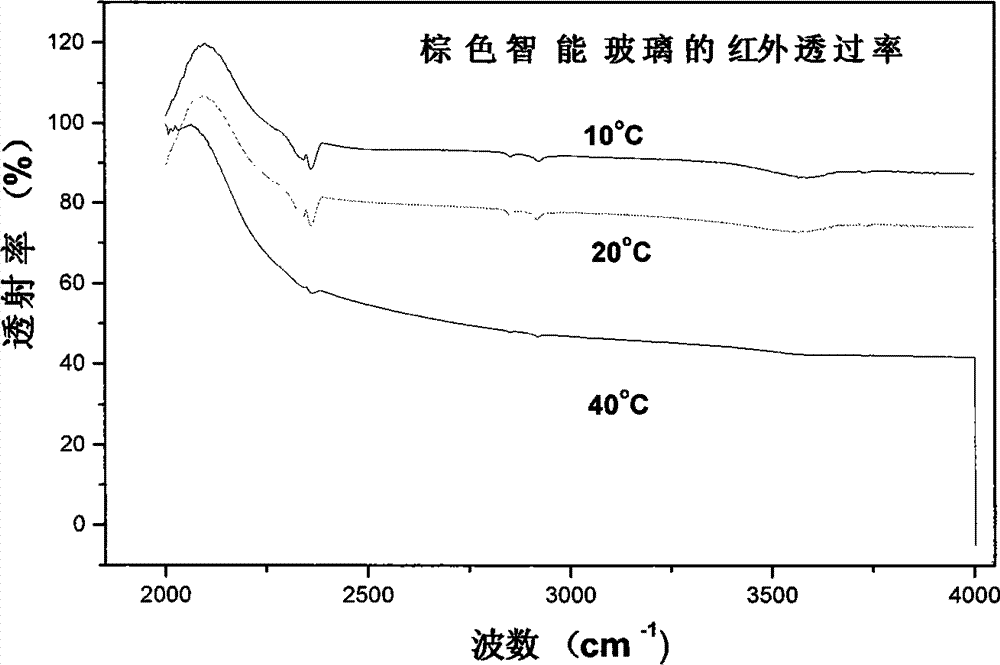
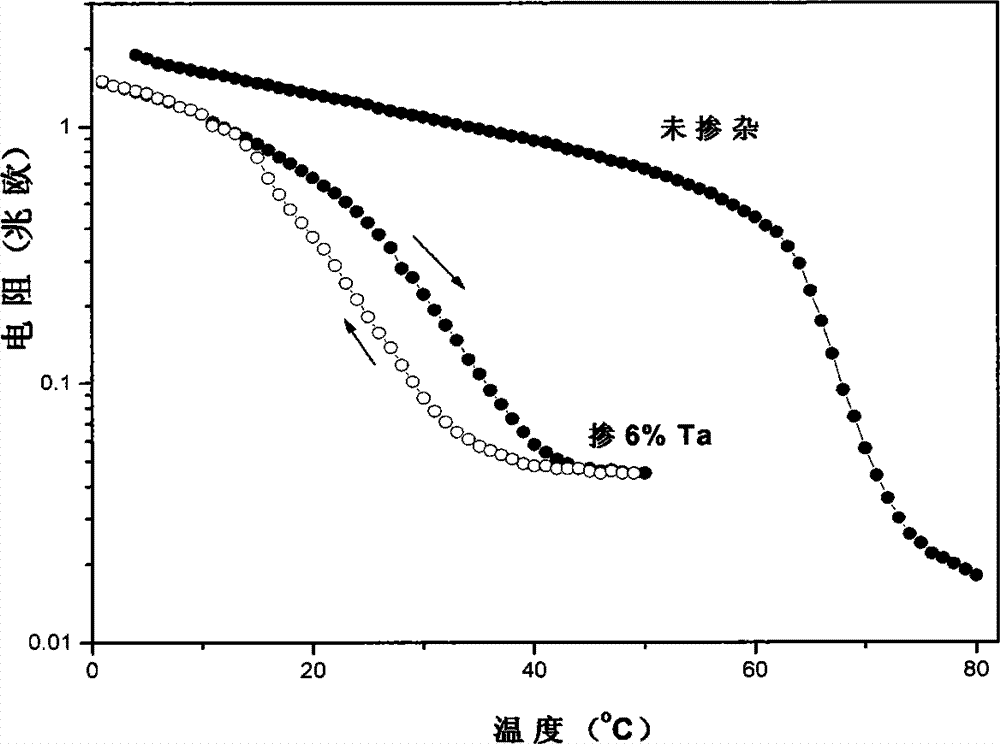
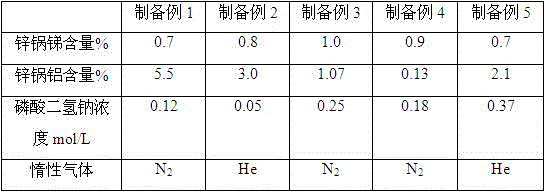
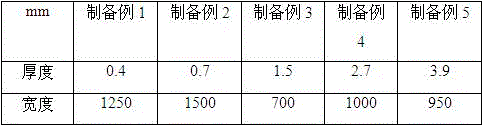
InactiveCN104261694ARapid large-area film formationImprove circulation speedSmart glassVanadium oxide
The invention relates to an industrial preparation method of smart glass capable of automatically regulating infrared transmittance. The industrial preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) conventionally cleaning glass, and then performing sputtering deposition of a Ti or Si elemental element film with the thickness of 5-20nm on the surface of the glass by an ion beam sputtering method as a crystallization inducing layer; (2) performing reactive sputtering deposition of a vanadium oxide film on the crystallization inducing layer by a direct current reactive magnetron sputtering method, wherein a reactive sputtering target is prepared by fusion of high-purity vanadium with the purity of 99.96% and doping elements with different atomic ratios; reactive sputtering source gas is Ar / O2 mixed gas, and the flow proportion of Ar / O2 is 5%-10%; and (3) performing heat treatment by adopting a fast heat treatment technology for heating by light of a halogen lamp after deposition of the vanadium oxide film, wherein the temperature in the whole heat treatment process is 450-550 DEG C, and the time is 10-20min; an annealing atmosphere adopts N2 / O2 mixed gas, N2 and O2 are formed by gasification of liquid nitrogen and liquid oxygen, and the flow proportion of N2 to O2 is (98%-99%): (2%-1%).
Owner:李金华
Preparation technology of galvanized steel sheet with continuous hot-dip spangles
ActiveCN106702101AGuaranteed mechanical propertiesImprove anti-corrosion performanceHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesAir knifeMechanical property
The invention relates to the technical field of galvanizing of steel sheets, and discloses a preparation technology of a galvanized steel sheet with continuous hot-dip spangles. The preparation technology comprises the following steps of uncoiling, and cleaning; annealing: sending a steel sheet into an annealing furnace to reduce and calcine, wherein the annealing atmosphere is a H2 (hydrogen) and N2 (nitrogen) mixed gas, and the annealing temperature is 720 to 800 DEG C; hot-dip: cooling the steel sheet by air, cooling to 470 to 520 DEG C at the average temperature, sending into a zinc pot, and performing hot-dip, wherein the temperature of the zinc pot is 455 to 470 DEG C, and the content of antimony in the zinc pot is 0.7 to 1.0% (in percentage by mass); spraying: enabling an air knife to scrape the excessive hot-dip liquid on the steel sheet, spraying and cooling, wherein the temperature of spraying liquid is 55 to 60 DEG C, and the spraying liquid is a monosodium phosphate water solution; flattening, and passivating; coiling. The preparation technology has the advantages that the production cycle is short, the spangles are small and uniform, and the mechanical property and anticorrosive property of the prepared steel sheet are excellent.
Owner:重庆万达薄板有限公司
Magnetic sensor and preparation technology thereof
InactiveCN104422906AIncreasing the thicknessHigh sensitivityMagnetic measurementsFilling materialsNitrogen
The invention discloses a magnetic sensor and a preparation technology thereof. The preparation technology comprises the following steps of depositing medium material on a substrate to form a first medium layer; forming a groove array on the first medium layer; enabling the width of an opening of a groove to be greater than the depth; depositing magnetic material to form a magnetic material layer; annealing in a magnetic field, wherein an annealing atmosphere is nitrogen, or inert gas or vacuum; preparing filling material, forming a filling material layer, filling the groove, and performing the photoetching technology; generating a pattern of the magnetic sensor, forming a sensing unit, and forming a magnetic conduction unit by using the groove, namely forming a three-axis sensor on a single chip; manufacturing a through hole and an electrode. The three-axis sensor and the preparation technology have the advantages that the technology process can be optimized, and the property of the sensor is improved.
Owner:QST CORP
Method for producing an easily deformable flat steel product, flat steel product, and method for producing a component from such a flat steel product
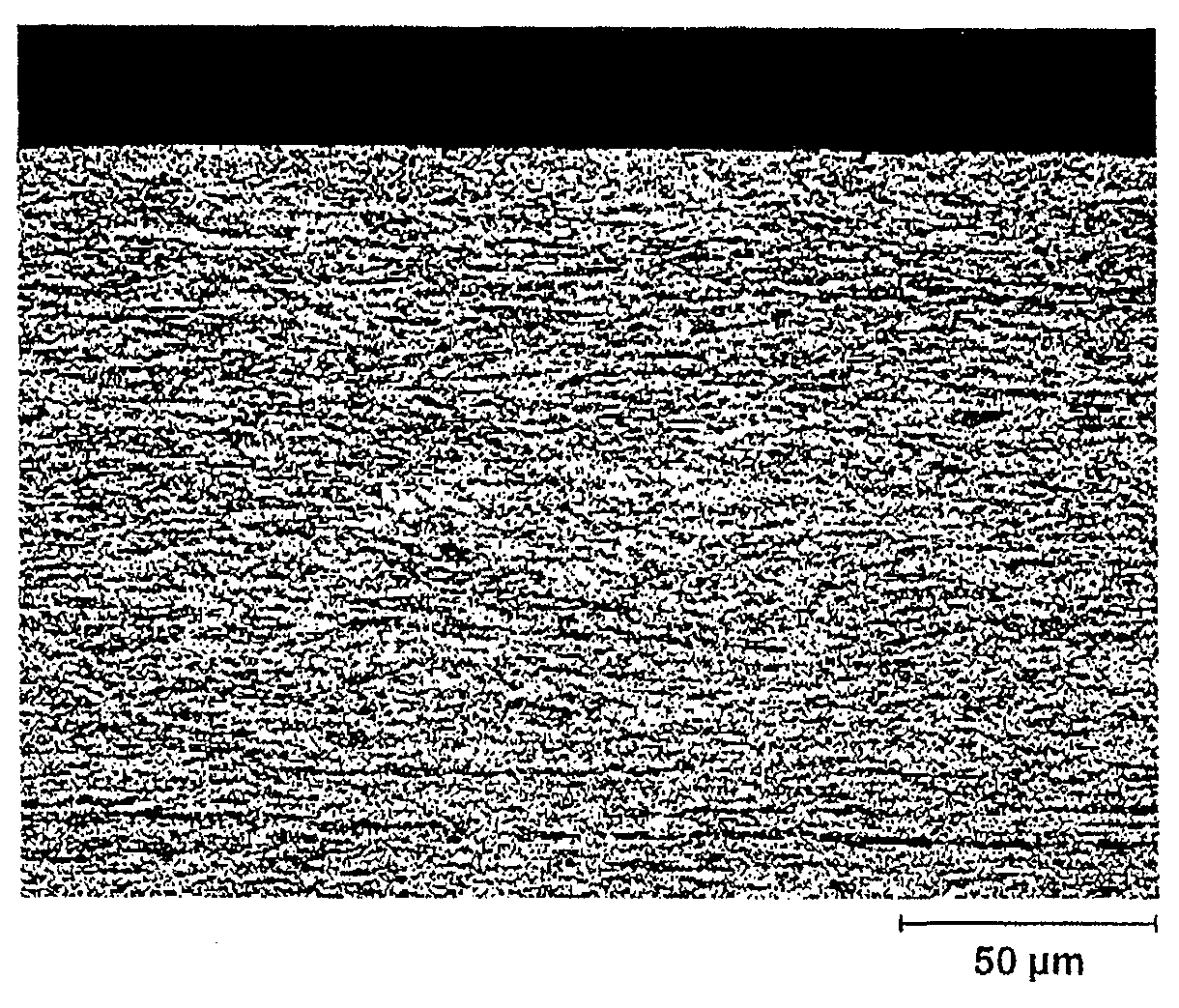
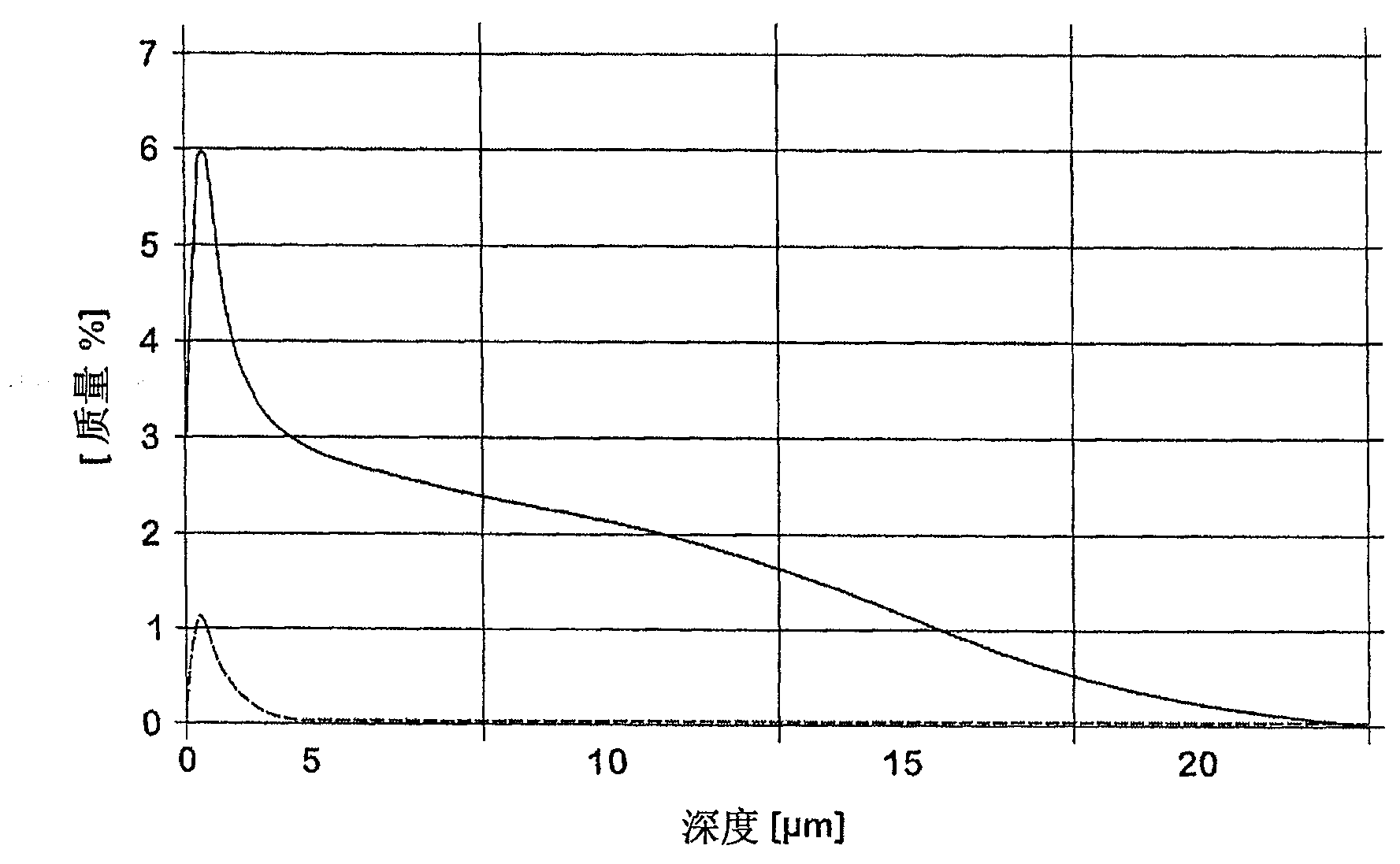
The invention relates to a method by means of which an easily deformable flat steel product having a carbon content of 0.1-0.4 wt % can be produced in a cost-effective manner. To this end, according to the invention, an annealing treatment is carried out under an annealing atmosphere comprising 0.1-25 vol % of H2, H2O, with the remainder being N2 and technically unavoidable impurities, and having a dew point of between -20 DEG C and +60 DEG C, wherein the ratio of H2O / H2 of the annealing atmosphere is no greater than 0.957.; The flat steel product is thereby heated to a holding temperature of 600-1100 DEG C in the course of the annealing treatment, at which it is held for a holding time of 10-360 s, so that the flat steel product obtained after the annealing treatment comprises a 10-200 [mu]m thick ductile edge layer (R) adjacent to the free surface thereof, having a ductility that is greater than the interior core layer (K) of the flat steel product covered by the edge layer. The invention further relates to a correspondingly produced flat steel product particularly suitable for hot or cold forming, and to a method for producing components made of such a flat steel product.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip and grain-oriented electrical steel strip obtained according to said process
ActiveUS20160111190A1Simple stepsReduce oxidationInorganic material magnetismSolid state diffusion coatingElectrical steelThin slab
A process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting, comprising the following process steps: a) smelting a steel, b) continuously casting the smelt by thin slab continuous casting, c′) heating up the thin slabs and subjecting the slabs to homogenization annealing at a maximum temperature of 1250° C., d) heating to a temperature between 1350° C. and 1380° C., e) continuously hot rolling the thin slabs to form a hot-rolled strip, f) cooling and reeling the hot-rolled strip to form a coil, g) annealing the hot-rolled strip after reeling and prior to a subsequent cold rolling step, h) cold rolling the hot-rolled strip to the nominal usable thickness, i) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing, j) applying an annealing separator (non-stick layer) to the strip surface of the cold-rolled strip, k) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to secondary recrystallization annealing, forming a finished steel strip having a pronounced Goss texture, and l) stress-free annealing the finished steel strip, which has been coated with an insulating layer, provides an improved process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting. This is achieved in that the recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing of the cold-rolled strip in process step h) comprises a decarburization annealing phase and a subsequent nitridation annealing phase, with an intermediate reduction annealing phase being interposed between the decarburization annealing phase and the nitridation annealing phase, and carried out at a temperature ranging from 820° C.-890° C., for a maximum period of 40 seconds, with a dry, gaseous annealing atmosphere, which contains nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) and acts on the cold-rolled strip, and which has a water vapor / hydrogen partial pressure ratio pH2O / pH2 of less than 0.10 and wherein a cold-rolled strip is obtained, which primary recrystallized grains have a circle equivalent mean size (diameter) between 22 μm and 25 μm.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
Method for fabricating plasma reactor parts
ActiveUS7919722B2Wave amplification devicesElectric discharge tubesPlasma reactorAnnealing atmosphere
A method of fabricating yttria parts is provided herein. In one embodiment, the method includes sintering a yttria sample, machining the sintered sample to form a part, and annealing the part by heating the part at a predetermined heating rate, maintaining the part at a constant annealing temperature, and cooling the part at a predetermined cooling rate. At least one of the sintering and annealing atmospheres is an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Bonding copper alloy wire for semiconductor device and manufacturing method of bonding copper alloy wire
ActiveCN104087780AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialOxidation resistant
The invention relates to a bonding copper alloy wire for a semiconductor device. The bonding copper alloy wire comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of copper, 0.5-1.5 parts of palladium and 0.0005-0.002 part of hydrogen. The invention also provides a manufacturing method of the bonding copper alloy wire. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of: (1) melting copper and palladium into a copper-palladium alloy melt, and then carrying out drawing process to obtain a copper-palladium alloy wire rod; (2) carrying out multi-pass drawing on the copper-palladium alloy wire rod to obtain a copper-palladium alloy wire, wherein during the drawing and after the drawing is completed, annealing treatment is carried out, and a mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen is adopted as the annealing atmosphere in the last-time annealing process; (3) after the last-time annealing process is completed, introducing the palladium-copper alloy wire into the aqueous solution of ethanol for cooling to obtain the bonding copper alloy wire. The bonding copper alloy wire disclosed by the invention has the advantages of relatively strong antioxidant capacity, relatively large bonding area and relatively high bonding strength when the ball bonding is carried out under an N2 atmosphere, strong conductivity and high reliability; the manufacturing method is simple and feasible.
Owner:NICHE TECH KAISER SHANTOU
Method for the hot-dip coating of a flat steel product containing 2-35 wt.% of Mn, and a flat steel product
A method by which a flat steel product containing 2-35 wt. % of Mn can be provided with a coating of Zn which adheres well by annealing at an annealing temperature Ta of 600-1100° C. for an annealing time of 10-240 s under an annealing atmosphere which has a reducing effect on the FeO present on the flat steel product and an oxidizing effect on the Mn contained in the steel substrate thereby forming a layer of Mn mixed oxide which covers the flat steel product at least in sections and then cooling the flat steel product to a temperature for bath entry and conveying it through a bath of molten Zn saturated within iron at a temperature of 420-520° C., within a dip time of 0.1-10 s.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip and grain-oriented electrical steel strip obtained according to said process
InactiveUS20160108493A1Affect strengthHigh chemical proportions of copperInorganic material magnetismFurnace typesWater vaporThin slab
With a process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting, comprising the following process steps: a) smelting a steel with a smelt which, in addition to iron (Fe) and unavoidable impurities, contains Si: 2.00-4.00 wt %, C: 0.025-0.100 wt %, Mn: 0.060-0.500 wt %, Cu: 0.200-0.550 wt %, Alsl: 0.010-0.030 wt %, S: <100 ppm, N: 80-120 ppm, and one or more elements from the group comprising Cr, V, Ni and Mo, each <0.100 wt %, b) continuously casting the smelt by thin slab continuous casting to form a strand having a thickness of 50-120 mm, and dividing the strand into thin slabs, c) heating up the thin slabs, preferably in a linear furnace, to a temperature above 1,050° C. and subjecting the slabs to homogenization annealing at a maximum temperature of 1,250° C., d) immediately prior to the first hot rolling pass of a subsequent hot rolling process, passing the slabs through an induction heating device, in particular, a high frequency induction heating device, and heating the thin slabs to a maximum temperature of 1,350° C., which is above the respective homogenization temperature of process step c), e) continuously hot rolling the thin slabs to form a hot strip having a thickness of 1.8 mm-3.0 mm, f) cooling and reeling the hot-rolled strip at a reeling temperature of less than 650° C. to form a coil, g) annealing the hot-rolled strip after reeling and prior to a subsequent cold rolling step at a temperature of between 910° C. and 1,140° C., h) cold rolling the hot strip in a first cold rolling stage to an (intermediate) thickness of 0.50 mm-0.80 mm, i) subjecting the resulting cold-rolled strip to recrystallization and decarburization annealing at a strip temperature ranging from 820° C.-890° C. for a period of 300-600 seconds in a gaseous annealing atmosphere which acts on the cold-rolled strip and contains nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2), and which has a water vapor / hydrogen partial pressure ratio pH2O / pH2 of 0.30 to 0.60, j) in a second cold rolling stage, cold rolling the cold strip which has been subjected to recrystallization and decarburization annealing to its (final) thickness or its nominal usable thickness of 0.15 mm-0.40 mm, k) applying an annealing separator (non-stick layer) containing MgO to the strip surface of the cold-rolled strip which has been rolled to its final thickness or usable thickness, l) subjecting the cold-rolled strip which has been coated with the annealing separator to secondary recrystallization annealing by high-temperature annealing in a bell-type furnace at a temperature of >1,150° C., forming a finished steel strip having a pronounced Goss texture, and m) coating the finished steel strip which has undergone secondary recrystallization annealing with an electrically insulating layer and then stress-free annealing or stress-relief annealing the coated finished steel strip, an improved process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting is provided, by which it is possible to introduce an inhibitor into the steel strip, which controls secondary grain growth during secondary recrystallization annealing in a high-temperature bell-type annealing furnace.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
Production method of 250 MPa-grade high-strength interstitial-free steel
ActiveCN112143860AImprove surface qualityHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesManganeseUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a production method of 250MPa-grade high-strength interstitial-free steel. A low-carbon, low-silicon, high-phosphorus manganese and Nb and Ti composite component system is adopted, through reasonable control over process temperature parameters, a front-section cooling and U-shaped coiling mode, high cold rolling reduction rate, stable pickling speed and stable control overannealing atmosphere, temperature and leakage point, the high-strength interstitial-free steel with yield strength larger than or equal to 250 Mpa, tensile strength larger than or equal to 440 Mpa, yield ratio smaller than or equal to 0.65, r value larger than or equal to 1.5, good deep drawing, good machining brittleness and good surface quality is obtained, and the high-strength interstitial-free steel is especially suitable for manufacturing of automobile stamping parts with certain stamping performance and high strength at the same time.
Owner:SD STEEL RIZHAO CO LTD
Method for improving copper oxidation resistance of authigenic nonmetal oxide composite film
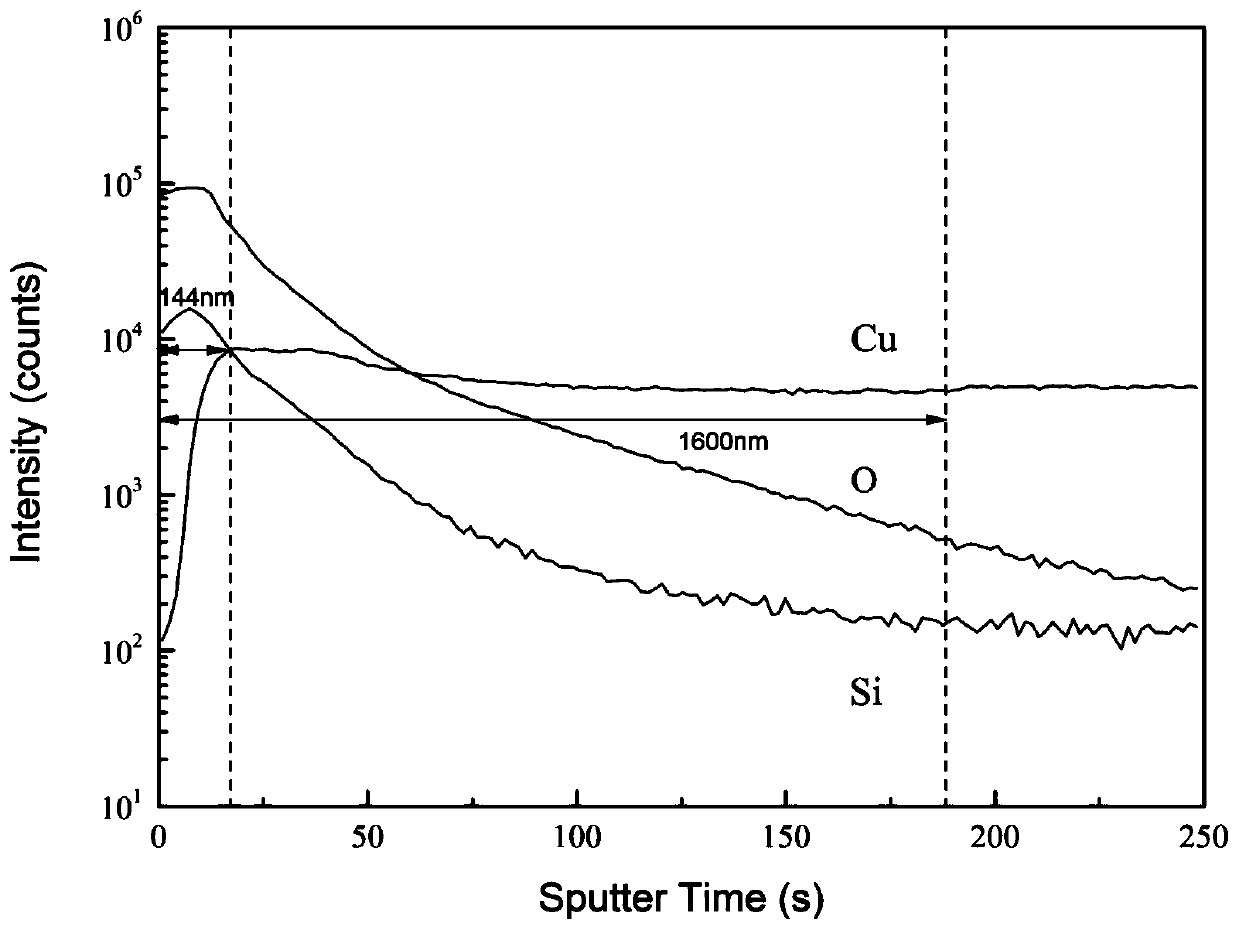
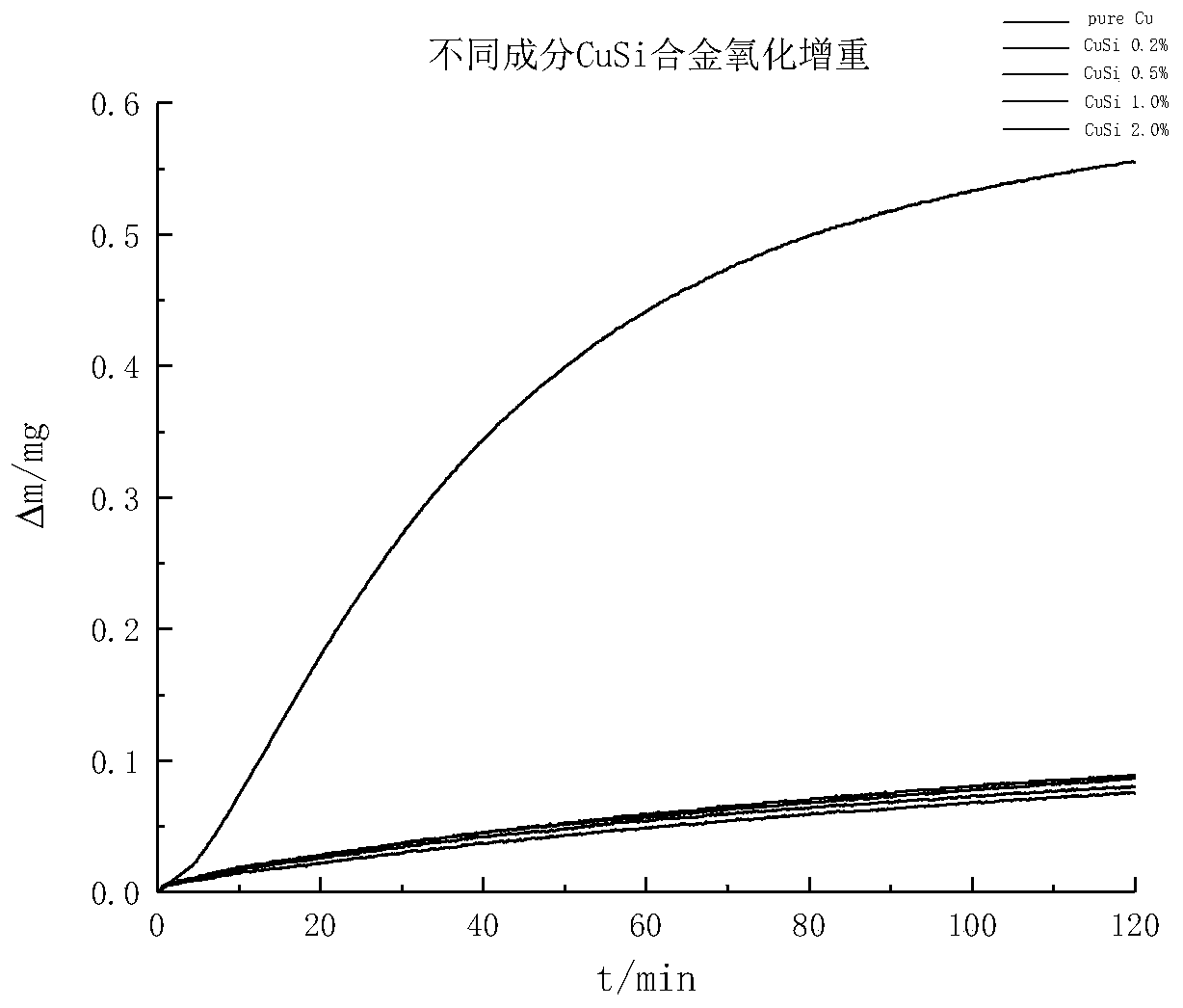
The invention provides a method for improving copper oxidation resistance of an authigenic nonmetal oxide composite film. Trace of Si elements are added into Cu so that a Cu@SiO2 composite attachmentfilm can be formed on the surface of Cu, and high-temperature oxidation resistance of the metal Cu and a product of the metal Cu is improved. By means of the method, trace of Si is mixed with Cu, repeated smelting is conducted in a vacuum smelting furnace, and a light doped CuSi alloy is manufactured. The added trace of Si elements are annealed in the Ar-20%H2 atmosphere, the trace of Si in the alloy is segregated to the surface of the alloy through the segregation effect and is reacted with residual O2 in the annealing atmosphere to generate SiO2, and therefore the Cu@SiO2 composite attachment film with a high melting point and stable performance can be formed, and it is ensured that a Cu metal matrix of the CuSi alloy is not oxidized under the high-temperature and pure-oxygen condition.By means of the method, the use reliability of copper-based parts and equipment is ensured, the cost is reduced, and industrial waste is reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip and grain-oriented electrical steel strip obtained according to said process
InactiveUS20160108494A1Simple stepsReduce oxidationInorganic material magnetismFurnace typesElectrical steelThin slab
A process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting, comprising the following process steps: a) smelting a steel, b) continuously casting the smelt by thin slab continuous casting, c′) heating up the thin slabs and subjecting the slabs to homogenization annealing at a maximum temperature of 1,250° C., d) heating to a temperature between 1.350° C. and 1.380° C., e) continuously hot rolling the thin slabs to form a hot-rolled strip, f) cooling and reeling the hot-rolled strip to form a coil, g) annealing the hot-rolled strip after reeling and prior to a subsequent cold rolling step, h) cold rolling the hot-rolled strip to the nominal usable thickness, i) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing, j) applying an annealing separator (non-stick layer) to the strip surface of the cold-rolled strip, k) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to secondary recrystallization annealing, forming a finished steel strip having a pronounced Goss texture, and l) stress-free annealing the finished steel strip, which has been coated with an insulating layer, provides an improved process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting. This is achieved in that the recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing of the cold-rolled strip in process step h) comprises a decarburization annealing phase and a subsequent nitridation annealing phase, with an intermediate reduction annealing phase being interposed between the decarburization annealing phase and the nitridation annealing phase, and carried out at a temperature ranging from 820° C.-890° C., for a maximum period of 40 seconds, with a dry, gaseous annealing atmosphere, which contains nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) and acts on the cold-rolled strip, and which has a water vapor / hydrogen partial pressure ratio pH2O / pH2 of less than 0.10 and wherein a cold-rolled strip is obtained, which primary recrystallized grains have a circle equivalent mean size (diameter) between 22 μm and 25 μm.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
Manufacturing method of silicon-based gallium nitride LED epitaxial structure
ActiveCN105914270AQuality improvementReduce the possibilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingLattice mismatchGallium nitride
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a silicon-based gallium nitride LED epitaxial structure. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (S1) with N2 and Al as raw materials, an AlN thin film is prepared on a silicon substrate, argon atoms are ionized into argon ions by plasma generated by magnetron sputtering, an aluminum target material is bombarded to sputter aluminum atoms and the aluminum atoms are migrated towards the silicon substrate and combined with nitrogen atoms to form an amorphous AlN thin film; (S2) the AlN thin film is heated for thermal annealing in an MOCVD cavity, a thermal annealing atmosphere is a mixed gas of nitrogen, hydrogen and an ammonia gas and the amorphous AlN thin film forms an AlN buffer layer of an AlN nano crystal nucleus structure; (S3) an insertion layer is formed on the AlN buffer layer in an epitaxial growth manner; and (S4) an n-type GaN layer, a quantum well light-emitting layer and a p-type GaN layer are formed on the insertion layer in an epitaxial growth manner. By the manufacturing method, the quality of the AlN film deposited by magnetron sputtering is improved; and the stress and the defect density caused by epitaxial film lattice mismatch are reduced.
Owner:FOCUS LIGHTINGS SCI & TECH
Nickel alloy base strip with cubic texture, and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a nickel alloy base strip with a cubic texture, and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation for an initial alloy billet: obtaining a nickel alloy cast ingot containing tungsten with atomic percent of 9.5% and carbon with atomic percent of 0.006%-0.009% through vacuum induction smelting, and obtaining the initial alloy billet through forging and hot-rolling; (2) cold-rolling for the alloy billet: carrying out cold-rolling on the obtained initial alloy billet until the thickness is 35[mu]m-55[mu]m and the total deformation amount is 98%, and obtaining a cold-rolled nickel alloy base strip; and (3) recrystallization heat treatment for the cold-rolled alloy base strip: carrying out recrystallization heat treatment on the obtained cold-rolled alloy base strip to obtain the nickel alloy base strip with a strong cubic texture, wherein the recrystallization heat treatment process is as follows: heat insulation is carried out for 2-2.5 hours at 1100-1280 DEG C, the heating speed is 3-5 DEG C / min, and the annealing atmosphere is pure hydrogen. The nickel alloy base strip with the cubic texture is provided with the strongcubic texture, free from ferromagnetic property, and high in strength.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Annealed Si-based InN nanorod heterojunction and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114657641AShorten migration distanceReduce recombination ratePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHeterojunctionNanopillar
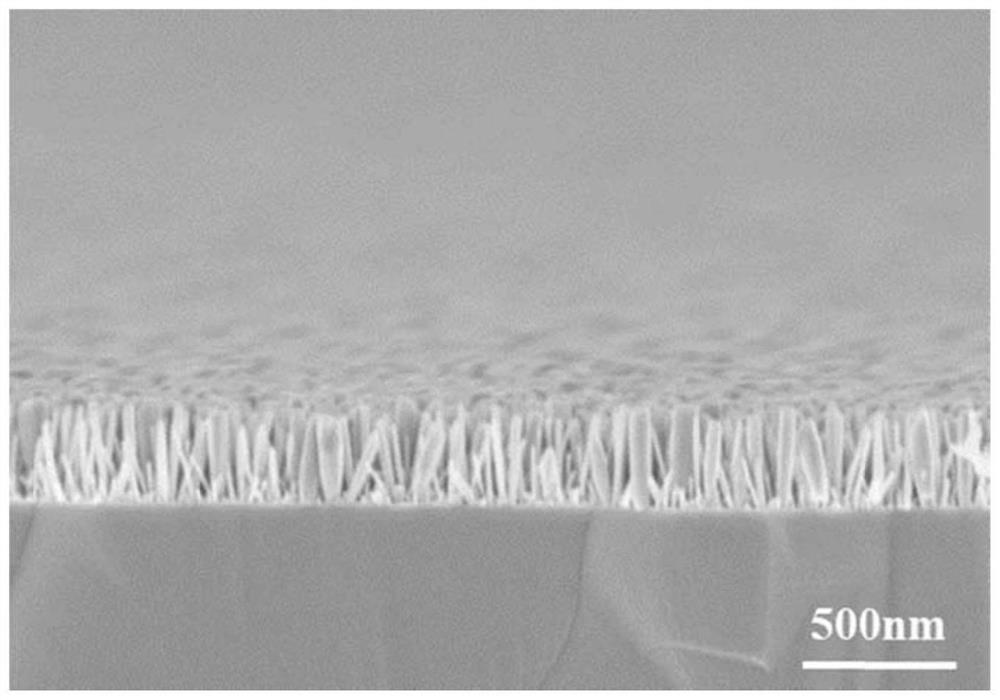
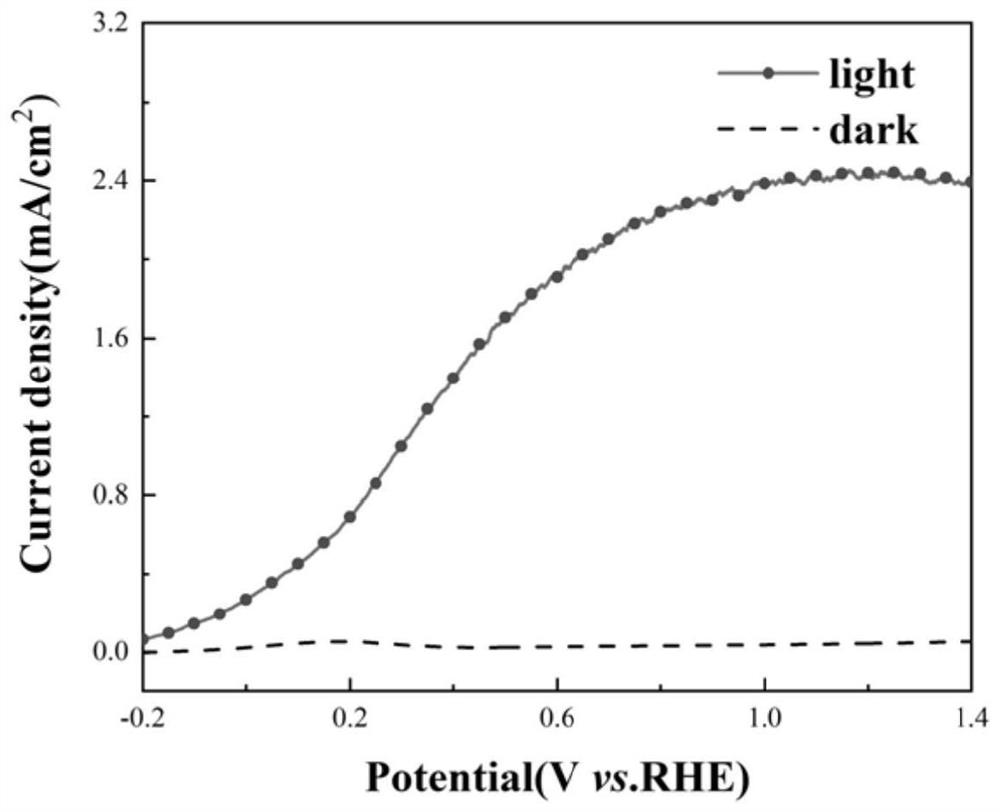
The invention discloses an annealed Si-based InN nanorod heterojunction as well as a preparation method and application of the annealed Si-based InN nanorod heterojunction. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) growing an InN nanorod on a Si substrate by adopting a molecular beam epitaxial growth process; (2) carrying out annealing treatment on the InN nanorod obtained in the step (1) to obtain a Si-based InN nanorod heterojunction; the annealing atmosphere is a sulfur atmosphere, an oxygen atmosphere or a selenium atmosphere under the protection of N2. The InN nanorod heterojunction comprises a substrate and an InN nanorod grown on the substrate, wherein the InN nanorod is annealed in different atmospheres to form the heterojunction. The Si-based InN nanorod heterojunction photoelectrode is prepared by adopting a method which is low in cost and simple in process. The heterojunction photoelectrode can be used for hydrogen production through photoelectrocatalysis water decomposition, the hydrogen production efficiency is greatly improved, and an effective strategy is provided for large-scale preparation of hydrogen energy through solar energy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Production method of antibacterial stainless steel drainer drawn piece
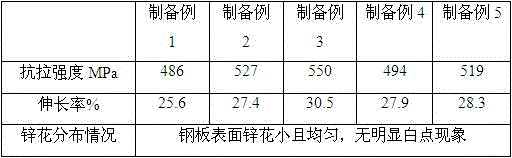
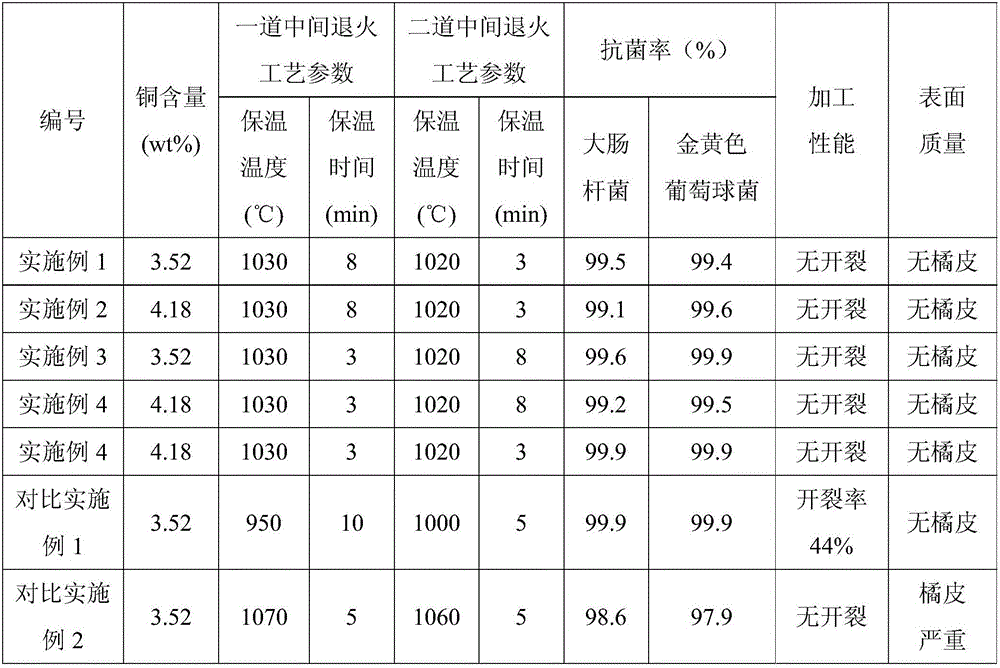
ActiveCN105755392AFlat surfaceDoes not affect processing performanceDomestic plumbingAusteniteAmmonia gas
The invention discloses a production method of an antibacterial stainless steel drainer drawn piece. The method sequentially comprises primary drawing, primary intermediate annealing, secondary drawing, secondary intermediate annealing, edge curling, coarse wire drawing and fine wire drawing; austenite stainless steel is used as a raw material, Cu ranges from 3.5wt% to 4.5wt%, C is less than or equal to 0.08wt%, Si is less than or equal to 1.0wt%, Mn is less than or equal to 2.0wt%, P is less than or equal to 0.045wt%, S is less than or equal to 0.03wt%, Ni ranges from 8wt% to 10.5wt%, Cr ranges from 17wt% to 19wt%, and the balance is Fe; the primary intermediate annealing is bright annealing, the annealing atmosphere is ammonia gas, the annealing temperature is 1,000-1,060 DEG C, and the annealing holding time is 2-10 min; the secondary intermediate annealing is bright annealing, the annealing atmosphere is ammonia gas, the annealing temperature is 1,010-1,050 DEG C, and the annealing holding time is 2-10 min. The drainer drawn piece produced with the production method has the bright, clean and flat surface and is low in cost and stable in antibacterial performance, and mass production is easy to realize.
Owner:JOMOO KITCHEN & BATHROOM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com