Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
126results about How to "Improve surface morphology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
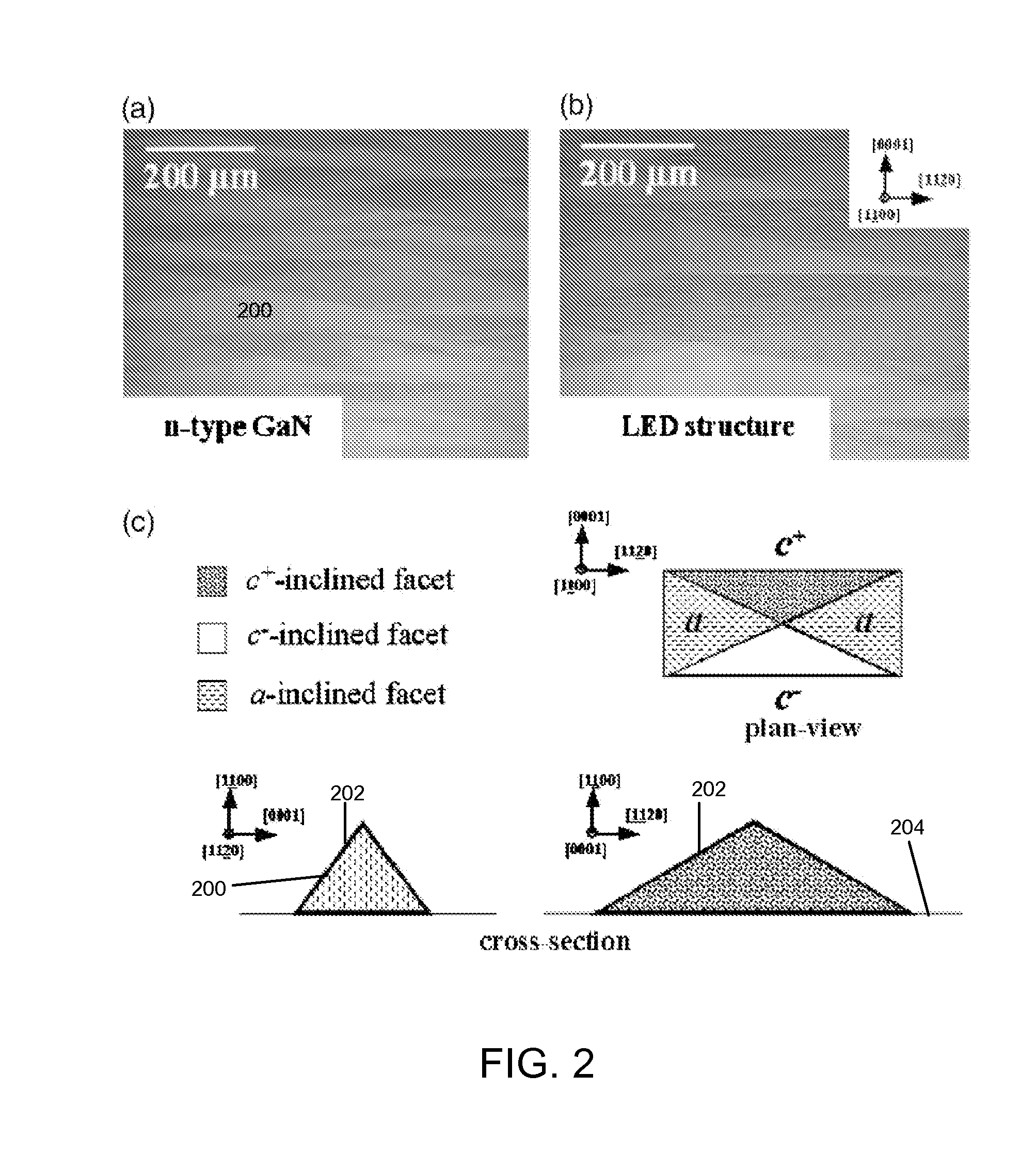
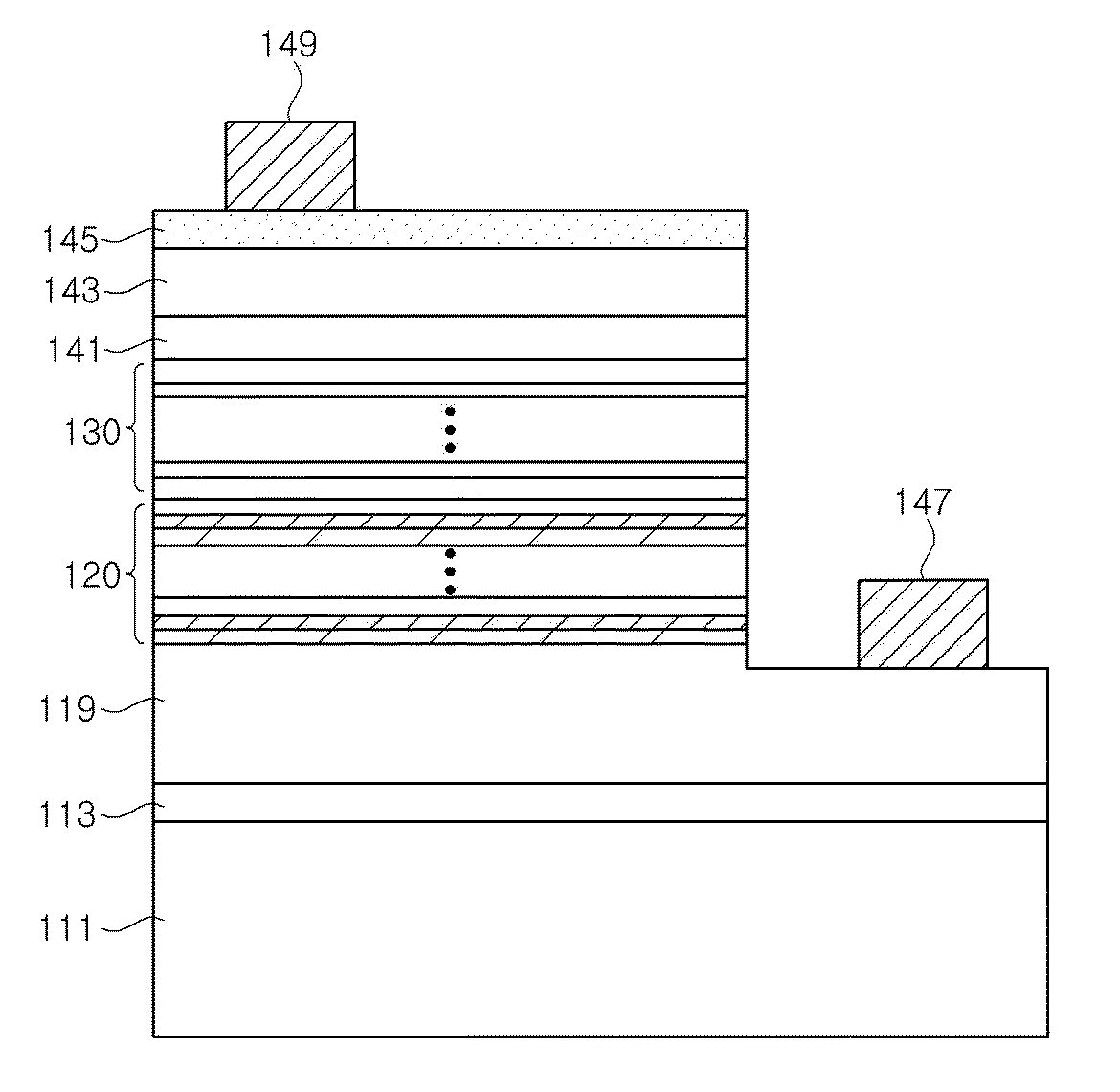
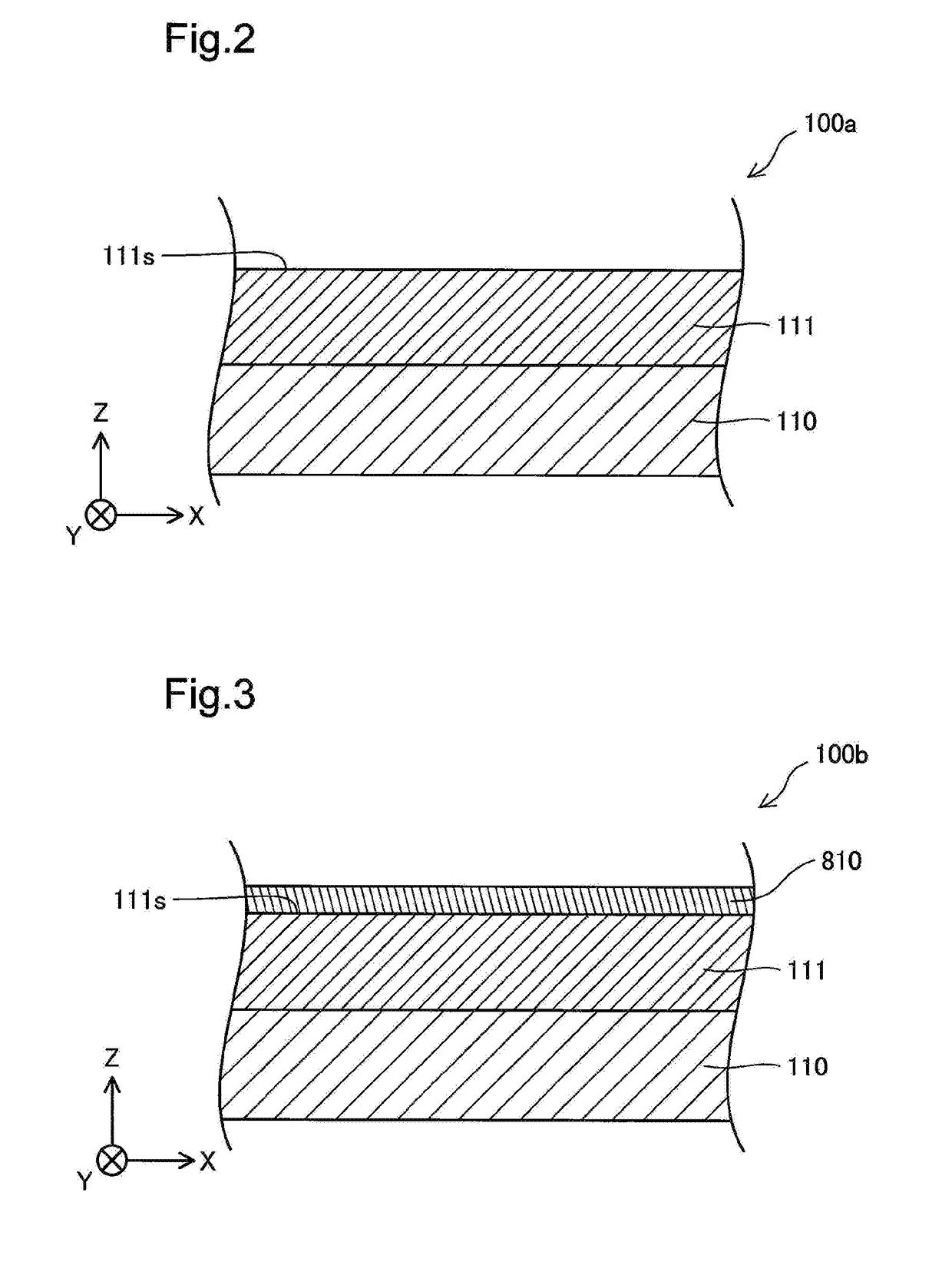
Method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor and nitride semiconductor element
ActiveUS8709843B2Improve surface morphologyReduce layeringPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSource materialCrystallinity
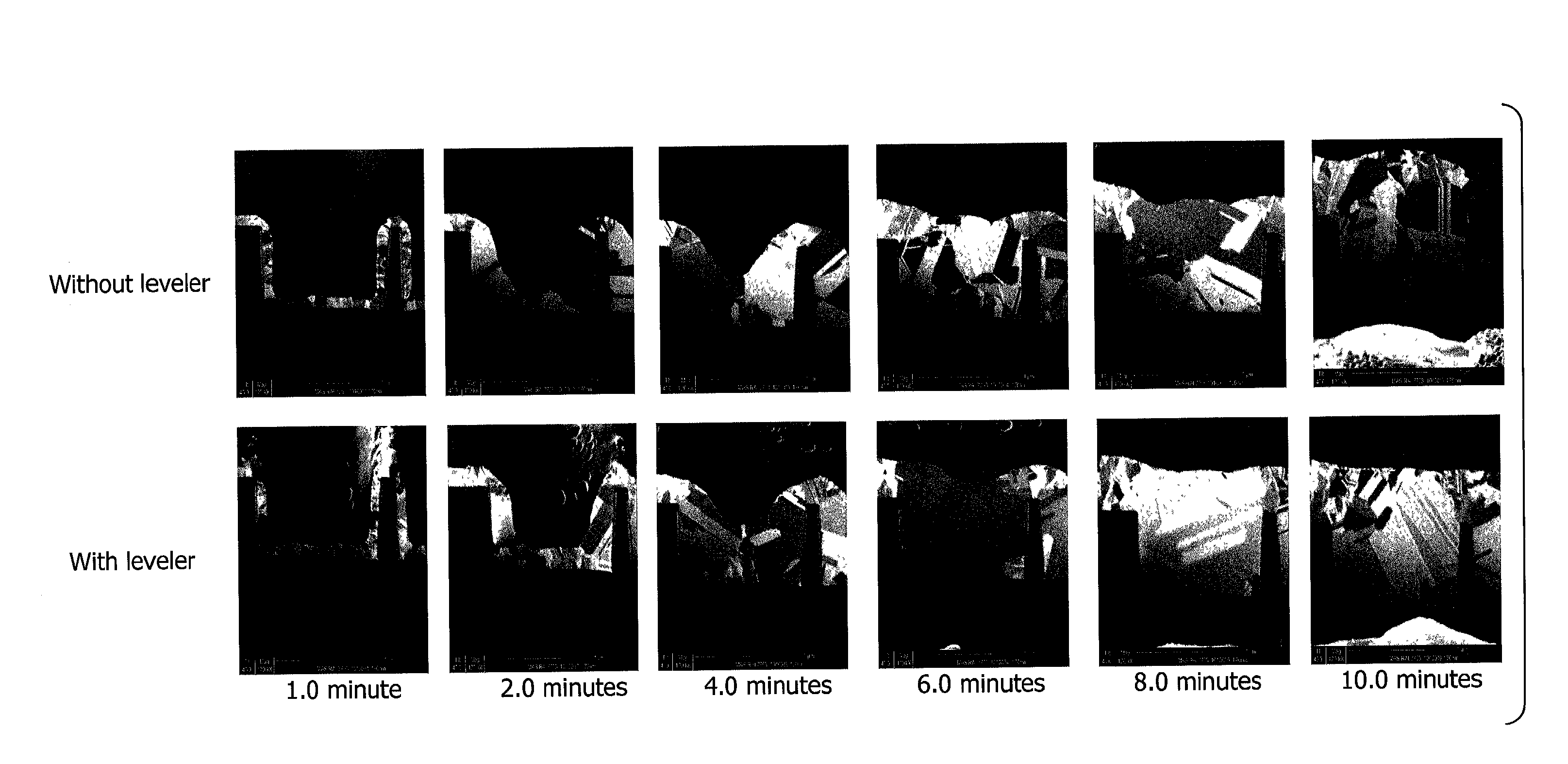
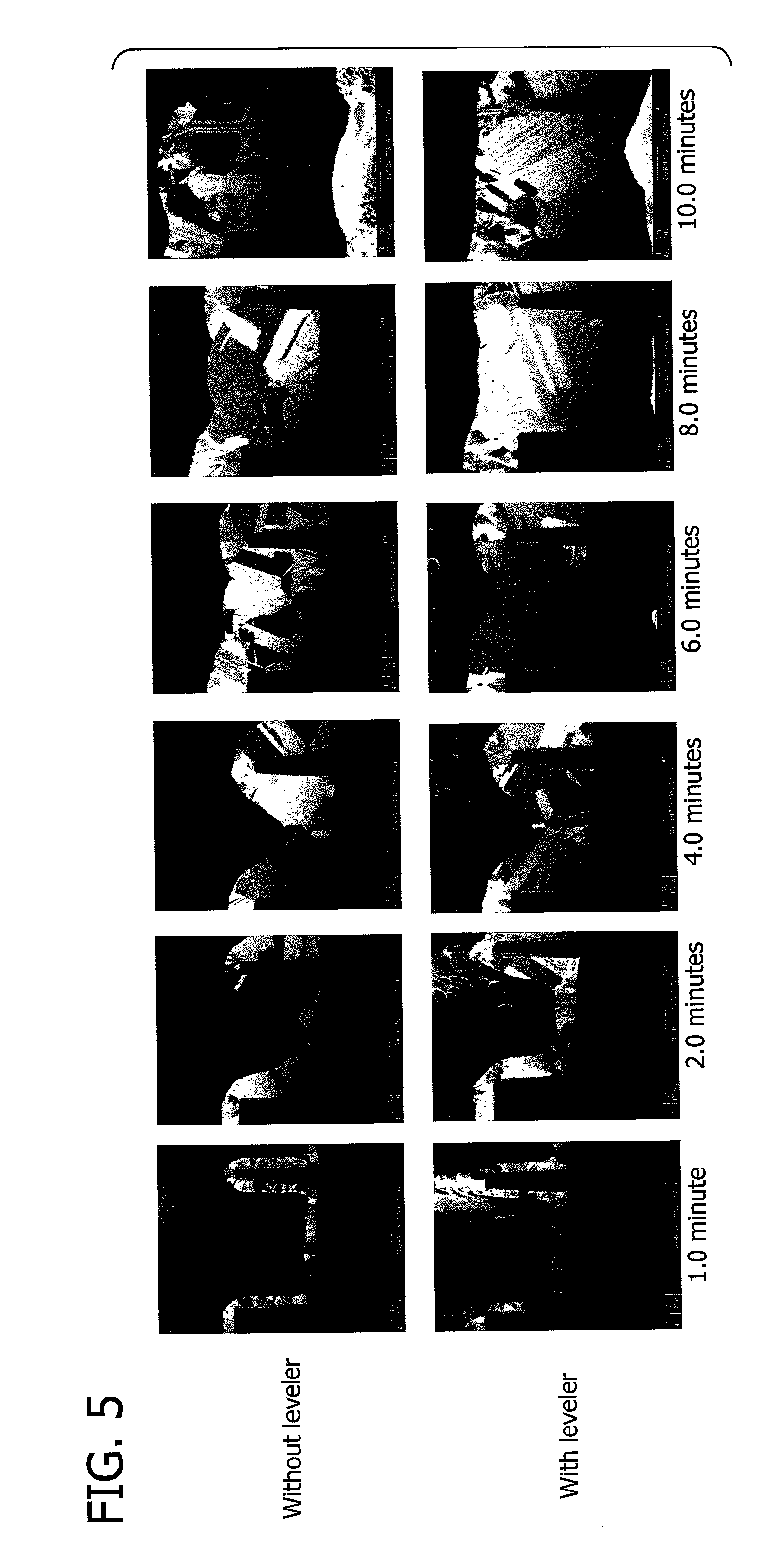
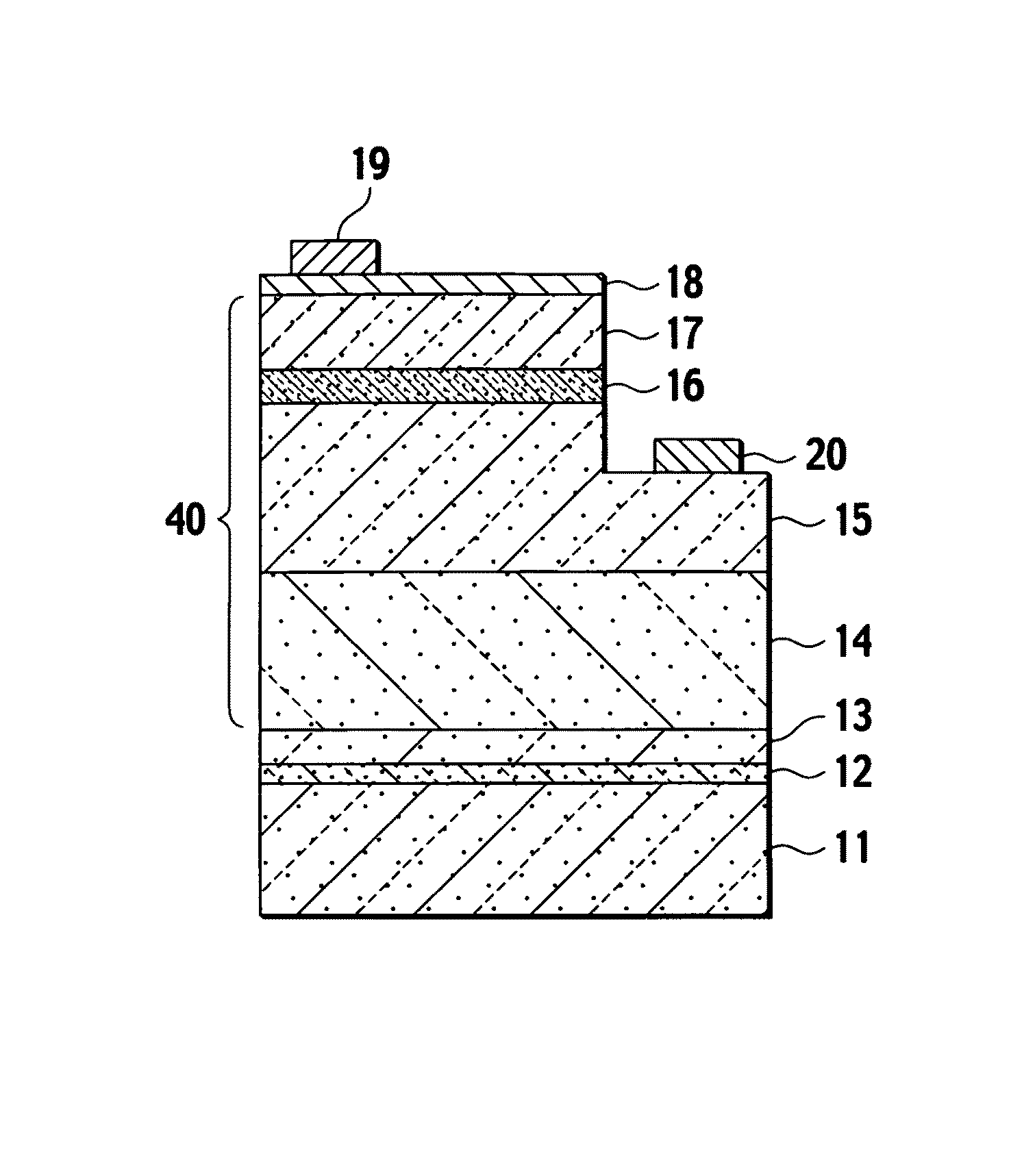
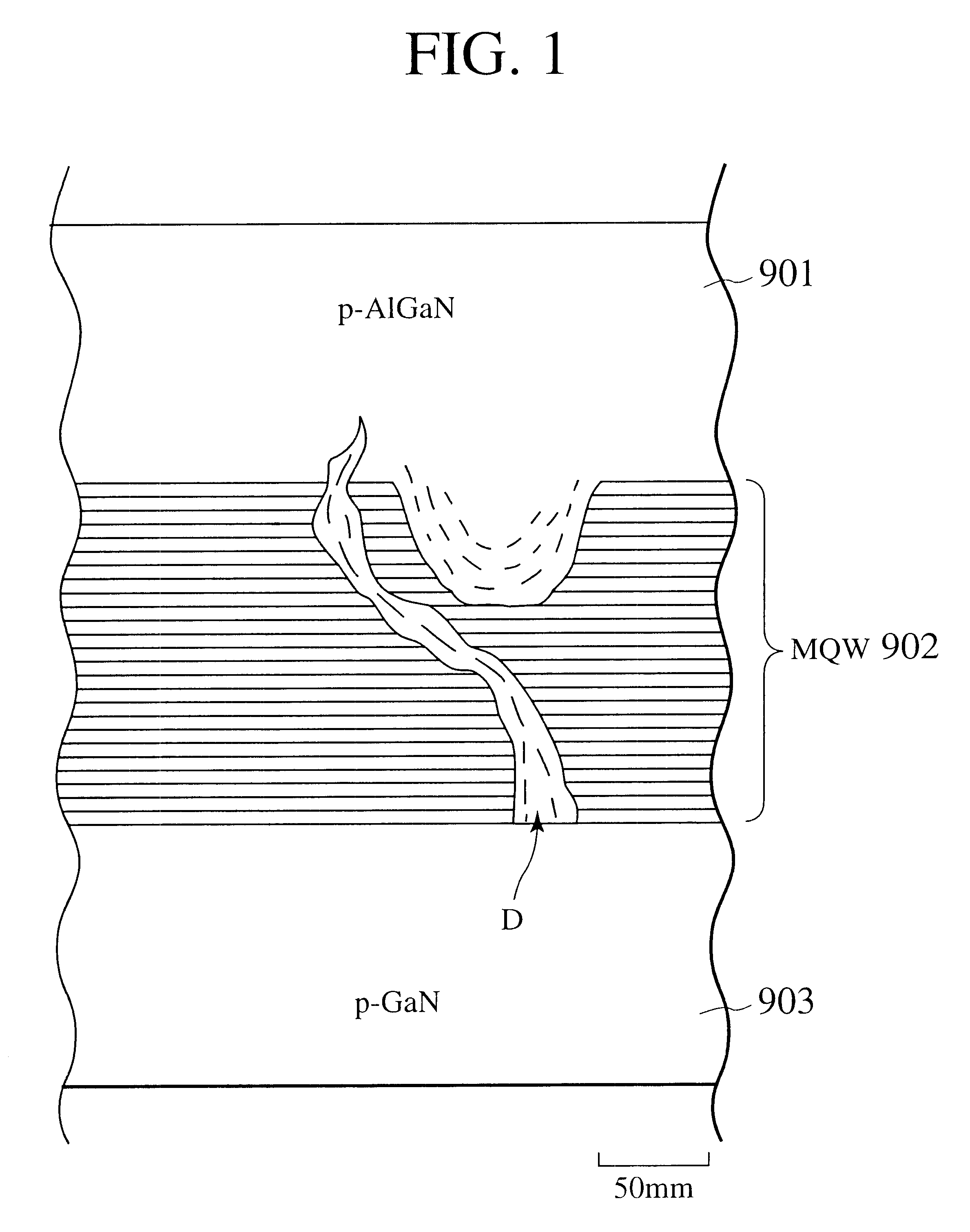
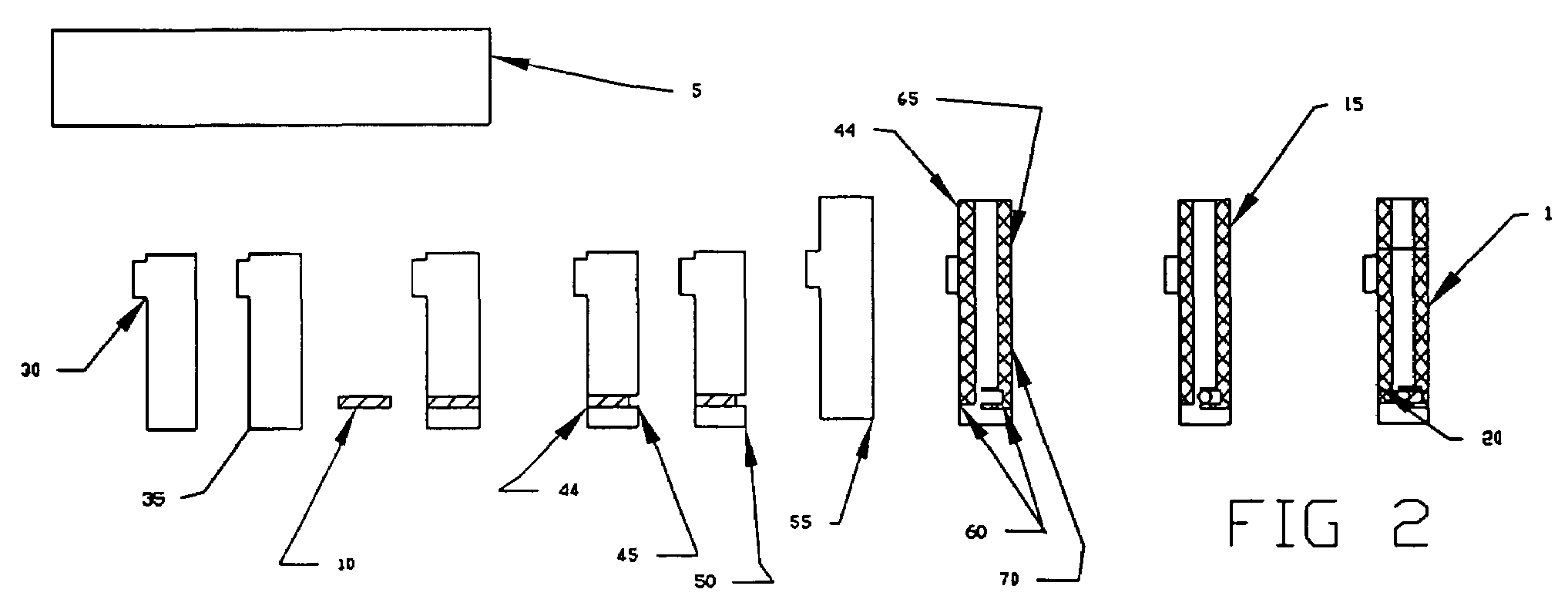
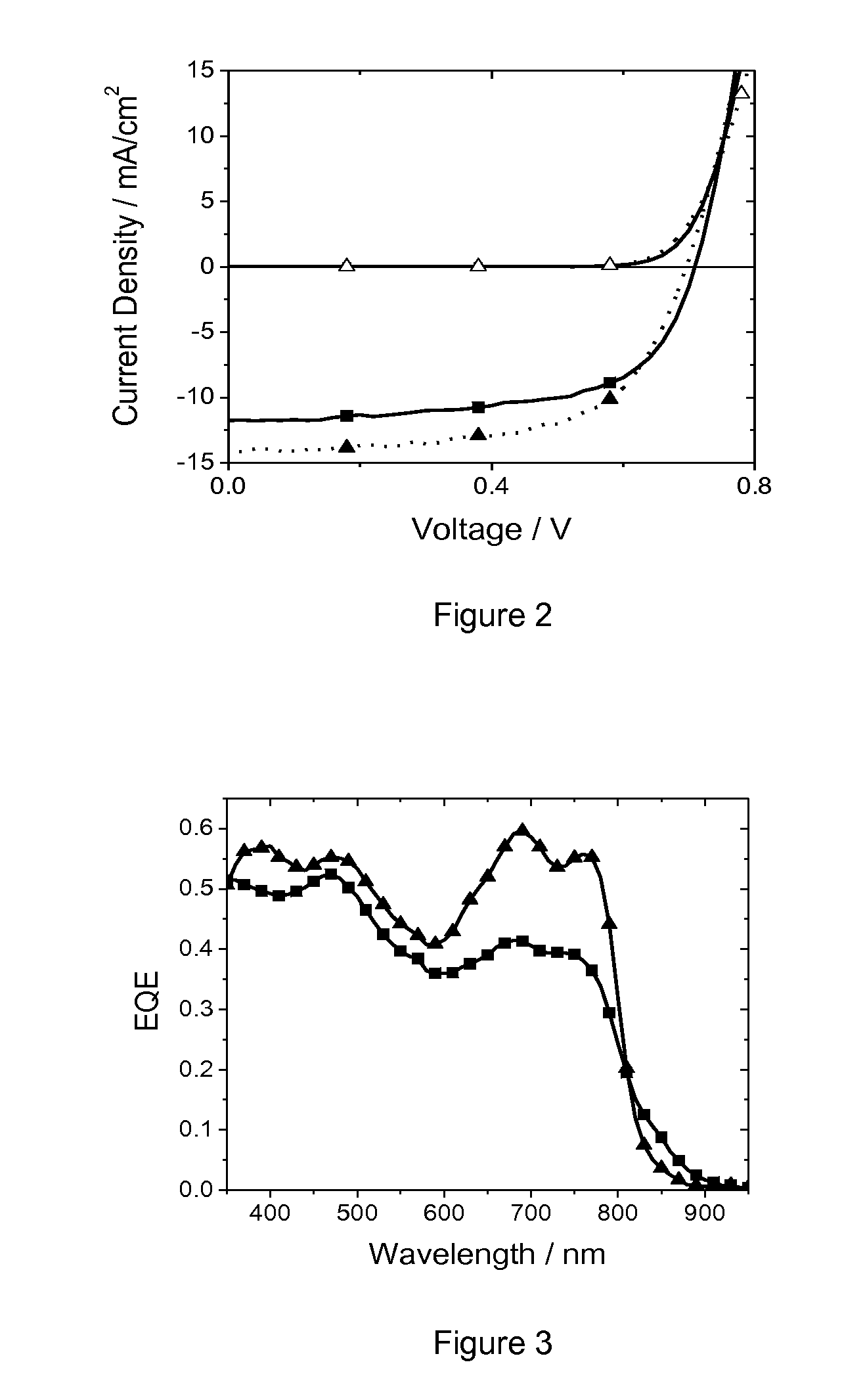
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a nitride semiconductor capable of improving the crystallinity and the surface state of the nitride semiconductor crystal formed on top of a high-temperature AlN buffer layer. An AlN buffer layer is formed on top of a growth substrate, and then nitride semiconductor crystals are grown on top of the AlN buffer layer. In a stage of manufacturing the nitride semiconductor, the crystal of the AlN buffer layer is grown at a high temperature of 900° C. or higher. In addition, an Al-source material of the AlN buffer layer is started to be supplied first to a reaction chamber and continues to be supplied without interruption, and then a N-source material is supplied intermittently.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method for preparing epitaxial-substrate and method for manufacturing semiconductor device employing the same
InactiveUS6627552B1Improve convenienceImprove surface morphologyPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSingle crystalSemiconductor
The present invention provides a method for preparing epitaxial-substrate, for growing a multilayered structure of GaN based semiconductor layers on the epitaxial-substrate so as to construct a semiconductor device such as blue-emitting laser diode and LED. The method for preparing the epitaxial-substrate encompasses (a) growing a first GaN based semiconductor layer on a bulk-substrate; (b) growing an InGaN based semiconductor layer on the first GaN based semiconductor layer; (c) growing a second GaN based semiconductor layer on the InGaN based semiconductor layer; and (d) separating the second GaN based semiconductor layer from the first GaN based semiconductor layer to provide the epitaxial-substrate. The epitaxial-substrate having a high crystallographic perfection and an excellent surface morphology is obtained simply and in a short time. The defect density of the single crystalline GaN based semiconductor layer film grown on the epitaxial-substrate is greatly reduced.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Vascular graft having a chemicaly bonded electrospun fibrous layer and method for making same
InactiveUS20030100944A1Improve surface morphologyGood tissue responseNon-woven fabricsCoatingsChemical LinkageElectrospinning
A vascular graft comprising a traditional graft material and an electrospun fibrous layer. The solvent used to reduce the material for the electrospun layer is also capable of reducing the graft material to a liquid solution. The electrospun layer is chemically bonded to the graft material, without adhesives, by either spraying the graft with the solvent prior to electrospinning or by assuring that a sufficient amount of residual solvent reaches the graft while electrospinning.
Owner:DATASCOPE INVESTMENT
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
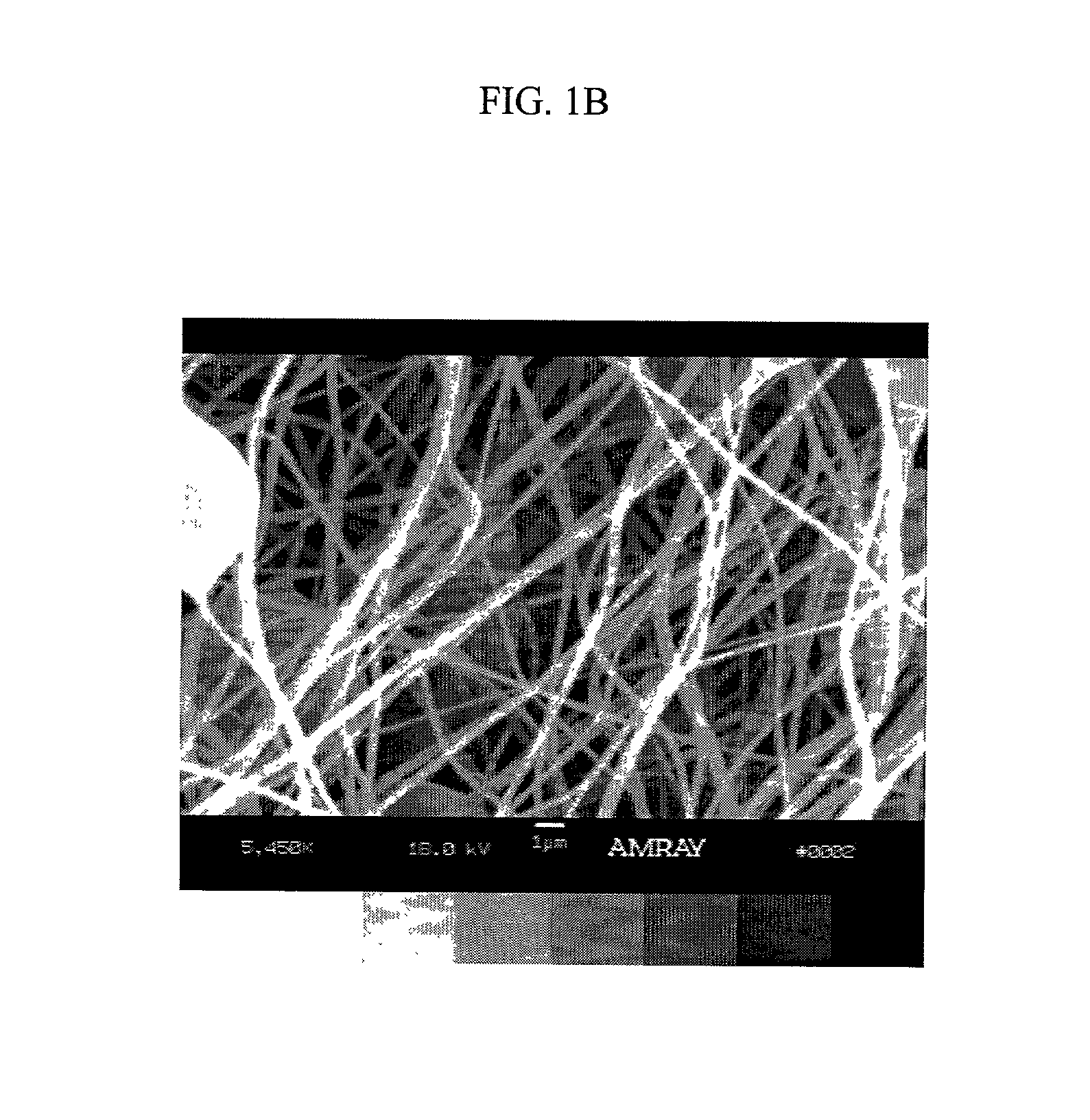
InactiveUS20050186333A1Accurate electronic readoutMinimizing strip to strip variationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSilver inkCarbon nanotube
A sensor system that detects a current representative of a compound in a liquid mixture features a multi or three electrode strip adapted for releasable attachment to signal readout circuitry. The strip comprises an elongated support which is preferably flat adapted for releasable attachment to the readout circuitry; a first conductor and a second and a third conductor each extend along the support and comprise means for connection to the circuitry. The circuit is formed with single-walled or multi walled nanotubes conductive traces and may be formed from multiple layers or dispersions containing, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-cloride. An active electrode formed from a separate conductive carbon nanotubes layer or suitable dispersion, positioned to contact the liquid mixture and the first conductor, comprises a deposit of an enzyme capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the compound and preferably an electron mediator, capable of transferring electrons between the enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the first conductor. A reference electrode also formed from a conductive carbon nanotube layer or suitable dispersion is positioned to contact the mixture and the second conductor. The system includes circuitry adapted to provide an electrical signal representative of the current which is formed from printing conductive inks made with nano size particles such as conductive carbon or carbon / platinum or carbon / silver, or carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide to form a conductive carbon nanotube layers. The multiple-electrode strip is manufactured, by then applying the enzyme and preferably the mediator onto the electrode. Alternatively the electrode can have a carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-cloride surface and or a conductive carbon or silver ink surface connecting leg. The carbon nanotube solution is first coated and patterned into electro shapes and the conductive carbon nanotubes, carbon or silver ink can be attached by printing the ink to interface with the carbon nanotube electro surface. A platinum electrode test strip is also disclosed that is formed from either nano platinum distributed in the carbon nanotube layer or by application or incorporation of platinum to the carbon nanotube conductive ink.
Owner:DOUGLAS JOEL S MR
Method to grow III-nitride materials using no buffer layer
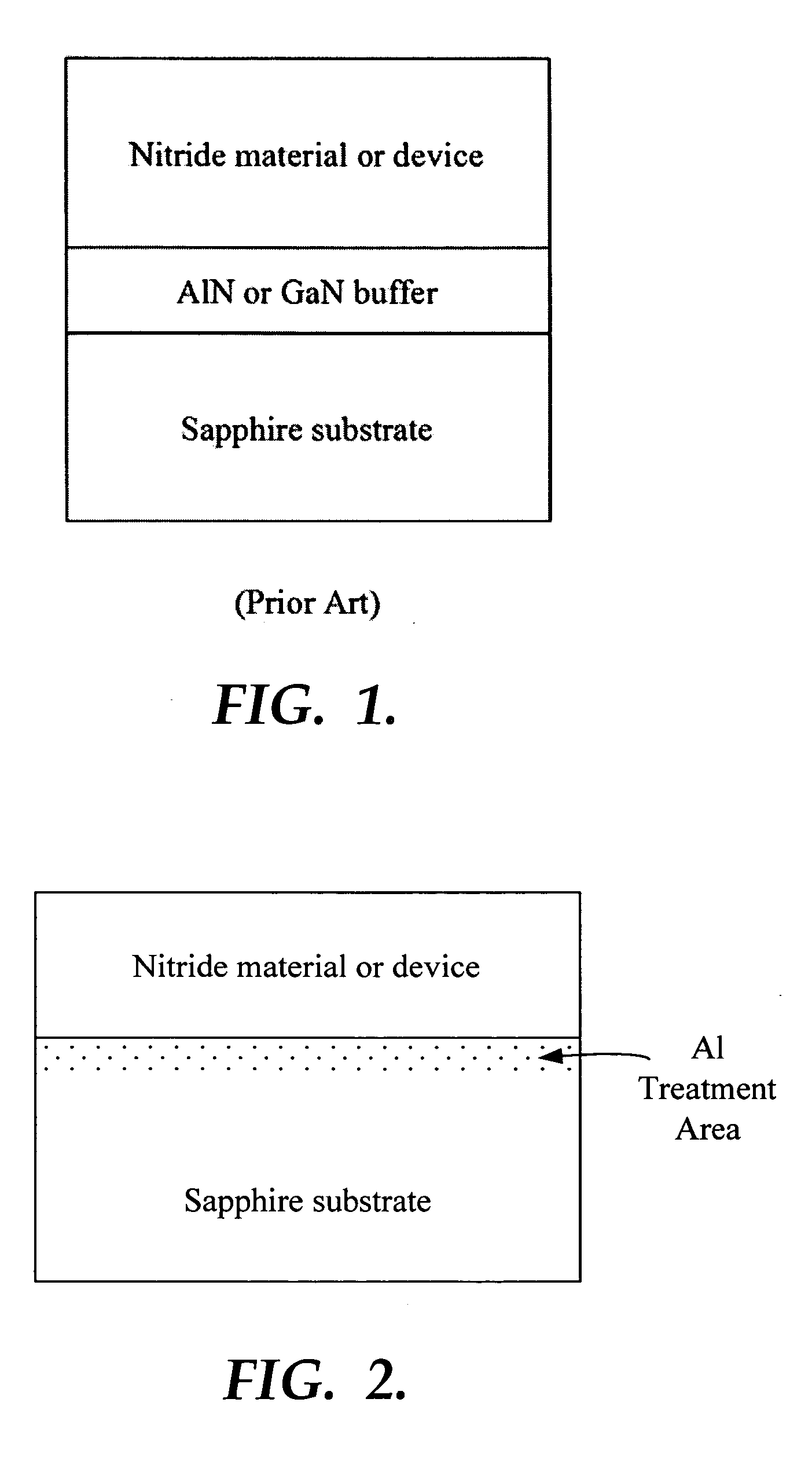
InactiveUS20060175681A1Improve crystal qualityImprove surface morphologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCrystallinityMaterials science
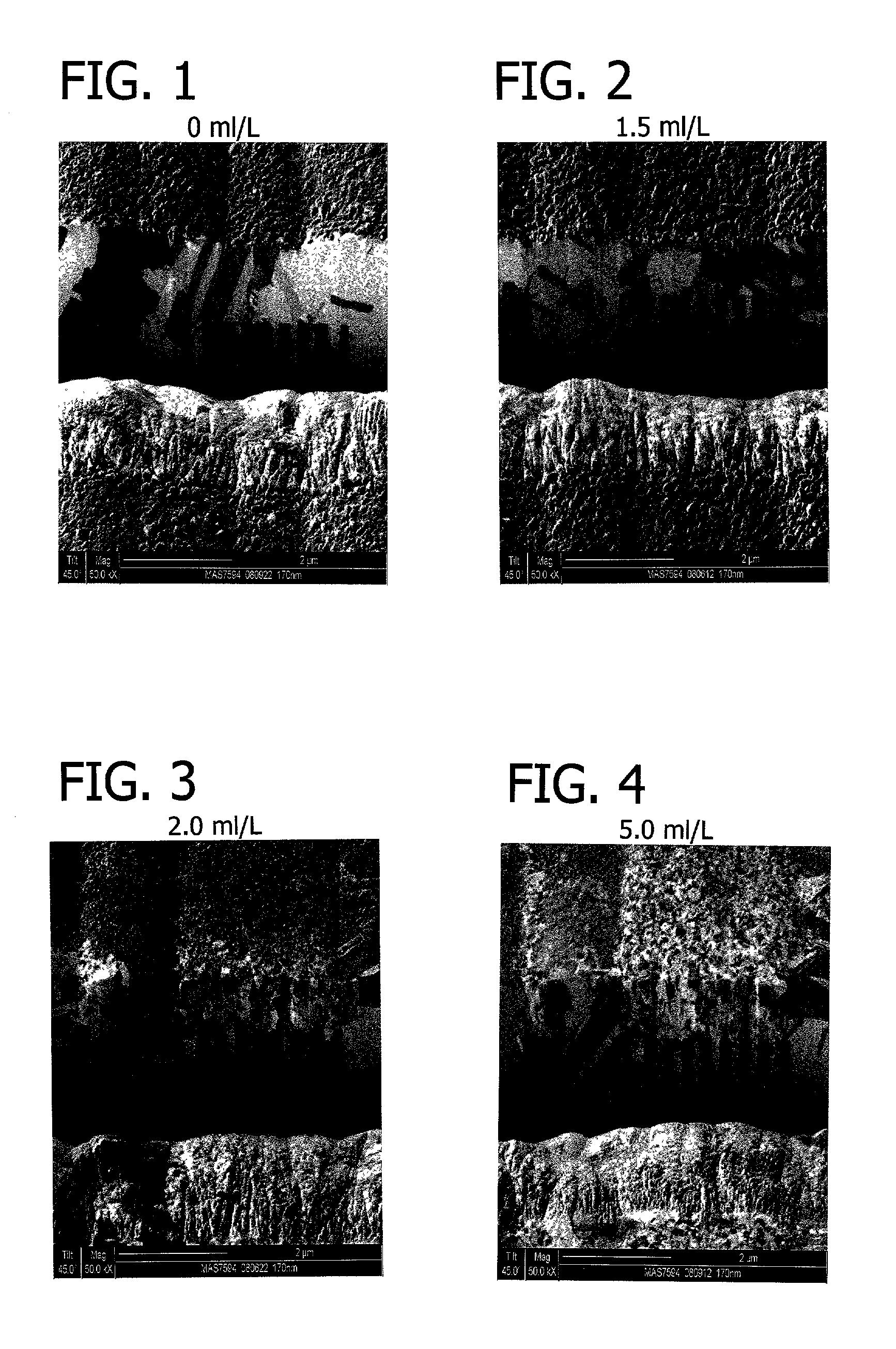
Disclosed is a method for growing nitride compound semiconductors on sapphire substrates where no low-temperature buffer layer is used. The nitride based compound semiconductor materials and devices grown by the method of the present invention have crystallinity and surface morphology at practical levels with high quality, high stability, and high yield.
Owner:III N TECH
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
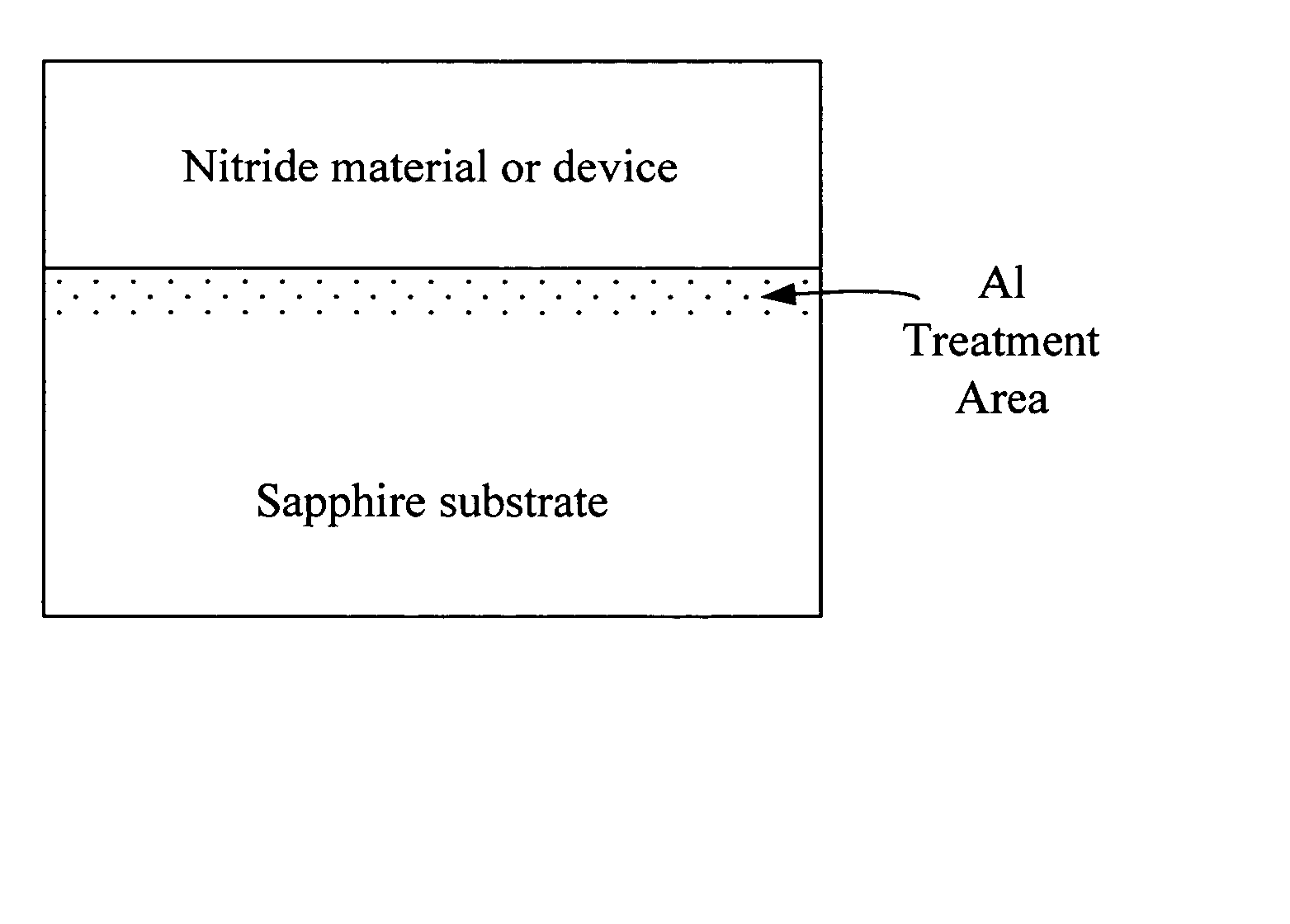
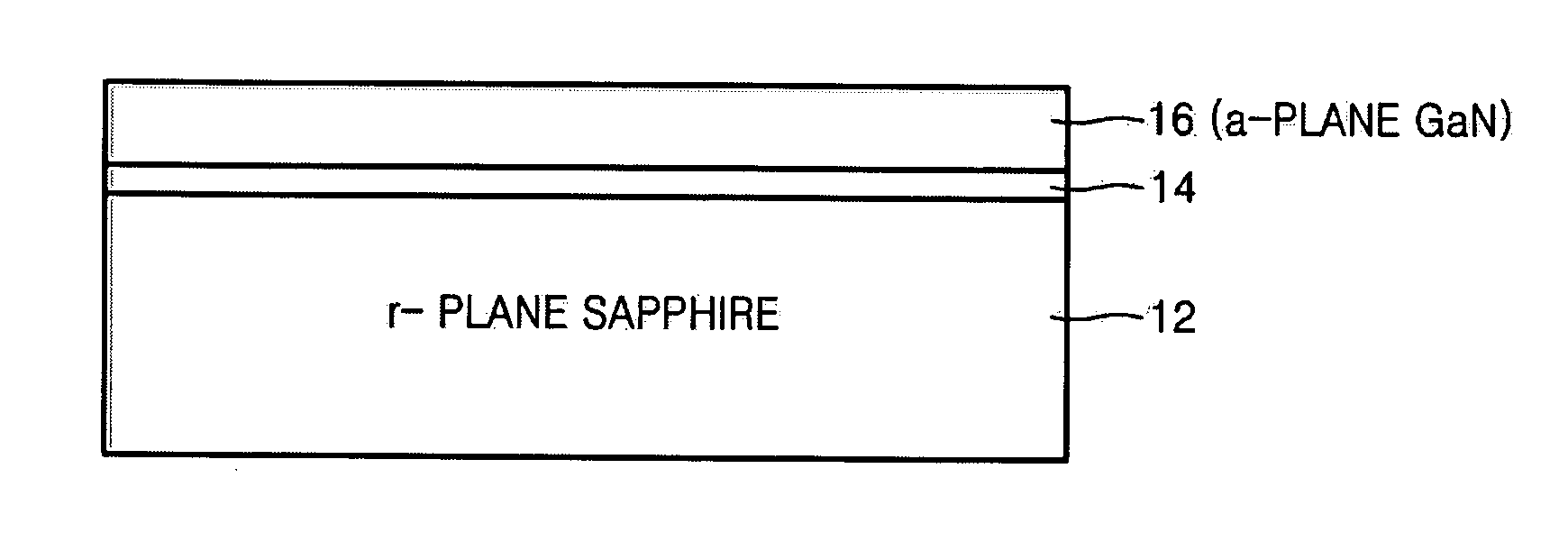
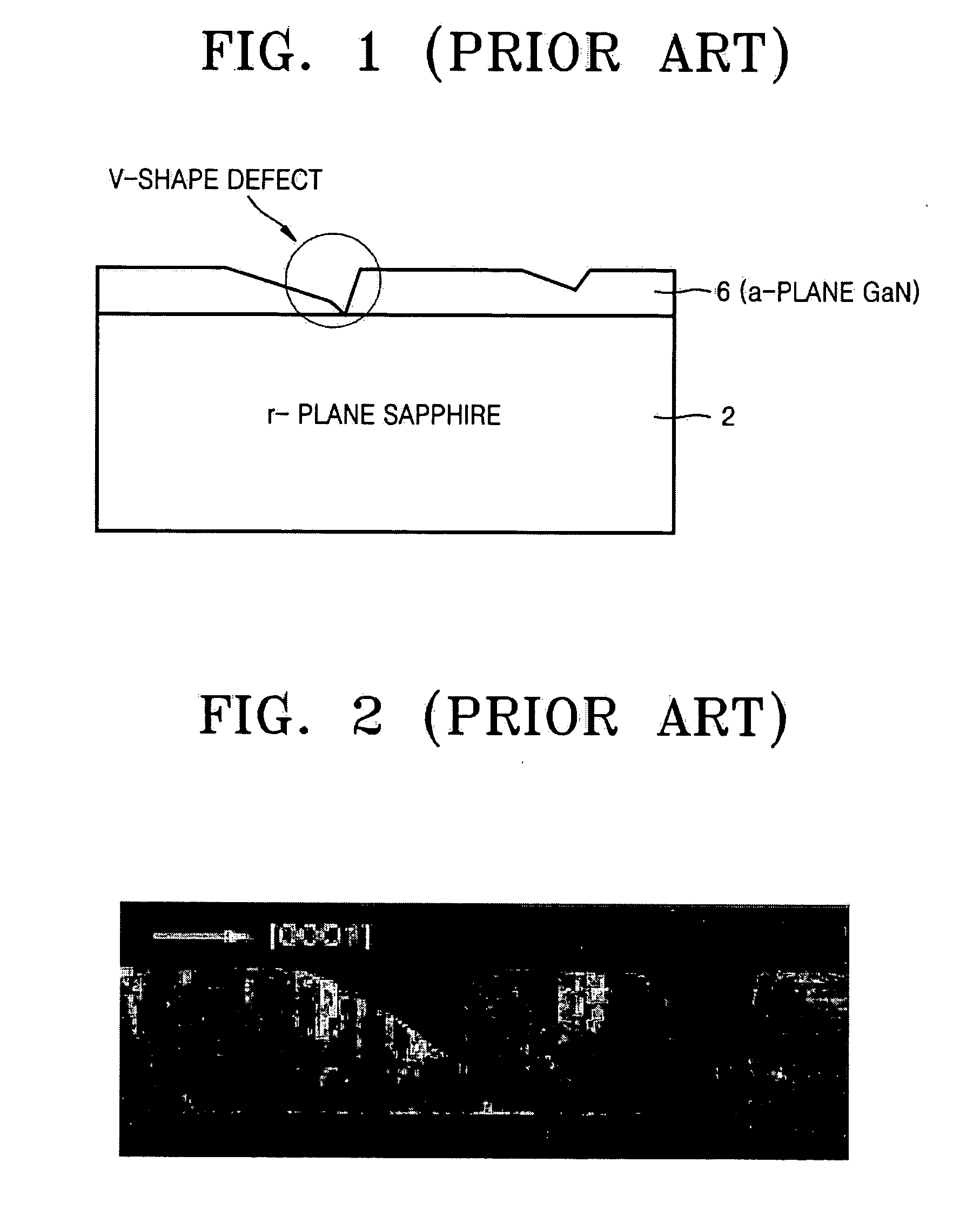
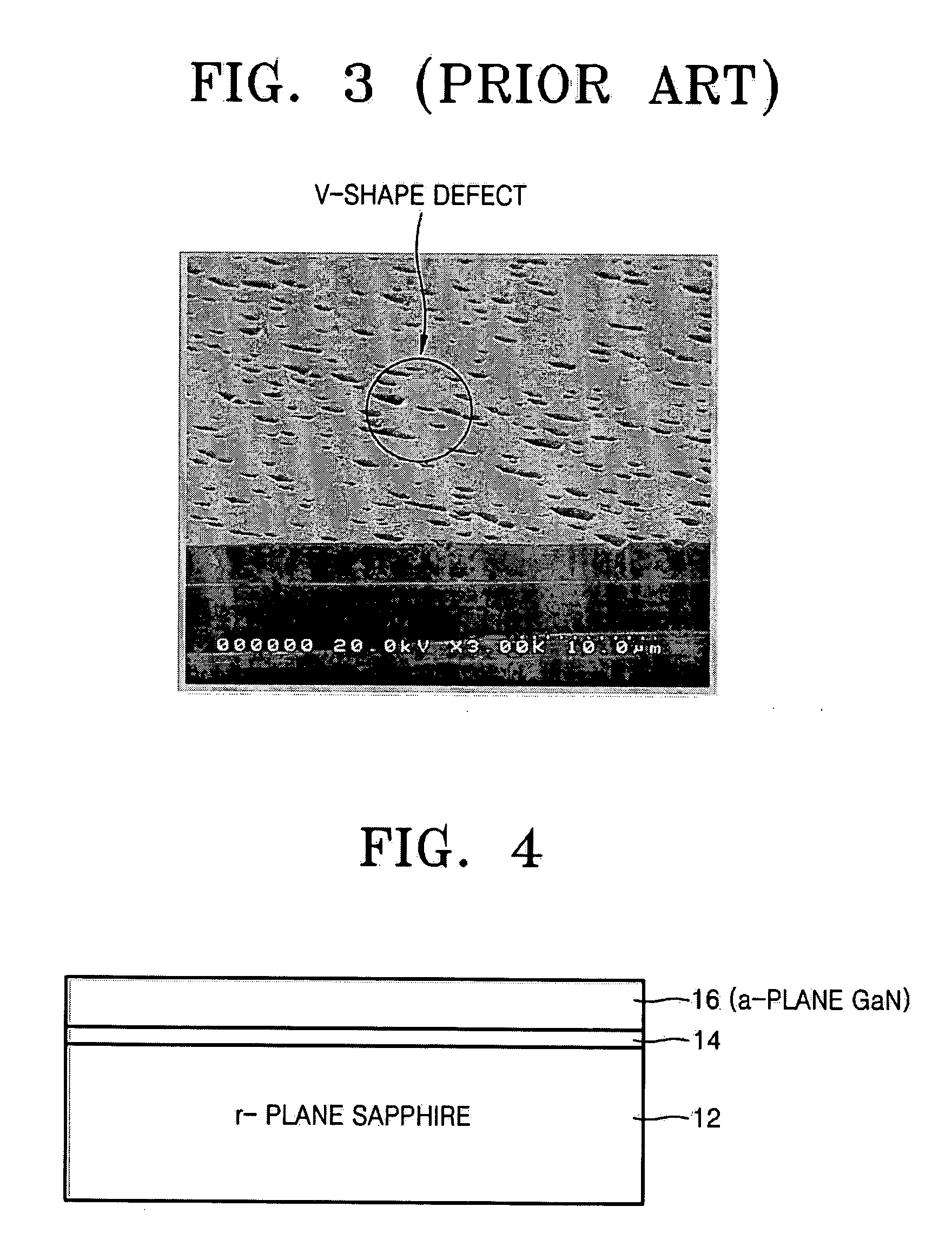
InactiveUS20070114563A1Improve surface morphologyPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsDevice materialNitrogen
Provided are semiconductor devices having improved surface morphology characteristics, and a method of fabricating the same. The semiconductor device includes: an r-plane sapphire substrate; an AlxGa(1-x)N(0≦×<1) buffer layer epitaxially grown on the r-plane sapphire substrate to a thickness in the range of 100-20000 Å in a gas atmosphere containing nitrogen (N2) and at a temperature of 900-1100° C.; and a first a-plane GaN layer formed on the buffer layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
InactiveUS7285198B2Flat surfaceImprove consistencyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsContact padAnalyte
An electrochemical test device for determining the presence or concentration of an analyte in an aqueous fluid sample comprises a substrate comprising a non-conductive material; a working electrode comprising a conductive film formed at least with carbon nanotubes, the working electrode having a first electrode area, a first lead and a first contact pad; a counter electrode comprising a conductive film formed at least with carbon nanotubes; a reagent capable of reacting with the analyte to produce a measurable change in potential which can be correlated to the presence or concentration of the analyte in the fluid sample, the reagent overlaying at least a portion of the first electrode area of the working electrode; and a reference electrode comprising a conductive coating formed at least with carbon nanotubes, the reference electrode having a third electrode area at least a portion of which is overlaid with a reference material.
Owner:DOUGLAS JOEL S MR
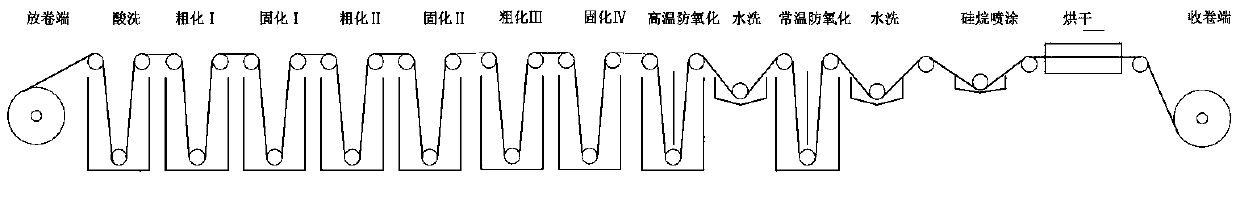
Method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor and nitride semiconductor element
ActiveUS20090269867A1Improve surface morphologyPrevent thermal deformationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSource materialCrystallinity
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a nitride semiconductor capable of improving the crystallinity and the surface state of the nitride semiconductor crystal formed on top of a high-temperature AlN buffer layer. An AlN buffer layer is formed on top of a growth substrate, and then nitride semiconductor crystals are grown on top of the AlN buffer layer. In a stage of manufacturing the nitride semiconductor, the crystal of the AlN buffer layer is grown at a high temperature of 900° C. or higher. In addition, an Al-source material of the AlN buffer layer is started to be supplied first to a reaction chamber and continues to be supplied without interruption, and then a N-source material is supplied intermittently.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Providing group v and group vi over pressure for thermal treatment of compound semiconductor thin films
InactiveUS20130056793A1Avoid lostPrevent loss of crystallinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for forming high quality, low resistivity Group III-V or Group II-VI compounds. In one embodiment, the method includes growing a compound semiconductor layer having a n-type or p-type dopant over a substrate, the compound semiconductor layer comprising at least a first component and a second component, and the second component has a vapor pressure relatively higher than the first component, forming a supplemental layer consisted essentially of the second component at or near an upper surface of the compound semiconductor layer, and anneal the substrate. A capping layer may be formed on the supplemental layer to help prevent loss of crystallinity of the second component at elevated temperatures. An overpressure of the second component gas may be provided onto an exposed surface of the substrate during annealing to enhance the surface morphology of the compound semiconductor layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Conjugated Polymers and Their Use in Optoelectronic Devices
ActiveUS20120186652A1Enhanced light absorptionGood charge transport characteristicNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSolubilityPhotodetector
Disclosed are certain polymeric compounds and their use as organic semiconductors in organic and hybrid optical, optoelectronic, and / or electronic devices such as photovoltaic cells, light emitting diodes, light emitting transistors, field effect transistors, and photodetectors. The disclosed compounds can provide improved device performance, for example, as measured by power conversion efficiency, fill factor, open circuit voltage, field-effect mobility, on / off current ratios, and / or air stability when used in photovoltaic cells or transistors. The disclosed compounds can have good solubility in common solvents enabling device fabrication via solution processes.
Owner:RAYNERGY TEK INC
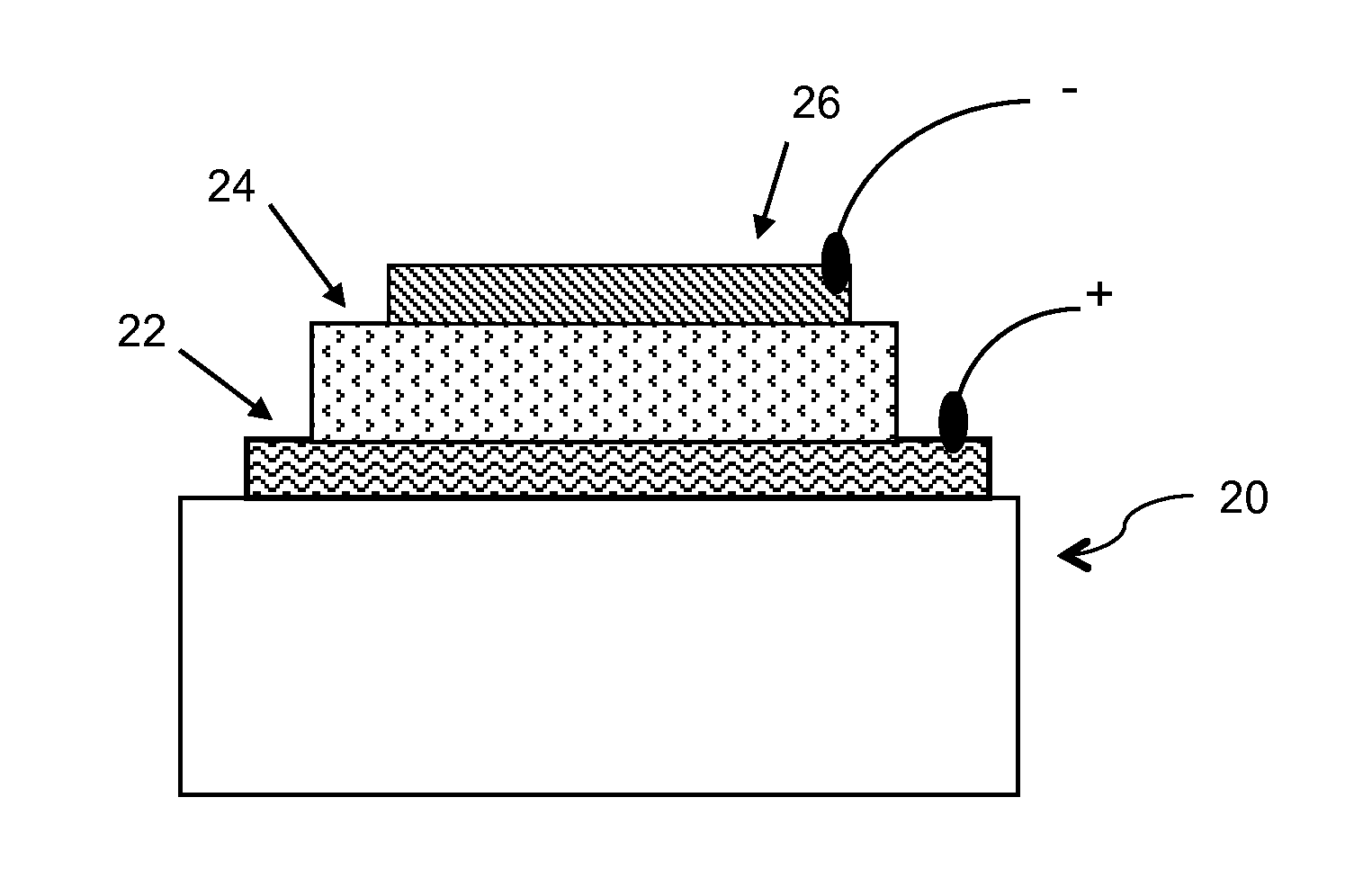
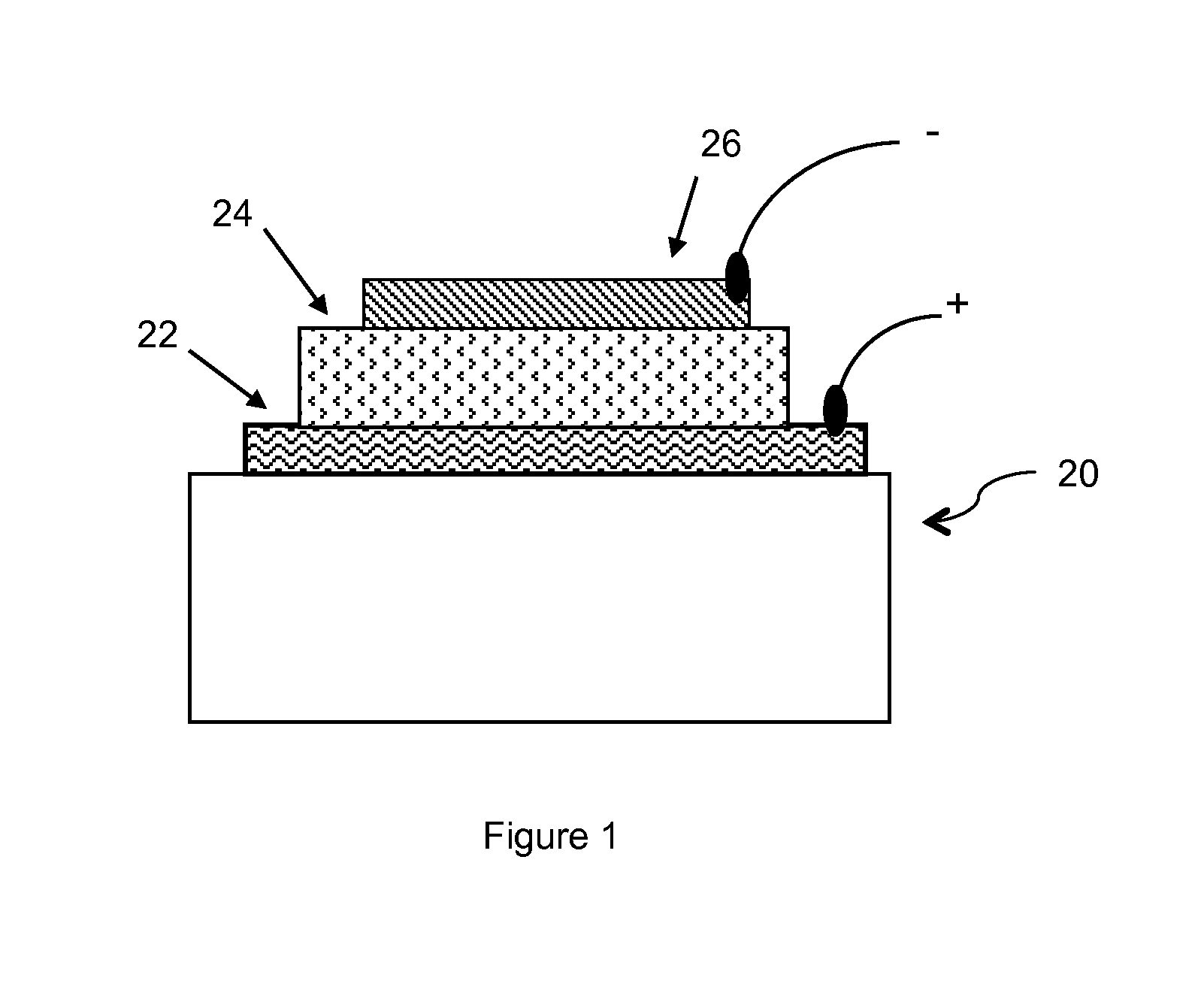
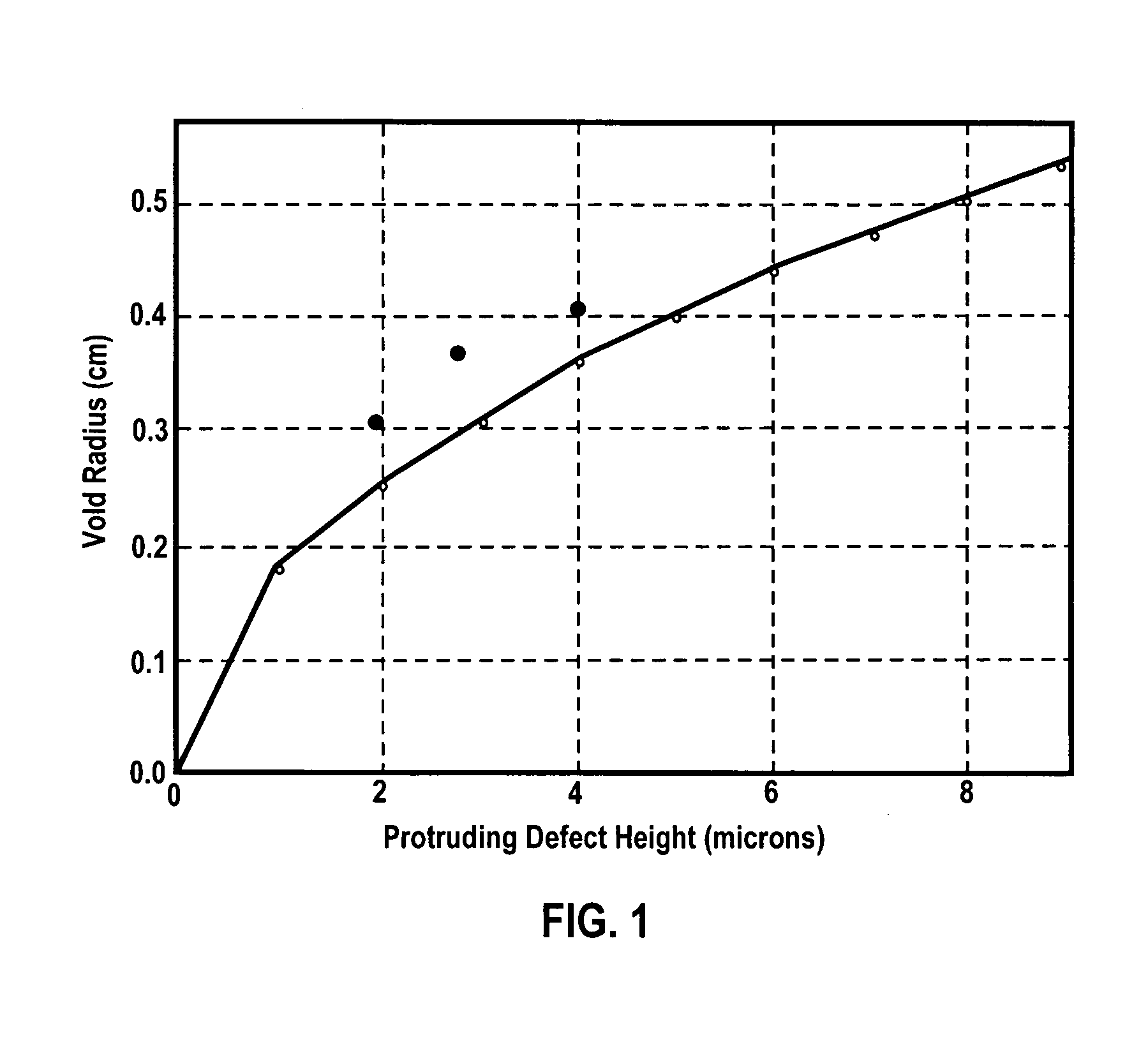
Defect reduction in electrodeposited copper for semiconductor applications
InactiveUS7316772B2Improve surface morphologyFew defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureWaferingMetallurgy
A method for electroplating a copper deposit onto a semiconductor integrated circuit device substrate having submicron-sized features, and a concentrate for forming a corresponding electroplating bath. A substrate is immersed into an electroplating bath formed from the concentrate including ionic copper and an effective amount of a defect reducing agent, and electroplating the copper deposit from the bath onto the substrate to fill the submicron-sized reliefs. The occurrence of protrusion defects from superfilling, surface roughness, and voiding due to uneven growth are reduced, and macro-scale planarity across the wafer is improved.
Owner:MACDERMID ENTHONE INC
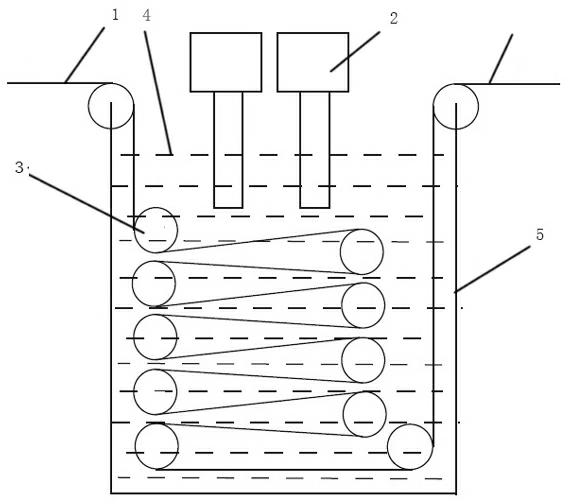
Carbon fiber surface treatment method based on ultrasonic strengthening
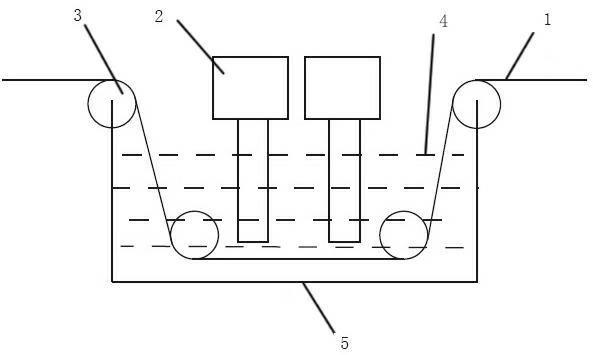
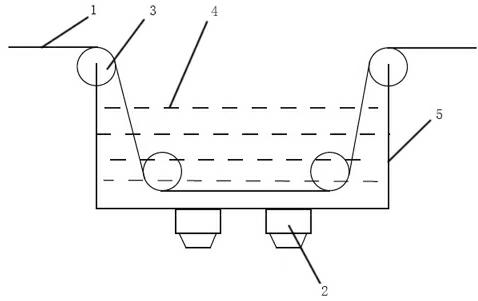
InactiveCN102628212AImprove surface morphologyImprove surface roughnessCarbon fibresUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to a carbon fiber surface treatment method based on ultrasonic strengthening, comprising the following steps of: soaking carbon fibers into liquid medium in a surface treatment tank, carrying out ultrasonic radiation on the liquid medium by virtue of an ultrasonic generator or an ultrasonic array which is arranged above or below the surface treatment tank, and adjusting ultrasonic processing time according to ultrasonic intensity and frequency, so as to achieve the aim of carrying out the surface treatment on the carbon fibers. The carbon fiber surface treatment method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that: surface morphology, surface roughness and the like of the carbon fibers are improved to improve mechanical properties of carbon fiber composite, and the oil stains produced in the production process of the carbon fiber composite are removed through ultrasonic cleaning at the same time that the carbon fiber is subjected to surface oxidation treatment; and compared with the other traditional methods, the carbon fiber surface treatment method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simple treatment equipment, simple and easy operation, no damage to environment, high treatment speed, high treatment efficiency, and easy implementation on assorted online production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
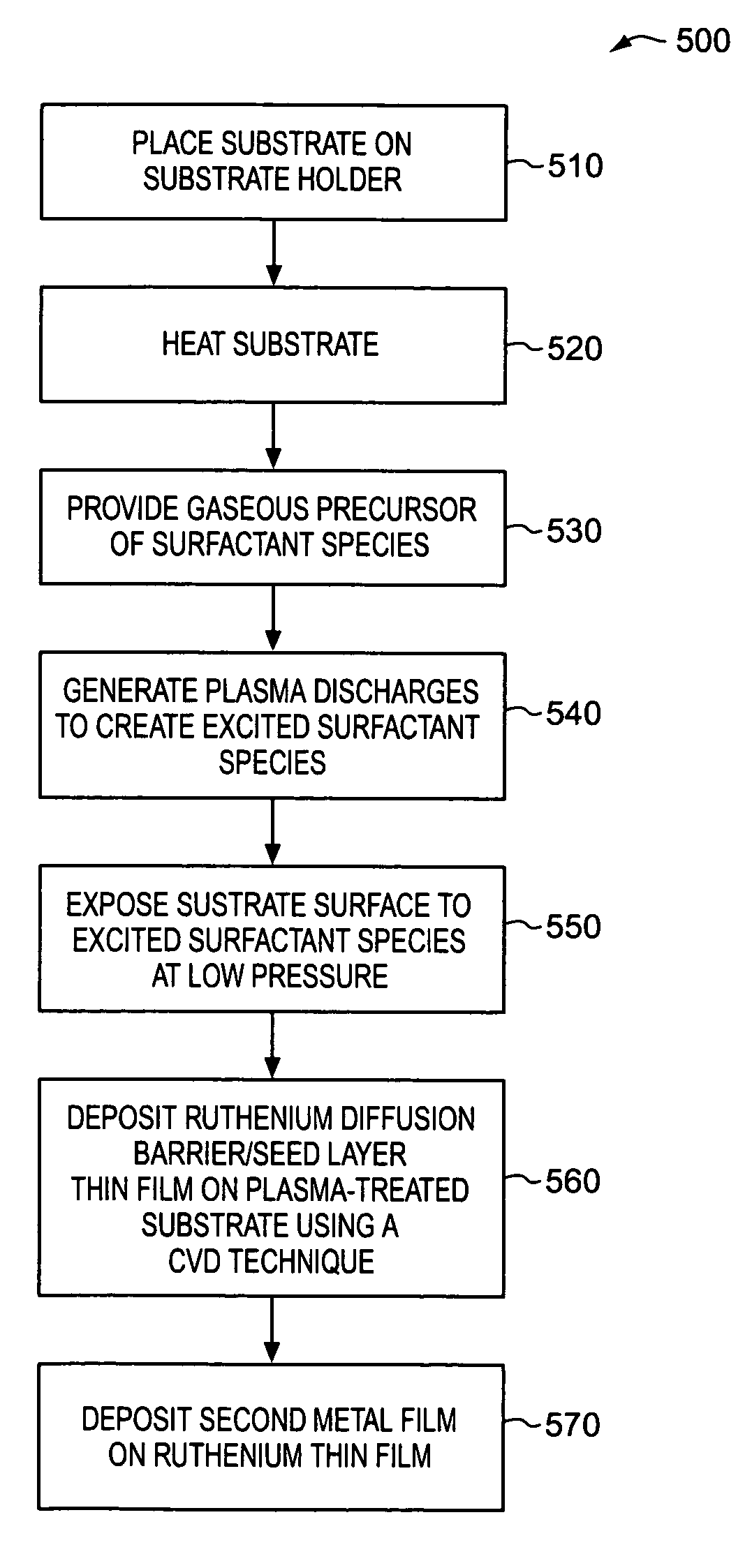
Surface treatment using iodine plasma to improve metal deposition
ActiveUS7041596B1Increase depositionShorten the timePretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumIodine
An excited surfactant species is created by generating plasma discharge in a surfactant precursor gas. A surfactant species typically includes at least one of iodine, led, thin, gallium, and indium. A surface of an integrated circuit substrate is exposed to the excited surfactant species to form a plasma-treated surface. A ruthenium thin film is deposited on the plasma-treated surface using a CVD technique.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Modified coarse aggregate, fiber nano recycled concrete prepared from modified coarse aggregate and preparation method of fiber nano recycled concrete
The invention belongs to the technical field of building materials, and particularly relates to a modified coarse aggregate with improved performance, excellent-performance fiber nano recycled concrete prepared from the modified coarse aggregate and a preparation method of the fiber nano recycled concrete. The preparation method includes the following steps that waste concrete test blocks and waste sintered bricks are crushed and screened to obtain a recycled coarse aggregate, and the recycled coarse aggregate is dried after being soaked with a nano silica sol to obtain a modified concrete coarse aggregate and a modified brick coarse aggregate; water, cement, fine aggregate, the modified concrete coarse aggregate, the modified brick coarse aggregate and polyvinyl alcohol fiber are preparedin proportion; the modified brick coarse aggregate, the modified concrete coarse aggregate, the cement and the fine aggregate are put into a stirrer and pre-stirred, the polyvinyl alcohol fiber is evenly dispersed and added, and dry mixing is carried out; water and a water reducer are sequentially added into the stirrer and stirred until the mixture is evenly mixed. Construction waste is effectively utilized to prepare the recycled concrete with certain performance indexes.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method for carbon dry gel
ActiveCN102104157AGood application effectHigh oxygen reduction reactivityCatalyst carriersCell electrodesNitrateSulfate
The invention relates to a carbon carrier of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell, in particular to a preparation method for carbon dry gel. The carbon dry gel is prepared by m-dihydroxybenzene, formaldehyde and a metal salt serving as raw materials, wherein the metal salt comprises a soluble nitrate, a carbonate, a sulfate, an acetate or a halide of one or more metal elements in an IVB group, a VB group, a VIB group, a VIIB group, a VIII group, an IB group and an IIB group; the m-dihydroxybenzene serving as a precursor and the formaldehyde are in the mol ratio of 2:1; the m-dihydroxybenzene and the metal salt are in the mol ratio of 10:1-500:1; and a high-stability carbon carrier is prepared by graphitizing mixed organic carbon dry gel at the high temperature of 1,500 to 3,500 DEG C. When serving as an anti-corrosion carbon material and being used as a cathode catalyst carrier of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell, the carbon dry gel has high anti-corrosion performance and high stability in an acidic and high-potential environment of cell operation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
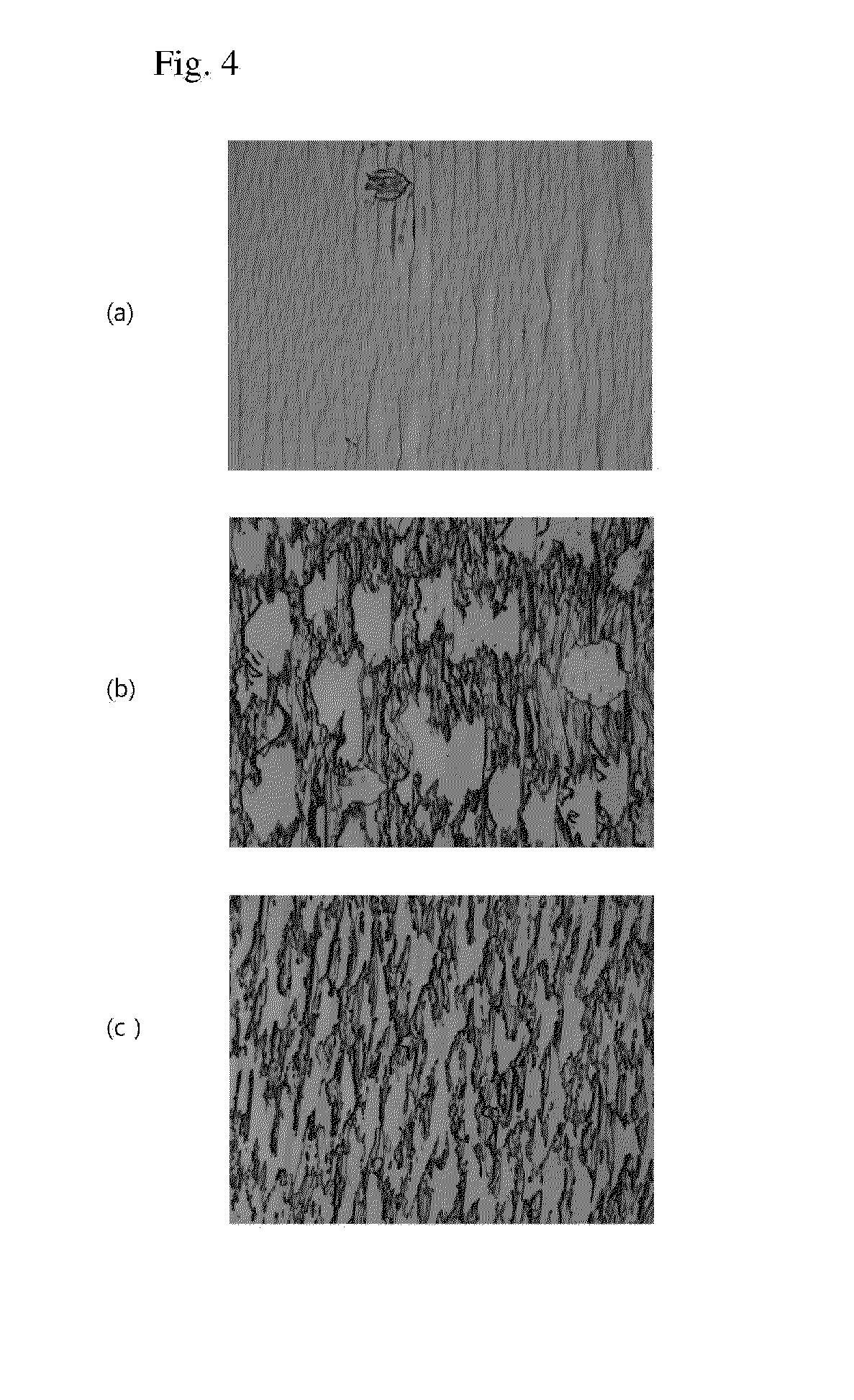
Method of improving surface morphology of (ga,al,in,b)n thin films and devices grown on nonpolar or semipolar (ga,al,in,b)n substrates
InactiveUS20100219416A1Improve scalabilityImprove surface smoothnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersLaserInert gas
A method for improving the growth morphology of (Ga,Al,In,B)N thin films on nonpolar or semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N substrates, wherein a (Ga,Al,In,B)N thin film is grown directly on a nonpolar or semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N substrate or template and a portion of the carrier gas used during growth is comprised of an inert gas. Nonpolar or semipolar nitride LEDs and diode lasers may be grown on the smooth (Ga,Al,In,B)N thin films grown by the present invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Self-masking defect removing method
InactiveUS20050186800A1Improve surface morphologySimplify the cleanup processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStructural engineering
A method for removing defects from a semiconductor surface is disclosed. The surface of the semiconductor is first coated with a protective layer, which is later thinned to selectively reveal portions of the protruding defects. The defects are then removed by etching. Finally, also the protective layer is removed. According to the method, inadvertent thinning of the surface is prevented and removal of the defects is obtained.
Owner:HRL LAB
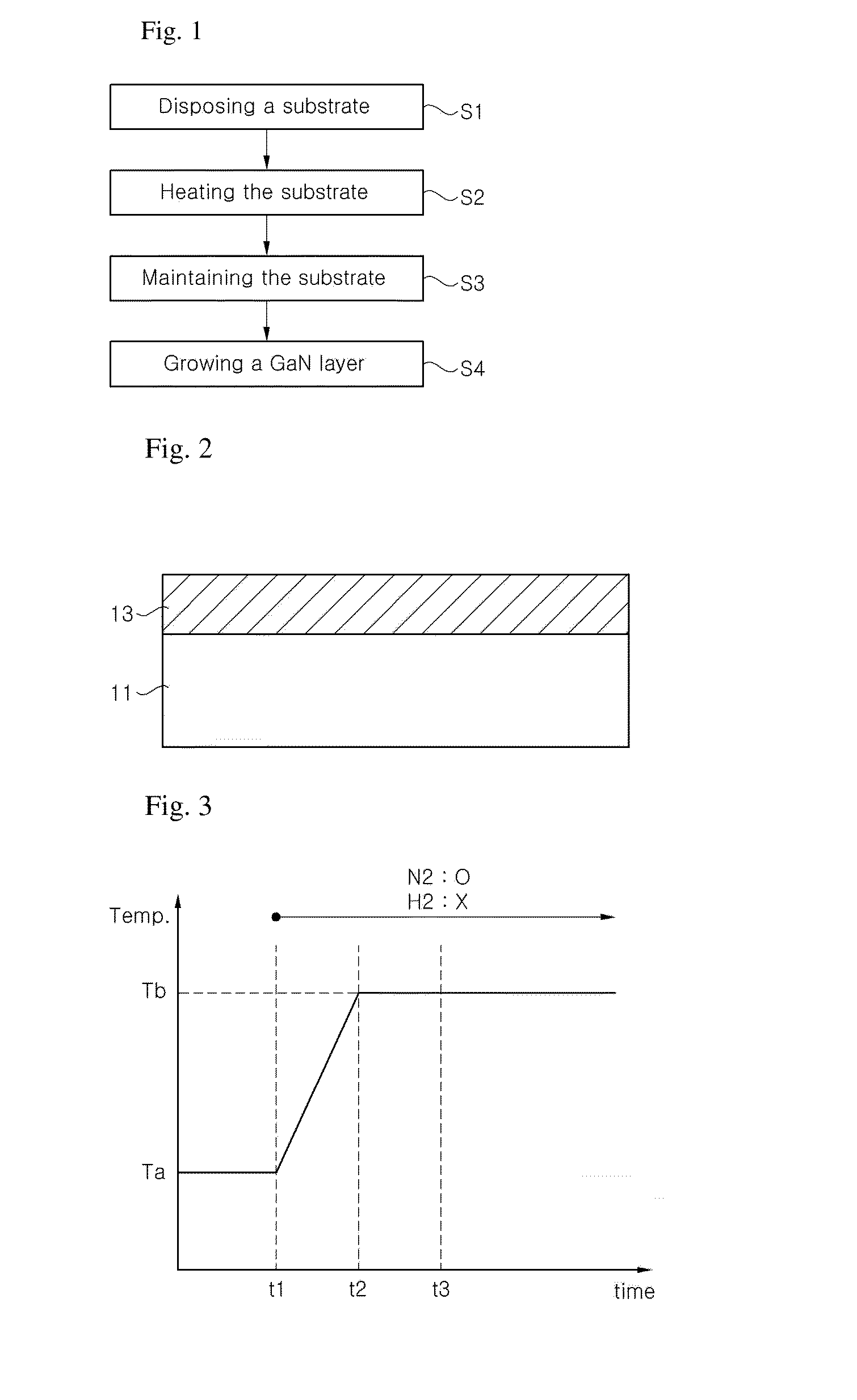
Method of fabricating nonpolar gallium nitride-based semiconductor layer, nonpolar semiconductor device, and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20130248818A1Improve surface morphologyImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideOrganic chemicals
A method of fabricating a nonpolar gallium nitride-based semiconductor layer is provided. The method is a method of fabricating a nonpolar gallium nitride layer using metal organic chemical vapor deposition, and includes disposing a gallium nitride substrate with an m-plane growth surface within a chamber, raising a substrate temperature to a GaN growth temperature by heating the substrate, and growing a gallium nitride layer on the gallium nitride substrate by supplying a Ga source gas, an N source gas, and an ambient gas into the chamber at the growth temperature. The supplied ambient gas contains N2 and does not contain H2.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
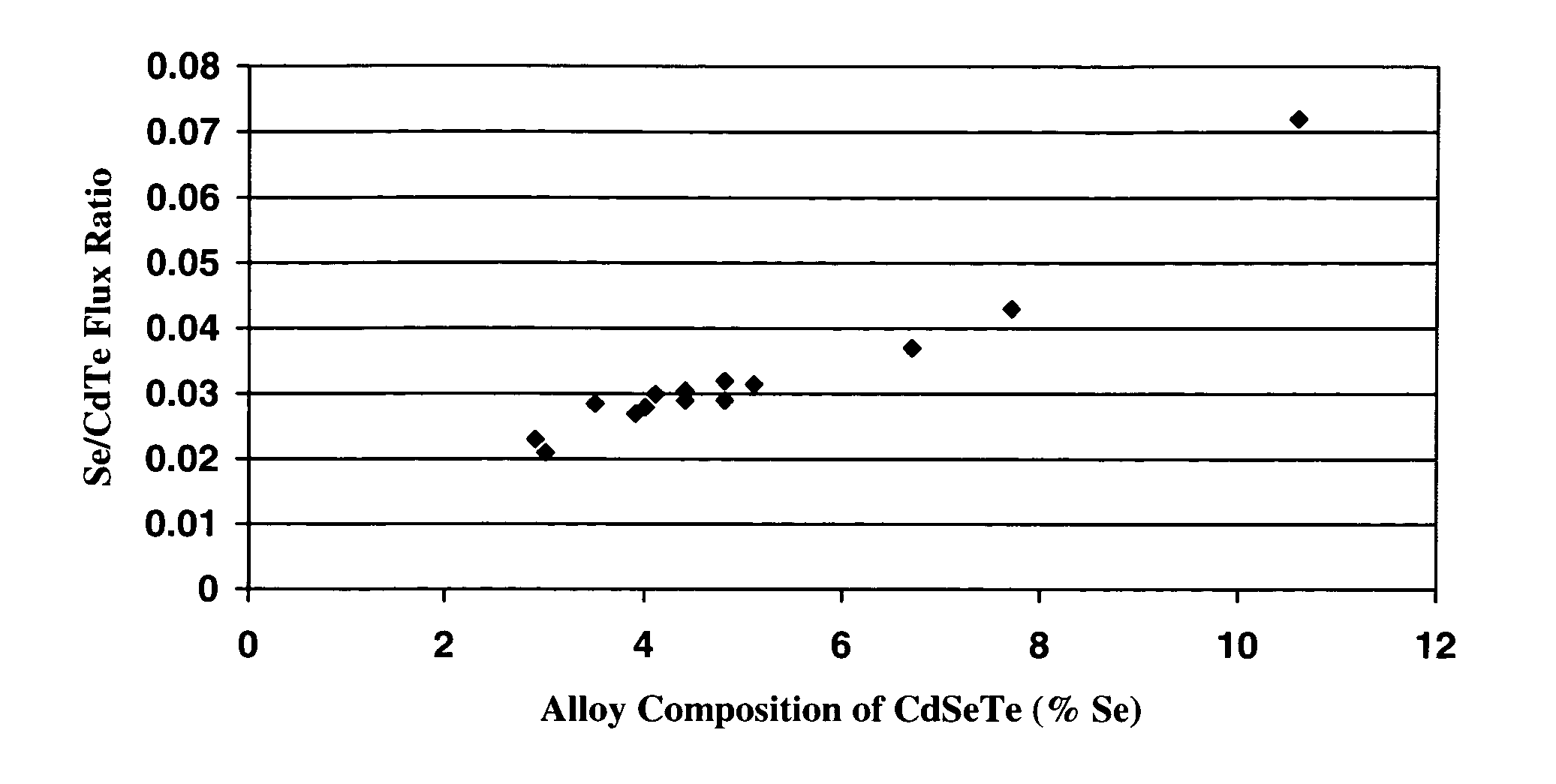
Molecular beam epitaxy growth of ternary and quaternary metal chalcogenide films
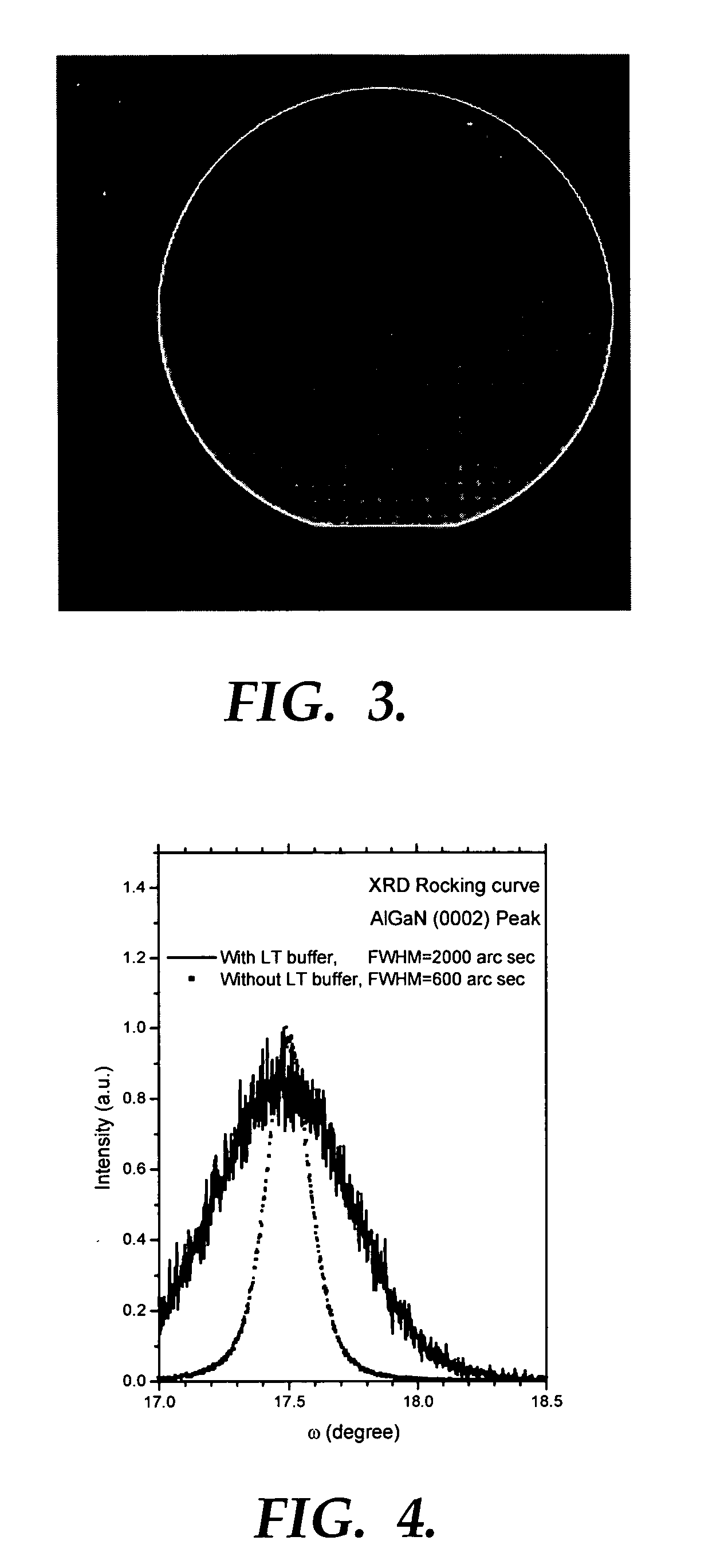
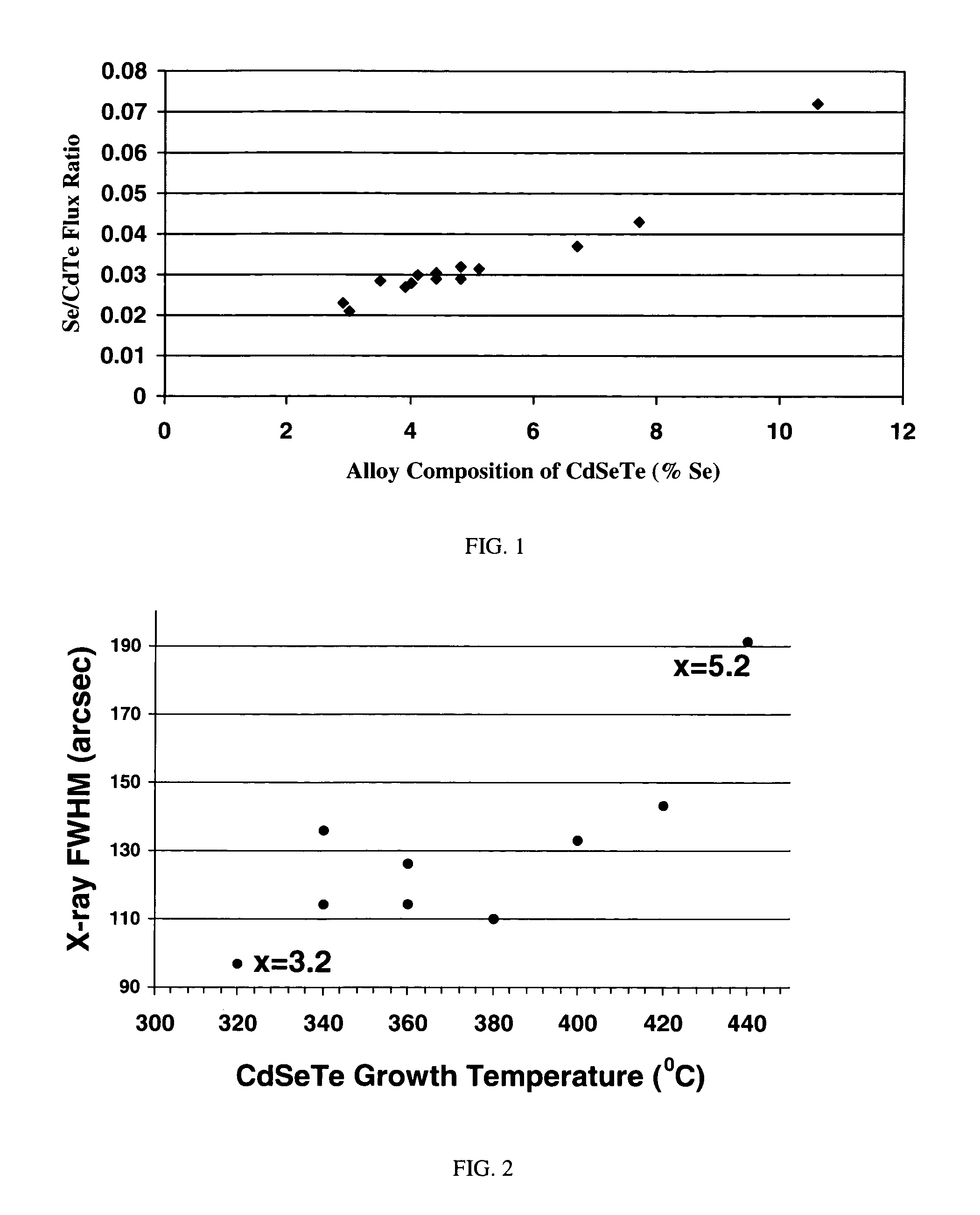
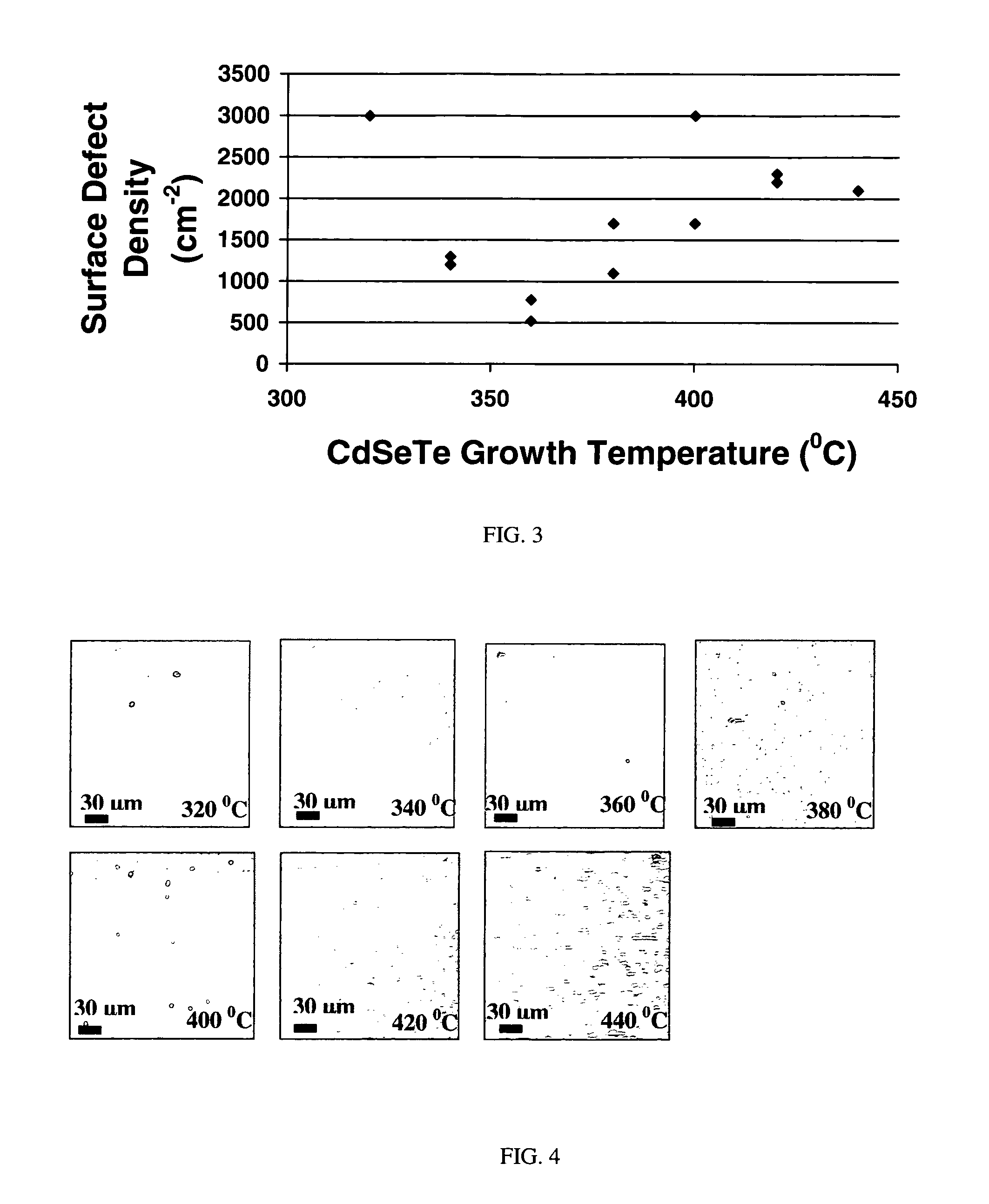
InactiveUS7518207B1Improve surface morphologyReduce surface defect densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationRocking curveSulfur
The ternary alloy CdSexTe1-x(2 1 1) and the quaternary alloy Cd1-zZnzSexTe1-x have been grown on Si(2 1 1) substrates using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). The growth of CdSeTe is facilitated using a compound CdTe effusion source and a Se effusion source while the growth of CdZnSeTe is facilitated using a compound CdTe effusion source, a compound ZnTe effusion source, and an elemental Se source. The alloy compositions (x) and (z) of CdSexTe1-x ternary compound and Cd1-zZnzSexTe1-x are controlled through the Se / CdTe and ZnTe / CdTe flux ratios. The rate of Se incorporation is higher than the rate of Te incorporation as growth temperature increases. As-grown CdSeTe with 4% Se and CdZnSeTe with 4% Zn+Se, which is substantially lattice matched to long-wavelength infrared HgCdTe materials, exhibits excellent surface morphology, low surface defect density (less than 500 cm2), and a narrow X-ray rocking curve (a full-width at half maximum of 103 arcsec).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
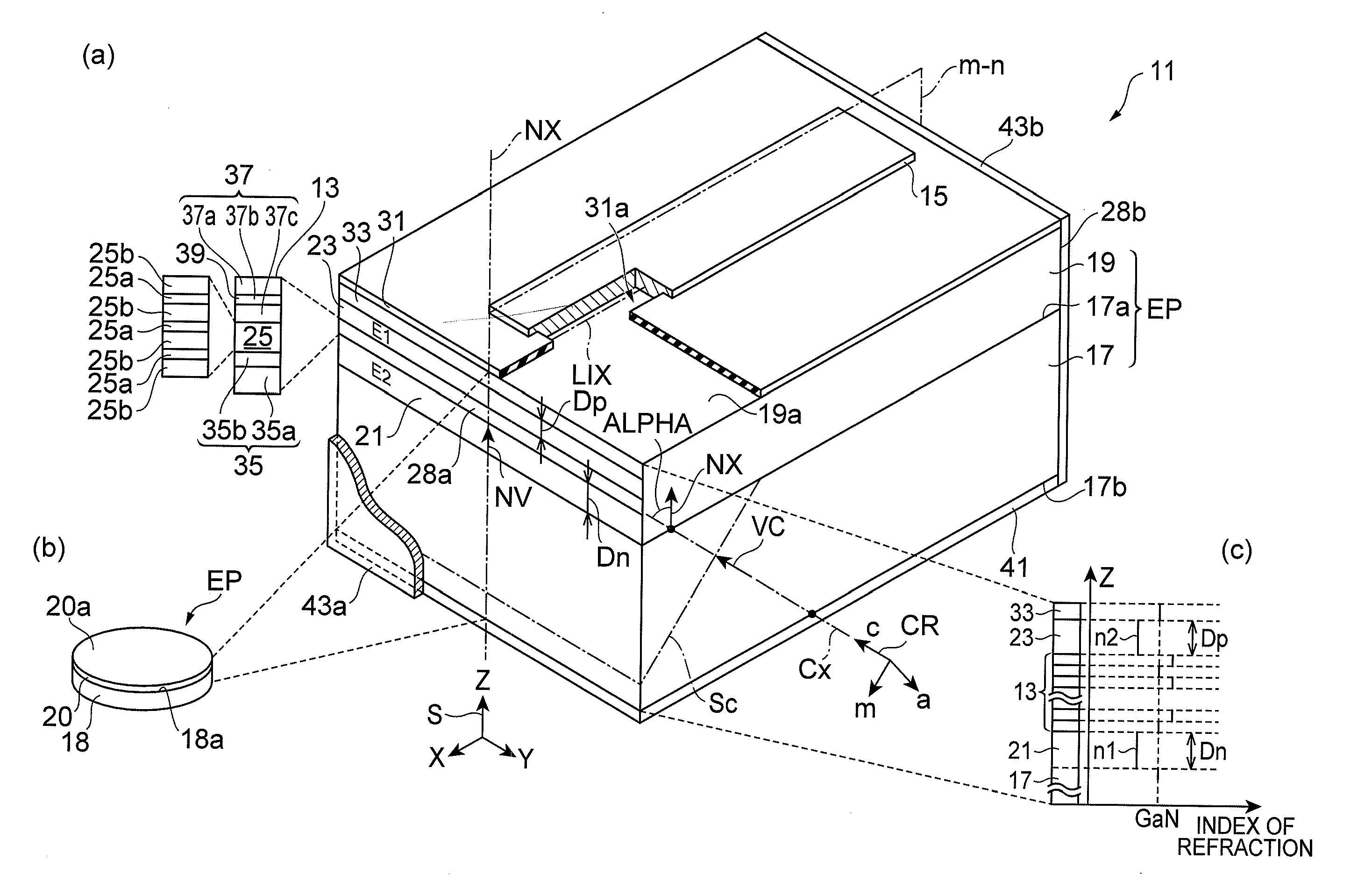
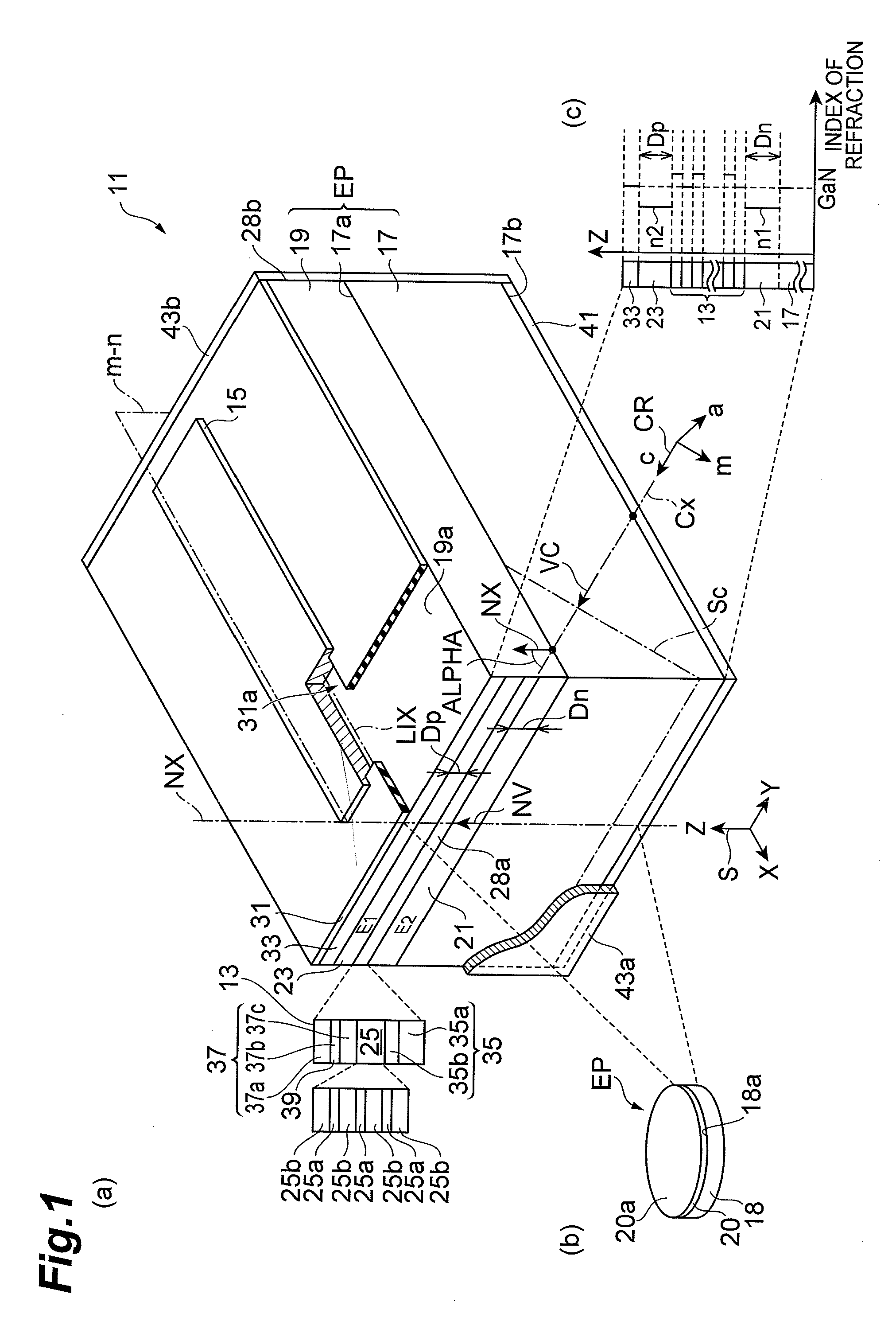
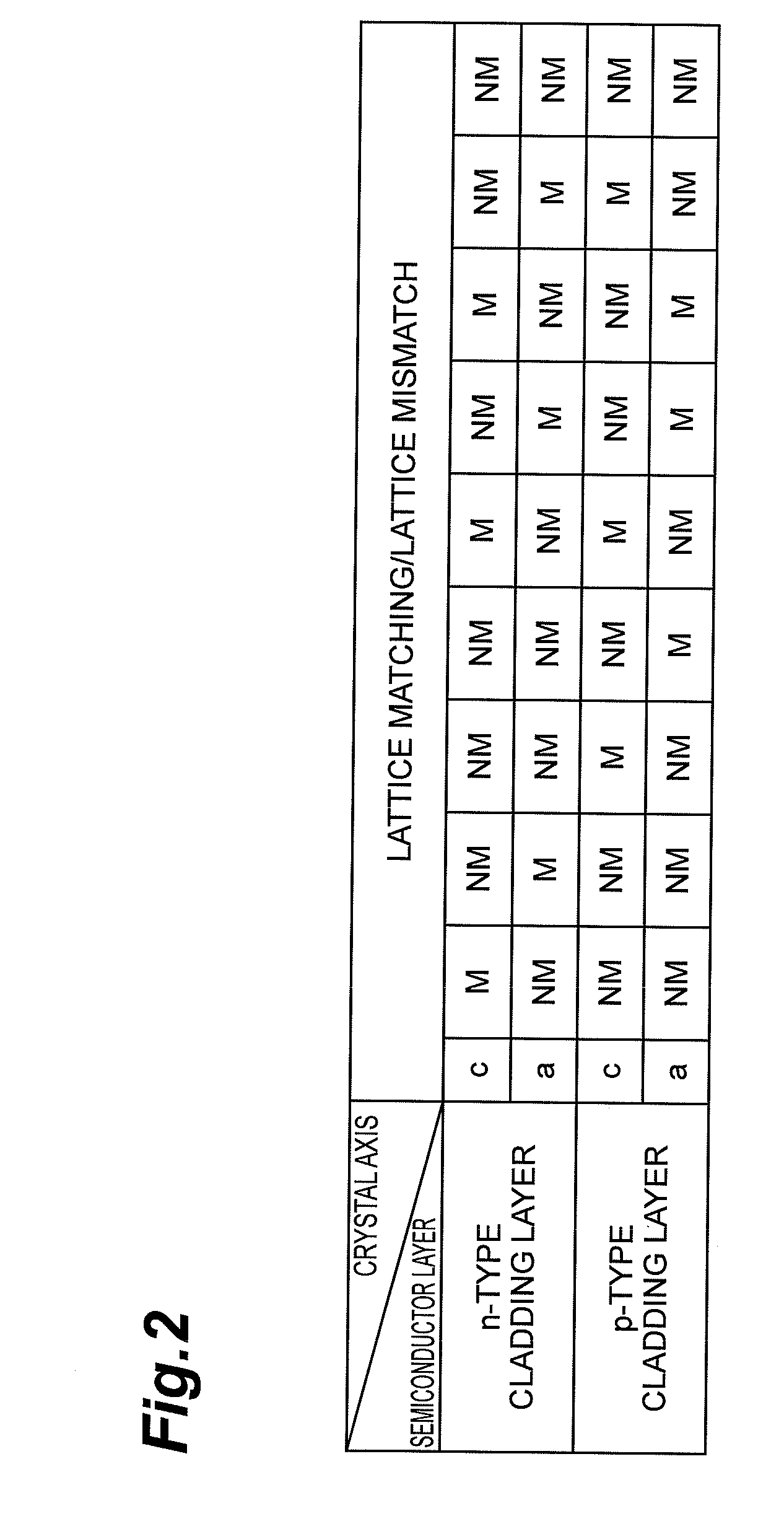
Group iii nitride semiconductor laser device, epitaxial substrate, method of fabricating group iii nitride semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20120327967A1Relieve pressureLower effective refractive indexLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumRefractive index
A nitride semiconductor laser device includes a p-type cladding layer, an active layer and an n-type cladding layer. The p-type cladding layer and the n-type cladding layer comprise indium and aluminum as group-III constituent. The n-type cladding layer, active layer and p-type cladding layer are arranged along the normal of a semi-polar semiconductor surface of a substrate. This surface tilts toward the m-axis of the hexagonal nitride by an angle of 63 degrees or more and smaller than 80 degrees from a plane orthogonal to a reference axis extending along the c-axis thereof. The active layer generates light having a peak wavelength in the range of 480 to 600 nm. The refractive indices of the n-type cladding layer and p-type cladding layer are smaller than that of GaN. The n-type cladding layer has a thickness of 2 μm or more while the p-type cladding layer has a thickness of 500 nm or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Cathode material, preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery containing same
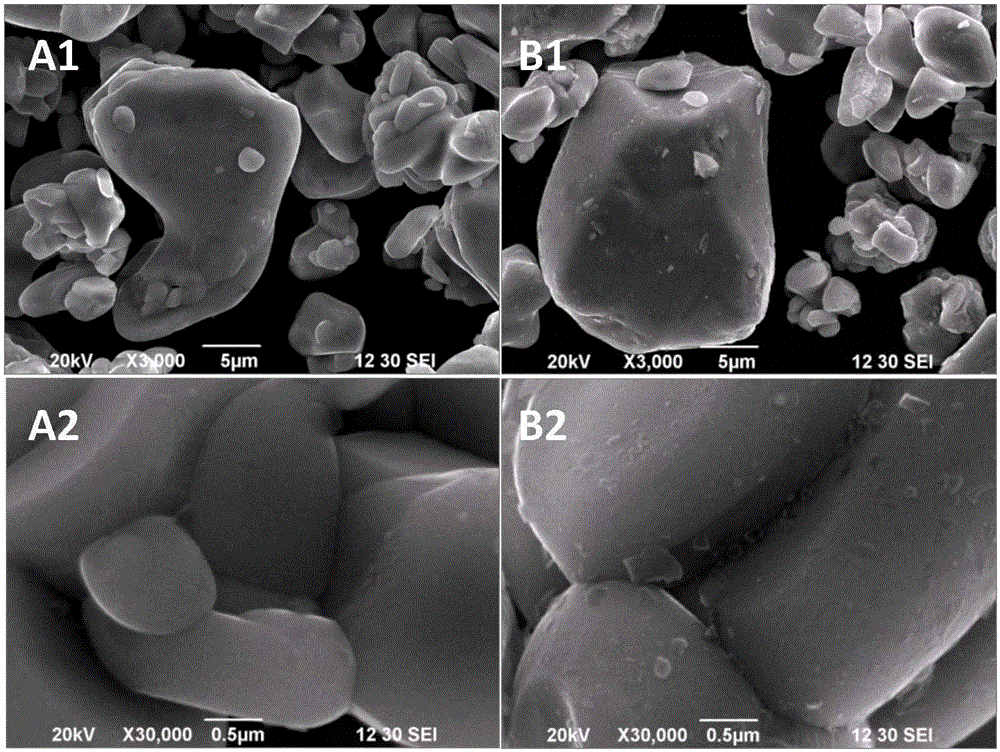
InactiveCN105098192AImprove stabilityImprove electronic conductivityCell electrodesSecondary cellsIndiumSodium-ion battery
The application relates to the field of processing of a lithium battery, in particular to a cathode material, a preparation method thereof and a lithium ion battery containing the same. The cathode material comprises a lithium-containing cathode material and an indium oxide cladding layer coated on the surface of the lithium-containing cathode material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding a soluble indium salt into a solution dissolved with an alkaline substance and stirring to form a sol; adding the lithium-containing cathode material into the sol and stirring to lead a generated sediment to be uniformly deposited and attached onto the surface of the lithium-containing cathode material; removing a liquid to obtain a lithium-containing cathode material solid body attached with the sediment; and roasting the lithium-containing cathode material solid body attached with the sediment to form the lithium ion cathode material coated with indium oxide on the surface. Compared with other inertia cladding materials such as aluminum oxide, the cathode material provided by the invention has the advantages that the electronic conductivity of indium oxide is excellent, and moreover, the discharging specific capacity, the cycling performance and the safety performance under high voltage can be obviously improved.
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
InactiveUS20080023327A1Improve consistencyFlat surfaceImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologySilver inkCarbon nanotube
A sensor system that detects a current representative of a compound in a liquid mixture features a multi or three electrode strip adapted for releasable attachment to signal readout circuitry. The strip comprises an elongated support which is preferably flat adapted for releasable attachment to the readout circuitry; a first conductor and a second and a third conductor each extend along the support and comprise means for connection to the circuitry. The circuit is formed with single-walled or multi walled nanotubes conductive traces and may be formed from multiple layers or dispersions containing, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-chloride. An active electrode formed from a separate conductive carbon nanotubes layer or suitable dispersion, positioned to contact the liquid mixture and the first conductor, comprises a deposit of an enzyme capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the compound and preferably an electron mediator, capable of transferring electrons between the enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the first conductor. A reference electrode also formed from a conductive carbon nanotube layer or suitable dispersion is positioned to contact the mixture and the second conductor. The system includes circuitry adapted to provide an electrical signal representative of the current which is formed from printing conductive inks made with nano size particles such as conductive carbon or carbon / platinum or carbon / silver, or carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide to form a conductive carbon nanotube layers. The multiple-electrode strip is manufactured, by then applying the enzyme and preferably the mediator onto the electrode. Alternatively the electrode can have a carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-chloride surface and or a conductive carbon or silver ink surface connecting leg. The carbon nanotube solution is first coated and patterned into electro shapes and the conductive carbon nanotubes, carbon or silver ink can be attached by printing the ink to interface with the carbon nanotube electro surface. A platinum electrode test strip is also disclosed that is formed from either nano platinum distributed in the carbon nanotube layer or by application or incorporation of platinum to the carbon nanotube conductive ink.
Owner:MYSTICMD
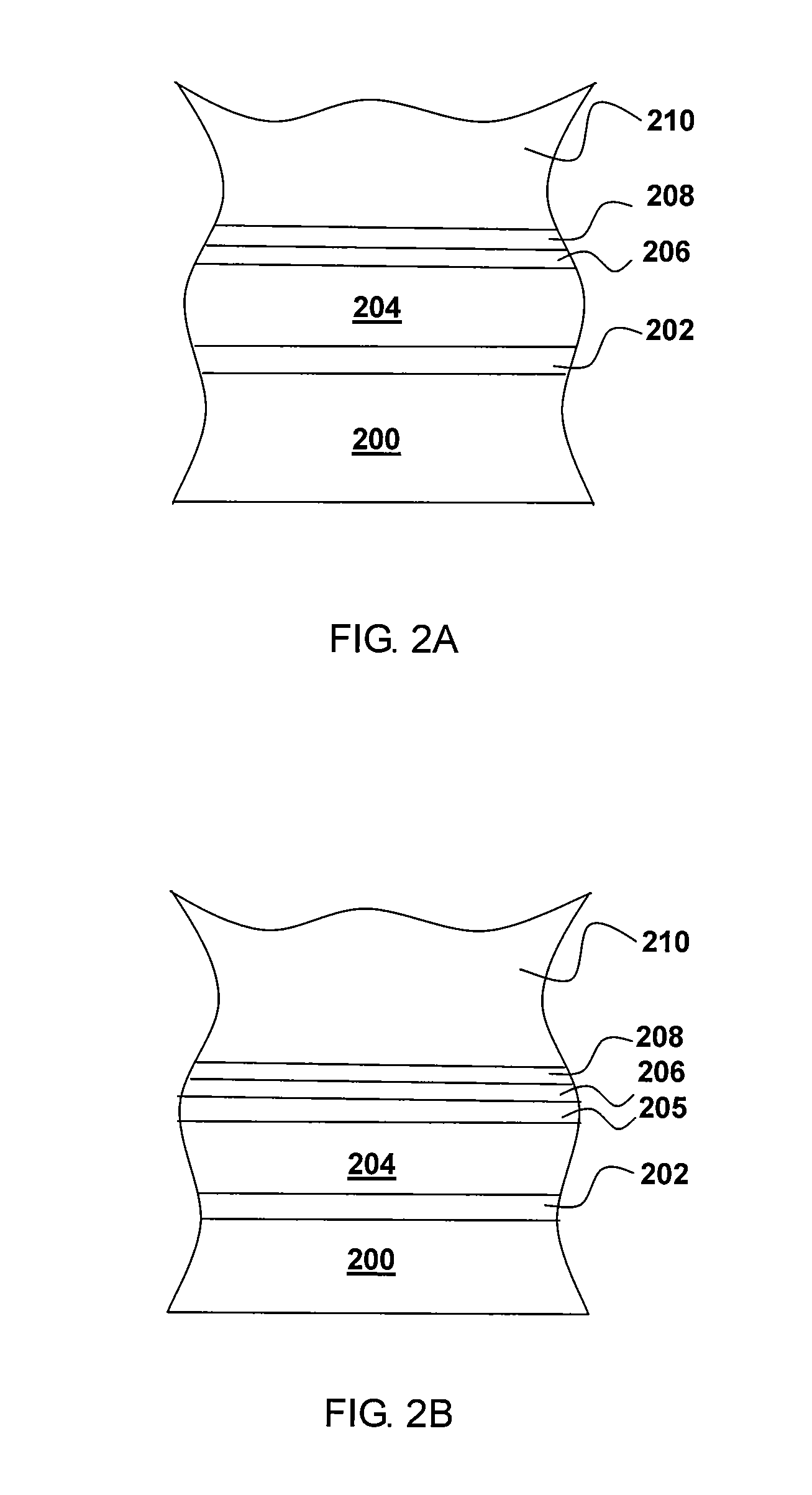
Ceramic and method of manufacturing the same, dielectric capacitor, semiconductor device, and element
InactiveUS7008669B2Reduce crystallizationImprove surface morphologyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyVacuum evaporation coatingCatalytic effectCeramic
A method of manufacturing a ceramic includes forming a film which includes a complex oxide material having an oxygen octahedral structure and a paraelectric material having a catalytic effect for the complex oxide material in a mixed state, and performing a heat treatment to the film, wherein the paraelectric material is one of a layered catalytic substance which includes Si in the constituent elements and a layered catalytic substance which includes Si and Ge in the constituent elements. The heat treatment includes sintering and post-annealing. At least the post-annealing is performed in a pressurized atmosphere including at least one of oxygen and ozone. A ceramic is a complex oxide having an oxygen octahedral structure, and has Si and Ge in the oxygen octahedral structure.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Gallium nitride-based semiconductor optical device, method of fabricating gallium nitride-based semiconductor optical device, and epitaxial wafer
InactiveUS20100220761A1Reduce piezoelectric effectImprove crystal qualityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIndiumGallium nitride
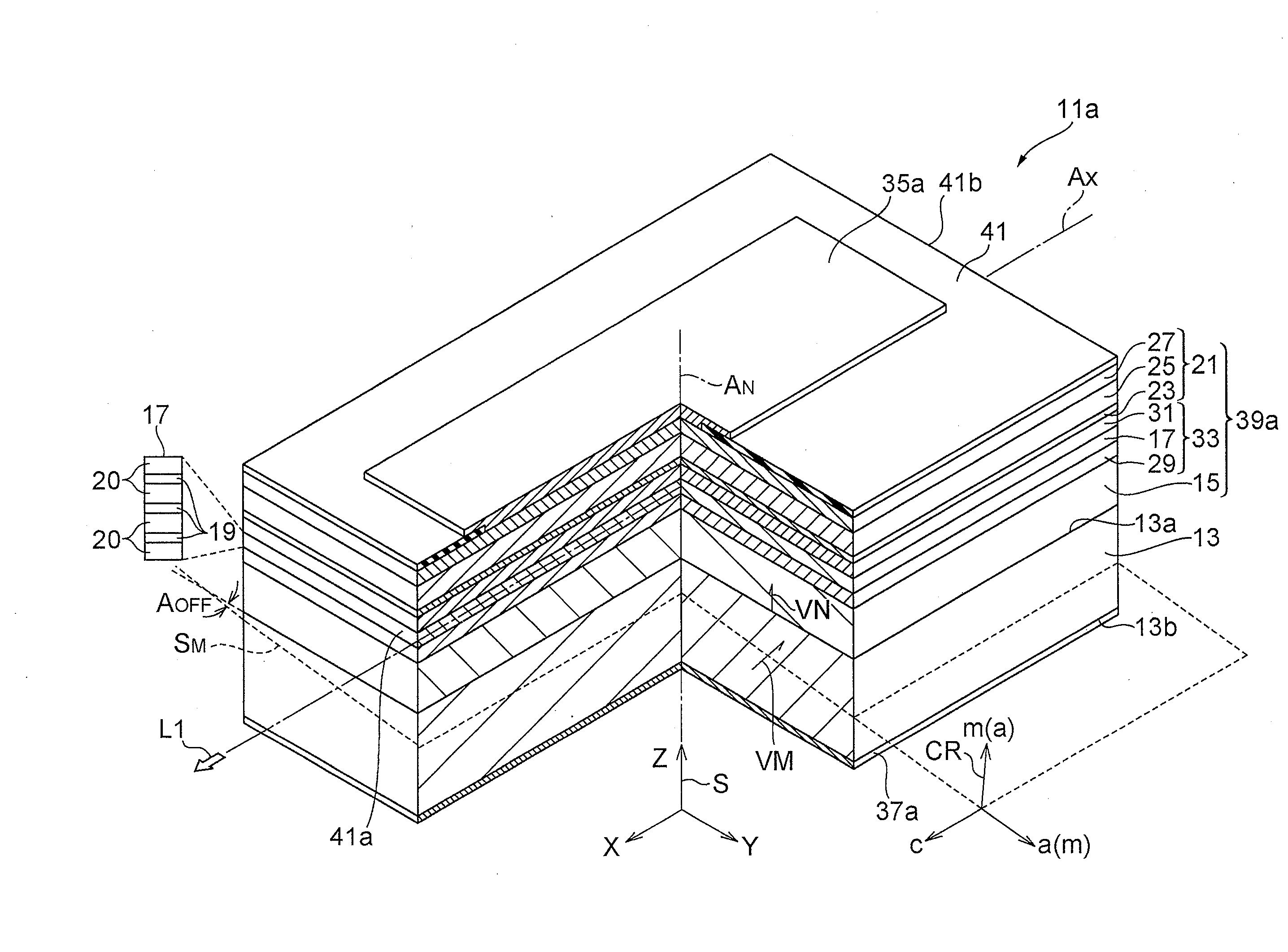
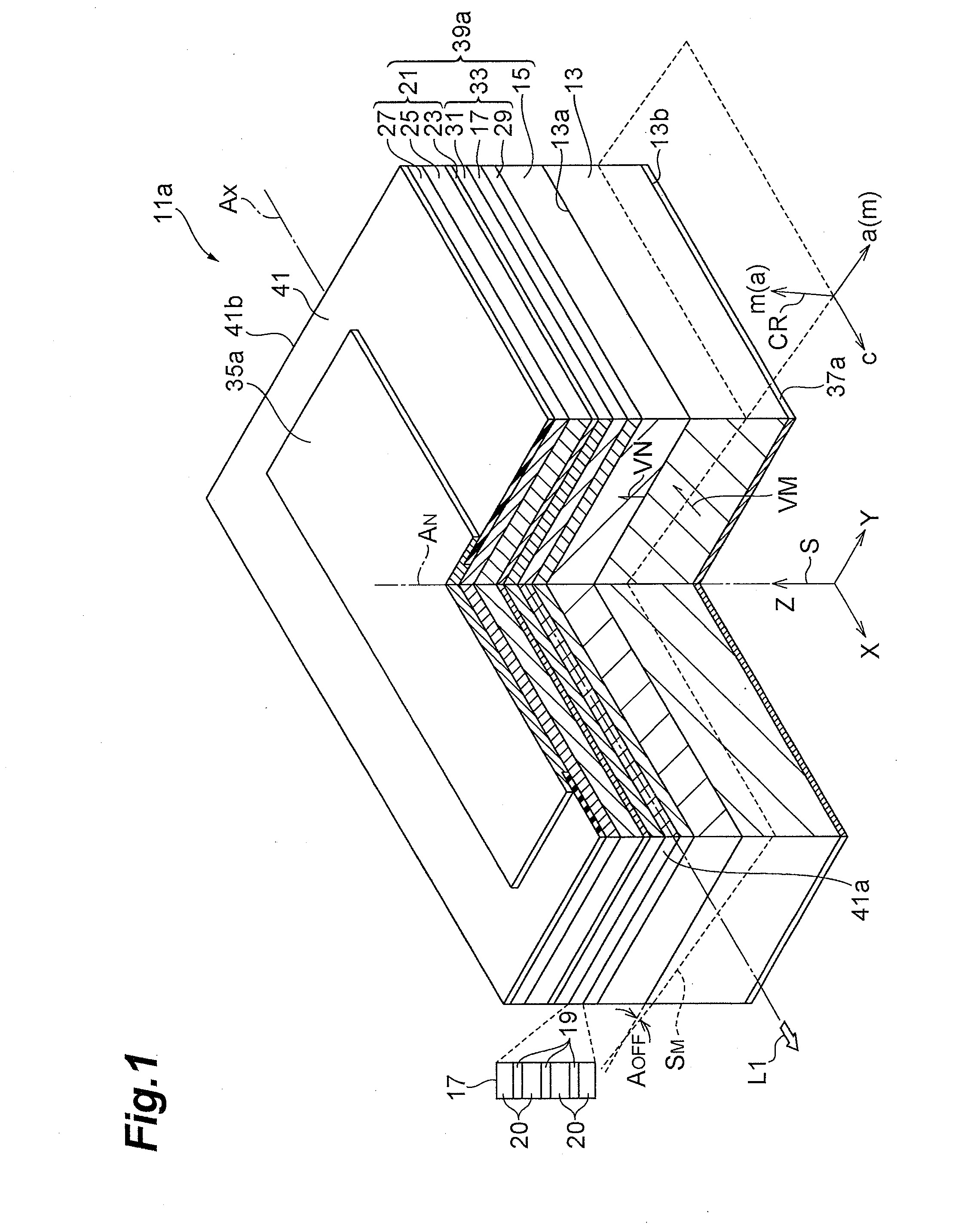
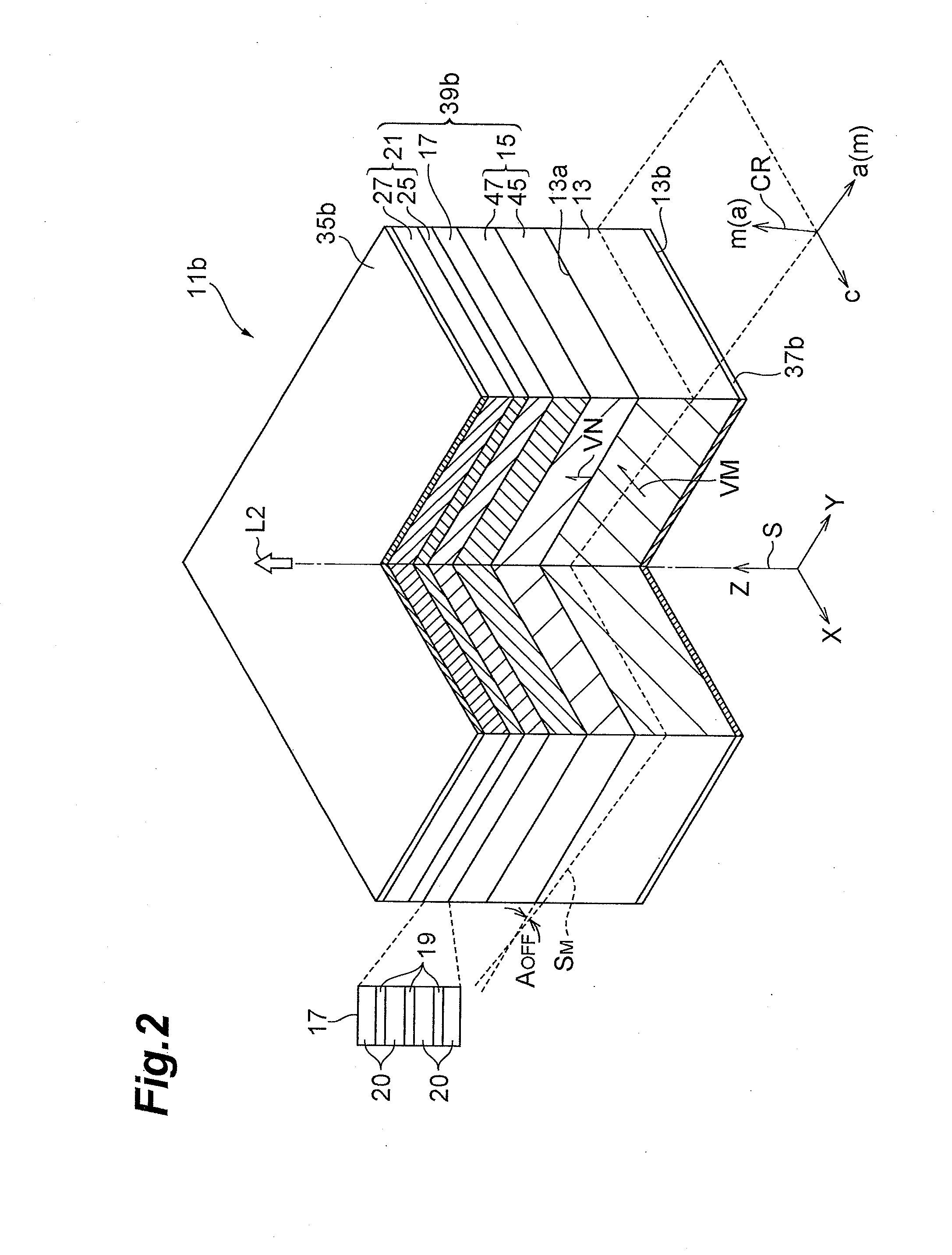
A gallium nitride-based semiconductor optical device is provided that includes an indium-containing gallium nitride-based semiconductor layer that exhibit low piezoelectric effect and high crystal quality. The gallium nitride-based semiconductor optical device 11a includes a GaN support base 13, a GaN-based semiconductor region 15, and well layers 19. A primary surface 13a tilts from a surface orthogonal to a reference axis that extends in a direction from one crystal axis of the m-axis and the a-axis of GaN toward the other crystal axis. The tilt angle AOFF is equal to the angle defined by a vector VM and a vector VN. The inclination of the primary surface is shown by a typical m-plane SM and m-axis vector VM. The GaN-based semiconductor region 15 is provided on the primary surface 13a. In the well layers 19 in an active layer 17, both the m-plane and the a-plane of the well layers 19 tilt from a normal axis AN of the primary surface 13a. The indium content of the well layers 19 is 0.1 or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Highly conductive and stable transparent conducting polymer films
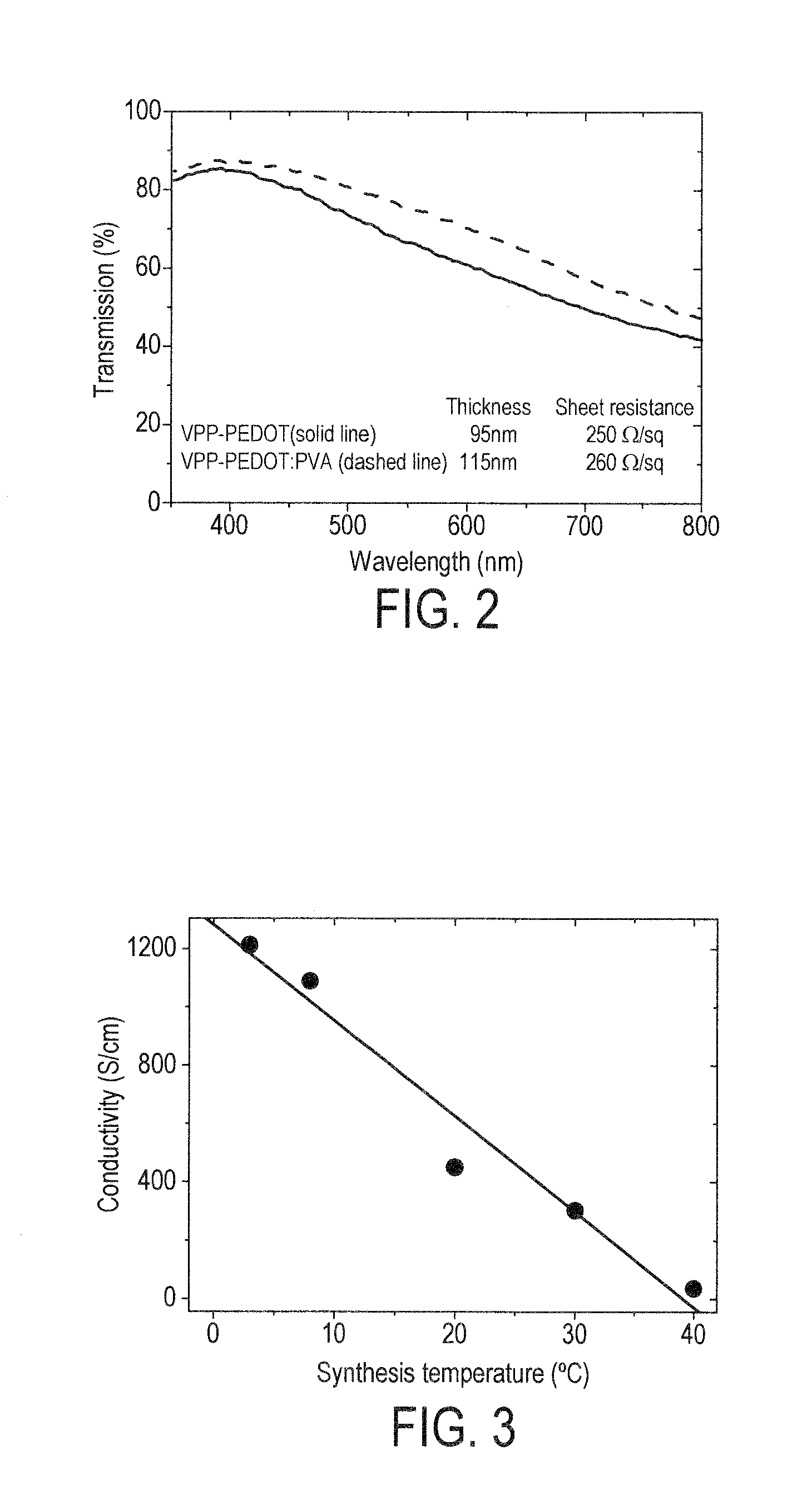
InactiveUS20100163808A1Improve adhesionGood substrate adhesionConductive materialOrganic conductorsPolymer chemistryPolymerization
The invention relates to a process for the synthesis of conducting polymer films by vapour phase polymerization. The invention relates particularly to the synthesis of polymerized thiophene films, for example poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) films.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Nitride semiconductor wafer and method of processing nitride semiconductor wafer
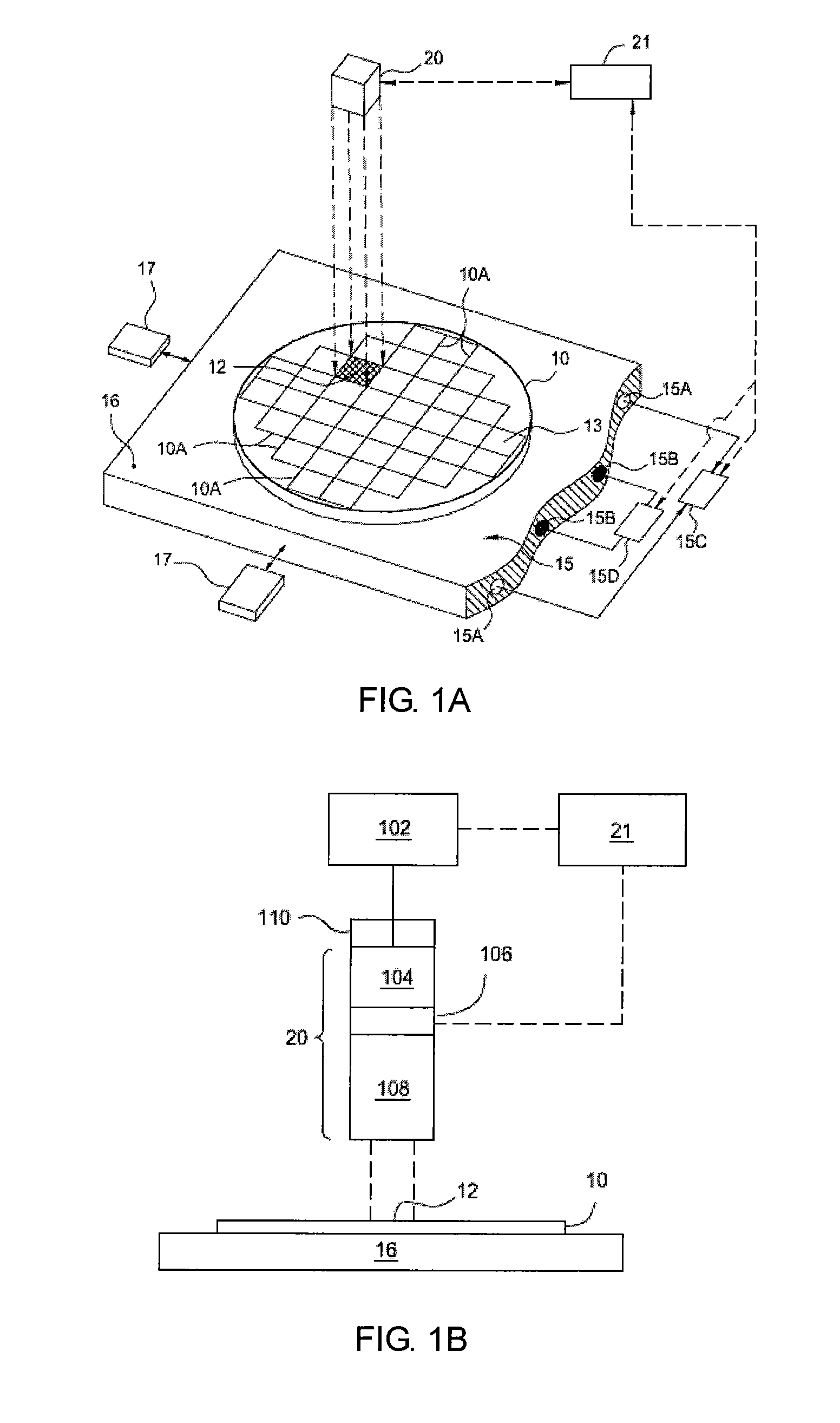
InactiveUS20050145879A1Suppress fluctuationsThickness of wafer is constantPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthWaferingGas phase
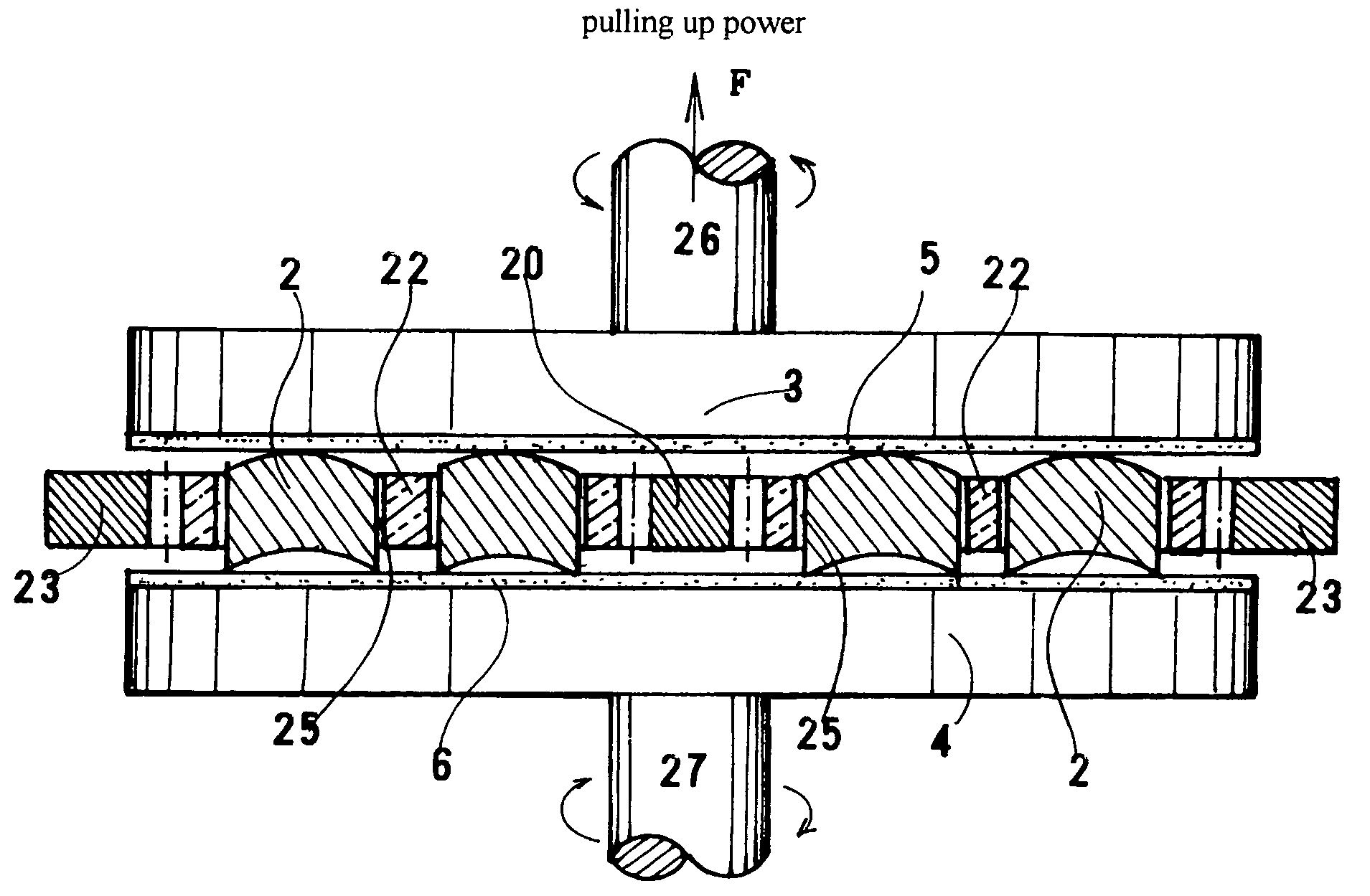
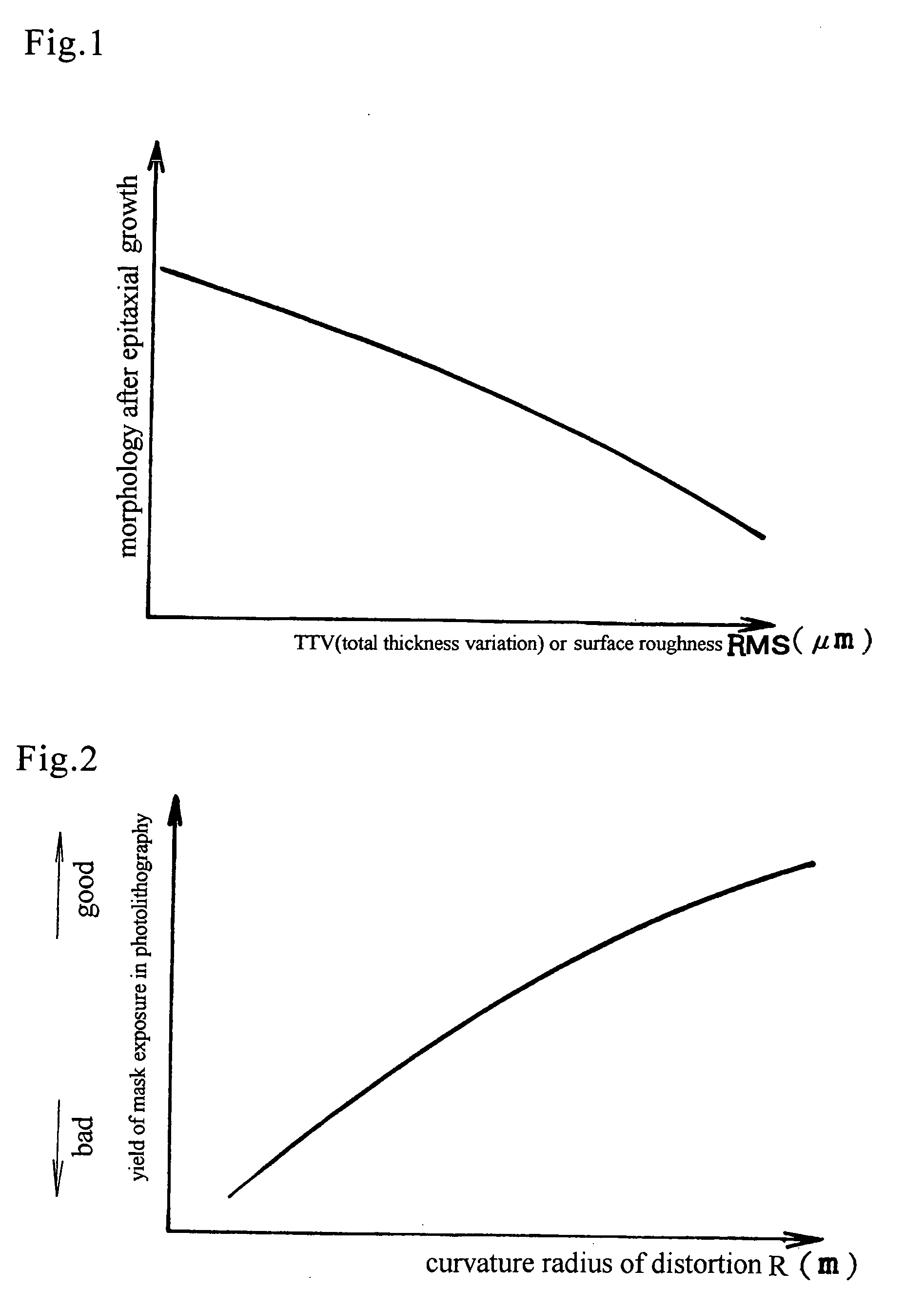
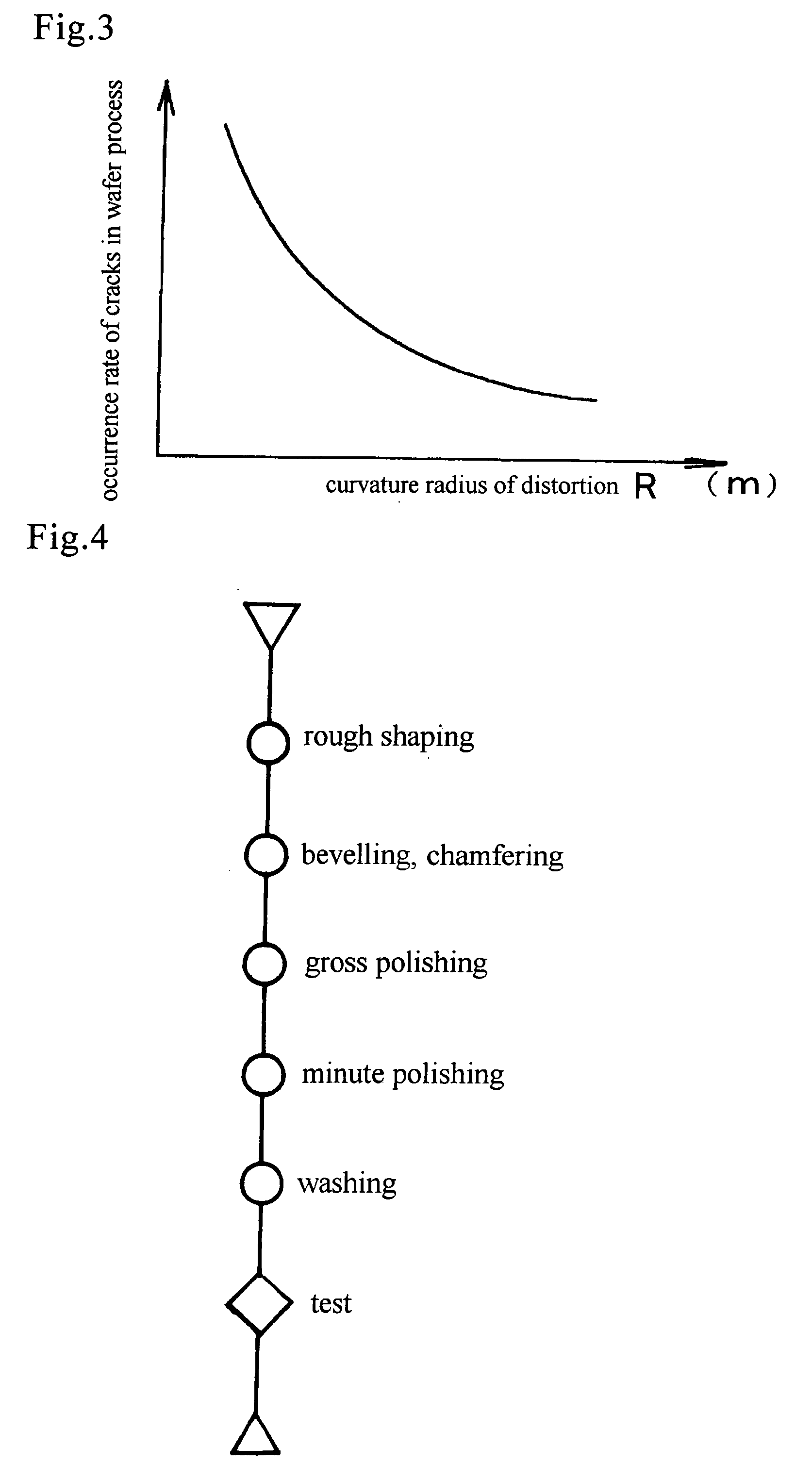
Nitride semiconductor wafers which are produced by epitaxially grown nitride films on a foreign undersubstrate in vapor phase have strong inner stress due to misfit between the nitride and the undersubstrate material. A GaN wafer which has made by piling GaN films upon a GaAs undersubstrate in vapor phase and eliminating the GaAs undersubstrate bends upward due to the inner stress owing to the misfit of lattice constants between GaN and GaAs. Ordinary one-surface polishing having the steps of gluing a wafer with a surface on a flat disc, bringing another surface in contact with a lower turntable, pressing the disc, rotating the disc, revolving the turntable and whetting the lower surface, cannot remedy the inherent distortion. The Distortion worsens morphology of epitaxial wafers, lowers yield of via-mask exposure and invites cracks on surfaces. Nitride crystals are rigid but fragile. Chemical / mechanical polishing has been requested in vain. Current GaN wafers have roughened bottom surfaces, which induce contamination of particles and fluctuation of thickness. Circular nitride wafers having a diameter larger than 45 mm are made and polished. Gross-polishing polishes the nitride wafers in a pressureless state with pressure less than 60 g / cm2 by lifting up the upper turntable for remedying distortion. Distortion height H at a center is reduced to H≦12 μm. Minute-polishing is a newly-contrived CMP which polishes the nitride wafers with a liquid including potassium hydroxide, potassium peroxodisulfate and powder, irradiates the potassium peroxodisulfate with ultraviolet rays. The CMP-polished top surface has roughness RMS of 0.1 nm≦RMS≦5 nm or more favorably 0.1 nm≦RMS≦0.5 nm. The CMP-polished bottom surface has roughness RMS of 0.1 nm≦RMS≦5000 nm or more favorably 0.1 nm≦RMS≦2 nm. TTV is less than 10 μm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130089973A1Reduce dislocation densityImprove surface morphologyLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
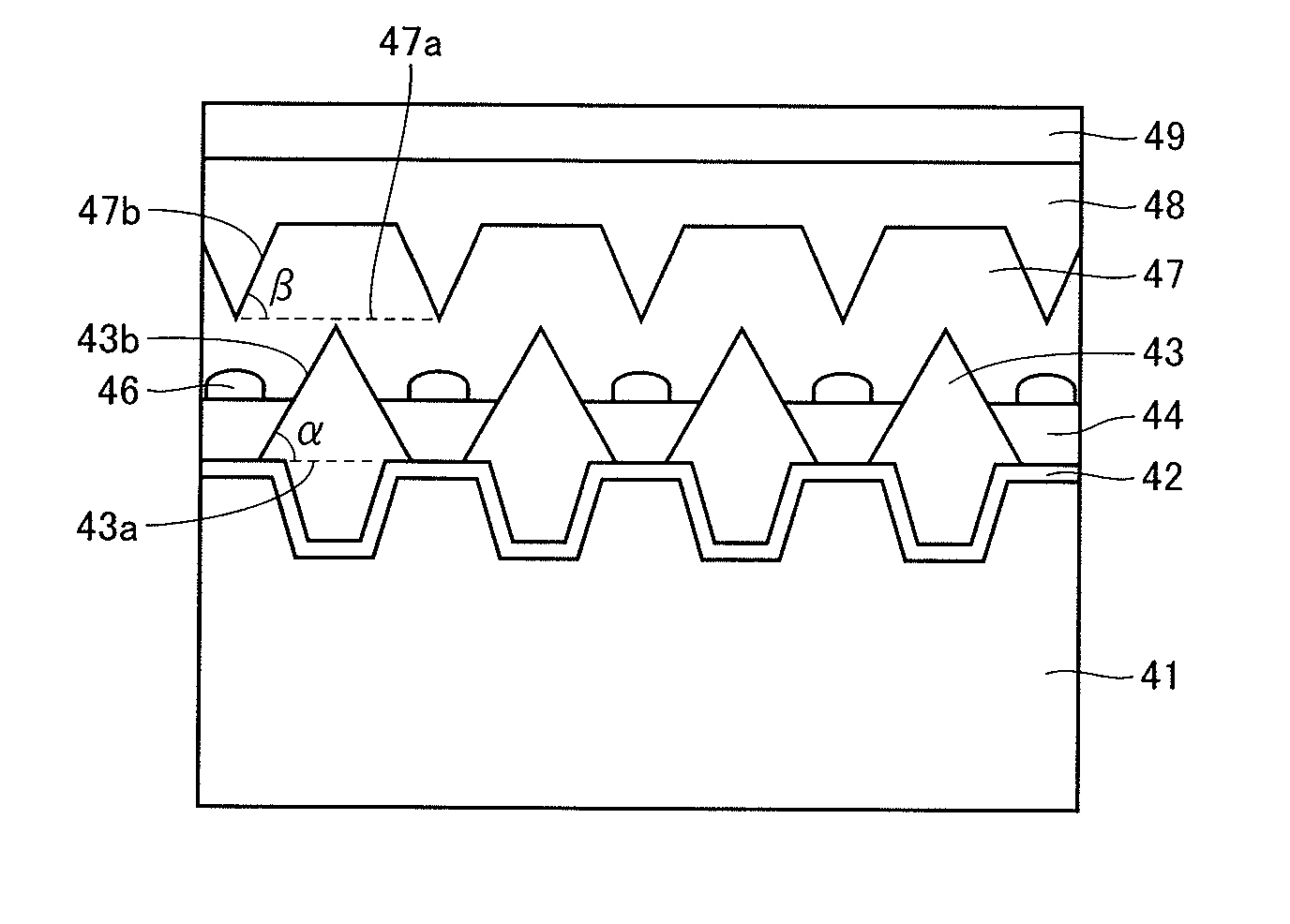
A method of manufacturing a nitride semiconductor device includes the step of forming a second nitride semiconductor layer having an inclined facet by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition, in which a molar flow ratio of a group V element gas to a group III element gas that are supplied to a growth chamber of a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition growth apparatus is set at 240 or less.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
Semiconductor device, method of manufacturing the same and power converter
ActiveUS20170077830A1Suppression problemIncrease displacementAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionNitrideCrystal growth
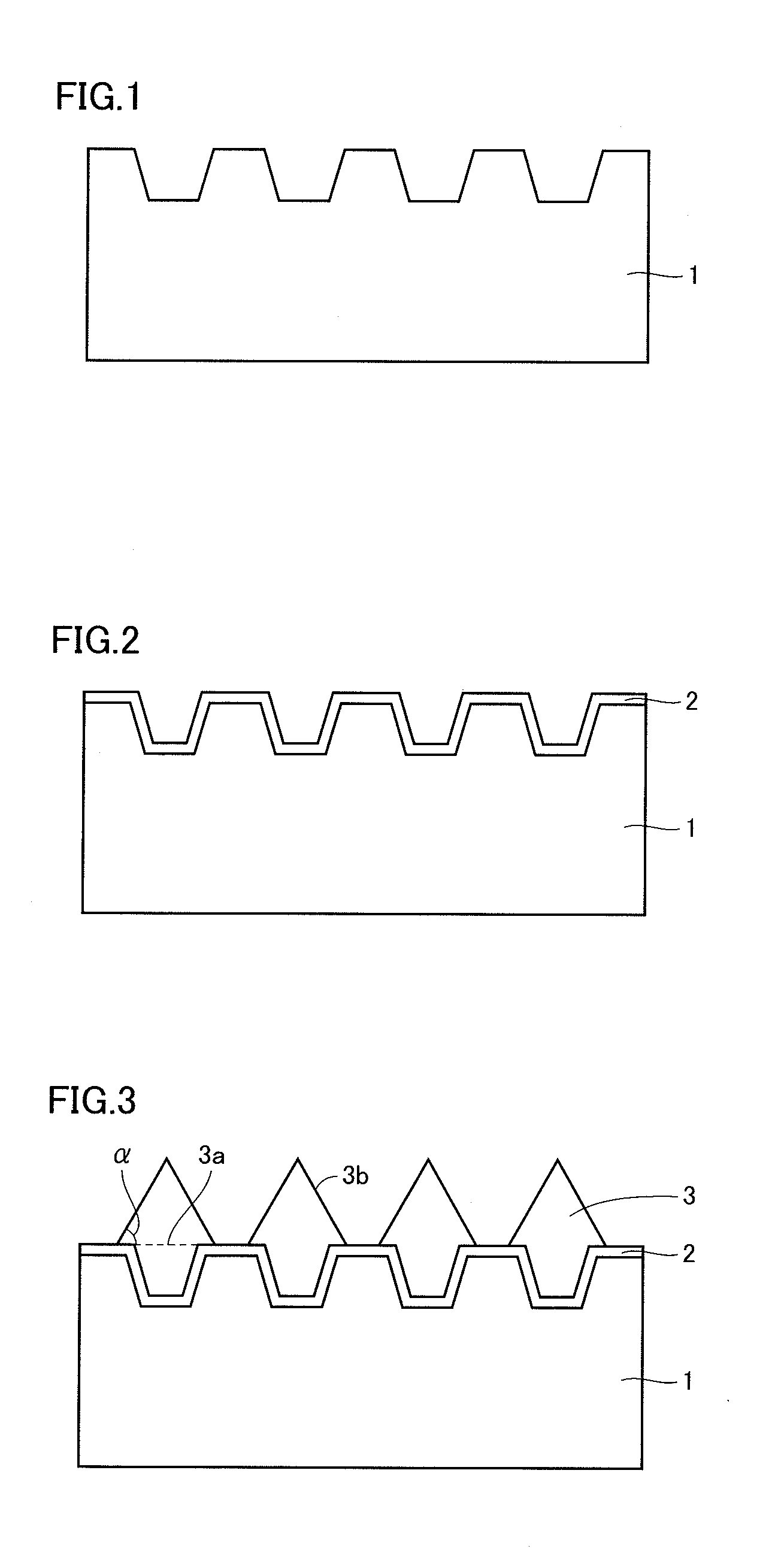
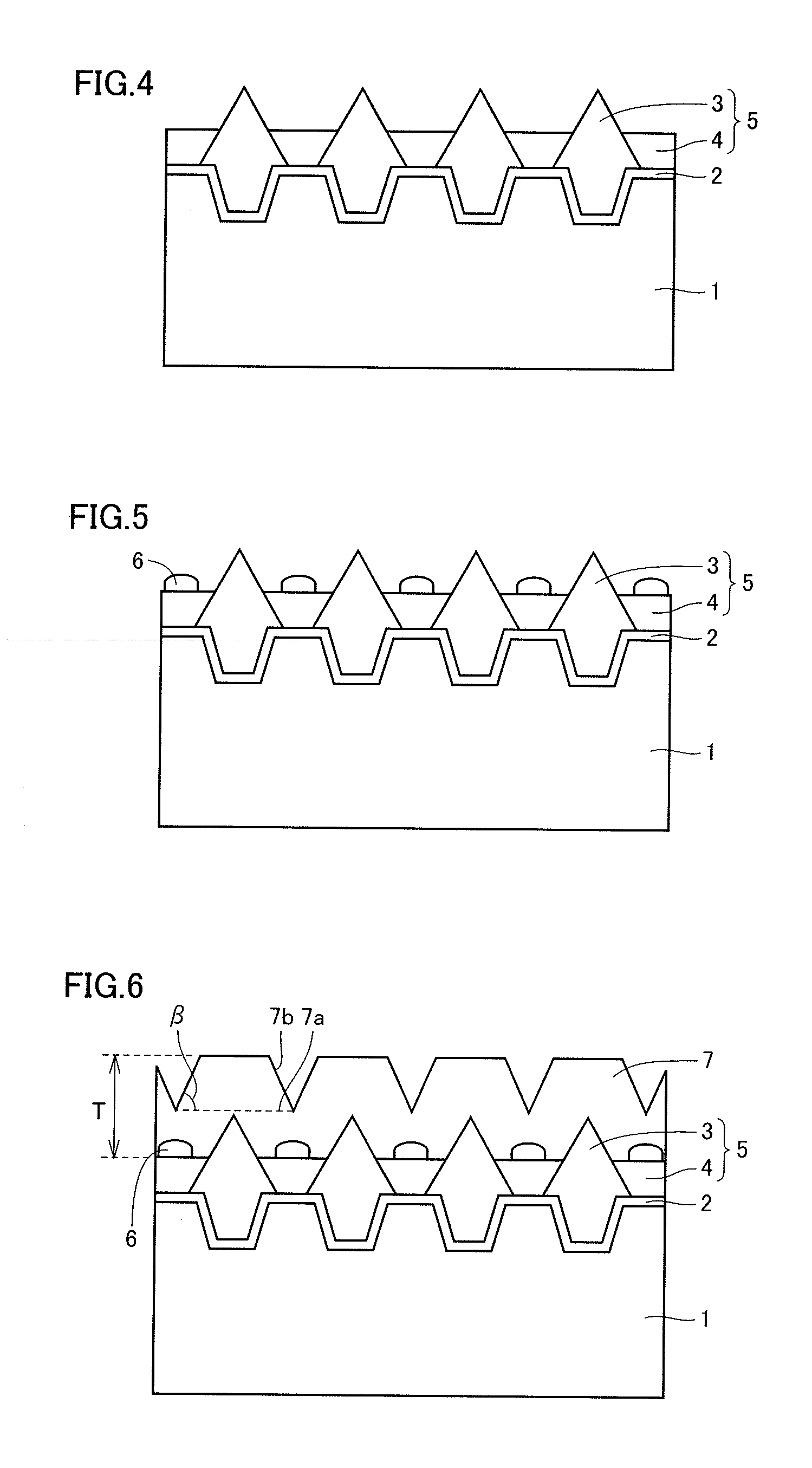
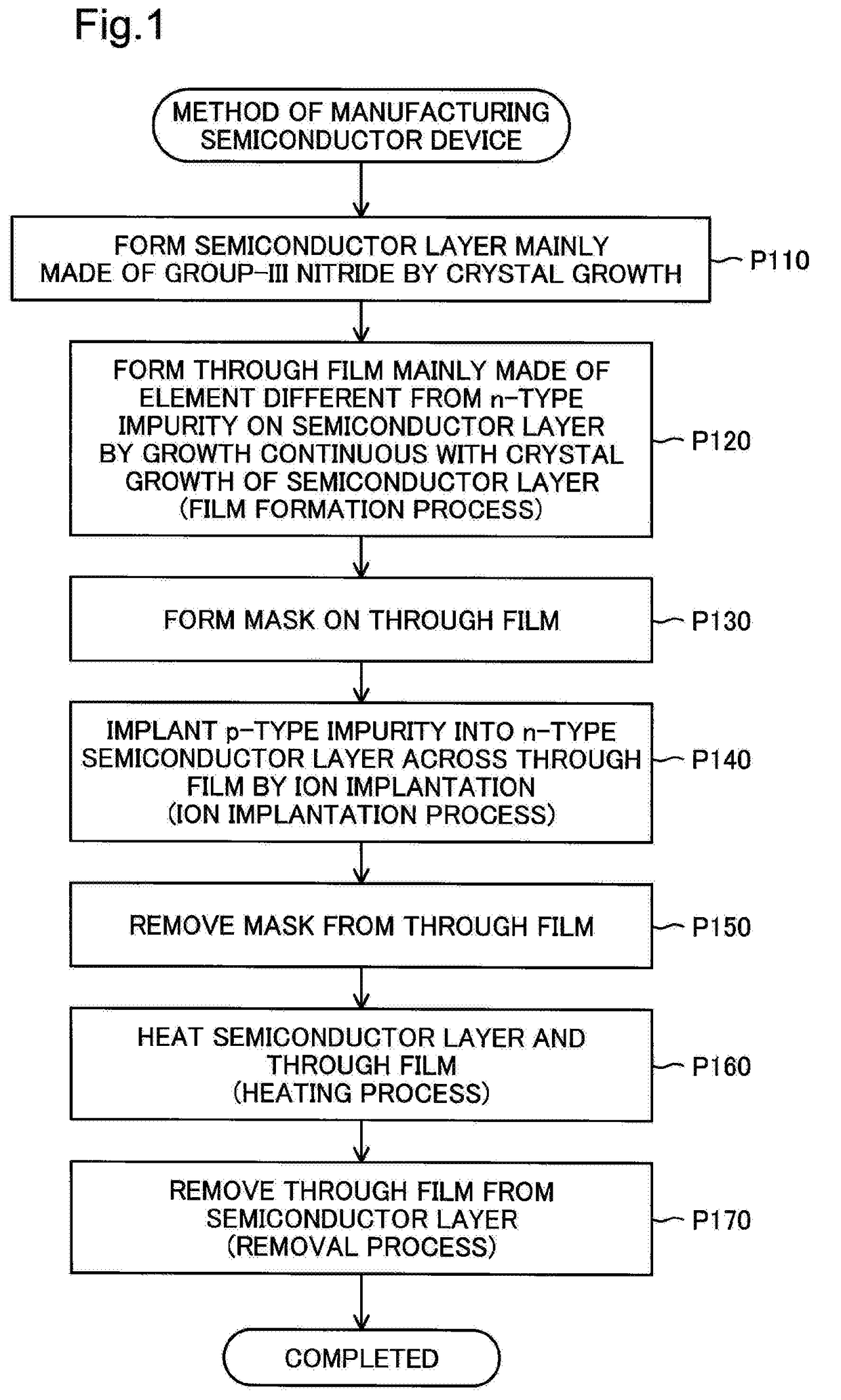
There is provided a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device. The method of manufacturing the semiconductor device comprises a process of forming a semiconductor layer that is mainly made of a group III nitride and has n-type characteristics, by crystal growth; a film formation process of forming a through film that is mainly made of an element different from an element serving as an n-type impurity relative to the group III nitride, by growth on the semiconductor layer continuous with crystal growth of the semiconductor layer; an ion implantation process of implanting a p-type impurity into the semiconductor layer across the through film by ion implantation; a heating process of heating the semiconductor layer and the through film after completion of the ion implantation process, so as to activate a region of the semiconductor layer in which the p-type impurity is ion-implanted, to a p-type semiconductor region; and a removal process of removing the through film from the semiconductor layer, after completion of the heating process. This configuration improves the surface morphology of the p-type semiconductor region formed by ion implantation.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
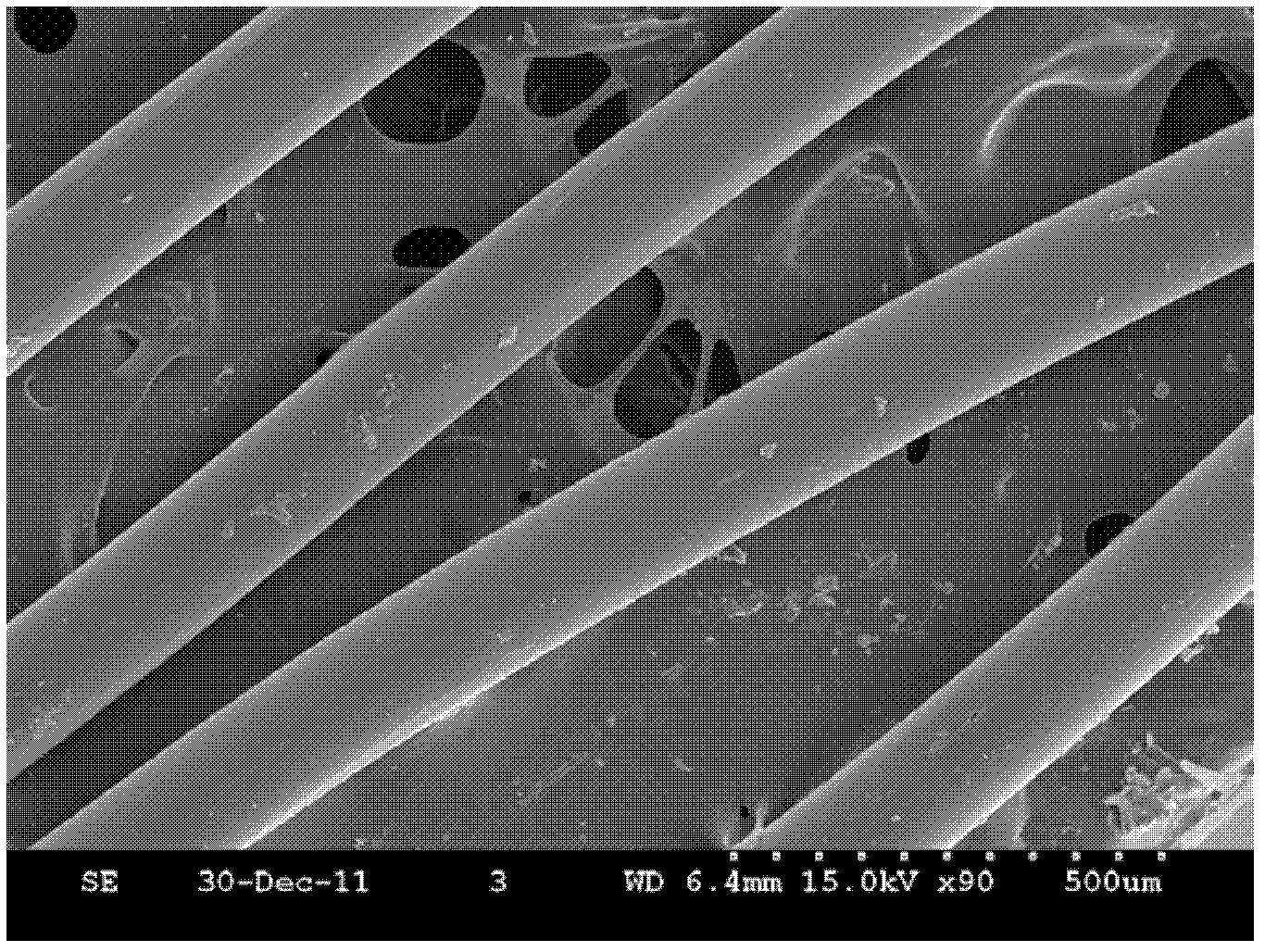
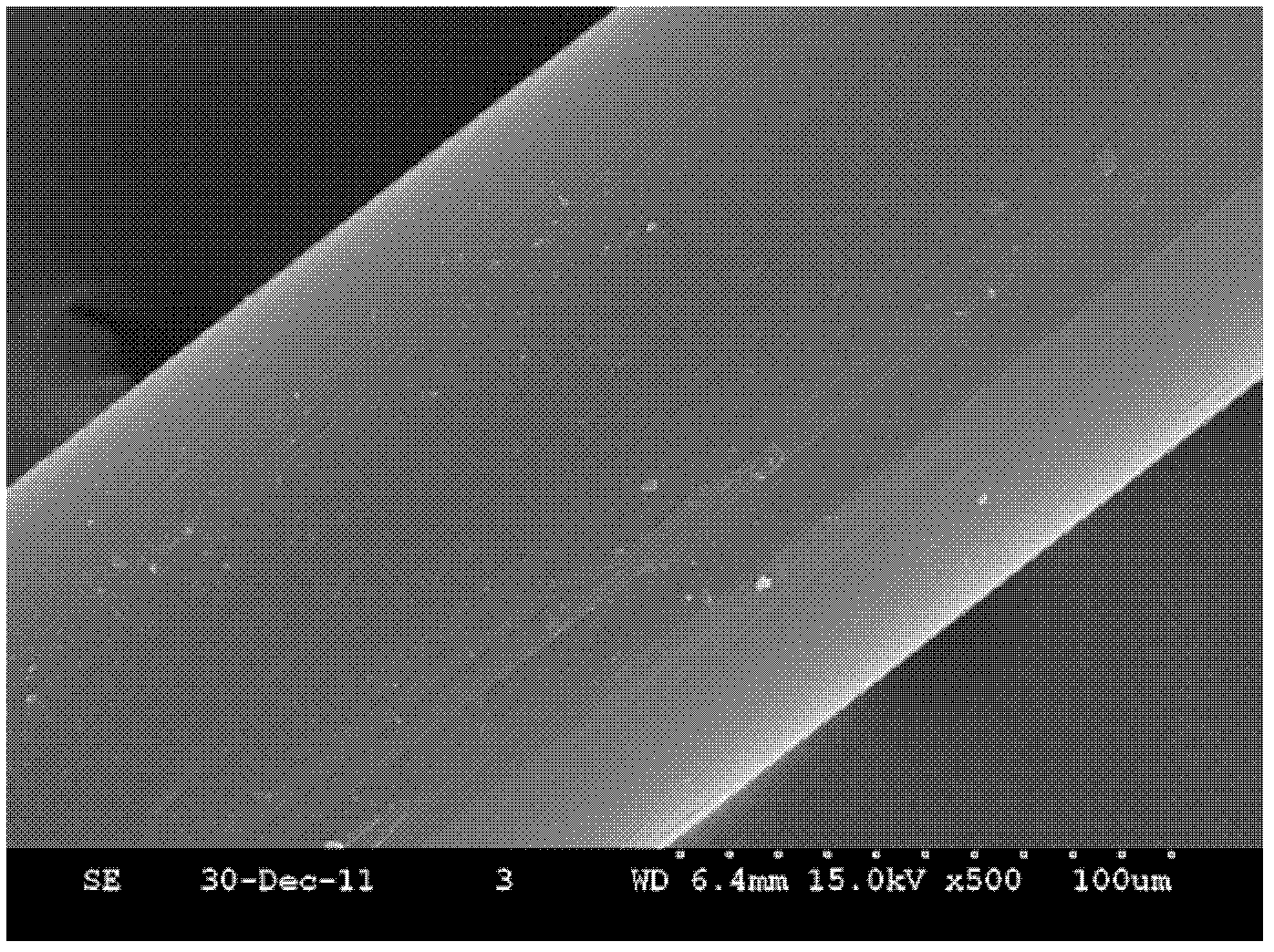
Production process of electrodeposited copper foil with shiny surface subjected to roughening
The invention discloses a production process of electrodeposited copper foil with a shiny surface subjected to roughening. The copper foil is subjected to acid pickling, roughening I, curing I, roughening II, curing II, curing III, curing IV, high-temperature anti-oxidation, water washing I, normal-temperature anti-oxidation, water washing II, silane spraying and drying in sequence; and the process conditions of the roughening I and the roughening II are that the current densities is 28 A / dm<2>-33 A / dm<2>, the temperature is 25 DEG C-35 DEG C, the sulfuric acid concentration is 160 g / l-180 g / l, the copper ion concentration is 7 g / l-13 g / l, the chloride ion concentration is 15 mg / l-30 mg / l, the sodium tungstate concentration is 0 mg / l-90 mg / l, the sodium molybdate concentration is 0 mg / l-70mg / l, and the cobalt sulfate concentration is 0 g / l-45 g / l. According to the process, tungsten, cobalt and molybdenum elements are added in the roughening procedures, so that the surface morphology of the copper foil is improved, and the anti-stripping strength of the electrodeposited copper foil is improved; and elements such as lanthanum or cerium are added in the high-temperature anti-oxidation process to form a special plating layer, and the structural morphology of the plating layer is changed, so that the anti-stripping strength and the corrosion resistance of the electrodeposited copper foil are improved.
Owner:JIANGDONG ELECTRONIC MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method of zirconium boride ceramic fibre
The invention relates to a preparation method of zirconium boride ceramic fibre, comprising the following steps of: (1) adding an aqueous solution containing a zirconium compound to an aqueous solution containing a boron compound, mixing evenly, dissolving a carbon source compound in the mixed solvent of ethanol and water, adding the mixed solvent of ethanol and water to the solution, adding an aqueous solution of complexing agents, mixing evenly, regulating pH value to be less than 4, and stirring for reaction for 10-16 hours to obtain a precursor solution; (2) mixing evenly a spinning addition agent and the precursor solution at the temperature between 30 and 70 DEG C and concentrating and defoaming the obtained mixture to obtain a precursor spinning solution of the zirconium boride ceramic fibre; (3) obtaining a precursor of the zirconium boride ceramic fibre from the spinning solution by a solvent spinning method at the temperature between 30 and 70 DEG C; and (4) obtaining the zirconium boride ceramic fibre by performing high temperature sintering on the precursor fibre. By adopting the method, ZrB2 ceramic nascent fiber with a better structure and performance can be obtained and the fiber with a promising prospect has the advantages of high temperature stability, low density, high heat conductivity and conductivity and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com