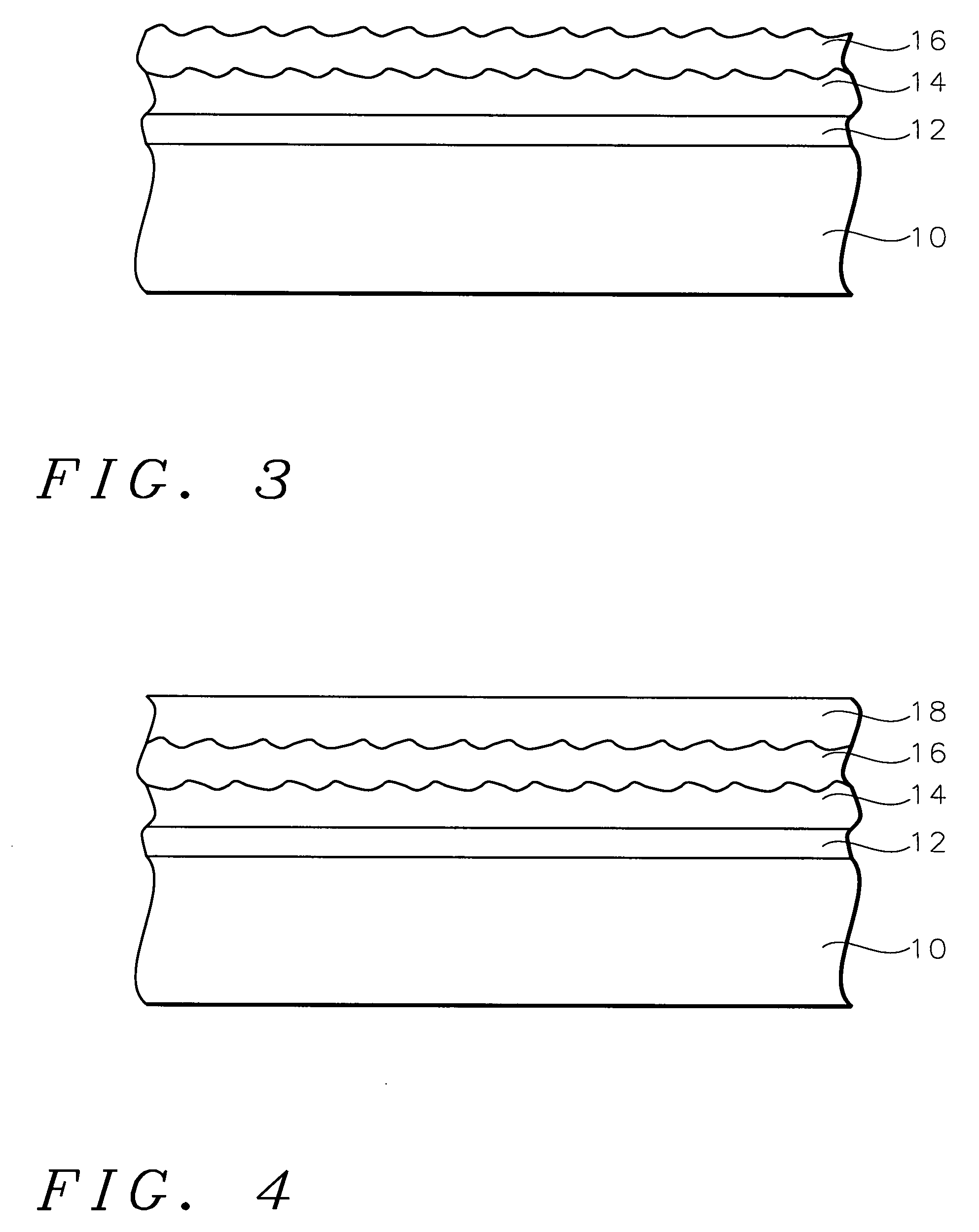
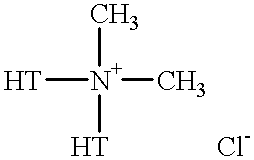
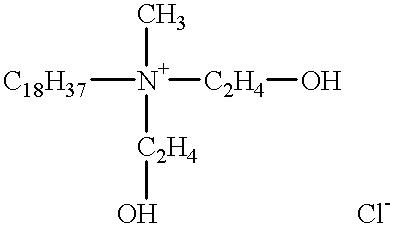
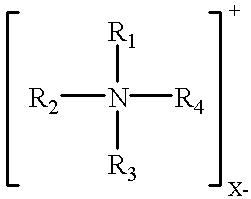Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3410 results about "Organic chemicals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Organic chemicals are chemical compounds that contain carbon as part of their molecular structure. Other elements that commonly make up these compounds are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and chlorine.
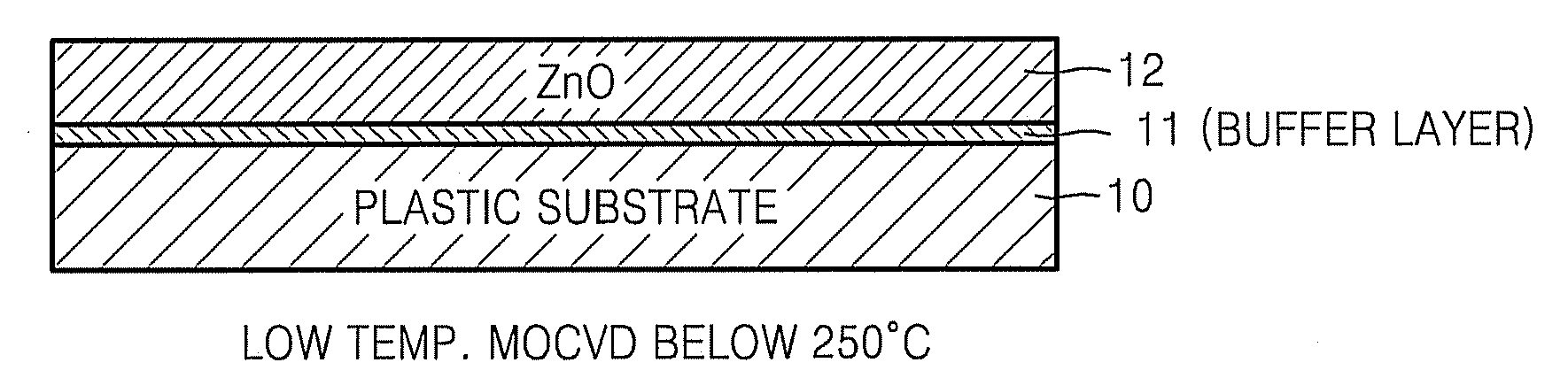
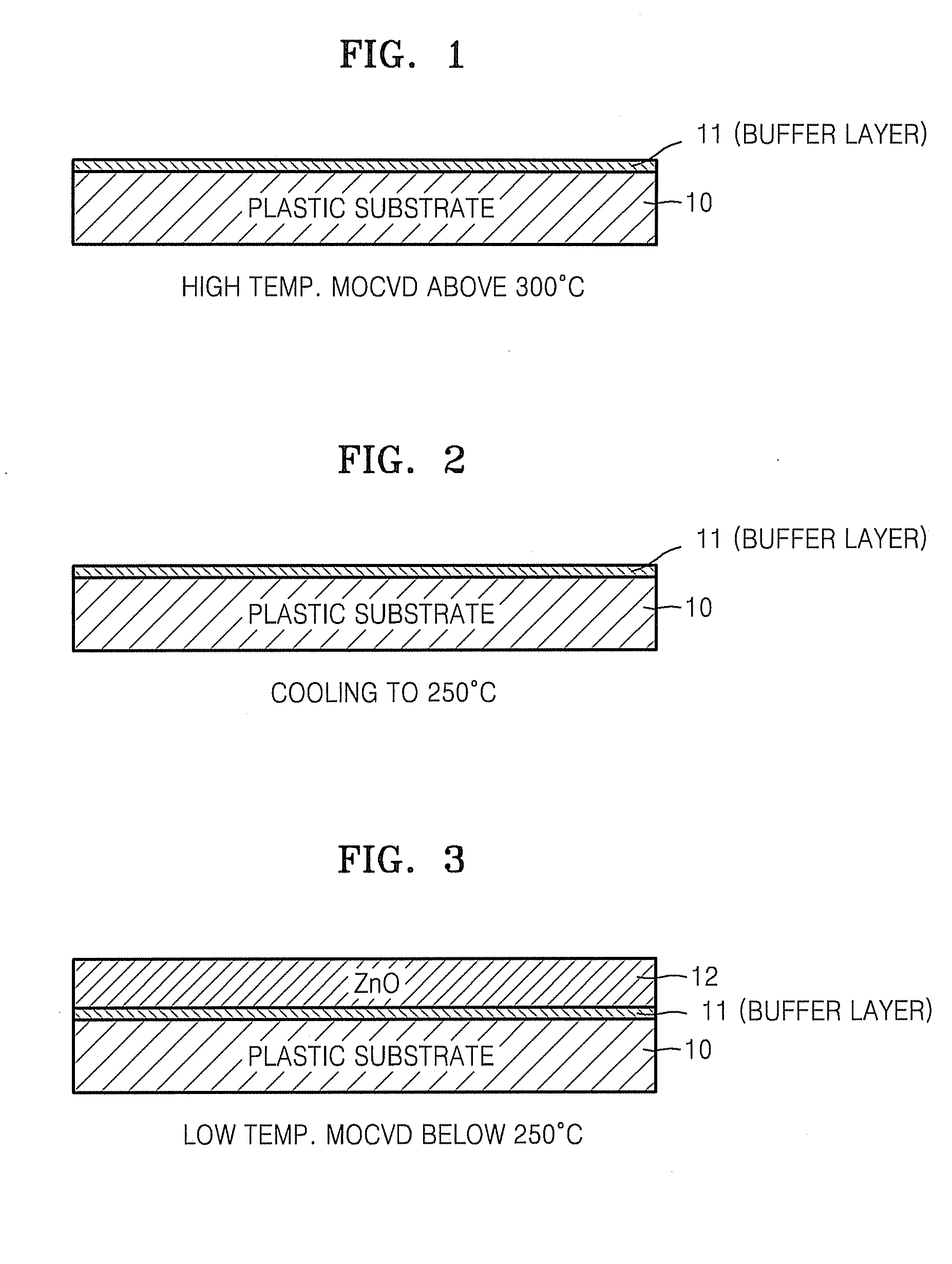
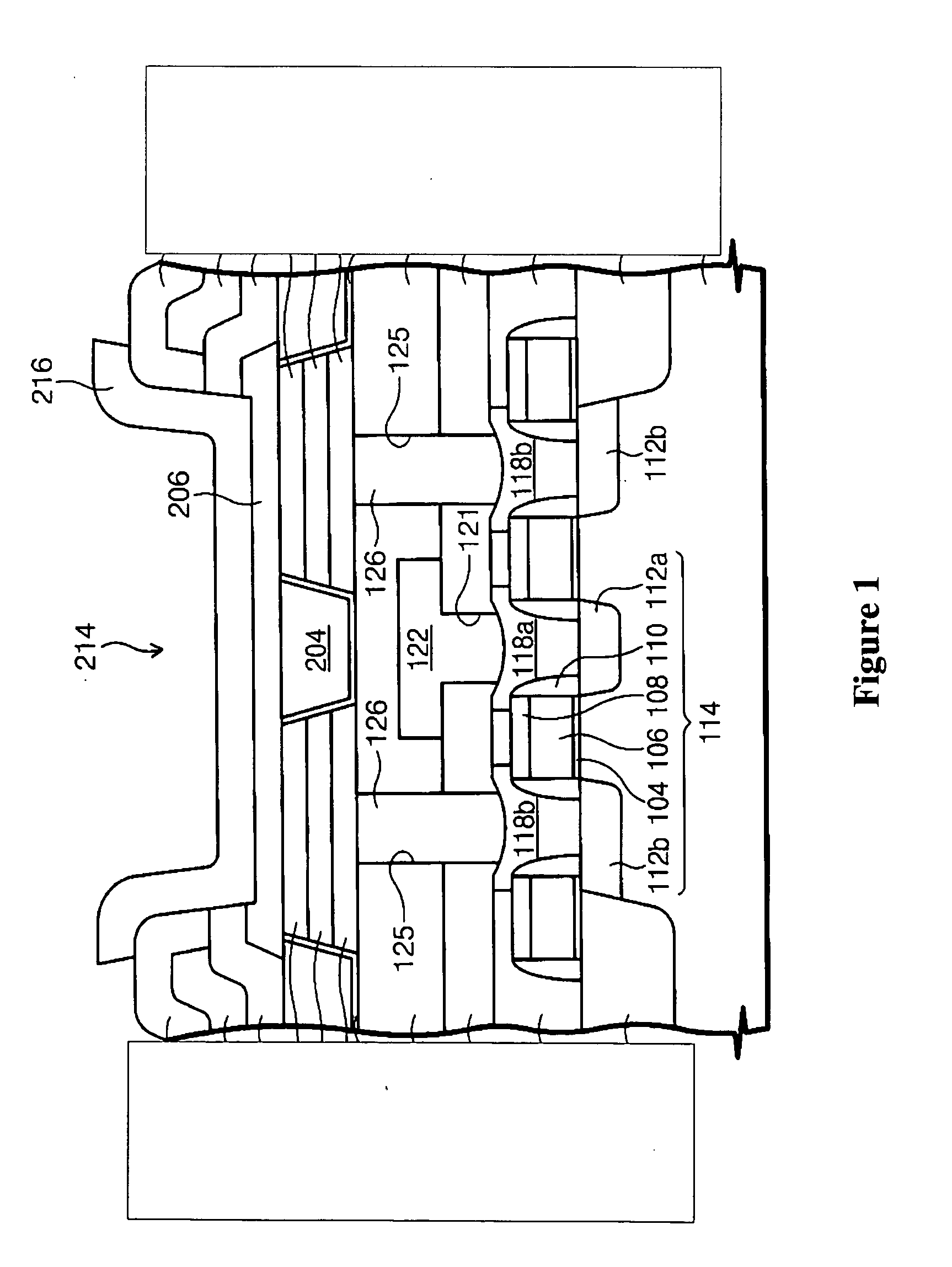
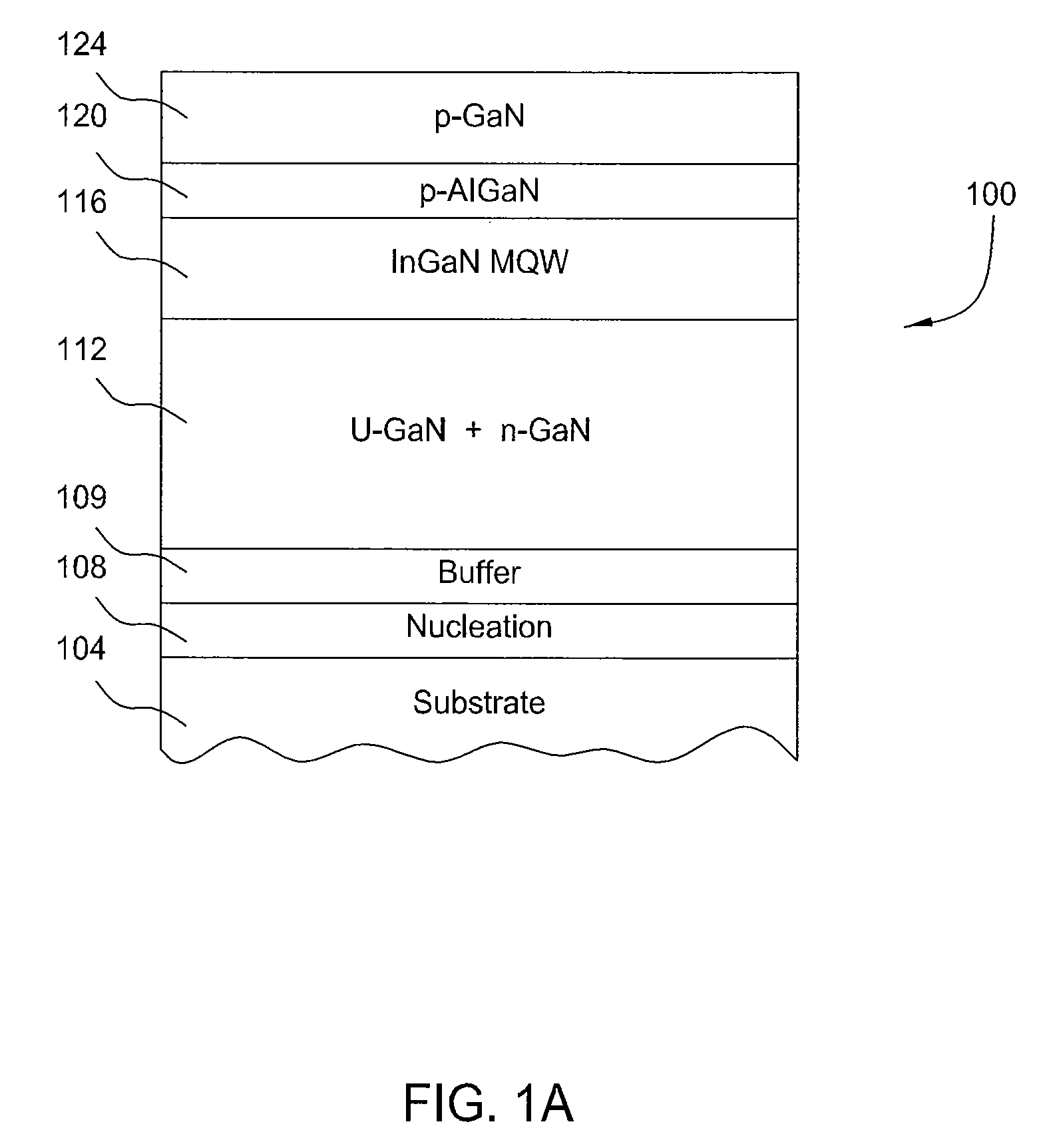
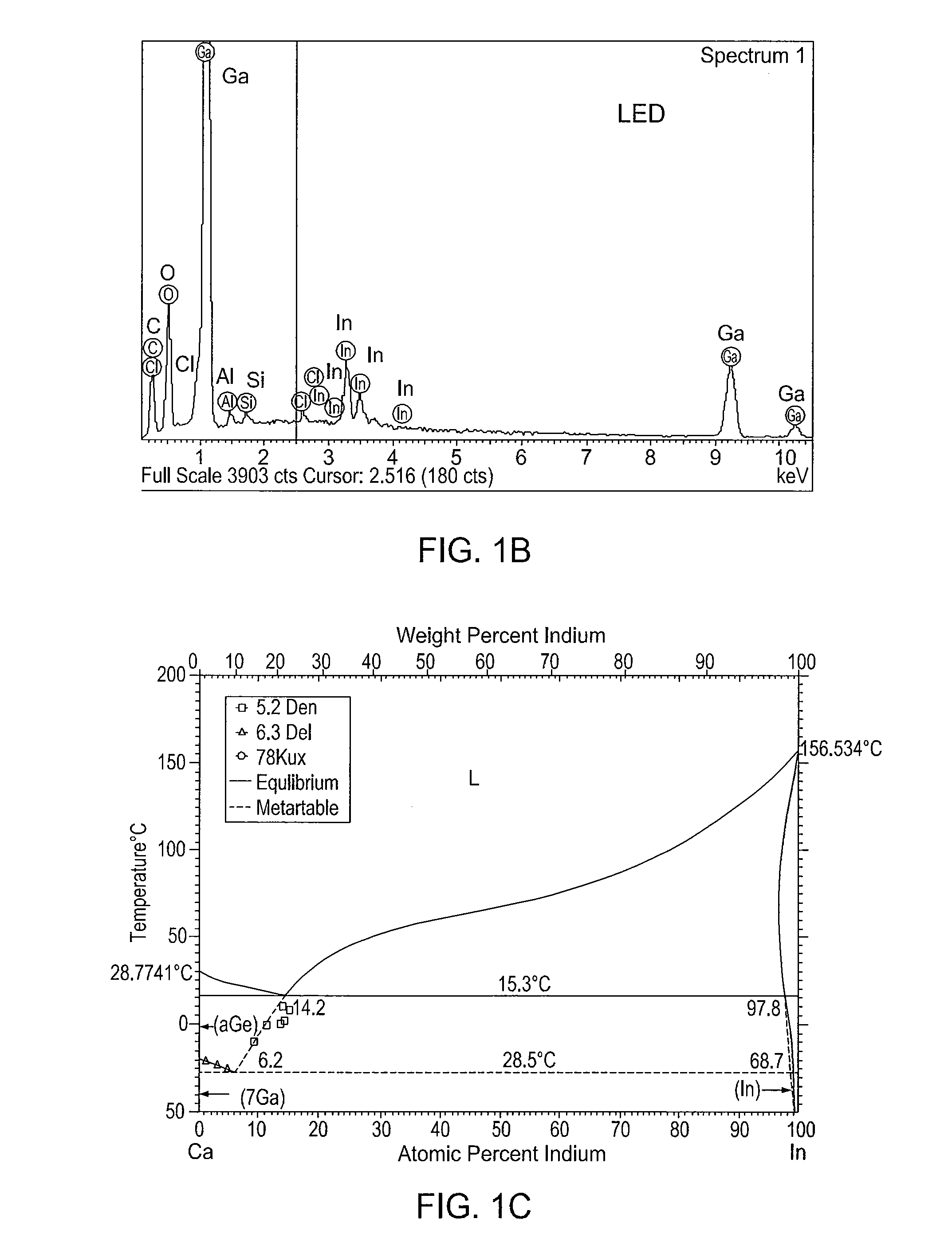
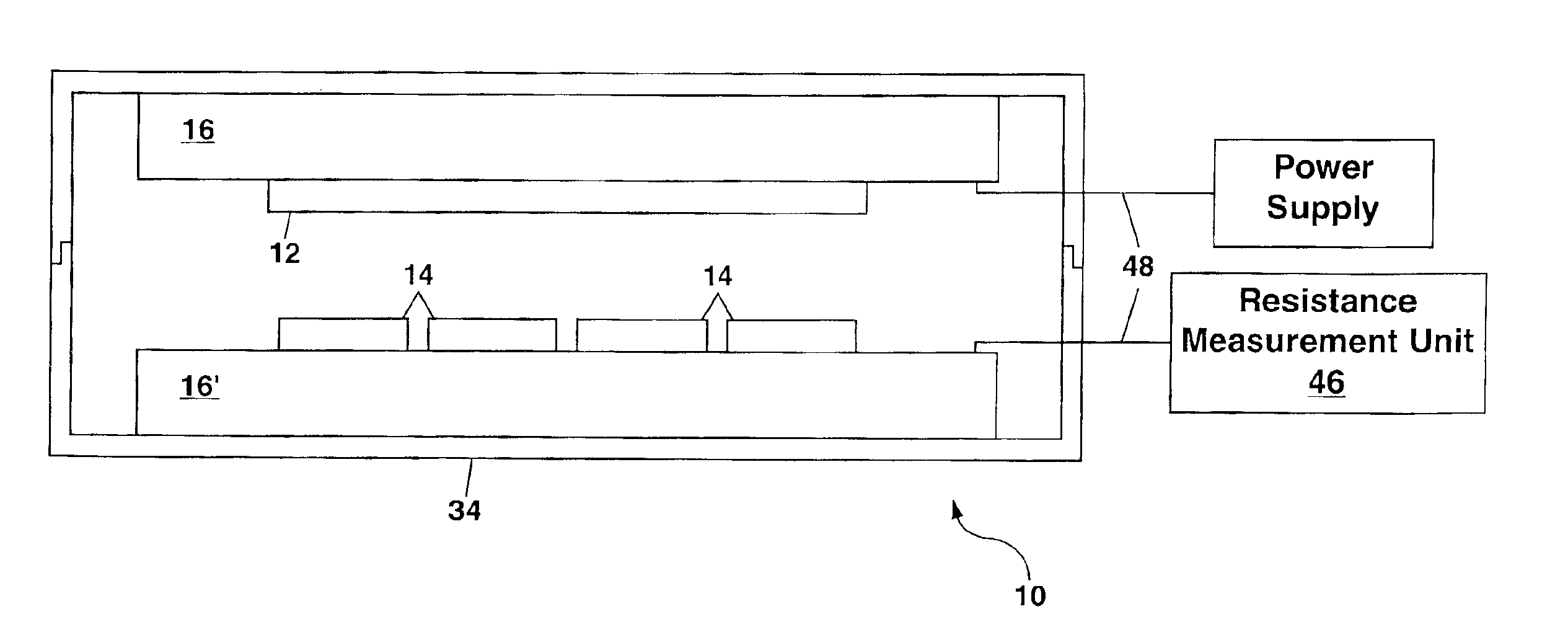
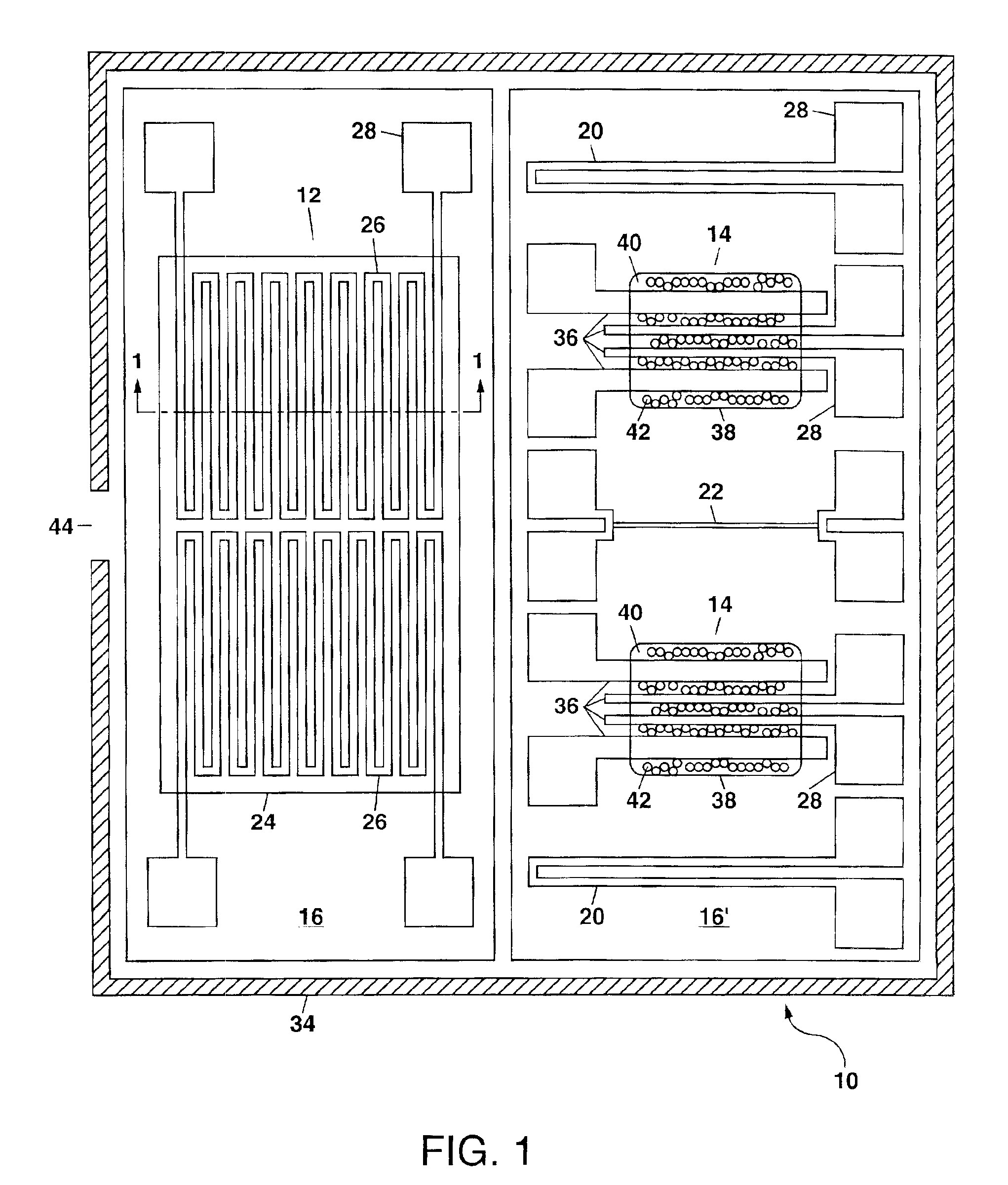
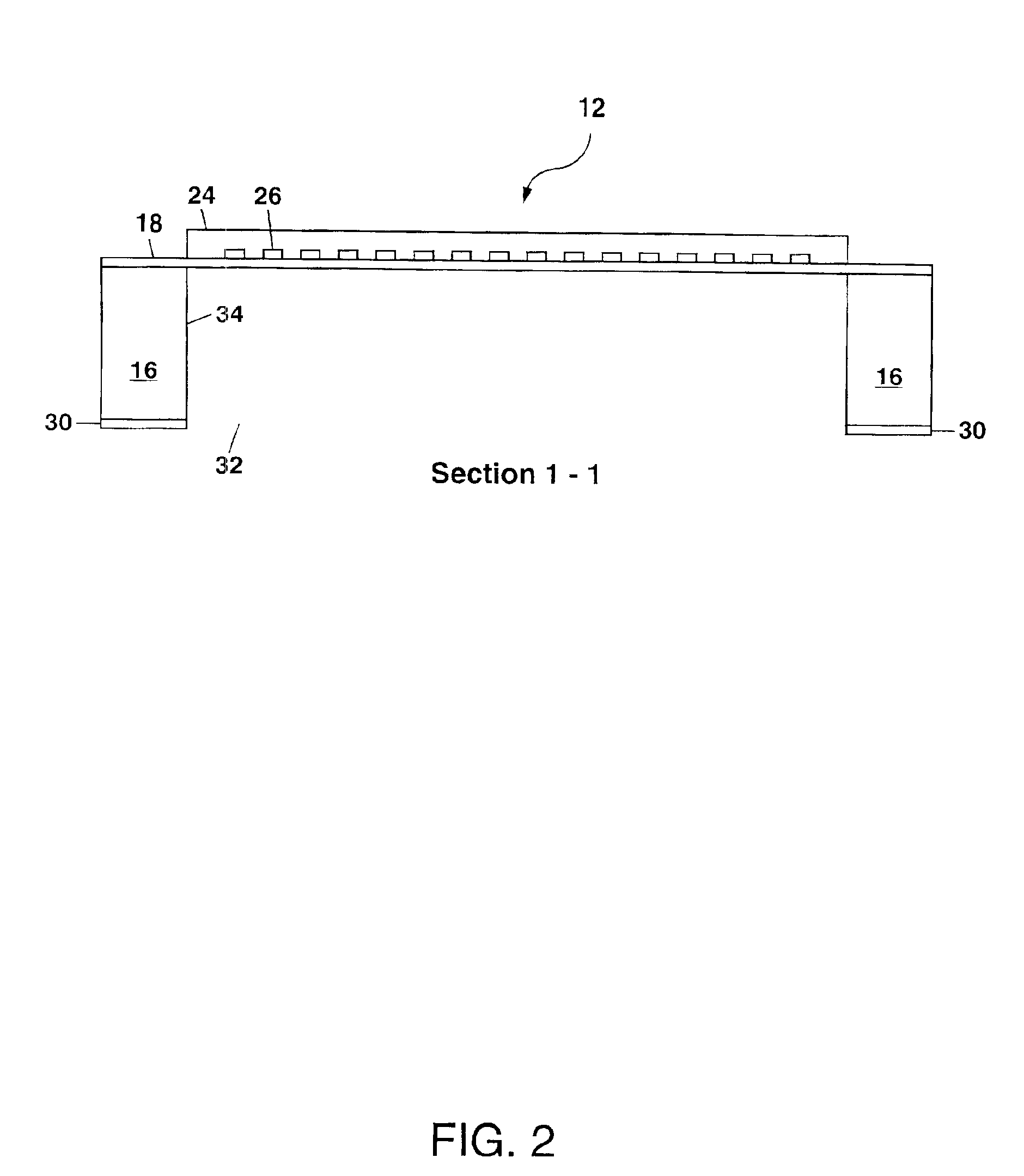
METHOD OF FABRICATING ZnO FILM AND THIN FILM TRANSISTOR ADOPTING THE ZnO FILM
InactiveUS20070172591A1Liquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical vapor depositionMetal
Provided is a method of fabricating a low temperature ZnO polycrystalline film and a thin film transistor (TFT) adopting the low temperature ZnO polycrystalline film. The method includes growing ZnO on a substrate at a first temperature for a first time using Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) to form a ZnO buffer layer, and heating the substrate at a temperature lower than the first temperature to grow ZnO on the ZnO buffer layer for a second time longer than the first time so as to form a ZnO film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment
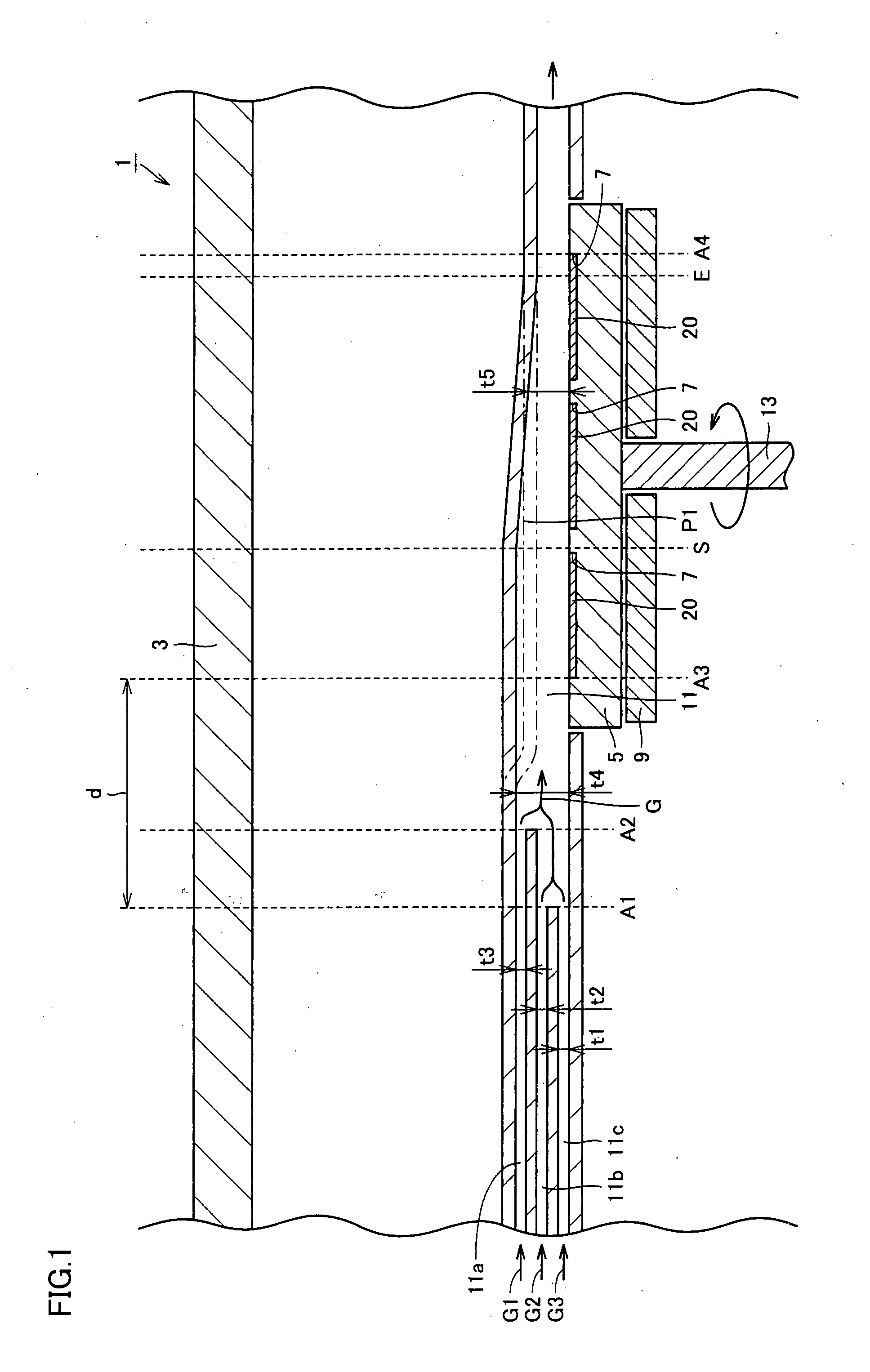
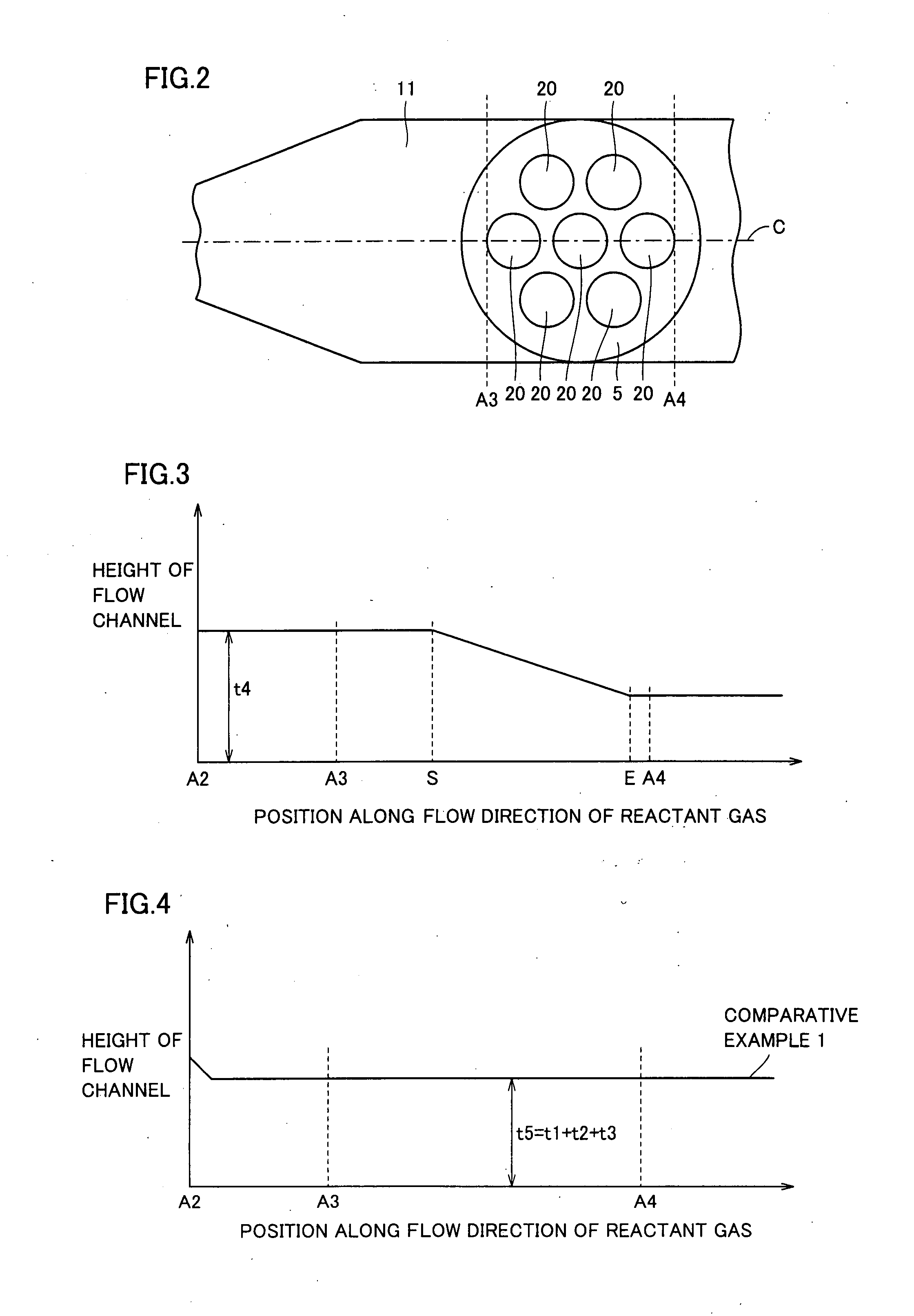
InactiveUS20080006208A1Uniform film thicknessImprove formation efficiencyAfter-treatment apparatusFrom chemically reactive gasesSusceptorProduct gas
Metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment is metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment for forming a film on a substrate by using a reactant gas, and includes a susceptor heating the substrate and having a holding surface for holding the substrate, and a flow channel for introducing the reactant gas to the substrate. The susceptor is rotatable with the holding surface kept facing an inner portion of the flow channel, and a height of the flow channel along a flow direction of the reactant gas is kept constant from a position to a position, and is monotonically decreased from the position to the downstream side. It is thereby possible to improve film formation efficiency while allowing the formed film to have a uniform thickness.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Bilayer inlet gas spray nozzle in use for metal-organic chemical vapor deposition device
This invention discloses a two-layer gas inlet blow head of a metal organic chemical gas phase deposit device including a closed shell having an upper gas inlet cavity and a lower gas inlet cavity, an upper escape pipe communicating with the upper gas cavity and reaction chamber is set between the upper-middle and the base plate and a lower escape pipe communicating with a lower gas inlet cavity and the reaction chamber is set between the lower plate and base plate characterizing that diameter of the lower escape pipe is layer than the upper and the upper is put in the lower. A cooling cavity is designed, the first reaction gas enters into the reaction chamber at the substrate surface from the upper and lower escape pipes separately.
Owner:南昌硅基半导体科技有限公司
Closed loop mocvd deposition control
InactiveUS20110308453A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseControl system
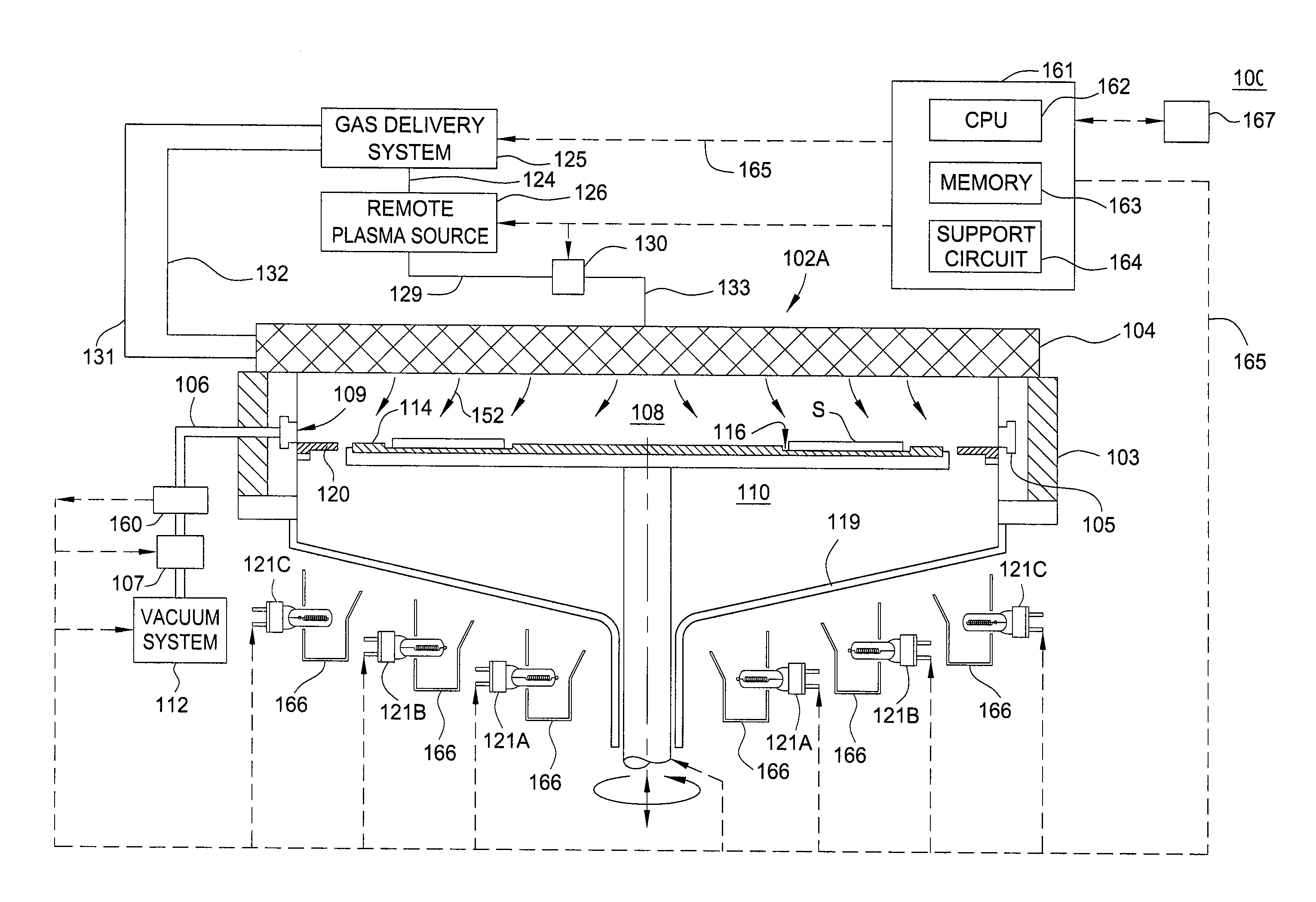
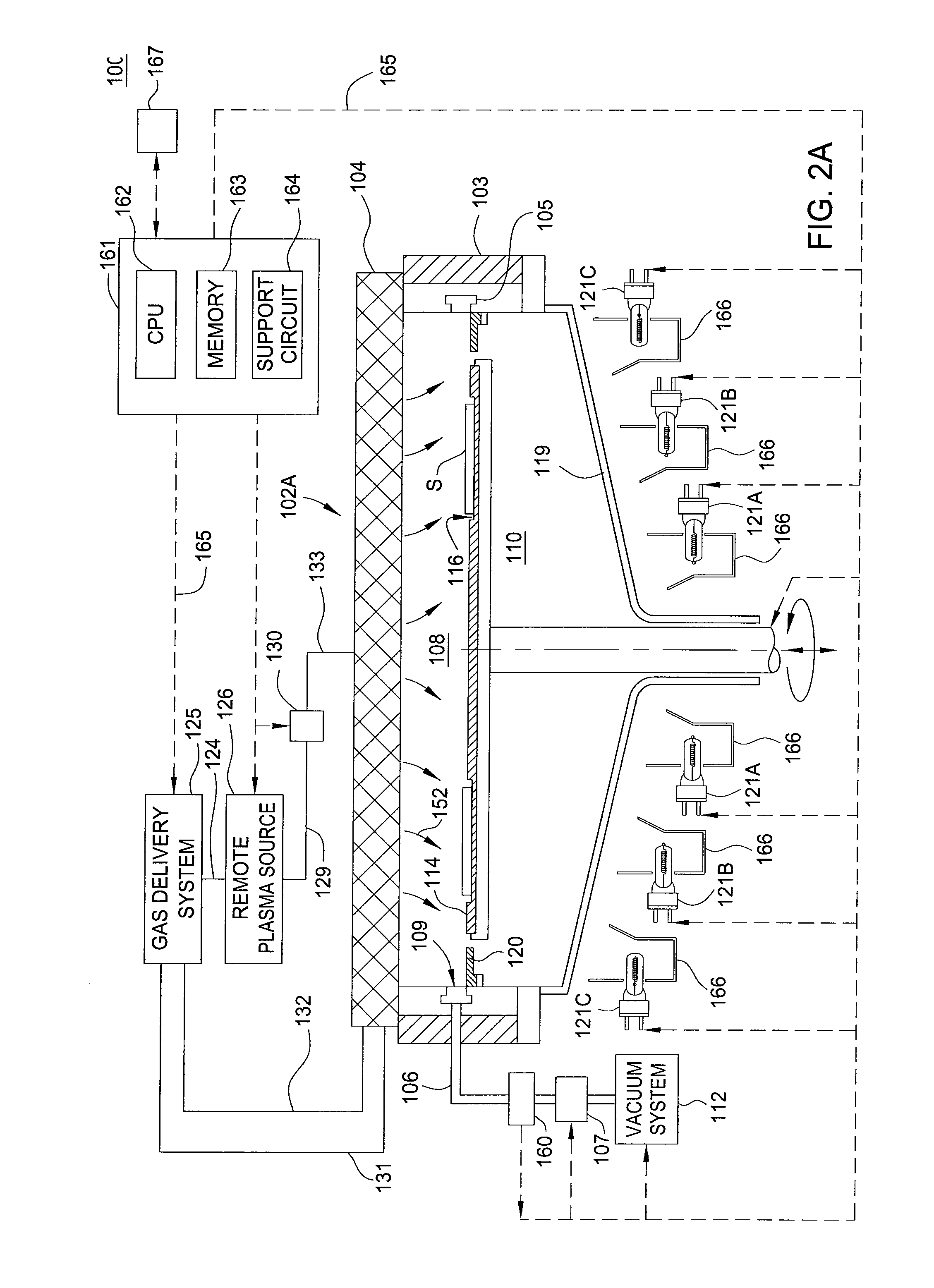
A method and apparatus are provided for monitoring and controlling substrate processing parameters for a cluster tool that utilizes chemical vapor deposition and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition. In one embodiment, a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) process is used to deposit a Group III-nitride film on a plurality of substrates within a processing chamber. A closed-loop control system performs in-situ monitoring of the Group III-nitride film growth rate and adjusts film growth parameters as required to maintain a target growth rate. In another embodiment, a closed-loop control system performs in-situ monitoring of film growth parameters for multiple processing chambers for one or more film deposition systems.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for forming a ferroelectric layer
InactiveUS20050019960A1Improve crystal structureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbideChemical vapor deposition
Methods and apparatus for depositing a layer including providing at least one precursor vapor to a process chamber, providing a gas to the process chamber, separate from the at least one precursor vapor, and forming a compound layer from the at least one precursor vapor and the gas on a wafer in the process chamber. The deposition may be a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) deposition method, a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) deposition method, an atomic layer deposition (ALD) deposition method, or other similar deposition method. The compound layer may be at least one of an oxide, nitride, carbide, or other similar layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Susceptor for MOCVD reactor
InactiveUS7122844B2Reducing unwanted impurityLess energySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesWaferingSusceptor
A susceptor for holding semiconductor wafers in an MOCVD reactor during growth of epitaxial layers on the wafers is disclosed. The susceptor comprises a base structure made of a material having low thermal conductivity at high temperature, and has one or more plate holes to house heat transfer plugs. The plugs are made of a material with high thermal conductivity at high temperatures to transfer heat to the semiconductor wafers. A metalorganic organic chemical vapor deposition reactor is also disclosed utilizing a susceptor according to the present invention.
Owner:CREE INC
Insulating gate AlGaN/GaN HEMT
InactiveUS7230284B2Reduce trappingReduce gate leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentDriving current
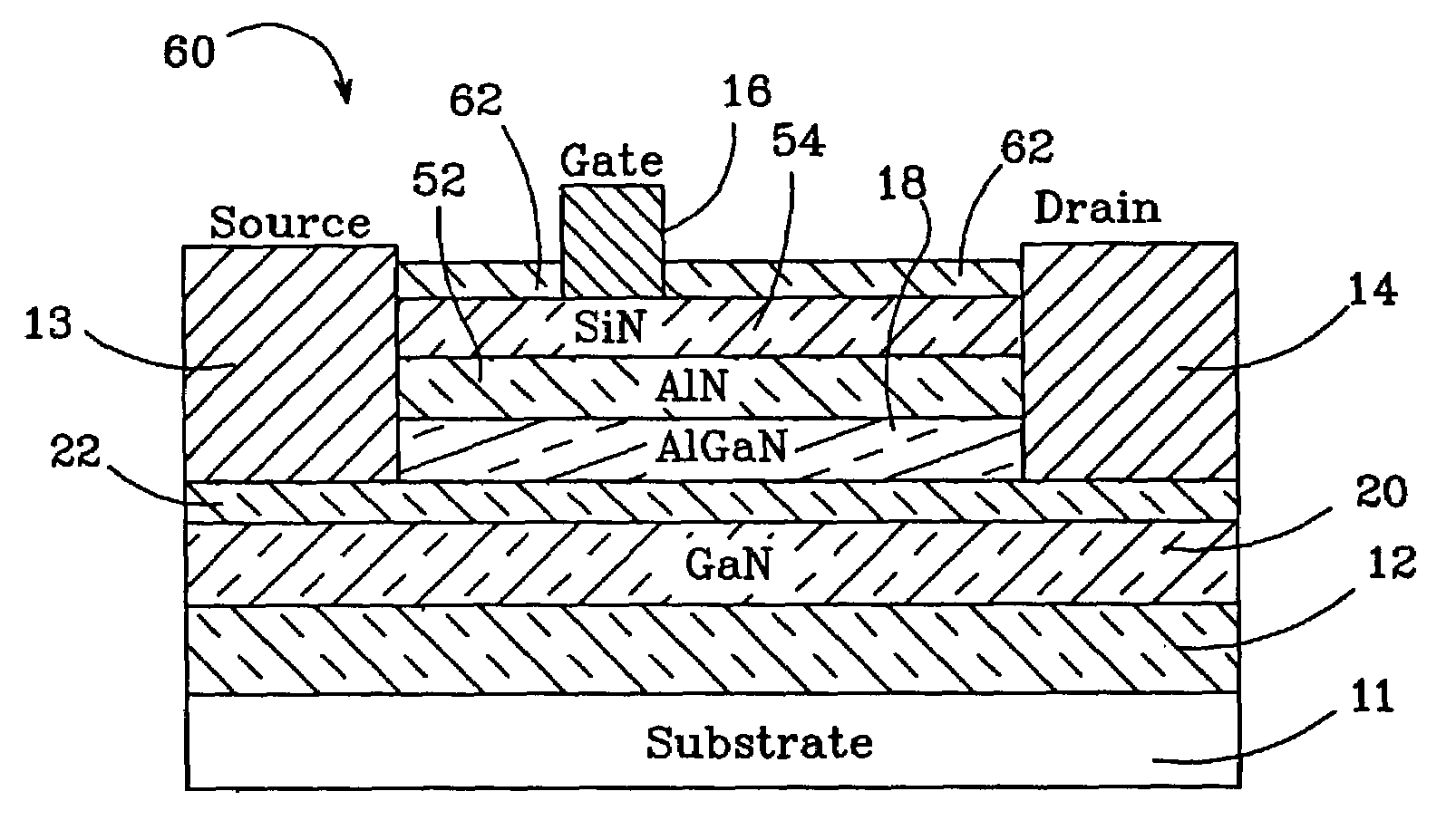
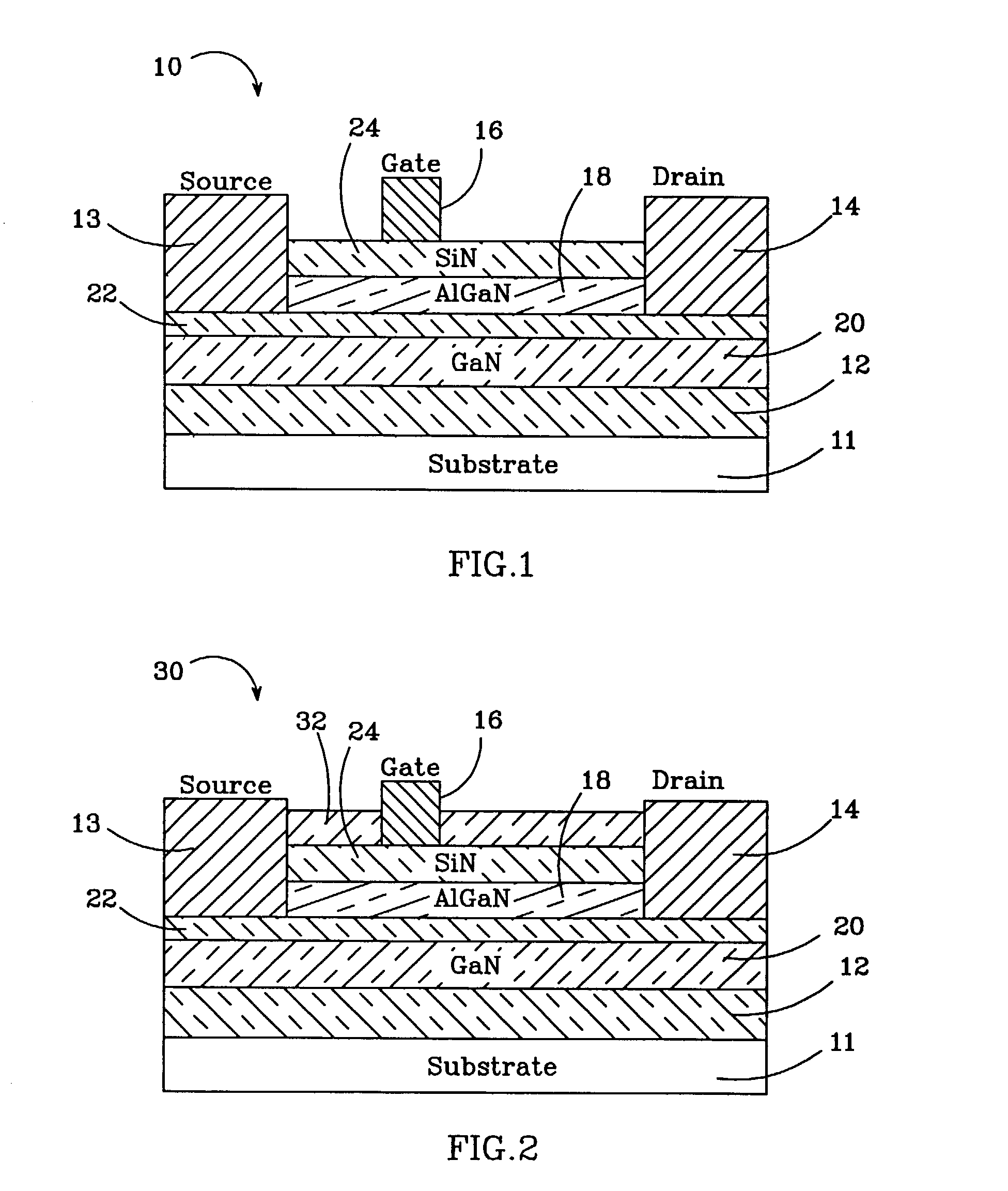
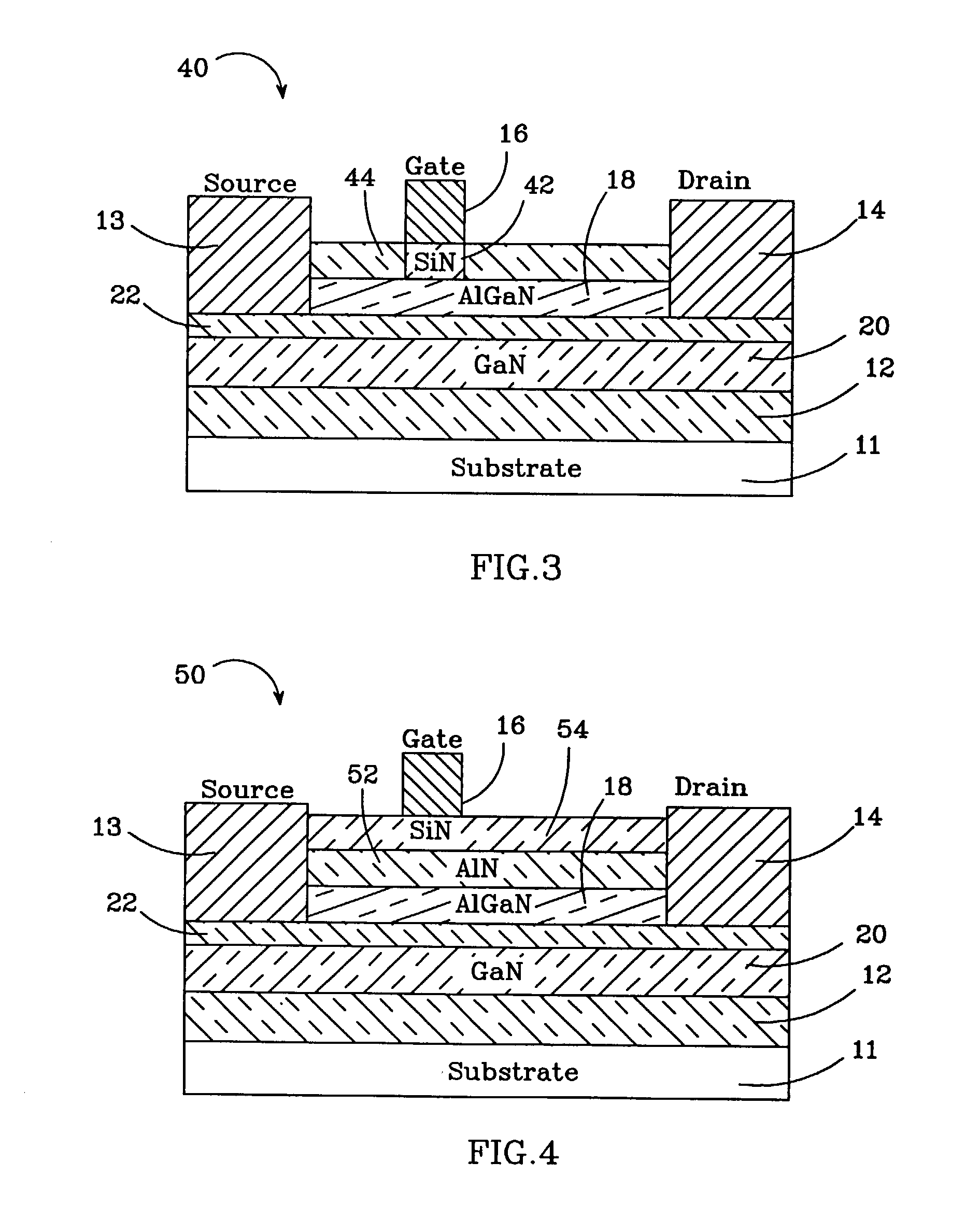
AlGaN / GaN HEMTs are disclosed having a thin AlGaN layer to reduce trapping and also having additional layers to reduce gate leakage and increase the maximum drive current. One HEMT according to the present invention comprises a high resistivity semiconductor layer with a barrier semiconductor layer on it. The barrier layer has a wider bandgap than the high resistivity layer and a 2DEG forms between the layers. Source and drain contacts contact the barrier layer, with part of the surface of the barrier layer uncovered by the contacts. An insulating layer is included on the uncovered surface of the barrier layer and a gate contact is included on the insulating layer. The insulating layer forms a barrier to gate leakage current and also helps to increase the HEMT's maximum current drive. The invention also includes methods for fabricating HEMTs according to the present invention. In one method, the HEMT and its insulating layer are fabricated using metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). In another method the insulating layer is sputtered onto the top surface of the HEMT in a sputtering chamber.
Owner:CREE INC
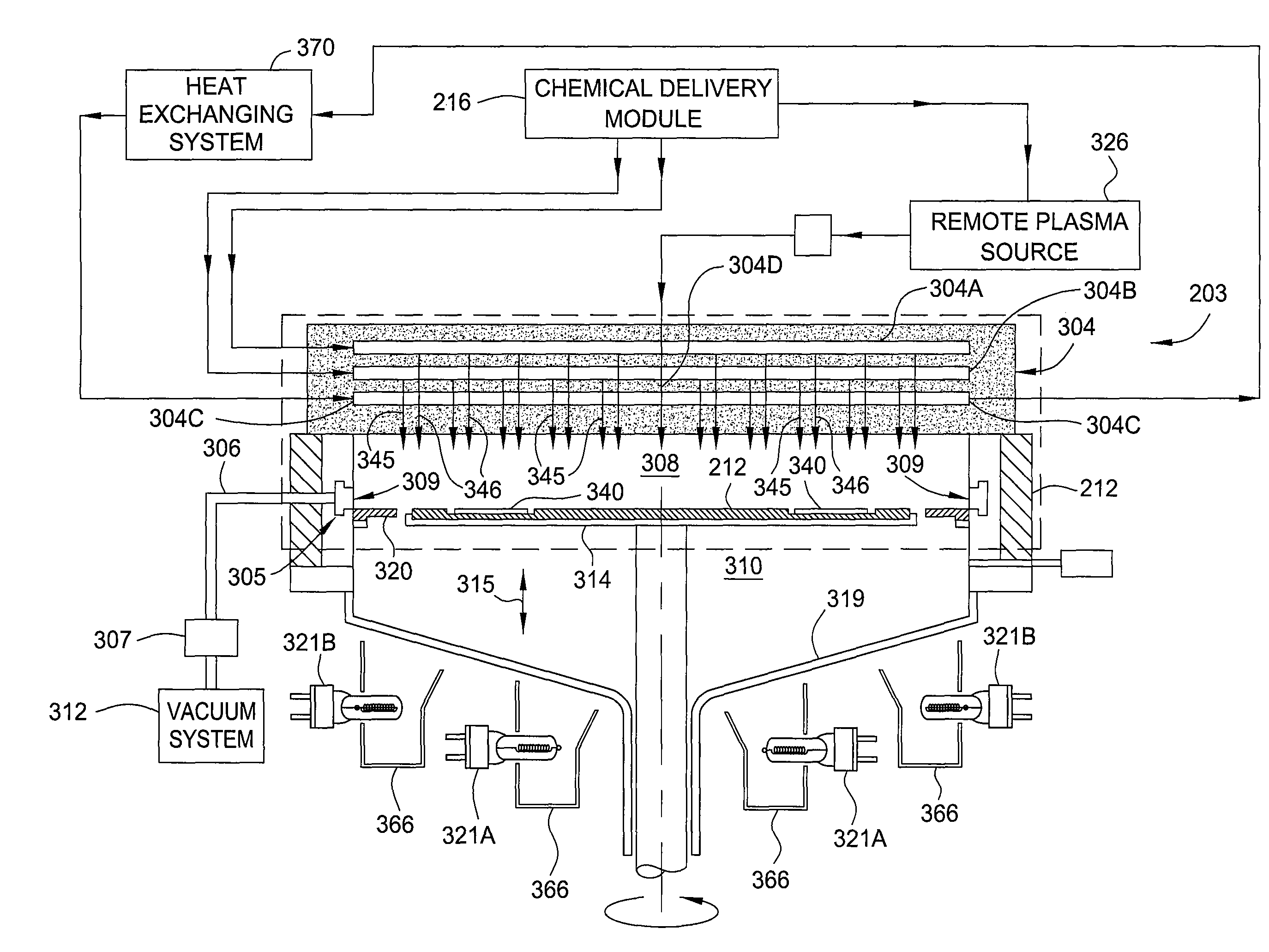
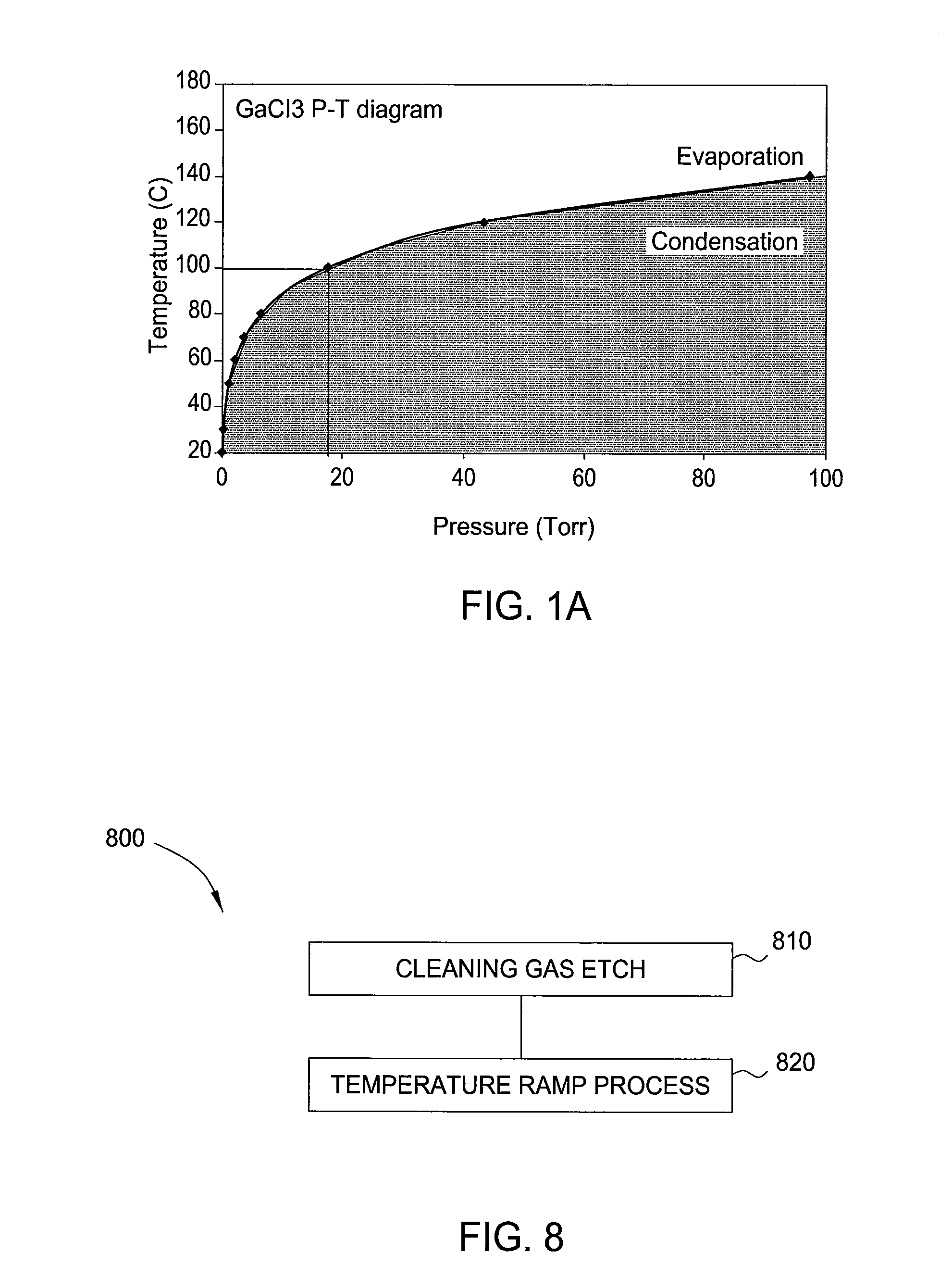
Decontamination of mocvd chamber using nh3 purge after in-situ cleaning
InactiveUS20100273291A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition processChemical vapor deposition
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to methods and apparatus for removing unwanted deposition build-up from one more interior surfaces of a substrate processing chamber after a substrate is processed in a chamber to form, for example, Group III-V materials by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) deposition processes and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition processes. In one embodiment, a method for removing unwanted deposition build-up from one or more interior surfaces of a substrate processing chamber is provided. The method comprises depositing one or more Group III containing layers over a substrate disposed in the substrate processing chamber, transferring the substrate out of the substrate processing chamber, and pulsing a halogen containing gas into the substrate processing chamber to remove at least a portion of the unwanted deposition build-up from one or more interior surfaces of the substrate processing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Mocvd single chamber split process for LED manufacturing
InactiveUS20100273290A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorGallium nitride
In one embodiment a method for fabricating a compound nitride semiconductor device comprising positioning one or more substrates on a susceptor in a processing region of a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) chamber comprising a showerhead, depositing a gallium nitride layer over the substrate with a thermal chemical-vapor-deposition process within the MOCVD chamber by flowing a first gallium containing precursor and a first nitrogen containing precursor through the showerhead into the MOCVD chamber, removing the one or more substrates from the MOCVD chamber without exposing the one or more substrates to atmosphere, flowing a chlorine gas into the processing chamber to remove contaminants from the showerhead, transferring the one or more substrates into the MOCVD chamber after removing contaminants from the showerhead, and depositing an InGaN layer over the GaN layer with a thermal chemical-vapor-deposition process within the MOCVD chamber is provided.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
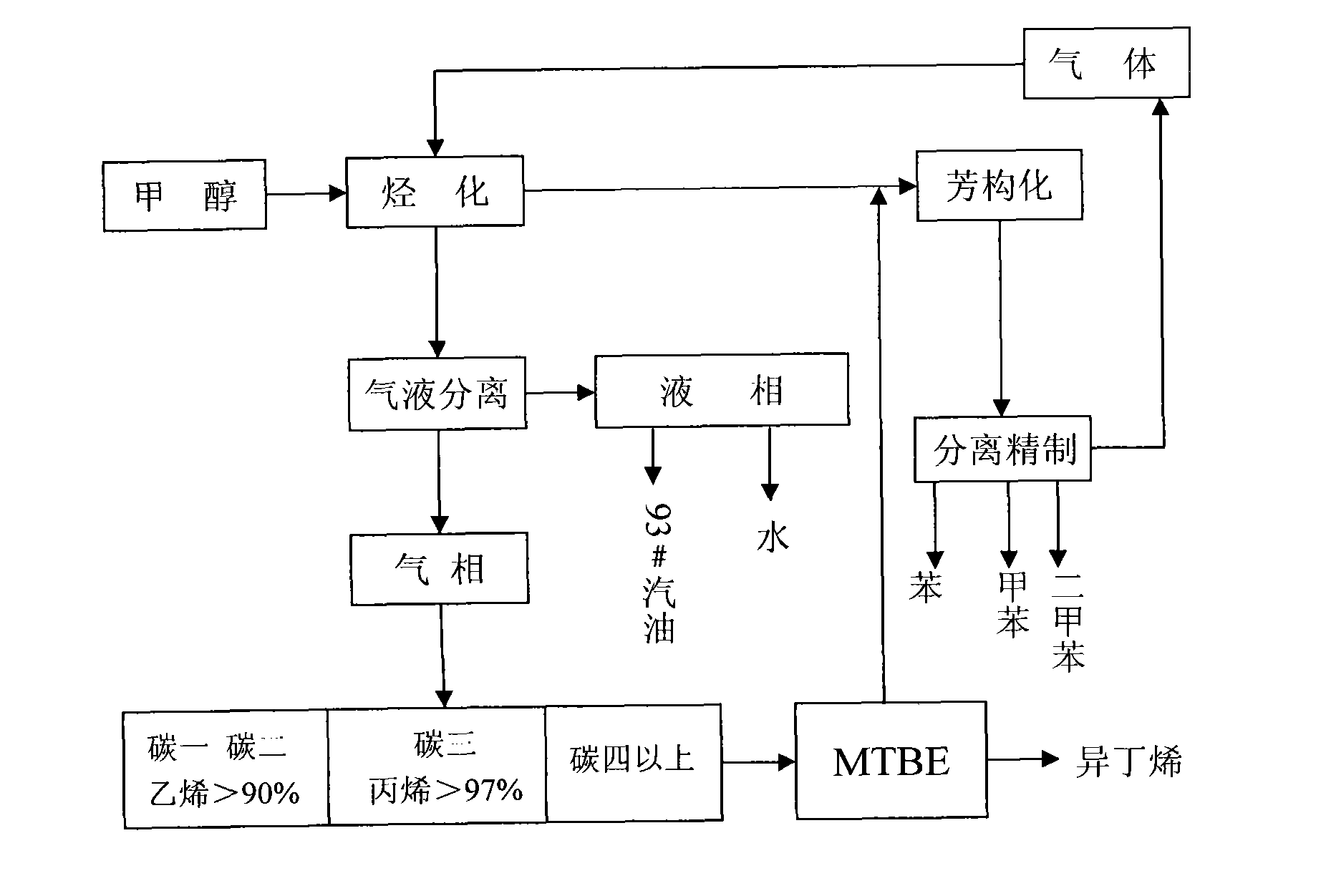
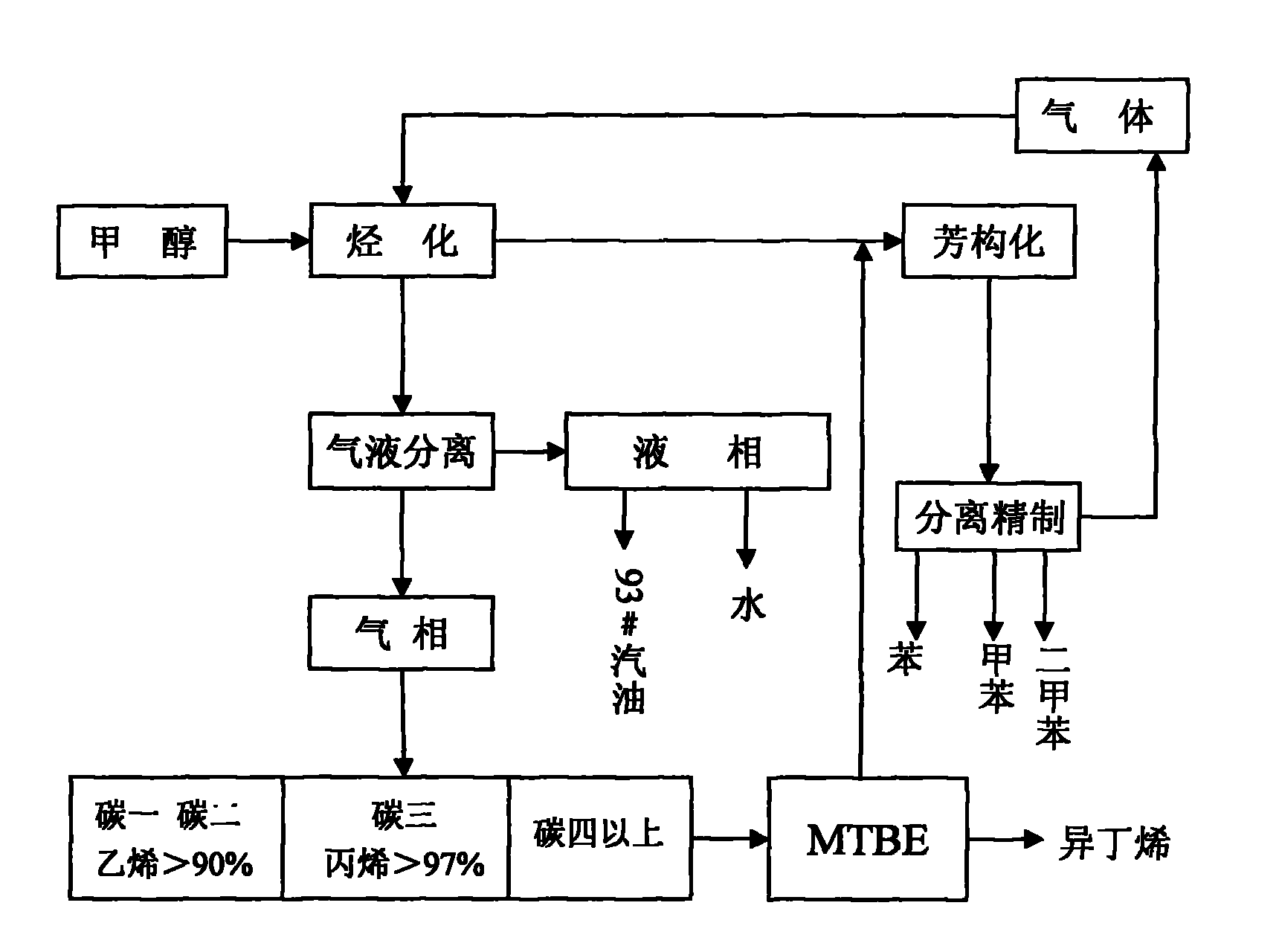
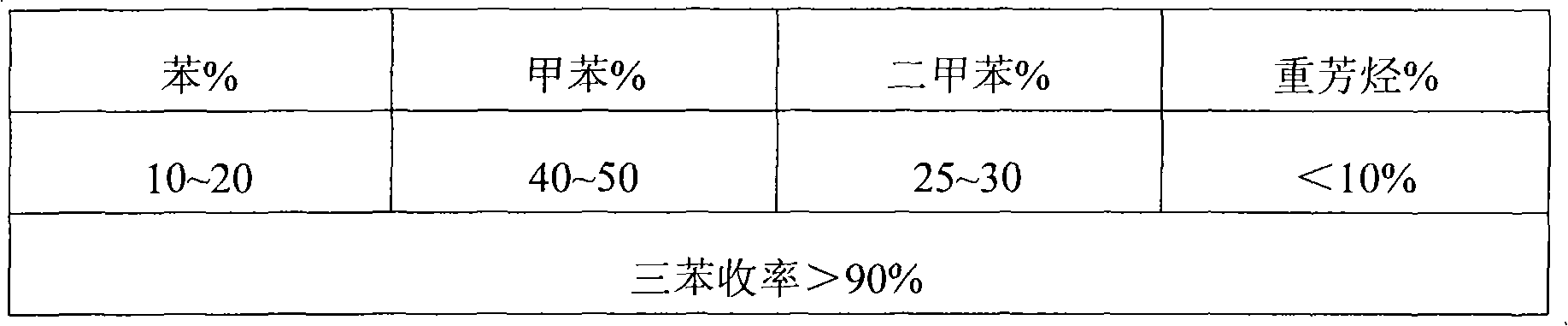
Process for producing low carbon olefin and arene parallel cogeneration gasoline by using methanol as raw material
InactiveCN102146010ALow costReduce energy consumptionHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionEnvironmental resistanceCogeneration
The invention discloses a process for producing low carbon olefin and arene parallel cogeneration gasoline by using methanol as a raw material. In the process, the methanol is used as the raw material and a molecular sieve catalyst is adopted to produce the low carbon olefin and arene parallel cogeneration gasoline by a methanol alkylation reaction and aromatization. In the process, the coal-based methanol is used as the raw material and can replace the conventional petroleum raw material to cogenerate a basis organic chemical raw material, and thus, the dependence degree of the conventional petrochemical industry on the petroleum can be reduced. Meanwhile, the process is also beneficial for reducing the foreign dependence degree of national petroleum, the strategic safety of energy and resources is improved, the production process of the process has low discharge, low pollution and low energy consumption, the requirements on green and environment protection are met, and the process has the advantages of low production cost and strong market competitiveness.
Owner:江苏煤化工程研究设计院有限公司 +2
Apparatus for sensing volatile organic chemicals in fluids
InactiveUS6902701B1High sensitivityHigh selectivityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationOperation modeChemiresistor
A chemical-sensing apparatus is formed from the combination of a chemical preconcentrator which sorbs and concentrates particular volatile organic chemicals (VOCs) and one or more chemiresistors that sense the VOCs after the preconcentrator has been triggered to release them in concentrated form. Use of the preconcentrator and chemiresistor(s) in combination allows the VOCs to be detected at lower concentration than would be possible using the chemiresistor(s) alone and further allows measurements to be made in a variety of fluids, including liquids (e.g. groundwater). Additionally, the apparatus provides a new mode of operation for sensing VOCs based on the measurement of decay time constants, and a method for background correction to improve measurement precision.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Process for low-temperature metal-organic chemical vapor deposition of tungsten nitride and tungsten nitride films
InactiveUS6884466B2Layered productsNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsTungsten nitrideNitrogen
Processes for producing tungsten nitride and tungsten nitride films are provided in which a tungsten carbonyl compound and a nitrogen-containing reactant gas are reacted at a temperature below about 600° C. Tungsten nitride precursors are also included which comprise a tungsten carbonyl compound capable of forming a tungsten nitride film in the presence of a nitrogen-containing reactant gas at a temperature of less than about 600° C. A process for forming a film by atomic layer deposition is also provided which includes introducing a substrate having a surface into a deposition chamber and heating the substrate to a temperature sufficient to allow adsorption of a tungsten source precursor or an intermediate thereof, and thereafter sequentially introducing by pulsing: a tungsten source precursor which is absorbed as a monolayer, a purging inert gas, a nitrogen-containing gas for reacting with the monolayer to form a first tungsten nitride layer on the substrate surface, and an inert purging gas, and repeating the sequence to form a film of desired thickness.
Owner:GELEST +1
Process For Producing Zno Transparent Conductive Film By Mocvd (Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) Method
InactiveUS20080032044A1Low costEliminate useChemical vapor deposition coatingPhotovoltaic energy generationWater vaporGas phase
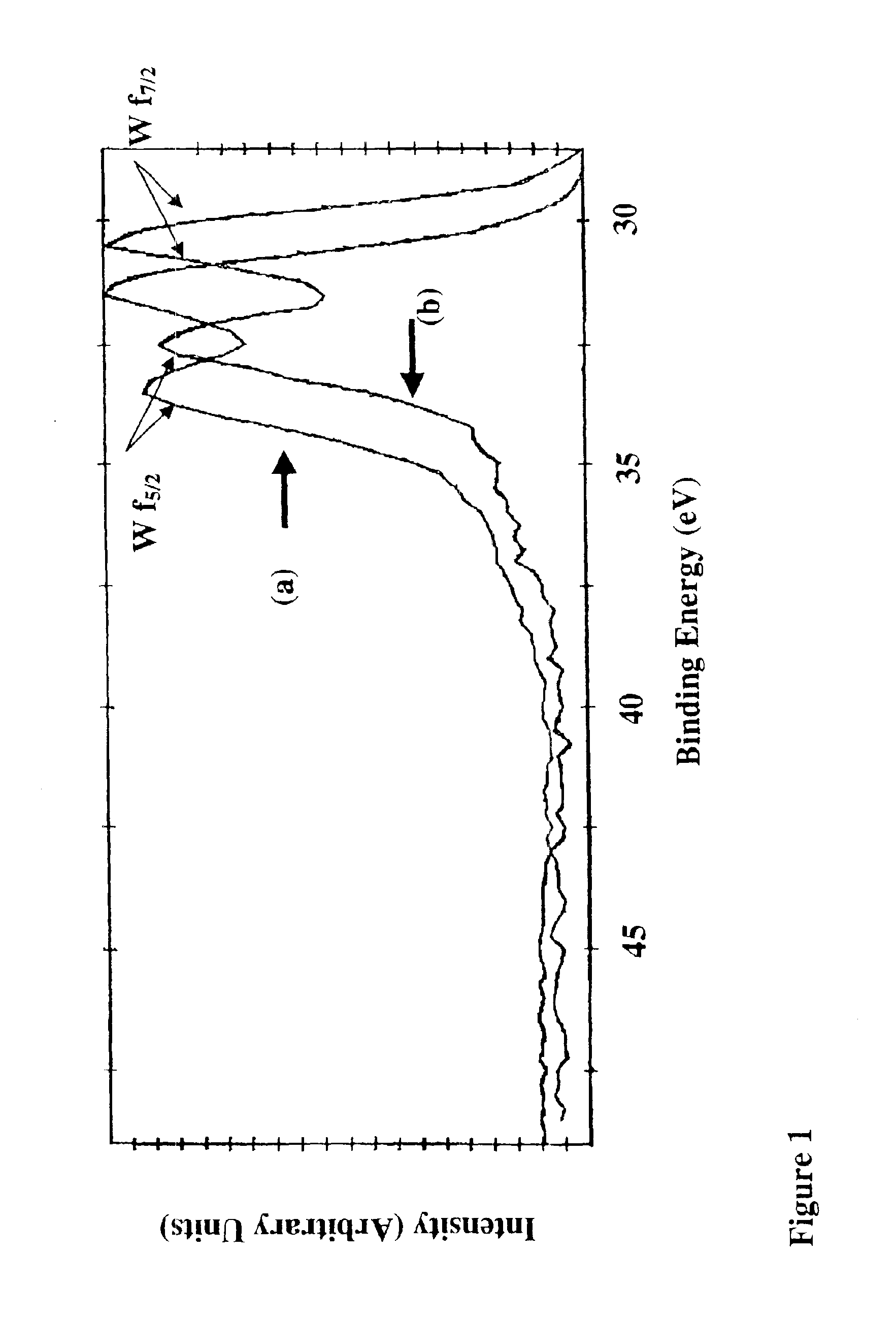
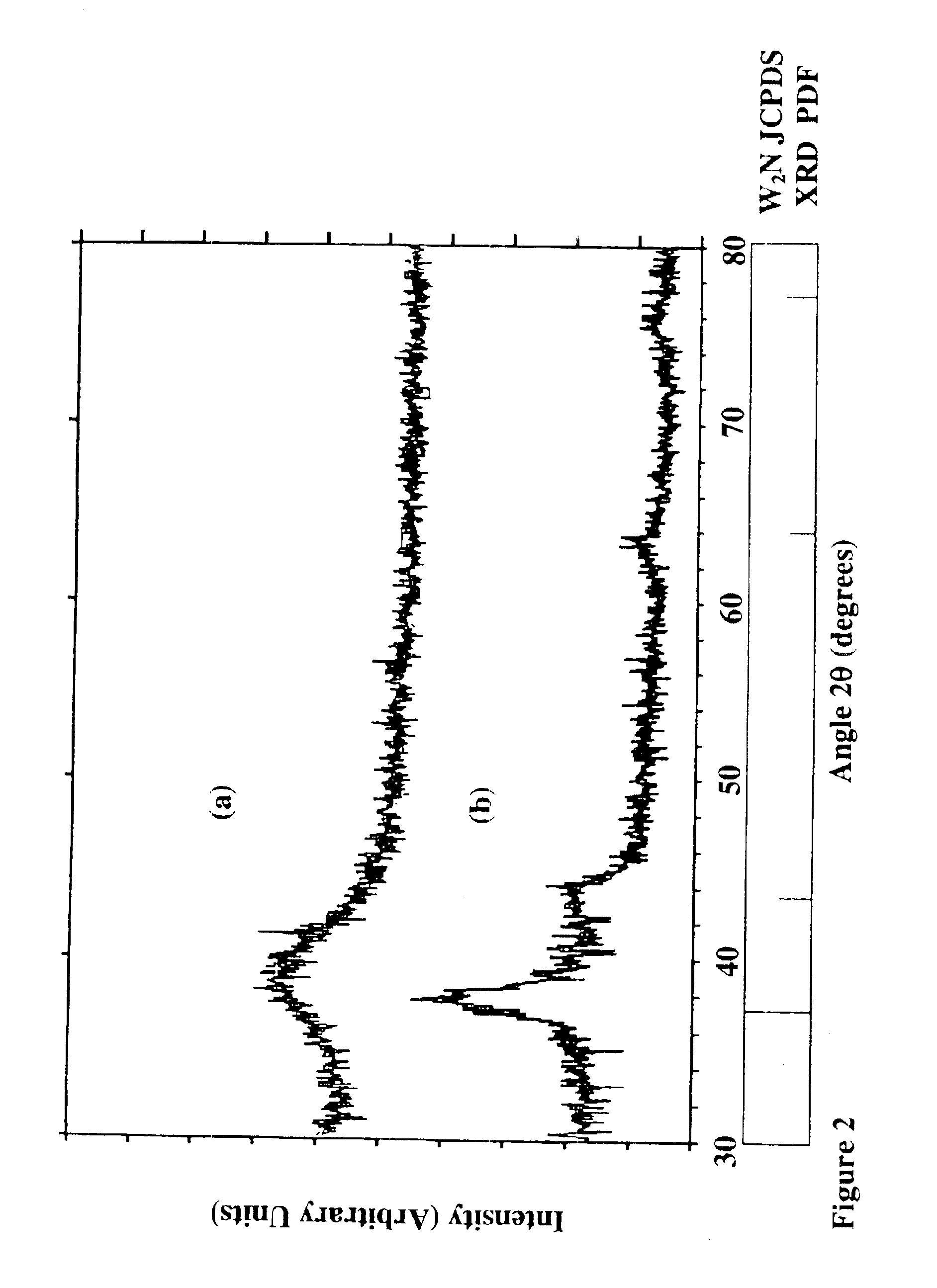
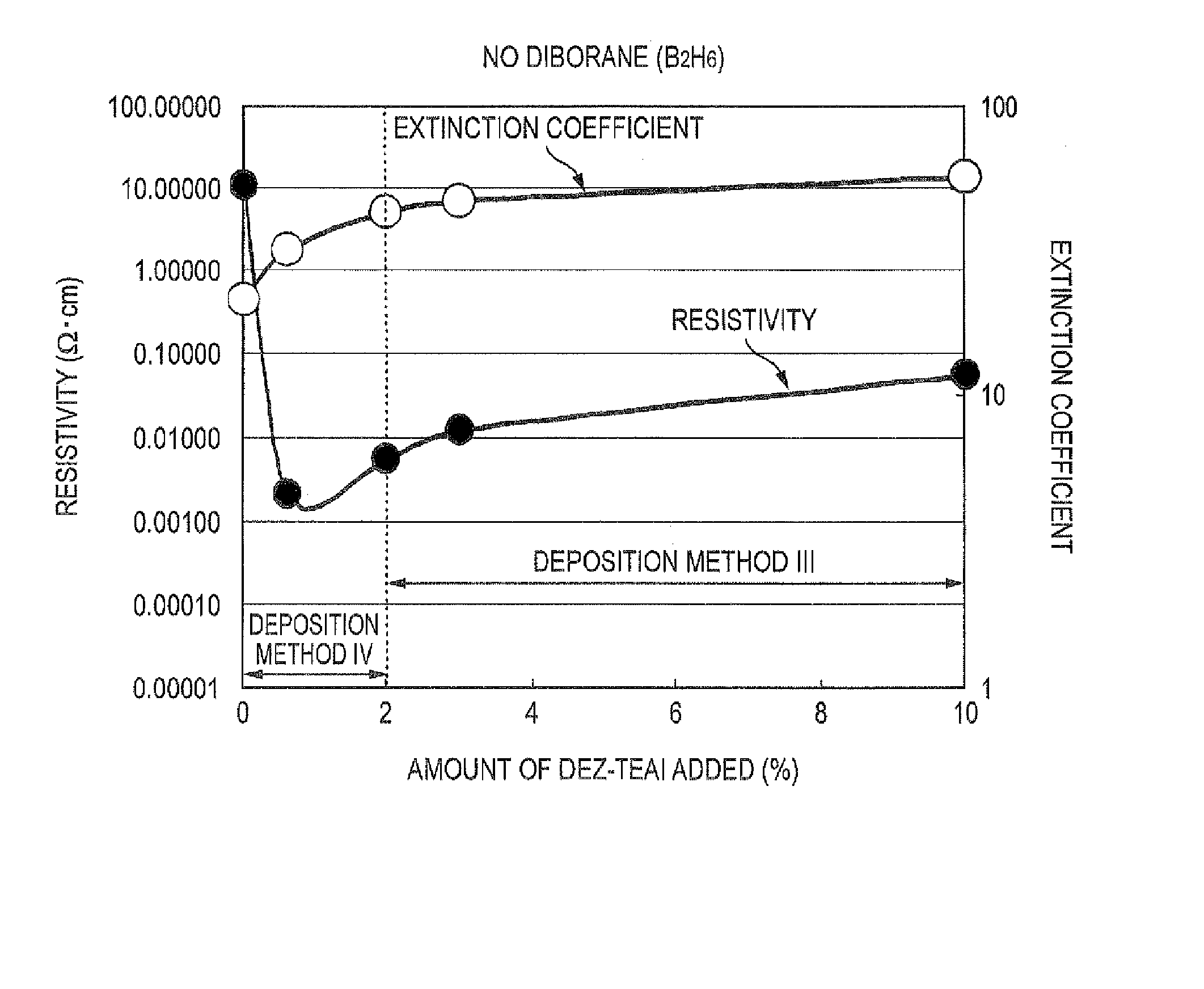
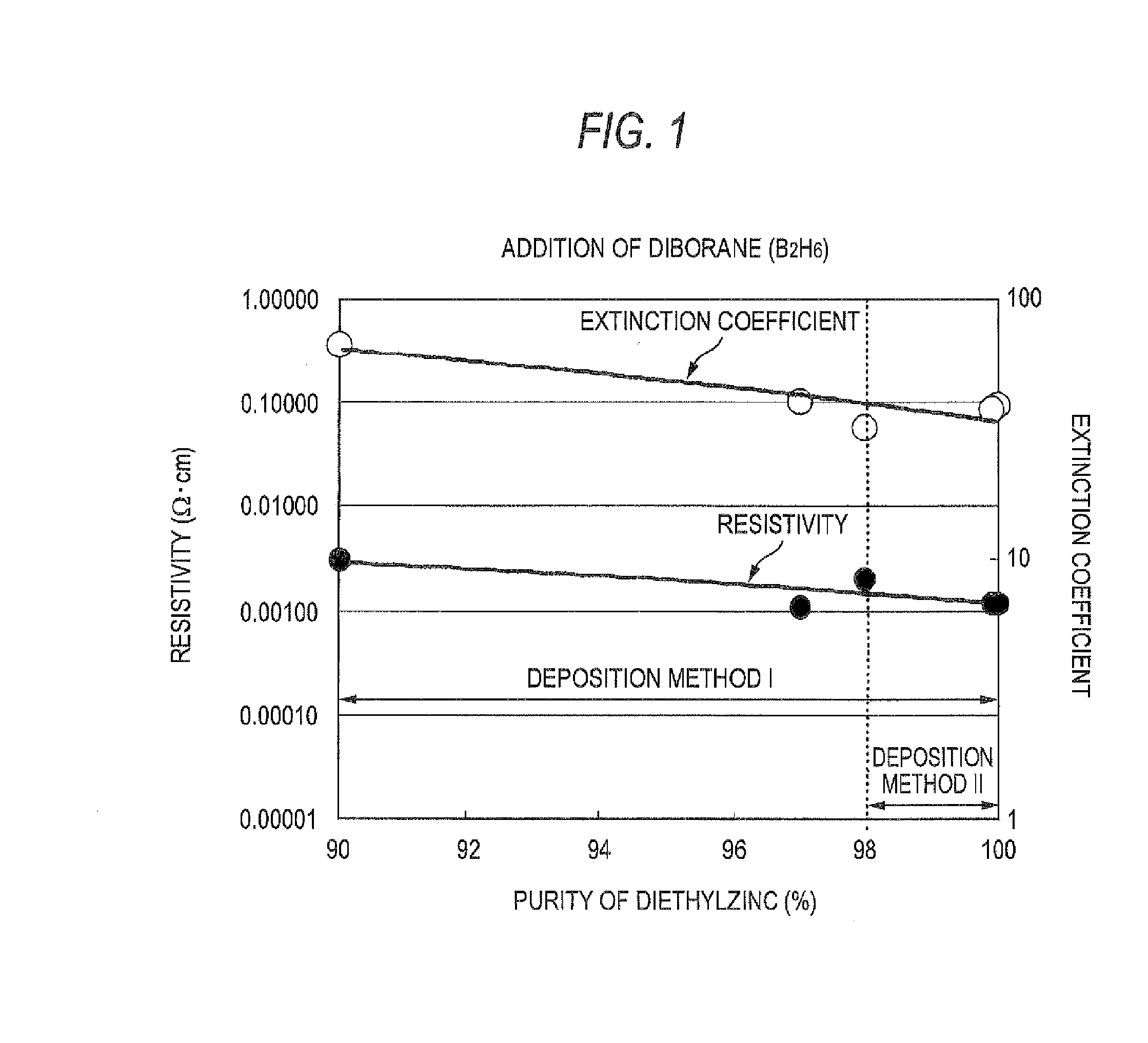
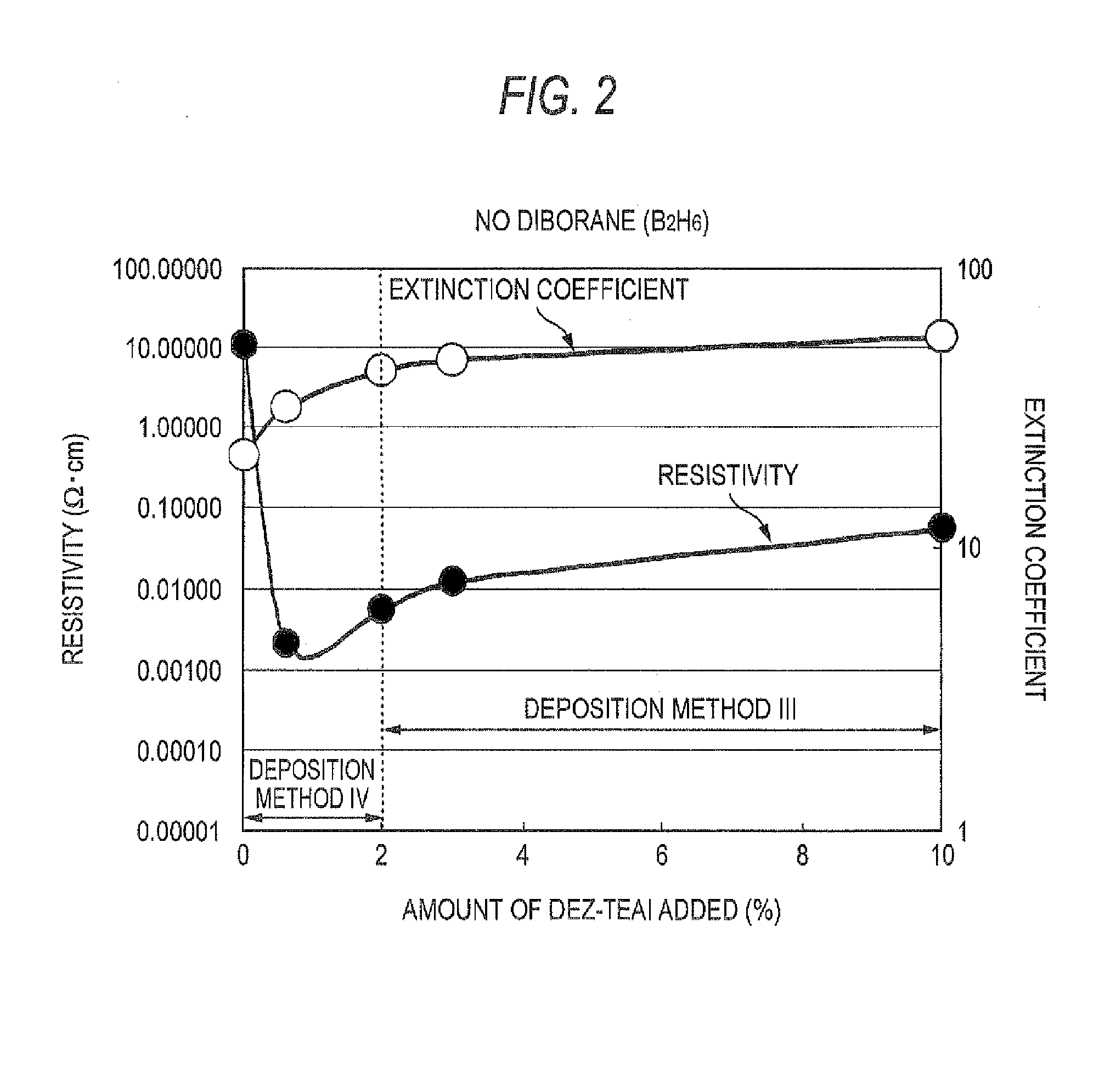
The triethylaluminum contained as an impurity in low-purity raw-material diethylzinc, which is inexpensive, is utilized as an additive to reduce the cost of film formation. Diethylzinc having a low purity (99.99-98% or 99.99-90%) is used as a raw material to produce a ZnO transparent conductive film by the MOCVD (metal-organic chemical vapor deposition) method. Water vapor (H2O) is used as an oxidizing agent and the triethylaluminum contained as an impurity in the raw material is utilized as an additive (diborane is further added as an additive) to cause the diethylzinc, the water vapor (H2O), and the triethylaluminum (and the diborane) to undergo a vapor-phase reaction to produce a ZnO transparent conductive film.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Method for synthesizing amphoteric slow-breaking quick-setting asphalt emulsifier
InactiveCN101712625AWide selectionWide adaptabilityOrganic compound preparationTransportation and packagingChemical synthesisSolubility
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a novel amphoteric slow-breaking quick-setting asphalt emulsifier, belonging to the technical field of organic chemical synthesis. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting oleic acid with polyamine to generate acid amide polyamine, and then adding chloroactic acid to generate halogenating reaction to prepare the asphalt emulsifier, wherein the polyamine is the mixture of diethylenetriamine and triethylene tetramine. The water solubility of the hydrophilic radical of the emulsifier synthesized by the process is stronger than those of like emulsifiers, thereby obviously lowering the critical micelle concentration (CMC) value, and the particles of the produced asphalt emulsion are finer, smoother and evener. The emulsifier can effectively prevent asphalt from settling, increases the storage stability of the asphalt emulsion, reasonably regulates the charge ratio, widens the selectivity on stone materials in the application of slurry seal construction, enables the mixing time to be sufficient, and has obvious quick-setting effect and improved project quality.
Owner:河南新友公路技术有限公司 +1
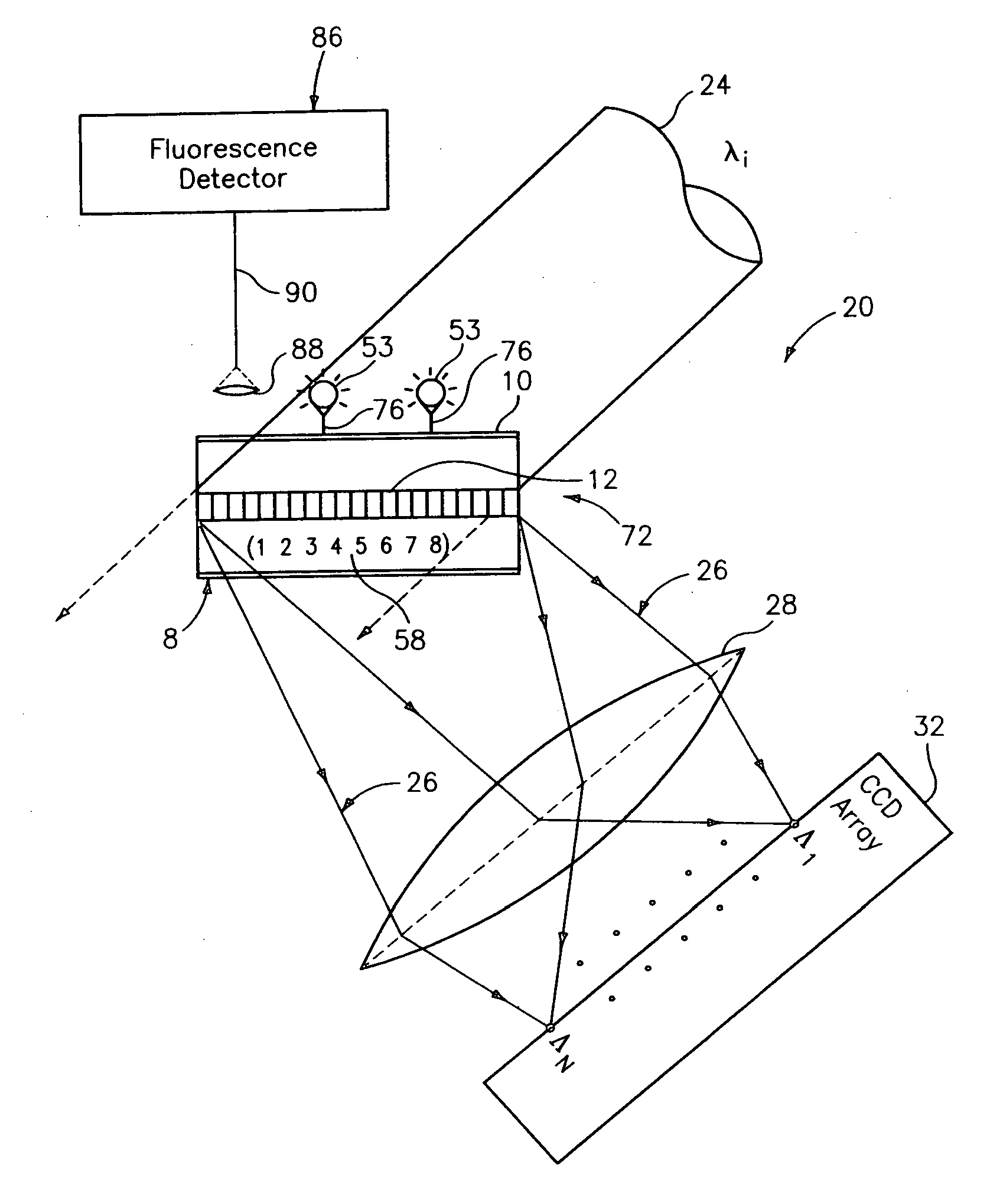
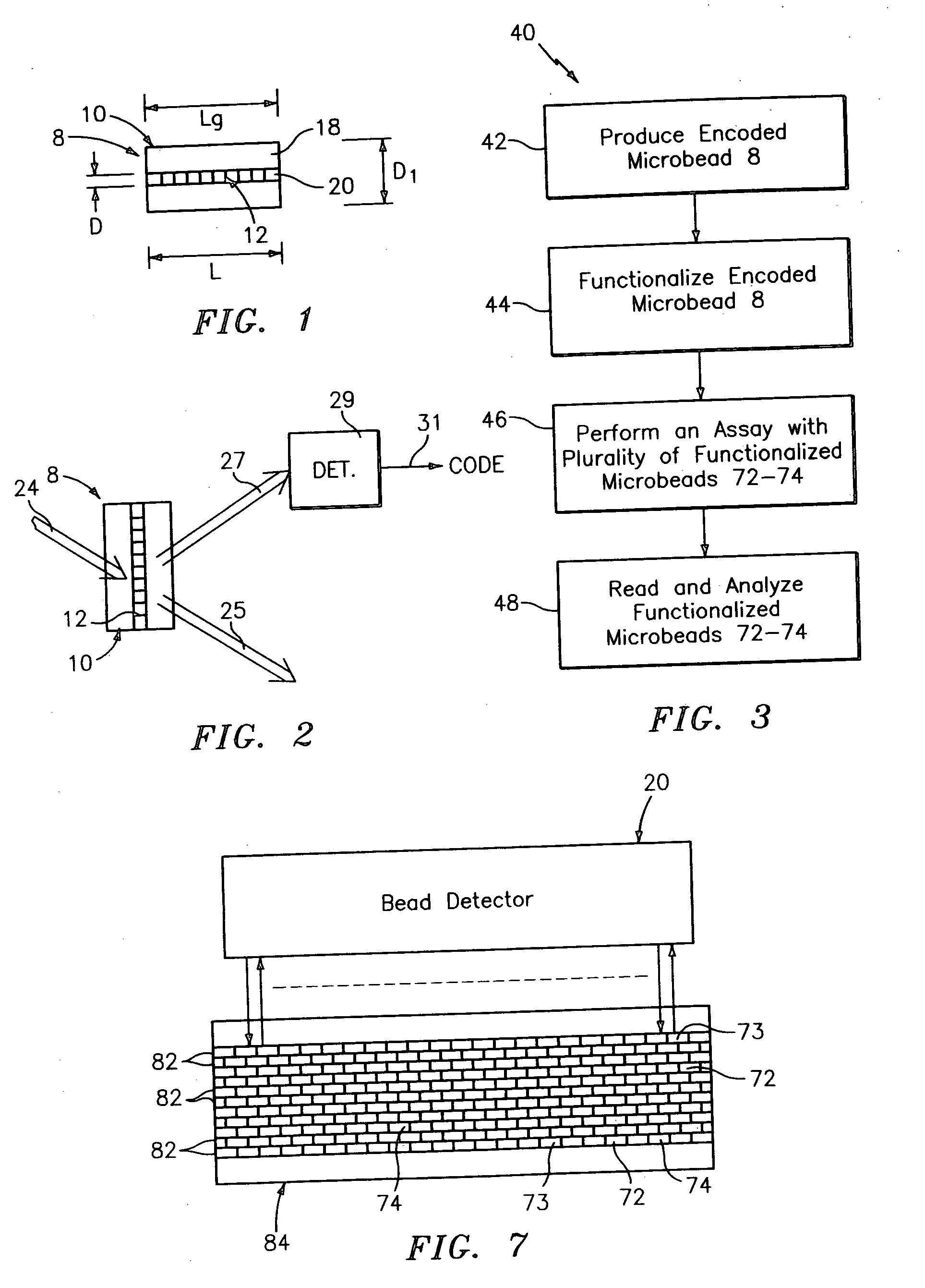
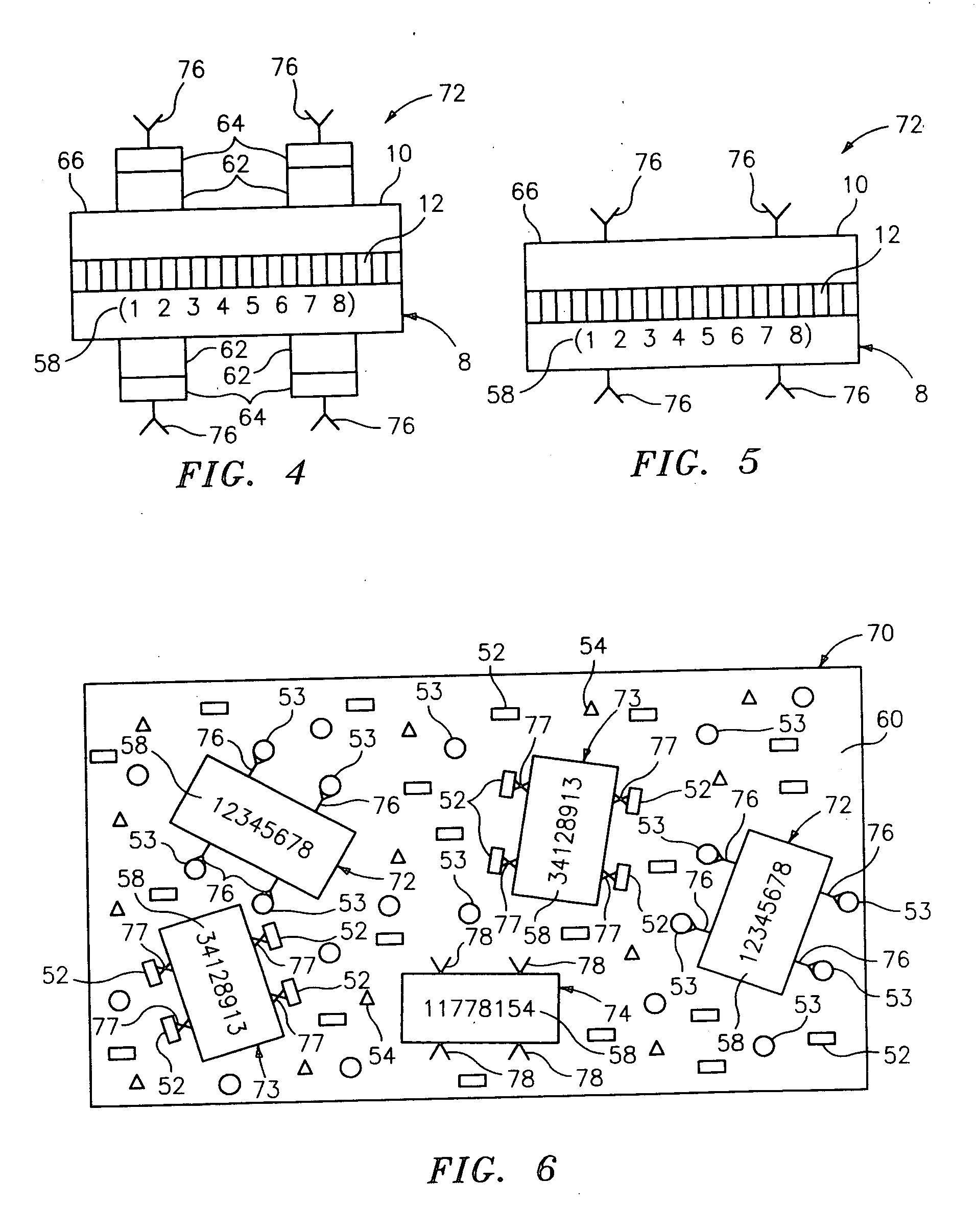
Diffraction grating-based encoded element having a substance disposed thereon
InactiveUS20060057729A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionMulti materialPolynucleotide
The present invention generally provides multicomponent articles of manufacture and methods of making them. In its broadest aspect, the invention provides a multicomponent article that includes a diffraction grating-based encoded element, wherein the encoded element includes an optical substrate having at least one surface, and an optical coding element; and a substance disposed on at least a portion of the surface of the substrate. The optical substrate may be made from a wide variety of materials. Importantly the multicomponent article may be a reagent particle wherein the substance includes a reagent. The reagent may be chosen from a wide range of biological macromolecules and oligomeric molecules, from any organic chemical or inorganic chemical compound including pharmaceutical agents and candidate pharmaceutical agents, modifications of any of them, and from any microbiological entity, a cell, and similar entities. In another aspect the invention provides a coded reagent library including a plurality of reagent particles described herein the preceding paragraphs. In another aspect the invention provides a method of preparing a multicomponent article including the steps of providing a diffraction grating-based encoded element, and binding a substance to a surface of said optical substrate. The invention also provides a method of preparing a coded reagent library. Additionally the invention provides a method of synthesizing a polynucleotide reagent on a multicomponent article.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
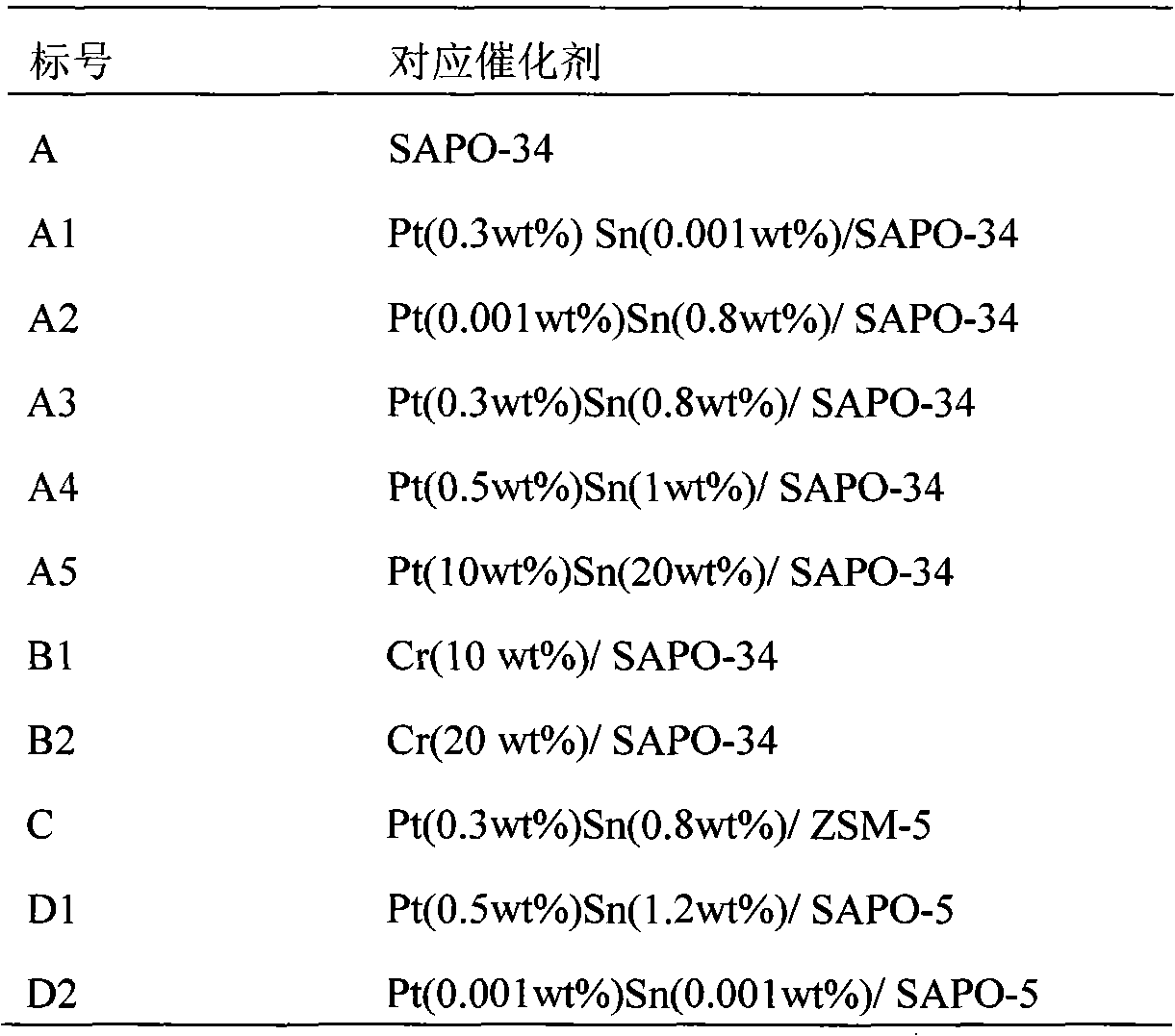
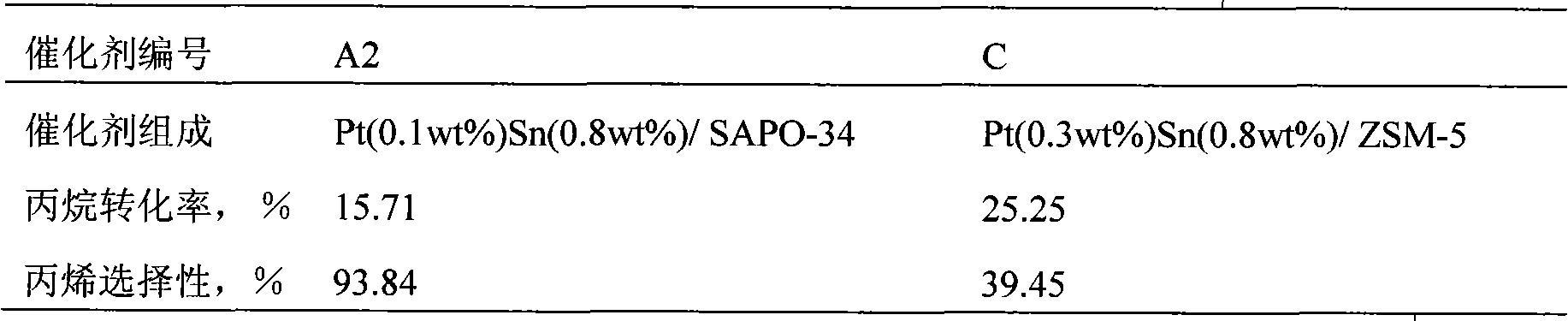
Catalyst for preparing olefin by dehydrogenating low-carbon alkane, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101623633AHigh selectivitySuitable for acidityCatalyst activation/preparationHydrocarbonsAlkaneMolecular sieve
The invention relates to a catalyst for preparing olefin by dehydrogenating low-carbon alkane, and a preparation method and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of the preparation of basic organic chemical raw materials. The catalyst is prepared by a dipping method of using an aluminium silicophosphate molecular sieve as a carrier, VIII group or VIB group elements as active constituents and IVA group elements as an auxiliary agent. In the process for preparing olefin by dehydrogenating low-carbon alkane, the catalyst is firstly reduced by hydrogen gas, then participates in a reaction, and is finally regenerated. Compared with the existing catalyst for preparing olefin by dehydrogenating low-carbon alkane, the catalyst has a pore shape selecting function and moderate acidity, thereby the selectivity of the low-carbon alkane can reach more than 90 percent in the process for preparing olefin by dehydrogenating low-carbon alkane. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple; the regeneration process flow of the reaction has a large choice, a fixed bed, a fluidized bed or a moving bed can be used as a reactor, and the catalyst can be regenerated in the reactor or outside the reactor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
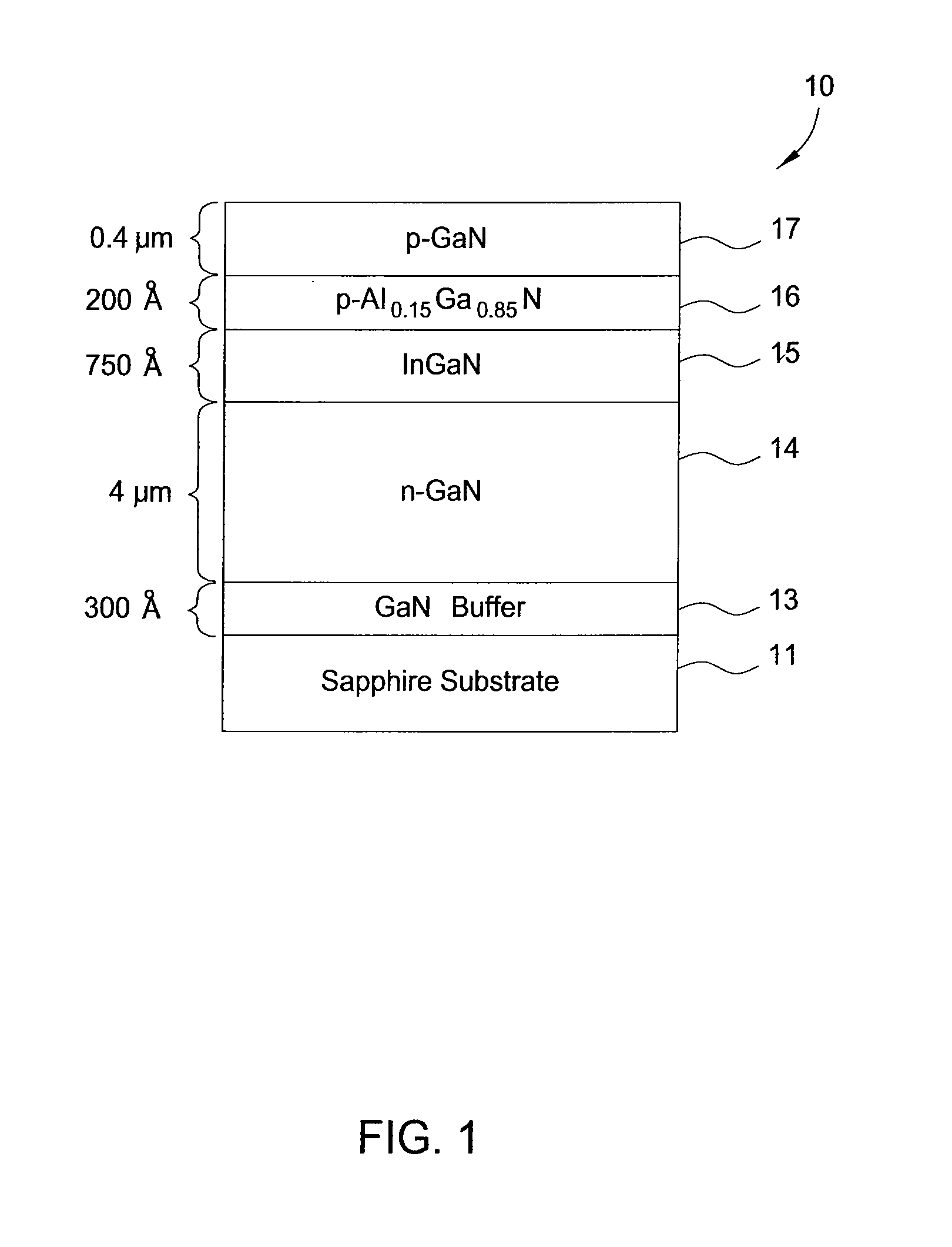
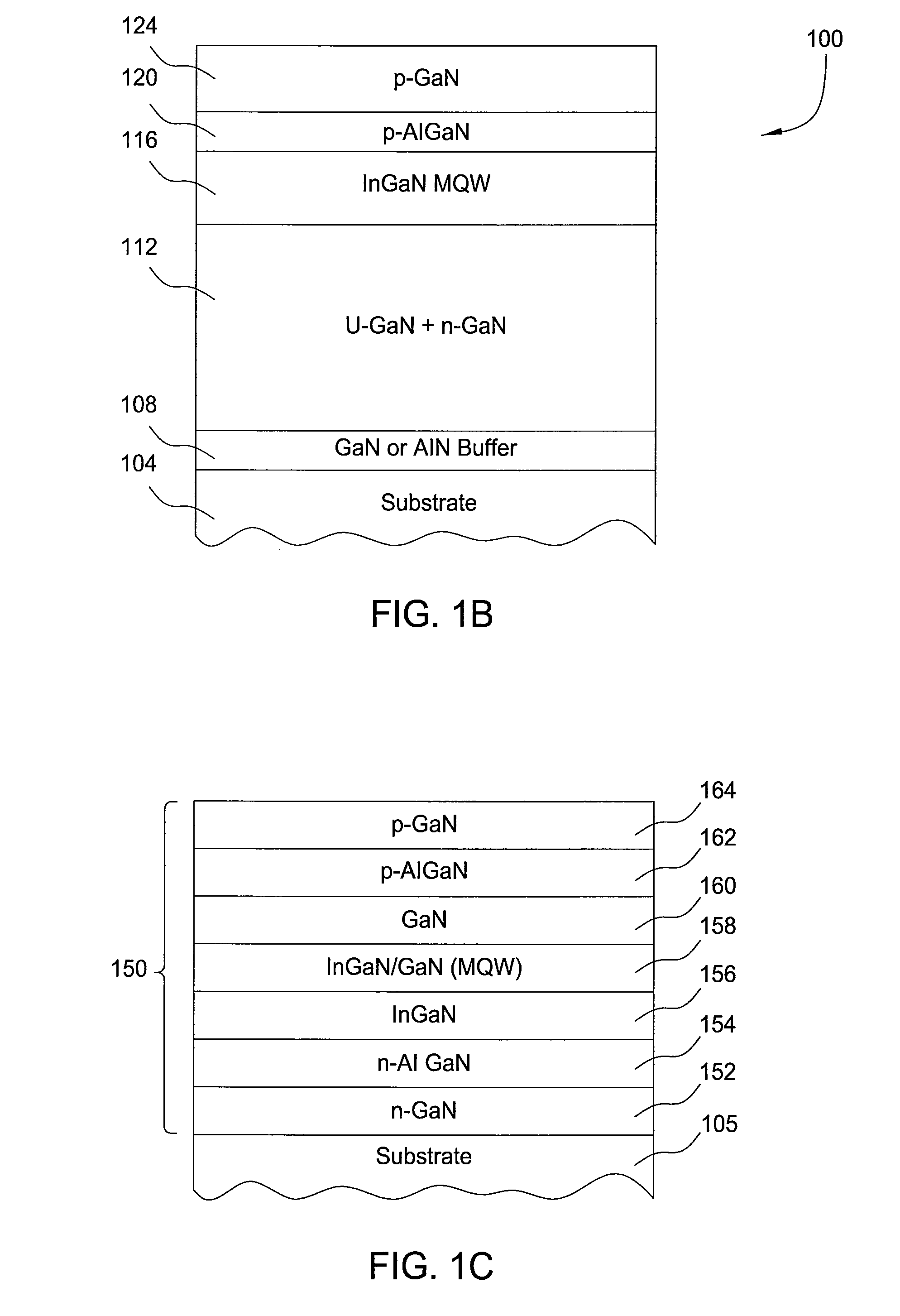
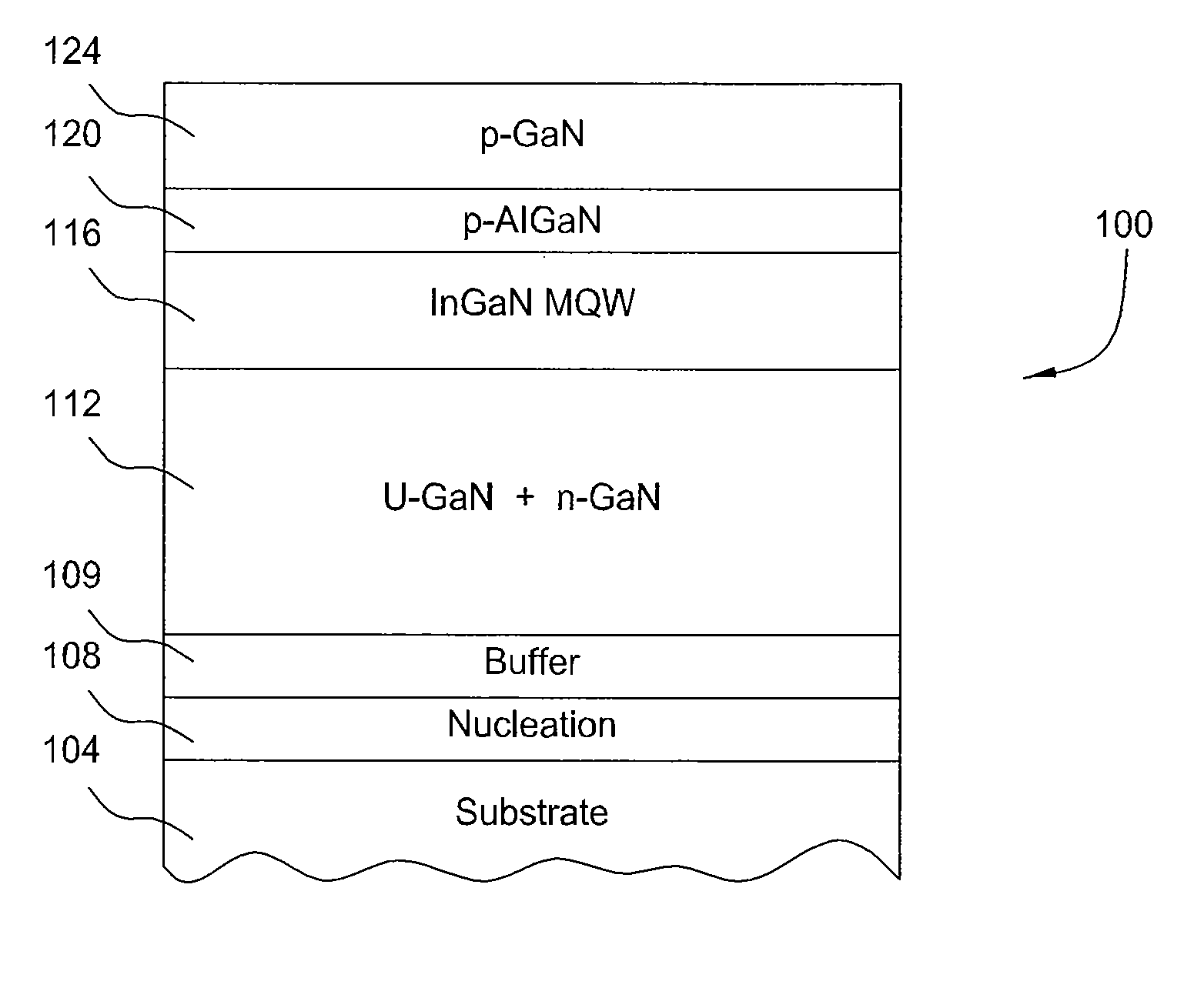
Growth of indium gallium nitride (InGaN) on porous gallium nitride (GaN) template by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD)
InactiveUS20090001416A1Increase indium incorporationLarge emissionsPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumGallium nitride
Si-doped porous GaN is fabricated by UV-enhanced Pt-assisted electrochemical etching and together with a low-temperature grown buffer layer are utilized as the template for InGaN growth. The porous network in GaN shows nanostructures formed on the surface. Subsequent growth of InGaN shows that it is relaxed on these nanostructures as the area on which the growth takes place is very small. The strain relaxation favors higher indium incorporation. Besides, this porous network creates a relatively rough surface of GaN to modify the surface energy which can enhance the nucleation of impinging indium atoms thereby increasing indium incorporation. It shifts the luminescence from 445 nm for a conventionally grown InGaN structure to 575 nm and enhances the intensity by more than two-fold for the growth technique in the present invention under the same growth conditions. There is also a spectral broadening of the output extending from 480 nm to 720 nm.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
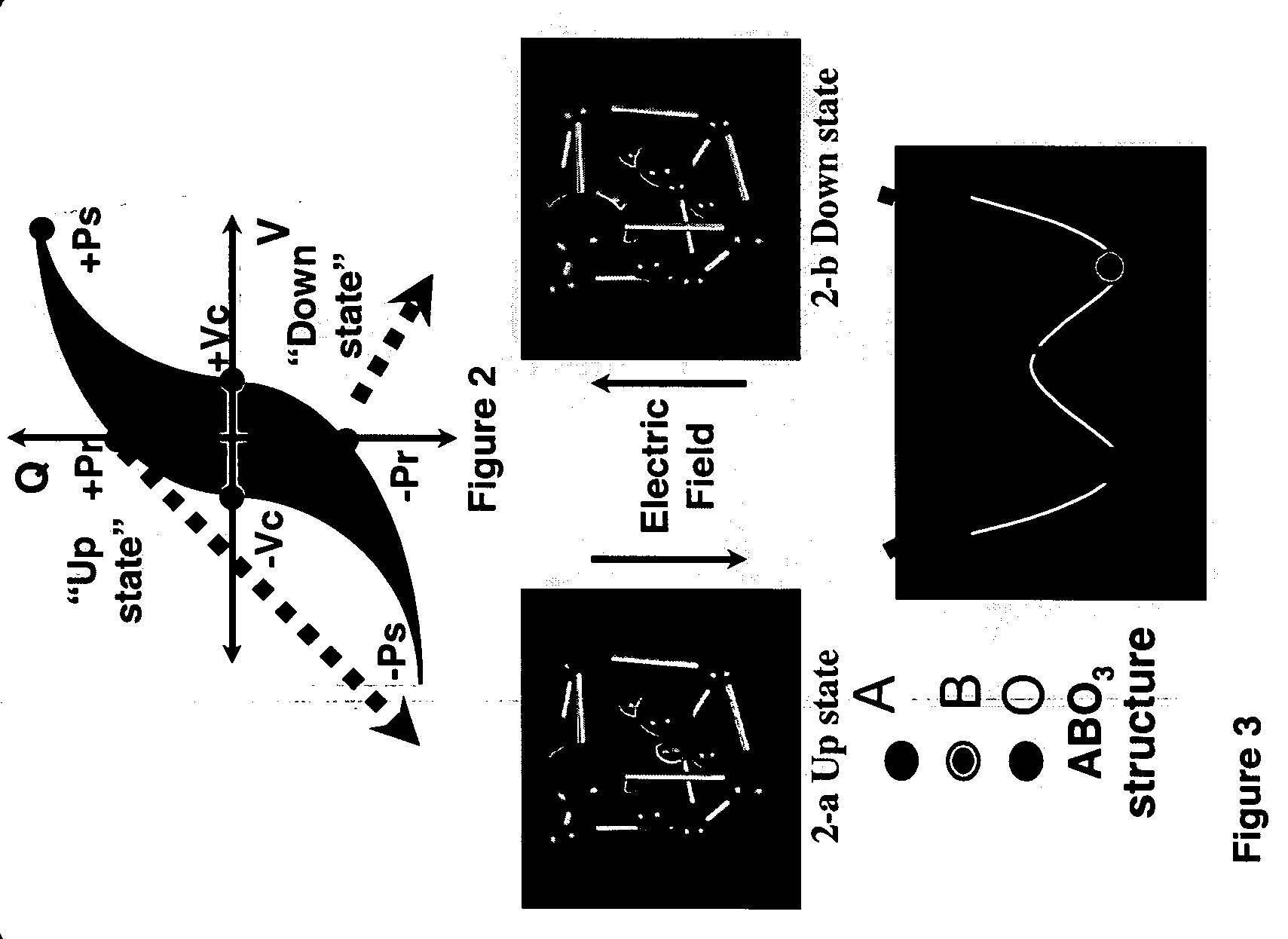
Clay/organic chemical compositions useful as additives to polymer, plastic and resin matrices to produce nanocomposites and nanocomposites containing such compositions
InactiveUS6380295B1Good dispersionImprove structural strengthCoatingsSilicon compoundsAmmonium compoundsWater dispersible
This invention is of a hybrid organoclay that consists of an organic chemical / phyllosilicate clay intercalate that has been ion-exchanged with quaternary ammonium compounds. Since this hybrid organoclay is hydrophobic, it can be washed in water to remove reaction salts and excess water soluble or water dispersible polymers to give a clean product via inexpensive means such as filtration. This allows a better dispersing composition to be prepared without the difficulties of isolation presented by prior art which uses energy intensive means to remove the bulk of the water from the final product and cannot be easily washed. In one aspect, the present invention provides a solid clay / chemical composition that comprises: (a) one or more smectite clays, (b) a quaternary ammonium compound which reacts via an ion exchange mechanism with the smectite clay, and (c) one or more non-anionic organic materials that intercalate with the clay. The invention is useful both as an ingredient to form nanocomposites and as a rheological additive.
Owner:ELEMENTIS SPECIALTIES INC
Method for grafting polymer on inorganic material surface
The present invention discloses a method of grafting a polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials. The polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol which contains amino or hydroxyl at the chain-end by a covalent bond or an ionic bond, or a compound containing glucose units is firstly fixed at the surface of the inorganic materials, so as to have a reductive organic chemical group on the surface; then a high cerium salt and a polymerizable monomer are added, the present invention makes use of the high cerium salt and the reductive organic group on the surface of the inorganic materials to constitute an oxidation-reduction initiation system, so as to initiate the monomer polymerization under the acidic condition, further to graft the polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials. The method of the present invention can graft the polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials easily, which has the advantages of simple reaction process, mild reaction condition and high grafting rate, so the present invention is particularly applicable for the grafting of a water-soluble polymer or a polymer hydrogel thin layer on the surface of the inorganic materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
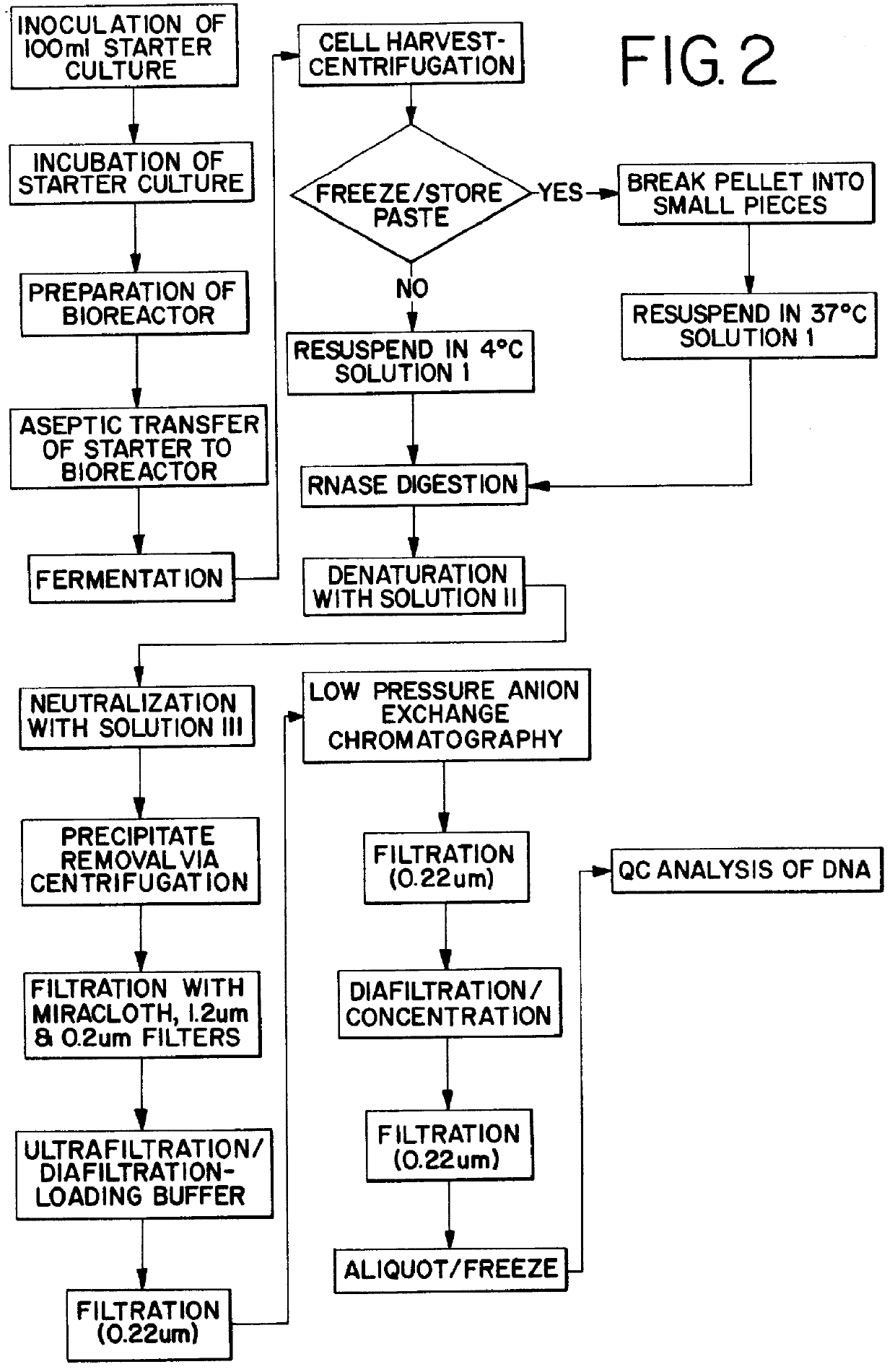
Methods for purifying nucleic acids
InactiveUS6011148AEasy to purifyImprove efficacySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsUltrafiltrationPlasmid dna
Methods are provided for producing highly purified compositions of nucleic acids by using tangential flow ultrafiltration. A scaleable process for producing pharmaceutical grade plasmid DNA, useful for gene therapy, is provided, which is efficient and avoids the use of toxic organic chemicals.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
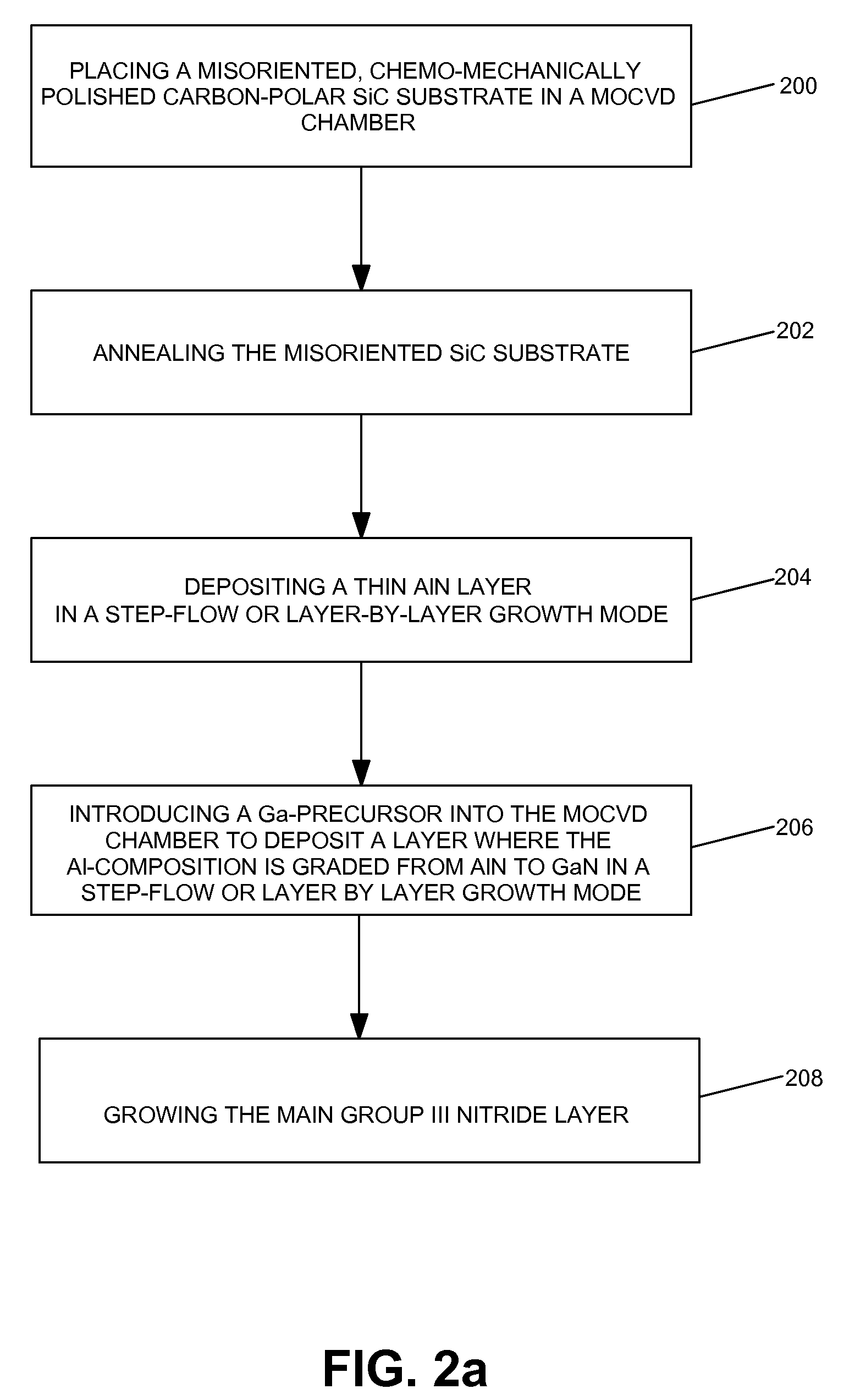
Method for heteroepitaxial growth of high-quality N-face GaN, InN, and AIN and their alloys by metal organic chemical vapor deposition
ActiveUS7566580B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseAlloy
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hotwall reactor and method for reducing particle formation in GaN MOCVD
InactiveUS20080050889A1Suppress formationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactor designChemical vapor deposition
Systems and methods to suppress the formation of parasitic particles during the deposition of a III-V nitride film with, e.g., metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) are described. In accordance with certain aspects of the invention, a hotwall reactor design and methods associated therewith, with wall temperatures similar to process temperatures, so as to create a substantially isothermal reaction chamber, may generally suppress parasitic particle formation and improve deposition performance.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
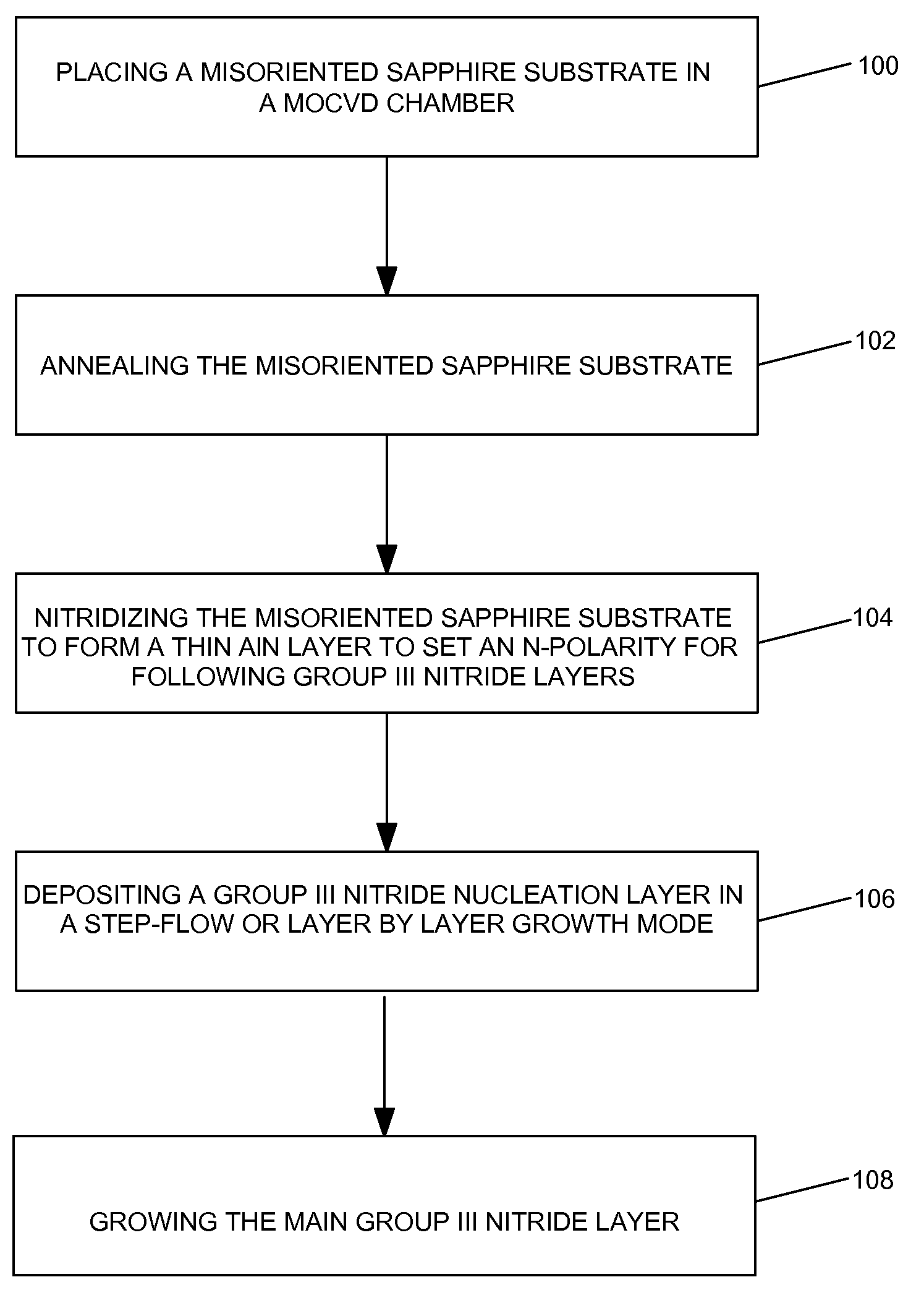
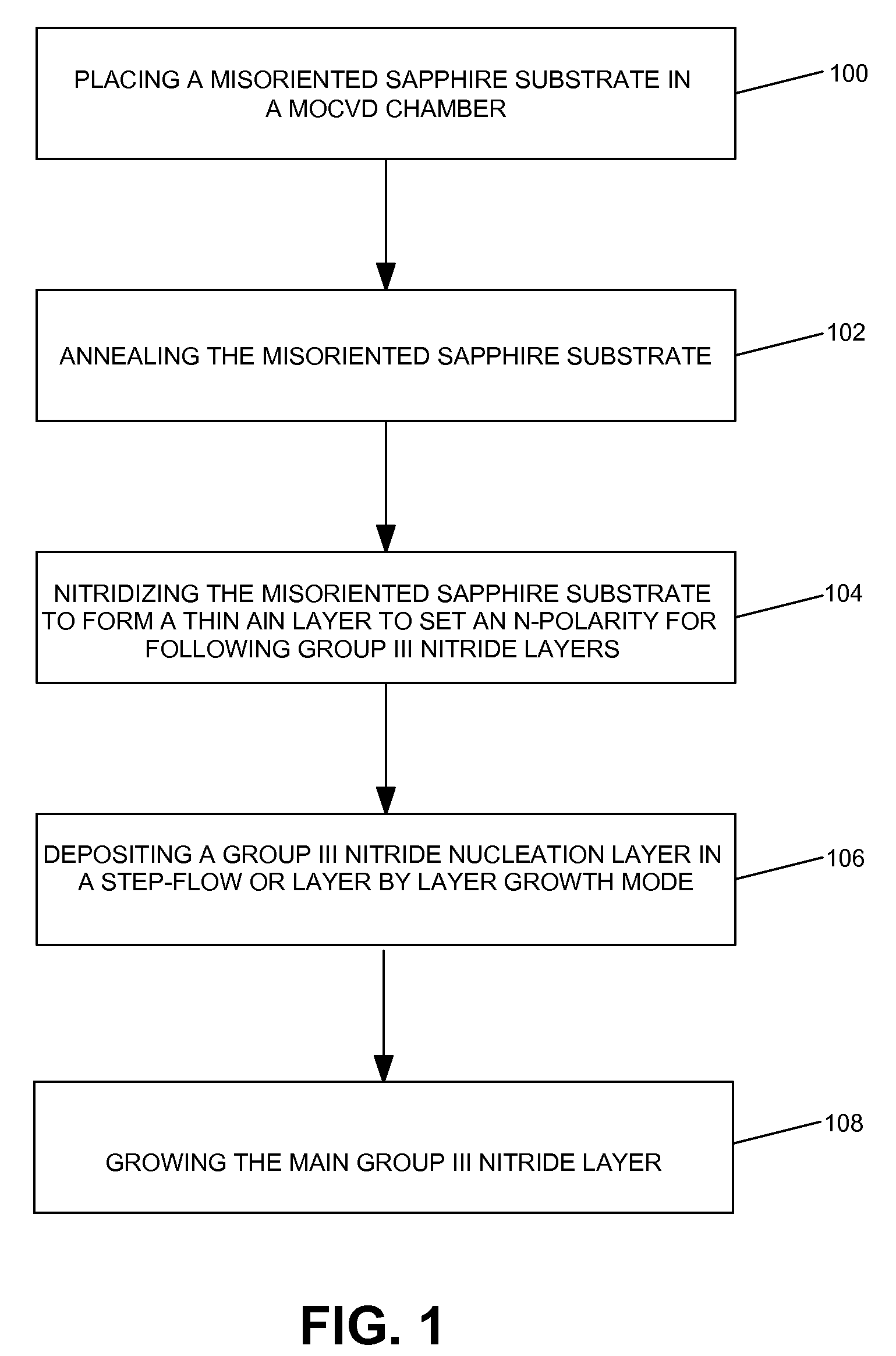
METHOD FOR HETEROEPITAXIAL GROWTH OF HIGH-QUALITY N-FACE GaN, InN, AND AlN AND THEIR ALLOYS BY METAL ORGANIC CHEMICAL VAPOR DEPOSITION
ActiveUS20080113496A1Enhanced charge transport propertiesPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAlloyChemical vapor deposition
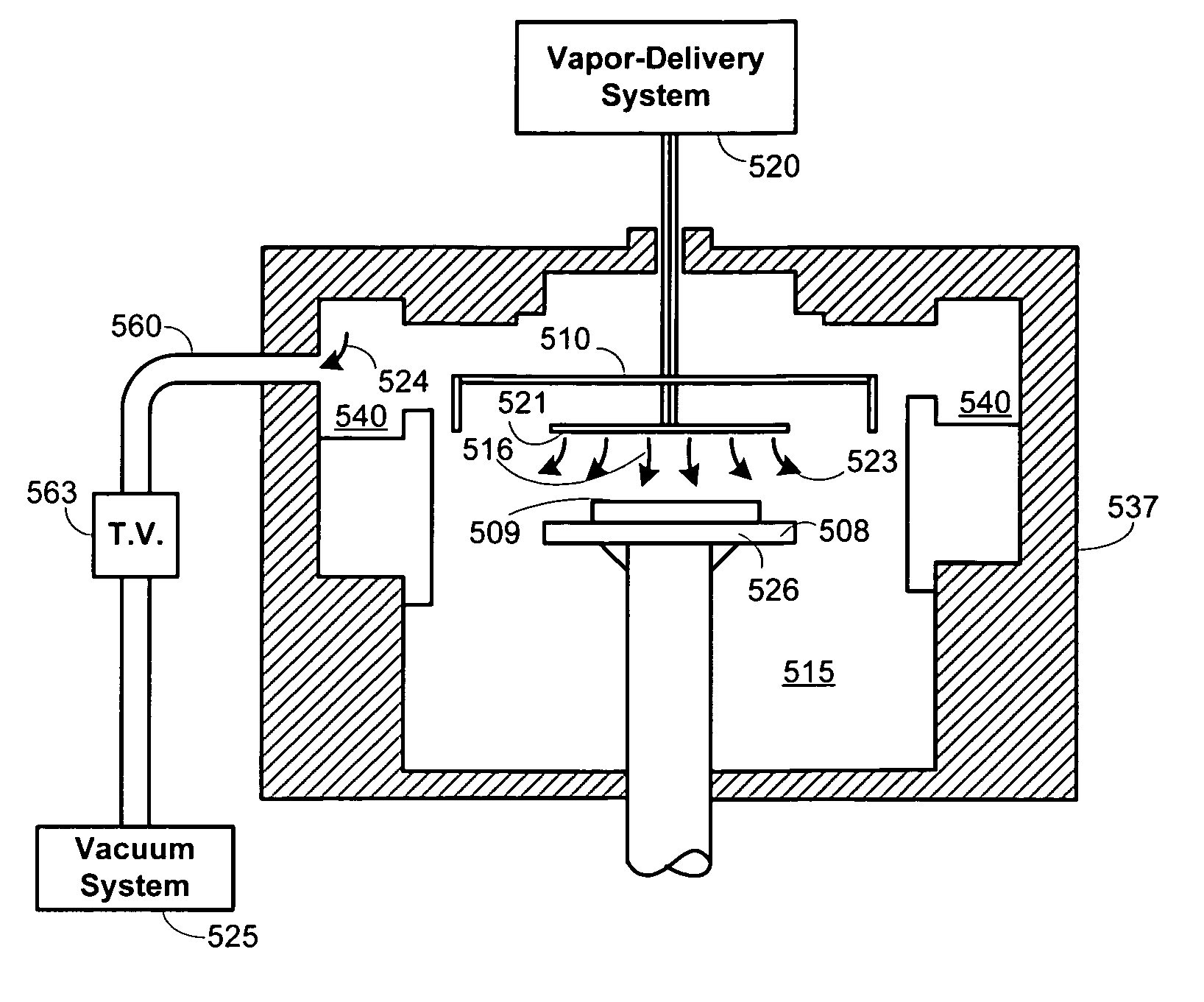
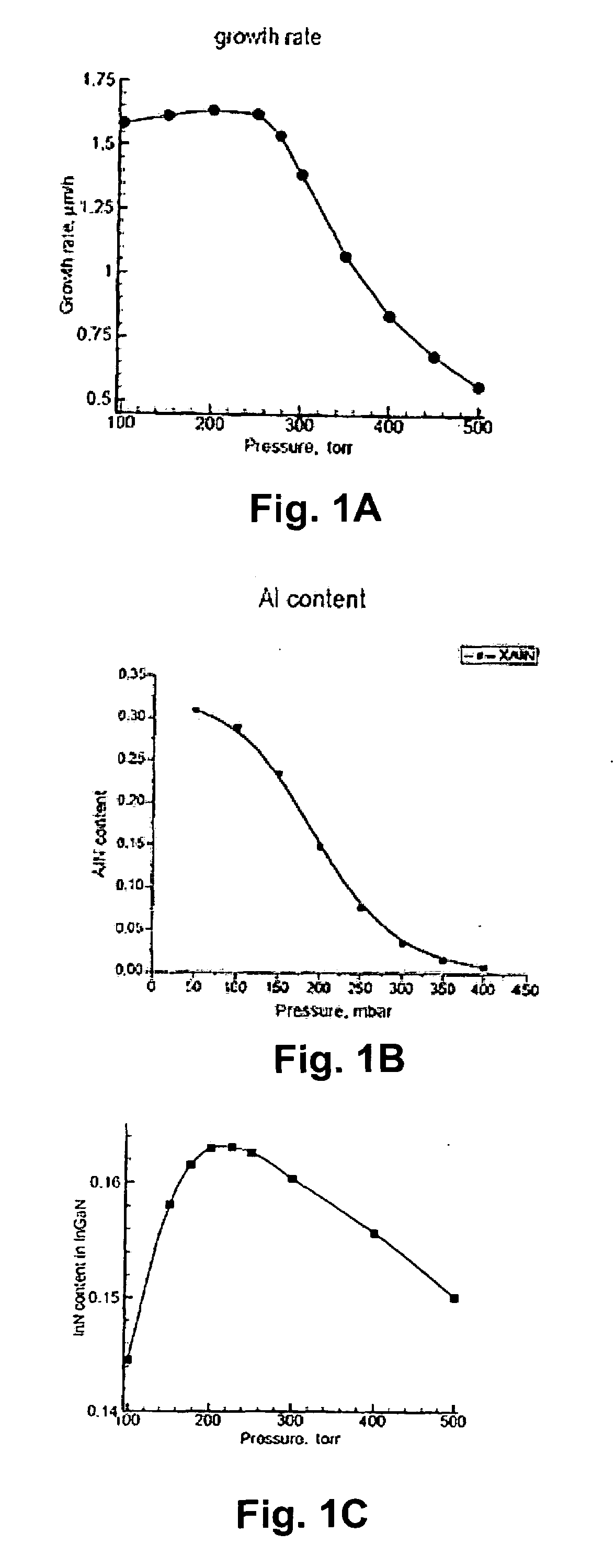
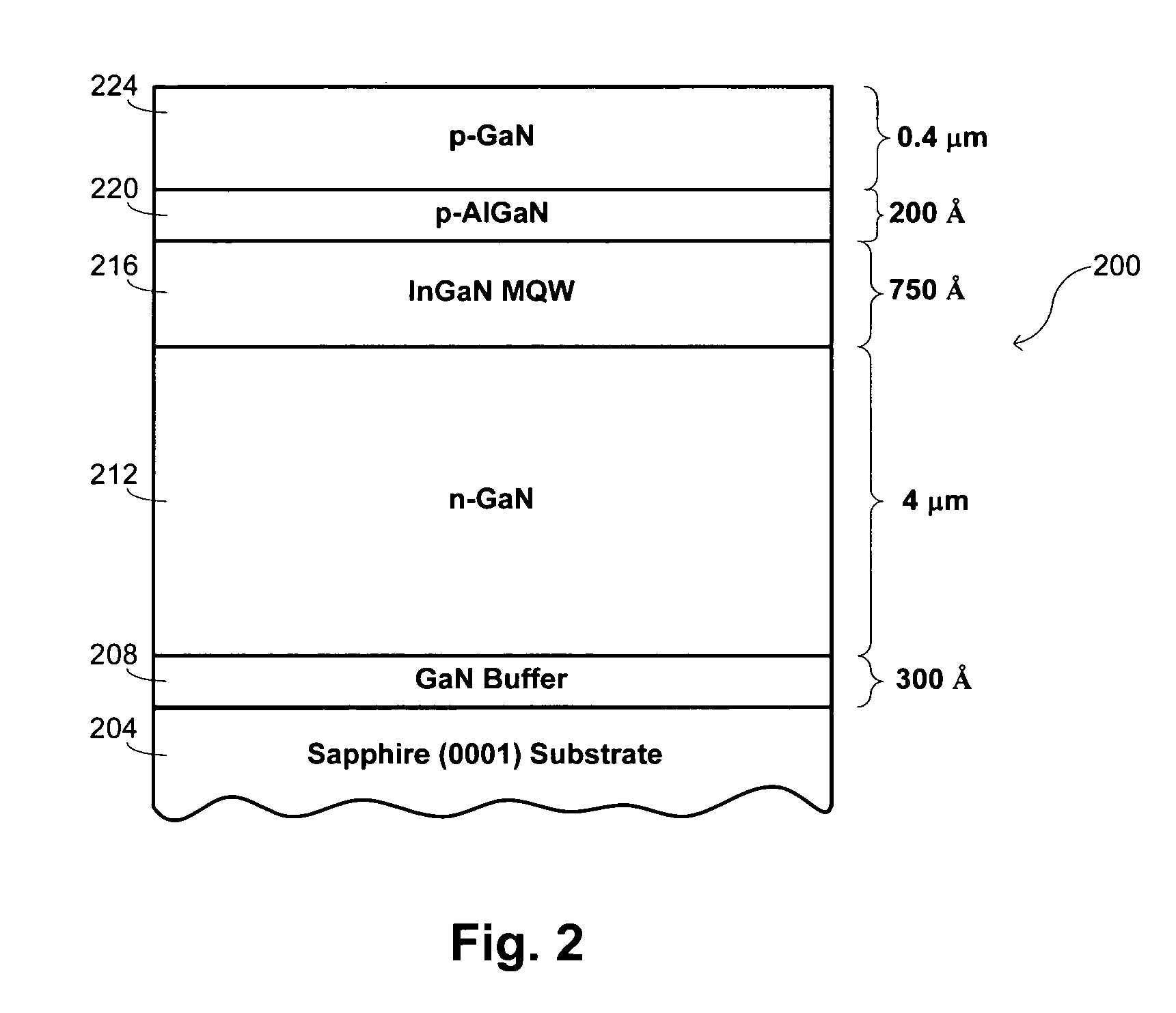
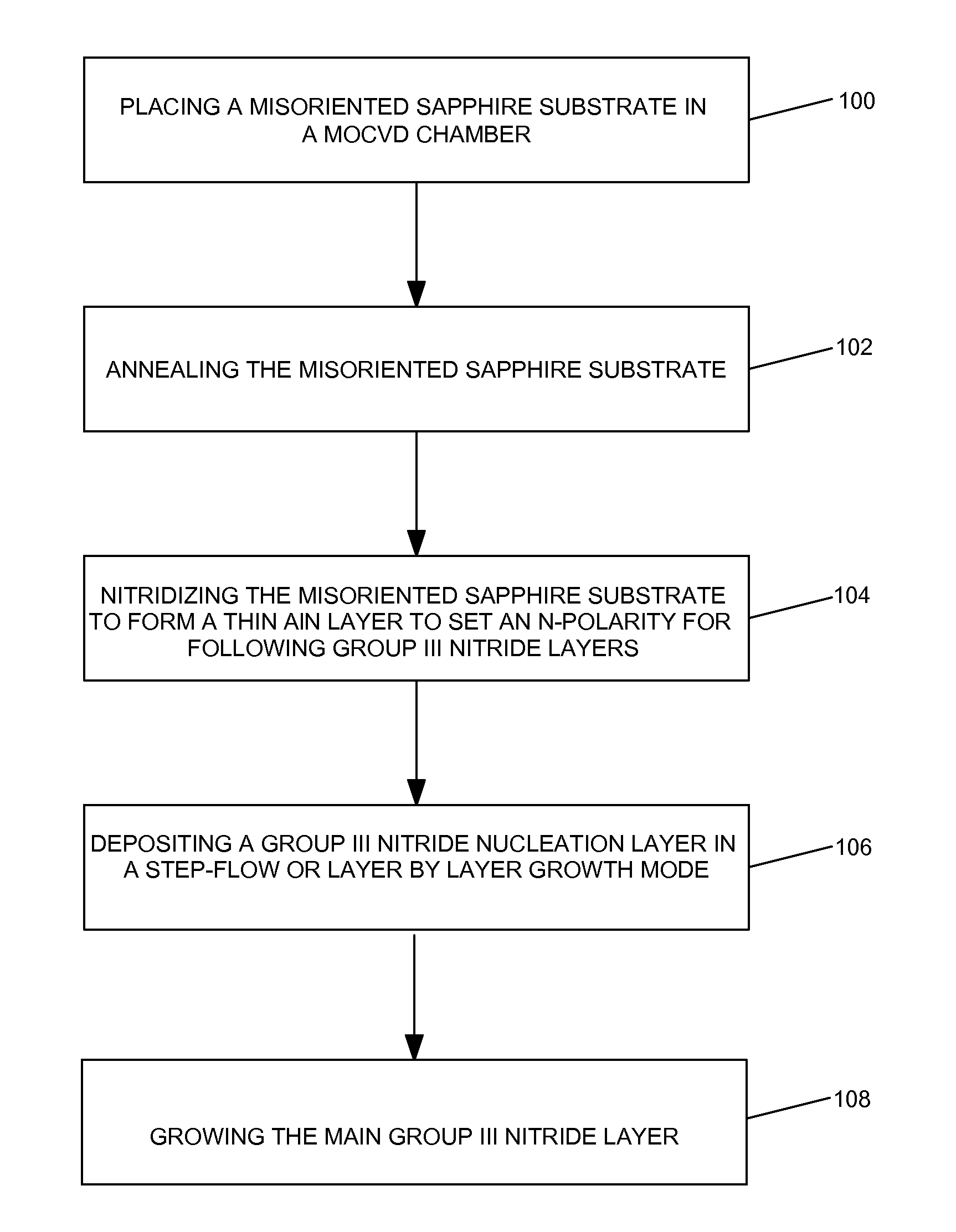
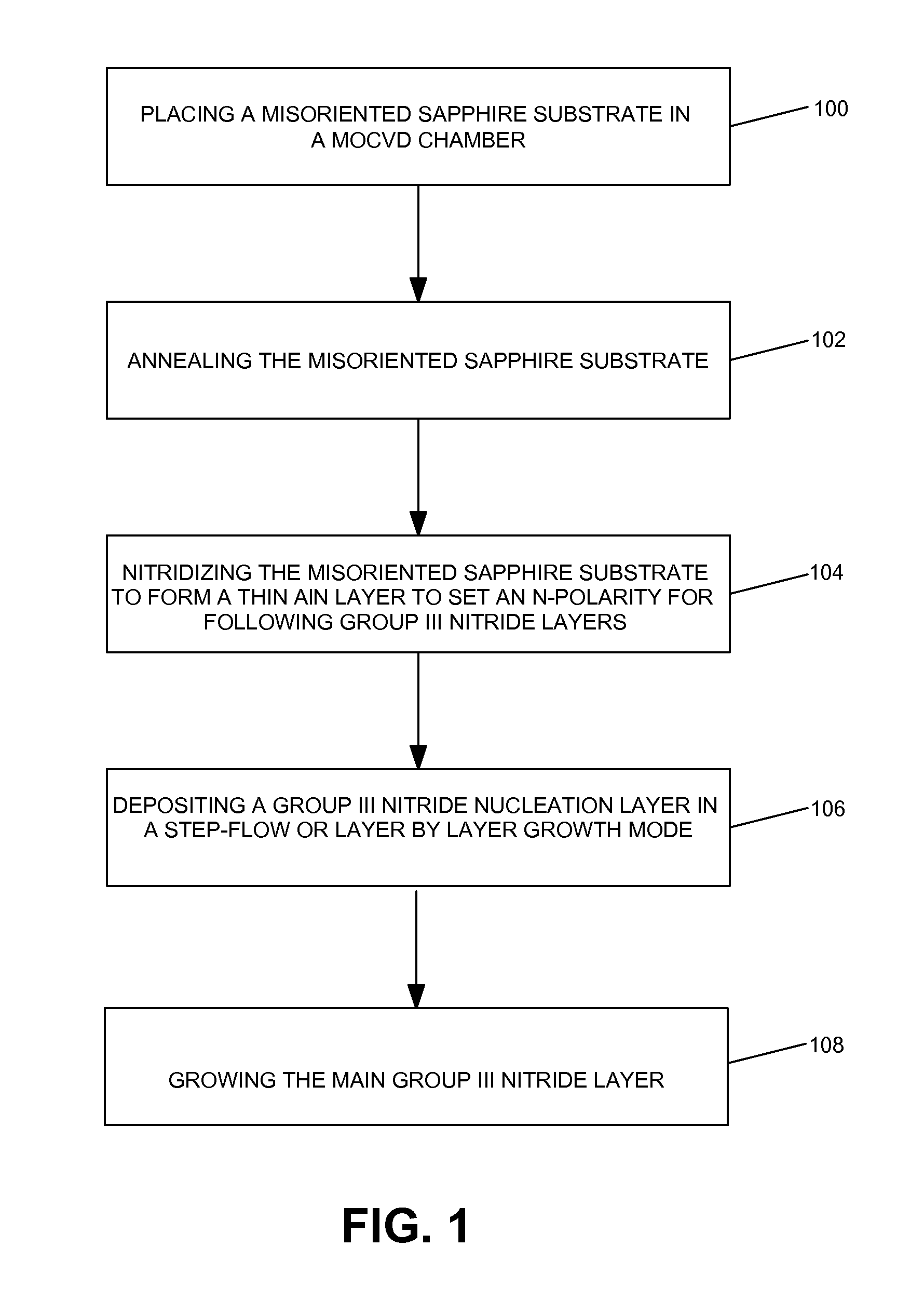
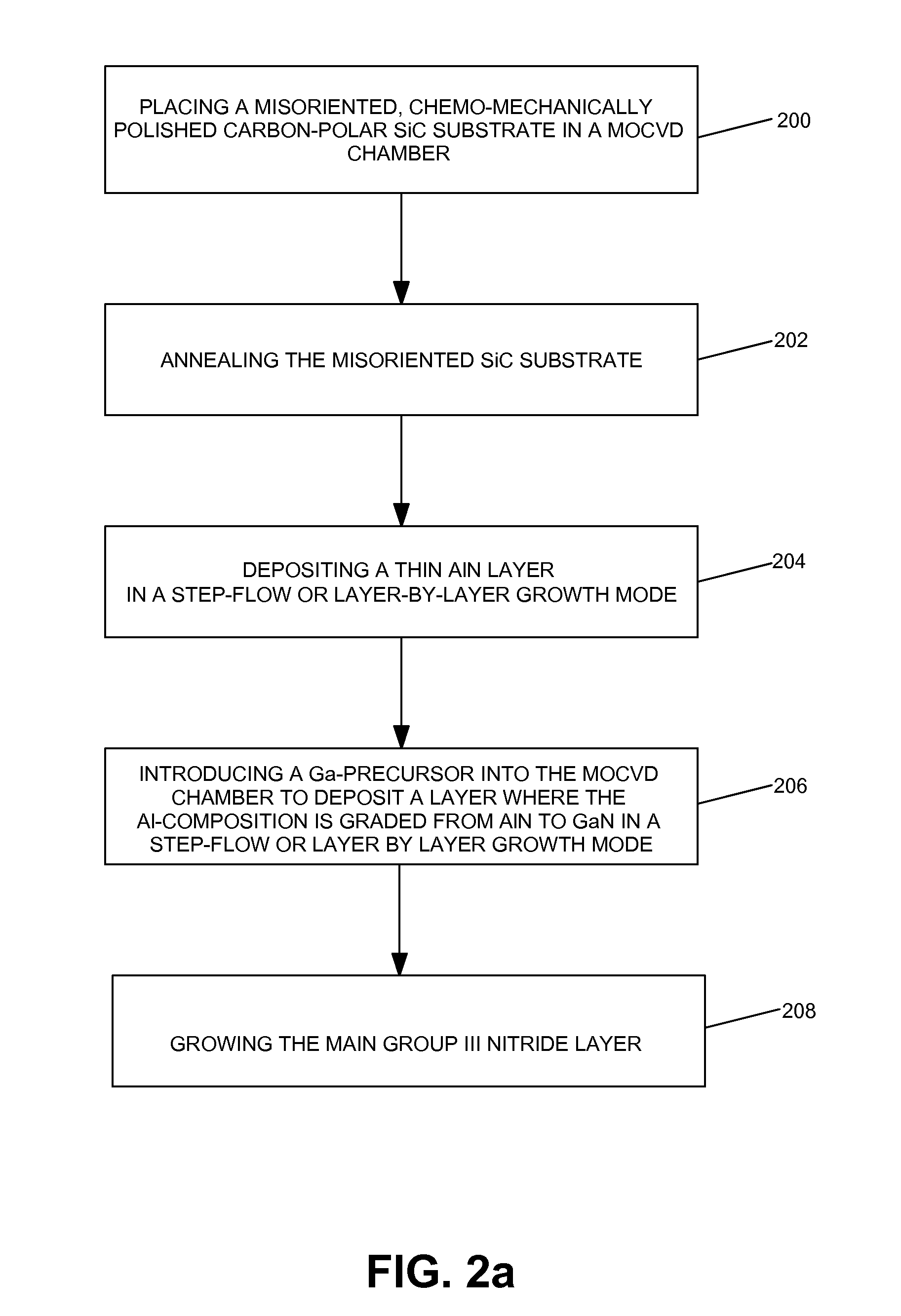
Methods for the heteroepitaxial growth of smooth, high quality films of N-face GaN film grown by MOCVD are disclosed. Use of a misoriented substrate and possibly nitridizing the substrate allow for the growth of smooth N-face GaN and other Group III nitride films as disclosed herein. The present invention also avoids the typical large (μm sized) hexagonal features which make N-face GaN material unacceptable for device applications. The present invention allows for the growth of smooth, high quality films which makes the development of N-face devices possible.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
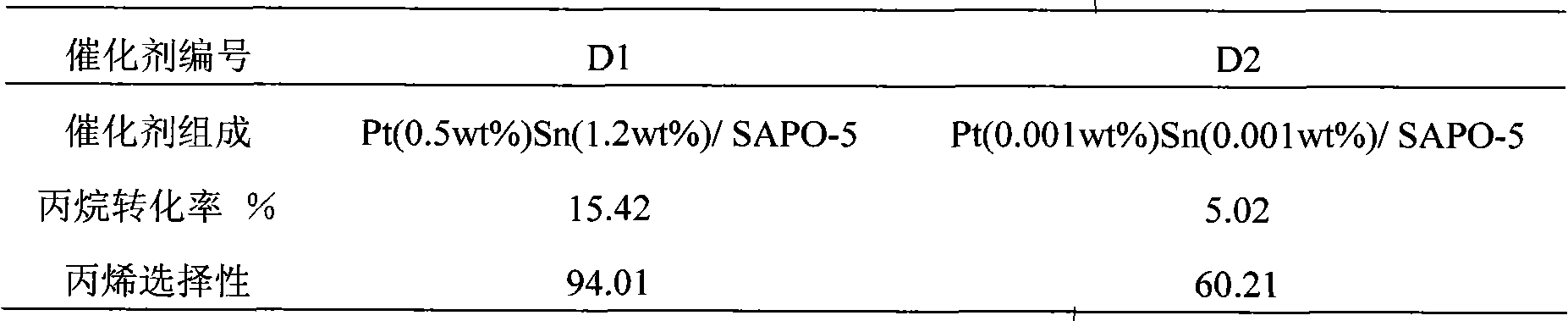
Catalyst for manufacturing olefin by low-carbon alkane dehydrogenation and application thereof
ActiveCN101773850AHigh selectivityHigh activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkaneRare-earth element
The invention discloses a catalyst for manufacturing olefin by low-carbon alkane dehydrogenation and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of preparation of basic organic chemical materials. The catalyst takes silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieve and alumina mixture as carriers, VIII group or IVA group elements as active components and alkaline-earth metal or rare-earth elements as auxiliary agents for the process of olefin preparation by ethane, propane, butane or pentane dehydrogenation. In the process of olefin preparation by low-carbon alkane dehydrogenation, catalyst is firstly reduced by hydrogen and then reacts, and finally the catalyst is in charcoaling regeneration and chlorination update; and reaction regeneration process flow has big choice, the reactor can adopt a fixed bed, a moving bed, a fluidized bed or a double-particle fluidized bed, and catalyst regeneration can be carried out in a device or out of the device. Compared with the existing catalyst for manufacturing olefin by low-carbon alkane dehydrogenation, the catalyst provided by the invention ensures that low-carbon alkane selectivity is above 95% in the olefin preparing process by low-carbon alkane dehydrogenation under high conversion rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low-pressure metal organic chemical vapour phase depositing apparatus for zinc oxide and process thereof
InactiveCN1644754AImprove crystal qualityImprove optical qualityFrom chemically reactive gasesChemical vapor deposition coatingTransport systemGas phase
The invention was about low voltage metal organic chemistry vapour deposition equipment and the preparation. The system was made up of gas transport system, reaction chamber, sample pretreatment chamber, control system, tail gas treatment system. The sample pretreatment chamber was made up of ectotheca, sample pallet shelf, sample desk, gas bleed spore, plasma generator, flange, plate valve of switch between the sample pretreatment chamber and reaction chamber, flange of plate valve, magnetic transmit bar, magnetic cannula, flange of transmit bar. Its advantages include increased the growing of ZnO film and uniformity, benefit for the P type and intermingle of high impedance.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +2
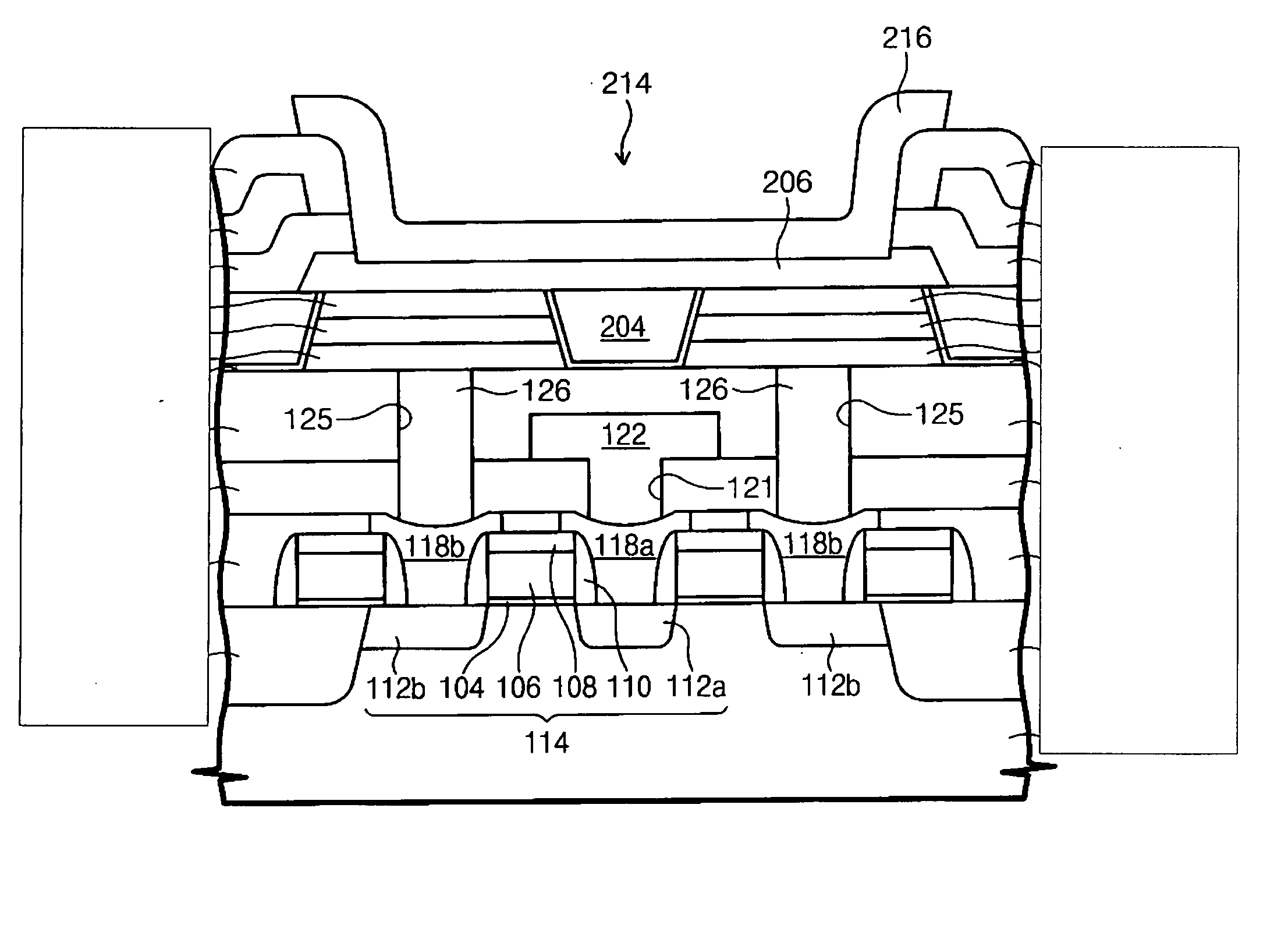
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20060267030A1Efficient removalEfficient reductionFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesDevice materialOrganic compound
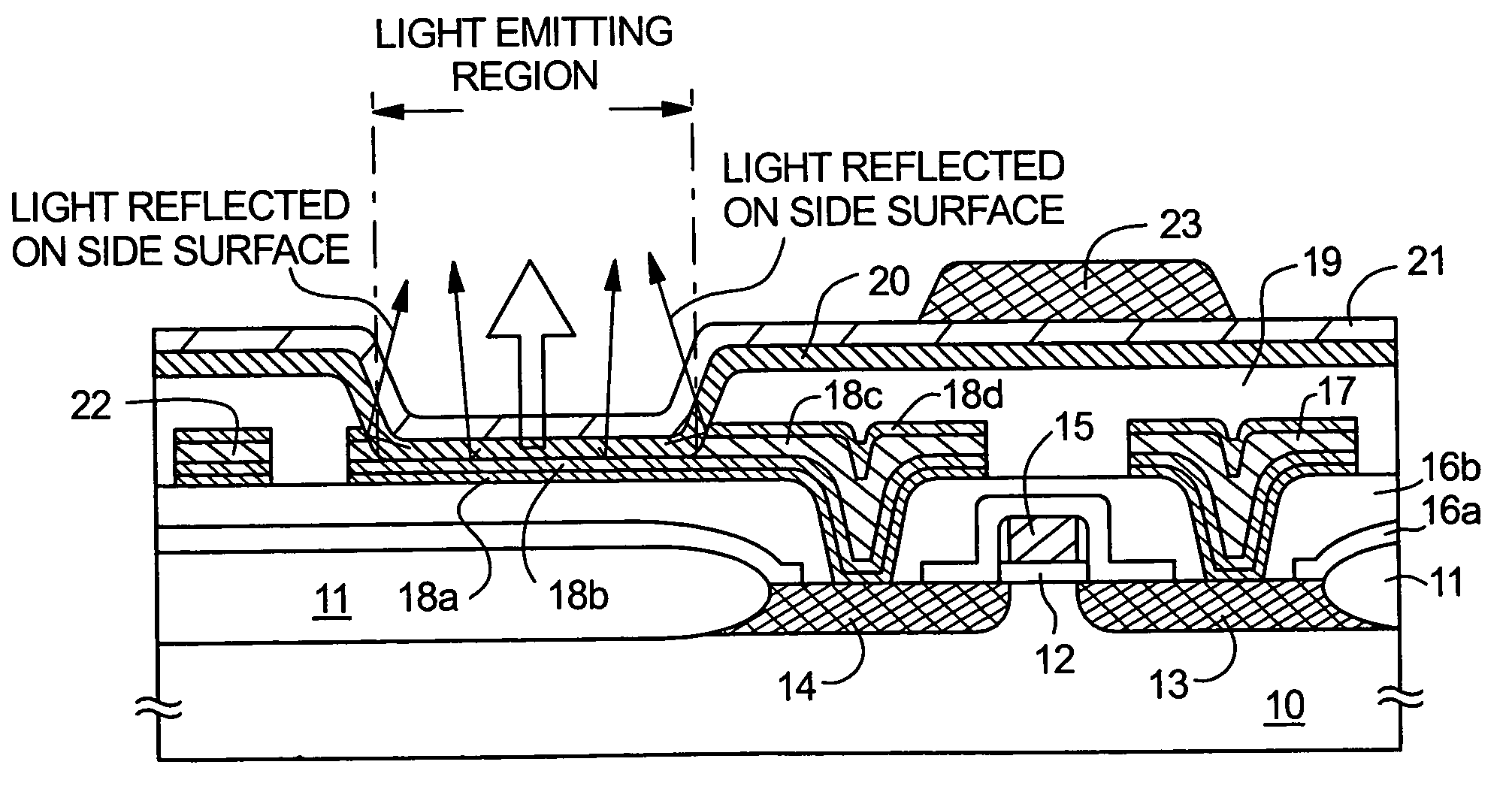
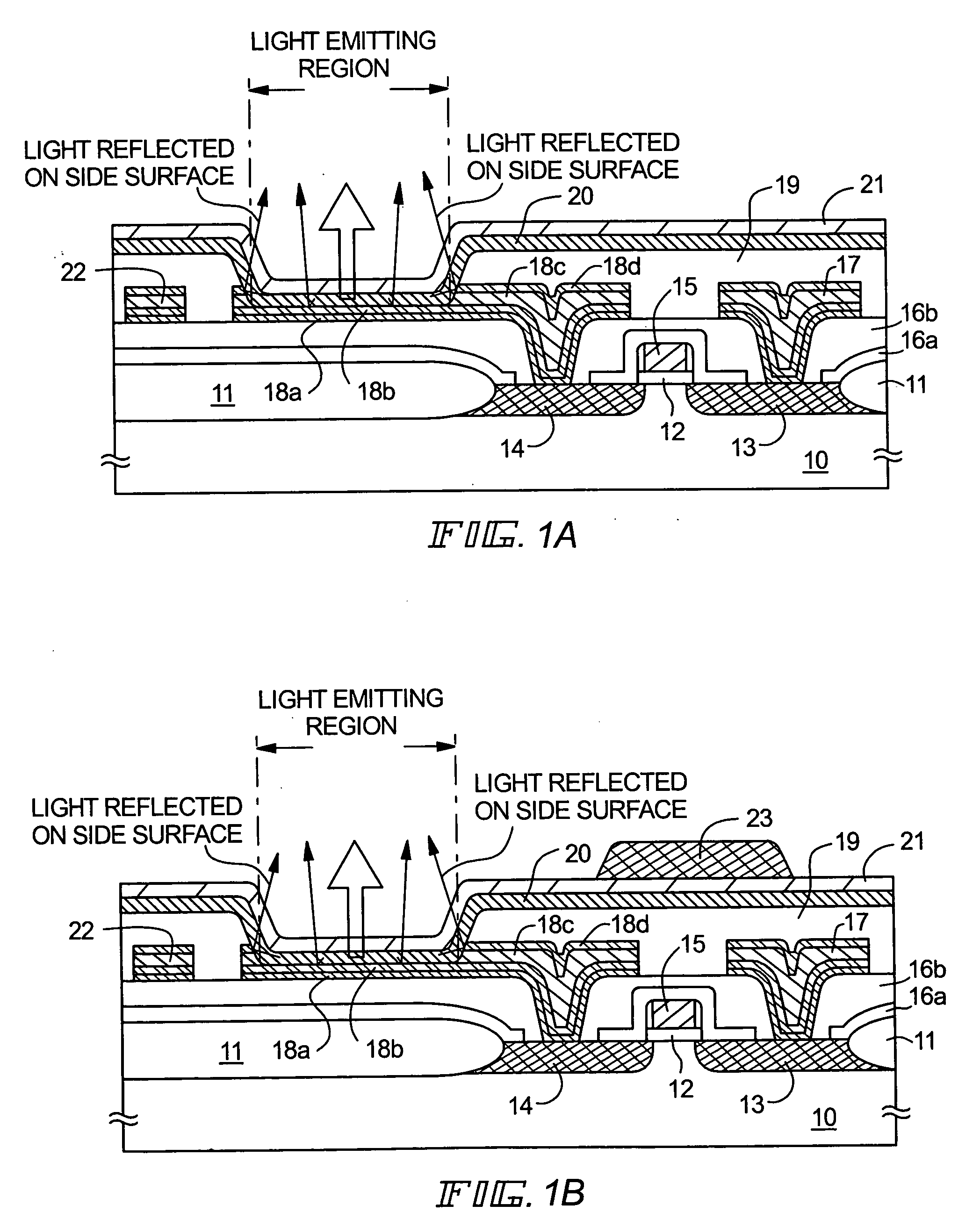
A FET is formed on a semiconductor substrate, a curved surface having a radius of curvature is formed on an upper end of an insulation, a portion of a first electrode is exposed corresponding to the curved surface to form an inclined surface, and a region defining a luminescent region is subjected to etching to expose the first electrode. Luminescence emitted from an organic chemical compound layer is reflected by the inclined surface of the first electrode to increase a total quantity of luminescence taken out in a certain direction.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
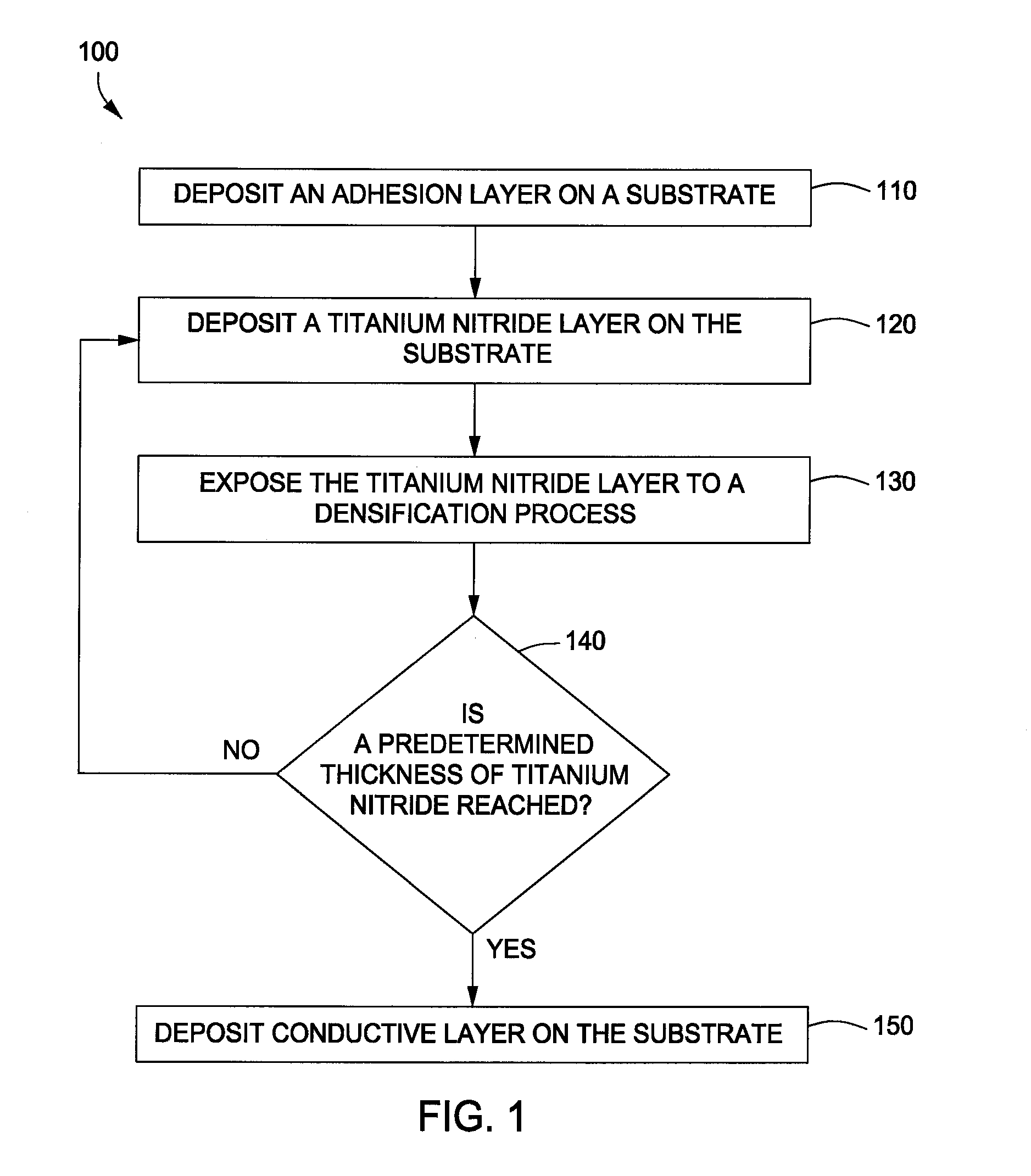
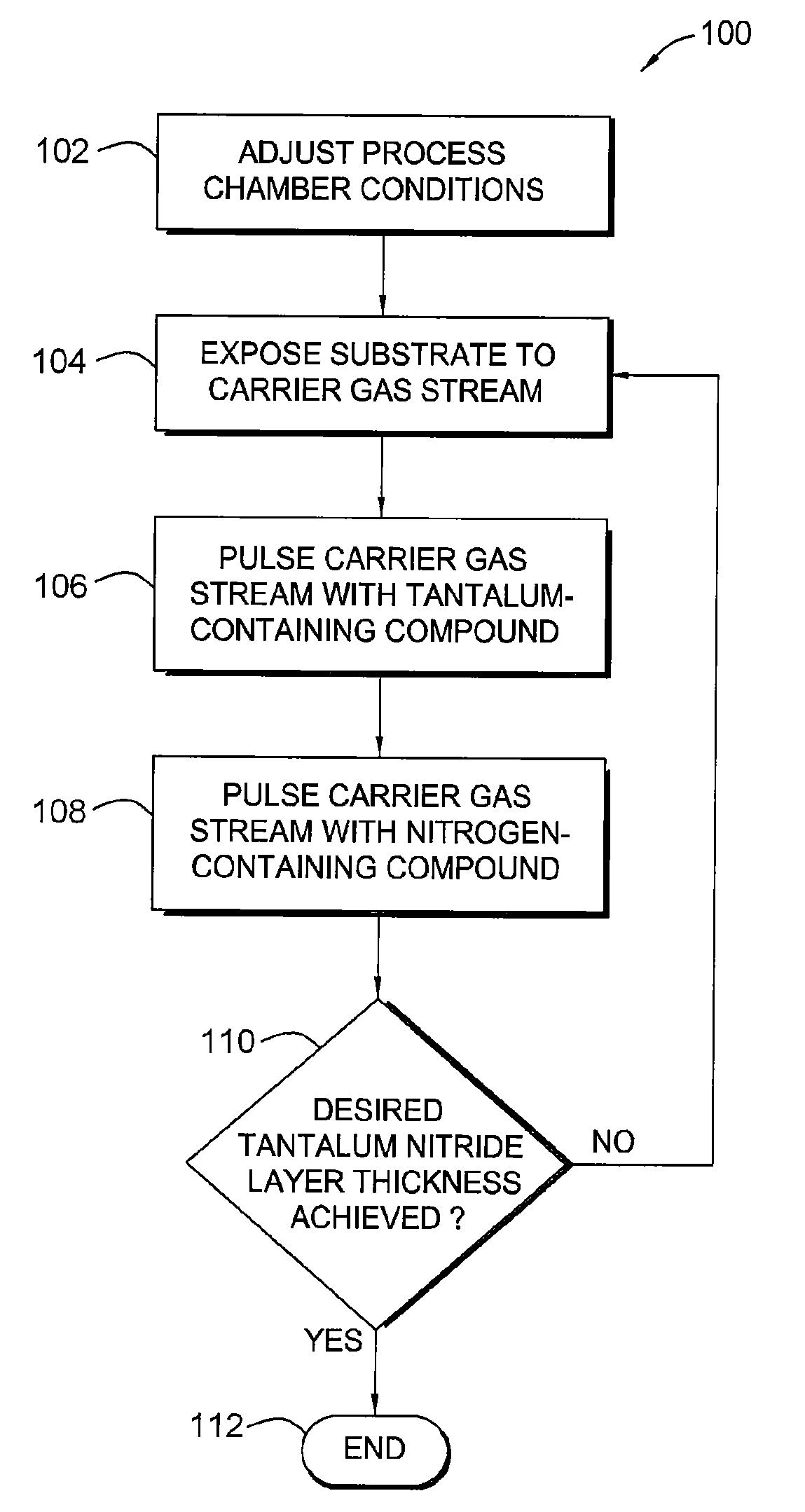
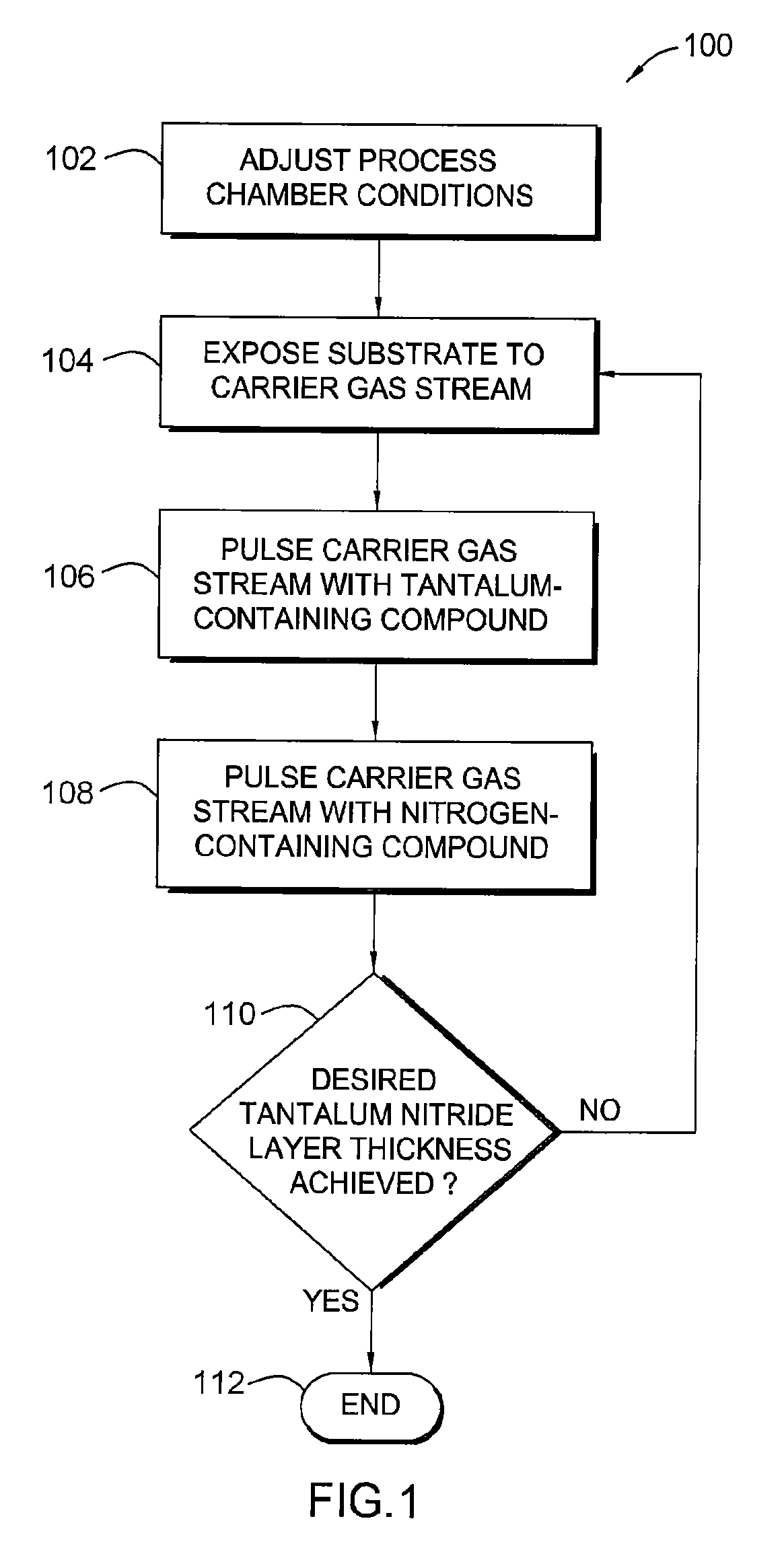
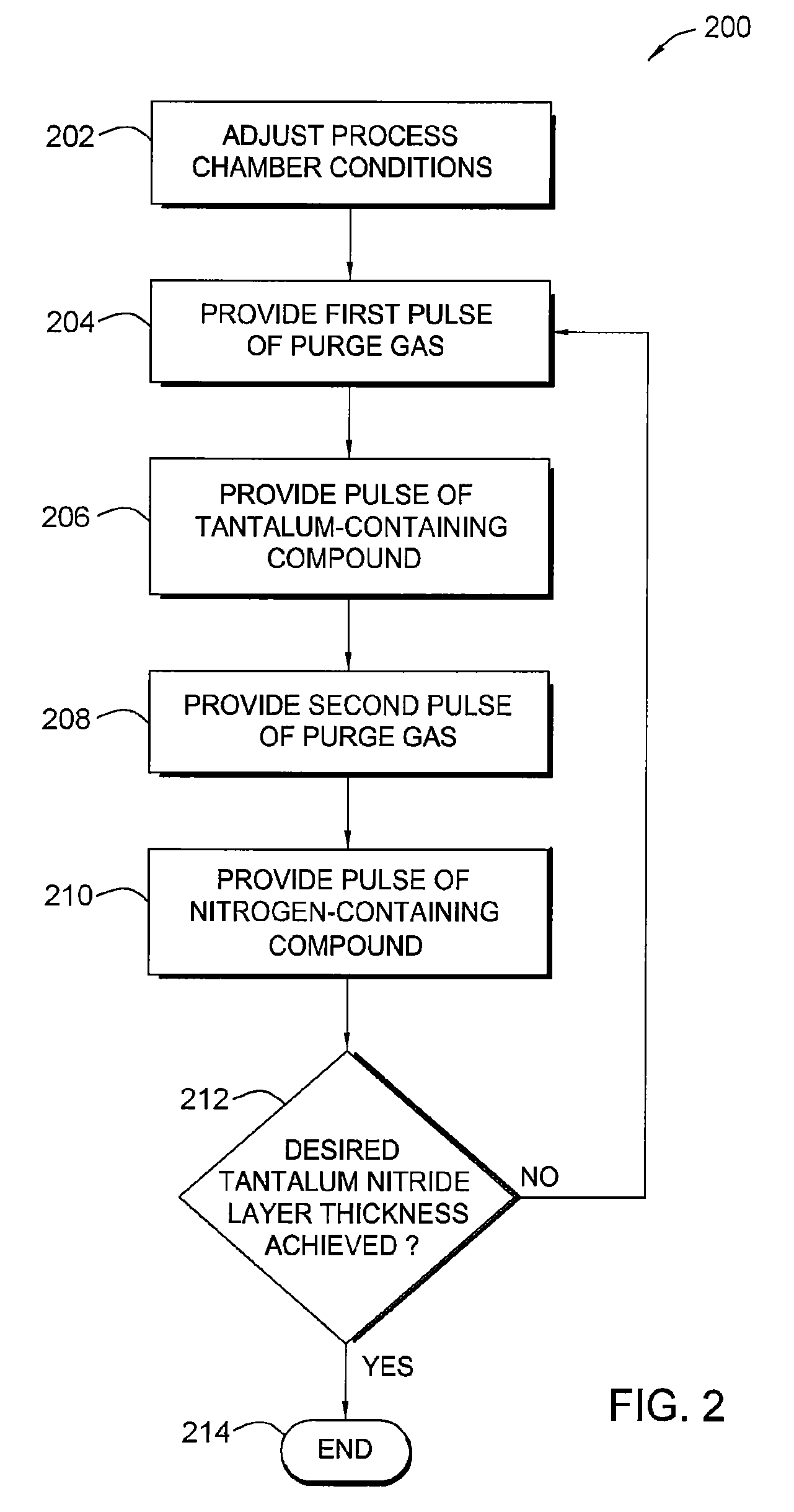
Deposition and densification process for titanium nitride barrier layers
InactiveUS20080085611A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideConductive materials
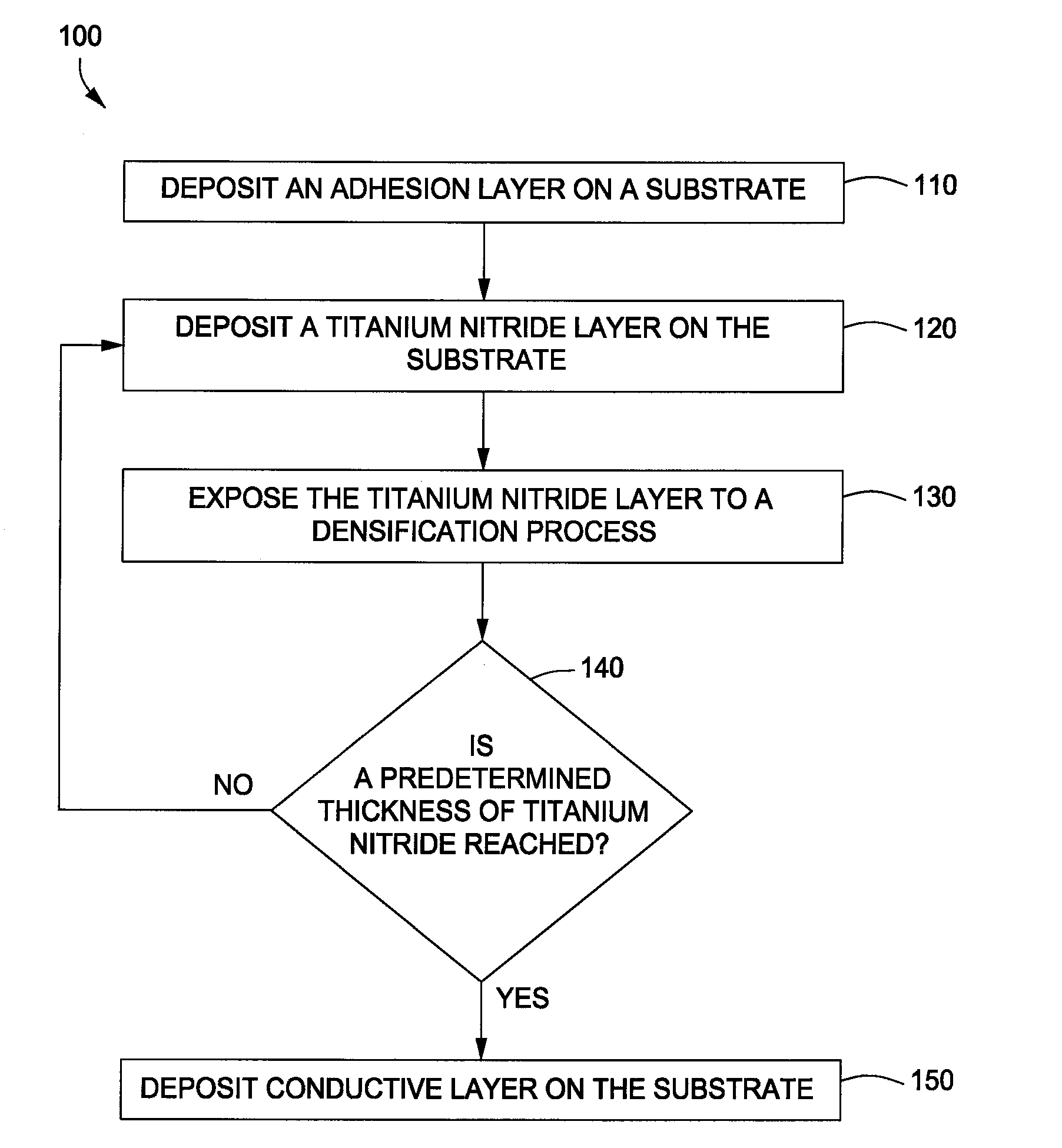
In one embodiment, a method for forming a titanium nitride barrier material on a substrate is provided which includes depositing a titanium nitride layer on the substrate by a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) process, and thereafter, densifying the titanium nitride layer by exposing the substrate to a plasma process. In one example, the MOCVD process and the densifying plasma process is repeated to form a barrier stack by depositing a second titanium nitride layer on the first titanium nitride layer. In another example, a third titanium nitride layer is deposited on the second titanium nitride layer. Subsequently, the method provides depositing a conductive material on the substrate and exposing the substrate to a annealing process. In one example, each titanium nitride layer may have a thickness of about 15 Å and the titanium nitride barrier stack may have a copper diffusion potential of less than about 5×1010 atoms / cm2.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for treating organic chemical waste water
InactiveCN101734817AEasy to handleReduce processing costsMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationHigh concentrationPretreatment method
The invention discloses a method for treating organic chemical waste water. In the method, after the pH value of the waste water is adjusted to 2.5-3.0, the organism which is hard to degrade is efficiently removed and the biochemical property of the waste water is enhanced through the aeration microelectrolysis, Fenton oxidization and coagulating sedimentation processes, and the Fe<2+> generated after the microelectrolysis reaction can be used for subsequent Fenton oxidization reaction, thereby reducing the treatment cost. The invention can be widely applied to treating various kinds of low concentration organic waste water which is hard to biodegrade, such as chemicals, pharmacy, and the like; and the treated water can directly reach the standard and be drained. The invention can also be used as a pretreatment method of the organic waste water with high concentration to improve the biochemical property of the waste water which is hard to biodegrade.
Owner:JIANGSU SUJING GROUP +1
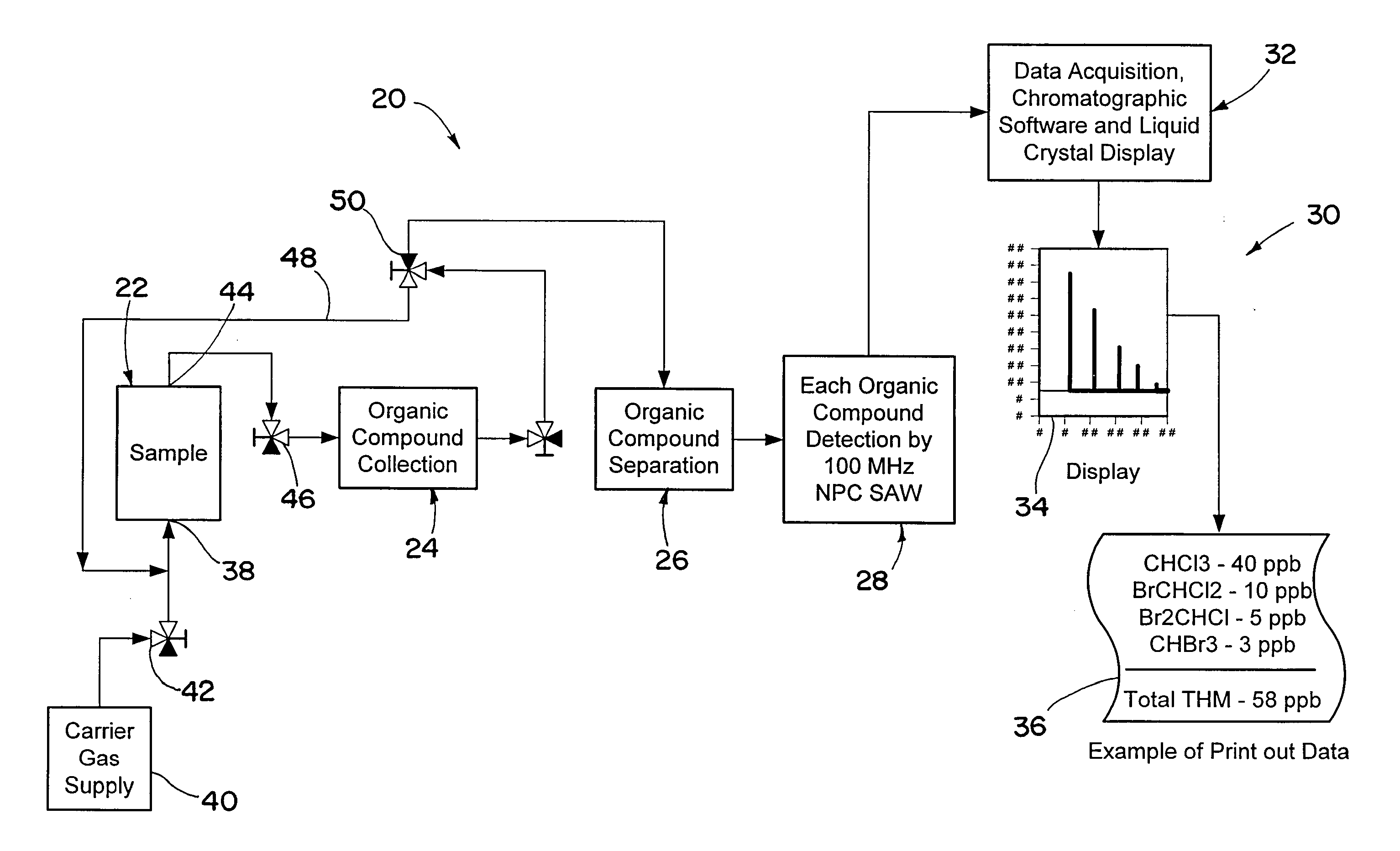
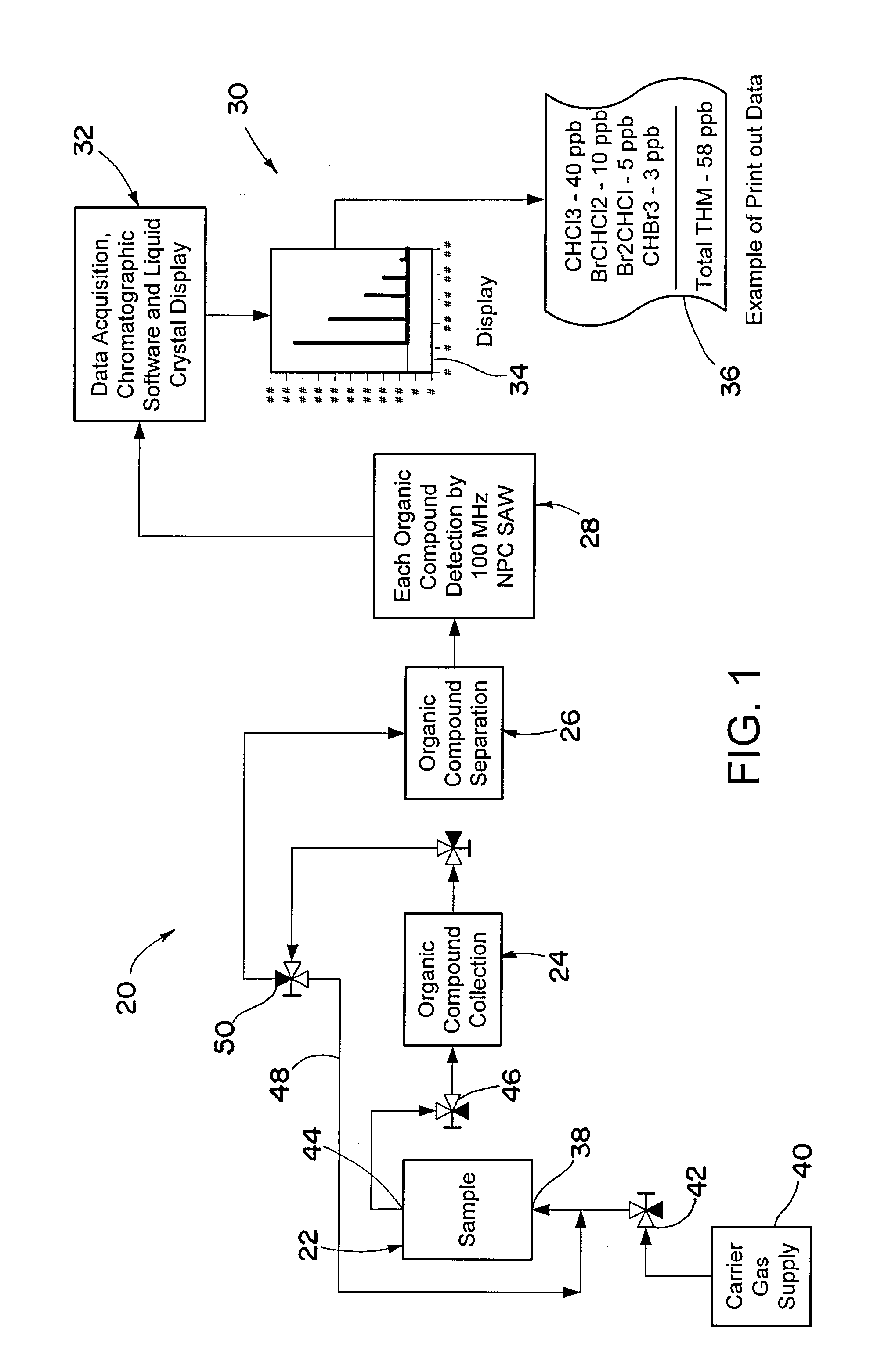
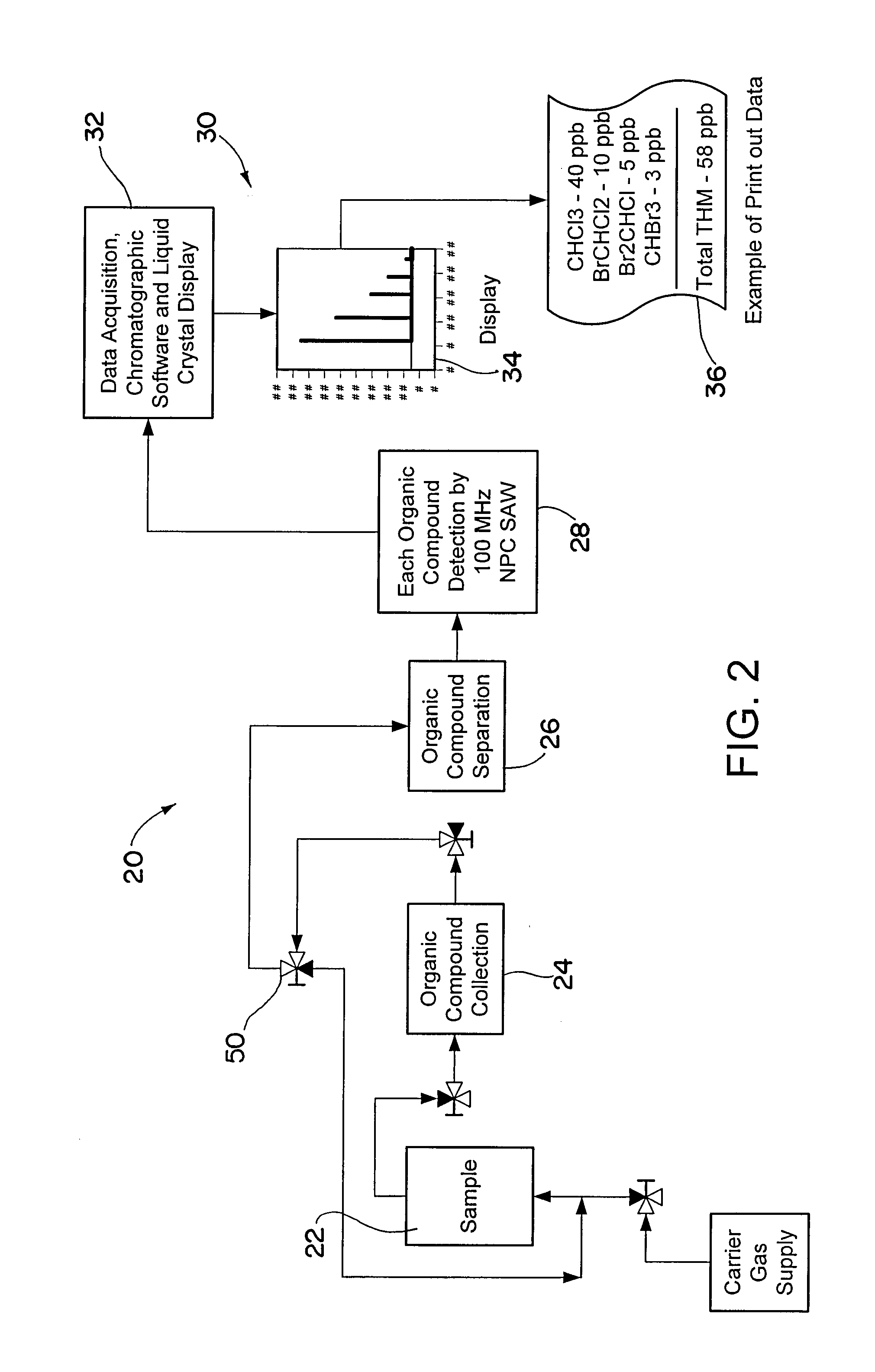
Portable analytical system for detecting organic chemicals in water
ActiveUS20080289397A1Easy to manufactureEliminate needMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersBromineBromoform
A portable analytical system for detecting organic chemicals in water comprising a miniature preconcentrator and a SAW detector, the latter being characterized by a nanoporous carbon coating that provides improved response compared to prior art polymer coatings, particularly when detecting low concentrations of trihalomethane chemicals, such as chloroform and bromoform.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
In-situ chamber treatment and deposition process
ActiveUS20100062614A1Improve uniformityReduce unevennessPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for treating the inner surfaces of a processing chamber and depositing a material on a during a vapor deposition process, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) or by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In one embodiment, the inner surfaces of the processing chamber and the substrate may be exposed to a reagent, such as a hydrogenated ligand compound during a pretreatment process. The hydrogenated ligand compound may be the same ligand as a free ligand formed from the metal-organic precursor used during the subsequent deposition process. The free ligand is usually formed by hydrogenation or thermolysis during the deposition process. In one example, the processing chamber and substrate are exposed to an alkylamine compound (e.g., dimethylamine) during the pretreatment process prior to conducting the vapor deposition process which utilizes a metal-organic chemical precursor having alkylamino ligands, such as pentakis(dimethylamino) tantalum (PDMAT).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com