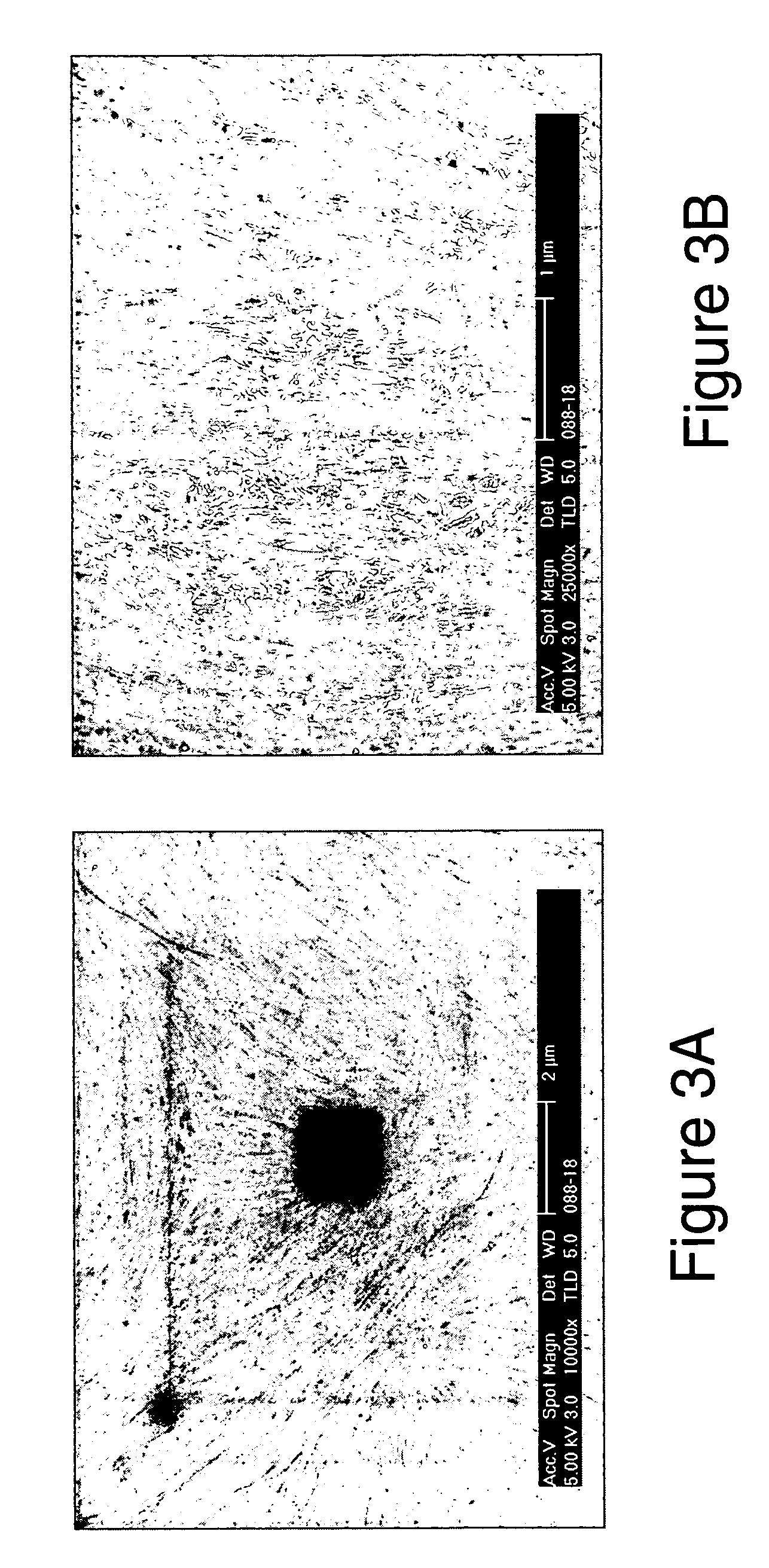
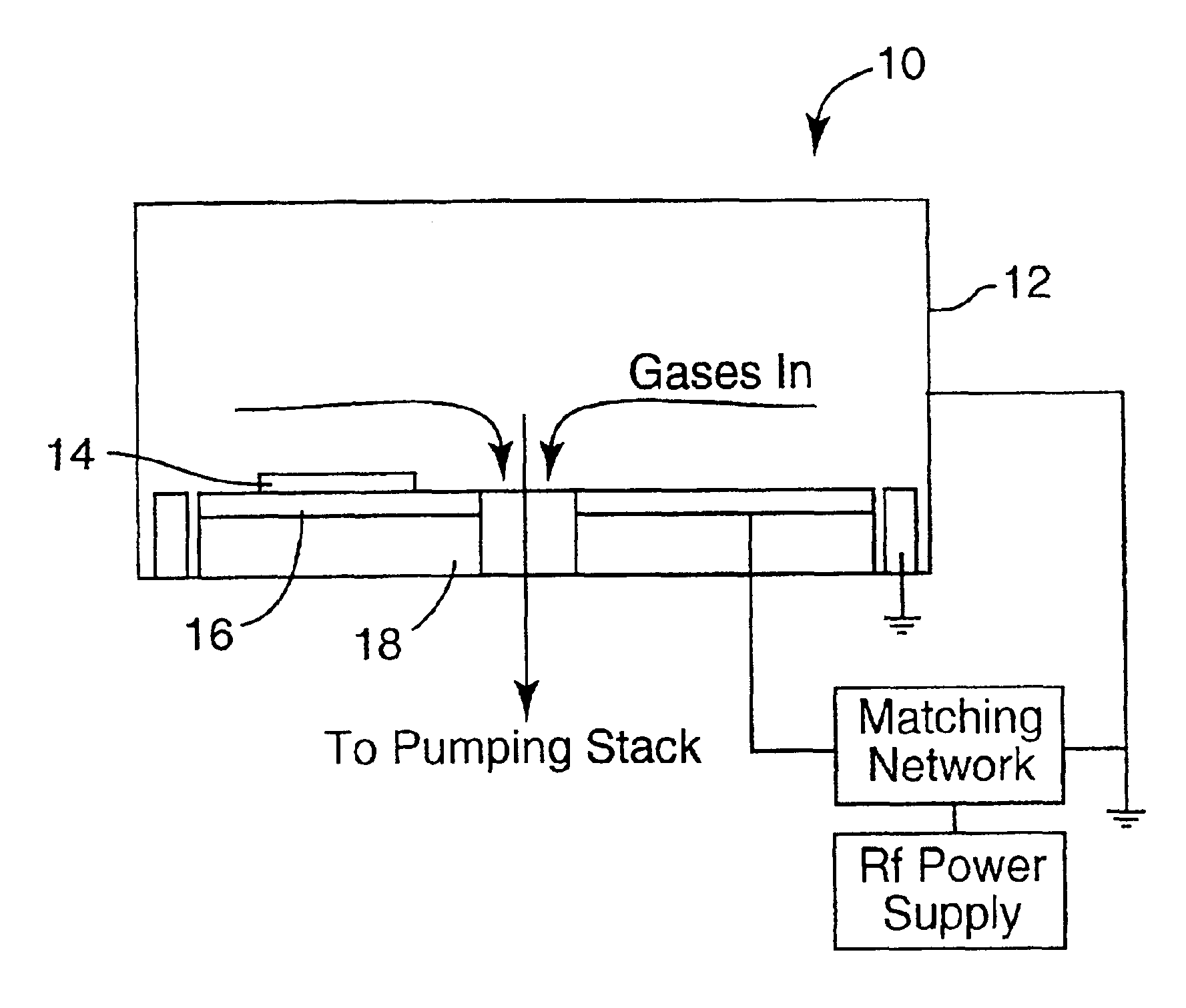
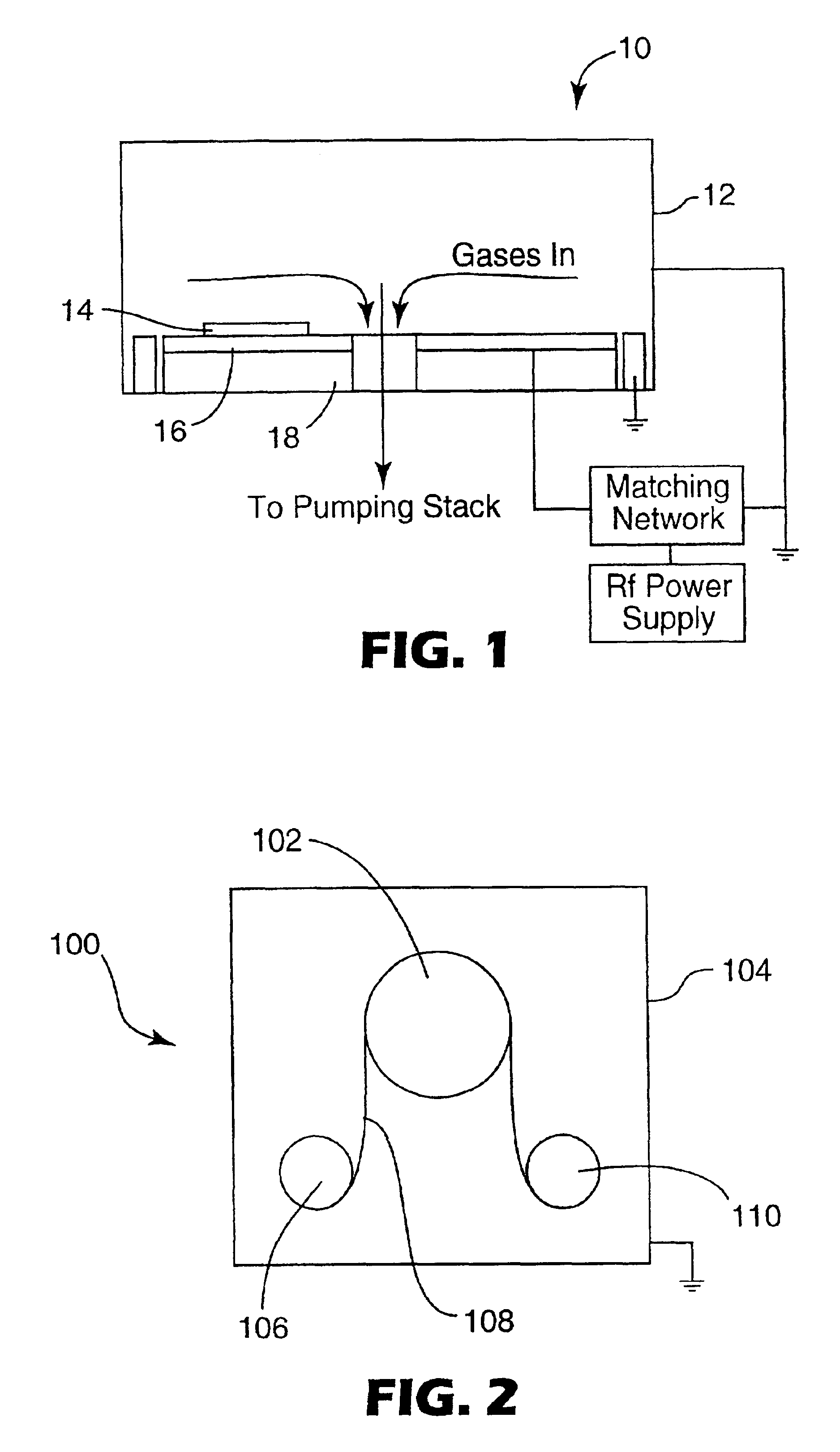
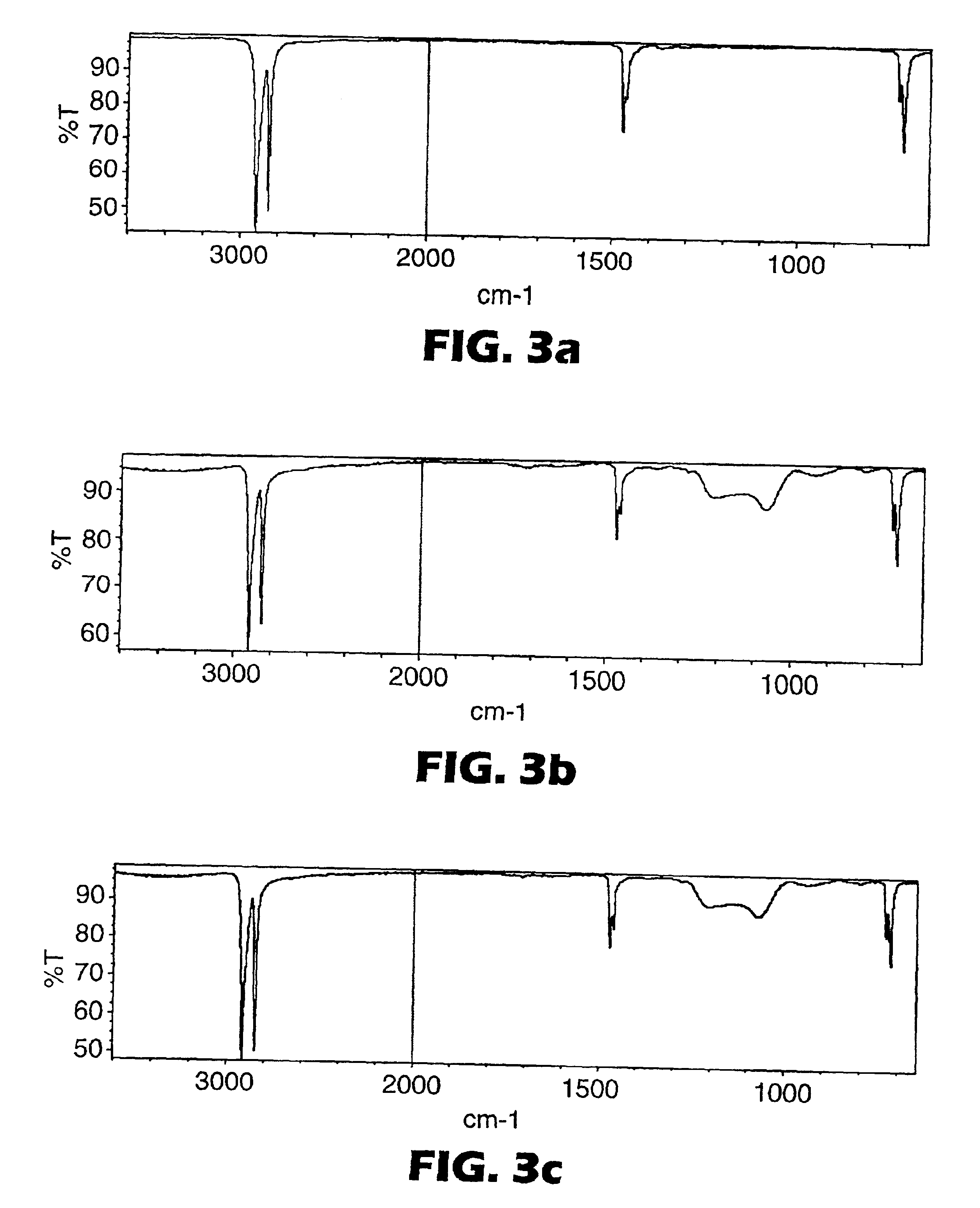
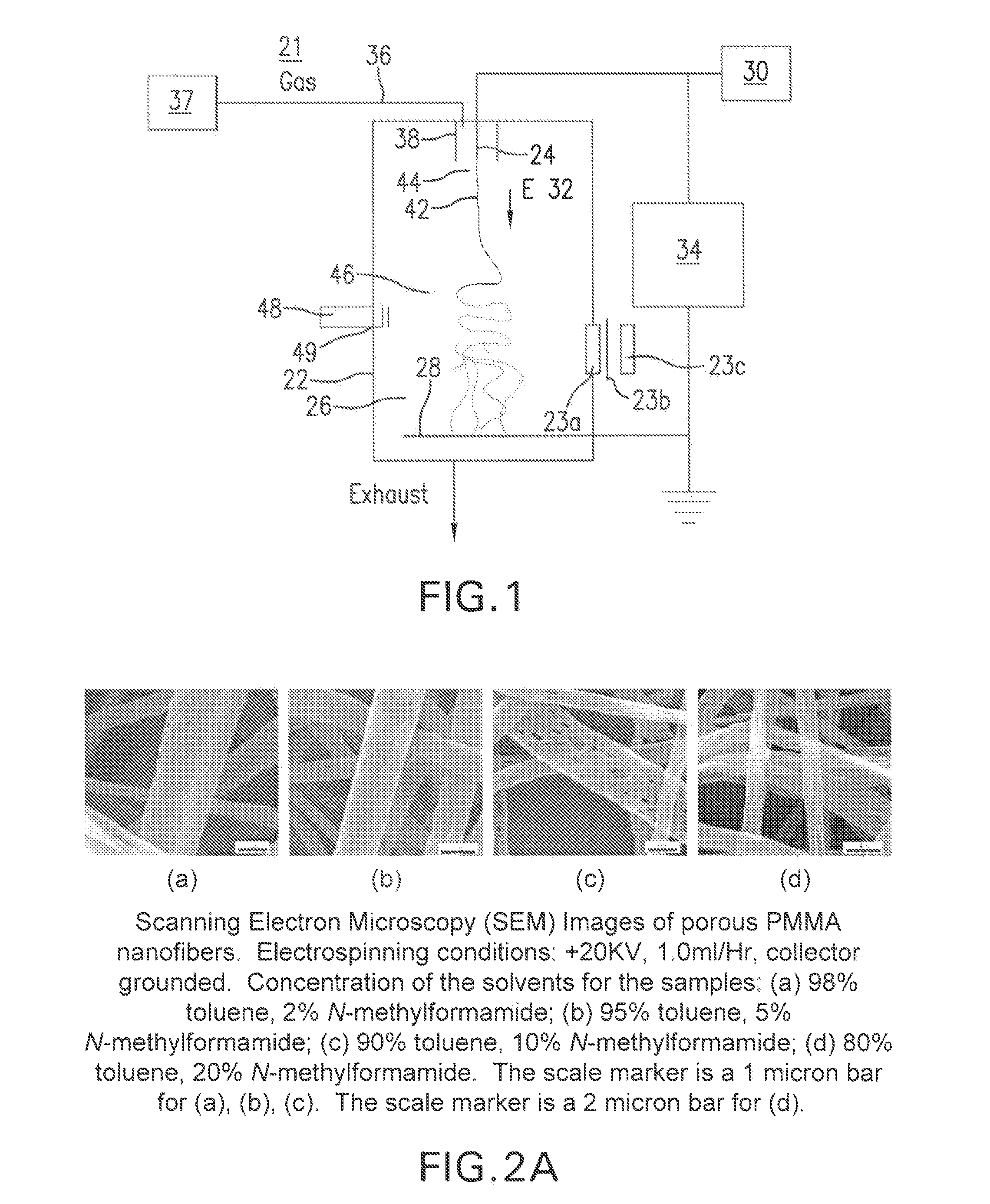
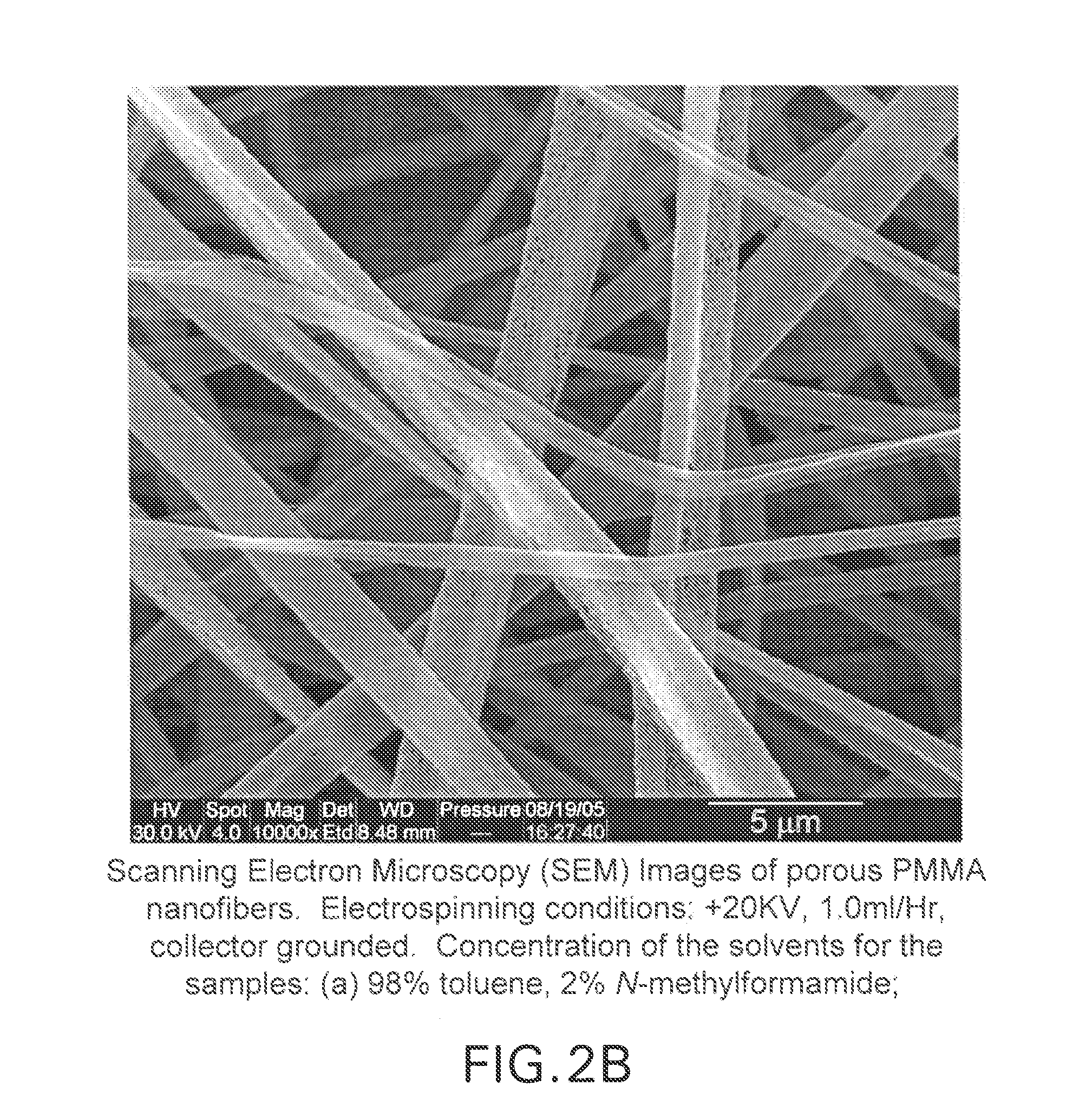
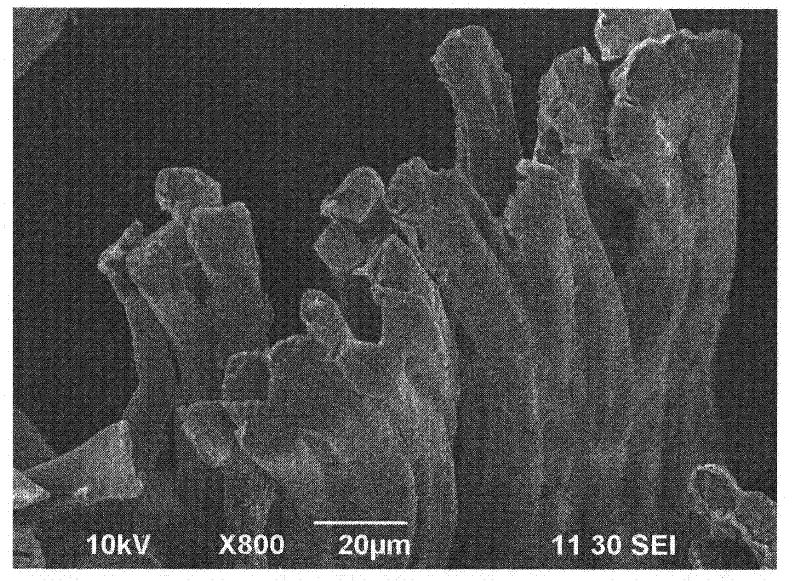
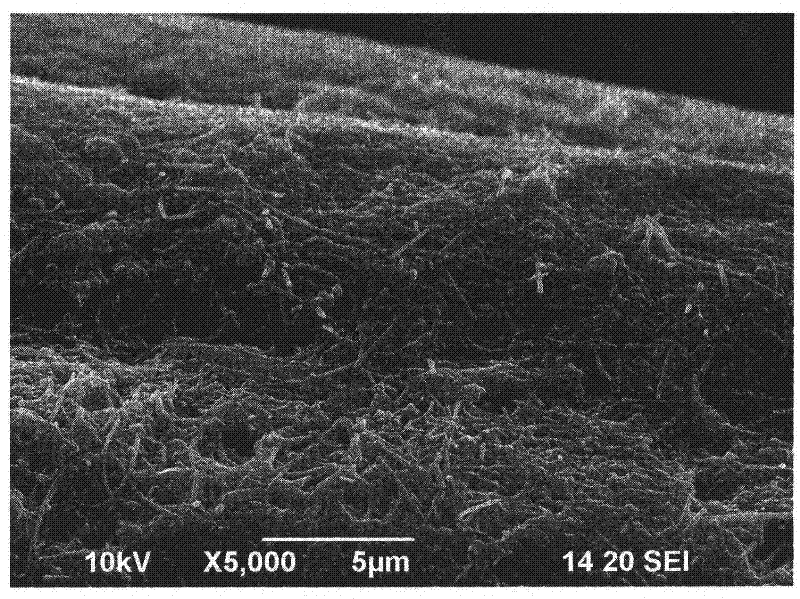
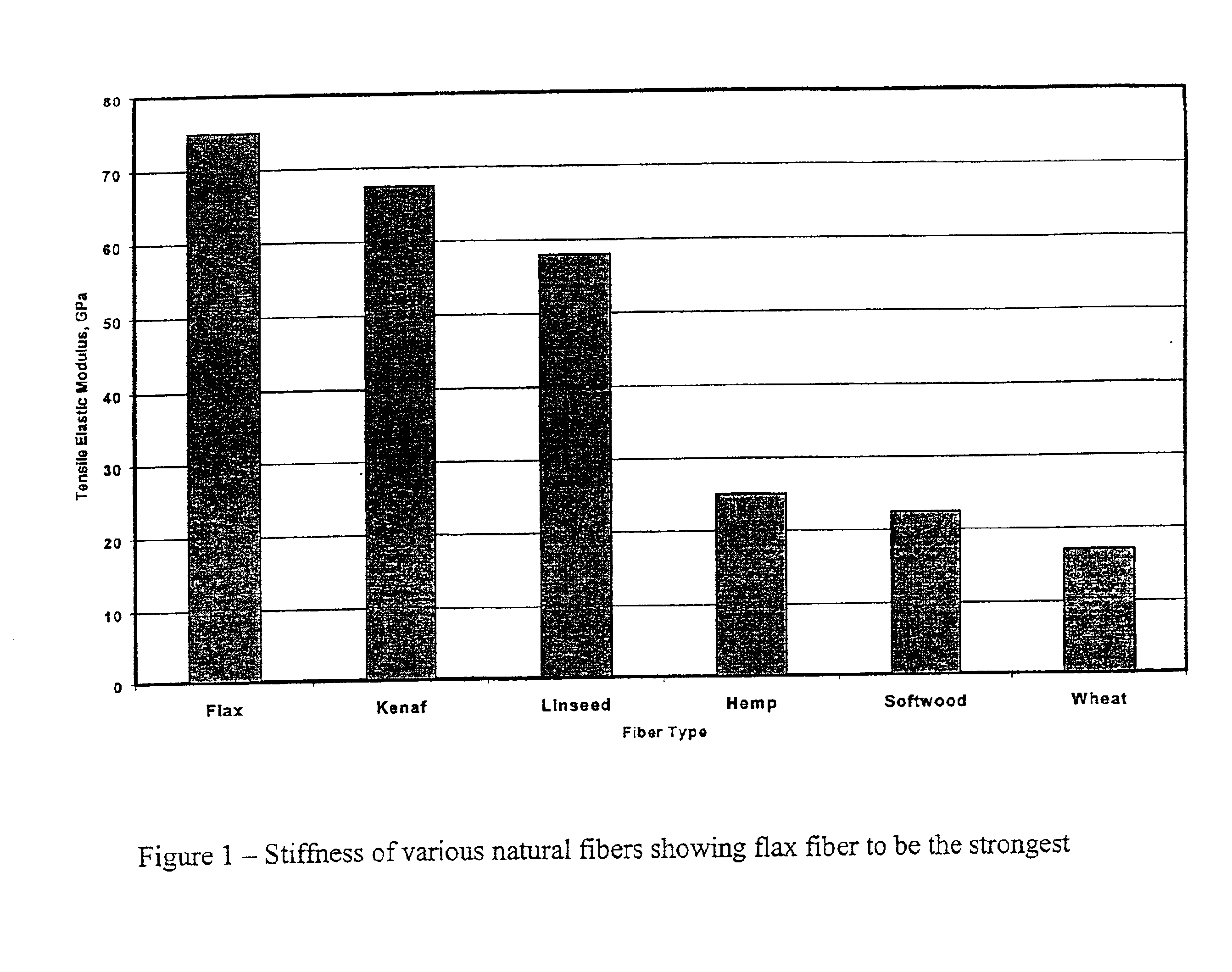
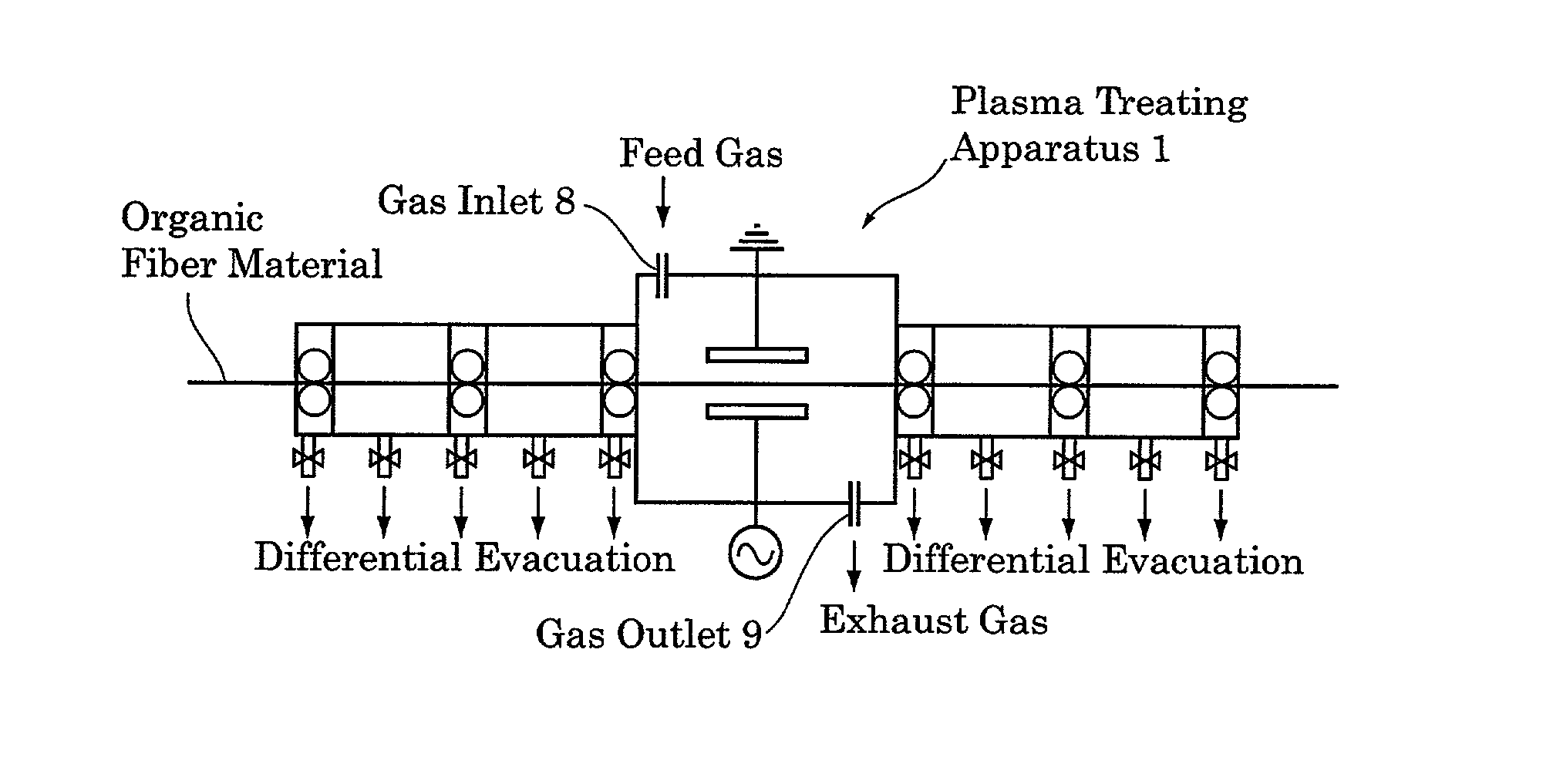
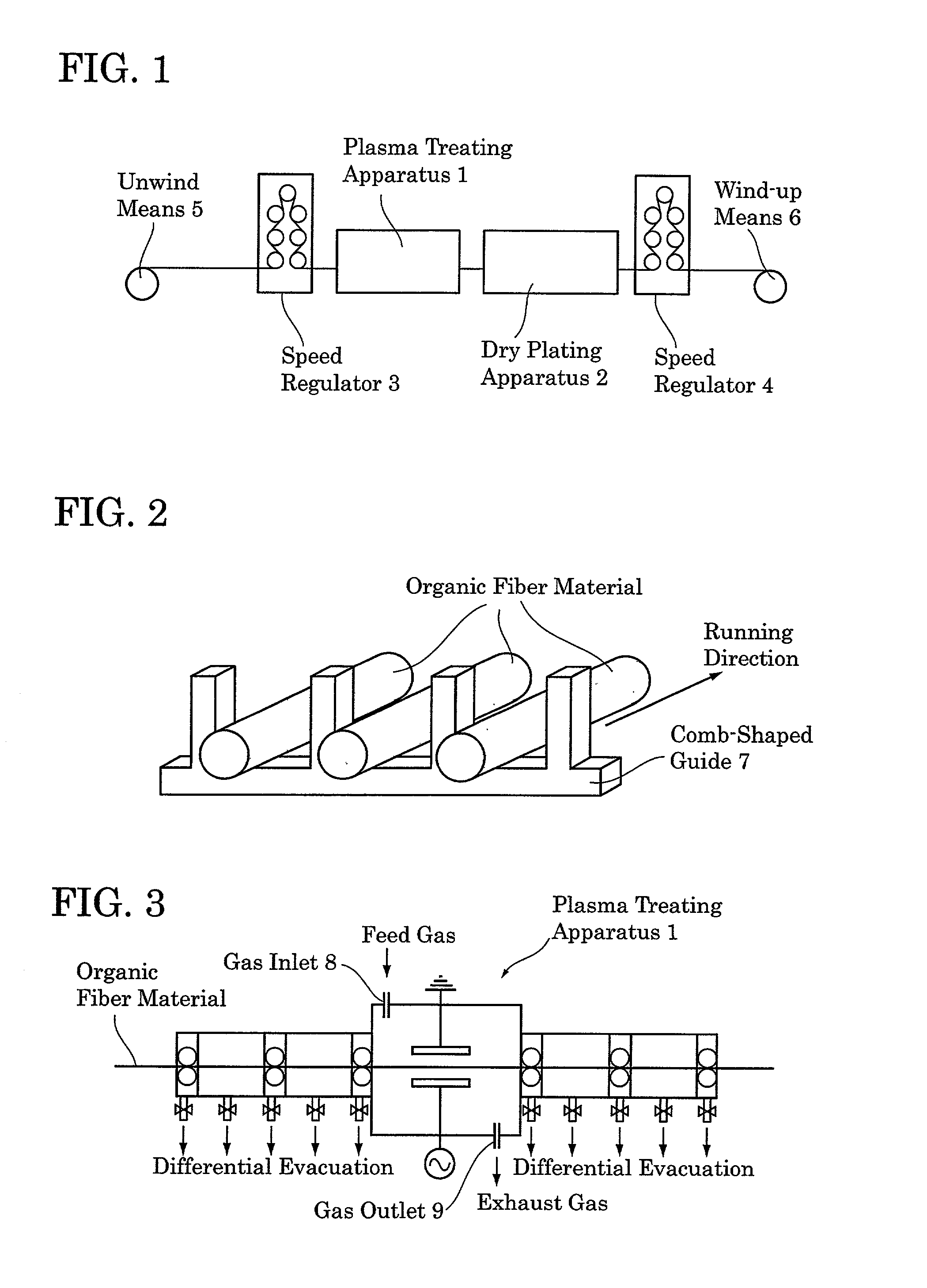
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1419results about "Ultrasonic/sonic fibre treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for hydrophilizing materials using hydrophilic polymeric materials with discrete charges
A method of rendering materials having hard and soft surfaces hydrophilic or more hydrophilic is disclosed. The method involves hydrophilizing such materials by applying a high energy treatment and charged particles and / or one or more hydrophilic polymeric materials with discrete charges to such materials.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
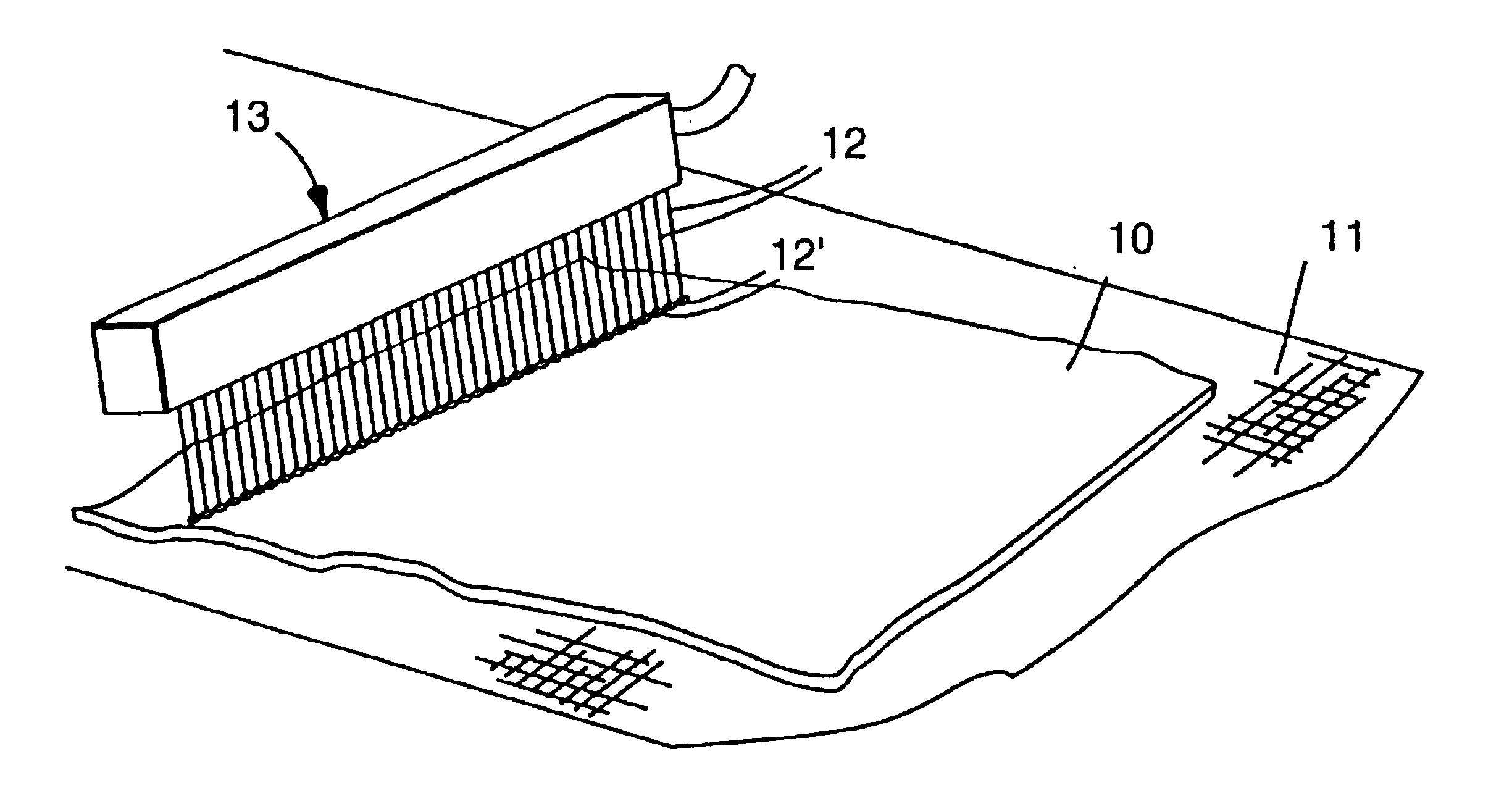
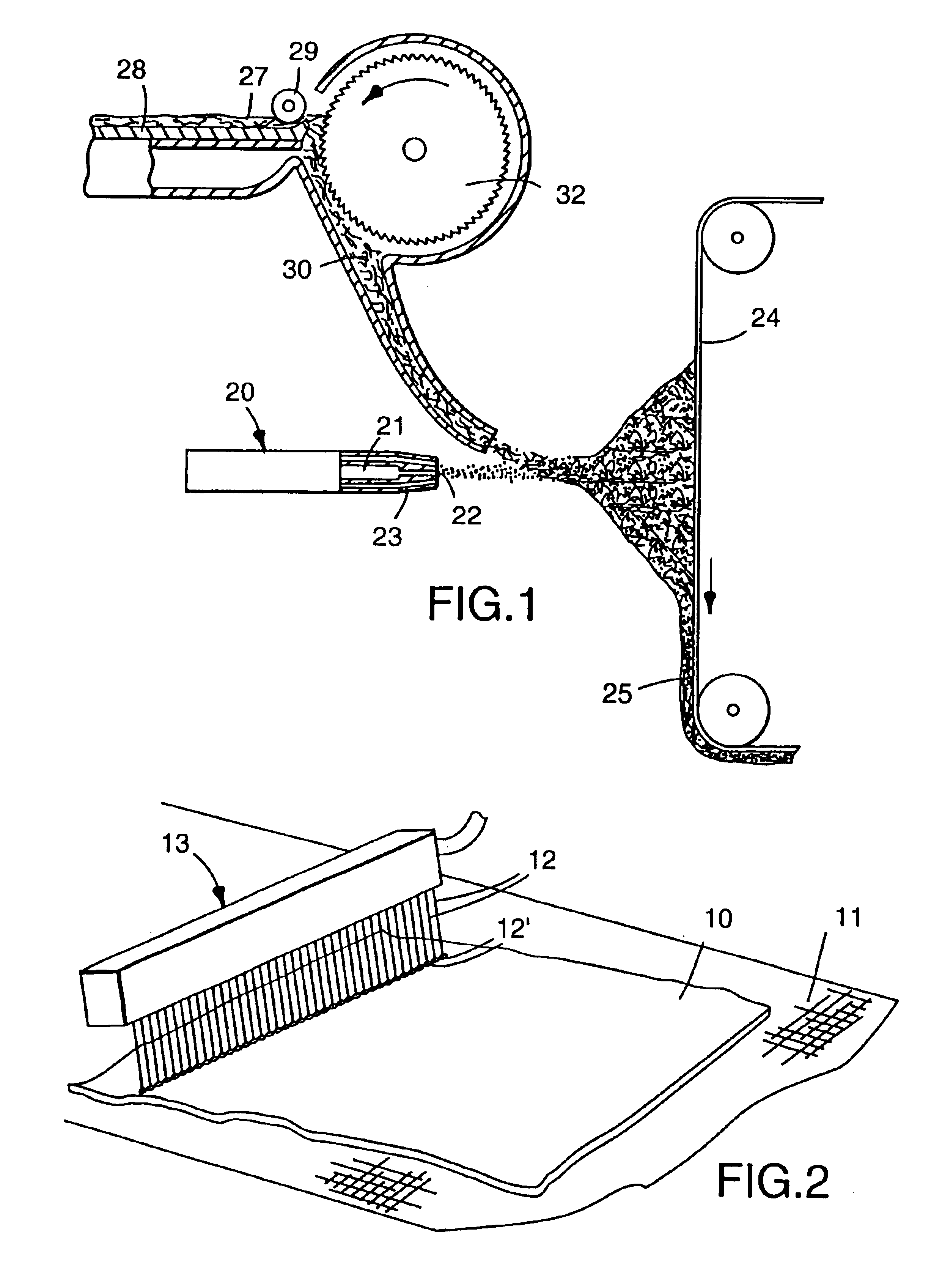
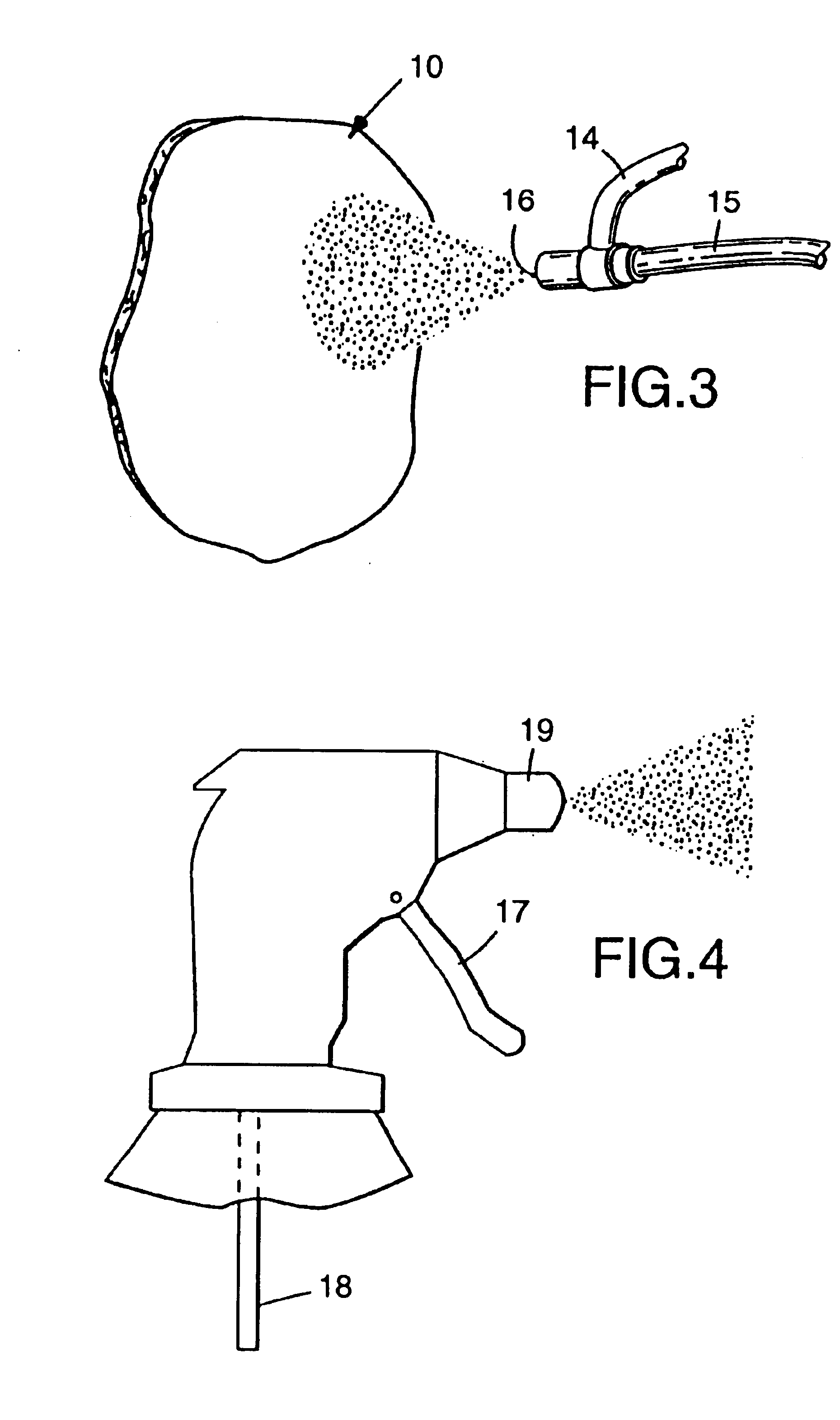
Electret filter media
InactiveUS6119691AReduce filtration efficiencyImprove filtering effectSynthetic fibresBreathing filtersMicrometerFilter media
An electret filter media, and mask, that is made of a nonwoven web of thermoplastic microfibers. The thermoplastic microfibers are of substantially the same composition, are nonconductive, and have an effective fiber diameter less than about 15 micrometers. The nonwoven web also has sufficient unpolarized trapped charge to exhibit an initial filtration quality factor of at least 0.31 when measured under the DOP Penetration and Pressure Drop Test.
Owner:3M CO
Electret filter media and filtering masks that contain electret filter media
InactiveUS6783574B1Reduce filtration efficiencyImprove filtering effectSynthetic fibresBreathing filtersFilter mediaRespiratory mask
Electret filter media comprising a nonwoven web of thermoplastic nonconductive microfibers having trapped charge, said charge provided by (1) subjecting the nonwoven web to a corona treatment, followed by (2) impingement of jets of water or a stream of water droplets on the web at a pressure sufficient to provide the web with filtration enhancing electret charge and (3) drying the web. This electret filter media may be used in a respiratory mask to provide extraordinarily good filtration properties.
Owner:3M CO
Aqueous carbon nanotube applicator liquids and methods for producing applicator liquids thereof
ActiveUS20060204427A1Low toxicityEasy to takeMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon fibresLiquid mediumVolumetric Mass Density
Certain applicator liquids and method of making the applicator liquids are described. The applicator liquids can be used to form nanotube films or fabrics of controlled properties. An applicator liquid for preparation of a nanotube film or fabric includes a controlled concentration of nanotubes dispersed in a liquid medium containing water. The controlled concentration is sufficient to form a nanotube fabric or film of preselected density and uniformity.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Plasma treatment of porous materials
InactiveUS6878419B2Improve wettabilityEfficient processingSemi-permeable membranesLayered productsCapacitanceMicrometer
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Absorbent sheet exhibiting resistance to moisture penetration
ActiveUS20040250969A1Reduce feelingsReduce wetted areaNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationWaxFiber
An absorbent paper sheet is treated with an aqueous wax dispersion such that the sheet includes a fused wax and emulsifier residue in an amount of from about 1 to about 20 weight percent of the sheet based on the combined weight of the fiber, wax residue and an emulsifier residue in the sheet. The fused wax emulsion operates to make at least one surface of the sheet laterally hydrophobic, exhibiting a moisture penetration delay of at least about 2 seconds and less than about 40 seconds as well as a typical contact angle with water at one minute of at least about 50 degrees. There is thus provided absorbent products which exhibit both absorbency and resistance to moisture penetration. The treated sheet further exhibits microbial barrier properties, impeding transfer of bacteria, for example, through the sheet. There are produced tissue products which resist moisture penetration from propelled liquids as well as sequester sorbed liquids in the interior of the tissue.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
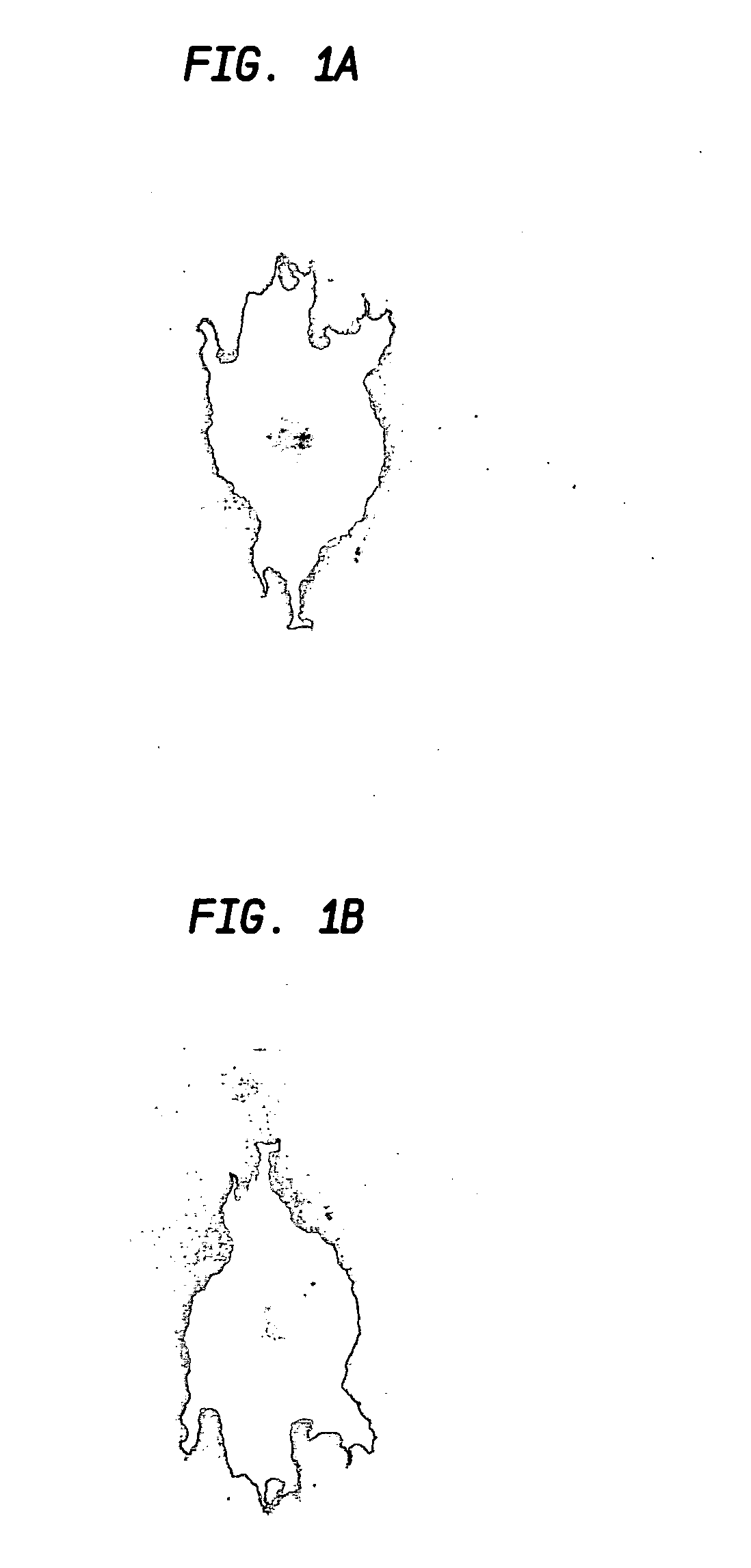
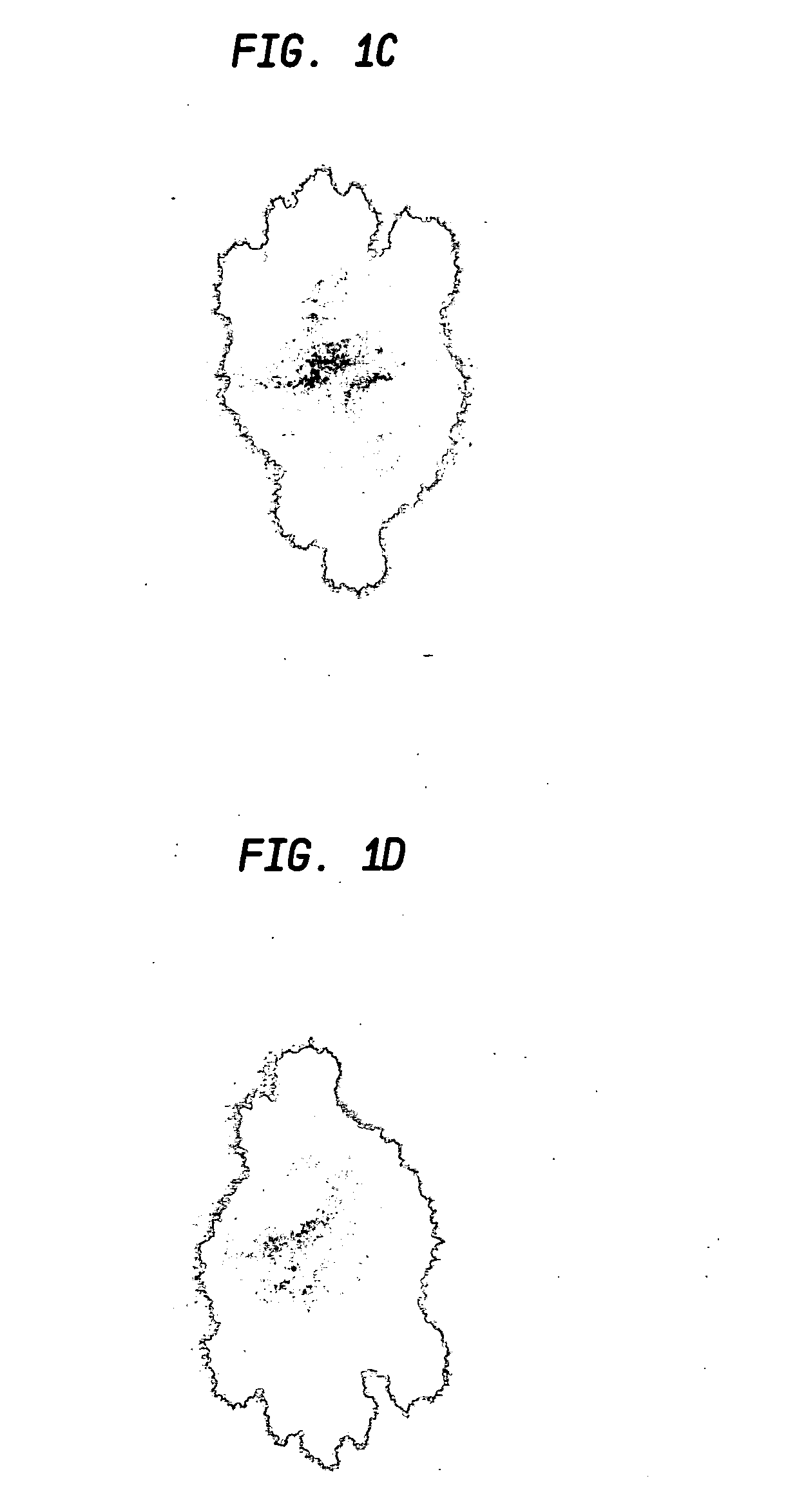
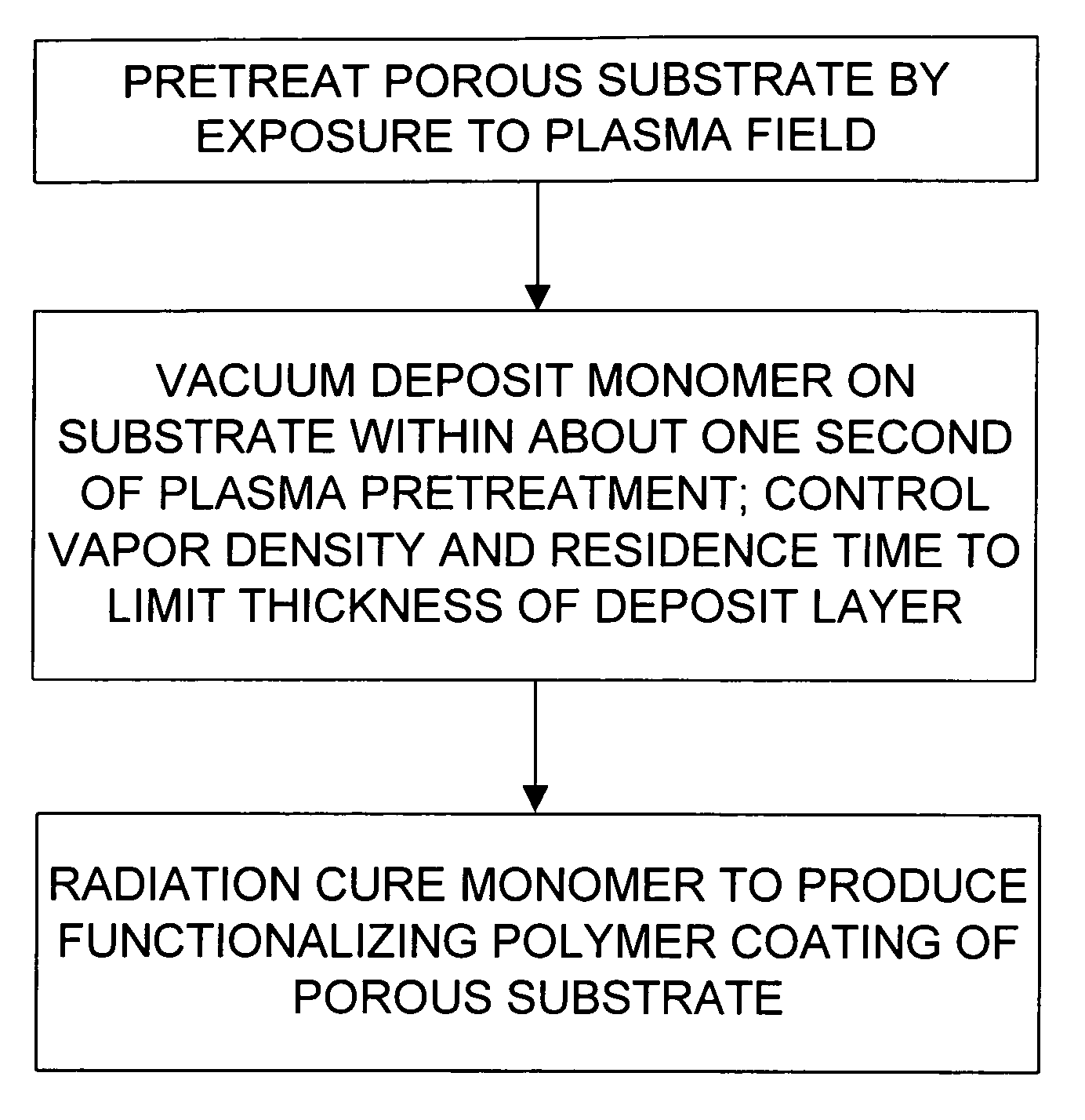
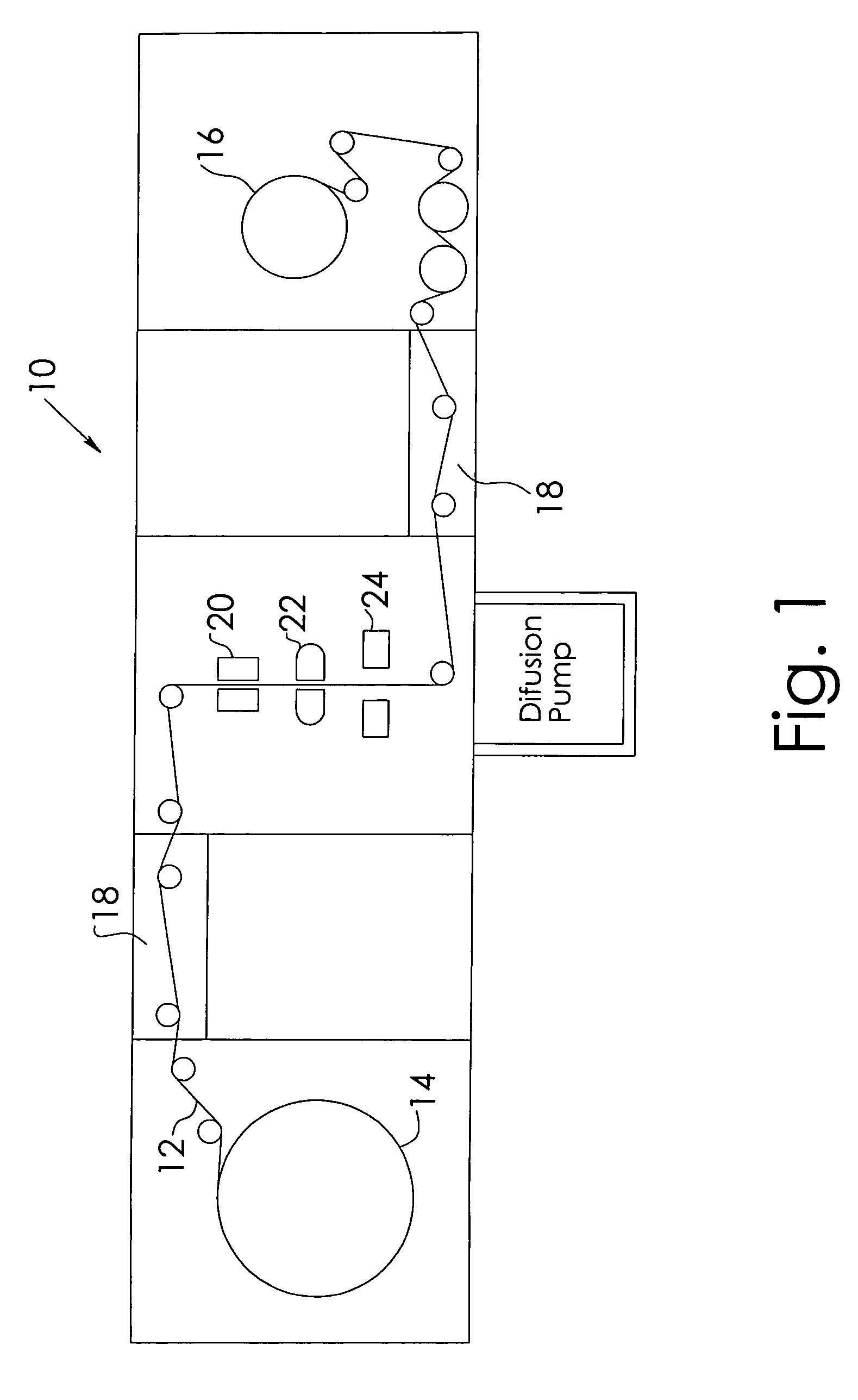
Functionalization of porous materials by vacuum deposition of polymers
InactiveUS7157117B2Improve reflectivityReduced durabilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesPorous substrateFiber
A porous substrate is pretreated in a plasma field and a functionalizing monomer is immediately flash-evaporated, deposited and cured over the porous substrate in a vacuum vapor-deposition chamber. By judiciously controlling the process so that the resulting polymer coating adheres to the surface of individual fibers in ultra-thin layers (approximately 0.02–3.0 μm) that do not extend across the pores in the material, the porosity of the porous substrate is essentially unaffected while the fibers and the final product acquire the desired functionality. The resulting polymer layer is also used to improve the adherence and durability of metallic and ceramic coatings.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Durable charged particle coatings and materials
This invention concerns coatings having high surface area materials and at least one metal ion adsorbed onto the high surface area material as well as substrates having the coating and methods of applying the coating. The substrates may be films, woven fabrics or may be nonwoven fabrics. The coatings have good odor and / or gas absorbing capabilities. Nonwoven fabrics include tissues, towels, coform materials, bonded carded webs, spunbond fabrics and so forth. The substrates may be made into storage and packaging material to reduce odor and retard the ripening of fruit. The substrates may be used in personal care products, to produce clothing for military and civilian applications and many other applications.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Rotary spinning processes for forming hydroxyl polymer-containing fibers
InactiveUS7655175B2Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberMaterials science
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Fibrillated bast fibers as reinforcement for polymeric composites
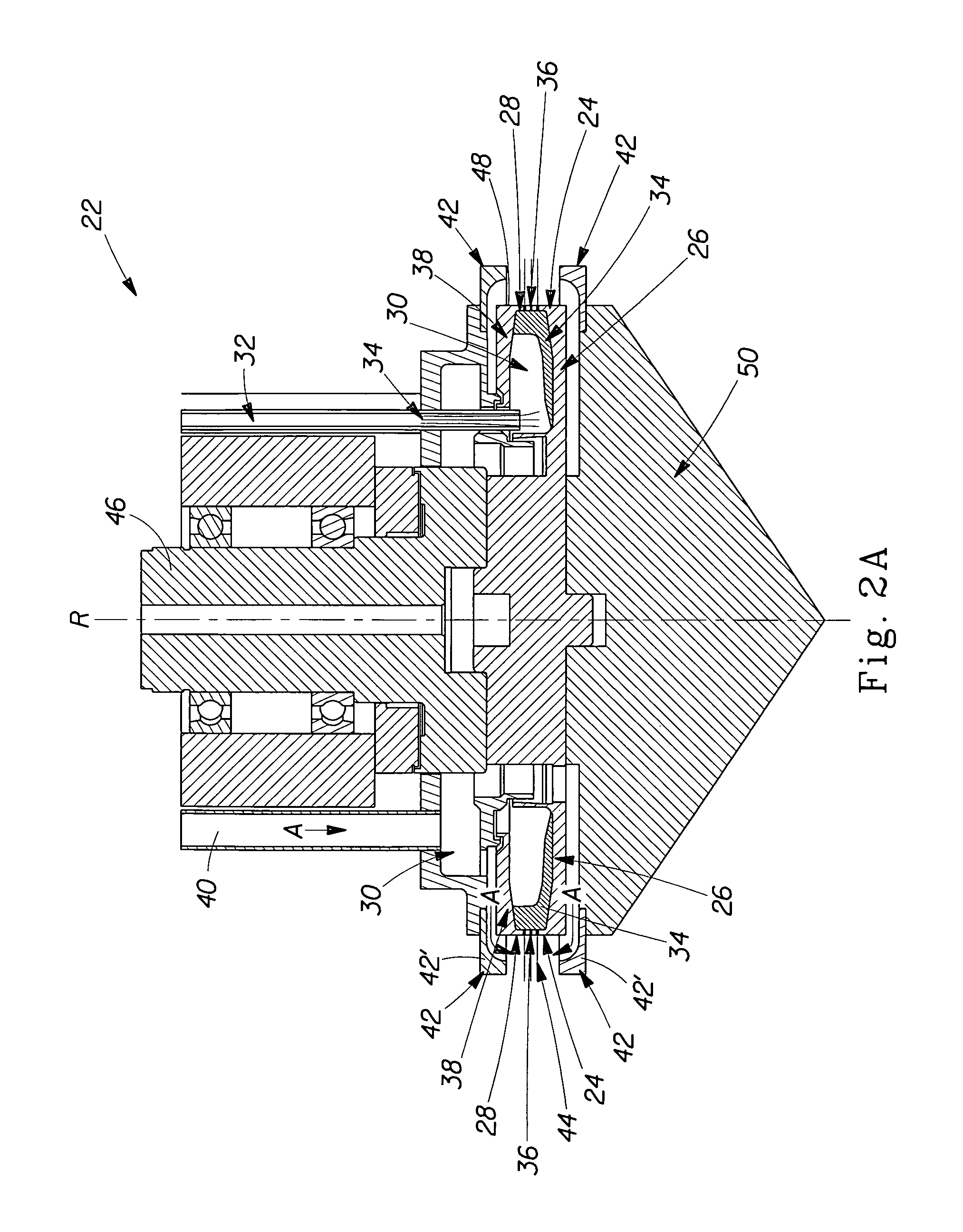
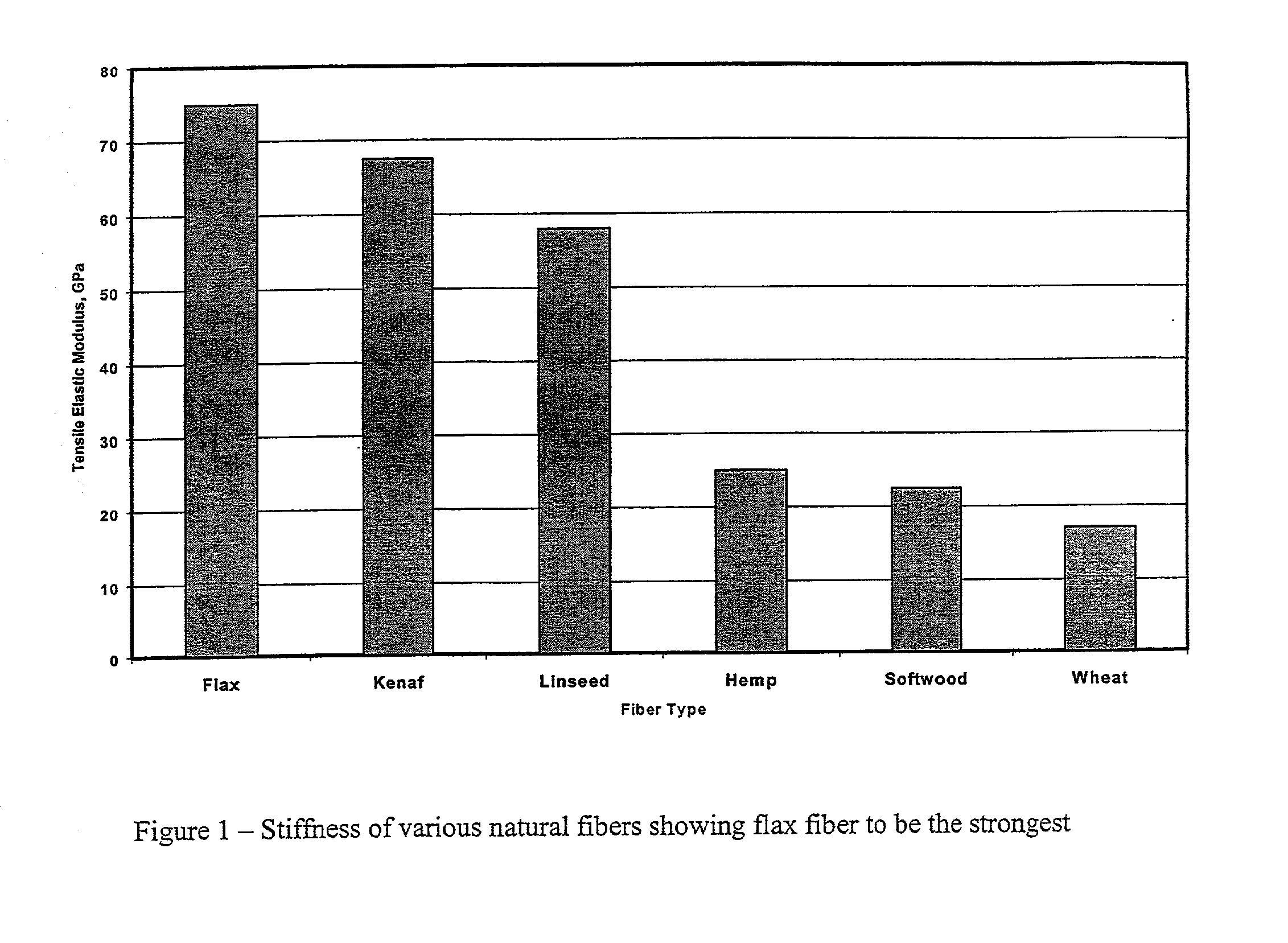
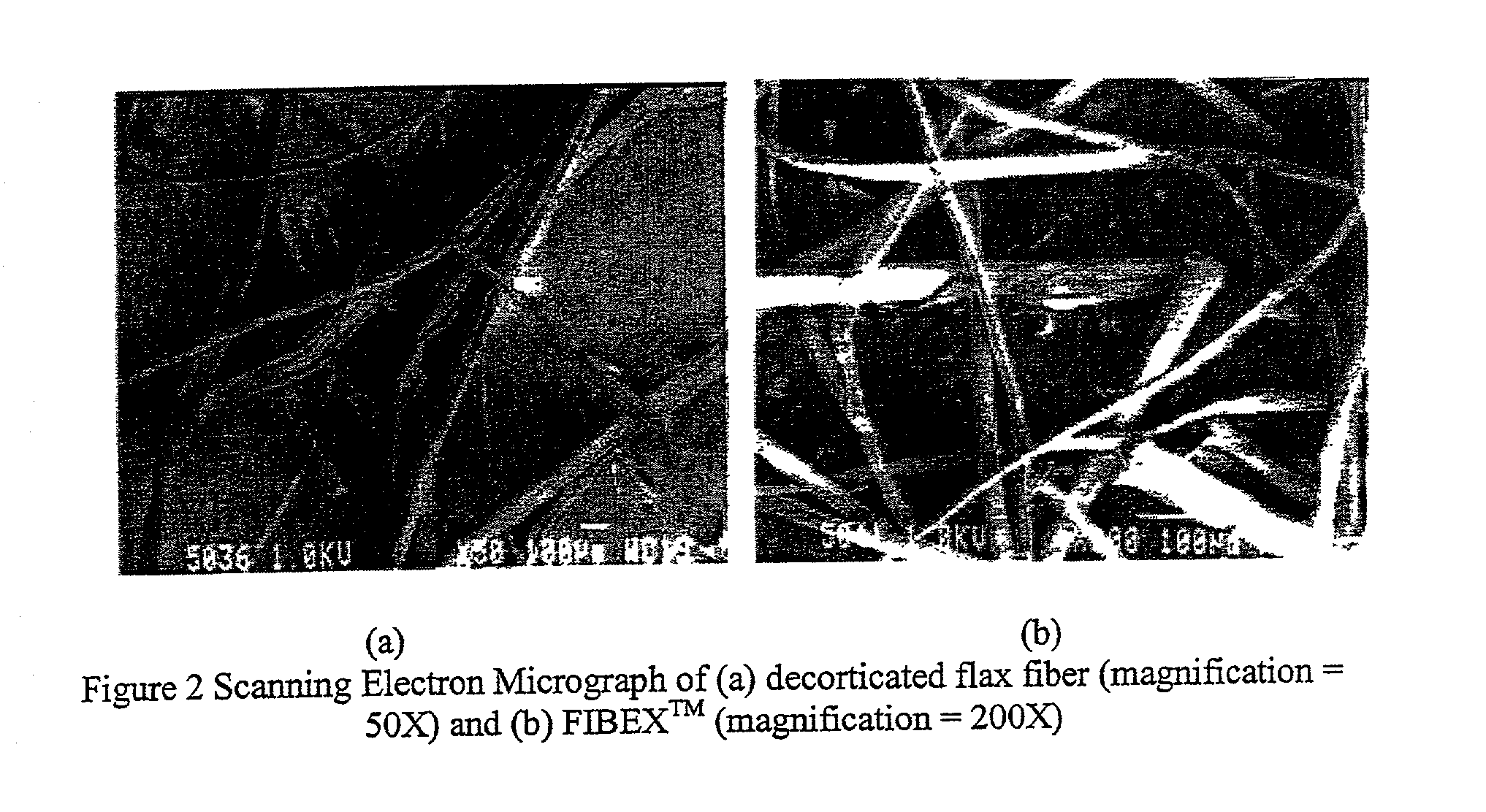
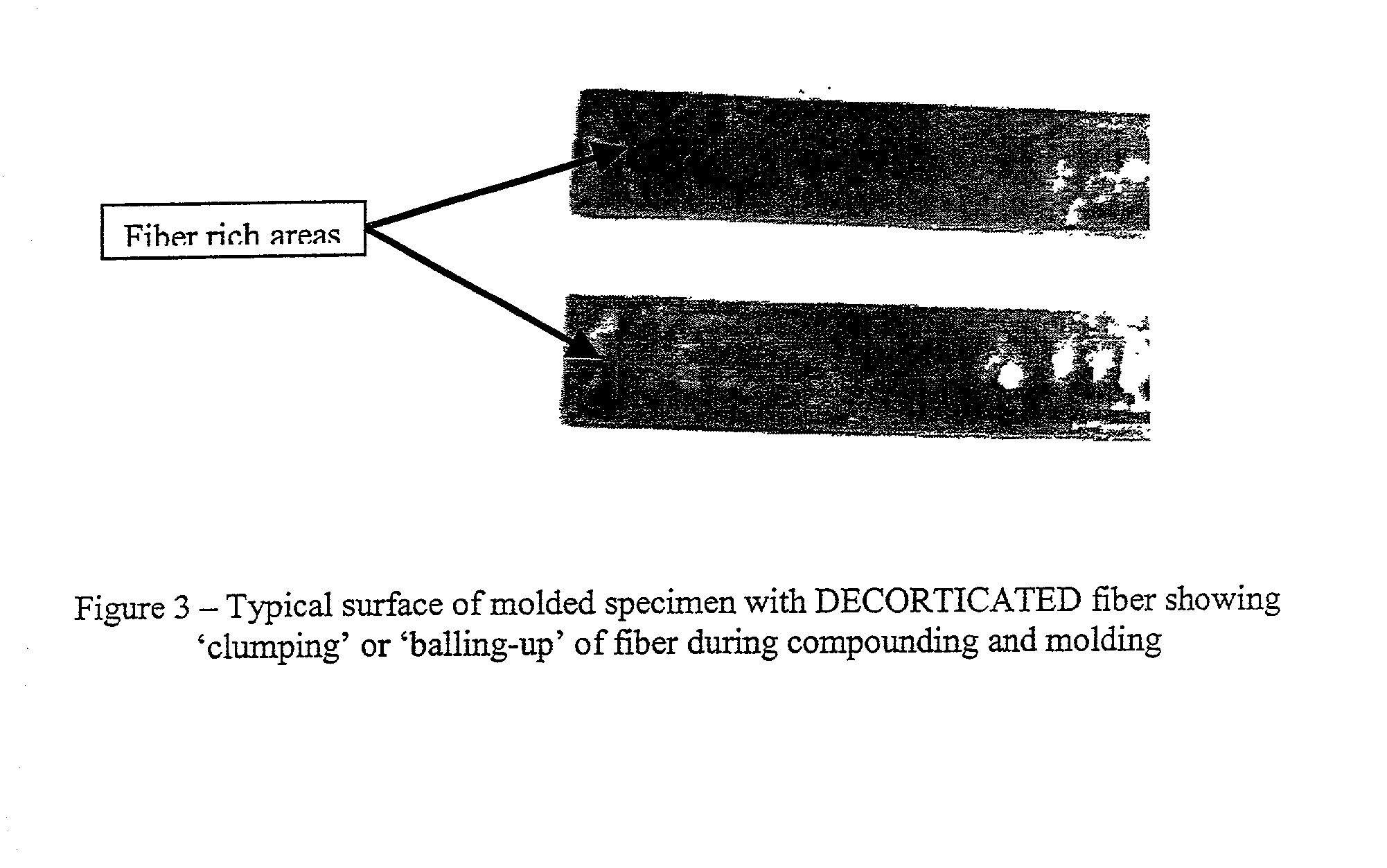
A decorticated bast fiber such as from flax that is particularly suitable as a reinforcement for polymeric resins, thermoplastic, and thermoset composites. The invention specifically overcomes past difficulties involving compounding and injection molding of composite specimens with bast fiber reinforcements. In one form, ultrasonic energy is applied to decorticated bast fibers to cause fibrillation.
Owner:ENG MECHANICS CORP OF COLUMBUS
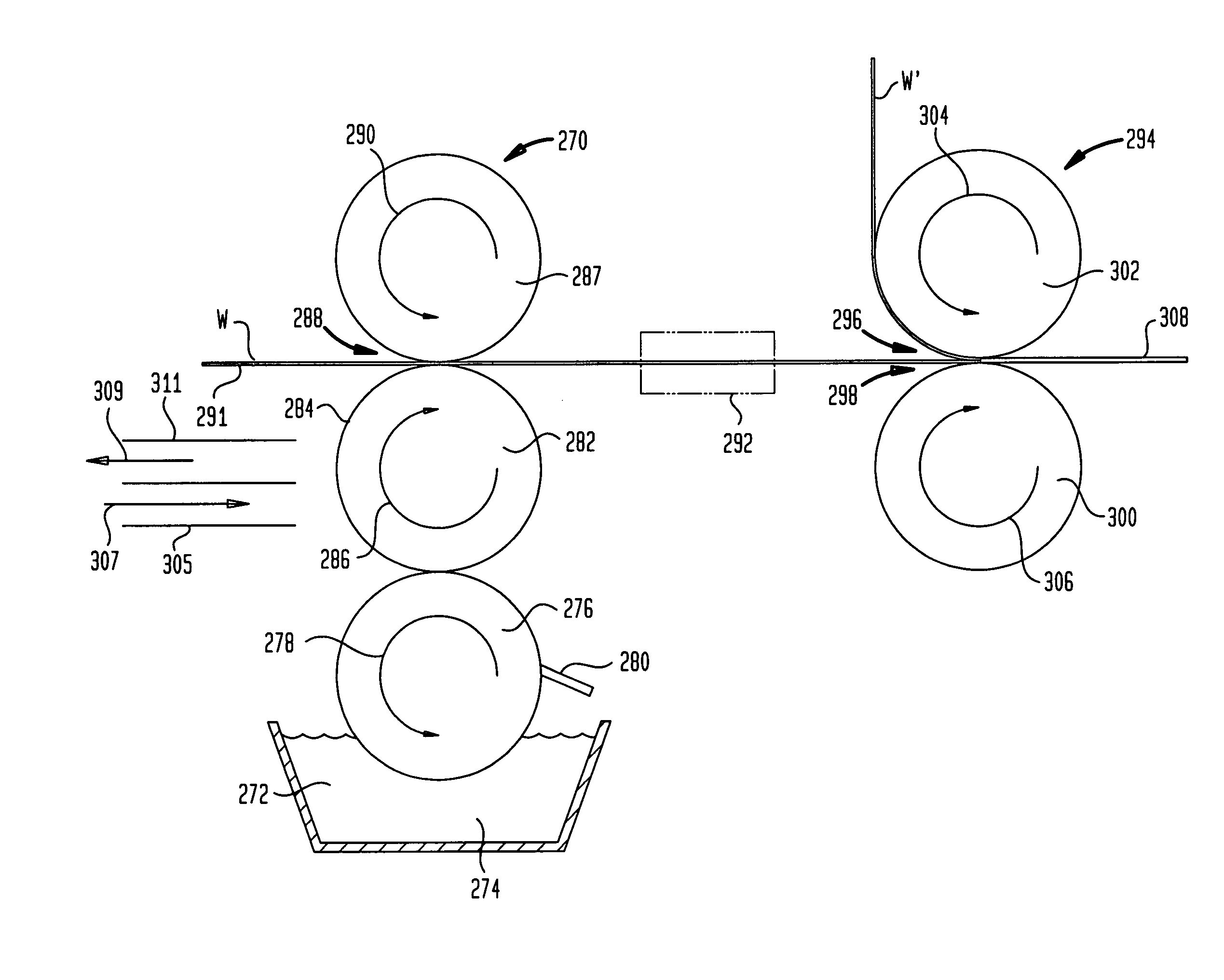
Atmospheric pressure plasma assembly
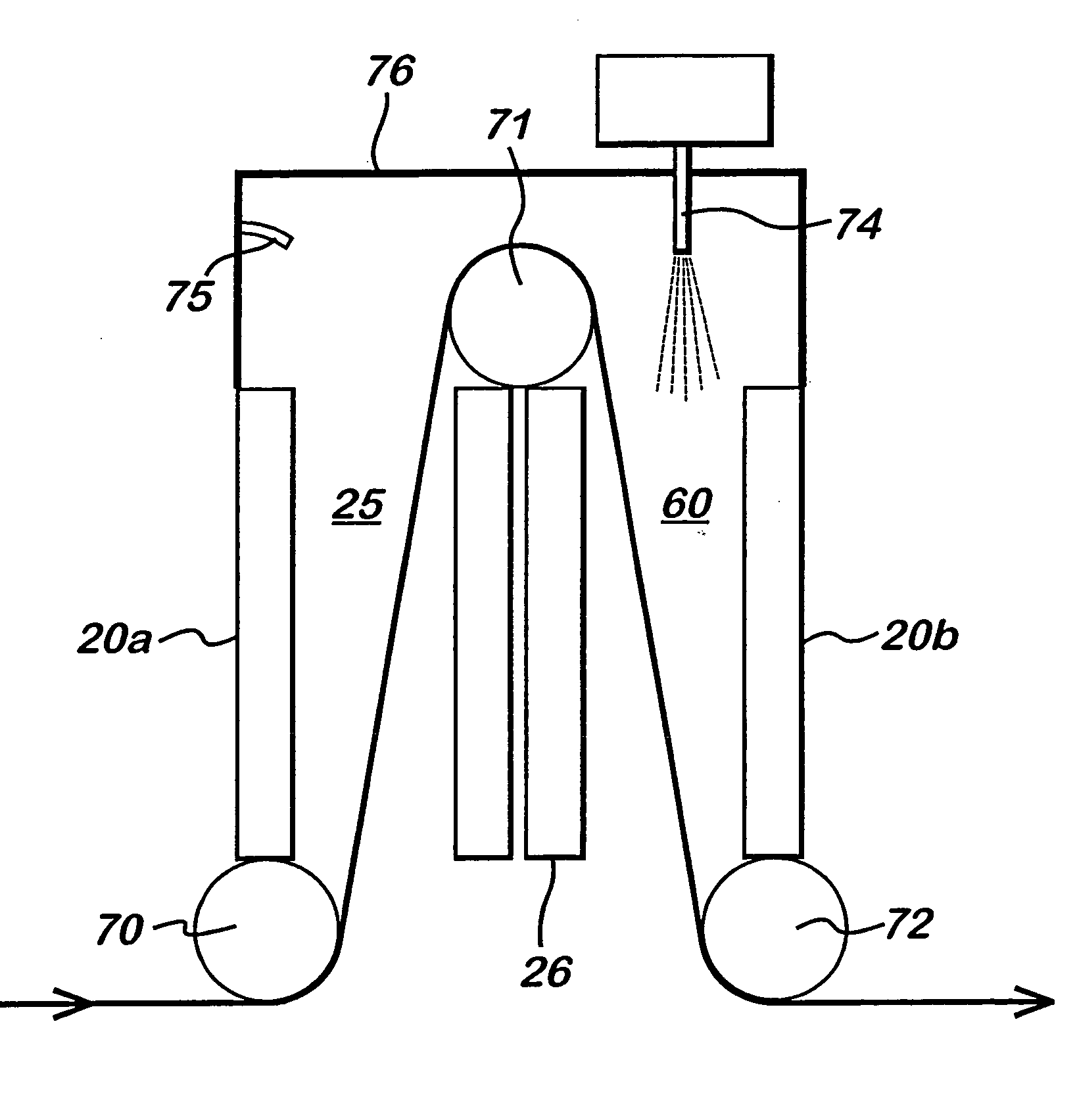
InactiveUS20050178330A1Efficient cooling agentEfficient electrodeElectric discharge tubesSurgeryPlanar electrodeDielectric plate
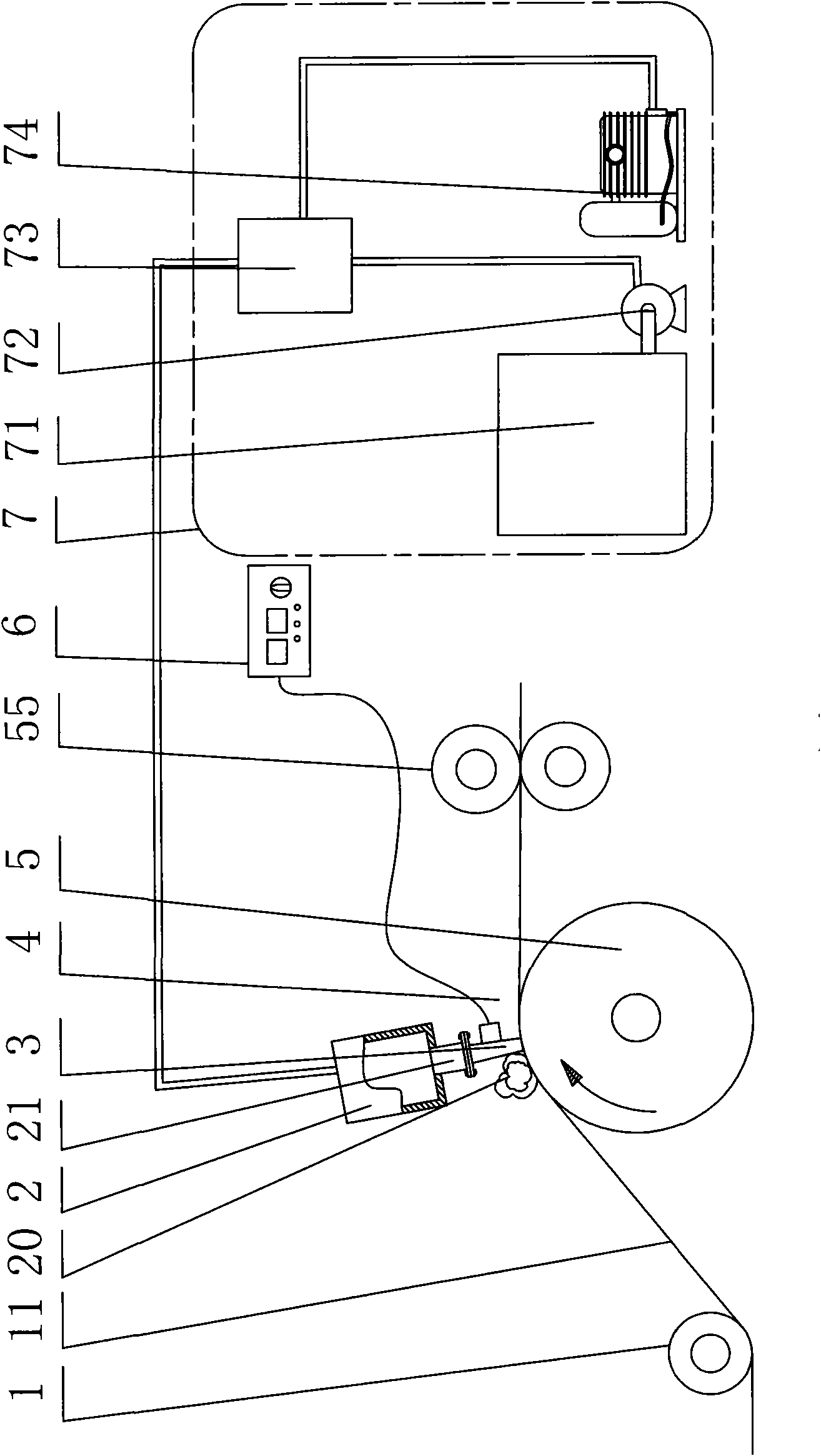
An atmospheric pressure plasma assembly (1) comprising a first and second pair of vertically arrayed, parallel spaced-apart planar electrodes (36) with at least one dielectric plate (31) between said first pair, adjacent one electrode and at least one dielectric plate (31) between said second pair adjacent one electrode, the spacing between the dielectric plate and the other dielectric plate or electrode of each of the first and second pairs of electrodes forming a first and second plasma regions (25,60) characterised in that the assembly further comprises a means of transporting a substrate (70,71,72) successively through said first and second plasma regions (25,60) and an atomiser (74) adapted to introduce an atomised liquid or solid coating making material into one of said first or second plasma regions.
Owner:DOW CORNING IRELAND
Porous and non-porous nanostructures and application thereof
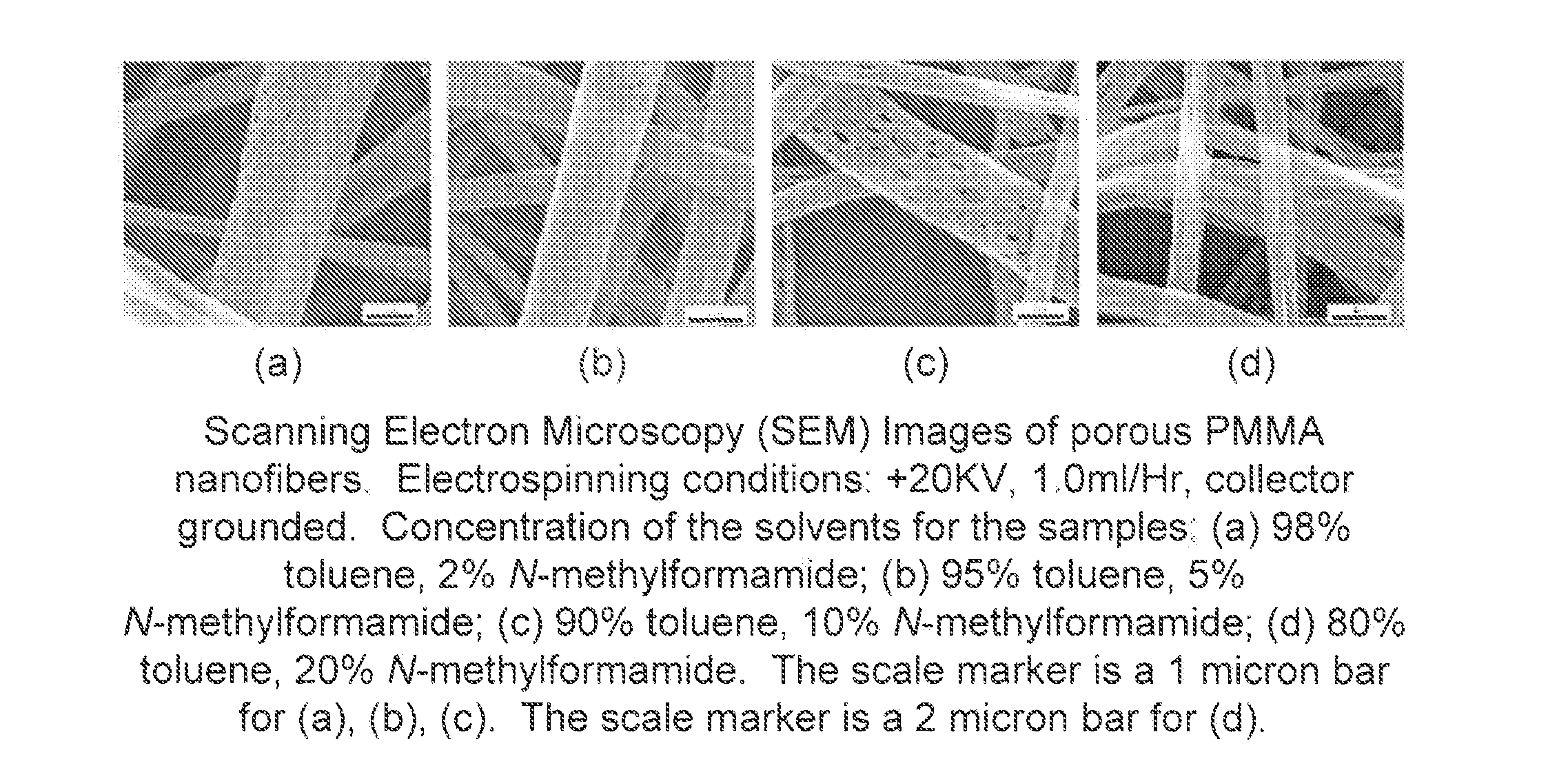
ActiveUS20110194304A1Increased process windowNatural cellulose pulp/paperPretreated surfacesNanoparticleNanofiber
A method for producing a fiber membrane of nanofibers that have both smooth and porous surface features. The method includes materials processing using polymer mixes with solvents and melt polymers with additives. The method includes nanomaterial incorporation onto a fiber structure after formation of the fiber structure. The fiber structure can be a part of a nanoparticle carrier material, a nanoparticle disposal medium, a lighting medium, and a catalysis medium.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Electroconductive fibers with carbon nanotubes deposited thereon, electroconductive threads, fiber structure, and process for producing same
ActiveCN102131980AImprove conductivityGood flexibilityFibre typesUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentPolymer scienceMicrometer
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
Tourmaline electret polylactic acid melt-blown non-woven cloth and manufacture method
InactiveCN103061038AGood dispersionHigh softening temperatureUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentNon-woven fabricsFiberFilter effect
The invention relates to tourmaline electret polylactic acid melt-blown non-woven cloth and a manufacture method. The tourmaline electret polylactic acid melt-blown non-woven cloth is manufactured through tourmaline modified polylactic acid melt-blown ultrafine fibers, wherein the diameter of the fiber ranges from 1 mu m to 10 mu m, and the tourmaline modified polylactic acid melt-blown ultrafine fiber is made of polylactic acid, tourmaline and assistant. The mass of the tourmaline is 1-3% of the mass of the polylactic acid, the assistant comprises coupling agent, dispersing agent and diluent, the mass of the coupling agent occupies 2-3% of that of the tourmaline, the mass of the dispersing agent occupies 1-3% of the mass of the tourmaline, and the mass of the diluent is three times as that of the coupling agent. The tourmaline electret polylactic acid melt-blown non-woven cloth is good in filtering effect, non-toxic, harmless and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for finishing wool fabric by compositing chitosan/TiO2
ActiveCN103981694AImprove the efficiency of grafting reactionGood antibacterialLiquid/gas/vapor removalUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentCooking & bakingPollution
The invention provides a method for finishing wool fabric by compositing chitosan / TiO2, which comprises the following steps: A)pretreating fabric; B)preparing composite finishing liquor, taking butyl titanate and dissolving in ethanol, adding diethanolamine, uniformly stirring and adding mixed liquor mixed by ethanol and water, heating, stirring under a backflow state to form nano TiO2 sol; adding chitosan, citric acid and sodium hypophosphate in the nano TiO2 sol, uniformly stirring to obtain the composite finishing liquor; C)finishing wool fabric, placing wool fabric in the composite finishing liquor, dipping and padding twice, wherein mangle expression is 85% and padding temperature is 50-65%; D)predrying; E)baking; F)washing; and G)drying. According to the finishing method, chitosan and nano TiO2 sol are employed as the composite finishing liquor, the finished wool fabric has good antibiosis, shrinkproof, ultraviolet resistance and anti-insolation performances; the finishing method generates no pollution on human body and environment, and the finished wool fabric has good hand feeling.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGXIN DYEING & FINISHING CO LTD
Absorbent sheet exhibiting resistance to moisture penetration
ActiveUS7300547B2Reduce feelingsReduce wetted areaNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationWaxFiber
An absorbent paper sheet is treated with an aqueous wax dispersion such that the sheet includes a fused wax and emulsifier residue in an amount of from about 1 to about 20 weight percent of the sheet based on the combined weight of the fiber, wax residue and an emulsifier residue in the sheet. The fused wax emulsion operates to make at least one surface of the sheet laterally hydrophobic, exhibiting a moisture penetration delay of at least about 2 seconds and less than about 40 seconds as well as a typical contact angle with water at one minute of at least about 50 degrees. There is thus provided absorbent products which exhibit both absorbency and resistance to moisture penetration. The treated sheet further exhibits microbial barrier properties, impeding transfer of bacteria, for example, through the sheet. There are produced tissue products which resist moisture penetration from propelled liquids as well as sequester sorbed liquids in the interior of the tissue.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Fibrillated bast fibers as reinforcement for polymeric composites
InactiveUS6767634B2Ultrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentThermoplasticPolymer resin
A decorticated bast fiber such as from flax that is particularly suitable as a reinforcement for polymeric resins, thermoplastic, and thermoset composites. The invention specifically overcomes past difficulties involving compounding and injection molding of composite specimens with bast fiber reinforcements. In one form, ultrasonic energy is applied to decorticated bast fibers to cause fibrillation.
Owner:ENG MECHANICS CORP OF COLUMBUS
Preparation method of soft and durable anti-penetrating material
ActiveCN107815870AIncreased durabilityGood flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentGrip property fibresFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of a soft and durable anti-penetrating material. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing shearing thickening liquid; (2) preparing a high performance fiber fabric with a special tissue structure, namely preparing a fabric from high performance fibers by virtue of a special tissue structure weaving process, putting the fabric into a vacuum drying oven, and drying at 120-150 DEG C for 2-3 hours; and (3) preparing the anti-penetrating material. According to the method, by virtue of reasonable tissue structure configuration on the fabric and plasma treatment on the shearing thickening liquid and the fabric, the shearing thickening liquid and the fabric are adequately compounded, so that the durabilityand flexibility of the anti-penetrating material are improved, and the soft and durable anti-penetrating material suitable for multiple environments of daily protective clothes of military police, armored military equipment, civil and industrial protection and the like is prepared.
Owner:江苏威之盾安防科技有限公司
Rubber-reinforcing fiber, process for producing the same, and rubber product and pneumatic tire each made with the same
InactiveUS20030000619A1Sufficient fatigue resistanceSolve the lack of resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsTyresFiberTitanium
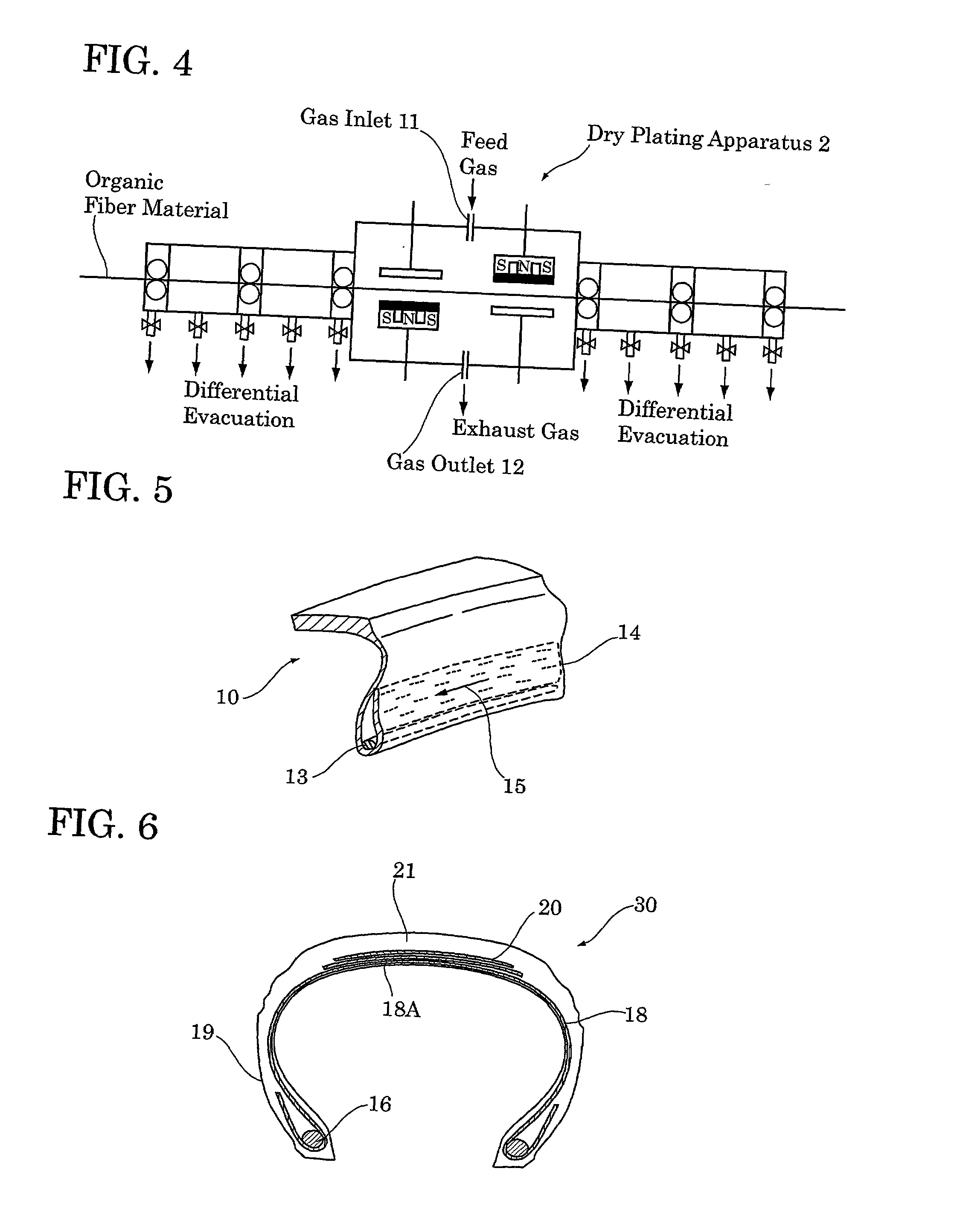
The rubber-reinforcing fiber of the present invention is provided with a coating layer of a thickness of 10 Å to 40 mum. The coating layer is formed by dry plating and contains at least one metal and / or metal compound selected from the group consisting of cobalt, zinc, copper, titanium, silver, nickel and compounds of the aforesaid metals. With such a coating layer, the rubber-reinforcing fiber of the present invention forms a firm adhesion to a rubber component and drastically improves the fatigue resistance and durability of a rubber article, particularly, a pneumatic tire.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Bacteriostatic antistatic multifunctional non-woven fabric
ActiveCN101638846AFine foamImprove stabilityFibre typesUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentUltravioletNonwoven fabric
The invention relates to a bacteriostatic antistatic multifunctional non-woven fabric which is fabricated by the steps of unwinding non-woven gray fabric; applying finishing agent by using an ultrasonic foam applicator; extruding out redundant finishing agent by using a rolling mill; and then drying by using a baking oven and winding. The finishing agent includes the following components: sodium dodecyl sulfate, hydroxyethyl cellulose, nanometer silver powder, penetrating agent JFC, nano-silica, gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, sorbitan ester, cetyltrimethyl ammonium chloride, methacrylic acid, beta-cyclodextrin and spices. The non-woven fabric has multiple functions of being antibacterial, anti-static, anti-ultraviolet, washing-resisting, fragrance lasting and the like. Especially the ultrasonic foam applicator is utilized to conduct foam finishing, and the finishing agent can be evenly penetrated in the fiber structure by means of the effect of ultrasonic waves, so as to lead nanometer material in the finishing agent and particles of the spices to disperse in the fabric and to be wrapped by organic matters to form a microcapsulation state, so that all functions and effects are lasting.
Owner:仙桃新发塑料制品有限公司
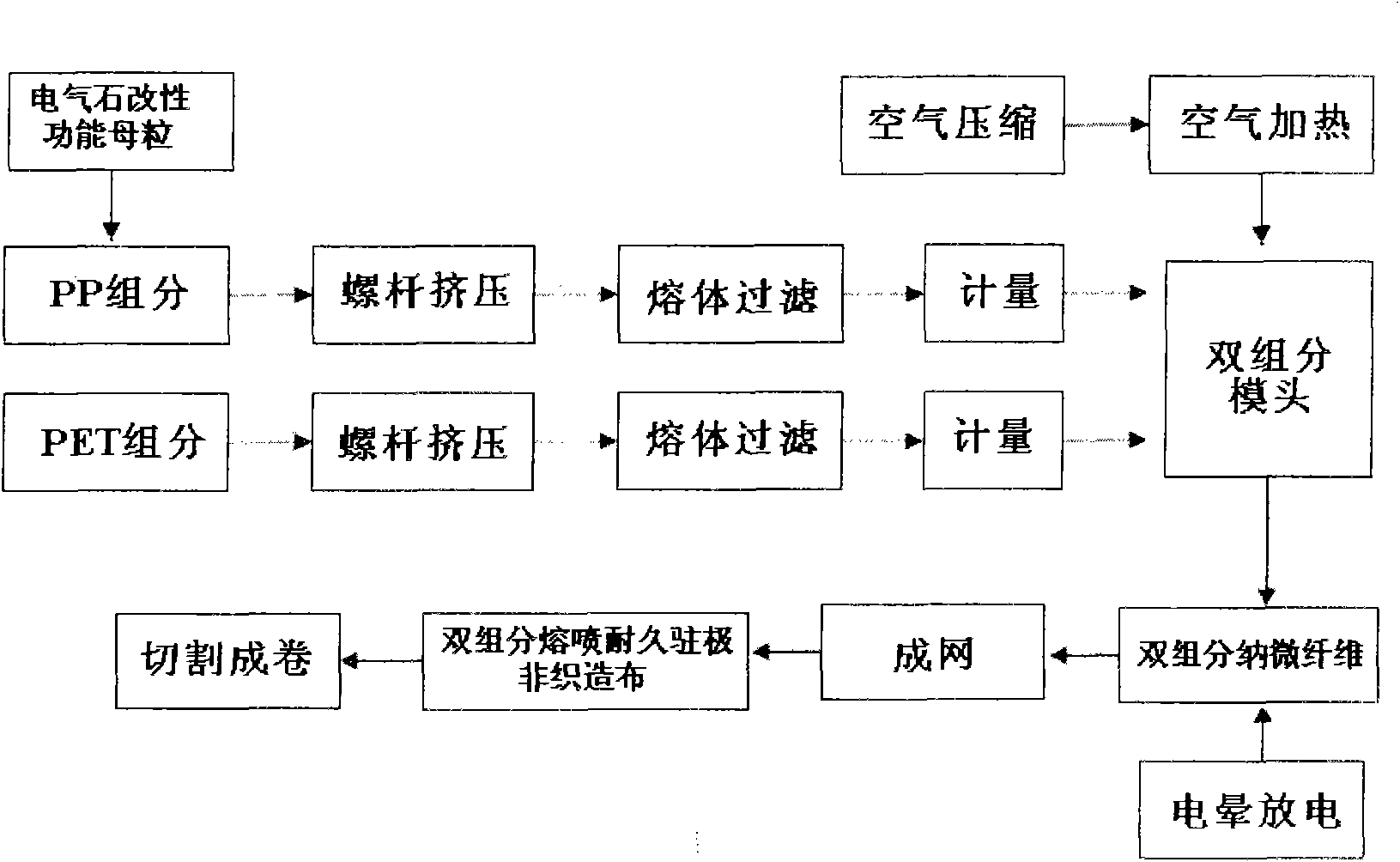
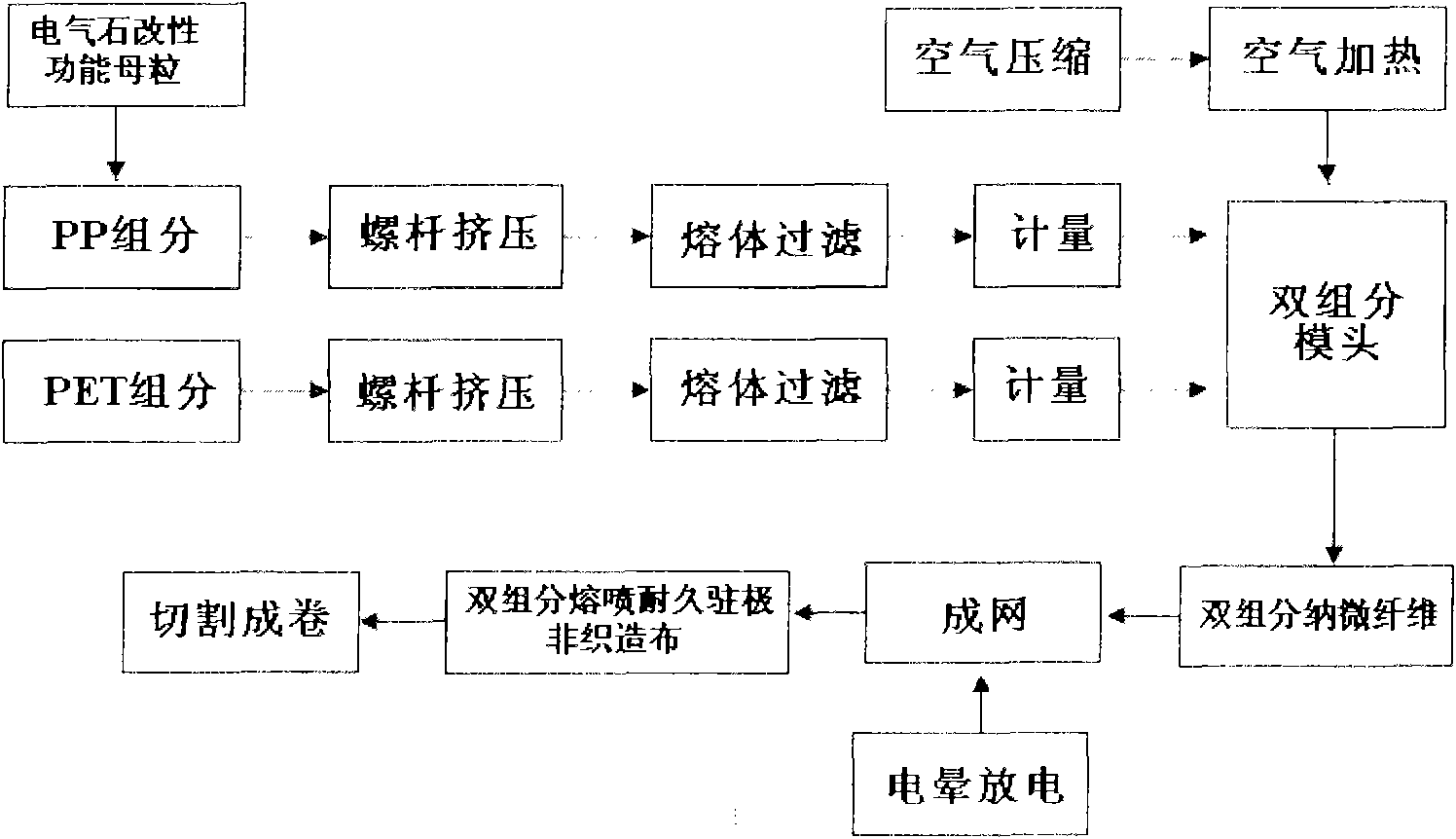
Double-component melt-blown durable electret non-woven fabric and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101591837ASoft touchImprove breathabilityElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureArtificial filament physical treatmentFiltrationThermal insulation
The invention relates to a double-component melt-blown durable electret non-woven fabric and a manufacturing method thereof. The non-woven fabric consists of tourmaline modified polypropylene / polyethylene glycol adipate (tourmaline modified PP / PET) parallel double-component melt-blown nano microfiber; and the fiber has the following components in percentage by mass: 20 to 80 percent of tourmaline modified PP, and 80 to 20 percent of PET. The method for manufacturing the non-woven fabric adopts the components in percentage by mass and the process steps of: (1) performing drying pre-treatment on the PET first; (2) then preparing a double-component melt-blown non-woven fabric by tourmaline modified PP / PET melt-blown composite spinning technology; and (3) finally obtaining the double-component melt-blown durable electret non-woven fabric by performing high-voltage corona discharge electret treatment on the non-woven fabric. The non-woven fabric can be used for durable high-efficiency filtration materials, and can also be applied to thermal insulation materials, antibacterial medical materials, oil absorption materials and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Durable charged particle coatings and materials
This invention concerns coatings having high surface area materials and at least one metal ion adsorbed onto the high surface area material as well as substrates having the coating and methods of applying the coating. The substrates may be films, woven fabrics or may be nonwoven fabrics. The coatings have good odor and / or gas absorbing capabilities. Nonwoven fabrics include tissues, towels, coform materials, bonded carded webs, spunbond fabrics and so forth. The substrates may be made into storage and packaging material to reduce odor and retard the ripening of fruit. The substrates may be used in personal care products, to produce clothing for military and civilian applications and many other applications.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
POSS-modified polypropylene melt-blown nonwoven fabric and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101724982AGood mechanical propertiesSoft touchUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentNon-woven fabricsPolymer scienceSilsesquioxane
The invention relates to a polyhedral silsesquioxane (POSS)-modified polypropylene melt-blown nonwoven fabric and a preparation method thereof. The nonwoven fabric is made of POSS-modified polypropylene melt-blown nano-micro fibers. According to the formula, the fibers comprise the following components in percentage by mass: PP 93-99 and POSS 1-7. The manufacturing method of the nonwoven fabric is based on the mass percentage formula of the fibers and comprises the following process steps: (1), adding POSS into polypropylene to prepare polypropylene functional mother particles; (2) preparing a POSS-containing polypropylene melt-blow nonwoven fabric; and (3) finally, processing the obtained nonwoven fabric with a high-voltage corona discharge electrets to obtain the POSS-modified polypropylene melt-blown nonwoven fabric. The nonwoven fabric is obviously improved in both mechanical property and filtering efficiency, and can be used in durable high-efficiency filter materials as well as heat insulation materials, antibacterial medical materials, oil absorbing materials and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Carbon nanotube pastes and methods of use
Dispersable pastes comprising single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) in water or in an organic solvent are prepared. The method of preparing the dispersable pastes comprises in general the following steps: a) removal of the catalyst used during the synthesis of SWNT; b) while the SWNT are still wet, addition of the appropriate amount of solvent, in a solvent / SWNT ratio which preferably varies between 30:1 and 100:1, depending on the desired viscosity of the paste; and c) high-energy horn sonication with a dismembrator probe. The resulting pastes are suitable for easy redispersion in solvents and incorporation in various matrices such as polymers. They are also suitable to be impregnated with metal precursors such as noble metal compounds for example, Pt. Appropriate drying and thermal treatments of the impregnated material produce metal-SWNT composites in which small metal clusters can be uniformly dispersed over the nanotube surface. These metal-SWNT composites may find applications as catalysts as well as electrodes for fuel cells, batteries, and capacitors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
A composite seam system
ActiveUS20050114989A1Small volumeReduce decreaseGarmentsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterAdhesive belt
A composite seam system including a narrow weld bead joining two panels of fabric and a seam tape applied thereon. The applied seam tape comprises a top layer, a reinforcing layer and an adhesive layer melted through the reinforcing layer and connecting the top layer to the fabric panels over the weld bead. The narrow weld bead and the small seam allowance of the fabric panels it joins allows the seam tape to be secured over the weld bead to the fabric panels while lying in a flat plane. The use of a narrow reinforcing layer of woven polyester, nylon or non-woven ultra-fine fibrous material in the seam tape allows the seam tape to be flexible enough to move with the fabric it joins, reducing the incidence of tape edge abrasion.
Owner:PATAGONIA
High-throughput efficient 2D net-shaped ultrafine nanofiber oil-water separation material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107557894AImprove throughputHigh porosityFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentFiberNanofiber
The invention discloses a high-throughput efficient 2D net-shaped ultrafine nanofiber oil-water separation material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a polymer solution is prepared from a selected polymer, a net is formed through electrostatic direct injection of the polymer solution, a spinneret vibrates in situ by the aid of external force inan electrostatic direct injection process to promote generation of charged droplets, the droplets are subjected to phase separation, and a uniform 2D net-shaped ultrafine nanofiber material is formedon the surface of a receiving substrate and is in a continuous and seamlessly stacked shape; then the obtained material is subjected to surface modification, and the 2D net-shaped ultrafine nanofiberoil-water separation material with selective surface and interface wetting property is obtained. The preparation process is simple, raw material limitations are few, and the net-shaped ultrafine nanofiber oil-water separation material has tiny meshes and good pore channel connectivity and has great application prospect in the fields of oil purification, oil-containing wastewater treatment and thelike.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
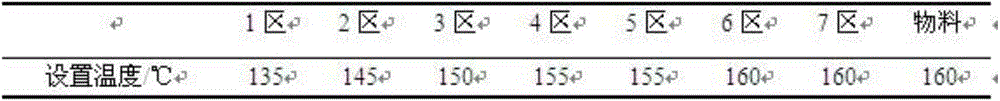
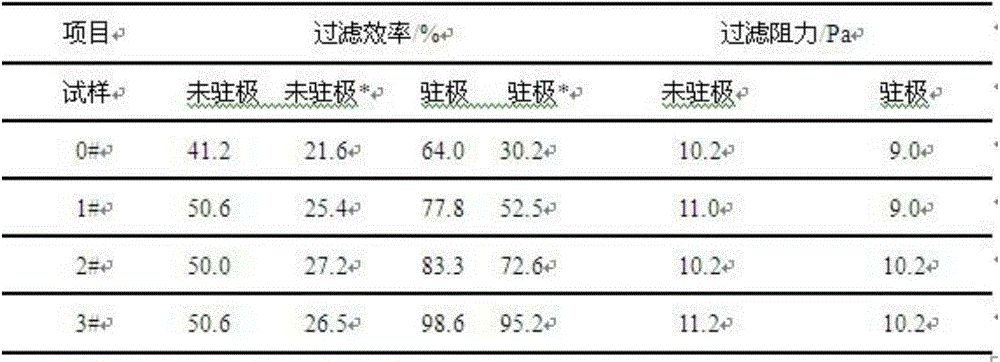
Melt-blow non-woven material capable of effectively filtering PM 2.5 particles, preparation method and production device
ActiveCN104153119AHigh filtration efficiencyImprove dust collection effectHeating/cooling textile fabricsUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentPorosityEngineering
The invention discloses a melt-blow non-woven material capable of effectively filtering PM 2.5 particles, a preparation method and a production device. The melt-blow non-woven material comprises, by weight percentage, 93-97 parts of polypropylene, 3-6 parts of electret master batch and 0.1-1 part of polyvinylidene fluoride. According to the melt-blow non-woven material capable of effectively filtering PM 2.5 particles, the polypropylene, the electret master batch and the polyvinylidene fluoride are compounded, the obtained melt-blow non-woven material is characterized by high porosity, the fiber diameter of smaller than two micrometers, large clogging capacity, high filtering efficiency and low resistance, an electret is good in charge storage performance after electret processing, the charge keeping rate can be above two years, and the electret can be used in a high-temperature and high-humidity environment. The product is environmentally friendly and free of pollution, has the advantages of being long in service life and wide in use range, and is particularly suitable for removing PM 2.5 particles in the air.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Aramid fiber reinforced PPESK base composite material interfacial modifying method
InactiveCN1978530AImprove performanceMeet the use requirementsFibre typesUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentKetoneOxygen
This invention is related to the interface modified method of aromatic fiber reinforced poly phthalazinone ehter sulfone ketone (PPESK) compound, using low-temperature plasma technology. The processed conditions are as follows: the atmosphere is oxygen, nitrogen, air, free ammonia or argon, the power is 10-400W, the time is 1-30 minutes, and the atmospheric pressure in the processing cavity is low pressure of 1-100Pa, normal pressure or high pressure of 1.01*105-106Pa. Etching the surface of Armoc aromatic fiber and modifying it by grafting, impregnating the modified Aromc aromatic fiber and the PPESK emulsion of 5-50% part by weight to prepare the prepreg of one-way fiber reinforced PPESK compound, and then preparing the said compound by using hot-pressed molding technology. The modified Aromc aromatic and the PPESK base can form a good interface layer, furthest realize the integrated performance of the compound, which is capable to meet the operating requirements of heat resistance and implement commercial processes in batch, continuity and large scale.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AERONAUTICAL ENG +1
Low bfs composite and process of making the same
InactiveUS20130059496A1Improve adhesionProtective equipmentLayered productsBallistic resistanceFibrous composites
Methods for producing composites useful for the formation of both soft and hard armor. More particularly, methods for the production of ballistic resistant fibrous composites having improved ballistic resistance properties, including low backface signature. The methods employ fiber surface treatments to improve the anchorage of substances applied onto fiber surfaces, achieving a low delamination tendency and corresponding benefits.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for protease-method wool felt-proofing treatment by using ultrasonic technology
InactiveCN103924439AHelps catalyze hydrolysisReduce processing timeBiochemical fibre treatmentUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentEngineeringUltrasonic technology
The invention discloses a method for protease-method wool felt-proofing treatment by using an ultrasonic technology, belongs to the application technical filed of wool fabric dyeing and finishing in the wool manufacturing industry and aims at solving the problems that the treating time is long, the felt-proofing rate is high and the fiber damage is large in a single protease method so as to realize the effect of optimizing wool fiber / wool top / wool fabric biological enzyme-method felt-proofing finishing. The felt proofing can be performed on wool under an ultrasonic condition, the protease catalytic hydrolysis speed is increased, the shedding off of a wool scale layer is accelerated, the protease method treating time is shortened, and the degradation of the protease to the inferiors of fibers is reduced. The synergistic effect of ultrasonic waves and the protease can replace a conventional chlorination method or single protease method felt-proofing method, so that the felt-proofing performance of wool fabrics is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com