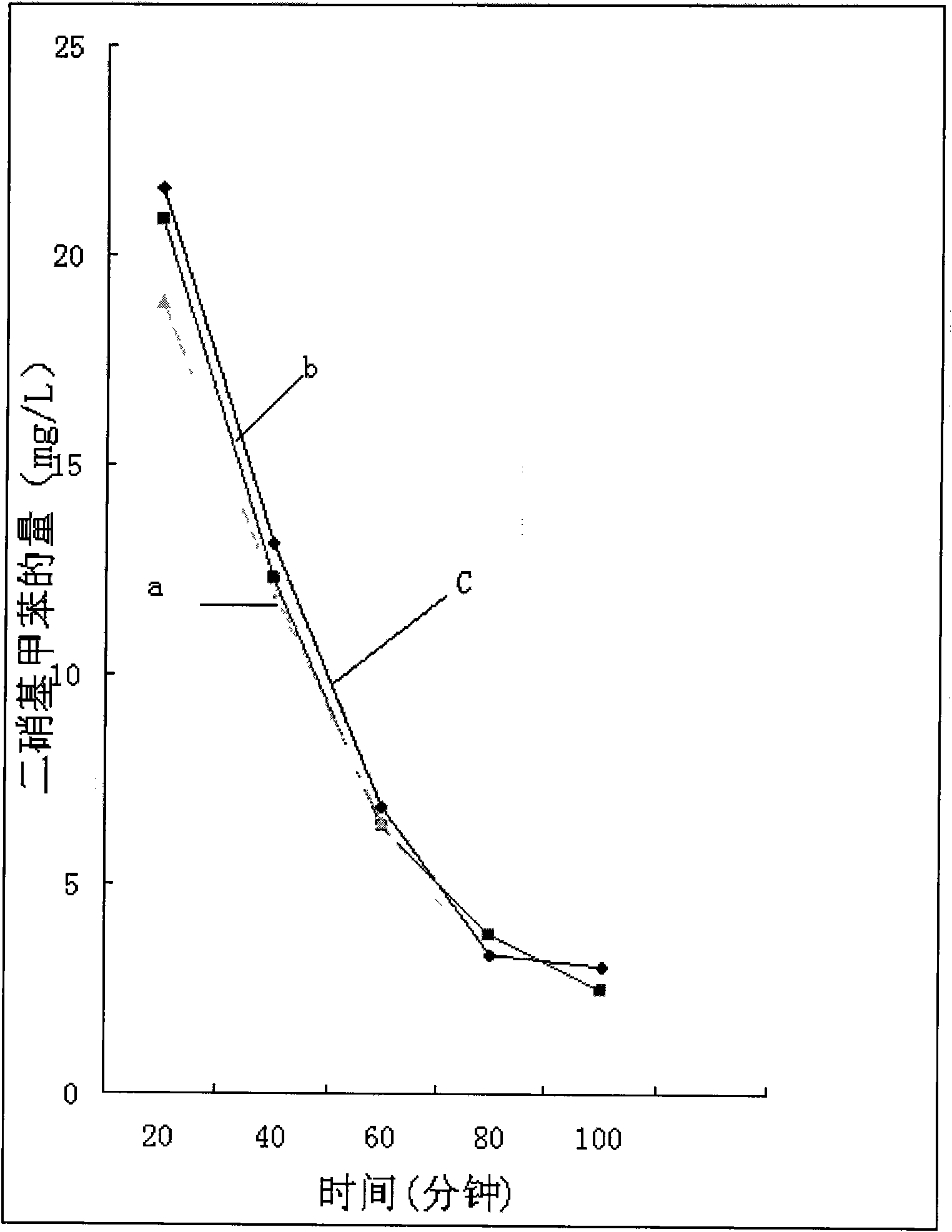
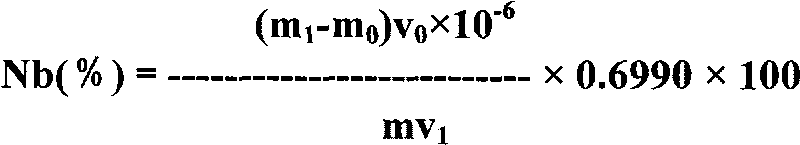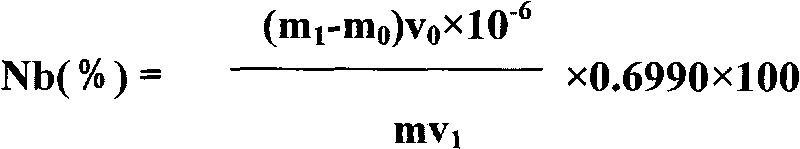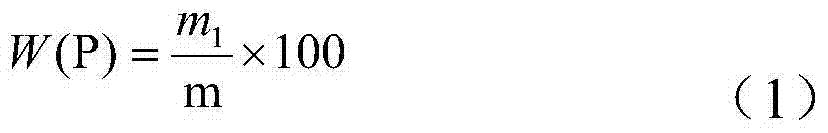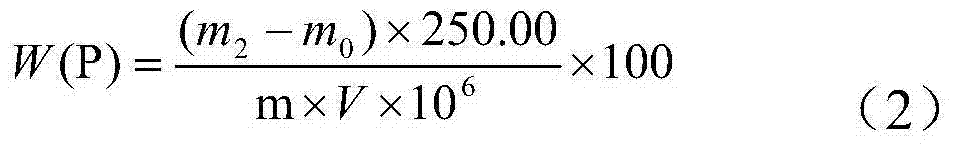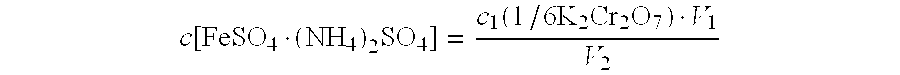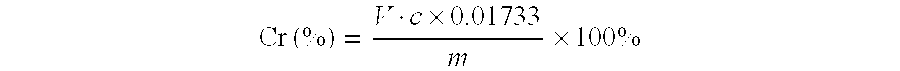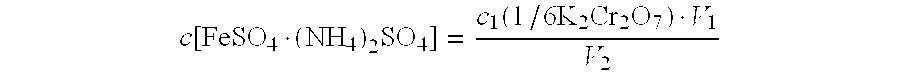Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
516 results about "Sodium peroxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sodium peroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Na₂O₂. This yellowish solid is the product of sodium ignited in excess oxygen. It is a strong base. This metal peroxide exists in several hydrates and peroxyhydrates including Na₂O₂·2H₂O₂·4H₂O, Na₂O₂·2H₂O, Na₂O₂·2H₂O₂, and Na₂O₂·8H₂O. The octahydrate, which is simple to prepare, is white, in contrast to the anhydrous material.
Oxygen fertilizer and preparation and application methods thereof
InactiveCN102584466ALift deathReduce economic costsFertilizer mixturesOxygen preparationSodium oxideChemistry
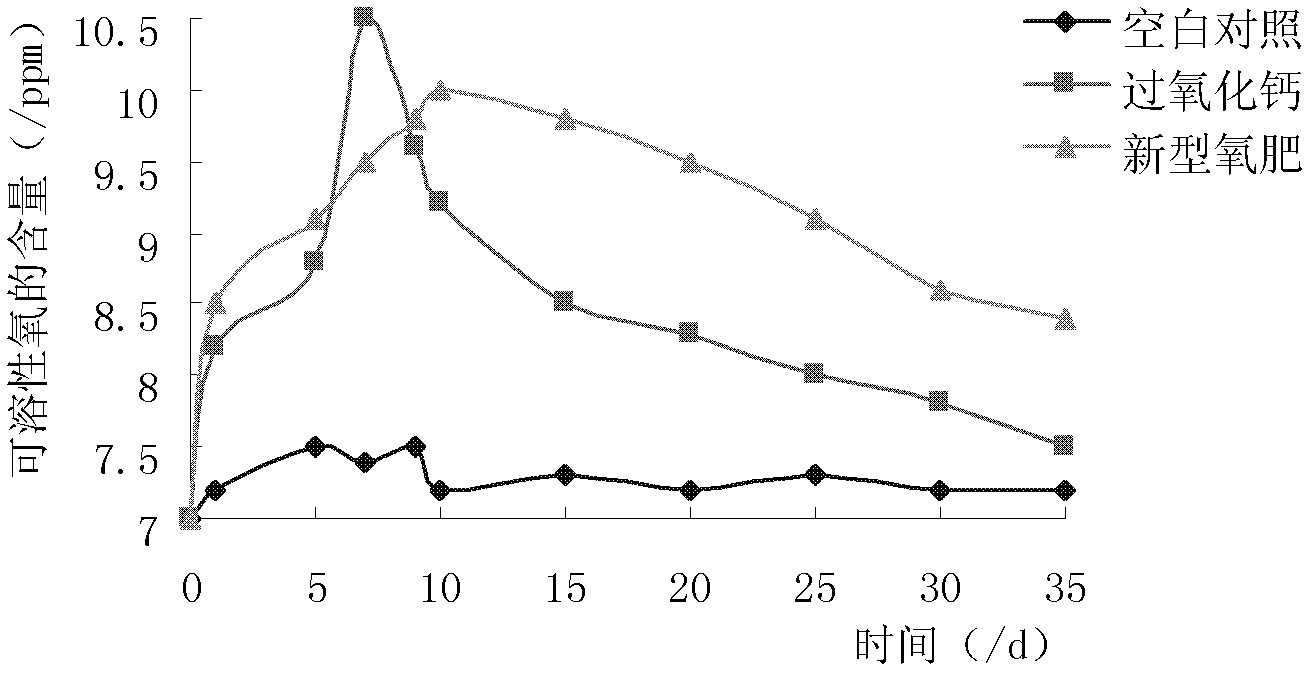
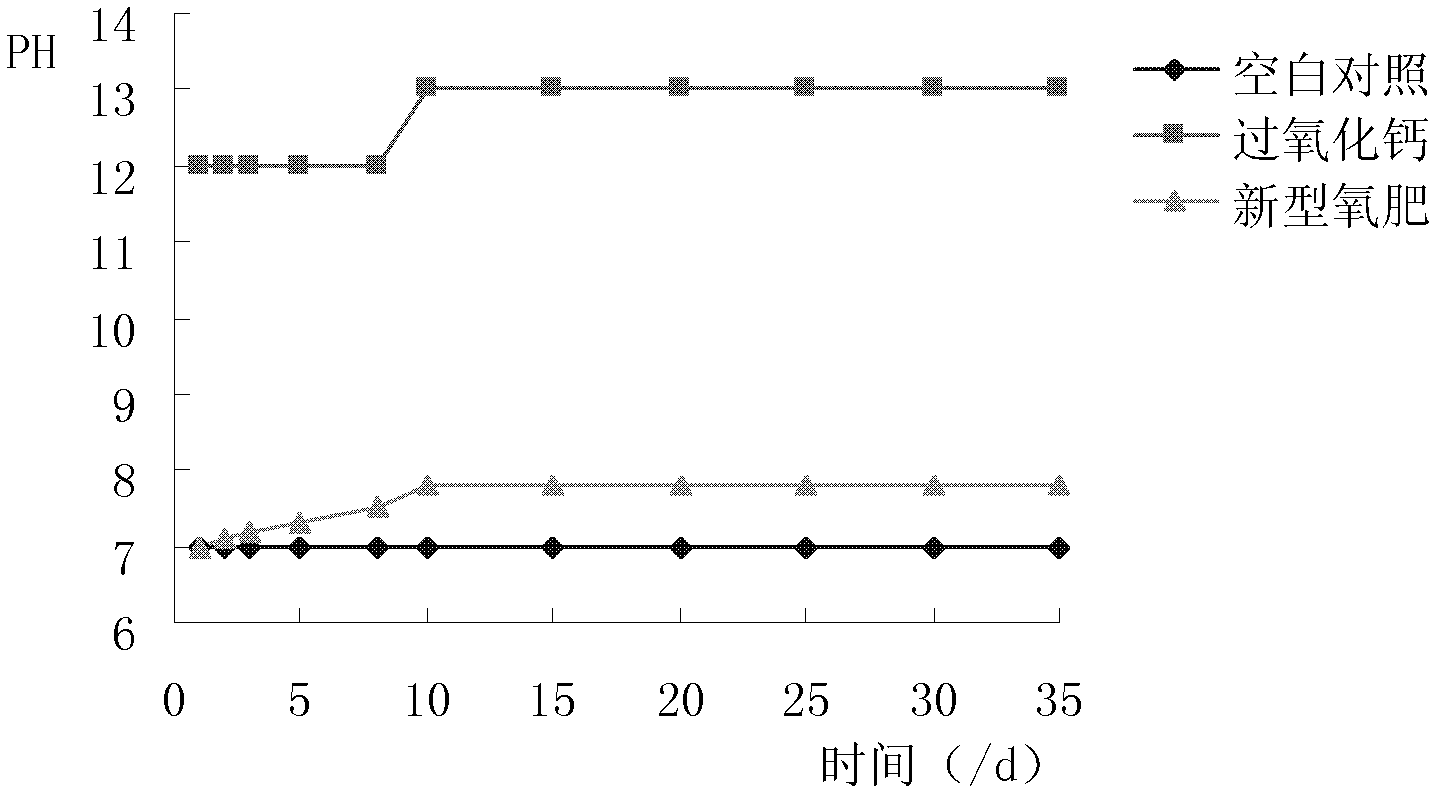
The invention discloses a novel oxygen fertilizer and preparation and application methods of the oxygen fertilizer. Mixtures of one or more of calcium peroxide, sodium peroxide and magnesium peroxide act as a core; nano chitosan doped with sodium alginate as the binding agent serves as a wrapping membrane; and the outer layer of the wrapping membrane is further wrapped by paraffin as a conditioner, so that a slow-release oxygen fertilizer is prepared. The oxygen fertilizer contains 70-75% of the core by weight, 20-25% of the wrapping membrane by weight, and 3-10% of the conditioner by weight and the particle diameter of the oxygen fertilizer particles is 3-10mm. The novel oxygen fertilizer prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention can supply oxygen to waterlogged plants for a long time and is convenient and simple to apply, simple in production process and environment-friendly, and saves time and labor and can be used widely.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Solid foamed drainage agent for natural gas well and preparation method of solid foamed drainage agent
InactiveCN103087698ANovel ingredientsStrong self-foaming abilityDrilling compositionBorehole/well accessoriesThioureaSURFACTANT BLEND
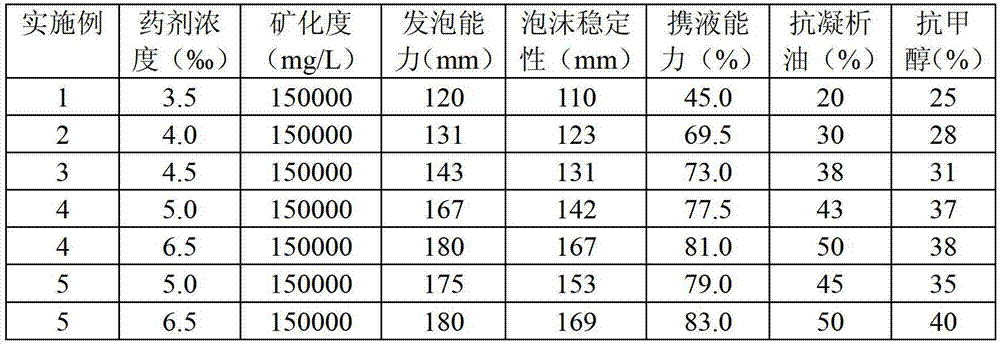
The invention discloses a solid foamed drainage agent for a natural gas well and a preparation method of the solid foamed drainage agent. The solid foamed drainage agent is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 25-30 percent of surfactant, 1-3 percent of imidazoline quaternary ammonium salt, 10-15 percent of sodium peroxide, 20-25 percent of citric acid and 30-40 percent of thiourea. The solid foamed drainage agent is novel in components, non-toxic and environment-friendly, strong in self-foaming capability and good in foaming stability and has the foaming stability to a maximum of 169mm, the liquid carrying capability to a maximum of 83 percent, the gas condensate resistance capability up to 50 percent, the methanol resistance capability up to 40 percent, the mineralization resistance capability of 200,000mg / L and the optimal effective concentration of 0.45-0.65 percent; and in addition, the solid foamed drainage agent is convenient to feed, has a corrosion inhibition effect and has the advantages of reducing the production cost and improving the working efficiency.
Owner:SHAANXI YUTENG IND
Sodium ion doped high-nickel ternary lithium battery positive electrode material and preparation method
The invention provides a sodium ion doped high-nickel ternary lithium battery positive electrode material and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing an 811-type NCM (Nickel Cobalt Manganese) ternary positive electrode precursor through a co-precipitation method; after drying and grinding the precursor, mixing the ground precursor with powdery sodium peroxide and lithium oxide; pre-firing and sintering under an oxygen-rich environment to prepare the sodium ion doped high-nickel ternary lithium battery positive electrode material. According to the method provided by the invention, the defects that Ni<2+> is difficulty effectively controlled to be released from and embedded into a lamellar structure in a sintering process so that a structure is changed in a desorption process and the capacity of lithium ions is reduced are effectively overcome; sodium peroxide is changed into a molten state in a pre-firing process and permeates into the precursor, so that the Ni<2+> is oxidized into Ni<3+>; meanwhile, a lithium layer is occupied and an interlayer structure is expanded; the Ni<2+> is prevented from being migrated into the lithium layer ina sintering process; technical effects that nickel and lithium mixed arrangement of the high-nickel NCM positive electrode material is reduced, the migration rate of lithium ions is improved and the circulating performance of the battery is improved are realized.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
All-solid-state integrated pH composite electrode device and preparation method of electrode
InactiveCN104007158AAvoid replacementSimple preparation processMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCopper wireMaterials science
The invention relates to an all-solid-state integrated pH composite electrode device and a preparation method of the electrode. The all-solid-state integrated pH composite electrode device comprises an Ag / AgCl reference electrode, an antimony electrode, a copper wire and an insulated rubber sleeve, wherein the antimony electrode is embedded at the bottom of a stainless steel hollow needle of the reference electrode through the insulated rubber sleeve; the reference electrode is formed by taking the stainless steel hollow needle as a substrate, electroplating a silver layer on the surface, performing ultrasonic cleaning by using deionized water, plating an AgCl layer on the surface, cleaning through deionized water, and finally coating the reference electrode by using perfluorinated sulfonic acid resin solution dissolved with supersaturated KCl; the antimony electrode is formed by oxidizing a common antimony electrode in molten sodium peroxide to form an oxidation layer film, coating the antimony electrode by using the perfluorinated sulfonic acid resin solution with the mass percent of 5-10 percent and forming a hydrogen ion selective semi-permeable membrane. The composite electrode has certain mechanical strength and piercing ability, and pH of solids, semi-solids, paste and solutions can be tested.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and equipment for mineralizing and degrading organic wastewater
InactiveCN101654297AReduce COD valueEfficient decompositionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by substance additionChemical industryPhosphate
The invention relates to a method and equipment for mineralizing and degrading organic wastewater, and belongs to the fields of chemical industry and environment. The equipment comprises a catalyst and wastewater treatment equipment which uses the catalyst. The catalyst for treating the wastewater comprises elementary substances such as palladium, rhodium, manganese, cobalt, copper, potassium, silver, lanthanum, iron, nickel, tungsten, ruthenium, titanium, cerium, sodium, osmium, gold, platinum, calcium, oxygen, bismuth and the like and oxide, superoxide, hyperoxide, halide, nitrate, sulfate,nitrite, carbonate, hydroxide, phosphate and the like thereof; the catalyst also comprises ozone, hydrogen peroxide, oxygen, sodium superoxide, sodium dioxide, calcium peroxide and calcium superoxide,and can be separately used or combined for use; and the dosage of the catalyst is 0.01g to 100Kg / ton. The wastewater treatment equipment mainly comprises a container, a water inlet pipe, a water outlet pipe, a valve, an ultraviolet lamp, a quartz tube, an aerator and an air pump. The catalyst and the wastewater are added into the container of the water treatment equipment through the water inletpipe at the top of the water treatment equipment; and the organic wastewater is treated through lighting catalysis. The method for treating the organic wastewater does not produce silt, and secondarypollutants. The equipment is simple and easy for operation.
Owner:武钦佩
Method for mineralizing and degrading organic waste water and processing equipment
InactiveCN101643266AReduce COD valueEfficient decompositionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by substance additionPhosphateCerium
The invention relates to a method for mineralizing and degrading organic waste water and processing equipment, which belong to the field of chemistry and environment. The method uses a catalyst and waste water treatment equipment using the catalyst. The catalyst for use in waste water treatment comprises simple substances such as palladium, rhodium, manganese, cobalt, copper, potassium, silver, lanthanum, iron, nickel, tungsten, ruthenium, titanium, cerium, sodium, osmium, gold, platinum, calcium, oxygen and bismuth as well as oxides, peroxides, superoxides, halides, nitrates, sulfates, nitrites, carbonates, hydroxides, phosphates and the like of the simple substances, and the catalyst also comprises ozone, hydrogen peroxide, oxygen, sodium superoxide, sodium dioxide, calcium peroxide andcalcium superoxide. The catalyst can be used alone or in combination at a dosage of 0.01 to 60 kilograms per ton. The catalyst and waste water are filled in a container in the water treatment equipment from a water inlet pipe on the top part of the water treatment equipment; and organic waste water is treated by photocatalysis. The method for treating the waste water does not generate silt and secondary pollution. The equipment is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Cold pad batch (CPB) dyeing method of pure cotton knitted fabric
InactiveCN102061611AOvercome chromatic aberrationOvercome the black air on the clothDyeing processVegetal fibresSodium silicateSodium hydroxide
The invention relates to a cold pad batch (CPB) dyeing method of a pure cotton knitted fabric. The invention provides a pure cotton knitted fabric pretreatment liquor comprising sodium peroxide, sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate for CPB dyeing of the pure cotton knitted fabric, a dye comprising reactive dye, an alkali agent and a penetrating agent and a method for CPB dyeing by applying the pretreatment liquor and the dye. The method solves the problems of color difference, cloth cover black gas, color dot, dyeing speck, and the like to a certain extent, and has the advantage of high color fixation of reaching higher than 85 percent.
Owner:日冠(福建)针纺织机械有限公司
Water quality improver for aquaculture
InactiveCN107285479ASpeed up the scope of improvementReduce BODAluminium silicatesSpecific water treatment objectivesArray data structureWater quality
The invention provides a water quality improver for aquaculture. The water quality improver comprises the following components in parts by weight: 23-28 parts of mineral powder, 2-4 parts of a bactericide, 6-10 parts of biological bacterium, 2-5 parts of a purifying agent, 3-6 parts of sodium peroxide, 0-4 parts of clay and a proper amount of water. According to the reasonable formula, the water quality is improved from multiple biochemical and physicochemical aspects, and the water quality improver has excellent adsorption, degradation and purification effects. Meanwhile, a certain nutritive material can be provided, and the breeding efficiency of aquatic organisms is effectively improved.
Owner:ANHUI HUANGHUAI VETERINARY MEDICINE
Method for preparing sodium chromate by mixing chromite and ferrochrome and device for method
The invention discloses a method for preparing sodium chromate by mixing chromite and ferrochrome and a device for the method. The method comprises the following steps: measuring and mixing chromite and ferrochrome with sodium carbonate, sodium nitrate and sodium peroxide; pelleting the mixture with extracted liquid sodium chromate in a pelletizer; drying in a drier; returning part of the clinker to a flame kiln after the material is dried and cooled, so that chromite and ferrochrome are decomposed and oxidized in the form of fused liquid phase in molten salts so as to obtain the clinker of sodium chromate; and continuously soaking, filtering and cleaning after the clinker is cooled so that a chromium chemical primary product of liquid sodium chromate is obtained, wherein the flame kiln comprises a U-shaped kiln body, a partition wall and a low-position molten salt suction port, wherein the partition wall and the low-position molten salt suction port are arranged in the U-shaped kiln body; one or more blowing oxygen lances and one or more charging holes are arranged at the top of the kiln body, and a smoke outlet is arranged on the upper side of the kiln; and one or more oxygen lances are arranged at the bottom of the kiln. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the oxidation rate is as high as 98%, the clinker extraction rate is as high as 99.97%, and the chromium yield is 97.96%.
Owner:HUBEI POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Ecological modifying agent for mineral substance water quality
InactiveCN101333022AViscousStrong oxidation abilityWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationChemical industrySodium Bentonite
The invention relates to a mineral water quality ecological modifying agent which is prepared by blending bentonite, alum, polyaluminium chloride and sodium dioxide in proportion; if the total amount is 1,000g, the weight proportion of each ingredient is as follows: 800-900g of bentonite, 40-80g of alum, 15-50g of polyaluminium chloride and 35-80g of sodium dioxide. The mineral water quality ecological modifying agent can be used for improving the aquaculture environment of fish ponds, balancing water ecological environment and enhancing unit fish yield per mu of fish ponds, and also can used for adsorbing blue algae, preventing the blue algae from doing harm to water, eliminating odor and protecting and improving water ecological environment; the water which derives from the treatment of chemical industry waste water, domestic sewage and the water of rivers, lakes, wells and pools can meet the national grade 1 and grade 2 water standards, and the precipitate from the water purification process can be recycled or used as feed or fertilizer, thus having low purifying treatment cost and high benefits.
Owner:唐子林
Heat pipe and heat-conducting medium thereof
InactiveCN102878838AImprove thermal efficiencyIncrease mobilityChemical industryIndirect heat exchangersZinc hydroxideHeat conducting
The invention relates to the technical field of heat-conducting components, in particular to a heat pipe with efficient heat-conducting effect and a heat-conducting medium thereof. The hot pipe comprises a metal pipe and the heat-conducting medium packaged in the metal pipe; and the heat-conducting medium is made from the following raw materials: 1,000g of deionized water, and 40-60g of potassium dichromate, 3-5g of boric acid, 8-12g of sodium perborate, 2-4g of sodium peroxide, 1-3g of calcium chloride, 6-10g of ethanol, 0.5-1g of manganese dioxide and 0.2-0.8g of zinc hydroxide, which are added into 1,000g of deionized water. By the technical scheme, a plurality of materials are cooperated with one another, and heat-conducting efficiency of a product is improved. By the heat pipe made from the heat-conducting medium, the heat-conducting efficiency is improved by 200-300% compared with that of the heat-conducting medium of an ordinary heat pipe, and the applicable temperature range of the heat pipe is wide.
Owner:东莞市焊宏爱法电子科技有限公司
Anti-interference metal/metal oxide pH electrode and preparation method
InactiveCN1869675AReduce volumeHigh mechanical strengthMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical synthesisDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses an anti-interference metal / metal oxide pH electrode and the preparing method, adopting metal wire with stable chemical properties as substrate, immersing the metal wire in the melted sodium peroxide for several minutes and forming hydrogen ion-sensitive active oxide film on the surface of the metal wire, then using fluorinated sulfonic acid resin to coat the active oxide film and forming hydrogen ion selective semipermeable membrane, which can transmit protons but stop other anions and cations outside, thus avoiding their interferences to pH electrode and simultaneously largely prolonging pH electrode service life. And the pH electrode has advantages of small bulk, high mechanical strength, and wide application range, etc, and the preparing method has simple process and low cost. And it has application values in the fields, such as chemical synthesis, dynamic monitoring of various power stations and waste management.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Combined determination method for main components in high-carbon ferrochrome slag
InactiveCN104897661AReduce preprocessingTime consumingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationDecompositionMolybdenum blue
A combined determination method for main components in high-carbon ferrochrome slag. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of: melting a high-carbon ferrochrome sample by a iron crucible; carrying out high-temperature melting decomposition by sodium peroxide; leaching in a 250ml plastic cup filled with water; acidifying and clarifying with sulfuric acid; placing at room temperature to obtain a high-carbon ferrochrome sample mother liquor; conducting constant volume analysis on the high-carbon ferrochrome mother liquor; decomposing the sample at one time; and respectively measuring the chemical composition of SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO and Cr2O3 by 1) determination of Cr2O3 by potassium permanganate oxidation and ammonium ferrous sulfate titration method, 2) determination of SiO2 by a silicon molybdenum blue spectrophotometric method, and 3) determination of Al2O3, MgO and CaO by an EDTA volumetric method. The method greatly reduces the analysis time (determination of SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO and Cr2O3 within four hours), while omits weighing and analysis of Al2O3 by a nickel crucible, and saves a lot of cost analysis.
Owner:HENAN AOXIN ALLOY
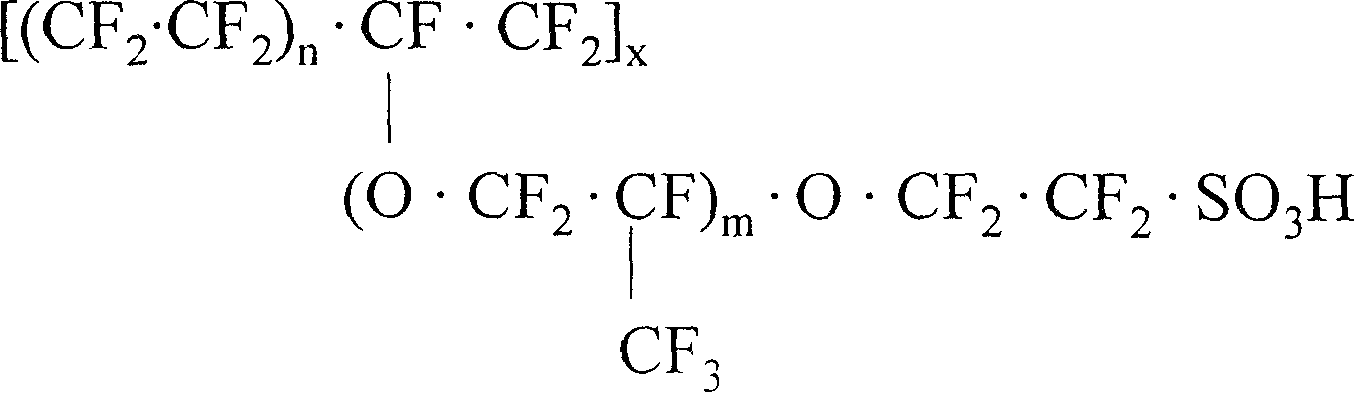
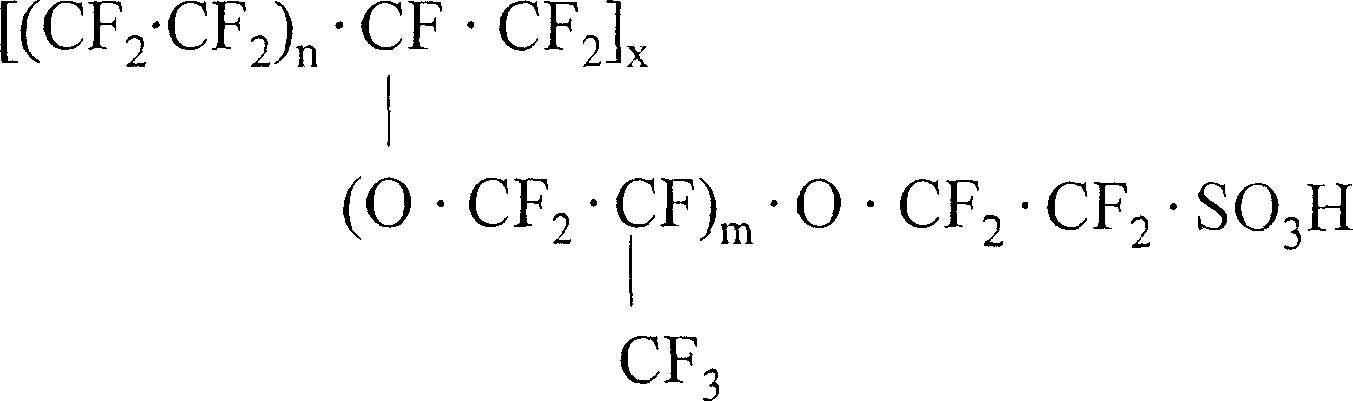
Method for measuring niobium content in tungsten carbide added with niobium or simultaneously added with tantalum and niobium
InactiveCN101762576AAvoid operabilityAvoid environmental pollutionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsHigh concentrationNiobium
The invention relates to a method for measuring a niobium content in tungsten carbide added with niobium or simultaneously added with tantalum and niobium, which comprises the following analytical steps that: after a sample is ground and sieved, the obtained product is melted by sodium peroxide, and the product is leached by hot water; after twice precipitations are carried out on the leached solution by using a coprecipitator to precipitate and using a gallotannic acid to precipitate, niobium or niobium and tantalum are separated from the main tungsten and other impurities, and then tartaric acid solution is prepared; when the prepared tartaric acid solution is in the sulphuric acid medium, the niobium and 5-Br-PADAP form a red chelate, the color depth is in positive proportion to the niobium content, hereby, the niobium content can be measured by photometry according to the working curve of the niobium; and if the sample comprises the niobium and tantalum simultaneously, the interference of tantalum to the measurement of the niobium content is eliminated by a method of adding excessive solution of high-concentration tartaric acid to carry out complexing and screening. The method of the invention has high precipitate recovery rate, simple and convenient operation, small interference, and good accuracy and repeatability.
Owner:JIANGXI RARE EARTH & RARE METALS TUNGSTEN GRP
Method for determining content of phosphorus in ferroniobium
ActiveCN104122219AAccurate determination of phosphorus contentSimple and fast operationColor/spectral properties measurementsHeteropoly acidSodium carbonate anhydrous
The invention provides a method for determining the content of phosphorus in ferroniobium. The method comprises the steps of melting anhydrous sodium carbonate, sodium peroxide and ferrocolumbium, cooling, adding perchloric acid, leaching, heating and boiling until a black muddy solution is changed to a green muddy solution; adding a sodium hydroxide solution and heating until boiling to obtain a mother solution; adding perchloric acid in the mother solution, adding a bismuth salt solution, a sodium thiosulfate solution and an ammonium molybdate mixed solution to enable the phosphorus in the mother liquid, bismuth ions and ammonium molybdate to react in a perchloric acid medium to generate phosphorus-bismuth-molybdenum heteropolyacid, wherein bismuth salt is dissolved in the perchloric acid and the solution is heated until dense perchloric acid smoke occurs, and therefore, the bismuth salt solution is obtained, and the ammonium molybdate mixed liquid is prepared from perchloric acid, ammonium molybdate and arabic gum; adding ascorbic acid to perform reduction reaction to obtain bismuth phosphomolybdenum blue containing a solution to be tested; and measuring the absorbancy of the bismuth phosphomolybdenum blue in the solution to be tested by adopting a spectrophotometric method and calculating the content of the phosphorus. The method is convenient to operate and can accurately determine the content of the phosphorus in the ferroniobium.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP JIANGYOU CHANGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL
Method and device for disinfecting, detoxifying and purifying water by using hydroxyl radicals
InactiveCN103723803ALow costIncrease profitWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processUltravioletTreated water
The invention relates to a method and a device for disinfecting, detoxifying and purifying water by using hydroxyl radicals. The method and the device mainly solve the technical problems that the existing water treatment method and the existing water treatment device cannot remove residual carcinogenic substances in water, and cannot remove overproof heavy metal and organic compounds. The method adopts the technical scheme that the method comprises the following steps that ozone is released to treated water; singlet-state atomic oxygen is generated through radiation of a plurality of mercury lamp ultraviolet lamp modules at UVC (ultraviolet C) 253.7nm or a plurality of LED (light-emitting diode) ultraviolet lamp modules at DUV (deep ultraviolet) LED 280nm; drinking water is continuously disinfected, detoxified and purified, so that the drinking water reaches a sanitary standard for domestic drinking water, and then is discharged; or reclaimed water of waste water is recycled; and zero discharge is reached. The device using the method comprises an ozone generator, an impeller, an aerator, a housing, the ultraviolet lamp modules, an ultrasonic device, a water inlet, a water outlet, an oxygen outlet, a sodium peroxide generation machine, a sodium peroxide collection tank and a sodium peroxide discharge pipe.
Owner:刘传林
Method for decomposing pesticide residues on fruits and vegetables and disinfecting tableware through hydroxyl radical and device adopting method
ActiveCN103652516ASolve efficiency problemsSolve processingFood preparationChemicalsHigh concentrationPesticide residue
The invention relates to a method for decomposing pesticide residues on fruits and vegetables and disinfecting tableware through hydroxyl radical and a device adopting the method, and mainly aims to solve the technical problems that the conventional fruit, vegetable, tableware and medical instrument disinfection method and the conventional fruit, vegetable, tableware and medical instrument disinfection device are low in pesticide residue removal efficiency, and poor in innocent treatment effect and medical instrument disinfection effect. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the method comprises the following steps of releasing ozone into water, irradiating the water through a UVC 253.7nm mercury lamp and ultraviolet lamp module to generate singlet elemental oxygen for blowing up the water to generate a high-concentration hydroxyl radical aqueous solution for disinfecting, detoxifying and purifying the pesticide residues on the fruits, the vegetables and fresh food or disinfecting tableware and medicament instruments. The device disclosed by the invention comprises an ozone generator, an impeller, an aerator, a shell, the ultraviolet lamp module, an ultrasonic device, a water outlet, a water inlet, a water pump, an oxygen outlet, a sodium peroxide generator, a sodium peroxide collection tank, a sodium peroxide discharging pipe, a hanging mechanism, and a closing cover.
Owner:刘传林
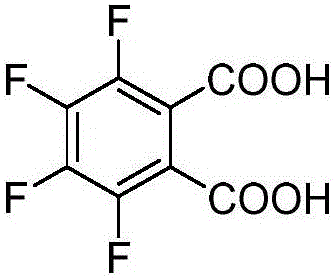
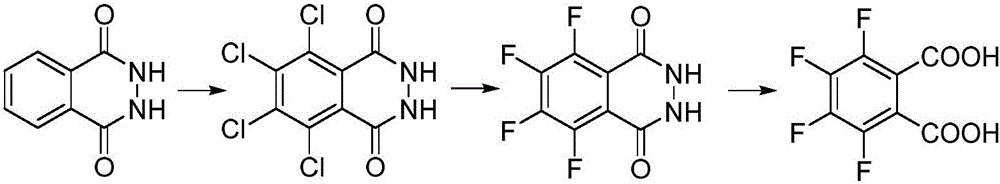
Synthesis method of 3, 4, 5, 6-tetrafluorophthalic acid
InactiveCN105693507AHigh yieldHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationDistillationPotassium fluoride
The invention discloses a synthesis method of 3, 4, 5, 6-tetrafluorophthalic acid, comprising the following steps: (1) adding phthalylhydrazine into mixed liquid of fuming sulfuric acid and diluted hydrochloric acid, then adding a catalyst I into the mixed liquid and stirring the mixture, controlling the filling of chlorine, and carrying out a thermal reaction; (2) adding potassium fluoride into a reaction device containing methyl alcohol, methylbenzene and a solvent I, heating up and then stirring the mixture, and carrying out atmospheric distillation on reaction liquid to recover the methyl alcohol and the methylbenzene; after that, under the protection of nitrogen, adding the tetrachloro phthalylhydrazine prepared in the step (1) and a catalyst II into the product, heating up to 120-200 DEG C and carrying out a fluoridation reaction; (3) adding the tetrachloro phthalylhydrazine and sodium peroxide which are prepared in the step (2) into water, carrying out a hydrolysis reaction for 2-8 hours at the temperature of 10-50 DEG C, then adjusting the acidity of the obtained reaction liquid until the pH value of the reaction liquid is equal to 1-4, carrying out suction filtration and drying to obtain the tetrafluorophthalic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for Determining Vanadium Content in a Tungsten Matrix with Added Vanadium or Simultaneously Added Chromium and Vanadium
InactiveUS20110318841A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationTungstateHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
A method for determining vanadium content in a tungsten matrix with singly added vanadium or simultaneously added chromium and vanadium, characterized in that a test sample is subjected to alkaline melting with sodium peroxide and water leaching followed by dry filtering, the chromium and vanadium in the filtrate are firstly reduced to low valences by a reducing agent, i.e. hydroxylamine hydrochloride, then the filtrate is adjusted to an acidity of 4-6 M with nitric acid, the vanadium is oxidized in a cold state to a high valence by potassium permanganate, and the high-valent vanadium forms a ternary complex with tungstate and orthophosphate, the darkness of the color of the ternary complex is directly proportional to the vanadium content, thus the vanadium content is determined colorimetrically, and the interference of chromium is eliminated with the fact that the potassium permanganate in a cold state in the acidic condition for vanadium determination oxidizes the vanadium but not the chromium. The method of the invention is relatively suitable for determining the macro-amount vanadium content in a tungsten matrix containing macro-amount vanadium singly or containing macro-amount vanadium and chromium simultaneously, the method is fast and accurate with a relative error less than 5%, which can fully satisfy the requirements of the production process for the determination.
Owner:HU YIQI
Method for simultaneously determining iodine, boron, tin and germanium elements in soil
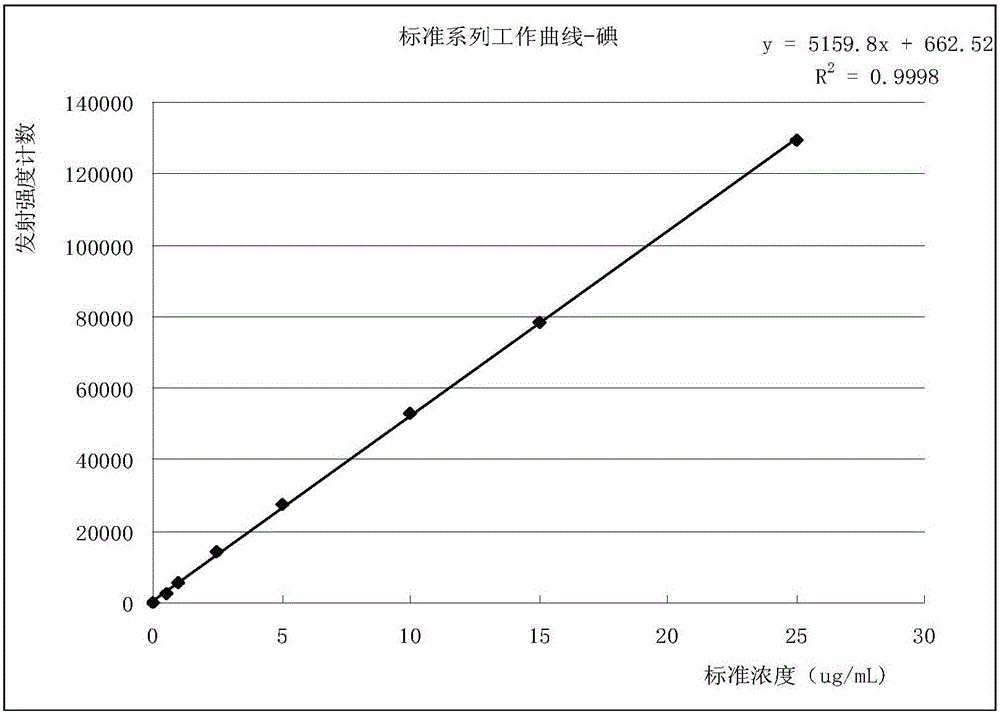
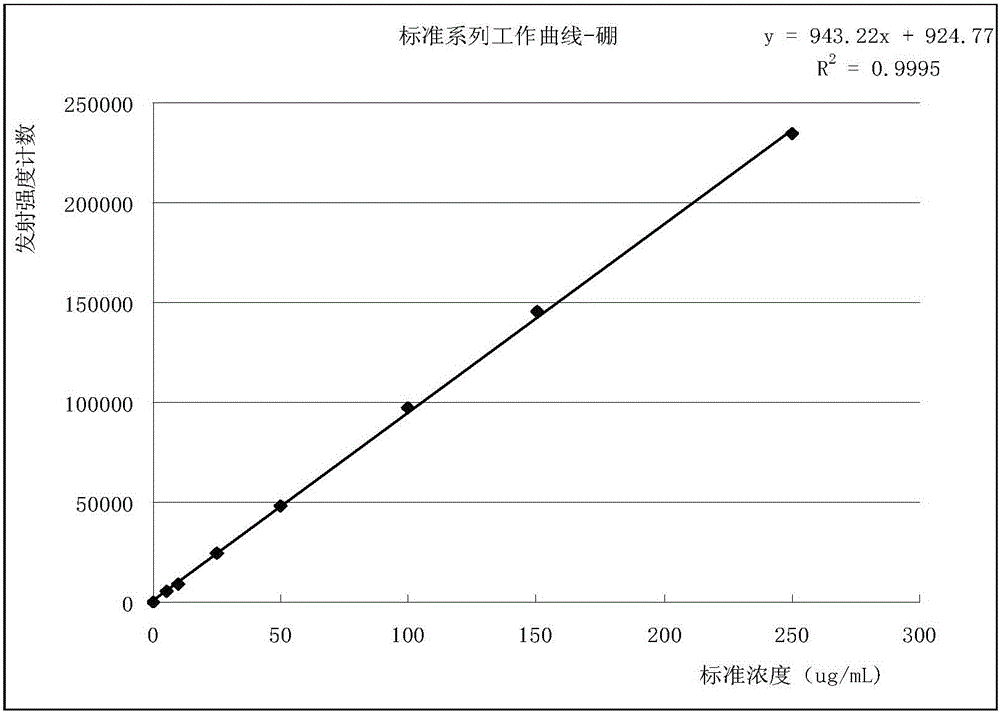
ActiveCN105758927AImprove work efficiencyHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopyRaw material
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining iodine, boron, tin and germanium elements in soil. The method comprises the following steps of pre-treating raw materials, preparing a determination solution, drawing a working curve and determining the content of each element in the soil, wherein the step of pre-treating the raw materials comprises the step of pre-treating with sodium oxide; a citric acid solution and cation resin are added into the pre-treated sample to prepare the determination solution; the obtained determination solution is determined by adopting an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously determining the plurality of elements including iodine, boron, tin and germanium in the soil, and is high in working efficiency and simple to operate; the inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry is used for determining; compared with an inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy, the method has the advantages of relatively high sensitivity, relatively low detection limit, relatively strong anti-interference capability, relatively high precision and the like. The detection limits of the detected elements that the iodine is 0.10Mug / g, the boron is 0.92Mu g / g, the tin is 0.29Mu g / g and the germanium is 0.02Mug / g, and are lower than the detection limits of the inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy.
Owner:广西壮族自治区地质矿产测试研究中心
Composite oxygen producer for adsorbing residual antibiotics in aquaculture water and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105036235AEnhance immune functionGood antibacterial effectWater/sewage treatment by substance additionWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processBreyniaAntibiotic Y
The present invention belongs to the field of aquaculture technology, and discloses a method for preparing a composite oxygen producer for adsorbing residual antibiotics in aquaculture water. The composite oxygen producer is prepared from the following components by weight: 70-90 parts of an oxygen supply component, 15-25 parts of a traditional Chinese medicine compound, 42-68 parts of an adsorption component, 2 -5 parts of a coating agent, 1-3 parts of a stabilizer and 1.3-1.8 parts of a sustained co-solvent. The oxygen supply component comprises 50-60 parts of sodium peroxide and 20-30 parts of calcium peroxide; the traditional Chinese medicine compound includes celandine, Chinese angelica, Radix Astragali, nephelium lappaceum, receptaculum nelumbinis, fruticose breynia juvenile branchlet and leaf, Hydrangea aspera Don and yucca; the adsorption component comprises 20-30 parts of Chinese medical stone, 6 -10 parts of a polymer material, 9-15 parts of diatomaceous earth and 7-13 parts of silica powder. Through compounding of a plurality of effective components, the obtained product has good oxygenation function and residual antibiotic adsorption function.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing stable chlorine dioxide with high purity by using gas stripping technique
InactiveCN1415534AHigh purityQuality improvementChlorine oxidesDispersed particle separationChlorine dioxideDesorption
A process for preparing high-purity stable ClO2 by desorption and stripping includes such steps as absorbing ClO2 gas by freezing water to obtain its aqueous solution, desorbing and stripping ClO2 from said aqueous solution, and reacting with sodium peroxide (or carbonate) solution. Its advantages are high quality and purity and no influence from impurities.
Owner:覃庆林
Method for controlling microorganisms
InactiveUS6045708APromote resultsBiocideWater/sewage treatment by substance additionMicroorganismBiotechnology
Owner:ERIKSSON JAN OLOF
Method for measuring phosphorus content in chromite
ActiveCN104181118AReasonable designThe result is stableColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalysis dataHeteropoly acid
The invention relates to a method for measuring phosphorus content in chromite. According to the method, a chromite sample is decomposed by high-temperature alkali fusion of sodium peroxide, the melt is extracted by hot water, phosphorus co-precipitates with elements such as iron, magnesium, manganese and the like, chromium enters the solution in a form of CrO4<2->, sodium hydroxide solution is used for washing so as to remove the chromium. The precipitate is subjected to acidolysis by hydrochloric acid and the precipitate subjected to acidolysis is then transferred into a volumetric flask. The test solution is separated, the pH value of the solution is adjusted by taking paranitrophenol as an indicator, phosphorus-molybdenum heteropoly acid is reduced to be phosphomolybdenum blue by taking ascorbic acid as a reducing agent in hydrochloric acid medium, and the light absorption value of the test solution is measured at the position of 680nm of a spectrophotometer. According to the technical scheme of the method, the design is reasonable, the relative standard deviation is less than 12%, and the recovery rate of standard addition reaches up to 96-99%; compared with the standard sample reference value, the method has the advantages that the analysis data is basically identical, the results are stable and accurate, simplicity and convenience are realized, and the operability is high.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Preparation method of graphene for super capacitor electrode material
InactiveCN104332325AMeet quality requirementsEasy accessHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceUltrasonic dispersion
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene for a super capacitor electrode material. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding concentrated sulfuric acid to crystalline graphite powder serving as a raw material, adding a strong oxidant and sodium nitrate at a temperature within the range of 0-10 DEG C, respectively, and stirring for 2-3 hours, next, slowly adding water, adding 1-2 hours and controlling the temperature within the range of 80-95 DEG C, centrifuging, washing with water and drying to obtain graphene oxide powder, adding the graphene oxide powder to a reducing agent solution controlling the temperature within the range of 75-85 DEG C, performing ultrasonic dispersion processing for 3-4 hours, and then cooling, settling, filtering by suction, washing and drying in vacuum to obtain the graphene. The graphene obtained by use of the preparation method has superior properties in application to a super capacitor; at the current density of 2A / G, the specific capacitance of the material reaches 141F / g, after 300 cycles at different current densities, the specific capacitance is still kept at 130F / g(2A / g); as a result, the material shows excellent rate and cyclic temperature properties.
Owner:JIANGSU YINJI CARBON TECH CO LTD
Method for quickly determining vanadium in coal mine containing scherbinaite
InactiveCN101666789AReflect true tasteShort timeAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationDecompositionSulphate Ion
The invention discloses a method for quickly determining vanadium in a coal mine containing scherbinaite. The invention has the following advantages that: (1) compared with the current widely-used method of sodium dioxide decomposition and ferrous ammonium sulphate titrating solution titration, the method for quickly determining vanadium only needs to lixiviate a sample ore at a lower temperatureinstead of decomposing the sample ore at a high temperature, and has the advantages of less time consumption and simple operation; (2) compared with the current widely-used method of sodium dioxide decomposition and ferrous ammonium sulphate titrating solution titration, the method for quickly determining vanadium requires a large number of samples, and the determined result can better reflect thereal quality of vanadium in a coal mine containing scherbinaite; and (3) the solution to be determined contains no solid matter, and therefore, colors can be clearly and definitely judged.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
High-clean methanol composite gasoline for vehicle and production thereof
The invention is about the high clearing methanol compound petrol which is composed of the methanol, the petrol, the acetone, the isopropyl ether, the isopropanol, the isoamylol, the tert-butyl alcohol and the synthetic addition agent. The addition agent is modulated by the ZnO, the Na2O2, the ferrum naphthenate and the isopropyl nitrate. The compound petrol can solve the problem of the corrosivity to the red copper and the swelling to the rubber. It can be mixed with the normal petrol arbitrarily and not need to change the structure of the engine, also it can remove the carbon and the colloid of the engine. The cost of the technique is low and the operability is high.
Owner:肖军
Greasy dirt flocculation deoiling device for industrial sewage
InactiveCN111606456AFully dispersedGood flocculation effectFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater contaminantsEnvironmental engineeringSewage
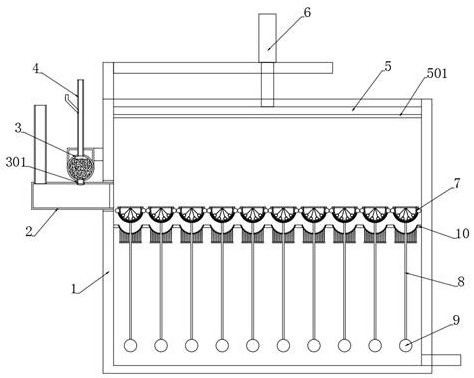
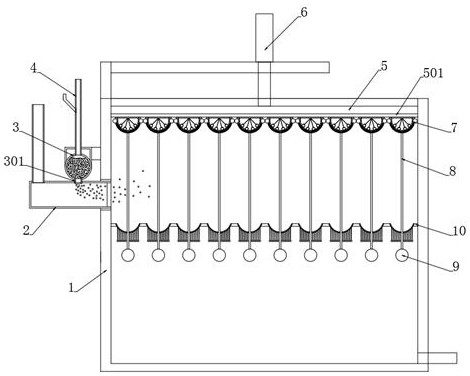
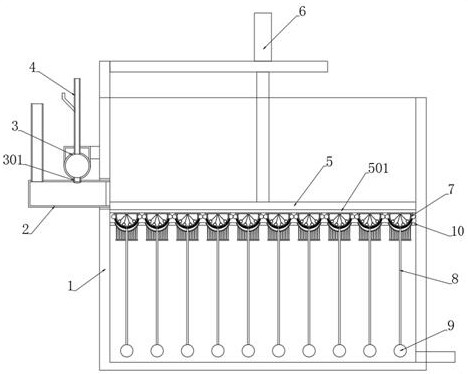
The invention discloses a greasy dirt flocculation deoiling device for industrial sewage. The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment. Upper elliptic adsorption layers coating thebottom end parts of adsorption floating balls are used for adsorbing greasy dirt flocculation particles on the water surface. After the flocculation operation is finished, sewage is discharged, the adsorption floating balls sink and abut against filtering oil guide mechanisms, meanwhile, an electric push rod presses down a sealing plate to enable the sealing plate to abut against the adsorption floating balls again, an electromagnet is electrified to magnetically attract a magnetic sealing cover plate, the electric push rod resets upward, the magnetic sealing cover plate and a gas stamping mechanism are pulled upwards, the gas stamping mechanism is separated from the filter holes of elliptic floating balls, sodium peroxide in the elliptic floating balls is diffused outwards to the upper elliptic adsorption layers through the filter holes, sodium peroxide powder generates sodium hydroxide and oxygen which can decompose greasy dirt particles when encountering water, the oxygen is used for scattering condensed particles to enable the greasy dirt particles to fall off easily, the gas stamping mechanism releases gas after being pulled to be broken, and the diffusion degree of the sodium peroxide powder is effectively improved.
Owner:施德琴
Auto cooling fluid
InactiveCN104087255AImprove stabilityGuaranteed cycleHeat-exchange elementsSilver carbonateSilver phosphate
The invention discloses auto cooling fluid, comprising the following raw materials in parts: 10-18 parts of diethylene glycol, 11-14 parts of oxalic acid, 13-15 parts of 1,2-propylene glycol, 12-15 parts of ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate, 8-12 parts of triethyl phosphonoacetate, 8-12 parts of glufosinate-ammonium, 5-8 parts of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid, 6-8 parts of styrene-acrylic-triazole, 6-7 parts of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, 6-9 parts of benzotriazole, 2-3 parts of dimeticone, 1-3 parts of hydroxyl silicone oil, 3-4 parts of a dimethyl silicone polymer, 3-5 parts of butanol, 1-3 parts of sodium hydroxide, 2-3 parts of sodium peroxide, 2-4 parts of potassium chlorate, 1-3 parts of silver carbonate, 2-5 parts of silver phosphate and 150-160 parts of purified water. The auto cooling fluid has good stability, the microbial flora can be inhibited and killed, floccules, flotage, sediments and the like are prevented, effective circulation of the cooling liquid is ensured, the fault of a cooling liquid circulating system is relieved and prevented, the anti-corrosion effect is good, corrosion to the cooling liquid circulation system can be reduced and delayed, the fault of the cooling liquid circulating system is reduced, and the service life of the auto cooling liquid is prolonged.
Owner:梁胜光
Method for Determining Chromium Content in a Tungsten Matrix with Added Chromium or Simultaneously Added Chromium and Vanadium
InactiveUS20110300634A1Accurate measurementMutual interferenceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTurbidityPrecipitation
A method for determining chromium content in a tungsten matrix with singly or simultaneously added chromium and vanadium, characterized in that a test sample is subjected to melting with sodium peroxide and hot water leaching; meanwhile said sodium peroxide is also used as an oxidizing agent to oxidize all the chromium to high valences; the main body of tungsten is coordinated by ammonium hydrogen fluoride to prevent tungstic acid from precipitating; precipitation and turbidity are avoided throughout the analysis, titration can be carried out in a quite clear condition with accurate and reliable results. In this invention, the clearness of the solution when titrating is very important for the accuracy of titrimetric analysis; the solution is always clear throughout the determination, ensuring that the interference with determination of chromium from vanadium is accurately and quantitatively eliminated; the interference from vanadium is eliminated by subtraction method, by means of titrating with ferrous ammonium sulfate standard solution after oxidation with potassium permanganate. In this invention, the determination method allows the determination to be carried out in the quite clear condition, and eliminates the interference from vanadium completely and quantitatively, thus the accuracy and speed of the determination of chromium content in a tungsten matrix with singly or simultaneously added chromium and vanadium are improved.
Owner:JIANGXI RARE EARTH & RARE METALS TUNGSTEN GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com