Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
160 results about "Bismuth chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bismuth chloride (or butter of bismuth) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula BiCl₃. It is a common source of the Bi³⁺ ion. In the gas phase and in the crystal, the species adopts a pyramidal structure, in accord with VSEPR theory.
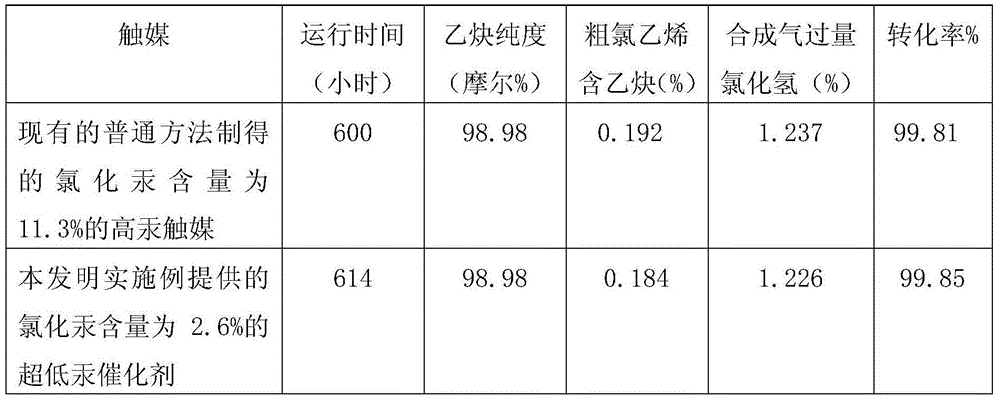
Low-mercury catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination
InactiveCN102380407AEasy to makeLow costPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionO-Phosphoric AcidPtru catalyst
Disclosed is a low-mercury catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. Mercuric chloride is carried on activated carbon. Raw materials comprise, by weight, 100 parts of activated carbon, 4-5 parts of mercuric chloride, 8-10 parts of total essential assistant, 1-5 parts of total non-essential assistant, wherein the essential assistant comprises 2-5 parts of bismuth chloride, 1-5 parts of cerium chloride, 1-5 parts of barium chloride and 2-5 parts of copper chloride; and the non-essential assistant comprises at least one of potassium chloride, phosphoric acid, zinc chloride and cuprous chloride. After being subjected to surface subtraction and drying on acid and oxidizing conditions, activated carbon is in reflux treatment with urea solution; and the catalyst can be prepared by soaking the treated activated carbon with HgC12 dissolved in hydrochloric acid and assistant solution sufficiently after urea is removed by steps of heating, washing the activated carbon with hydrochloric acid and finally drying the same. The carrying capacity of mercuric chloride in the catalyst is lower so that cost for the catalyst is reduced and consumption of mercury resources is decreased. Furthermore, activity and stability of the low-mercury catalyst are much higher than those of the existing high-mercury catalyst, and reforming rate and selectivity of reaction of vinyl chloride can be 99.7% and be higher than 99.8%. Accordingly, the low-mercury catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination is suitable for industry production and is environment-friendly.
Owner:CHENGDU HUIEN FINE CHEM
Ultralow-mercury catalyst and production process thereof
InactiveCN103551139AReduce manufacturing costLow in Mercury ChlorideCatalyst carriersPreparation by halogen halide additionVoid ratioPotassium
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG KECHUANG ADDITIVES CO LTD
Nanometer bismuth/carbon composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108134090AAvoid the case of bulky bismuth metalEvenly distributedMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline accumulatorsCarbon compositesPotassium borohydride
The invention relates to a nanometer composite material, in particular to a nanometer bismuth / carbon composite material and a preparation method thereof. A nanometer bismuth and carbon compound is obtained by taking various carbon materials as a substrate, bismuth nitrate, bismuth chloride, bismuth sulfate, bismuth acetate, bismuth citrate and the like as a bismuth source, water containing an organic complexing agent, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol or other mixture as a solvent and sodium borohydride, potassium borohydride, hydrazine hydrate and the like as a reducing agent and by an absorption-thermal decomposition-reduction method. According to the method, a solution containing bismuth ions is absorbed to a surface of a carbon material, remaining solution is filtered, the bismuth oxide / bismuth and carbon compound is obtained after drying and thermal treatment, and the nanometer bismuth / carbon composite material is finally obtained by reduction reaction. In the composite material obtained by the method, metal bismuth particles are uniformly distributed in surfaces of carbon particles in nanometer size, and a phenomenon that a large amount of bismuth can be agglomerated by a traditional bismuth reduction method is prevented.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composite copper-based catalyst, preparation method and application thereof in the production of vinyl chloride
ActiveCN109821546AHigh activityImprove stabilityPreparation by halogen halide additionCatalyst activation/preparationCeriumPotassium
The invention provides a composite copper-based catalyst, a preparation method and an application thereof in the production of vinyl chloride. The preparation method of the composite copper-based catalyst includes the following steps: soaking acid-treated activated carbon in a solution containing copper salt and an auxiliary agent, and drying and roasting to obtain the composite copper-based catalyst, wherein the auxiliary agent is one or more of ferric chloride, cerium chloride, tin chloride, barium chloride, manganese chloride, zinc chloride, cobalt chloride, lanthanum chloride, nickel chloride, bismuth chloride and potassium chloride; and the mass ratio of the acid-treated activated carbon, the copper salt and the auxiliary agent is 100: 5: 1-100: 10: 5. The catalyst is environment-friendly, low in cost, simple in process and short in production period. The catalyst shows high activity, selectivity and good stability in the reaction of hydrochlorination of acetylene to produce the vinyl chloride, and is expected to be a good substitute for a mercury catalyst.
Owner:鄂尔多斯市瀚博科技有限公司
Preparation method of ultra-thin BiOCl nano-sheet photocatalyst
ActiveCN106492849AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic dyeHydrothermal synthesis
The invention belongs to the field of catalysts, and particularly relates to a preparation method of an ultra-thin BiOCl nano-sheet. According to the method, the catalyst is synthesized by the aid of a hydrothermal method and takes chlorination 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazole as chlorine sources, so that the thickness of the prepared photocatalyst BiOCl nano-sheet is 2-3nm, the thickness of the photocatalyst BiOCl nano-sheet prepared by taking bismuth chloride as chlorine sources is 50nm, the thickness of the photocatalyst BiOCl nano-sheet prepared by taking sodium chloride as chlorine sources is 450nm, and the catalytic efficiency of photocatalytic degradation organic dye rhodamine B is high. The photocatalyst is synthesized by the aid of the hydrothermal method and simple to prepare, the preparation method is green and environmentally friendly, and different chlorine sources are selected, so that the thickness of the nano-sheets can be adjusted.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
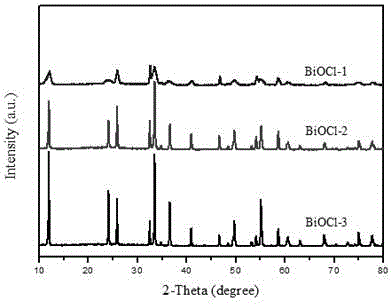
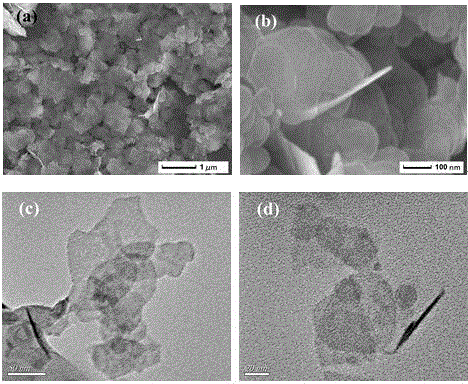
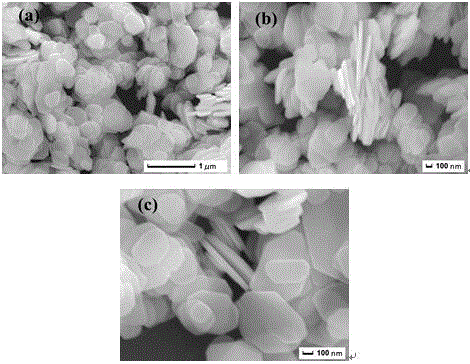
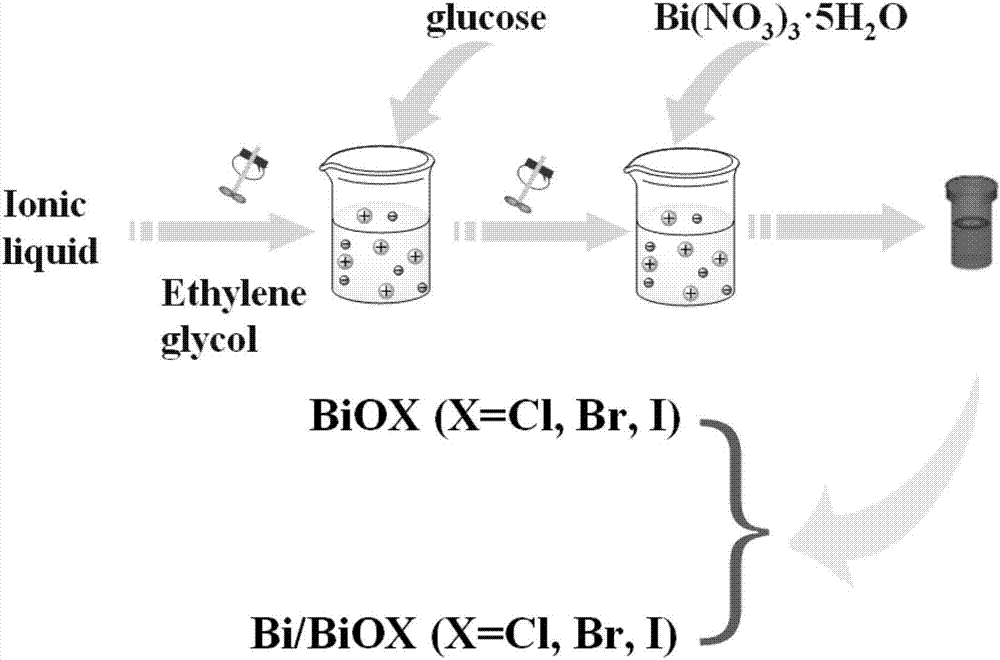
Preparation method and application of bismuth metal auto-doping halogenated bismuth oxide
InactiveCN106938340AImprove photoelectric performanceHigh detection sensitivityAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBismuth compoundsPhotodetectorIonic liquid
The present invention provides a method for preparing bismuth metal self-doped bismuth oxyhalide and its application, which is carried out according to the following steps: first, take the ionic liquid containing halogen and put it into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reaction kettle, Next, add ethylene glycol and fully dissolve it; then add glucose and bismuth pentahydrate bismuth nitrate into the reaction kettle and stir until they are evenly mixed; carry out constant temperature thermal reaction, and naturally cool to room temperature after the reaction is completed; wash the solid product with alcohol , washed with water, centrifuged and dried to obtain a bismuth metal self-doped bismuth oxyhalide material. The electrode material used in the present invention is bismuth oxyhalide self-doped with bismuth metal that responds in the visible light region. Its superior photoelectric properties have been explored, and the application of bismuth oxyhalide-based materials in the field of optoelectronics has been broadened, and it has also found new opportunities for photoelectric detection. A new type of material.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Aluminium/water reaction controllable-hydrogen catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103861645AImprove conversion rateThe market is well suppliedHydrogenOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHigh activityBall mill
The invention discloses an aluminium / water reaction controllable-hydrogen catalyst. The aluminium / water reaction controllable-hydrogen catalyst comprises the following materials in percent by weight: (a) 75%-85% of metal aluminium powder; (b) 5%-12% of mixture of bismuth chloride, sodium chloride and potassium chloride; (c) 5%-15% of mixture of metal calcium powder and metal zinc powder. A preparation method of the catalyst comprises the steps of: (1) fully stirring according to the proportion with 90% of aluminium powder and 10% of bismuth chloride, sodium chloride and potassium chloride, and mixing into an Al-BiCl3 base material; (2) fully stirring according to the proportion with 90% of Al-BiCl3 base material and 10% of metal calcium powder and metal zinc powder, and mixing into an Al-BiCl3 main material; (3) putting the Al-BiCl3 main material into a ball mill to carry out ball-milling for more than 5 hours so as to prepare a high-activity Al-BiCl3 composite material; (4) mixing and stirring the high-activity Al-BiCl3 composite material and polyacrylamide aqueous solution, preparing into blocks and then drying.
Owner:卢少辉
Inorganic/organic hybrid photochromic material, preparation method and application
ActiveCN102965095AChange color quicklyObvious phenomenonTenebresent compositionsBenzyl ViologenPhotochromic sunglasses
The invention relates to an inorganic / organic hybrid photochromic material, a preparation method and an application, which belongs to the inorganic / organic hybrid photochromic material field, and relates to a synthetic method and an application of a benzyl viologen bismuth chloride inorganic / organic hybrid photochromic compound. The benzyl viologen bismuth chloride inorganic / organic hybrid photochromic compound has excellent photochromism performance, is fast to change color under the irradiation of UV and visible light, and also fast to fade while being heated and placed in a darkroom, the material can be used in the fields of light information storage, protection decoration, fake resistance and authentic identification, secrecy, optical switch device, light information converter, photochromic sunglass lens used for radiation protection, diaphragm material and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of high fluorescence efficiency Cs2AgxNa1-xInncl6 dual-layer perovskite
InactiveCN109777403AHigh fluorescence yieldEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceEthanol
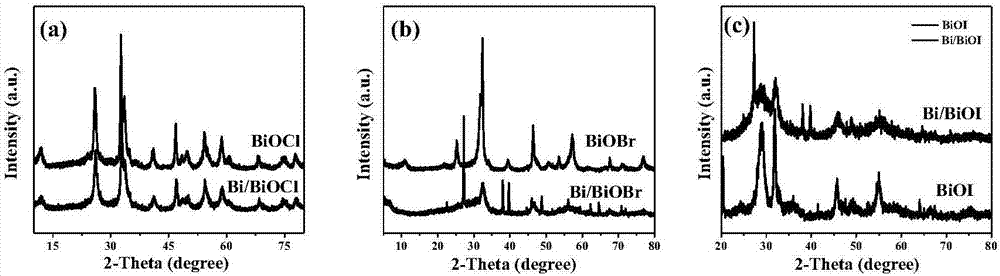
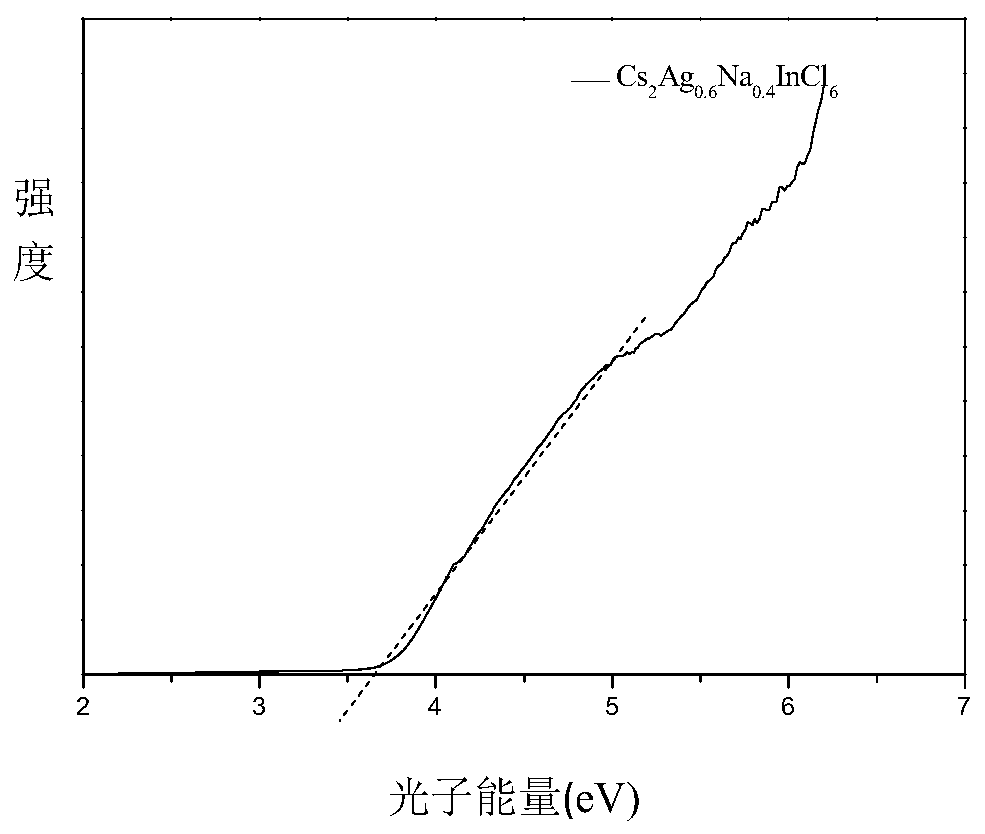
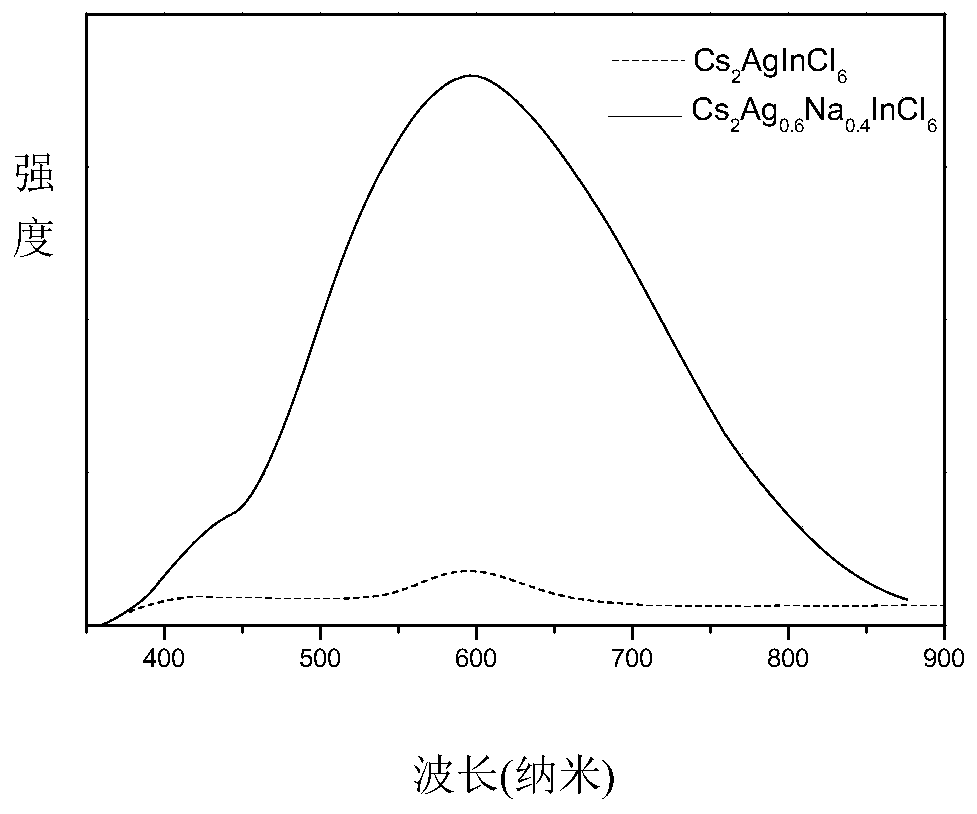
The invention relates to a preparation method of high fluorescence efficiency Cs2AgxNa1-xInncl6 dual-layer perovskite and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nanomaterial preparation. Themethod comprises the steps that firstly, caesium chloride, sodium chloride, silver chloride and indium chloride are mixed and ground, the mixture is gradually hardened from fluffy white powder and isattached to a container wall, and then the powder is softened and continues to be ground until the mixture becomes fluffy white powder again; then, bismuth chloride is added for continuous grinding, and the obtained product is cleaned through ethyl alcohol and dried for 2 hours at the vacuum condition of 60-350 DEG C so as to obtain the high fluorescence efficiency Cs2AgxNa1-xInncl6 dual-layer perovskite. According to the method, Na+ alloying and Bi3+ trace doping of Cs2AgInC16 are achieved through mechanical grinding, and the fluorescence yield of the perovskite is greatly increased; meanwhile, the method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the method is simple, and industrial production is easily achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for synthesizing flaky pearlized bismuth oxychloride
ActiveCN101804965ASolve processing problemsSimple processHalogen oxides/oxyacidsState of artEcological environment
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing flaky pearlized bismuth oxychloride, which belongs to the technical field of inorganic material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a bismuth chloride solution; 2) preparing acidified pure water; 3) dropwisely adding the bismuth chloride solution to hydrolyze and synthetize the flaky pearlized bismuth oxychloride; and 4) processing into finished flaky pearlized bismuth oxychloride. The method has the advantages of easy amplification, convenient regulation and control, and strong controllability. The product obtained by using the method has the advantages of uniform dispersibility, good glossiness and stable property, and has broad market prospects in the fields of inorganic pigments, pearlized buttons, pearlized decorations and the like. The invention solves the problem of difficulty in waste water treatment after production in the prior art, and protects the ecological environment.
Owner:HUNAN SHIZHUYUAN NON FERROUS METAL
Display element
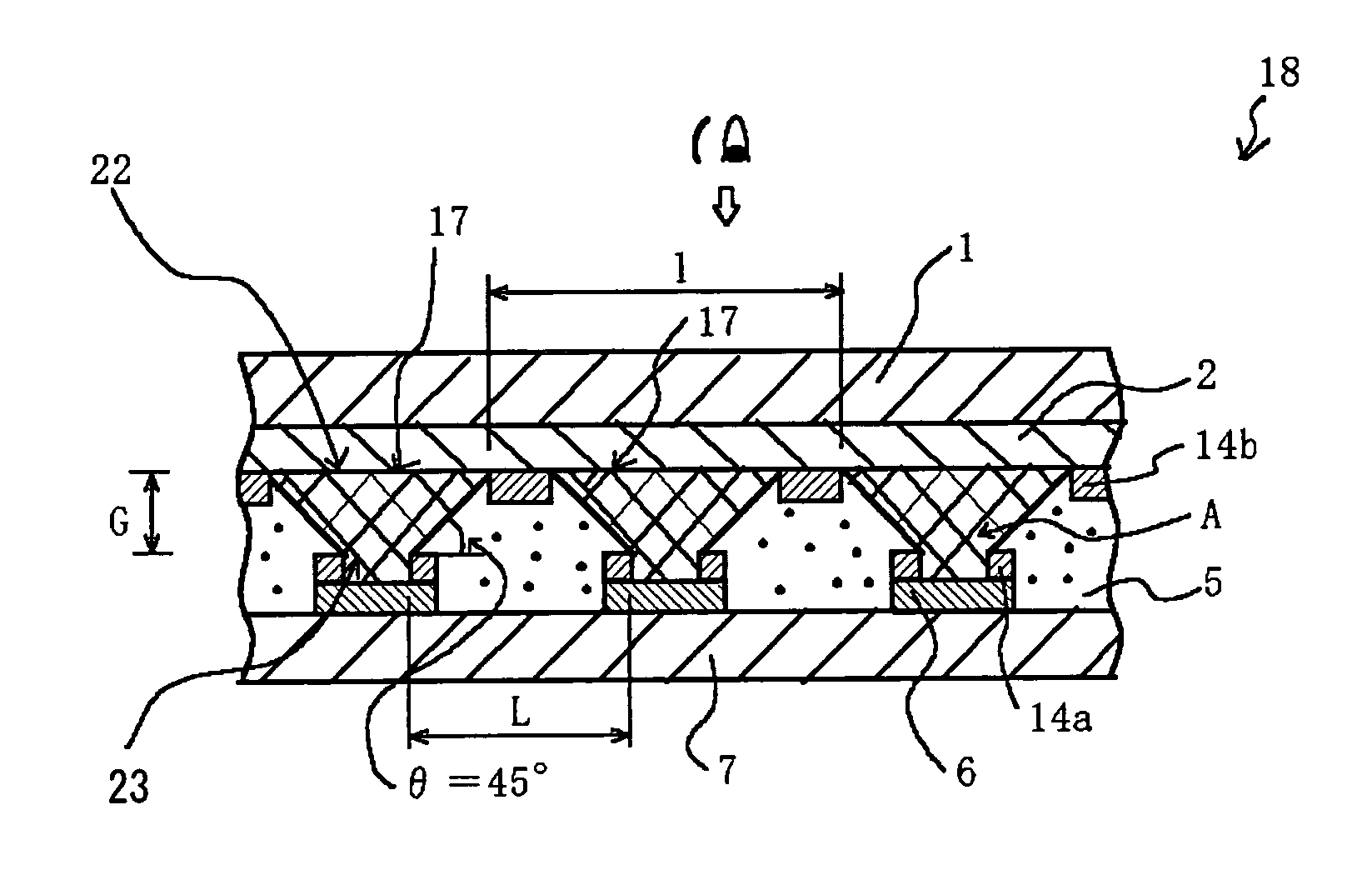
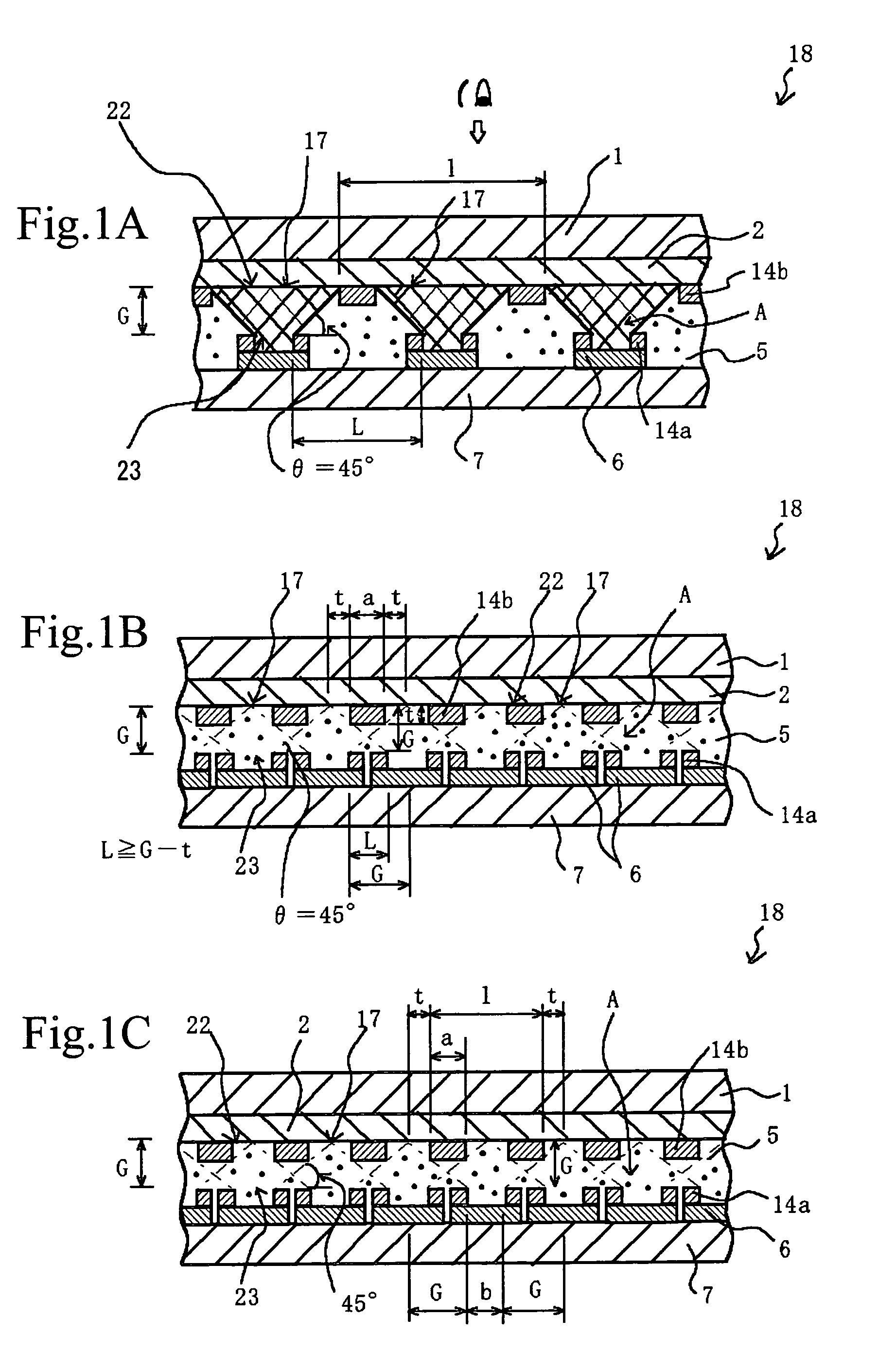
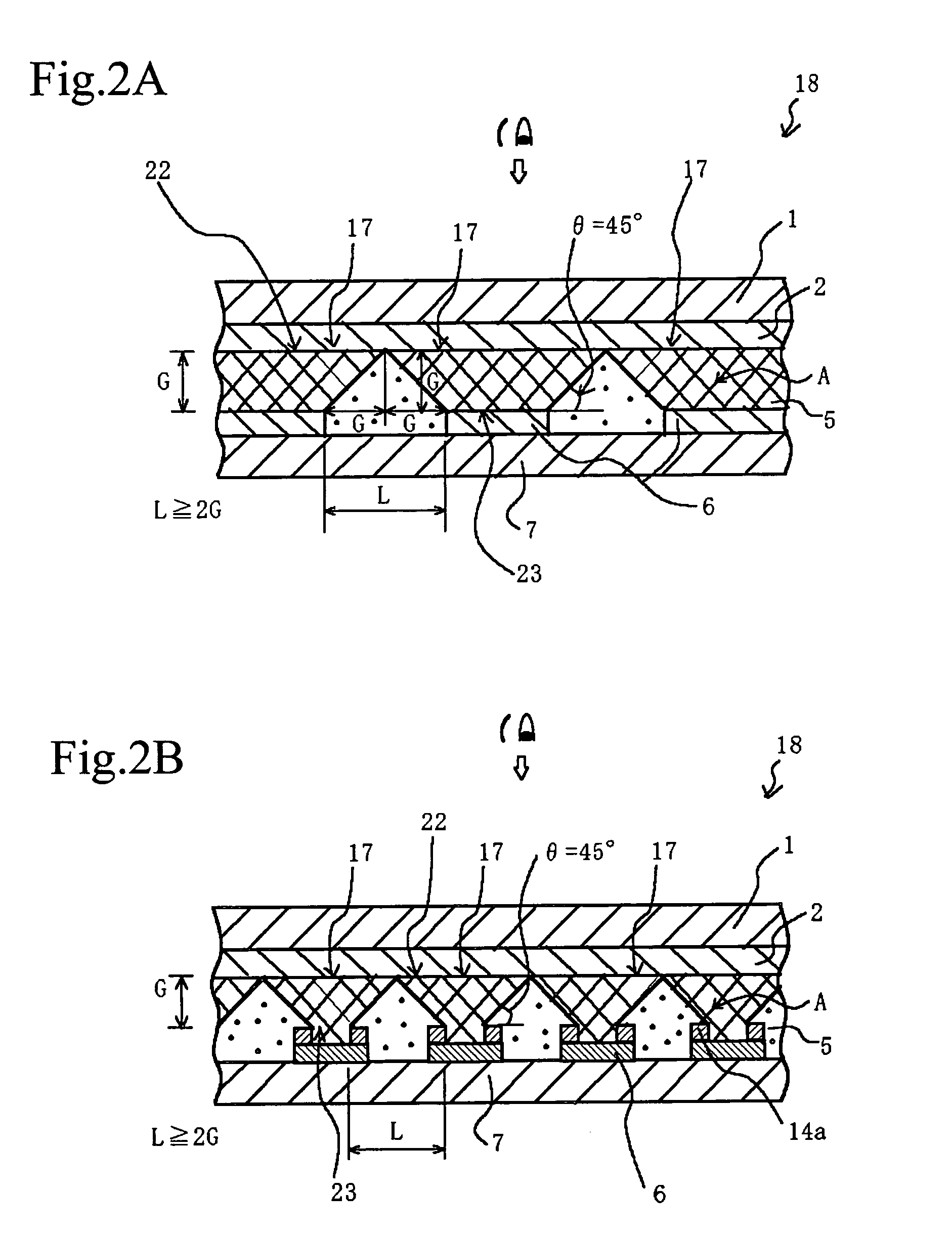
InactiveUS7057789B2Effectively prevent ionEffectively prevent ions from invading the adjacent pixelsFuel cell auxillariesCell component detailsDissolutionElectrochemistry
A display element not causative of crosstalk, ensures sharp display, and can be driven at a low energy is disclosed. In the display element (18), a polymer solid electrolyte layer (5) which contains a colorant material such as bismuth chloride or AgI, capable of causing deposition, dissolution or color change based on electrochemical reduction or oxidation, is disposed between transparent pixel electrodes (2) and opposing electrodes (6), and at least the transparent pixel electrodes (2) are covered with an insulating material (14b) in an area exclusive of at least pixel portions (17).
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Bismuth base hydrogen storage material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101513994AUniform sizeSingle formCell electrodesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsTe elementSolvent
The invention relates to a bismuth base (bismuth selenide, bismuth telluride) hydrogen storage material and a preparation method thereof, relating to low temperature liquid phase synthesis of bismuth base material and the application thereof on hydrogen storage, lithium storage and electrode material. The invention is characterized in that water is taken as solvent, bismuth salts such as bismuth nitrate, bismuth chloride and the like as a bismuth source, and water-soluble tellurium (selenium) acid salts (such as sodium tellurite, selenium substituted sodium sulfate, sodium selenite) or tellurium (selenium) acids (such as orthotelluric acid, tellurous acid and selenous acid) as a tellurium source (selenium) source; proper coordination agents (such as nitrilotriacetic acid, hexamethylene diamine tetraacethyl and the like) and reducing agents (such as vitamin C, sodium borohydride and the like) are added for liquid phase reaction synthesis at the low temperature of 60-80 DEG C. The bismuth selenide crystal grains prepared by the invention take on flower shapes with the sphere diameter of 1-6mum, and the bismuth telluride crystal grains take on sheet shapes with nanometer diameter; the hydrogen storage performance reaches over 100mAh.g. The method has the advantages of cheap raw material, simple technique, convenient operation, easy mass production, etc.
Owner:中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所苏州研究院
Manganese-bismuth-iron-phosphor permanent magnetic alloy plating solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104790000AGood chemical stabilitySimple preparation processLiquid applicationManganeseIron(II) chloride
The invention discloses a manganese-bismuth-iron-phosphor permanent magnetic alloy plating solution and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of metal plating electro-deposition. The manganese-bismuth-iron-phosphor permanent magnetic alloy plating solution contains ferrous chloride, manganese chloride, bismuth chloride, and a proper amount of water, and additionally comprises boric acid, sodium hypophosphate, sodium citrate and ascorbic acid. Each component of the plating solution is, by weight, 35-45 parts of boric acid, 30-45 parts of sodium hypophosphate, 5-15 parts of ferrous chloride, 55-65 parts of manganese chloride, 4-10 parts of bismuth chloride, 35-45 parts of sodium citrate, and 1-5 parts of ascorbic acid. The invention also provides the preparation method of the manganese-bismuth-iron-phosphor permanent magnetic alloy plating solution, and the preparation method comprises: taking a Pt sheet as an anode, taking a workpiece to be plated as a cathode; and carrying out plating in the plating solution, wherein the temperature of the plating solution is 20-40 DEG C and the voltage while plating is 2.0-5.0V. The plating solution is high in chemical stability and low in cost and has no pollution. The preparation method is simple and controllable; a prepared manganese-bismuth-iron-phosphor permanent magnetic alloy plating layer is high in corrosion resistance and good in magnetic performance; and the plating solution is mainly applied to the fields such as surface decoration of hardware products and magnetic materials.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +1
Bismuth sulfide nanorod with CT (computed tomography) angiography function, nano-composite material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102633304AShape is easy to controlUniform sizeX-ray constrast preparationsNanotechnologyBismuth sulfideSolvent
The invention discloses a bismuth sulfide nanorod with a CT (computed tomography) angiography function, a nano-composite material and preparation thereof. The preparation method of the bismuth sulfide nanorod comprises the following steps of: (1) dissolving bismuth chloride in a solvent in an ultrasonic manner to get a solution A; (2) dissolving sulfur powder or thiacetamide in the solvent in the ultrasonic manner to get a solution B; and (3) increasing the temperature of the solvent to 80-180 DEG C under the protection of argon, sequentially adding the solution A and the solution B, stirring to realize complete reaction, cooling, and then adding ethanol for centrifugation so as to get the bismuth sulfide nanorod, wherein the solvent is selected from oleyl amine, ethylene glycol and glycerin. The oleyl amine and a metal salt type compound are added into a toluene solution of the bismuth sulfide nanorod, stirring is performed at room temperature, and the ethanol is added for centrifugation so as to get the nano-composite material. The method disclosed by the invention is fast, simple and convenient, and the prepared bismuth sulfide nanorod and the nano-composite material thereof have the advantages of controllable appearance, uniform size and low cost and have excellent CT signals.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy, preparing method thereof and application
InactiveCN109652684AHigh activityImprove the performance of hydrogen production by hydrolysisHydrogen productionPotassiumCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy. The hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy comprises raw materials including, by mass percent, 90 to 95% of Al and 5 to10% of an additive. The additive is one or multiple of a metal element, metallic oxide and metal chloride, the metal element comprises one or multiple of magnesium, antimony, zinc, lead, cadmium, bismuth, tin, potassium and sodium, the metallic oxide comprises one or multiple of magnesium oxide, antimony oxide, zinc oxide, lead oxide, cadmium oxide, bismuth oxide, tin oxide, potassium oxide and sodium oxide, and the metal chloride comprises one or multiple of magnesium chloride, antimony chloride, zinc chloride, lead chloride, cadmium chloride, bismuth chloride, tin chloride, potassium chloride and sodium chloride. In the hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy, the cost of hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy is greatly reduced while hydrogen production is ensured. The invention further provides a preparing method of the hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy and application.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Environment-friendly non-mercury catalyst for acetylene-method chloroethylene synthesis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103386315AAvoid pollutionImprove conversion ratePhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionCeriumCuprous chloride
The invention discloses an environment-friendly non-mercury catalyst for acetylene-method chloroethylene synthesis and a preparation method thereof. According to the non-mercury catalyst disclosed by the invention, a precious metal chloride, namely any of gold chloride, platinum chloride and palladium chloride, is adopted as a main active substance, wherein the content of the precious metal chloride accounts for 0.5-5% of the weight of the catalyst; an assistant active ingredient is one or more than one of non-precious metal chlorides, namely bismuth chloride, cuprous chloride, cerium chloride and zinc chloride, wherein the content of the non-precious metal chlorides accounts for 1-10% of the weight of the catalyst; and a support is one of coconut shell charcoal, fruit shell charcoal and coal charcoal. The non-mercury catalyst is prepared by a conventional impregnation method. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple and is environmental-friendly, few byproducts are generated, the stability of the prepared catalyst is good, the environmental pollution caused by mercury catalysts is avoided, the service life of the catalyst is prolonged, the acetylene conversion ratio can reach 96-99%, and the selectivity to chloroethylene is not lower than 98%.
Owner:湖北随州双星生物科技有限公司
Novel bismuth selenate photocatalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105195180AHigh synthetic yieldHigh purityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPtru catalystNanoparticle
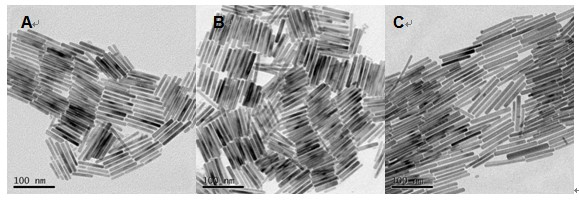
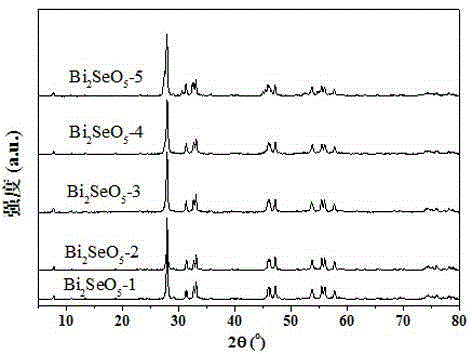
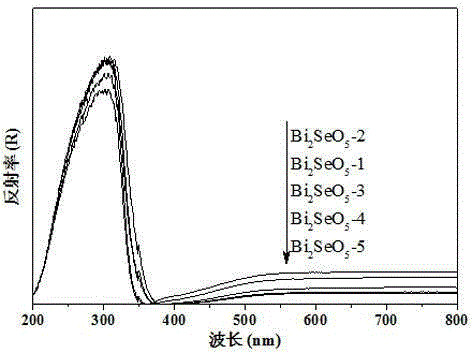
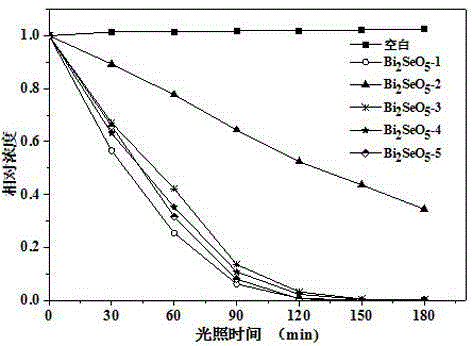
The invention discloses a n novel bismuth selenate photocatalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and environment pollution treatment. The bismuth selenate photocatalyst is Bi2SeO5. Bismuth chloride and selenium powder are taken as initiators, a hydro-thermal synthesis method is firstly employed for preparing a bismuth selenide precursor, and then a thermooxidizing method is employed for preparing the Bi2SeO5 nanometer particle with photocatalytic activity. The prepared bismuth selenate photocatalyst is capable of efficiently degrading organic pollutants in water and indoor formaldehyde and other VOC substances, and possesses efficient decoloring degradation effects on pollutants in printing and dyeing wastewater. The preparation technology is simple, low in cost, and green and environment-friendly in production process. The obtained catalyst is high in stability, accords with practical production demand and possesses relatively large application potential.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
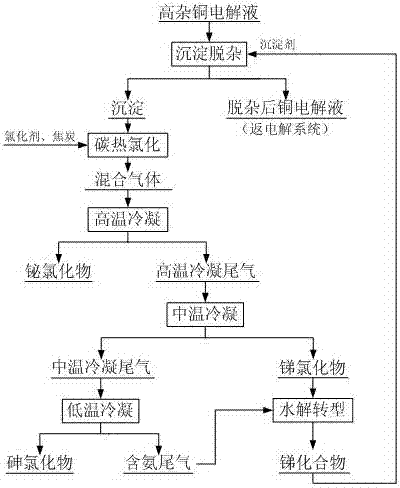
Method for carrying out precipitate impurity removal on copper electrolyte and carrying out chlorination regeneration on precipitant
ActiveCN107164785AEfficient removalHigh removal rateElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for carrying out precipitate impurity removal on a copper electrolyte and carrying out chlorination regeneration on a precipitant. The method comprises the following steps: adding an antimony compound in the copper electrolyte to remove co-precipitates containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth, then directly returning the copper electrolyte to an electrolysis system after the impurity removal, and comprehensively recovering the precipitates containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth by means of carbochlorination and gradient temperature-control condensation. The carbochlorination is carried out on the precipitates to obtain a mixed gas containing arsenic chlorides, antimony chlorides and bismuth chlorides under the action of coke and a chlorinating agent; high-temperature condensation is carried out on the mixed gas to obtain the bismuth chlorides and high-temperature condensation tail gas; medium-temperature condensation is carried out on the high-temperature condensation tail gas to obtain the antimony chlorides and medium-temperature condensation tail gas; low-temperature condensation is carried out on the medium-temperature condensation tail gas to obtain the arsenic chlorides and ammonia-containing tail gas; and the antimony chlorides and the ammonia-containing tail gas are slowly added in water, hydrolysis transformation is carried out on the antimony chlorides and the ammonia-containing tail gas to obtain the antimony compound, and the antimony compound is returned to a precipitate impurity removal procedure as the precipitant. The process method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being short in process flow, simple to operate, high in removal rate, free from the emission of 'three wastes', capable of repeatedly using the precipitant, low in cost and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Non-mercury septum paper for laminated cell
InactiveCN101271968AAvoid dischargePrevent precipitationCell component detailsThioureaPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a mercury-free diaphragm paper for a laminated cell, which is composed of a substrate and a coating, wherein, the coating is composed of a solid polymer electrolyte and bismuth chloride which is an inorganic mercury-substitute inhibiter; the solid polymer electrolyte is prepared by coordinated ionic liquid and PVA, PAM and starch; the coordinated ionic liquid is prepared by heating and melting urea, thiourea, zinc butter and ammonium chloride according to a certain proportion. The inorganic mercury-substitute inhibiter, bismuth chloride, in the coating of the invention can form a dense covering layer on the surface of a zinc electrode and form a good metallic film, thus realizing inhibition effect, reducing the discharge resistance of the battery and improving the capacity of the battery.
Owner:LIAOYUAN HONGTU LI ION BATTERY DIAPHRAGM TECH
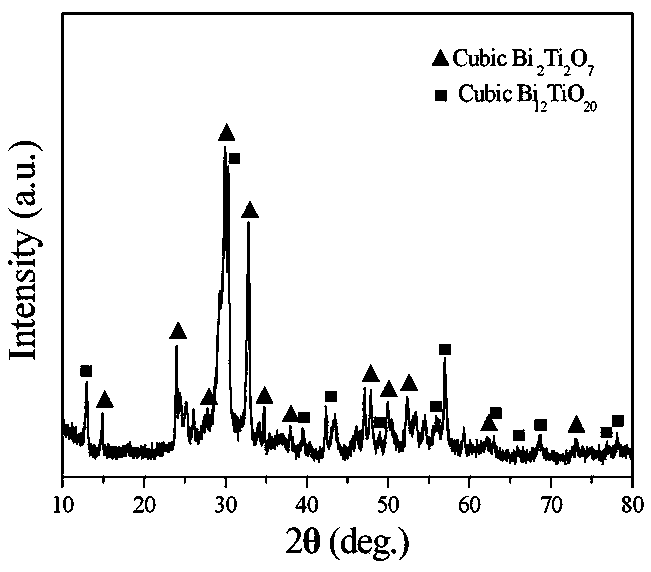
Bismuth titanate nanoneedle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103466703AReduced post-processingLow costMaterial nanotechnologyBismuth compoundsActive agentPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a bismuth titanate nanoneedle and a preparation method of the bismuth titanate nanoneedle, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. The bismuth titanate nanoneedle is composed of cubic Bi2Ti2O7 and Bi12TiO20 crystalline phases and is about 1-micron long. The diameter of the tip of the nanoneedle is about 10 nanometers. According to the preparation method, bismuth chloride and tetrabutyl titanate are used as raw materials, and water is used as a solvent, wherein the molar ratio of the bismuth chloride to the tetrabutyl titanate is 1:1; the bismuth chloride, the tetrabutyl titanate and the water are mixed uniformly before being placed in a reaction vessel and sealed at the temperature of 100-180 DEG C to preserve heat for 4-24 hours; the weight of the bismuth chloride and the tetrabutyl titanate is not larger than 10% of the weight of the water, and the white flocculent bismuth titanate nanoneedle can be obtained at last. The preparation process is simple, and surfactants are not needed; the raw materials and the preparation process do not cause pollution to the environment, meet the environmental requirements and conform to the development direction of the modern industry; a large number of the bismuth titanate nanoneedles can be prepared.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
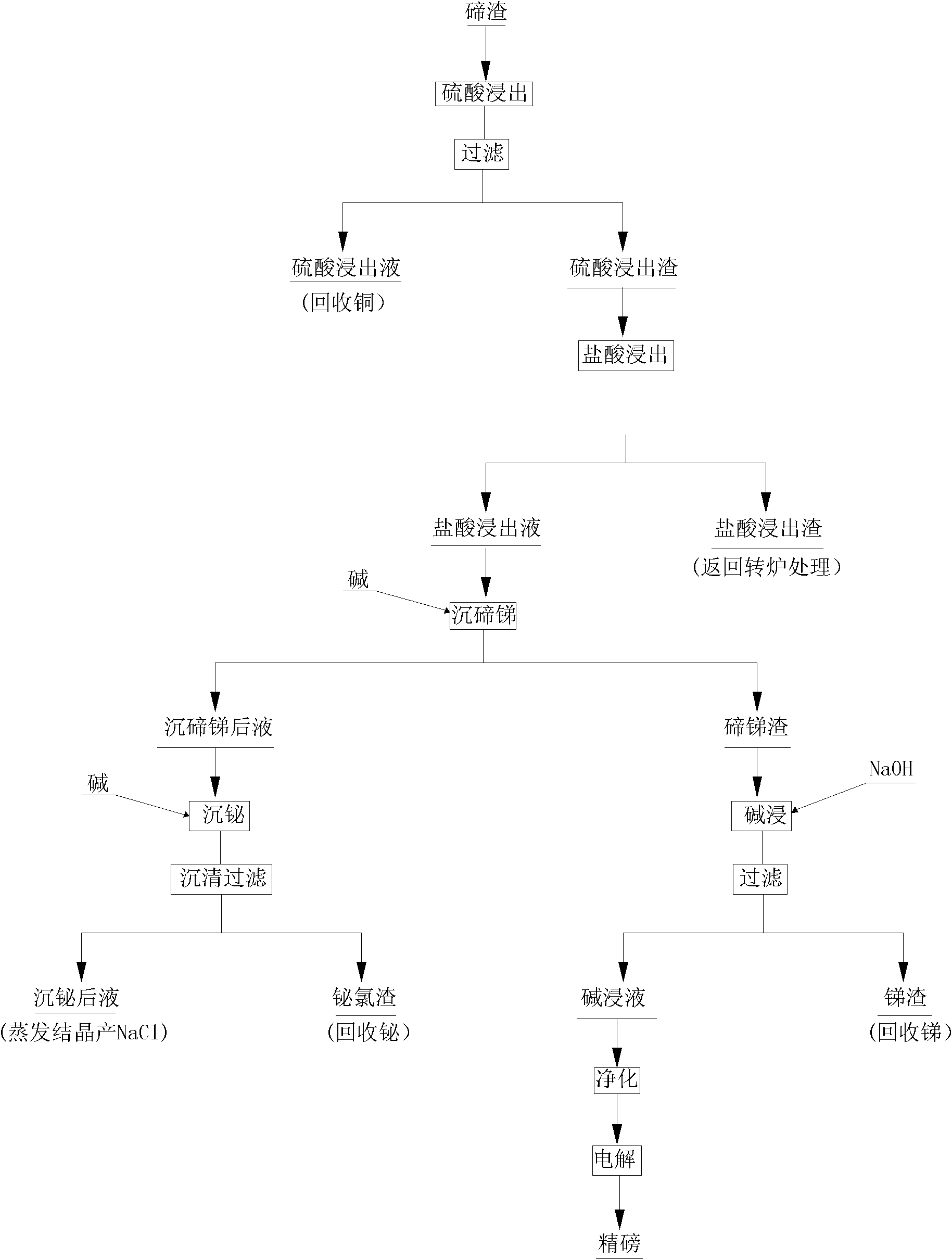
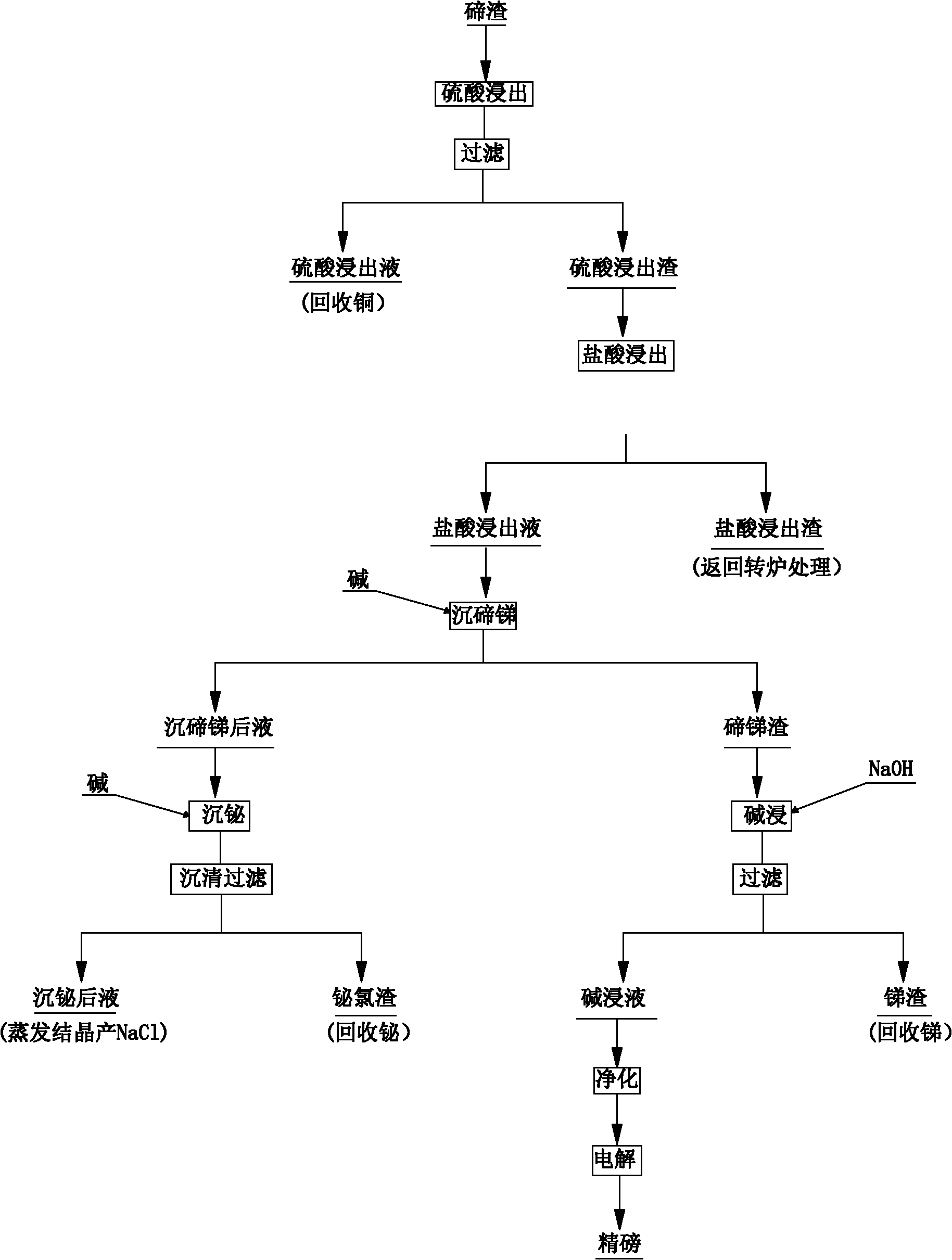
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from low-grade tellurium slag
ActiveCN102002597AImprove direct yieldIncrease sedimentation rateSelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementSlagMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from low-grade tellurium slag, and aims to provide the method for comprehensively recovering the valuable metals from the low-grade tellurium slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: A, crushing and grinding the tellurium slag until the tellurium slag is below 80 meshes, stirring and leaching with a sulfuric acid and filtering to obtain sulfuric acid leach liquor and sulfuric acid leach residue; B, stirring and leaching the sulfuric acid leach residue obtained in the step A with a hydrochloric acid, cooling and filtering to obtain hydrochloric acid leach liquor and hydrochloric acid leach residue; C, stirring the hydrochloric acid leach liquor obtained in the step B, and adding alkali to precipitate tellurium and antimony so as to obtain liquor obtained after tellurium and antimony precipitation and tellurium and antimony slag; D, leaching the tellurium and antimony slag obtained in the step C with sodium hydroxide for 2 to 4 hours and filtering to obtain alkaline leach liquor and antimony slag; and E, adding the alkali into the liquor obtained after tellurium and antimony precipitation obtained in the step C to precipitate bismuth, settling and filtering to obtain bismuth chloride slag and recovering the bismuth. The method is mainly used for comprehensively recovering the valuable metals such as copper, bismuth, antimony, tellurium and the like from the low-grade tellurium slag.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
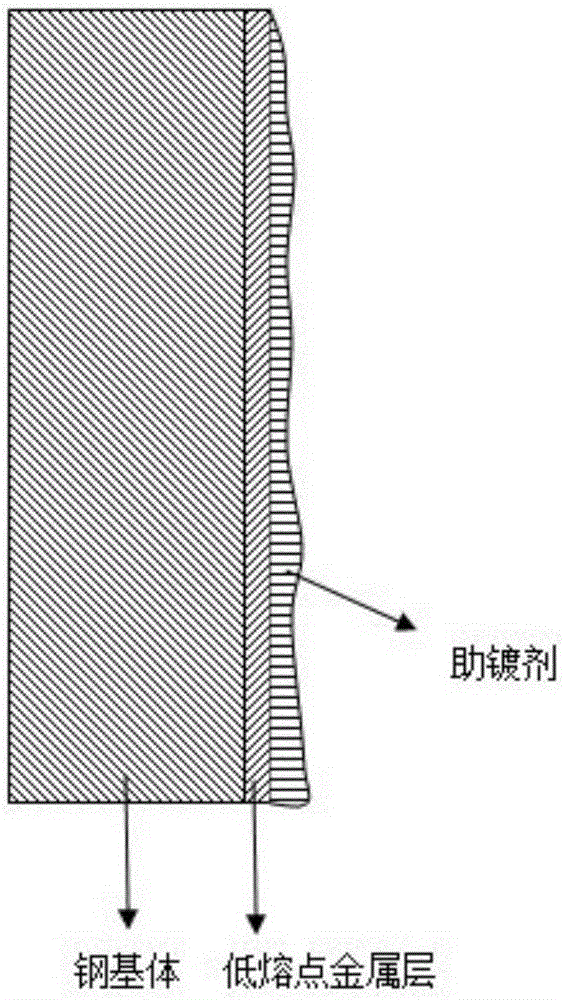
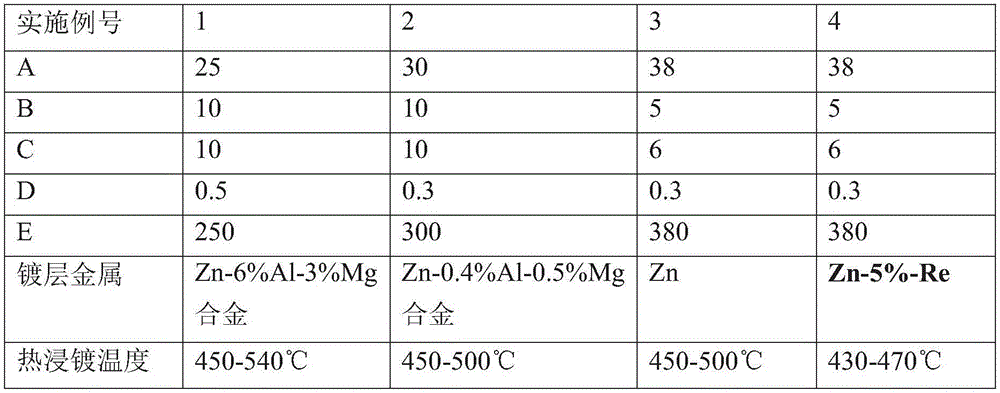
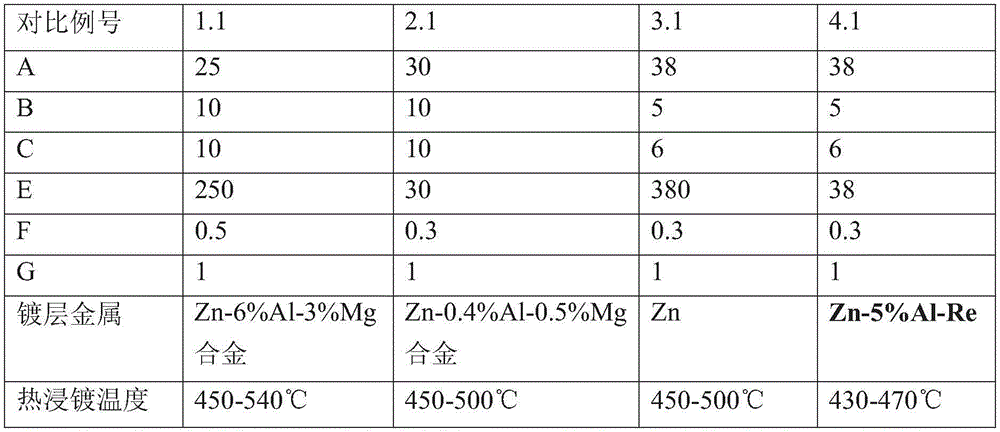
Plating assisting agent for batch hot-dip coating of Galfan and preparation method of plating assisting agent
ActiveCN105220099ASolve the problem of missing plating that is easy to occurSolving Missing Plating ProblemsHot-dipping/immersion processesCeriumLanthanum
The invention relates to a plating assisting agent for batch hot-dip coating of Galfan and a preparation method of the plating assisting agent. The plating assisting agent is characterized in that according to the formula of calculation of each liter of plating assisting agent, the plating assisting agent comprises 80-180 g of ZnCl2, 10-30 g of alkali chloride, 10-30 g of bismuth chloride and / or tin chloride, 2-10 g of transition metal element chloride which does not contain rear earth elements or zinc chloride and can be dissolved in water, 5-25 g of calcium chloride, 1-10 g of rare earth chloride, 15-25 ml of industrial hydrochloric acid and the balance water, wherein the rare earth chloride comprises at least one of lanthanum chloride and cerium chloride.
Owner:TIANJIN GONGDA GALVANIZING EQUIP CO LTD
Plating assistant and plating assisting solution for hot dip galvanizing and zinc alloy coating
InactiveCN104372280ANo surface defectsIncrease productivityHot-dipping/immersion processesPotassiumZinc alloys
The invention relates to a plating assistant and plating assisting solution for hot dip galvanizing and zinc alloy coating. The invention is characterized in that the plating assistant is composed of the following salts in parts by weight: 25-40 parts of zinc chloride, 5-10 parts of ammonium chloride, 5-10 parts of potassium chloride and 0.1-1 part of bismuth chloride. The plating assisting solution is a solution prepared from any plating assistant, water and hydrochloric acid. The zinc chloride concentration of the plating assisting solution is 250-400 g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN GONGDA GALVANIZING EQUIP CO LTD +1
Mercury-free catalyst for synthesizing vinyl chloride by acetylene method and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106975500AHigh activityHigh selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionEvaporationHigh activity
The invention relates to a mercury-free catalyst for synthesizing vinyl chloride by an acetylene method and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of using an acetic acid solution to soak coconut husk activated carbon for 8 to 24h, and using deionized water to wash the activated carbon to neutral state, so as to obtain a pretreated carrier; then, while stirring at normal temperature, dissolving ruthenium trichloride, cuprous chloride and bismuth chloride into a hydrochloric acid solution, impregnating the solution into the pretreated coconut husk activated carbon under the vacuum atmosphere, performing rotary evaporation, and drying, so as to obtain the required catalyst. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the mercury-free catalyst has high activity and selectivity when the acetylene is catalyzed to synthesize the vinyl chloride; the mercury-free catalyst uses the mercury-free active component, the green and environment-friendly effects are realized, the multiple sets of auxiliary equipment are not needed, the difficulty in preparation is low, the production technology is simple, and the preparation method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Method of manufacturing stibium doped bismuth telluride nano-wire
InactiveCN101492155AHigh crystallinityMild reaction conditionsBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsEthylenediamineNanowire
The invention relates to a method for preparing a stibium doped bismuth telluride nanowire, which comlprise: firstly adding antimony chloride, bismuth chloride and disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate into water to form a complex solution; dissolving orthotelluric acid in the water to form an aqueous solution of the orthotelluric acid; mixing the complex solution and the aqueous solution of the orthotelluric acid, and adding overweight reducer into the mixed solution for a reflux reaction at a temperature of between 80 and 120 DEG C for 4 to 6 hours; and after the completion of the reaction, cooling the mixed solution, separating a precipitate, and washing and drying the precipitate to obtain the stibium doped bismuth telluride nanowire. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation, and low energy consumption; and the prepared stibium doped bismuth telluride nanowire has good crystallinity.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Preparation method and application of small-size bismuth oxychloride/bismuth oxybromide chip
InactiveCN106040268ASmall sizeIncreased absorption spectral rangeGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsBismuth oxybromideHeating time
The invention discloses a hydrothermal preparation method for a small-size bismuth oxychloride / bismuth oxybromide chip. The method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing bismuth ions in the presence of chloride ions and bromide ions so as to form a bismuth oxychloride / bismuth oxybromide crystal nucleus; controlling heating time and temperature and a template in an enclosed container so as to form a bismuth oxychloride / bismuth oxybromide chip with a controllable size; and carrying out cooling, cleaning and drying so as to obtain a high-purity bismuth oxychloride chip having a controllable size and directly grown on a substrate. The method provided by the invention adopts the principle of direct hydrolysis of bismuth chloride, only has one reactant, is simple in process flow and low in cost, can control the size of the produced chip by changing heating time and temperature and the template, and is a preparation method with commercial utilization value. The prepared bismuth oxychloride chip is extensively applied to the fields of photocatalysts and devices thereof.
Owner:燕园众欣纳米科技(北京)有限公司
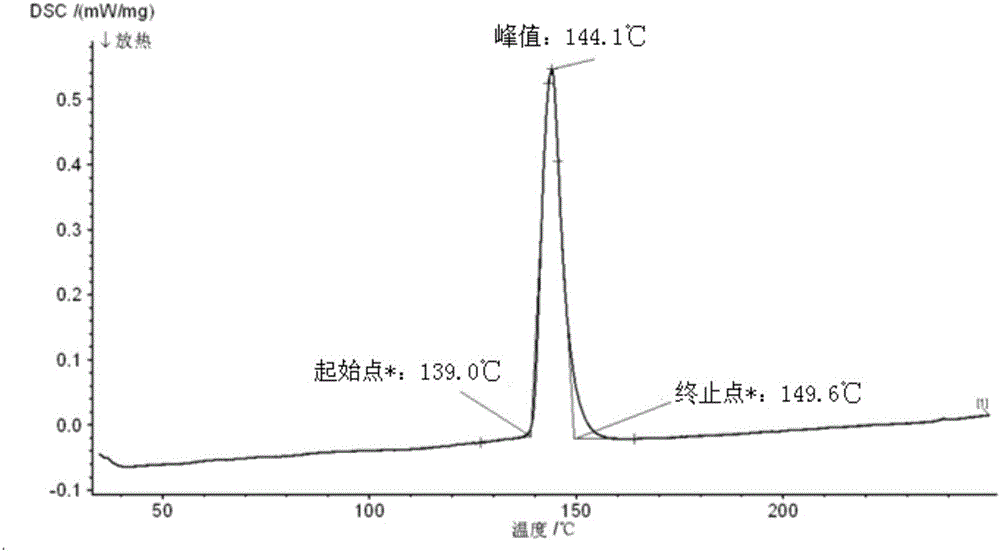
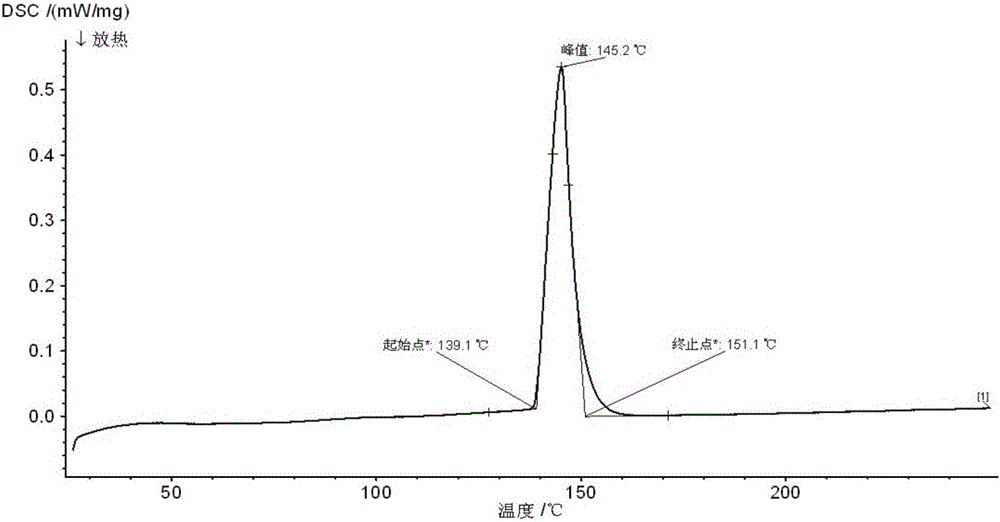
Corrosion-resistant low-temperature solder for photovoltaic solder strip and preparation method of corrosion-resistant low-temperature solder
ActiveCN105014254ALow melting pointImprove corrosion resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaDip solderingPorous carbon
The invention discloses corrosion-resistant low-temperature solder for a photovoltaic solder strip and a preparation method of the corrosion-resistant low-temperature solder. The solder comprises, by weight, 55%-60% of Bi, 0-0.01% of Sb, 0-0.0005% of Al, 0-0.0005% of Zn and the balance tin. The method comprises the following steps that a proper amount of the tin and bismuth is heated to 280 DEG C to 300 DEG C, and mixed melt is obtained; a proper amount of bismuth chloride is added to cover the surface of the mixed melt, then heat preservation is carried out, temperature is reduced to below 180 DEG C after stirring of 15-20 minutes, and molten solder is obtained; and finally the molten solder is filtered through porous carbon, the filtered molten solder is cast, and the corrosion-resistant low-temperature solder is obtained. According to the solder, the content of the key component Bi is controlled, it is measured that the melting point is close to 139 DEG C, the temperature difference of a solid phase and a liquid phase is only about 12 DEG C, and the phenomenon of segregation can be effectively avoided in dip soldering and other welding processes with the high cooling rate; the content of impurities is controlled to be low, so that the melting point of the prepared solder is low, and the corrosion resistance of the prepared solder is high.
Owner:SUZHOU YOURBEST NEW TYPE MATERIALS +1
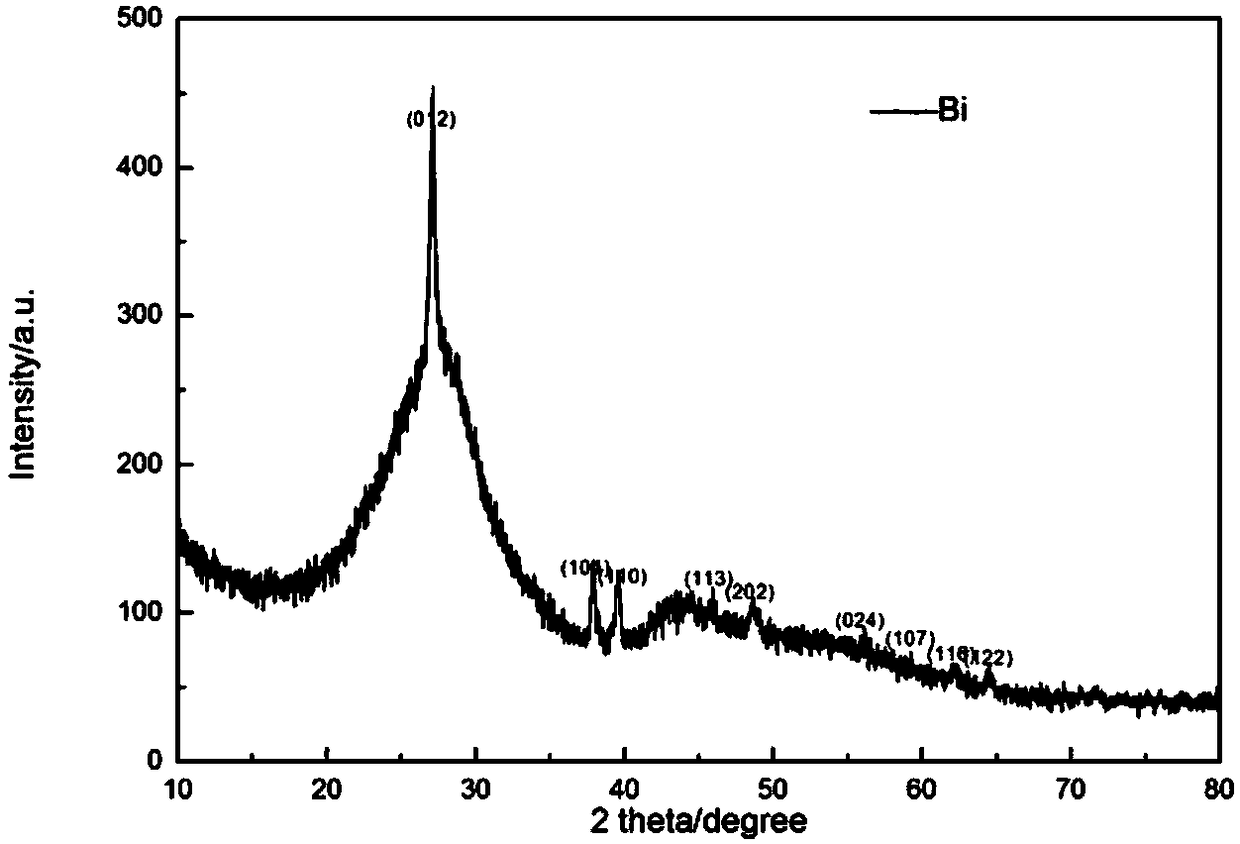
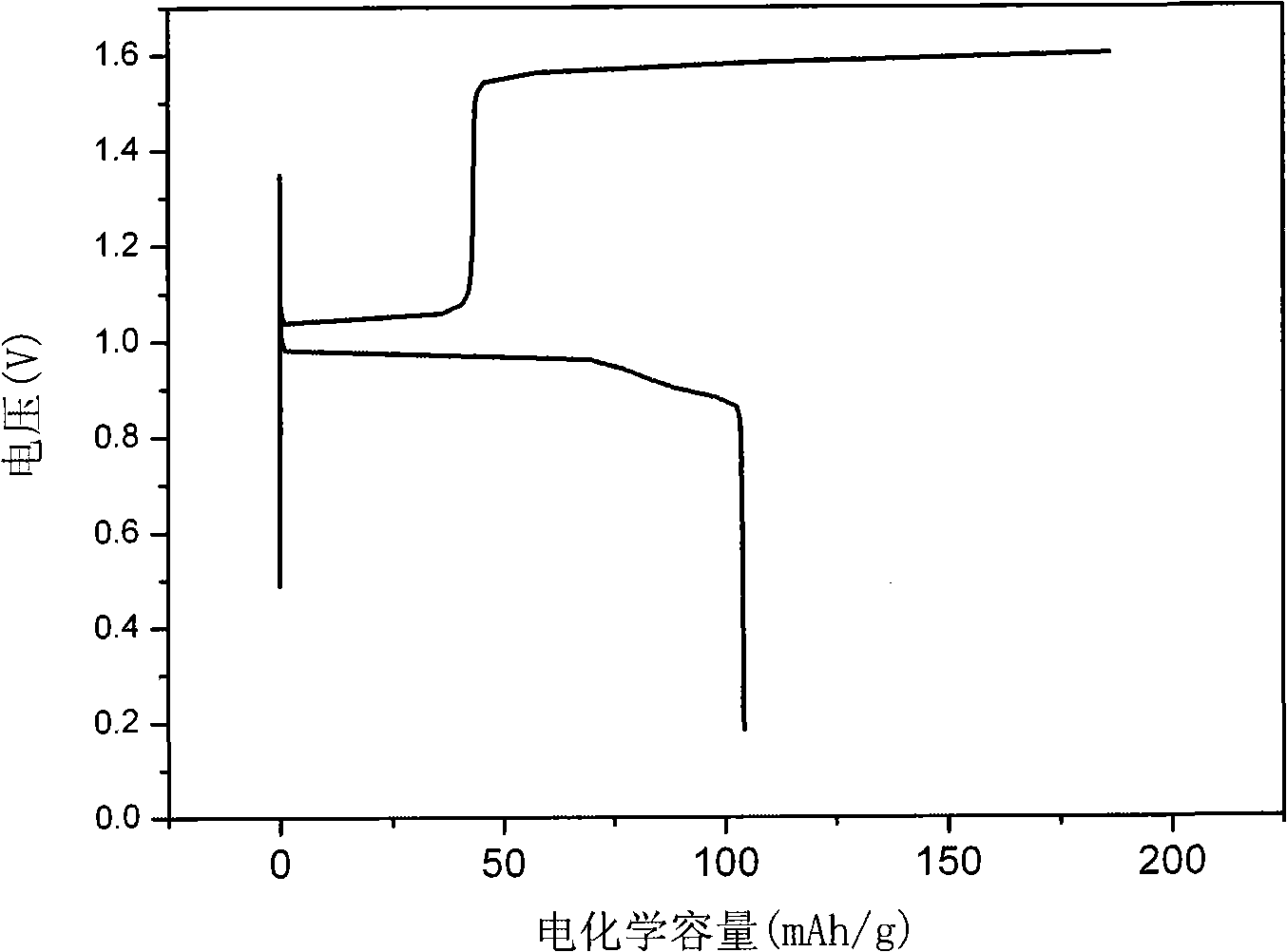
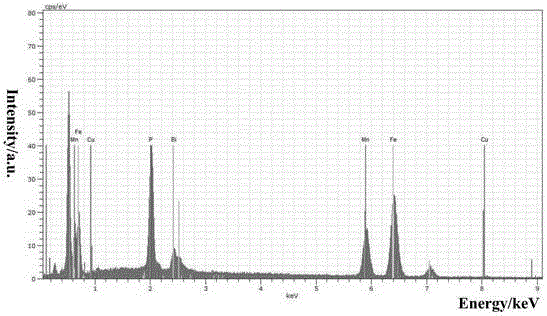
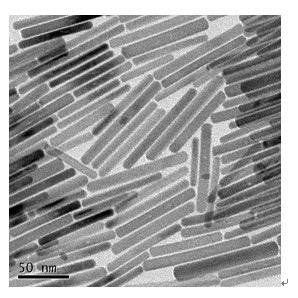
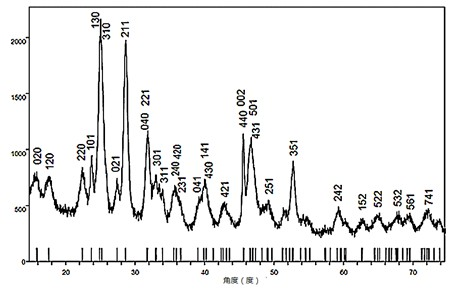
Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets
InactiveCN105200520AHigh crystallinityGood dispersionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsDispersityCrystallinity
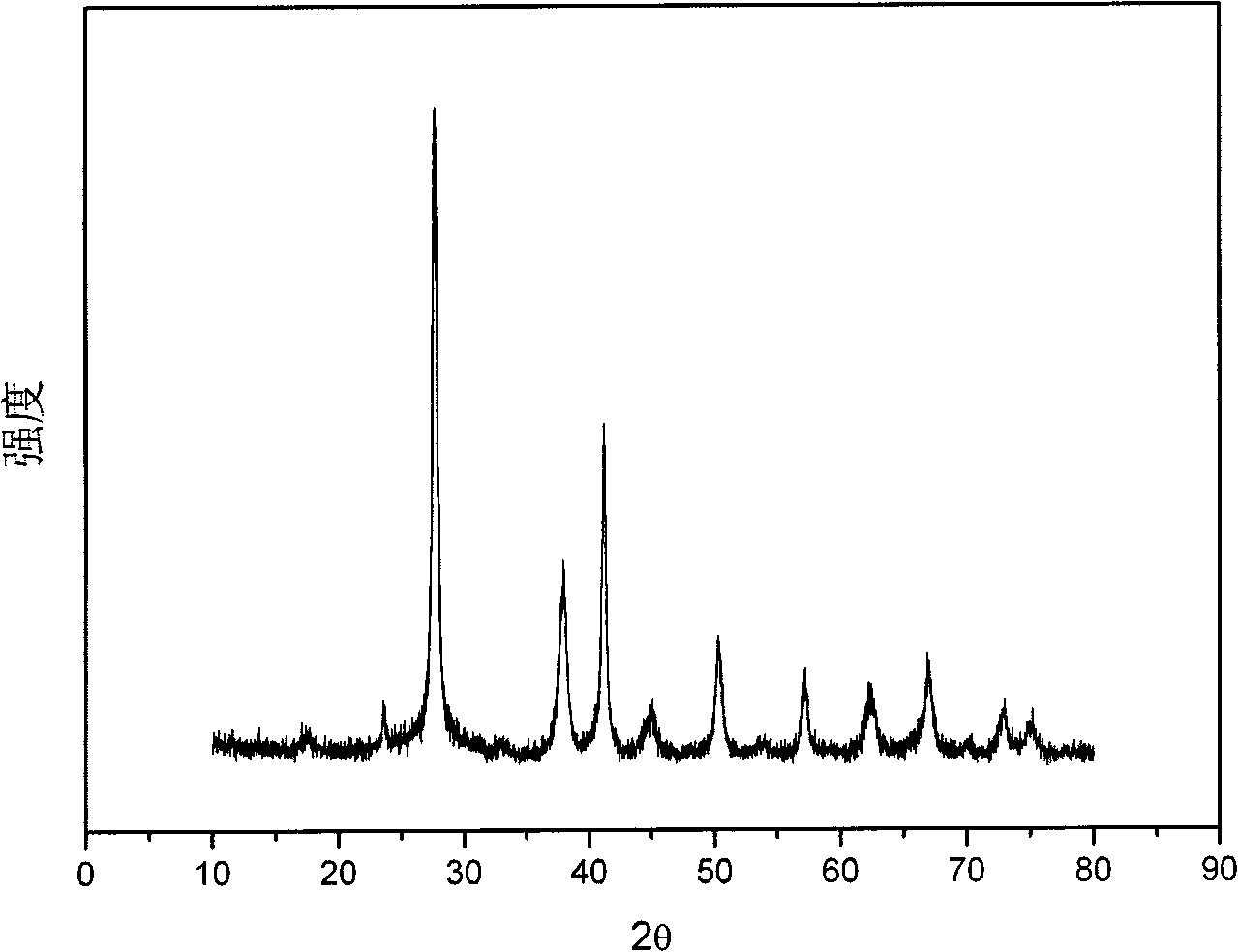
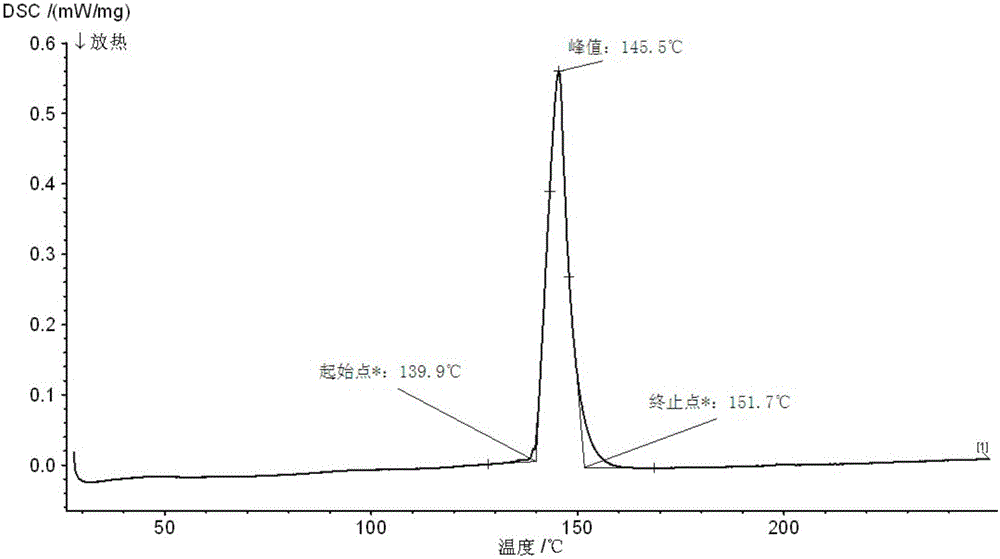
The invention discloses a method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets, which comprises the following steps: adding tellurium powder, selenium powder and an organic solvent into a high-pressure reaction kettle, stirring for 15-35 minutes, adding bismuth chloride, continuing stirring for 15-35 minutes, sealing the reaction kettle, keeping the temperature at 180-200 DEG C for 12-48 hours, carrying out solvothermal reaction, cleaning the reaction product with deionized water and anhydrous ethanol 1-3 times, carrying out vacuum drying, and collecting to obtain the end product Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets. A solvothermal process is adopted, diethylenetriamine is used as the solvent, and the bismuth chloride, tellurium simple-substance powder and selenium simple-substance powder are used as precursors to synthesize the adjustable-component Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets without the assistant of other surfactants; and the obtained Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets have favorable crystallinity and dispersity. The preparation method is low in environmental pollution, simple in process and easy to operate and popularize, and has important research value and wide application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Bismuth compounds composite
InactiveUS8308986B1Maintain good propertiesElectrode and associated part arrangementsDischarge tube/lamp detailsBismuth compoundRadiation shield
A heavily filled bismuth compound composite having a polymer matrix and a bismuth compound therein. The bismuth compound may be bismuth oxide, or other bismuth compounds. The polymer may be any of a very wide range of materials or combinations thereof. Binder, secondary fillers or other third components may be added. By means of use of various bismuth compounds, polymers, and third components, the physical, radiological and electrical properties of the finished products may be tailored to achieve desired properties. In addition, the invention teaches that radiation shielding, insulators, and combined radiation shield / insulators may be fashioned from the composite. A wide range of production methods may be employed, including but not limited to liquid resin casting.
Owner:STUART MCCORD
Preparation method of Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles and nanometer material made of Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles
InactiveCN103418333AUnrivaled Adsorption CapacityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesHigh absorptionPotassium
The invention relates to a preparation method of Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles and a nanometer material made of the Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing proper amount of bismuth salt and dissolving the bismuth salt in certain amount of water, and under the condition of magnetic stirring, adding a nitric acid solution with certain concentration; dissolving proper amount of molybdate in the obtained solution, and adjusting the pH value with ammonia water with certain concentration; pouring the mixed solution into a crucible, and performing microwave reaction. The obtained product is sequentially washed with water and absolute ethyl alcohol for multiple times, and is dried. The bismuth salt is one type from or a mixture of bismuth chloride, bismuth nitrate and bismuth sulfate. The molybdate is one type from or a mixture of ammonium molybdate, potassium molybdate and cadmium molybdate. Through changing of solution pH value, reactant concentration and microwave frequency, the Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles with different sizes can be obtained. Due to different electric charges on the surfaces of the Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles, the Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles are subjected to electrostatic interaction with different ionic pigments, so that the Bi<3.64>Mo<0.36>O<6.55> nanometer particles show high selectivity and high absorption capability in respect of absorbability.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com













![Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/88fc781e-5f84-4d4b-98ec-6a8d782b060f/151009144052.PNG)
![Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/88fc781e-5f84-4d4b-98ec-6a8d782b060f/151009144058.PNG)
![Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets Method for preparing Bi2(SexTe[1-x])3 monocrystal nanosheets](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/88fc781e-5f84-4d4b-98ec-6a8d782b060f/151009144105.PNG)