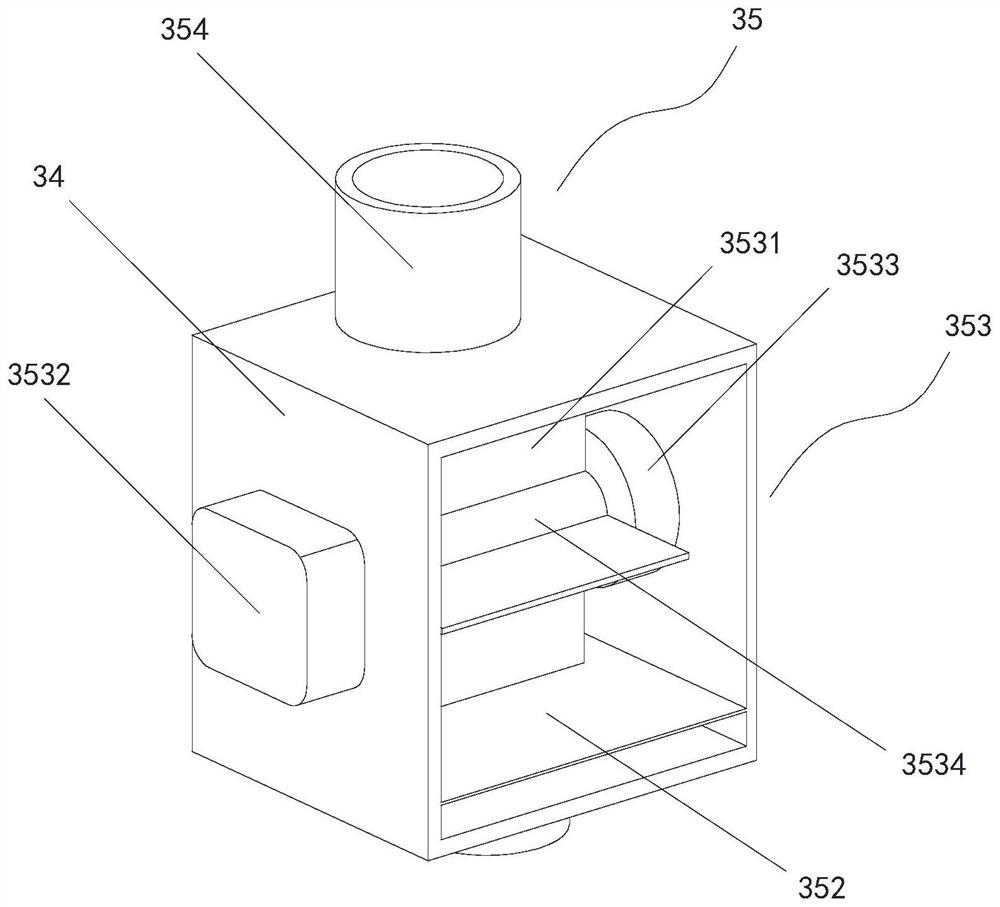
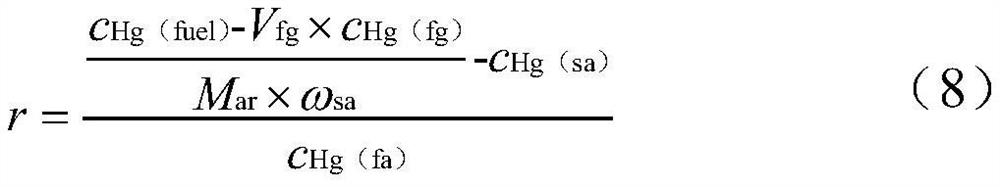Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Mercury (element)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum (/haɪˈdrɑːrdʒərəm/ hy-DRAR-jər-əm). A heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is liquid at standard conditions for temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature.
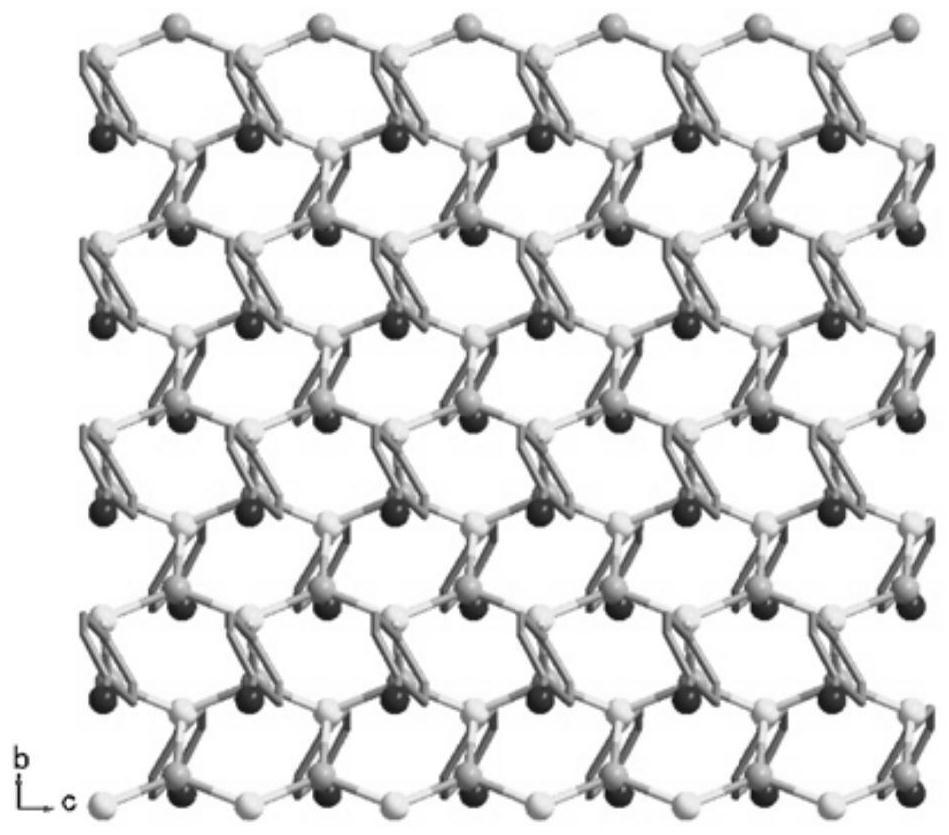
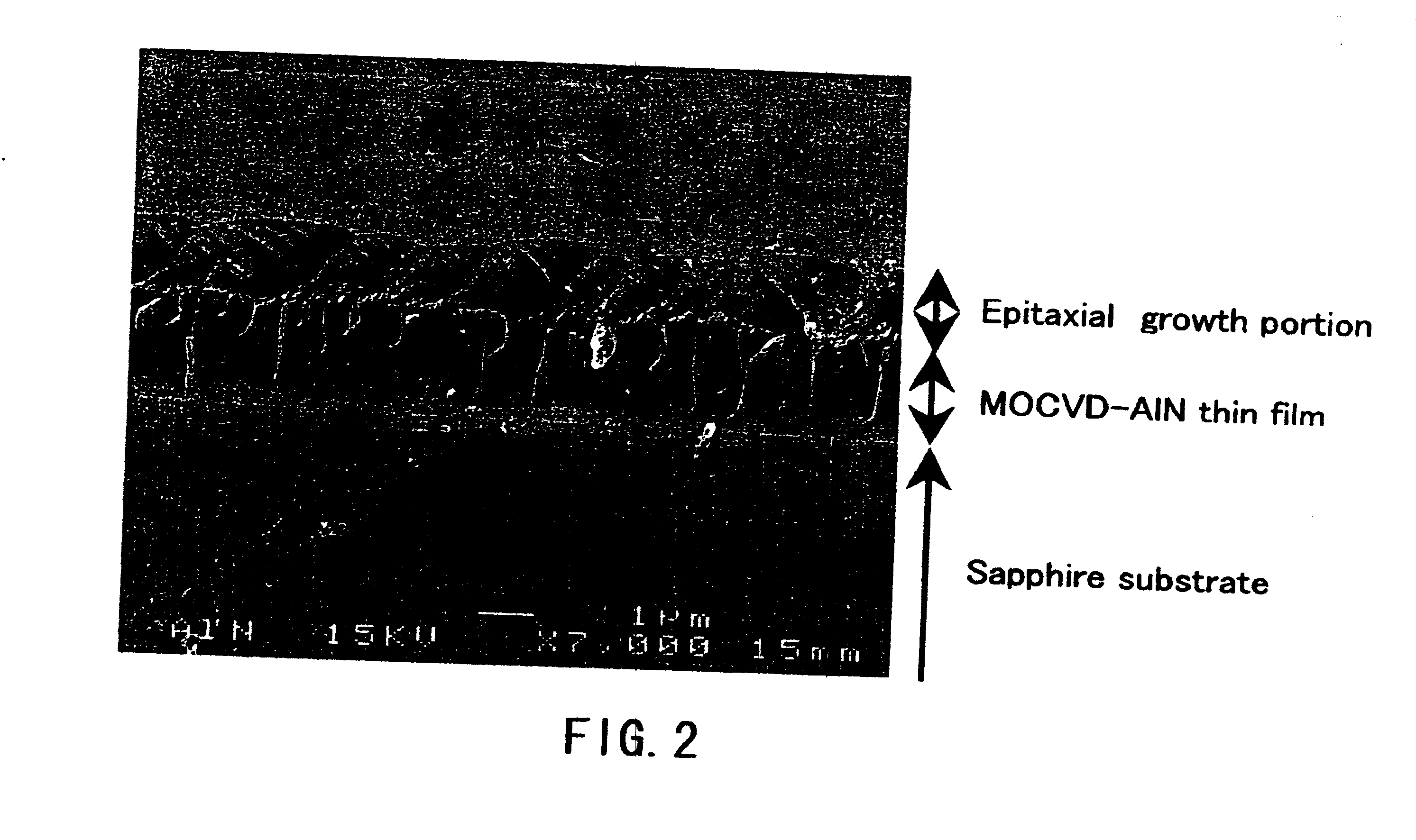
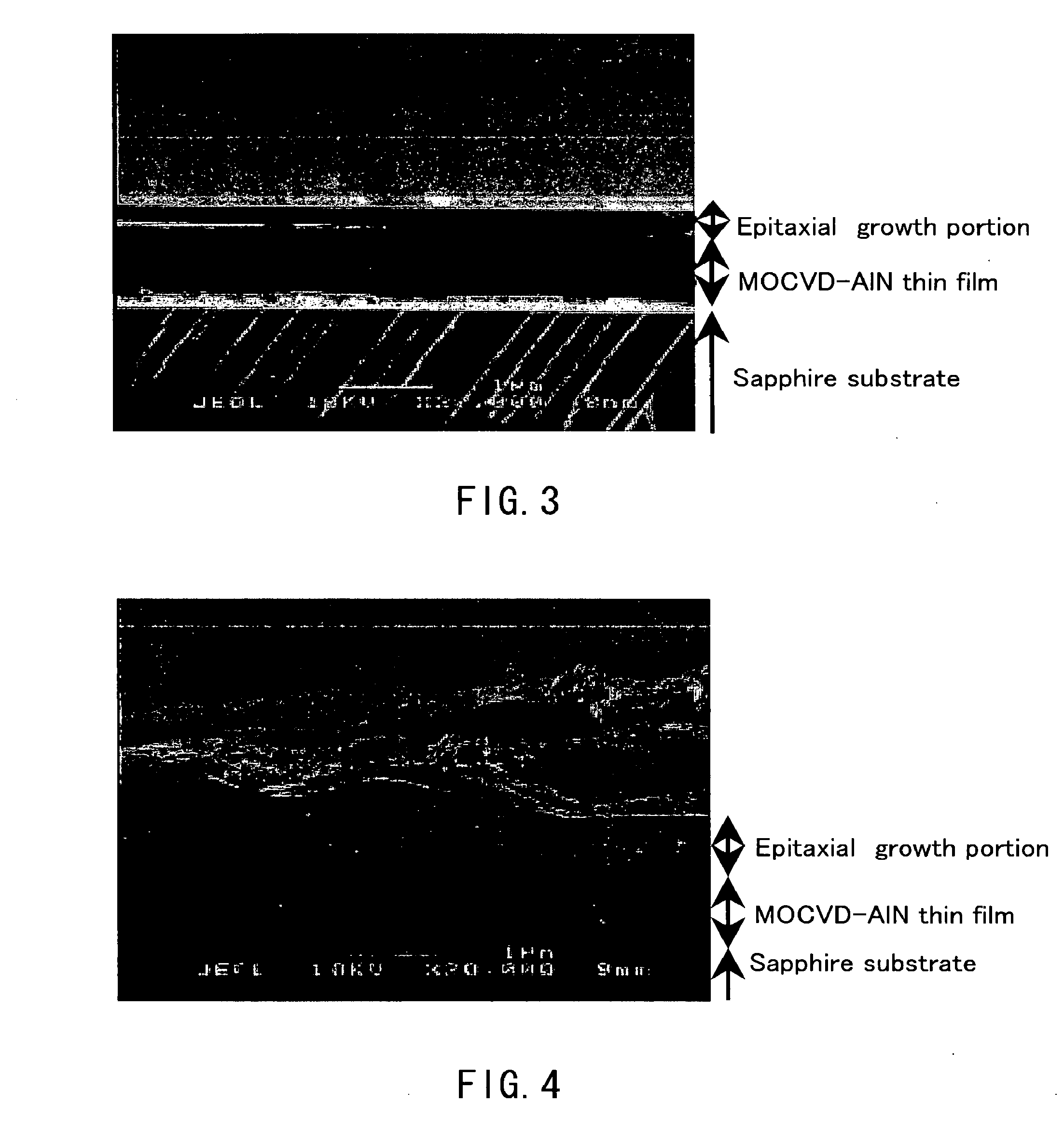
Process For Producing Aluminum Nitride Crystal And Aluminum Nitride Crystal Obtained Thereby
InactiveUS20080008642A1Mild production conditionsQuality improvementFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthIndiumAlkaline earth metal
The present invention provides a method for producing aluminum nitride crystals under mild pressure and temperature conditions. In the production method of aluminum nitride crystals, aluminum nitride crystals are formed and grown in the presence of nitrogen-containing gas by allowing aluminum and the nitrogen to react with each other in a flux containing the following component (A) and component (B), or a flux containing the following component (B). (A) At least one element selected from the group consisting of the alkali metal and the alkaline-earth metal. (B) At least one element selected from the group consisting of tin (Sn), gallium (Ga), indium (In), bismuth (Bi) and mercury (Hg).
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Catalyst and process for hydrocracking hydrocarbon-containing feedstocks
ActiveUS20040138059A1Improve spatial resolutionCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesNitrogenPore diameter
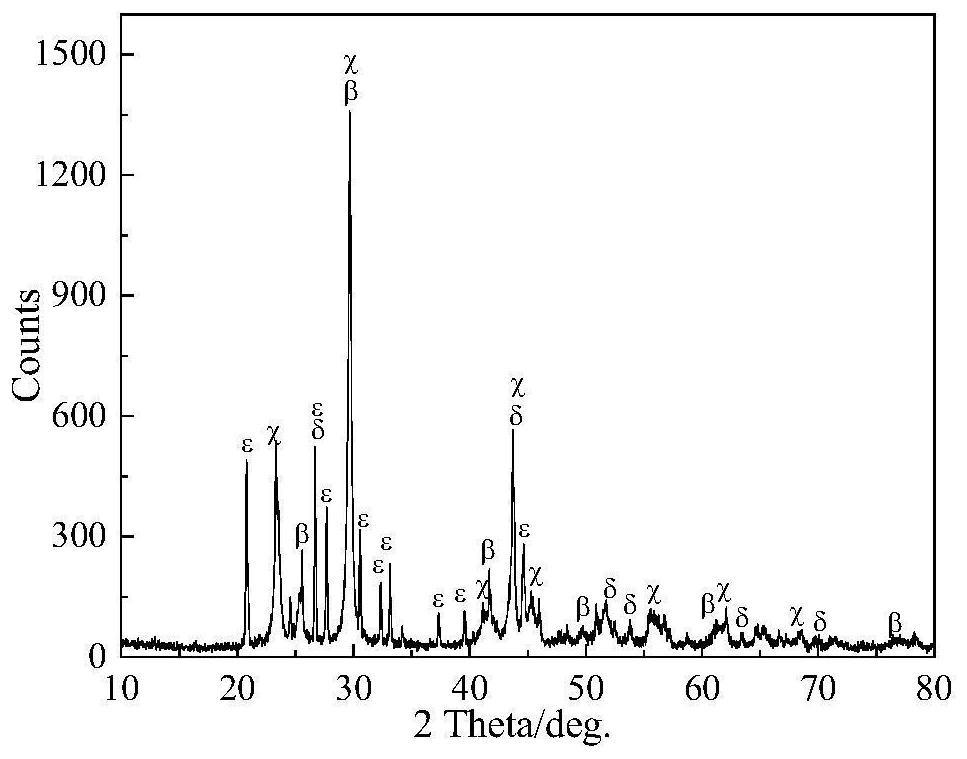
This invention relates to silico-aluminum substrates, catalysts, and the hydrocracking and hydrotreatment processes that use them. The catalyst comprises at least one hydro-dehydrogenating element that is selected from the group that is formed by elements of group VIB and group VIII of the periodic table and a non-zeolitic silica-alumina-based substrate that contains an amount of more than 5% by weight and less than or equal to 95% by weight of silica (SiO2) and has the following characteristics: A mean pore diameter, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed between 20 and 140 Å, a total pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed between 0.1 ml / g and 0.6 ml / g, a total pore volume, measured by nitrogen porosimetry, encompassed between 0.1 ml / g and 0.6 ml / g, a BET specific surface area encompassed between 100 and 550 m<2> / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 140 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 160 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 200 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 500 Å, of less than 0.01 ml / g, an X diffraction diagram contains at least the main lines that are characteristic of at least one of the transition aluminas contained in the group that consists of the alpha, rho, chi, eta, gamma, kappa, theta and delta aluminas.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Thermographic recording material with improved image tone and/or stability upon thermal development
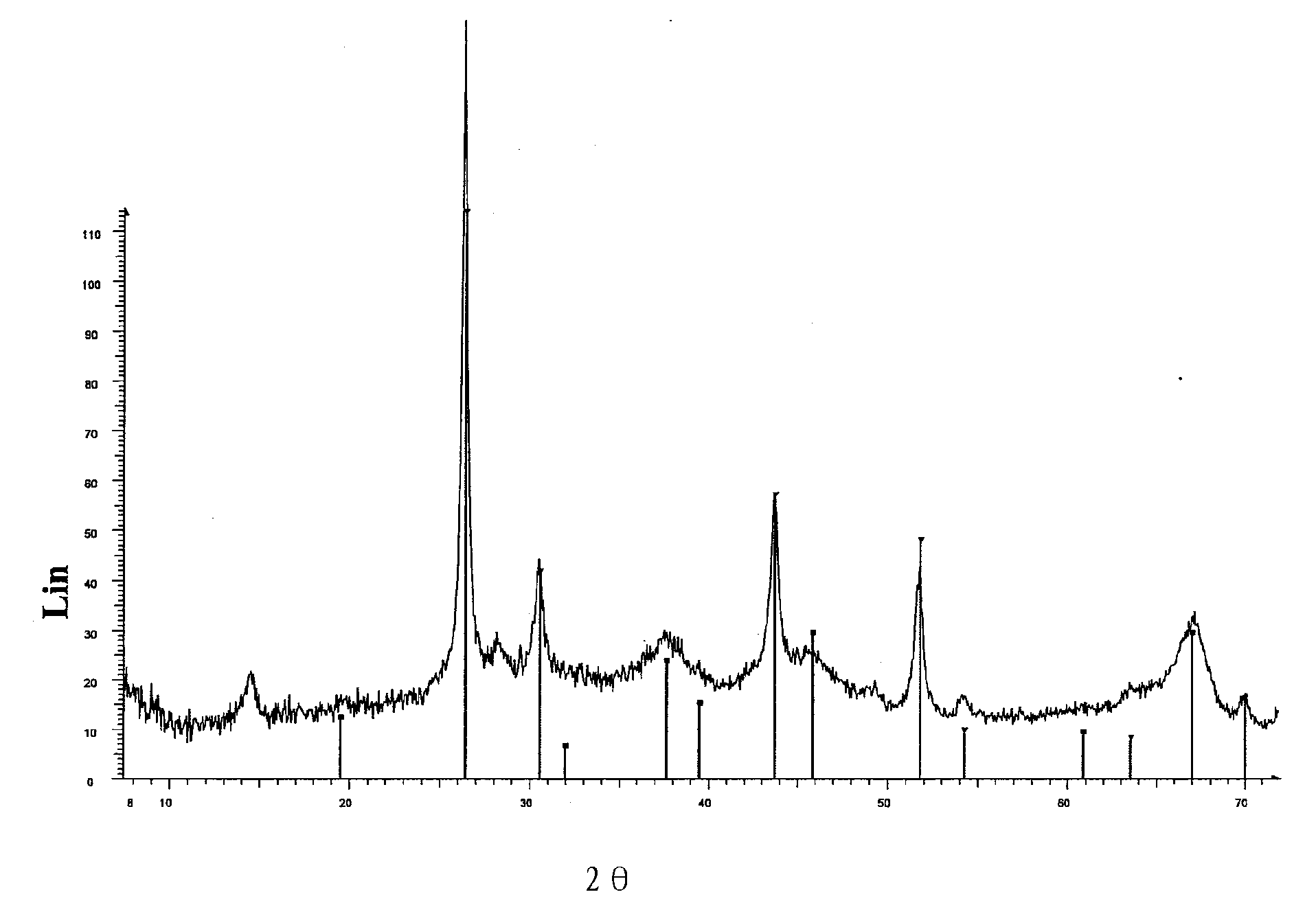
InactiveUS6096486AImprove wear resistanceAvoid local deformationX-ray/infra-red processesOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventDiffractometer
A recording material comprising a support and a thermosensitive element containing silver behenate, an organic reducing agent therefor in thermal working relationship therewith and a binder, wherein the silver behenate is not associated with mercury and / or lead ions and when the recording material is irradiated with a copper K alpha 1 X-ray source the ratio, normalized to a quantity of silver in the recording material of 1 g per m2 thereof, of the sum of the peak heights of the X-ray diffraction lines attributable to silver behenate at Bragg angles, 2 THETA , of 6.01 DEG , 7.56 DEG , 9.12 DEG , 10.66 DEG , 12.12 DEG and 13.62 DEG to the sum of the peak heights of the X-ray diffraction lines at Bragg angles, 2 THETA , of 25.60 DEG , 35.16 DEG and 43.40 DEG of NIST standard 1976, rhombohedral Al2O3, determined with the same X-ray diffractometer in the same state of adjustment, is greater than 0.85; production processes for particles of substantially light-insensitive organic silver salt comprising silver behenate with these X-ray characteristics in the presence and substantial absence of organic solvent.
Owner:AGFA HEALTHCARE NV
Method for measuring metallic element mercury in soil
ActiveCN103196892AImprove measurement accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationTest samplePre treatment
The invention discloses a method for measuring metallic element mercury in soil. The method comprises the steps of pre-treating a sample, drawing a solution working curve and measuring, wherein the pre-treating step comprises digesting various soil samples through an acid and treating the soil samples at high temperature to form a solution to be measured; and meanwhile, the measuring step comprises measuring the metallic element mercury through inductive coupling plasma atom emission spectrography, and selecting proper working parameters to quickly obtain the content of mercury in the test sample. The solution pre-treatment step in the measuring method is simple and economical; the measuring process is simple, the linear range is wide, and the operation is simple and quick; and meanwhile, the interference of different elements in the soil can be avoided during the measuring process.
Owner:广西益土检测技术有限公司
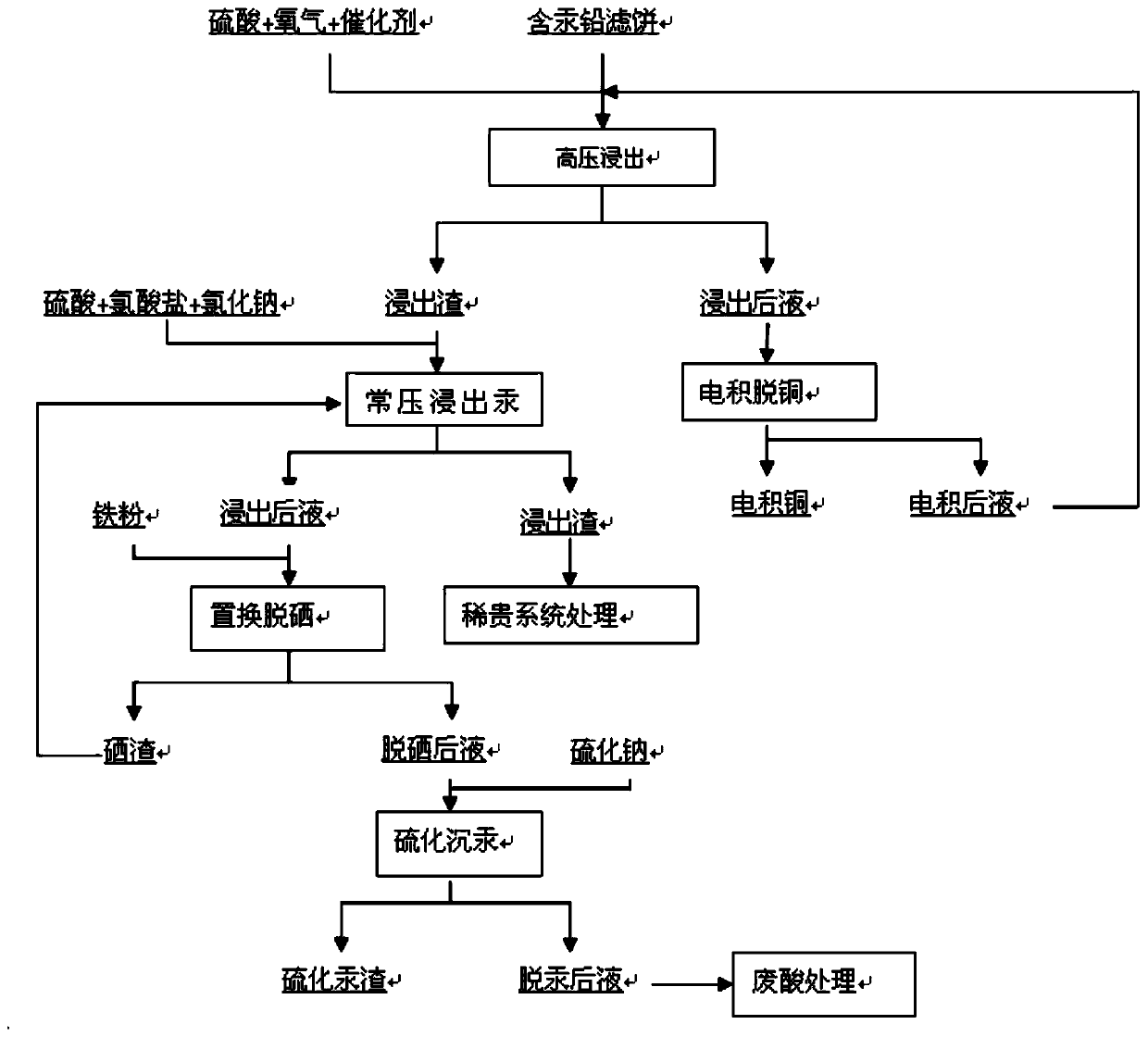
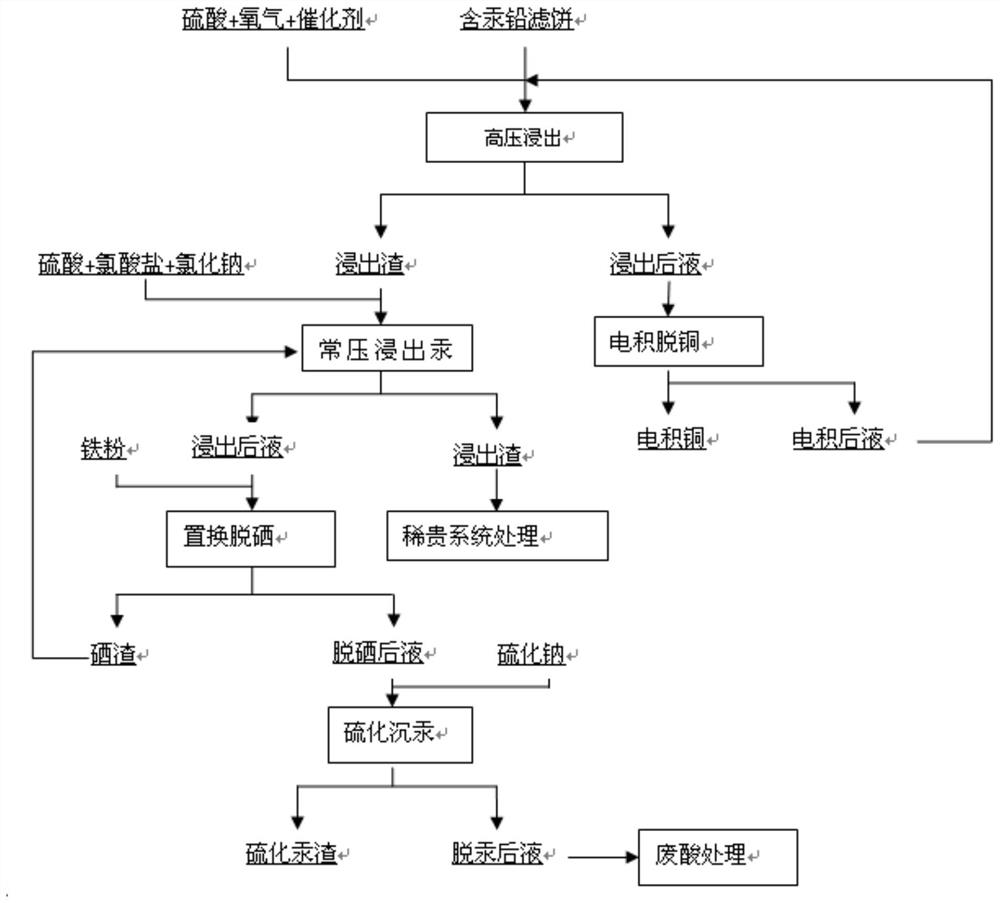
Treatment process of copper, mercury, selenium, lead, gold and silver in copper smelting lead filter cake
ActiveCN109971962AImprove leaching effectImprove overall recoveryPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementVulcanizationSlag
The invention provides a treatment process of copper, mercury, selenium, lead, gold and silver in a copper smelting lead filter cake. The process mainly comprises following steps of low-temperature high-pressure oxidizing leaching of copper, normal-pressure oxidizing leaching and removal of mercury, replacement of selenium and vulcanization mercury sediment and further comprises rare precious system treatment and electrodeposition copper removal treatment. The treatment process is thorough in copper, mercury, selenium, lead, gold and silver separating effect, the gold, silver and selenium arebasically and completely enriched in the slag phase, the copper recycling rate is about 96%, the leaching rate of mercury is above 90%, and the aim of comprehensively treating valuable elements is achieved.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Analysis method for determining hydromorphone hydrochloride bulk drug element impurities
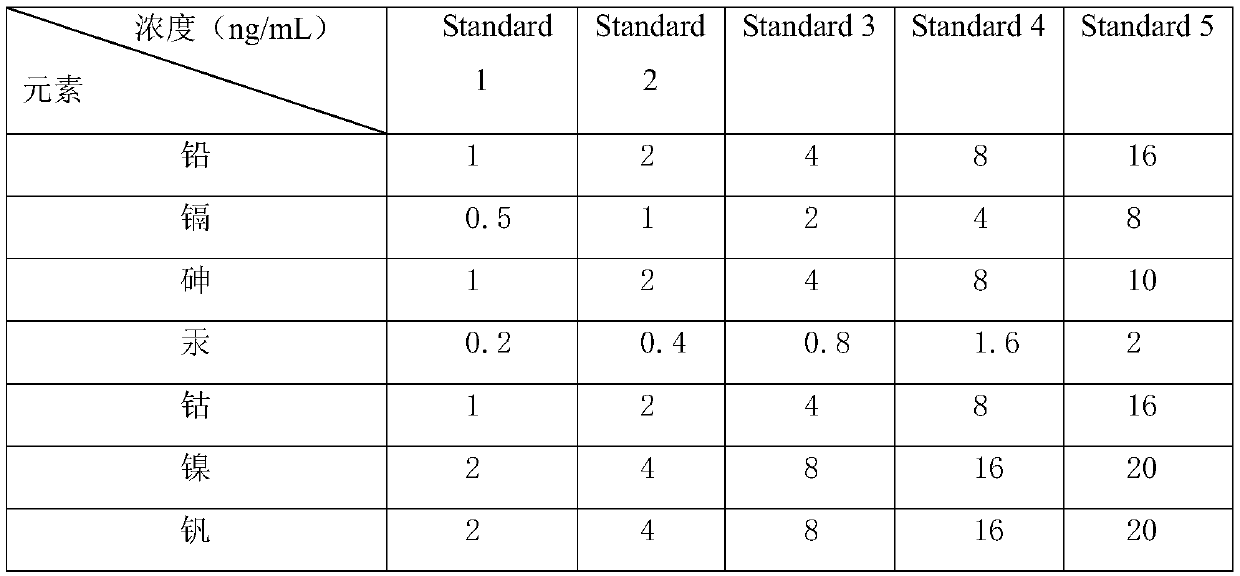
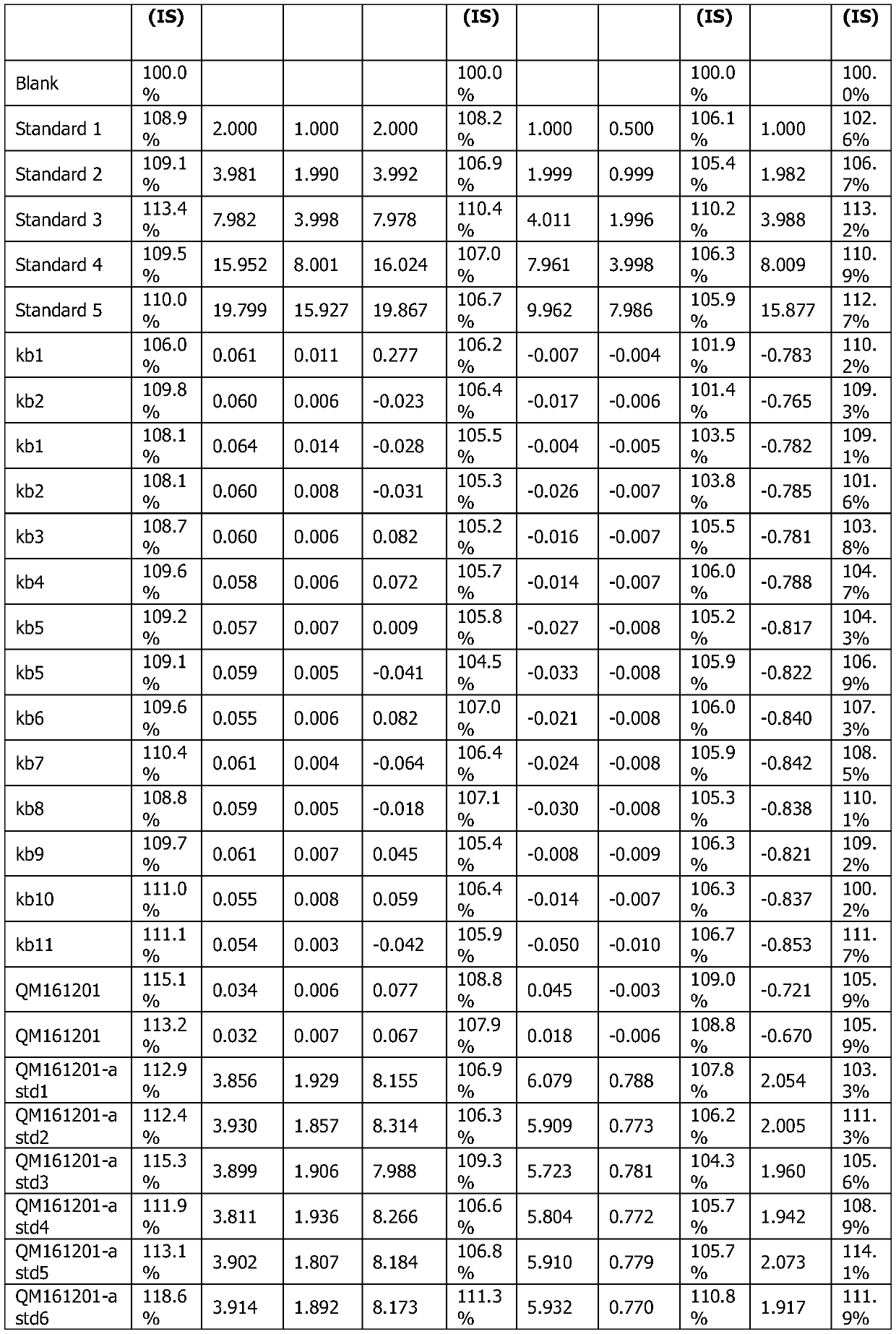
PendingCN110988105ASolve the recovery rate failureReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHYDROMORPHONE HYDROCHLORIDEIndium
The invention relates to an analysis method for determining hydromorphone hydrochloride bulk drug element impurities. The method comprises the steps of system applicability, standard curve preparation, internal standard solution preparation, sample preparation and standard recovery sample preparation, and standard curve drawing, detection limit, sample, and standard recovery rate detection. According to the method, the simultaneous determination of seven elements is split into simultaneous determination of six metal elements, namely arsenic, cadmium, lead, cobalt, nickel and vanadium and independent determination of mercury (Hg); the acid removing temperature is reduced from 150 DEG C to 130 DEG C, the problem that the recovery rate of the mercury element does not reach the standard is solved, the recovery rate can be increased to about 90%; and interference of the mercury (Hg) element on other elements due to the strong memory effect can be reduced through independent measurement. Germanium, indium, bismuth and scandium internal standards are selected, so that the influence of signal drift and matrix effect on measurement can be effectively reduced.
Owner:YICHANG HUMANWELL PHARMA
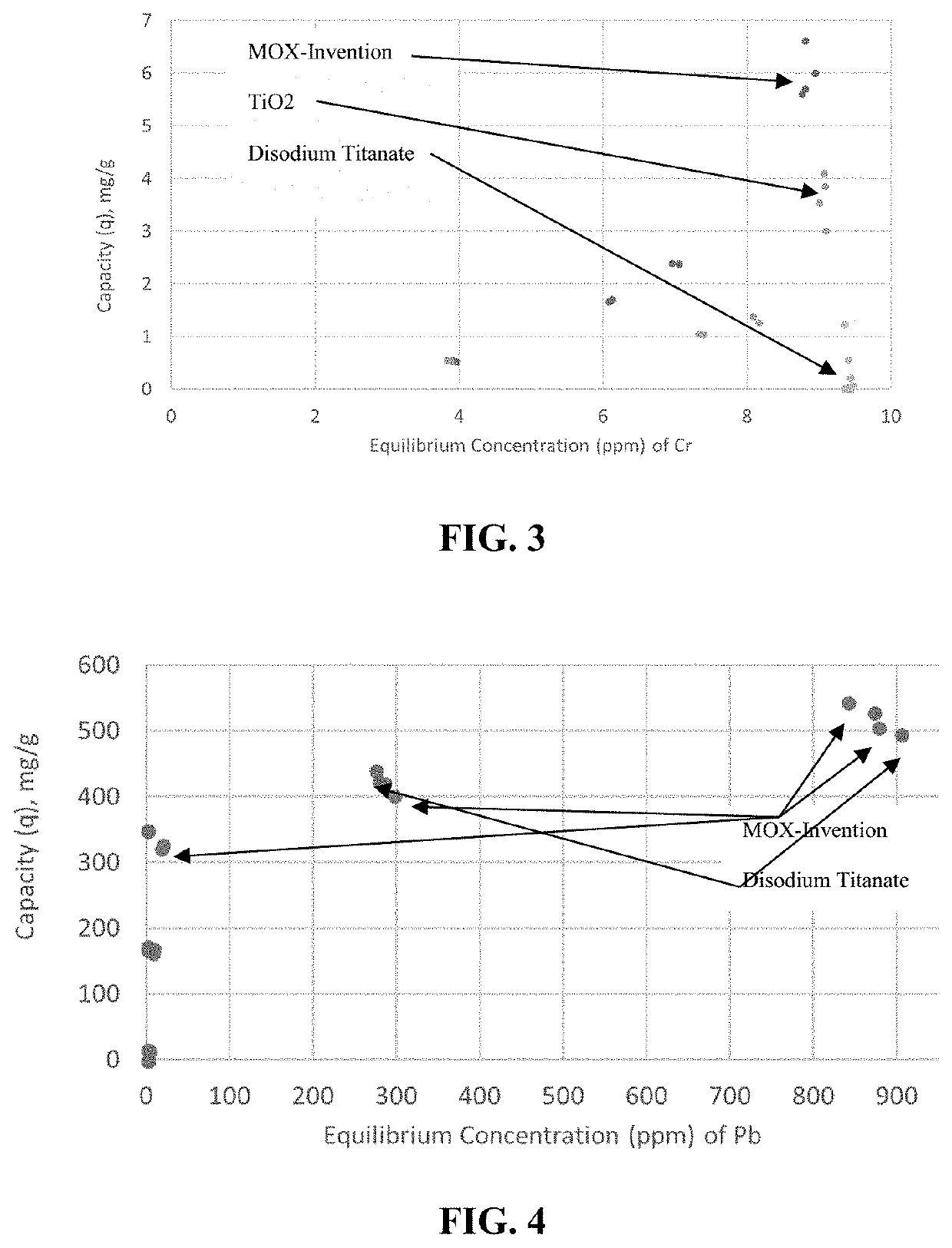
High capacity adsorbent for oxyanions and cations and method for making the same
ActiveUS20200254438A1Reduce adsorptionIncrease capacityOther chemical processesAnion exchangersTitanium zirconiumCerium
An alumina-based adsorbent and method of making exhibiting high affinity and capacity towards cations and oxyanions in a broad pH range and presence of large excess of competitive ions. Alumina based adsorbent is a mixed oxide of alumina existing in tetra-, penta-, and octahedral coordination at specific ratio, and oxides of polyvalent metals of elements titanium, zirconium, tin, cerium, lanthanum, iron, or combinations thereof. The alumina-based adsorbent may be used for selective removal of oxyanions of fluoride, phosphorus, arsenic, chromium, and / or selenium, and / or cations of lead, mercury, cadmium, copper, and / or zinc, from drinking water, industrial streams and wastes, in medicine and food industry.
Owner:GRAVER TECH LLC
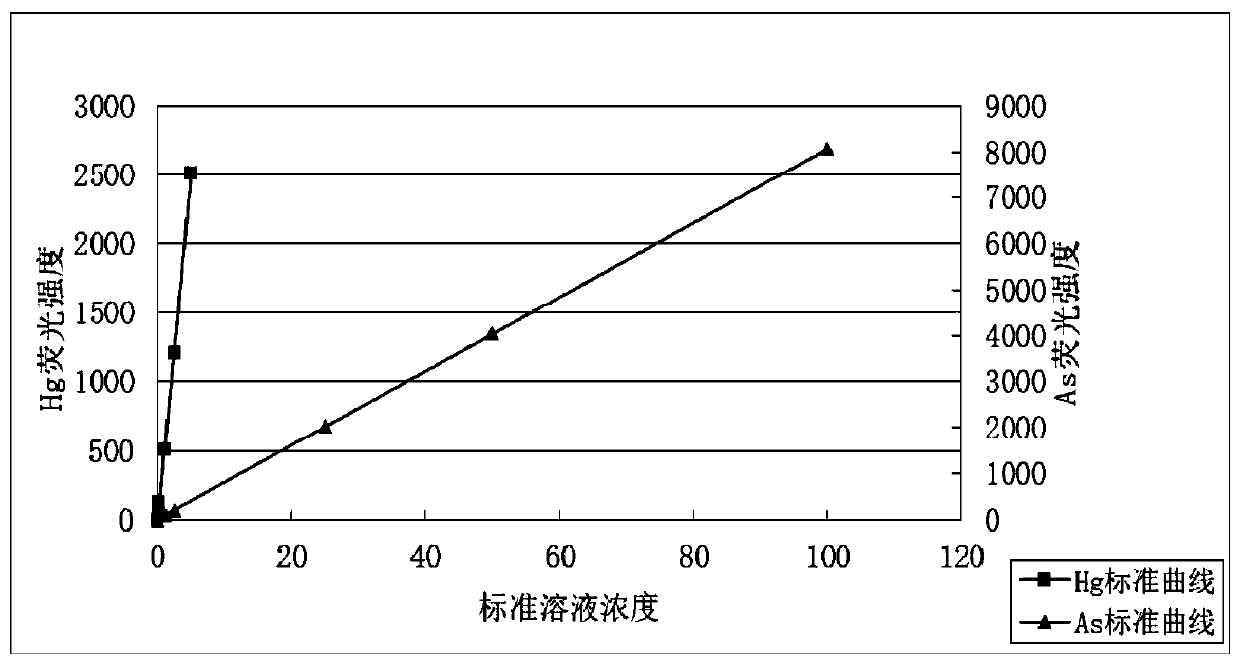
Method for detecting mercury and arsenic in marine sediments
InactiveCN109781684AContent rapid detectionEasy to handleFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltimate tensile strengthOcean sediment
The invention discloses a method for detecting mercury and arsenic in marine sediments. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a mixed standard solution: preparing the mixedstandard solution of mercury and arsenic; (2) preparing a to-be-detected solution: preparing the to-be-detected solution containing mercury and arsenic samples, wherein the to-be-detected solution contains mercury and arsenic elements; (3) selecting the mixed standard solution of mercury and arsenic obtained in the step (1), and making a mercury and arsenic standard curve through an atomic fluorescence spectrometer; and (4) measuring the mercury element and the arsenic element in the to-be-detected solution through the atomic fluorescence spectrometer to obtain detection values of fluorescence intensites of the mercury element and the arsenic element, and comparing the detection values with standard curves of mercury and arsenic to obtain the content of the mercury element and the contentof the arsenic element in the to-be-detected solution, thereby obtaining the content of the mercury element and the content of the arsenic element in the marine sediments. The method can simultaneously detect the content of mercury and the content of arsenic in the marine sediments, reduces the pretreatment and detection steps, and improves the working efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ANALYSIS CHINA NAT ANALYTICAL CENT GUANGZHOU
Novel method for repairing heavy metal cadmium, arsenic, mercury, lead and chromium combined polluted soil
PendingCN114192565AFacilitated releaseFast complete passivationContaminated soil reclamationDichromate ionSoil material
The invention discloses a novel method for repairing heavy metal cadmium, arsenic, mercury, lead and chromium combined polluted soil, and relates to the technical field of soil repairing. The inventor improves the remediation material and method for the heavy metal compound contaminated soil, soil acidification is accelerated through an acidification material and a first passivation material, arsenic passivation fixation and dichromate ion reduction are conducted through acidification and oxidation-reduction reaction in the acidification process, meanwhile, release of adsorbed chromium, cadmium, mercury and lead is accelerated, and the remediation effect of the heavy metal compound contaminated soil is improved. And then a soil pH increasing material and a second passivation material are added, so that cadmium, mercury, lead and chromium cations are rapidly and completely passivated, and the two-step operation can realize complete fixation of cadmium, arsenic, mercury, lead and chromium pollution elements in the polluted soil and thorough remediation.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Novel method for repairing soil polluted by heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium
PendingCN114029333AAchieve fixAchieve fixationContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceMercury (element)
The invention discloses a novel method for repairing soil polluted by heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium. The repairing method comprises two steps for repairing the soil polluted by the heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium: the first step is to add composite materials such as a sulfur-containing material and a phosphorus-containing material, and carry out soil acidification process to enhance release of positive ions of the heavy metals such as cadmium, lead and mercury, wherein through an oxidation-reduction reaction in the soil acidification process, hexavalent chromium is reduced into harmless trivalent chromium; and the second step is to add a composite combination material and a passivation material for improving the pH value of the soil, so that passivation and fixation of heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium are realized in the process of improving the pH value of the soil. The method has the outstanding advantages of being rapid in acidification, accurate in acidification, thorough in repair, high in safety, simple in repair link and the like. By applying the combination material and the method disclosed by the invention, a complete repair of soil in single-element pollution or combined pollution of heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium can be realized.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
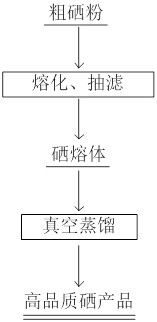
Method for deeply removing arsenic and mercury in crude selenium
PendingCN113548647AEfficient removalRealize mass productionChemical industryProcess efficiency improvementSlagFiltration
The invention discloses a method for deeply removing arsenic and mercury in crude selenium, which belongs to the technical field of purification of scattered metals. As arsenic and mercury are easy to volatilize together with selenium through distillation, and impurities arsenic and mercury in selenium are relatively complex in components and partially exist in the form of compounds, and are difficult to deeply remove through simple filtration. The method comprises the following steps of melting a crude selenium raw material in a reaction kettle, carrying out suction filtration under a negative pressure condition to realize separation of a main element selenium from large-particle arsenic and mercury so as to obtain a selenium melt with relatively high purity, carrying out vacuum distillation on the collected selenium melt or a condensed selenium ingot in a vacuum furnace, volatilizing and condensing selenium in a steam form, thereby realizing further separation of the main elements selenium, arsenic and mercury, deeply removing arsenic and mercury in the crude selenium slag, and well realizing recycling of hazardous wastes.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Material sorting method
Disclosed is a material sorting method, which processes ores by means of the difference of X-ray linear absorption coefficients and removes elements with high atomicity from elements with low atomicity. The method in a mine reduces pollution and transport cost. One embodiment of the invention is that impurities having sulfur, silicate, mercury, arsenic and radioactive elements are discharged from coal, which reduces the amount and toxicity of coal ashes, and reduces energy consumed by discharging and cleaning flue gas from coal combustion. The removal of discharge elements improves thermal efficiency and reduces pollution and carbon footmark of power generation.
Owner:MINERAL SEPAREJSHN TECHZ INK
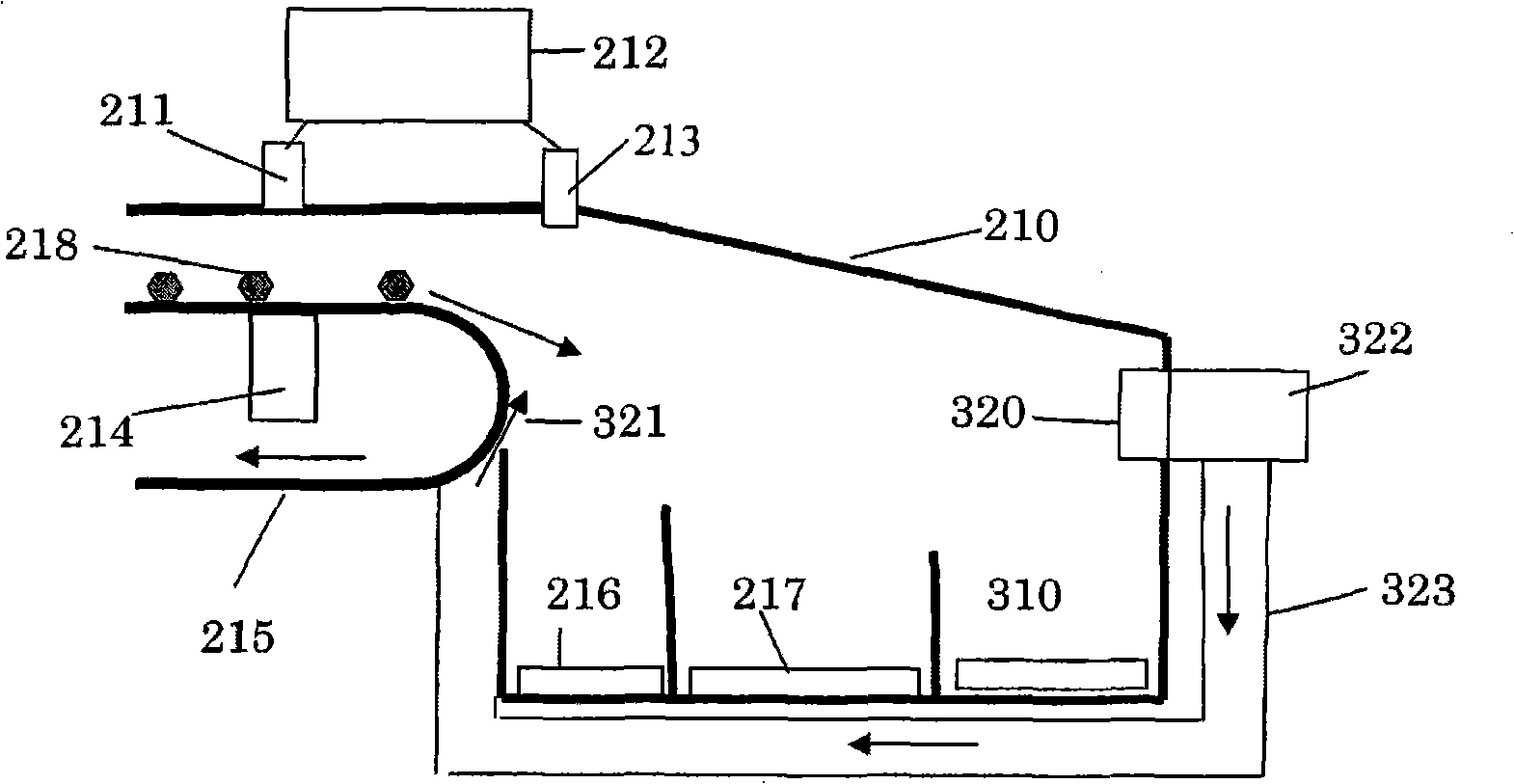
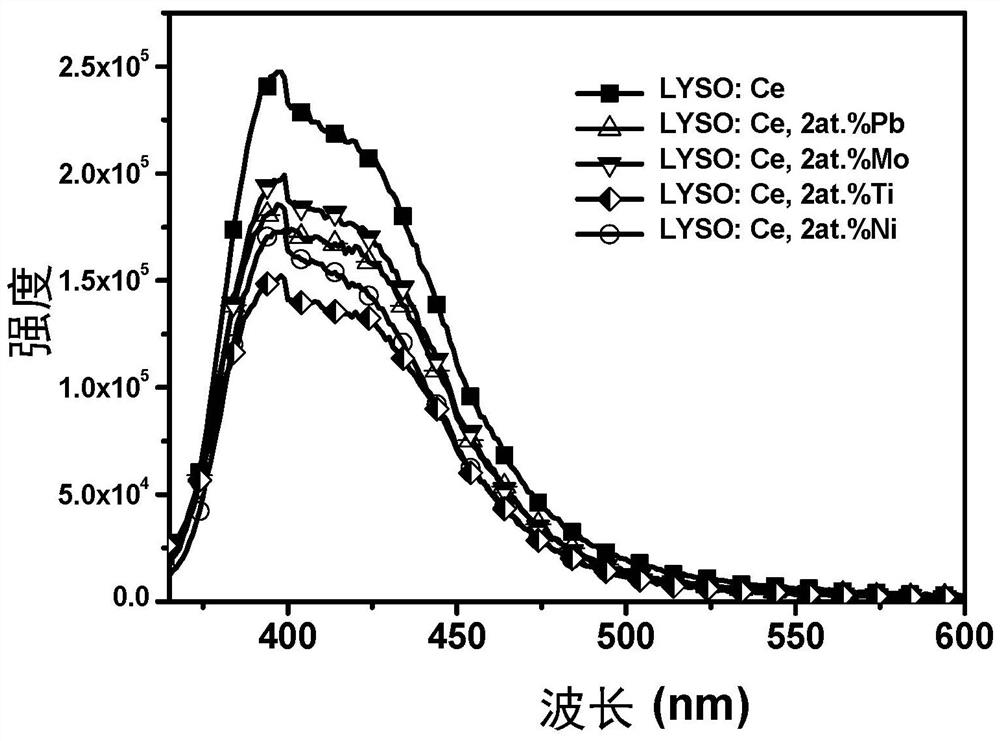
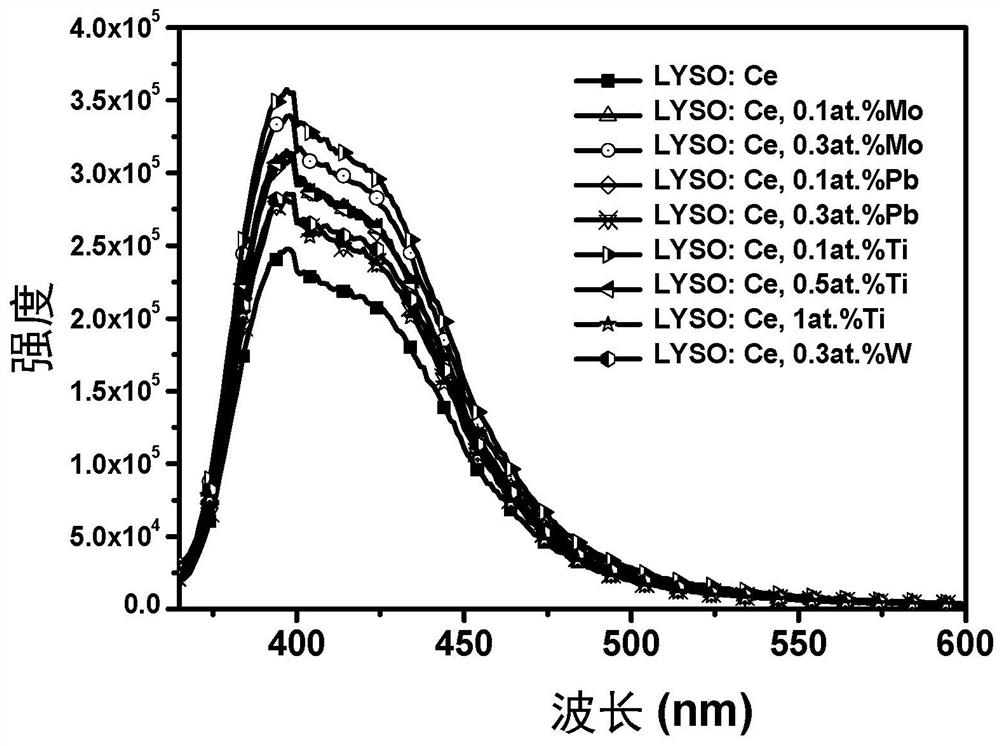
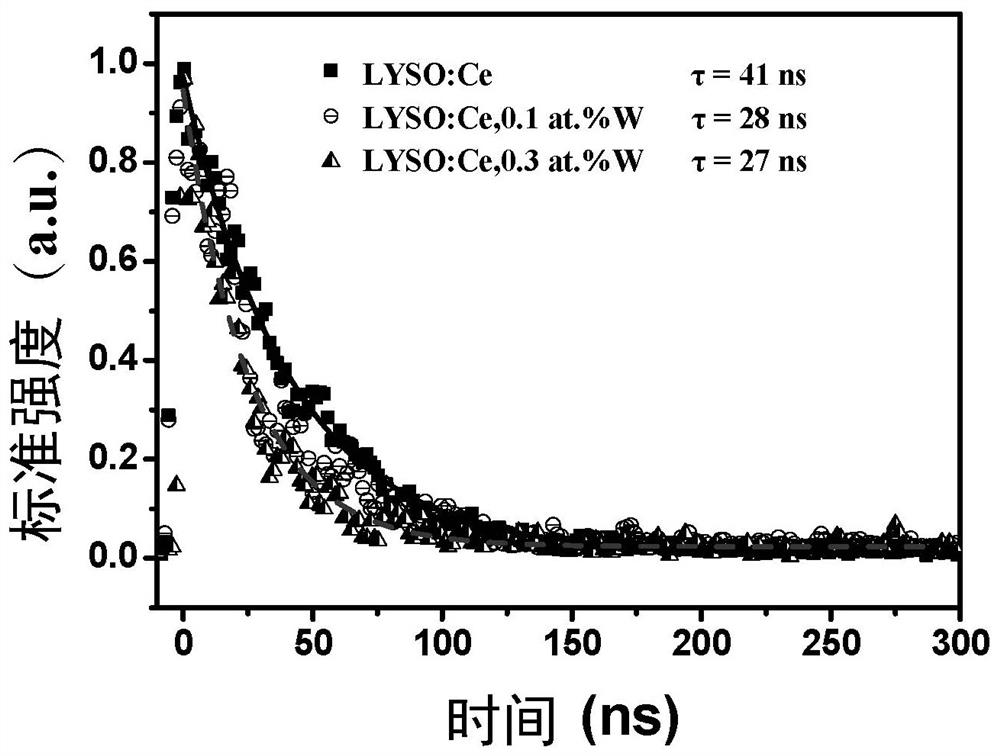
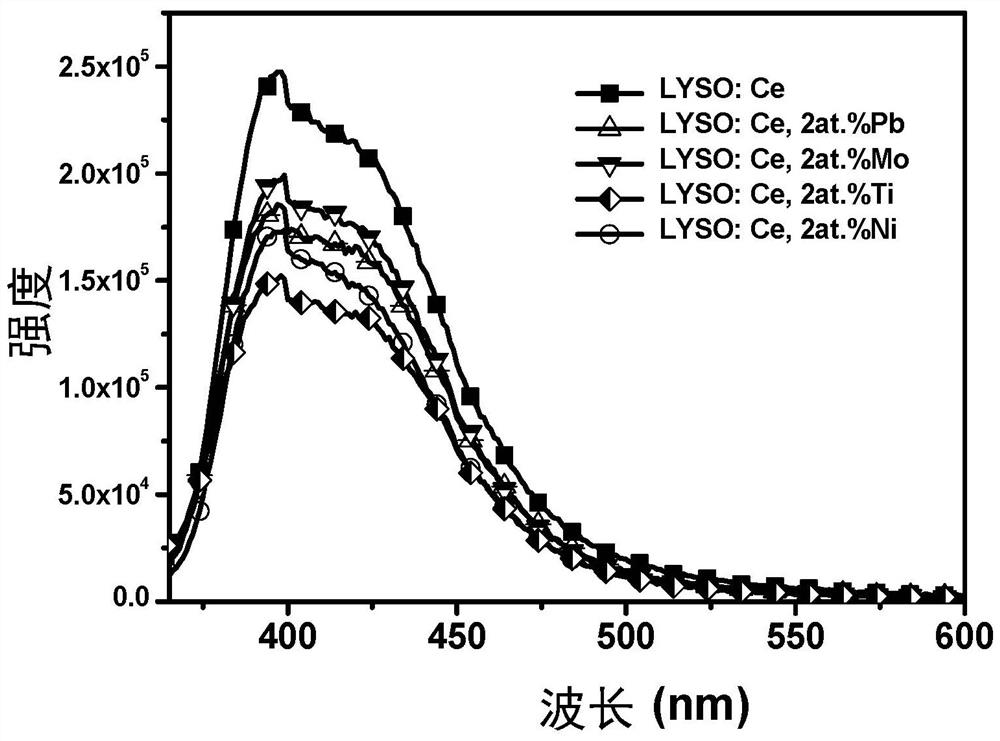
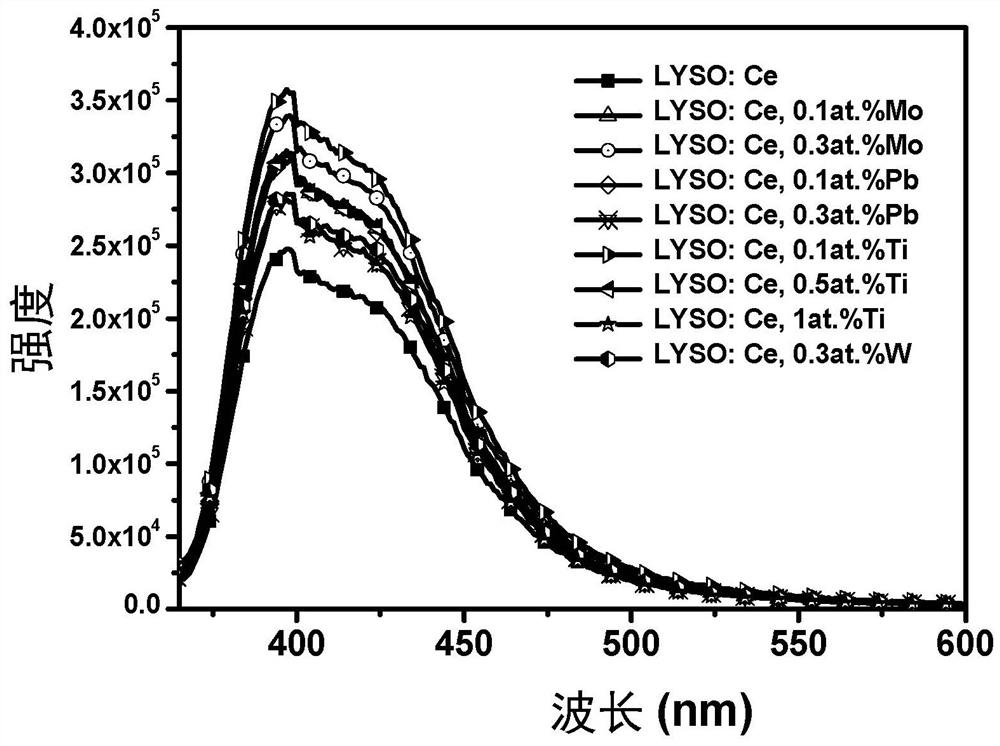
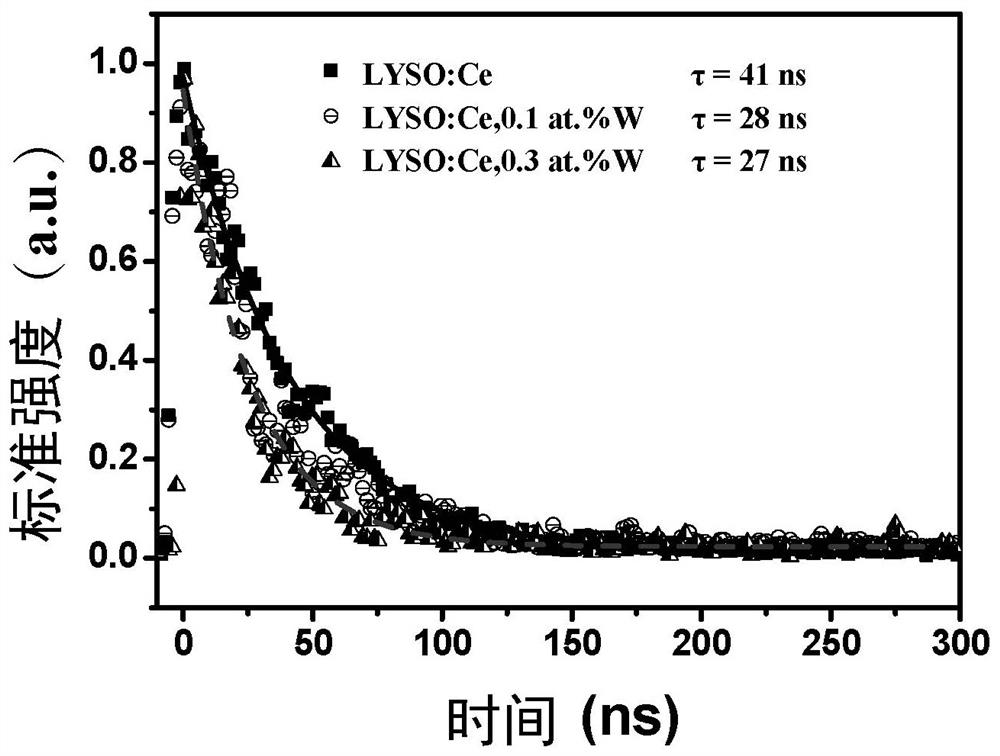
Strong electron-withdrawing element doped rare earth orthosilicate scintillating material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112390278AShorten the timeShorten rise timePolycrystalline material growthMeasurement with scintillation detectorsRheniumIndium
The invention relates to a strong electron-withdrawing element doped rare earth orthosilicate scintillating material and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the strong electron-withdrawing element doped rare earth orthosilicate scintillating material is RE2 (1-x-y + delta / 2) Ce2xM2y-delta Si (1-delta) M delta O5, wherein RE is a rare earth ion, and x is more than0 and less than or equal to 0.05; M is a strong electron-withdrawing doping element, and y is greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.015; 0 < = delta < = 10<-4>; M is selected from at least one oftungsten W, lead Pb, molybdenum Mo, tellurium Te, antimony Sb, bismuth Bi, mercury Hg, silver Ag, nickel Ni, indium In, zinc Zn, thallium T1, niobium Nb, titanium Ti, tantalum Ta, tin Sn, cadmium Cd,technetium Tc, zirconium Zr, rhenium Re and gallium Ga.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
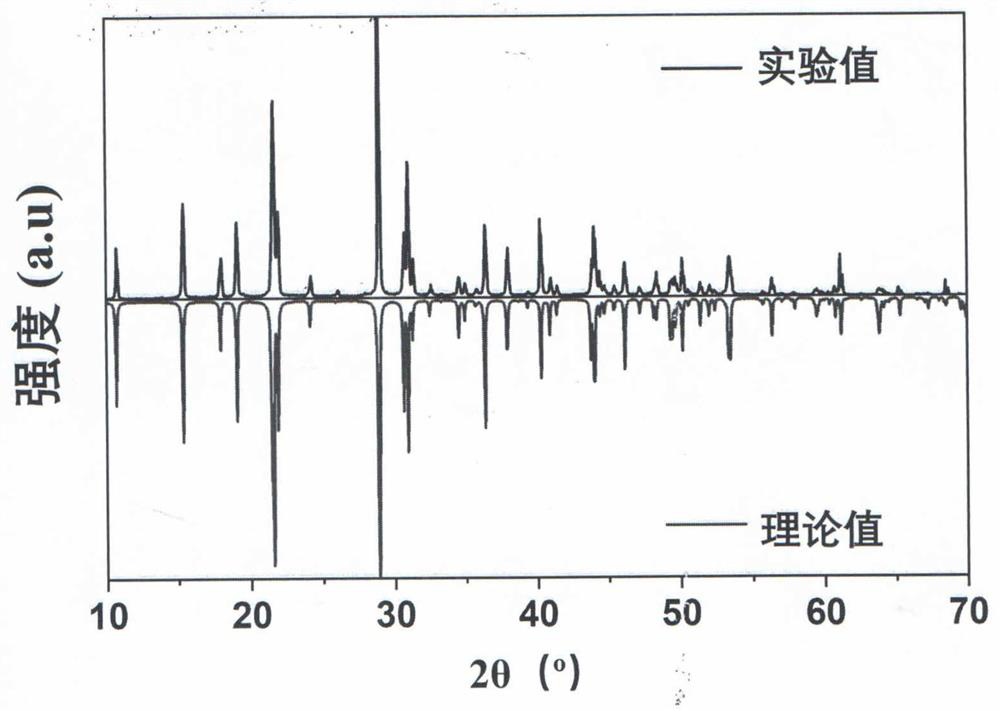
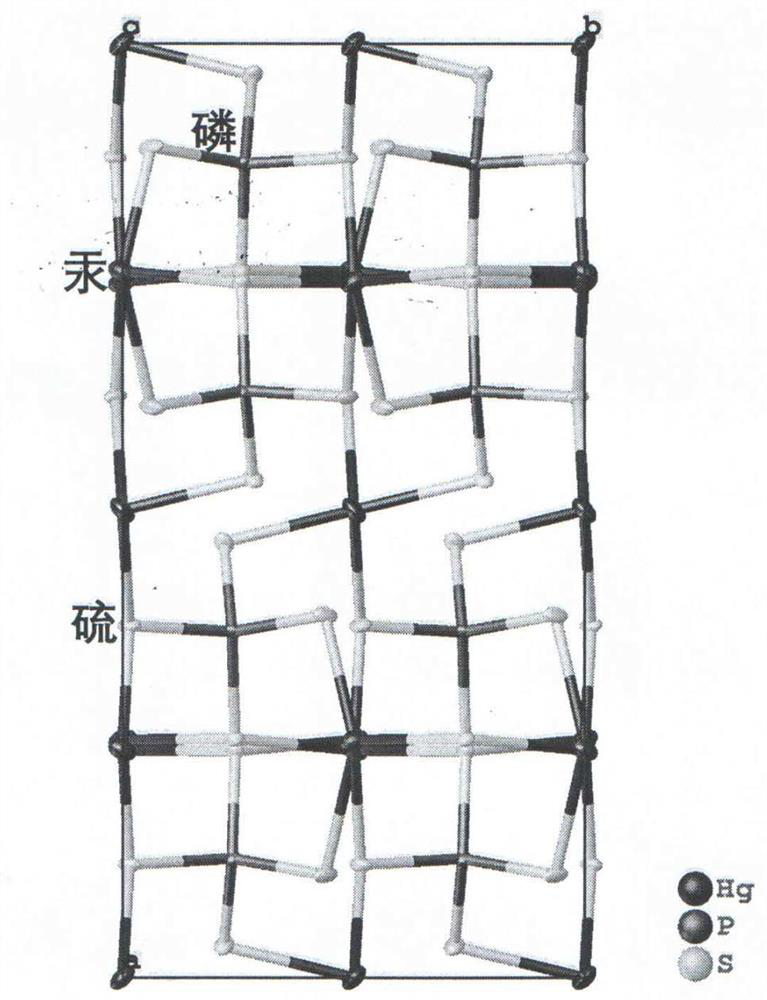
Compound sulfur-phosphorus-cadmium and sulfur-phosphorus-mercury, sulfur-phosphorus-cadmium and sulfur-phosphorus-mercury infrared nonlinear optical crystal, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113060711ALarge nonlinear optical effectHigh hardnessPolycrystalline material growthPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsNonlinear optical crystalCrystal system
The invention relates to compound sulfur-phosphorus-cadmium and sulfur-phosphorus-mercury, a sulfur-phosphorus-cadmium and sulfur-phosphorus-mercury infrared nonlinear optical crystal and a preparation method and application thereof, the molecular general formula of the compounds is A3P2S8, in the formula, A is a transition element Cd or Hg, the chemical formula of sulfur-phosphorus-cadmium is Cd3P2S8, and the molecular weight is 655.70; the chemical formula of sulfur phosphorus mercury is Hg3P2S8, and the molecular weight is 920.23; the crystal does not have a symmetric center and belongs to an orthorhombic crystal system, the space group is Aba2, and the cell parameters of Cd3P2S8 are as follows: a = 16.214 (3) angstroms, b = 8.07 (5) angstroms, c = 8.993 (6) angstroms, alpha = beta = gamma = 90 degrees, and Z = 4; and the cell parameters of the Hg3P2S8 are as follows: a is equal to 16.52 (2) angstroms, b is equal to 8.223 (10) angstroms, c is equal to 9.293 (11) angstroms, alpha= beta=gamma is equal to 90 degrees, and Z is equal to 4. The infrared nonlinear optical crystal is prepared by adopting a high-temperature melt spontaneous crystallization method, a chemical vapor transport method, a fluxing agent method or a crucible descent method. The material has the advantages of being large in nonlinear optical effect, wide in light-transmitting wave band, large in hardness, good in mechanical performance, not prone to fragmentation and deliquescence and easy to process and store, and can be used for manufacturing infrared nonlinear optical devices.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
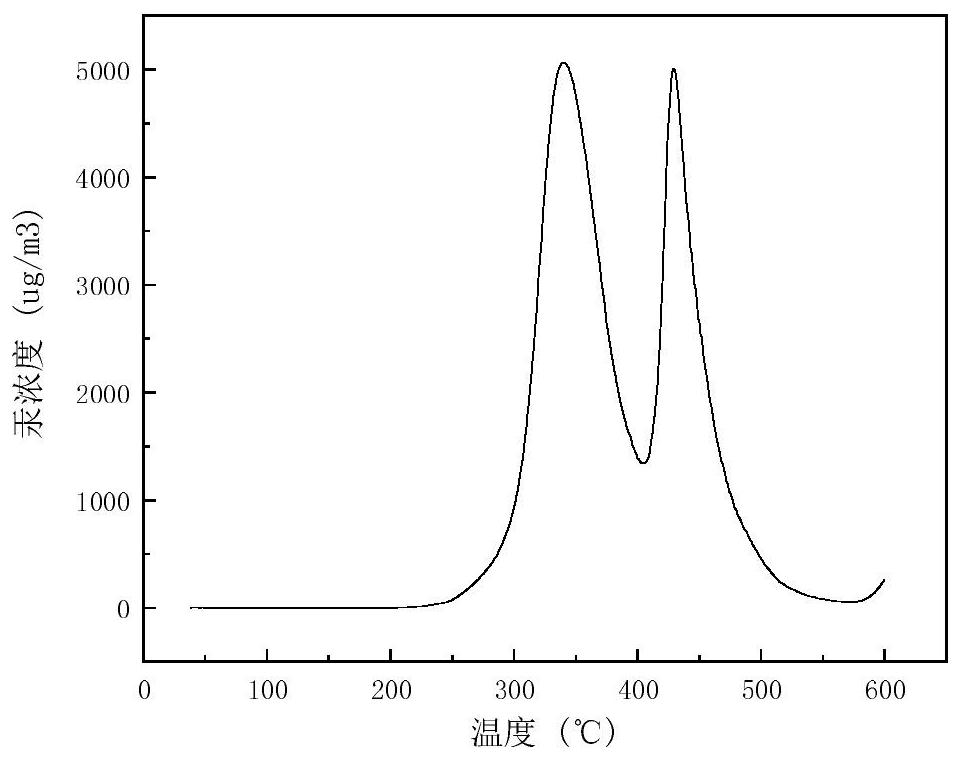
Method for calculating ratio of fly ash to large slag based on mercury concentration measurement
PendingCN113985003ALess measuring workEliminate the effects of large measurement uncertaintiesFuel testingCombustionSlag
The invention discloses a method for calculating the ratio of fly ash to large slag based on mercury concentration measurement. The measurement work of the mass flow of fly ash and slag is replaced by the test analysis of the mercury element content of each related substance, and the ash-slag ratio r is determined by adopting a mercury balance basic formula and an iterative calculation method. Based on the method, the measurement work of the fly ash mass flow and the slag mass flow is omitted, the influence of large uncertainty of mass flow measurement is eliminated, the unburned carbon heat loss can be calculated more conveniently and accurately, and the boiler combustion condition can be evaluated more conveniently and accurately. In addition, the recycling value of the fly ash can be further analyzed and evaluated through test analysis data of ash elements.
Owner:XIAN THERMAL POWER RES INST CO LTD
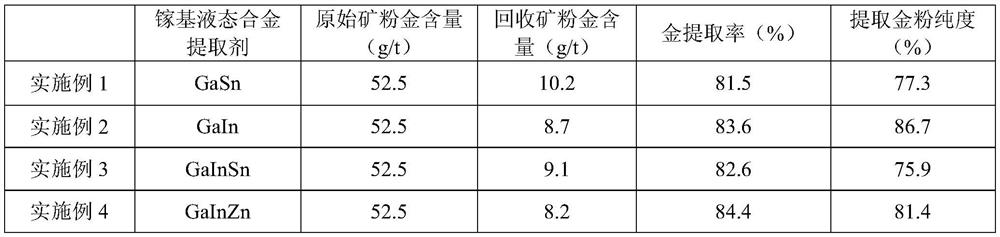
A kind of preparation method of low-melting point five-element gallium-based liquid alloy
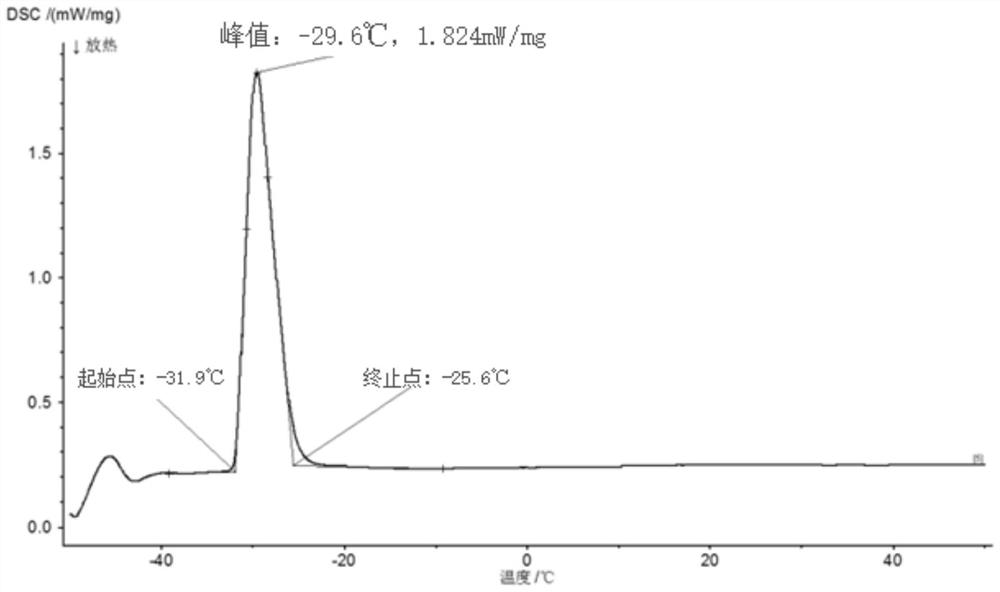
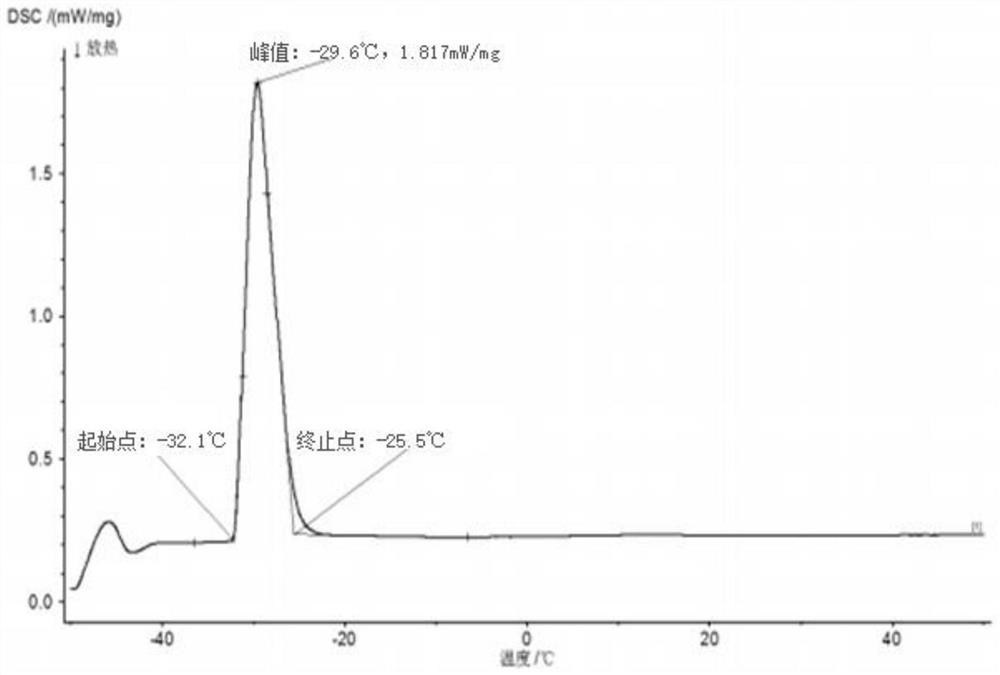
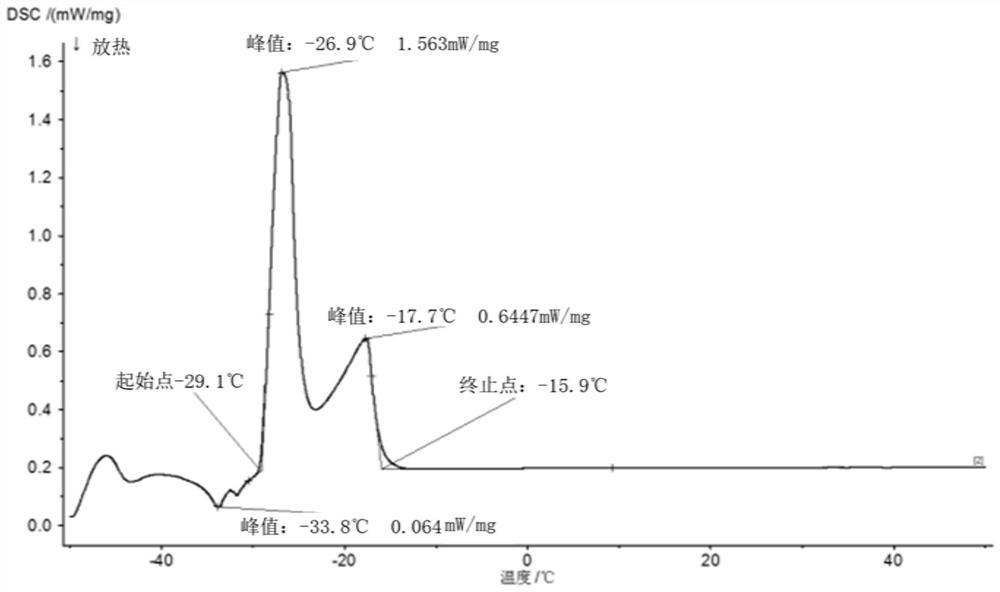
The invention discloses a method for preparing a low-melting point five-element gallium-based liquid alloy, which belongs to the field of material metallurgy. The present invention adopts the atmosphere smelting method or the gallium dissolving method, and prepares the alloy according to the mass percentage of 83.80%-83.99% of gallium, 12.20% of indium, 3.60% of tin, 0.20% of zinc, and 0.01%-0.20% of aluminum. The preparation method of a gallium-based liquid metal with an ultra-low melting point of the present invention can obtain the gallium-based liquid metal with a melting point of -32°C, the preparation method is simple, and it is easy to promote industrial production. The melting point of the gallium-based liquid alloy obtained in the present invention is similar to that of mercury, and the alloy is safe and non-toxic, can replace mercury products, solve potential environmental pollution threats, and have wide applications in new technology fields such as flexible electronics, wearable devices, and bionic robots. prospect.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
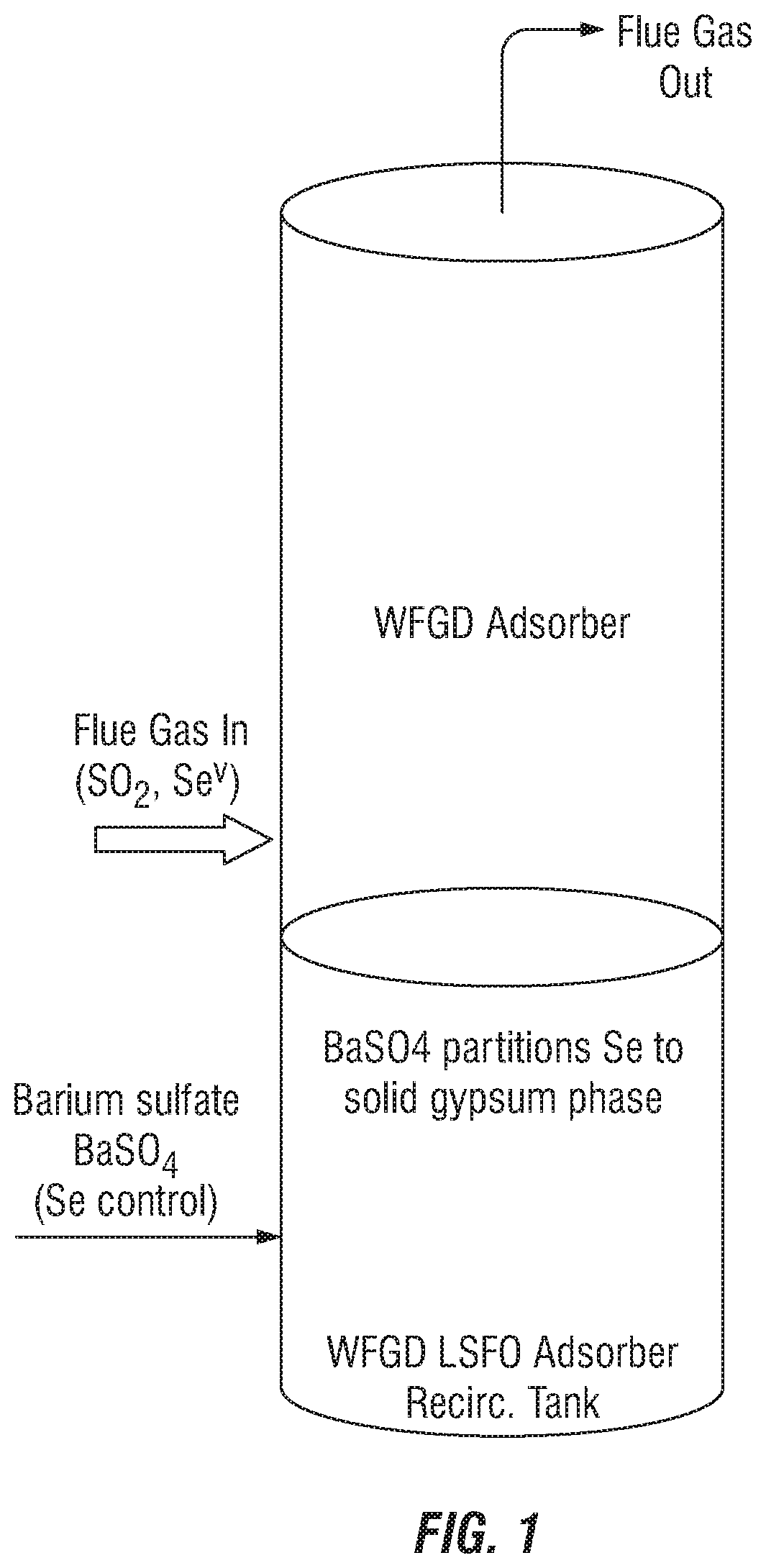
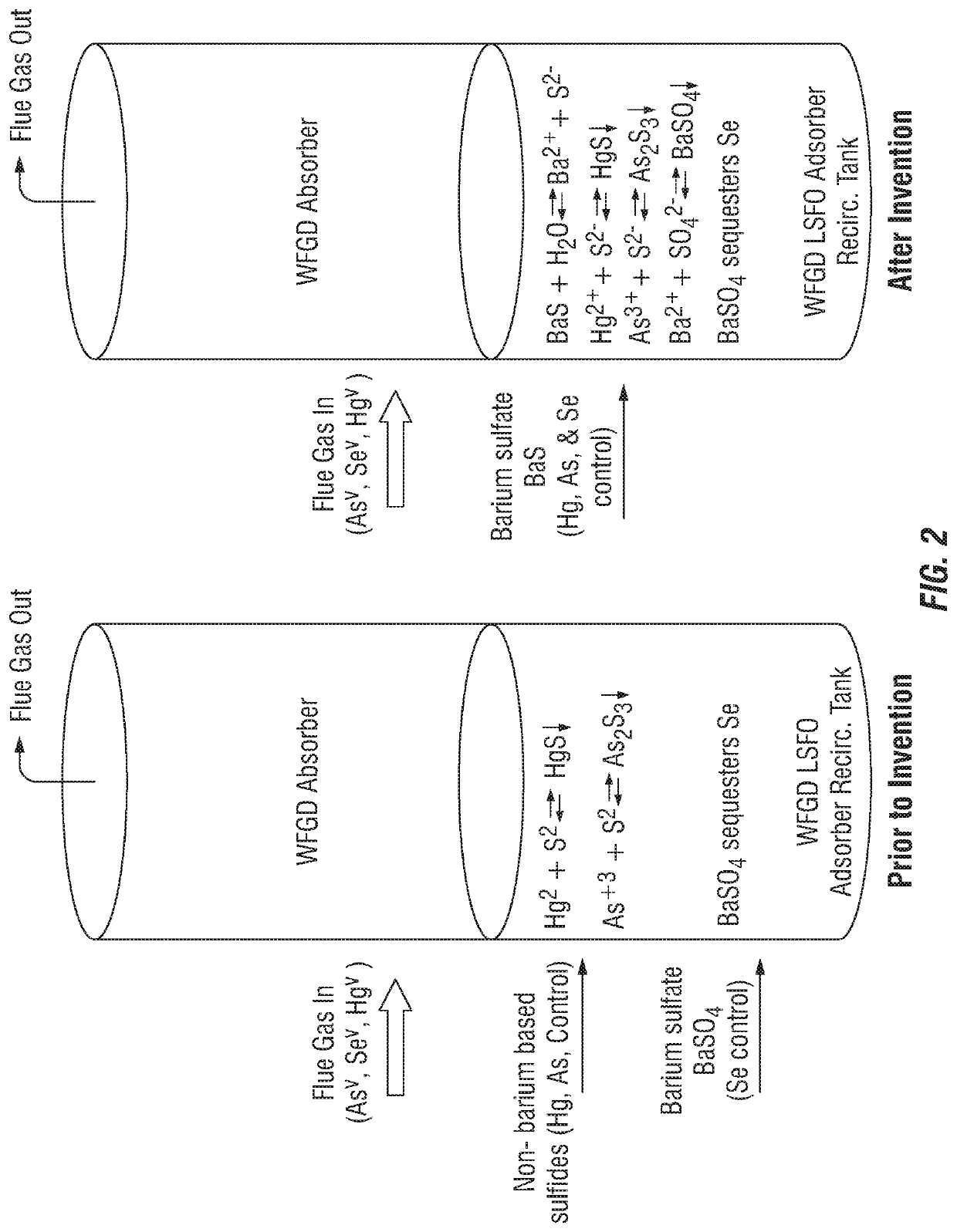
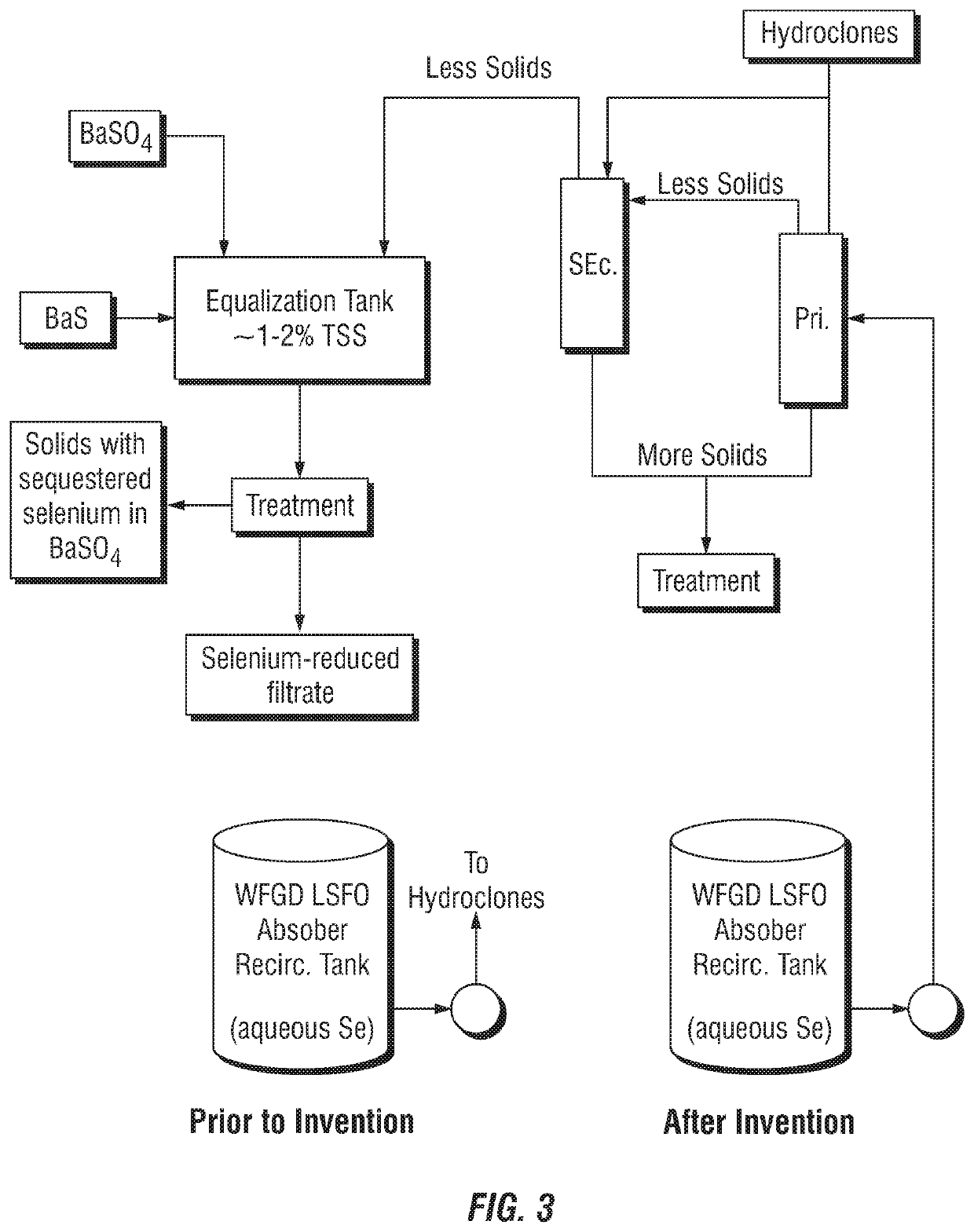
Control of aqueous arsenic, selenium, mercury or other metals from flue gas
ActiveUS11319233B2Cost-effective methodsReduce the amount requiredWater treatment parameter controlGas treatmentFlue gasMercury (element)
The invention pertains to methods of reducing dissolved elements such as arsenic, selenium and mercury in aqueous solutions using, for example, various barium compounds to partition said elements to a solid phase. Such methods are particularly useful for reducing such elements at various points in coal and oil-fired power plants prior to final waste water treatment.
Owner:STEVE FEENEY CONSULTING LLC
A process for treating copper, mercury, selenium, lead and gold and silver in lead filter cake of copper smelting
ActiveCN109971962BImprove leaching effectImprove overall recoveryPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSlagMercury (element)
The invention provides a treatment process of copper, mercury, selenium, lead, gold and silver in a copper smelting lead filter cake. The process mainly comprises following steps of low-temperature high-pressure oxidizing leaching of copper, normal-pressure oxidizing leaching and removal of mercury, replacement of selenium and vulcanization mercury sediment and further comprises rare precious system treatment and electrodeposition copper removal treatment. The treatment process is thorough in copper, mercury, selenium, lead, gold and silver separating effect, the gold, silver and selenium arebasically and completely enriched in the slag phase, the copper recycling rate is about 96%, the leaching rate of mercury is above 90%, and the aim of comprehensively treating valuable elements is achieved.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Capture mass composed of elemental sulphur deposited on porous support for capturing heavy metals
ActiveCN103505983AImprove adsorption capacityGas treatmentDispersed particle separationMercury (element)Environmental engineering
The application relates to a capture mass composed of elemental sulphur deposited on a porous support for capturing heavy metals. The present invention concerns the elimination of the heavy metals, in particular mercury and possibly arsenic and lead, present in a dry or moist gaseous effluent (1) by means of the capture mass (2) comprising the porous support at least part of which is of low mesoporosity and an active phase based on sulphur. The invention is advantageously applicable to the treatment of gas of industrial origin, synthesis gas or natural gas.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Treatment method for coalescence demercuration of mercury-containing wastewater and application
PendingCN113072154AChange the surface charge propertiesAchieve aggregationProcess efficiency improvementWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFiltrationMercury (element)
The invention provides a treatment method for coalescence demercuration of mercury-containing wastewater and application, and relates to the technical field of water demercuration treatment. On the basis of the action principle that alkyl mercaptan can change the surface charge of the mercury element and can generate surface adsorption-bridging-coalescence with the mercury element, the mercury element in the wastewater is selectively removed. The treatment method comprises the following steps of: adding a solution A containing a sulfydryl compound into mercury-containing wastewater for mixing reaction, and coalescing the sulfydryl compound and the mercury element to form a mercury coalescence; and then carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mercury coalescence and the mercury-removed wastewater through air flotation (or filtration) to obtain the mercury coalescence and the mercury-removed wastewater. According to the treatment method, the interference on a solution system is small, the coalescence degree of other metals except mercury is low, the mercury removal effect is good, and the formed mercury coalescence is high in mercury content and easy to recycle subsequently.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Rapid detector and detection method for heavy metal mercury in water
PendingCN111982597AAccurate measurementWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMercury (element)Physical chemistry
The invention discloses a rapid detector and a detection method for heavy metal mercury in water; an upper-layer collecting pipe, a middle-layer collecting pipe and a bottom-layer collecting pipe areused for respectively collecting water at the upper section, the middle section and the lower section of a water body to be detected; the water collected at the upper section, the middle section and the lower section are fused, and large-volume impurities in the fused water are filtered, so that the free state of mercury metal in the water entering a fusion tank is separated by a crushing turbine, and the mercury element content of the water entering a detection table can be measured more accurately.
Owner:江苏博微检测技术有限公司
A kind of mineral gold extraction method based on mercury-free liquid alloy
The invention provides a method for extracting mineral gold based on a mercury-free liquid alloy, which includes the following steps: 1) taking a gallium-based alloy and soaking it in an anti-oxidation solution, then adding gold-containing ore powder, heating and stirring to obtain a mixed solution; 2) ) After the mixed solution is left to stand, it is filtered and separated to obtain liquid metal; 3) The liquid metal is cooled to room temperature, and the gold element is extracted from the liquid metal by electric field decomposition. The invention provides a mineral gold extraction method based on a mercury-free liquid alloy, which has a clear principle, simple equipment, safe and convenient operation process, does not need to use any mercury or cyanide and other substances in the whole process, is green and environmentally friendly, and has low loss of liquid metal. With continuous recycling, the extraction effect is obvious, the cost is low and controllable, and it is expected to be widely promoted.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV +1
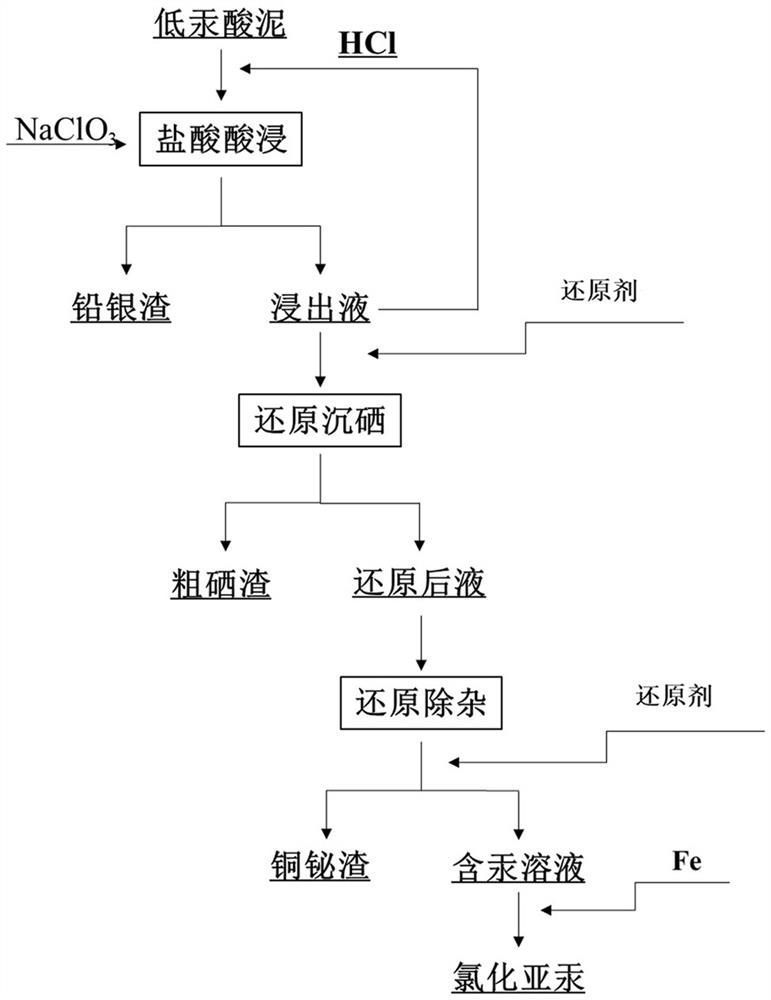
Method for recovering mercury from nonferrous metallurgy low-mercury acid mud by adopting wet process technology
InactiveCN113388746ASolve difficult to recycleEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumSodium chlorateMercury (element)
The invention discloses a method for recovering mercury from a nonferrous metallurgy low-mercury acid mud by adopting a wet process technology, the mercury in a acid mud is extracted by adopting the wet process technology in the whole process by carrying out component analysis on a low-mercury acid mud generated in a nonferrous metallurgy industry, so that a purpose of recovering the mercury is achieved. The technological process comprises the steps of acid leaching of a sodium chlorate hydrochloride system, centrifugal separation, reduction selenium deposition, reduction copper and bismuth removal and reduction mercury deposition. According to the method for recovering the mercury from the nonferrous metallurgy low-mercury acid mud by adopting the wet process technology, process design is reasonable, the properties of various chemical elements and compounds thereof in different condition states are fully utilized, extraction and recovery of the mercury in the low-mercury acid mud are realized, extraction and separation of lead, silver, selenium, copper, bismuth and other elements are also realized, and high economic benefits are provided. The method is environment-friendly and high in utilization rate of each part of resources, and has industrial application value.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
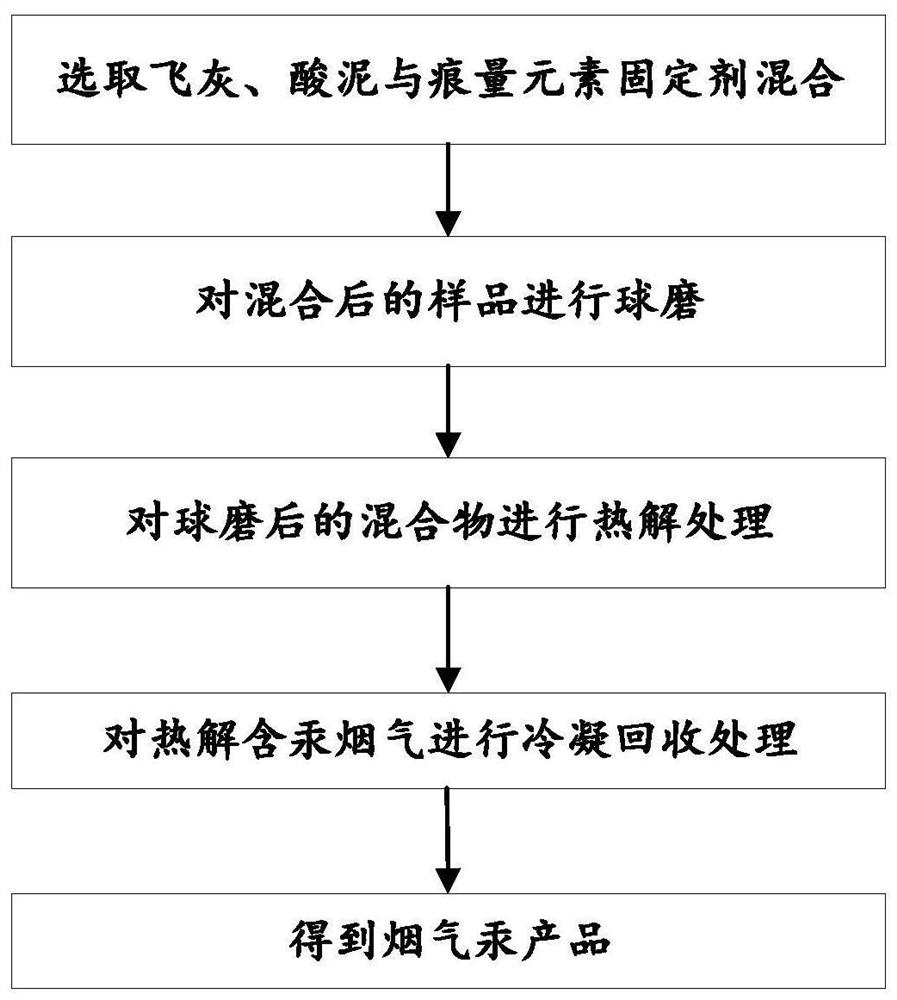
Method for recovering mercury in nonferrous smelting solid waste
InactiveCN112430739AAvoid interferencePrevent volatilizationProcess efficiency improvementMercury (element)Arsenic
The invention discloses a method for recovering mercury in nonferrous smelting solid waste. The method comprises the following steps of: performing ball milling treatment on mercury-containing solid waste and an arsenic-selenium fixing agent, performing pyrolysis treatment on the obtained mixed material, and condensing and recovering mercury from the pyrolysis flue gas. By adopting the method, toxic and harmful trace elements such as arsenic and selenium can be effectively inhibited from volatilizing into the flue gas, and mercury in the solid waste pyrolysis flue gas is efficiently recovered,so that mercury resources are recycled, the economic benefits of nonferrous smelting are improved, and environmental pollution is fully avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Capture block consisting of elemental sulfur deposited on a porous support for heavy metal capture
The present application relates to capture blocks consisting of elemental sulfur deposited on a porous support for capturing heavy metals. The invention relates to the removal of heavy metals, in particular mercury and possibly arsenic and lead, present in dry or wet gaseous effluents (1) by means of a capture block (2) containing at least a portion with a low Mesoporous porous support, and sulfur-based active phase. The invention is advantageously suitable for the treatment of gases of industrial origin, synthesis gas or natural gas.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
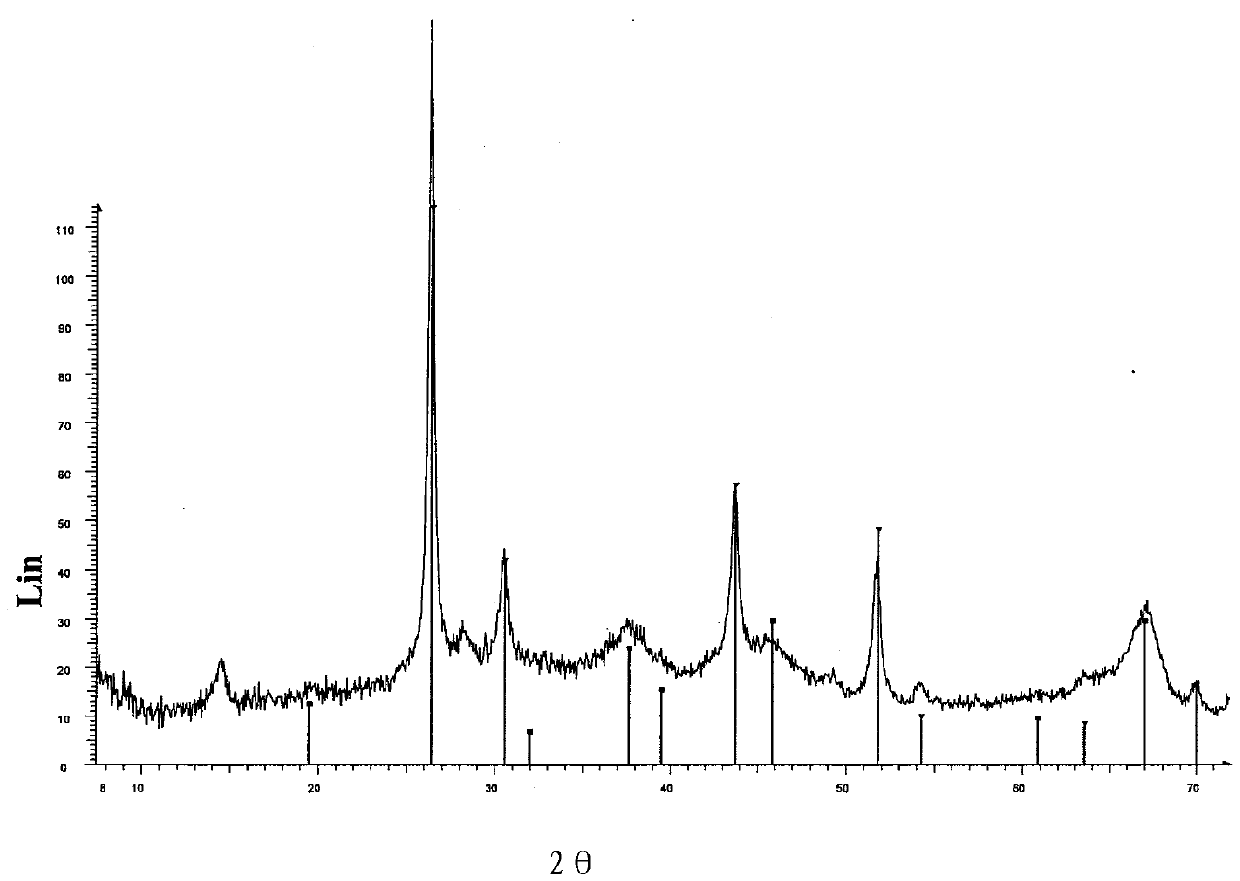
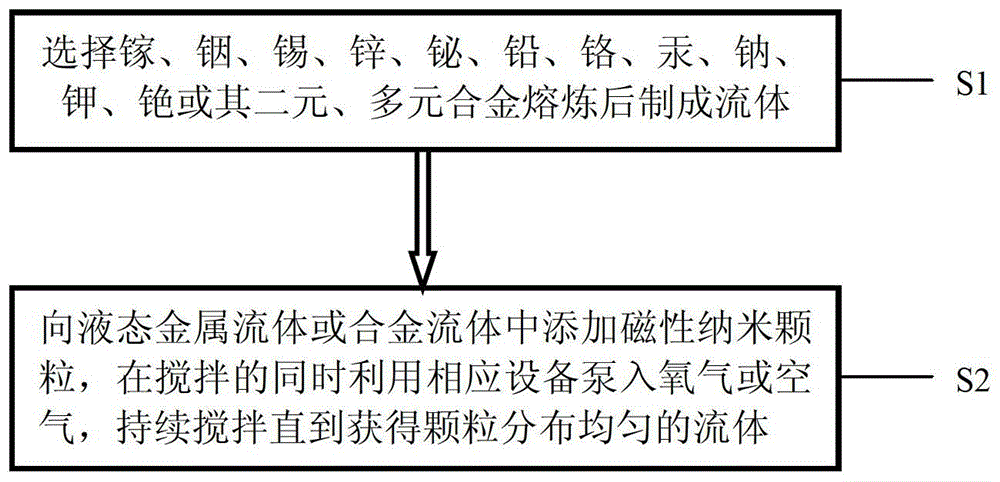
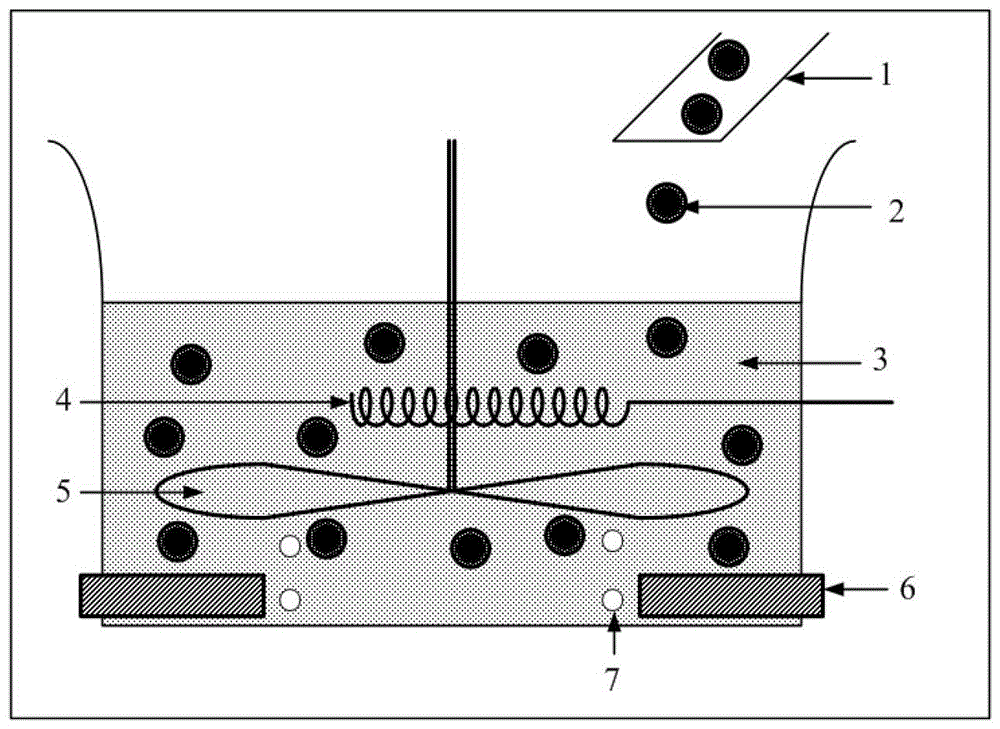
A kind of magnetic nano metal fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104124031BHigh thermal conductivityImprove liquidityMaterial nanotechnologyMagnetic liquidsIndiumMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a magnetic nano-metal fluid, which comprises: liquid metal gallium, indium, tin, zinc, bismuth, lead, chromium, mercury, sodium, potassium, cesium or their binary or multiple alloys, and magnetic Nanoparticles, the volume ratio of the magnetic nanoparticles to the liquid metal / alloy is less than or equal to 50%:1. The present invention actively introduces oxygen through a specific oxygen supply mechanism to regulate the adhesion between fluid and particles, and uses metal gallium, indium, tin, zinc, bismuth, lead, chromium, mercury, sodium, potassium, cesium or their binary or multi-element alloys as the base A magnetic nanofluid with high thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity, good fluidity, and low volatility and leakage can be obtained very quickly and efficiently.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for sorting materials
Disclosed herein is the use of differences in x-ray linear absorption coefficients to process ore and remove elements with higher atomic number from elements with lower atomic numbers. Use of this dry method at the mine reduces pollution and transportation costs. One example of said invention is the ejection of inclusions with sulfur, silicates, mercury, arsenic and radioactive elements from coal. This reduces the amount and toxicity of coal ash. It also reduces air emissions and the energy required to clean stack gases from coal combustion. Removal of said ejected elements improves thermal efficiency and reduces the pollution and carbon footprint for electrical production.
Owner:MINERAL SEPAREJSHN TECHZ INK
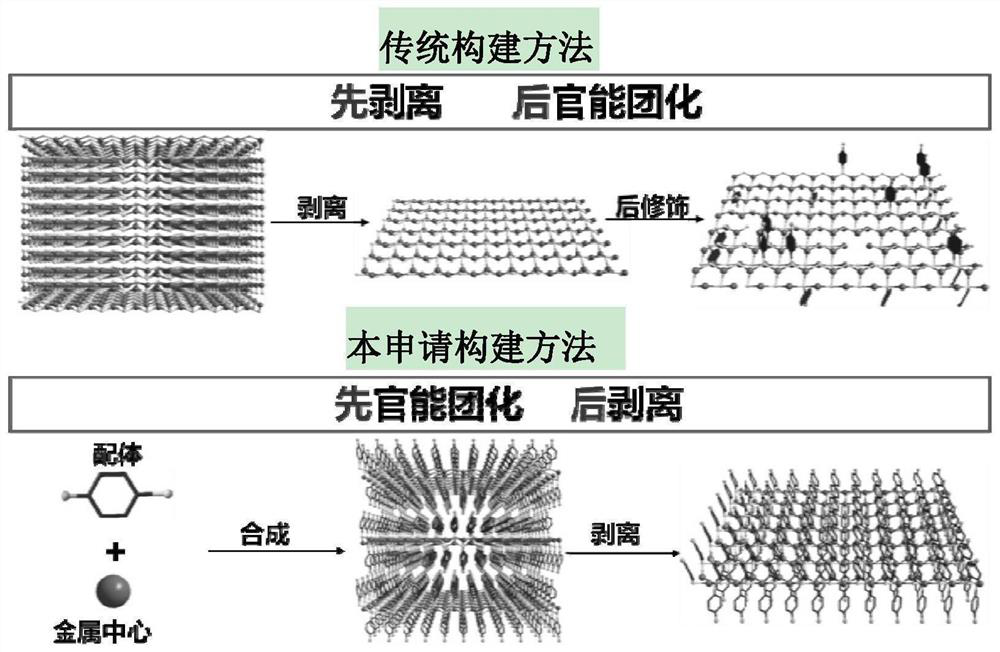
A kind of two-dimensional material, nano sheet and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111960976BUniform and orderly full coverageStrong designabilityThiol preparationOrganic chemistry methodsO-Phosphoric AcidIndium
The application provides a two-dimensional material having the chemical formula (X‑Y‑Z) a m b , X is selected from hydroxyl, ether group, carboxyl group, aldehyde group, carbonyl group, aliphatic group, nitro group, amino group, amido group, sulfonic acid group, phosphoric acid group, cyano group, thiocyano group, hydrocarbon group, substituted hydrocarbon group, halogen at least One; Y is selected from at least one of hydrocarbon group, substituted hydrocarbon group, heteroaryl group, substituted heteroaryl group; Z is selected from at least one of hydroxyl group, thiol group, selenol group, telluryl group; M is selected from Iron, chromium, manganese, copper, lead, zinc, tin, cobalt, nickel, antimony, mercury, cadmium, bismuth, gold, silver, platinum, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium, tantalum, At least one of tungsten, molybdenum, gallium, indium, thallium, germanium, rhenium, scandium, yttrium, thorium and lanthanide metal elements; a and b are each independently 1-6. The functional groups grafted on the surface of the two-dimensional material based on structural design have the advantages of known distribution, distribution area, and modification rate.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of strongly electron-withdrawing element doped rare earth orthosilicate scintillation material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112390278BShorten the timeShorten rise timePolycrystalline material growthMeasurement with scintillation detectorsIndiumElectron doping
The invention relates to a strong electron-withdrawing element-doped rare earth orthosilicate scintillation material and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the strong electron-withdrawing element-doped rare earth orthosilicate scintillation material is: RE 2(1‑x‑y+δ / 2) Ce 2x M 2y‑δ Si (1‑δ) M δ O 5 ; where RE is rare earth ion, 0<x≤0.05; M is a strong electron-withdrawing doping element, 0<y≤0.015; and 0≤δ≤10 ‑4 ; The M is selected from tungsten W, lead Pb, molybdenum Mo, tellurium Te, antimony Sb, bismuth Bi, mercury Hg, silver Ag, nickel Ni, indium In, zinc Zn, thallium Tl, niobium Nb, titanium Ti, tantalum Ta , at least one of tin Sn, cadmium Cd, technetium Tc, zirconium Zr, rhenium Re and gallium Ga.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Performance trapping mass and use thereof in heavy metal trapping
ActiveUS9561487B2Purified more effectivelyLow investment costGas treatmentOther chemical processesGas phaseTrapping
The present invention concerns the elimination of heavy metals, in particular mercury and possibly arsenic and lead, present in a gaseous or liquid effluent by means of a capture mass comprising a support essentially based on alumina obtained by the gel method and at least one element selected from the group constituted by copper, molybdenum, tungsten, iron, nickel and cobalt. The invention is advantageously applicable to the treatment of gas of industrial origin, synthesis gas, natural gas, gas phase condensates and liquid hydrocarbon feeds.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com