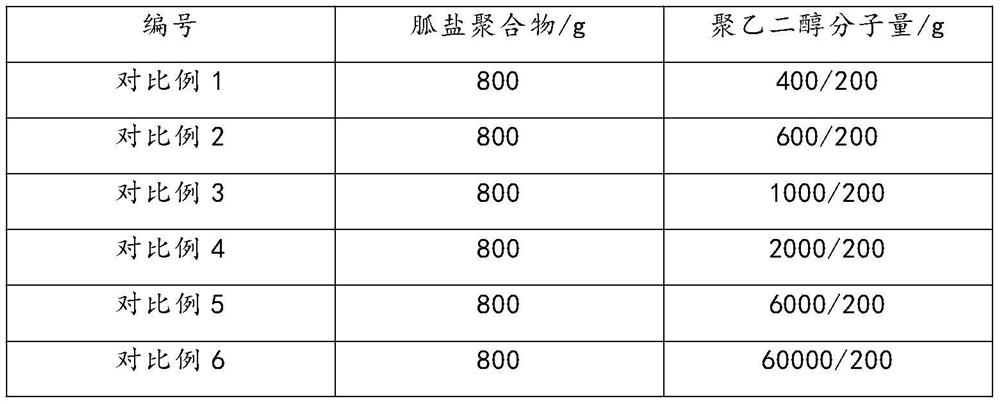
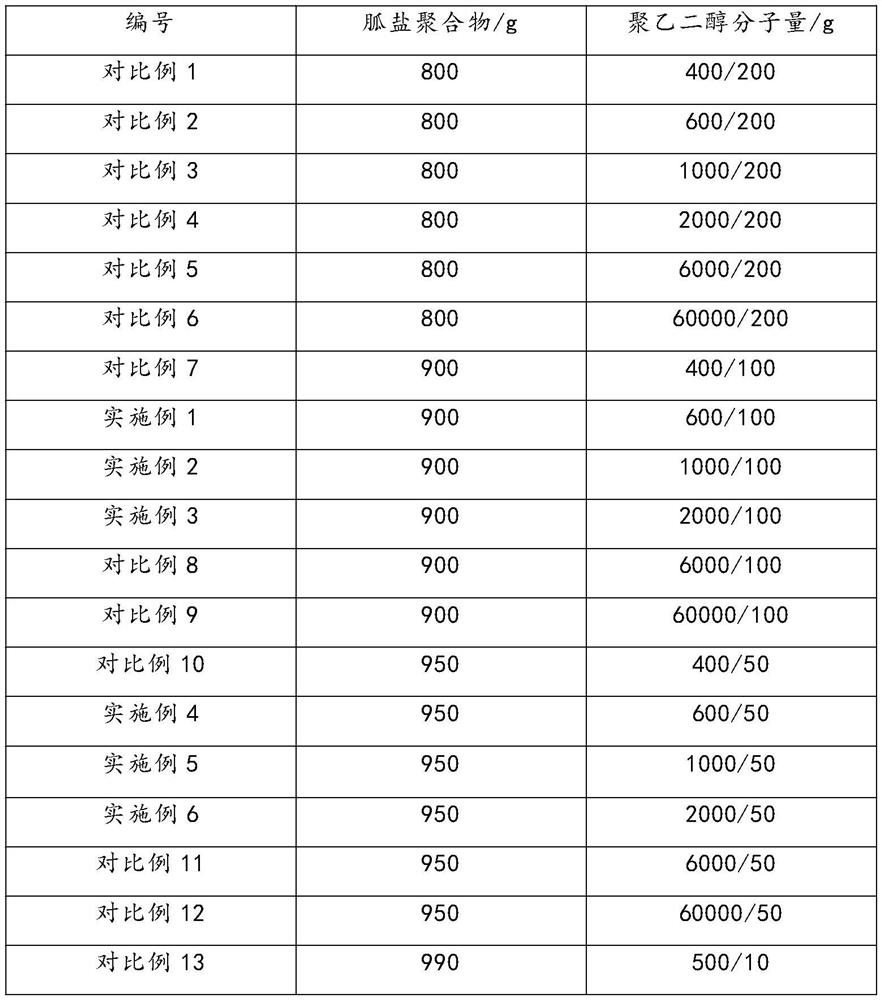
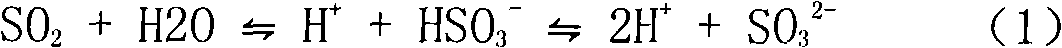Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
342 results about "Dioctyl Sulfosuccinates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Docusate, also known as docusate salts or dioctyl sulfosuccinate, is a laxative of the stool softener type used to treat constipation. It is considered a good choice in children who have hard feces. For constipation that occurs as a side effect of opiate use, it may be used alone or with a stimulant laxative.
Chinlon filament winding oil
The invention discloses chinlon filament winding oil which comprises the following components by weight: white oil, an antistatic agent PK, an emulsifier MOA3, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate and auryl oleate. The invention has the advantages of a reasonable formula, a good utilization effect and low production cost.
Owner:王琳
Flue gas desulfurization synergist and using method thereof
InactiveCN102091510AImprove solubilityReduce consumptionDispersed particle separationGlutaric acidAdipic acid
The invention discloses a flue gas desulfurization synergist which comprises the following components in percent by weight: 30-80 percent of adipic acid or glutaric acid, 5-30 percent of one of sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate, and 1-50 percent of dioctyl sulfosuccinate sodium salt. A using method of the flue gas desulfurization synergist is characterized by comprising the steps of: firstly, preparing lime into limestone slurry of 50-300PPm, adding 300-1000mg / L of gas desulfurization synergist in the limestone slurry, mechanically stirring uniformly, and then pumping the limestone slurry added with the gas desulfurization synergist into a desulfuration reaction tower by using a limestone slurry pump. By using the gas desulfuration synergist, the desulfuration efficiency is improved by 5-15 percent, the consumption of limestone is reduced, the scale formation and the blockage of equipment are reduced, and the operation electric energy is saved.
Owner:马鞍山市鸿伟环化有限公司
Sterilizing stripper dedicated for oilfield injection water and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102177913AGood peeling effectImprove the bactericidal effectBiocideFungicidesPhosphoniumSulfate-reducing bacteria
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and particularly relates to a sterilizing stripper dedicated for oilfield injection water and a preparation method thereof. The sterilizing stripper dedicated for the oilfield injection water is characterized by compounding the following materials in percentage by weight: 15 to 35 percent of tetrakis hydroxymetyl phosphonium sulfuric, 10 to 35 percent of dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of sodium dioctylsulfosuccinate, and the balance of deionized water. The preparation method comprises the followingsteps: adding the deionized water into a reaction kettle; and adding the tetrakis hydroxymetyl phosphonium sulfuric, the dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride and the sodium dioctylsulfosuccinate, and stirring for 40 to 50 minutes at normal temperature. By the method, the stripping performance of the sterilizing stripper and the killing performance to bacteria, particularly sulfate reducing bacteria, are improved; the sterilizing stripper has strong sterilization capability, good penetration and remarkable stripping effect; and the preparation process is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:山东合润环境科技有限公司
Environment-friendly high-strength water-resisting and mildew-resisting adhesive for plywood and preparation method of environment-friendly high-strength water-resisting and mildew-resisting adhesive
InactiveCN105542683AReduced effectReduce hydrogen bondingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch adhesivesBond ForceP-hydroxybenzoic acid
The invention discloses an environment-friendly high-strength water-resisting and mildew-resisting adhesive for a plywood and a preparation method of the environment-friendly high-strength water-resisting and mildew-resisting adhesive. The environment-friendly high-strength water-resisting and mildew-resisting adhesive is prepared from the following raw materials including polyvinyl alcohol, cassava starch, dibutyl phthalate, sodium pyrosulfite, tannic acid, jade powder, calcium silicate hydrate, asbestos powder, p-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, hydroquinone, sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, triethyltin chloride, phenyl mercury oleate, borax and the like. The polyvinyl alcohol and the cassava starch are subjected to a cross-linking reaction so that crystallization degrees of the polyvinyl alcohol and the cassava starch are reduced and a new cross-linking structure is formed, and furthermore, the thermal stability of the adhesive is improved; the borax is added and the polyvinyl alcohol and the starch can be subjected to further cross linking, so that the cross-linking degree and the initial viscosity of the adhesive are improved, and furthermore, the water resistance and the bonding force of the adhesive can be improved; the triethyltin chloride, the phenyl mercury oleate, the p-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide and the like are added so that the mildew-resisting capability of the plywood can be improved.
Owner:倪协照
Environment-friendly type PVC (polyvinyl chloride) synthetic leather and production method thereof
InactiveCN104278539AImprove breathabilityReduce potential threatsSynthetic resin layered productsTextiles and paperPolyamidePolyvinyl chloride
The invention discloses environment-friendly type PVC (polyvinyl chloride) synthetic leather. The environment-friendly type PVC synthetic leather is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of polyvinyl chloride resin SG-5 (PVCSG-5), 15-30 parts of polyvinyl chloride resin SG-8 (PVCSG-8), 10-15 parts of egg shell powder, 3-6 parts of rice bran, 2-5 parts of rice husk, 2-4 parts of wollastonite powder, 0.2-0.5 part of aluminum oxide, 40-70 parts of trioctyl citrate, 15-30 parts of trimethyl citrate, 1-2 parts of isopropanolamine, 0.5-1 parts of lactose, 0.2-0.5 part of calcium chloride, 0.5-1.5 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 1-2 parts of turkey red oil, 0.5-1 part of polyamide epichlorohydrin, 5-10 parts of pigment and 5-10 parts of modifying additives. The PVC synthetic leather uses agricultural wastes as filling materials, is environmentally-friendly, can improve the air permeability and toughness and is suitable for practical production use, and energy can be saved.
Owner:ANHUI HUIAN ARTIFICAL LEATHER
Moisture-resistant epoxy resin paint for transformer
ActiveCN103013269AImprove consistencyImprove surface qualityPretreated surfacesCoatingsTransformerMelamine formaldehyde resin
The invention discloses moisture-resistant epoxy resin paint for a transformer. The moisture-resistant epoxy resin paint is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 125-135 parts of modified epoxy resin, 20-30 parts of phenolic resin, 15-20 parts of melamino-formaldehyde resin, 10-20 parts of anti-rust pigment zinc phosphate, 5-6 parts of phthalic acid diethylene glycol acrylate, 1-2 parts of polyacrylic acid, 0.3-0.5 part of fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether ammonium sulfate, 0.2-0.4 part of isopropyl tri(dioctyl pyrophosphoric acid acyloxy) titanate, 0.1-0.3 part of dicumyl peroxide, 0.2-0.6 part of monoethanolamine, 0.1-0.3 part of defoamer polydimethylsiloxane, and 0.1-0.2 part of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate. According to the invention, a finished product of emulsion prepared by using the modified epoxy resin is used as a main film-forming material, so that the entire production process is stable and is easy to control, the product consistency is improved greatly, and the stability among batches is good; and the phthalic acid diethylene glycol acrylate is selected as the solvent, so that the odor of the finished product is improved greatly, and environment pollution is reduced when the phthalic acid diethylene glycol acrylate is used in production.
Owner:铜陵常江传动工具有限公司
Mould-proof shrink-proof cleaning agent for wool fabrics and preparation method of cleaning agent
The invention relates to a mould-proof shrink-proof cleaning agent for wool fabrics and a preparation method of the cleaning agent. The cleaning agent comprises the components in parts by mass as follows: 4-8 parts of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 2-5 parts of sodium alkyl sulfate, 1-3 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 5-12 parts of dimethyl distearylammonium chloride, 0.5-3 parts of sodium dichloro isocyanurate, 4-10 parts of ester quaternary ammonium salt, 0.2-0.5 part of permethrin, 4-7 parts of carboxymethyl cellulose, 0.2-0.6 part of essence and 50-80 parts of deionized water. According to the mould-proof shrink-proof cleaning agent for the wool fabrics and the preparation method of the cleaning agent, the cleaning agent has soft, anti-static, shrink-proof, antibacterial, mould-proof and moth-proof functions simultaneously and is obvious in dirt-removing effect, and the cleaned wool fabrics become fragrant and soft.
Owner:NANTONG CITY TONGZHOU DISTRICT DADA HEMP TEXTILE
Printing and dyeing auxiliary
The invention relates to the field of auxiliaries, in particular to a printing and dyeing auxiliary. The printing and dyeing auxiliary is prepared from, by mass, 10-12 parts of coconut oil acid diethanolamide, 5-8 parts of sodium sulfite, 1-2 parts of ethylene oxide, 6-20 parts of polyethylene glycol dilaurate, 18-25 parts of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 2-4 parts of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 3-8 parts of borax and 2-3 parts of barium chloride. By means of the barium chloride, the bath ratio in the printing and dyeing process can be effectively reduced, the usage of water is reduced, the cost is lowered, the usage amount of dye can be reduced, the color fastness is improved, and the auxiliary is environmentally friendly, free of toxicity and harmless to human bodies.
Owner:TONGXIANG CITY SWEATER VOCATIONAL TECHNICAL SCHOOL
Metal part electroplating method
The invention discloses a metal part electroplating method. The metal part electroplating method includes the steps that a, film pasting is conducted, i.e., the surface of a metal part to be electroplated is covered with an anti-electroplating film coinciding with the portion, not needing electroplating, of the metal part; b, electroplating is conducted, i.e., the metal part with the surface covered with the anti-electroplating film is subjected to electrocoppering, electronickelling and electrogalvanizing, wherein an electrogalvanizing solution for electrogalvanizing is composed of 100-150 mg / L of sodium hydroxide, 5-10 mg / L of ethylenediamine, 25-30 mg / L of triethanolamine, 50-130 mg / L of alkaline tetra-iso-propyl amine, 10-15 mg / L of zinc sulfate, 40-59 mg / L of sodium citrate, 25-39 mg / L of phosphorous acid, 40-55 mg / L of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate and 25-67 mg / L of antimony potassium tartrate, and meanwhile electroplating parameters are set; and c, film removal is conducted, i.e., the anti-electroplating film on the metal part is removed after electroplating is completed. By means of the metal part electroplating method, the electroplating cost is reduced and the occurrence rate of hydrogen brittleness is also reduced.
Owner:WUXI QIAOYANG MACHINERY MFG
Water-based glass paint containing modified diatomite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103102759ANo precipitation and stratificationStrong cohesionCoatingsPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsForeign matterWater based
The invention discloses water-based glass paint containing modified diatomite and a preparation method thereof. The water-based glass paint comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 55-65 of acrylate emulsion, 8-10 of water-based amino resin, 1-3 of dipropylene glycol mono butyl ether, 10-15 of pure water, 0.4-0.6 of fatty acid polyglycol ester, 0.2-0.4 of a defoaming agent, namely polyoxypropylene glycerol ether, 0.2-0.6 of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 0.3-0.5 of zinc oxide, 0.2-0.4 of adhesion promoter BOK-M-208, 0.3-0.5 of flatting agent L-350, 0.3-0.5 of modified diatomite, 0.3-0.1 of fumed silica and 0.8-1.2 of water-based silicone coupling agent A800. The water-based glass paint produced by the invention has no bubbles, no agglomerates, no foreign matters and recipitation stratification, can be infinitely diluted with water and reduce the cost and is environment-friendly; a paint film has very strong cohesion and adhesive force as well as high strong abrasive resistance at a room temperature; the added modified diatomite and fumed silica serve as thickening agents so that the adhesive force of the paint film is enhanced; and the added water-based silane coupling agent further enhances the adhesive force of the paint film.
Owner:合肥市科睦佰水性材料有限公司
Wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106172434AAchieve bactericidal effectRealize functionBiocideCovering/liningsGlycoside formationGlucoside
The invention discloses a wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent and a preparation method thereof. The wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent comprises, by mass, 5-25% of disodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate, 5-20% of alkyl glycosides, 5-20% of alkyl glucoside quaternary ammonium, 5-15% of octylisothiazolinone, and the balance of deionized water. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent and a use method of the wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent. The wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent prepared through the preparation method of the wall covering sterilization and mildew inhibition agent is added to a wall covering according to a mass ratio of 0.1-0.5:100. The above assistant has strong inhibiting and killing effects on common bacteria and fungi, also has sterilizing and mildew inhibiting effects, and also has the advantages of good biodegradability and low cost.
Owner:NINGDE NORMAL UNIV
Low-melting-point compound suspension and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105432604AMeet environmental protection requirementsWide application areaBiocideAnimal repellantsOctanolDodecylbenzenesulfonic acid
The invention discloses a low-melting-point compound suspension. The low-melting-point compound suspension comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5 to 55 parts of a low-melting-point compound, 1 to 7 parts of a moisturizing agent, 2 to 5 parts of a dispersant, 0.5 to 3 parts of a stabilizing agent, 2 to 6 parts of an anti-freezing agent, 0.1 to 0.5 part of a preservation, 1 to 8 parts of a thickening agent, 0.1 to 0.5 part of an anti-foaming agent, 1 to 15 parts of a special auxiliary agent, and the balance of water; the low-melting-point compound is a compound with the melting point between 35 and 70 DEG C; the auxiliary agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 8 to 40 parts of isooctyl alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, 8 to 30 parts of calcium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 6 to 20 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 6 to 18 parts of octanol, and 3 to 5 parts of liquid paraffin. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the suspension. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing uniformly, grinding, adding the thickening agent and stirring uniformly. The low-melting-point compound suspension is high in fluidity, obvious in medicinal effect, easy to prepare, and low in production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANFENG BIOLOGICAL SCI
Anti-rust oil for auto parts and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses anti-rust oil for auto parts and a preparation method thereof. The anti-rust oil for auto parts is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 55-60 parts of liquid paraffin, 2-4 parts of barium petroleum sulfonate, 4-6 parts of phenyltriethoxysilane, 6-8 parts of triethanolamine, 3-5 parts of zinc naphthenate, 1-3 parts of dodecenylsuccinic acid, 2-4 parts of dodecyl sodium silicate, 5-7 parts of hydroxy ethidene diphosphonic acid, 8-10 parts of palmitic acid, 35-40 parts of nanosilicon dioxide, 2-3 parts of 2,6-di-tertiary butyl p-cresol, 1-3 parts of polymethacrylate, 2-4 parts of tributyl phosphate, 3-4 parts of ammonium oxalate and 2-4 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate. By using liquid paraffin as a main material, the anti-rust oil disclosed by the invention is not only energy-saving and environment-friendly, but also is good in corrosion resistance, water resistance and flame retardance, and strong in adhesive force on auto parts. Meanwhile, the anti-rust oil which is environment-friendly and free of environmental pollution is green and environment-friendly paint and can be widely applied to surface anti-rust and protective decorative operation of auto parts.
Owner:HEFEI ZHENGTUO DECORATION MATERIALS CO LTD
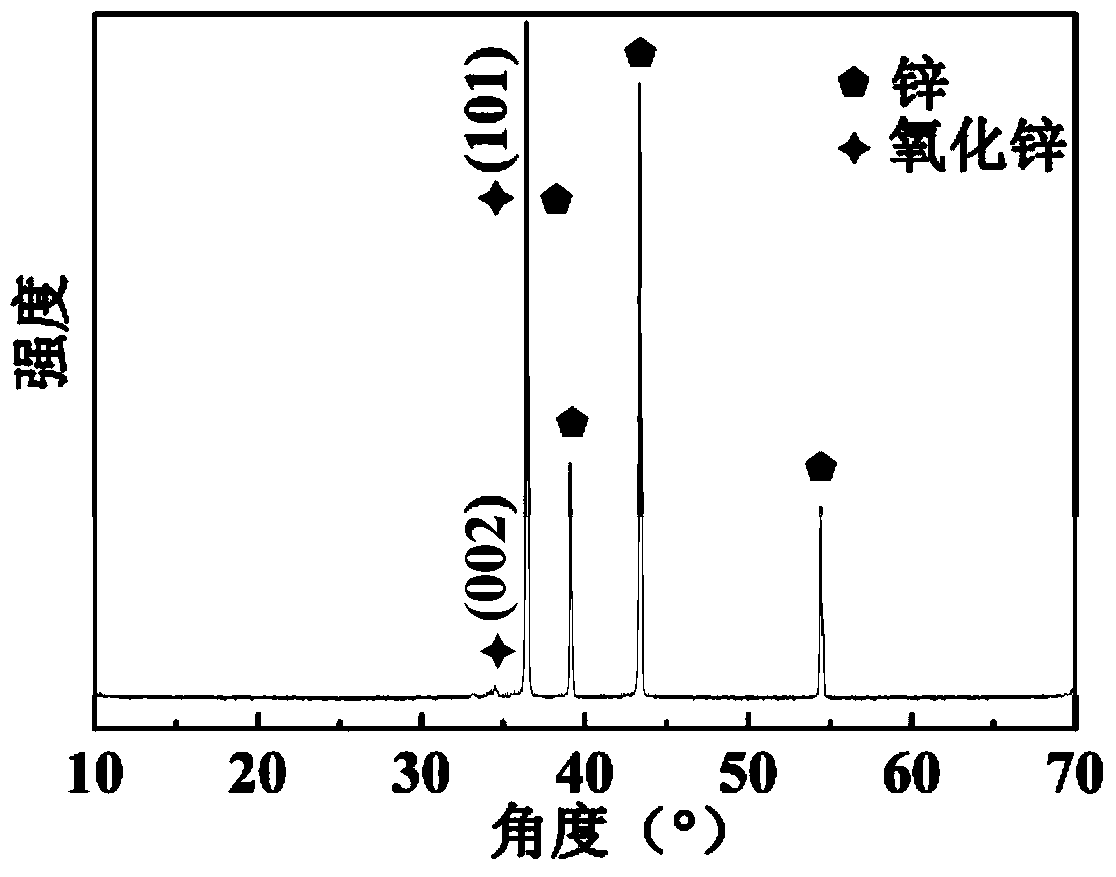
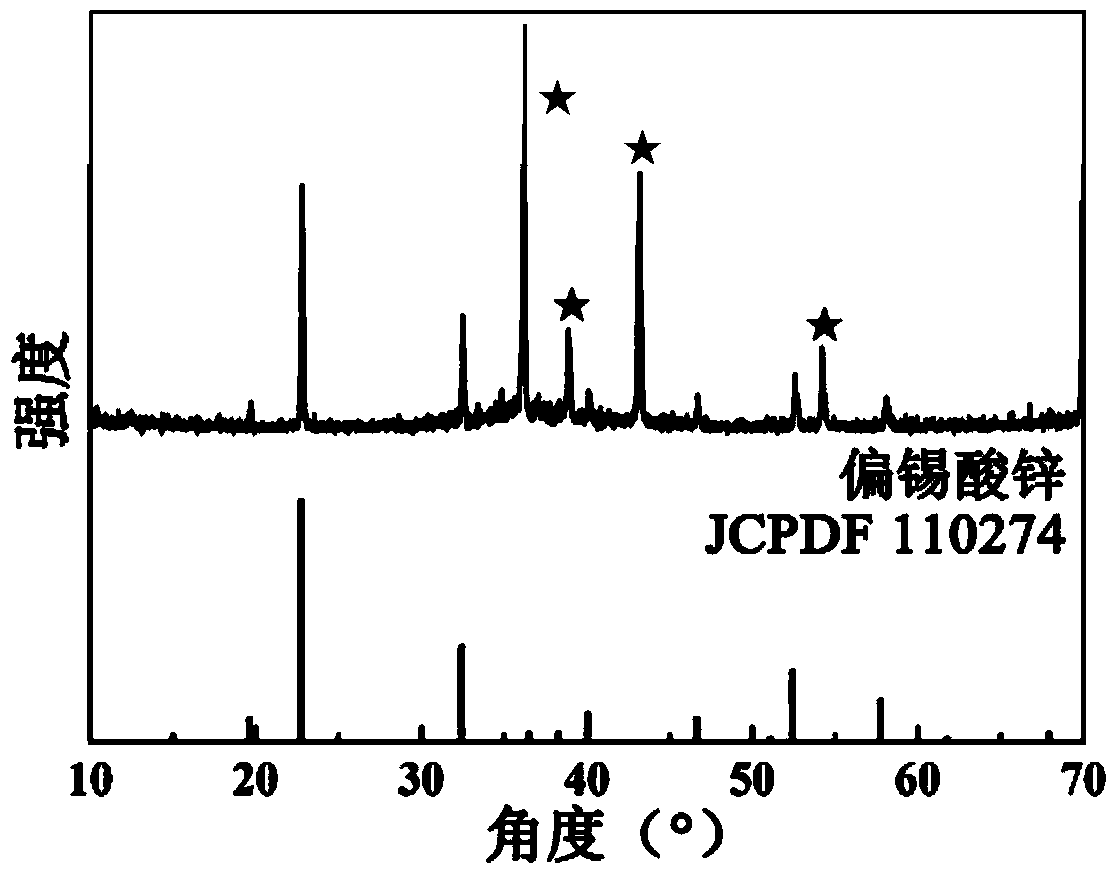
Preparation method of ZnSnO3 nano material with high gas sensitivity
InactiveCN103466691AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsTin compoundsNanotechnologyAlcoholPotassium
The invention provides a preparation method of a ZnSnO3 nano material with high gas sensitivity. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting a 1*1cm<2> zinc plate into an autoclave containing 30mL of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate solution of which the concentration is 1.5g / L, putting the autoclave into an electric heating constant-temperature air dry oven, heating for 2 hours at 100 DEG C, taking out the zinc plate after reaction, and rinsing the zinc plate by using absolute ethyl alcohol and distilled water sequentially; putting the zinc plate into an autoclave containing 0.75g of urea, 0.15-0.35g of potassium stannate and 30mL of ethanol solution; putting the autoclave into the electric heating constant-temperature air dry oven, and heating for 0.5-10 hours at 80-170 DEG C; collecting the zinc plate and a deposit obtained through reaction, rinsing by using absolute ethyl alcohol and distilled water sequentially, and drying in the electric heating constant-temperature air dry oven for 10 hours at 60 DEG C to obtain a final product. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in operation, mild in reaction condition and low in energy consumption, and the obtained product is uniform in shape.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Wool and cashmere printing and dyeing auxiliary
The invention relates to the field of production auxiliaries of wool products, in particular to a wool and cashmere printing and dyeing auxiliary. The wool and cashmere printing and dyeing auxiliary comprises sodium carboxy methyl cellulose, sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, citric acid, ethylene oxide, amino silicon oil, di-rhamnolipid, peroxidase and deionized water. The wool and cashmere printing and dyeing auxiliary comprises, by mass, 10-15 parts of sodium carboxy methyl cellulose, 3-8 parts of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 12-16 parts of citric acid, 8-14 parts of ethylene oxide, 5-10 parts of amino silicon oil, 3-6 pars of di-rhamnolipid, 1-3 parts of peroxidase and 40-60 parts of deionized water. According to the wool and cashmere printing and dyeing auxiliary, due to the combination ratio of the carboxy methyl cellulose, the citric acid and the amino silicon oil, dyeing and fixation of the dye on a wool and cashmere product are effectively improved, color fastness is improved, the color increasing and protecting performance can be improved, and the dyeing effect is ensured.
Owner:TONGXIANG PUYUAN WOOLEN KNITTING TECH SERVICE CENT
Metal cutting fluid and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of machining lubrication, in particular to a type of metal cutting fluid suitable for a cutting machining procedure and a preparation method of the metal cutting fluid. The metal cutting fluid comprises the following components in parts by weight: 60-80 parts of a mixture consisting of triethanolamine, silicone oil, phosphate, polyether and alkylated aromatics, 10-20 parts of a mixture consisting of fatty, stearic acid and lauryl sodium sulfate, 3-5 parts of sodium molybdate, 3-5 parts of boron amine, 1-2 parts of sulfurized olefin, 5-15 parts of deionized water, 0.5-1 part of nanometer antiwear agent, 1.5-3 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate and 1-2.5 parts of tetradecyl benzyl dimethyl ammonium chloride. The metal cutting fluid provided by the invention has the prominent capabilities of anti-oxidization, corrosion resistance, stability, hard water resistance, bacterial contamination-deterioration resistance in the processes of cutting machining, high-speed cutting and heavy-load cutting machining, and can be reused for a long time.
Owner:SHENYANG CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
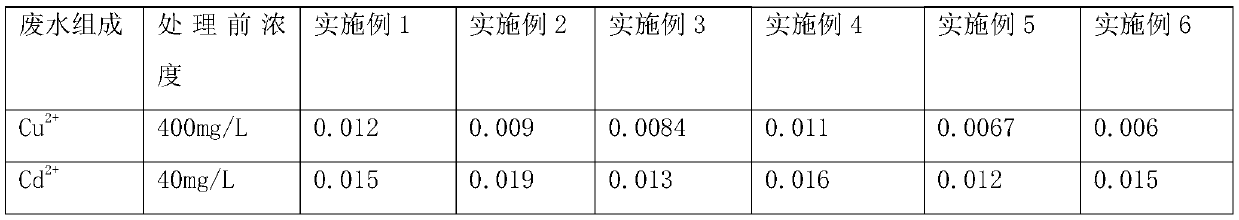
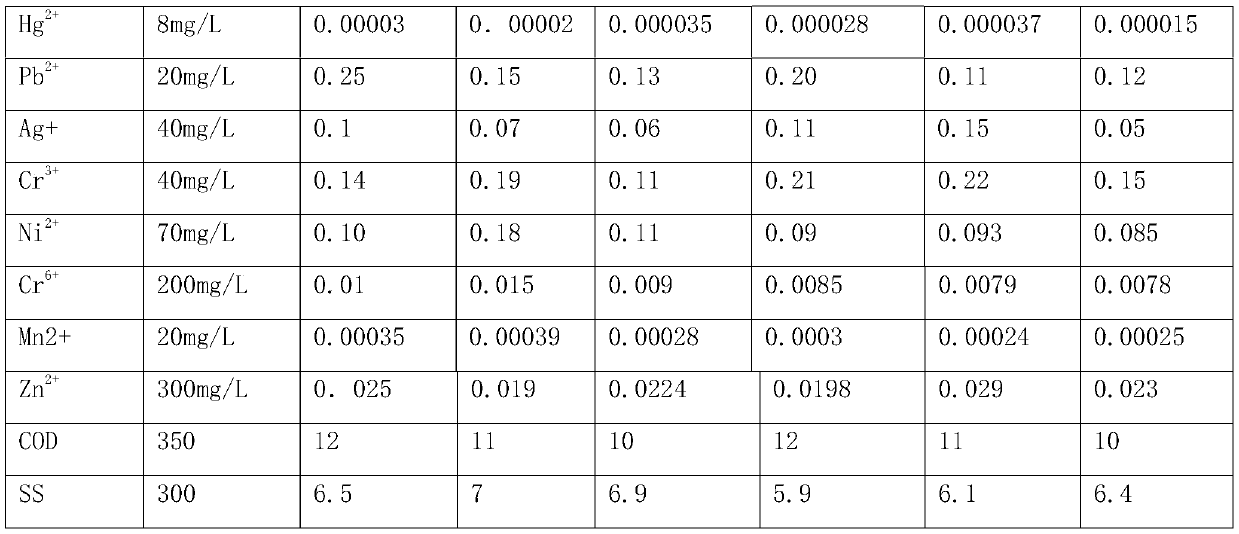
Treating agent for jointly removing heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater
The invention discloses a treating agent for jointly removing heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater. Raw materials comprise polystyrene divinylbenzene resin microspheres, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, a dithiocarbamate, polyethyleneimine, glutaraldehyde, black wattle tannin, poly(2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid), maleic anhydride, dialkyl dithiophosphate, polyaspartic acid, 2-amino-3-mercaptopropionylchitosan, polyethyleneimine sodium xanthate, mercaptoacetic acid, dibutyl phthalate, polyepoxysuccinic acid, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, a cross-linking agent and a coupling agent. The treating agent can be used to jointly remove heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater under coexistence ions, is not influenced by ion interference, and can form stable compounds precipitate with most monovalent and bivalent heavy metal ions such as Fe<2+>, Ni<2+>, Pb<2+>, Ag<+>, Zn<2+>, Cd<2+>, Hg<2+>, Ti <+>, Cr<3+> and the like for precipitation, so that the purpose of removing heavymetal ions is achieved. The removal effect can be achieved regardless of the concentrations of the heavy metal ions in wastewater. When a plurality of metal ions coexist, the metal ions can be simultaneously removed. When heavy metal ions exist in a form of complex salt (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), tetramine and the like), a good removal effect can also be achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING VOCATIONAL INST OF ENG
Permeability-increasing and coagulation-accelerating wetting agent for wet-type dust control
ActiveCN105778867AReduce surface tensionIncrease surface tensionOther chemical processesDust removalSucrosePhosphate
The invention discloses a permeability-increasing and coagulation-accelerating wetting agent for wet-type dust control. The permeability-increasing and coagulation-accelerating wetting agent comprises 0.5%-2% of cocamidopropyl betaine, 0.15%-0.8% of butylnaphthalenesulfonic acid sodium salt, 0.2%-1% of trimethyl-1-propanaminium iodide, 0.2%-1% of sucrose fatty acid ester, 1%-3% of corn starch grafting sodium acrylate, 0.5%-1.5% of isooctanol phosphate, 0.06%-0.35% of sodium alcohol ether sulphate, 0.5%-1.3% of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 0.2%-1.2% of polyacrylamide, 0.1%-0.8% of chitin derivative-carboxymethyl chitosan, 0.1%-0.2% of polyaspartic acid, 0.3%-0.6% of calcium chloride and the balance water. The ermeability-increasing and coagulation-accelerating wetting agent for wet-type dust control has the advantages that wetting ability of water for coal is enhanced and water molecules can wrap coal dust particles quickly, so that coagulation and falling of the coal dust particles are facilitated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Silicon aerogel material preparation method
The invention belongs to the field of chemical industry materials, and more particularly relates to a silicon aerogel material preparation method. The preparation method comprises: a) mixing silicate, water, an auxiliary agent and an organic solvent, and carrying out a hydrolysis reaction under an acid condition to obtain a sol, wherein the auxiliary agent is one or a plurality of materials selected from hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate and sodium glycocholate; b) carrying out a condensation polymerization reaction on the sol under an alkaline condition to obtain a wet gel material; and c) carrying out a drying treatment on the obtained wet gel material to obtain the silicon aerogel material. According to the preparation method of the present invention, the auxiliary agent is added during the silicon aerogel material preparation process, wherein the mechanical strength of the silicon aerogel material can be increased through the addition of the auxiliary agent.
Owner:BEIJING BOTIANZIRUI TECH CO LTD
Efficient environment-friendly penetrant for fabric pretreatment and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-efficiency environment-friendly penetrating agent for fabric pretreatment, which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 2 parts of isomeric tridecanol polyoxyethylene ether -4 parts, 4-7 parts of secondary alkyl sodium sulfonate, 2-3 parts of polyoxyethylene oleate, 1-3 parts of phytic acid, 5-8 parts of alkyl glycoside, 2- 6 parts, 6-12 parts of sodium N-dodecyl-β-alanine, 2-5 parts of methyl salicylate, 4-6 parts of clove, 1-2 parts of defoamer, 1-2 parts of wetting agent 2 parts, 40-80 parts of deionized water. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the high-efficiency and environment-friendly penetrating agent, which has good penetrating performance, excellent emulsifying effect, good decontamination and dispersing performance, low foam, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali resistance, good stability, excellent oxidation resistance, green Environmental protection, no damage to the fabric.
Owner:SUZHOU SANHE KAITAI COLORED THREAD WEAVING CO LTD
Method and solution for electrogalvanizing surface of zinc alloy workpiece comprising blind hole
The invention discloses a method and solution for electrogalvanizing the surface of a zinc alloy workpiece comprising a blind hole. The method orderly comprises the steps of cleaning, activating, electrogalvanizing, reactivating and passivating the surface of the zinc alloy workpiece. The electrogalvanizing solution is characterized in that: the solution contains the following components per liter: 0.5 to 2 g of acridine, 0.05 to 0.2 g of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, and the balance of common acidic galvanizing components. The electrogalvanizing solution adjusts the pH value to between 5.0 and 6.0 when the electrogalvanizing is performed, the temperature of the solution is kept between 20 and 30 DEG C, and the cathode current density is between 1 and 3 A / dm<3>. The method and the solution have the advantages that: the electrogalvanizing solution has little corrosion to the matrix of a zinc alloy after a corrosion inhibitor is added; and the throwing power of the blind hole is high after a wetting agent is added into the electrogalvanizing solution; a finally obtained electrogalvanized layer has good binding force, good the throwing power, and good compactness and corrosion resistance; and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Mildew-proof agent for silk fabric
InactiveCN103741460AWon't breakHas antibacterial and antifungal effectsAnimal fibresPolyethylene glycolStearate
The invention discloses a mildew-proof agent for a silk fabric. The mildew-proof agent consists of the following components in parts by weight: 10-14 parts of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 12-15 parts of amino silicon oil, 6-9 parts of sorbitan stearate, 6-9 parts of polyethylene glycol monostearate, 10-15 parts of vinyl polysiloxane, 10-17 parts of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, 12-16 parts of N,N-nickel dibutyldithiocarbamate, 12-18 parts of titanium isopropylate, 22-25 parts of ethylene glycol, 10-18 parts of tetrabutyl titanate and 50-70 parts of water. The mildew-proof agent has the beneficial effects that (1) excellent bacteria-resisting and mildew-proofing effects are achieved; (2) a finished fabric is high in washing fastness and soft in handfeel; and (3) the mildew-proof agent is prepared by adopting a simple preparation process, is nontoxic and harmless to human bodies, and does not damage silks in the silk fabric.
Owner:WUJIANG CITY QIDU TOWN MIAOGANG YADI KNITTING GARMENT FACTORY
Novel antistatic finishing agent composition for polyester fabric
The invention discloses a novel antistatic finishing agent composition for a polyester fabric. The novel antistatic finishing agent composition is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 18 to 25 parts of ethyl acrylate, 1 to 5 parts of sodium oleate, 5 to 8 parts of magnesium stearate, 15 to 20 parts of polyethylene glycol diamine, 15 to 20 parts of coconut oil acid monoethanolamine, 16 to 19 parts of dimethyl terephthalate, 11 to 15 parts of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 4 to 8 parts of sodium pyrophosphate, 2 to 4 parts of potassium tartrate, 50 to 60 parts of ethyl alcohol and 70 to 90 parts of deionized water. The antistatic finishing agent has softening and smoothening effects, and friction force between polyester fabrics can be reduced, so that the antistatic finishing agent has good antistatic effect; the prepared antistatic finishing agent is biologically degraded easily, and environment pollution is not caused.
Owner:HUZHOU LIHUA YUJIE UNION TEXTILE
Instant degerming and virus-removing master batch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111748416AImprove liquidityEasy to useInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsSodium stearateButanedioic acid
Owner:青岛拜士特新材料有限公司
Concrete air-added heat preservation brick and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105541386AHigh compressive strengthImprove bending strengthSolid waste managementCeramicwareBrickTitanium nitride
A concrete air-added heat preservation brick is prepared from, by weight, 115-125 parts of ordinary Portland cement, 100-110 parts of composite filler, 7-9 parts of reinforced filler, 7-8 parts of composite forming agent, 9-10 parts of additive and 55-62 parts of papermaking wastewater. The composite filler is prepared from coal ash, titanium nitride, metakaolin and ceramic polishing waste. The reinforced filler is prepared from polycrystal mullite cellucotton and chopped glass fiber. The composite forming agent is prepared from dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, alkyl polyglucoside and pentaerythritol stearate. The additive is prepared from ammonium polyphosphate, sodium dehydroacetate, pine tar and a polycarboxylates high performance water-reducing agent. The concrete air-added heat preservation brick has the advantages of quite outstanding high pressure resistance and high bending strength, and is good in heat preservation effect.
Owner:吉安市第四建筑工程有限公司
Sterilization washing powder containing zinc pyrithione antibacterial agent and preparation method of sterilization washing powder
ActiveCN111690469ARapid sterilizationEfficient sterilizationOrganic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsButanedioic acidThioketone
The invention provides sterilization washing powder containing a zinc pyrithione antibacterial agent and a preparation method of the sterilization washing powder, and belongs to the technical field ofantibiosis. The sterilization washing powder containing the zinc pyrithione antibacterial agent is prepared by the following method: S01, preparing a composite antibacterial agent from a guanidine salt polymer and polyethylene glycol according to a ratio through a physical mixing method; S02, mixing the guanidine salt polymer / polyethylene glycol antibacterial agent with a zinc-loaded antibacterial agent, zinc pyrithione and dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate to prepare the composite antibacterial agent containing zinc pyrithione. The composite antibacterial agent is added into a washing formula system such as washing powder, soap powder and the like and can be quickly dissolved and dispersed to release guanidine salt polymers, zinc ions and zinc pyrithione antimicrobial ingredients when clothes are washed and is easy to disperse in the washing process, and achieves the effects of quick sterilization and degerming.
Owner:青岛拜士特新材料有限公司
High-content stable prinsepia utilis royle oil microemulsion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106031705ASolve the problem of poor solubility in water-based systemsImprove stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPreservativePrinsepia utilis
The invention discloses high-content stable prinsepia utilis royle oil microemulsion and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of oil microemulsification. The prinsepia utilis royle oil microemulsion is prepared from 10-20 parts of prinsepia utilis royle oil, 3-7 parts of tween-65, 2-7 parts of span-80, 2-6 parts of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 3-7 parts of carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin, 4-8 parts of cocamidopropyl betaine, 5-12 parts of glycerin, 2-4 parts of n-butyl alcohol, 0.1-0.3 part of a preservative and 130-160 parts of deionized water. The preparation method of the prinsepia utilis royle oil microemulsion comprises the steps of mixing, stirring, shearing and the like. The prepared prinsepia utilis royle oil microemulsion has the advantages of being small in particle size, good in storage stability property and excellent in dissolving property.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Antistatic finishing agent for silk fabrics
ActiveCN103741457AHas antibacterial and antistatic effectsGood effectAnimal fibresFiberDimethyl terephthalate
The invention discloses an antistatic finishing agent for silk fabrics, which is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 11-15 parts of sodium diethylhexyl sulfosuccinate, 10-15 parts of lactose, 6-9 parts of starch, 19-26 parts of alcohol, 3-4 parts of essence, 3-5 parts of lanolin polyethenoxy ether, 6-9 parts of ethyl acrylate, 3-5 cocoyl monoethanolamine, 3-6 parts of dimethyl terephthalate and 4-8 parts of sodium pyrophosphate. The antistatic finishing agent for silk fabrics has favorable antimicrobial and antistatic effects; the finished fabric has favorable washing fastness and soft feeling; and the preparation technique is simple, is nontoxic and harmless to the human body, and can not destroy the cocoon fibers in the silk fabric.
Owner:WUJIANG DALONG JET WEAVING
Preparation method for architectural glass heat insulation coating
InactiveCN105131743AGood weather resistanceGood chemical resistanceHyaluronic acid coatingsChitin coatingsArchitectural glassAntioxidant
The invention provides a preparation method for an architectural glass heat insulation coating. The preparation method includes the steps that ATO nanometer powder, lecithin, triethoxy-1H,1H,2H,2H-tridecafluoro-n-octylsilane and dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate are added into deionized water and stirred, then silicon carbide whiskers are added, a sodium hydroxide solution with the mass concentration of 1% is dripped on the stirring condition, stirring continues to be carried out until no precipitation is generated, and precipitation is filtered, washed with deionized water and dried to obtain heat insulation powder; the heat insulation powder, SiO2 particles and a silane coupling agent KH-570 are mixed, and the mixture is ground on a ball grinder to obtain functional powder; the functional powder, polytetrafluoroethylene wax powder, perchlorovinyl resin, zinc phosphate, polyacrylamide, mannitol, chitosan, an uvioresistant agent and an antioxidant are mixed and stirred to obtain the architectural glass heat insulation coating. The coating has excellent weather resistance, chemical resistance, waterproof performance and hardness performance.
Owner:江苏耀兴安全玻璃有限公司
Electroplating method of metal piece
The invention discloses an electroplating method of a metal piece. The electroplating method comprises steps as follows: a, film pasting: the to-be-electroplated metal piece is covered with an anti-electroplating film coinciding with the part which does not need electroplating; b, electroplating: the metal piece covered with the anti-electroplating film is electroplated with copper, nickel and zinc respectively, wherein an electroplating solution for zinc electroplating comprises 60-90 mg / L of benzyl pyridinium sodium carboxylate, 15-30 mg / L of triethanolamine, 50-130 mg / L of alkalized tetra-isopropylamine, 10-15 mg / L of zinc sulfate, 40-59 mg / L of sodium citrate, 25-39 mg / L of phosphorous acid, 40-55 mg / L of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate and 25-67 mg / L of antimony potassium tartrate, and meanwhile, electroplating parameters are limited; c, film removal: the anti-electroplating film on the metal piece is removed after electroplating. According to the electroplating method, the electroplating cost is reduced, and the phenomenon of hydrogen embrittlement is reduced.
Owner:WUXI JIABANG ELECTRIC POWER PIPE FACTORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com