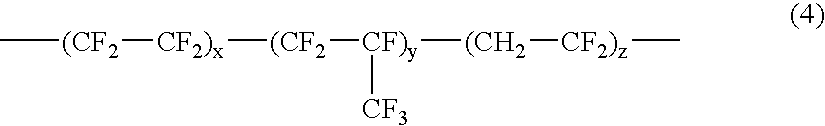Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1450 results about "Anti reflective" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
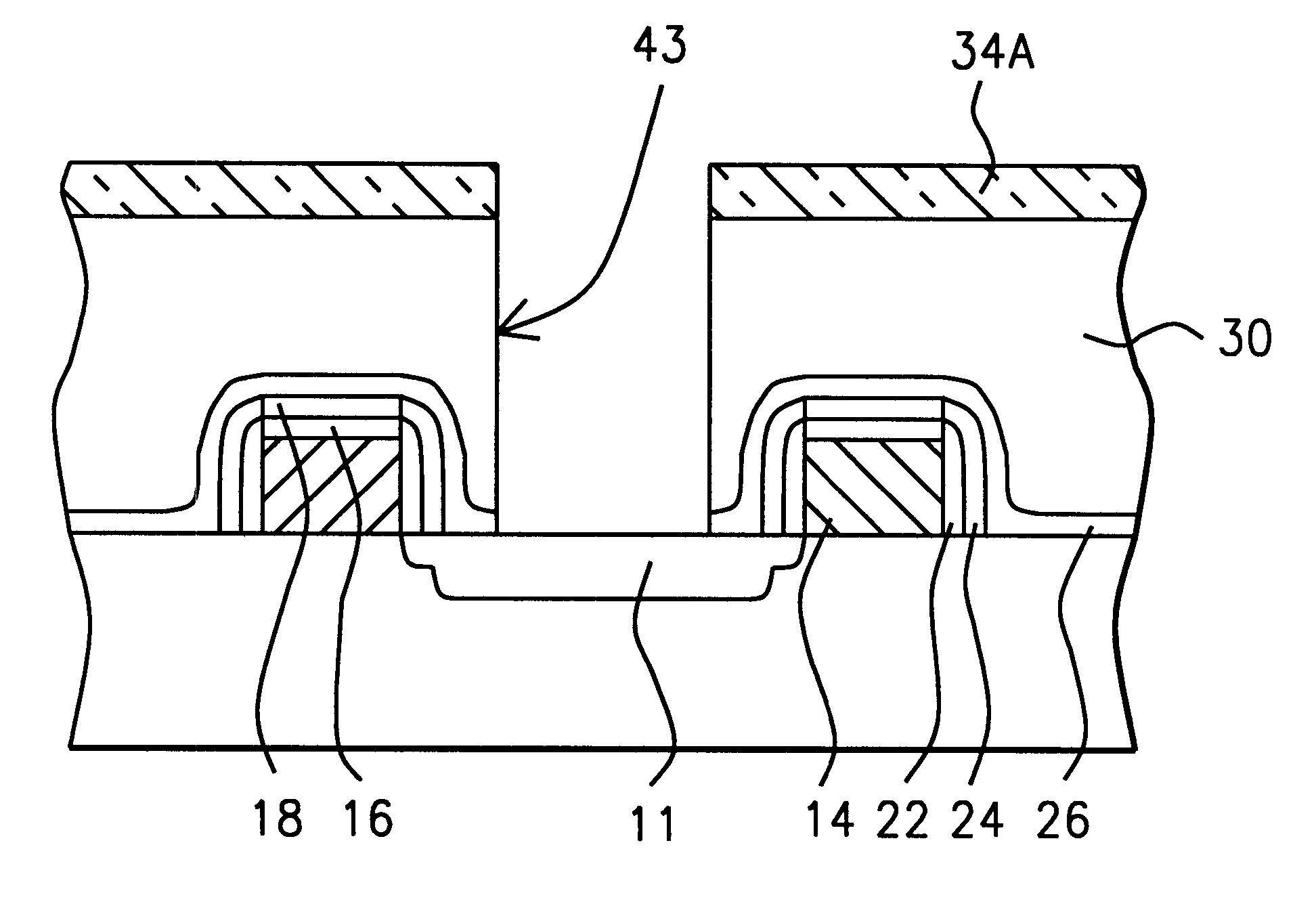
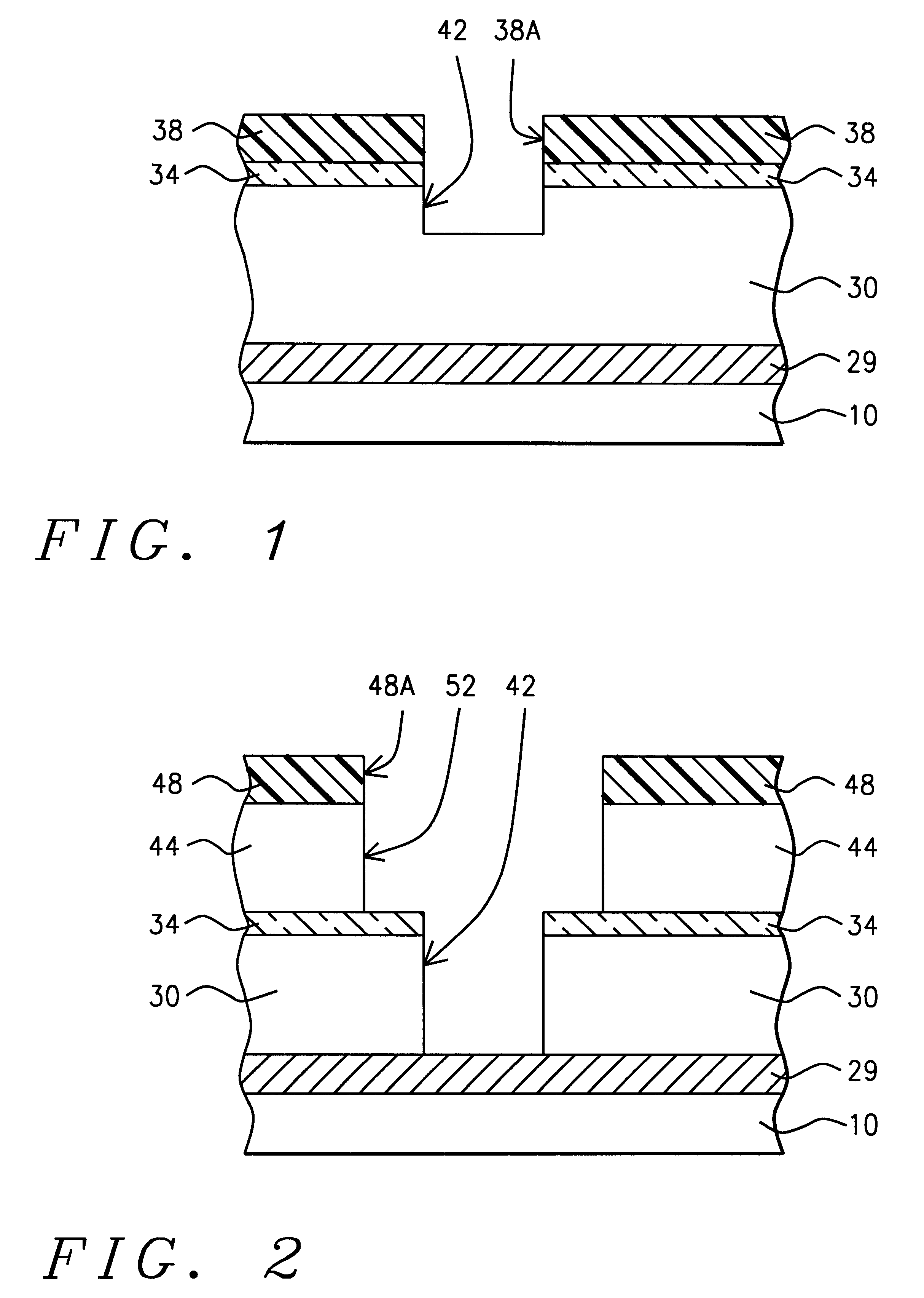
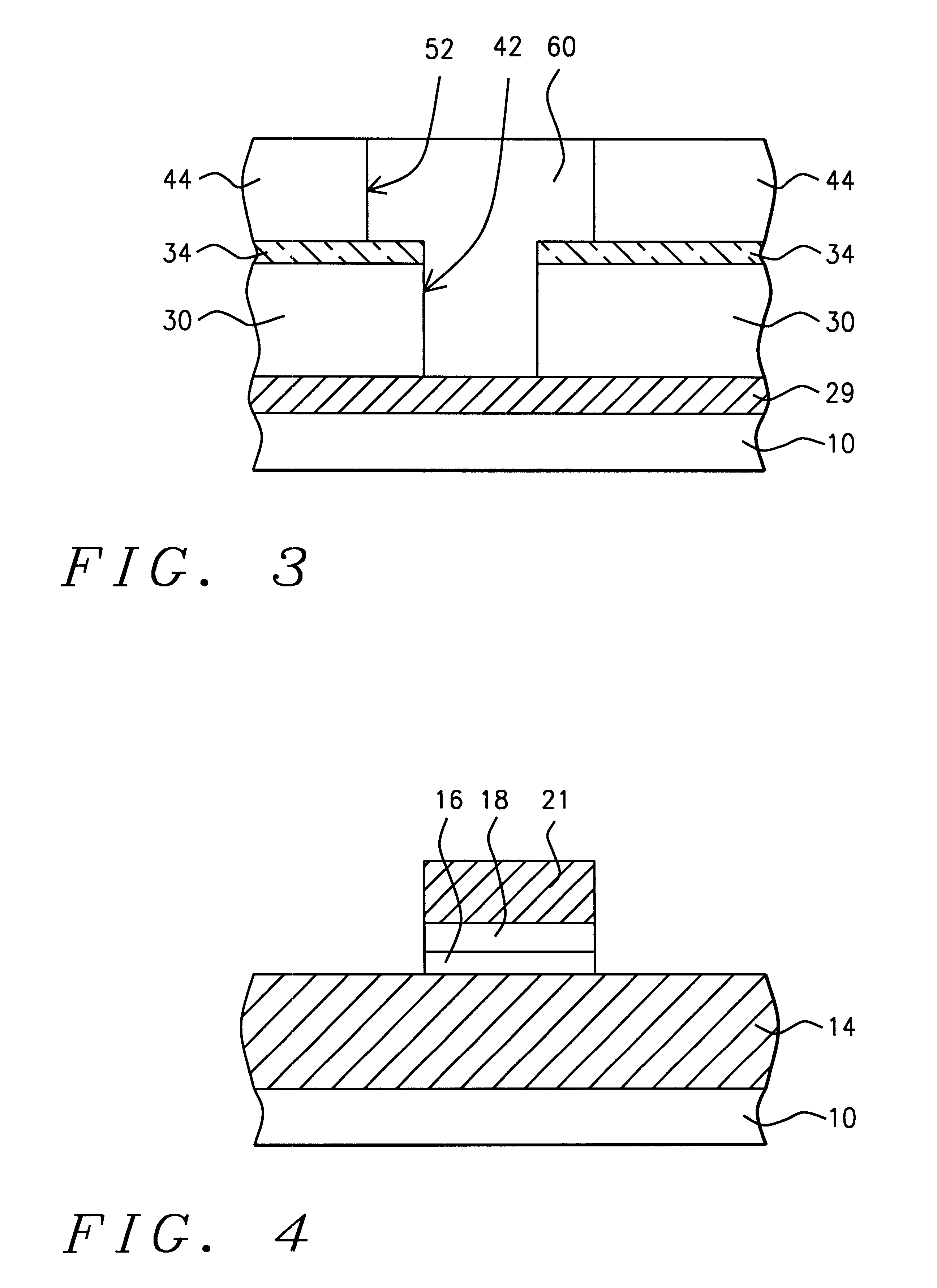
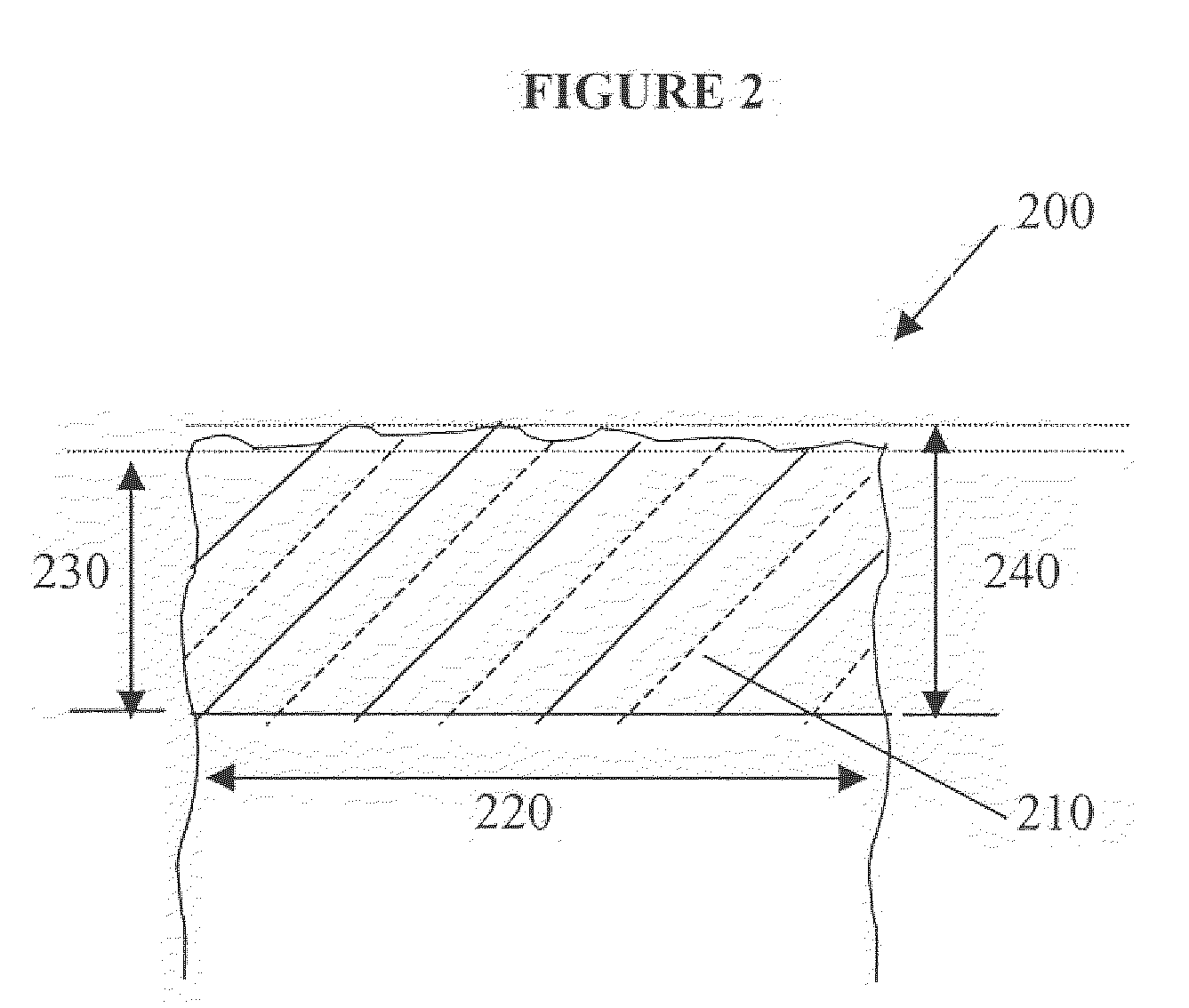
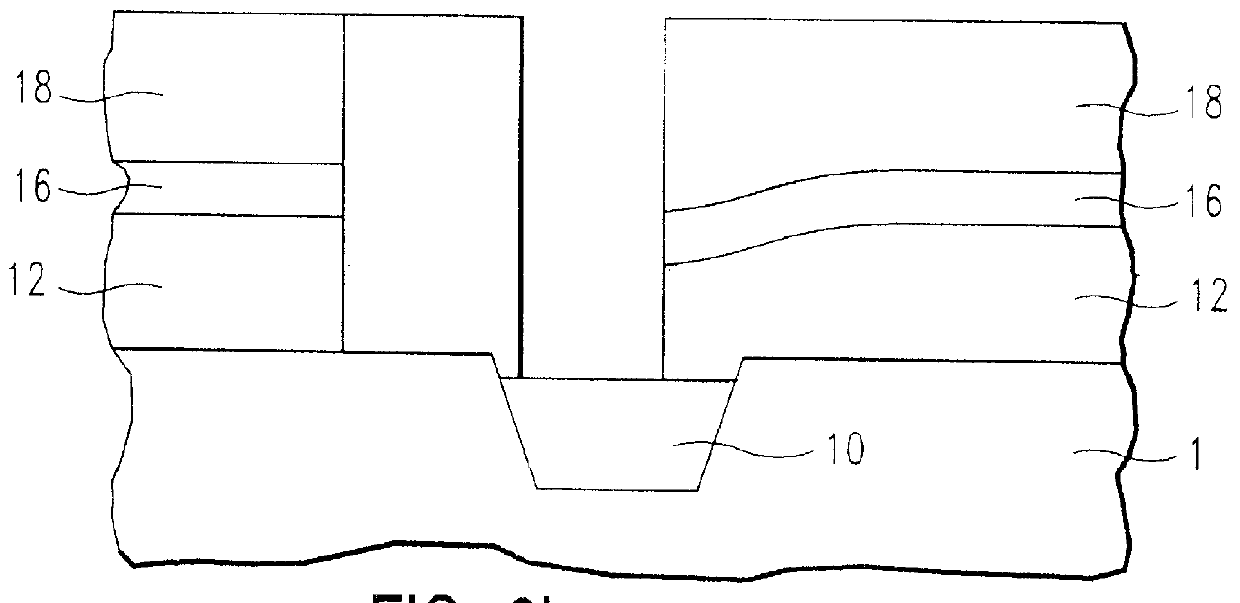
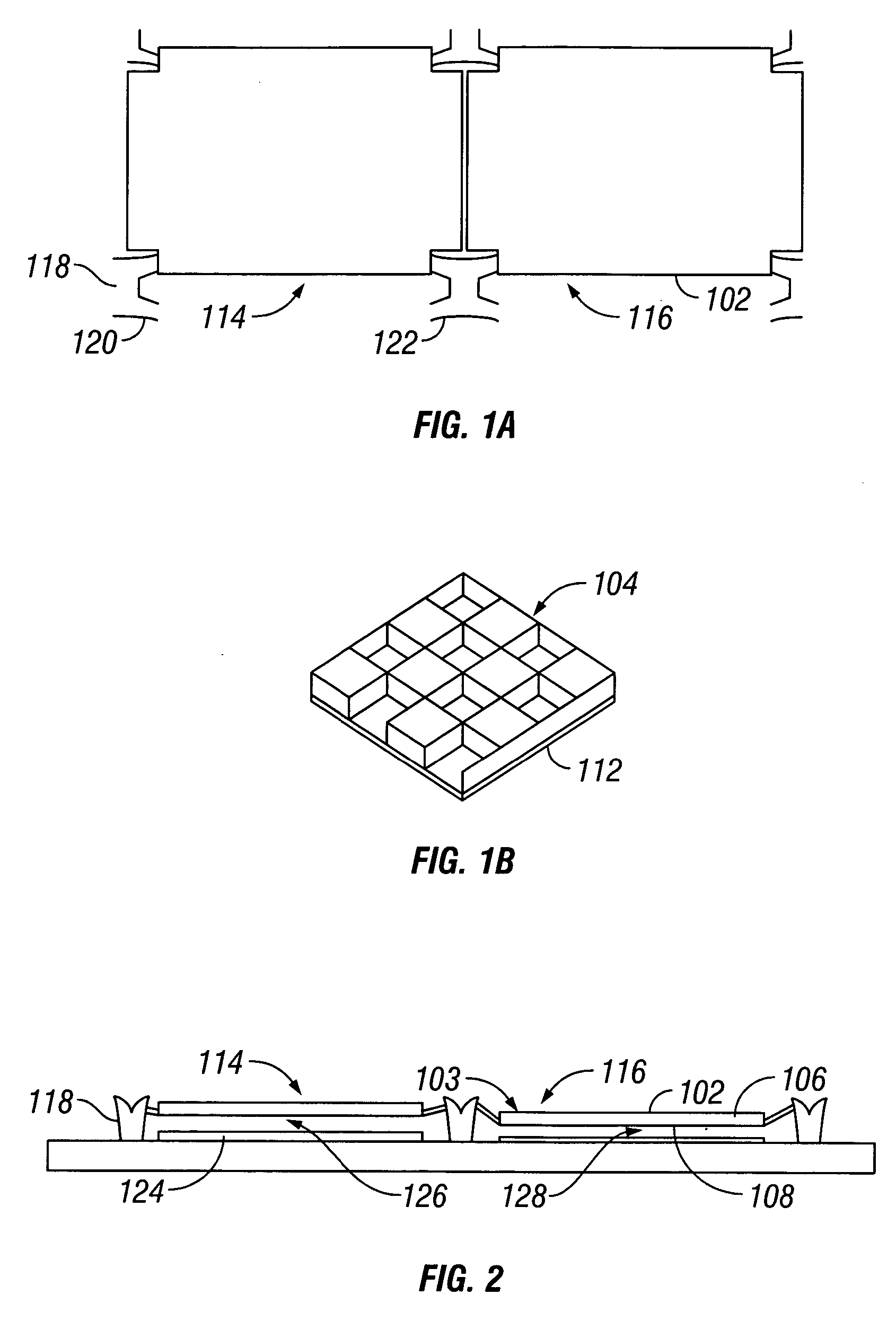
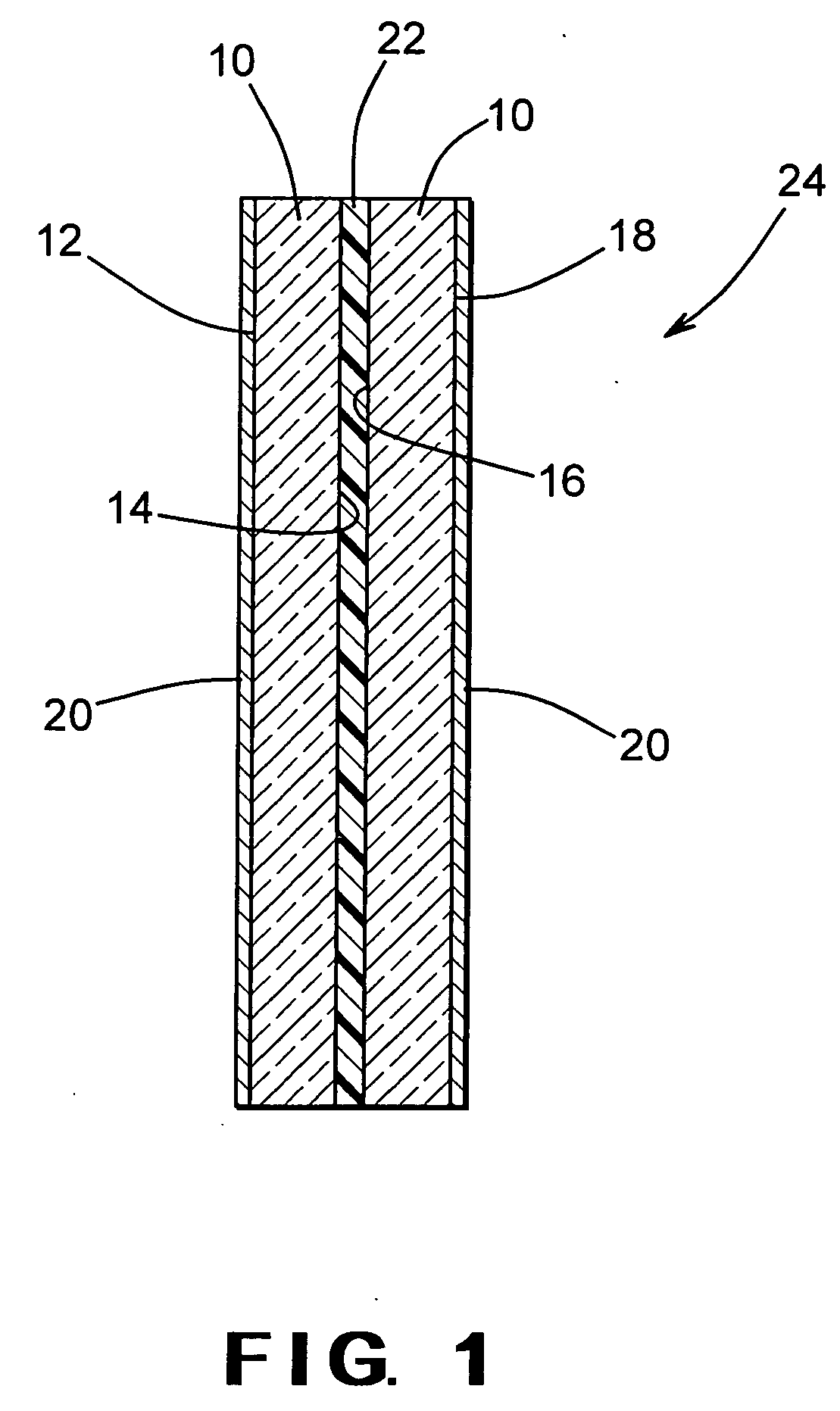
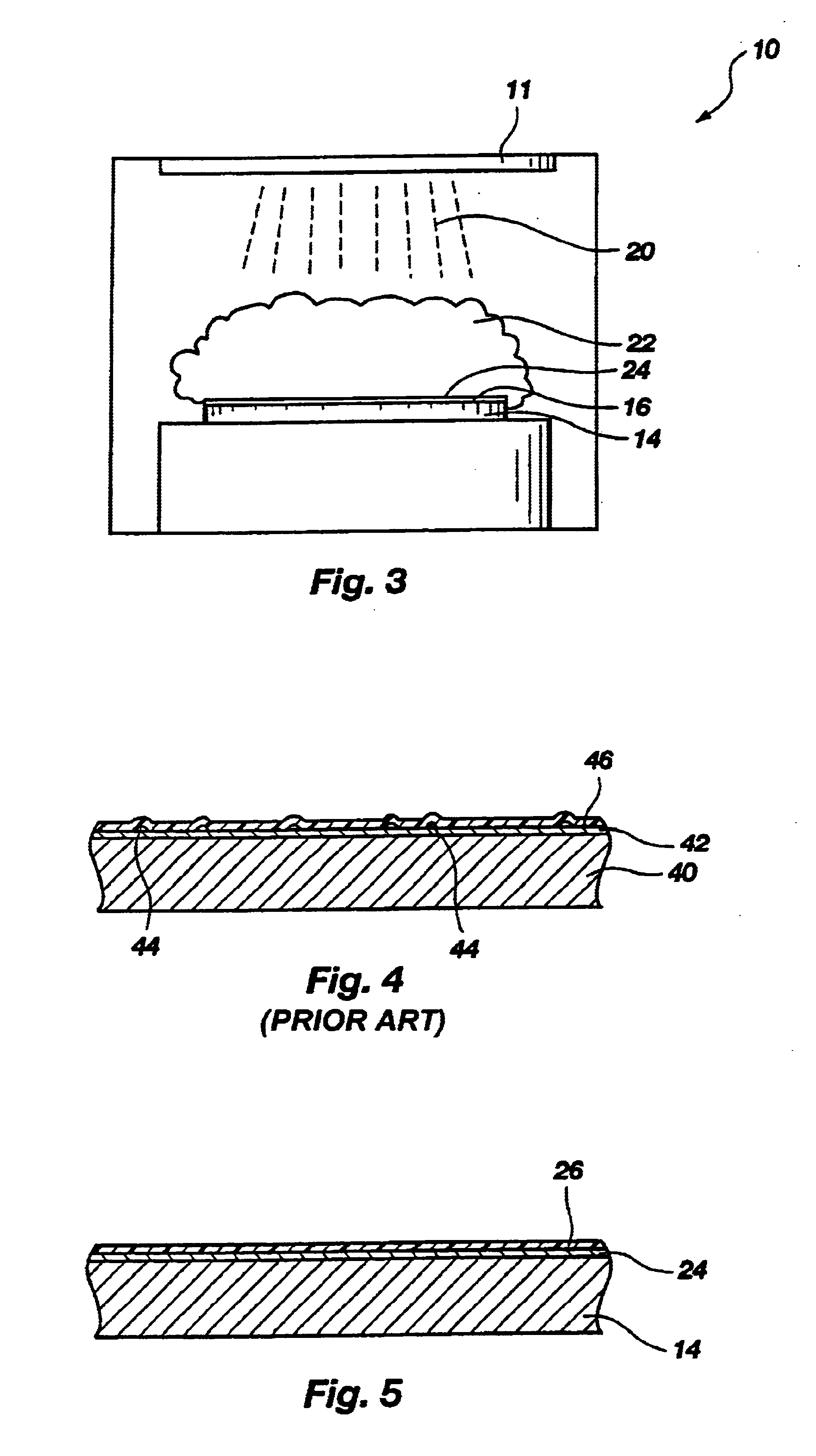
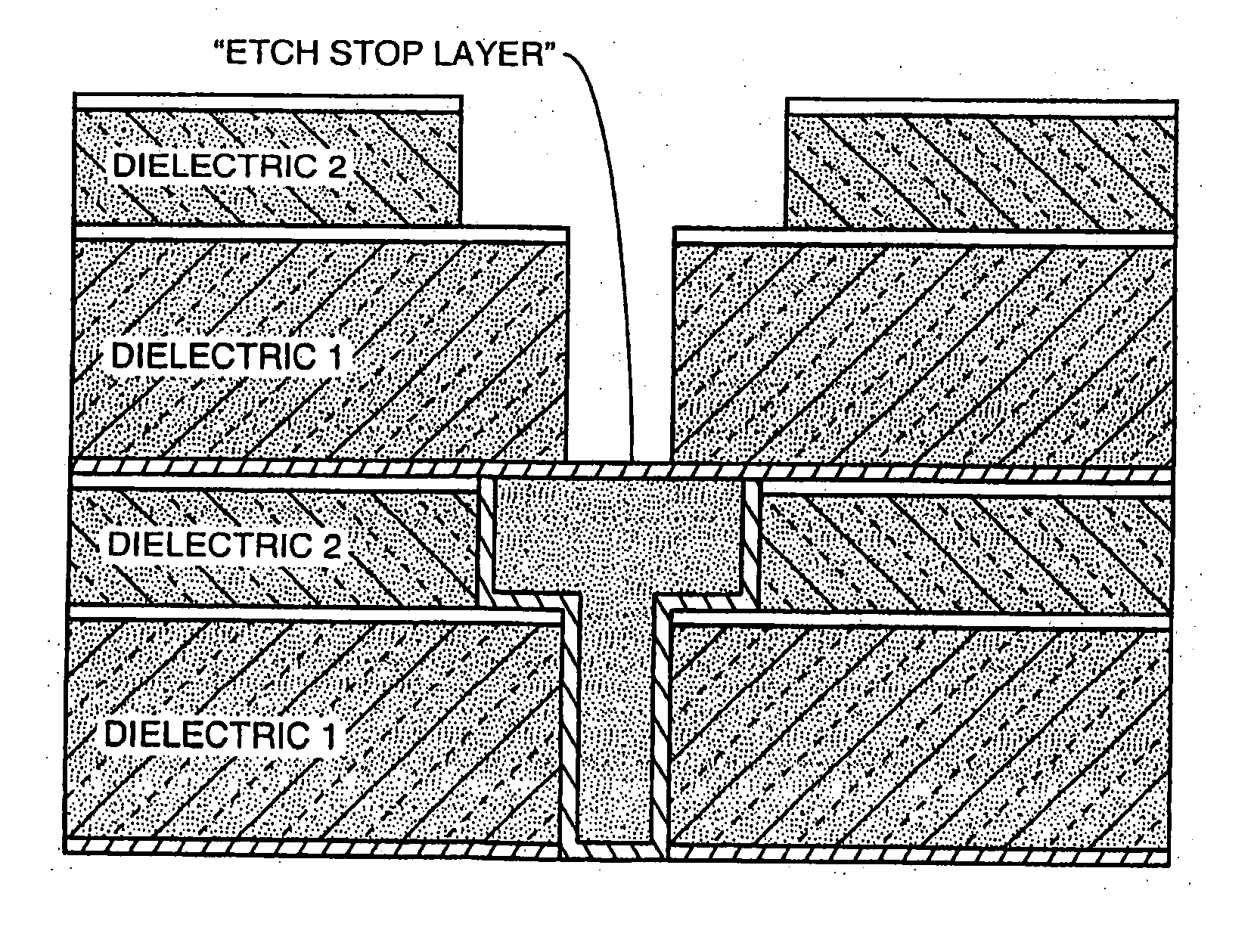
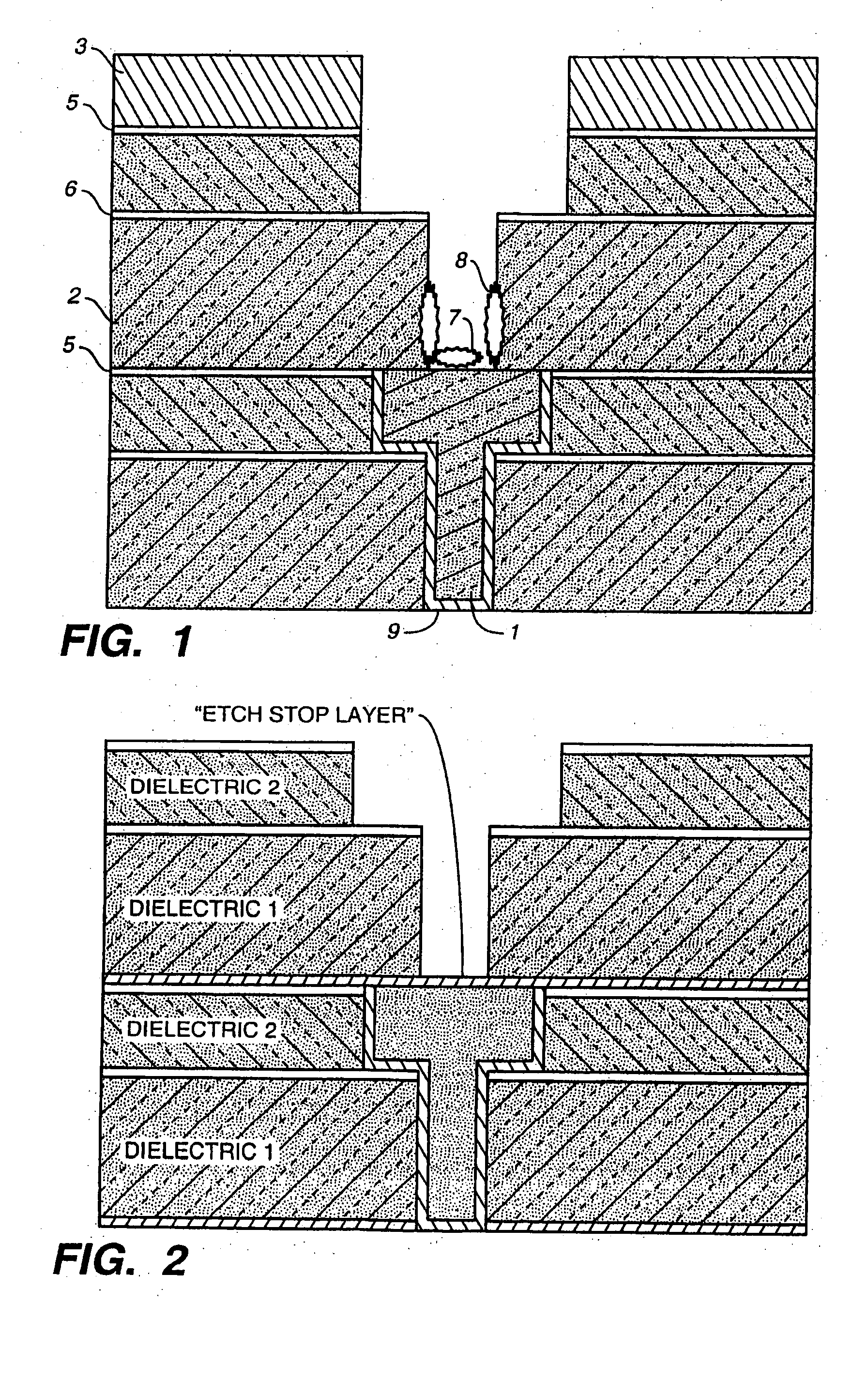
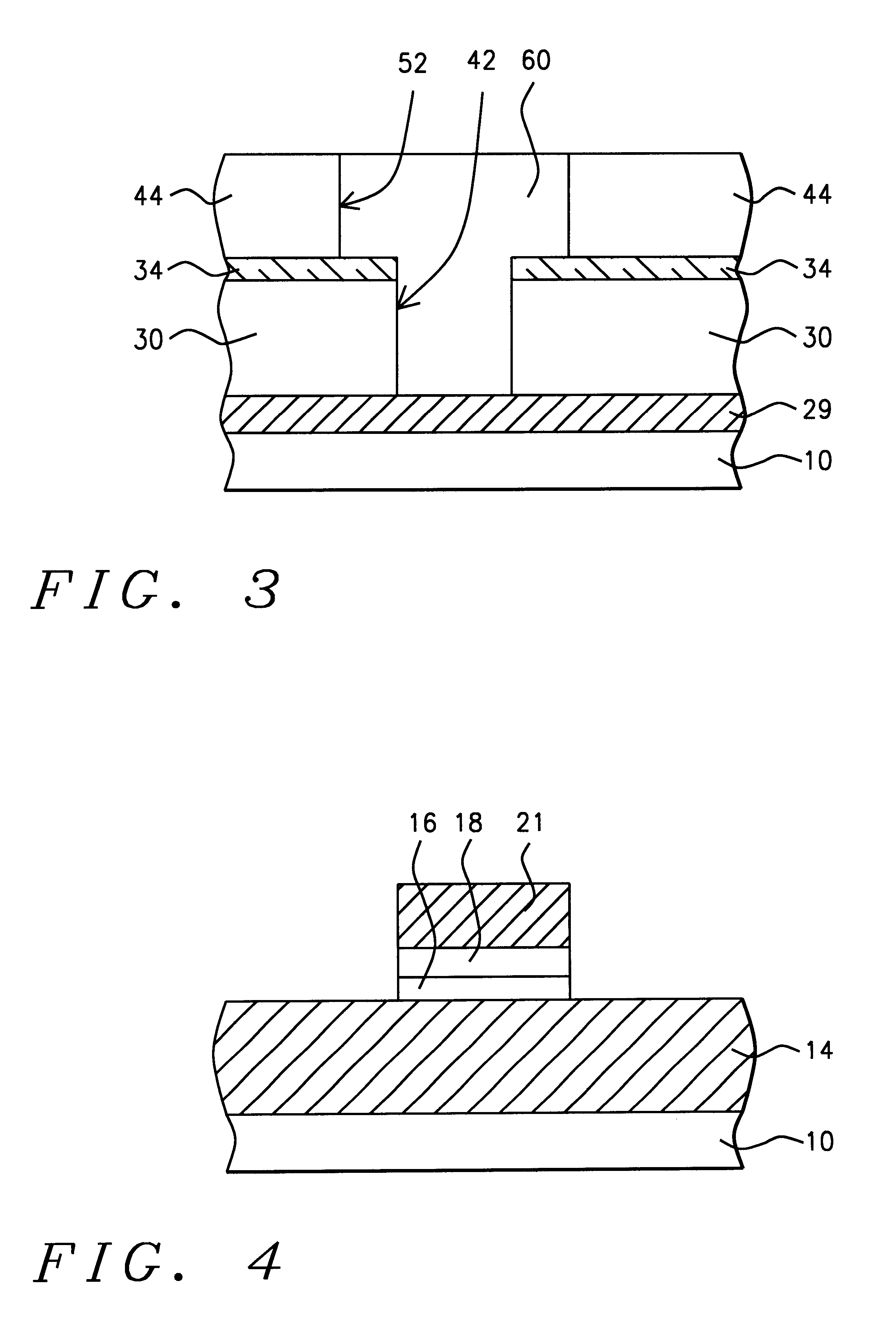
High selectivity Si-rich SiON etch-stop layer
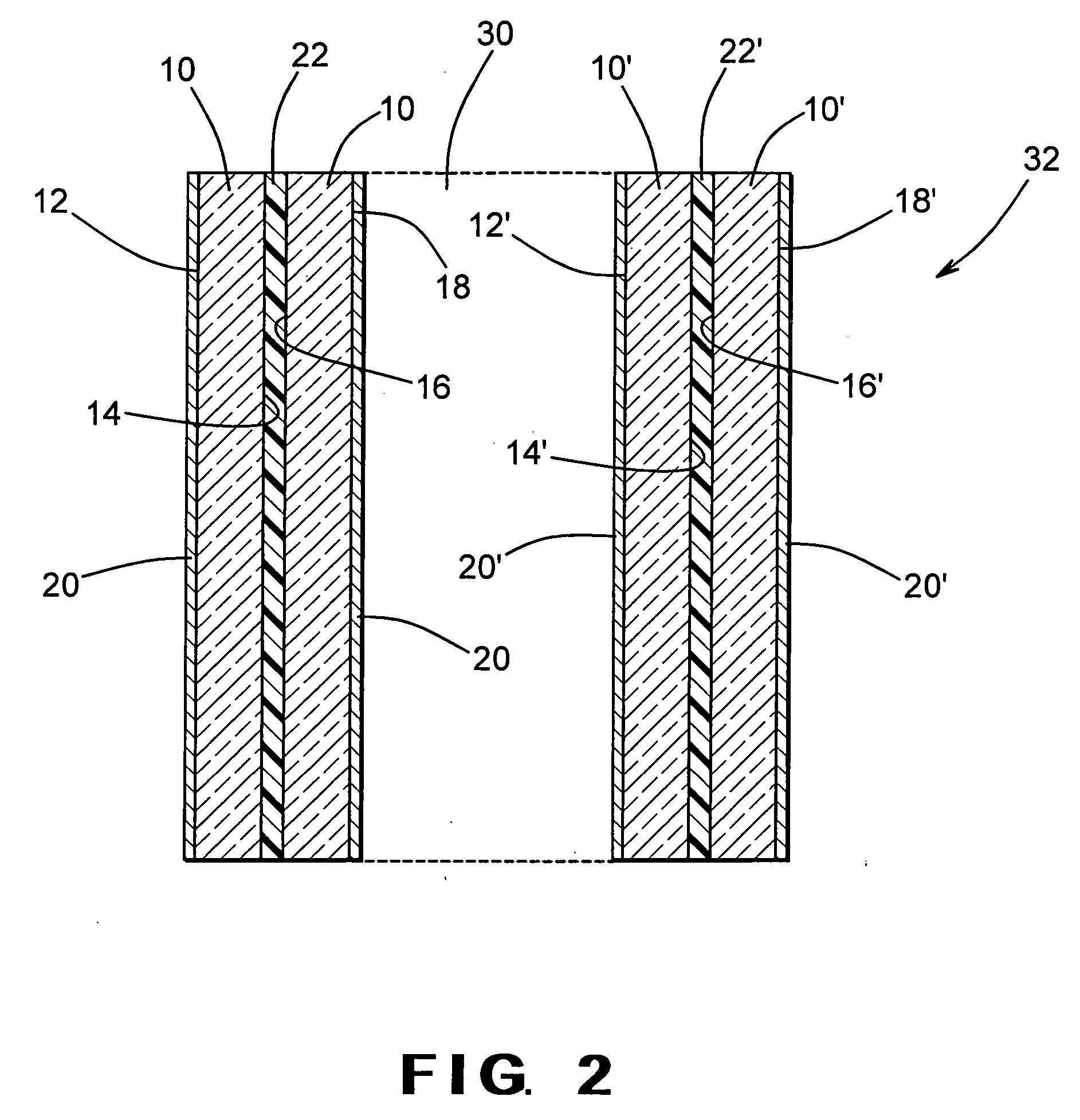
The present invention provides an anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer and two compatible oxide etch processes. The Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer can be used as a hard mask in a dual damascene structure and as a hard mask for over a polysilicone gate. The invention has the following key elements: 1) Si rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) ARC layer, 2) Special Silicon oxide Etch process that has a high selectivity of Si-Rich SiON to silicon oxide or SiN; 3) Special Si Rich SiON spacer process for a self aligned contact (SAC).A dual damascene structure is formed by depositing a first dielectric layer. A novel anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer is deposited on top of the first dielectric layer. A first opening is etched in the first insulating layer. A second dielectric layer is deposited on the anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer. A second dual damascene opening is etched into the dielectric layers. The anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynnitride (SiON) etch barrier layer can also serve as an ARC layer during these operations to reduce the amount of reflectance from conductive region to reduce distortion of the photoresist pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Thin Films and Methods of Making Them
InactiveUS20020197831A1Increase productionImprove device yieldTransistorMaterial nanotechnologyAnti-reflective coatingSilicon membrane
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> Thin, smooth silicon-containing films are prepared by deposition methods that utilize a silicon-containing precursor. In preferred embodiments, the methods result in Si-containing films that are continuous and have a thickness of about 150 Åor less, a surface roughness of about 5 Å rms or less, and a thickness non-uniformity of about 20% or less. Preferred silicon-containing films display a high degree of compositional uniformity when doped or alloyed with other elements. Preferred deposition methods provide improved manufacturing efficiency and can be used to make various useful structures such as wetting layers, HSG silicon, quantum dots, dielectric layers, anti-reflective coatings (ARC s), gate electrodes and diffusion sources.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Fluoropolymer coating compositions with olefinic silanes for anti-reflective polymer films
InactiveUS20060147177A1Low compositionIncreased durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistrySilanesRefractive index
An economic, optically transmissive, stain and ink repellent, durable low refractive index fluoropolymer composition for use in an antireflection film or coupled to an optical display. In one aspect of the invention, the composition is formed from the reaction product of a fluoropolymer, a C═C double bond group containing silane ester agent, and an optional multi-olefinic crosslinker. In another aspect of the invention, the composition further includes surface modified inorganic nanoparticles. In another aspect, the multi-olefinic crosslinker is an alkoxysilyl-containing multi-olefinic crosslinker.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
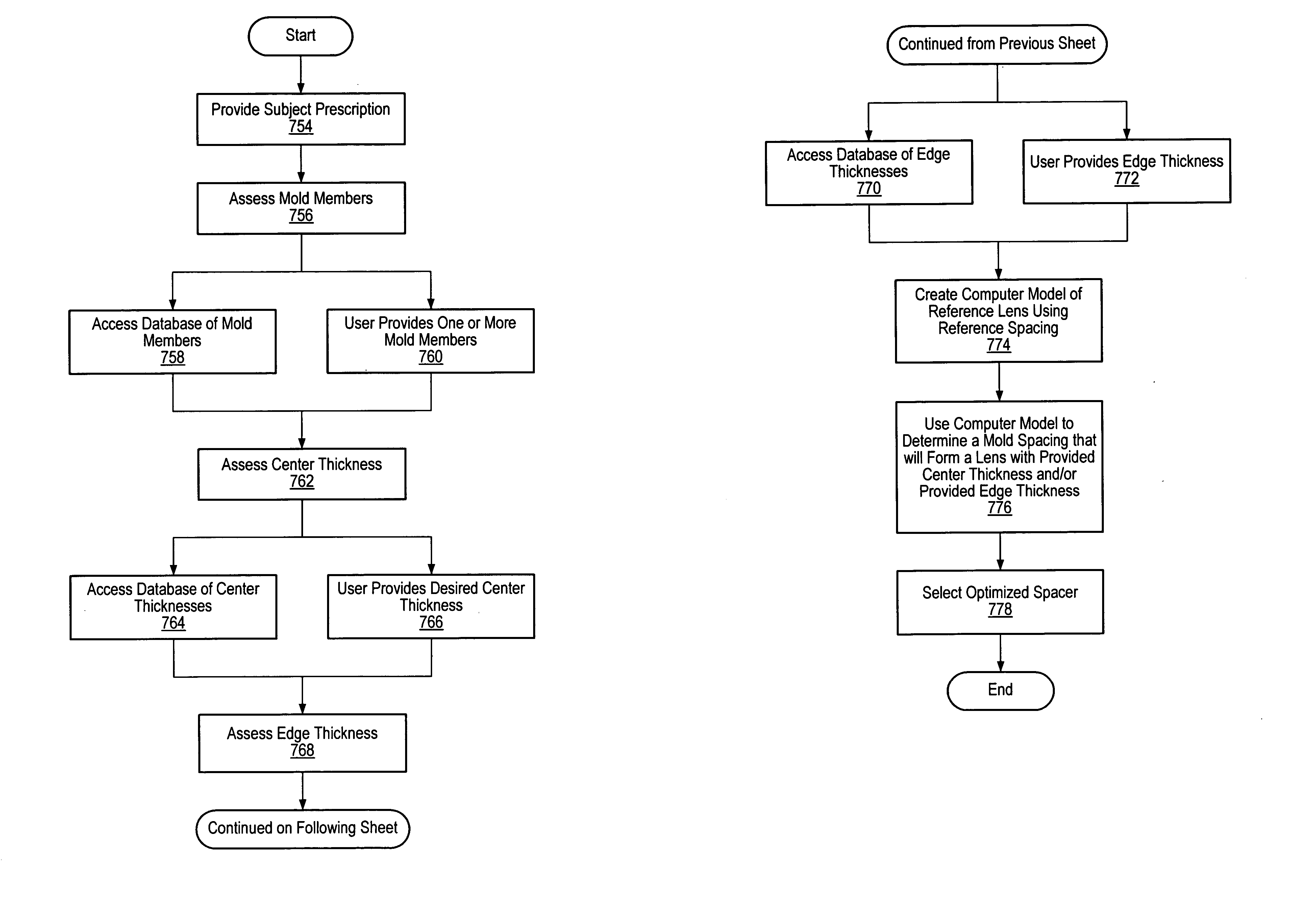
Lens forming systems and methods
Described herein are methods and systems for forming lenses. In one embodiment, systems for use in forming eyeglass lenses are described that include one or more LED lights. The LED lights may be used to cure lens forming compositions and coating compositions. In other embodiments, methods of determining an appropriate spacing for mold members are described. In other embodiments, methods of forming anti-reflective coatings, photochromic coatings, hardcoat coatings, and combinations thereof, on eyeglass lenses, are described.
Owner:VISION DYNAMICS
Process for defining a pattern using an anti-reflective coating and structure therefor
InactiveUS6030541ADecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingPhotoresist
A pattern in a surface is defined by providing on the surface a hard mask material; depositing an anti-reflective coating on the hard mask material; applying a photoresist layer on the anti-reflective coating; patterning the photoresist layer, anti-reflective layer and hard mask material; and removing the remaining portions of the photoresist layer and anti-reflective layer; and then patterning the substrate using the hard mask as the mask. Also provided is a structure for defining a pattern in a surface which comprises a surface having a hard mask material thereon; an anti-reflective coating located on the hard mask material; and a photoresist located on the anti-reflective coating. Also provided is an etchant composition for removing the hard mask material which comprises an aqueous composition of HF and chlorine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Spatial light modulator with integrated optical compensation structure
A spatial light modulator comprises an integrated optical compensation structure, e.g., an optical compensation structure arranged between a substrate and a plurality of individually addressable light-modulating elements, or an optical compensation structure located on the opposite side of the light-modulating elements from the substrate. The individually addressable light-modulating elements are configured to modulate light transmitted through or reflected from the transparent substrate. Methods for making such spatial light modulators involve fabricating an optical compensation structure over a substrate and fabricating a plurality of individually addressable light-modulating elements over the optical compensation structure. The optical compensation structure may be a passive optical compensation structure. The optical compensation structure may include one or more of a supplemental frontlighting source, a diffuser, a black mask, a diffractive optical element, a color filter, an anti-reflective layer, a structure that scatters light, a microlens array, and a holographic film.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Filter for displaying, display unit and production method therefor
InactiveUS20030156080A1High color purityGood colorMagnetic/electric field screeningStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceCopper foil
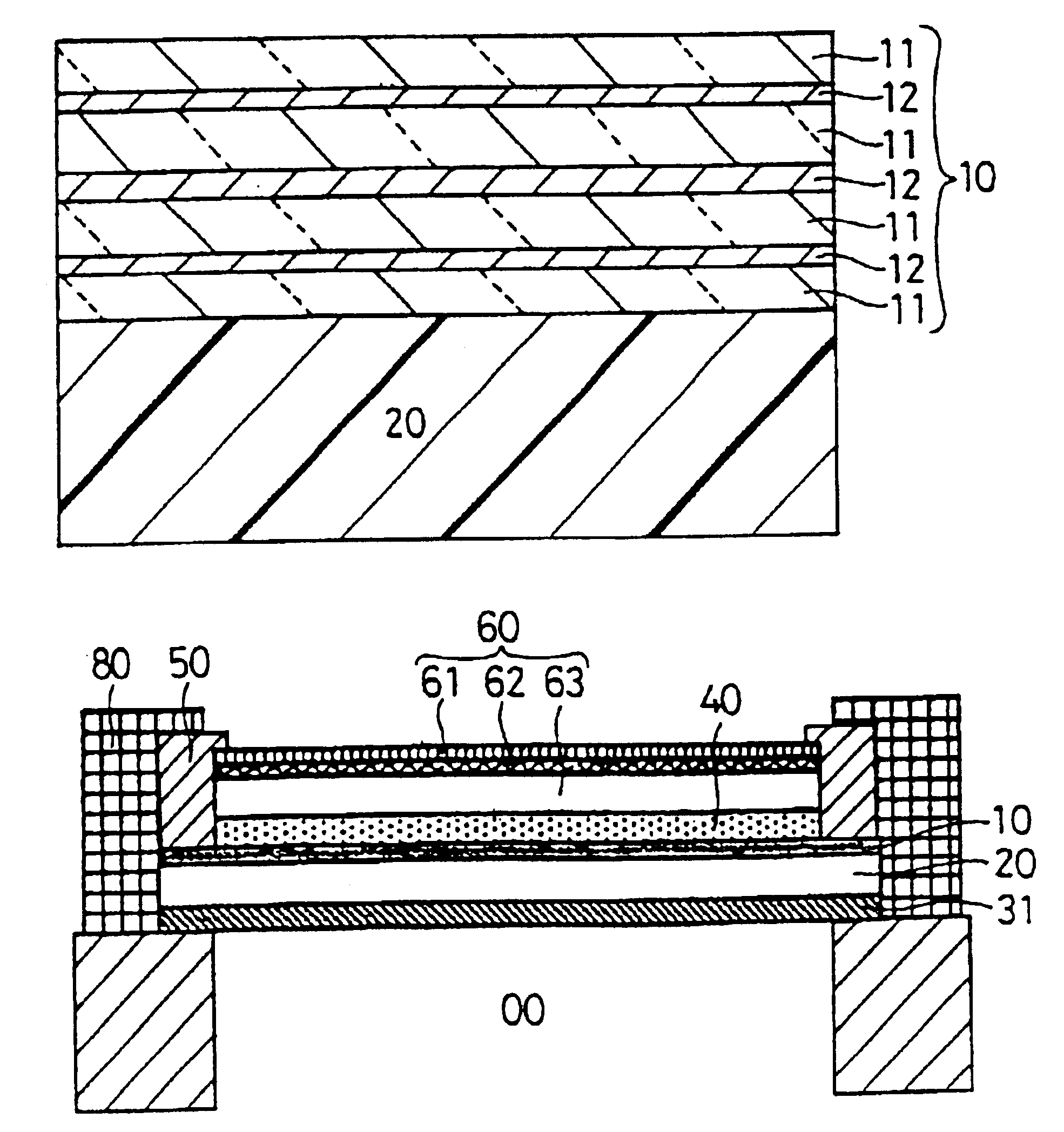
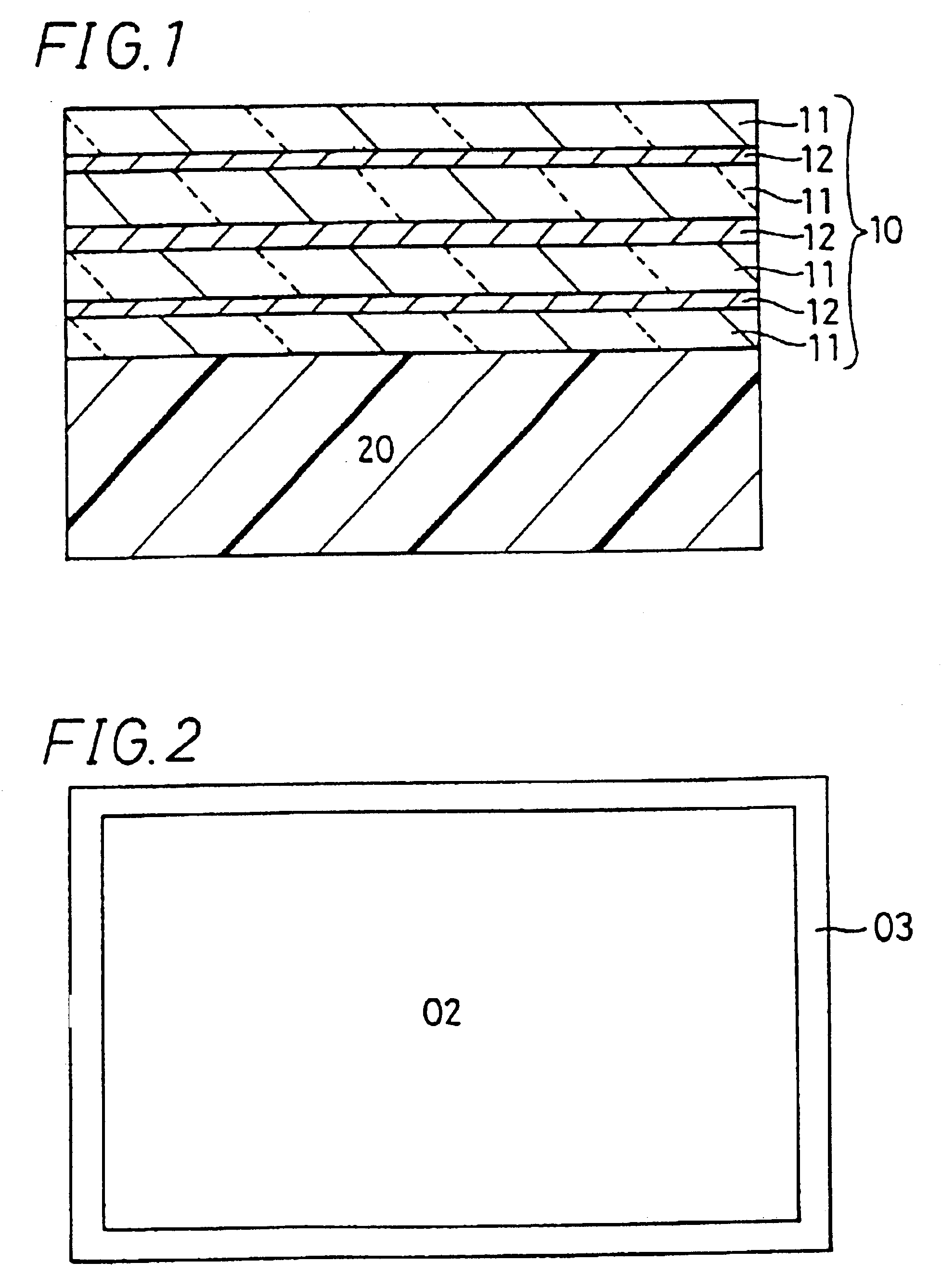
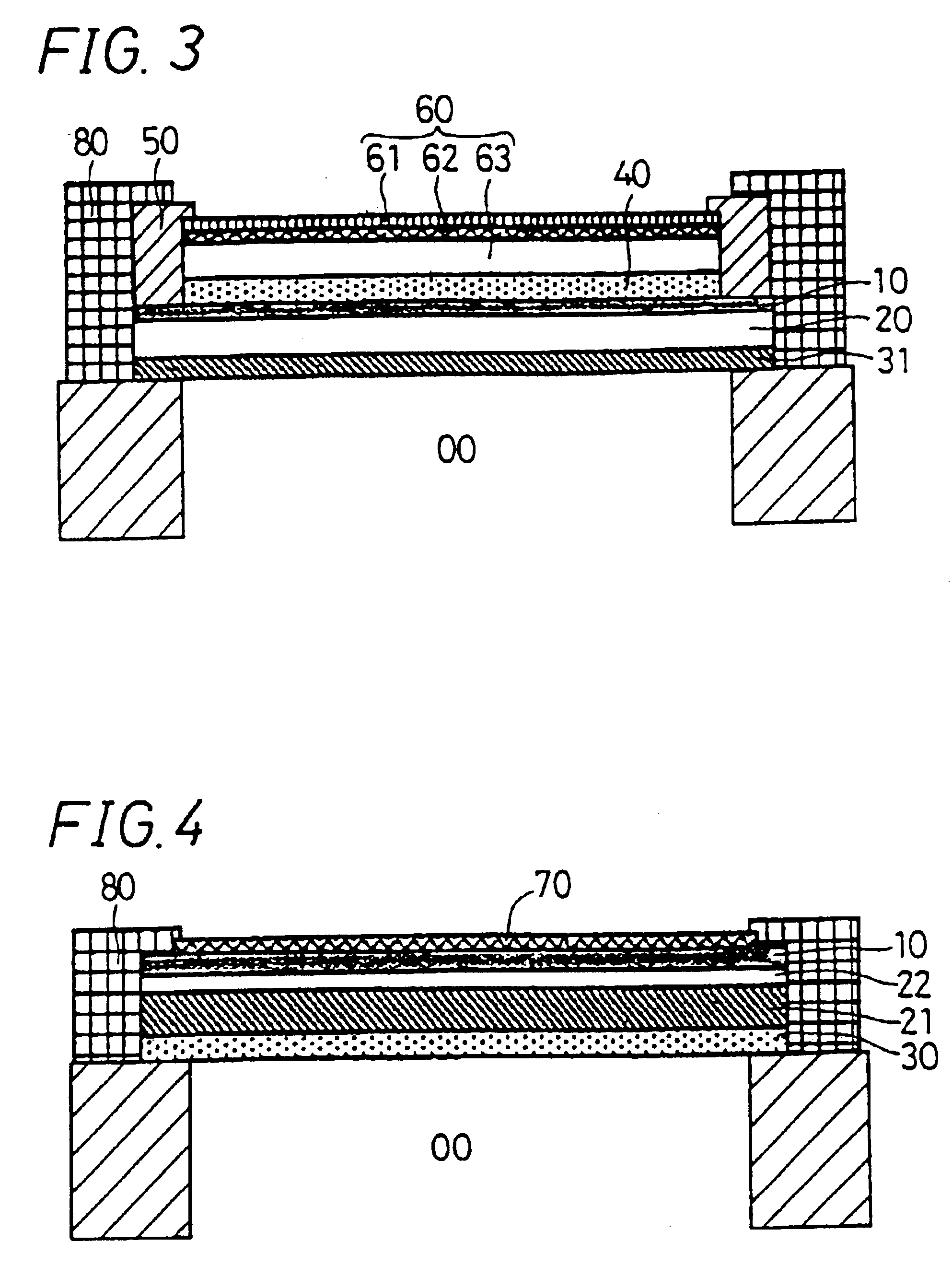
The display filter is constituted by laminating a transparent adhesive layer (C) 31 containing dye, a polymer film (B) 20, a transparent electrically conductive layer (D) 10, a transparent adhesive layer (E) 40, and a functional transparent layer (A) 60 having an anti-reflection property, a hard coat property, a gas barrier property, an antistatic property and an anti-fouling property sequentially in this order, adhered on a display area 00; on this occasion, the transparent electrically conductive layer (D) 10 is grounded to a ground terminal of the display via an electrode 50 and an electrically conductive copper foil adhesive tape 80.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Spatial light modulator with integrated optical compensation structure
A spatial light modulator comprises an integrated optical compensation structure, e.g., an optical compensation structure arranged between a substrate and a plurality of individually addressable light-modulating elements, or an optical compensation structure located on the opposite side of the light-modulating elements from the substrate. The individually addressable light-modulating elements are configured to modulate light transmitted through or reflected from the transparent substrate. Methods for making such spatial light modulators involve fabricating an optical compensation structure over a substrate and fabricating a plurality of individually addressable light-modulating elements over the optical compensation structure. The optical compensation structure may be a passive optical compensation structure. The optical compensation structure may include one or more of a supplemental frontlighting source, a diffuser, a black mask, a diffractive optical element, a color filter, an anti-reflective layer, a structure that scatters light, a microlens array, and a holographic film.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
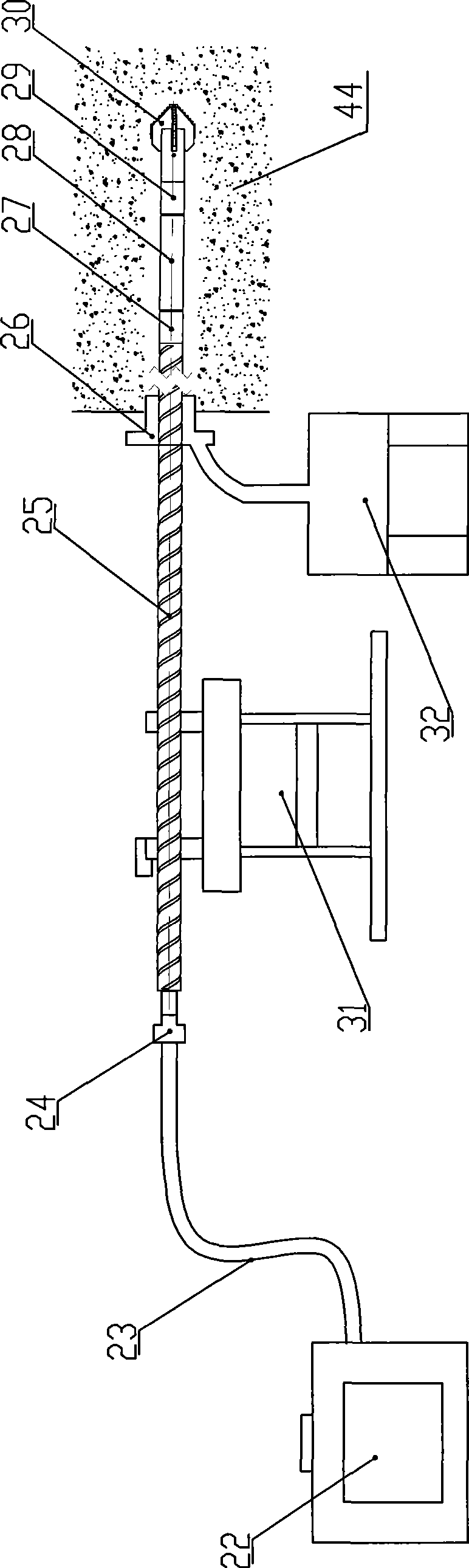
In-hole drilling tool integrating drilling, slotting and punching coal seam and using method thereof
InactiveCN101532391AGuaranteed cleanlinessAvoid enteringDrill bitsLiquid/gas jet drillingHigh pressure waterHigh pressure
The invention discloses an in-hole drilling tool integrating drilling, slotting and punching a coal seam and a using method thereof. The in-hole drilling tool comprises a water supple device or an air supple device, a high-pressure sealing drill pipe, a slotting and punching valve and a drill bit. The water supply device and the air supply device are connected with the high-pressure sealing drill pipe at an orifice. The slotting and punching valve is installed between the high-pressure sealing drill pipe and the drill bit. The in-hole drilling tool is essentially used for drilling and anti-reflective outburst eliminating after drilling of soft outburst coal seam. The using method is as follows: after the drilling construction is finished, a water supplier with a pressure release valve is used for starting a high-pressure pumping station to improve the pressure and the flux for water supply; high-pressure water current at the pumping station drives the slotting and punching valve to act for closing an axial liquid passage and opening a radial liquid passage; and high-pressure jet current realizes slotting or punching through a cutting nozzle or a punching nozzle. The invention has novel design and easy operation, is safe and reliable, improves the outburst elimination efficiency and realizes the integrated operation of drilling, slotting or punching and outburst eliminating.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
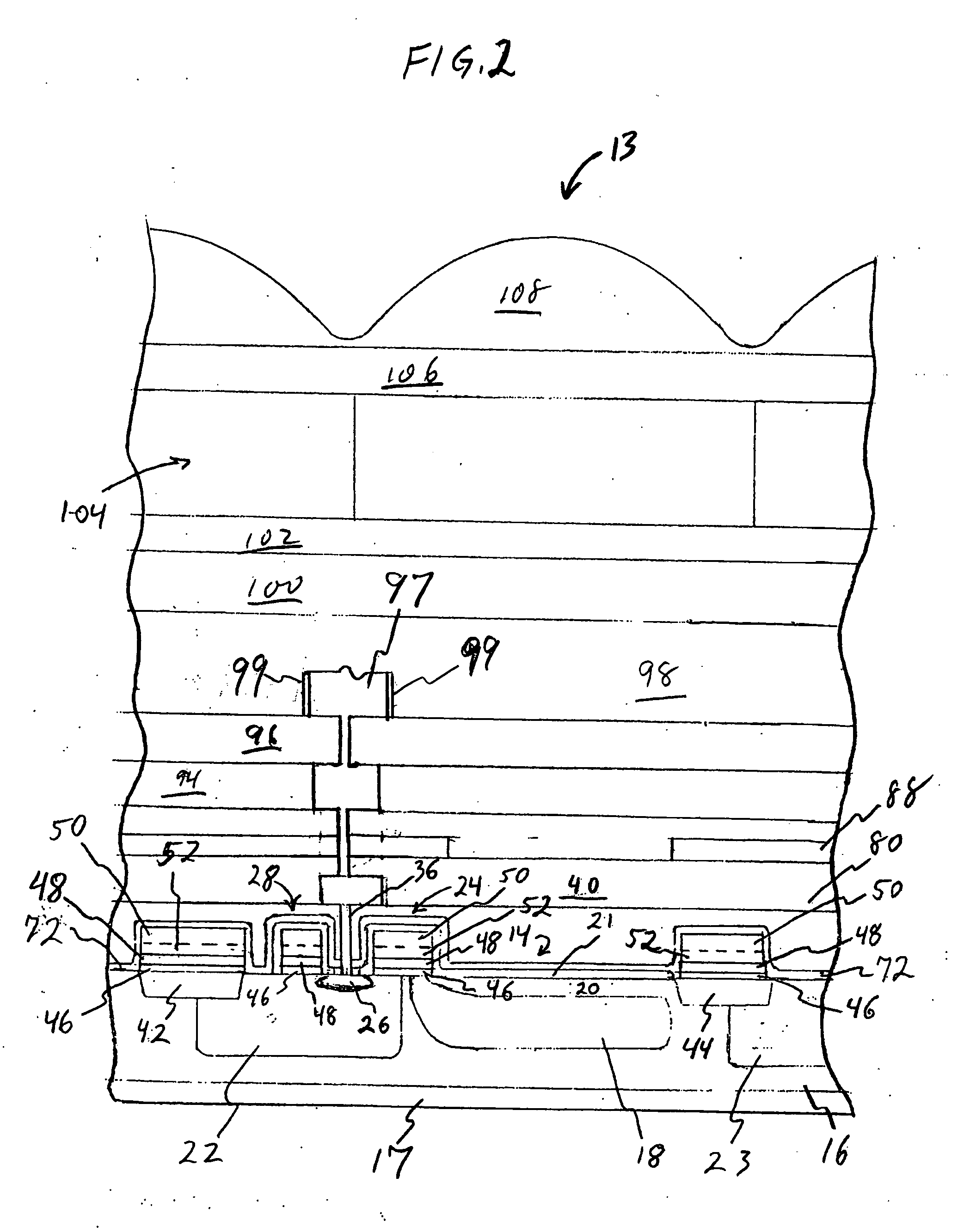
Resistive touch panel using removable, tensioned top layer
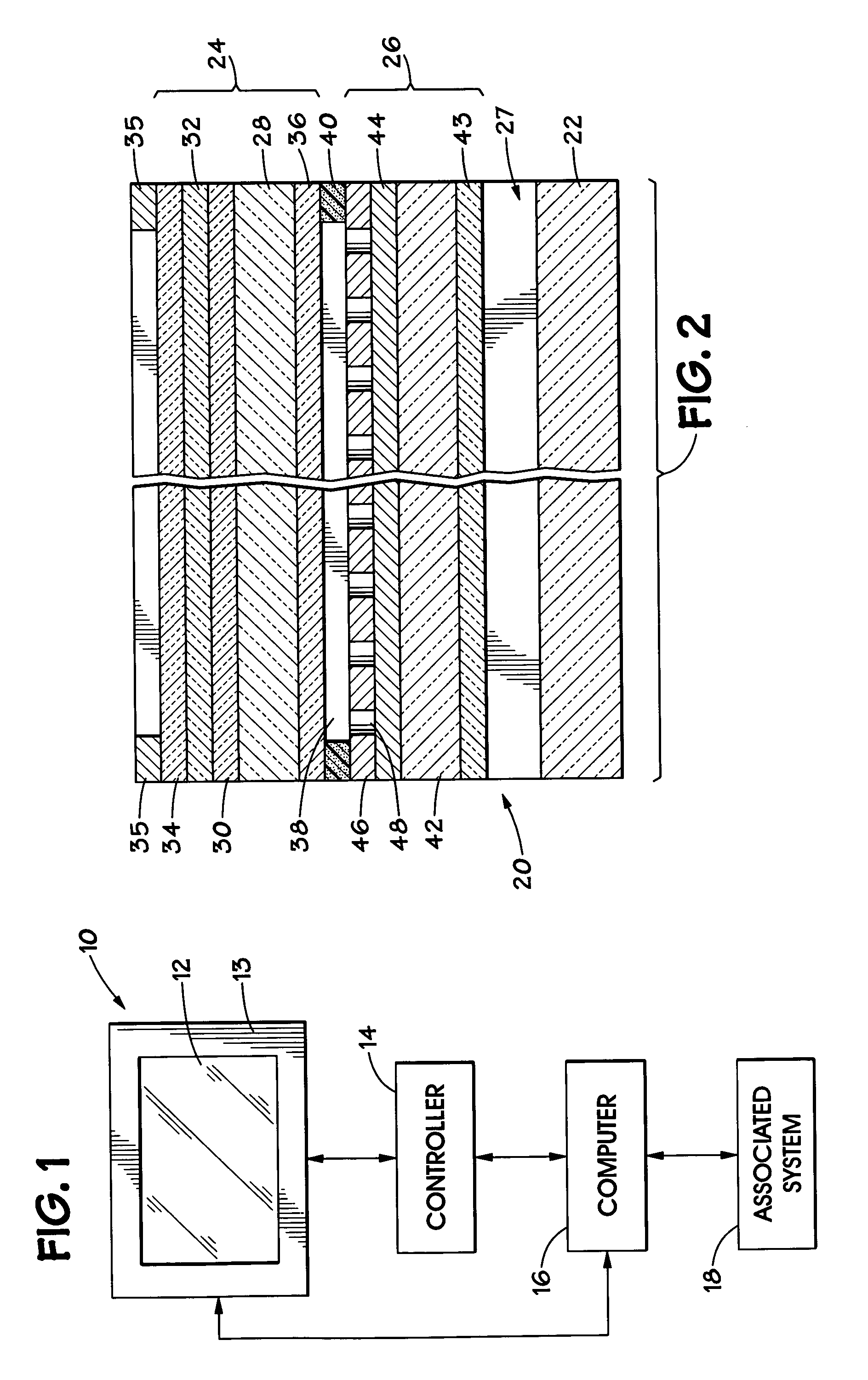
Sunlight can damage a conventional touch screen display and cause the display to be quite difficult to read. Furthermore, conventional touch screen displays are easily damaged, and, once damaged, the entire touch screen is replaced. To address these concerns, a touch panel includes anti-reflective coatings on the surfaces of the top plate and the base plate that are open to the air. These coatings substantially reduce reflections and make the touch screen easier to read in direct sunlight. In particular, the anti-reflective coating used on the upper surface of the base plate is dielectric in nature to reduce reflectivity even further. This dielectric coating includes openings to an underlying conductive layer so that an electrical contact is made when a user deflects the top plate into the base plate. Also, the top plate may be detachably coupled to the base plate, advantageously by double stick adhesive tape, so that only the top plate is replaced when damaged. In one embodiment, the top plate is placed in tension within a frame to prevent wrinkling. Furthermore, a resistive voltage divider may be fabricated on the base plate. The resistive voltage divider may include a substantially continuous strip of resistive material disposed on the conductive layer of the base plate, and a plurality of conductive traces disposed on the dielectric layer of the base plate and coupled to the resistive material in selected locations.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Composition and process for post-etch removal of photoresist and/or sacrificial anti-reflective material deposited on a substrate
ActiveUS20050197265A1Cationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAnti-reflective coatingPhotoresist
A composition and process for removing photoresist and / or sacrificial anti-reflective coating (SARC) materials from a substrate having such material(s) thereon. The composition includes a base component, such as a quaternary ammonium base in combination with an alkali or alkaline earth base, or alternatively a strong base in combination with an oxidant. The composition may be utilized in aqueous medium, e.g., with chelator, surfactant, and / or co-solvent species, to achieve high-efficiency removal of photoresist and / or SARC materials in the manufacture of integrated circuitry, without adverse effect on metal species on the substrate, such as copper, aluminum and / or cobalt alloys, and without damage to SiOC-based dielectric materials employed in the semiconductor architecture.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Display filter, display apparatus, and method for production of the same
InactiveUS6965191B2Cathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersDisplay deviceEngineering
The display filter is constituted by laminating a transparent adhesive layer (C) 31 containing dye, a polymer film (B) 20, a transparent electrically conductive layer (D) 10, a transparent adhesive layer (E) 40, and a functional transparent layer (A) 60 having an anti-reflection property, a hard coat property, a gas barrier property, an antistatic property and an anti-fouling property sequentially in this order, adhered on a display area 00; on this occasion, the transparent electrically conductive layer (D) 10 is grounded to a ground terminal of the display via an electrode 50 and an electrically conductive copper foil adhesive tape 80.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
High density plasma CVD process for making dielectric anti-reflective coatings
InactiveUS6060132ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesResistAnti-reflective coating
An improved process for preparing nitrogen containing substrates selected from the group consisting of silicon oxynitride, silicon nitride and titanium nitride films and silicon dioxide cap films characterized by prevent resist contamination when used as dielectric anti-reflective coatings, using a high density plasma CVD system, comprising: providing a processing chamber holding a wafer in a vacuum sufficient to enable O2 to be used as an oxygen source without risk of explosion in a plasma generating region of the processing chamber; introducing a gaseous mixture selected from the group consisting of SiH4 / O2 / N2 or SiH4 / O2 / N2 / Ar into the processing chamber; and subjecting the processing chamber to a RF electrical signal of sufficient frequency to create a high density plasma in the plasma generating region of said processing chamber, whereby said wafer is processed by resulting high density plasma generated by said RF electrical signal.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Method for constructing anti-reflection microstructure using single layer nanometer particle as etching blocking layer
InactiveCN101308219ASimple methodBase variableSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsSurface patternLight energy
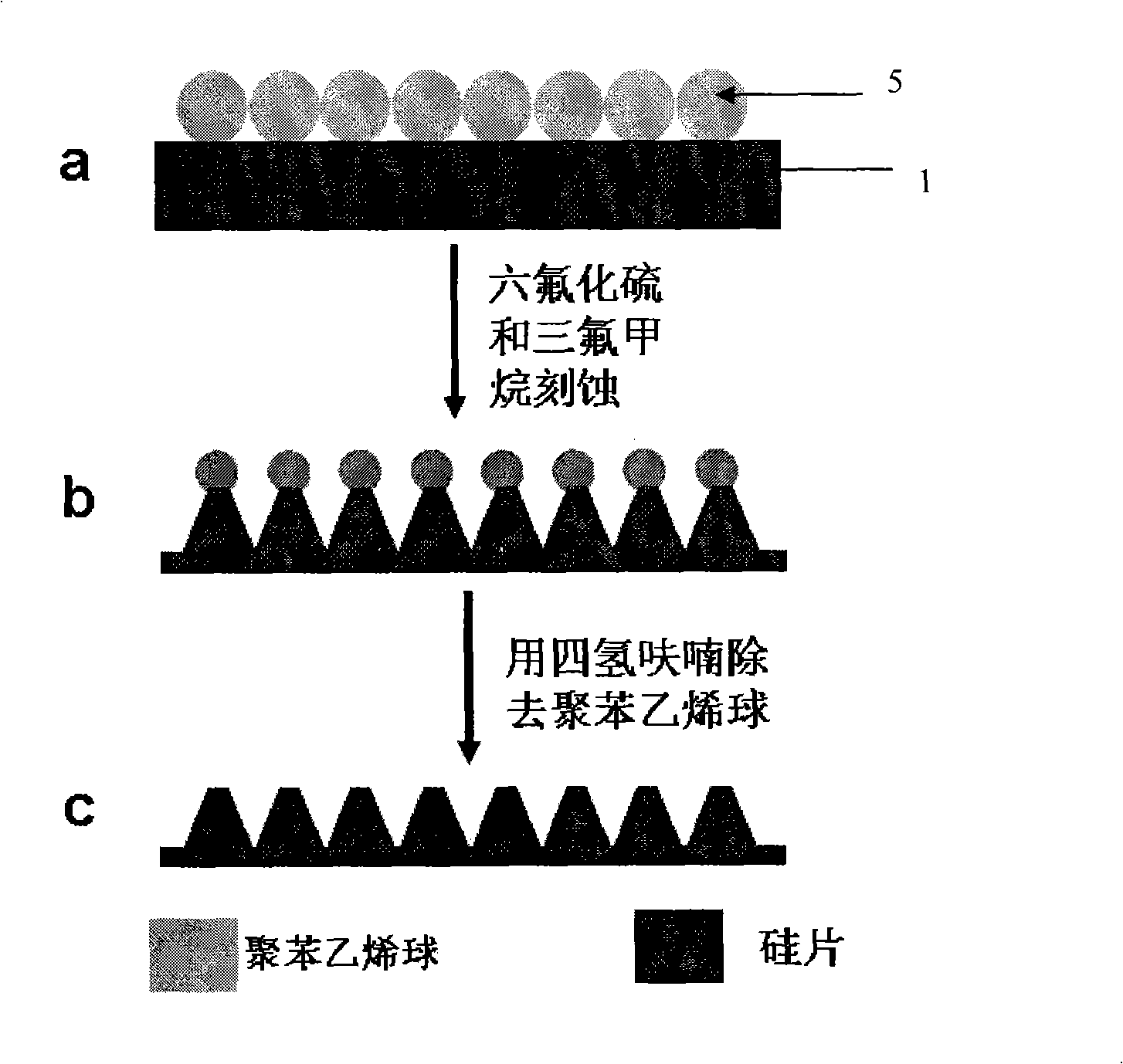
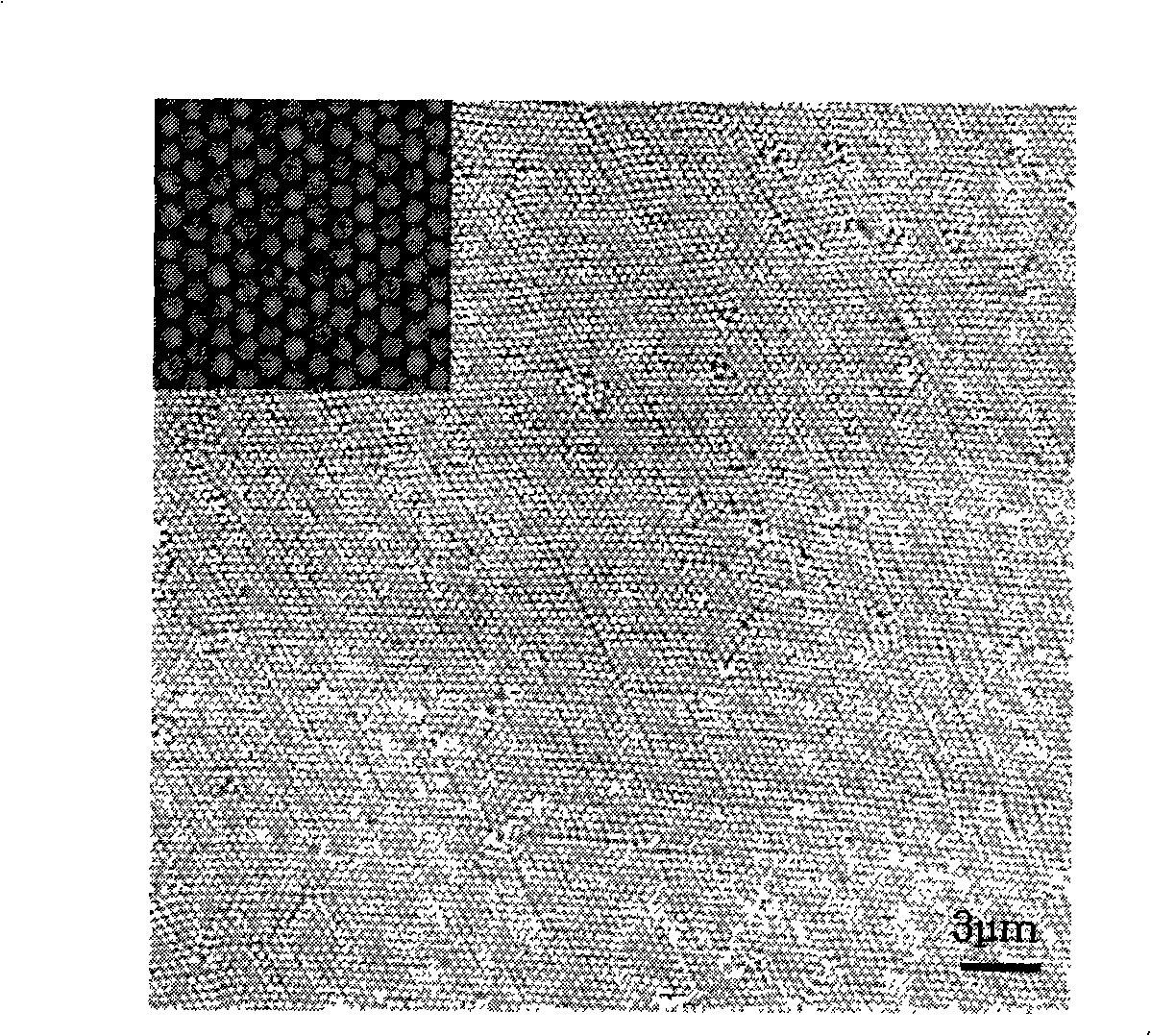
The invention belongs to the surface patterning microstructure construction technique, which relates to a method for constructing a microstructure with anti-reflection performance on a foundation base by combining the self-assembly technique with the reactive ion beam etching technique. The method is to take monolayer polymeric micro-spheres, silicon dioxide micro-spheres and nano-particles of metal or metal oxides as a barrier layer and implement the RIE etching to the foundation base, then an approximate cone-shaped microstructure is constructed on the foundation base, and the structure has extreme high anti-reflection performance, thereby effectively improving the light energy utilization rate, reducing the interference of veiling glare in an optical system, increasing the optical transmittance, and further improving the sensitivity and stability of the optical system, and the method can be used for constructing large-area anti-reflection structures. The method of the invention has advantages of simple operation, changeable foundation base, strong applicability, good repeatability, low cost, high efficiency, adjustable anti-reflective applied wavelength and conformity to industrialized standards, and can be used for making photoelectric devices such as solar batteries and white light sensors.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Anti-Reflective and Anti-Soiling Coatings with Self-Cleaning Properties
ActiveUS20120040179A1Evenly distributedUniform depositionLayered productsRecord information storageSoil propertiesSilanes
The embodiments of the invention are directed to coatings and their uses. More particularly, the embodiments of the invention are directed to coating compositions that include silane-based precursors that are used to form coatings through a sol-gel process. The coatings so formed are characterized by anti-reflective, abrasion resistant, and anti-soiling properties. The coatings also have extended weatherability to heat, humidity, and protection against ambient corrosives. The coatings formed from the compositions described herein have wide application, including, for example, use as coatings on the outer glass of solar cells.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Anti-reflective, thermally insulated glazing articles
A laminated glass unit having at least two sheets of glass separated and bonded by a polymeric interlayer material, and further having multi-layer thin film coatings on each of the unbonded surfaces of the at least two glass sheets, is disclosed. Two or more of such laminated glass units can be utilized in various configurations to form an insulated glass unit. The thin films deposited on the unbonded glass surfaces have anti-reflective, iridescence-suppressing and solar control properties when suitable configurations, materials and layer thicknesses are chosen. The laminated glass unit and insulated glass units of the invention exhibit an excellent combination of low visible light reflectance and thermal insulating properties.
Owner:PILKINGTON NORTH AMERICA INC
Method of decontaminating process chambers, methods of reducing defects in anti-reflective coatings, and resulting semiconductor structures
InactiveUS6670284B2Reduce the degree of distortionReduce exposureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnti-reflective coatingSemiconductor structure
A method for fabricating a substantially smooth-surfaced anti-reflective coating on a semiconductor device structure including generating a plasma from an inert gas in a process chamber in which the anti-reflective coating is to be deposited. The anti-reflective coating may include silicon, oxygen and nitrogen, and is preferably of the general formula Si.sub.x O.sub.y N.sub.z, where x equals 0.40 to 0.65, y equals 0.02 to 0.56 and z equals 0.05 to 0.33. Preferably, x+y+z equals one. The method may also include fabricating a silicon nitride layer over the anti-reflective coating. A semiconductor device which includes a silicon nitride layer over the anti-reflective coating has a density of less than about 40,000 particles or surface roughness features in the silicon nitride of about 120-150 nanometers dimension per eight inch wafer. Accordingly, a mask that is subsequently formed over the silicon nitride layer has a substantially uniform thickness and is substantially distortion-free.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Remover compositions for dual damascene system
InactiveUS20050266683A1Avoid corrosionAvoid inhibitionNon-surface-active detergent compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricAnti-reflective coating
A new remover chemistry based on a choline compound, such as choline hydroxide, is provided in order to address problems related to removal of residues, modified photoresists, photoresists, and polymers such as organic anti-reflective coatings and gap-fill and sacrificial polymers from surfaces involved in dual damascene structures without damaging the dielectrics and substrates involved therein. An etch stop inorganic layer at the bottom of a dual damascene structure may or may not be used to cover the underlying interconnect of copper. If not used, a process step of removing that protective layer can be avoided through a timed etch of the via in trench-first dual damascene processes.
Owner:EKC TECH
Low-power eyewear for reducing symptoms of computer vision syndrome
Computer eyewear for reducing the effects of Computer Vision Syndrome (CVS). In one embodiment, the eyewear comprises a frame and two lenses. In some embodiments, the frame and lenses have a wrap-around design to reduce air flow in the vicinity of the eyes. The lenses can have optical power in the range from about +0.1 to +0.25 diopters, or from about +0.125 to +0.25 diopters, for reducing accommodation demands on a user's eyes when using a computer. The lenses can also include prismatic power for reducing convergence demand on a user's eyes when sitting at a computer. The lenses can also include a partially transmissive mirror coating, tinting, and anti-reflective coatings. In one embodiment, a partially transmissive mirror coating or tinting spectrally filters light to remove spectral peaks in fluorescent or incandescent lighting.
Owner:GUNNAR OPTIKS LLC
Spin-on anti-reflective coatings for photolithography
Anti-reflective coating materials for ultraviolet photolithography include at least one absorbing compounds and at least one pH tuning agent that are incorporated into spin-on materials. Suitable absorbing compounds are those that absorb around wavelengths such as 365 nm, 248 nm, 193 nm and 157 nm that may be used in photolithography. Suitable pH tuning agents not only adjust the pH of the final spin-on composition, but also influence the chemical performance and characteristics, mechanical performance and structural makeup of the final spin-on composition that is part of the layered material, electronic component or semiconductor component, such that the final spin-on composition is more compatible with the resist material that is coupled to it. More specifically, the pH tuning agent strong influences the polymeric characteristics, the structural makeup and the spatial orientation that results in increasing the surface properties of the anti-reflective coating for optimal resist performance. In other words, a pH tuning agent that merely adjusts the pH of the spin-on material without influencing the mechanical properties and structural makeup of the spin-on composition or the coupled resist material is not contemplated herein. A method of making absorbing and pH tuned spin-on materials includes combining at least one organic absorbing compound and at least one pH tuning agent with at least one silane reactant during synthesis of the spin-on materials and compositions.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
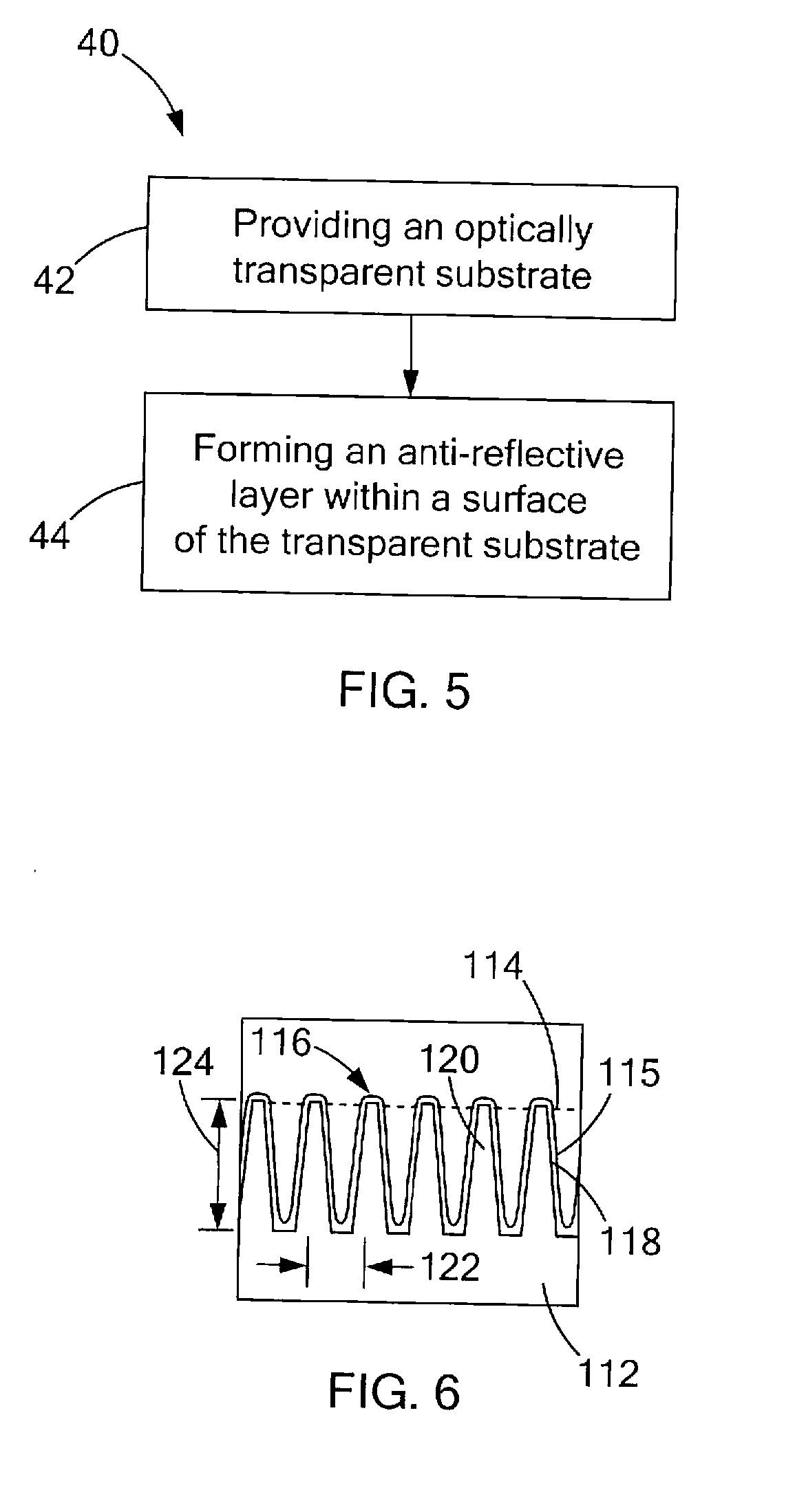
Transparent Anti-reflective article and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS20090231714A1Minimize light diffractionSimilar shapeElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNano structuringRefractive index
A transparent anti-reflective article includes a transparent substrate having a first refractive index and a first surface. An anti-reflective layer is formed within the first surface of the transparent substrate through use of one of nanosphere lithography, deep ultra-violet photolithography, electron beam lithography, and nano-imprinting. The anti-reflective layer includes a subwavelength nano-structured second surface including a plurality of protuberances. Such protuberances have a predetermined maximum distance between adjacent protuberances and a predetermined height for a given wavelength such that the anti-reflective layer includes a second refractive index lower than the first refractive index to minimize light diffraction and random scattering therethrough. The predetermined height is approximately equal to a quarter of the given wavelength divided by the second refractive index.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
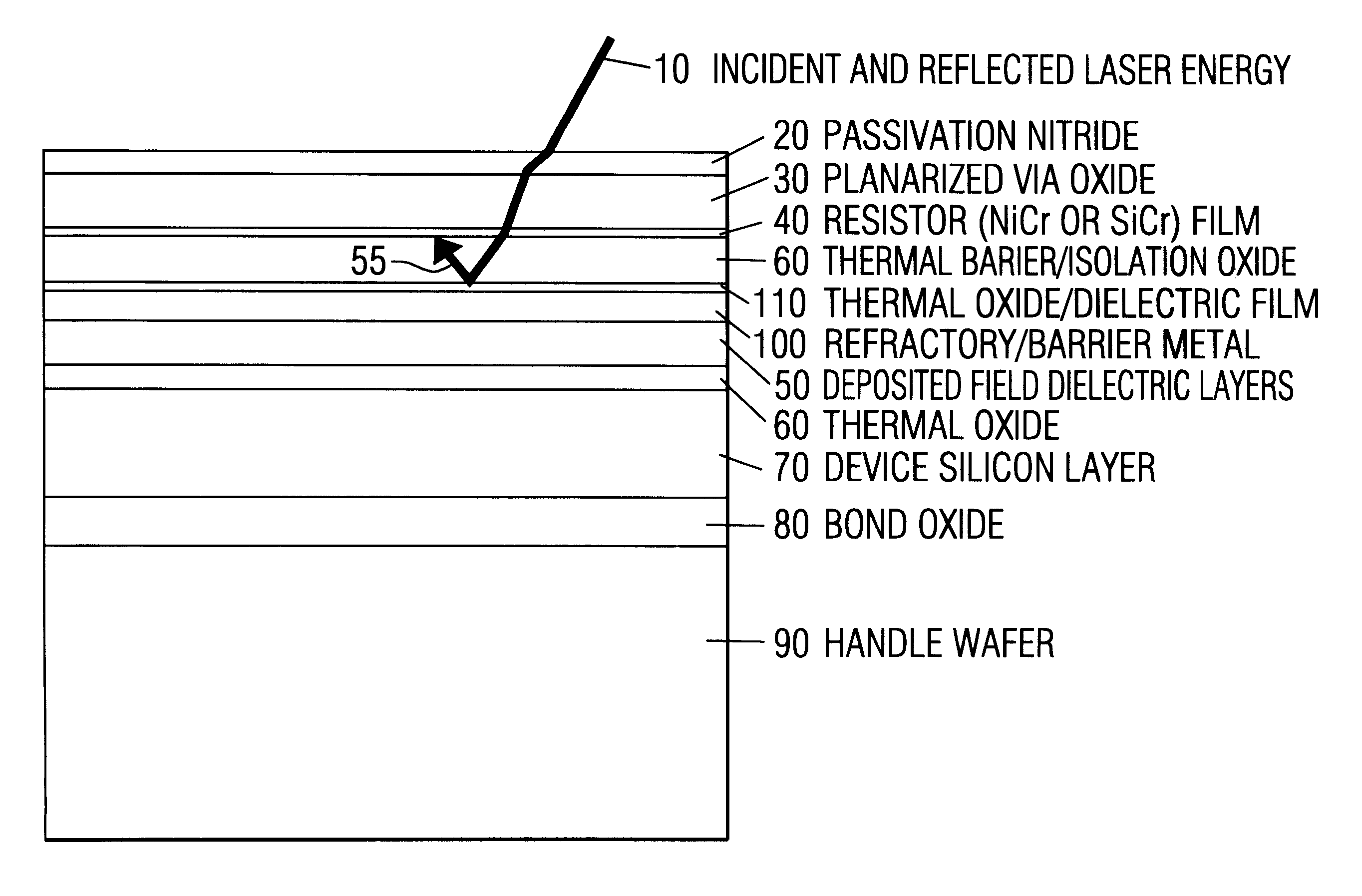
Use of barrier refractive or anti-reflective layer to improve laser trim characteristics of thin film resistors
InactiveUS6259151B1Reducing inaccuracy behaviorOptical wave guidanceSolid-state devicesTitaniumReflective layer
A precision resistor of NiCr or SiCr has a refractive and thermal barrier layer beneath the resistor. The refractive barrier is a layer of refractory metal. The refractory metal prevents the incident laser beam of a laser trimmer penetrating lower layers of the device. Unwanted reflections and refractions caused by lower layers are avoided. The reflective barrier layer is a material selected from the group consisting of tungsten, titanium, molybdenum, TiSi2l3,14, CoSi215, MoSi2, TaSi2 and WSi2.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Coating composition, coating film thereof, antireflection coating, antireflection film, image display, and intermediate product
InactiveUS20030096102A1Good dispersibilityGood dispersionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsMetallurgyRefractive index
A coating material capable of forming a high-quality thin film having a regulated refractive index; a coating film formed from the coating material; an antireflection coating comprising the coating film; an antireflection film to which the antireflection coating is applied; and an image display. The coating composition comprises (1) rutile-form titanium oxide having primary particle diameter of 0.01 to 0.1 mum and coated with an inorganic compound for reducing or eliminating the photocatalytic activity and with an organic compound having an anionic polar group and / or an organometallic compound, (2) a binder ingredient curable with an ionizing radiation, (3) a dispersant having an anionic polar group, and (4) an organic solvent. The coating film formed from the coating composition is suitable for forming a light-transmitting layer constituting or contained in a single- or multi-layer antireflection coating (17), in particular, a medium-refractive-index layer (18), high-refractive-index layer (19), or hard coat layer (16) having a high refractive index.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Index tuned antireflective coating using a nanostructured metamaterial
InactiveUS20090071537A1Reduce interfacial resistanceIncrease the effective surfaceDecorative surface effectsNanoopticsRefractive indexSolar cell
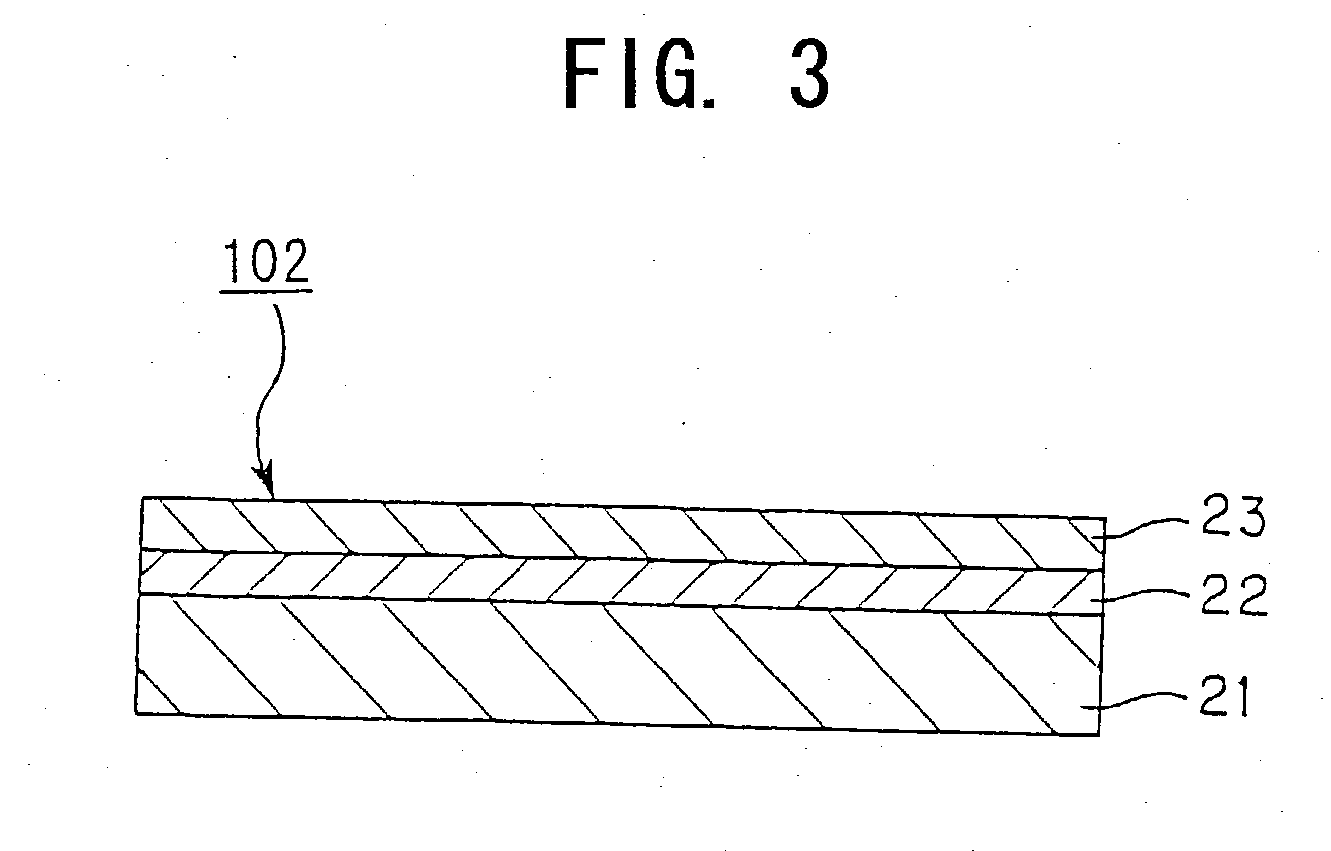
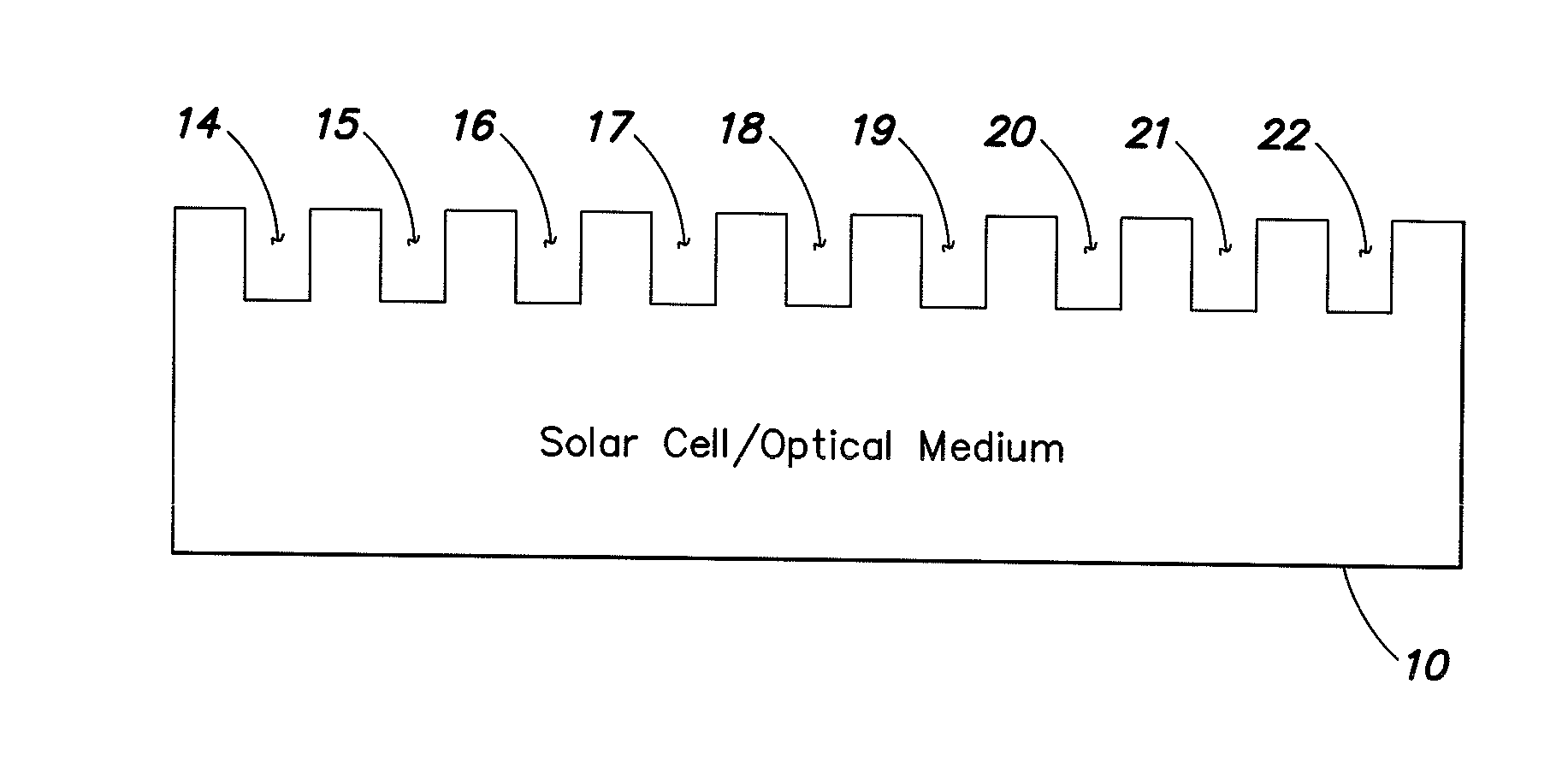
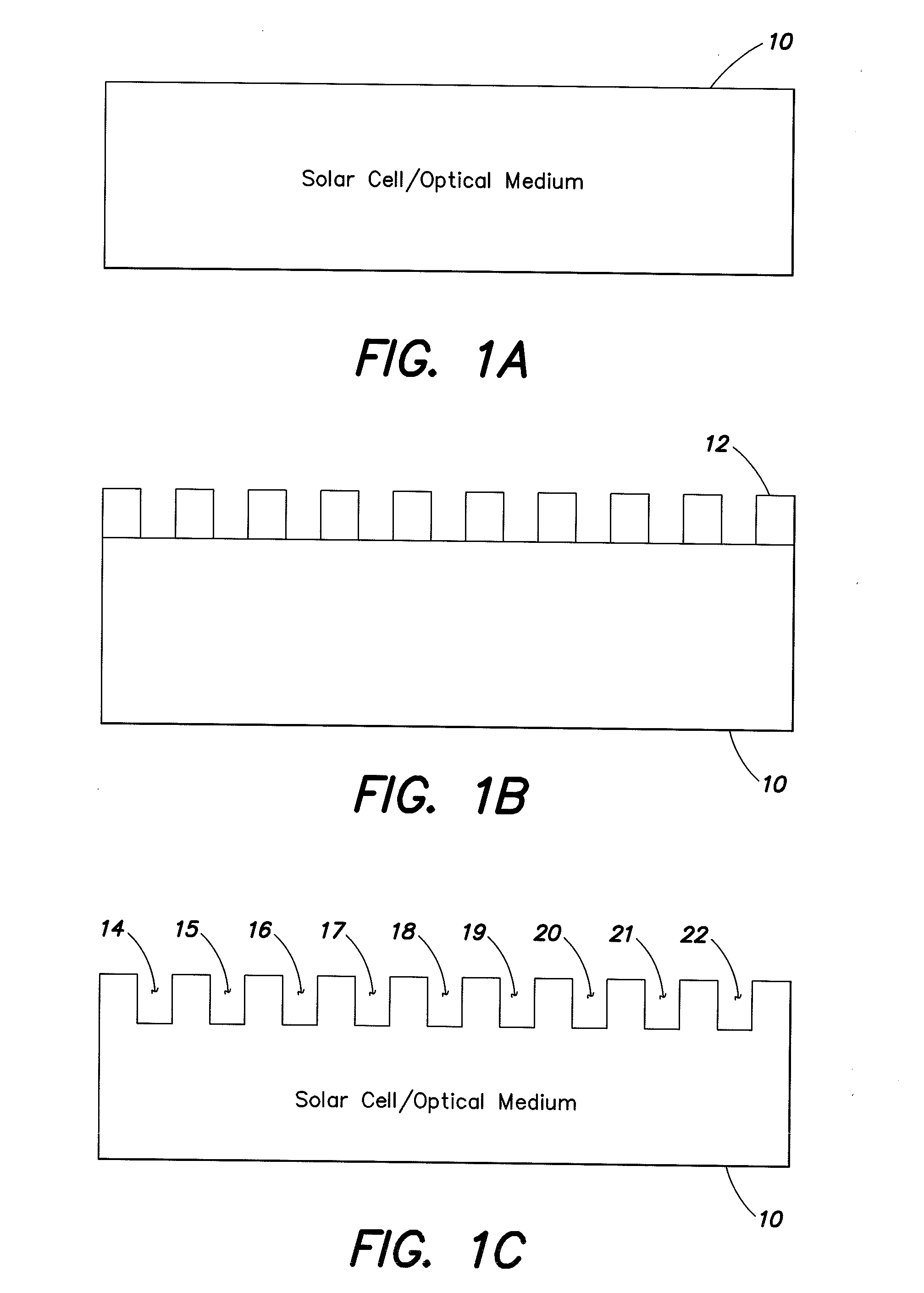
An anti-reflective layer solar cell / optical medium is provided by nanostructuring the surface of the optical material into which light transmission is desired. The surface of the optical material is etched through a nanoporous polymer film etch mask to transfer the porous pattern to the optical material. The resultant nanostructured layer is an optical metamaterial since it contains structural features much smaller than the wavelength of light and the presence of these structural features change the effective index of refraction by controlling the degree of porosity in the nanostructured layer and also by controlling the thickness of the porous layer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Anti-reflective coatings using vinyl ether crosslinkers
InactiveUS20070207406A1High percent solubilityReduce production processOrganic chemistrySilver halide emulsionsVinyl etherAnti-reflective coating
Novel, developer soluble anti-reflective coating compositions and methods of using those compositions are provided. The compositions comprise a polymer and / or oligomer having acid functional groups and dissolved in a solvent system along with a cross linker, a photoacid generator, and optionally a chromophore. The preferred acid functional group is a carboxylic acid, while the preferred crosslinker is a vinyl ether crosslinker. In use, the compositions are applied to a substrate and thermally crosslinked. Upon exposure to light (and optionally a post exposure bake), the cured compositions will decrosslink, rendering them soluble in typical photoresist developing solutions (e.g., alkaline developers). In one embodiment, the compositions can be used to form ion implant areas in microelectronic substrates.
Owner:BREWER SCI
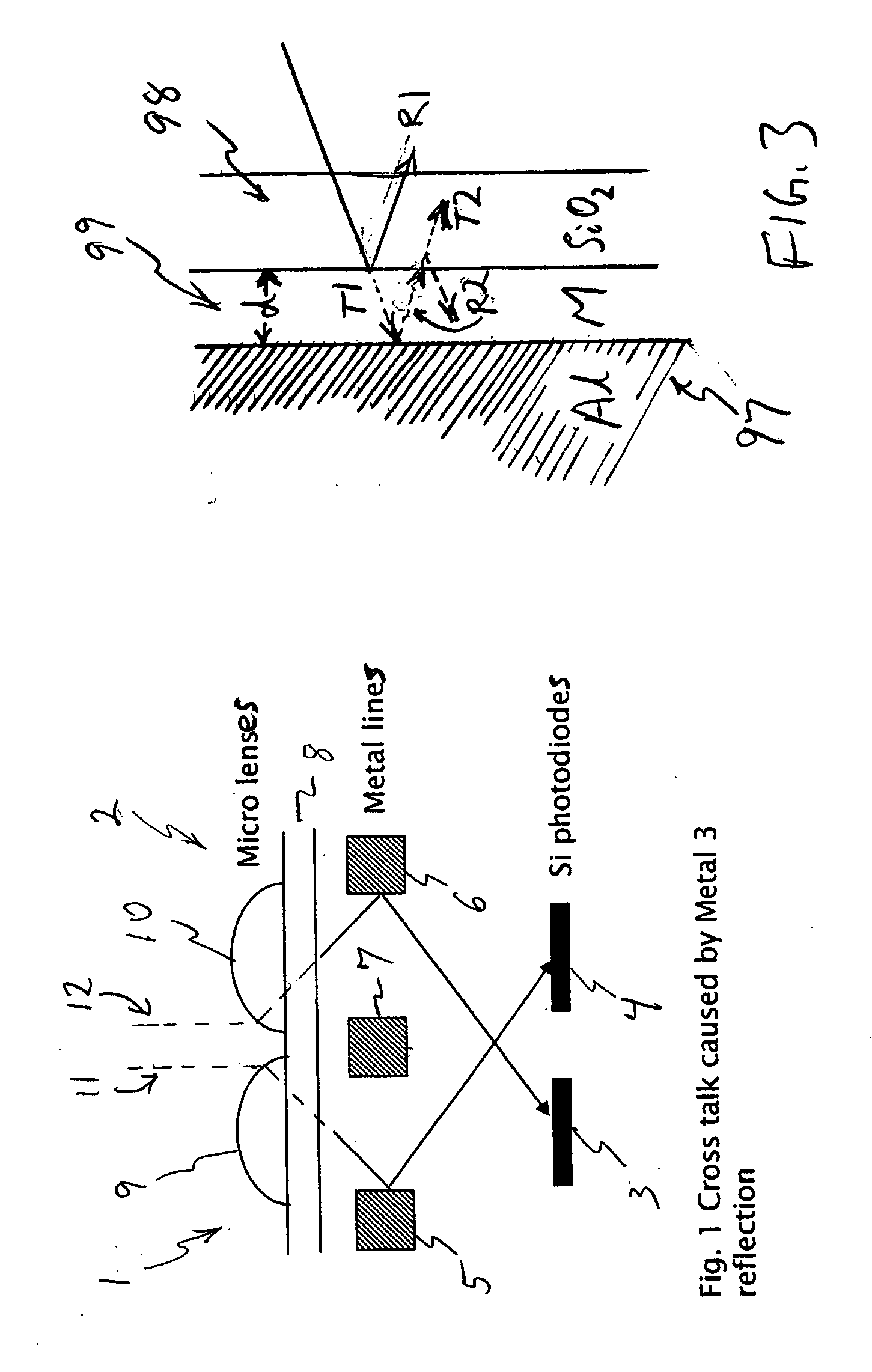
Solid-state imager and formation method using anti-reflective film for optical crosstalk reduction
InactiveUS20070045642A1Mitigate optical crosstalkSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesRefractive indexLight reflection
Conductive lines in an imaging device are coated with an anti-reflective film to reduce crosstalk caused by light reflecting from the conductive lines. An interface results between the anti-reflective film and the surface of the conductive line surface. A second interface exists between the anti-reflective film and an overlying insulating layer. The anti-reflective film is formed from a material having a complex refractive index such that reflectance is reduced at each of the two interfaces. The anti-reflective film also can be light absorbing to provide further reductions in light reflection and consequent crosstalk.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Resistive touch panel using removable, tensioned top layer
InactiveUS20040095332A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAnti-reflective coatingElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Metal catalyst technique for texturing silicon solar cells
InactiveUS6329296B1Improve throughputDiminish current extractionDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologySilicon solar cell
Textured silicon solar cells and techniques for their manufacture utilizing metal sources to catalyze formation of randomly distributed surface features such as nanoscale pyramidal and columnar structures. These structures include dimensions smaller than the wavelength of incident light, thereby resulting in a highly effective anti-reflective surface. According to the invention, metal sources present in a reactive ion etching chamber permit impurities (e.g. metal particles) to be introduced into a reactive ion etch plasma resulting in deposition of micro-masks on the surface of a substrate to be etched. Separate embodiments are disclosed including one in which the metal source includes one or more metal-coated substrates strategically positioned relative to the surface to be textured, and another in which the walls of the reaction chamber are pre-conditioned with a thin coating of metal catalyst material.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
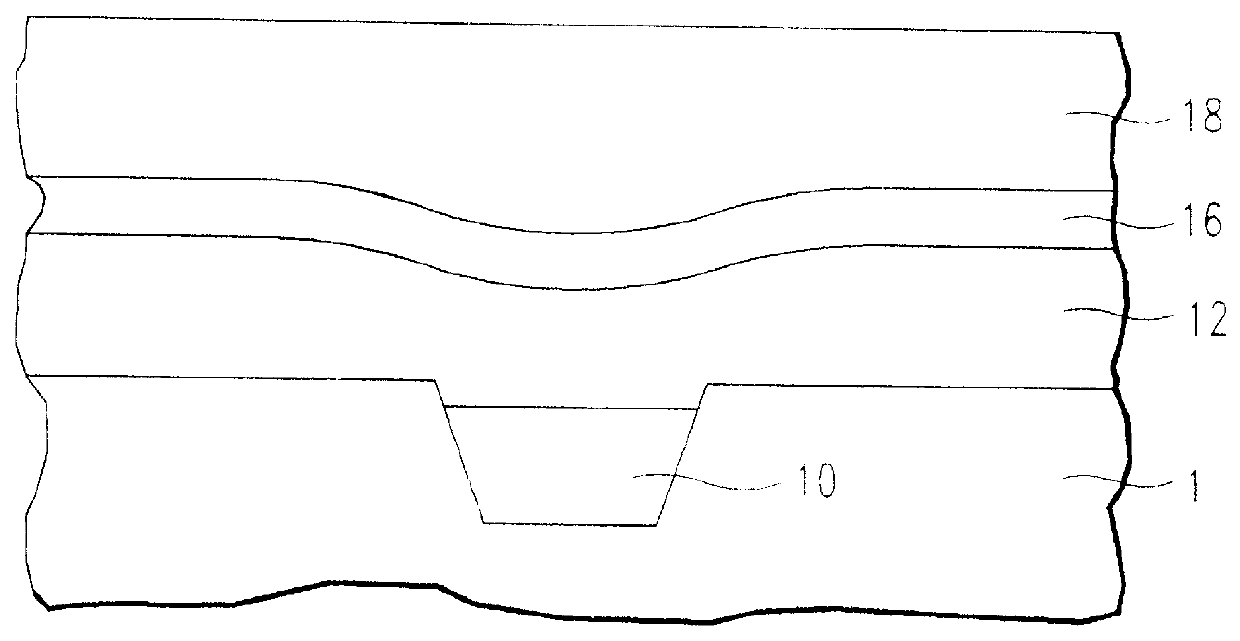
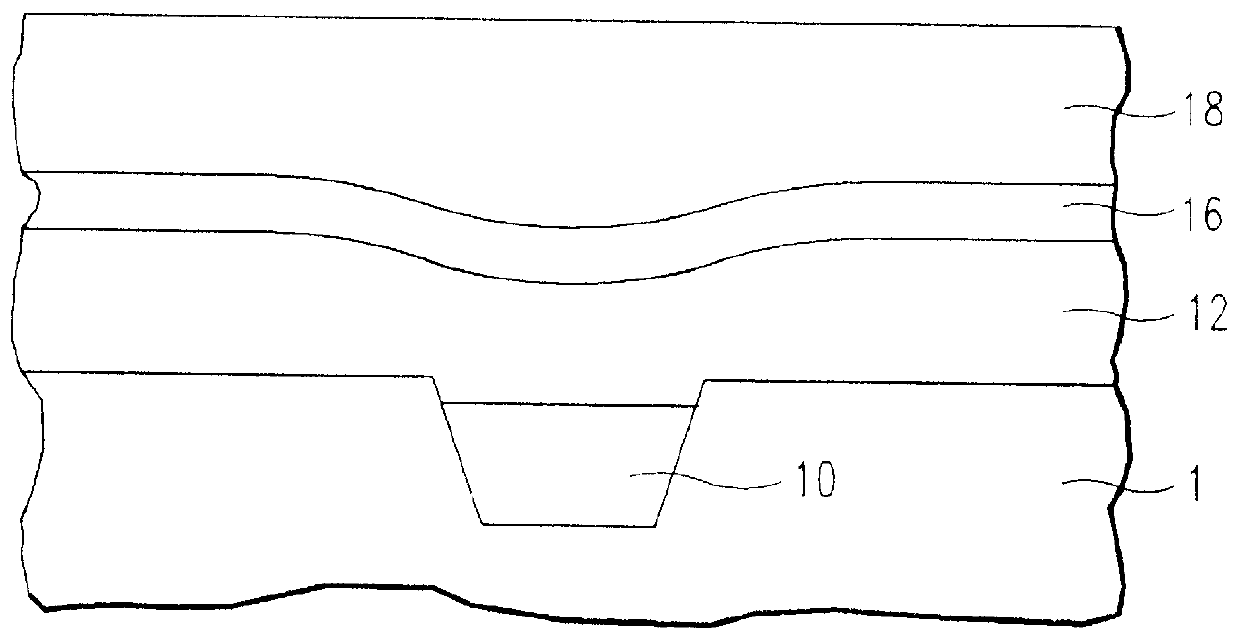
High selectivity Si-rich SiON etch-stop layer
InactiveUS6245669B1Superior light absorption qualityReduce RC delaySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSilicon oxide
The present invention provides an anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer and two compatible oxide etch processes. The Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer can be used as a hard mask in a dual damascene structure and as a hard mask for over a polysilicon gate. The invention has the following key elements: 1) Si rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) ARC layer, 2) Special Silicon oxide Etch process that has a high selectivity of Si-Rich SiON to silicon oxide or SiN; 3) Special Si Rich SiON spacer process for a self aligned contact (SAC).A dual damascene structure is formed by depositing a first dielectric layer. A novel anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer is deposited on top of the first dielectric layer. A first opening is etched in the first insulating layer. A second dielectric layer is deposited on the anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer. A second dual damascene opening is etched into the dielectric layers. The anti-reflective Si-Rich Silicon oxynitride (SiON) etch barrier layer can also serve as an ARC layer during these operations to reduce the amount of reflectance from conductive region to reduce distortion of the photoresist pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High transmittance, low emissivity coatings for substrates
InactiveUS6838159B2High light transmittanceLow emissivityMirrorsOptical filtersAngle of incidenceOptical property
The present invention provides a coating for a transparent substrate which exhibits a “neutral” color through a wide range of angles of incidence of light. The coating employs a base coat adjacent the transparent substrate having a thickness of no more than about 275 Å and may include two reflective metal layers having an intermediate layer of an anti-reflective metal oxide therebetween and an outer anti-reflective layer of metal oxide over the second reflective metal layer. If so desired, the coating of the invention may include an abrasive-resistant overcoat as its outermost layer. This overcoat is desirably formed of an abrasive-resistant metal oxide, such as zinc oxide applied at a thickness which does not significantly affect the optical properties of said coated substrate.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com