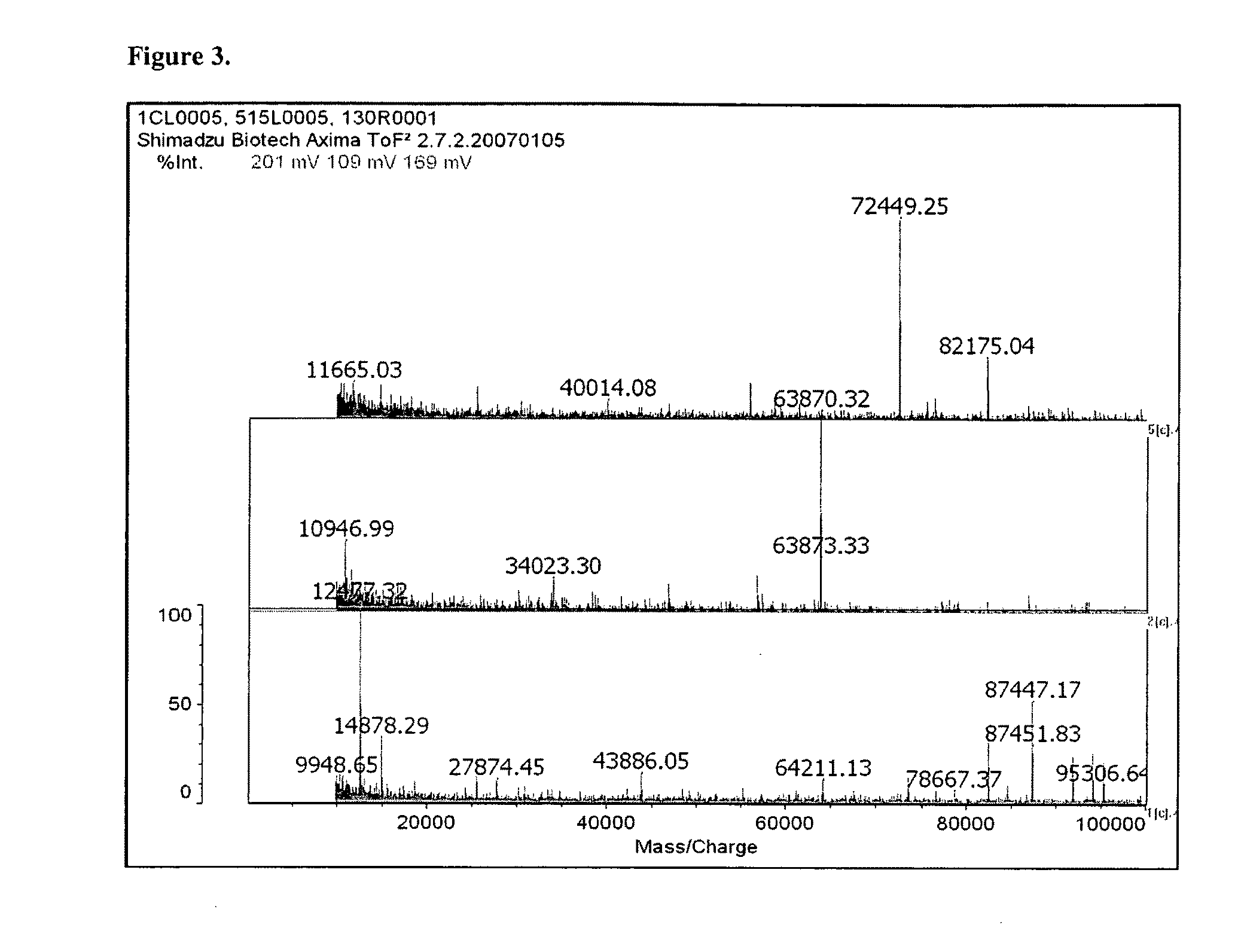
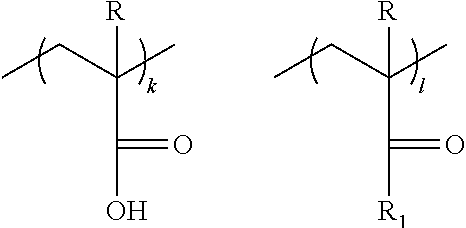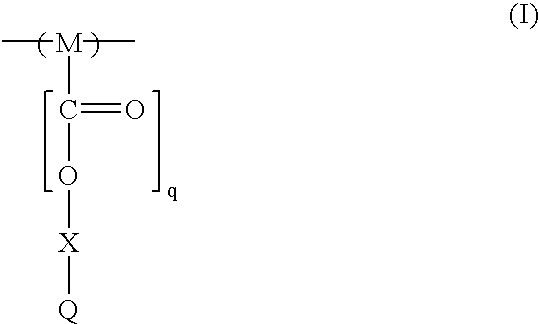Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
439 results about "Post exposure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
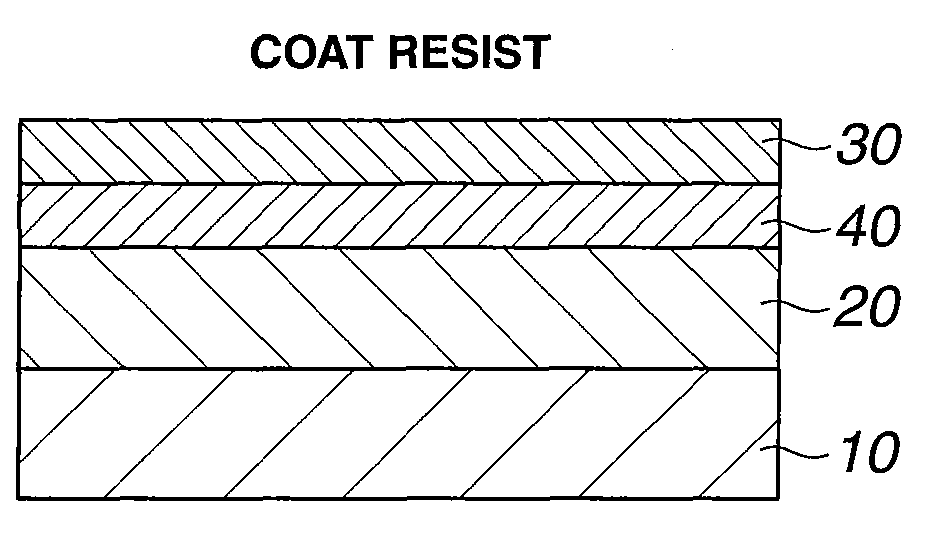
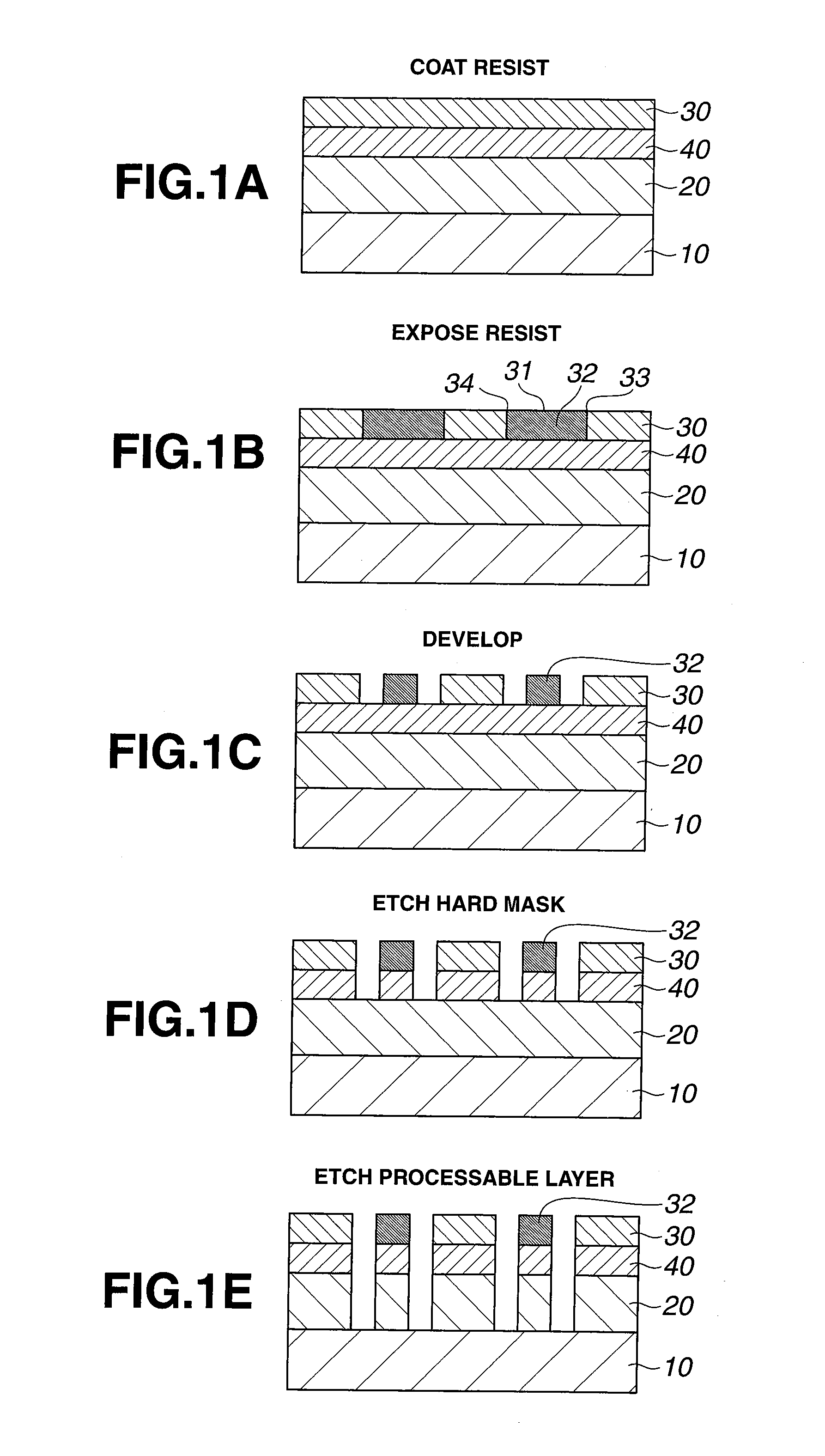
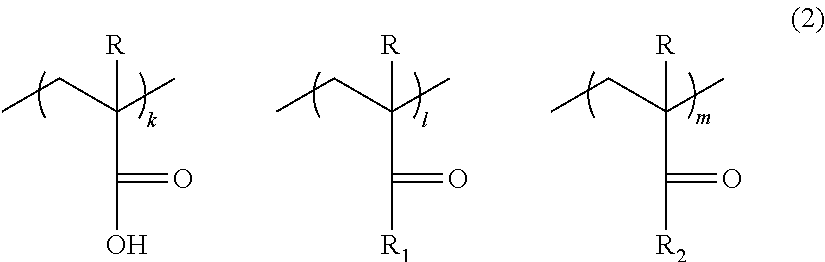
Photoresist monomers, polymers thereof, and photoresist compositions containing the same
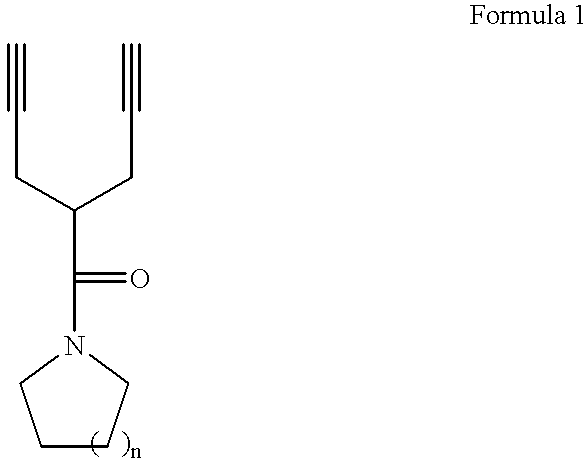
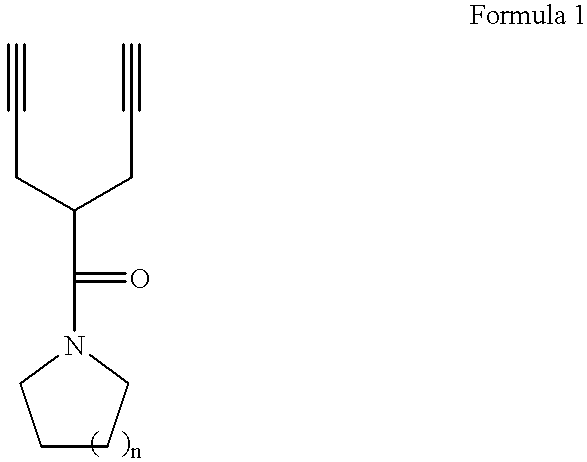
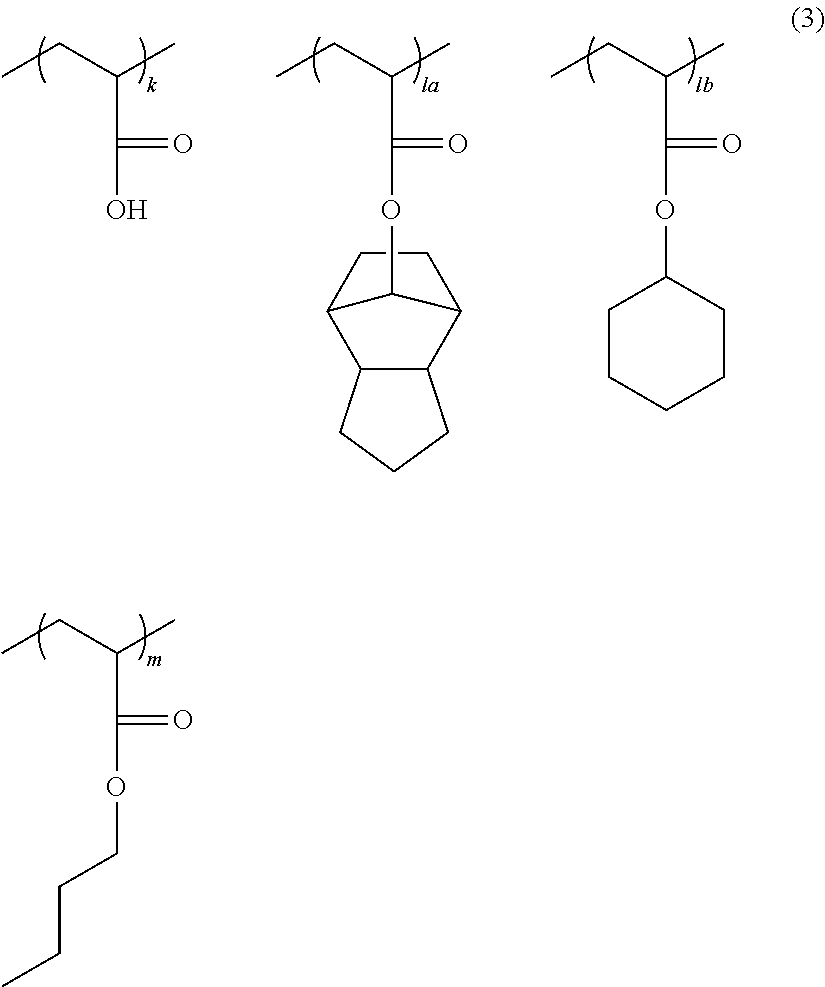
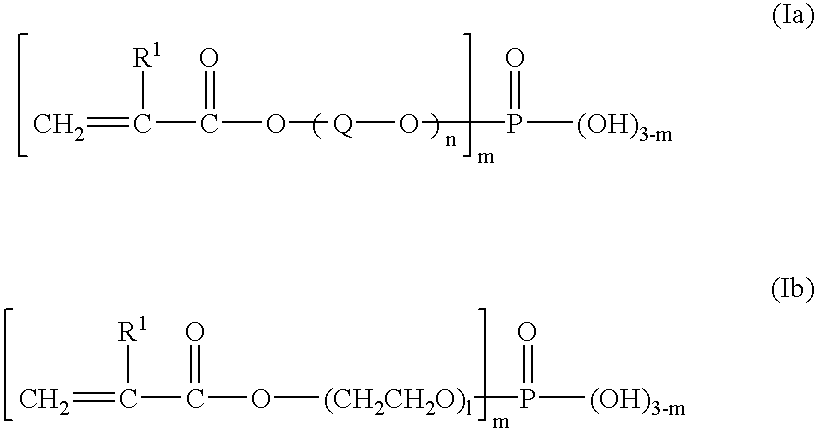
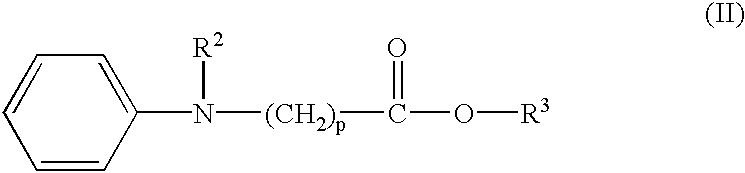
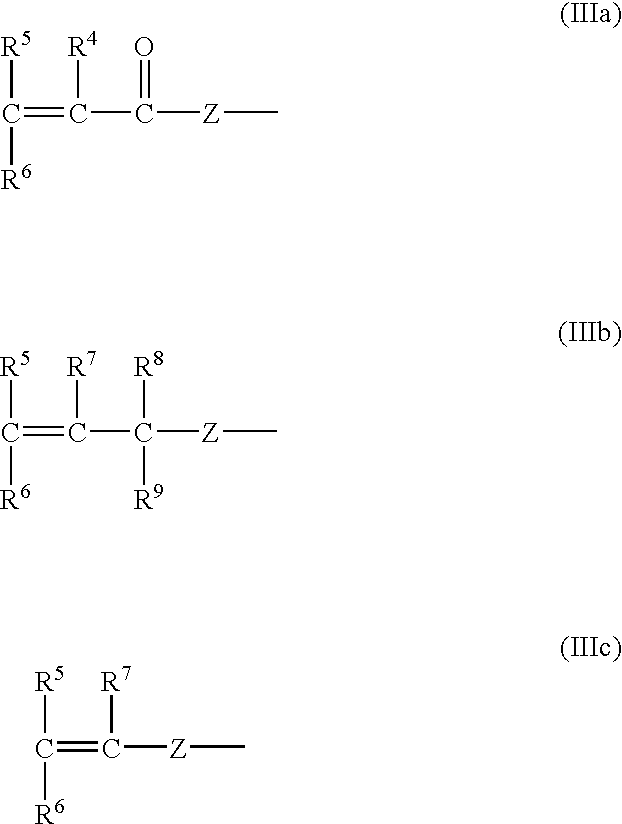
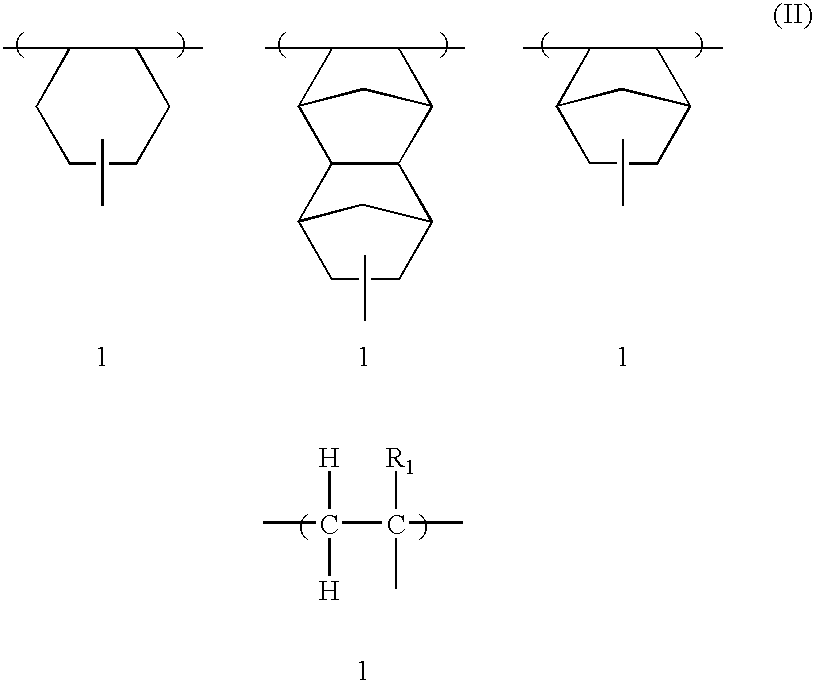
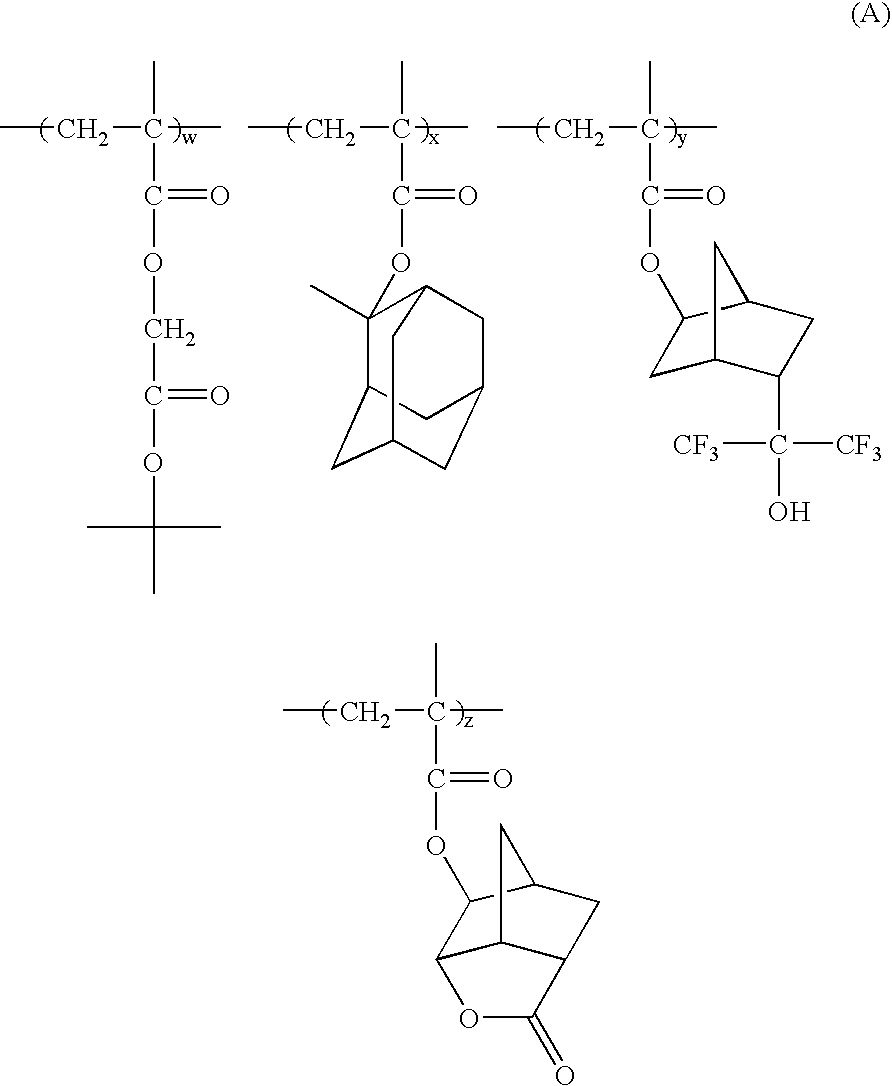
Dipropargyl acetamide derivatives of following Formula 1 which are photoresist monomers, polymers thereof, and photoresist compositions containing the same. The photoresist polymer has high etching resistance, adhesiveness and post-exposure delay stability. As a result, the photoresist composition is suitable to form a fine pattern in a deep ultraviolet region.wherein, n is an integer from 0 to 5.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
High speed negative-working thermal printing plates
Negative working thermally imageable elements useful as lithographic printing plate precursors and methods for their use are disclosed. The elements have a substrate, a layer of imageable composition over the substrate, and, optionally, an overcoat layer over the layer of imageable composition. The imageable composition has an allyl-functional polymeric binder. Optimum resolution and on-press performance can be attained without a post-exposure bake. The elements do not require a post-exposure bake and can be used in on-press development applications.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
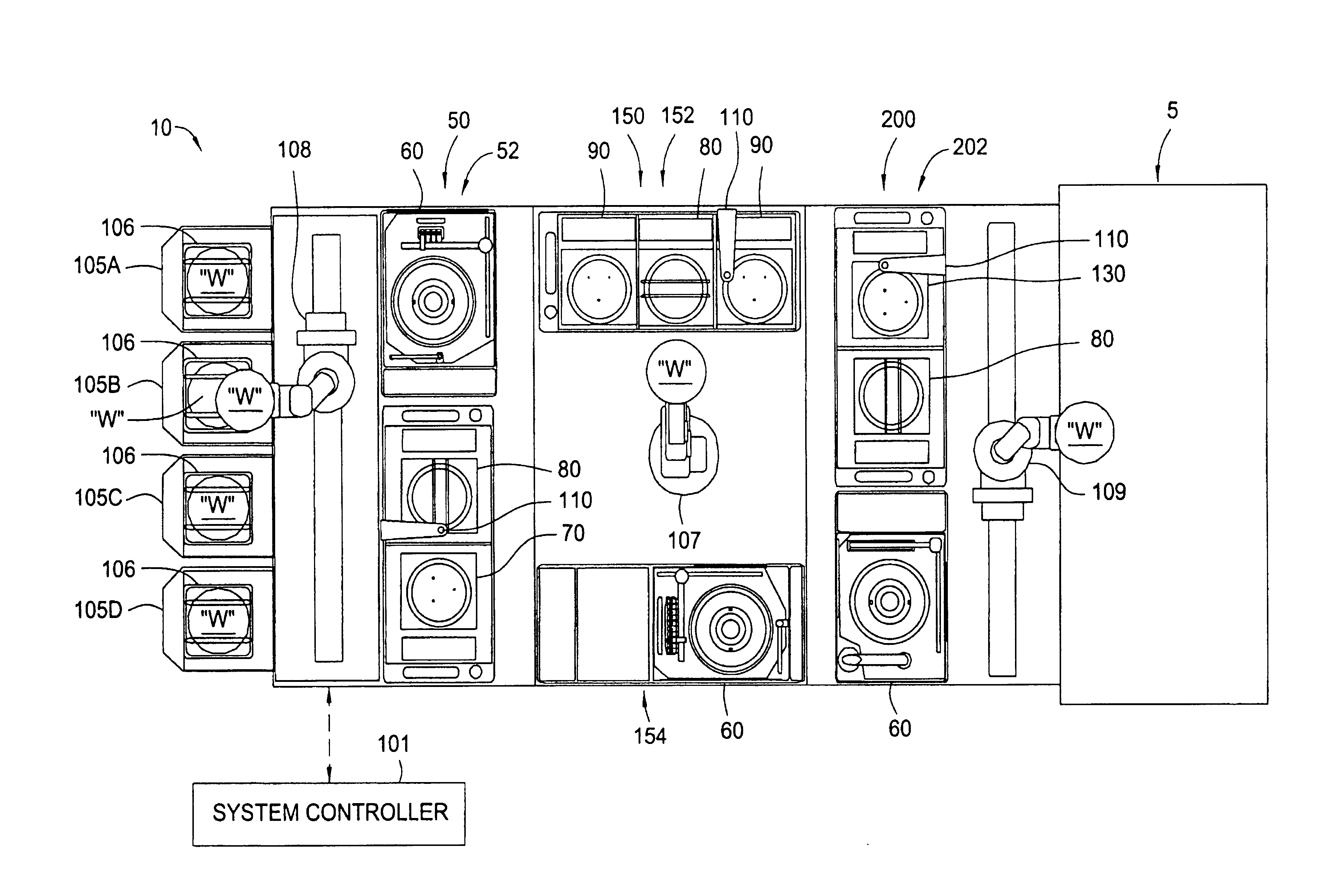
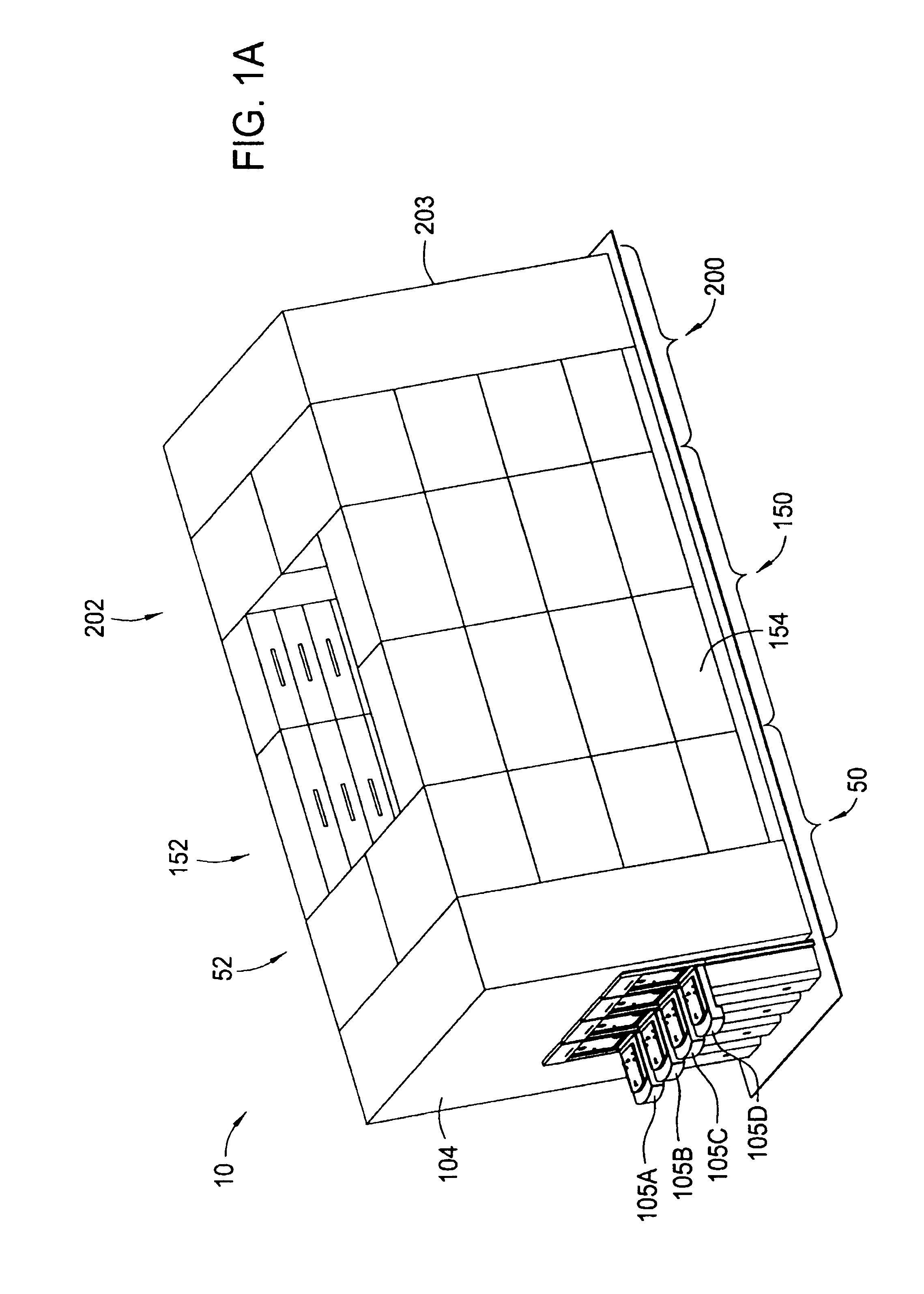
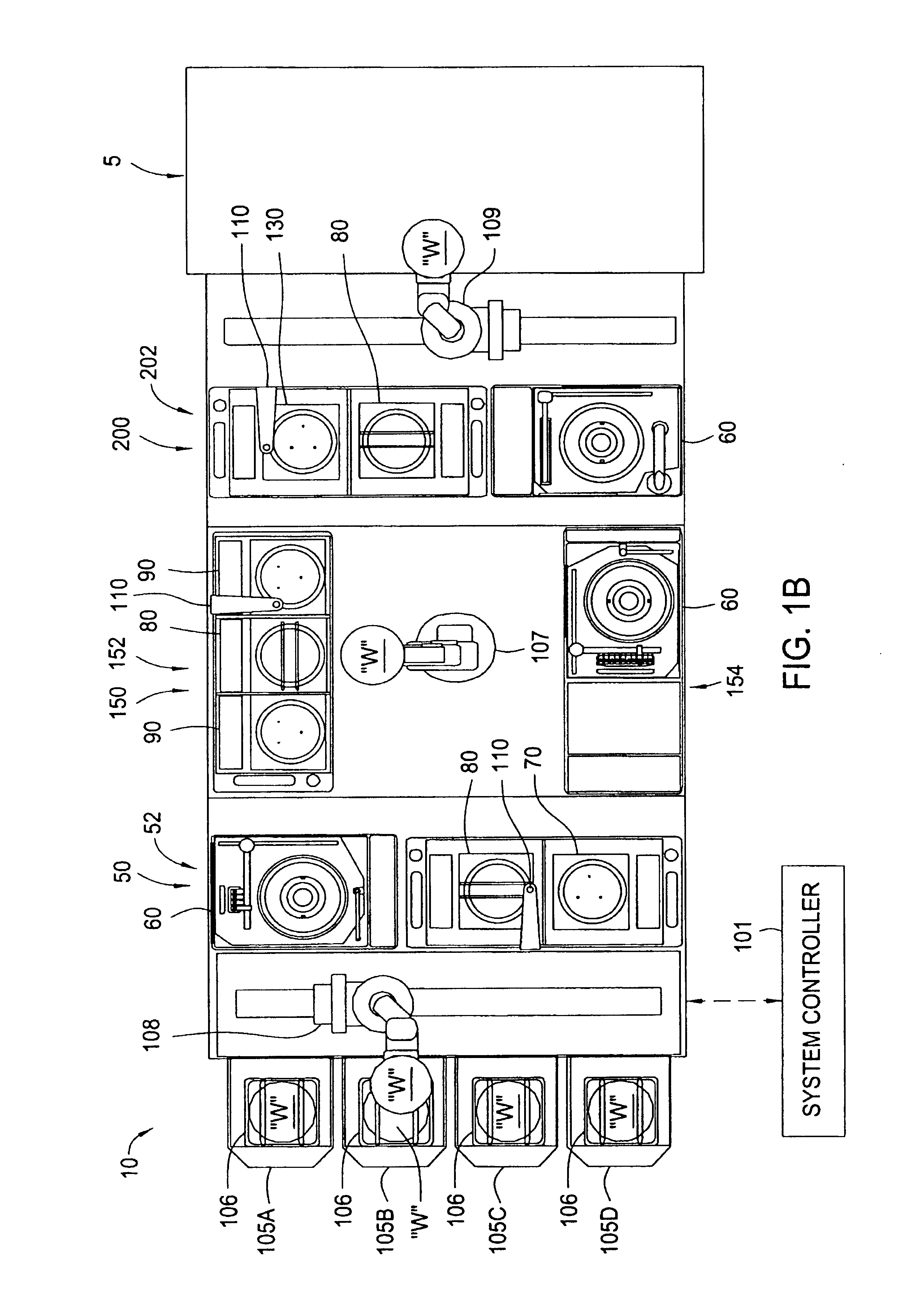
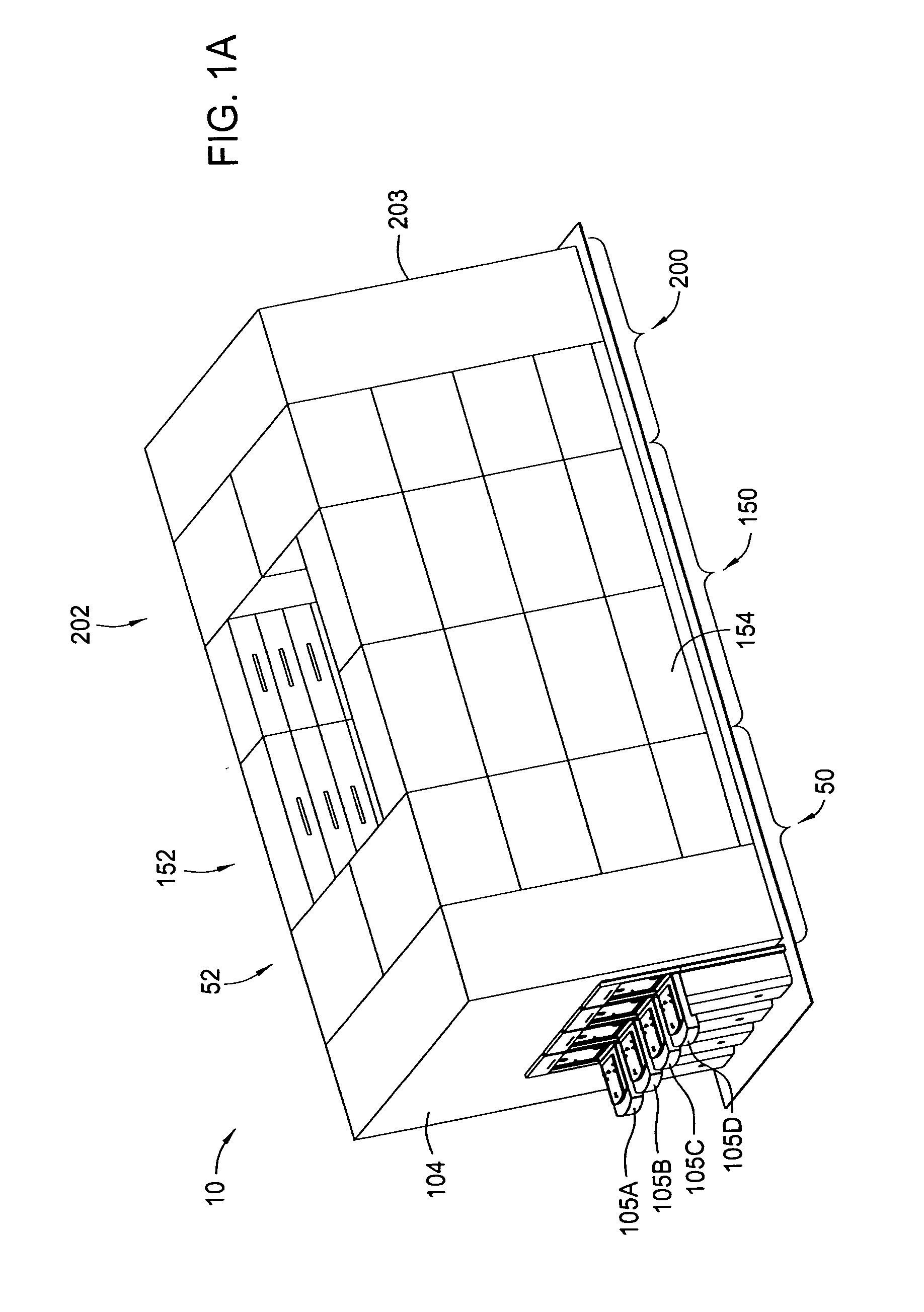
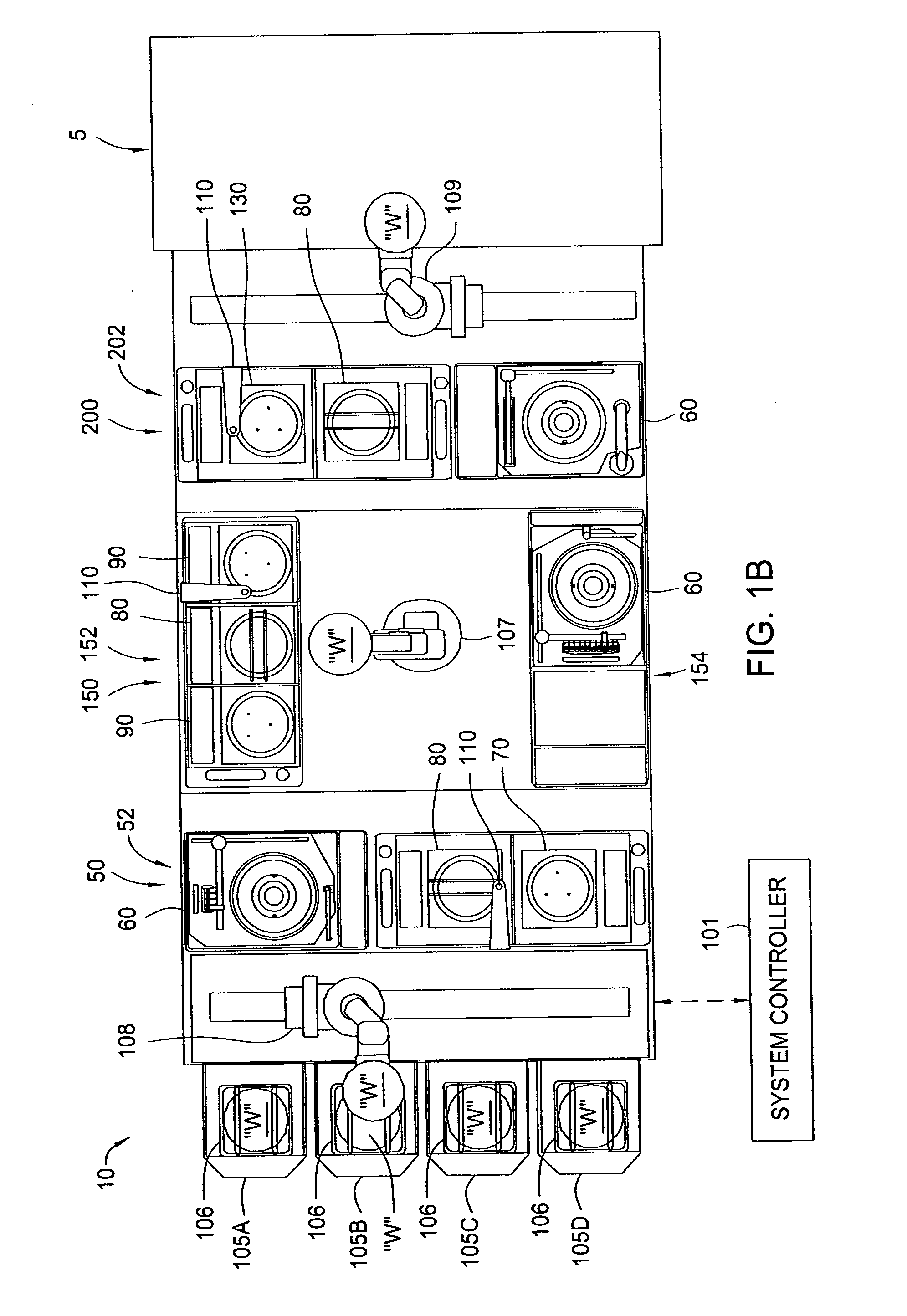
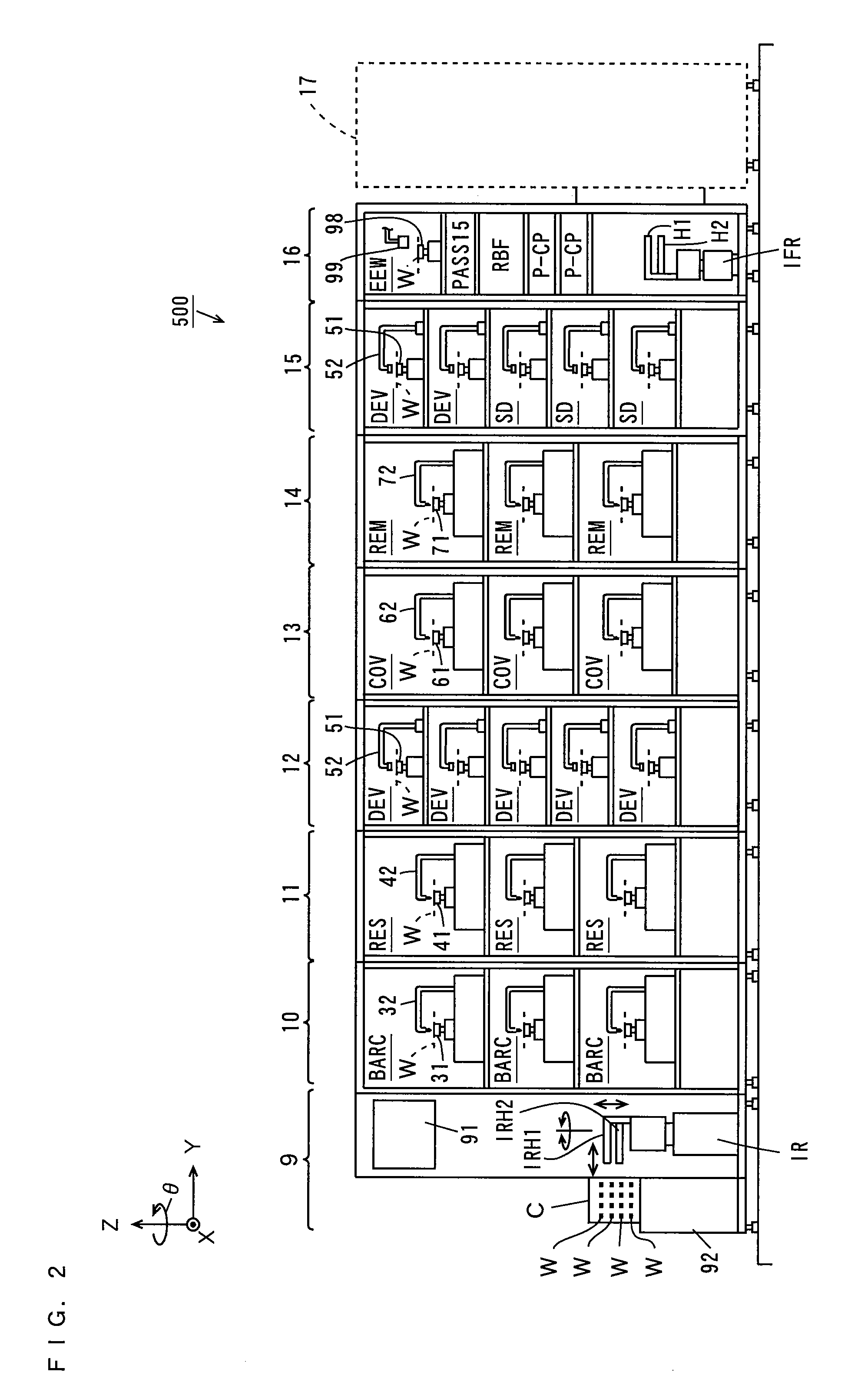
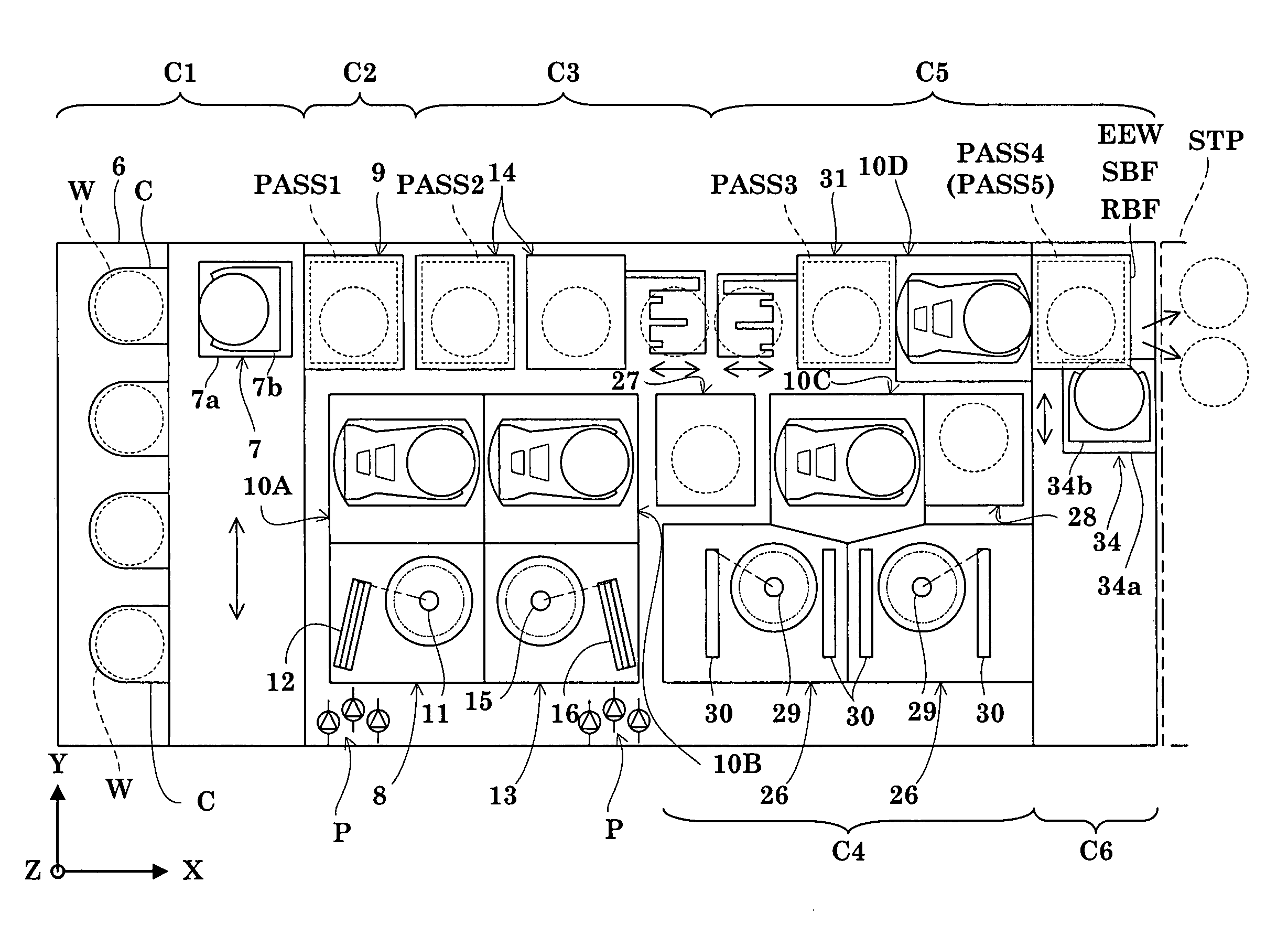
Cluster tool architecture for processing a substrate
ActiveUS20060130750A1Temperature controlMore repeatable wafer processing historyLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLithography processEngineering
Embodiments generally provide an apparatus and method for processing substrates using a multi-chamber processing system (e.g., a cluster tool) that has an increased system throughput, increased system reliability, substrates processed in the cluster tool have a more repeatable wafer history, and also the cluster tool has a smaller system footprint. In one embodiment, the cluster tool is adapted to perform a track lithography process in which a substrate is coated with a photosensitive material, is then transferred to a stepper / scanner, which exposes the photosensitive material to some form of radiation to form a pattern in the photosensitive material, which is then removed in a developing process completed in the cluster tool. In track lithography type cluster tools, since the chamber processing times tend to be rather short, and the number of processing steps required to complete a typical track system process is large, a significant portion of the time it takes to process a substrate is taken up by the processes of transferring the substrates in a cluster tool between the various processing chambers. In one embodiment of the cluster tool, the cost of ownership is reduced by grouping substrates together and transferring and processing the substrates in groups of two or more to improve system throughput, and reduces the number of moves a robot has to make to transfer a batch of substrates between the processing chambers, thus reducing wear on the robot and increasing system reliability. In one aspect of the invention, the substrate processing sequence and cluster tool are designed so that the substrate transferring steps performed during the processing sequence are only made to chambers that will perform the next processing step in the processing sequence. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to improve the coater chamber, the developer chamber, the post exposure bake chamber, the chill chamber, and the bake chamber process results. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to increase the reliability of the substrate transfer process to reduce system down time.
Owner:SCREEN SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
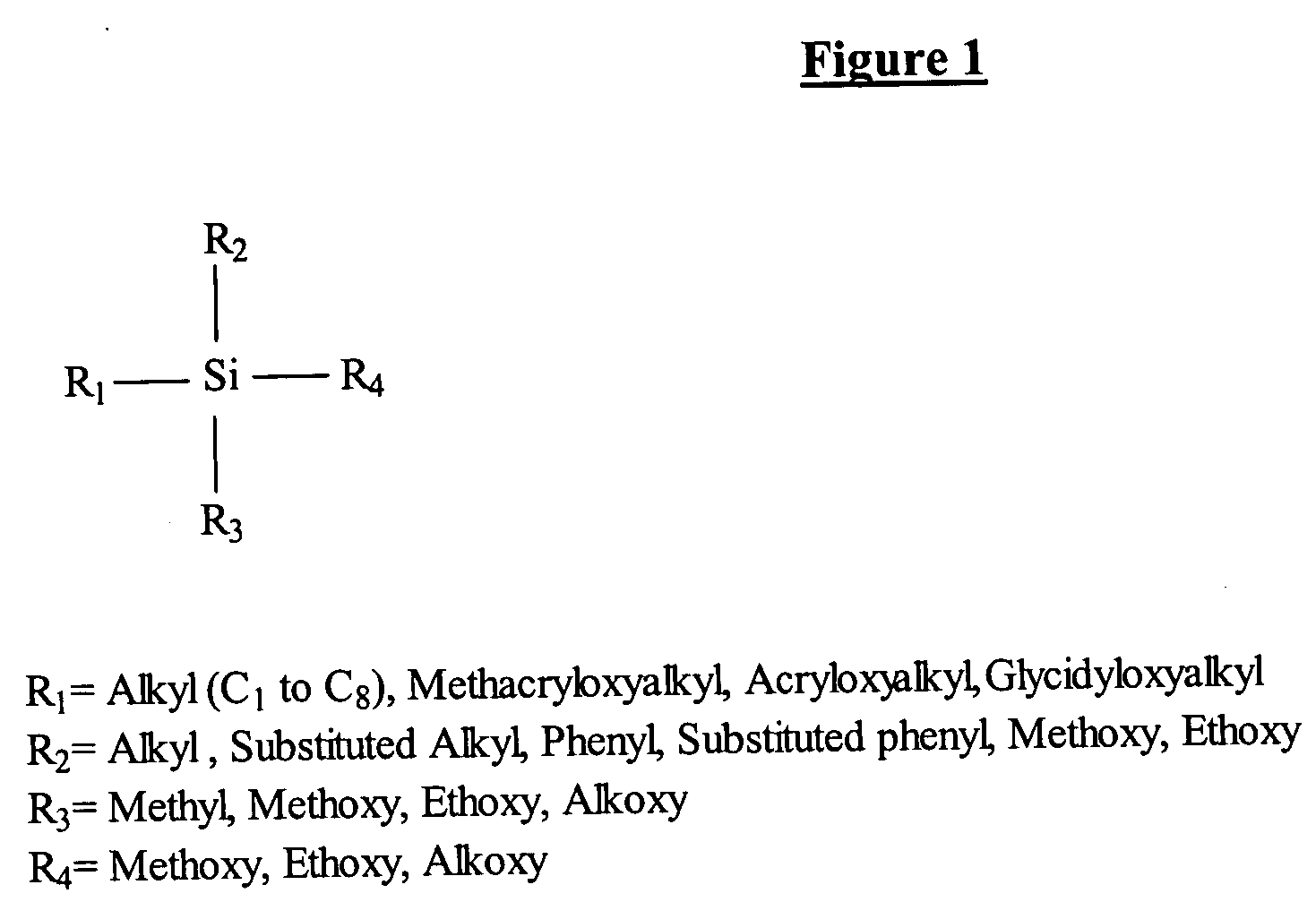
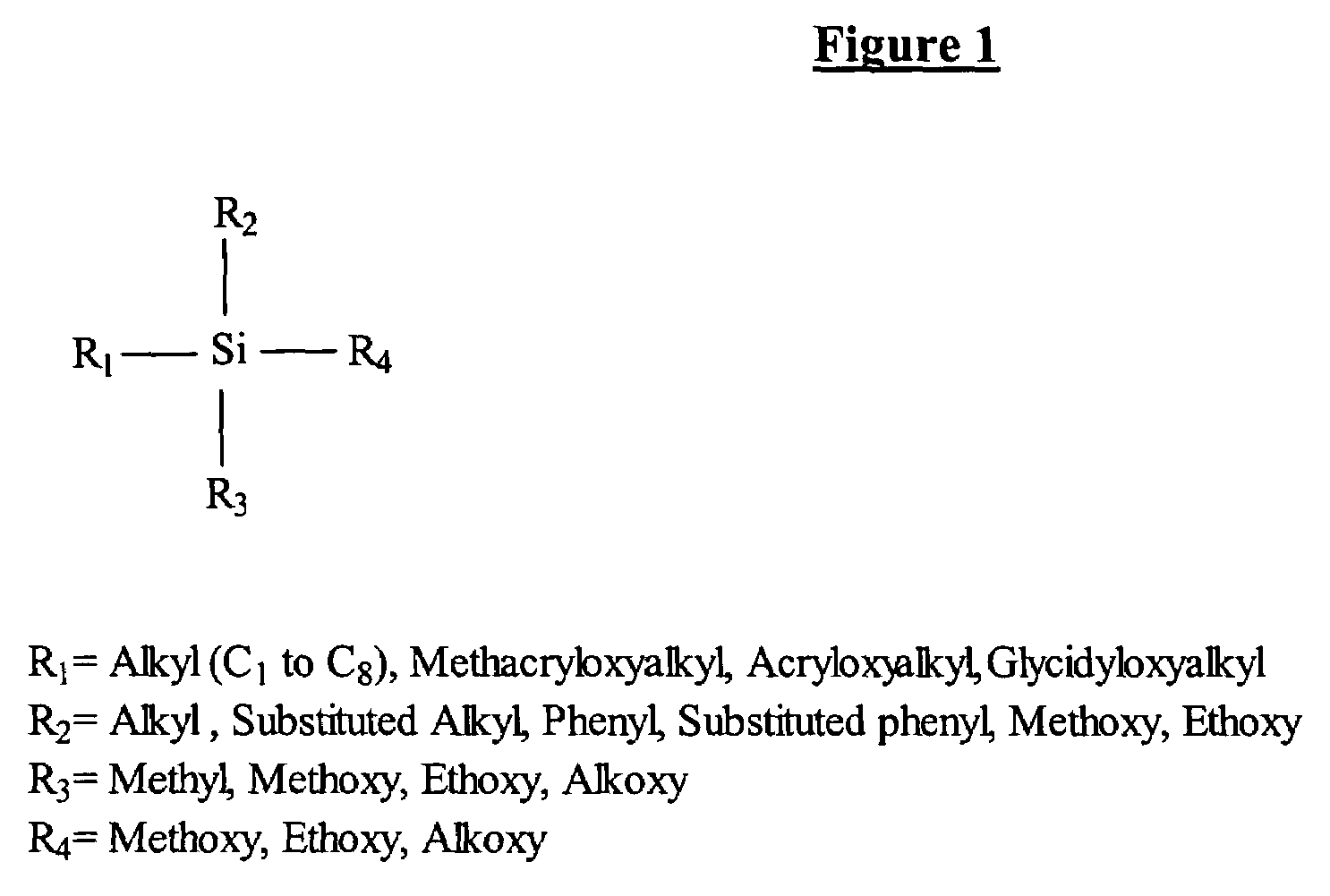
High performance sol-gel spin-on glass materials
InactiveUS20050022697A1Improve adaptabilityIncrease flexibilityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPhotomechanical apparatusSilanesRoom temperature
Hybrid sol-gel materials are provided, which may be produced by the reaction of an alkyl or dialkyl substituted trialkoxysilane or dialkoxysilane reacting with a silane diol, wherein said alkyl group has from 1 to 8 carbon atoms. A process is also provided for patterning the sol-gel spin-on glass material by: a) coating a substrate with the spin-on glass material; b) exposing the coated substrate of step a) to UV illumination in a desired pattern; c) post-exposure baking the coated substrate of step b) at a temperature from 100° C. to 120° C. for 30 to 60 minutes; d) cooling the coated substrate of step c) to room temperature; e) removing the non-exposed areas of the coating on the coated substrate of step d); f) drying the coated substrate of step e); g) hard baking the coated substrate of step f) at a temperature from 120° C. and 150° C. for 1 to 3 hours.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Methods for producing pattern-forming body
InactiveUS7252923B2Improve accuracyEffect can be problematicMaterial nanotechnologyPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringPost exposure
A method of producing a pattern-forming body with high accuracy with no need for a post-exposure treatment and without allowing any photocatalyst to remain in the resultant pattern-forming body and whereby any problematic effect of the photocatalyst in the pattern-forming body is eliminated. The method includes providing a photocatalyst-containing layer-sided substrate and a pattern-forming body substrate having a characteristic-changeable layer, which is changed by the effect of the photocatalyst in the photocatalyst-containing layer, and a light-shading part formed as a pattern in such a manner that the photocatalyst-containing layer and the characteristic-changeable layer are brought into contact with each other, followed by exposure on the side of the pattern-forming body substrate to change the characteristics of the characteristic-changeable layer of the exposed part, followed by removing the photocatalyst-containing layer-sided substrate.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Digital stereo photographic system
The invention provides a complete system for three-dimensional (3D) (stereo) still photography in a digital format. This includes capturing the image or photo, viewing, printing and projecting it. Intermediate steps would include downloading images to a computer, editing, enhancing or modifying, saving, recording photo images to other storage medium, and the printing of still photos. This invention is a significant advancement of the traditional analog film stereo slides, in that the digital format will allow viewing of the image in the camera in 3D, prior to, during, immediately after exposure and at any other time after exposure. With significant computer processing capability after exposure in editing, enhancing, color correcting, adding text and art, the images are further improved. The system includes the ability to view images, in 3D (stereo), in the camera, in a hand held viewer, on a computer screen on a standard television set as well as printed pairs or in anaglyph formats. The images can also be viewed with conventional digital projectors using conventional polarized glasses. The camera is also a significant advancement over the standard digital still cameras because it provides the three-dimensional image capture in a digital format. It also retains the full 2-dimensional capability of digital photography.
Owner:NEWBERY REVOCABLE TRUST INDENTURE
Anti-reflective coatings using vinyl ether crosslinkers
InactiveUS20070207406A1High percent solubilityReduce production processOrganic chemistrySilver halide emulsionsVinyl etherAnti-reflective coating
Novel, developer soluble anti-reflective coating compositions and methods of using those compositions are provided. The compositions comprise a polymer and / or oligomer having acid functional groups and dissolved in a solvent system along with a cross linker, a photoacid generator, and optionally a chromophore. The preferred acid functional group is a carboxylic acid, while the preferred crosslinker is a vinyl ether crosslinker. In use, the compositions are applied to a substrate and thermally crosslinked. Upon exposure to light (and optionally a post exposure bake), the cured compositions will decrosslink, rendering them soluble in typical photoresist developing solutions (e.g., alkaline developers). In one embodiment, the compositions can be used to form ion implant areas in microelectronic substrates.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Cluster tool architecture for processing a substrate
InactiveUS20060134330A1More repeatable wafer processing historyReduced footprintProgramme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLithography processEngineering
Embodiments generally provide an apparatus and method for processing substrates using a multi-chamber processing system (e.g., a cluster tool) that has an increased system throughput, increased system reliability, substrates processed in the cluster tool have a more repeatable wafer history, and also the cluster tool has a smaller system footprint. In one embodiment, the cluster tool is adapted to perform a track lithography process in which a substrate is coated with a photosensitive material, is then transferred to a stepper / scanner, which exposes the photosensitive material to some form of radiation to form a pattern in the photosensitive material, which is then removed in a developing process completed in the cluster tool. In track lithography type cluster tools, since the chamber processing times tend to be rather short, and the number of processing steps required to complete a typical track system process is large, a significant portion of the time it takes to process a substrate is taken up by the processes of transferring the substrates in a cluster tool between the various processing chambers. In one embodiment of the cluster tool, the cost of ownership is reduced by grouping substrates together and transferring and processing the substrates in groups of two or more to improve system throughput, and reduces the number of moves a robot has to make to transfer a batch of substrates between the processing chambers, thus reducing wear on the robot and increasing system reliability. In one aspect of the invention, the substrate processing sequence and cluster tool are designed so that the substrate transferring steps performed during the processing sequence are only made to chambers that will perform the next processing step in the processing sequence. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to improve the coater chamber, the developer chamber, the post exposure bake chamber, the chill chamber, and the bake chamber process results. Embodiments also provide for a method and apparatus that are used to increase the reliability of the substrate transfer process to reduce system down time.
Owner:SOKUDO CO LTD
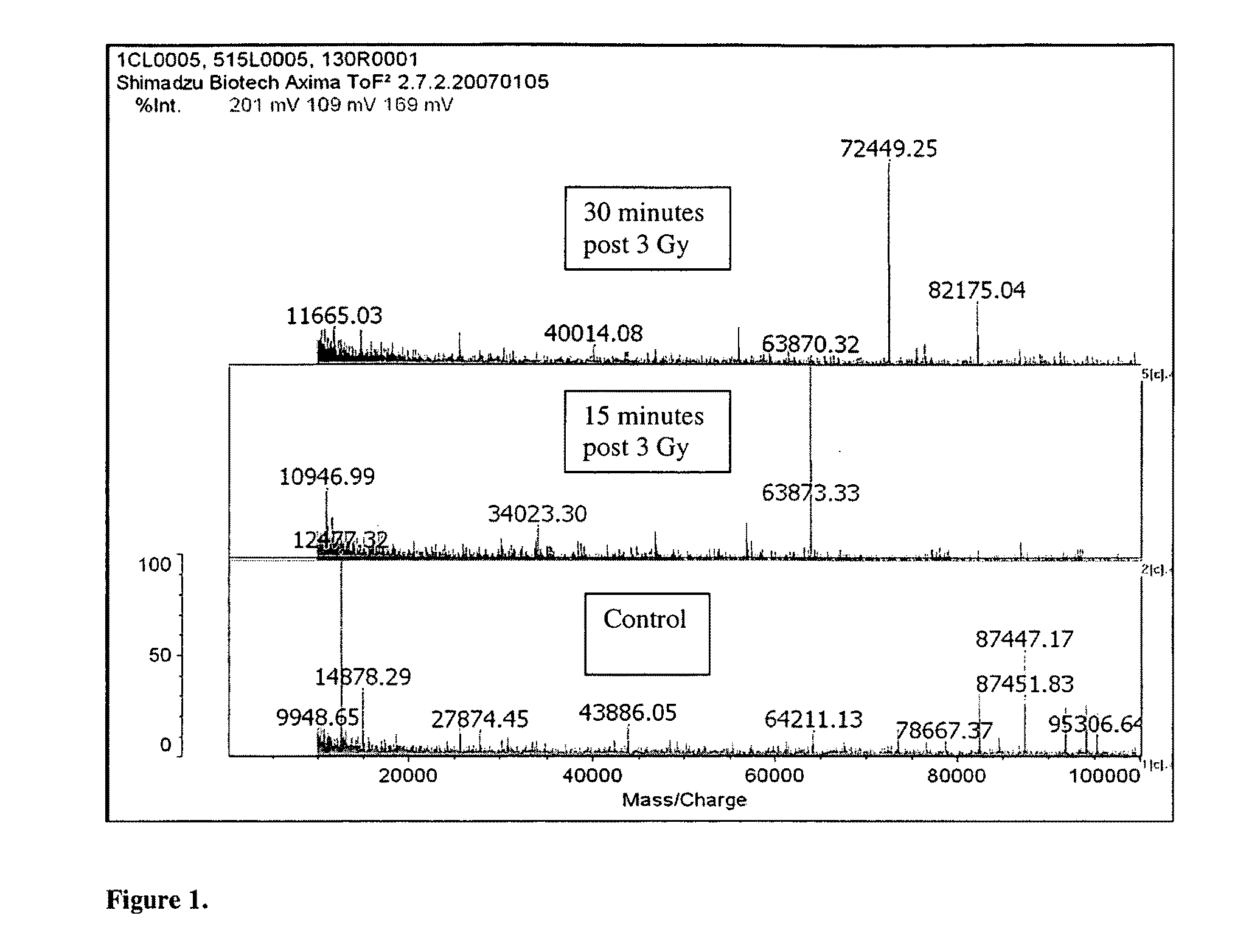
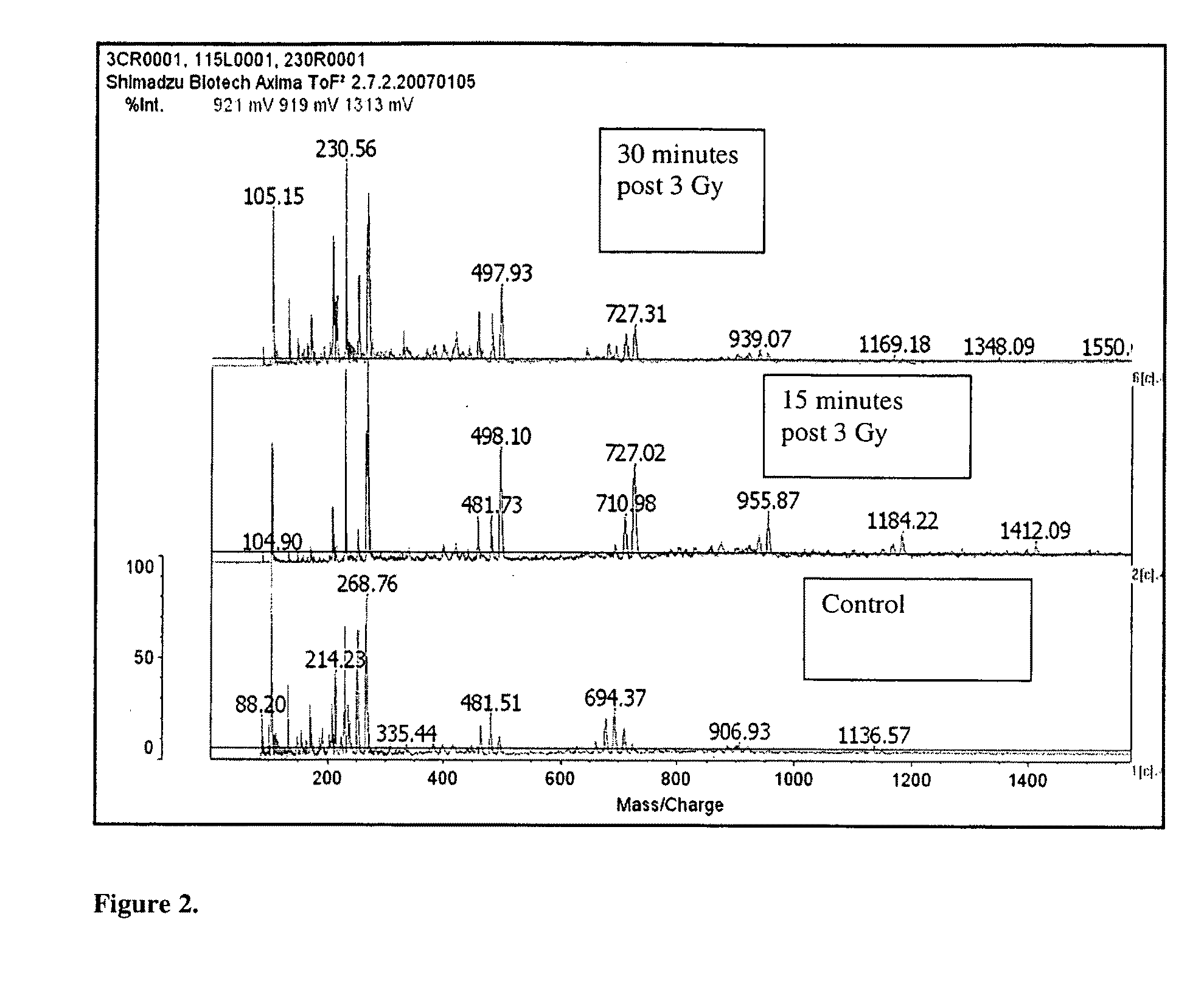
Biomarkers of ionizing radiation
ActiveUS20090289182A1Rapid inexpensiveLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementParticle spectrometer methodsDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides novel radiation associated markers. The radiation associated markers may be one or more of albumin, LTGF-β, or any protein or peptide listed in any one of Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 provided herein. The present invention also provides methods of assessing exposure to ionizing radiation by determining the presence of one or more radiation associated markers. The methods may optionally include quantifying one or more of the radiation associated markers. The methods may further include comparing the amount of one or more radiation associated markers in the sample determined to be present in the sample with either (i) the amount determined for temporally matched, normal samples or (ii) the amount determined for samples obtained from individuals or subjects that have not been exposed to an elevated level of ionizing radiation. The present invention further provides a method of predicting outcome in a subject after exposure to elevated levels of ionizing radiation. Further, the present invention provides a method of determining the amount of radiation therapy that has been delivered to a particular tissue. Also, the present invention provides kits for assessing the likelihood of significant damage, death, illness or medical complications post exposure to elevated levels of ionizing radiation by determining the presence or absence or by quantifying the amount of one or more radiation associated markers.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Patterning process
ActiveUS20090081595A1Increase contrastFunction increaseResist coatingPhotosensitive materialsSolubilityResist
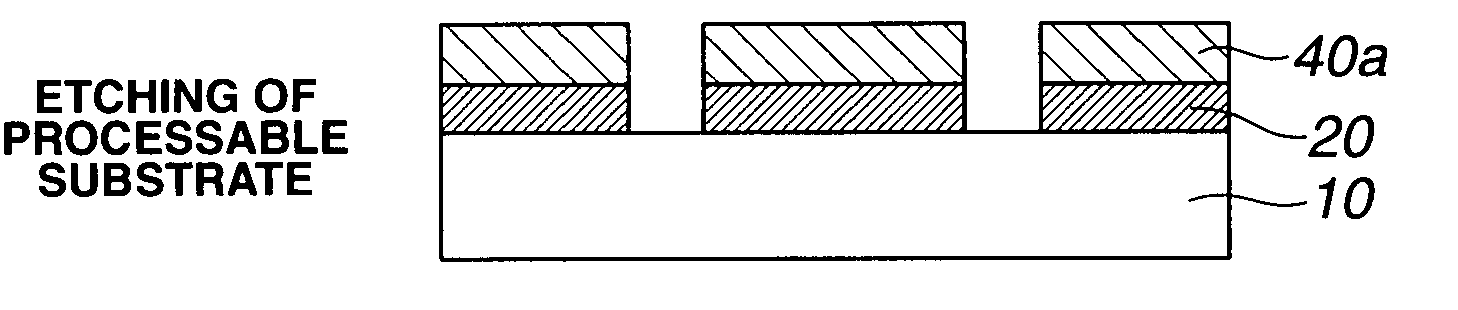
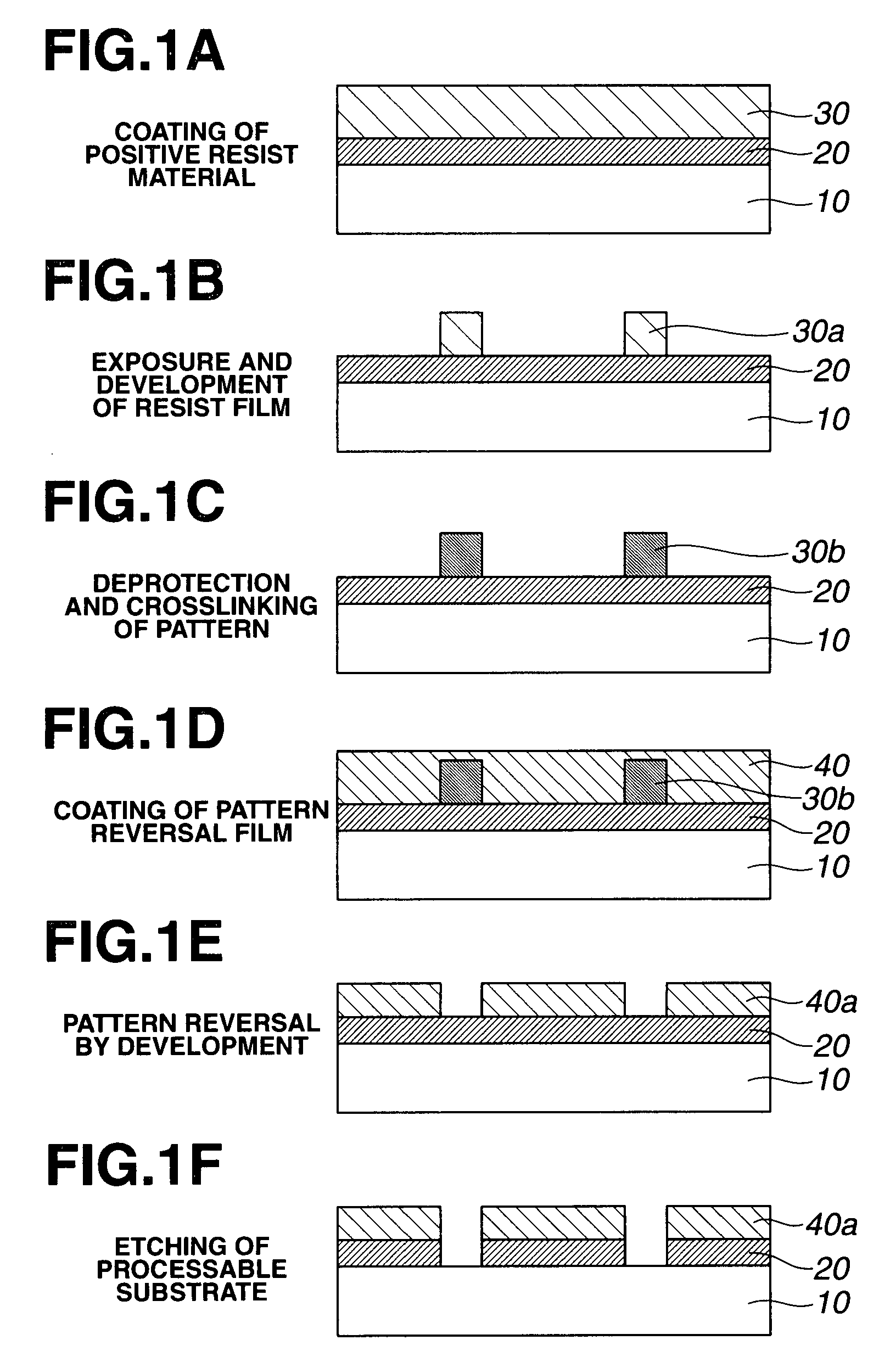
A pattern is formed through positive / negative reversal by coating a chemically amplified positive resist composition comprising an acid labile group-bearing resin, a photoacid generator, and an organic solvent onto a substrate, prebaking the resist composition, exposing the resist film to high-energy radiation, post-exposure heating, and developing the exposed resist film with an alkaline developer to form a positive pattern; irradiating or heating the positive pattern to facilitate elimination of acid labile groups and crosslinking for improving alkali solubility and imparting solvent resistance; coating a reversal film-forming composition thereon to form a reversal film; and applying an alkaline wet etchant thereto for dissolving away the positive pattern.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
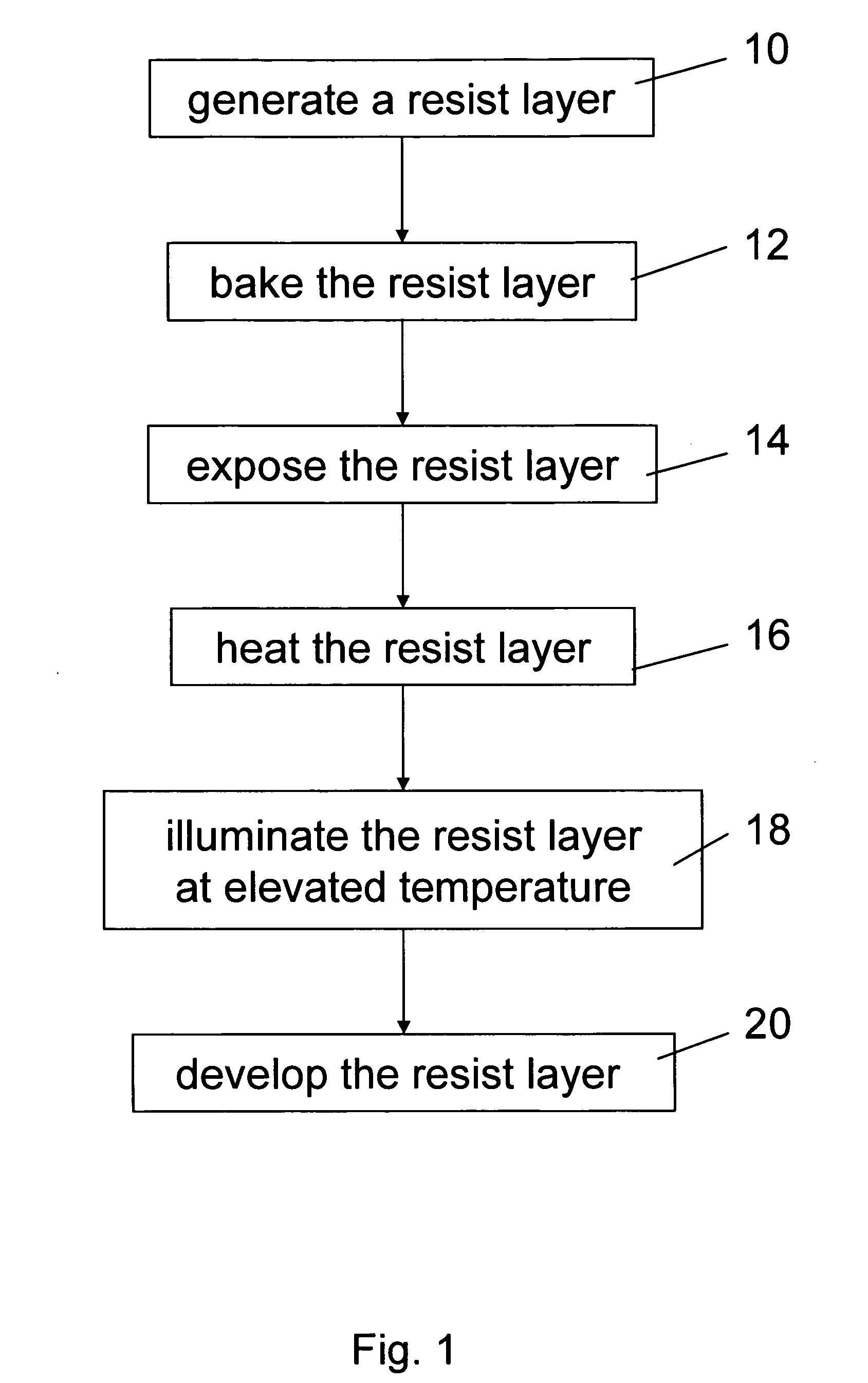
Post exposure resist bake
InactiveUS7396482B2Reduce morbidityFully removedDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistPhotoacid
A preferred embodiment of the invention provides a method for forming an integrated circuit. The method comprises forming a resist layer on a substrate. Preferably, the photoresist layer comprises a photo acid generator (PAG). Embodiments include irradiating the resist through a mask to generate a photoacid in the resist, heating the resist at a first temperature, and then heating the resist at a second temperature. Heating at the first temperature evaporates water from the resist. Heating at the second temperature deprotects the resist.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
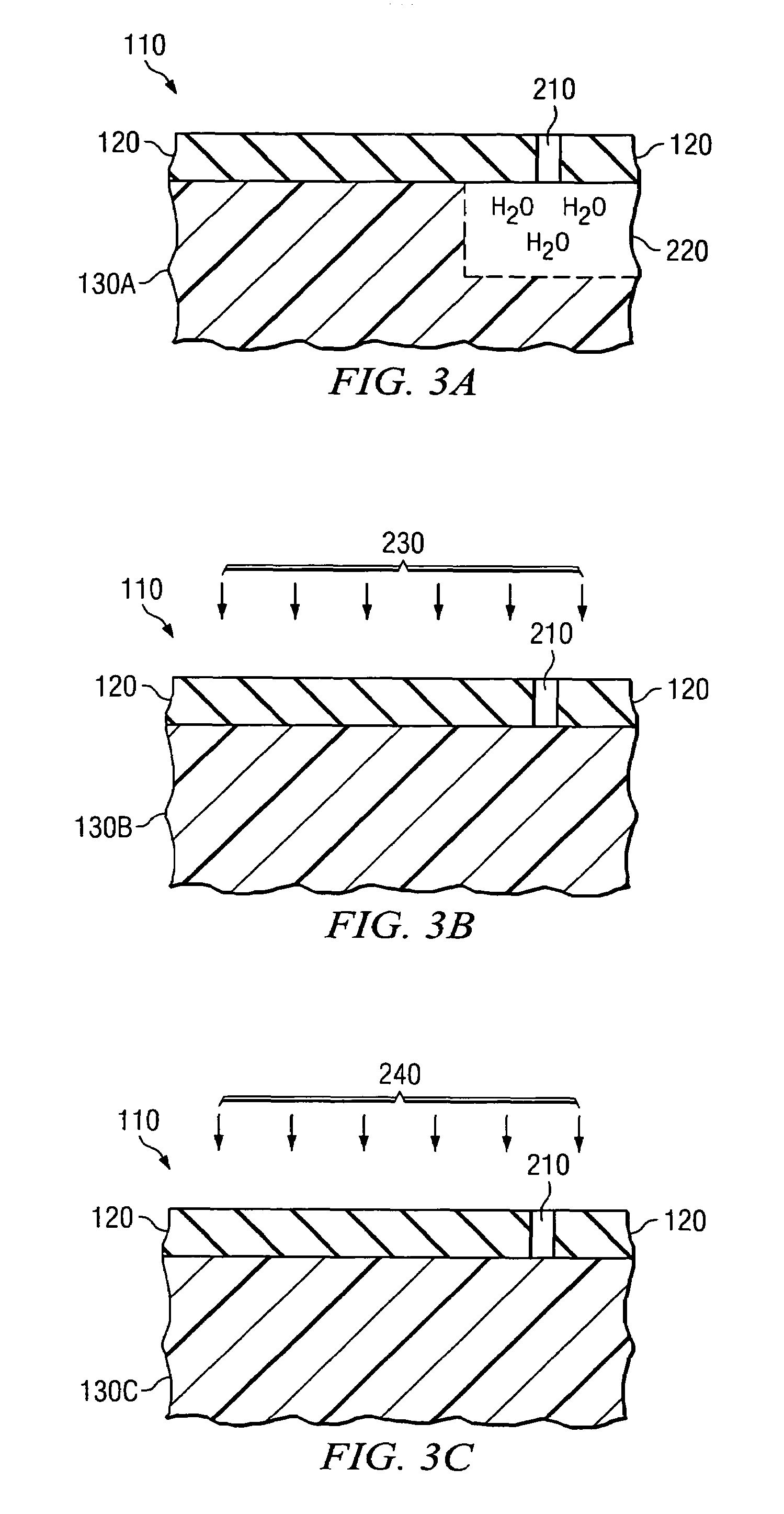
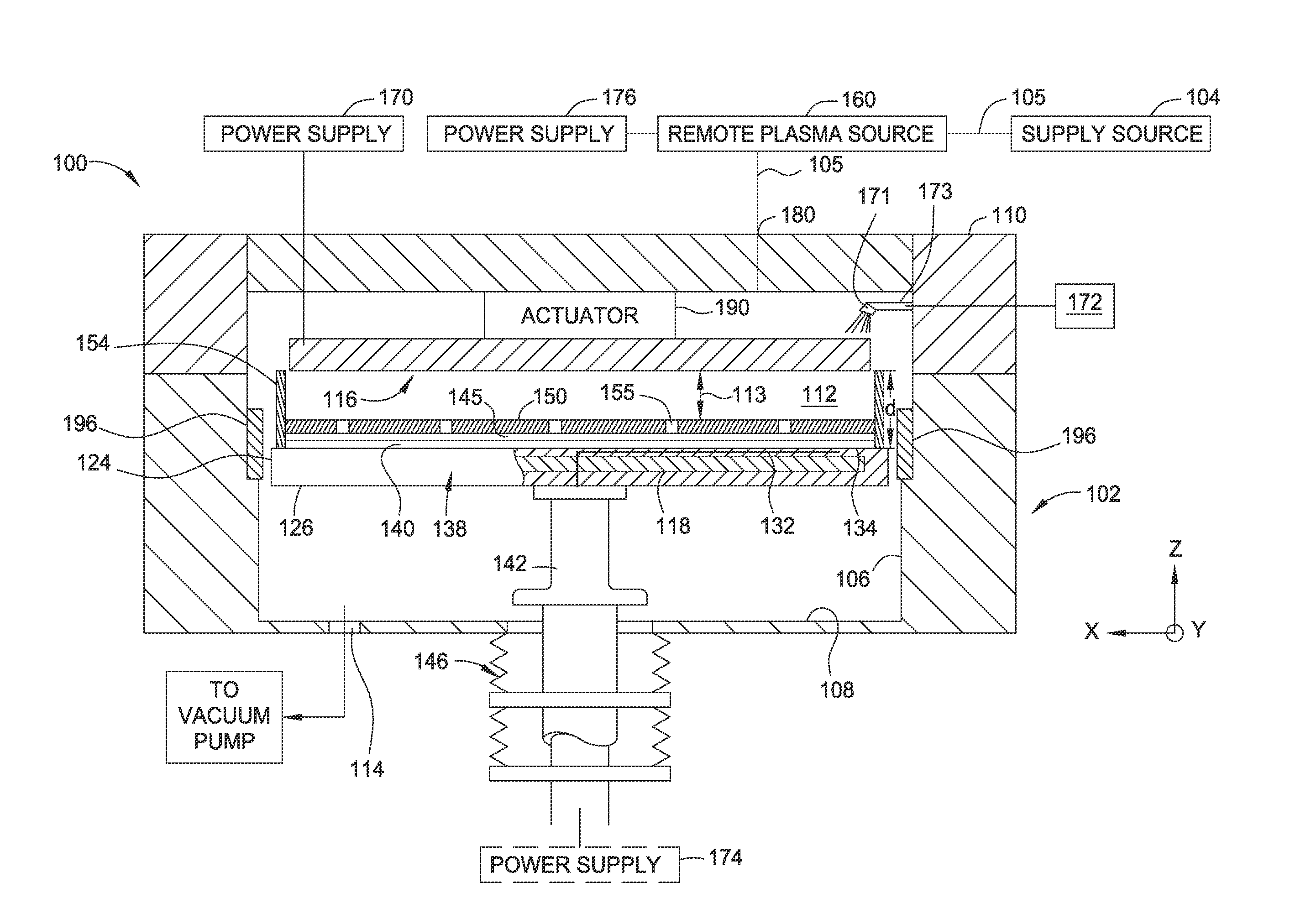
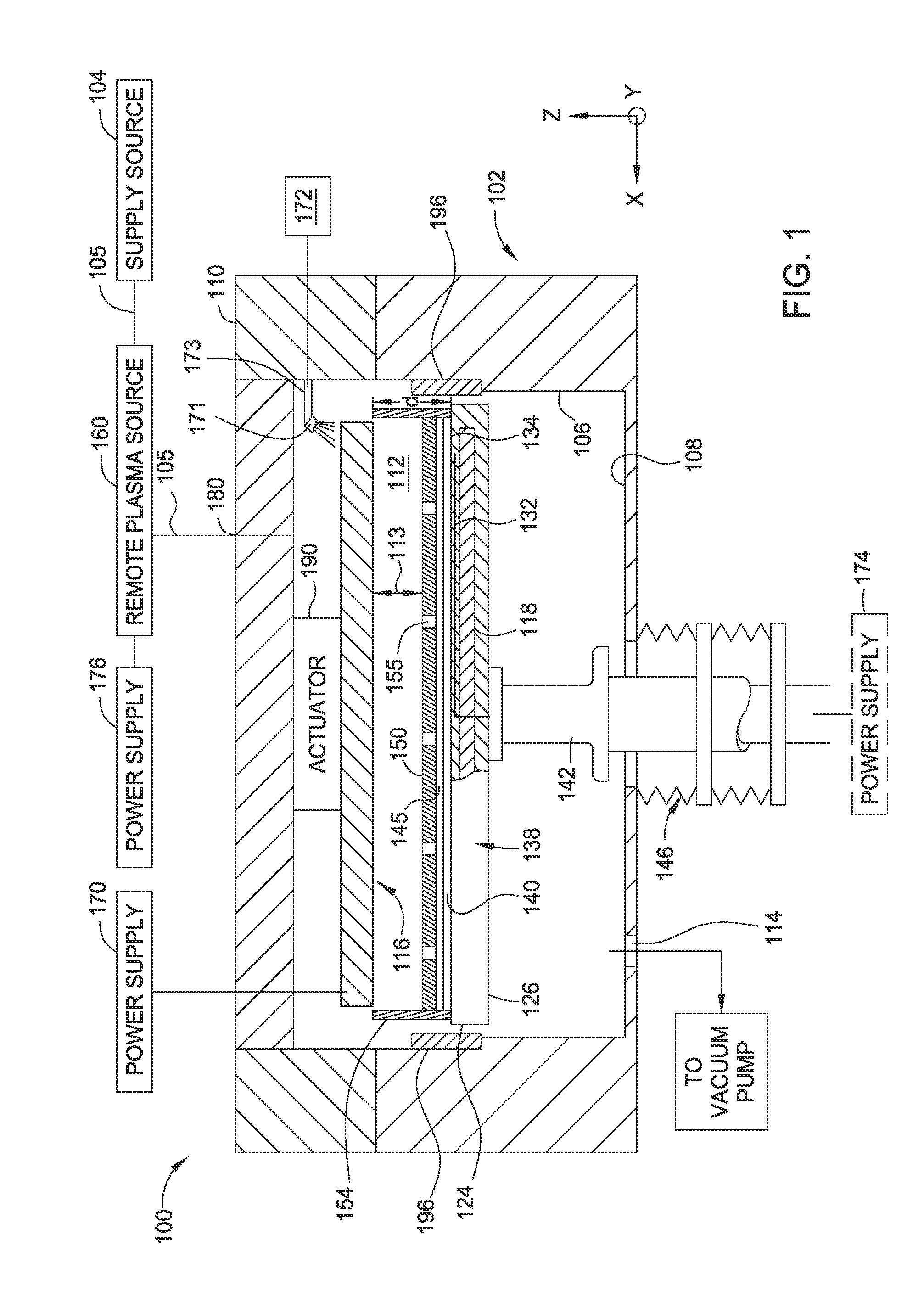
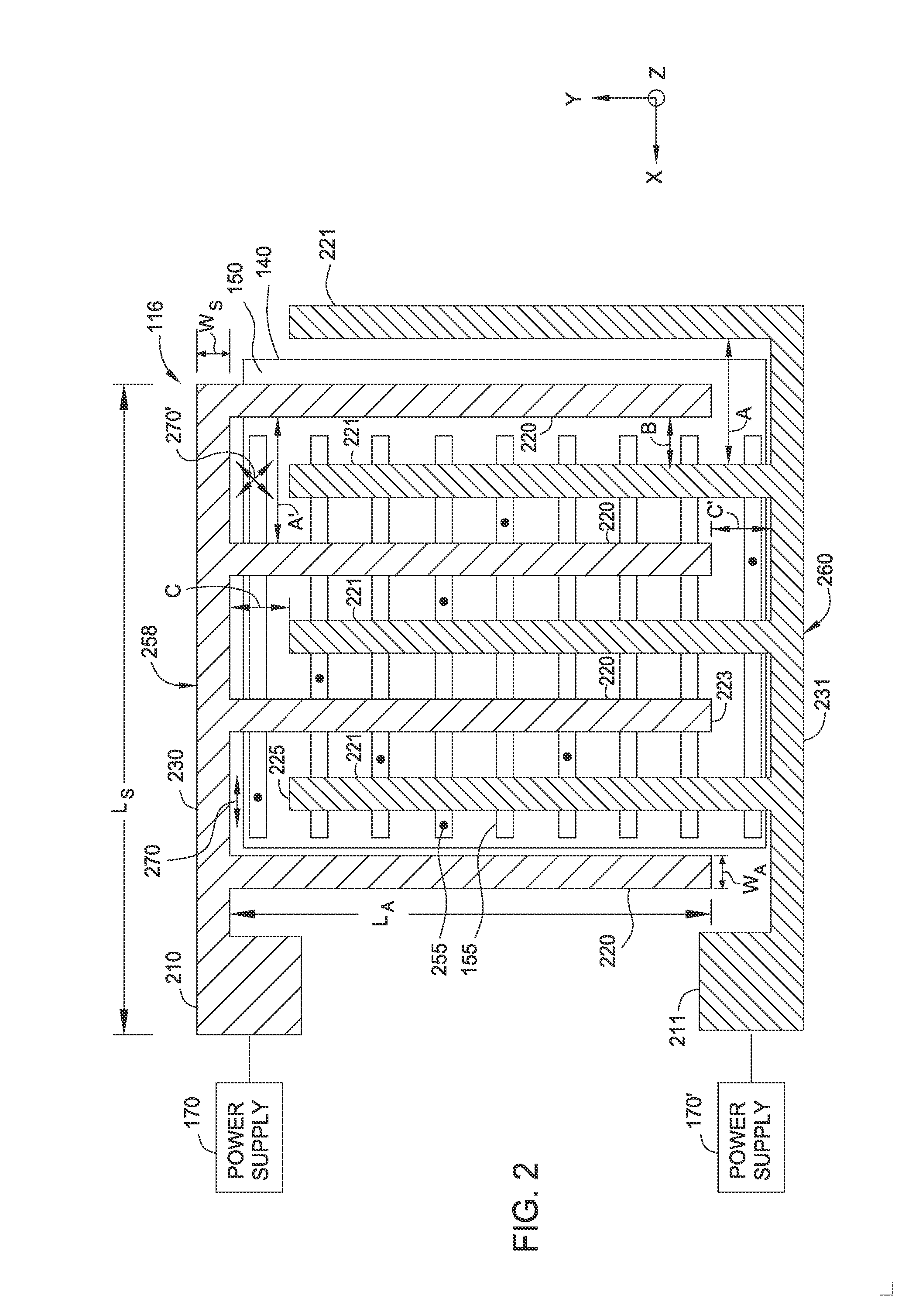
Immersion field guided exposure and post-exposure bake process
ActiveUS20160357107A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringPost exposure
Methods disclosed herein provide apparatus and method for applying an electric field and / or a magnetic field to a photoresist layer without air gap intervention during photolithography processes. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a processing chamber comprising a substrate support having a substrate supporting surface, a heat source embedded in the substrate support configured to heat a substrate positioned on the substrate supporting surface, an electrode assembly configured to generate an electric field in a direction substantially perpendicular to the substrate supporting surface, wherein the electrode assembly is positioned opposite the substrate supporting surface having a downward surface facing the substrate supporting surface, wherein the electrode assembly is spaced apart from substrate support defining a processing volume between the electrode assembly and the substrate supporting surface, and a confinement ring disposed on an edge of the substrate support or the electrode assembly configured to retain an intermediate medium.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Patterning process and resist composition
InactiveUS20110091812A1Resolution is doubledPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage resolutionOrganosolv
The process forms a pattern by applying a resist composition onto a substrate to form a resist film, baking, exposure, post-exposure baking, and development. The resist composition comprises a polymer comprising recurring units having an acid labile group and substantially insoluble in alkaline developer, a PAG, a PBG capable of generating an amino group, a quencher for neutralizing the acid from PAG for inactivation, and an organic solvent. A total amount of amino groups from the quencher and PBG is greater than an amount of acid from PAG. An unexposed region and an over-exposed region are not dissolved in developer whereas only an intermediate exposure dose region is dissolved in developer. Resolution is doubled by splitting a single line into two through single exposure and development.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
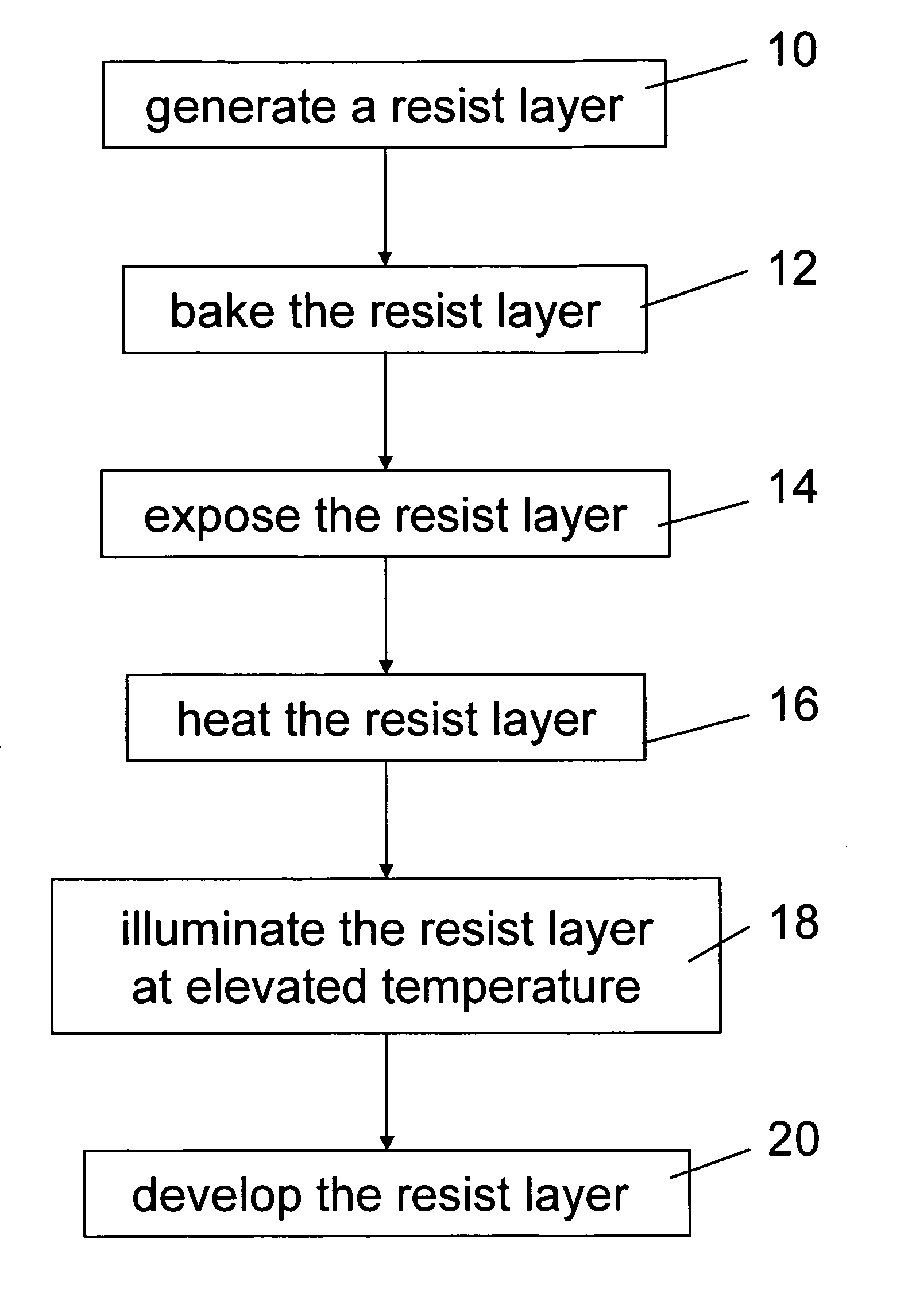
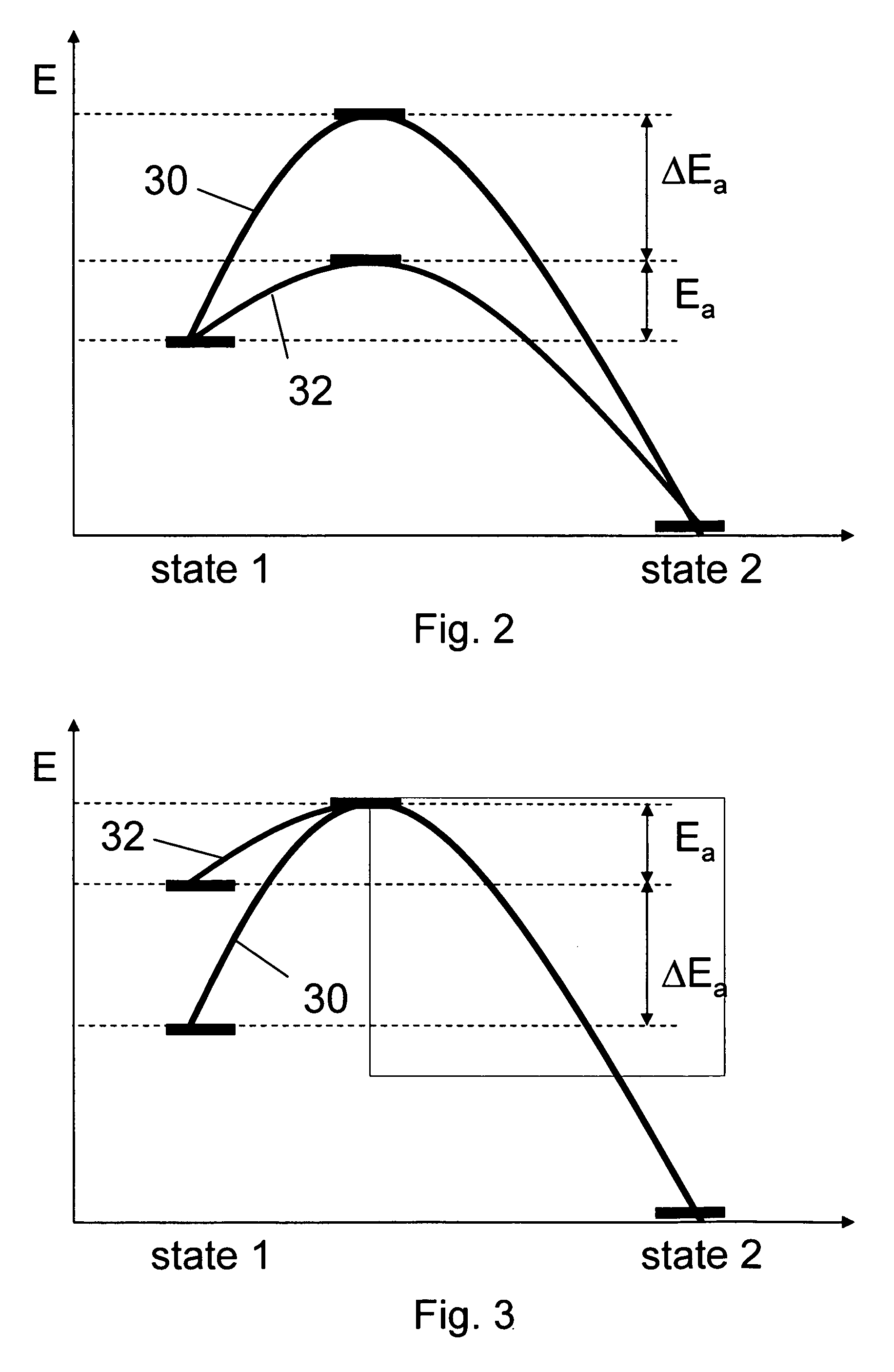
Method and apparatus for a post exposure bake of a resist
InactiveUS20060269879A1Reduce blurReduce diffusePhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhotosensitive material processingResistSolubility
Method and Apparatus for A Post Exposure Bake Of A Resist In a Method for patterning a chemically amplified resist layer, the resist layer is provided on a substrate, the resist layer comprising resist molecules in a first state with a first solubility. Predetermined regions of the resist layer are exposed to a first radiation to generate a catalytic species in the exposed predetermined regions of the resist layer. The resist layer is exposed to a second radiation and resist molecules in the predetermined regions of the resist layer are converted from the first state into a second state with a second solubility, the conversion of a resist molecule being catalyzed by the catalytic species, and the activation energy of the catalyzed conversion of the resist molecule being lowered by the absorption of the second radiation in the resist molecule. The resist layer is developed with a predetermined developer.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Material for formation of resist protection film and method of forming resist pattern therewith
InactiveUS7879529B2Improve featuresHighly accurate resistOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsLithography processAcrylic resin
In the liquid immersion lithography process, by simultaneously preventing deterioration of a resist film and deterioration of an immersion liquid employed during liquid immersion lithography which uses various immersion liquids, including water, resistance to post exposure delay of the resist film can be improved without increasing the number of processes, thereby making it possible to form a high resolution resist pattern using liquid immersion lithography. Furthermore, it is possible to apply a high refractive index liquid immersion medium, used in combination with the high refractive index liquid immersion medium, thus making it possible to further improve pattern accuracy. Using a composition comprising an acrylic resin component having characteristics which have substantially no compatibility with a liquid in which a resist film is immersed, particularly water, and are also soluble in alkaline, a protective film is formed on the surface of a resist film used.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Method for treating photosensitive lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS6558875B1Satisfactory image strengthX-ray/infra-red processesPhotosensitive materialsLaser lightEngineering
A method for treating a photosensitive lithographic printing plate, which comprises exposing the photosensitive lithographic printing plate to laser light, developing with a developer containing an alkali metal silicate and then carrying out post-exposure treatment, said photosensitive lithographic printing plate being prepared by forming a photopolymerizable photosensitive layer having a film thickness of from 1.2 to 4 g / m2 and further forming a protective layer having a film thickness of from 2 to 8 g / m2 on a support having a centerline average height (Ra) of at least 0.35 mum.
Owner:AGFA NV
Method of preparing optically imaged high performance photomasks
InactiveUS20030027083A1Uniform critical dimensionLong stable periodRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContinuous waveLength wave
One principal embodiment of the disclosure pertains to a method of optically fabricating a photomask using a direct write continuous wave laser, comprising a series of steps including: applying an organic antireflection coating over a surface of a photomask which includes a chrome-containing layer; applying a chemically-amplified DUV photoresist over the organic antireflection coating; post apply baking the DUV photoresist over a specific temperature range; exposing a surface of the DUV photoresist to the direct write continuous wave laser; and, post exposure baking the imaged DUV photoresist over a specific temperature range. The direct write continuous wave laser preferably operates at a wavelength of 244 nm or 257 nm. In an alternative embodiment, the organic antireflection coating may be applied over an inorganic antireflection coating which overlies the chrome containing layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High performance sol-gel spin-on glass materials
InactiveUS7393469B2Improve adaptabilityIncrease flexibilityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPhotomechanical apparatusSilanesRoom temperature
Hybrid sol-gel materials are provided, which may be produced by the reaction of an alkyl or dialkyl substituted trialkoxysilane or dialkoxysilane reacting with a silane diol, wherein said alkyl group has from 1 to 8 carbon atoms. A process is also provided for patterning the sol-gel spin-on glass material by: a) coating a substrate with the spin-on glass material; b) exposing the coated substrate of step a) to UV illumination in a desired pattern; c) post-exposure baking the coated substrate of step b) at a temperature from 100° C. to 120° C. for 30 to 60 minutes; d) cooling the coated substrate of step c) to room temperature; e) removing the non-exposed areas of the coating on the coated substrate of step d); f) drying the coated substrate of step e); g) hard baking the coated substrate of step f) at a temperature from 120° C. and 150° C. for 1 to 3 hours.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
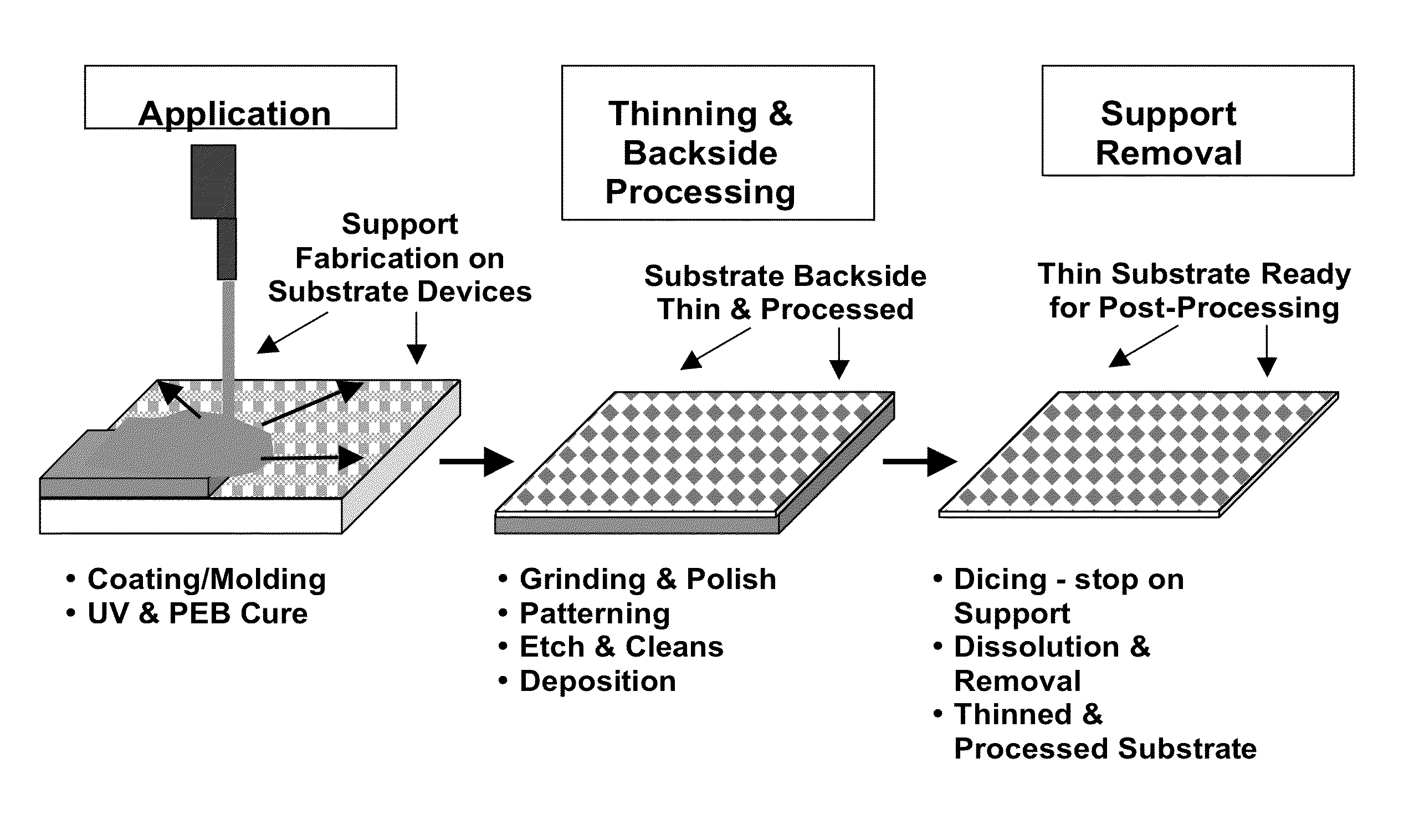
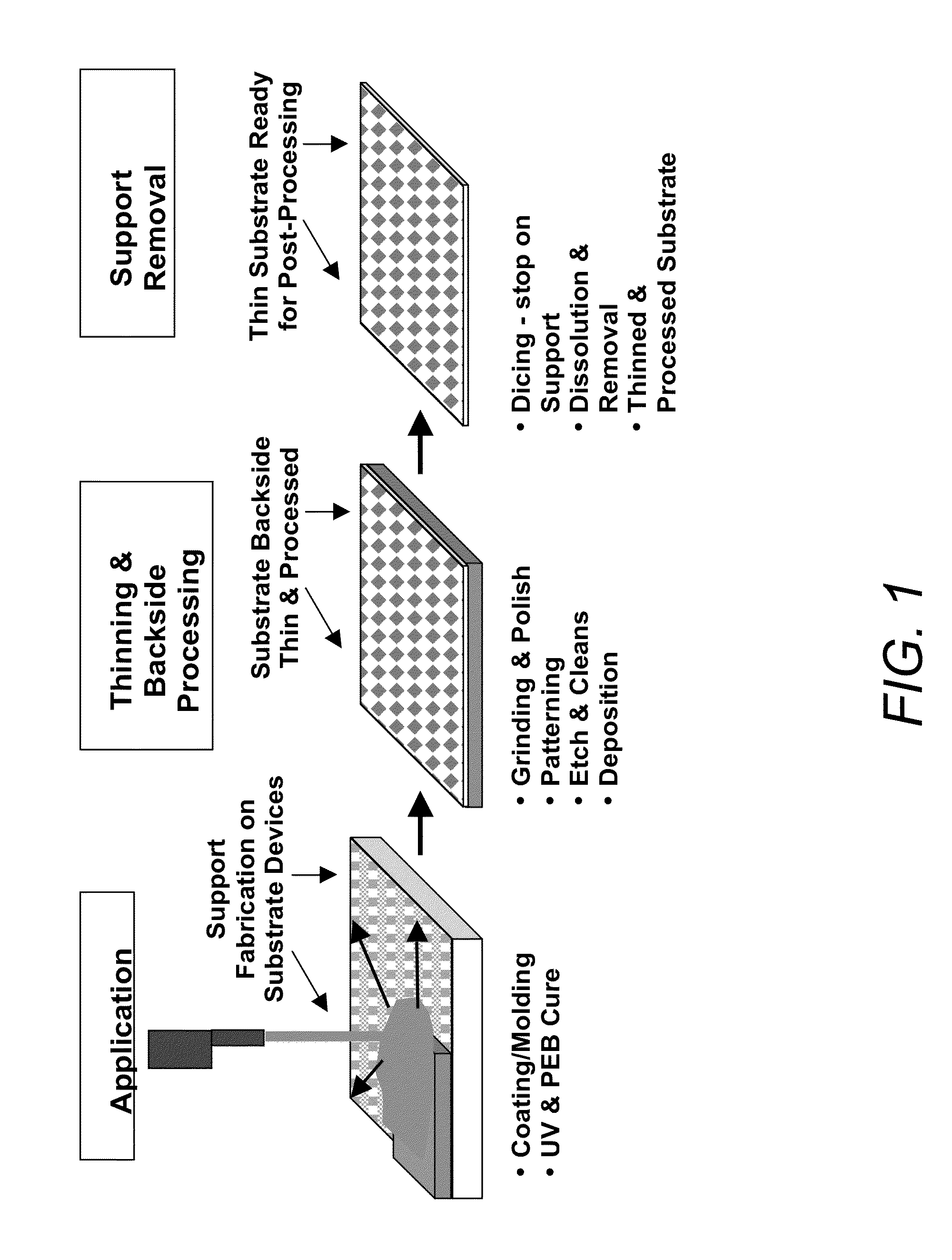
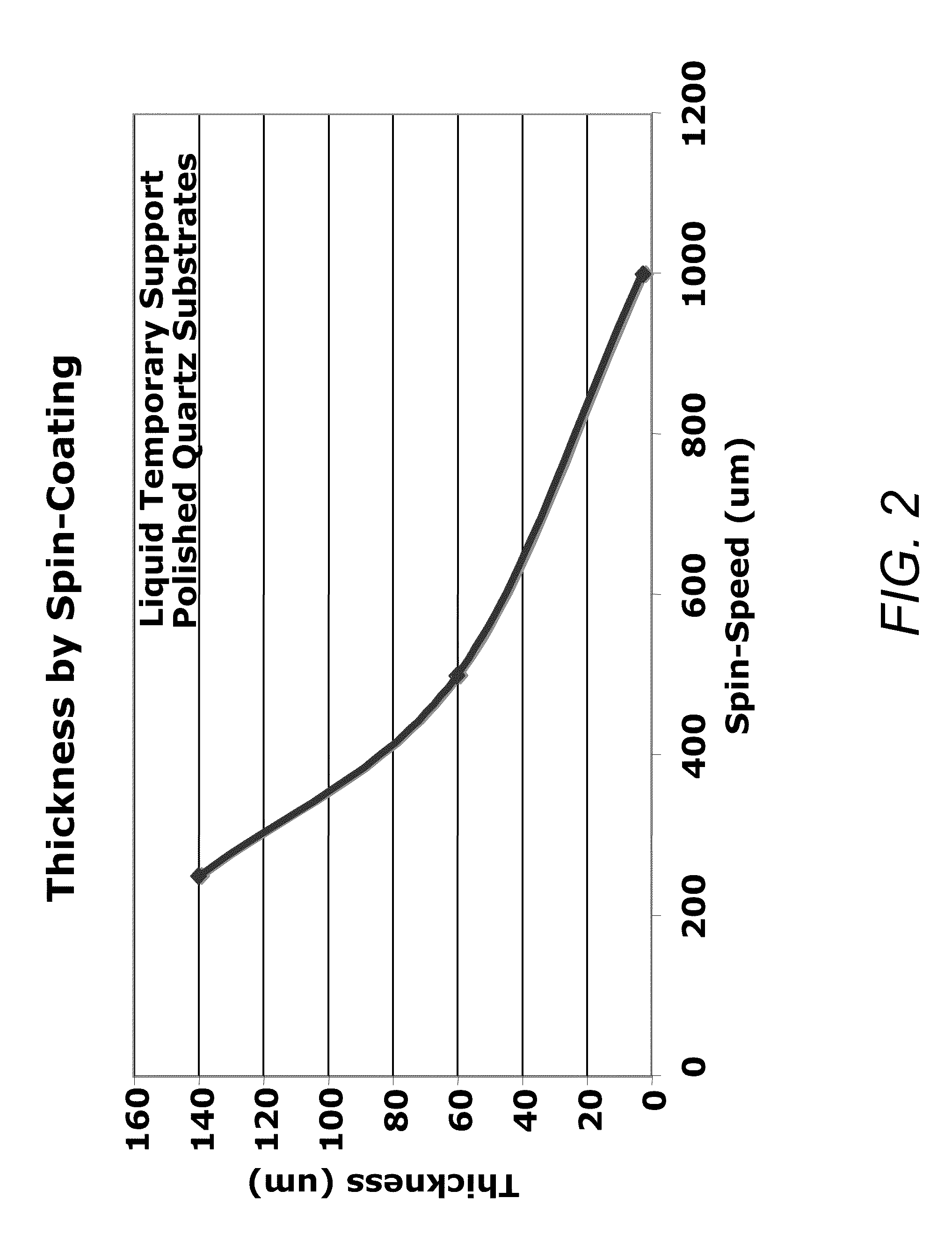
Rapid fabrication of a microelectronic temporary support for inorganic substrates
InactiveUS20100264566A1Eliminate useEliminate damageLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid layerOutgassing
A method for fabricating a rigid temporary support used for supporting inorganic substrates during processing includes providing an inorganic substrate comprising a first surface to be processed and a second surface opposite to the first surface. Next, applying a liquid layer to the second surface of the inorganic substrate and then curing the applied liquid layer and thereby forming a rigid temporary support attached to the second surface of the inorganic substrate. Next, processing the first surface of the inorganic substrate while supporting the inorganic substrate upon the rigid temporary support. The curing includes first exposing the applied liquid layer to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and then performing a post exposure bake (PEB) at a temperature sufficient to complete the curing of the applied liquid layer and to promote outgassing of substances.
Owner:SUSS MICRO TEC LITHOGRAPHY
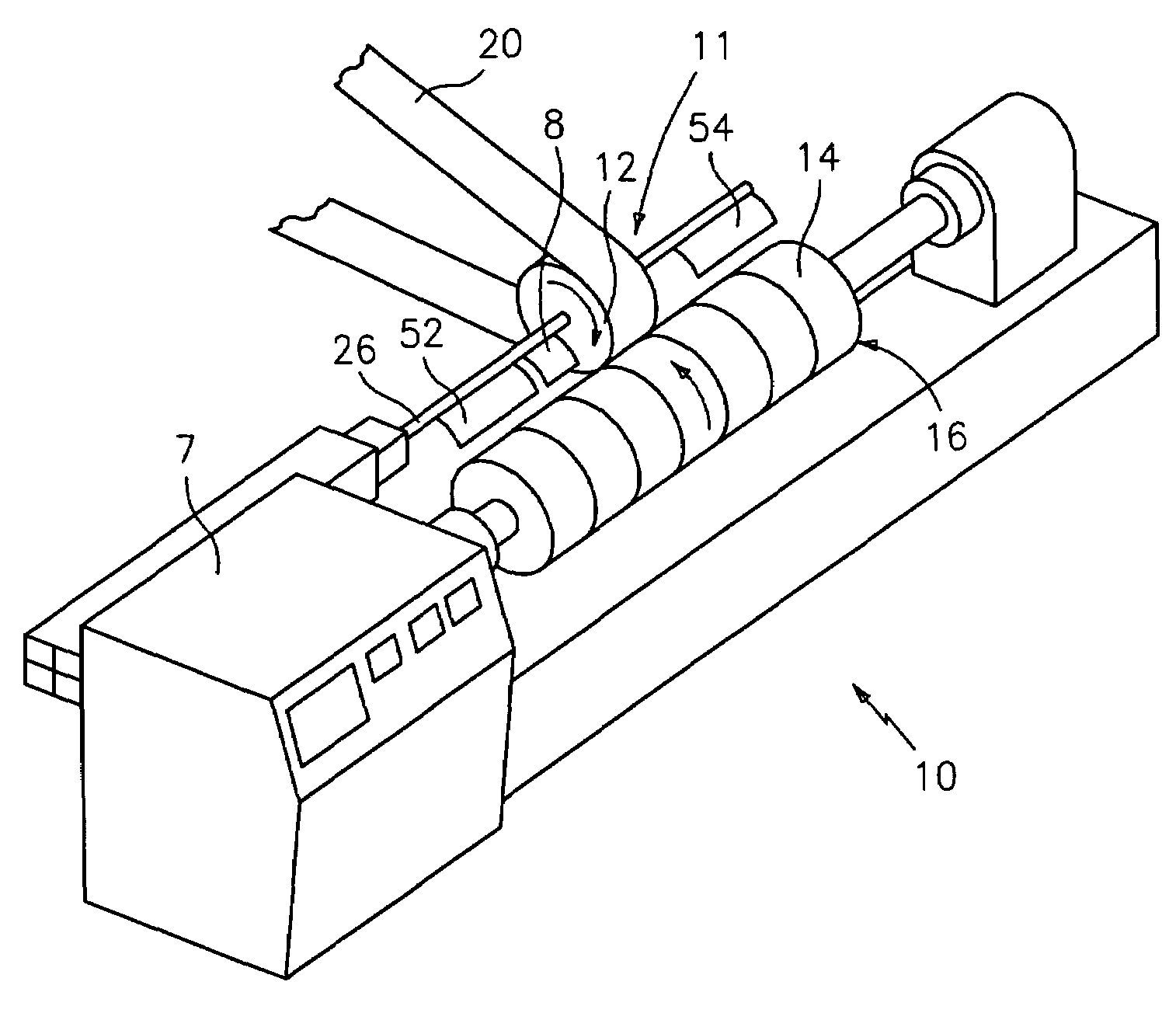
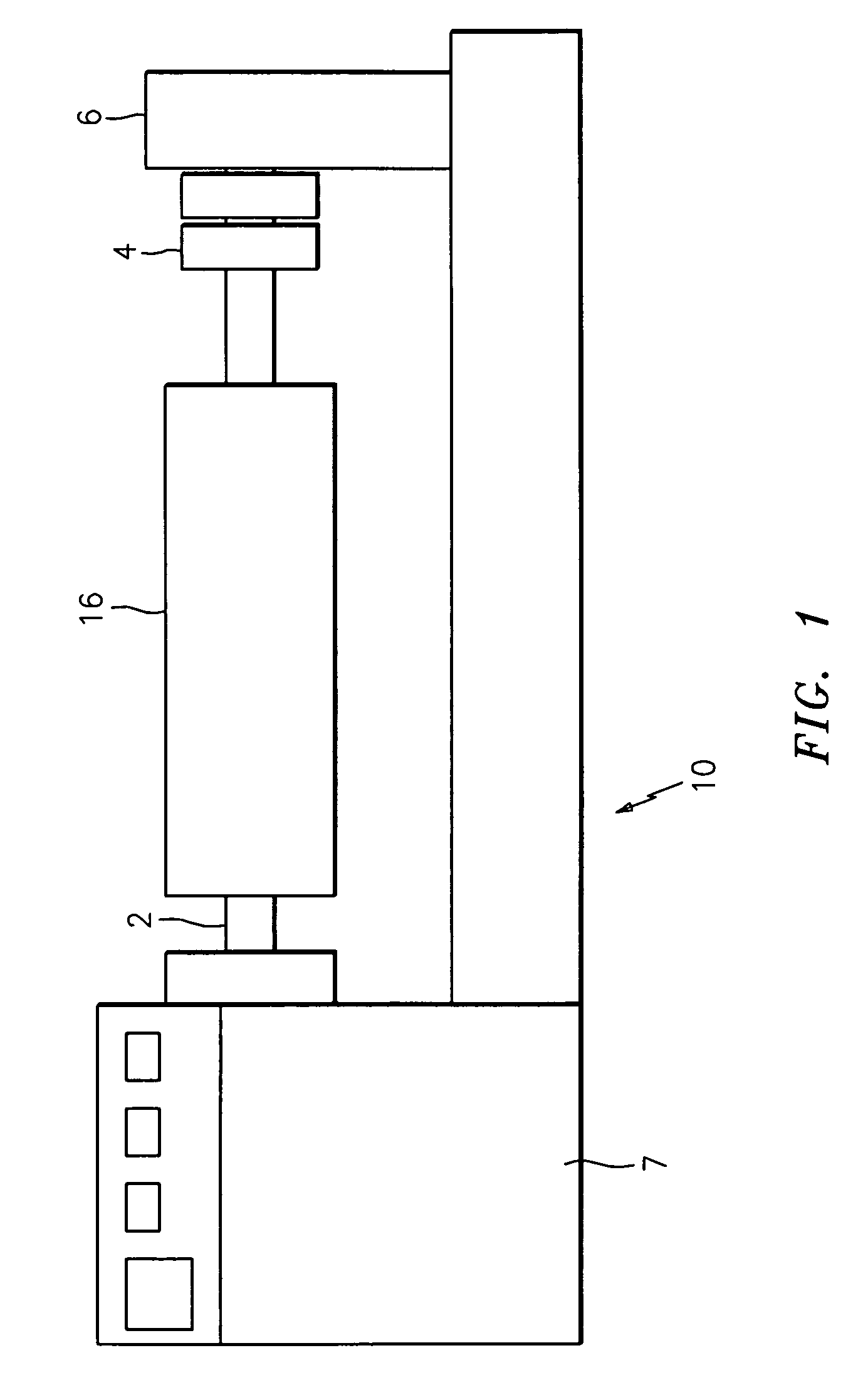
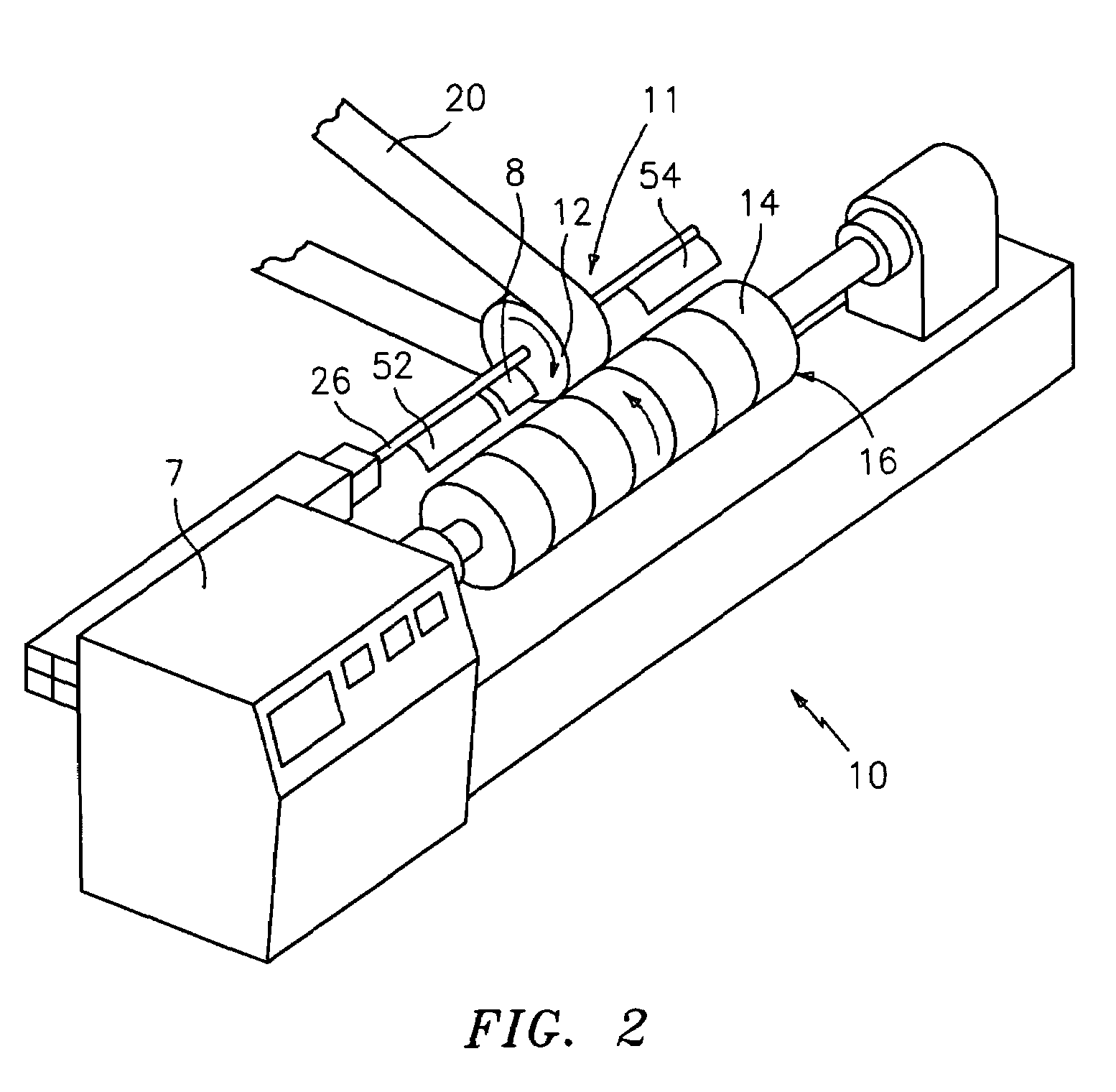
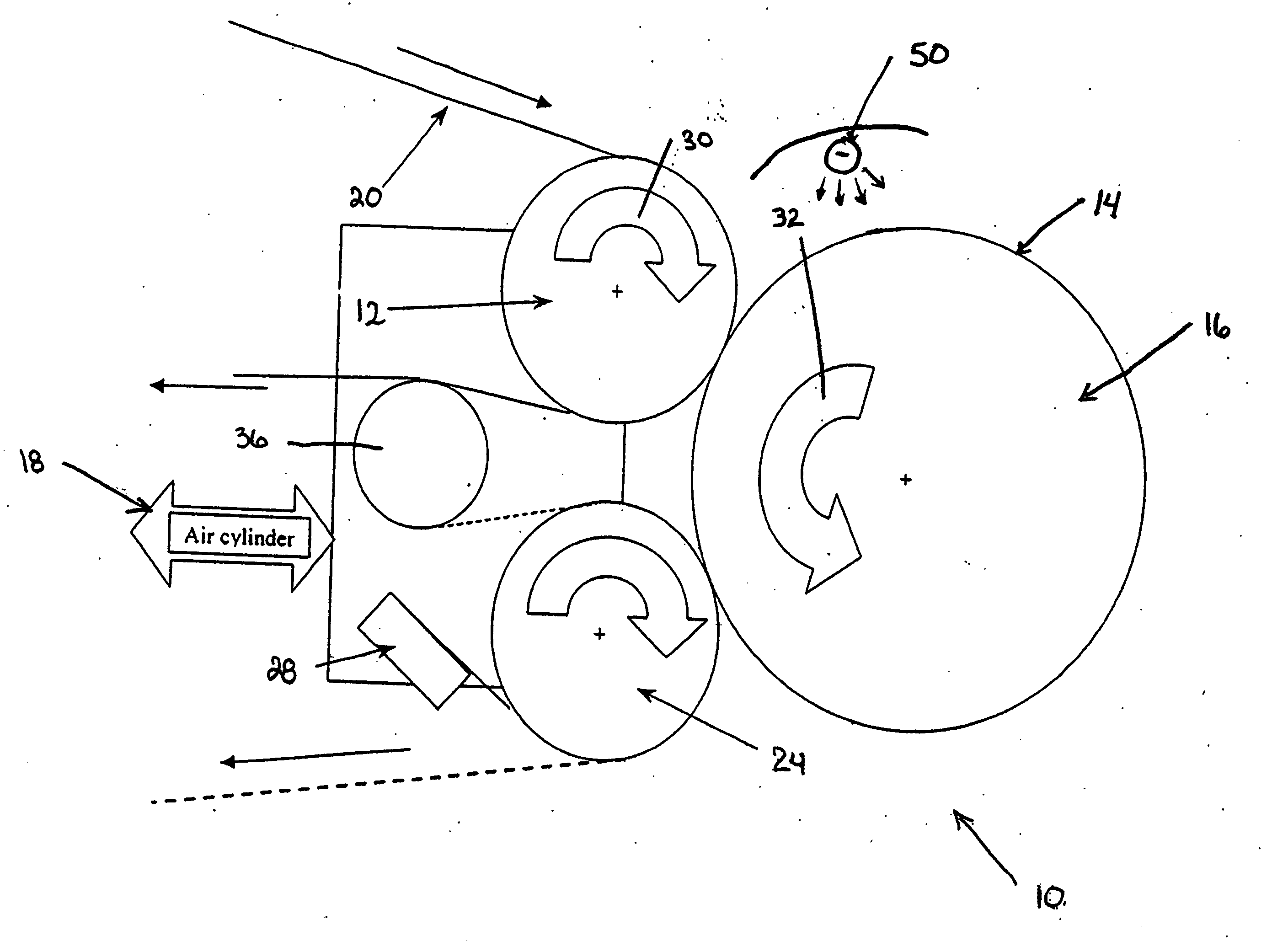
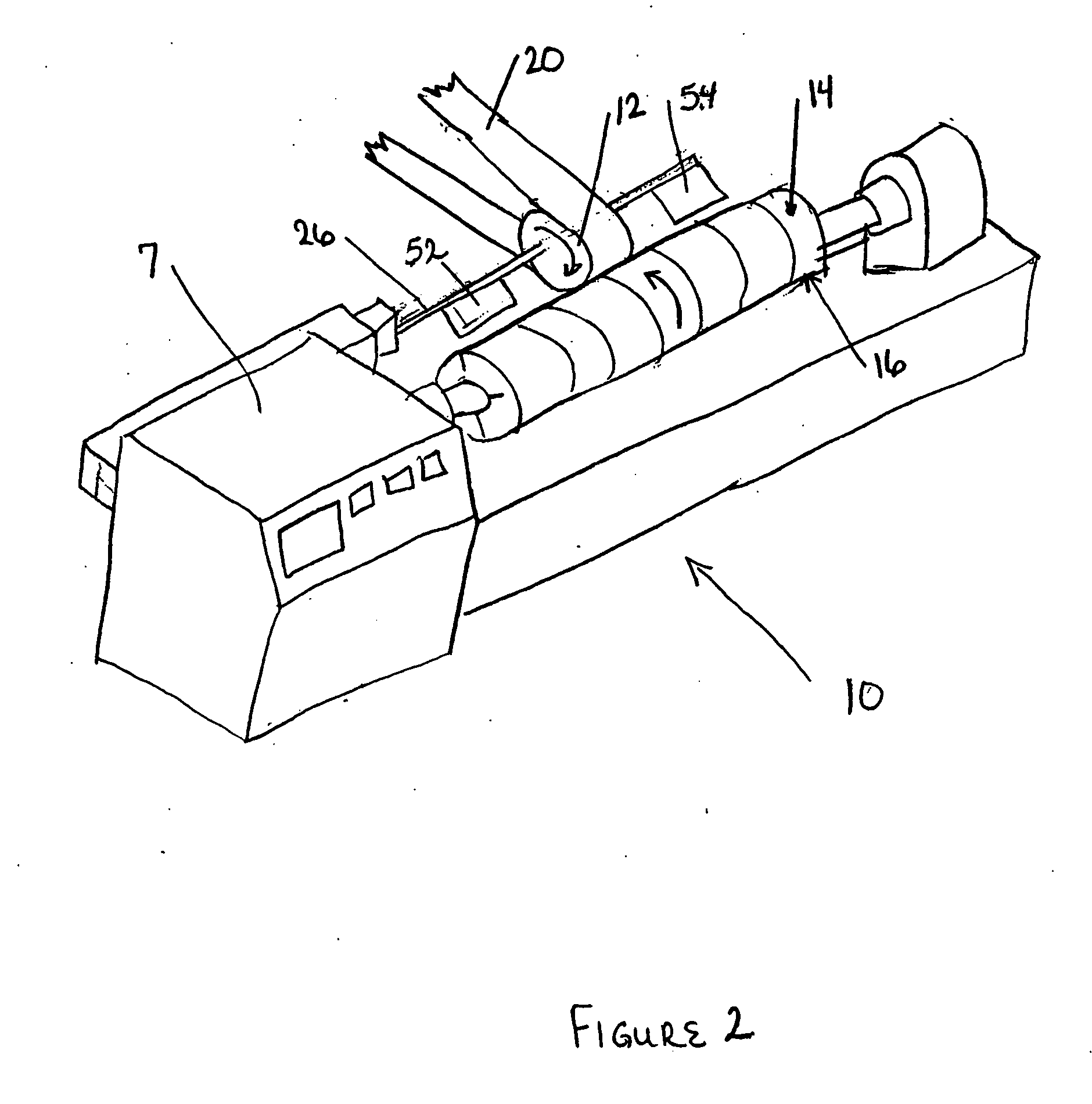
Flexo processor
ActiveUS7237482B2The process is convenient and fastGood flexibilityPlaten pressesMulticolor photographic processingHeat sensitivePost exposure
An improved flexo processor and a method of using the improved flexo processor to increase the flexibility of both the type and the size of the flexographic printing element that may be processed. The novel thermal plate processor system is capable of processing both flat and round photosensitive printing elements with only minimal changes to the system. The thermal plate processor system may also include means for exposure and post-exposure / detack in the same system.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
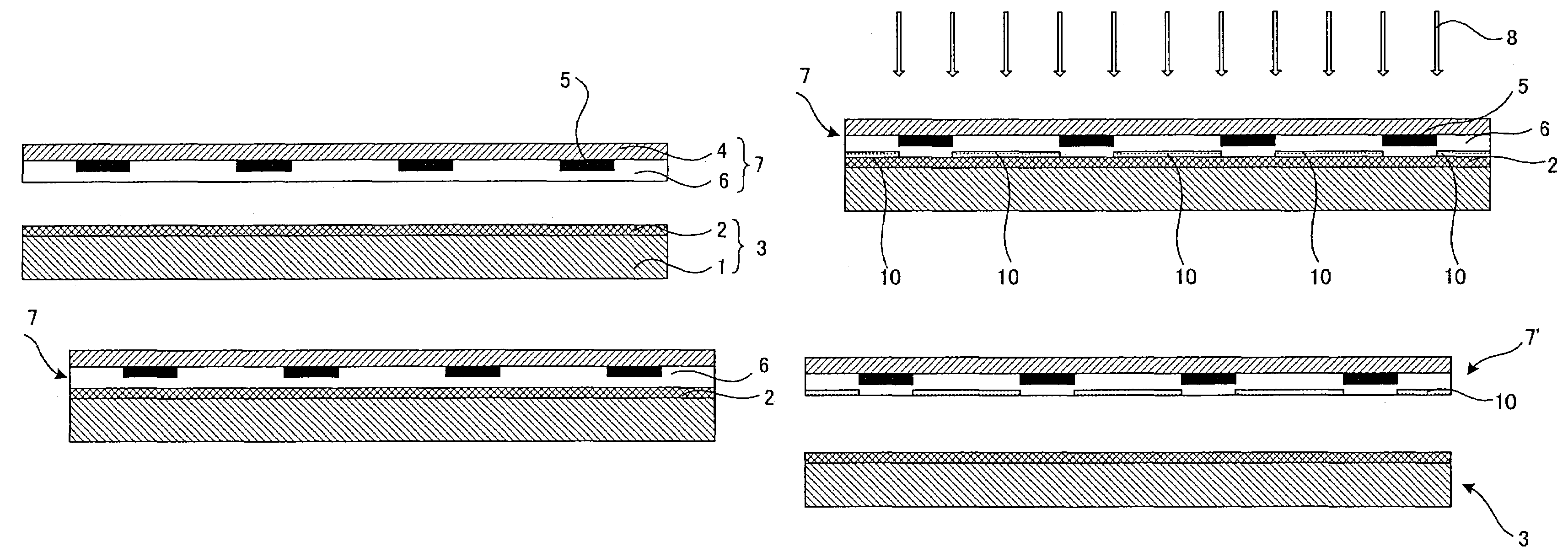
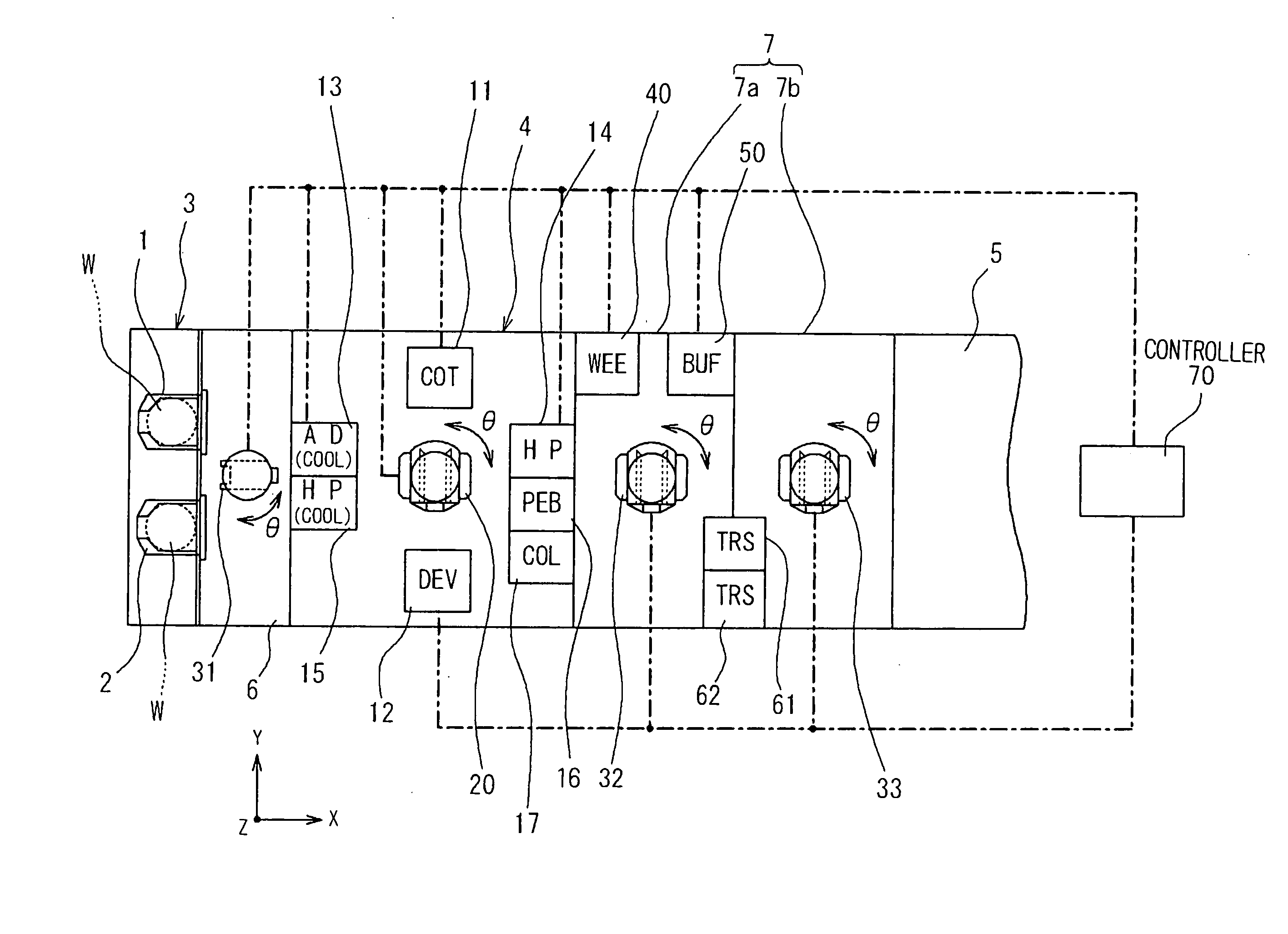
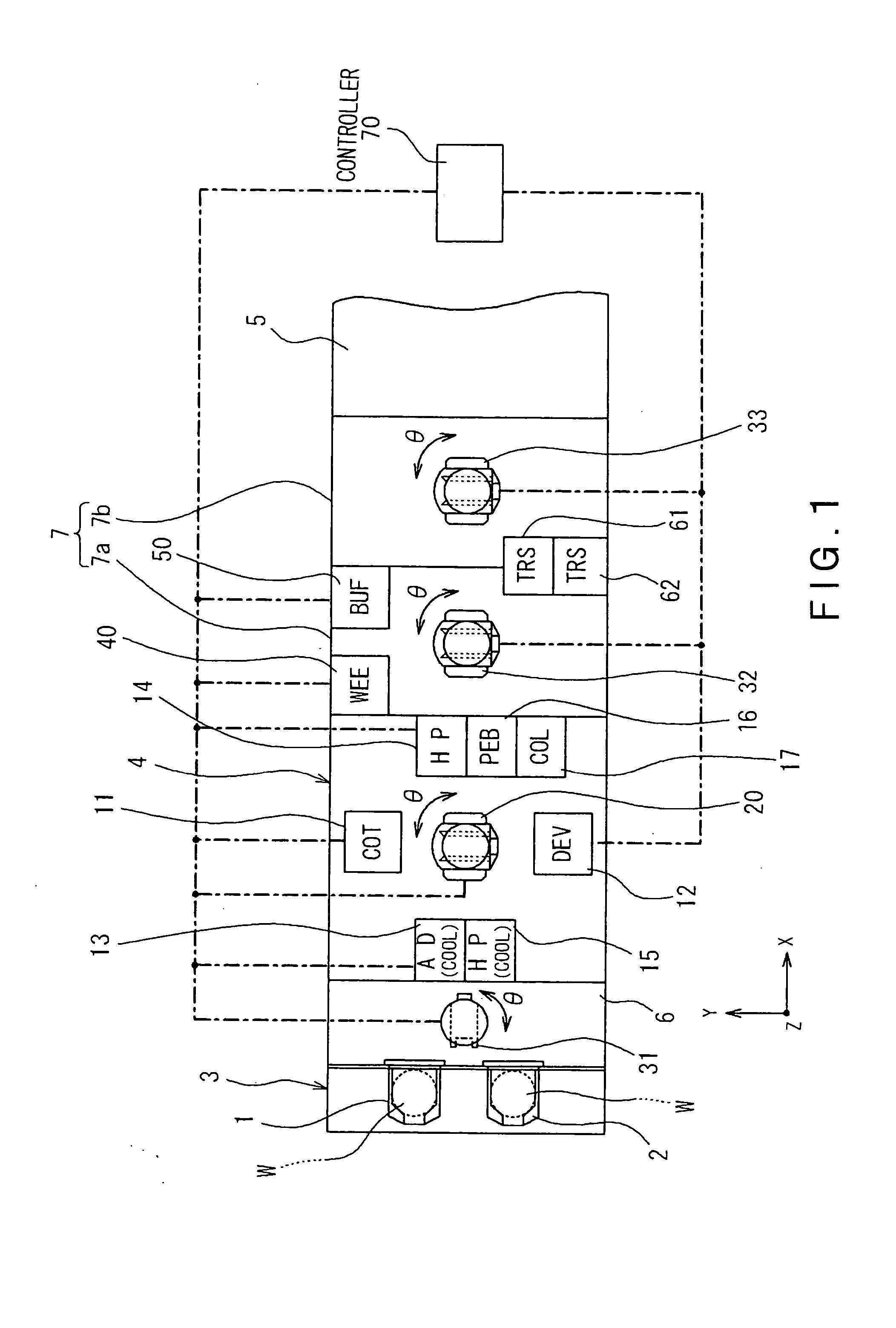
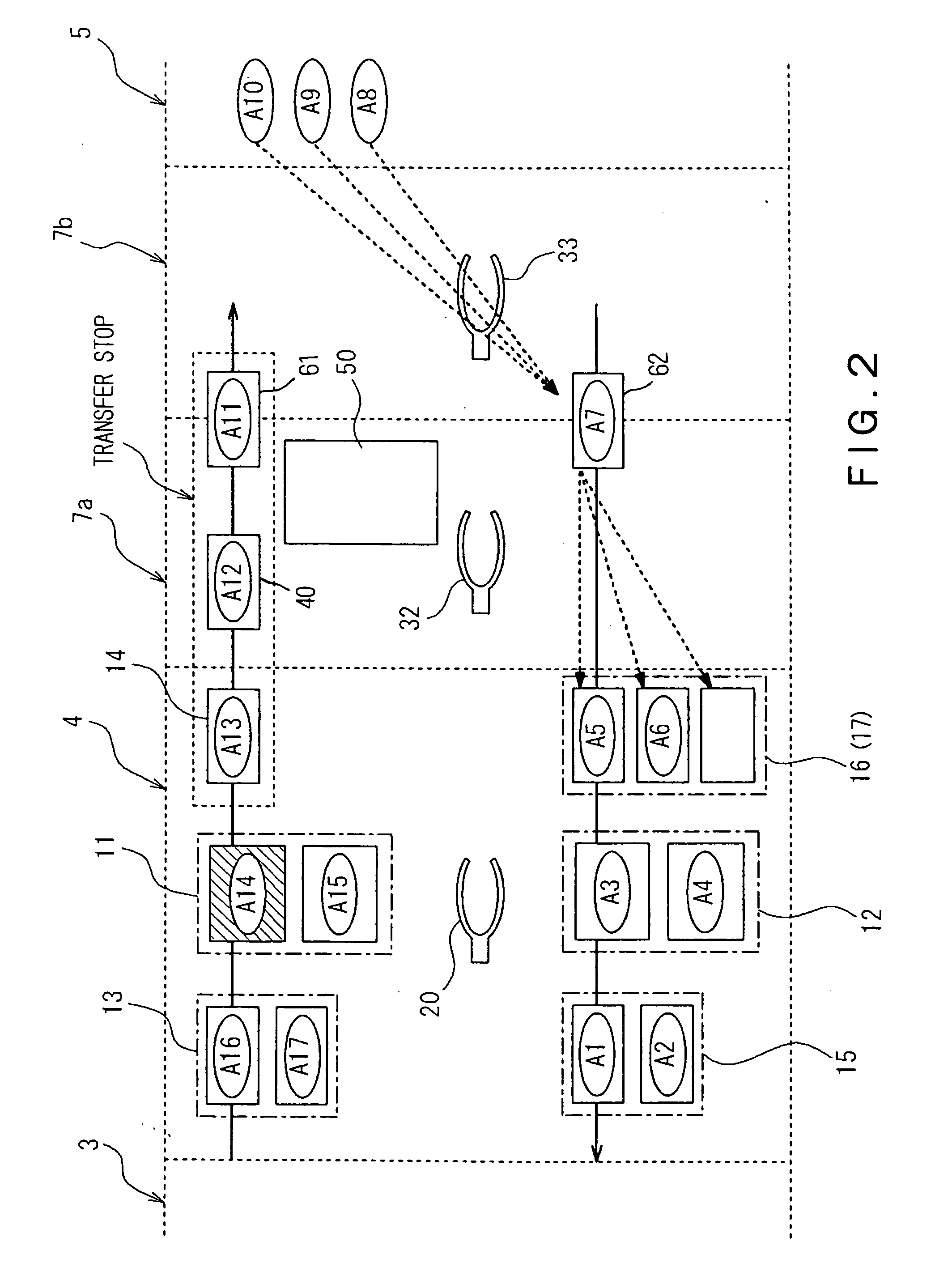
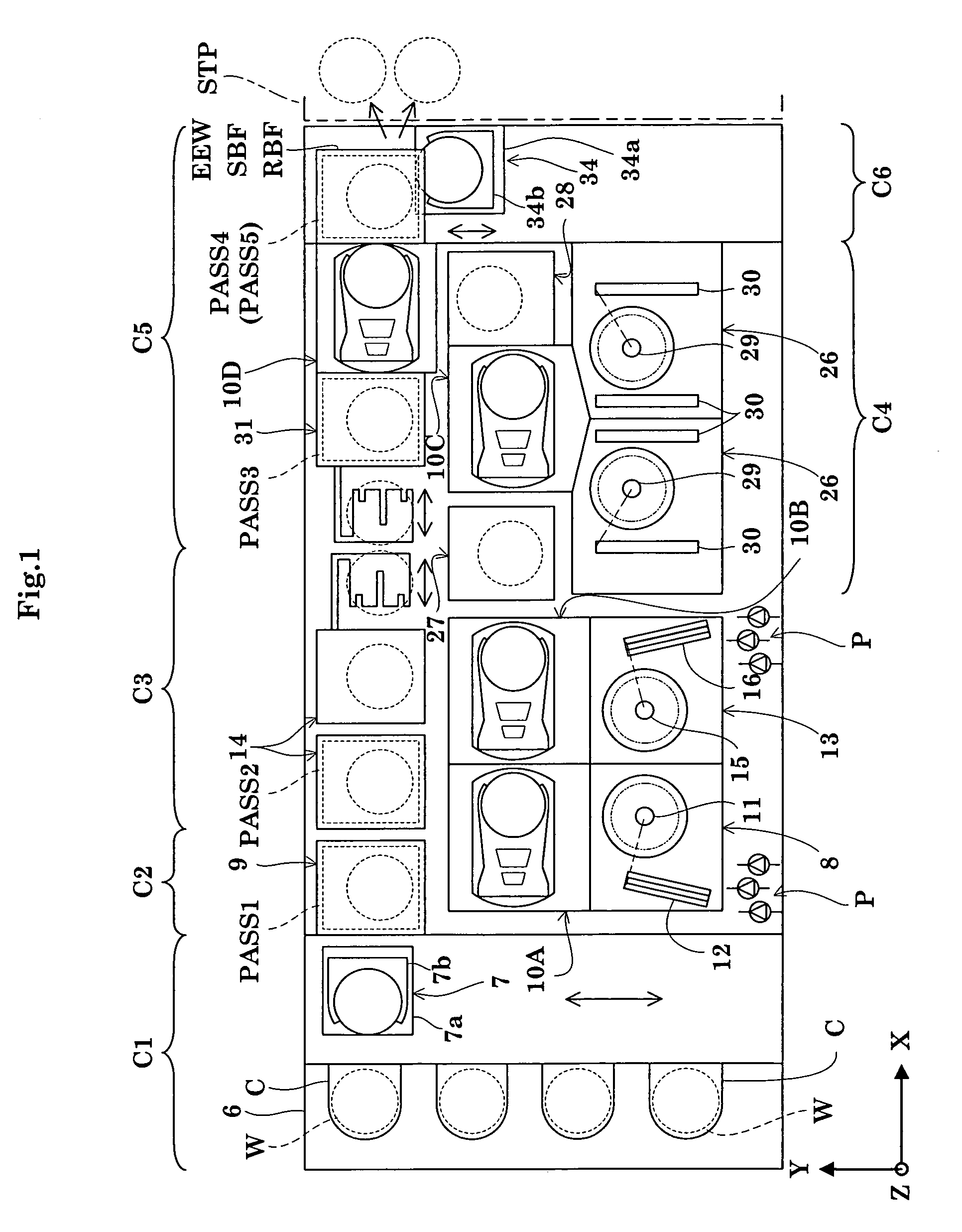
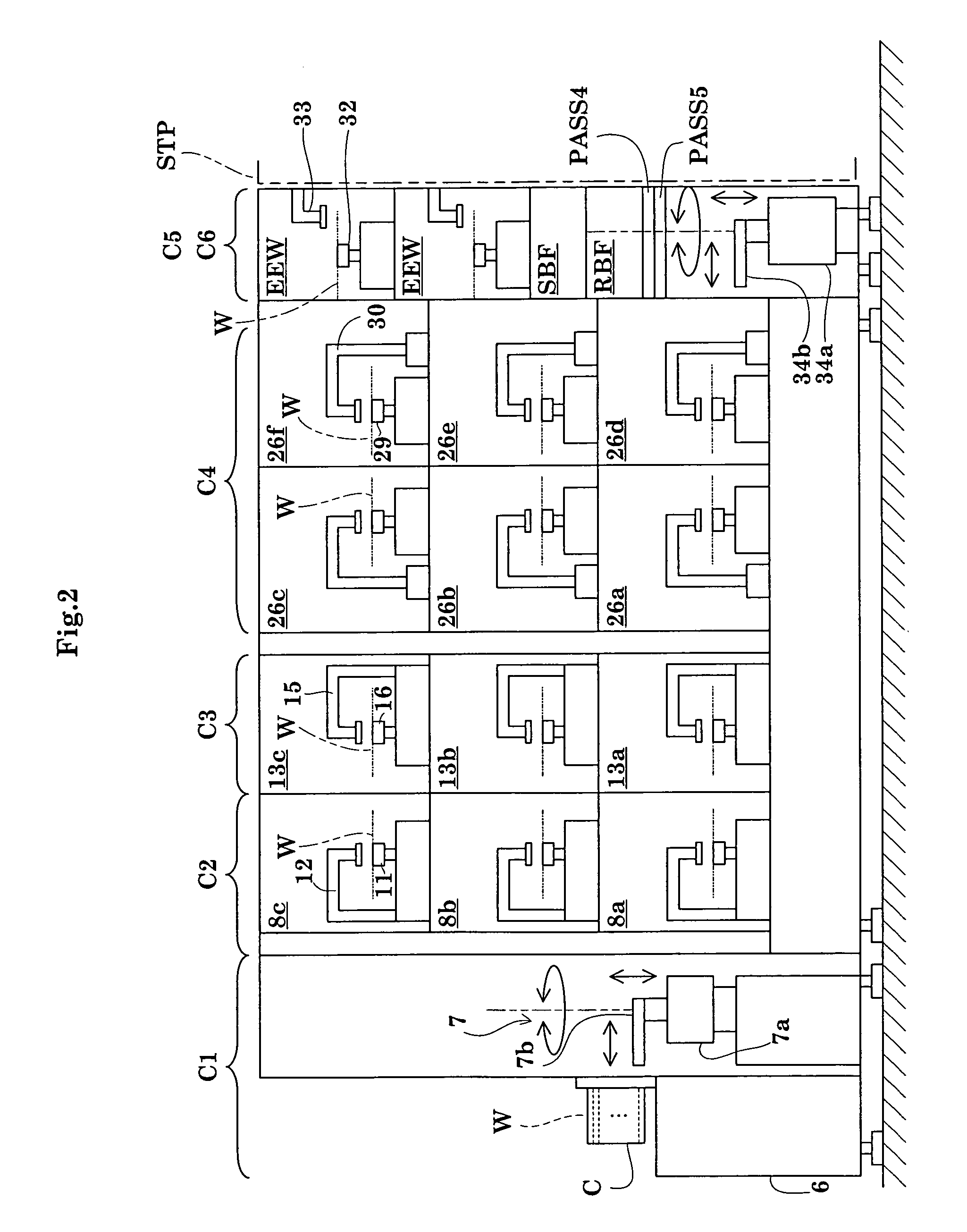
Substrate transporting and processing apparatus, fault management method for substrate transport and processing apparatus, and storage medium storing fault management program
InactiveUS20070219660A1Avoid increase in time intervalLow yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial data processing applicationsResistCooking & baking
Disclosed is a countermeasure to be taken when a fault occurs in one of process modules 11-17 or a transport module 20 that makes it impossible to transport substrates to a process module positioned downstream of a post-exposure baking module 15 in accordance with a predetermined transport schedule in a post-exposure substrate transport path that starts from an exposure apparatus 5 and goes through the post-exposure baking (PEB) module 15, a developing module 12, and a post-development baking module 15. In this instance, part of post-exposure processes to a post-exposure baking process are continuously performed to the exposed substrates and the wafers W having been subjected to the PEB process are loaded into a buffer module 32 and temporarily stored in the buffer module 32 until the fault is cleared. This prevents increase in the time period from an exposure process completion to the post-exposure baking process even when the fault occurs, thereby avoiding defective line width the circuit pattern of a resist, particularly a chemically amplified resist.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
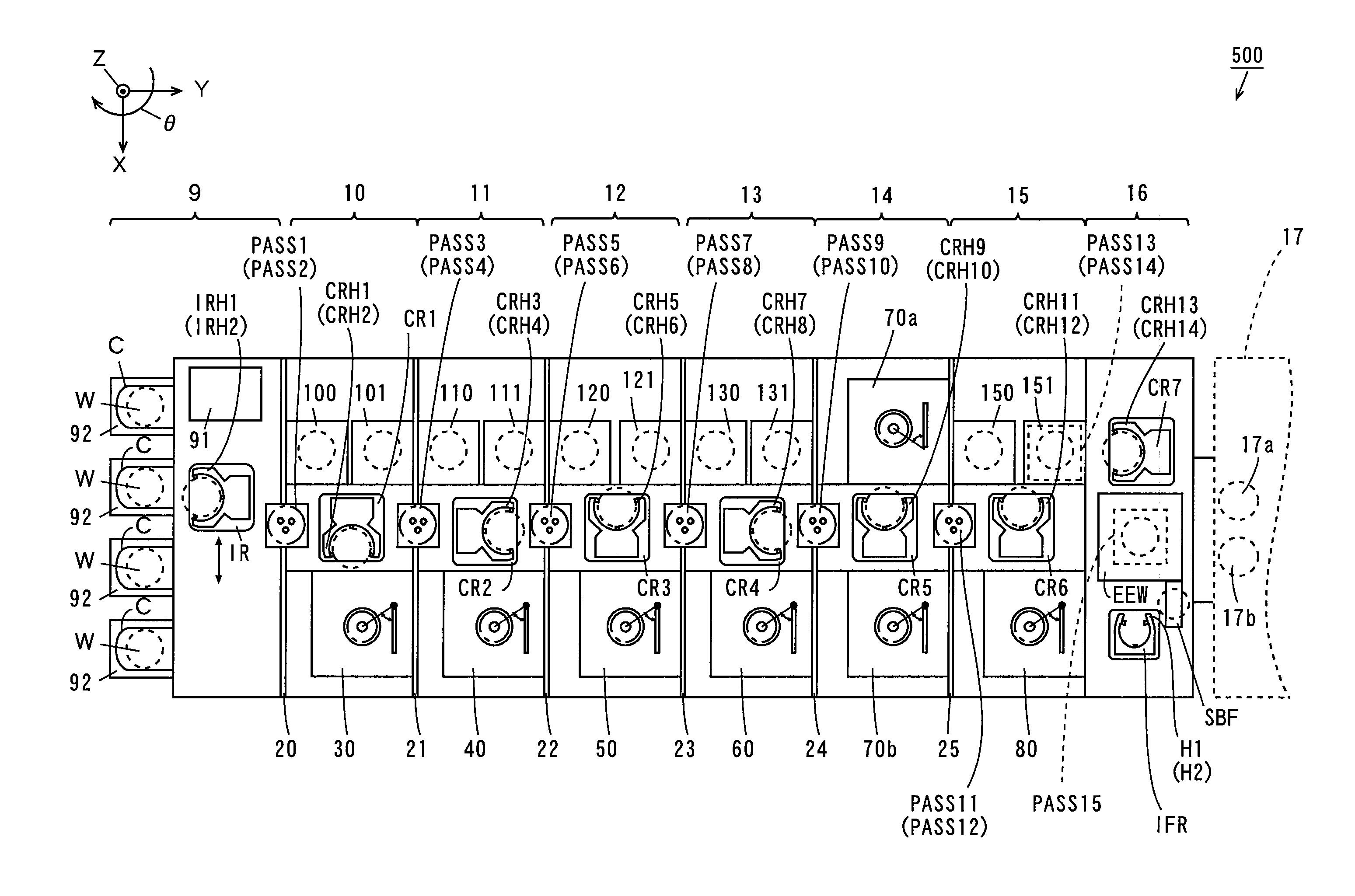
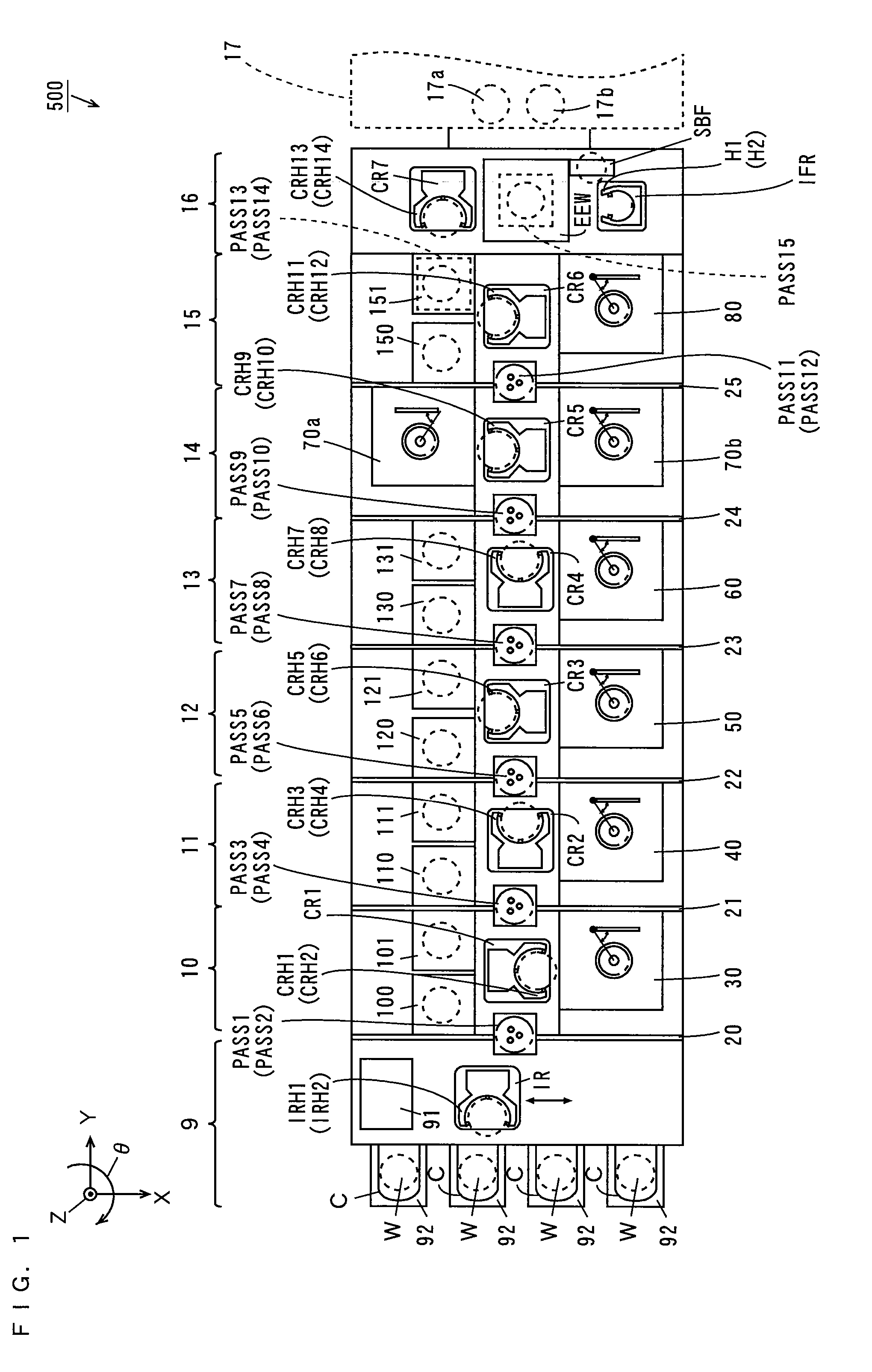
Substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070071439A1Operation is troublesomeLiquid processingPhotomechanical apparatusPulp and paper industryPost exposure
The transporting process from cleaning and drying processing of a substrate in a cleaning / drying processing unit in a cleaning / drying processing group to post-exposure bake (PEB) of the substrate in a thermal processing group for post-exposure bake in a cleaning / drying processing block is described below. First, after the substrate after exposure processing is subjected to the cleaning and drying processing in the cleaning / drying processing group, a sixth central robot takes out the substrate from the cleaning / drying processing group and carries that substrate into the thermal processing group for post-exposure bake in the cleaning / drying processing block.
Owner:SOKUDO CO LTD
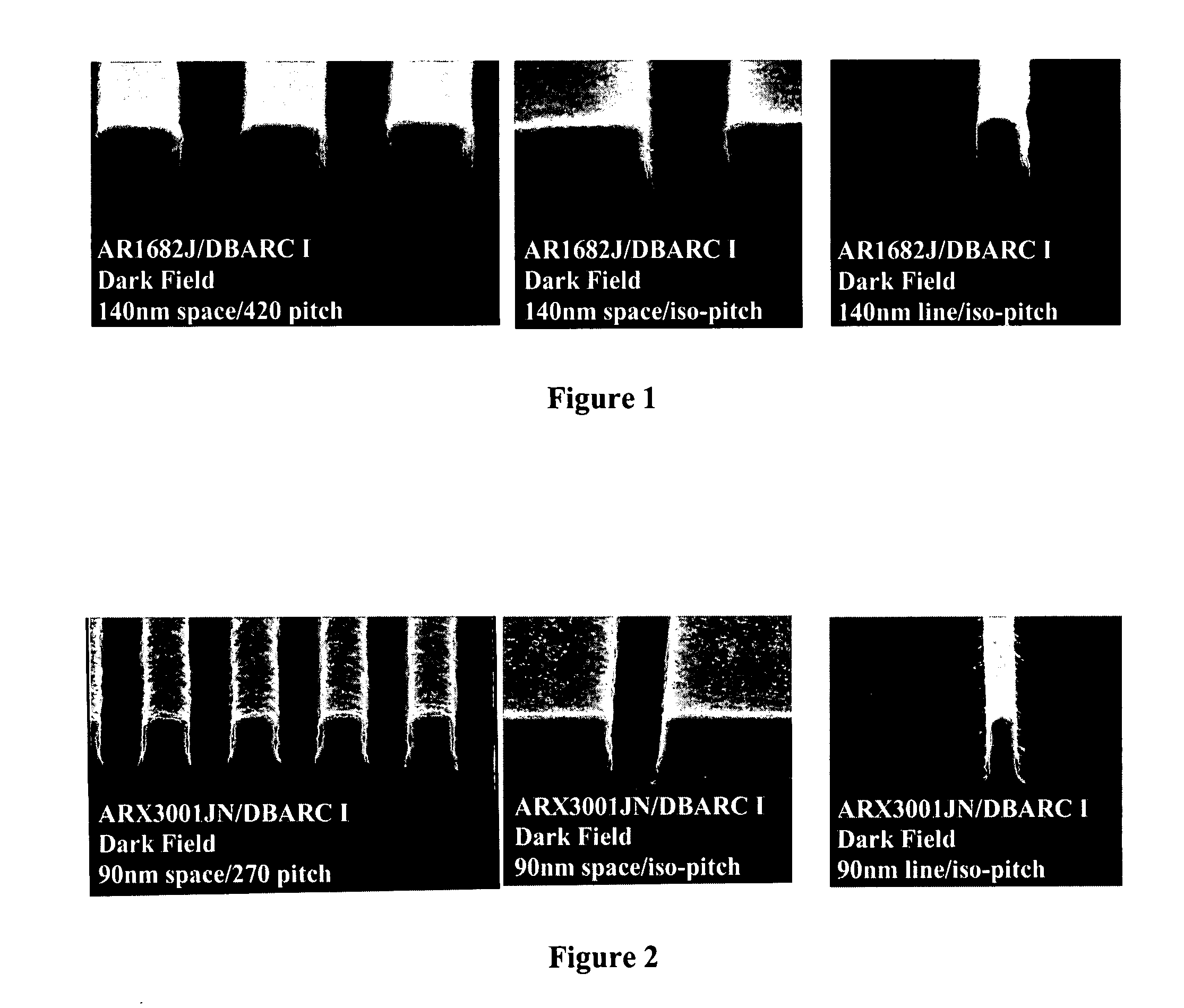
Radiation-Sensitive, Wet Developable Bottom Antireflective Coating Compositions and Their Applications in Semiconductor Manufacturing
InactiveUS20090098490A1Eliminates scummingReduce scumPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusPhotoacidPhotoacid generator
The present invention is directed to novel radiation-sensitive, wet developable bottom antireflective coating (DBARC) compositions and their use in semiconductor device manufacturing. The DBARC compositions contain a photoacid generator that produces a photoacid upon exposure to activating radiation. In a photolithographic imaging process, the relatively strong photoacid reduces or eliminates scumming. Further, the relatively large size of the photoacid limits its diffusion through the DBARC, thus minimizing or preventing undercut. The inventive method also limits diffusion of the photoacid by controlling the temperature of the post-exposure baking step. Use of the DBARC compositions with a photoresist in photolithography results in highly resolved features having essentially vertical profiles and no scumming and no undercut, which is critical as microelectronics and semiconductor components become increasingly miniaturized.
Owner:JSR MICRO
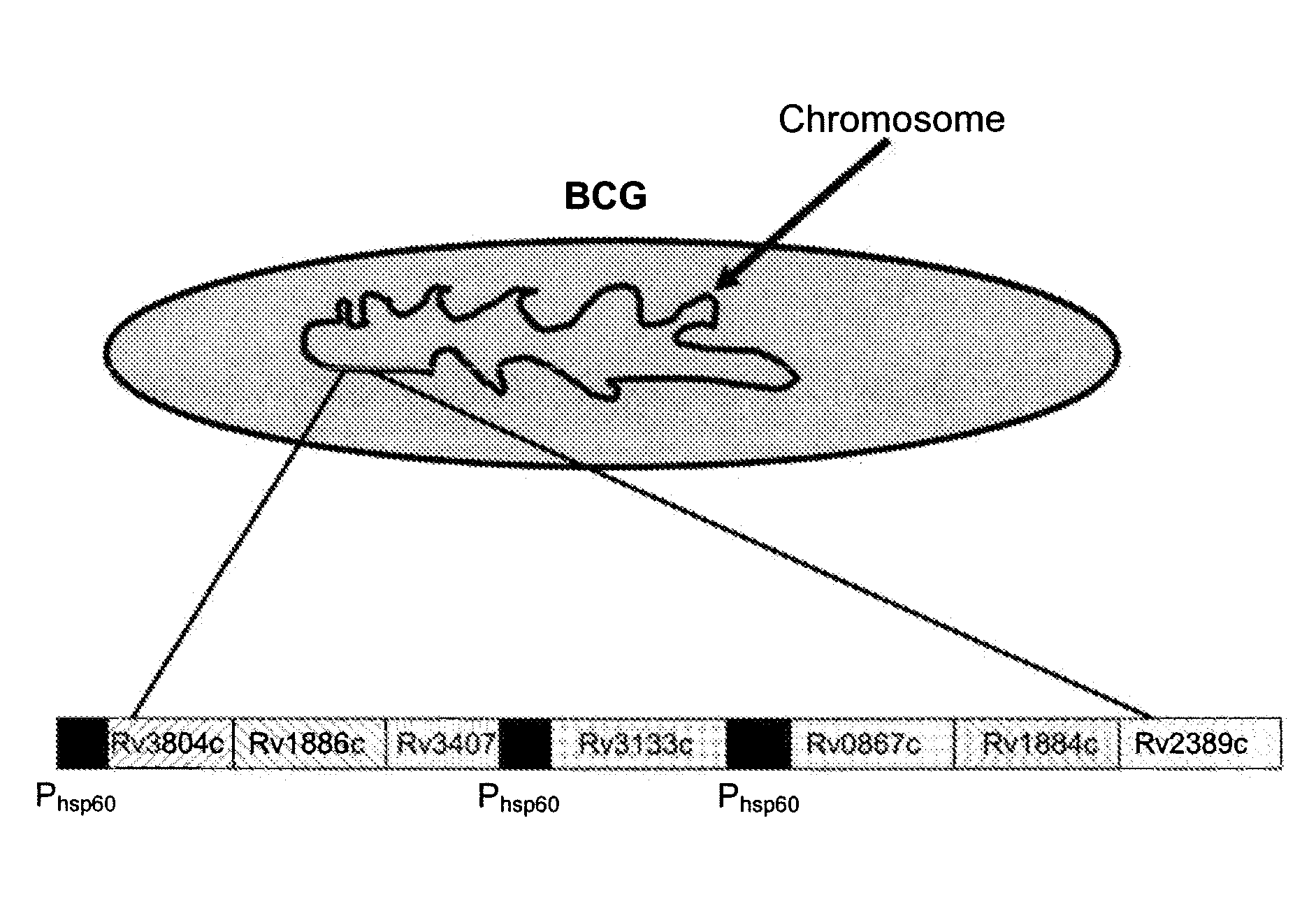
Novel recombinant bcg tuberculosis vaccine designed to elicit immune responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis in all physiological stages of infection and disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
Method of preparing optically imaged high performance photomasks
InactiveUS6703169B2Radiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContinuous waveWavelength
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
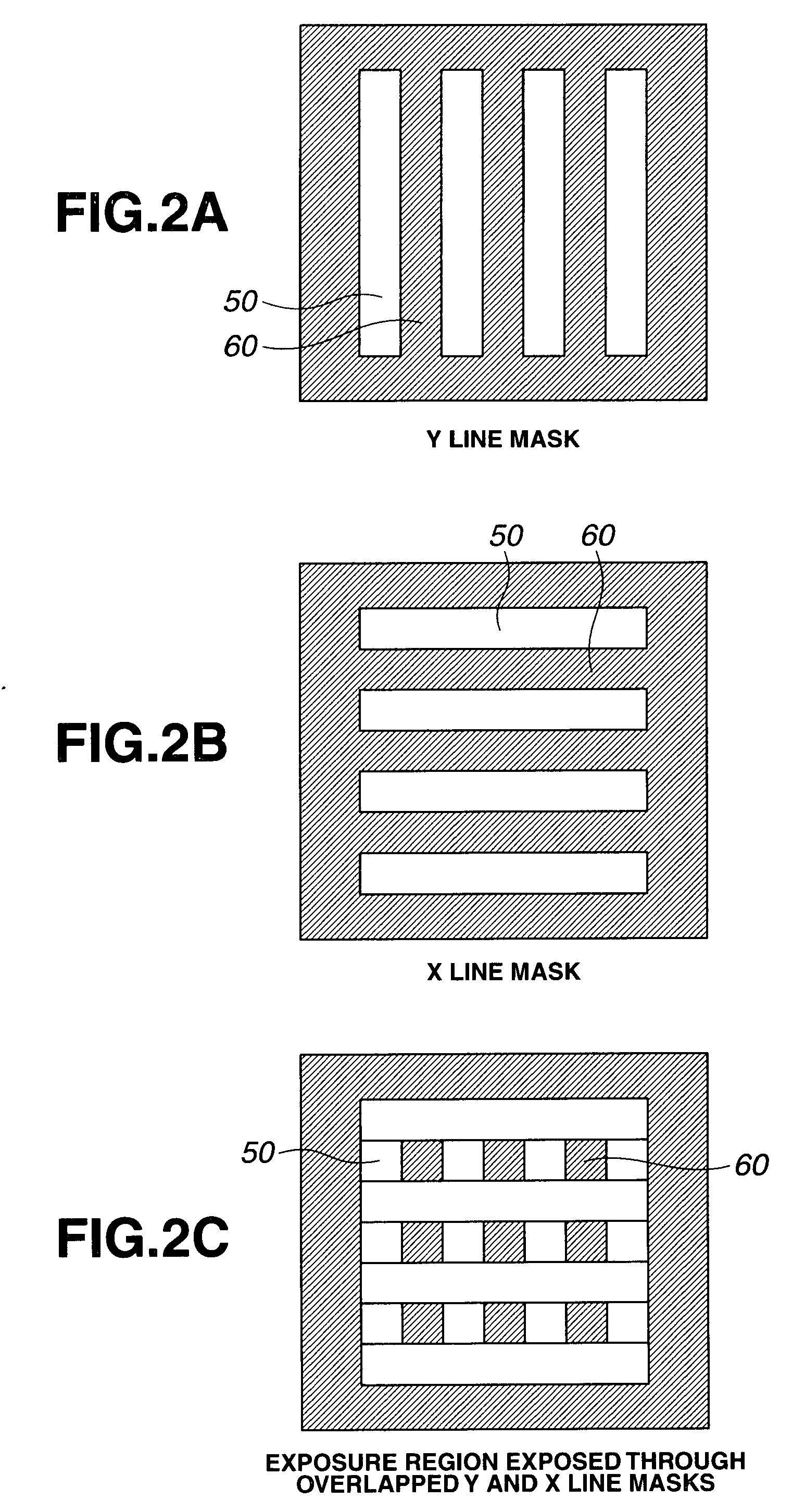
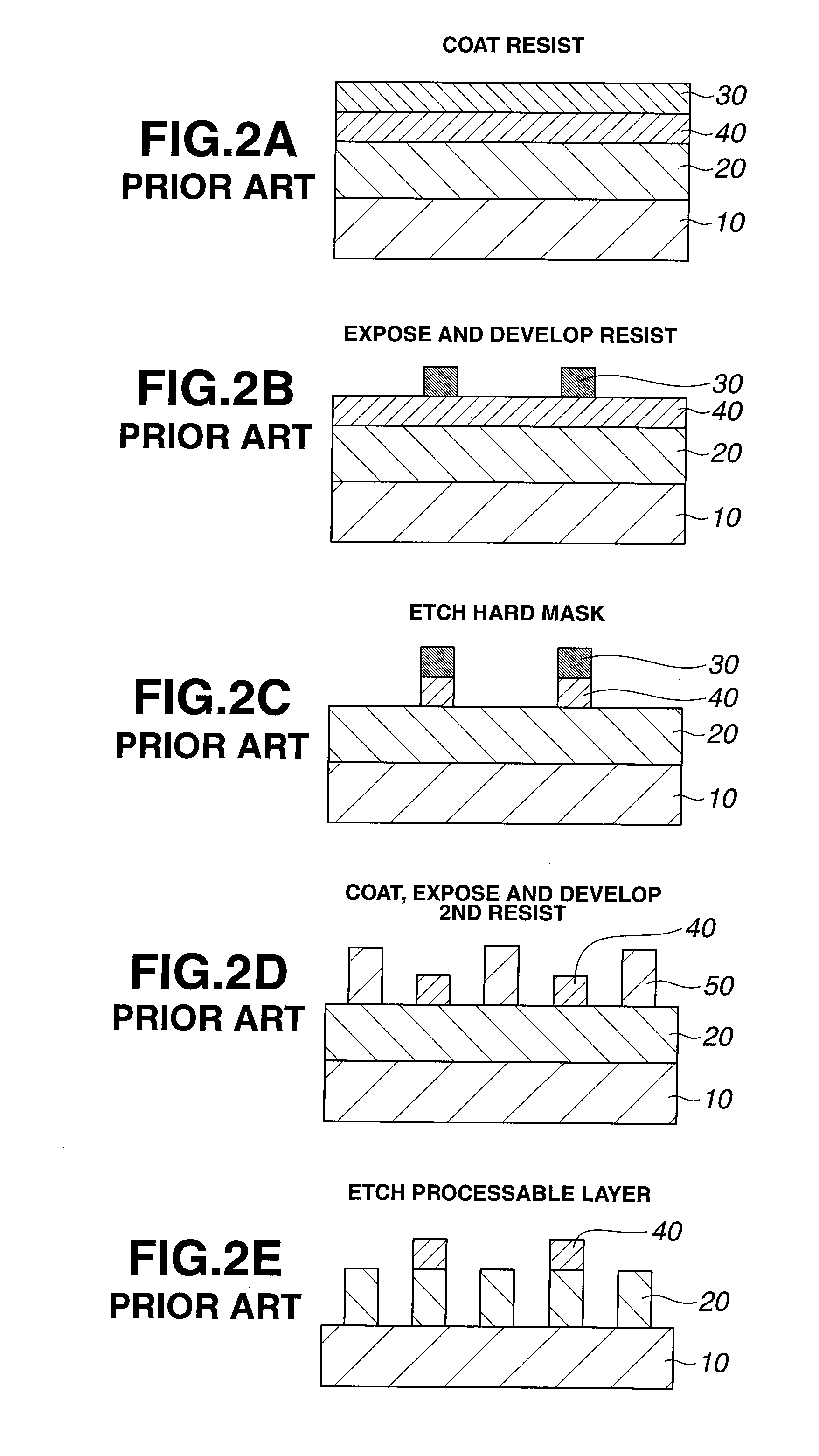
Plural interleaved exposure process for increased feature aspect ratio in dense arrays
InactiveUS6451508B1Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEngineering
A method for exposing a workpiece in a dual exposure step-and-repeat process starts by forming a design for a reticle mask. Deconstruct the design for the reticle mask by removing a set(s) of the features that are juxtaposed. Form unexposed resist on the workpiece. Load the workpiece and the reticle mask into the stepper. Expose the workpiece through the reticle mask. Reposition the workpiece by a nanostep. Then expose the workpiece through the reticle mask after the repositioning. Test whether the plural exposure process is finished. If the result of the test is NO the process loops back to repeat some of the above steps. Otherwise the process has been completed. An overlay mark is produced by plural exposures of a single mark. A dead zone is provided surrounding an array region in which printing occurs subsequent to exposure in an original exposure. Stepper-framing-blades are moved over the dead zone to prevent additional exposures after an initial exposure. Alternatively, the workpiece can be fully exposed first by stepping a series of full steps, then going back to the starting position, making a nanostep to reset the starting position and re-exposing from the reset starting position in the same way with full steps from the nanostepped position.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
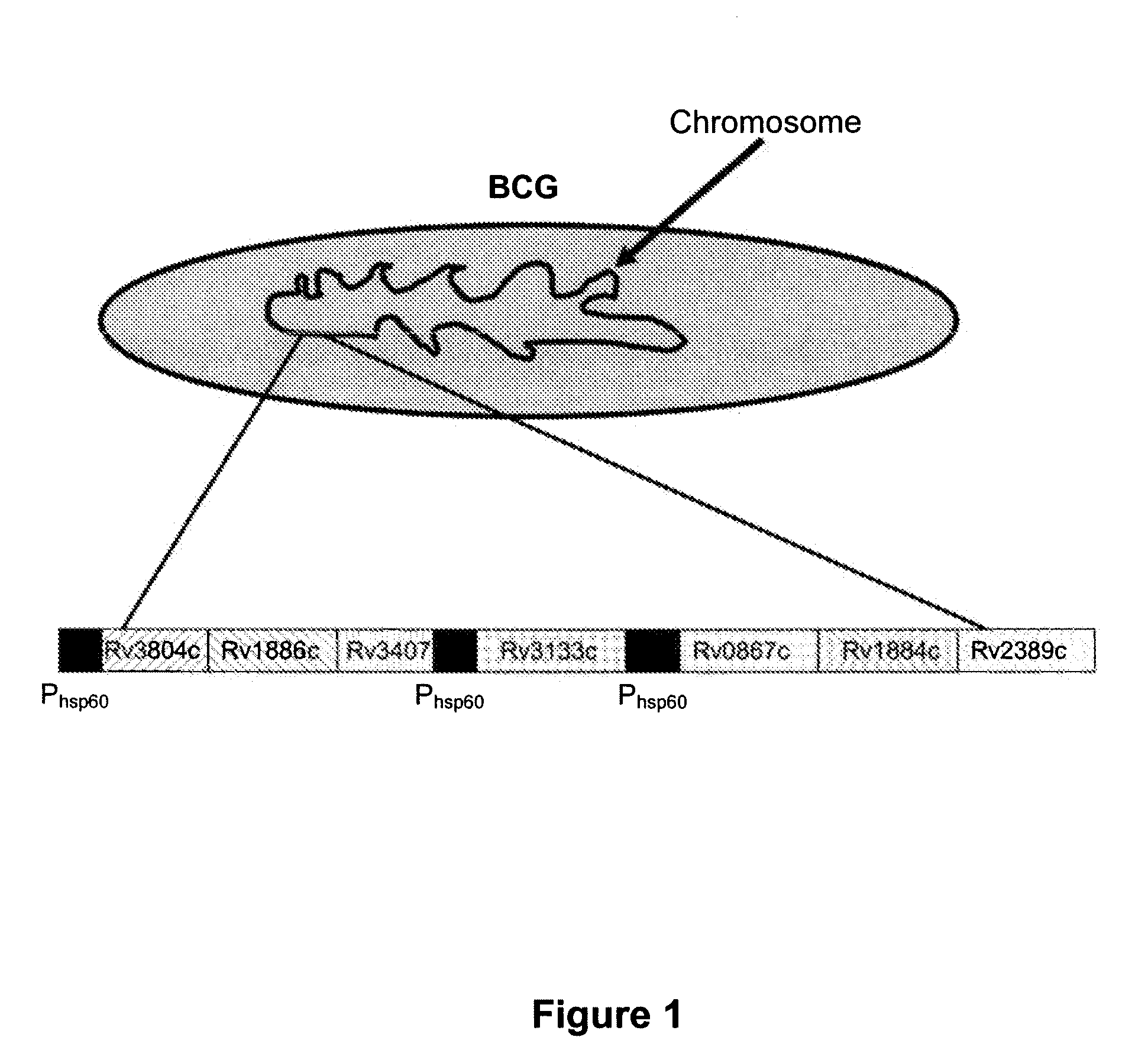
Novel Recombinant BCG Tuberculosis Vaccine Designed to Elicit Immune Responses to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in all Physiological Stages of Infection and Disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
193nm resist with improved post-exposure properties
InactiveUS7087356B2High resolution lithographic performanceGood exposure dose latitudePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistAcid catalyzed
Acid-catalyzed positive resist compositions which are imageable with 193 nm radiation and / or possibly other radiation and are developable to form resist structures of improved development characteristics and improved etch resistance are enabled by the use of resist compositions containing imaging polymer component comprising an acid-sensitive polymer having a monomeric unit with a pendant group containing a remote acid labile moiety.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Substrate treating apparatus
ActiveUS7323060B2Reduce distractionsEfficient transferLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid processingComputer modulePost exposure
A forward direction-only path (first substrate transport path) is formed for transporting substrates in a forward direction to pass the substrates on to an exposing apparatus. A separate, substrate transport path (second substrate transport path) is formed exclusively for post-exposure bake (PEB). Substrate transport along each path is carried out independently of substrate transport along the other. A fourth main transport mechanism is interposed as a predetermined substrate transport mechanism between transfer points consisting of a buffer acting as a temporary storage module for temporarily storing the substrates and a post-exposure bake (PEB) unit corresponding to a predetermined treating unit. This arrangement forms the path for transporting the substrates between the buffer and the PEB unit, to allow PEB treatment of the substrates to be performed smoothly. Similarly, the substrates are transported smoothly to the buffer.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Flexo processor
ActiveUS20050211121A1Good flexibilityThe process is convenient and fastPlaten pressesMulticolor photographic processingPost exposureEmbedded system
An improved flexo processor and a method of using the improved flexo processor to increase the flexibility of both the type and the size of the flexographic printing element that may be processed. The novel thermal plate processor system is capable of processing both flat and round photosensitive printing elements with only minimal changes to the system. The thermal plate processor system may also include means for exposure and post-exposure / detack in the same system.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com