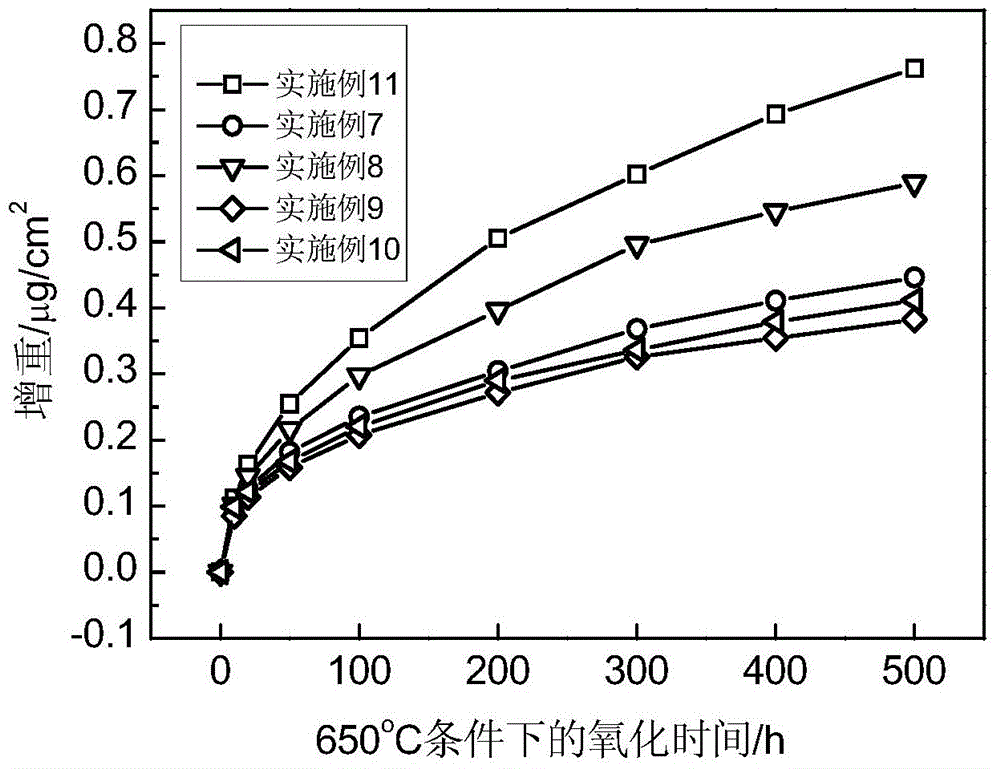
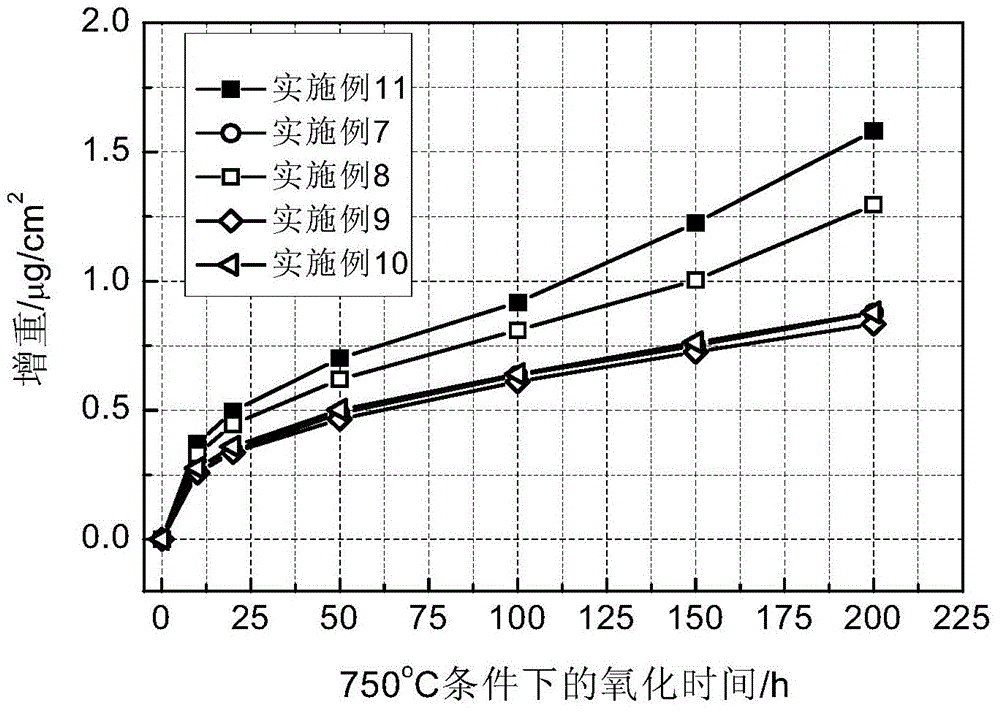
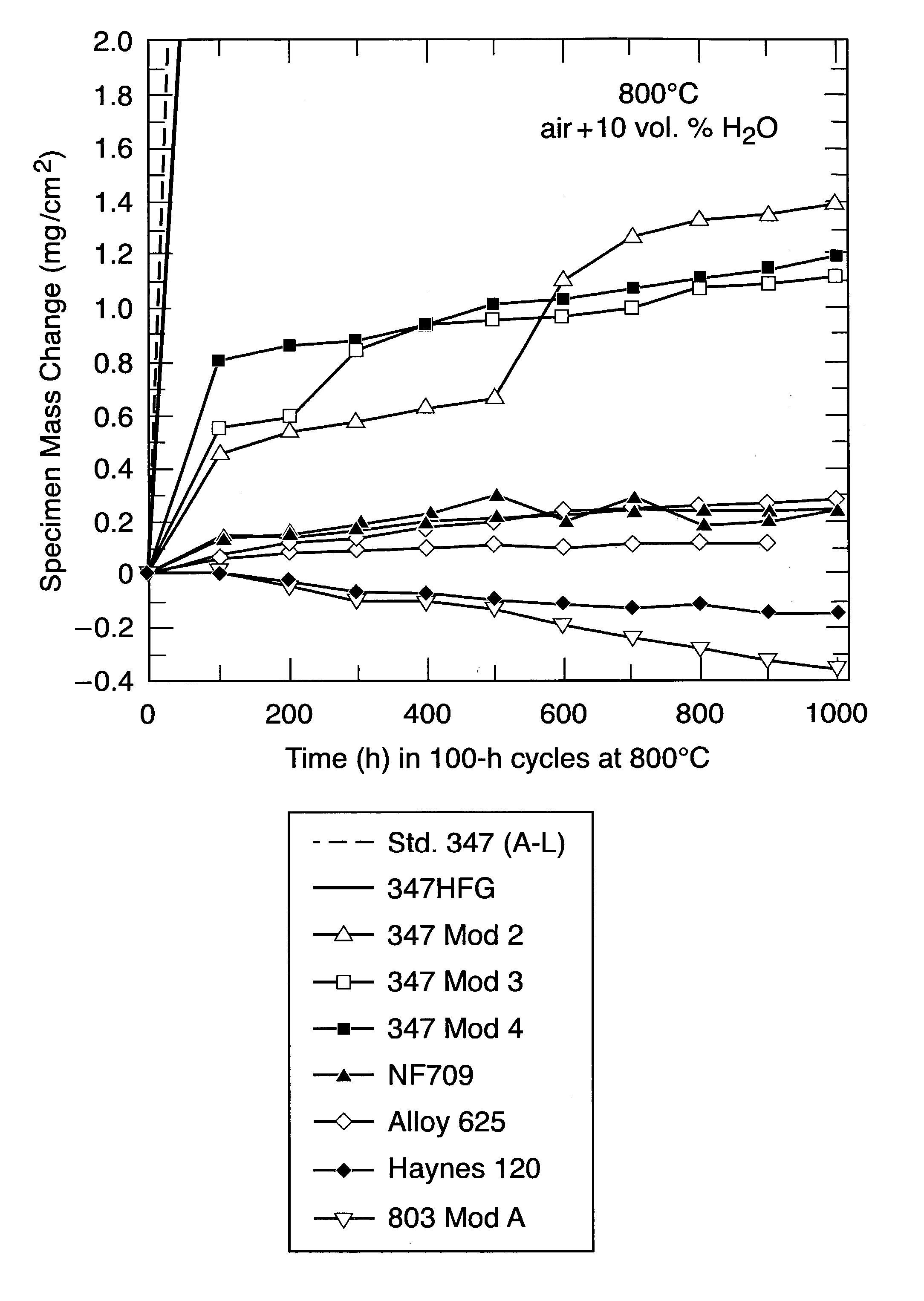
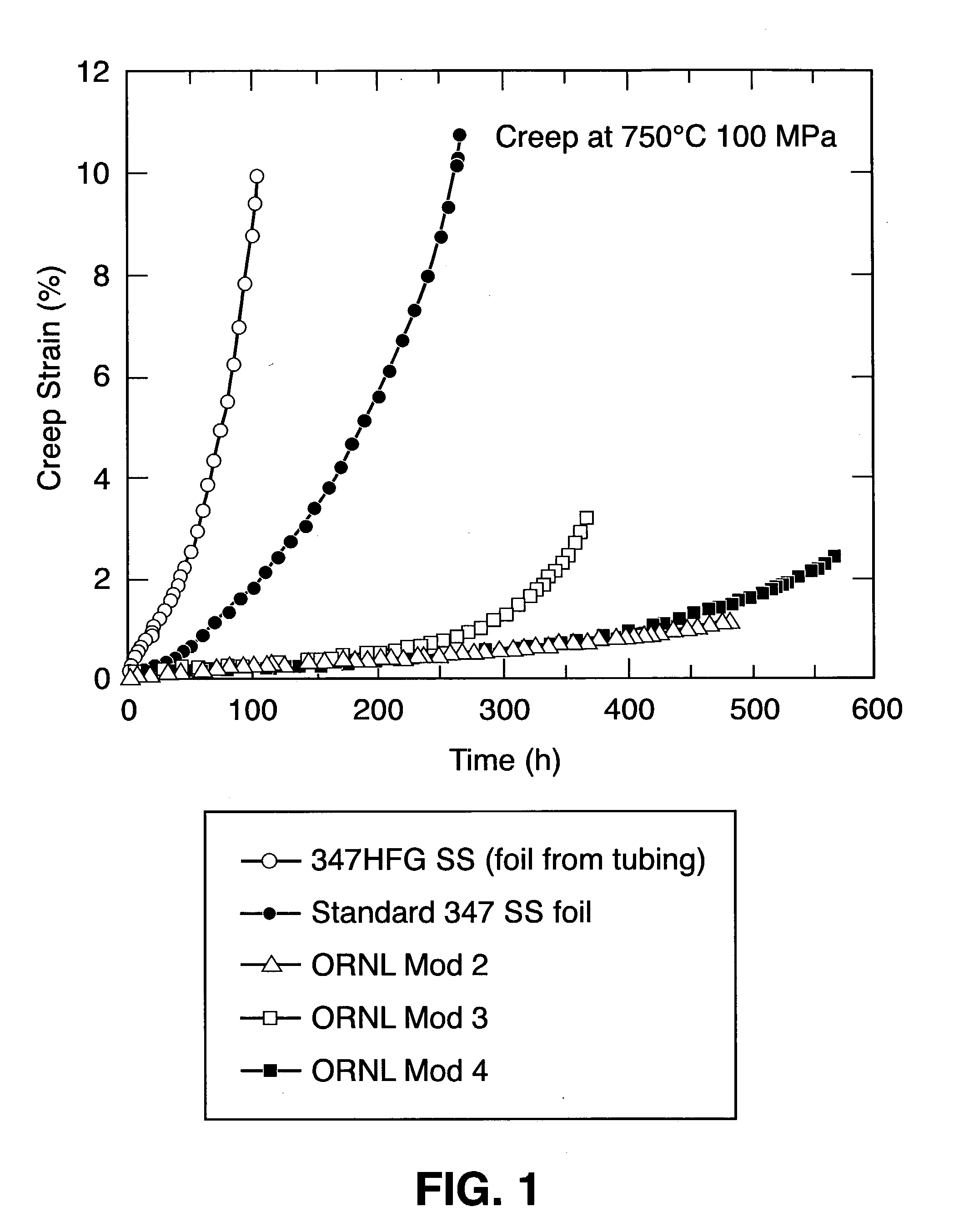
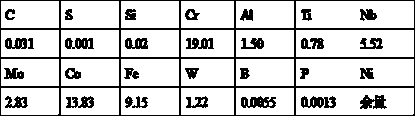
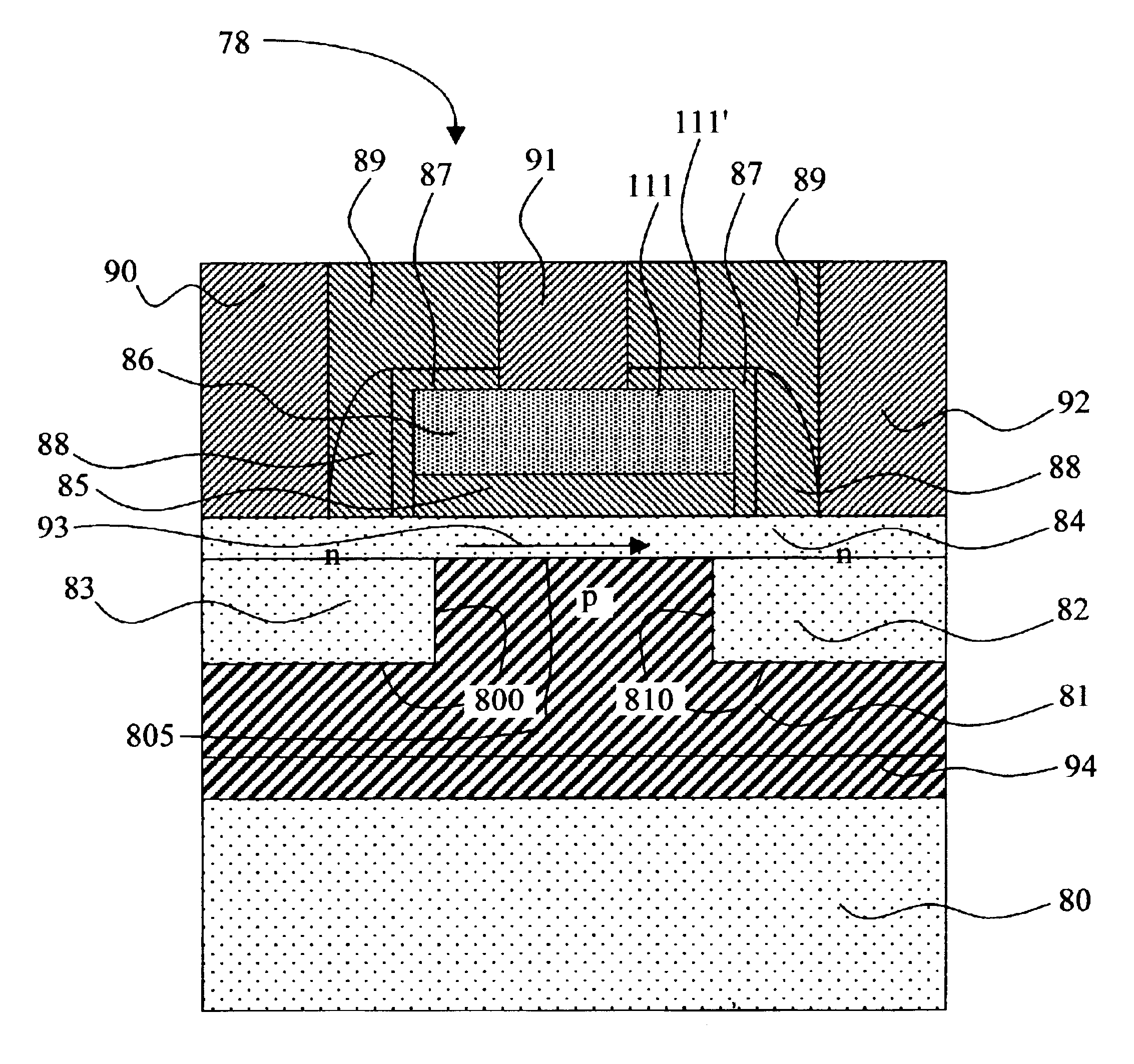
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2852 results about "Alloy composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
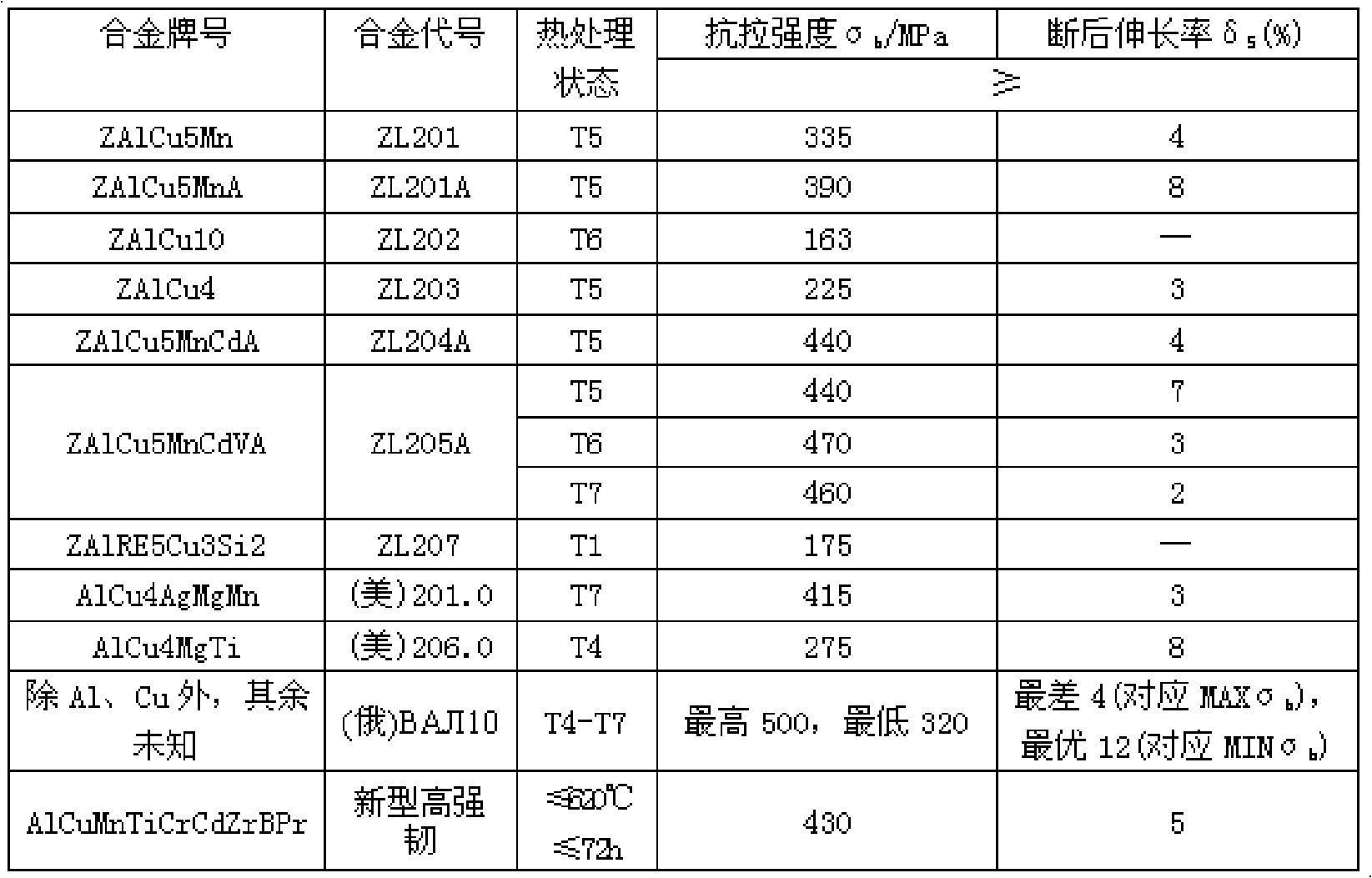
High-strength cast aluminium alloy material
The invention discloses a high strength casting aluminum alloy material. The alloy comprises the following compositions in weight percent: 2.0 to 6.0 percent of Cu, 0.05 to 1.0 percent of Mn, 0.01 to 0.5 percent of Ti, 0.01 to 0.2 percent of Cr, 0.01 to 0.4 percent of Cd, 0.01 to 0.25 percent of Zr, 0.005 to 0.04 percent of B, 0.05 to 0.3 percent of Pr, the balance being Al and trace impurity elements. The invention adopts the advanced alloy composition design and the micro alloying design. Based on taking Al-Cu-Mn as main compositions, the material finds reasonable micro alloy elements (Ti, Cr, B, Zr and rare earth, etc.), determines the ranges of compositions of the micro alloy elements, is capable of realizing the function of replacing precious and rare metals such as Ag and V, etc., and lowers the formula cost by 5 to 10 percent.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +2
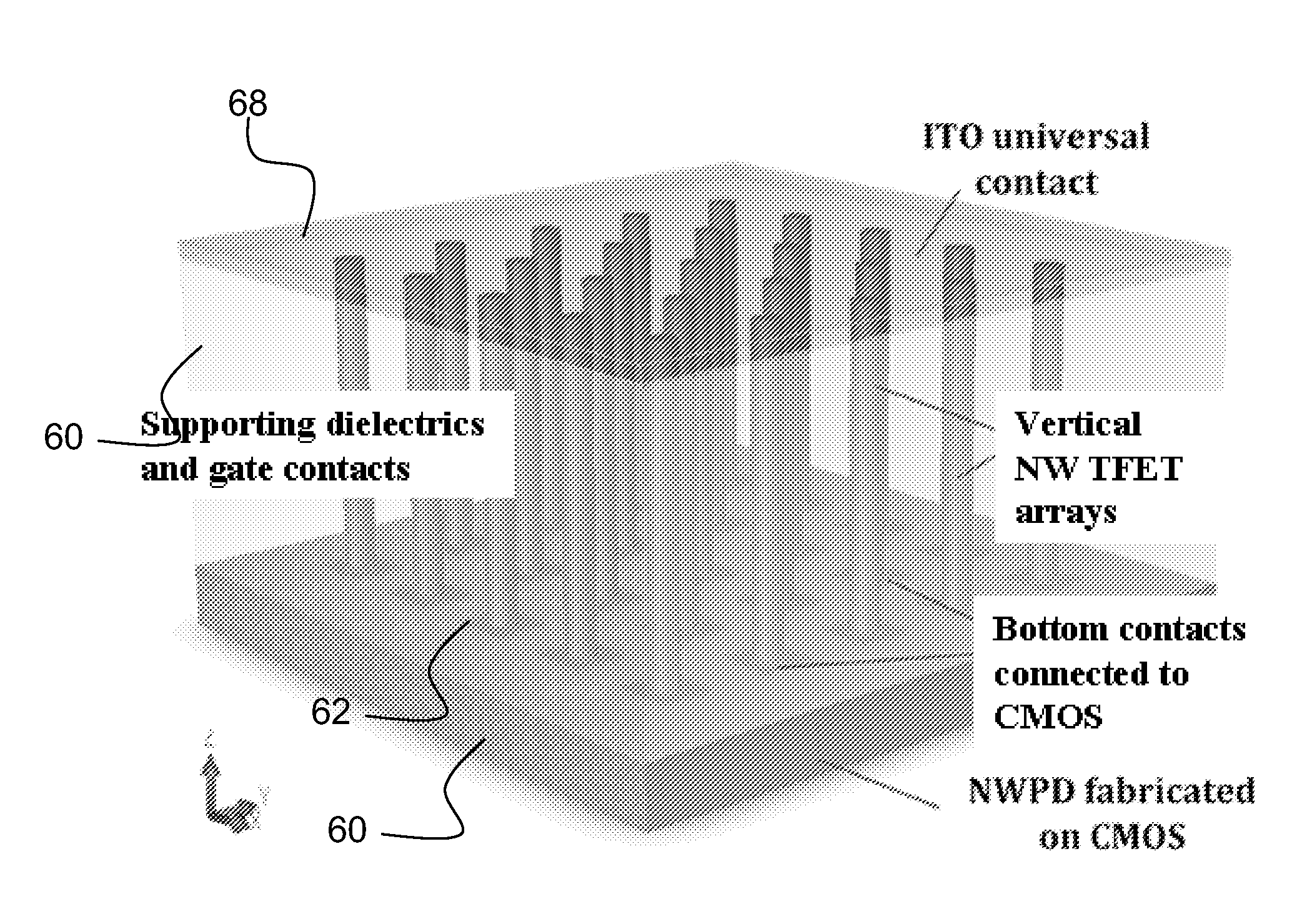
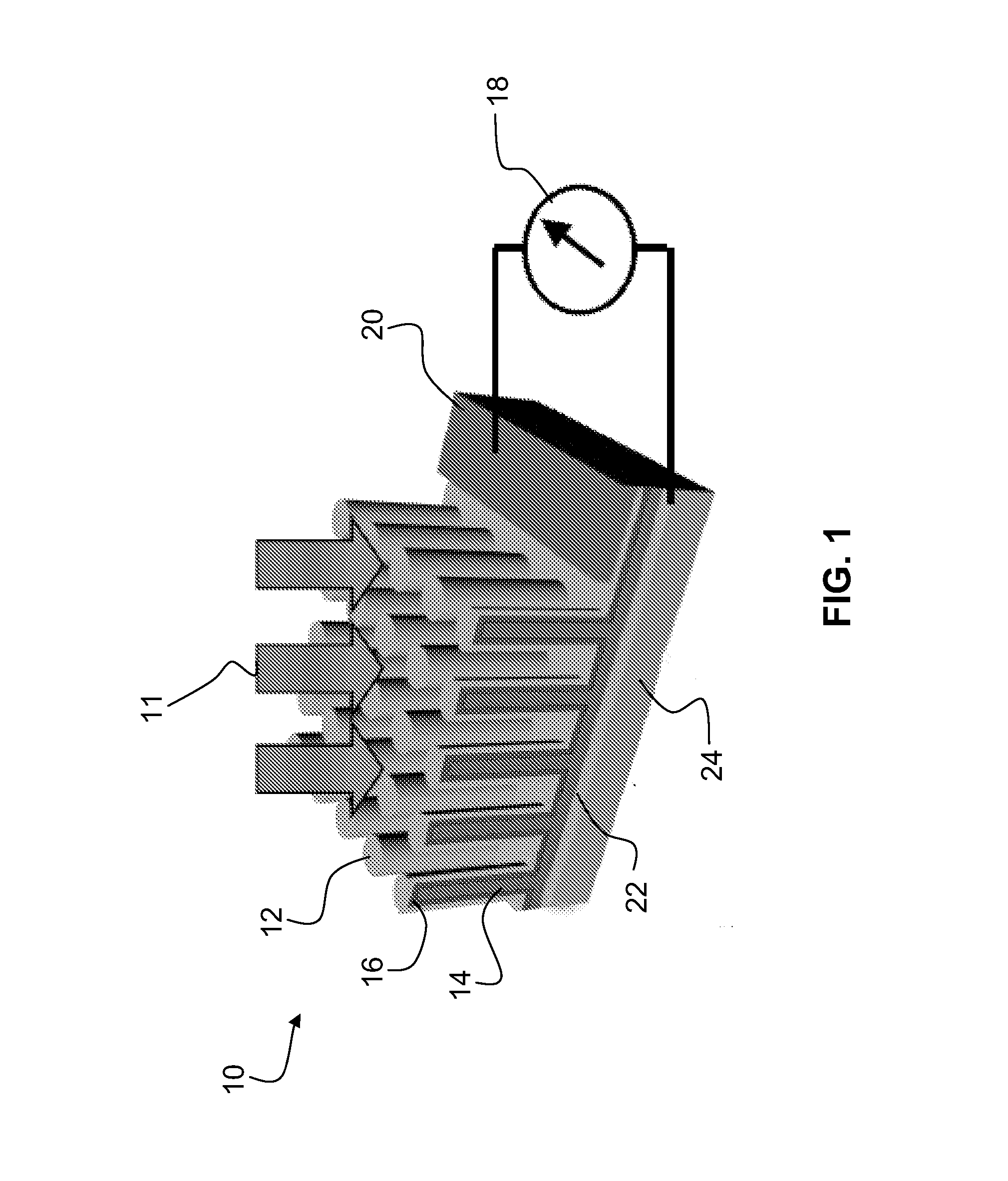
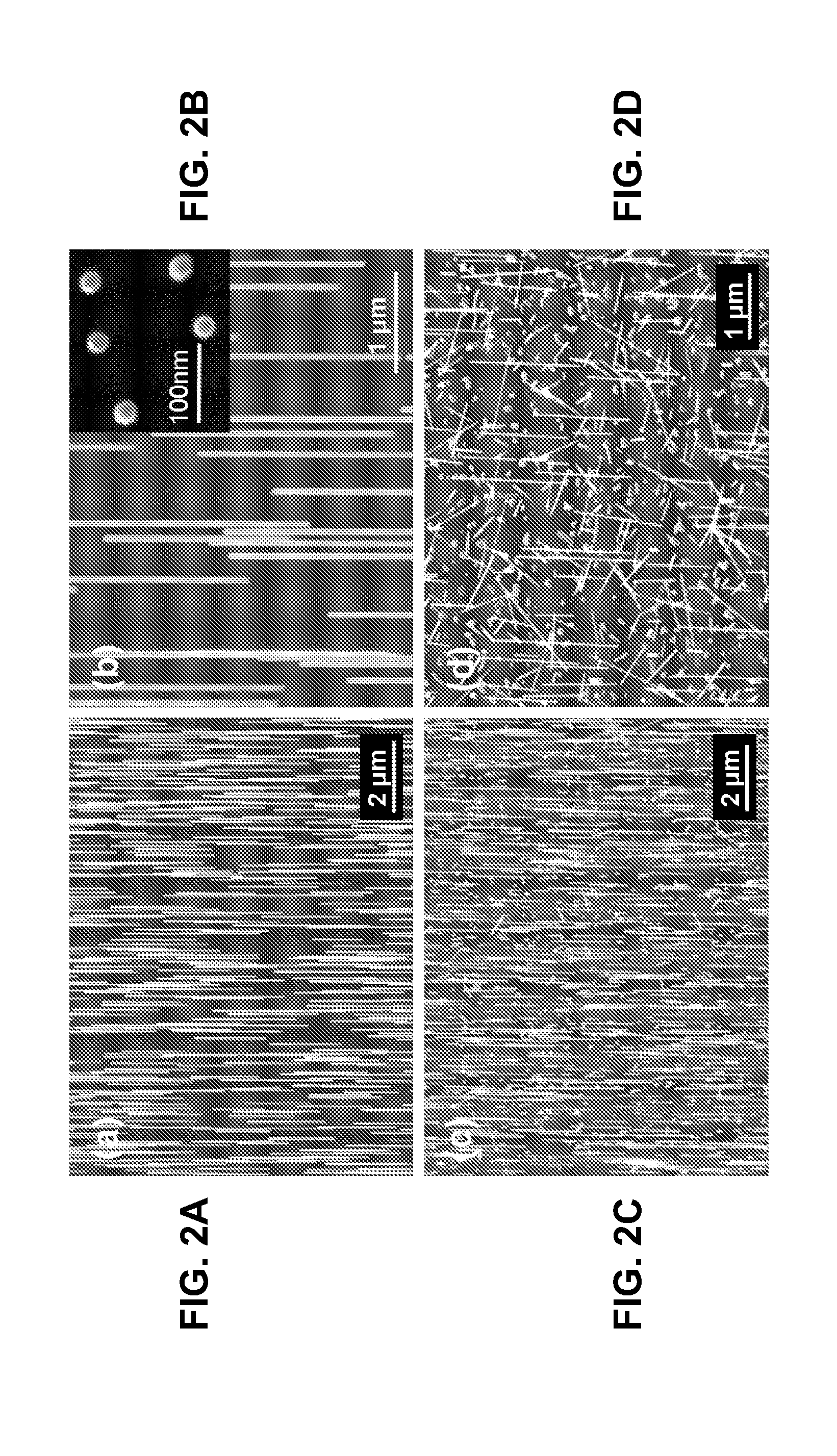
Vertical group iii-v nanowires on si, heterostructures, flexible arrays and fabrication
ActiveUS20110253982A1Promote absorptionReduce distanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesNanowire arrayCore shell
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for direct heteroepitaxial growth of vertical III-V semiconductor nanowires on a silicon substrate. The silicon substrate is etched to substantially completely remove native oxide. It is promptly placed in a reaction chamber. The substrate is heated and maintained at a growth temperature. Group III-V precursors are flowed for a growth time. Preferred embodiment vertical Group III-V nanowires on silicon have a core-shell structure, which provides a radial homojunction or heterojunction. A doped nanowire core is surrounded by a shell with complementary doping. Such can provide high optical absorption due to the long optical path in the axial direction of the vertical nanowires, while reducing considerably the distance over which carriers must diffuse before being collected in the radial direction. Alloy composition can also be varied. Radial and axial homojunctions and heterojunctions can be realized. Embodiments provide for flexible Group III-V nanowire structures. An array of Group III-V nanowire structures is embedded in polymer. A fabrication method forms the vertical nanowires on a substrate, e.g., a silicon substrate. Preferably, the nanowires are formed by the preferred methods for fabrication of Group III-V nanowires on silicon. Devices can be formed with core / shell and core / multi-shell nanowires and the devices are released from the substrate upon which the nanowires were formed to create a flexible structure that includes an array of vertical nanowires embedded in polymer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Broad spectrum solar cell
InactiveUS7217882B2Increase profitImprove matchPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEnergy spectrumMultijunction photovoltaic cell
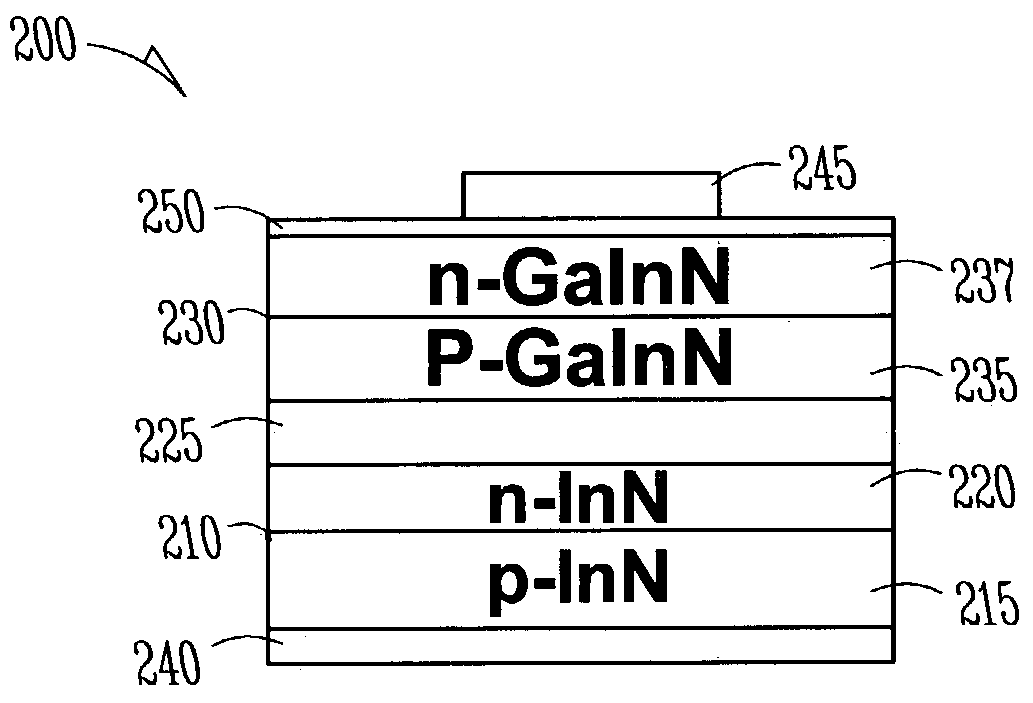
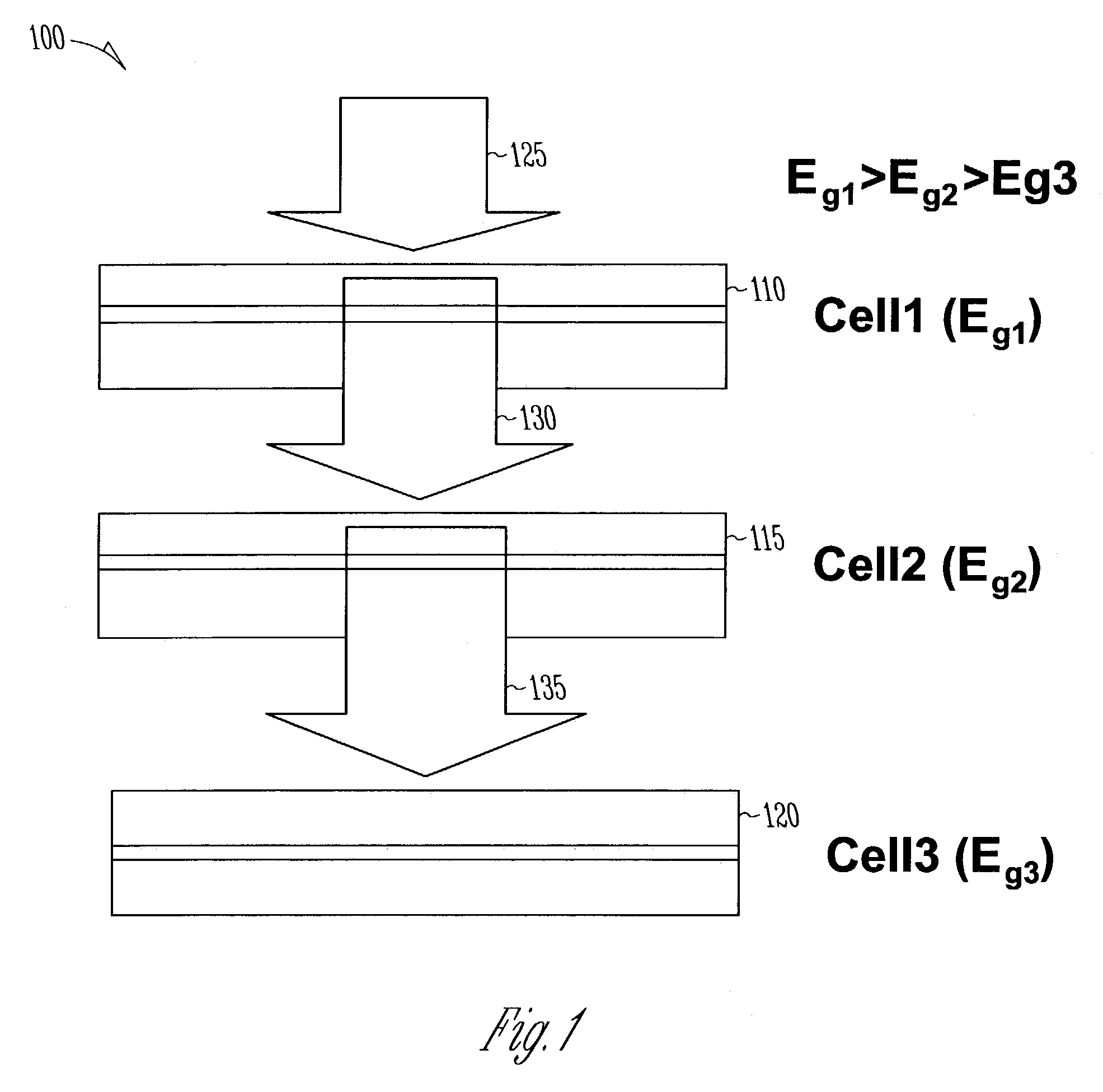
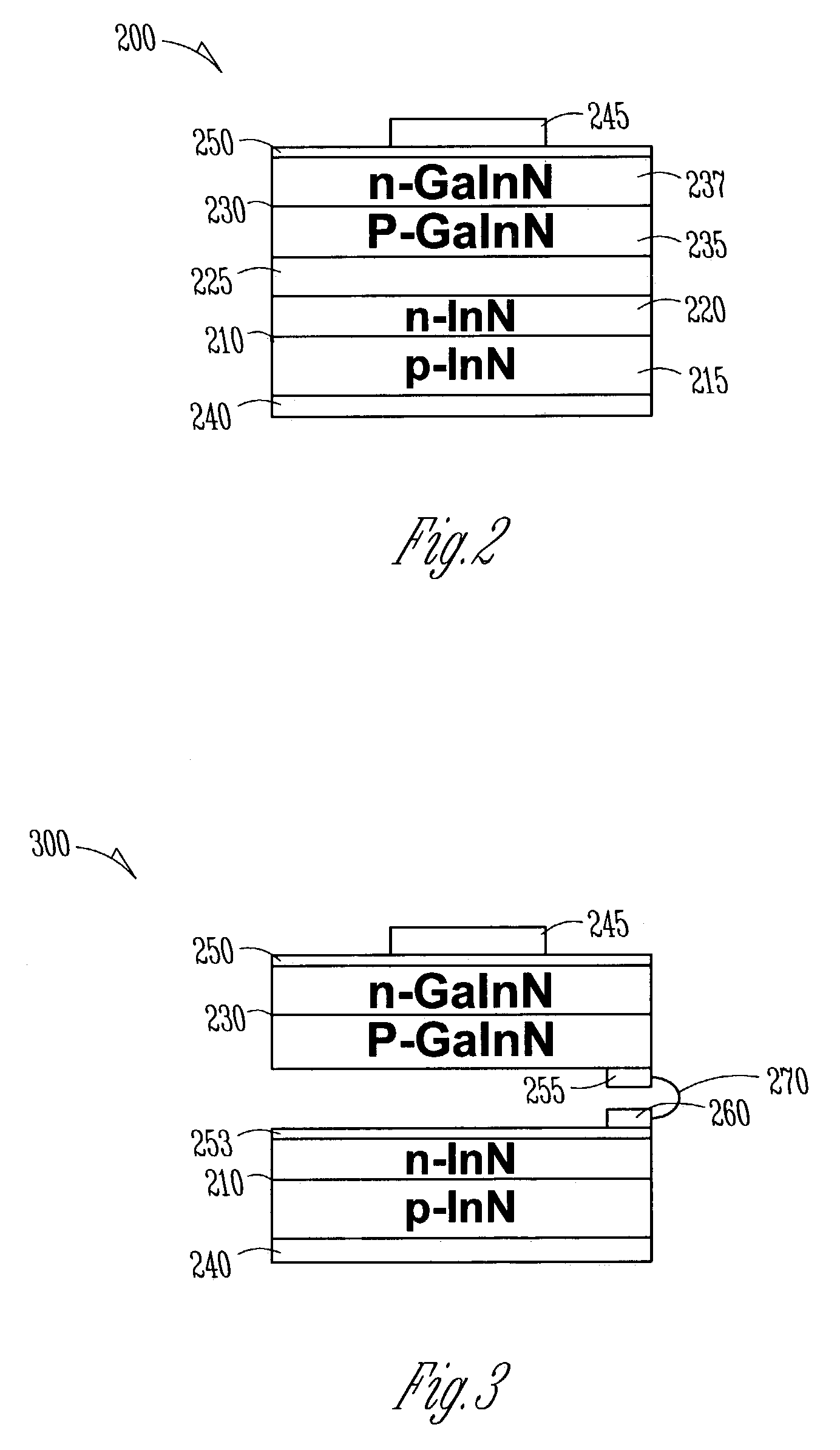
An alloy having a large band gap range is used in a multijunction solar cell to enhance utilization of the solar energy spectrum. In one embodiment, the alloy is In1−xGaxN having an energy bandgap range of approximately 0.7 eV to 3.4 eV, providing a good match to the solar energy spectrum. Multiple junctions having different bandgaps are stacked to form a solar cell. Each junction may have different bandgaps (realized by varying the alloy composition), and therefore be responsive to different parts of the spectrum. The junctions are stacked in such a manner that some bands of light pass through upper junctions to lower junctions that are responsive to such bands.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
7000 series aluminum alloy material and preparation method thereof
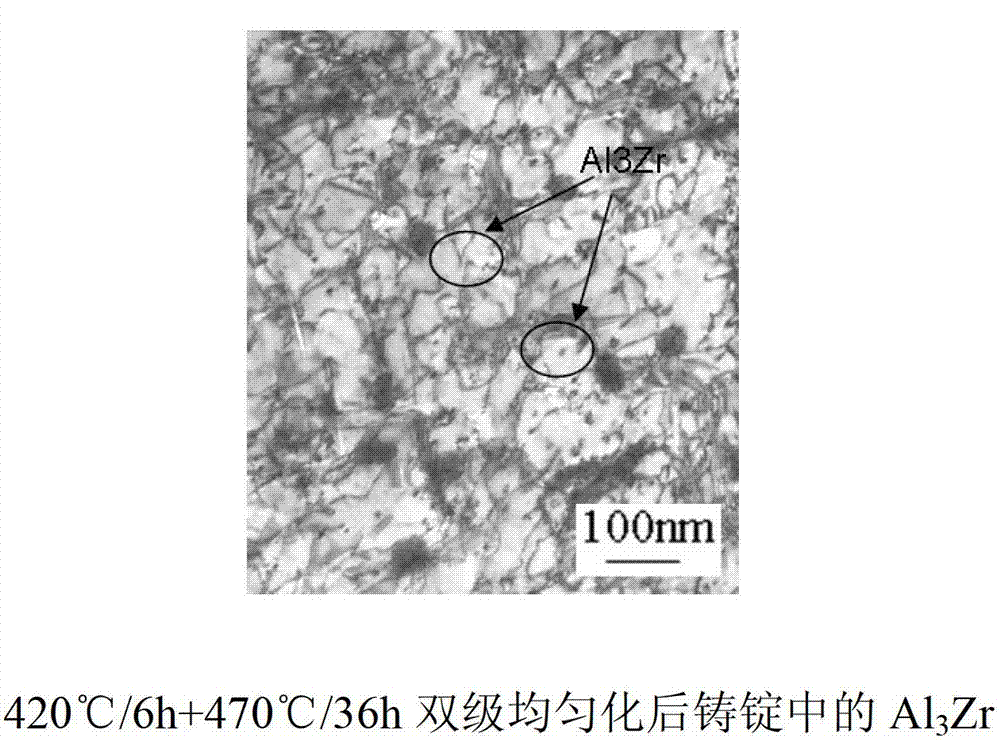
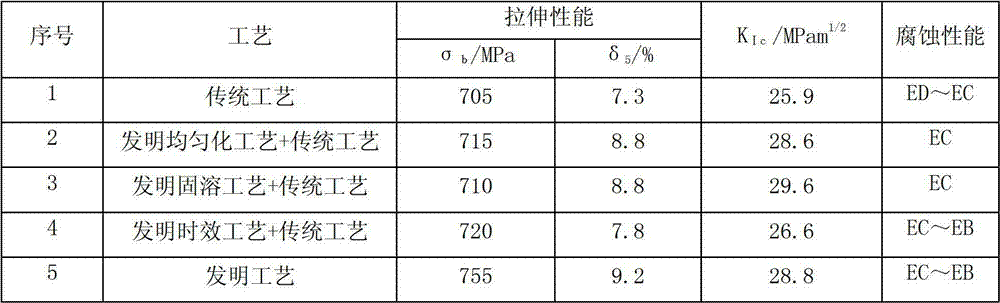
The invention relates to a 7000 series aluminum alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum alloy material has alloy components of, by weight: 7.6-11.0% of Zn, 1.2-3.0% of Mg, 1.3-2.6% of Cu, 0.04-0.30% of Zr, 0.10-0.60% of Cr, no more than 0.08% of Si, no more than 0.10% of Fe, no more than 0.10% of Ti, no more than 0.15% of total other impurities (wherein the content of single other impurity is no more than 0.05%), and balance of Al. The alloy elements Zr and Cr can be added optionally or simultaneously. The materials are prepared according to the alloy composition; the raw materials are molten; in-furnace refining and standing are carried out; and the material is cast into alloy ingots with required specifications. The alloy ingots are subjected to a preferable graded uniformization process, and is forged or extruded, such that the alloy ingots are molded; the molded materials are subjected to graded solid solution treatment, and are quenched; and artificial forced aging is carried out, such that the material can be processed into parts. The microstructures of the material are uniform, and the property of the material is stable. The ultimate tensile strength of the material can be more than 750MPa. The extensibility of the material is higher than 10%. The T-L direction KIc of the material reaches 28MPam1 / 2.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Making colloidal ternary nanocrystals
InactiveUS20100289003A1Short radiative lifetimeFluorescence stabilizationPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNanocrystalSemiconductor
A method of making a colloidal solution of ternary semiconductor nanocrystals, includes providing binary semiconductor cores; forming first shells on the binary semiconductor cores containing one of the components of the binary semiconductor cores and another component which when combined with the binary semiconductor will form a ternary semiconductor, thereby providing core / shell nanocrystals; and annealing the core / shell nanocrystals to form ternary semiconductor nanocrystals containing a gradient in alloy composition.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Multifunctional metal-graphite nanocrystals
InactiveUS20080213189A1High resolutionShrink tumorPowder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsMRI contrast agentPolyethylene glycol
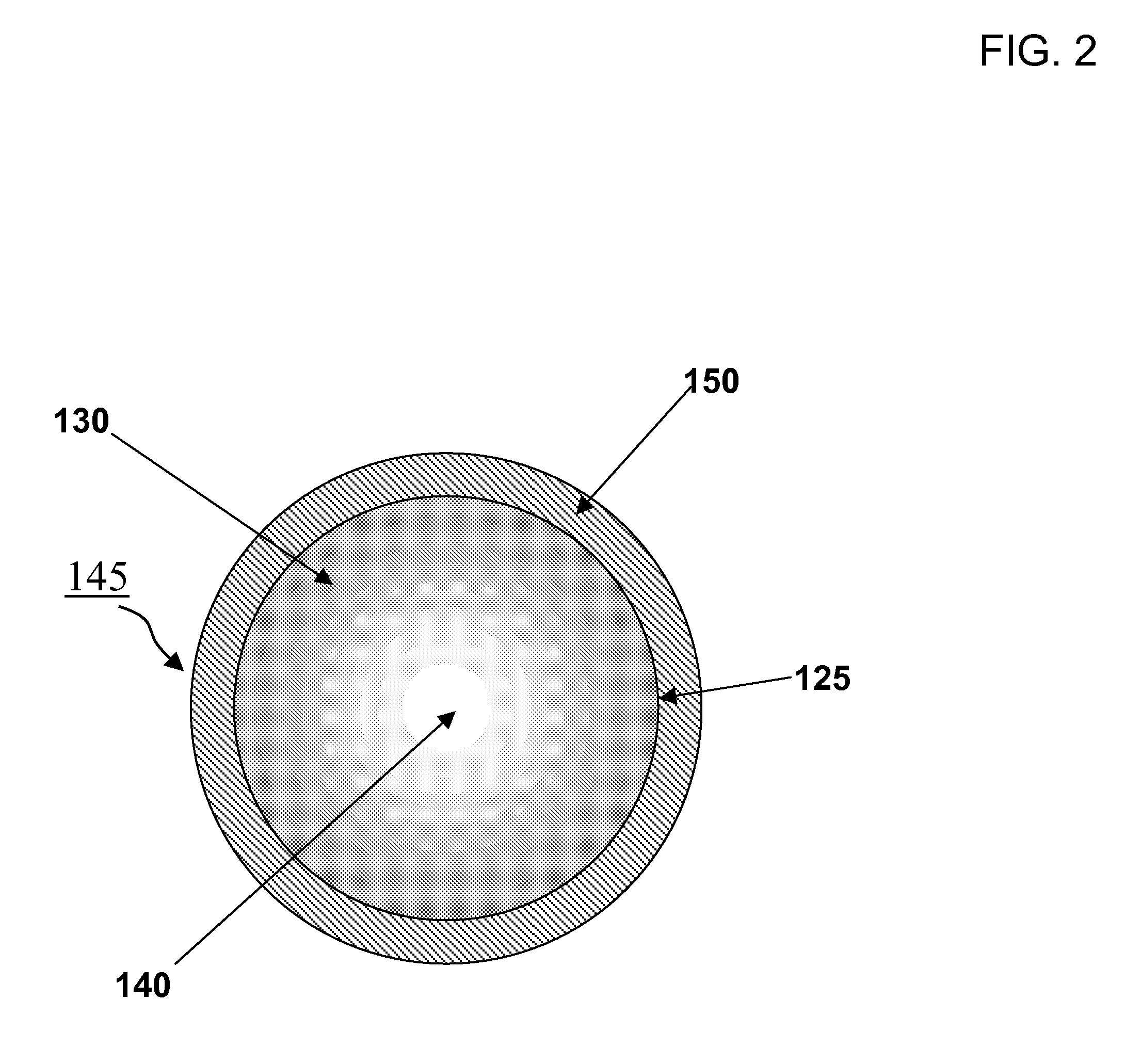
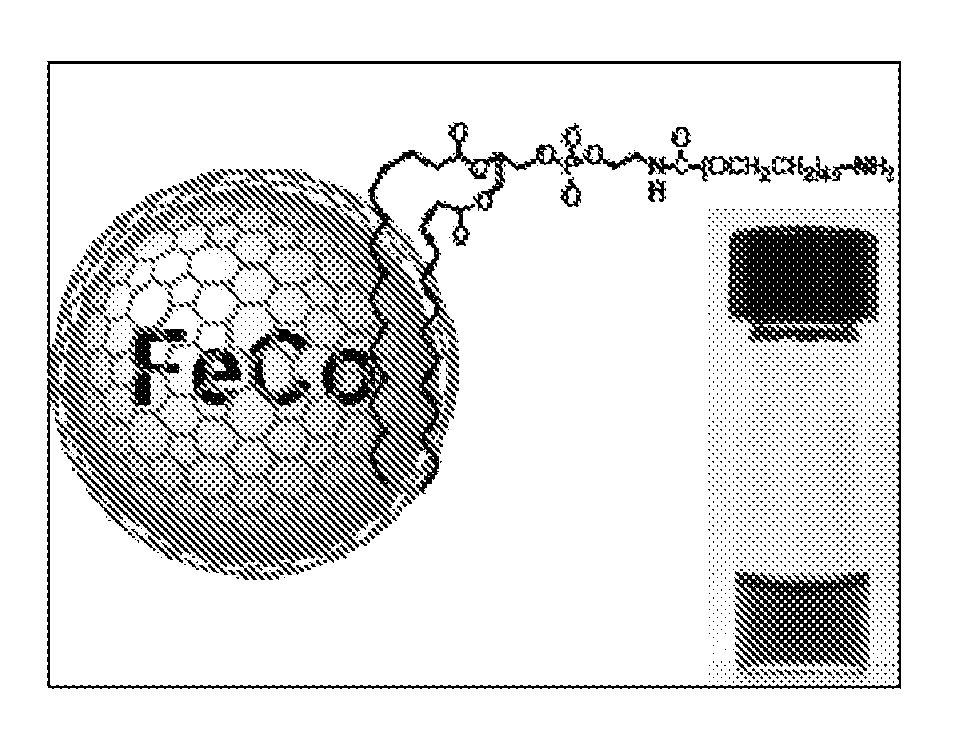
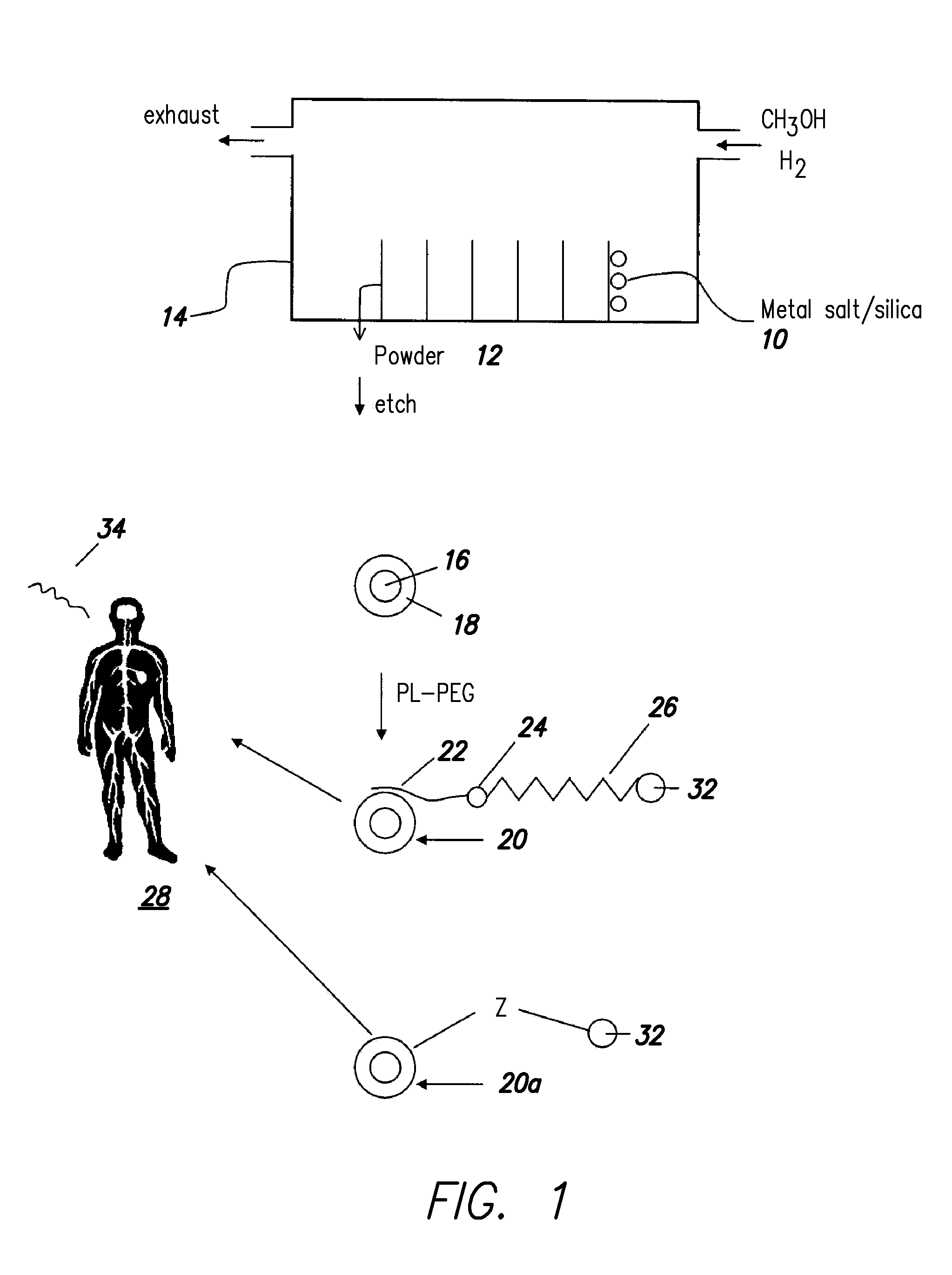
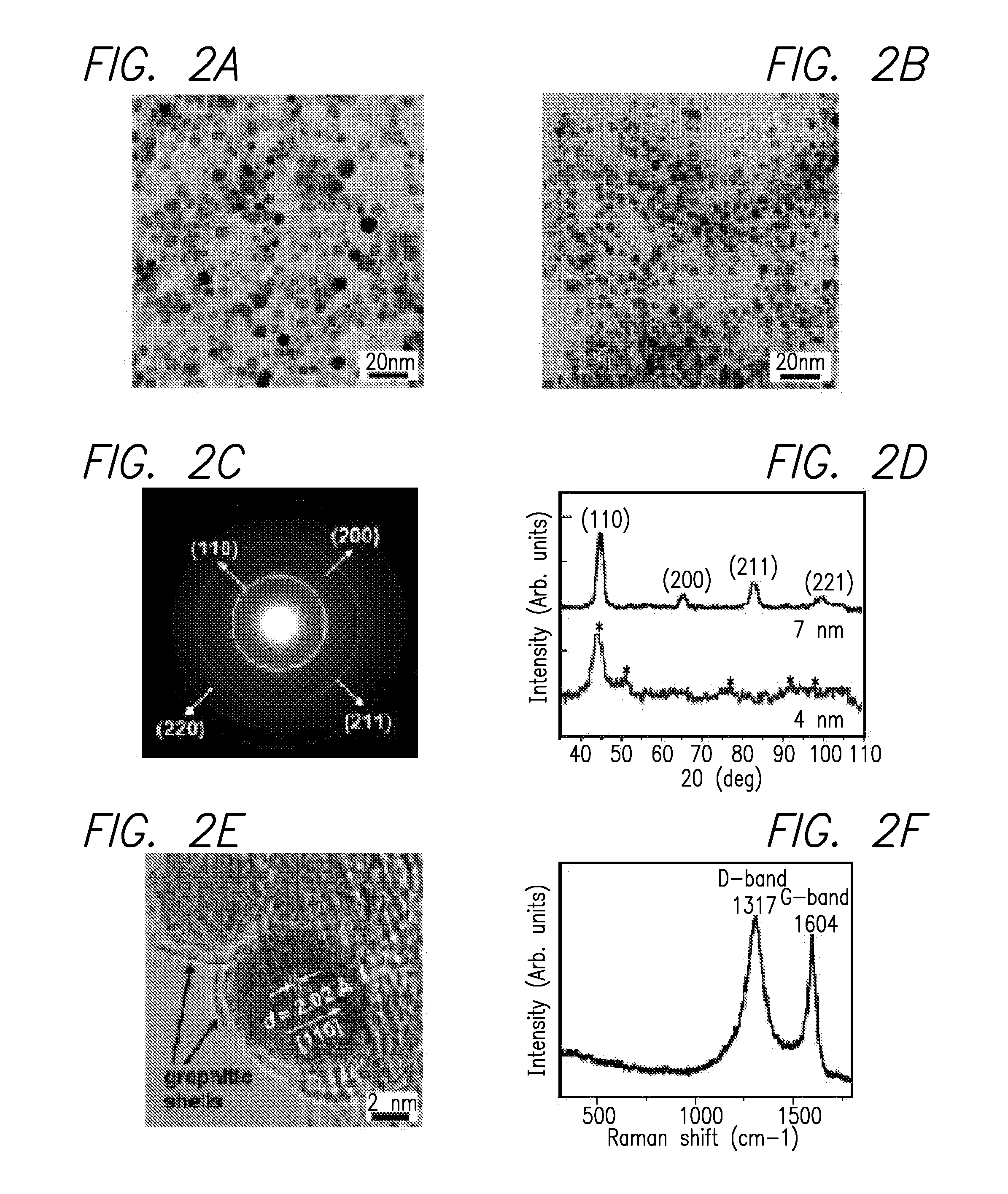
Disclosed are nanocrystals comprising metals and metal alloys, which are formed by a process that results in a layer of graphite in direct contact with the metallic core. The nanocrystals may be used in vivo as MRI contrast agents, X-ray contrast agents, near IR (NIR) heating agents, drug delivery, protein separation, catalysis etc. The nanocrystals may be further functionalized with a hydrophilic coating, e.g., phospholipid-polyethylene glycol, which improves in vivo stability. The process comprises chemical vapor deposition of metals adsorbed onto silica as a fine powder, in conjunction with a carbon containing gas, which coats the metal particles. The silica is then etched away. Preferred metals include iron, gold, cobalt, platinum, ruthenium and mixtures thereof, e.g., FeCo and AuFe. The process permits control of the alloy compositions, size, and other characteristics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Device containing non-blinking quantum dots
InactiveUS20090109435A1Short radiative lifetime propertyReduced life-timeRadiation pyrometryDischarge tube luminescnet screensQuantum dotNanocrystal
An optoelectronic device including two spaced apart electrodes; and at least one layer containing ternary core / shell nanocrystals disposed between the spaced electrodes and having ternary semiconductor cores containing a gradient in alloy composition and wherein the ternary core / shell nanocrystals exhibit single molecule non-blinking behavior characterized by on times greater than one minute or radiative lifetimes less than 10 ns.
Owner:NANOCO TECH LTD
Novel heat-resisting titanium alloy and processing and manufacturing method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of titanium-based alloys, and particularly relates to a novel heat-resisting titanium alloy and a processing and manufacturing method and application thereof. The processing and manufacturing method comprises the composition elements of alloy components, smelting, heat processing, heat treatment and the like, wherein the alloy components are as follows (in percentage by weight): 5.4%-6.3% of Al, 3.0%-5.0% of Sn, 2.5%-6.4% of Zr, 0.0%-0.96% of Mo, 0.25%-0.5% of Si, 0.2%-0.5% of Nb, 0.3%-3.4% of Ta, 0.2%-1.6% of W, 0.0%-0.07% of C, less than or equal to 0.17% of O, less than or equal to 0.03% of Fe and the balance of Ti and inevitable impurity elements. The novel heat-resisting titanium alloy disclosed by the invention can obtain different matching of tensile strength, plasticity, permanence, creep strength and heat stability through the combination of different heat processing process and heat treatment processes, can be used for manufacturing parts, namely blades, coil assemblies and the like which are positioned on the high-temperature parts of an advanced aircraft engine, is used for a long time within a range of 600-650 DEG C, can also be used for manufacturing high temperature-resistant structural members, namely aerospace craft skin and the like, is used for a short time at about 700 DEG C and can be used as a material and the like used for high temperature-resistant corrosion-resistant valves of an automobile and a boiler.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
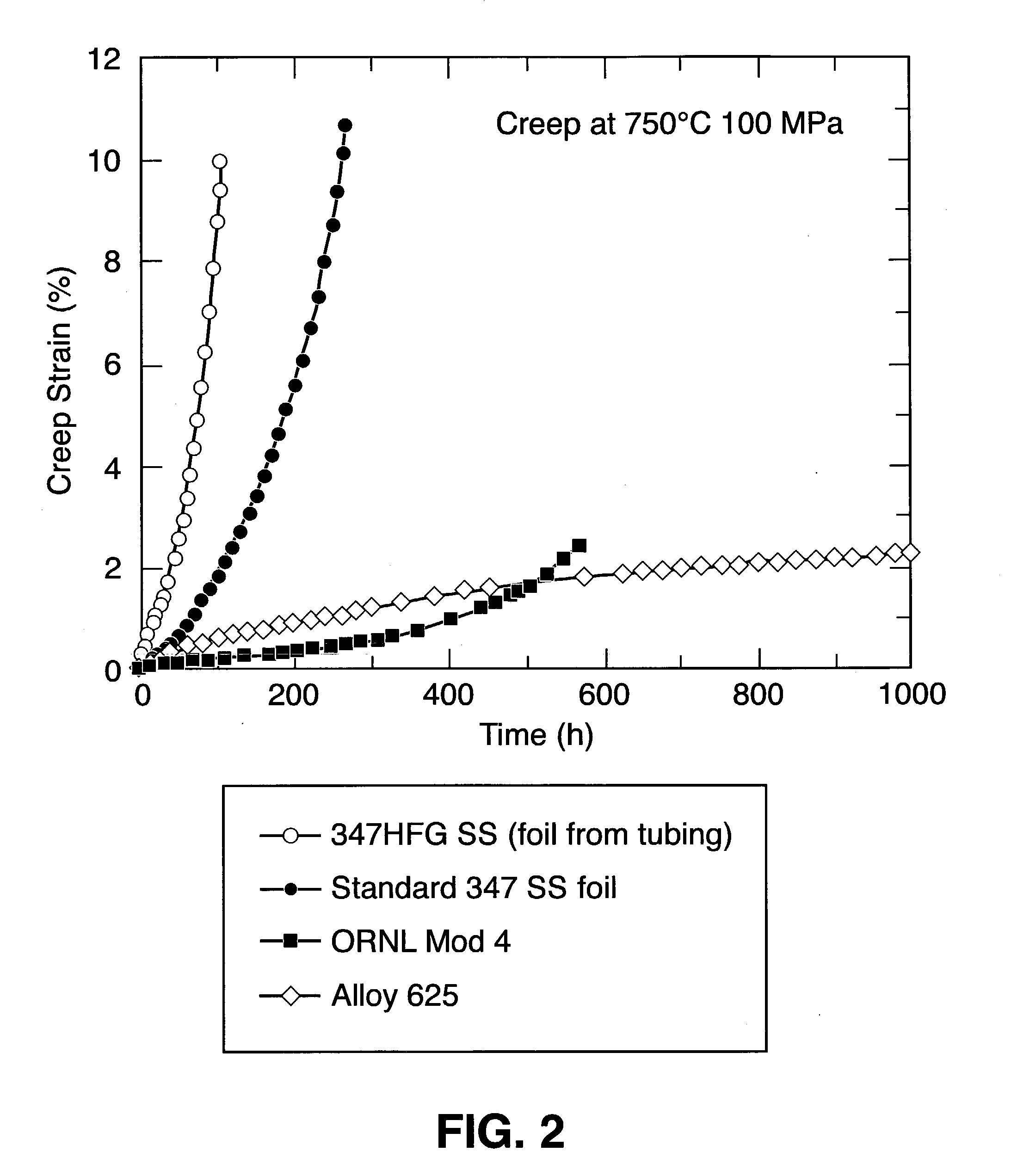
Wrought stainless steel compositions having engineered microstructures for improved heat resistance
InactiveUS20040191109A1Increase heatIncrease resistanceHeat exchange apparatusHeat resistanceAustenite
A wrought stainless steel alloy composition includes 12% to 25% Cr, 8% to 25% Ni, 0.05% to 1% Nb, 0.05% to 10% Mn, 0.02% to 0.15% C, 0.02% to 0.5% N, with the balance iron, the composition having the capability of developing an engineered microstructure at a temperature above 550° C. The engineered microstructure includes an austenite matrix having therein a dispersion of intragranular NbC precipitates in a concentration in the range of 10<10 >to 10<17 >precipitates per cm<3>.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Amorphous soft magnetic alloy and inductance component using the same
InactiveUS20070175545A1Excellent in amorphous-forming abilityExcellent soft magnetic propertiesTransformers/inductances detailsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMetallurgyInductor
To provide an amorphous soft magnetic alloy having a supercooled liquid region and excellent in amorphous-forming ability and soft magnetic properties, by selecting and optimizing an alloy composition, and to further provide a ribbon, a powder, a high-frequency magnetic core, and a bulk member each using such an amorphous soft magnetic alloy. The amorphous soft magnetic alloy has a composition expressed by a formula of (Fe1-αTMα)100-w-x-y-zPwBxLySiz, wherein unavoidable impurities are contained, TM is at least one selected from Co and Ni, L is at least one selected from the group consisting of Al, V, Cr, Y, Zr, Mo, Nb, Ta, and W, 0≦α0.98, 2≦w≦16 at %, 2≦x≦16 at %, 0<y≦10 at %, and 0≦z≦8 at %).
Owner:TOKIN CORP +1
Device containing non-blinking quantum dots
InactiveUS7777233B2Reduced life-timeShort radiative lifetime propertiesRadiation pyrometryDischarge tube luminescnet screensQuantum dotNanocrystal
An optoelectronic device including two spaced apart electrodes; and at least one layer containing ternary core / shell nanocrystals disposed between the spaced electrodes and having ternary semiconductor cores containing a gradient in alloy composition and wherein the ternary core / shell nanocrystals exhibit single molecule non-blinking behavior characterized by on times greater than one minute or radiative lifetimes less than 10 ns.
Owner:NANOCO TECH LTD
Steel plate for hot stamping, hot stamping process and hot-stamped member
ActiveCN104846274ALow austenitizing temperatureQuenching temperature is lowShaping toolsFurnace typesHot stampingMartensite transformation
The invention relates to a steel plate for hot stamping, a hot stamping process and a hot-stamped member. The steel plate for hot stamping is characterized by comprising, by weight, 0.18 to 0.42% of C, 4 to 8.5% of Mn and 0.8 to 3.0% of Si and Al, with the balance being Fe and avoidable impurities, wherein the alloy component of the steel plate satisfy the condition that the actual measured value of martensite phase transformation beginning temperature is no more than 280 DEG C. A manufacturing method for the hot-stamped member comprises the following steps: heating a material to 700 to 850 DEG C and carrying out stamping; then carrying out cooling in a die or air cooling or cooling in other manners to 150 to 260 DEG C below the martensite phase transformation beginning temperature; and heating the stamped member to 160 to 450 DEG C, maintaining the temperature for 1 to 100,000 s, carrying out tempering heat treatment and cooling the stamped member to room temperature. The hot-stamped member prepared in the invention has yield strength of no less than 1200 MPa, tensile strength of no less than 1600 MPa and total elongation percentage of no less than 10%.
Owner:EASYFORMING STEEL TECH CO LTD
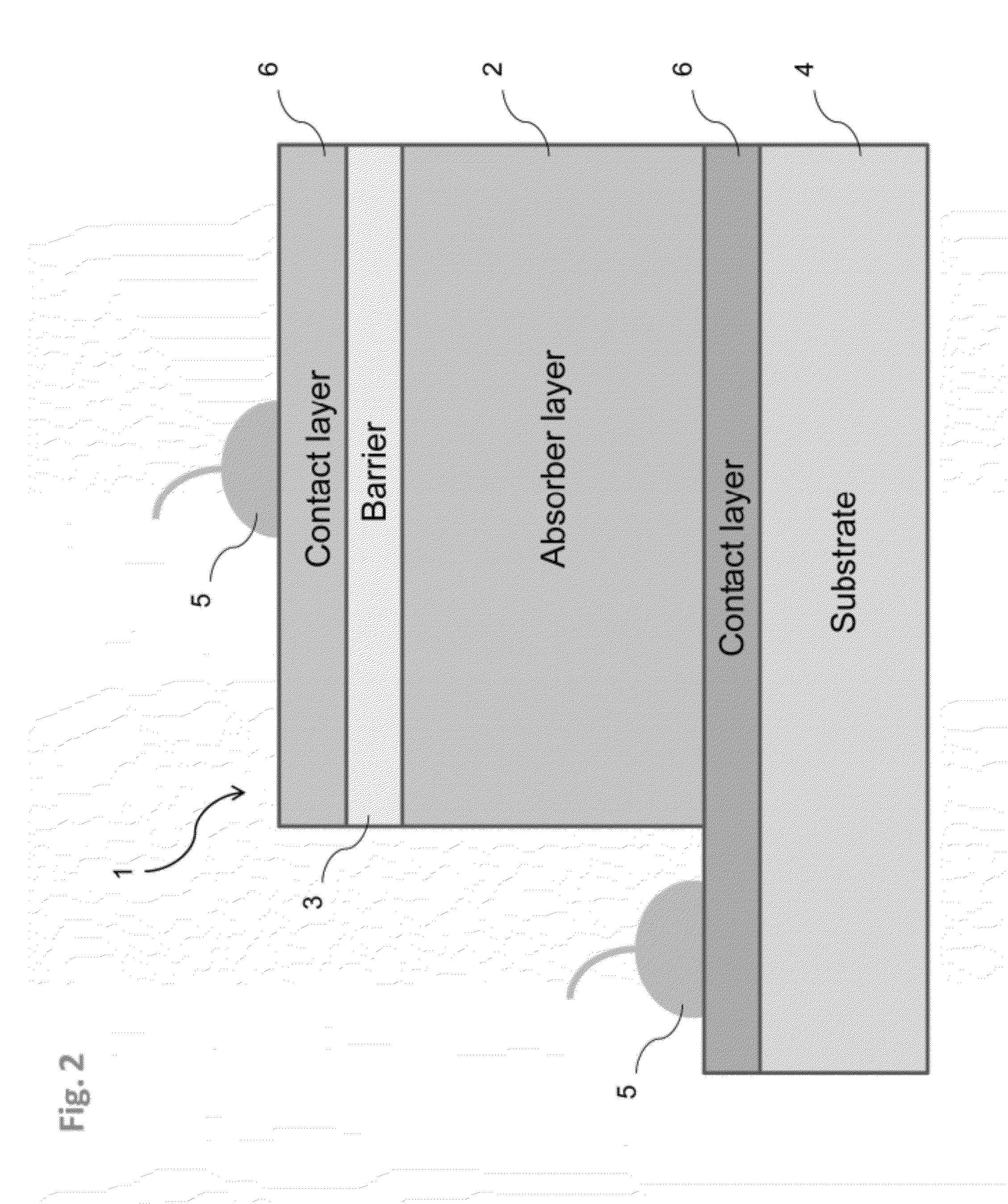
Barrier infrared detector
ActiveUS20120145996A1Minimally strainedFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesPower flowOperability
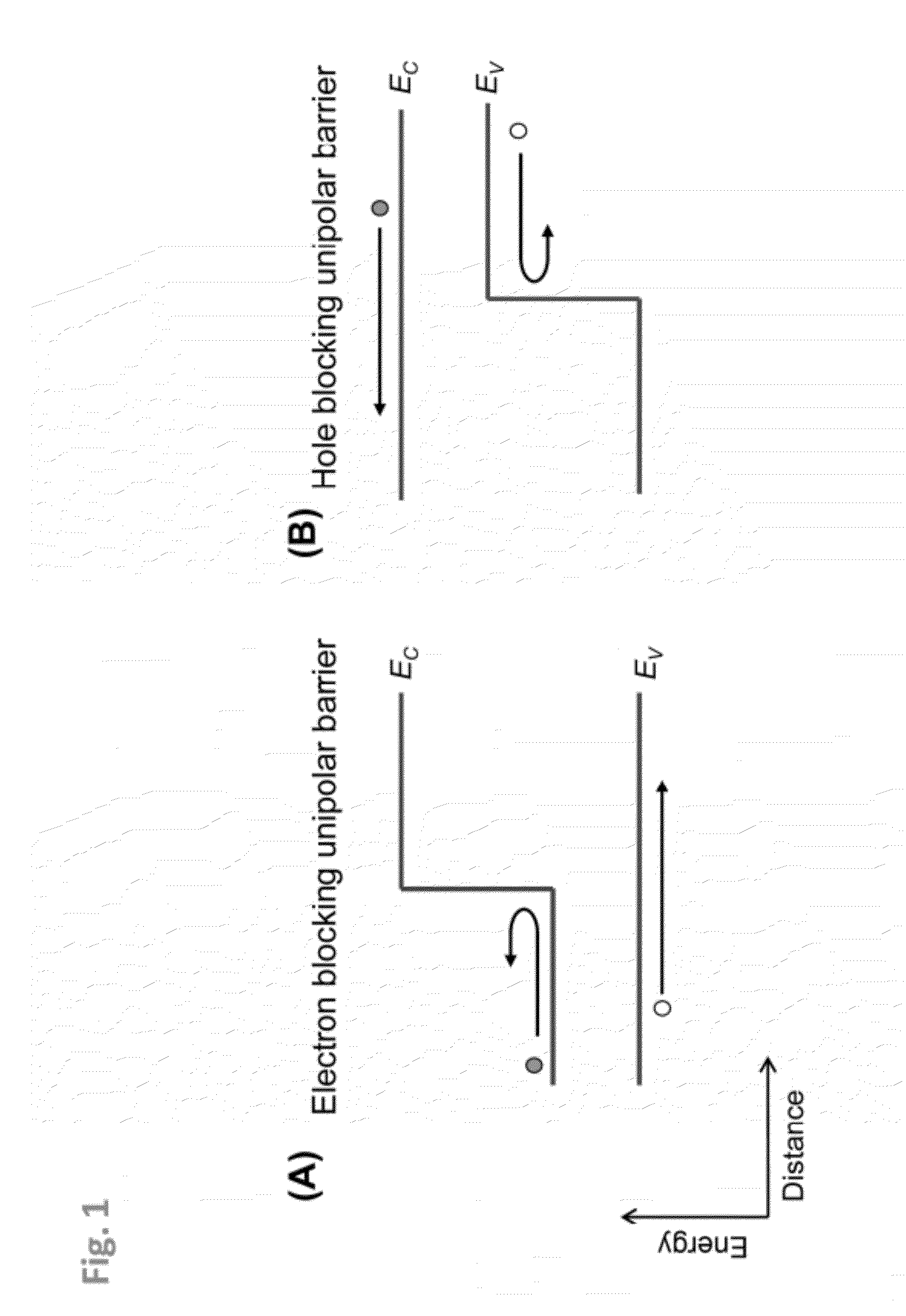
A superlattice-based infrared absorber and the matching electron-blocking and hole-blocking unipolar barriers, absorbers and barriers with graded band gaps, high-performance infrared detectors, and methods of manufacturing such devices are provided herein. The infrared absorber material is made from a superlattice (periodic structure) where each period consists of two or more layers of InAs, InSb, InSbAs, or InGaAs. The layer widths and alloy compositions are chosen to yield the desired energy band gap, absorption strength, and strain balance for the particular application. Furthermore, the periodicity of the superlattice can be “chirped” (varied) to create a material with a graded or varying energy band gap. The superlattice based barrier infrared detectors described and demonstrated herein have spectral ranges covering the entire 3-5 micron atmospheric transmission window, excellent dark current characteristics operating at least 150K, high yield, and have the potential for high-operability, high-uniformity focal plane arrays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
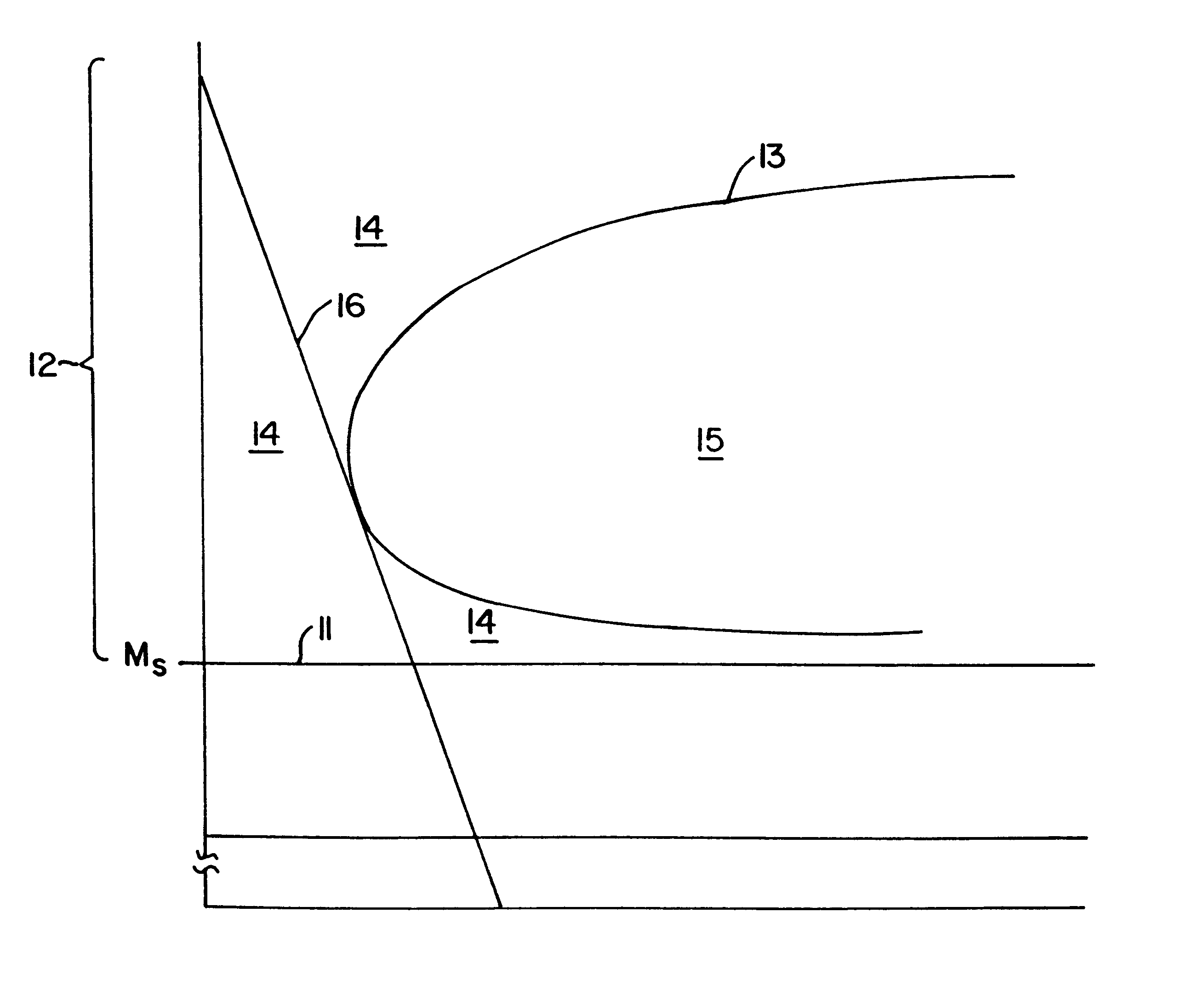
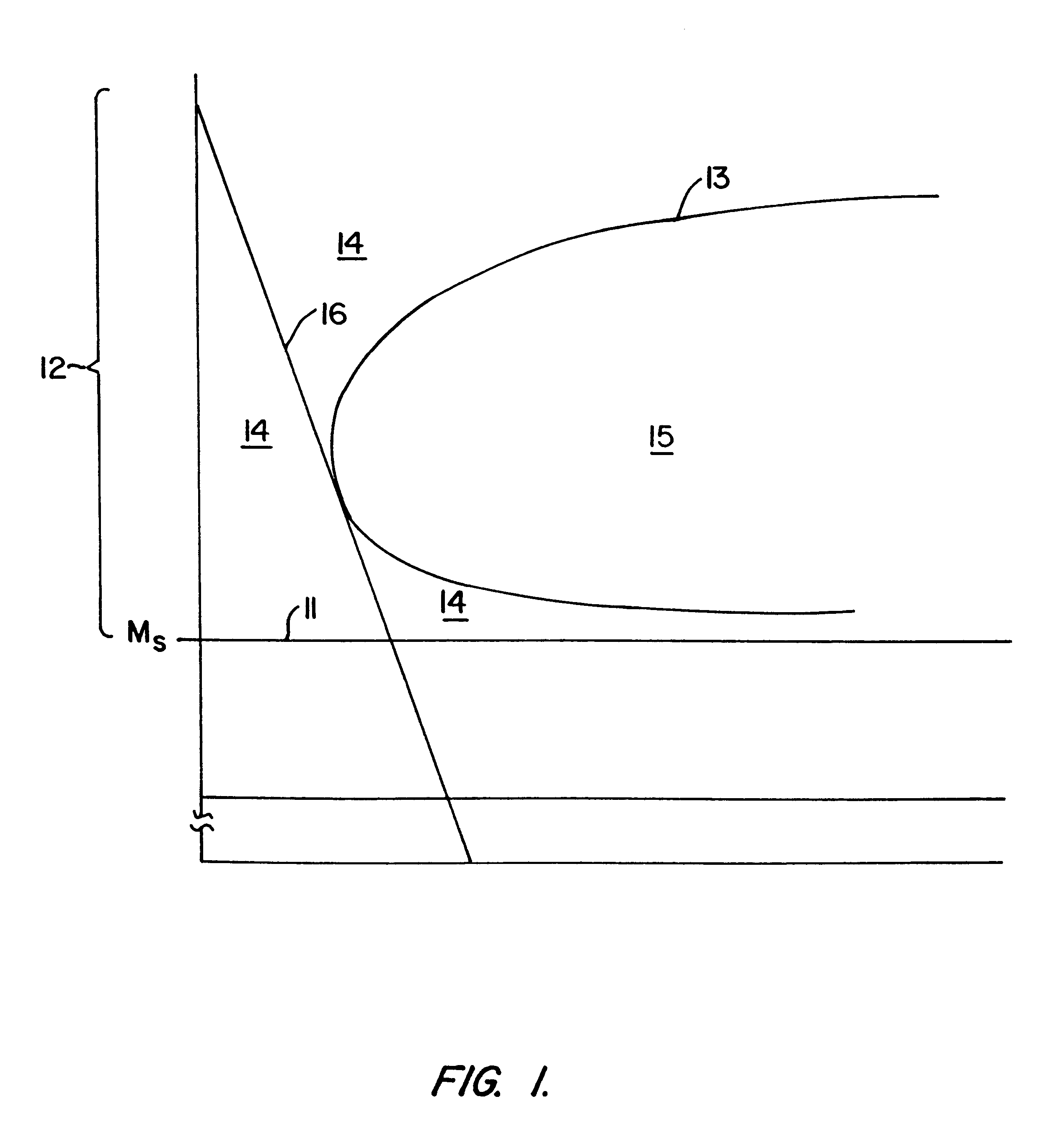
Low-carbon steels of superior mechanical and corrosion properties and process of making thereof
InactiveUS6273968B1Simple structureAccelerated corrosionFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCrystal twinningCarbide
Alloy steels that combine high strength and toughness with high corrosion resistance are achieved by a dislocated lath microstructure, in which dislocated martensite laths that are substantially free of twinning alternate with thin films of retained austenite, with an absence of autotempered carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides in both the dislocated martensite laths and the retained austenite films. This microstructure is achieved by selecting an alloy composition whose martensite start temperature is 350° C. or greater, and by selecting a cooling regime from the austenite phase through the martensite transition region that avoids regions in which autotempering occurs.
Owner:CMC STEEL FABTORS
Niobium-containing zirconium alloy for nuclear fuel claddings
InactiveUS6261516B1Improve corrosion resistanceIncrease resistanceOptical rangefindersFuel elementsNiobiumManganese
The invention presented herein relates to a niobium-containing zirconium alloy for use in nuclear fuel cladding. The Zr alloy of this invention with superior corrosion resistance is characterized as comprising an alloy composition as follows:1) niobium (Nb), in a range of 0.8 to 1.2 wt. %; one or more elements selected from the group consisting of iron (Fe), molybdenum (Mo), copper (Cu) and manganese (Mn), in a range of 0.1 to 0.3 wt. %, respectively; oxygen (O), in a range of 600 to 1400 ppm; silicon (Si), in a range of 80 to 120 ppm; and the balance being of Zr,2) Nb, in a range of 1.3 to 1.8 wt. %; tin (Sn), in a range of 0.2 to 0.5 wt. %; one element selected from the group consisting of Fe, Mo, Cu and Mn, in a range of 0.1 to 0.3 wt. %; O, in a range of 600 to 1400 ppm; Si, in a range of 80 to 120 ppm; and the balance being of Zr,3) Nb, in a range of 1.3 to 1.8 wt. %; Sn, in a range of 0.2 to 0.5 wt. %; Fe, in a range of 0.1 to 0.3 wt. %; one element selected from the group consisting of chromium (Cr), Mo, Cu and Mn, in a range of 0.1 to 0.3 wt. %; O, in a range of 600 to 1400 ppm; Si, in a range of 80 to 120 ppm; and the balance being of Zr, and4) Nb, in a range of 0.3 to 1.2 wt. %; Sn, in a range of 0.4 to 1.2 wt. %; Fe, in a range of 0.1 to 0.5 wt. %; one element selected from the group consisting of Mo, Cu and Mn, in a range of 0.1 to 0.3 wt. %; O, in a range of 600 to 1400 ppm; Si, in a range of 80 to 120 ppm; and the balance being of Zr.
Owner:KOREA HYDRO & NUCLEAR POWER CO LTD +1
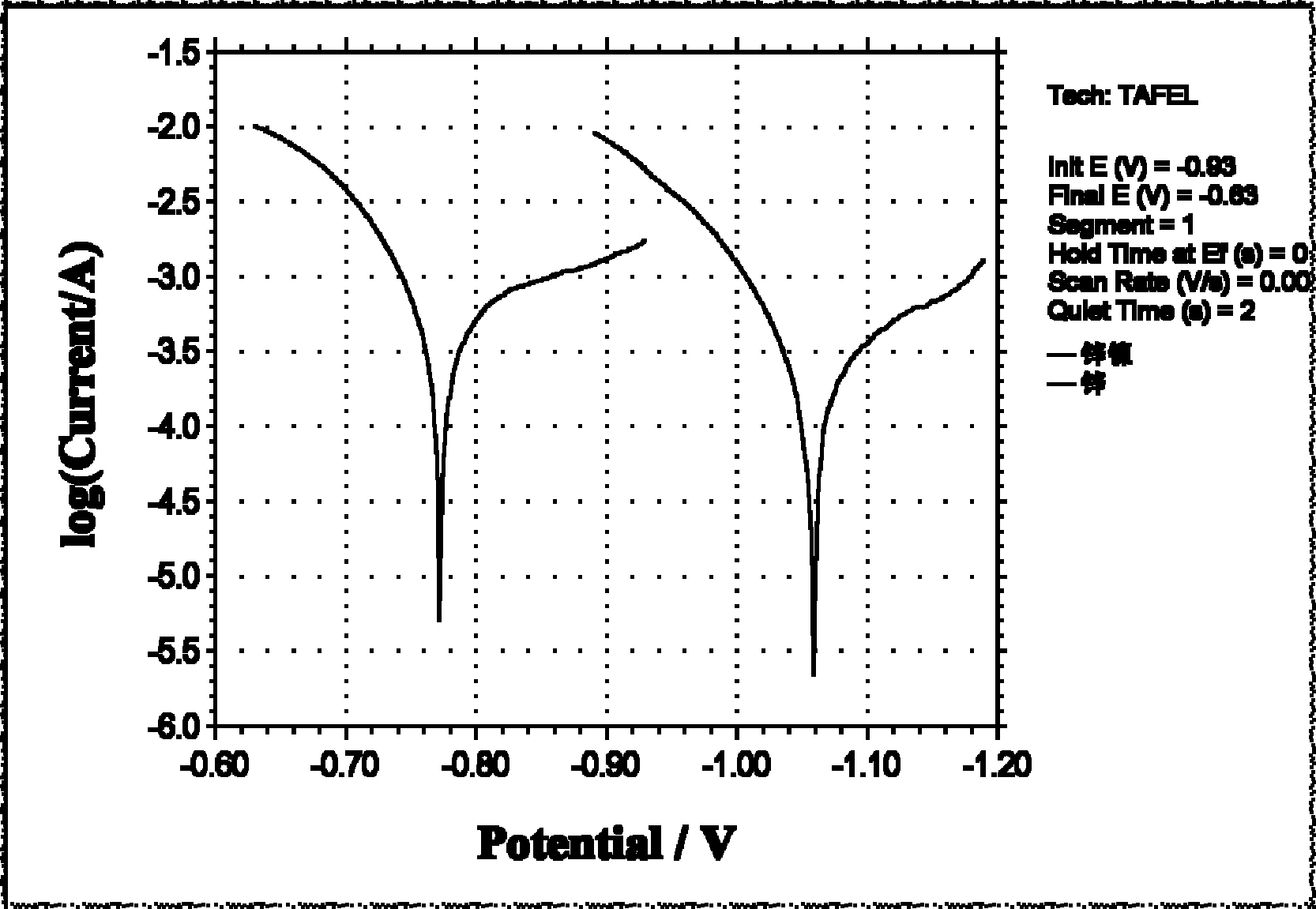
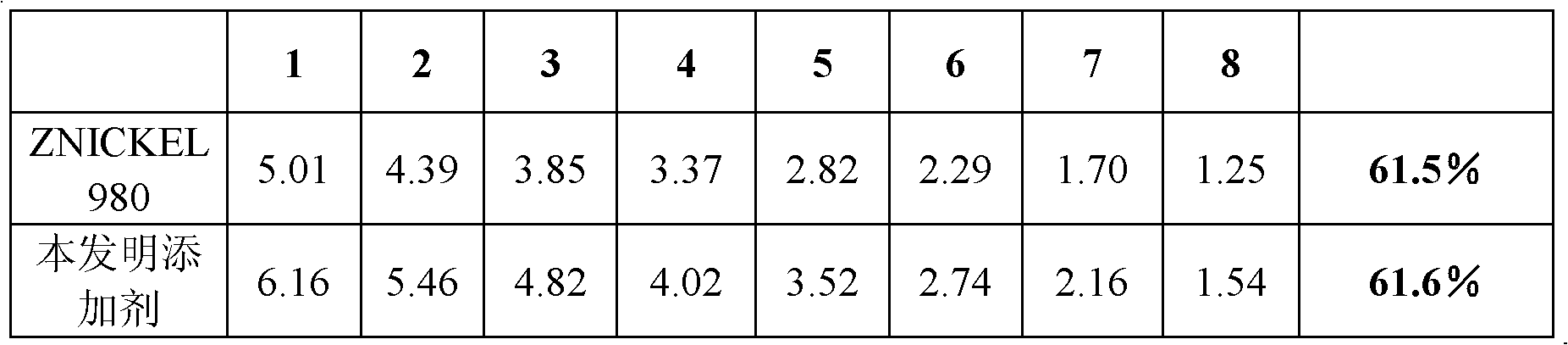
Alkaline electroplating Zn-Ni alloy additive, electroplating solution and preparation method
The invention relates to an alkaline electroplating Zn-Ni alloy additive, an electroplating solution and a preparation method. The additive comprises the following components in parts by weight: 3.5 to 4.5 parts of nickel complex agent, 6 to 8 parts of nickel source, 7 to 8.5 parts of zinc complex agent, 1.5 to 2.5 parts of brightening agent and 0.2 to 0.3 part of throwing agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding zinc oxide into dissolved sodium hydroxide, stirring and dissolving; adding the zinc complex agent, the nickel complex agent, nickel replenisher, the brightening agent and the throwing agent in turn; and stirring to ensure that the mixture is mixed uniformly so as to prepare the electroplating solution containing the additive. The alkaline electroplating Zn-Ni alloy additive can acquire excellent metal distribution and constant alloy composition within a wide current density range, has stable nickel content of the plating in a range of between 12 and 15 percent, excellent corrosion resistance which is over five times more than a conventional zinc coating, excellent dispersive power and higher current efficiency, and can be used for barrel plating or rack plating with small coating stress, high ductility and excellent brightness.
Owner:济南德锡科技有限公司
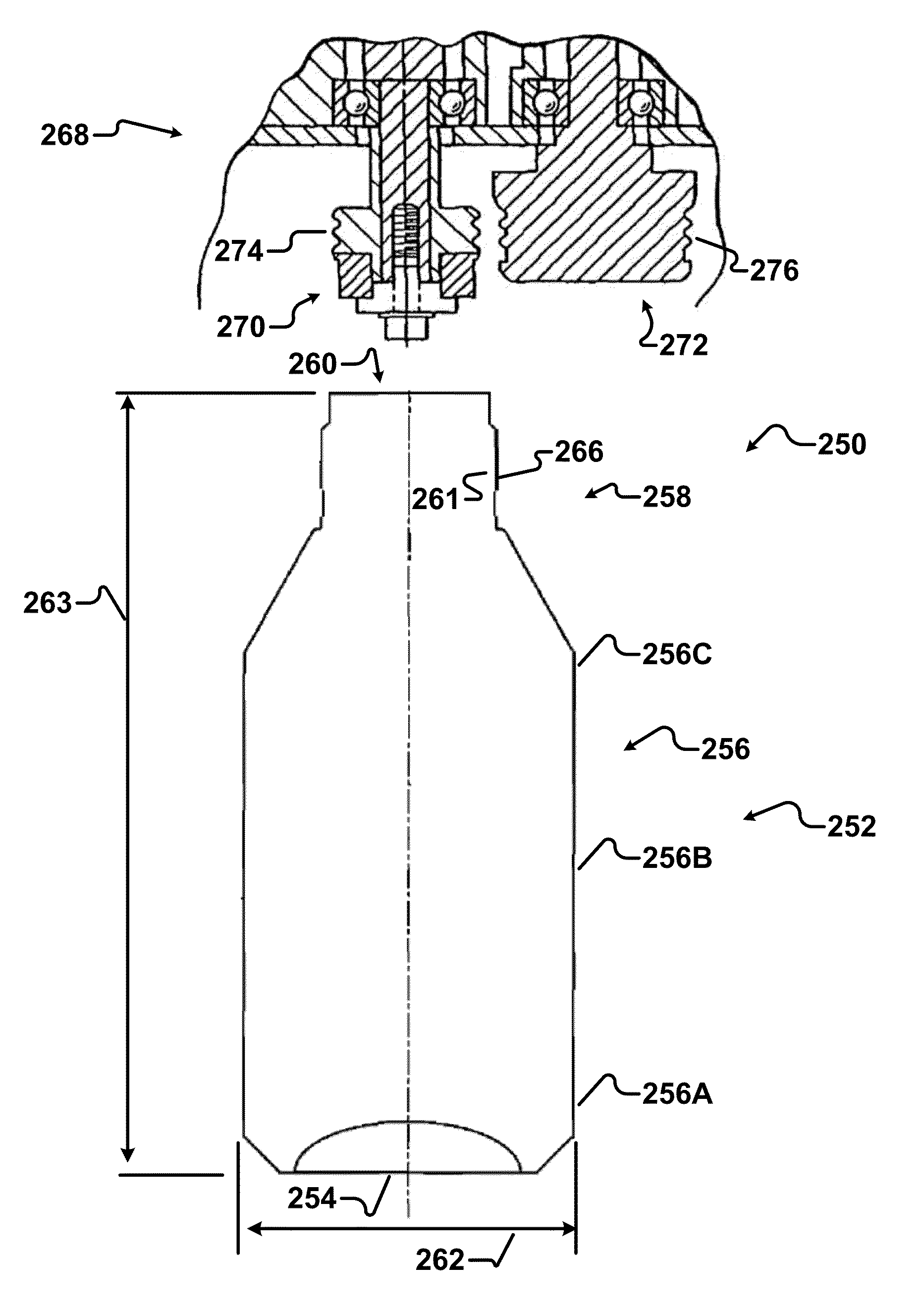
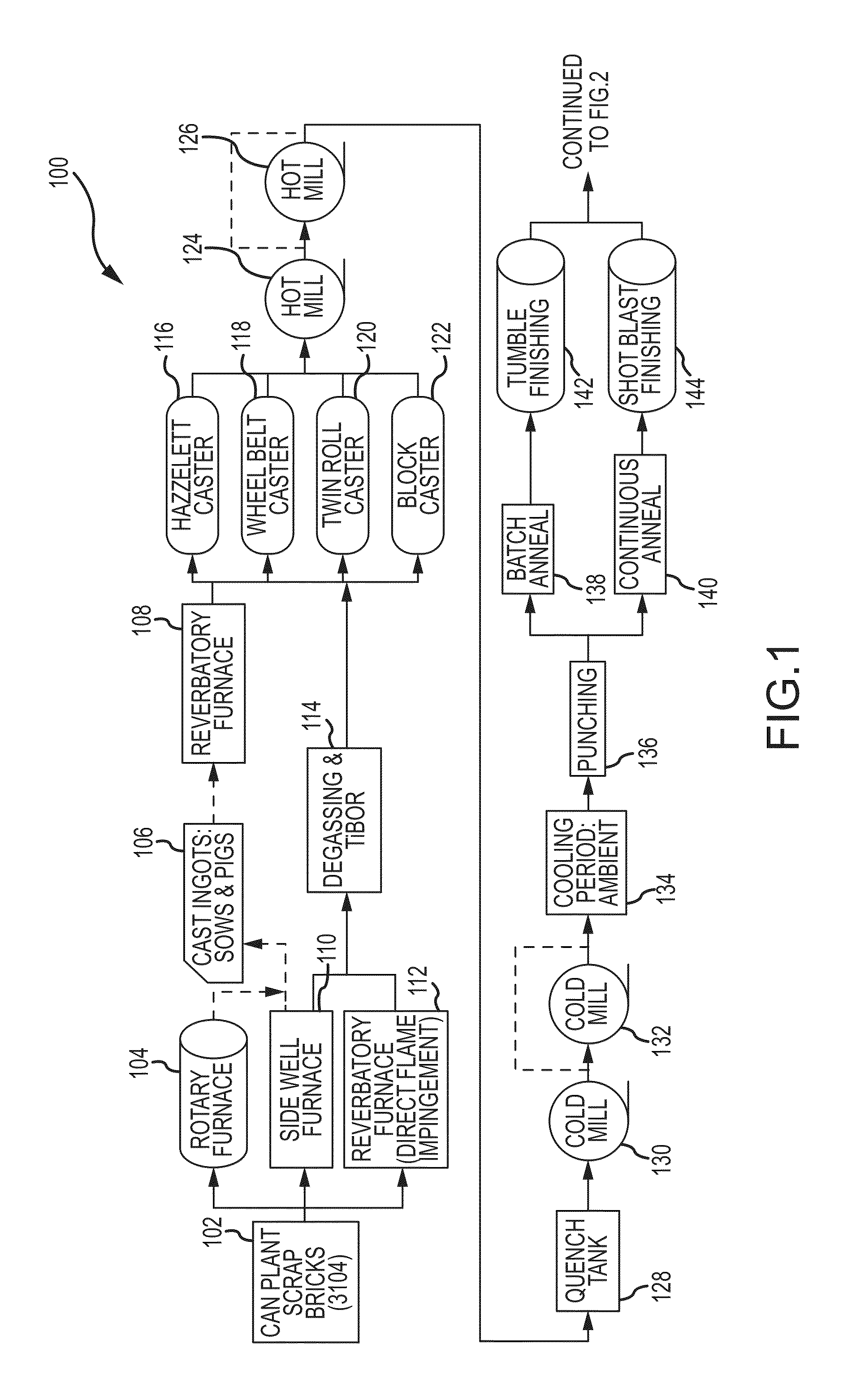
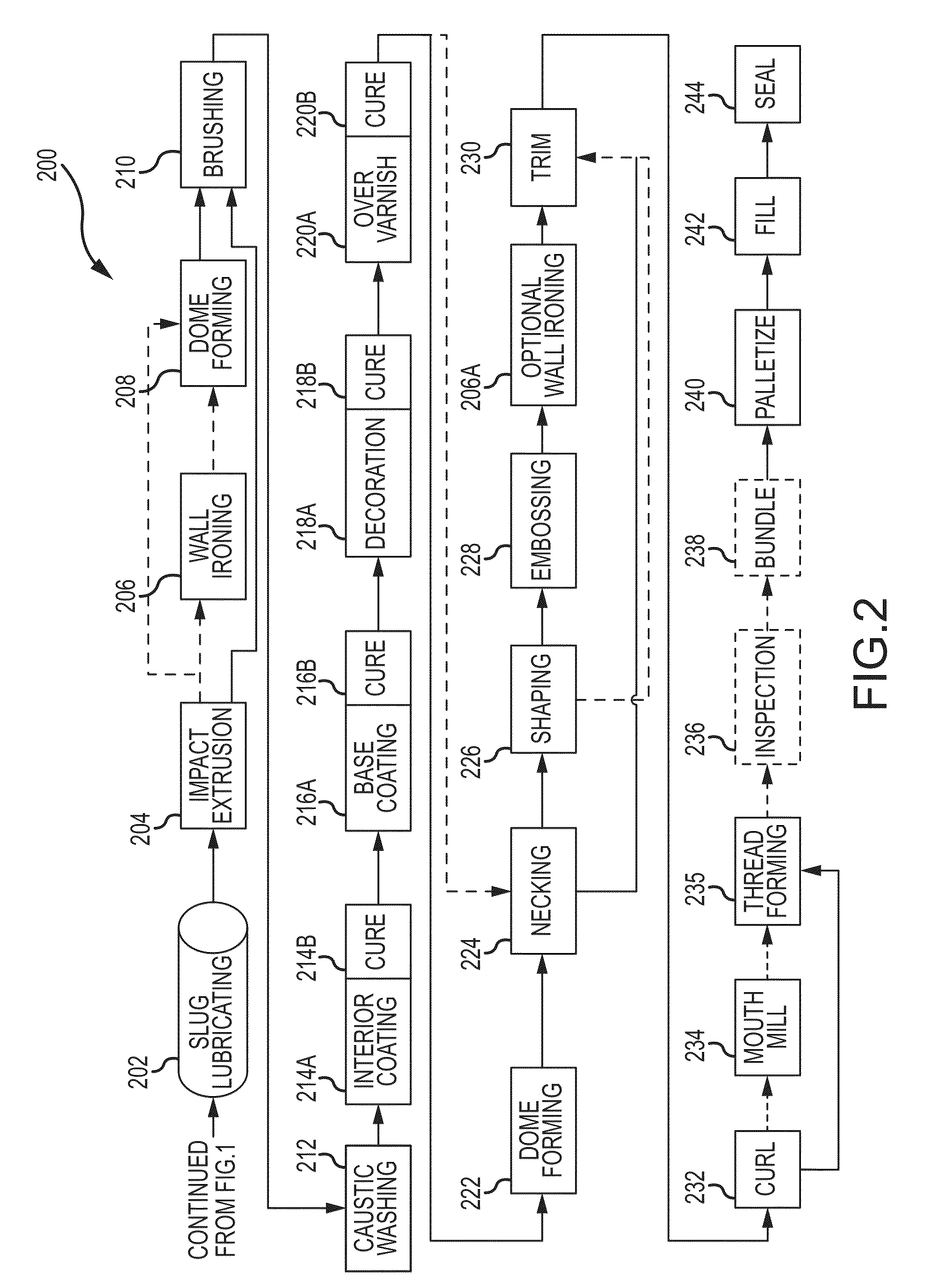
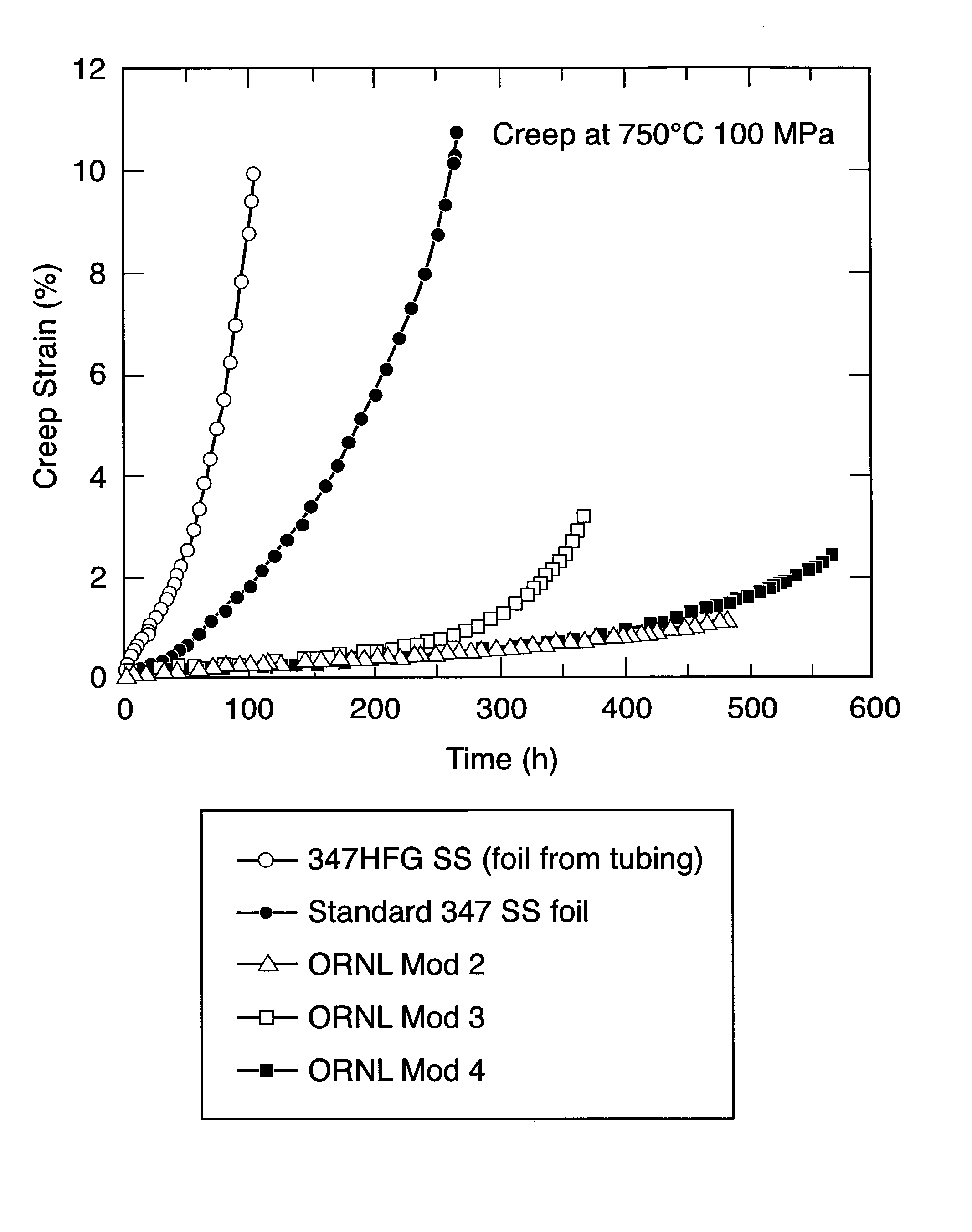
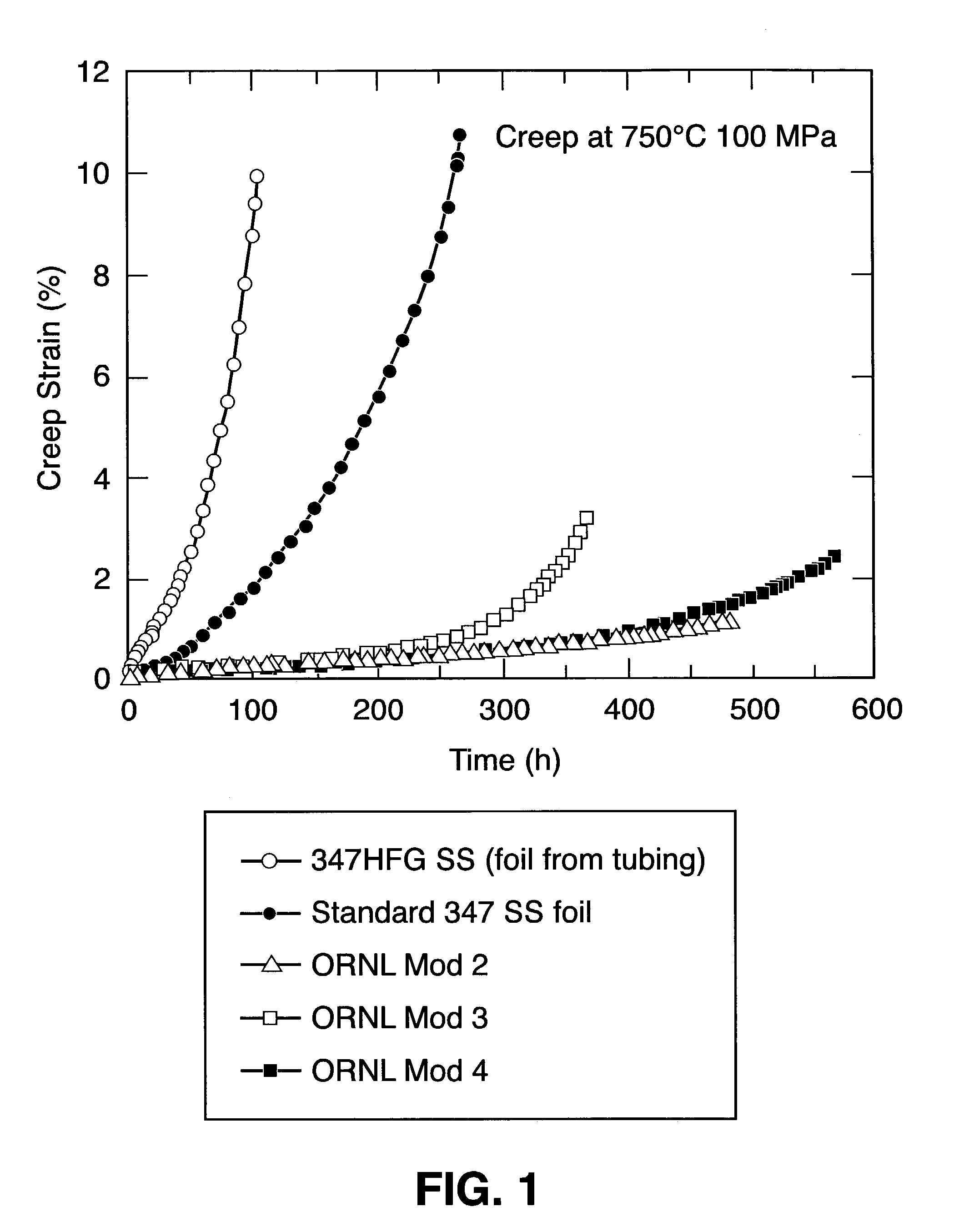
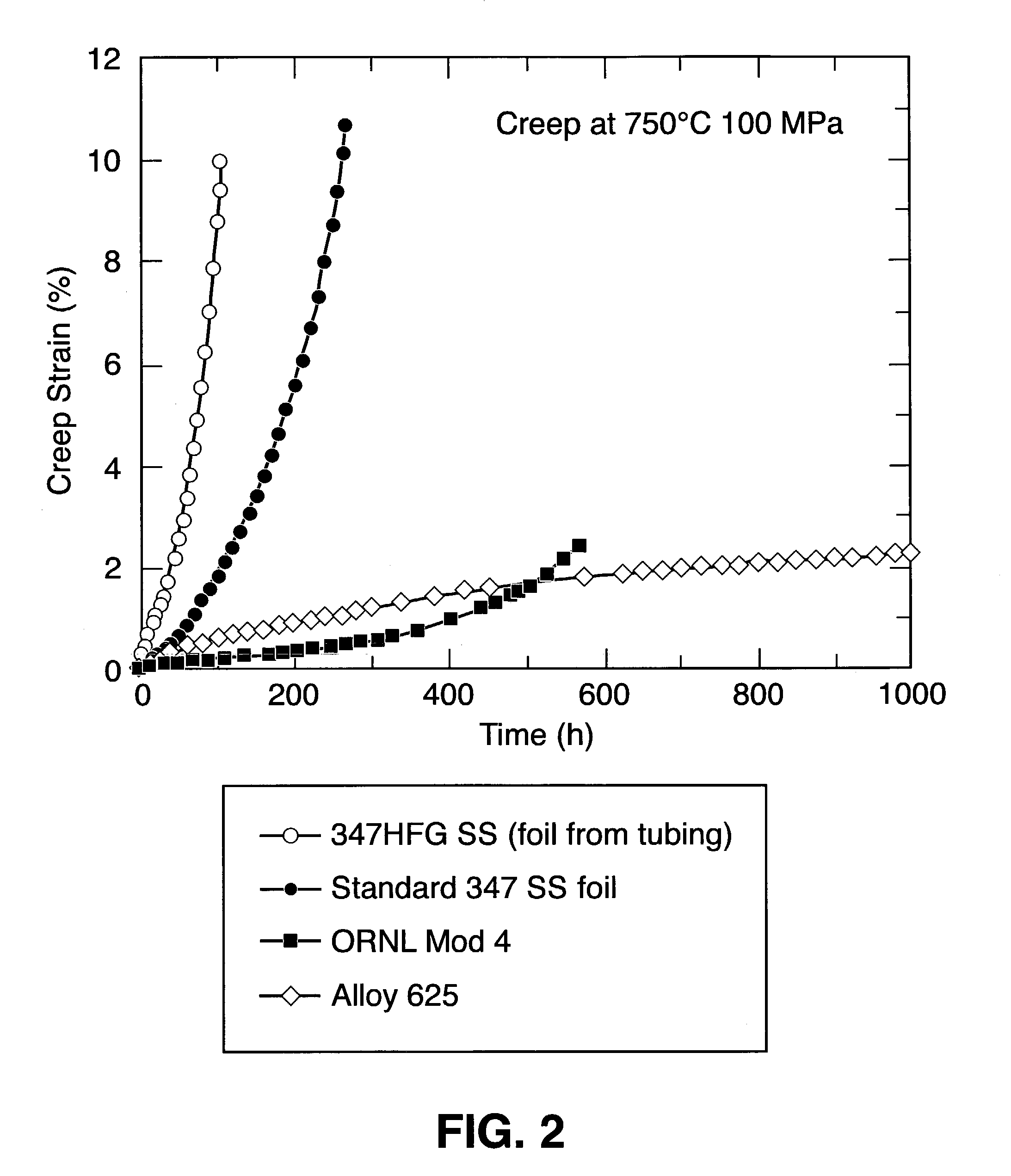
Aluminum impact extruded bottle with threaded neck made from recycled aluminum and enhanced alloys
ActiveUS20140298641A1High mechanical strengthLow costMetal rolling stand detailsClosure capsBottleUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates generally to forming a threaded neck in a metal bottle manufactured by a process known as impact extrusion. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods, apparatus and alloy compositions used in the impact extrusion manufacturing of containers and other articles with sufficient strength characteristics to allow threading the container necks to receive a threaded closure on the threaded neck.
Owner:BALL CORP
Wrought stainless steel compositions having engineered microstructures for improved heat resistance
A wrought stainless steel alloy composition includes 12% to 25% Cr, 8% to 25% Ni, 0.05% to 1% Nb, 0.05% to 10% Mn, 0.02% to 0.15% C, 0.02% to 0.5% N, with the balance iron, the composition having the capability of developing an engineered microstructure at a temperature above 550° C. The engineered microstructure includes an austenite matrix having therein a dispersion of intragranular NbC precipitates in a concentration in the range of 1010 to 1017 precipitates per cm3.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Lattice matchable alloy for solar cells
InactiveUS20110232730A1Improve performancePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsIndiumSolar cell
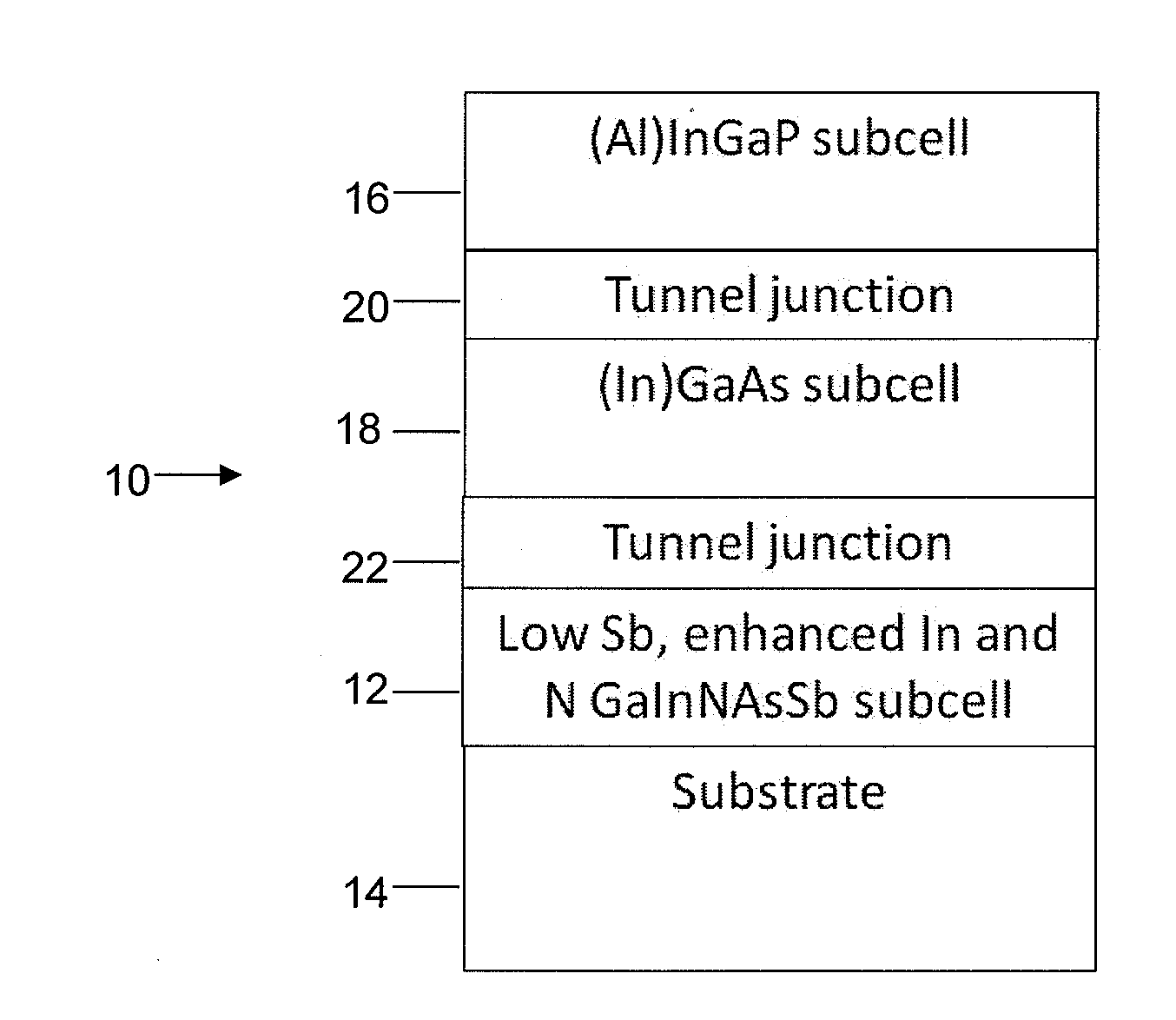
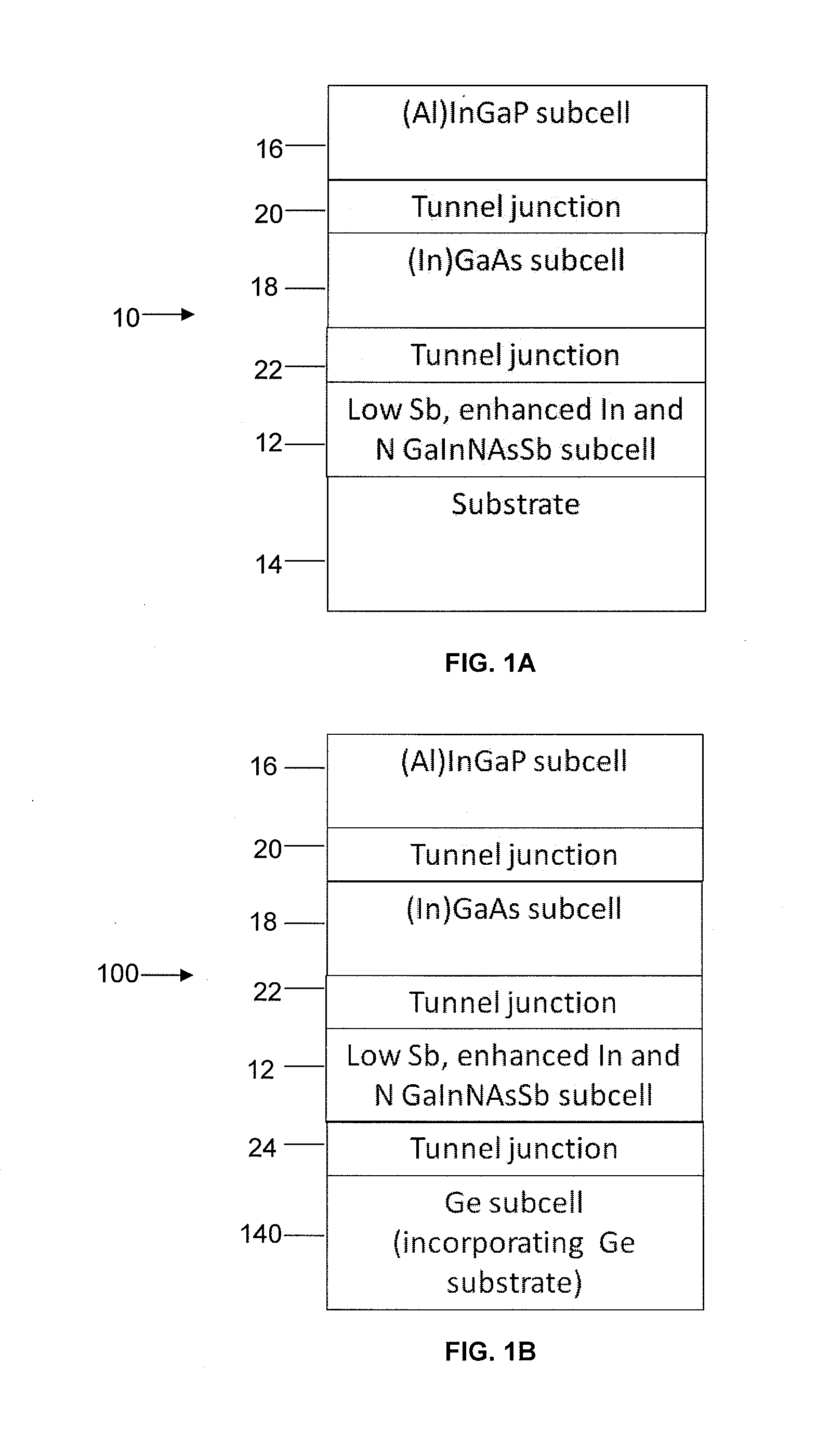
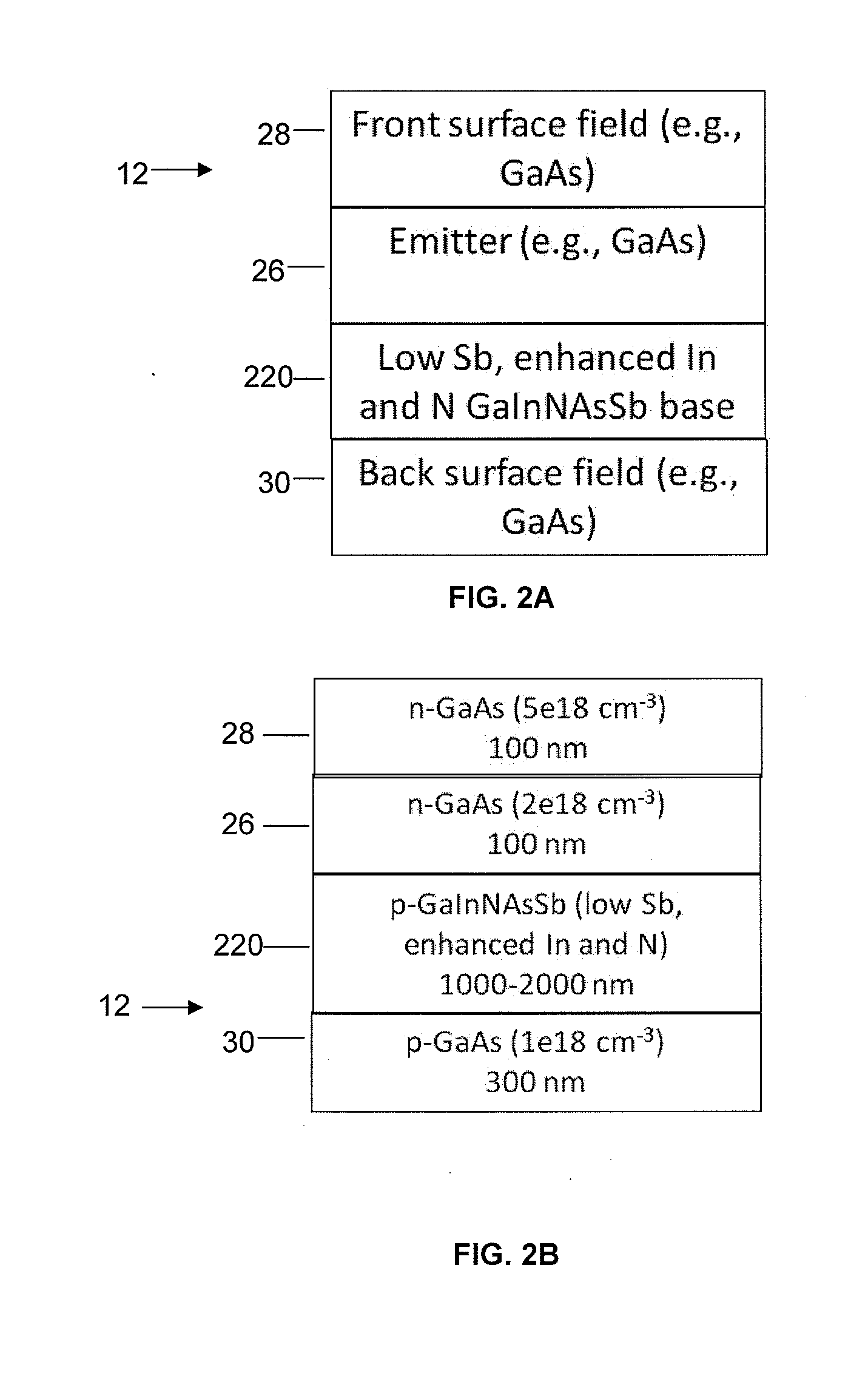
An alloy composition for a subcell of a solar cell is provided that has a bandgap of at least 0.9 eV, namely, Ga1-xInxNyAs1-y-zSbz with a low antimony (Sb) content and with enhanced indium (In) content and enhanced nitrogen (N) content, achieving substantial lattice matching to GaAs and Ge substrates and providing both high short circuit currents and high open circuit voltages in GaInNAsSb subcells for multijunction solar cells. The composition ranges for Ga1-xInxNyAs1-y-zSbz are 0.07≦x≦0.18, 0.025≦y≦0.04 and 0.001≦z≦0.03.
Owner:CACTUS MATERIALS INC
Nickel-base high-temperature alloy with low density and high melting point and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to high-temperature alloy technology, and in particular provides an isometrical cast nickel-base high-temperature alloy with low density, high incipient melting temperature and good casting property and a preparation process thereof, which can be used for floating tile materials of a combustion chamber. The alloy comprises the following compositions by mass percentage: 0.03 to 0.06 percent of C, 5 to 12 percent of Cr, 5.5 to 6.5 percent of Al, 3 to 8 percent of Co, 3 to 7 percent of W, 2 to 4 percent of Mo, 1.6 to 3.2 percent of Nb, 0.01 to 0.03 percent of B, 0.008 to 0.025 percent of Y and the balance of Ni. A vacuum induction furnace is adopted to smelt a master alloy, and a smelting crucible is a CaO crucible or a MgO crucible; and the operation process comprises the following steps: putting alloying elements such as carbon, chromium, cobalt, tungsten, molybdenum and niobium in proportion and a nickel plate into the crucible; melting the alloy when the vacuum degree reaches between 50 and 0.1 Pa; and after completion of the melting, refining for 30 to 300 seconds at a temperature of between 1,550 and 1,600 DEG C, cutting off electricity, forming a film, breaking the film to add Al and Al-Y and Ni-B interalloy for uniform stirring, and casting a master alloy pig at a temperature of between 1,450 and 1,500 DEG C. The invention solves the problems of low incipient melting temperature, poor plasticity and inoxidability and the like of the nickel-base high-temperature alloy.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rare earth aluminum alloy, and method and device for preparing same
The invention discloses a rare earth aluminum alloy, and a method and a device for preparing the same. The alloy contains at least one rare earth metal of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, lutetium, scandium and yttrium, the content of raw earth is 5 to 98 weight percent, and the balance is aluminum and inevitable impurities. The device for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy is characterized in that: a) graphite serves as an electrolysis bath, a graphite plate is an anode, a tungsten bar is a cathode and a molybdenum crucible serves as a rare earth aluminum alloy receiver; b) the diameter of the tungsten bar is 30 to 55 mm; and c) the anode of the graphite consists of a plurality of graphite plates. The rare earth aluminum alloy, and the method and the device for preparing the same have the advantages that: the alloy has uniform components, little segregation and low impurity content; technology for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy through fusion electrolysis can maximally replace a process for preparing single medium-heavy metal through metallothermic reduction, greatly reduce energy consumption and the emission of fluorine-containing tail gas and solid waste residue, improve current efficiency and metal yield and reduce the consumption of auxiliary materials and the energy consumption; and the rare earth aluminum alloys with different rare earth contents can be obtained by controlling different electrolytic temperatures and different cathode current densities.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Smelting technique of novel nickel-iron-base high-temperature alloy GH4169D
The invention discloses a smelting technique of a novel nickel-iron-base high-temperature alloy GH4169D, which aims to smelt the novel high-temperature alloy GH4169D consumable ingot which has the advantages of lower raw material cost and favorable hot working properties in industrial production as well as high stability at high temperature. The scheme of the smelting technique is as follows: on the basis of the GH4169 alloy composition, the Fe content is lowered, the sum and proportion of Al and Ti are adjusted, and proper P and B are added; and by adopting a triple (VIM+PESR+VAR) smelting technique, proper slag and technological parameters are selected, and the burning loss of Al and Ti in the protective-atmosphere electroslag smelting process is controlled to obtain the precise contents of Al and Ti. The technique enhances the metallurgical quality of the high-temperature alloy, and fills up the blank of the high-temperature alloy in the aspect of the application temperature between 650 DEG C and 750 DEG C; the GH4169D alloy has the high strength, favorable hot working property and weldability of the GH4169 alloy, and has the high application temperature and other comprehensive properties of the GH4738 alloy; and the GH4169D alloy has long-term stability at 700 DEG C.
Owner:FUSHUN SPECIAL STEEL SHARES
6063 aluminium alloy with high strength and elongation coefficient an dproduction thereof
The invention opened a high strength and high extensibility 6063 Al alloy which contain the Cu, Mn, chrome, Fe, Zn, Ti, Al. The process is: a, founding: adding the material to the furnace melting stir ring and skimming coving refining skimming and refining thermal retardation casting ingot. b extruding and heat processing: isotroping air cooling, heating extruding quenching cutting cooling stretching straightening aging treatment product. The process has improved the mechanics of the alloy, also the elongation percentage (60%) and the intensity (40%). The tensile strength has been improved to 280-300 MPa, the elongation percentage is improved to 13%. So it satisfy the windows and the curtain wall's need.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Al-Mg-Sc-Zr series aluminum alloy composition for selective laser melting technology and preparation method for molding part
ActiveCN108486433AImprove performanceIncrease contentAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySolubilitySelective laser melting
The invention discloses an Al-Mg-Sc-Zr series aluminum alloy composition for selective laser melting technology and a preparation method for a molding part. The composition comprises, by mass, 6-15% of Mg, 0.5-4% of Sc, 0.7-3% of Zr, 0.5-2% of Mn and the balance aluminum. An aluminum alloy molding part are prepared by smelting of master alloy, preparation of metal powder, preparation of aluminum alloy molding parts and heat treatment processes. According to the elective laser melting technology, the solubility of Mg, Sc and Zr alloy elements in aluminum matrix is greatly improved, the concentration of solid solution strengthening elements and dispersion strengthening particles in the aluminum alloy is increased, and the mechanical property of the aluminum alloy is improved. According to the aluminum alloy obtained by preparation of the selective laser melting technology, the highest density is 99.8%, the highest extension strength sigma b reaches 550 MPa, the yield strength sigma0.2 reaches 520 MPa, the plastic deformation rate of about 12 % is maintained, and the Al-Mg-Sc-Zr series aluminum alloy composition for the ctive laser melting technology and the preparation method for themolding part is applied to complicated structural parts with higher mechanical properties.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High speed lateral heterojunction MISFETs realized by 2-dimensional bandgap engineering and methods thereof
InactiveUS6927414B2Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionCMOS
A method for forming and the structure of a strained lateral channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry is described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a single crystal semiconductor substrate wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region. The invention reduces the problem of leakage current from the source region via the hetero-junction and lattice strain while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials and alloy composition.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
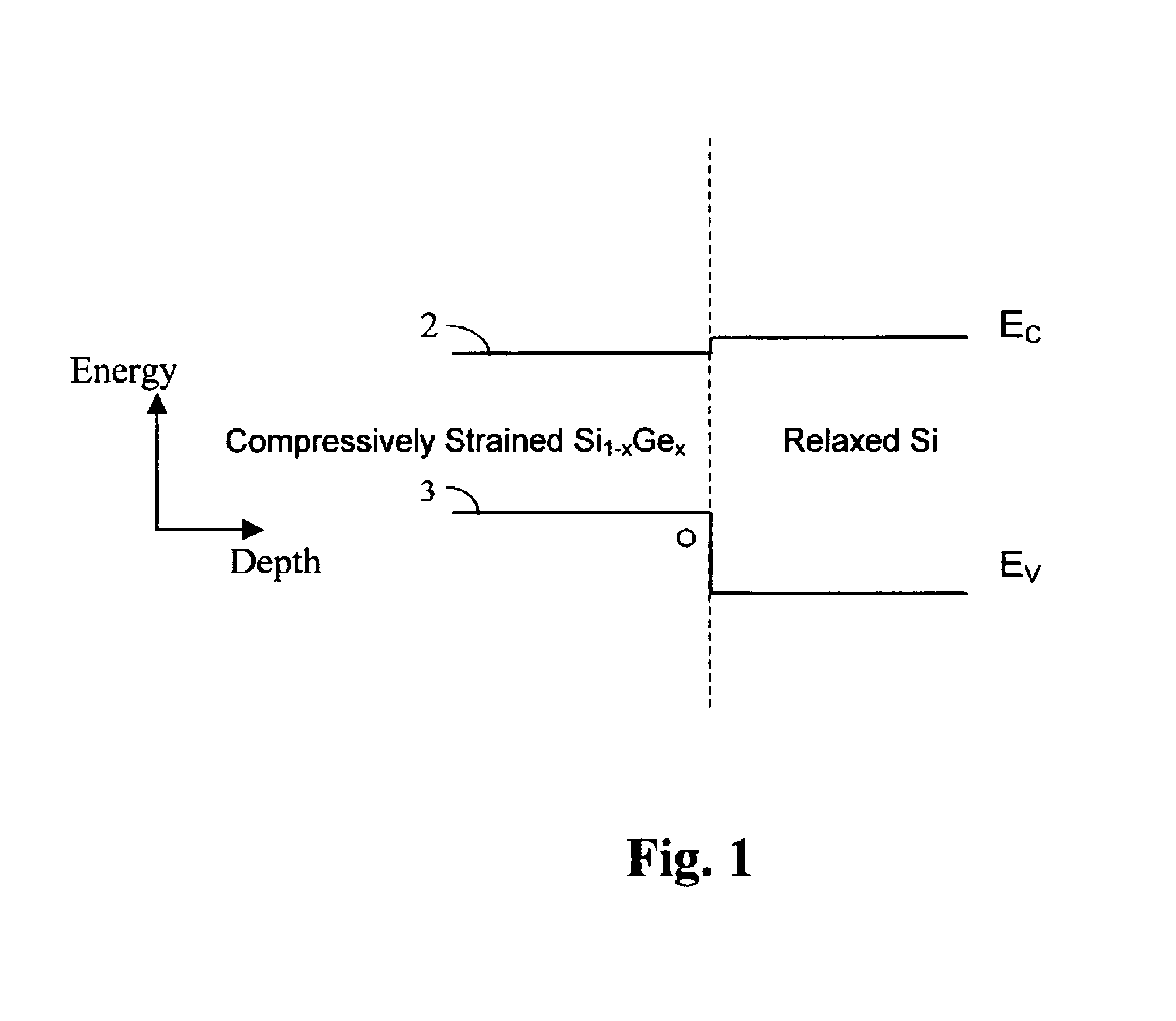
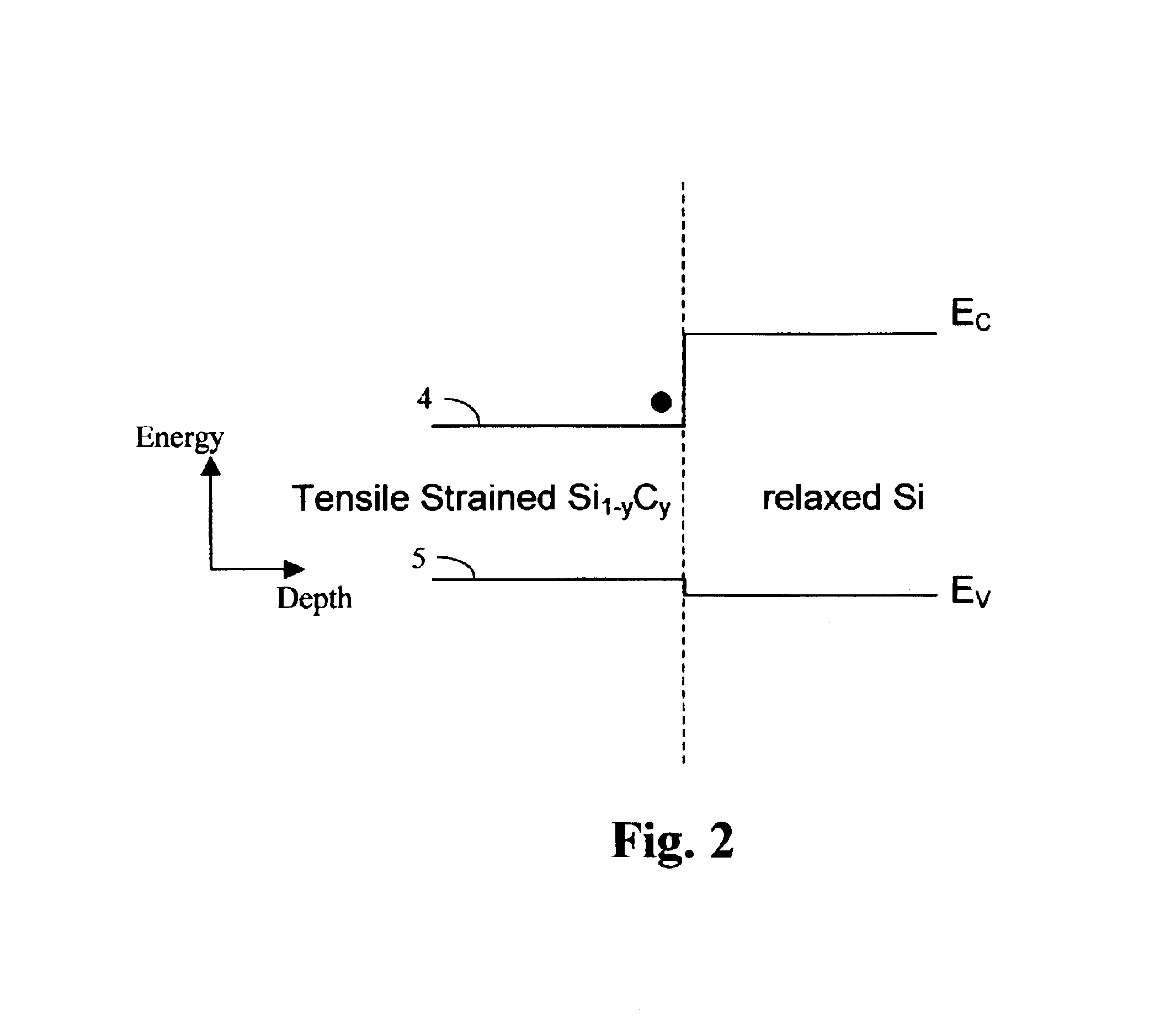
Compositionally graded metallic plates for planar solid oxide fuel cells
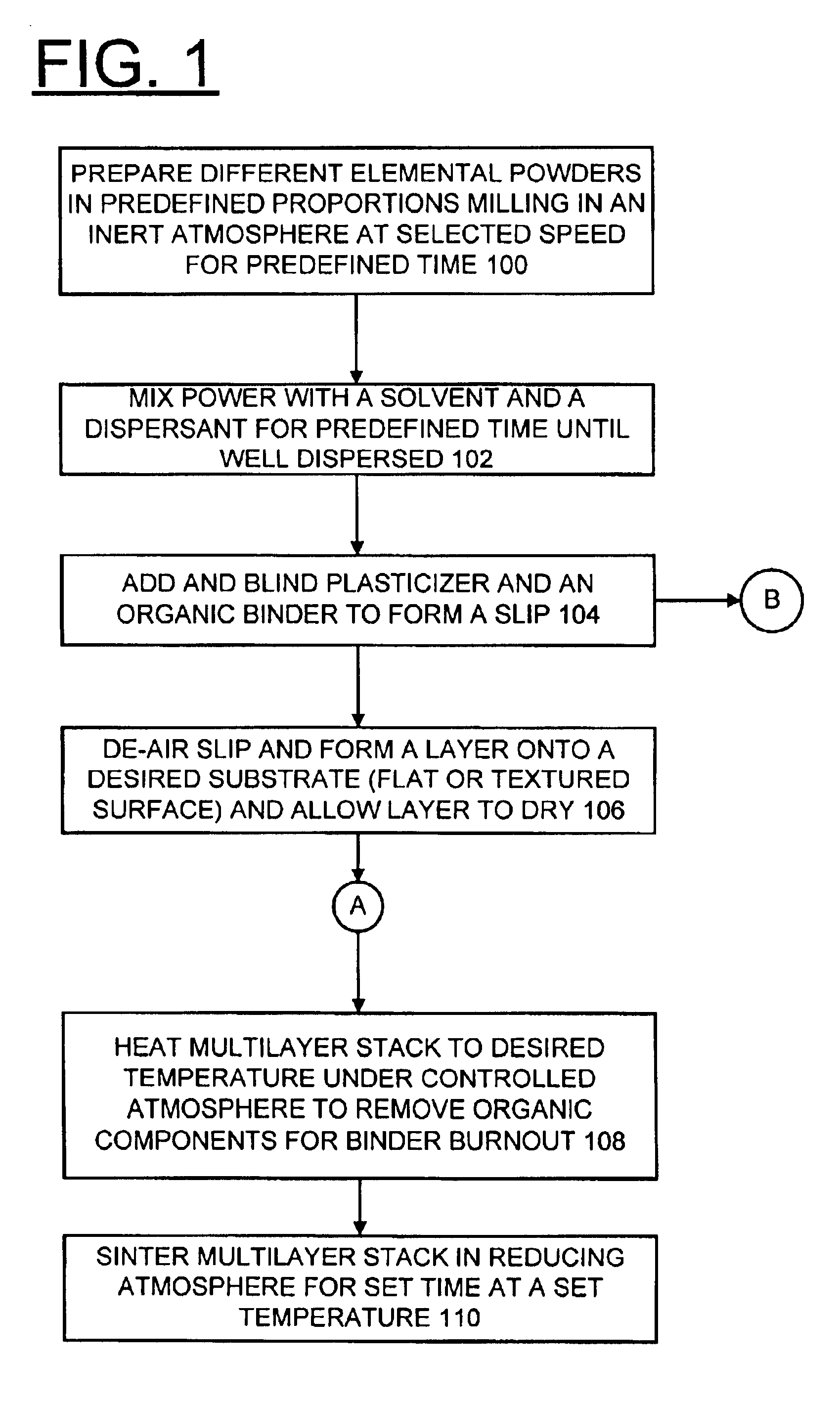
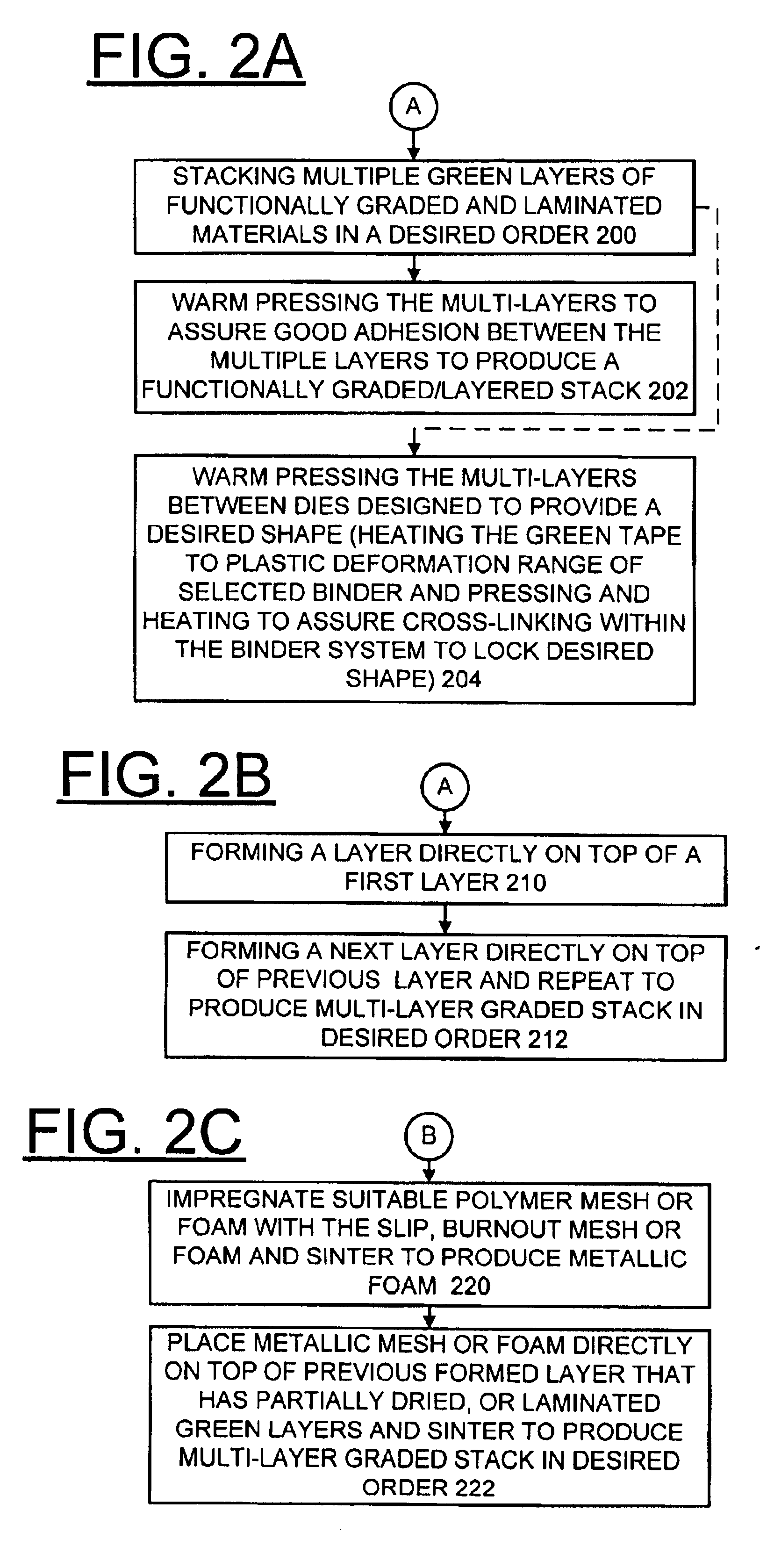
A method for preparing compositionally graded metallic plates and compositionally graded metallic plates suitable for use as interconnects for solid oxide fuel cells are provided. The method of the invention, utilizing powder metallurgy, enables making metallic plates of generally any desired composition to meet the corrosion requirements of fuel cells and other applications, and enables making metallic plates of graded composition from one surface of the plate to the other. A powder of the desired alloy composition is obtained, then solvents, dispersants, a plasticizer and an organic binder are added to form a slip. The slip is then formed into a layer on a desired substrate that can be flat or textured. Once dried, the layer is removed from the substrate and the binder is burned out. The layer is sintered in a reducing atmosphere at a set temperature for a predefined duration specific to the materials used and the desired final properties.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Microbolometer infrared detector elements and methods for forming same
ActiveUS20100133536A1Improved stability and performance characteristicImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial analysis by optical meansDopantMicrobolometer
Microbolometer infrared detector elements that may be formed and implemented by varying type / s of precursors used to form amorphous silicon-based microbolometer membrane material / s and / or by varying composition of the final amorphous silicon-based microbolometer membrane material / s (e.g., by adjusting alloy composition) to vary the material properties such as activation energy and carrier mobility. The amorphous silicon-based microbolometer membrane material / s materials may include varying amounts of one or more additional and optional materials, including hydrogen, fluorine, germanium, n-type dopants and p-type dopants.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
Methods for forming dispersion-strengthened aluminum alloys
In accordance with an exemplary embodiment, a method of forming a dispersion-strengthened aluminum alloy metal includes the steps of providing a dispersion-strengthened aluminum alloy composition in a powdered form, directing a low energy density laser beam at a portion of the powdered alloy composition, and withdrawing the laser beam from the portion of the powdered alloy composition. Subsequent to withdrawal of the laser beam, the portion of the powdered alloy composition cools at a rate greater than or equal to about 106° C. per second, thereby forming the dispersion-strengthened aluminum alloy metal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
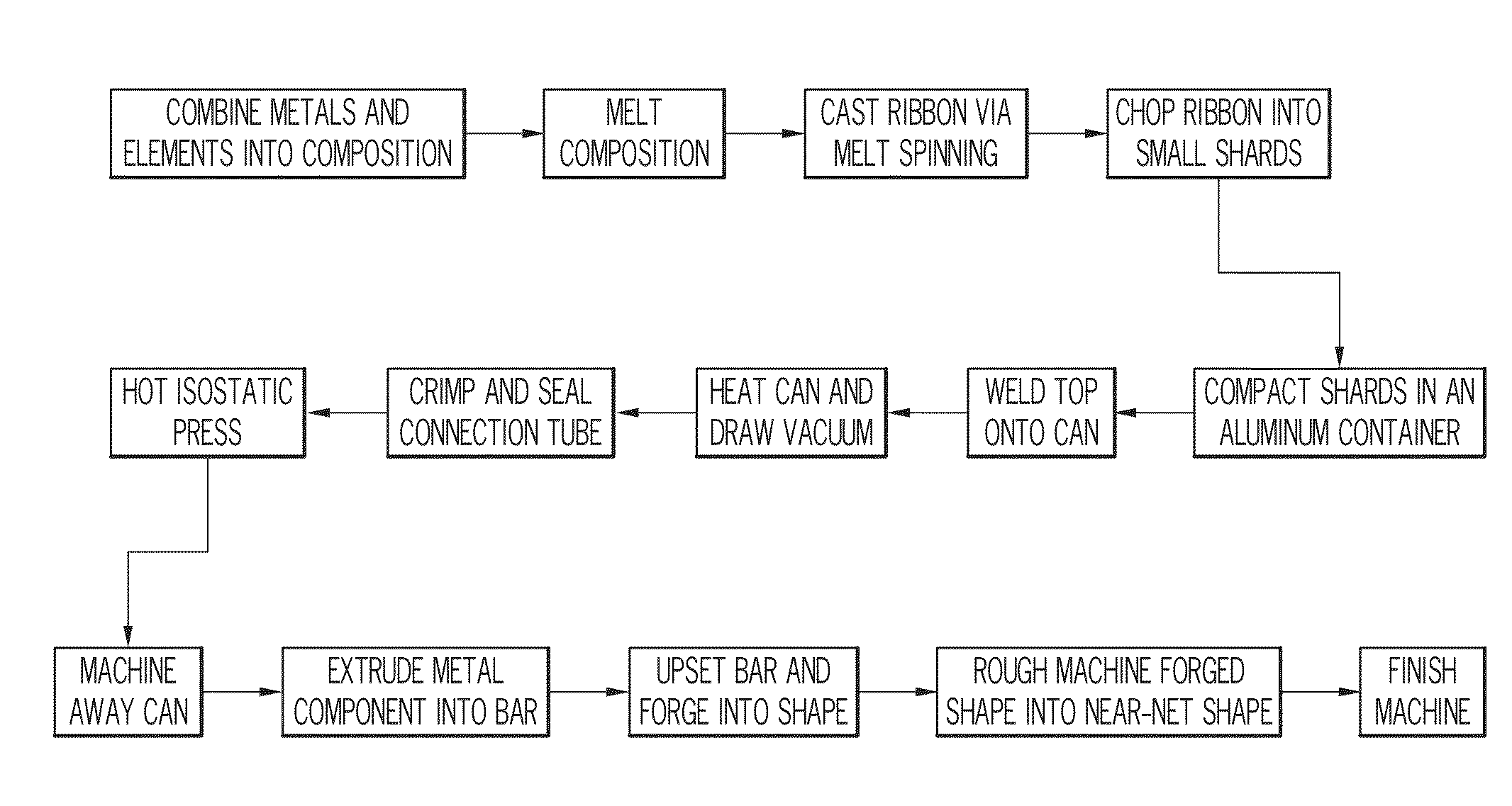
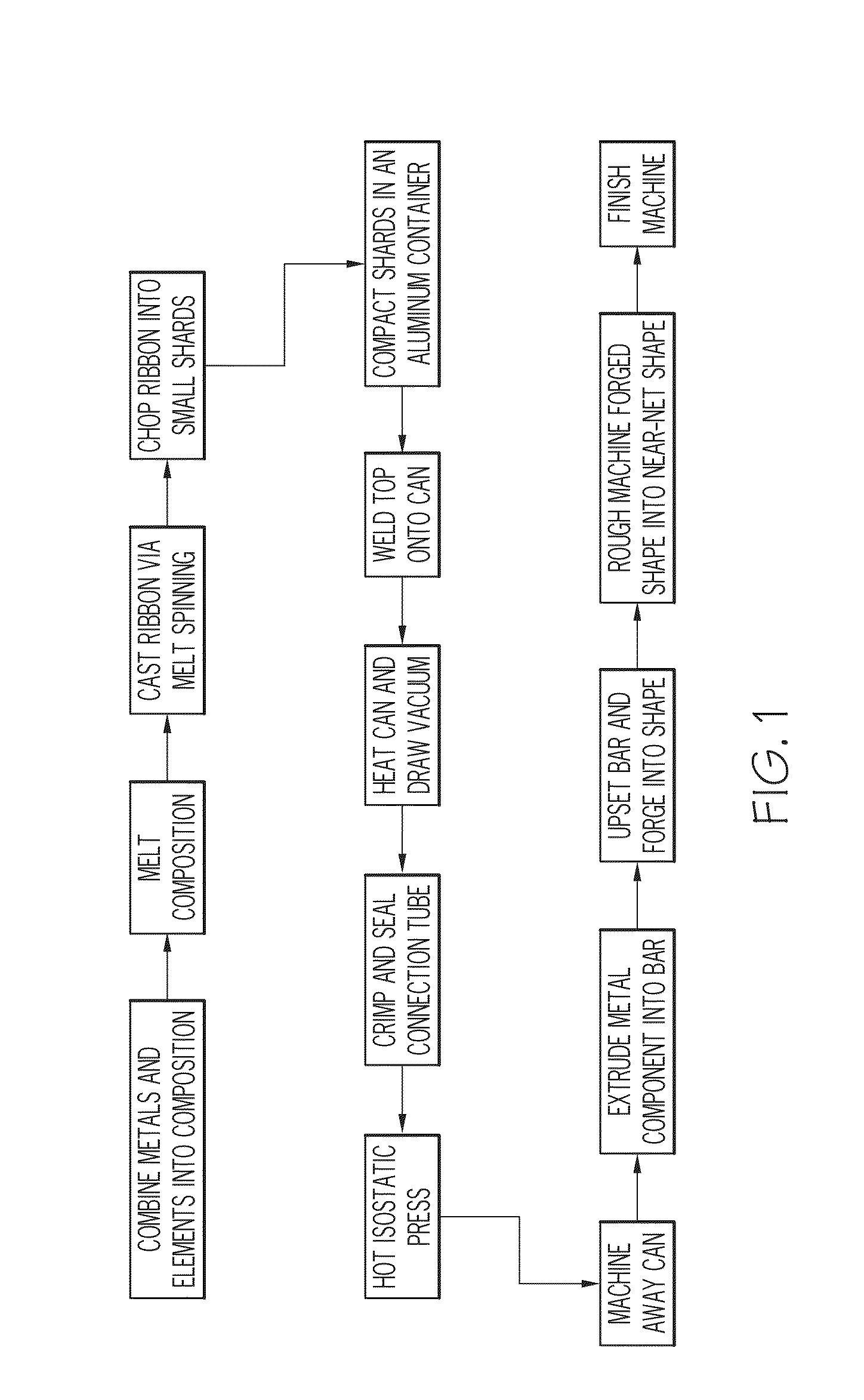
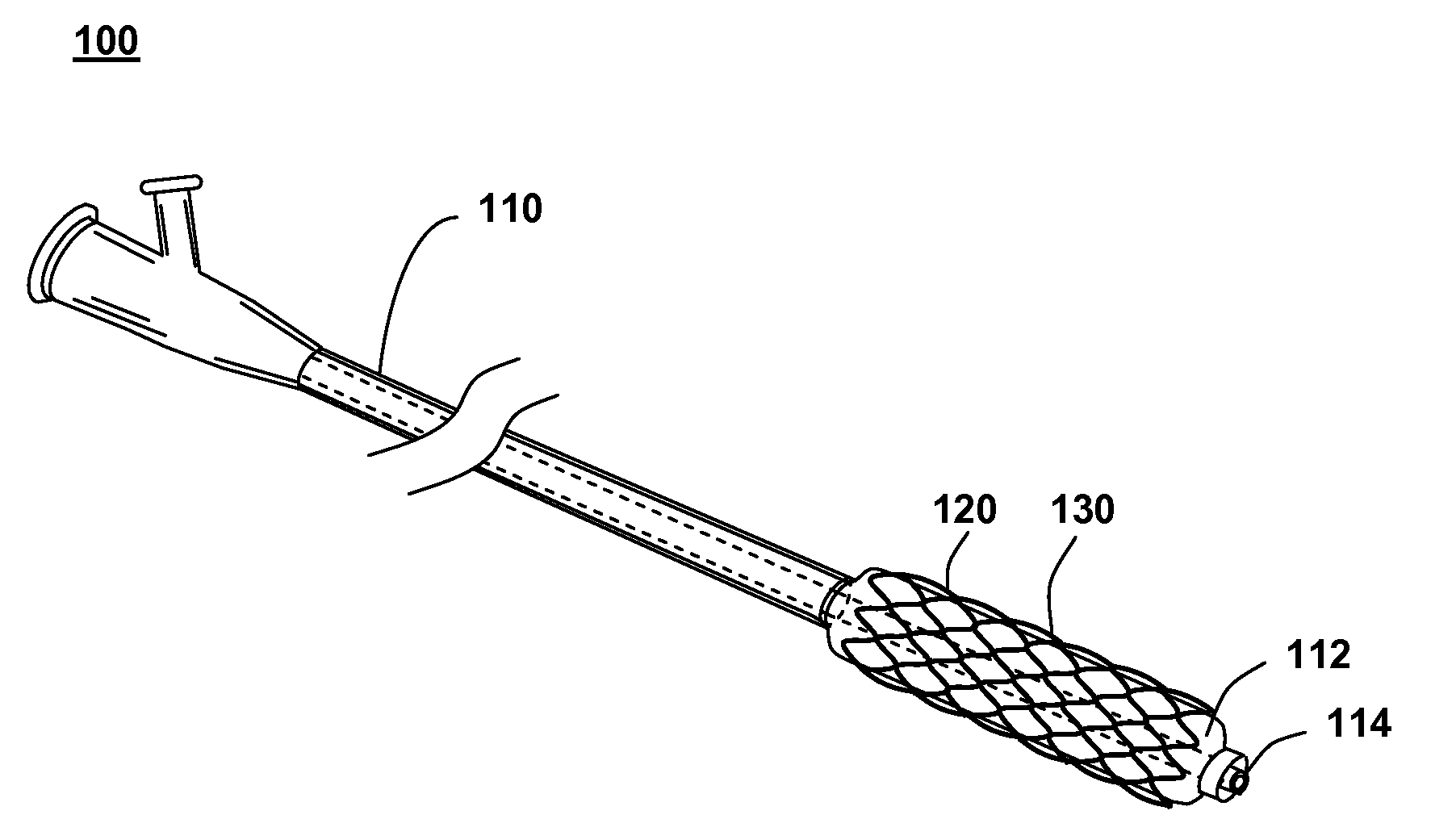
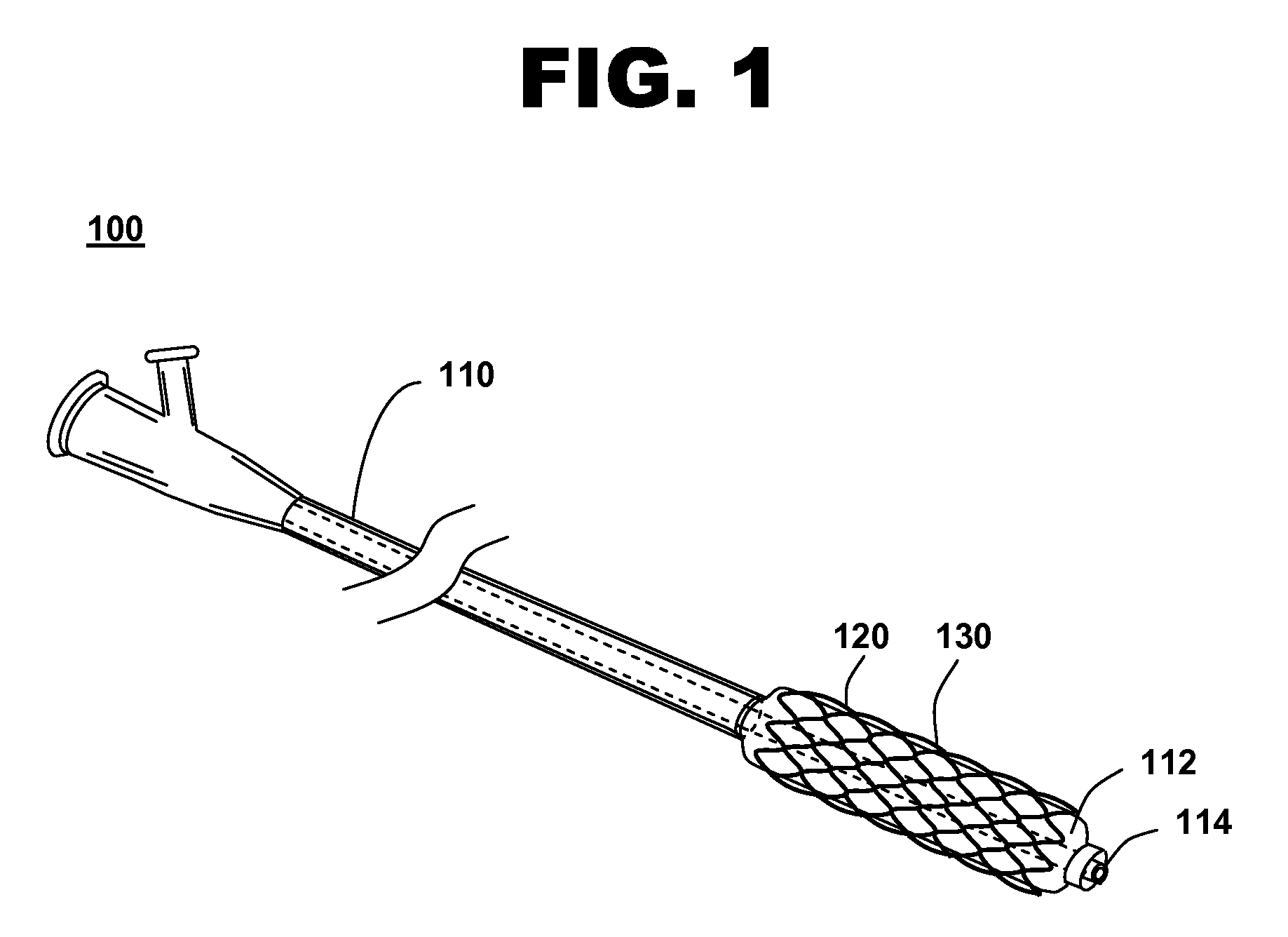
Controlled Porosity Stent
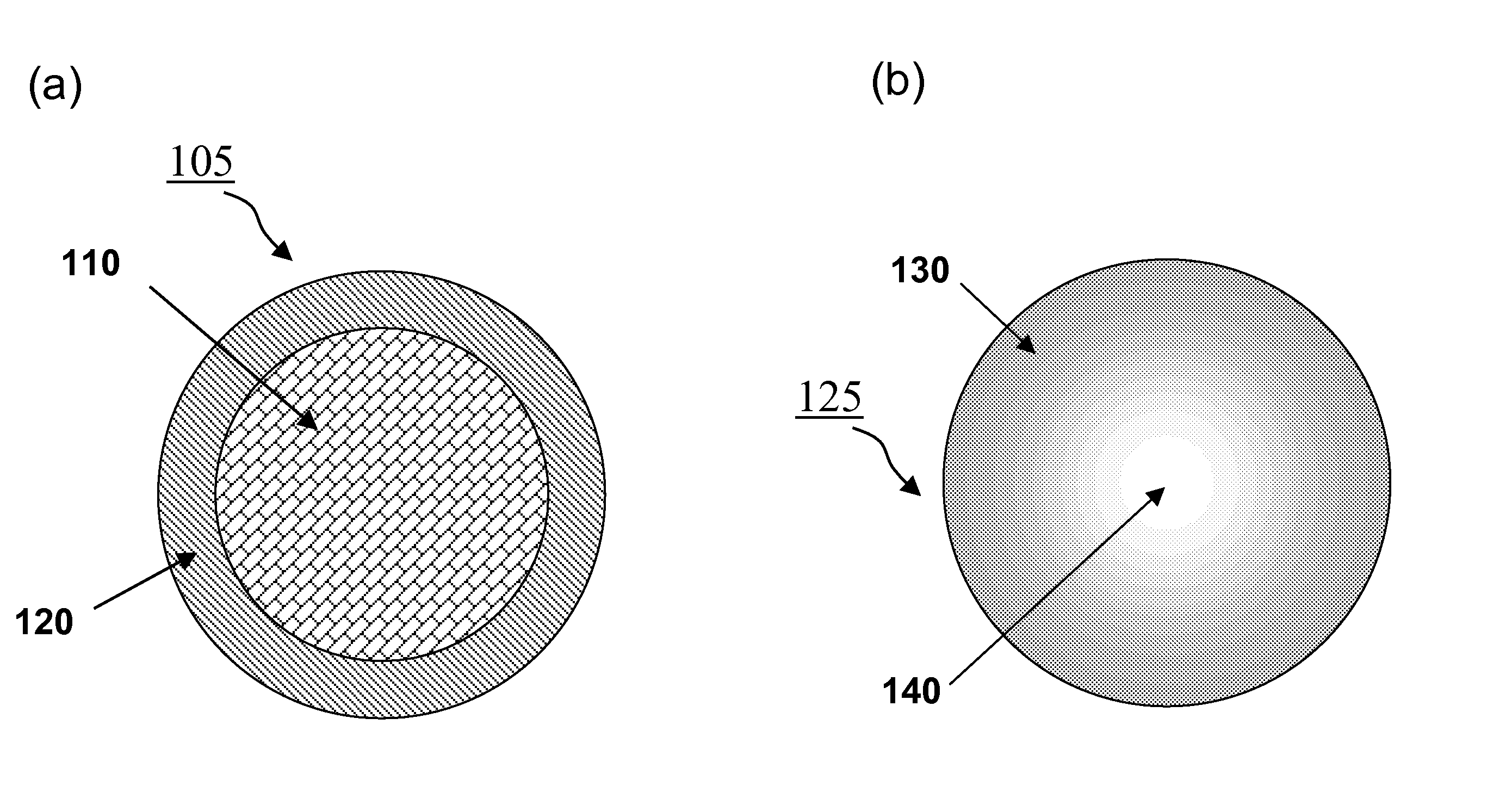
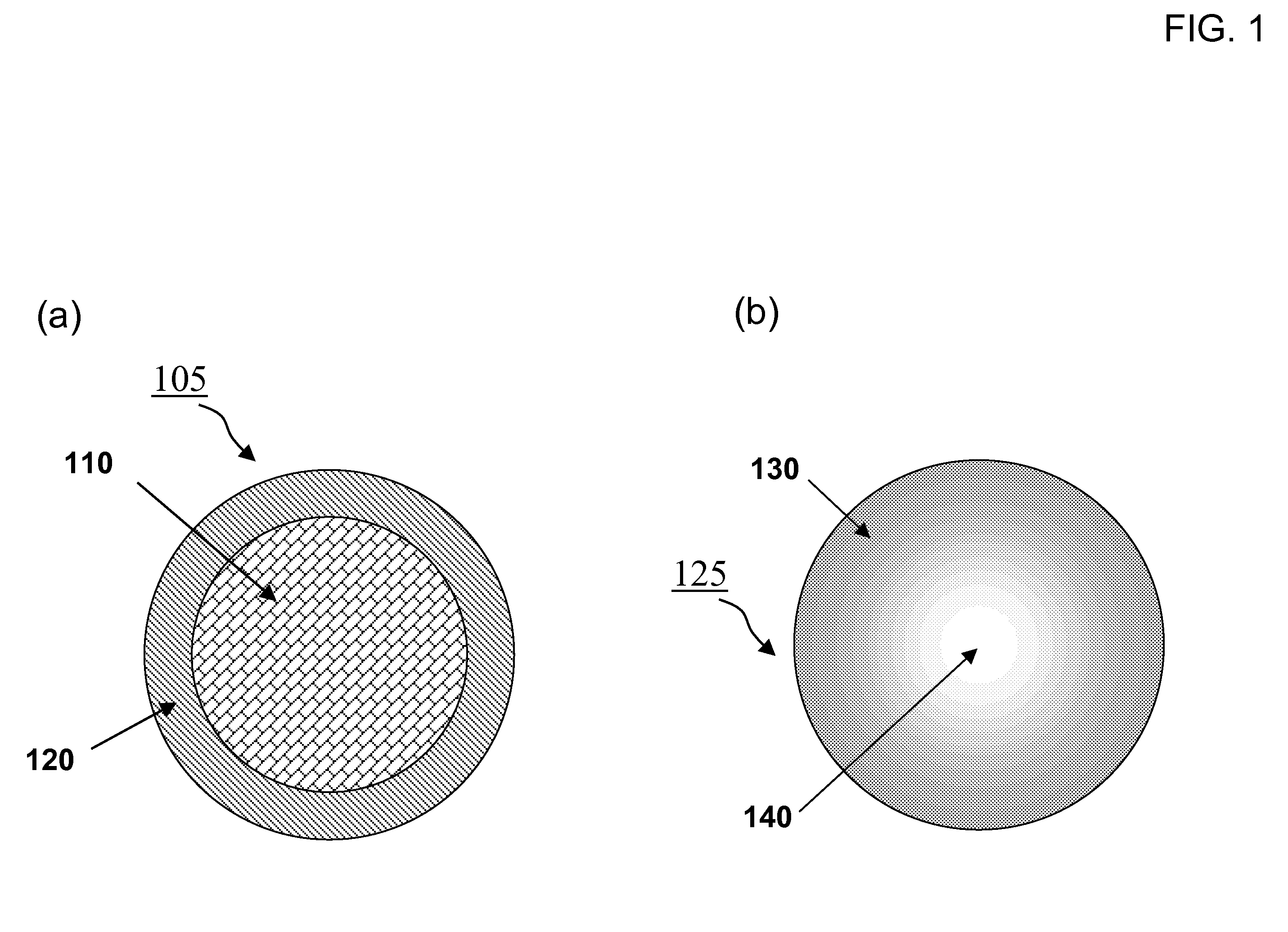
A method of manufacturing a stent includes forming a stent blank including a predetermined alloy composition, the alloy composition including at least base element and at least one sacrificial element and forming a stent framework from the stent blank. The method further includes removing at least a portion of the sacrificial element and forming at least one pore based on the removal. A method of manufacturing a vascular treatment system includes forming a stent blank including a predetermined alloy composition including at least one base element and at least one sacrificial element. The method further includes forming a stent framework and removing at least a portion of the sacrificial element. The method also includes forming at least one pore based on the removal, bending the stent framework to a delivery shape, and attaching the bent stent framework including the formed pores to a catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Electromigration-resistant and compliant wire interconnects, nano-sized solder compositions, systems made thereof, and methods of assembling soldered packages
InactiveUS20070001280A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal particleElectronic packaging
A nano-sized metal particle composite includes a first metal that has a particle size of about 50 nanometer or smaller. A wire interconnect is in contact with a reflowed nanosolder and has the same metal or alloy composition as the reflowed nanosolder. A microelectronic package is also disclosed that uses the reflowed nanosolder composition. A method of assembling a microelectronic package includes preparing a wire interconnect template. A computing system includes a nanosolder composition coupled to a wire interconnect.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com