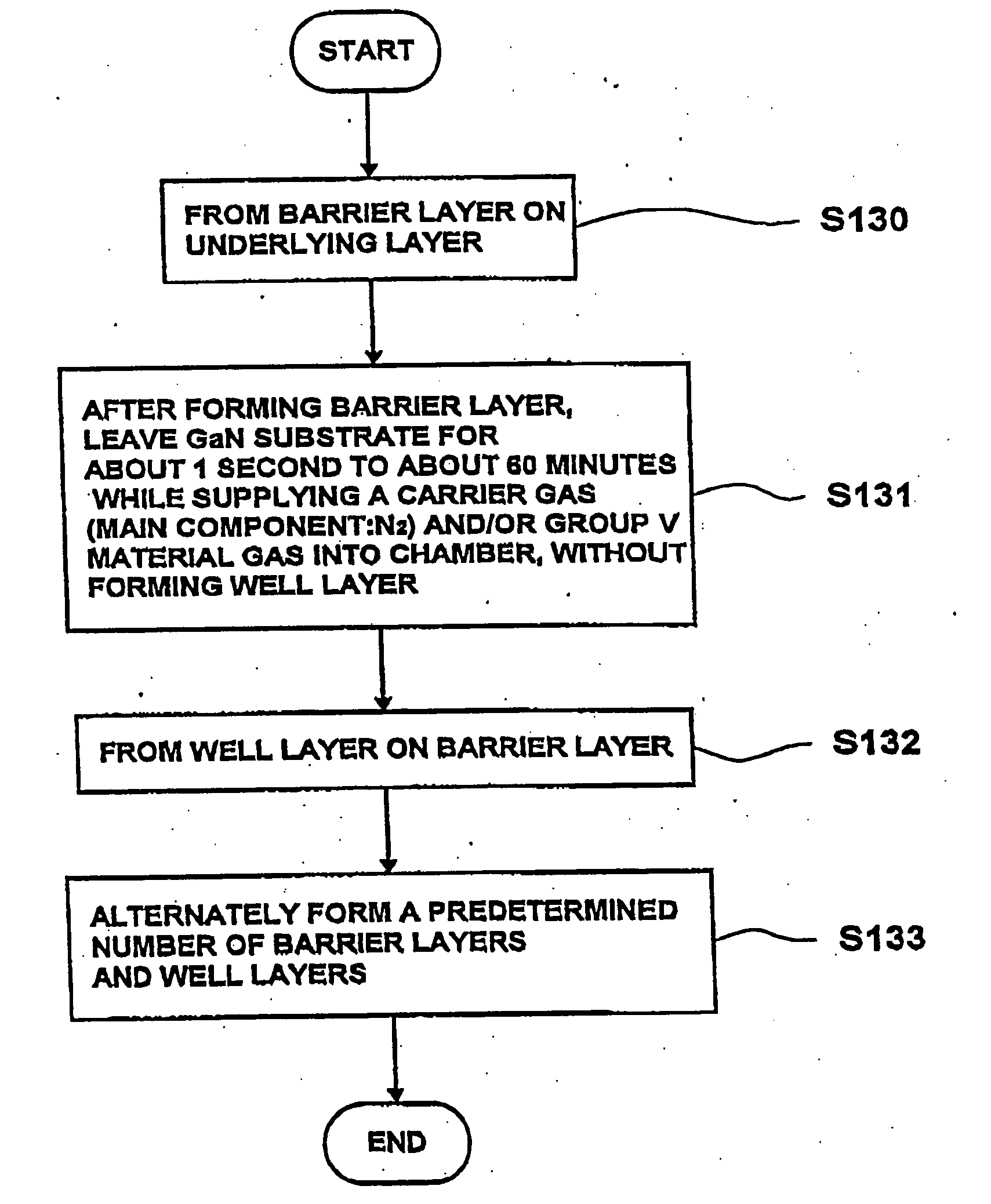
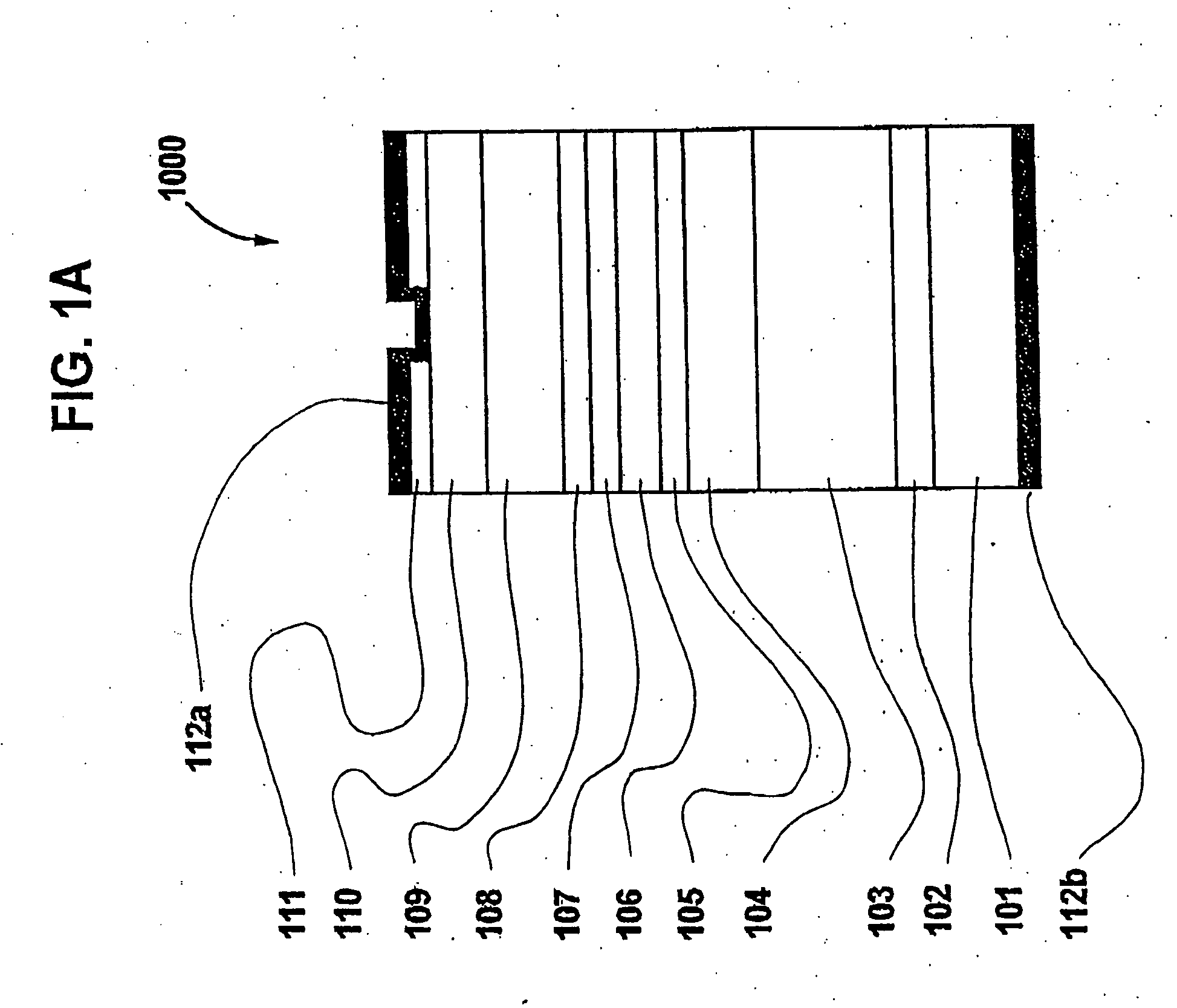
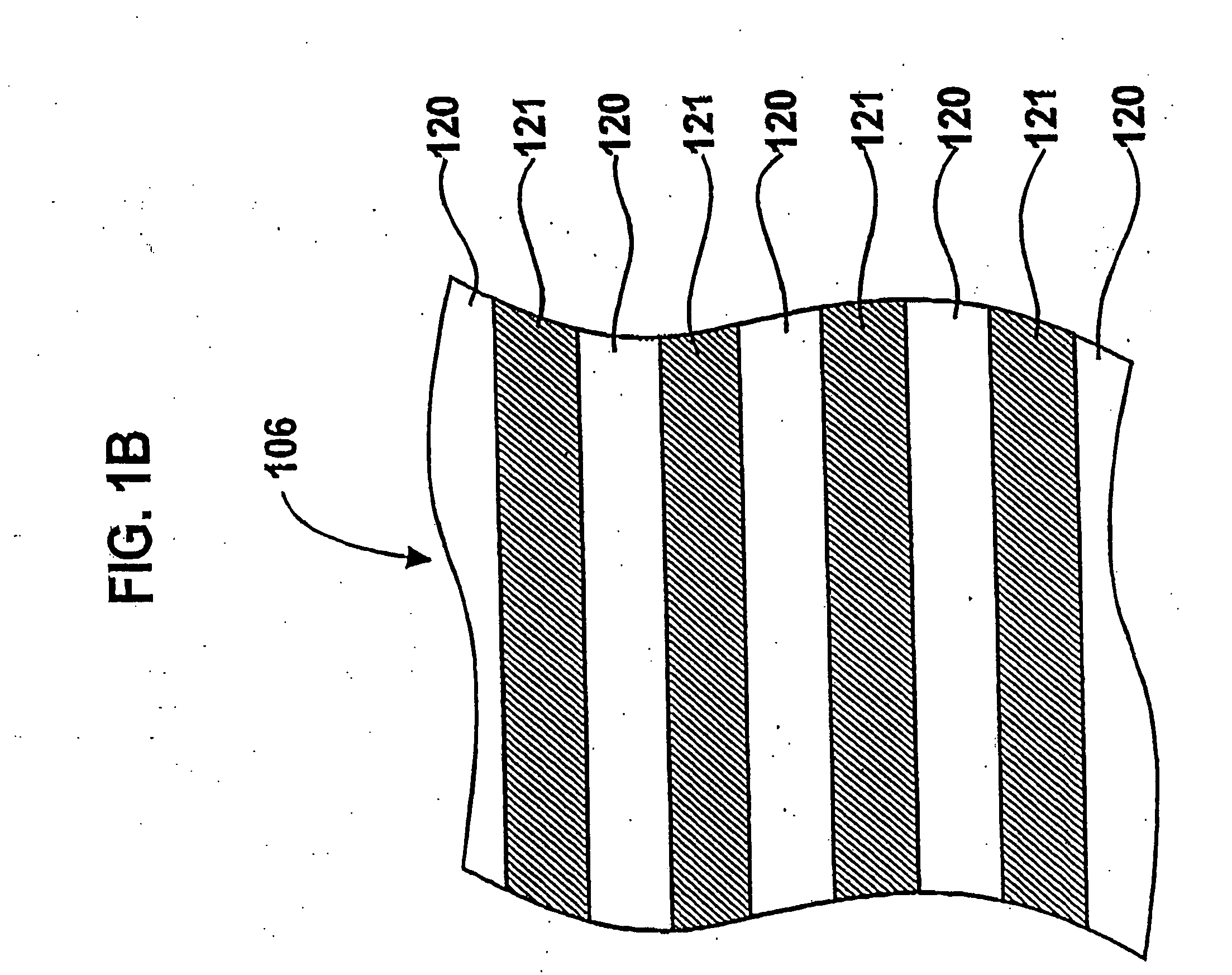
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Acceptor doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
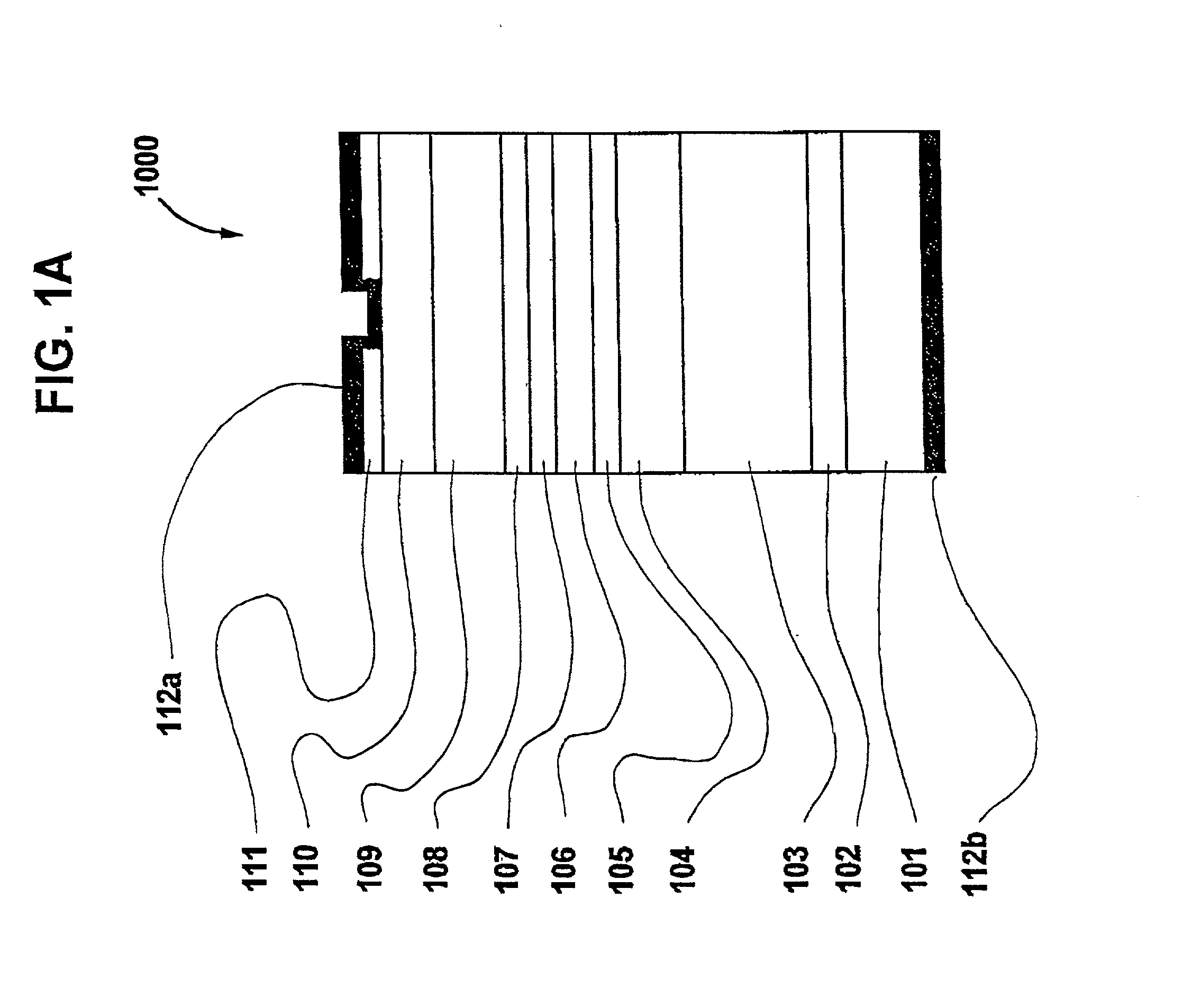
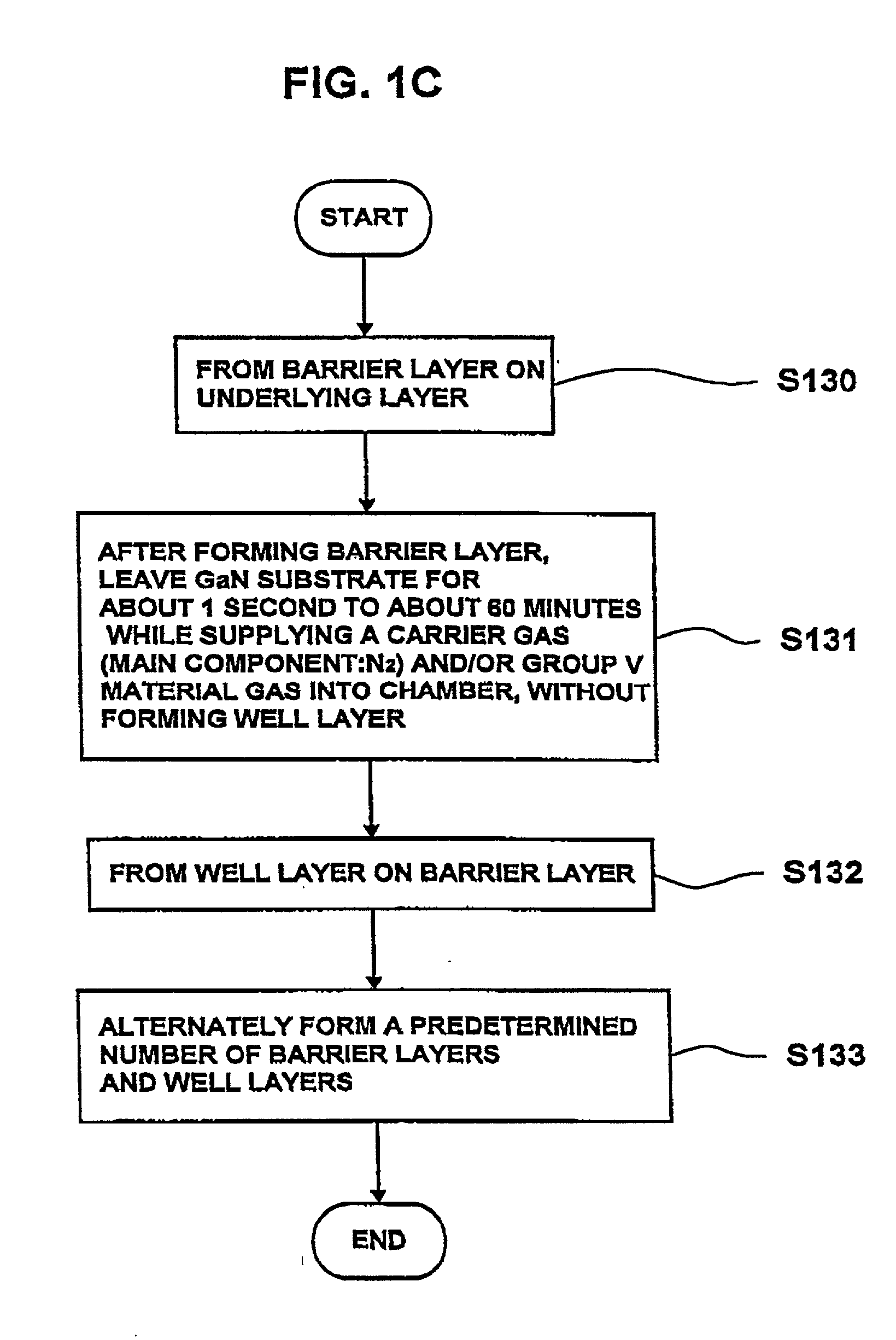
Nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and method for producing the same
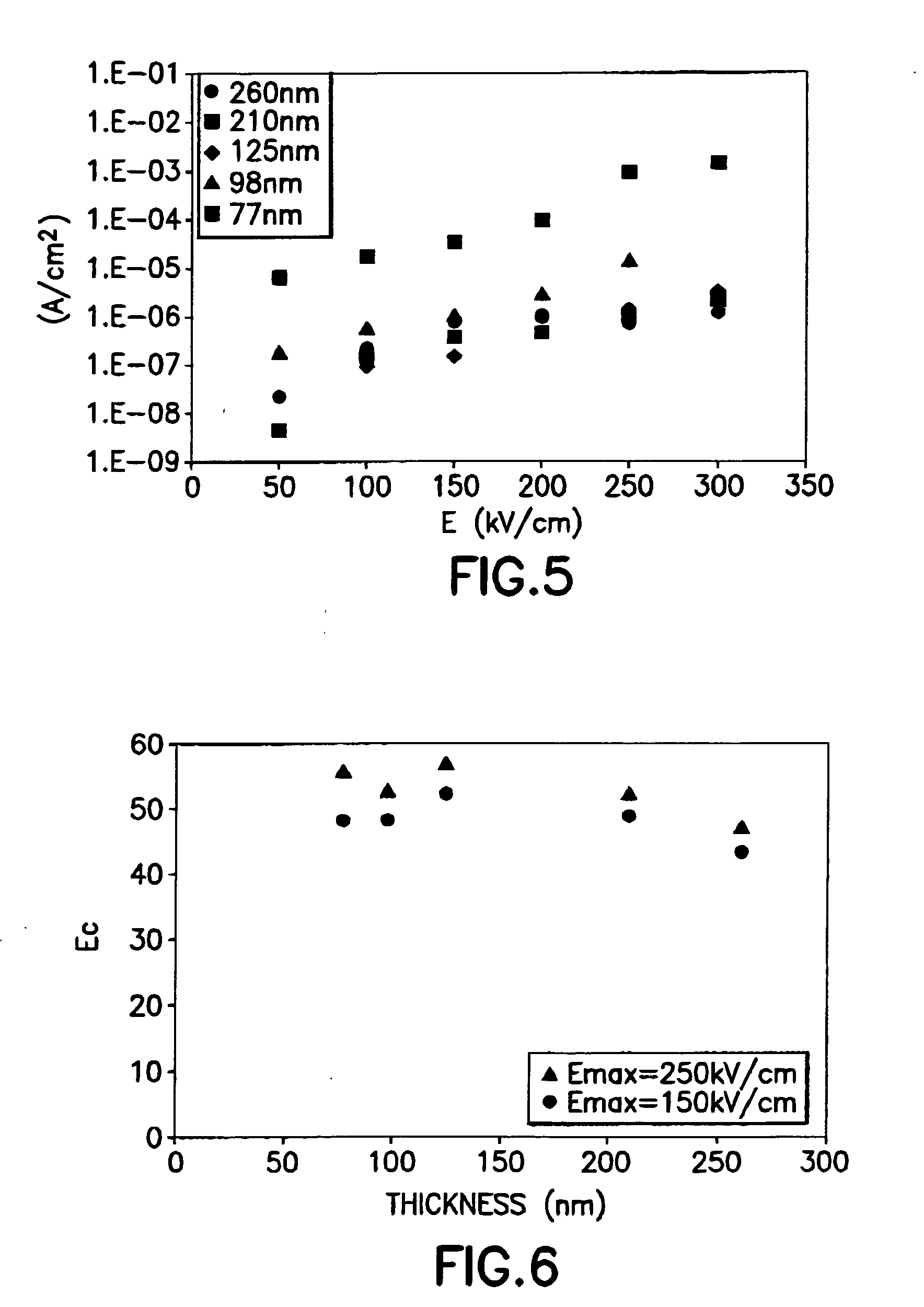
InactiveUS20010030329A1Low working voltageLaser detailsLaser active region structureCrystal orientationActive layer
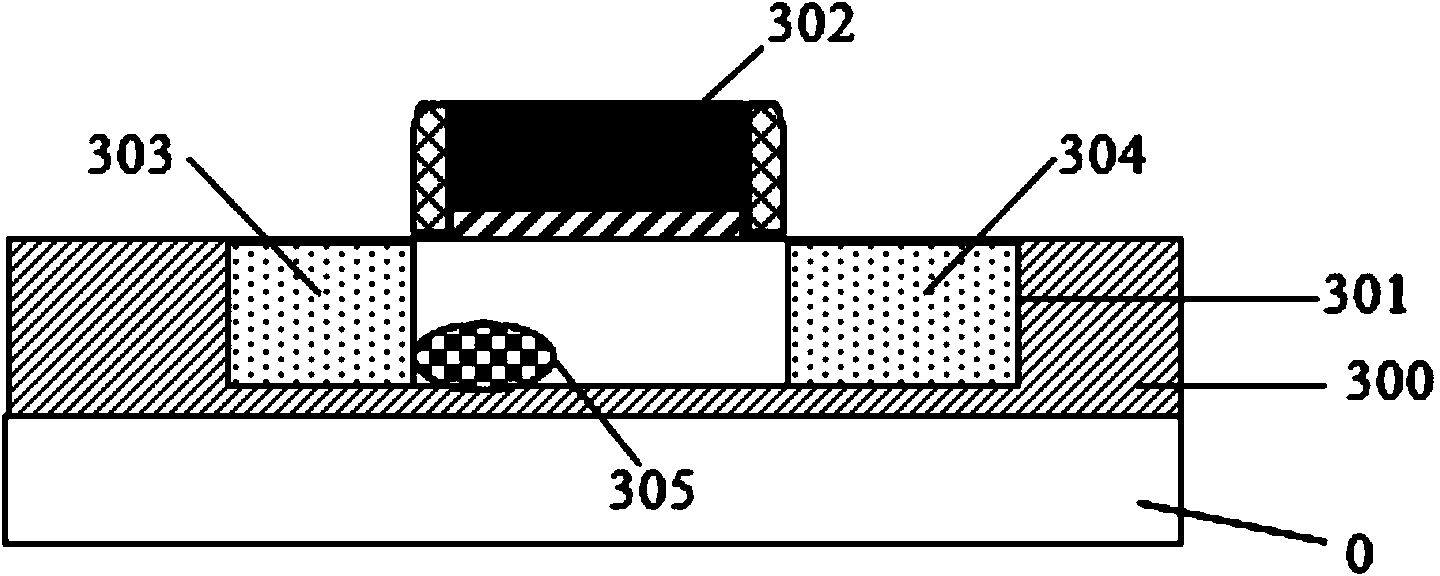
A nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device includes: a GaN substrate having a crystal orientation which is tilted away from a <0001> direction by an angle which is equal to or greater than about 0.05° and which is equal to or less than about 2°, and a semiconductor multilayer structure formed on the GaN substrate, wherein the semiconductor multilayer structure includes: an acceptor doping layer containing a nitride compound semiconductor; and an active layer including a light emitting region.
Owner:SHARP KK
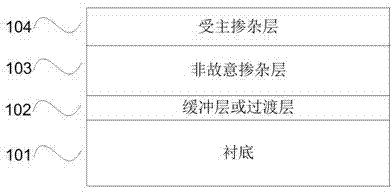
Preparation method of p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material
ActiveCN102903615AEasy to desorbImprove bindingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDimethylhydrazineSemiconductor materials
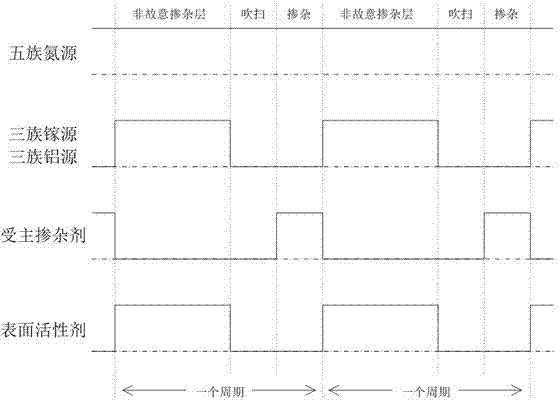
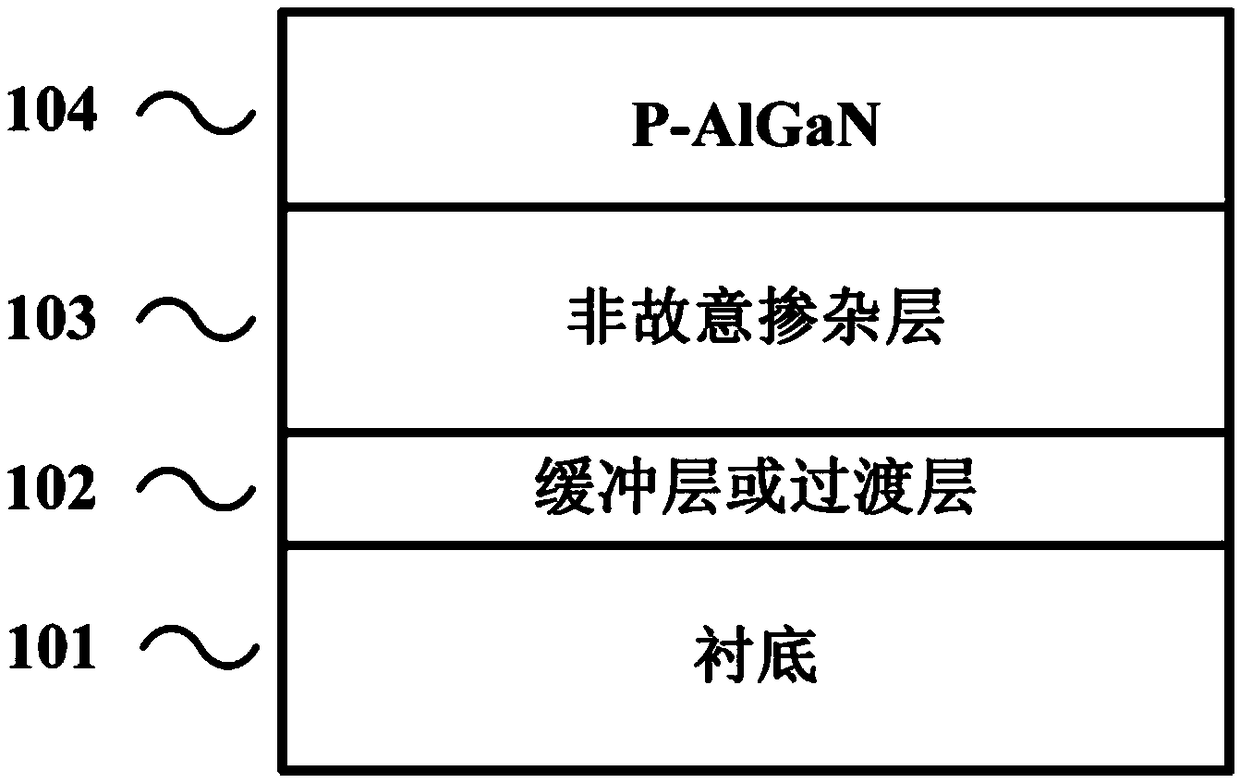
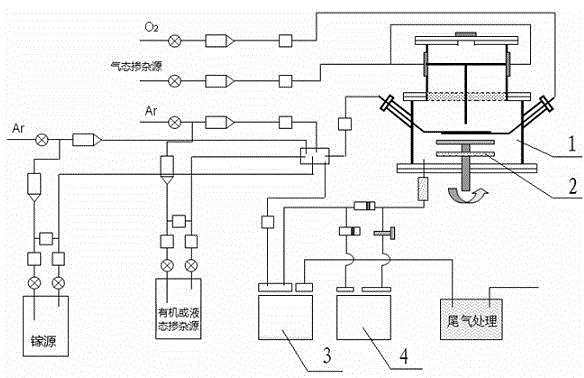
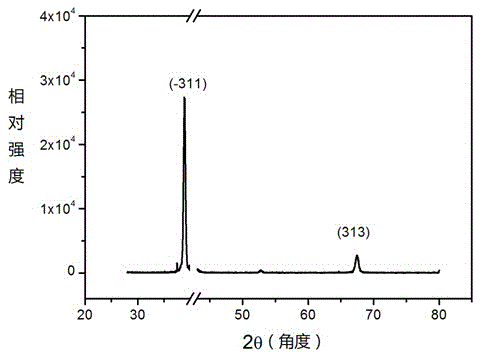
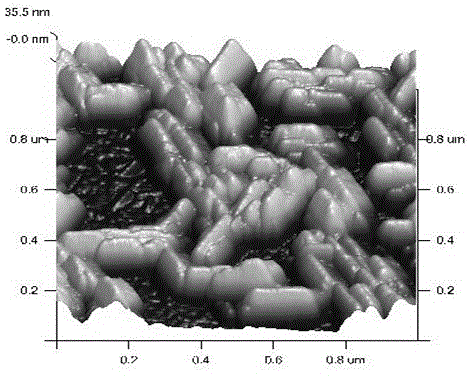
The invention discloses a preparation method of a p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material. A substrate, and a buffer layer or a transition layer, an unintended doped layer and an acceptor doped layer grown on the substrate from bottom to top are contained; in a growth process of the structure, ammonia or nitrogen dimethylhydrazine is used as a five-group nitrogen source; trimethyl gallium or TEGa used as a three-group gallium source, trimethylaluminium or triethyl aluminum used as a three-group aluminium source, and trimethylindium or TEIn used as a three-group indium source are collectively called three-group metal sources; and the trimethylindium or the TEIn is also used as a surface active agent and used in the acceptor doped layer. According to the method, the trimethylindium or the TEIn is used as the surface active agent to assist growth, and simultaneously, the acceptor doped layer is prepared by adopting a delta doping method. According to the method, the doping efficiency of acceptor doped magnesium atoms is increased, and simultaneously, the self-compensation effect is suppressed, so that the p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material with favorable crystalline quality and high hole concentration is obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS7064357B2Low operation voltage and currentLaser detailsLaser active region structureCrystal orientationActive layer
A nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device includes: a GaN substrate having a crystal orientation which is tilted away from a <0001> direction by an angle which is equal to or greater than about 0.05° and which is equal to or less than about 2°, and a semiconductor multilayer structure formed on the GaN substrate, wherein the semiconductor multilayer structure includes: an acceptor doping layer containing a nitride compound semiconductor; and an active layer including a light emitting region.
Owner:SHARP KK
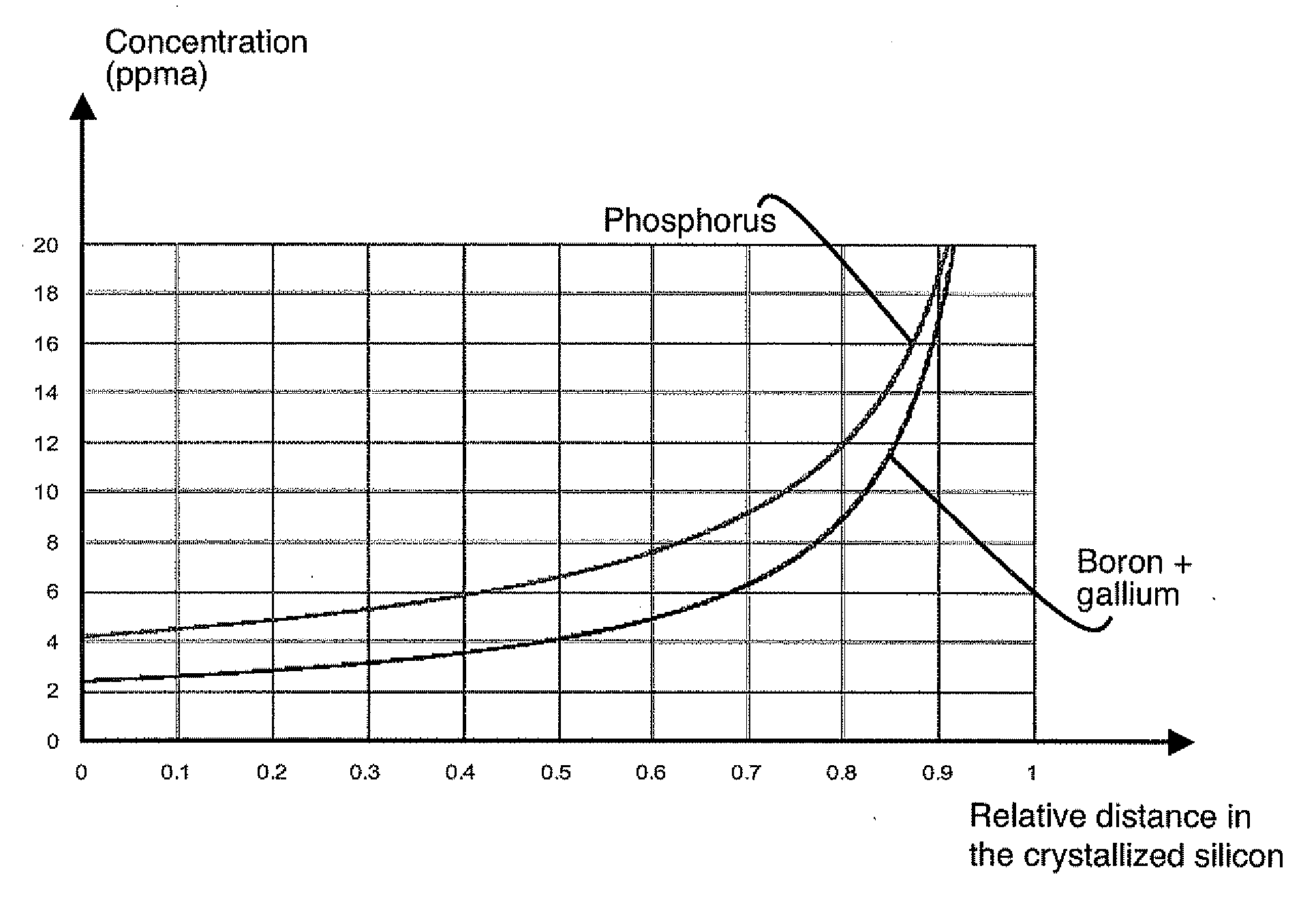
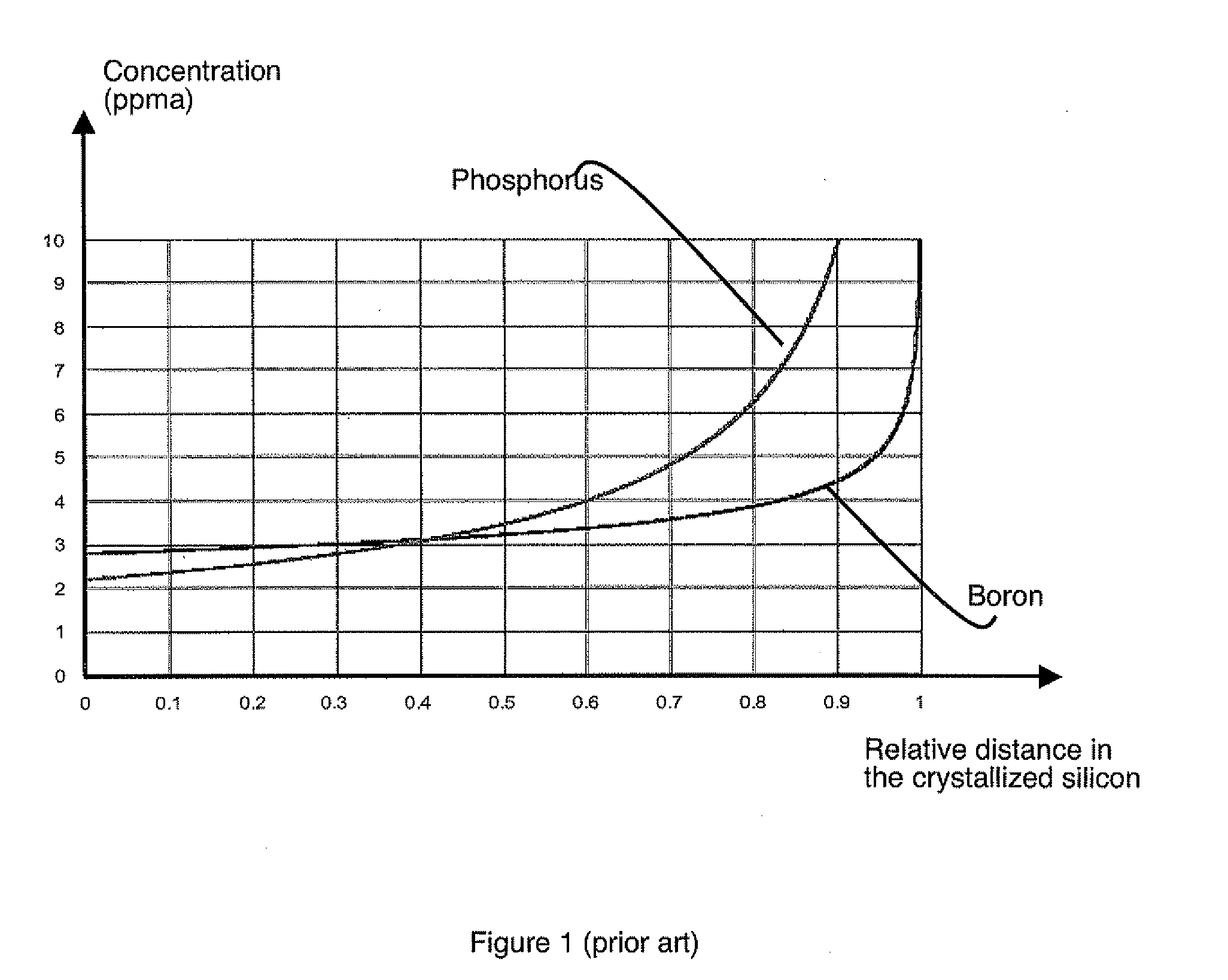
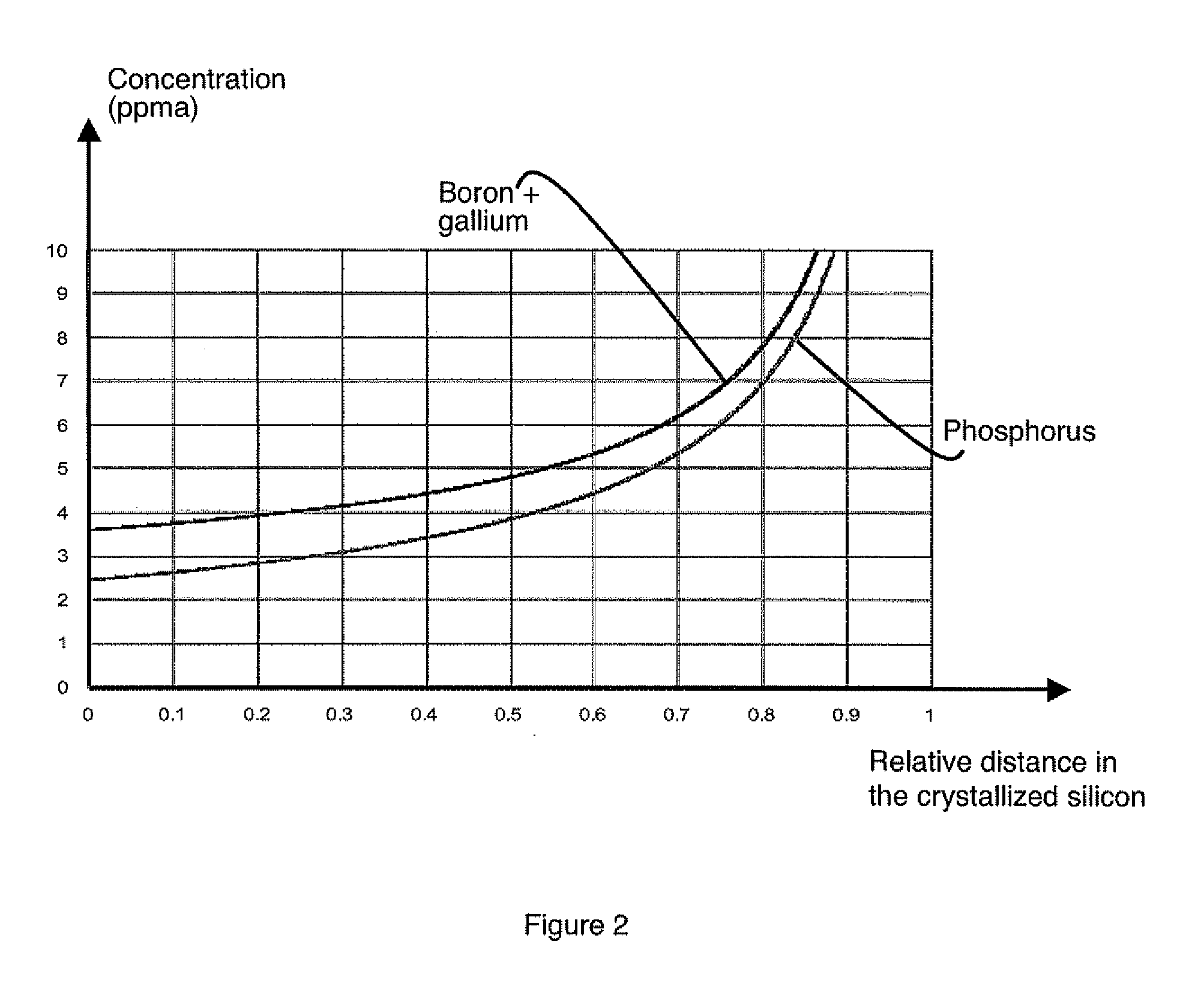
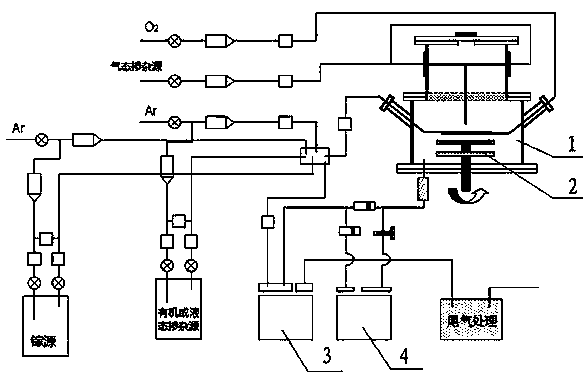
Method for producing photovoltaic-grade crystalline silicon by addition of doping impurities and photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20110030793A1Easy to implementImprove conversion efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureDopantCrystalline silicon
Production of photovoltaic grade crystalline silicon is achieved by crystallization of a molten silicon feedstock, the sum of the initial donor doping element and acceptor doping element concentrations whereof is greater than 0.1 ppma, and both the acceptor and donor doping element concentrations whereof are less than 25 ppma. At least a predefined quantity of a doping material having a segregation coefficient of less than 0.1 is added to the feedstock. This addition enables a crystallized silicon to be produced the difference between the donor and acceptor doping profiles whereof is comprised between 0.1 and 5 ppma over at least 50% of the solidified silicon. A silicon presenting a concentration of at least one of the dopants is greater than or equal to 5 ppma and a difference less than or equal to 5 ppma between these two types of dopant is integrated in a photovoltaic cell.
Owner:APOLLON SOLAR SAS
Preparation method of gallium oxide film with hole conduction characteristic as well as gallium oxide film with hole conduction characteristic
ActiveCN103469173AAcceptor doping is efficient and stableChemical vapor deposition coatingPhysical chemistryOxygen
The invention provides a preparation method of a gallium oxide film with a hole conduction characteristic as well as the gallium oxide film with the hole conduction characteristic. The preparation method of the gallium oxide film with the hole conduction characteristic comprises the following steps: placing a substrate in a growing tray in a sealed reaction chamber, heating the tray to a temperature which is 10-200 DEG C higher than the expected growing temperature of the gallium oxide film, and thermally treating the substrate; after reducing the temperature of the tray to the predetermined growing temperature, continuously exhausting air to the reaction chamber in a predetermined pressure range; introducing a gallium source, an oxygen source and a doping source to the reaction chamber so as to realize the epitaxial growth of the gallium oxide film; when the growing process of the gallium oxide film is finished, carrying out in-situ thermal treatment to the gallium oxide film or directly cooling and sampling the gallium oxide film slowly or carrying out thermal treatment after sampling to obtain the gallium oxide film with the hole conduction characteristic. The method provided by the invention is scientific and reasonable in step, overcomes many problems in the prior art, provides an effective acceptor doping path, and can be used for preparing gallium oxide films with different hole concentrations.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Doping-assisted defect control in compound semiconductors
InactiveUS20050020033A1High resistivityGood reproducibilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrappingHigh resistivity
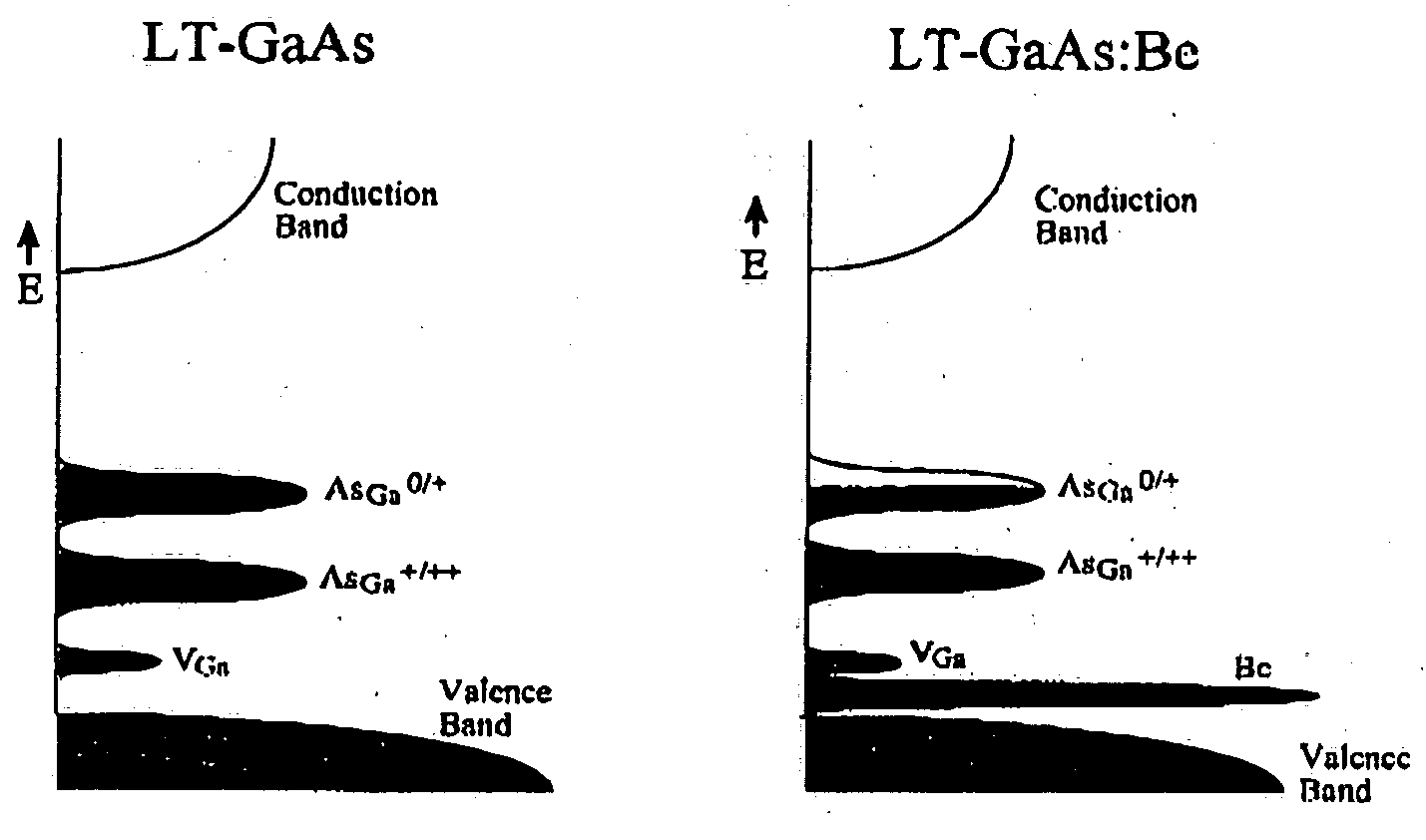
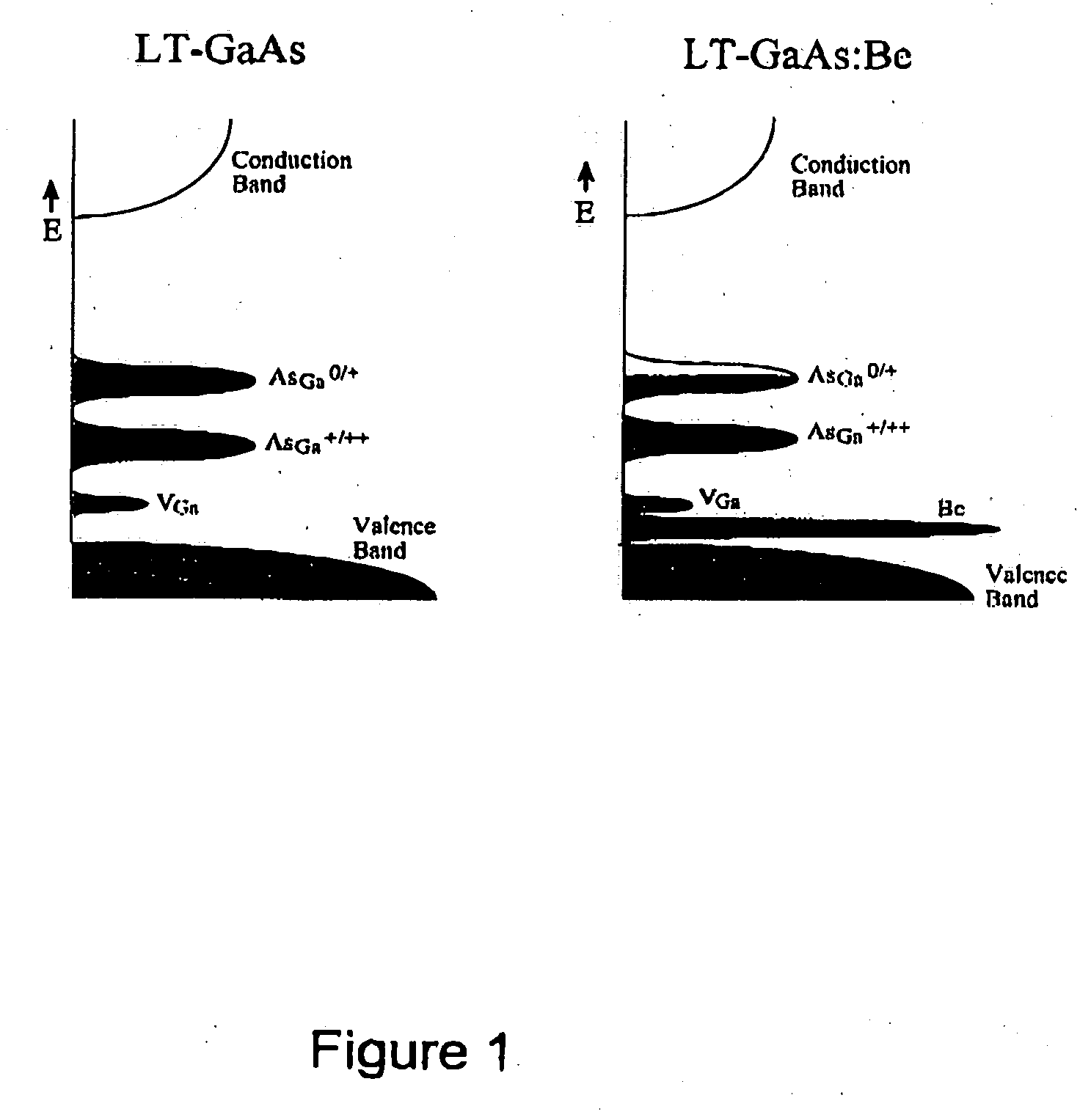
The present invention relates to the production of thin film epilayers of III-V and other compounds with acceptor doping wherein the acceptor thermally stabilizes the epilayer, stabilize the naturally incorporated native defect population and therewith maintain the epilayer's beneficial properties upon annealing among other advantageous effects. In particular, balanced doping in which the acceptor concentration is similar to (but does not exceed) the antisite defects in the as-grown material is shown to be particularly advantageous in providing thermal stability, high resistivity and ultrashort trapping times. In particular, MBE growth of LT-GaAs epilayers with balanced Be doping is described in detail. The growth conditions greatly enhance the materials reproducibility (that is, the yield in processed devices). Such growth techniques can be transferred to other III-V materials if the growth conditions are accurately reproduced. Materials produced herein also demonstrate advantages in reproducibility, reliability and radiation hardening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Scalable lead zirconium titanate (PZT) thin film material and deposition method, and ferroelectric memory device structures comprising such thin film material
InactiveUS6984417B2Thin/thick film capacitorGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesLead zirconate titanateOptoelectronics
A novel lead zirconium titanate (PZT) material having unique properties and application for PZT thin film capacitors and ferroelectric capacitor structures, e.g., FeRAMs, employing such thin film material. The PZT material is scalable, being dimensionally scalable, pulse length scalable and / or E-field scalable in character, and is useful for ferroelectric capacitors over a wide range of thicknesses, e.g., from about 20 nanometers to about 150 nanometers, and a range of lateral dimensions extending to as low as 0.15 μm. Corresponding capacitor areas (i.e., lateral scaling) in a preferred embodiment are in the range of from about 104 to about 10−2 μm2. The scalable PZT material of the invention may be formed by liquid delivery MOCVD, without PZT film modification techniques such as acceptor doping or use of film modifiers (e.g., Nb, Ta, La, Sr, Ca and the like).
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060189012A1Low operation voltage and currentLaser detailsLaser active region structureCrystal orientationAcceptor doping
A nitride compound semiconductor light emitting device includes: a GaN substrate having a crystal orientation which is tilted away from a <0001> direction by an angle which is equal to or greater than about 0.05° and which is equal to or less than about 2°, and a semiconductor multilayer structure formed on the GaN substrate, wherein the semiconductor multilayer structure includes an acceptor doping layer containing a nitride compound semiconductor; and an active layer including a light emitting region.
Owner:SHARP KK
CdTe solar cell by using V-Se film as back contact layer
The invention aims to eliminate the defects of copper or back contact layer materials containing copper in a CdTe cell and avoid the negative influence of copper diffusion on the performance of the CdTe solar cell. A copper-free V-S material is added between an absorbing layer and a metal back electrode in the basic structure of the CdTe solar cell and is taken as a back contact layer of the CdTe solar cell, thus an ohmic contact of the CdTe solar cell can be realized, the depletion region of the solar cell can be widened, the interface recombination can be reduced, the bypass resistance can be increased, the filling factor can be increased and the conversion efficiency can be improved. Since an acceptor doping agent, such as copper, is not used in the invention, the cell does not have attenuation after being used or stored for a long term, and the device has good stability.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
P-ZnO thin film and preparation thereof
InactiveCN1440053AGood controllability of doping concentrationImprove stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringDifferential pressure
The P-ZnO film of this invention is the codoped p-ZnO film by using N as the acceptor doping source and Al as the donor doping source with doping concentration of 1.8X10 to the power 15 cm-3 - 4.5X10 to the power 18 cm-3. The preparation method for it is to use magnetic control sputtering method by using ZnxAl1-x as target material (1>x>0.6) and the doping concentration can be controlled by regulating the different differential pressure ratio of N gas and high purified O2 or Ar to be inputted as well as by regulating the Al content in the target material so that the good stability and controllability can be obtained for the doping concentration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Radio frequency semiconductor device
ActiveUS8134224B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRadio frequency signalSilicon oxide
A semiconductor device receiving as input a radio frequency signal having a frequency of 500 MHz or more and a power of 20 dBm or more is provided. The semiconductor device includes: a silicon substrate; a silicon oxide film formed on the silicon substrate; a radio frequency interconnect provided on the silicon oxide film and passing the radio frequency signal; a fixed potential interconnect provided on the silicon oxide film and placed at a fixed potential; and an acceptor-doped layer. The acceptor-doped layer is formed in a region of the silicon substrate. The region is in contact with the silicon oxide film. The acceptor-doped layer is doped with acceptors.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
III nitride-based double-heterojunction phototransistor
InactiveCN105742399AAvoid compensatory effectsImprove light incident efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesElectron injectionPhotocurrent
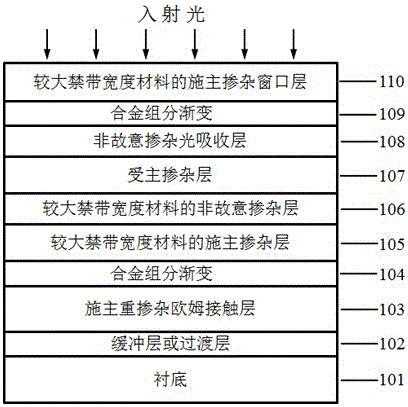
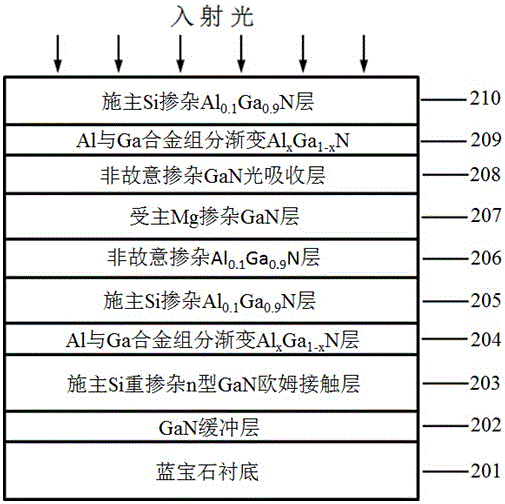
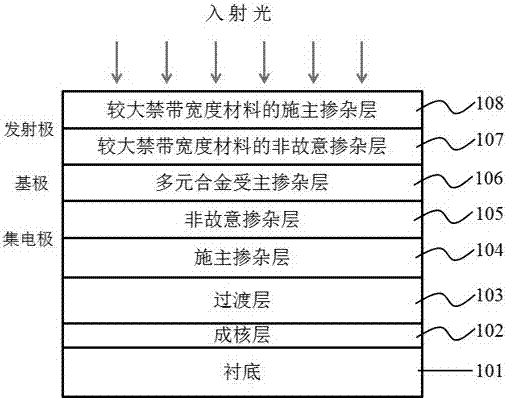
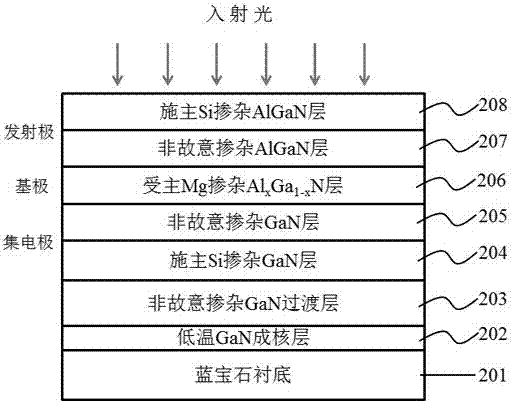
The invention provides an III nitride-based double-heterojunction phototransistor, belongs to the technical field of semiconductor devices and provides an III nitride-based double-heterojunction phototransistor and a preparation method thereof. The III nitride-based double-heterojunction phototransistor comprises a substrate and an epitaxial layer, wherein the epitaxial layer grows on the substrate; and the epitaxial layer sequentially comprises a buffer layer or a transition layer, a donor heavily-doped ohmic contact layer, an alloy composition gradient layer, a donor doped layer of a relatively broad band gap material, an unintentionally doped layer of the relatively broad band gap material, an acceptor doped layer, an unintentionally doped light absorption layer, the alloy composition gradient layer and a donor heavily-doped window layer of the relatively broad band gap material from bottom to top. By an overhead collector region structure, with the III nitride multi-element alloy material with a relatively broad band gap light absorption layer as the window layer of an incident light, the quantum efficiency is improved; and the number of photo-generated holes is increased, so that the photocurrent gain of the device is improved. A reverse heterojunction is adopted as an emitter junction in a lower emitter region; and the unintentionally doped layer of the relatively broad band gap material is introduced as an acceptor-doped diffusion barrier layer and a base region-emitter region heterointerface energy band sag compensation layer, so that the electron injection efficiency of the transistor is improved. The III nitride-based double-heterojunction phototransistor has the characteristics of high photocurrent gain, stable device performance and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Non-halogen flame retardant resin composition and electric wire and cable using the same
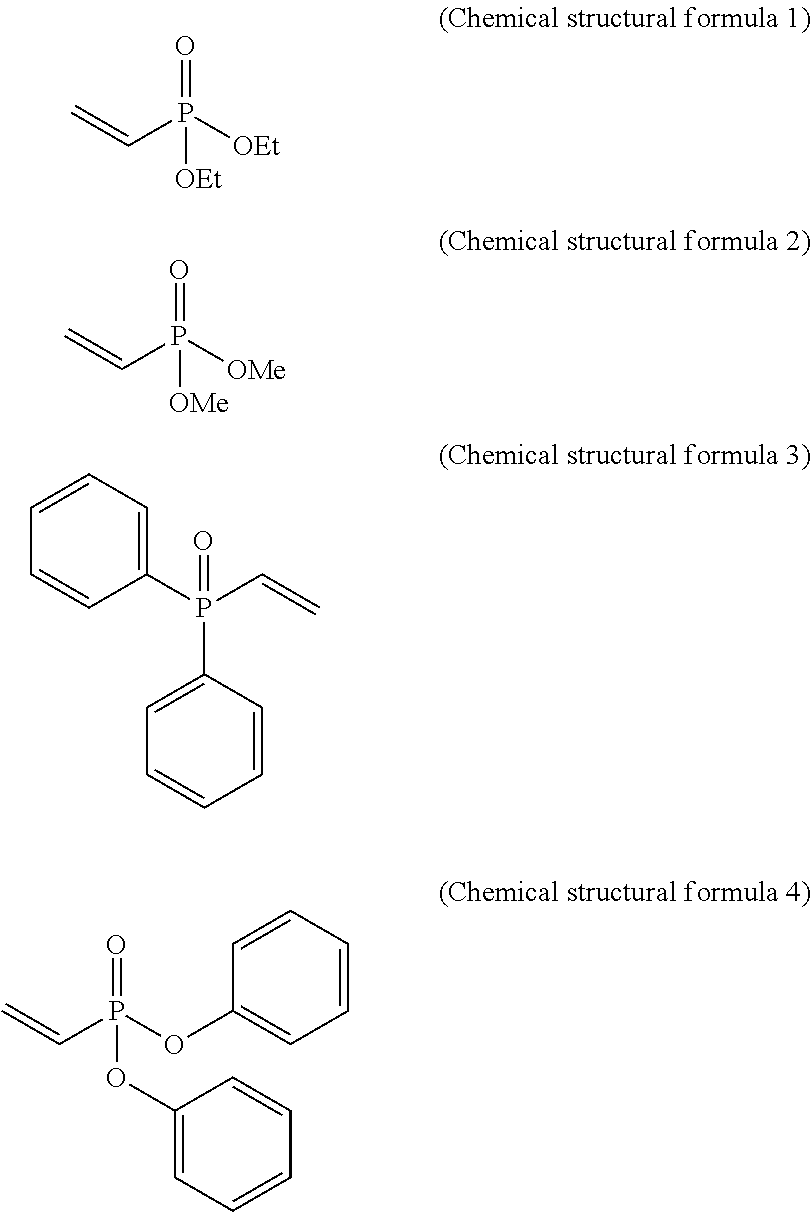
InactiveUS20110198105A1Improve flame retardant propertiesImprove colorabilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsConductive materialPolyolefinHalogen
An electric wire and cable made of a non-halogen flame retardant resin composition has a modified polyolefin resin composition comprising a polyolefin resin grafted with a phosphate compound having a vinyl group, and an acid acceptor doped to the modified polyolefin resin.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
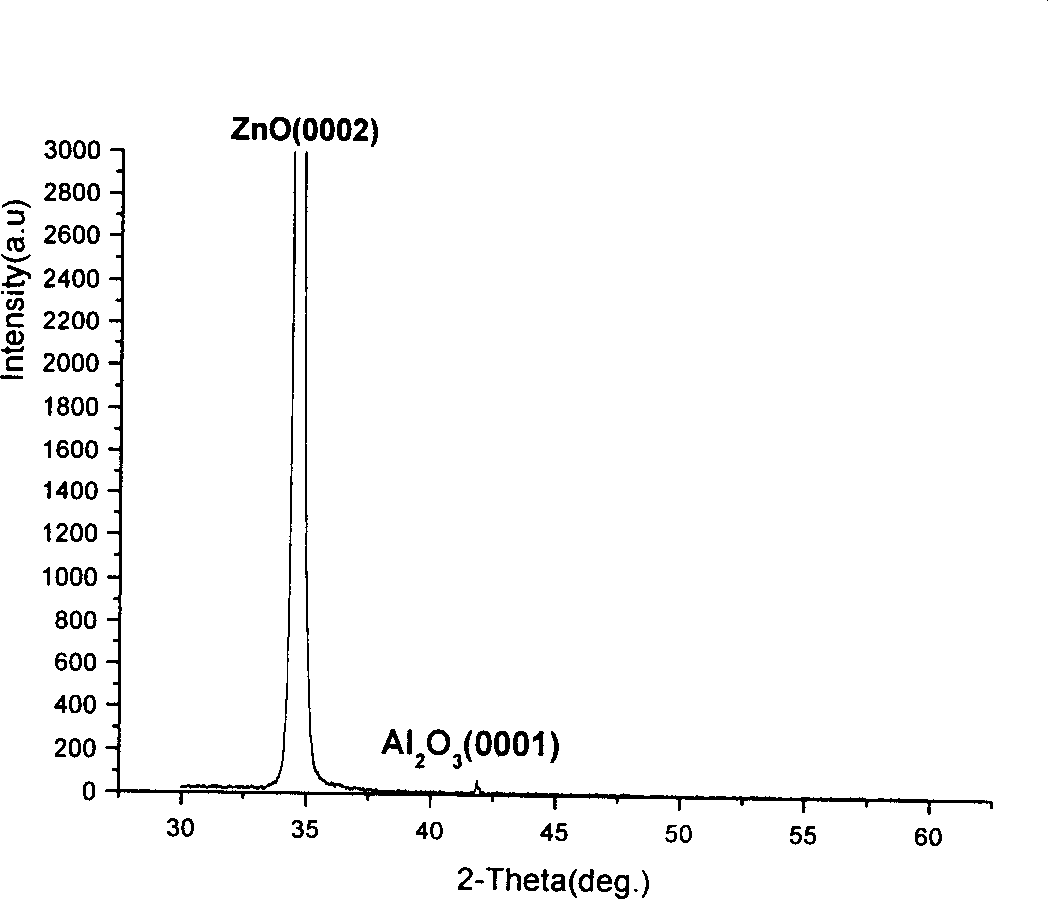
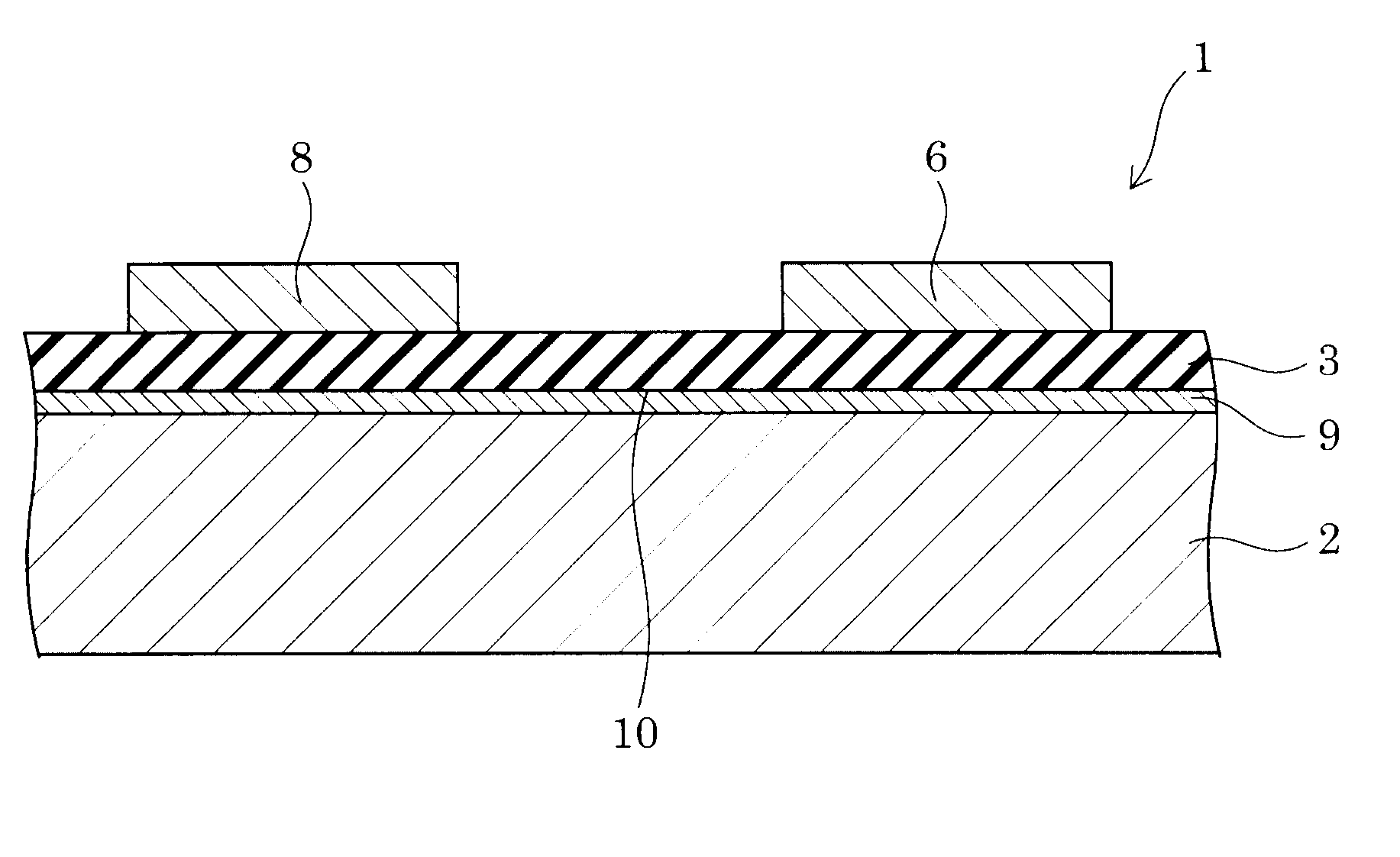
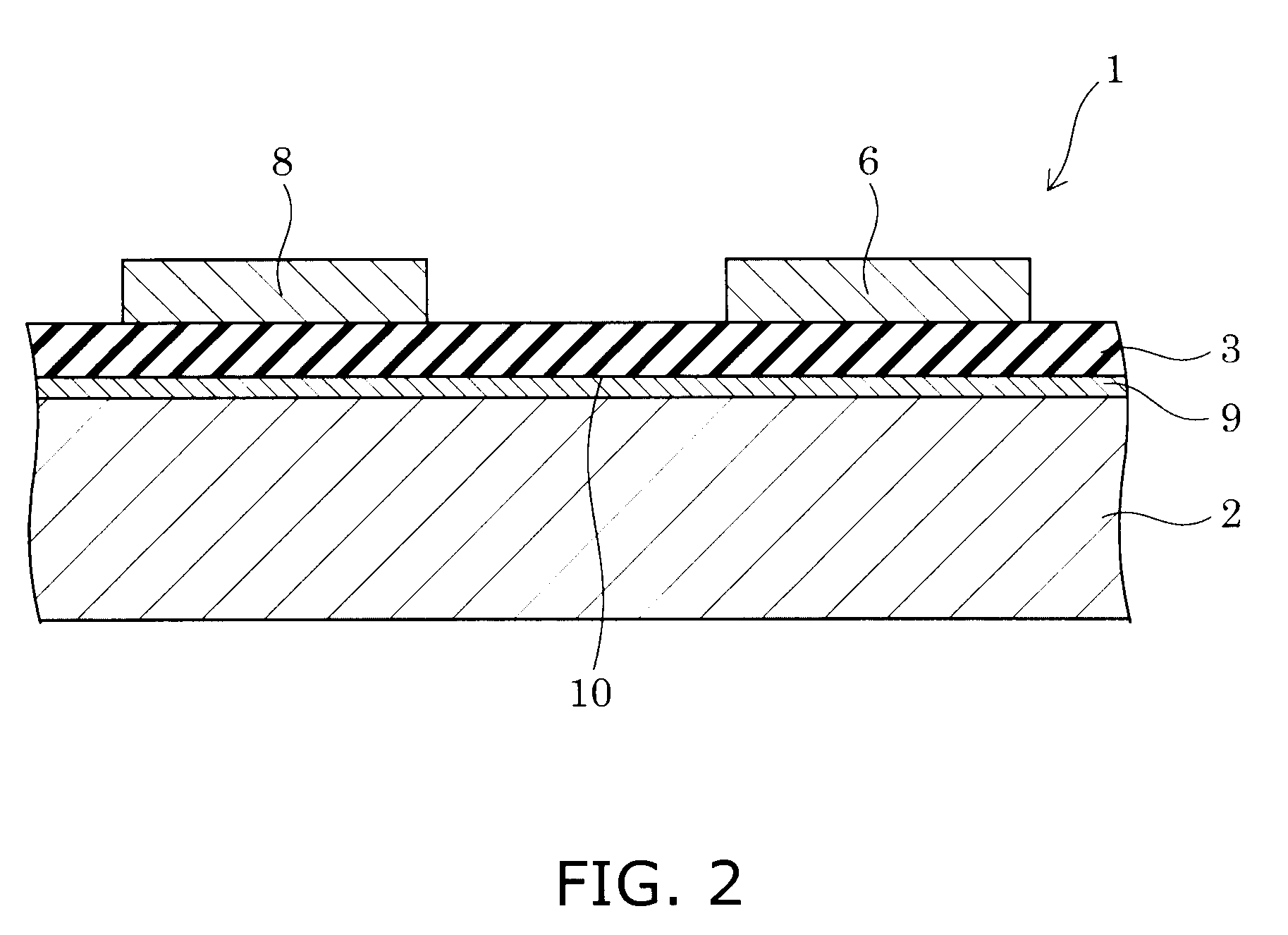
ZnO SEMICONDUCTOR ELEMENT
InactiveUS20110114938A1Flatness can be worsenedStable in natureSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
Provided is a ZnO-based semiconductor device in which, in the case of forming a laminate including an acceptor-doped layer made of a ZnO-based semiconductor, the properties of a film can be stabilized by preventing deterioration of the flatness of the acceptor-doped layer or a layer after the acceptor-doped layer and an increase of crystal defect in the layer, without lowering the concentration of an acceptor element.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
PMOS device and preparation method thereof
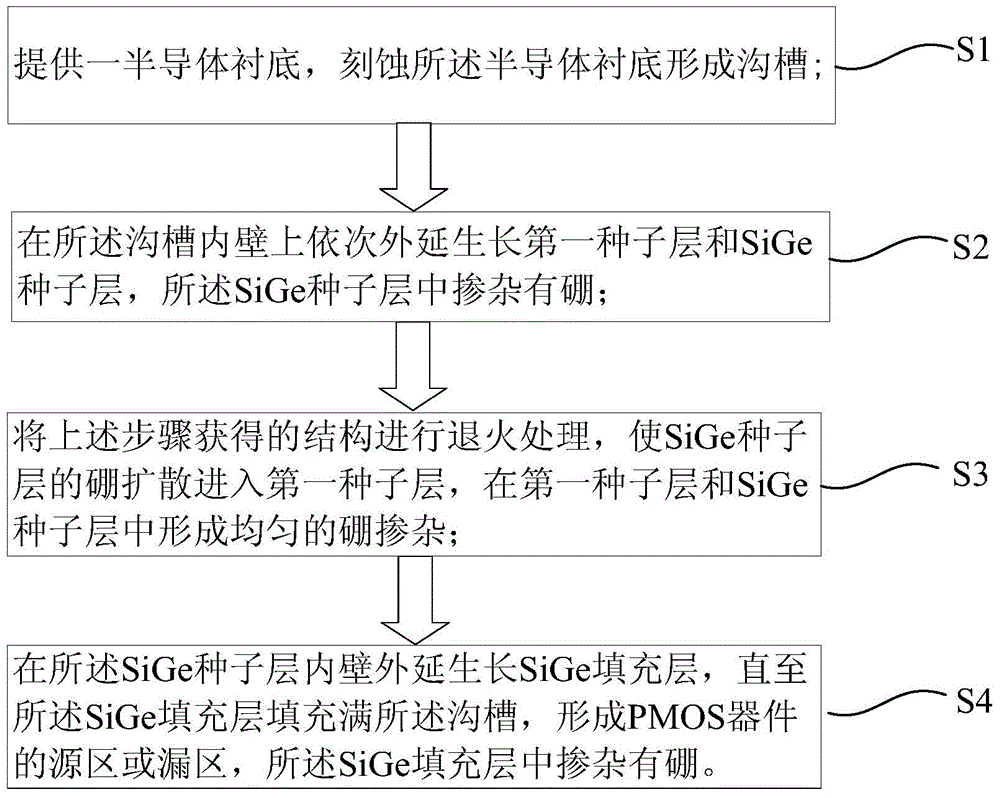
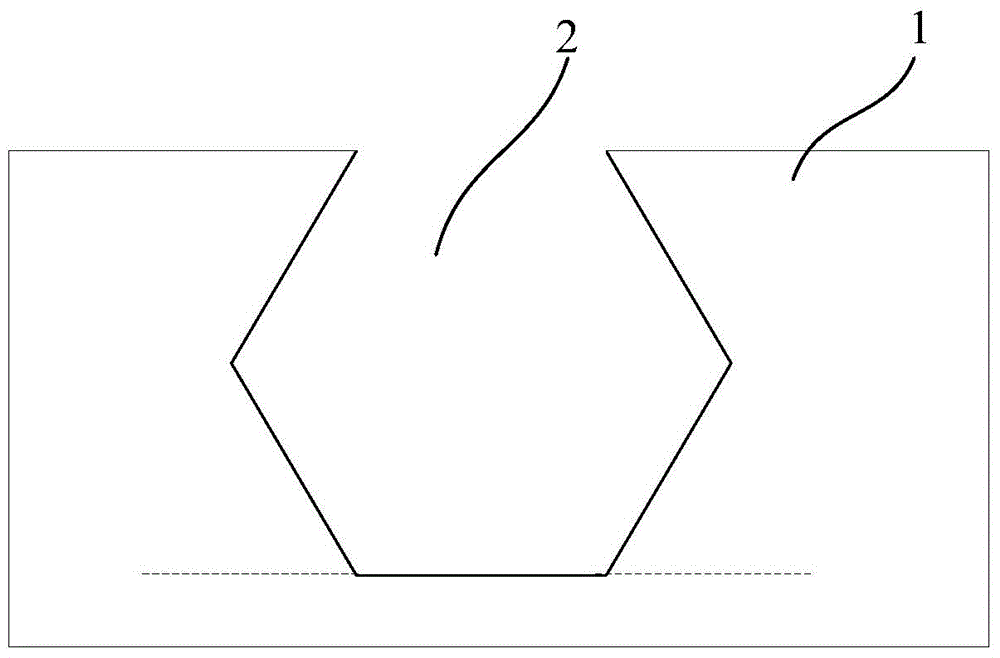
ActiveCN104576391AReduce dislocationReduce defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAcceptor dopingSemiconductor
The invention provides a PMOS device and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method at least includes the following steps: forming a groove in a semiconductor substrate; sequentially growing a first seed layer and a SiGe seed layer in an epitaxial manner on the inner wall of the groove, wherein boron is doped in the SiGe seed layer; annealing the obtained structure, enabling boron in the SiGe seed layer to diffuse in the first seed layer, and forming uniform boron doping in the first seed layer and the SiGe seed layer; growing a SiGe filling layer until a source region or drain region formed by the groove, of the PMOS device is filled with the SiGe filling layer, wherein the SiGe filling layer is doped with boron. According to the invention, acceptor doped ions in the SiGe seed layer diffuse in the first seed layer through the annealing process, so as to be uniformly distributed in the SiGe seed layer and the first seed layer, as a result, accumulation of doped ions at the Si and SiGe interfaces is avoided, resistance at the source region and the drain region is reduced, and improvement on hole mobility is facilitated.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Growth method of p-type AlGaN semiconductor material
ActiveCN108987256AReduced Displacement Formation EnergyImprove retentionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDimethylhydrazineIndium
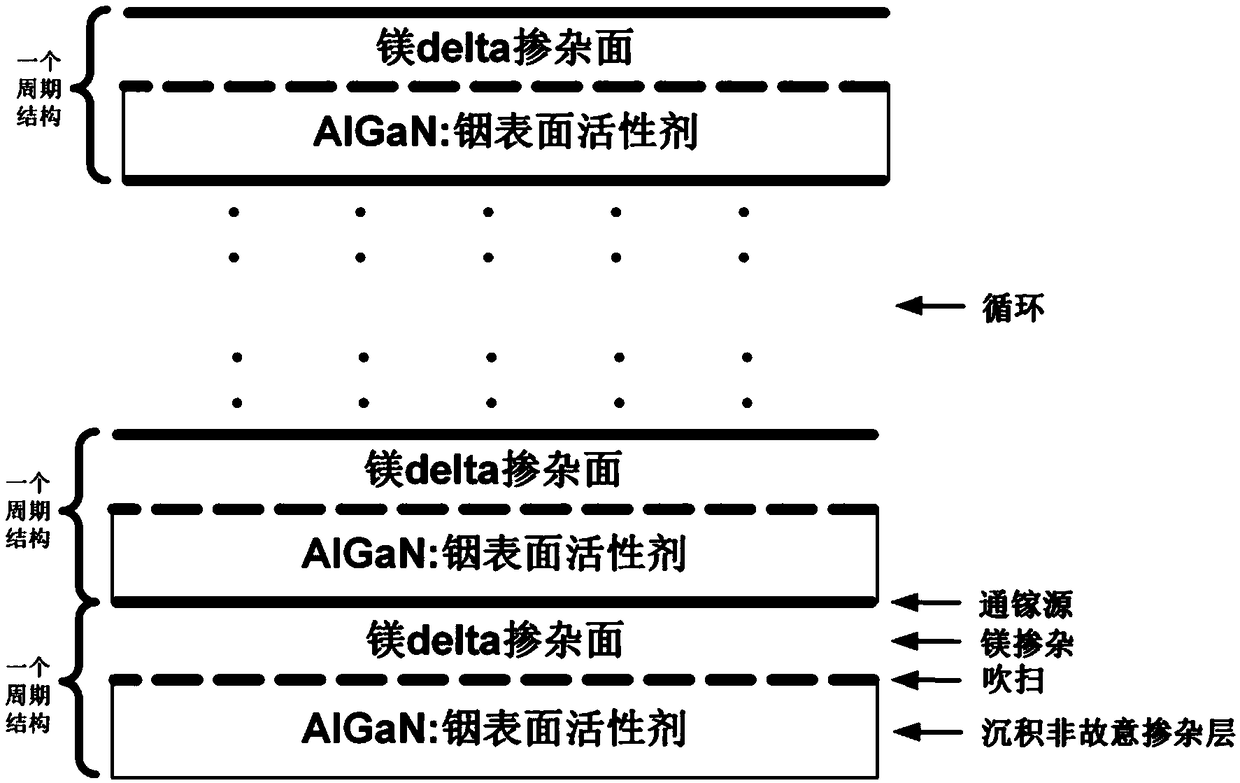
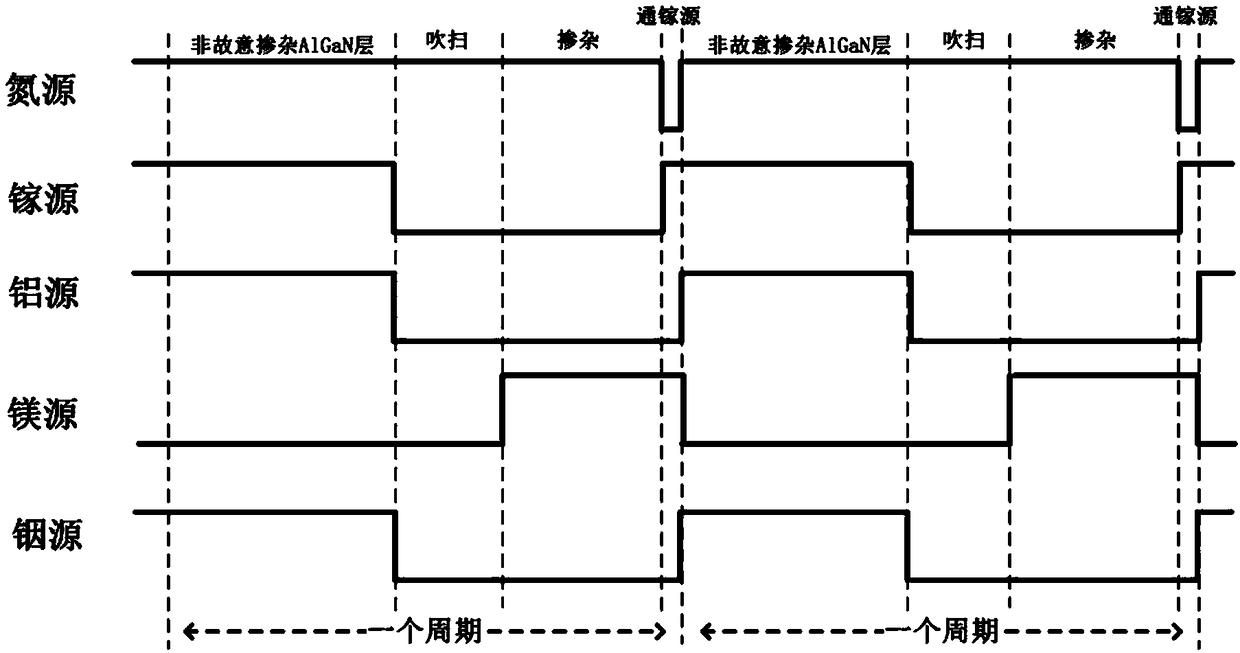
The invention discloses a growth method of p-type AlGaN semiconductor material, the semiconductor material is grown by a technical method of adding a gallium source through step into a surfactant-assisted magnesium delta doping, Ammonia gas or dimethylhydrazine nitrogen is used as group V nitrogen source in the growth of p-type AlGaN semiconductor material, Trimethylgallium or triethylgallium is used as a Group III gallium source, trimethylaluminum or triethylaluminum is used as a Group III aluminum source, trimethylindium or triethylindium is used as a Group III indium source, collectively referred to as a Group III metal source, and trimethylindium or triethylindium is also used as a surfactant in the acceptor doping layer. The method of the invention can improve crystal quality, increase doping concentration of acceptor doped magnesium atoms, reduce acceptor ionization energy by enhancing valence band modulation, and further suppress self-compensation effect, thereby obtaining p-type AlGaN semiconductor material with high crystal quality and high hole concentration.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
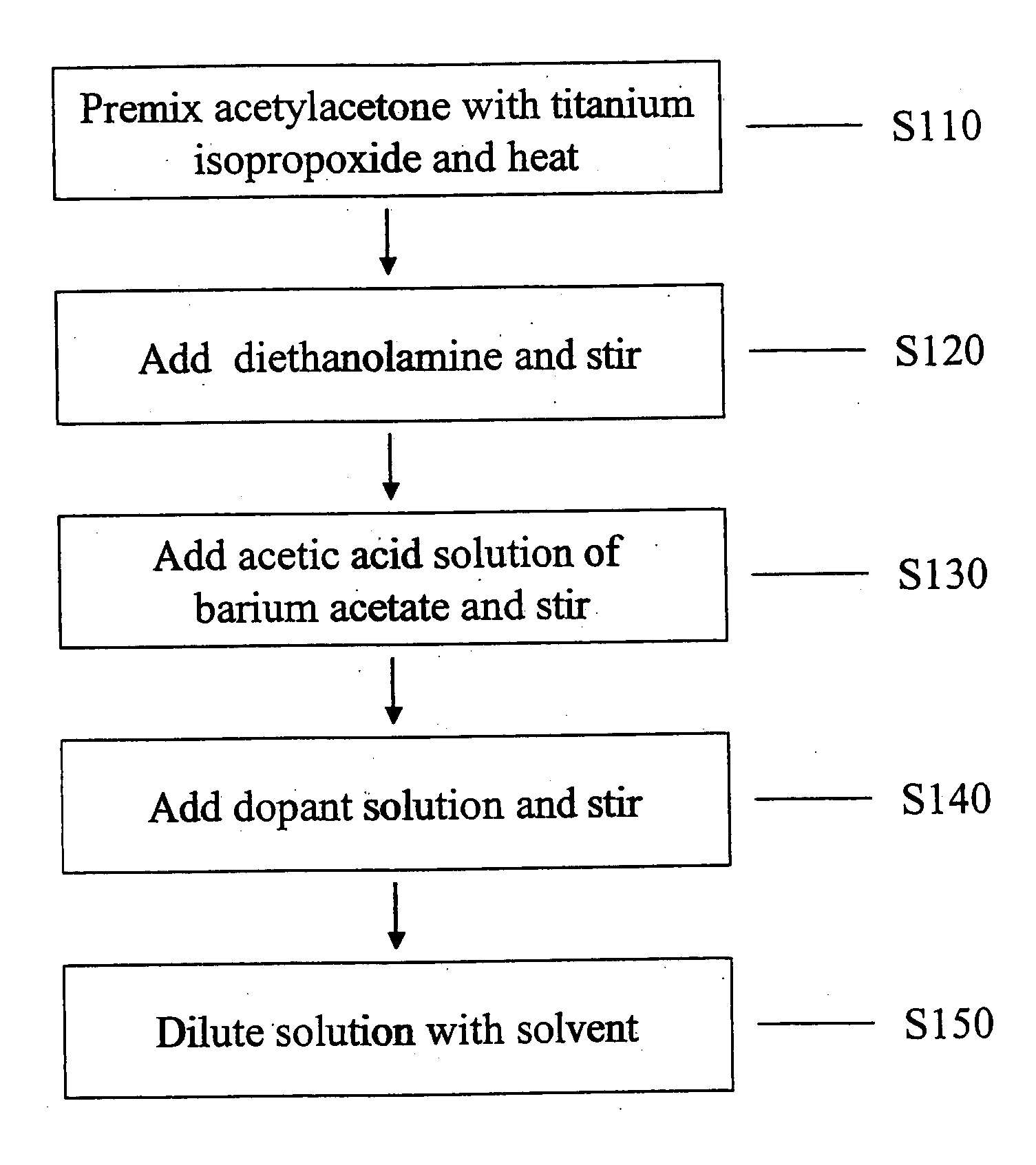
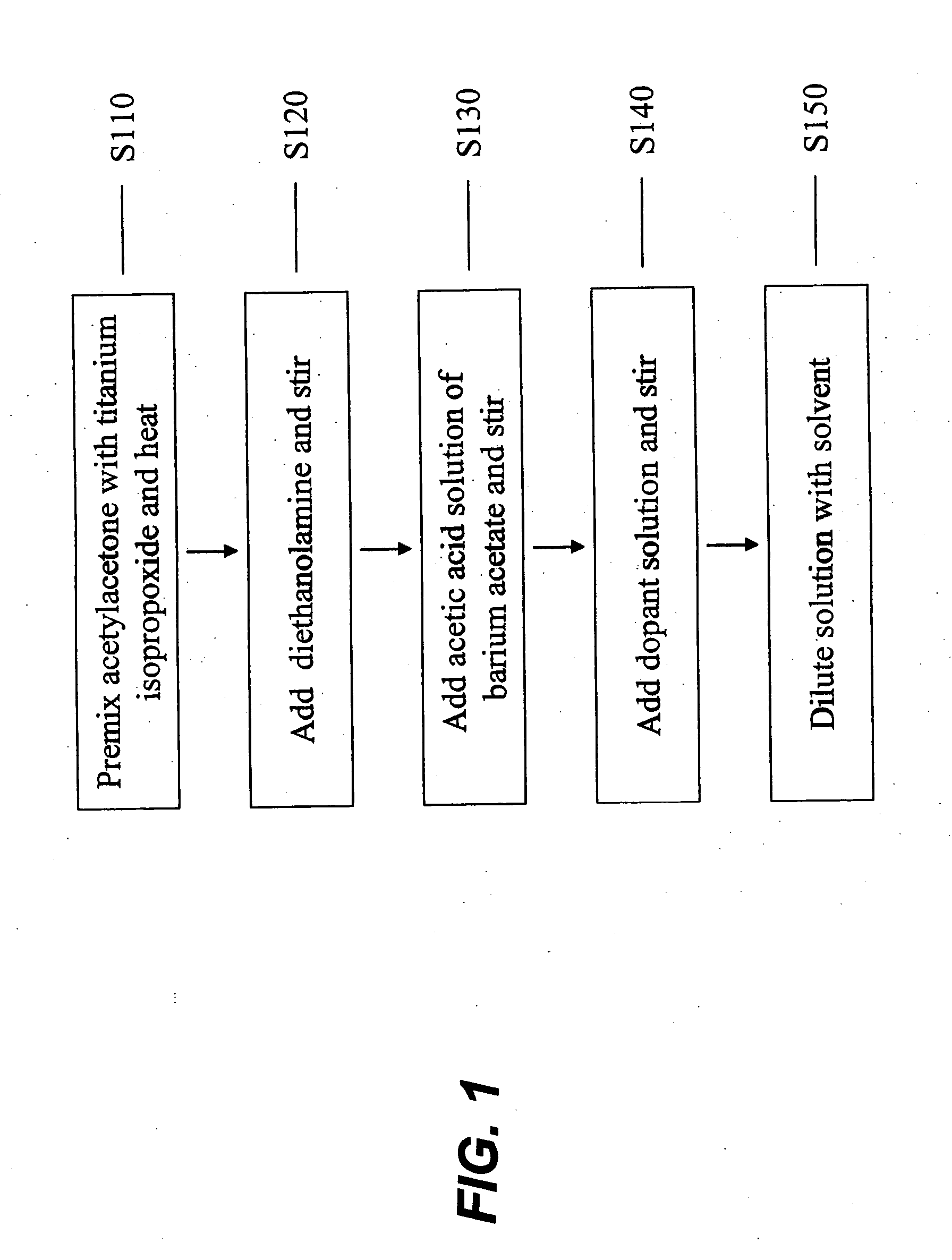
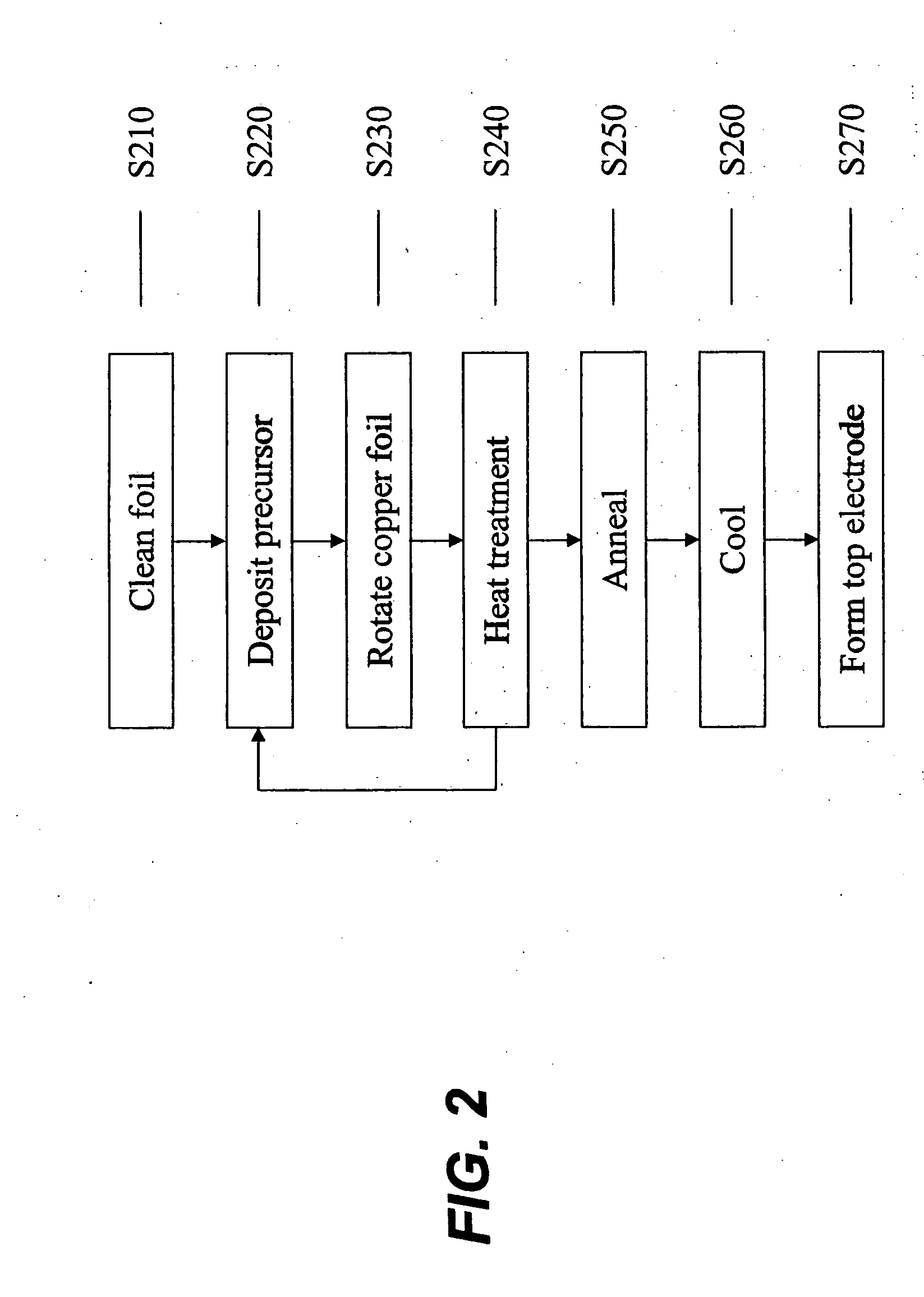
Acceptor doped barium titanate based thin film capacitors on metal foils and methods of making thereof
The present invention is directed to a dielectric thin film composition comprising: (1) one or more barium / titanium-containing additives selected from (a) barium titanate, (b) any composition that can form barium titanate during firing, and (c) mixtures thereof; dissolved in (2) organic medium; and wherein said thin film composition is doped with 0.002-0.05 atom percent of a dopant comprising an element selected from Sc, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Ca, Zn, Al, Ga, Y, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Yb, Lu and mixtures thereof and to capacitors comprising such compositions.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Phthalocyanine rare earth organic infrared semiconductor light guide detector
ActiveCN101969101AControllable electrical parametersHigh controllabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsPhotoconductive detector
The invention relates to the technical field of photoelectron, in particular to a phthalocyanine rare earth organic infrared semiconductor light guide organic semi-conductor detector. The detector of the invention comprises a substrate, a metal or transparent conductive electrode, an organic infrared photosensitive material layer and the like. The detector is characterized in that the photosensitive material is phthalocyanine rare earth with a sandwich structure; the electrical parameters of the photosensitive material of the organic infrared semiconductor light guide detector are controllable, so that electric resistance of a device can be adjusted within a scope of three orders of magnitude by acceptor doping, the performance regulation of the device and the compatibility with the infrared system are enhanced; the photosensitive material is an organic infrared semiconductor material which can be used to fabricate a large-area and low-cost infrared photoconductive detector responsive to infrared light with the wavelength of 1.3-1.8 micron on a silicon substrate integrated circuit, a cheap substrate glass, a quartz plate and a flexible plastic substrate and has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, controllable performances and the like.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Modulation method being able to achieve magnetic torque nonvolatile orientation of magnetic film
ActiveCN104617215ARegulatory performanceSimple structureMagnetostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMagnetostrictive material selectionHeterojunctionVoltage pulse
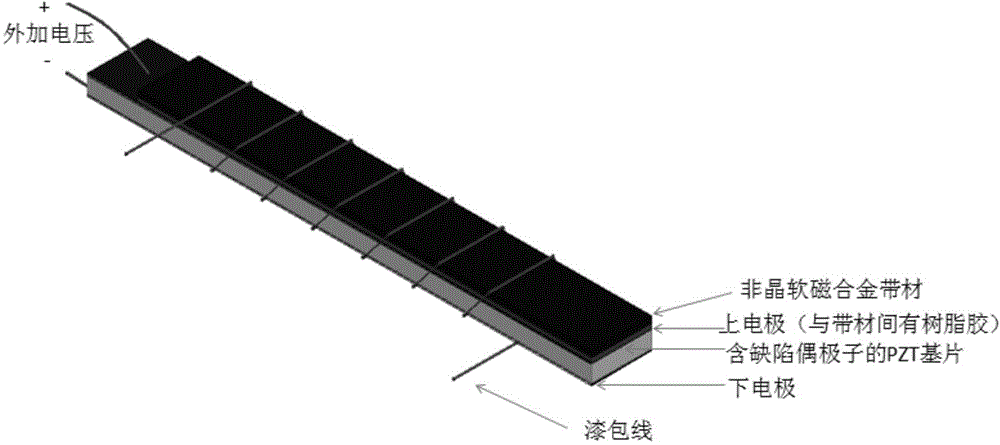
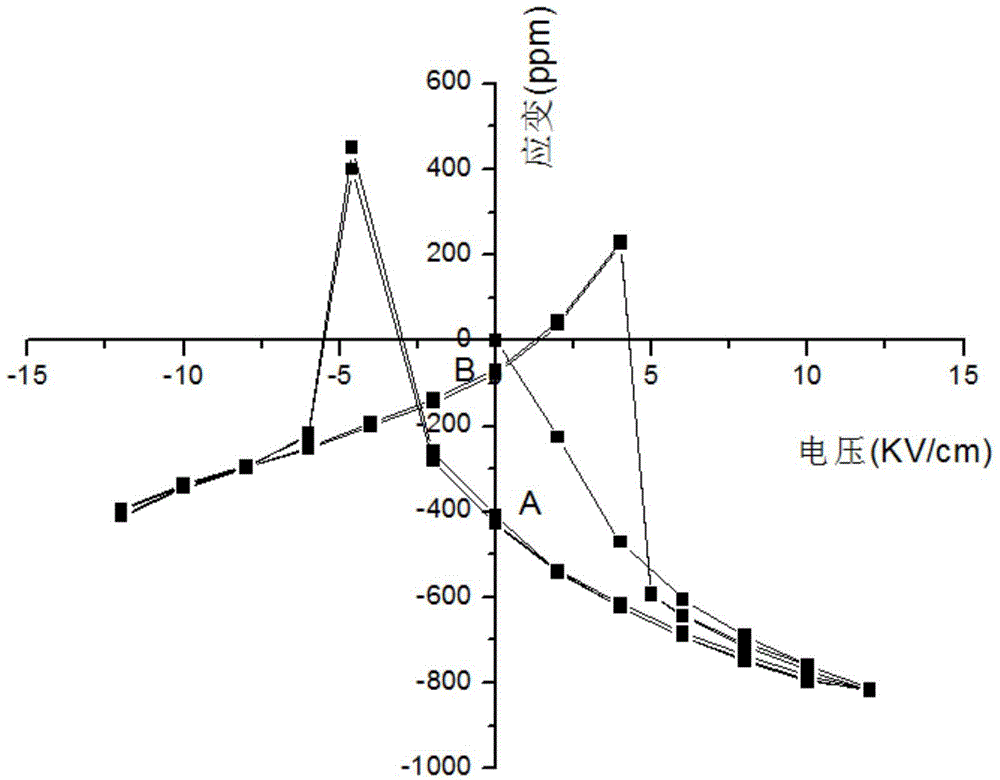
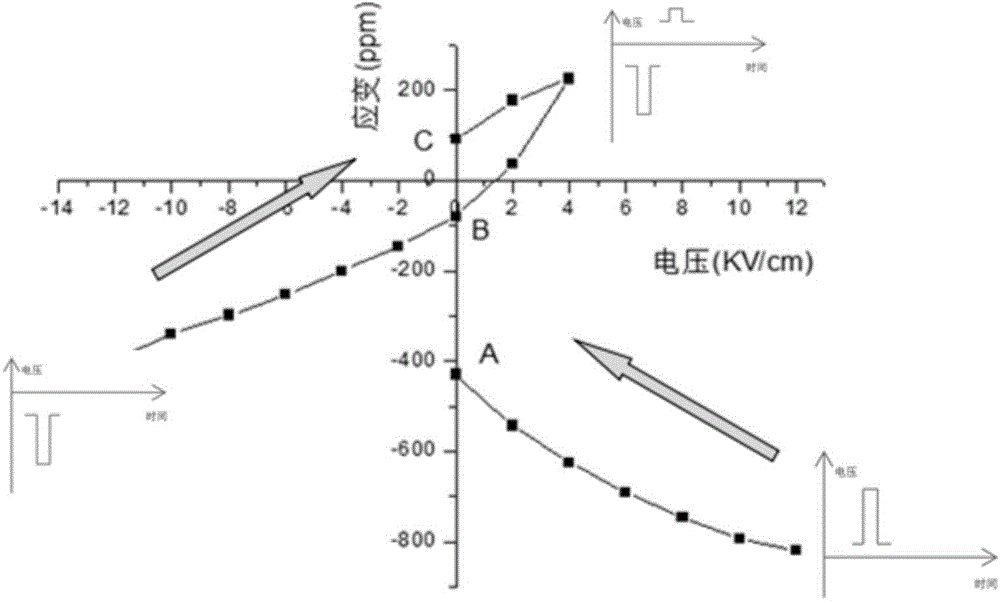
The invention provides a multi-ferric heterojunction and a modulation method for achieving magnetic torque nonvolatile orientation of magnetic film based on the multi-ferric heterojunction, and belongs to the technical field of electronic material. The multi-ferric heterojunction uses cheap polycrystal PZT ceramic containing defect dipoles as a piezoelectric substrate, an elargol is coated on one side thereof for being used as an electrode, the other side is polished and then plated or glued with a magnetic film having magnetostriction features; the polycrystal PZT ceramic substrate containing the defect dipoles is obtained by polarizing and aging the polycrystal PZT ceramic substrate after being acceptor doped. By applying a specific voltage pulse to the multi-ferric heterojunction, three nonvolatile transformation states can be generated in the magnetic film after removing the externally applied voltage, thus achieving the stable nonvolatile magnetic torque modulation effect. The modulation method is simple and convenient in operation, easy to be achieved, and good in modulation effect; the modulation method has a wide application range in the field of nonvolatile electric field pulse modulation magnetic devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
III nitride-based heterojunction phototransistor
ActiveCN107195709AImprove absorption efficiencyGood compensationSemiconductor devicesUltraviolet lightsAlloy
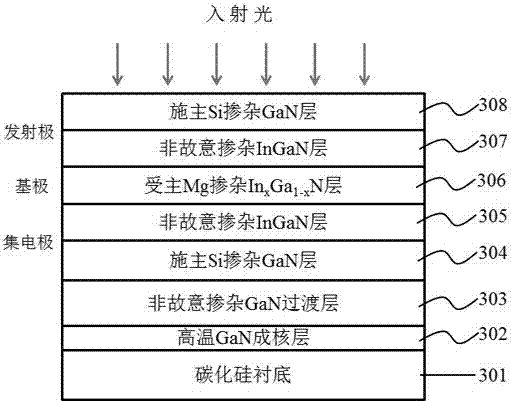
The invention relates to the technical field of visible light and ultraviolet light detectors and more particularly, relates to an III nitride-based heterojunction phototransistor. The III nitride-based heterojunction phototransistor comprises a substrate and an III nitride epitaxial layer growing on the substrate, wherein the III nitride epitaxial layer comprises a nucleating layer, a transition layer, a donor doping layer, an unintentionally doping layer, a multicomponent alloy acceptor doping layer, an unintentionally doping layer with a large band gap material, and a donor doping layer with a large band gap material sequentially from bottom to top. According to the III nitride-based heterojunction phototransistor, alloy components and the doping concentration graded base are adopted, an additional accelerated electric field is generated, transition of electrons through the base is accelerated, the possibility of being composited in the base is reduced, and the photoelectric gains and the detection sensitivity are further improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Technique for preparing Li doping ZnO ceramic target material
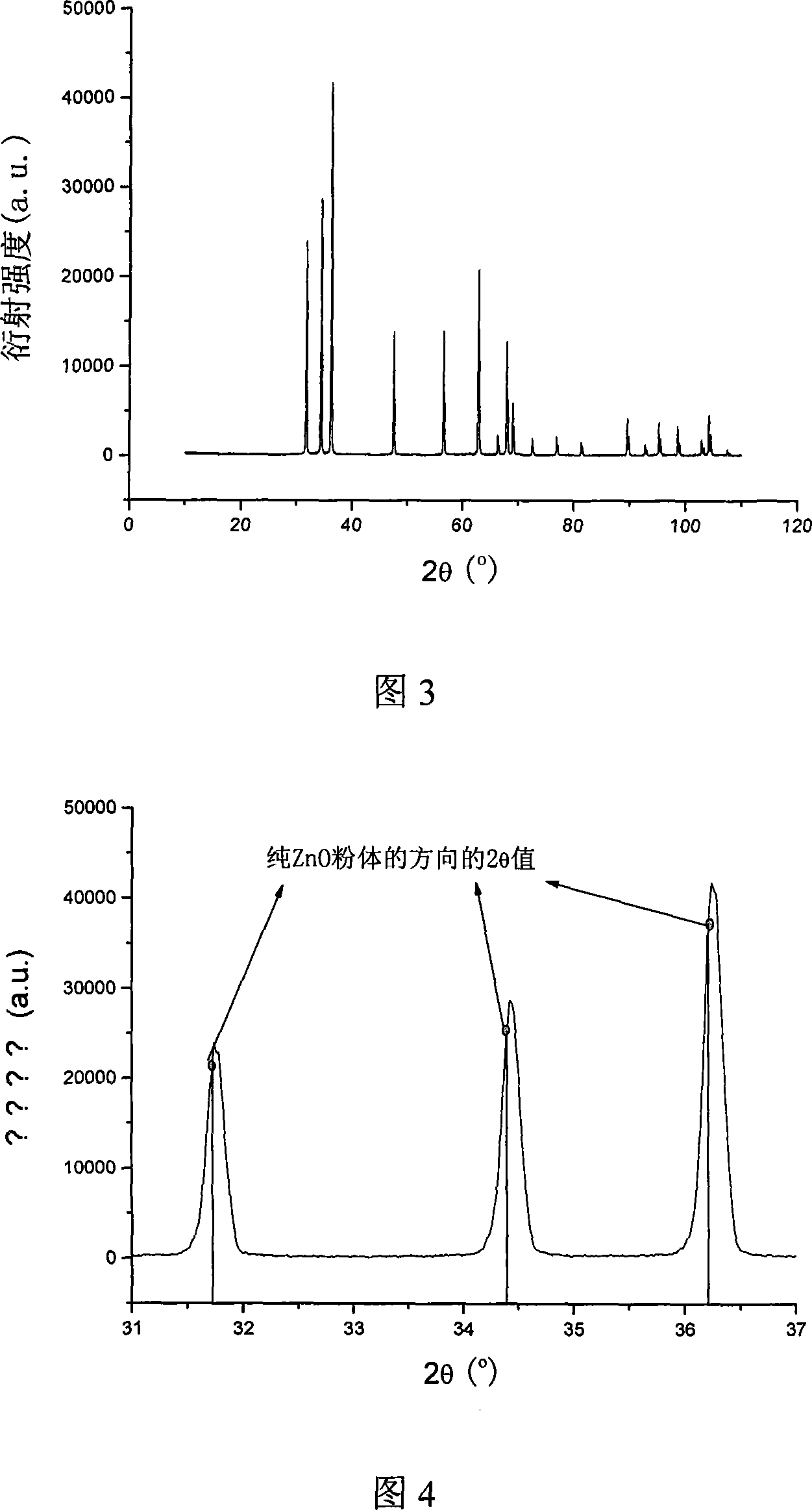
The invention relates to a preparation technique of ceramic target with Li doped with ZnO, which pertains to the preparation technical field of ceramic target material. The process is that: zinc nitrate, lithium nitrate, urea and glycine are fully mixed then put into a beaker; the obtained material is added with deionized water, and is stirred, so as to lead the material to be fully melt; the melted solution is heated and sent into an evaporator, leading combustion reaction to be occurred and synthesizing Li doped with ZnO powder body; the powder body is grinded, then is sintered in a discharging plasma sintering furnace; the obtained product is the Li doped with ZnO ceramic target. The invention has the advantages of raw material being easy to be obtained, short process period, high purity and being evenly doped; in addition, acceptor doping is realized for the element Li used for substituting for Zn in lattice ZnO, and the using of the ceramic target is in favor of the preparation of Li doped with a P-typed ZnO film.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Silicon infrared optical detector structure and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN105932077AProcess compatibleFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSingle crystalAcceptor doping
The invention relates to a silicon infrared optical detector structure and a manufacturing method therefor. A super-heavy doped silicon single crystal material with weight compensation is taken as an infrared photoelectric conversion material; a super-heavy donor doped silicon single crystal material with weight acceptor compensation or a super-heavy acceptor doped silicon single crystal material with weight donor compensation is singly adopted for absorbing infrared light to generate electron-hole pairs; or the super-heavy donor doped silicon single crystal material with weight acceptor compensation and the super-heavy acceptor doped silicon single crystal material with weight donor compensation are adopted concurrently to form a PN junction for absorbing infrared light to generate the electron-hole pairs. According to the silicon infrared optical detector structure, the donor impurity and the acceptor impurity are heavily doped in the silicon single crystal material concurrently, so that a donor impurity energy band and an acceptor impurity energy band are formed in a forbidden band at the same time; meanwhile, an energy band tail connected with a conduction band and an energy band tail connected with a valence band are formed as well, so that the energy levels of the impurities participate in the infrared photon absorption and electron and hole jumps; and therefore, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the silicon material at the near infrared communication waveband is improved.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
Scalable lead zirconium titanate (PZT) thin film material and deposition method, and ferroelectric memory device structures comprising such thin film material
InactiveUS20060115596A1Tin organic compoundsThin/thick film capacitorLead zirconate titanateOptoelectronics
A novel lead zirconium titanate (PZT) material having unique properties and application for PZT thin film capacitors and ferroelectric capacitor structures, e.g., FeRAMs, employing such thin film material. The PZT material is scalable, being dimensionally scalable, pulse length scalable and / or E-field scalable in character, and is useful for ferroelectric capacitors over a wide range of thicknesses, e.g., from about 20 nanometers to about 150 nanometers, and a range of lateral dimensions extending to as low as 0.15 μm. Corresponding capacitor areas (i.e., lateral scaling) in a preferred embodiment are in the range of from about 104 to about 10−2 μm2. The scalable PZT material of the invention may be formed by liquid delivery MOCVD, without PZT film modification techniques such as acceptor doping or use of film modifiers (e.g., Nb, Ta, La, Sr, Ca and the like).
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Preparation method of gallium oxide film with hole-conducting properties and gallium oxide film with hole-conducting properties
The invention provides a preparation method of a gallium oxide film with a hole conduction characteristic as well as the gallium oxide film with the hole conduction characteristic. The preparation method of the gallium oxide film with the hole conduction characteristic comprises the following steps: placing a substrate in a growing tray in a sealed reaction chamber, heating the tray to a temperature which is 10-200 DEG C higher than the expected growing temperature of the gallium oxide film, and thermally treating the substrate; after reducing the temperature of the tray to the predetermined growing temperature, continuously exhausting air to the reaction chamber in a predetermined pressure range; introducing a gallium source, an oxygen source and a doping source to the reaction chamber so as to realize the epitaxial growth of the gallium oxide film; when the growing process of the gallium oxide film is finished, carrying out in-situ thermal treatment to the gallium oxide film or directly cooling and sampling the gallium oxide film slowly or carrying out thermal treatment after sampling to obtain the gallium oxide film with the hole conduction characteristic. The method provided by the invention is scientific and reasonable in step, overcomes many problems in the prior art, provides an effective acceptor doping path, and can be used for preparing gallium oxide films with different hole concentrations.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Inductor capable of realizing tristate nonvolatile modulation and modulation method thereof
ActiveCN104599826ASensitive difference is obviousPreserve the regulatory effectTransformers/inductances magnetic coresInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureVoltage pulseImpedance matching
The invention provides an inductor capable of realizing tristate nonvolatile modulation and a modulation method of the inductor for realizing thee different inductance values, and belongs to the technical field of electronic devices. The inductor capable of realizing the tristate nonvolatile modulation comprises a polycrystal PZT (Pb-Zr-Ti) ceramic substrate which comprises a defect dipole, a metal electrode, a noncrystal soft magnetic alloy strip magnetic film and an enamelled wire, wherein the polycrystal PZT ceramic substrate which comprises the defect dipole is obtained in a manner that the polycrystal PZT ceramic substrate is subjected to polarization and ageing processing after being subjected to acceptor doping. Voltage pulse is applied to an upper electrode and a lower electrode of the PZT substrate, and a transition state of three types of nonvolatility is generated in the noncrystal soft magnetic alloy strip magnetic film after external voltage is removed so as to regulate the inductance value. The modulation method has the advantages of simpleness in operation, good performance and low energy consumption and has a wide application prospect in filtering, tuning, impedance matching and other functional electronic circuit systems which need to be realized by the inductor.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
P type conductive film Nb<x>W<1-x>S<2> and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105047696AReduce internal stressHigh Hall MobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRadio frequency magnetron sputteringField-effect transistor
The invention relates to a p type conductive film Nb<x>W<1-x>S<2> and a preparation method thereof. WS2 is doped with Nb, and a p type semiconductor is formed by acceptor doping. Nb is doped into WS2 to reduce the band gap value of WS2 properly, and can improve the electron mobility. The p tyoe conductive film Nb<x>W<1-x>S<2> can be formed by doping Nb into WS2, the internal stress of the film is relatively low, and higher Hall mobility can be obtained. A Nb<x>W<1-x>O<2>film is deposited on a Si substrate in an RF magnetron sputtering method, and then vulcanized to generate the Nb<x>W<1-x>S<2> film, and in situ annealing is carried out. The p type conductive film Nb<x>W<1-x>S<2> is lower in the inner structures, higher in the Hall mobility, and can serve as channel material of a p type field effect transistor.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080224253A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRadio frequency signalSilicon oxide
A semiconductor device receiving as input a radio frequency signal having a frequency of 500 MHz or more and a power of 20 dBm or more is provided. The semiconductor device includes: a silicon substrate; a silicon oxide film formed on the silicon substrate; a radio frequency interconnect provided on the silicon oxide film and passing the radio frequency signal; a fixed potential interconnect provided on the silicon oxide film and placed at a fixed potential; and an acceptor-doped layer. The acceptor-doped layer is formed in a region of the silicon substrate. The region is in contact with the silicon oxide film. The acceptor-doped layer is doped with acceptors.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
SOI NMOS ESD device and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103996679ALower breakdown voltageImprove electrostatic discharge abilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcceptor dopingIon implantation
The invention provides an SOI NMOS ESD device and a preparing method thereof. In a bulk silicon region, an ESD acceptor doping ion implantation region is formed on the bottom of a channel, being close to and making contact with the side edge of a drain region, and being far away from a source region and the surface of the bulk silicon region, and therefore the ESD acceptor doping ion implantation region can be applied to an SOI device; the ESD acceptor doping ion implantation region located at the position can guide ESD trigger currents to flow through the bulk silicon region, the depth range of the bulk silicon region is larger than that of the drain region, the effect of electrostatic discharge is improved, and breakdown voltage of the drain region is decreased.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Near-infrared visible-light OPV iodine-doped photovoltaic organic detector
ActiveCN105355793AControllable electrical parametersHigh controllabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceOrganic semiconductor
The invention relates to the field of photoelectronic techniques, in particular to a photoconductive organic semiconductor detector. The invention discloses a near-infrared visible-light OPV iodine-doped photovoltaic organic detector, which comprises a substrate, wherein functional layers are arranged on the substrate. The organic detector comprises the substrate (1), a metal or transparent conductive pole (3), a hole transmission layer (4), an organic photosensitive layer (2) and the like, and is characterized in that the organic photosensitive layer (2) is made of an OPV material, after acceptor-doping of iodine and has photoelectric response to near-infrared light, of a solar cell. The organic photosensitive layer is a common OPV material of a typical solar cell, is subjected to effective acceptor-doping of iodine in order to achieve response to near-infrared bands. The near-infrared visible-light OPV iodine-doped photovoltaic organic detector has the advantages of being easy to achieve large area and large array, having controllable resistance of photosensitive layer material, being able to achieve flexible processing and the like, and has important application value in military, civil use and some specific fields.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Low-potential-gradient voltage-sensitive-capacitance dual-functional titanium dioxide ceramic material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105418066ALower potential gradientBoth pressure-sensitive and capacitive dual functionsCapacitanceAntimony trioxide
The invention relates to a low-potential-gradient voltage-sensitive-capacitance dual-functional titanium dioxide ceramic material and a preparing method thereof, and belongs to the field of semiconductor electronic materials. The titanium dioxide ceramic material is characterized in that micron-sized titanium dioxide is used as a body, micron-sized additives including niobium pentoxide, silicon dioxide, samarium oxide, manganese dioxide and antimonous oxide are added, the mixture is fully mixed through wet ball grinding, dried, granulated, formed in a compression mode, subjected to rubber discharging at low temperature and sintered at high temperature to prepare voltage-sensitive-capacitance dual-functional titanium dioxide ceramic, wherein high valence ions such as niobium pentoxide and antimony pentoxide generated by converting antimonous oxide in an oxidized mode in the firing process are used for donor doping to achieve semi-conductivity of titanium dioxide crystalline grains, and samarium oxide and other low valence ions are used for acceptor doping to improve related electrical properties. The average size of the crystalline grains is larger than 9 micrometers, the potential gradient ranges from 2.3 V / mm to 13.1 V / mm, the nonlinear coefficient ranges from 2 to 4.13, the relative dielectric constant epsilon r ranges from 4.6*10<4> to 9.5*10<4> (1kHz), and the loss angle tan delta ranges from 0.11 to 0.57. The titanium dioxide ceramic material has low potential gradient and a good capacitance function.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com