Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55results about How to "Prolong sintering time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing ultra-fine crystal WC-Co hard alloy
A preparation method of superfine crystal WC-Co hard alloys belongs to the field of high-performance functional materials. The powder mixture is composed of 8-11wt percent of Co, 0.001-0.7wt percent of VC, 0.001-0.8wt percent of Cr3C2, and WC with a grain size of 0.2-0.5 micron in balance. The powder mixture is weighed at the given weight ratio and then subjected to alloying treatment under such conditions that the ball-milling time is 15-60 min, the rotational speed of ball mill is 800-1400 r / min-1, the ratio of media-to-material is 5:1 to 10:1; and the level of ball milling media is 5-10 mm above the surface of the ball-milled material, so that the powder mixture is pre-formed to form a pre-forming blank with a density of 50-70 percent. The pre-forming blank is further processed into superfine WC-Co hard alloy by the ultra-high pressure sintering process in a six-face presser, under the following conditions: sintering voltage of 1.25-1.40V, sintering pressure of 10-12GPa, and sintering time of 60-120s. The method has the advantages that the powder is rapidly densified upon an extremely-high pressure and heating simultaneously; and the obtained produce has full density and high hardness (up to 93.1HRA) while the grain size of WC remains almost unchanged.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Preparation method of porous film
ActiveCN106000123AControl pore structureHigh porosityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesChemical reactionAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a porous support body; (2) preparing a thick size containing raw material powder, a binder, a dispersant and a pore forming agent; (3) loading the size onto the porous support body, and drying to make a film billet; (4) sintering the film billet to make a porous film precursor; (5) removing the pore forming agent from the precursor to obtain a porous film with the thickness of 5-3,000 [mu]m, the average aperture of 0.05-100 [mu]m and the porosity of 40-90%. The preparation method has the following advantages: firstly, no chemical reaction occurs between the pore forming agent and the raw material powder, so that the ingredients of the porous film cannot be damaged; secondly, the pore forming agent is excellent in thermal stability and always occupies a certain space (place) in the sintering process; after sintering, the pore forming agent is removed, holes or pores are generated in situ; therefore, the whole technological process is simple, the hole structure of the porous film is easy to control, and the porosity is remarkably improved.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
Porous material prepared from solid wastes
InactiveCN108558254AIncrease varietyWide range of usesCeramic materials productionCeramicwarePorosityPrill
The invention belongs to the field of environment protection and relates to porous material prepared from solid wastes. The porous material is prepared from, by weight, 50-97% of solid waste parent material, 1-20% of a forming agent, 1-15% of a foaming agent and 1-15% of fluxing agent. By the arrangement, shortcomings that the porous material prepared from existing solid wastes require clay consumption, and the porous material is difficult to control, long in sintering time, high in energy consumption and severe in requirement of process control are overcome; the porous material prepared fromthe solid wastes is widely applicable and adjustable in particle size and shape, volume density, porosity size and percentage of close area of the porosity can be adjusted in a wide range, clay consumption is not needed, and short sintering time is achieved.
Owner:ZEROWASTE ASIA PTE LTD
Porous film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105854633AImprove uniformityLow filtration accuracySemi-permeable membranesMembranesSlurryMetal
The invention discloses a porous film which comprises a filtering layer and a porous support, wherein the filtering layer is composed of dendritic metal substance powder and / or metal substance oxide powder. A preparation method for the porous film comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring the raw material powder and the porous support, wherein the raw material powder is the dendritic metal substance powder and / or the metal substance oxide powder; 2) preparing slurry; 3) loading the slurry on the surface of the porous support, drying and preparing into a film blank; 4) sintering the film blank and cooling, thereby acquiring the porous film. Firstly, the dendritic metal substance powder is stacked and formed into the pores of the porous film, the complex hole-forming process is avoided and the porosity is high and is easy to control; the filtering layer composed of the dendritic metal substance powder and / or the metal substance oxide powder is stable in physico-chemical property, long in service life and free from mutual reaction; the complex phase-forming process is avoided; the component of the porous film is easy to control.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
Preparation method of WC-Co-cBN composite material
The invention belongs to the technical field of material preparation and in particular relates to a preparation method of a WC-Co-cBN composite material. The preparation method of the WC-Co-cBN composite material comprises the following steps: firstly weighing WC, metal Co powder and cBN raw material in proportion, uniformly mixing, mixing by carrying out ball milling, drying the mixed raw materials in a drying oven at the temperature of 50-200 DEG C, then sieving with a sieve of 100-300 meshes, putting the dried raw materials into a mould, then placing the mould into a hot-pressing sintering furnace, heating the sintering furnace to 1200-1400 DEG C at a speed of 30-50 DEG C / min, insulating for 5-30 minutes, and maintaining pressure to be 20-50MPa, so that the WC-Co-cBN composite material is obtained. The preparation method of the WC-Co-cBN composite material has the advantages that the hot-pressing method is adopted, the sintering temperature is low, sintering time is short, and no phase transformation of cBN can be guaranteed while the WC-Co-cBN composite material has high shrinkage percentage and high volume density; meanwhile, hot pressing energy consumption is low, cost is low, operation is easy, and safety coefficient is high.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
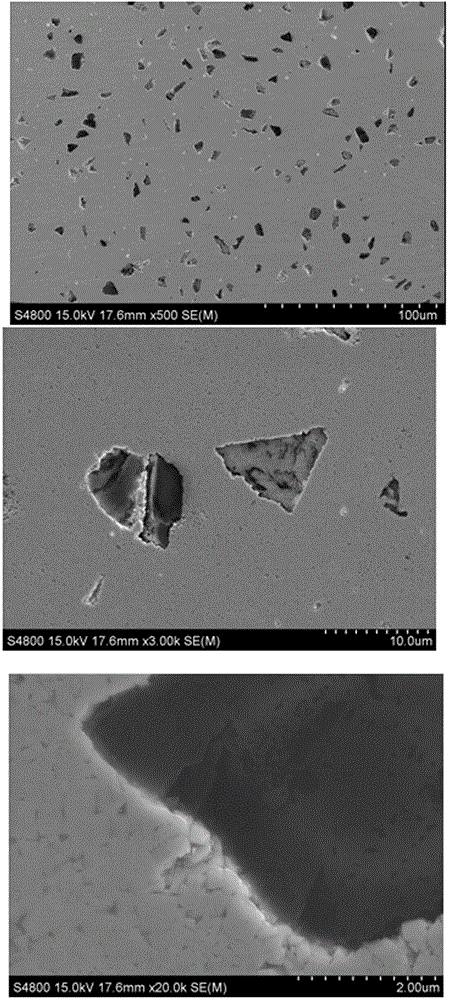
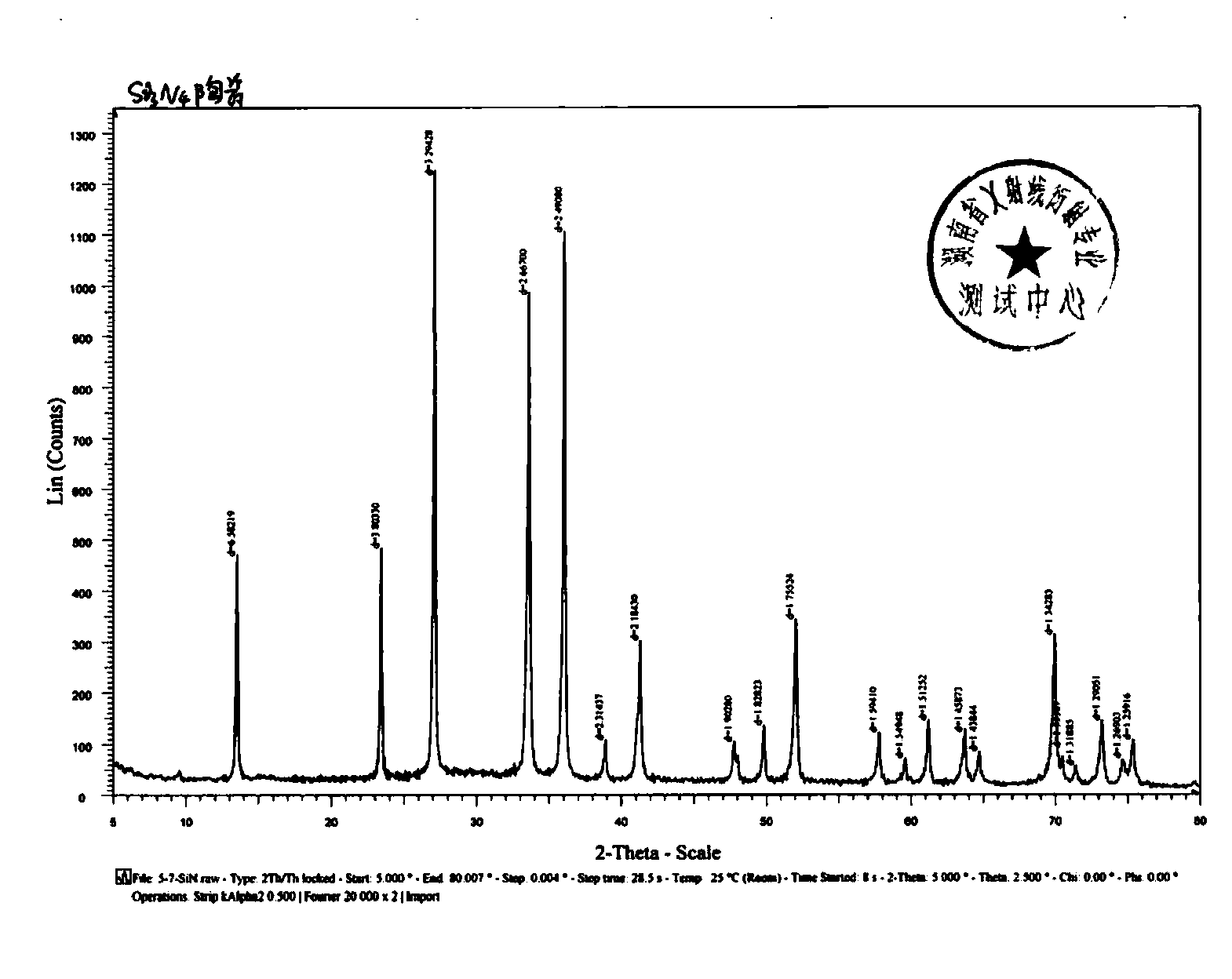
Microwave sintering preparation method of high purity silicon nitride ceramic lift tube for low-pressure casting
The invention discloses a microwave sintering preparation method of a high purity silicon nitride ceramic lift tube for low-pressure casting. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing silicon nitride powder and an additive in a ball milling machine, carrying out wet method ball milling to obtain material slurry, drying and granulating the slurry, placing the granules into a mould, pressing, and forming so as to obtain a lift tube blank; and placing the blank into a sintering cavity to carry out microwave sintering so as to obtain the high purity silicon nitride ceramic lift tube; wherein the sintering cavity is prepared by overlapping corundum and mullite round tubes and graphite round tubes, and the upper opening and the lower opening of the sintering cavity are both provided with a graphite round plate. The preparation method utilizes the special wave bands of microwaves to couple the silicon nitride composite material to generate heats, the material is consumed to heat the composite material as a whole, the optimized microwave sintered structure is matched with the structural characteristics of high purity silicon nitride ceramic lift tube, and thus the utilization rate and efficiency of microwaves is maximized. The preparation method has the advantages of good sintering quality, high yield rate, low sintering temperature, short sintering time, and low sintering energy consumption.
Owner:HENGYANG KAIXIN SPECIAL MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Nitride ceramic material microwave sintering method
The invention discloses a nitride ceramic material microwave sintering method. According to the invention, a nitride ceramic blank is placed between graphite plates, and microwave sintering is carried out under a protective atmosphere in a microwave sintering device. A microwave frequency value range is 2.45GHz, a microwave sintering temperature is 500-3000 DEG C, and a temperature maintaining time is 0-50h. The protective atmosphere is composed of nitrogen gas or argon gas or a mixed gas of nitrogen and hydrogen. The pressure is normal pressure. Different from traditional convection, conduction or radiation heating method, according to the invention, heat is produced through the coupling of a special band of microwave and the basic structure of the material. With the medium loss of the material, the material is heated with an integral heating manner. The method has the advantages of low sintering temperature, short temperature maintaining time, low energy consumption, and the like. The sintered material has good performances and considerable economic benefit.
Owner:HENGYANG KAIXIN SPECIAL MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Microwave rapid sintering method for high-quality aluminum nitride ceramic substrates
The invention discloses a microwave rapid sintering method for high-quality aluminum nitride ceramic substrates. The method belongs to microwave firing of ceramic materials and comprises the following steps: after discharging glue, putting aluminum nitride ceramic substrate blanks into an auxiliary heating insulation structure in a microwave sintering cavity, uniformly spraying boron nitride powder among the blanks, wherein the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate blanks are overlapped orderly and the auxiliary heating insulation structure comprises an aluminum nitride fiber plate, a boron nitride sagger and a high-purity graphite plate; sintering in a nitride atmosphere containing 6-10% of hydrogen under the conditions that the microwave sintering frequency is 2.45GHz, the normal-pressure microwave sintering temperature is 1700-1750 DEG C and the heating rate is 8-10 DEG C per minute; preserving the heat for two hours, cooling along with a furnace, opening the furnace and taking out the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate blanks when the temperature is below 400 DEG C, thus obtaining high-quality aluminum nitride ceramic substrate sintering bodies which are small in deformation and has a heat conductivity being greater than 150W / (m K). Different from a conventional methods adopting a convection, conduction or radiation heating manner, the method adopts a heating manner that the microwave with a special waveband is used to be coupled with basic structures of the materials so as to generate heat and the materials are heated completely by adopting medium loss of the materials; and in combination with special microwave sintering structures and sintering process, the method is capable of rapidly and uniformly sintering the materials and has the advantages of low sintering temperature, short time, low energy consumption, high quality and high efficiency.
Owner:XINHUA TIANHE MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Method for shortening sintering time of resistant material of electric furnace at time of opening new furnace
The present invention discloses a method used for shortening the sintering time of the refractory material of an electric furnace when a novel furnace is opened. Before the production of the first furnace of the newly opened furnace, a layer of petroleum coke recarbonizer is spread uniformly on the ramming material that has been arranged on the slope of the bottom of the furnace. The method can shorten the sintering time of the refractory material of the electric furnace when a novel furnace is opened, save the energy consumption of the electric furnace, and improve the quality of electric steelmaking. At the same time, the method ensures the excellent sintering effects of the refractory material on the bottom of the furnace, and prolongs the service life of the refractory material.
Owner:JIANGSU SUZHOU STEEL GRP
Fracturing propping agent for shale gas exploitation and preparation method of fracturing propping agent
ActiveCN104830308AMeet mining requirementsLow densityFluid removalDrilling compositionShale gasAluminium
The invention belongs to the technical field of gas (oil) exploitation auxiliaries and discloses a fracturing propping agent for shale gas exploitation and a preparation method of the fracturing propping agent. The fracturing propping agent is composed of, by weight, 43-55% of bauxite, 43-55% of shale, 1-3% of barium carbonate and 1-2% of boric acid, wherein BaCO3 is added as a fluxing agent and a binding agent to prevent sintering by lowering the sintering temperature, a certain quantity of monoclinic celsian excellent in acid resistance is generated by Al2O3 and SiO2 to form a protective film on the surface of the propping agent, and accordingly the propping agent can be protected from corrosion of acidic and alkaline substances of rock stratums. The calcination temperature can be lowered by the boric acid, mullite in growth can be slowly wrapped by celsian melts by prolonging of sintering time, and accordingly porosity of blanks can be guaranteed to further improve compressive strength of the propping agent. In addition, corrosion resistance of the propping agent is improved owing to own acid resistance of the boric acid, and adverse effects of K2O, Na2O and the like in raw materials on acid solution can be reduced.
Owner:HENAN TIANXIANG NEW MATERIALS
Solid oxide type fuel cell-use electrode support substrate and production method therefor
InactiveUS7351492B2Increase resistanceHigh stressFinal product manufactureCell electrodesPorosityFuel cells
Disclosed is an electrode support substrate for a fuel cell which is even, gives a small fluctuation in gas permeability, and is capable of carrying out printing of an anodic electrode with high adhesiveness, and which comprises a ceramic sheet having a porosity of 20 to 50%, a thickness of 0.2 to 3 mm and a surface area of 50 cm2 or more wherein the variation coefficient of measured values of the gas permeable amounts of areas measured by the method according to JIS K 6400 ranges from 5 to 20% and further the surface roughness measured with a laser optical manner three-dimensional shape measuring device may be 1.0 to 40 μm as the maximum roughness depth (Rmax) thereof.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
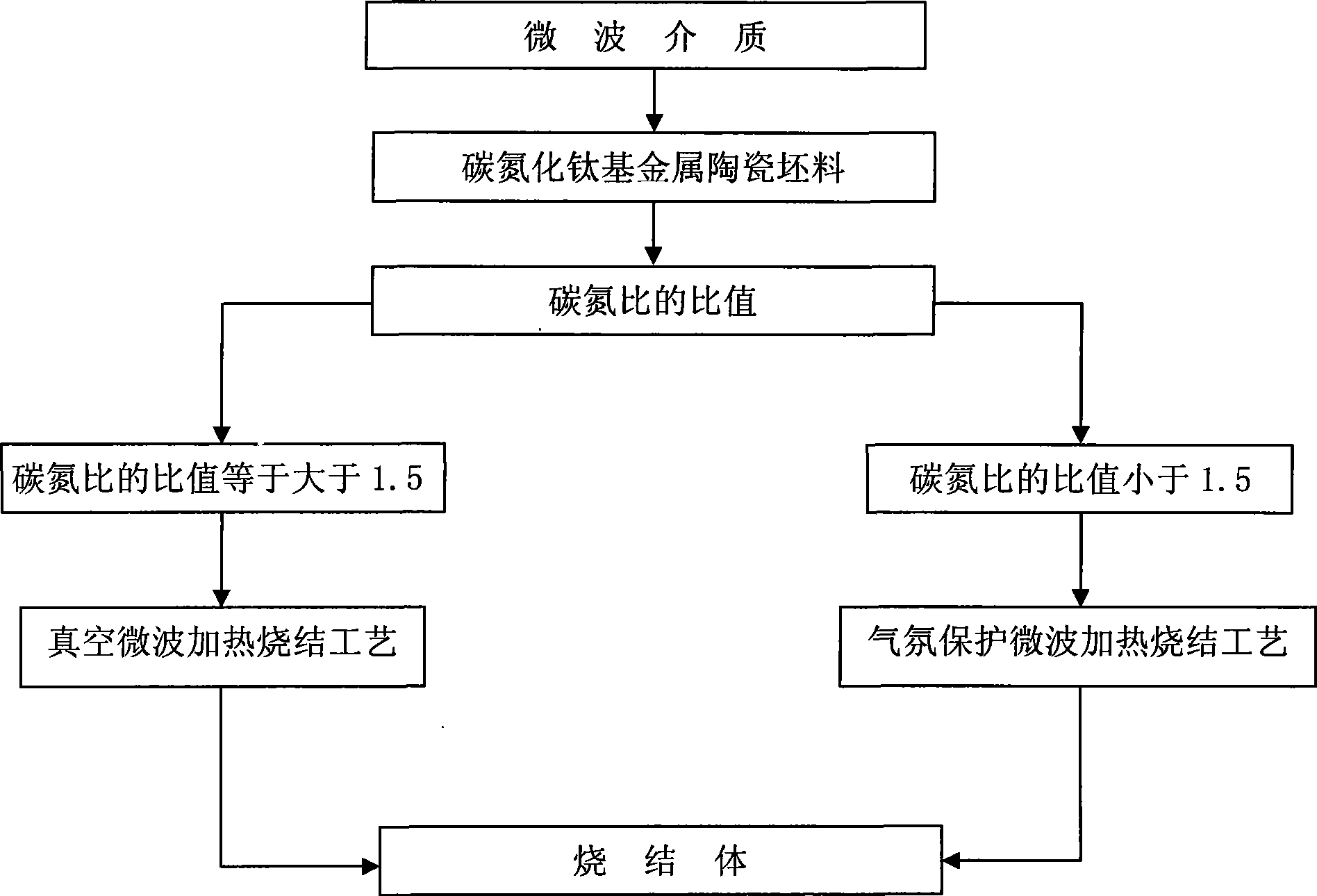
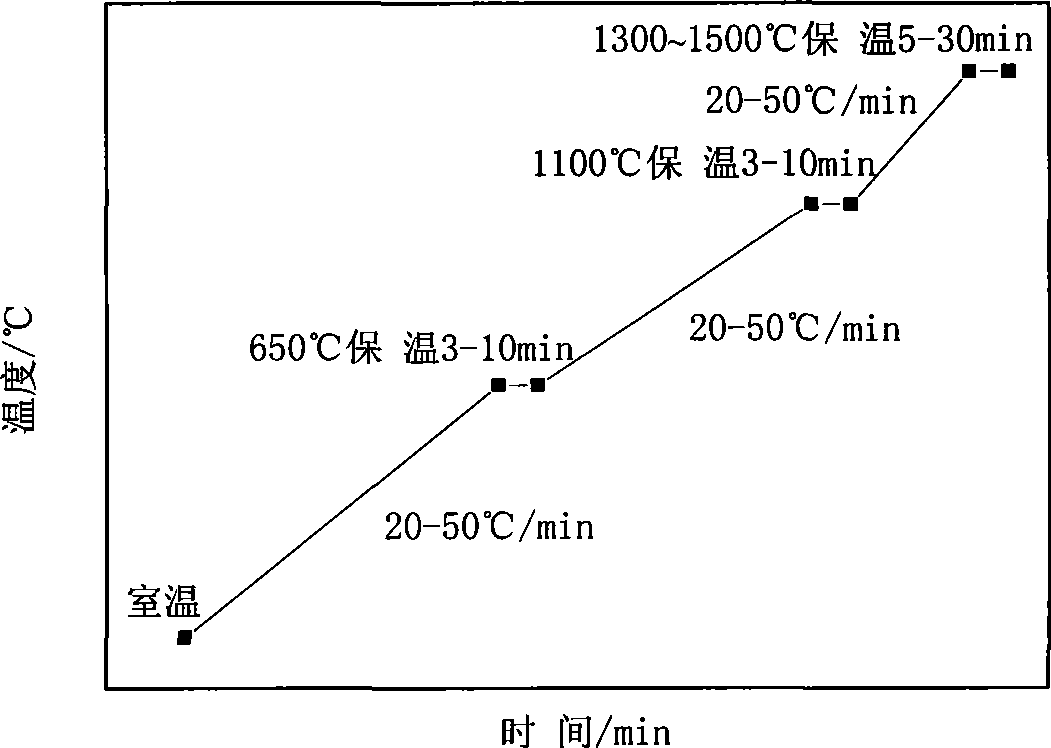
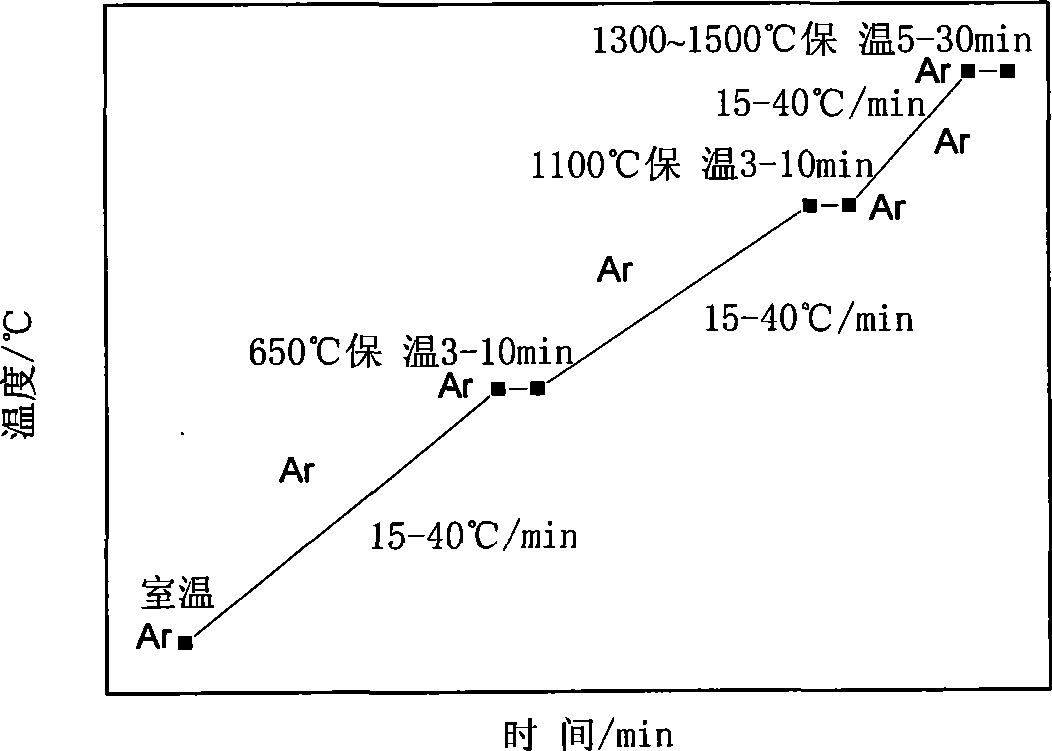
Microwave sintering of superfine grain base titanium carbonitride
The utility model provides microwave sintering of an ultra-fine grain titanium carbonitride group cermet. A 300MHz to 8GHz microwave frequency medium is used as a heat source to enable a billet of the ultra-fine grain titanium carbonitride group cermet to absorb microwave energy to complete the sintering process. During the sintering process, vacuum and atmosphere protection microwave heating and sintering techniques are adopted respectively according to the ratio of carbon to nitrogen of the billet of the ultra-fine grain carbon titanium nitride cermet. The 300MHz to 8GHz microwave frequency is used to heat and sinter the billets of the titanium carbonitride group cermet with different ratio of carbon to nitrogen and vacuum microwave sintering and atmosphere protection microwave sintering technological proposals are used respectively for the billets of the titanium carbonitride group cermet with the different ratio of carbon to nitrogen, which overcomes the defects of the prior vacuum or atmosphere protection sintering techniques, such as low heating efficiency, long sintering time, large energy consumption, serious environment pollution and oversized grains, and the like. The microwave sintering can be widely applied to sintering other ceramics, ceramic matrix composites and intermetallic compound materials with stronger microwave absorbing capacity.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Quick change method of converter tap hole
The invention discloses a quick change method of a converter tap hole. The quick change method is mainly used for solving the technical problems that in the prior art, the replacement time of a converter tap hole is long, the replacement operation is complex, and the replacement quality is poor. According to the technical scheme, the quick change method of the converter tap hole comprises the steps of preparing a mounting hole for the new tap hole; mounting the new tap hole; filling a gap between the new tap hole with a refractory material and the mounting hole of the new tap hole in a converter body; and after 5-8 minutes since grouting is completed, returning the converter to a zero position, so that replacement of the new tap hole is completed. By means of the method, rapid replacementof the converter tap hole is achieved, and the replacement quality is controllable.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Glass composition and electrode composition for solar cell using same
InactiveCN105939976AReduced series resistanceImprove fill factorNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPhotovoltaic energy generationFill factorGlass transition
Owner:DONGJIN SEMICHEM CO LTD
A method for eliminating cracks in metal material additive manufacturing and improving mechanical properties
ActiveCN108994304BReduce residual stressEliminate cracksAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMetallic materialsStress relief
The invention provides a method for eliminating metal material additive manufacturing cracks and improving mechanical properties, and belongs to the technical field of additive manufacturing. According to the method, stress relief annealing and spark plasma sintering treatment are carried out on additive manufacturing forming parts in sequence. The stress relief annealing comprises the following steps that the temperature is increased to the annealing temperature in a protective atmosphere, and the temperature is kept; the annealing temperature is (0.3-0.4)T; and the temperature of the spark plasma sintering is (0.8-0.9)T, and the time is 10-20 min. According to the method, the stress relief annealing of specific parameters and SPS sintering of specific parameters are adoptedon metal obtained throughadditive manufacturing in sequence, so that not only are the product cracks eliminated, but also the mechanical property is greatly improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
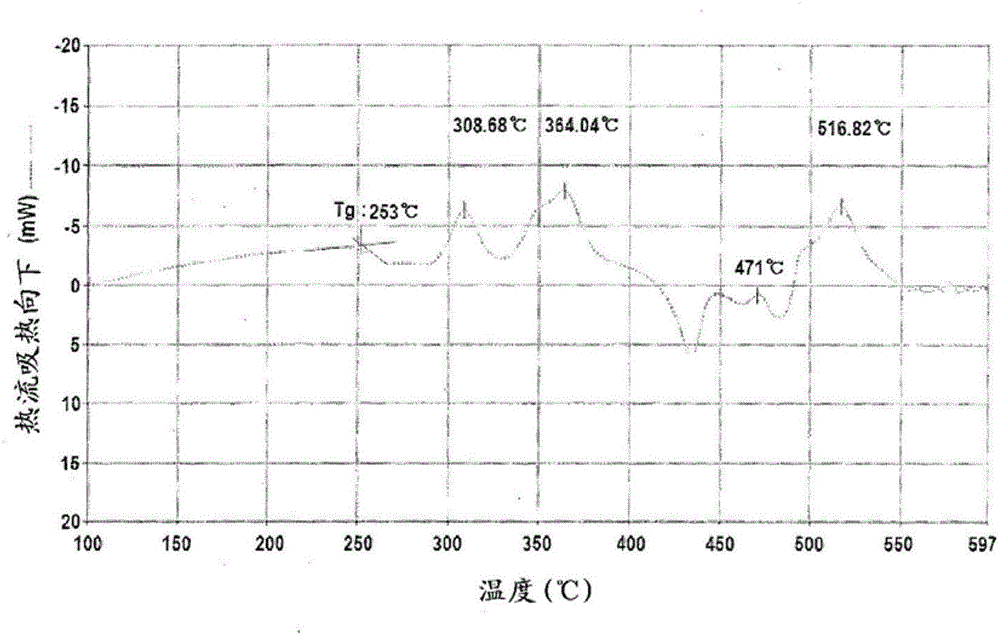
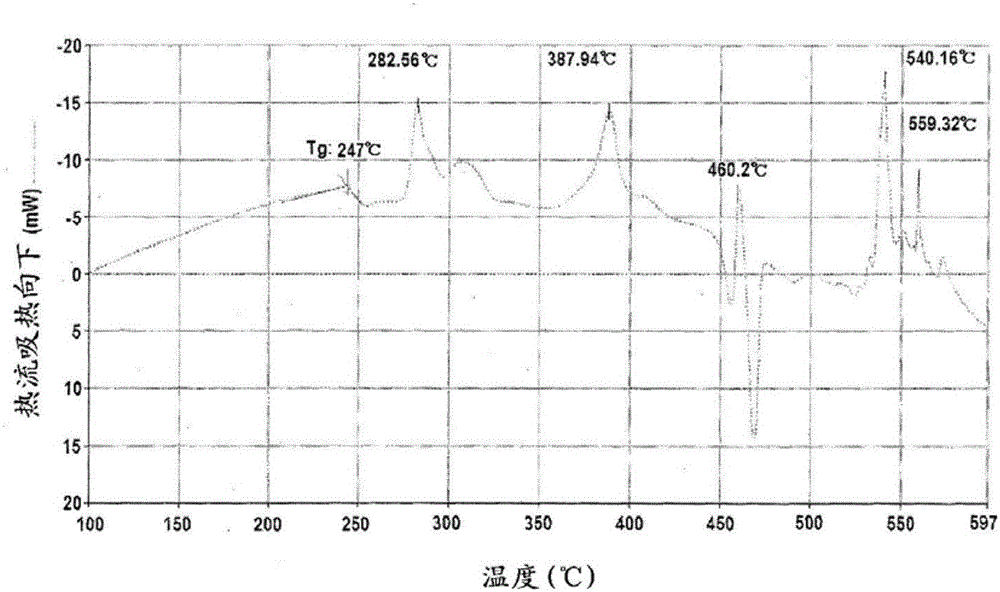
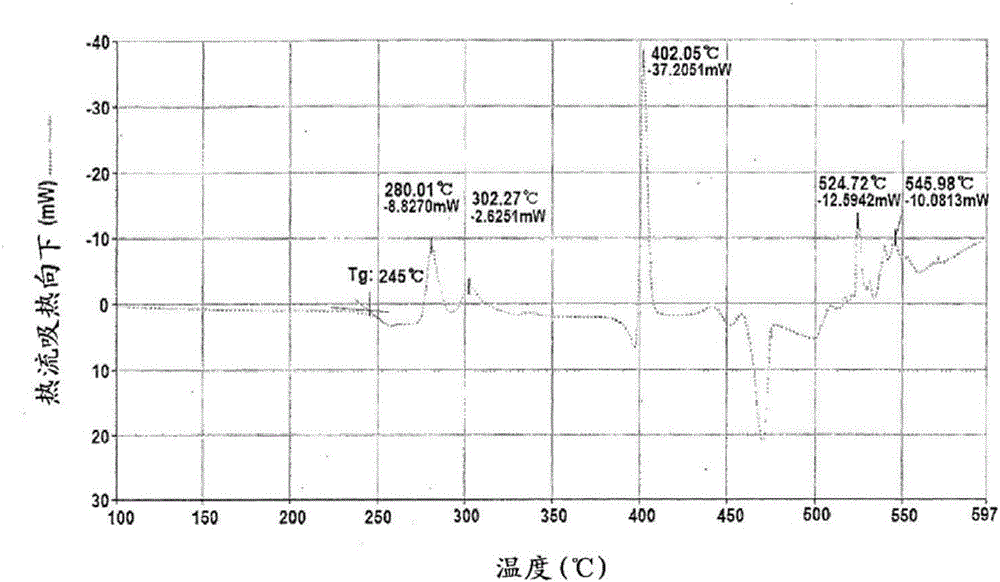
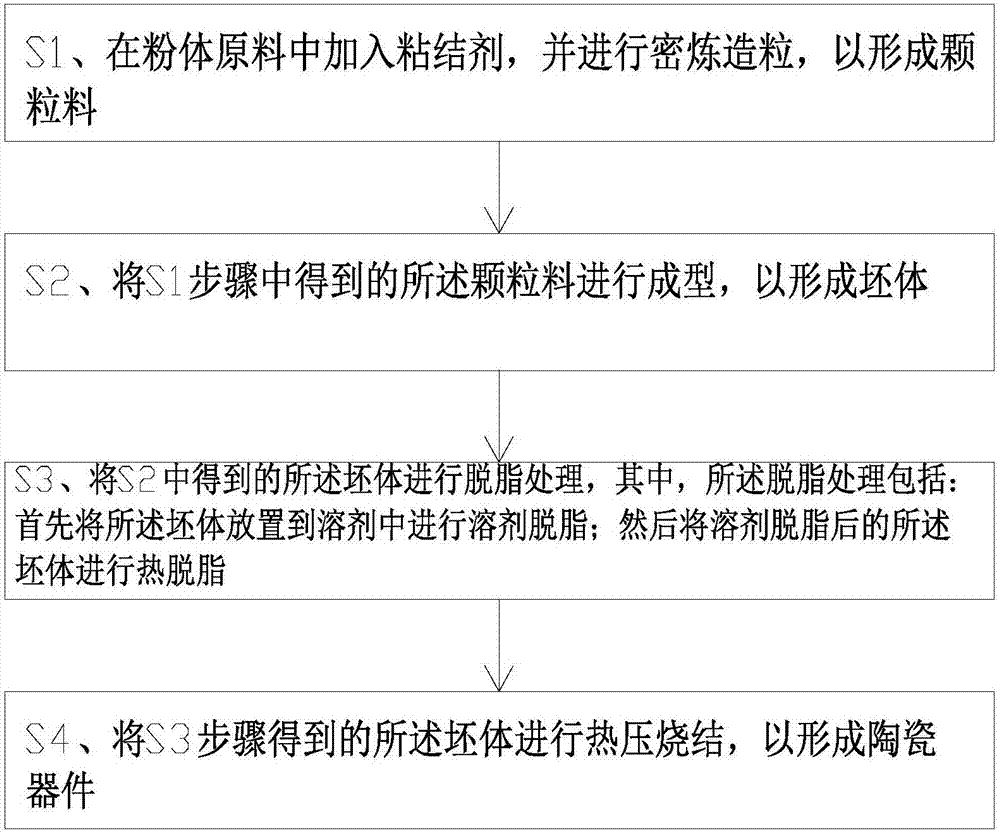
Preparation method of ceramic device
InactiveCN107382311AProlong sintering timeRaise the sintering temperatureSlip casting mouldsSolvent degreasingRaw material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ceramic device, which comprises the steps of S1, adding a binding agent to a powder raw material and performing internal mixing and granulation to form a granule, S2, performing molding on the granule obtained in Step S1 to form a body, S3, performing degreasing treatment on the body obtained in Step S2, and S4, performing hot press sintering on the body obtained in Step S3 to form the ceramic device, wherein the degreasing treatment comprises the steps of placing the body in a solvent, performing solvent degreasing, and then performing hot degreasing on the body subjected to the solvent degreasing.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
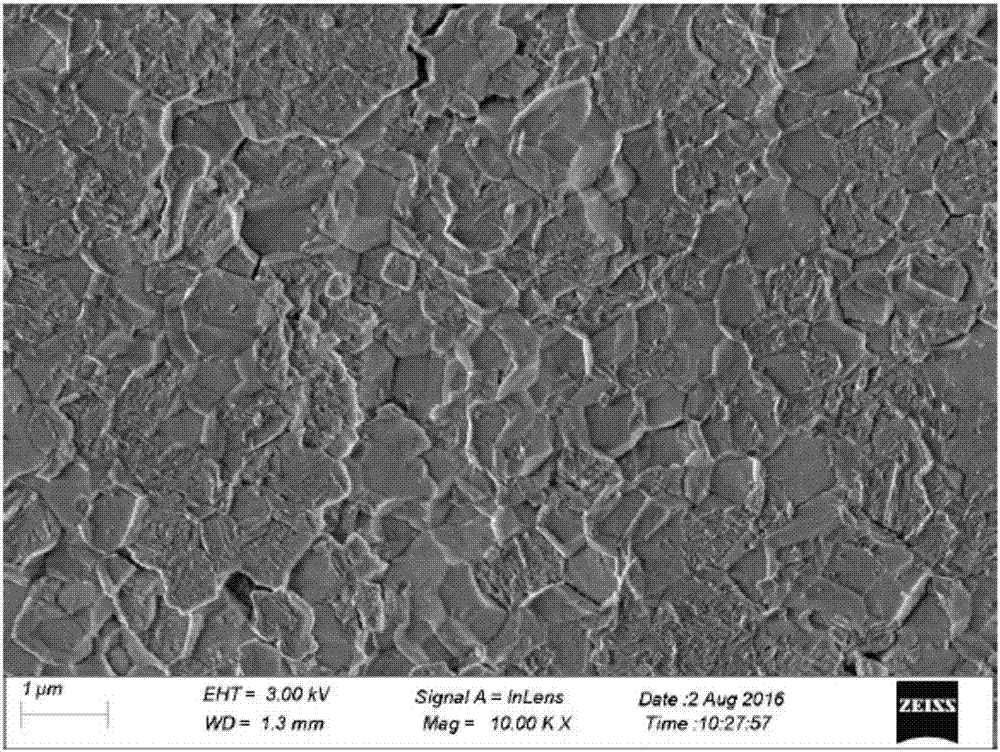
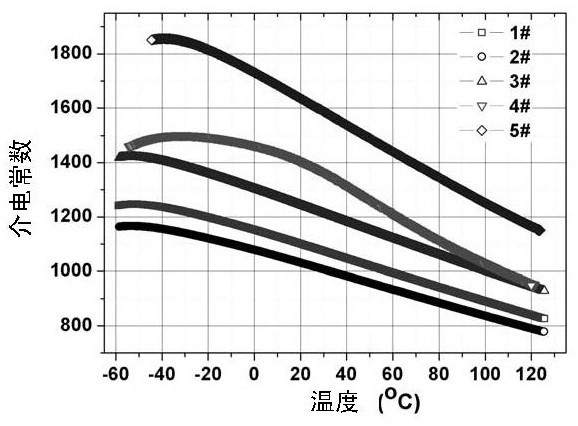
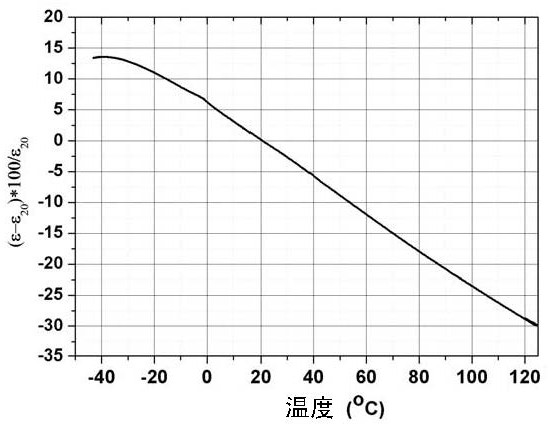
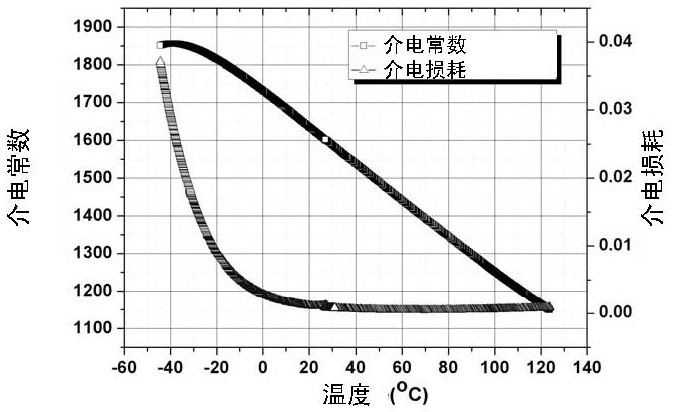
Barium strontium titanate-based dielectric ceramic material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111763082AReduce defectsImprove electrical resistanceStrontium titanateBarium strontium titanate
The invention relates to a barium strontium titanate-based dielectric ceramic material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composition formula of the barium strontium titanate-based dielectric ceramic material comprises the following components: aBaTiO3+bSrTiO3+cTiO2+dBiO5+e MgO+fAl2O3+gCaO+hSiO2, wherein a, b, c, d, e, f, g and h are molar percentages of the components; 20 < = a < = 50 mol%; 15 < = b < = 30 mol%, 10 < = c < = 20 mol%, 0 < = d < = 10 mol%, 0 < = e < = 35 mol%, 0 < = f < = 6 mol%, 0 < = g < = 6 mol%, 0 < = h < = 1 mol%, and a + b + c + d + e + f + g + h= 100 mol%.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for producing high-purity magnesia by adopting double-layer sintering spray gun vertical kiln
The invention discloses a process for producing high-purity magnesia by adopting a double-layer sintering spray gun vertical kiln and relates to the technical field of preparation of high-purity magnesia. The process comprises the following specific steps: firstly performing grinding treatment on a caustic-burned magnesia powder with a particle size of 150-200 mm, grinding by adopting a ball mill,ending grinding after the material fineness of 95 percent of the caustic-burned magnesia powder is less than 325 meshes, then ball-pressing by adopting a ball press machine, health-preserving and drying after the end of ball-pressing, then enabling a dried magnesium ball to enter the kiln, preheating the temperature of the vertical kiln to 800-1000 DEG C, opening a first-layer spray gun to calcine till the sintering zone temperature is 1200-1500 DEG C, opening a second-layer spray gun to calcine till the sintering zone temperature is 1800-2000 DEG C after the end of calcination by the first-layer spray gun, finally cooling to 150-200 DEG C through a cooling zone and going out of the kiln by adopting a furnace discharge conveyer to prepare the high-purity magnesia. The process disclosed bythe invention has the benefits that a double-layer sintering spray gun structure is adopted, the sintering time is prolonged, and the purpose of producing the high-density and high-purity magnesia isachieved.
Owner:营口金岱国际科技有限公司
Preparation method of high-voltage ultra-small-capacity non-solid electrolyte tantalum electrolytic capacitor
ActiveCN110797216AHigh strengthNot easy to drop blocks and missing cornersCapacitor manufactureElectrolysisTantalum capacitor
The invention belongs to the technical field of tantalum capacitor preparation and particularly relates to a preparation method of a high-voltage ultra-small-capacity non-solid electrolyte tantalum electrolytic capacitor. The method is characterized in that pressing density is improved, a molding mode is changed, the increasing sintering temperature and sintering time are increased, so the strength of a tantalum core is enhanced, tantalum cores are not easy to fall off and have unfilled corners, impurities in tantalum powder are effectively removed, a tantalum core with excellent electrical performance is obtained through an improved forming method, aging process treatment is combined, so the voltage of the prepared non-solid electrolyte tantalum capacitor can reach 180V, the capacitance can reach 0.047 mu F, and the non-solid electrolyte tantalum capacitor has the characteristics of high voltage and ultra-small capacitance.
Owner:CHINA ZHENHUA GRP XINYUN ELECTRONICS COMP ANDDEV CO LTD
Mfg. method of cals photocatalyst for hydrogen prodn and method for generating hydrogen therewith
InactiveCN1121271CProlong sintering timePromote activityCadmium sulfidesHydrogen productionPhotocatalysisOxide
A method for producing CdS-based photocatalyst for hydrogen generation and a method for producing hydrogen in the presence of CdS. Dissolve the compound containing Cd and M in water, after the M value reaches 0.001-20.00, add H to it 2 S or Na 2 S any reactant, stir to get Cd[M]S precipitate, wash the precipitate with water, and vacuum dry the washed precipitate in a nitrogen (flow) atmosphere at a temperature of 105-150 ℃ for 1.5-3.0 Hours later, add a liquid phase m-containing compound to the dried Cd[M]S precipitate for doping treatment, so that the m content in the entire photocatalyst reaches 0.10 to 5.00% by weight, and the photocatalyst with the following formula I is produced. m(a) / Cd[M(b)]S(I) (in the above general formula, m represents the metal doped as an electron acceptor, which is made from Ni, Pd, Pt, Fe, Ru, Co or their oxides One or more substances selected from; a represents the weight % of m, and its value is 0.10 to 5.00. M is a promoter selected from V, Cr, Al, P, As, Sb, Pb, and b represents M / (Mole % of (M+Cd), its value is 0.001~20.00.) Make the above-mentioned photocatalyst, contact with the water that adds 0.05~1.0 mole sodium sulfite reducing agent and 0.05~1.0 mole sodium sulfide electron donor to suspend it, while stirring While irradiating the light in the visible light region adjusted by the filter and sunlight, it reacts to generate hydrogen.
Owner:株式会社青丘 +1
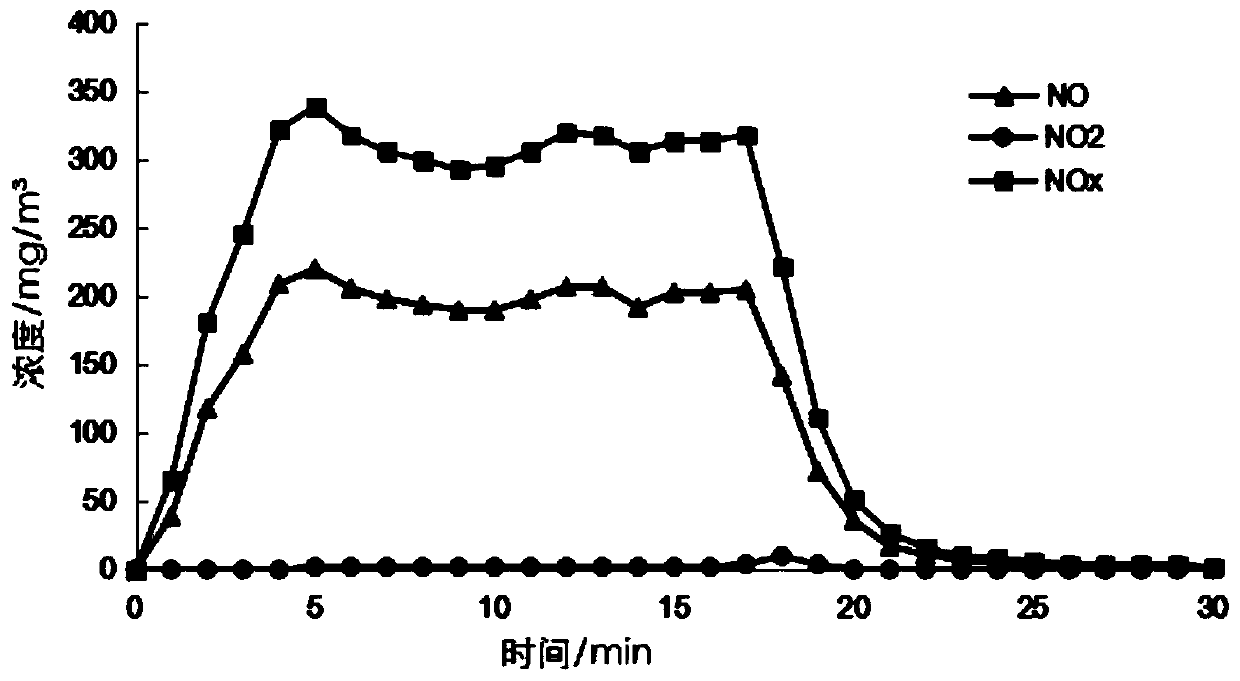
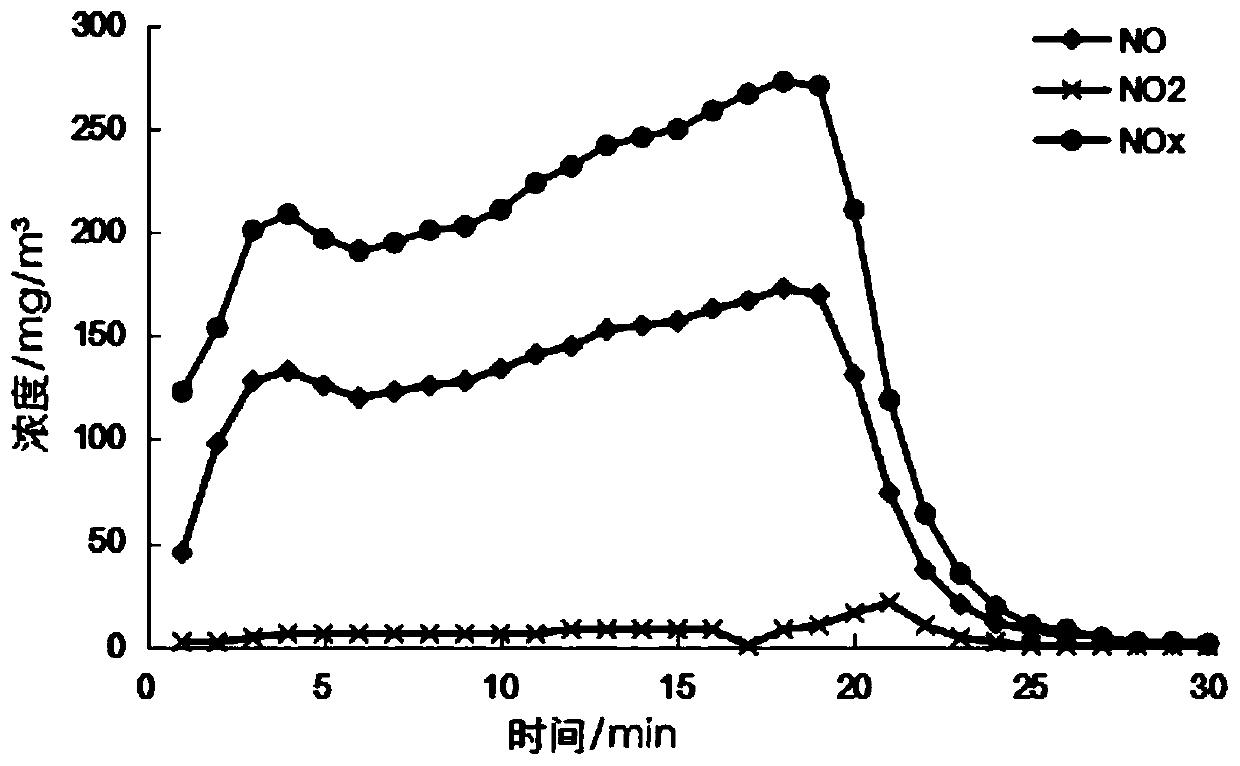
Iron ore sintering method capable of simultaneously improving sinter reducibility and reducing nitrogen oxide emission
The invention belongs to the technical field of iron ore sintering, and particularly relates to an iron ore sintering method capable of simultaneously improving sinter reducibility and reducing nitrogen oxide emission. The method comprises the steps of batching, primary mixing, secondary mixing, distributing, ignition and sintering, wherein low-carbon alcohol is added in the secondary mixing step.The inventor found through research that adding an appropriate amount of the low-carbon alcohol into the secondary mixing can adjust the sintering temperature during the sintering process and prolongthe sintering time. The sinter reducibility can be improved and also the nitrogen oxide emission is significantly reduced. Particularly, compared with a blank test, the content of ferrous oxide in the sinter can be reduced from 11% to 9.6%, and the sinter reducibility is significantly improved; at the same time, compared with the blank test, the total concentration of nitric oxide and nitrogen oxide in sintering flue gas is decreased.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
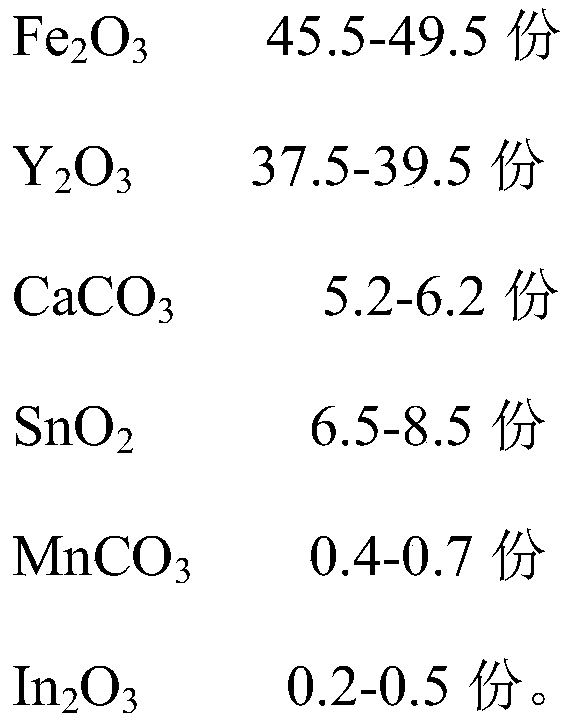
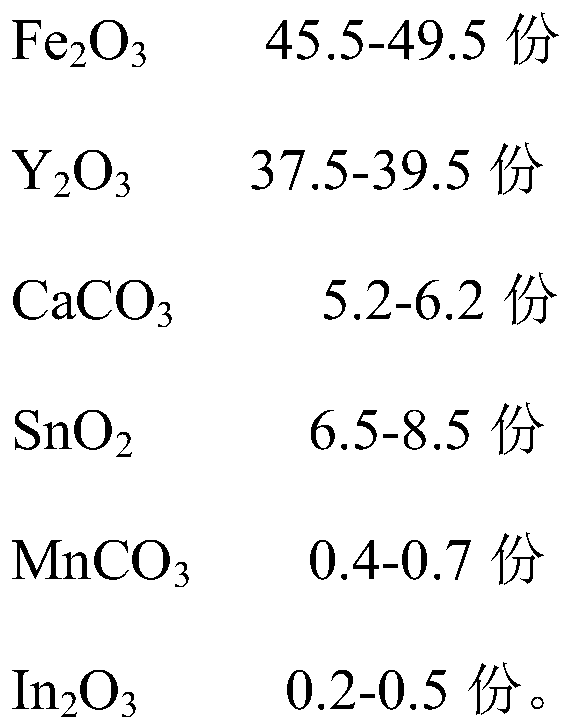
Microwave ferrite magnetic sheet, preparation method and applications thereof
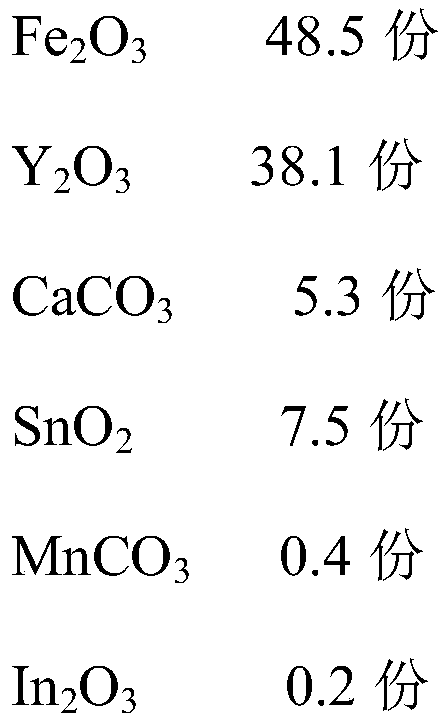
The invention provides a microwave ferrite magnetic sheet, a preparation method and applications thereof. The raw materials of the magnetic sheet comprise a main raw material and an auxiliary raw material, wherein the main raw material comprises an oxide of a Fe element and an oxide of a Y element, and the auxiliary raw material comprises Ca element, Sn element, Mn element and In element. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) mixing the raw materials according to the formula ratio, and carrying out first crushing to obtain a first crushing material; 2) pre-sintering the first crushing material to obtain a pre-sintered material; 3) carrying out second crushing on the pre-sintered material to obtain a second crushing material; and (4) granulating and molding the second crushing material, and sintering to obtain the microwave ferrite magnetic sheet. According to the microwave ferrite magnetic sheet provided by the invention, the saturation magnetization intensity of thematerial is improved by adjusting the formula, so that the size of an isolator is reduced, and the high saturation magnetization intensity can increase the bandwidth of a device.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Method for preparing ultra-fine crystal WC-Co hard alloy
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A preparation method of a high-voltage ultra-small capacity non-solid electrolyte tantalum electrolytic capacitor
ActiveCN110797216BHigh strengthNot easy to drop blocks and missing cornersCapacitor manufactureElectrolysisTantalum capacitor
The invention belongs to the technical field of tantalum capacitor preparation, in particular to a method for preparing a high-voltage ultra-small capacity non-solid electrolyte tantalum electrolytic capacitor. By increasing the compaction density, changing the molding method, and increasing the sintering temperature and sintering time, the strength of the tantalum core is improved. Reinforced, the tantalum core is not easy to drop blocks and corners, and the impurities in the tantalum powder are effectively removed. Through the improved formation method, a tantalum core with excellent electrical properties is obtained. Combined with the aging process, the prepared non-solid electrolyte tantalum The voltage of the capacitor can reach 180V, and the capacitance can reach 0.047μF, which has the characteristics of high voltage and ultra-small capacitance.
Owner:CHINA ZHENHUA GRP XINYUN ELECTRONICS COMP ANDDEV CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of wc-co-cbn composite material
The invention belongs to the field of material preparation technology, and particularly relates to a method for preparing WC-Co-cBN composite materials. In the present invention, WC, metallic Co powder and cBN raw materials are first weighed in proportion and mixed evenly, and the ball mill is used for mixing. After the ball-milled mixed raw materials are dried in an oven at 50~200°C, they are then sieved through 100~300 mesh. After processing, put the dried raw materials into the mold and place them in a hot-pressing sintering furnace. The sintering furnace heats up to 1200~1400℃ at a speed of 30~50℃ / min and keeps it warm for 5~30 minutes. The pressure is maintained at 20 ~50MPa, WC-Co-cBN composite material was obtained. The present invention adopts the hot-pressing sintering method, with low sintering temperature and short sintering time, which can ensure that the cBN does not phase change, and can also make the material have a large shrinkage rate and high volume density, and the hot-pressing sintering energy consumption is small and the cost is low. Low, easy to operate, high safety factor.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
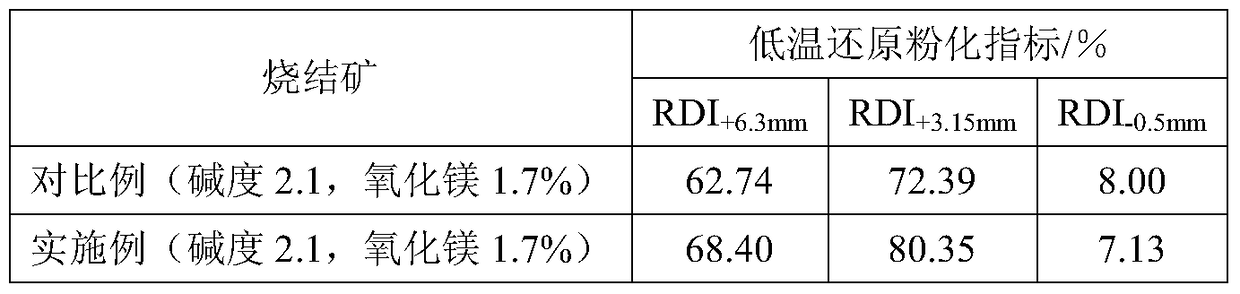
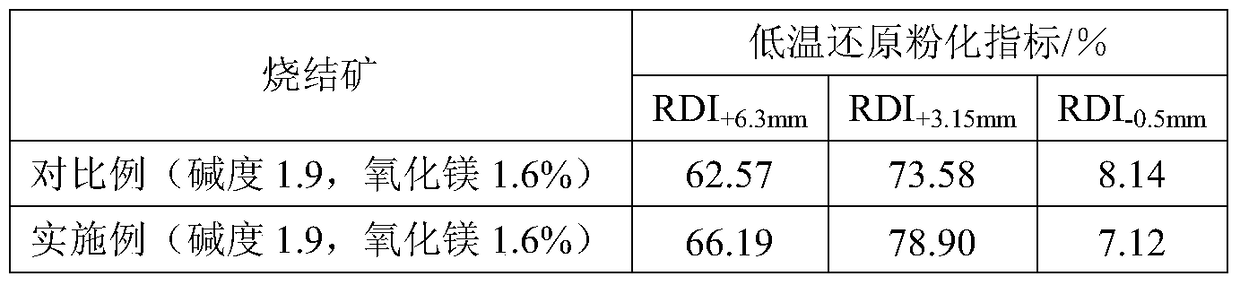
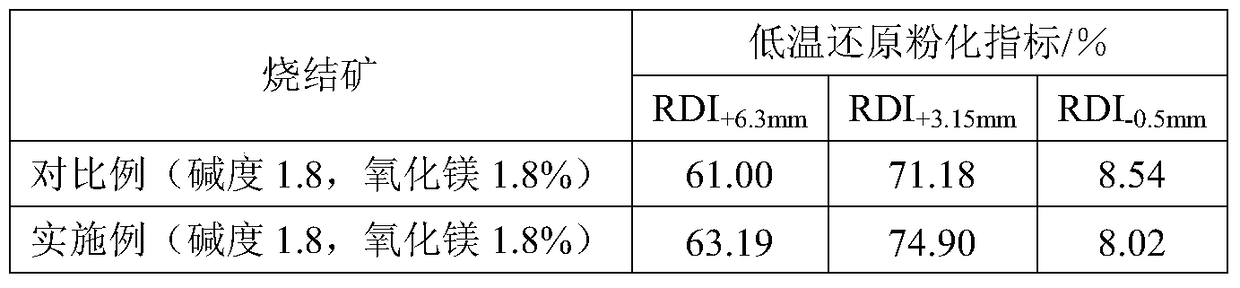
A method for improving the pulverization rate of low-temperature reduction of sintered ore
The invention discloses a method for improving low-temperature reduction powdering rate of sintered ores. Sintering raw materials are an iron-bearing mineral, a fusing agent and solid fuel. The method comprises the steps that firstly the iron-bearing mineral, the fusing agent and the coke powder are mixed, the mixture is screened respectively according to the three granularity levels of below 3 mm, 3-5 mm and above 5 mm, the mixture with the granularity level above 5 mm is put at the bottommost end of a material layer on a sintering trolley, the mixture with the granularity level of 3-5 mm and added with coking fly ash is put in the middle of the material layer on the sintering trolley, and the mixture with the granularity level below 3 mm and added with coking fly ash is put on the upmost portion of the material layer on the sintering trolley. The problem that the coking fly ash does not easily form sphere kernels and is difficult to adsorb is overcome, a large number of by-products of a coking plant are used, accordingly coke powder resources are saved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
High-strength core-preparing precoated sand and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN102688977BHigh strengthHigh melting pointFoundry mouldsFoundry coresHexamethylenetetraminePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a high-strength core-making coated sand. The weight ratio of each component is iron sand 4.8%-14.7%, mixed resin 1.65%-1.76%, urotropine 0.18%-0.24%, stearic acid Calcium 0.07%-0.11%, water 0.34%-0.54%, and the rest is silica sand. The preparation process is as follows: heating the base raw sand to 125-135°C and then adding it into the sand mixer; adding 1.7%-1.8% mixed resin with a weight of 1.7%-1.8% of the base raw sand into the sand mixer, mixing and grinding; when mixing When the temperature of the sand in the sand machine drops to 102-108°C, add urotropine solution and continue to mix and grind; when the temperature of the sand in the sand mixer drops to 70-75°C, add calcium stearate, mix and grind and then sieve Separation and cooling to obtain finished sand. The invention effectively controls the formation of N2, suppresses subcutaneous stomatal defects as high as 96%, breaks through the barriers of the prior art, and truly prevents the formation of nitrogen stomata.
Owner:西峡县众德汽车部件有限公司
Tungsten alloy target material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102139371BReduce heatingTake advantage ofVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh densityHigh energy
Owner:FOSHAN JUSHITAI POWDER METALLURGY CO LTD
Preparation method of porous film
ActiveCN106000123BControl pore structureHigh porositySemi-permeable membranesMembranesChemical reactionPore diameter
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a porous support body; (2) preparing a thick size containing raw material powder, a binder, a dispersant and a pore forming agent; (3) loading the size onto the porous support body, and drying to make a film billet; (4) sintering the film billet to make a porous film precursor; (5) removing the pore forming agent from the precursor to obtain a porous film with the thickness of 5-3,000 [mu]m, the average aperture of 0.05-100 [mu]m and the porosity of 40-90%. The preparation method has the following advantages: firstly, no chemical reaction occurs between the pore forming agent and the raw material powder, so that the ingredients of the porous film cannot be damaged; secondly, the pore forming agent is excellent in thermal stability and always occupies a certain space (place) in the sintering process; after sintering, the pore forming agent is removed, holes or pores are generated in situ; therefore, the whole technological process is simple, the hole structure of the porous film is easy to control, and the porosity is remarkably improved.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
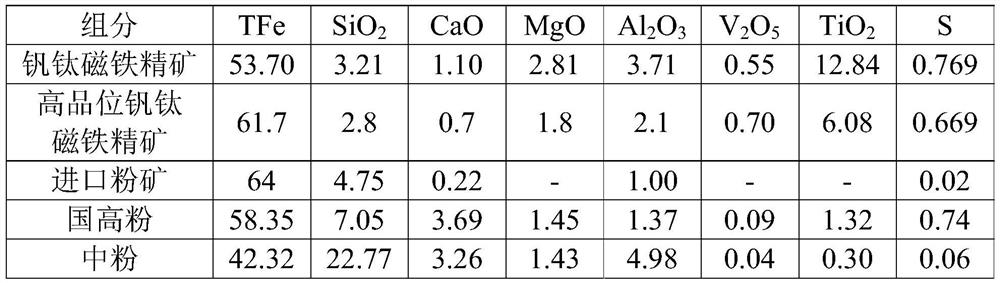
A method for improving the quality of sintered ore of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate
ActiveCN110564953BIncrease the average particle sizeIncreased drum strengthOre concentrateRaw material
The invention relates to the technical field of iron and steel metallurgy, and discloses a method for improving the quality of vanadium titanium magnetite concentrate sinter. The method comprises thefollowing steps: (1) drily mixing a sintering raw material and return mine, and thus obtaining a dry material; (2) adding water to the obtained dry material for primary mixing and secondary mixing, and controlling the water content of the obtained sintering mixture to be 7-7.2 wt%; and (3) distributing, igniting and sintering the obtained sintering mixture. High-grade vanadium titanium magnetite concentrate is added into vanadium titanium magnetite concentrate, and meanwhile the water content of the sintering mixture and the ratio of active ash in the sintering raw material are controlled to improve the tumbler strength of the sinter, so the quality of the vanadium titanium sinter is improved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com