Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
168 results about "YTTRIUM FLUORIDE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yttrium(III) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula YF3. It is not known naturally in 'pure' form. The fluoride minerals containing essential yttrium include tveitite-(Y) (Y,Na)6Ca6Ca6F42 and gagarinite-(Y) NaCaY(F,Cl)6. Sometimes mineral fluorite contains admixtures of yttrium.
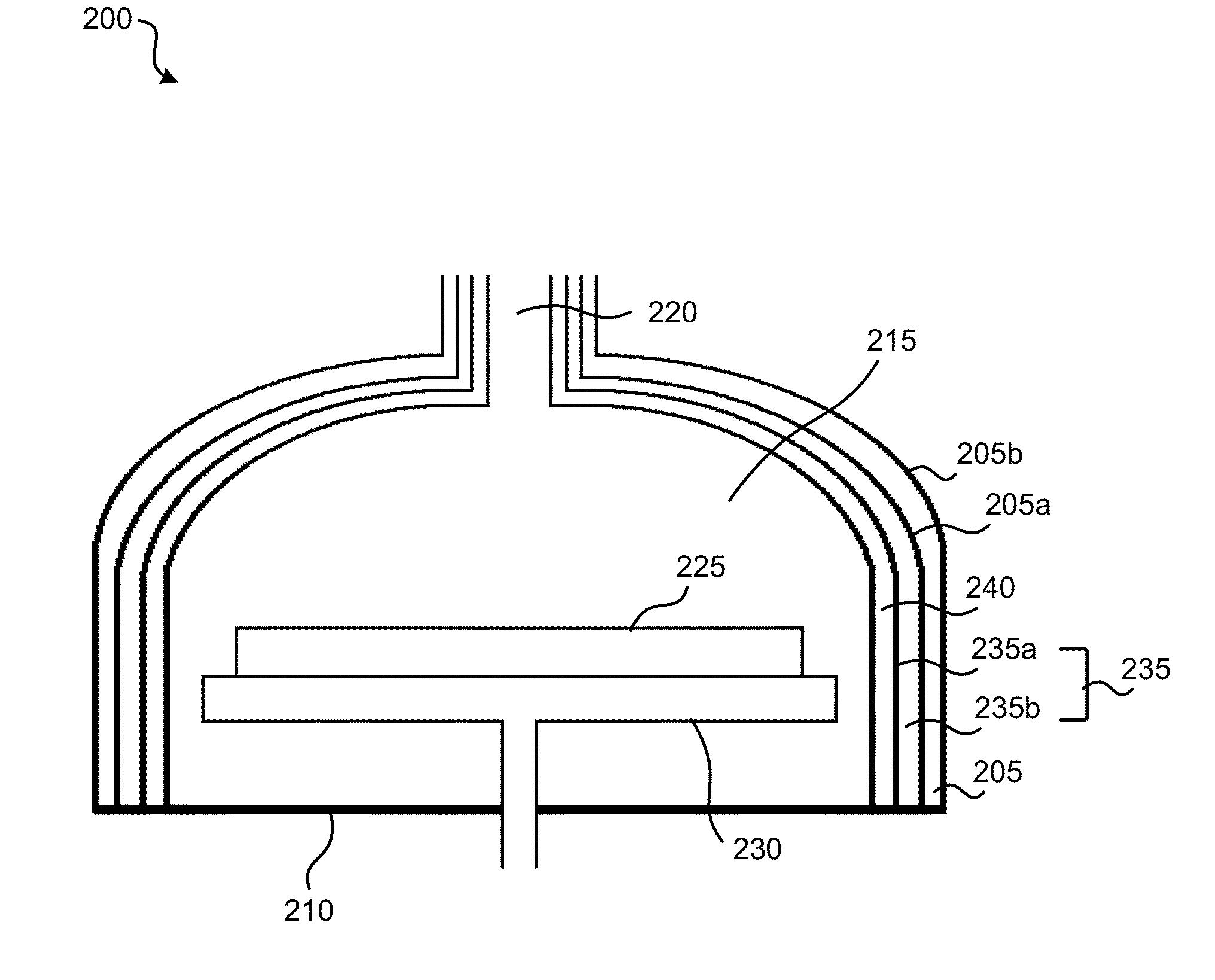
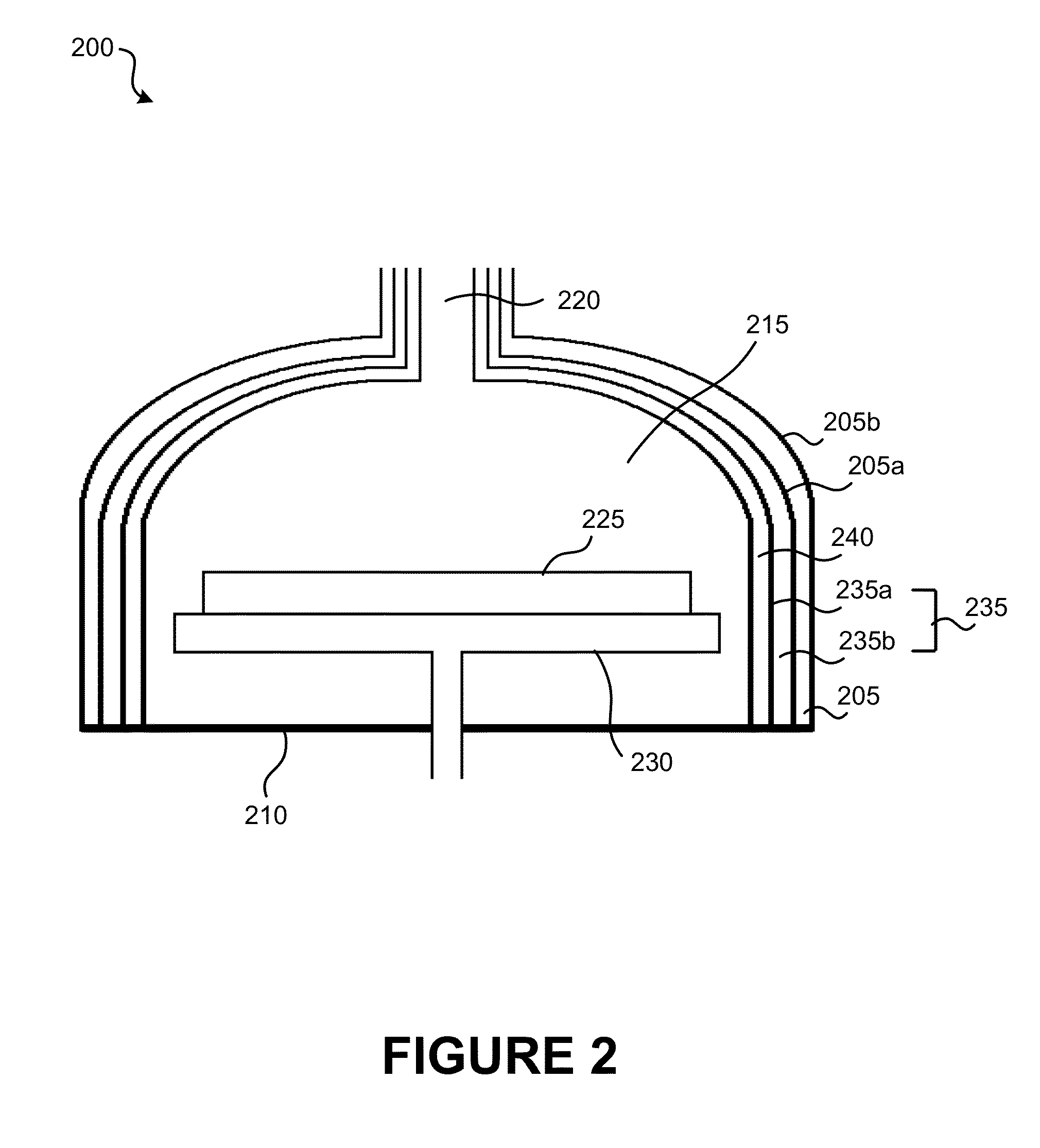
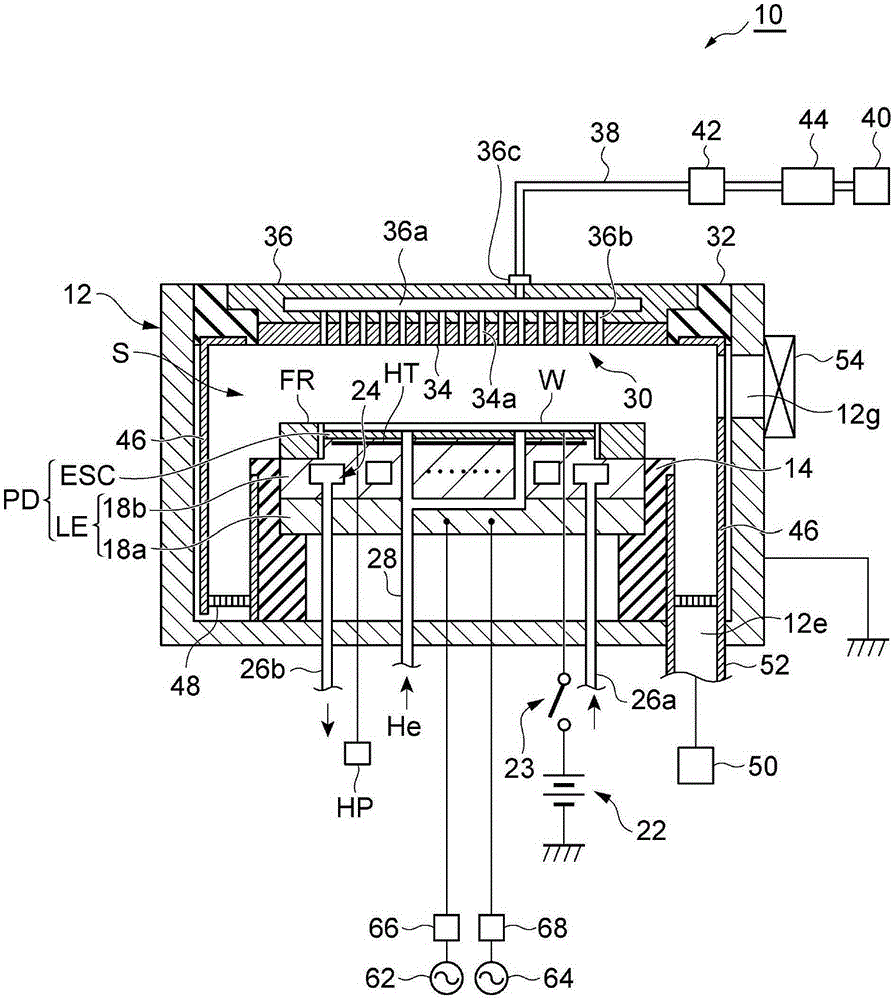
Conductive, plasma-resistant member
InactiveUS20070248832A1Improve corrosion resistanceSuppress particle contaminationMolten spray coatingNatural mineral layered productsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
An electrically conductive, plasma-resistant member adapted for exposure to a halogen-based gas plasma atmosphere includes a substrate having formed on at least part of a region thereof to be exposed to the plasma a thermal spray coating composed of yttrium metal or yttrium metal in admixture with yttrium oxide and / or yttrium fluoride so as to confer electrical conductivity. Because the member is conductive and has an improved erosion resistance to halogen-based corrosive gases or plasmas thereof, particle contamination due to plasma etching when used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment or flat panel display manufacturing equipment can be suppressed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
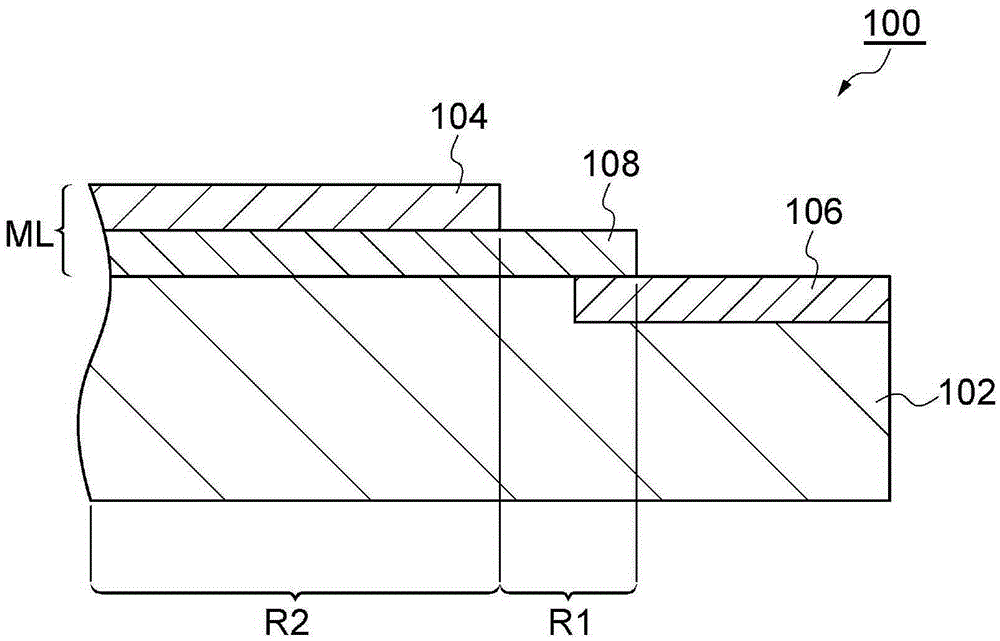
Multilayer rare-earth oxide coatings and methods of making
InactiveUS20130115418A1Control roughness/smoothnessPrecise maintenanceLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingRare earthOptoelectronics
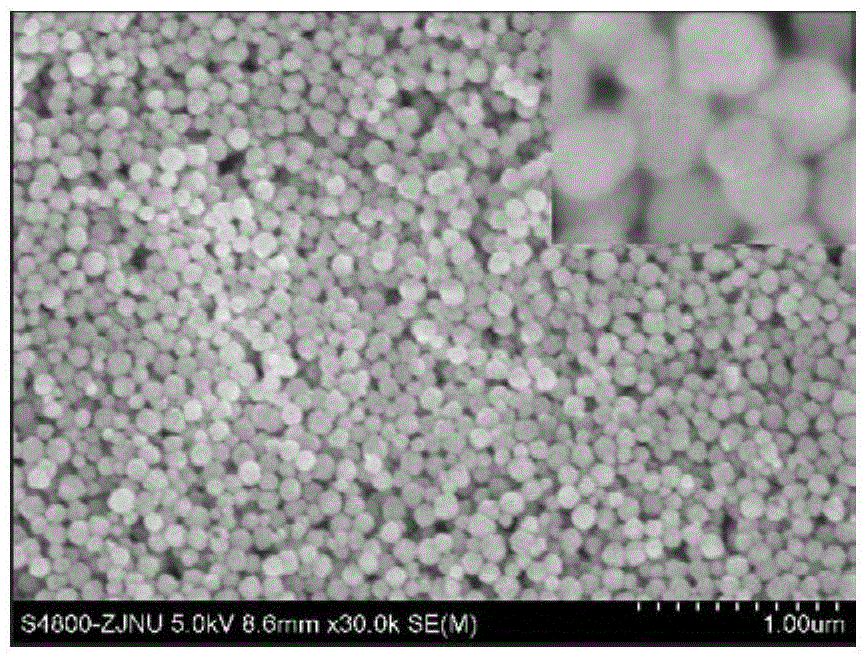
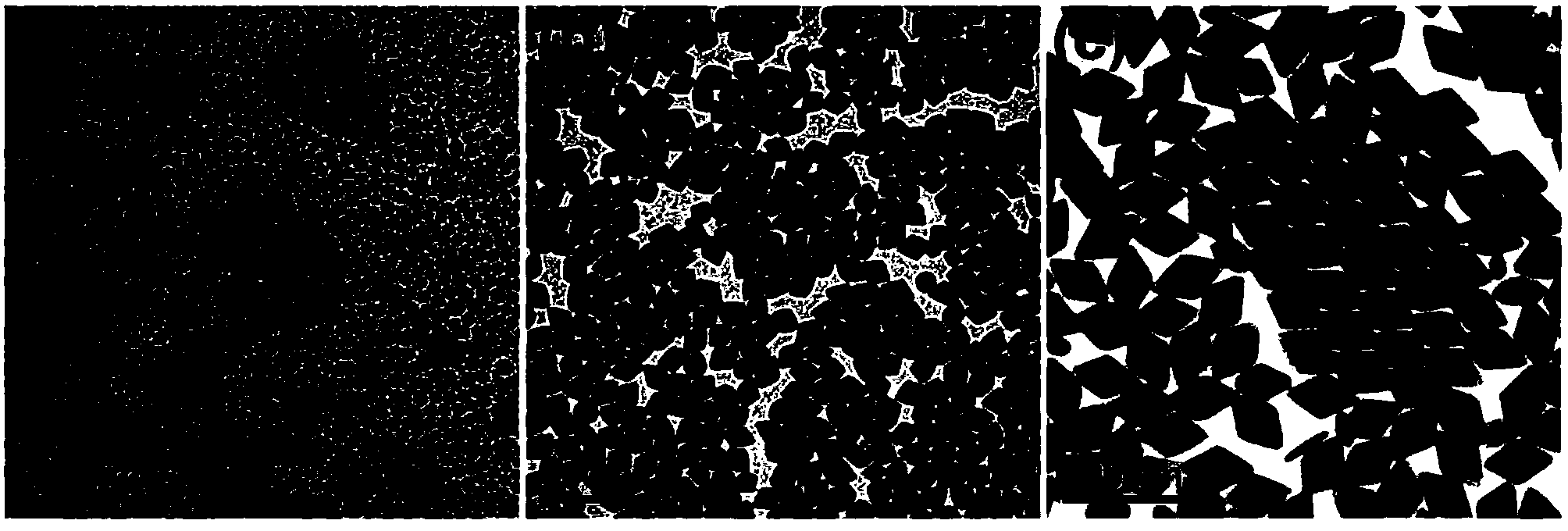
Embodiments relate to a coated substrate and a method of making and using the same. A plasma-spray coated layer may be formed on a substrate, wherein the plasma-sprayed coated layer comprises a rare-earth oxide (e.g., yttrium oxide), a rare-earth fluoride (e.g. yttrium fluoride), or a rare-earth silicate (e.g. yttrium silicate). An exposed surface of the plasma-spray coated layer may be irradiated to form a treated portion of the layer, wherein the treated portion of the layer has a mean spacing of local peaks (S value) between about 100 and 200 microns. A second layer may be formed on the treated portion of the plasma-spray coated layer, wherein the second layer comprises a dielectric material.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
Graphene and rare earth up-conversion fluorescent composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102952547AImprove responseRaw materials are non-toxicLuminescent compositionsRare earthUp conversion
The invention provides a graphene and rare earth up-conversion fluorescent composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of: using a graphite powder as a raw material to prepare graphite oxide by a Hummer method; conducting ultrasonic dispersion on 5-85mg of graphite oxide into 24-60mL of water; then adding Y (NO3), Yb (NO3) and Er (NO3) in a total molar weight of 0.05-1mmol by a stoichiometric ration of 78:20:2 into the graphite oxide dispersion; adding 0.02-0.5g of NaF and stirring for 5-10min; transferring the mixture to a 100mL reactor; reacting for 4-24h at 200-240 DEG C; naturally cooling to room temperature; centrifuging for separation and washing the reaction product with deionized water twice to obtain a graphene and yttrium fluoride up-conversion fluorescent powder composite material, which comprises a mixture of two or three selected from the followings: graphene-YF3:Yb, Er; graphene-(alpha) NaYF4:Yb, Er; and graphene-(beta) NaYF4:Yb, Er. The method provided by the invention is simple, employs non-toxic raw materials, and can change type of the earth up-conversion fluorescent material and up-conversion fluorescence properties of a final composite material by simply adjusting conditions of a hydrothermal reaction.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Upconversion fluorescent ink for inkjet printer and preparation method of upconversion fluorescent ink
The invention discloses an upconversion fluorescent ink for an inkjet printer. The upconversion fluorescent ink comprises, by weight, 1-10 parts of rare-earth doped upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles, 1600-2000 parts of ink solvent and 300-800 parts of thickener, the rare-earth doped upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles are sodium yttrium fluoride nanoparticles co-doped by rare-earth activator and rare-earth sensitizer, the rare-earth activator is erbium, thulium or holmium, and the rare-earth sensitizer is ytterbium or erbium. The upconversion fluorescent ink for the inkjet printer has the advantages of good anti-counterfeiting effect and long fixation time and storage life and can realize individualized instant anti-counterfeiting printing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
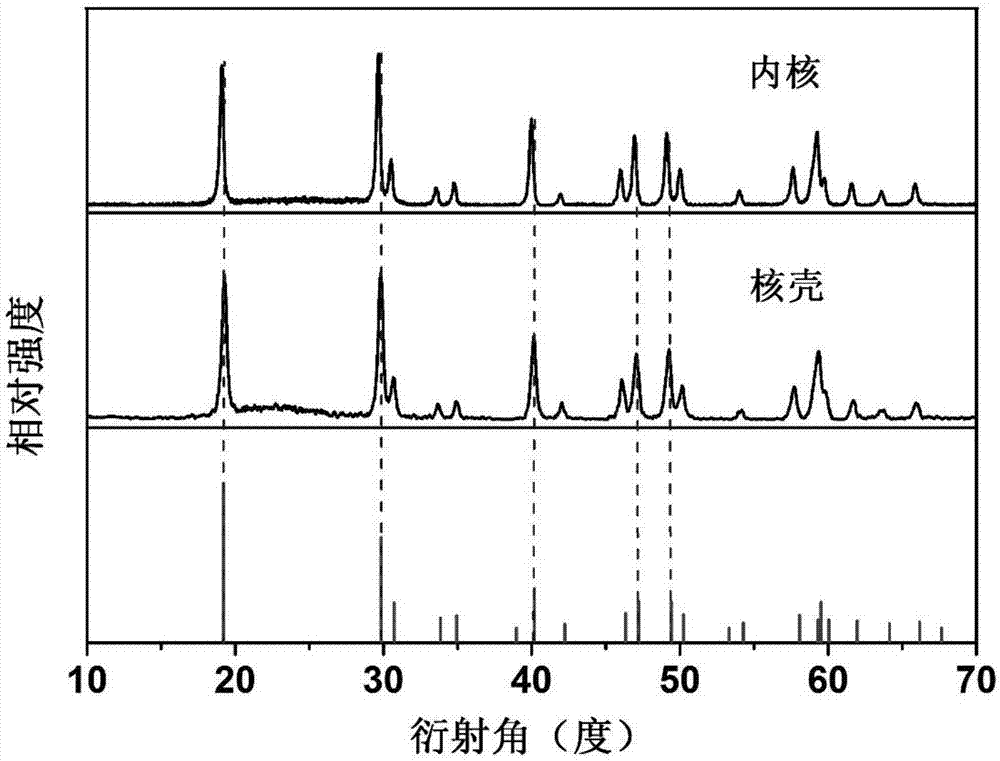
Rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride nanometer material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107033905AGood monodispersityImprove luminous efficiencyNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsBiological imagingRare earth
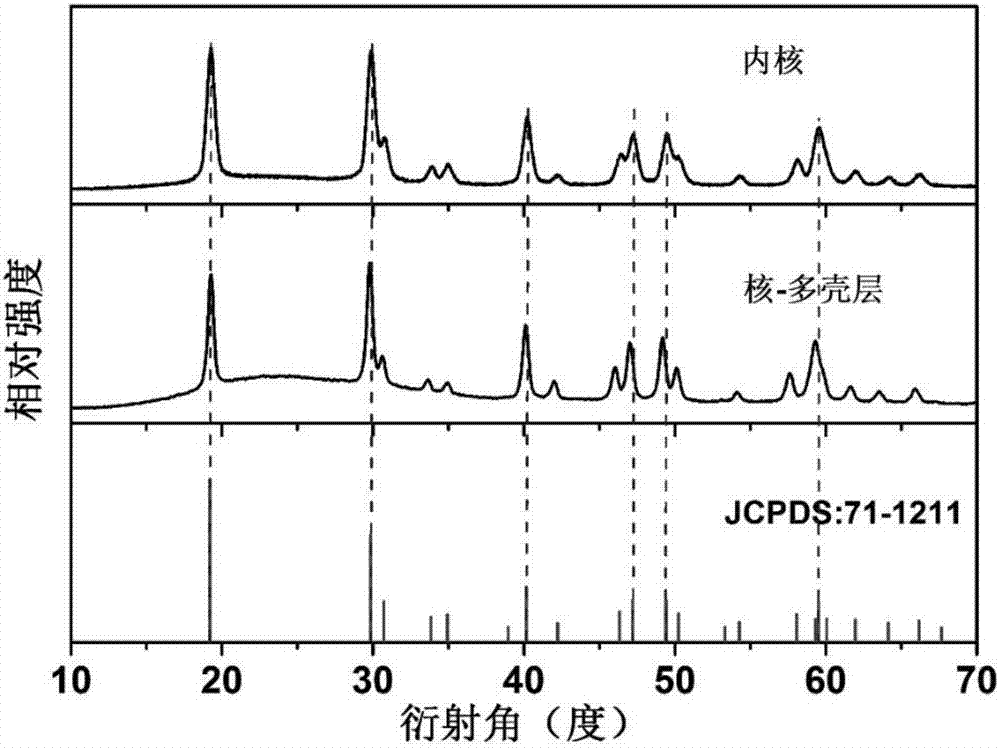
The invention relates to a rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride nanometer material and a preparation method and application thereof. A modified high-temperature coprecipitation method is adopted to synthesize the rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride nanometer material with upper conversion / lower transfer luminescence, at the same time, epitaxial growth is conducted on the basis of a core, a mono-layer core-shell structure nanometer material which is uniformly covered can be obtained, and a lithium yttrium fluoride based multi-layer core-shell nanometer material is further prepared. The three prepared and obtained materials are good in monodispersity, uniform in particle size and excellent in luminescent property, after acid pickling treatment, water-soluble nanometer particles can be used for biological detection and biological imaging.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Atomic layer deposition of protective coatings for semiconductor process chamber components
ActiveCN107313027ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingFluorideAtomic layer deposition
The invention relates to atomic layer deposition of protective coatings for semiconductor process chamber components. A multi-component coating composition for a surface of a semiconductor process chamber component comprising at least one first film layer of a yttrium oxide or a yttrium fluoride coated onto the surface of the semiconductor process chamber component using an atomic layer deposition process and at least one second film layer of an additional oxide or an additional fluoride coated onto the surface of the semiconductor process chamber component using an atomic layer deposition process, wherein the multi-component coating composition is selected from the group consisting of YOxFy, YAlxOy, YZrxOy and YZrxAlyOz.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Conductive, plasma-resistant member
InactiveUS7655328B2Solve the lack of resistanceReduce abnormal dischargeMolten spray coatingNatural mineral layered productsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
An electrically conductive, plasma-resistant member adapted for exposure to a halogen-based gas plasma atmosphere includes a substrate having formed on at least part of a region thereof to be exposed to the plasma a thermal spray coating composed of yttrium metal or yttrium metal in admixture with yttrium oxide and / or yttrium fluoride so as to confer electrical conductivity. Because the member is conductive and has an improved erosion resistance to halogen-based corrosive gases or plasmas thereof, particle contamination due to plasma etching when used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment or flat panel display manufacturing equipment can be suppressed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
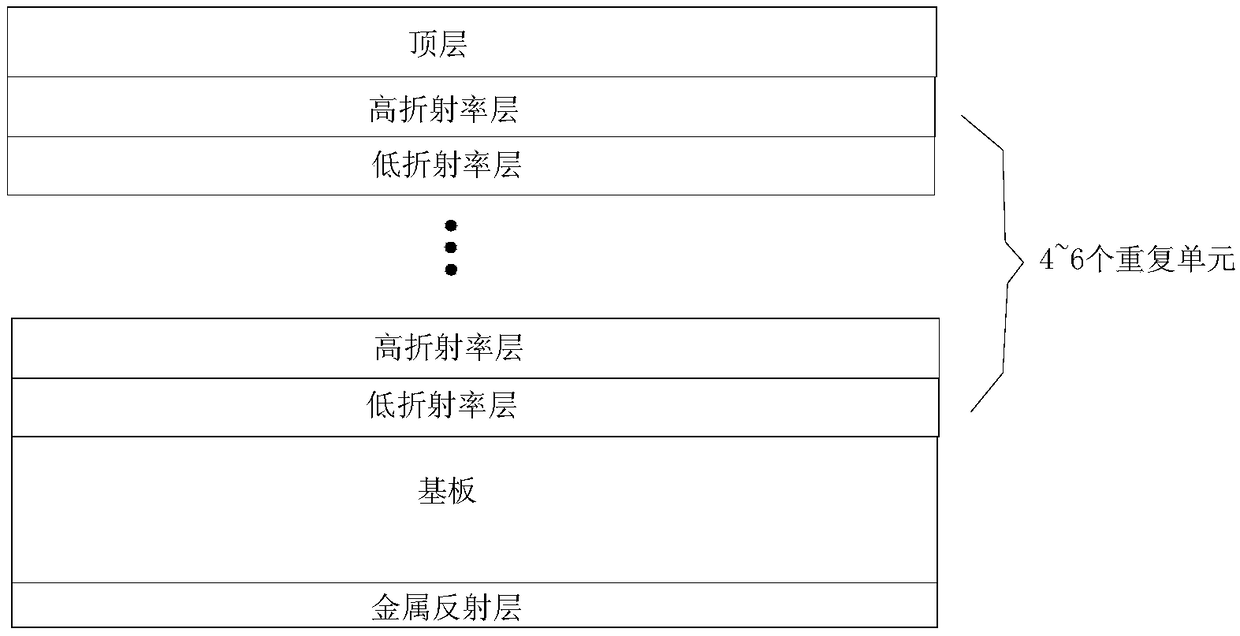
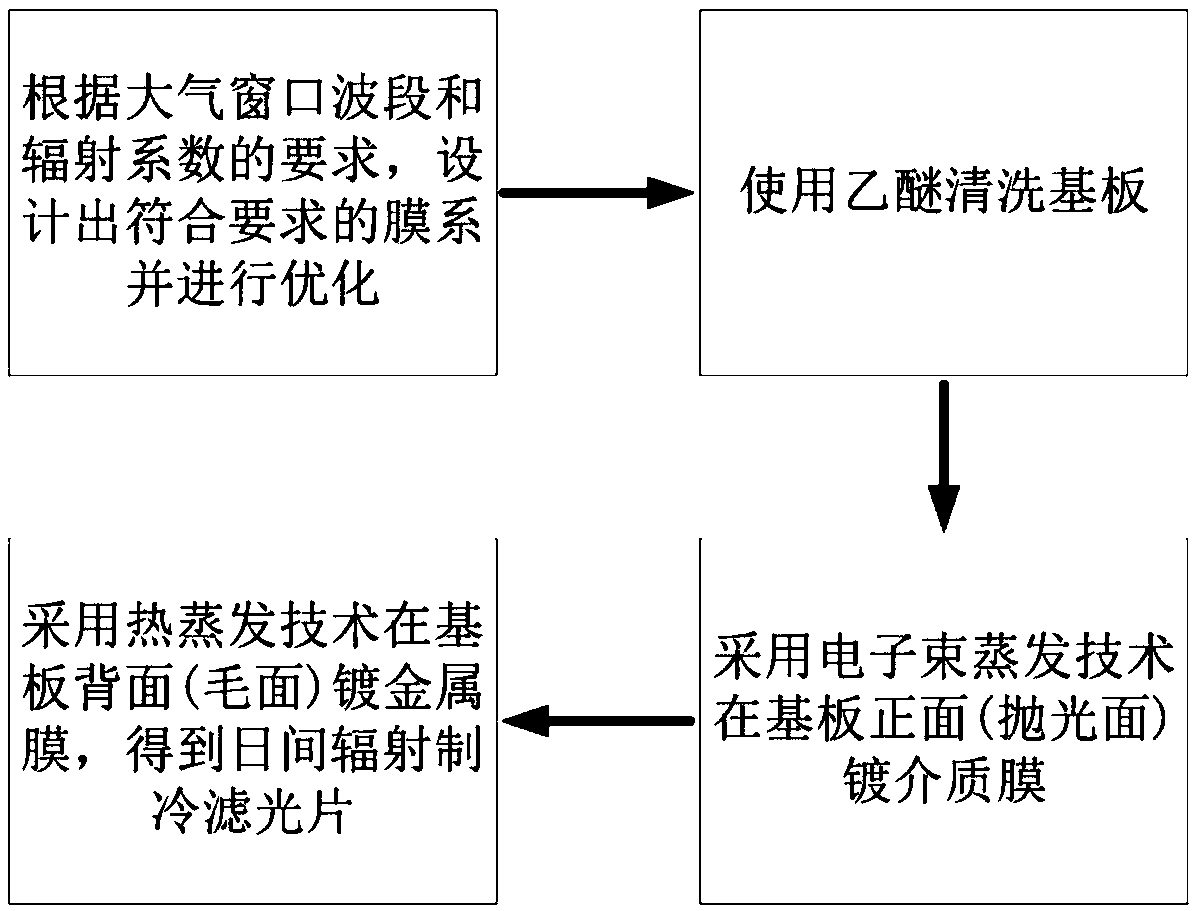
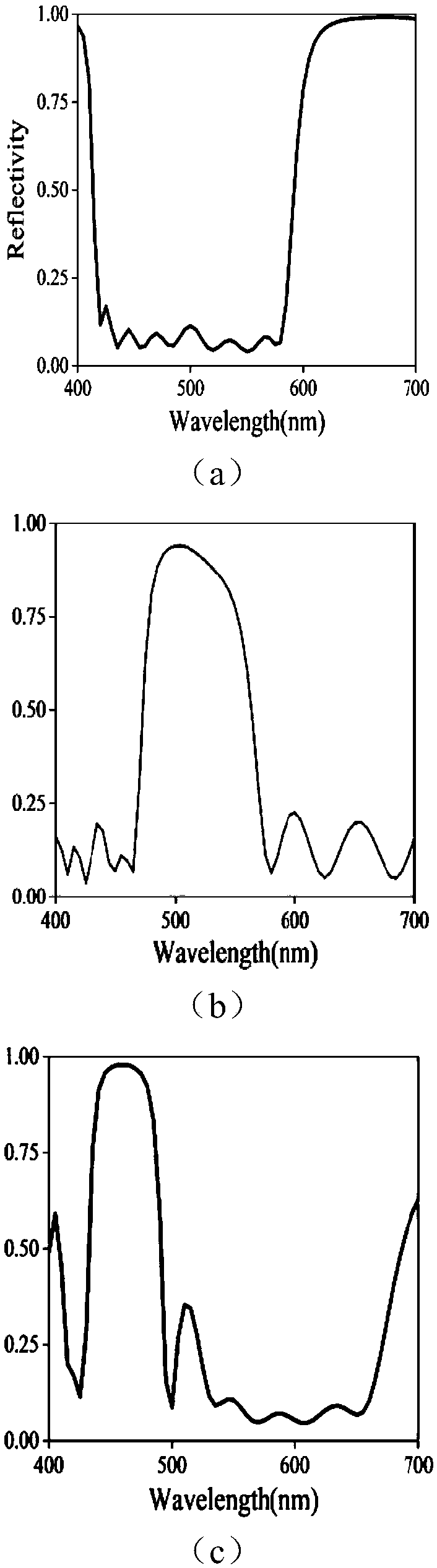
Radiation refrigeration optical filter, method for preparing same and application of radiation refrigeration optical filter
ActiveCN108710169ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costMountingsSilicon dioxideResonant absorption
The invention discloses a radiation refrigeration optical filter which comprises a substrate. A single surface of the substrate is polished, a metal reflecting layer is arranged on a rough surface ofthe substrate, and an intermediate layer and a top layer are sequentially arranged on the polished surface of the substrate; the intermediate layer comprises layers A and layers B which are alternately arranged; the thicknesses of each layer A and each layer B are 50-400 nm; the layers A are made of silicon dioxide or aluminum oxide, and the layers B are made of titanium dioxide or silicon nitrideor silicon carbide; alternatively, the layers A are made of titanium dioxide or aluminum oxide, and the layers B are made of silicon dioxide or silicon nitride or silicon carbide; the top layer is made of ytterbium fluoride or yttrium fluoride or zinc sulfide; multi-resonant absorption enhancers in wavebands of atmospheric transparent windows (with the wavebands of 8-13 micrometers) are jointly formed by the intermediate layer and the top layer. Compared with the traditional optical filters, the radiation refrigeration optical filter has the advantages that the radiation refrigeration opticalfilter can work in intense light for a long time, and radiation refrigeration can be passively implemented by the radiation refrigeration optical filter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
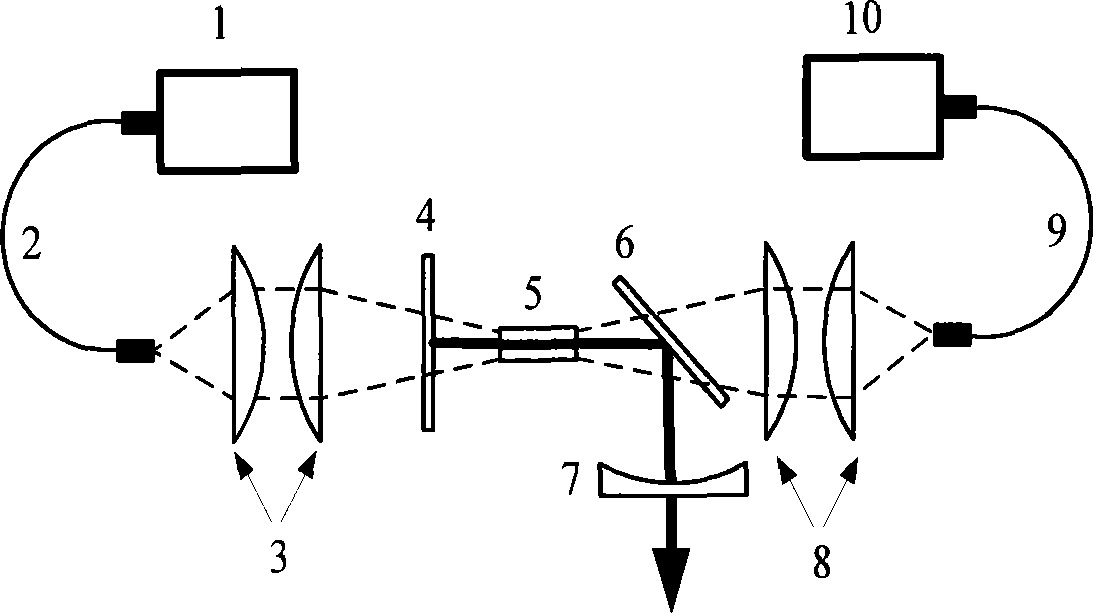
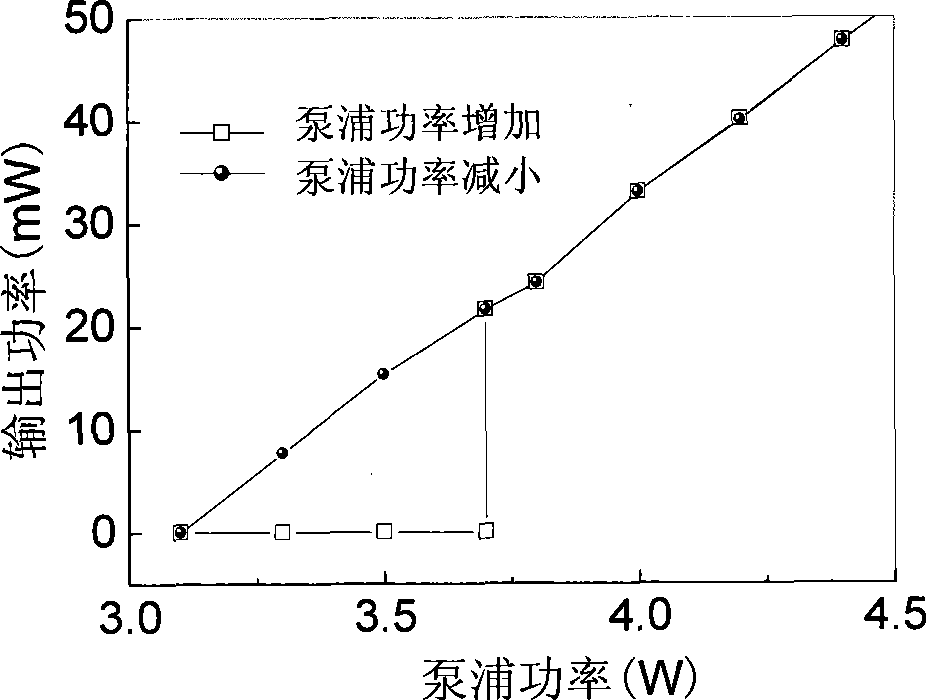
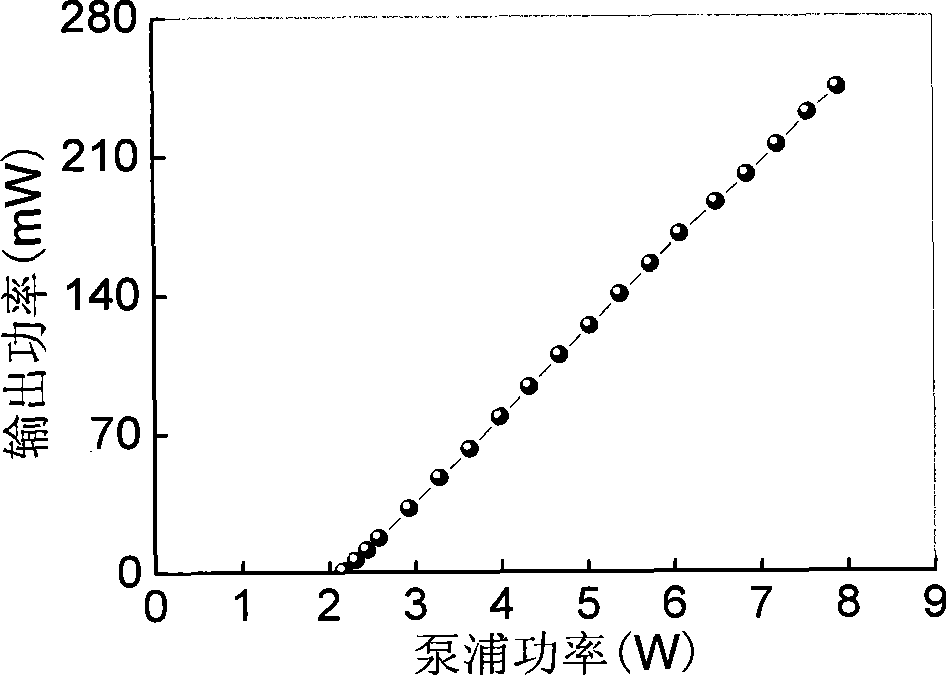
Bistable Tm,Ho:YLE laser with bistable zone and adjustable width -
InactiveCN101465513AReduce volumeSimple structureOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavityLithium
The invention provides an optical bistable Tm, Ho:YLF laser, the width of pumping bistable area of a laser diode end surface of which can be adjusted; the optical bistable Tm, Ho:YLF laser comprises a laser diode pumping source, an optical fiber, a coupling lens, a resonant cavity and a thulium and holmium codoping lithium yttrium fluoride crystal; the optical bistable Tm, Ho:YLF laser is characterized in that: pumping light given off by the two laser diode pumping sources enters in the resonant cavity by respectively passing through the optical fiber and the coupling lens; the resonant cavity is an L-shaped right-angle folding cavity which is composed of a back-cavity mirror, a 45 degrees plane folding mirror and an output mirror; the front end of the resonant cavity is the back-cavity mirror, the rear end thereof is the 45 degrees plane folding mirror, and the lower end thereof is the output mirror; the thulium and holmium codoping lithium yttrium fluoride crystal is arranged in the resonant cavity. The laser has small volume, simple structure and low cost; by injecting pumping light to an absorption area, the absorption performance of the absorption area is changed, thus achieving the purpose of adjusting the width of the bistable area and leading the laser to have large adjusting magnitude and convenient usage.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
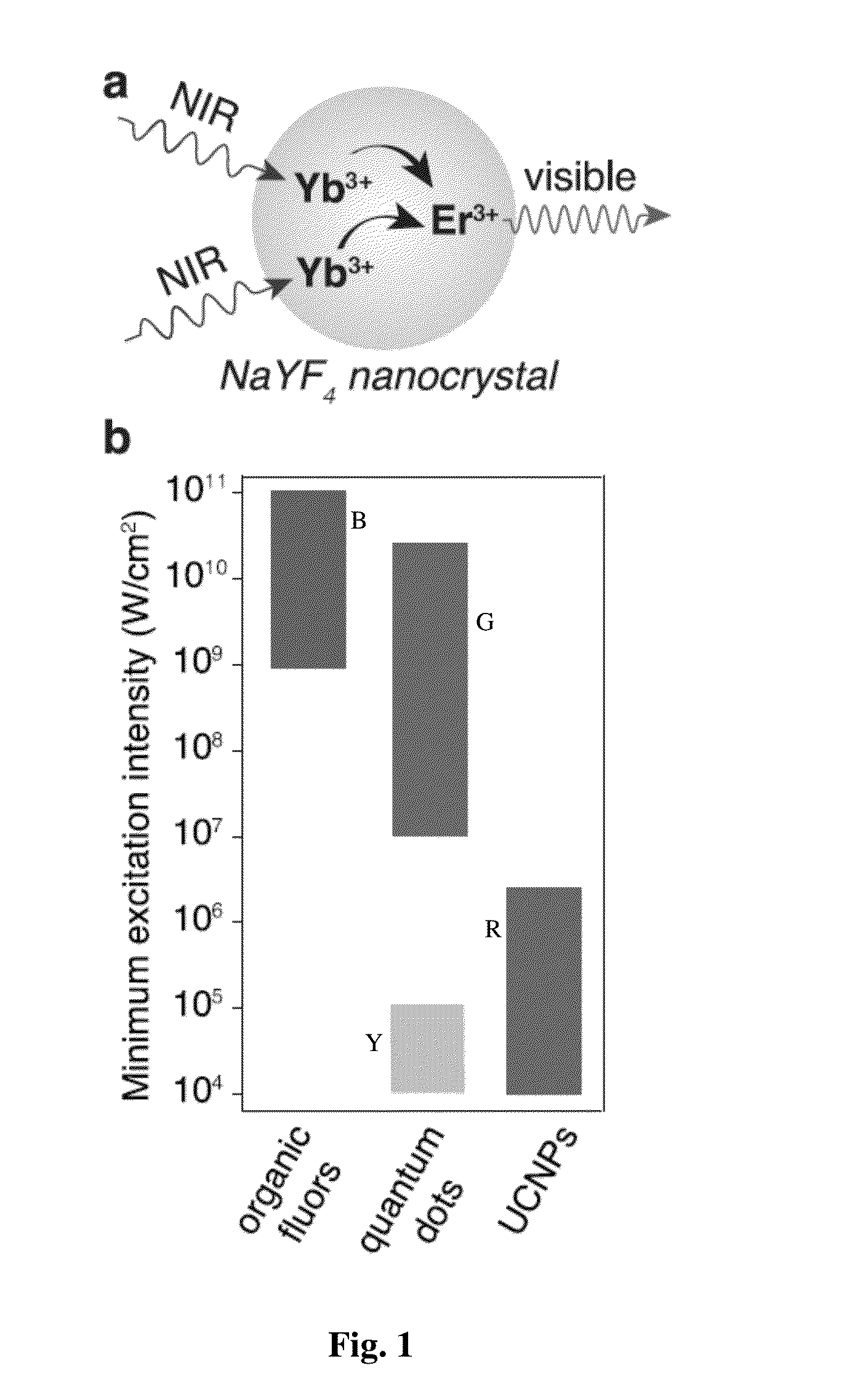
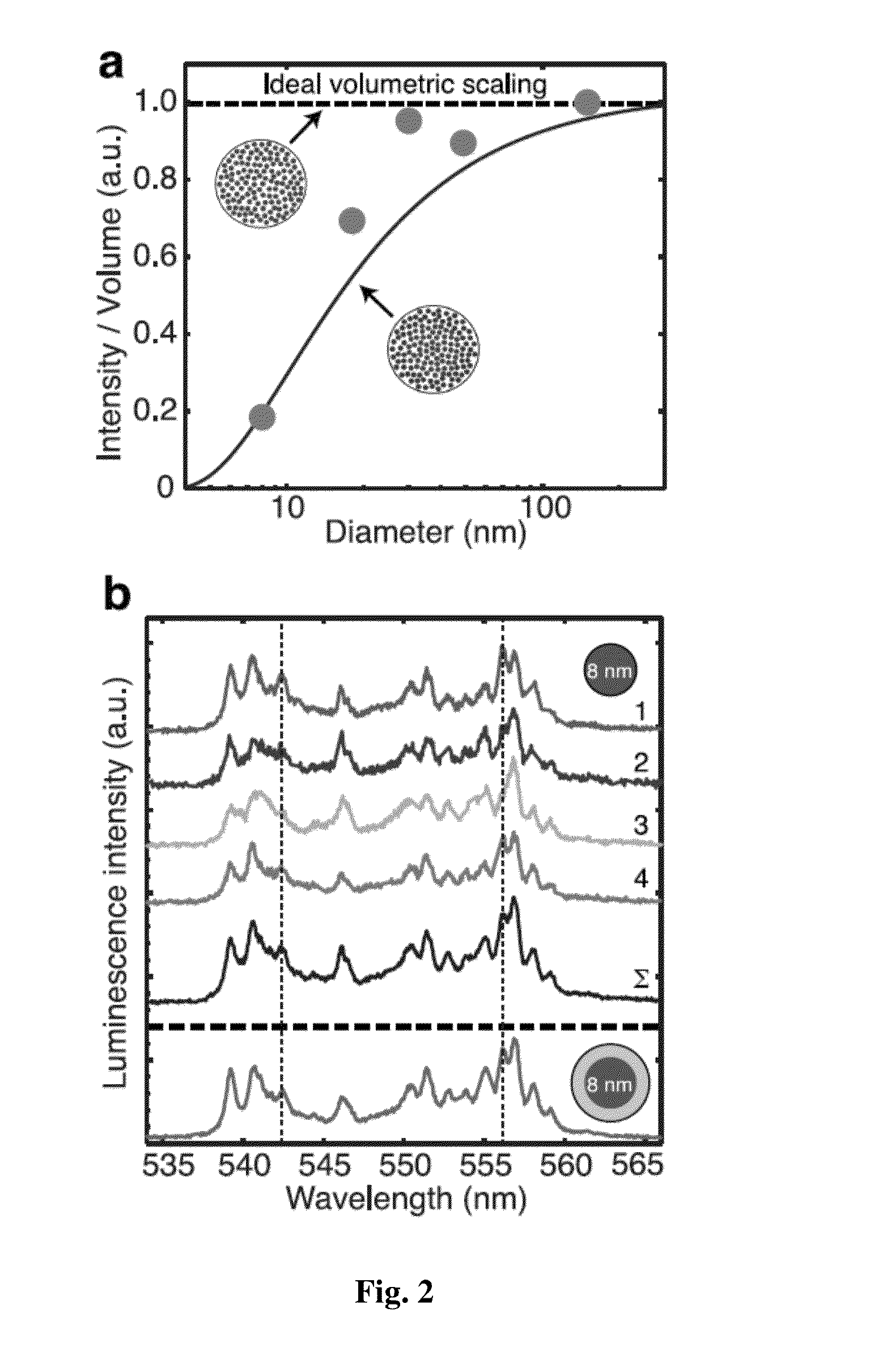
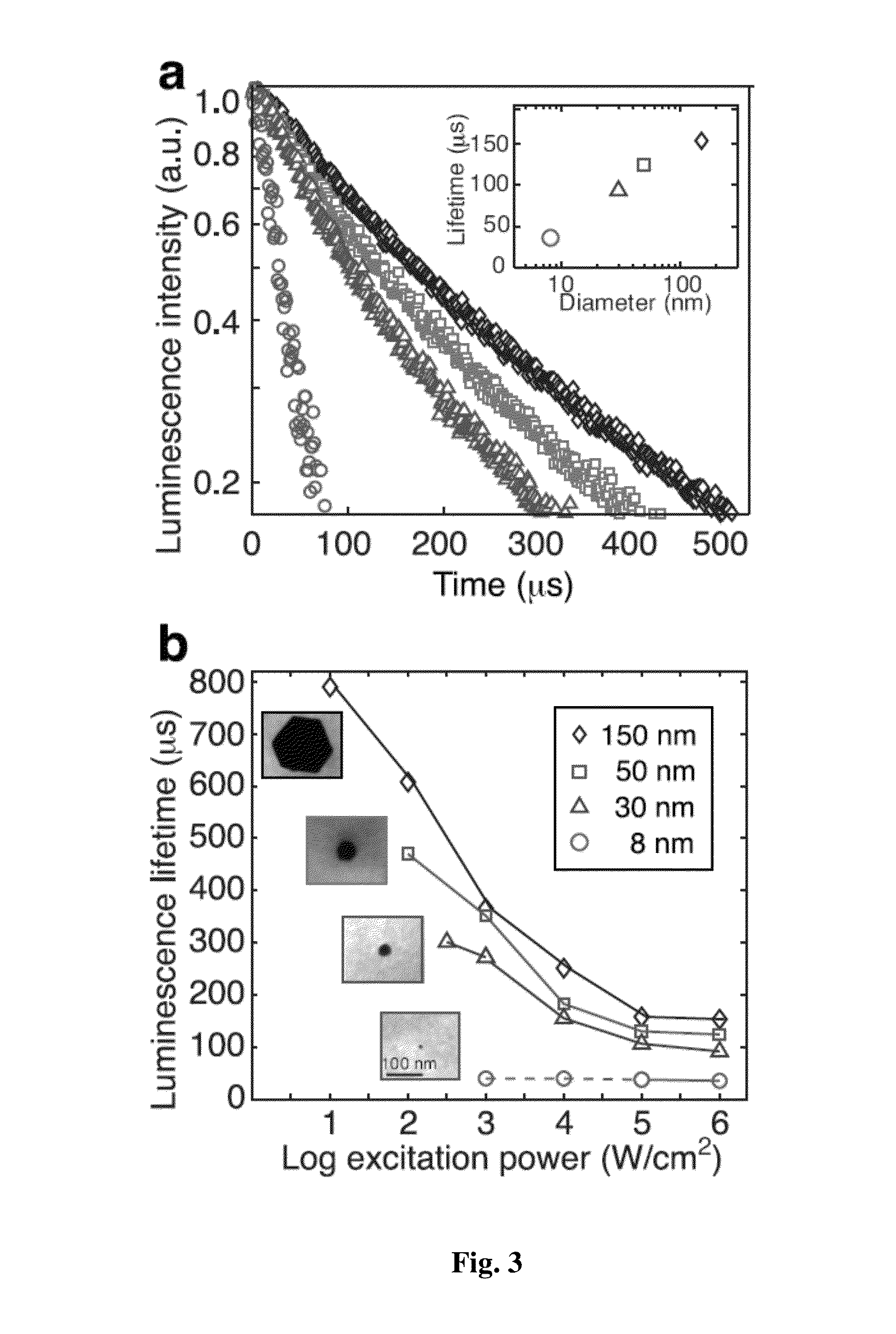
Engineering Bright Sub-10-nm Upconverting Nanocrystals for Single-Molecule Imaging
InactiveUS20150241349A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryImaging conditionLanthanide
Various embodiments of the invention describe the synthesis of upconverting nanoparticles (UCNPs), lanthanide-doped hexagonal β-phase sodium yttrium fluoride NaYF4:Er3+ / Yb3 nanocrystals, less than 10 nanometers in diameter that are over an order of magnitude brighter under single-particle imaging conditions than existing compositions, allowing visualization of single UCNPs as small (d=4.8 nm) as fluorescent proteins. We use Advanced single-particle characterization and theoretical modeling is demonstrated to find that surface effects become critical at diameters under 20 nm, and that the fluences used in single-molecule imaging change the dominant determinants of nanocrystal brightness. These results demonstrate that factors known to increase brightness in bulk experiments lose importance at higher excitation powers, and that, paradoxically, the brightest probes under single-molecule excitation are barely luminescent at the ensemble level.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Erbium-doped barium-yttrium-fluoride-nanocrystalline containing transparent oxyfluoride glass ceramic and preparation thereof
The invention relates to erbium-doped transparent glass ceramic containing nanocrystalline barium yttrium fluoride and the preparation method thereof, which relates to the field of luminescent material. The components of glass ceramic are (mole ratio): 40SiO2-25Al2O3-xBaCO3-10YF3-yBaF2-zErF3 (x=5-20, z=0.1-3.0, y=25-x-z). The invention is prepared by melt-spinning technique and adopts SiO2, Al2O3, BaCO3, YF3, BaF2 and ErF3 powder as raw materials, and the raw materials are well mixed, heated to 1300-1600 DEG C and the temperature is preserved for 1-4 hours, and then melting fluid is prepared into vitreous body; the vitreous body is annealed to relieve internal stress, continues to be heated to 650-800 DEG C, the temperature is preserved for 1-10 hours, and the obtained nanocrystalline has extremely high solid solubility of erbium ion. With the infrared excitation, the up-conversion emission intensity of the glass ceramic is greatly improved by adjusting heat treatment temperature.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing Er-Yb co-blended yttrium fluoride up-conversion luminescence hollow nanofibers
InactiveCN102965762AInorganic material artificial filamentsHollow filament manufactureUpconversion luminescenceMaterials preparation
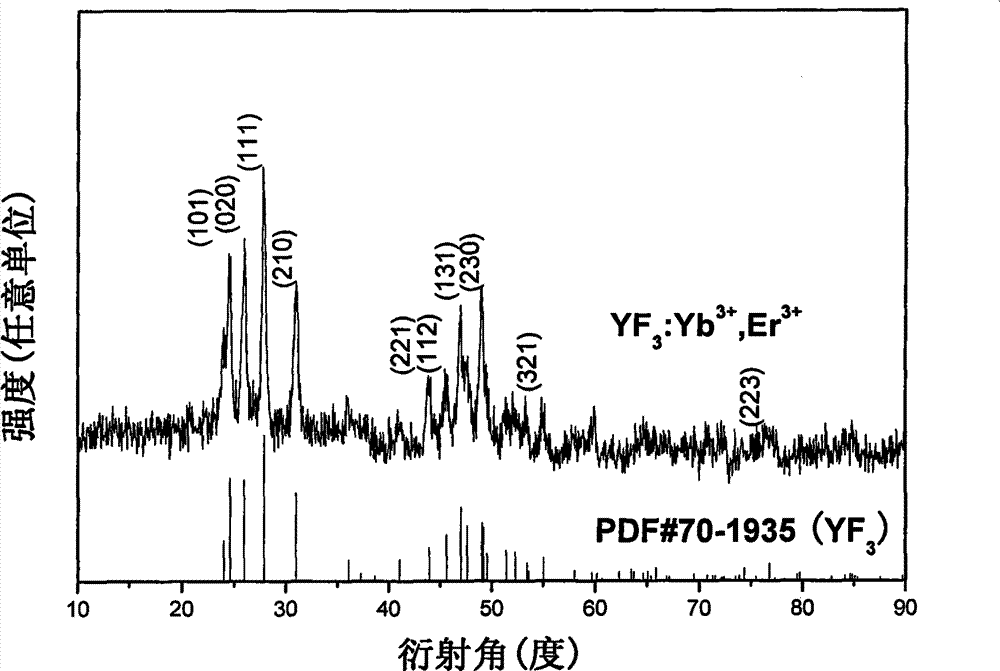
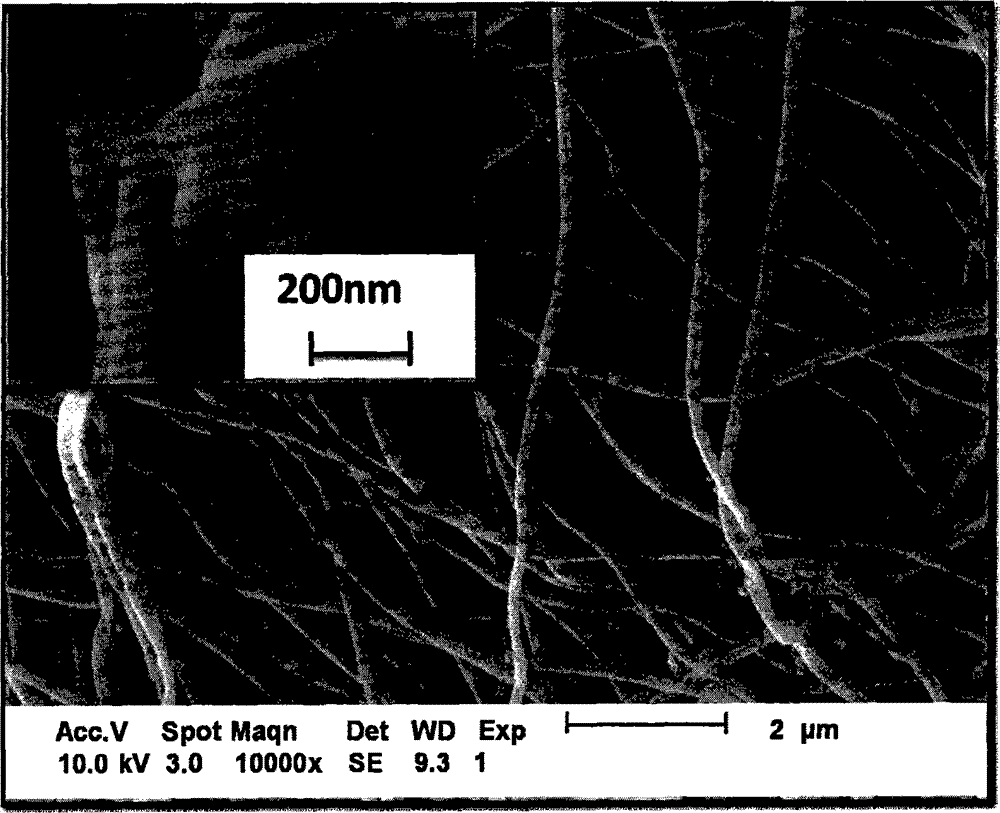
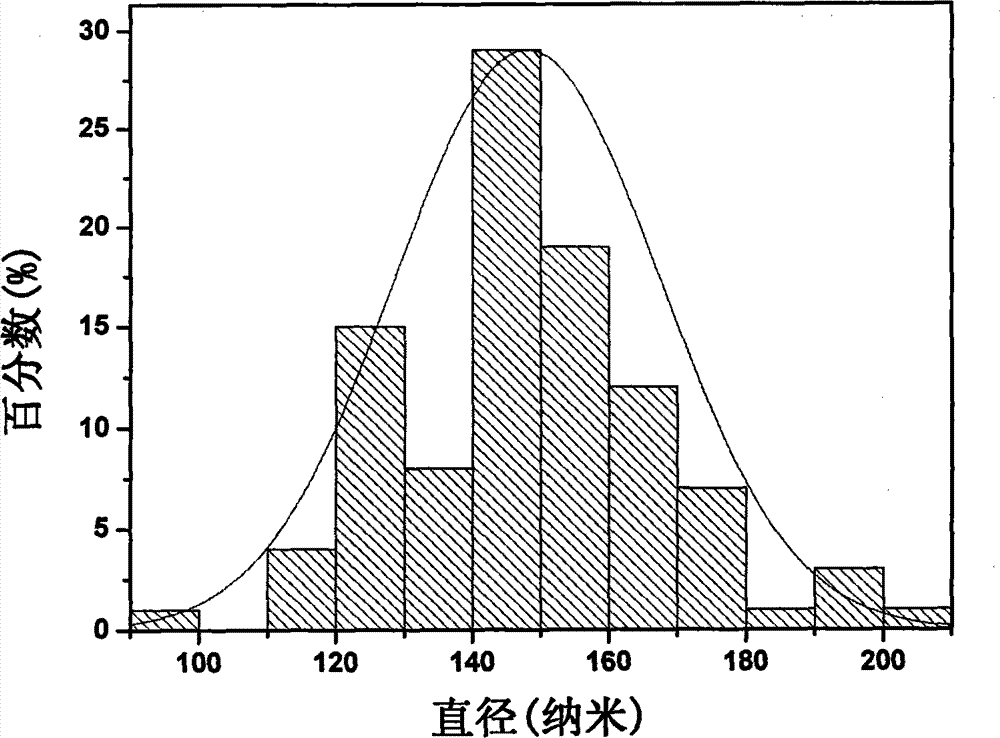
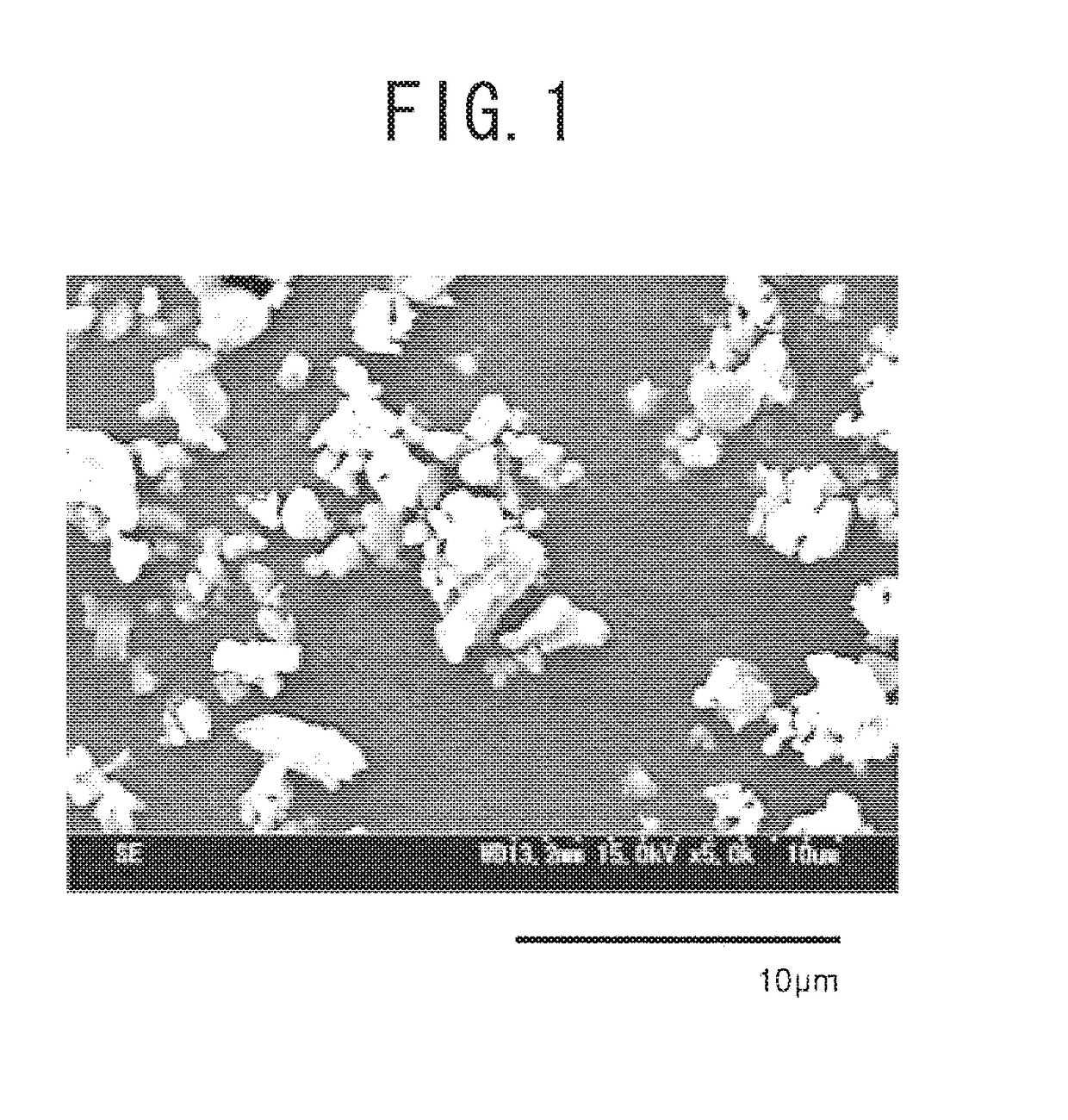
The invention relates to a method for preparing Er-Yb co-regenerated yttrium fluoride up-conversion luminescence hollow nanofibers, belong to the technical field of nano-material preparation. The invention comprises four steps: (1) preparing a spinning liquid; (2) preparing a PVP / [Y(NO3)3+Er(NO3)3+Yb(NO3)3] original composite fiber by using a uniaxial electrospinning technology; (3) preparing Y2O3:Er<3+>, Yb<3+> hollow nanofibers by heating the composite fiber; and (4) preparing YF3:Er<3+>, Yb<3+> hollow nanofibers by using a double crucible method. The YF3:Er<3+>, Yb<3+> hollow nanofibers have a good crystallinity, a diameter of 148 + / - 20 nm, and a length of more than 30 [mu]m. The hollow nanofibers are important green fluorescent materials. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, can be mass-produced, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Composite photocatalytic antibacterial material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105772040AAvoid yieldAvoid energy consumptionBiocidePhysical/chemical process catalystsSolventUltrasonic dispersion
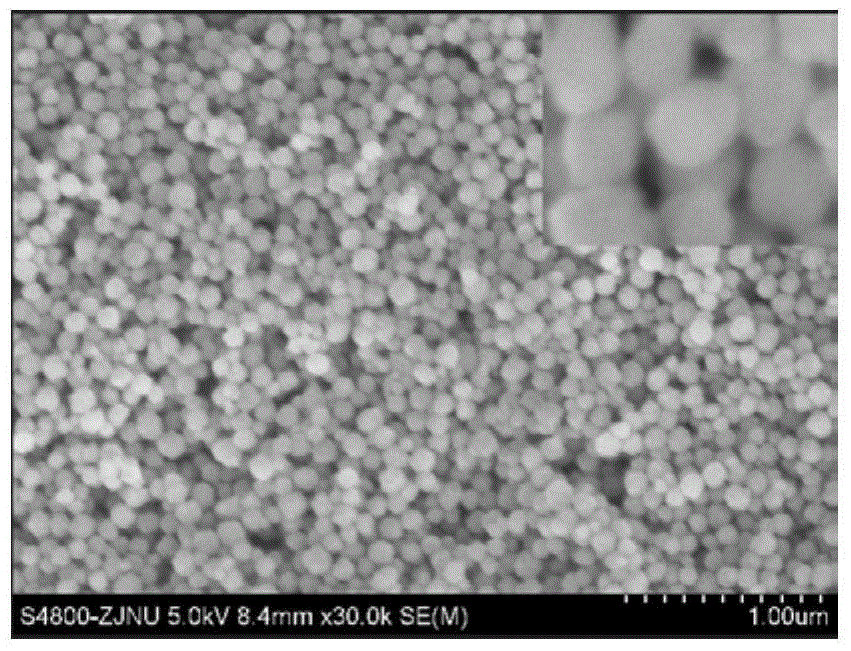
The invention discloses a composite photocatalytic antibacterial material and a preparation method thereof; particularly, a ytterbium-erbium co-doped sodium yttrium fluoride (NaYF4:Yb,Er) and manganese-doped zinc oxide are combined to prepare the photocatalytic antibacterial material driven by visible / near-infrared light. The preparation method comprises the steps: together dissolving sodium chloride, yttrium acetate, ytterbium acetate, erbium acetate and ammonium fluoride in an ethylene glycol / water mixed solvent, and carrying out a microwave assisted solvothermal reaction to obtain NaYF4:Yb,Er spherical nanoparticles; dispersing the NaYF4:Yb,Er in an isopropanol / water / ammonia water mixed solvent, adding tetraethyl orthosilicate, and carrying out hydrolysis for 5 h, to obtain an NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2 core-shell structure; and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion of the NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2 in diethylene glycol, adding a zinc salt and a manganese salt, carrying out a heating reflux reaction at the temperature of 180 DEG C for 1-6 h, then washing, drying, and calcining for 2 h at the temperature of 500 DEG C to obtain the product. The material can convert the visible / near-infrared light into UV / visible light, manganese-doped zinc oxide absorbs the UV / visible light to produce electrons-holes, and the electrons-holes act on the environment to produce free radicals to participate in a sterilization process, and the material can be used in the field of photodynamic therapy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Slurry for thermal spraying, sprayed coating, and method for forming sprayed coating
ActiveUS20170088930A1Good effectEasy to produceMolten spray coatingPowdery paintsThermal sprayingMetallurgy
To provide a slurry for thermal spraying. In the slurry, even when spray particles precipitate, the precipitates easily disappear. The present invention provides a slurry for thermal spraying including spray particles and a dispersion medium. The spray particles have an average circularity in a plan view of 0.85 or less. The spray particles preferably have an average circularity of 0.6 or more. The spray particles may include yttrium fluoride and an yttrium oxyfluoride.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Yttrium fluoride spray material, yttrium oxyfluoride-deposited article, and making methods
ActiveUS20170114440A1Increase oxygen concentrationReduce fluorine concentrationMolten spray coatingElectric discharge tubesYTTRIUM FLUORIDESpray coating
An yttrium fluoride spray material contains Y5O4F7 and YF3, and has an average particle size of 10-60 μm and a bulk density of 1.2-2.5 g / cm3. The Y5O4F7 and YF3 in the yttrium fluoride spray material consist of 30 to 90% by weight of Y5O4F7 and the balance of YF3. A sprayed coating of yttrium oxyfluoride is obtained by atmospheric plasma spraying of the spray material.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Efficient refining agent for smelting aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an efficient refining agent for smelting an aluminum alloy. The efficient refining agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 6-8 parts of plant ash, 8-10 parts of bentonite, 3-5 parts of wollastonite in powder, 3.5-5.5 parts of celestite powder, 0.5-2 parts of graphite powder, 3-5 parts of jade powder, 2-4 parts of quartz sand, 8-10 parts of magnesium hydroxide, 8-10 parts of lithium chloride, 6-8 parts of zinc chloride, 3-4 parts of calcium chloride, 2-4 parts of barium chloride, 4-5 parts of potassium fluosilicate, 1-2 parts of potassium tripolyphosphate, 2-3 parts of sodium sulfate, 1-2 parts of sodium metasilicate, 7-8 parts of rare earth carbonate, 0.1-1.0 part of boron oxide, 0.8-1.2 parts of yttrium fluoride and 3-5 parts of cerium oxide. The efficient refining agent can be used for effectively removing nonmetallic inclusions from an aluminum alloy melt and reducing the loss of rare earth elements in the alloy, and has a good degassing effect; and when the efficient refining agent is used for refining, aluminum dross is separated thoroughly, so that the porosity and oxide inclusions in an alloy casting are obviously reduced, and the comprehensive performance of an aluminum alloy profile is improved.
Owner:XUZHOU NAILI MACROMOLECULE TECH CO LTD
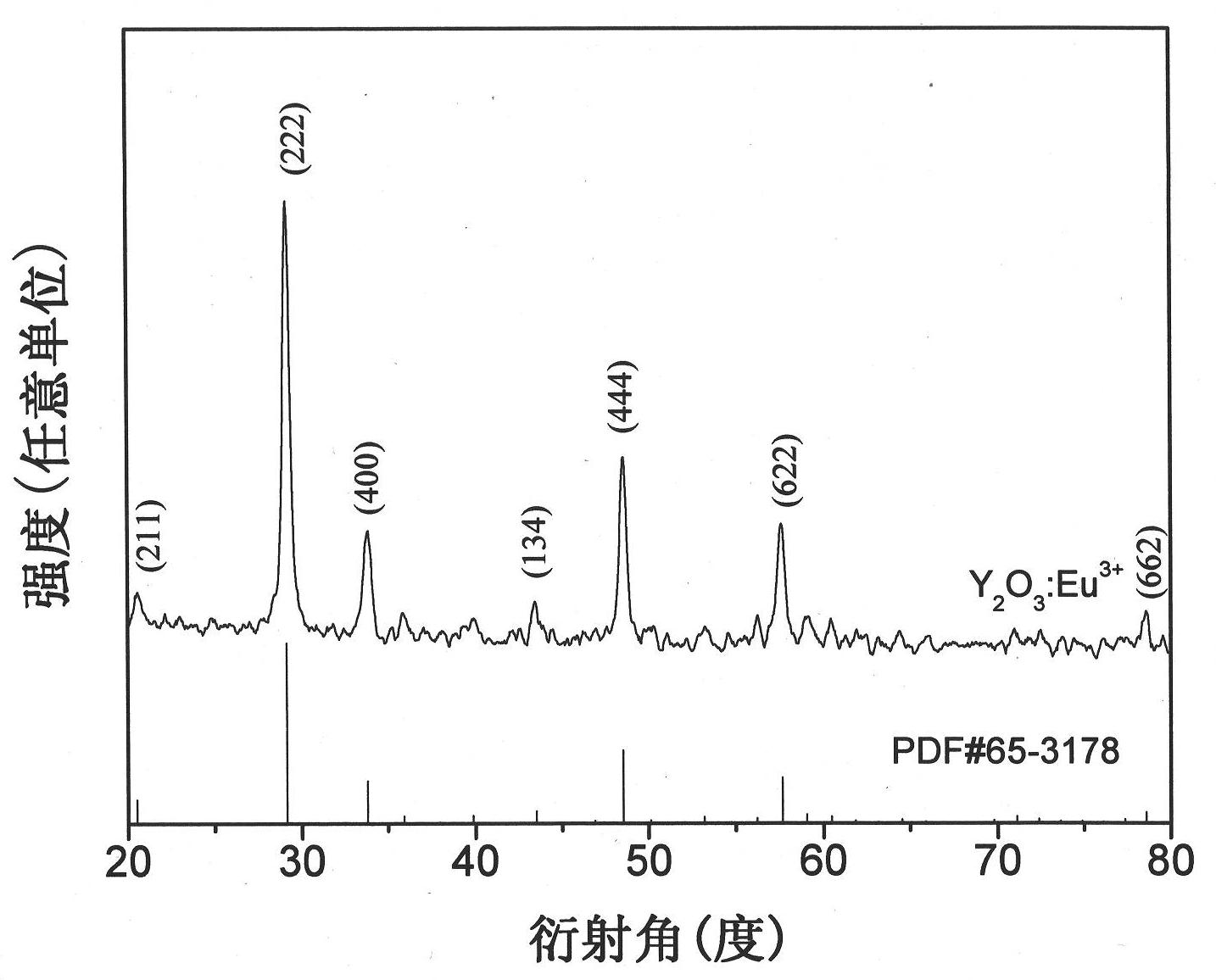
Method for preparing europium-doped yttrium fluoride nano fiber/polymer composite nano fiber
InactiveCN102031586AFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberMaterials preparation
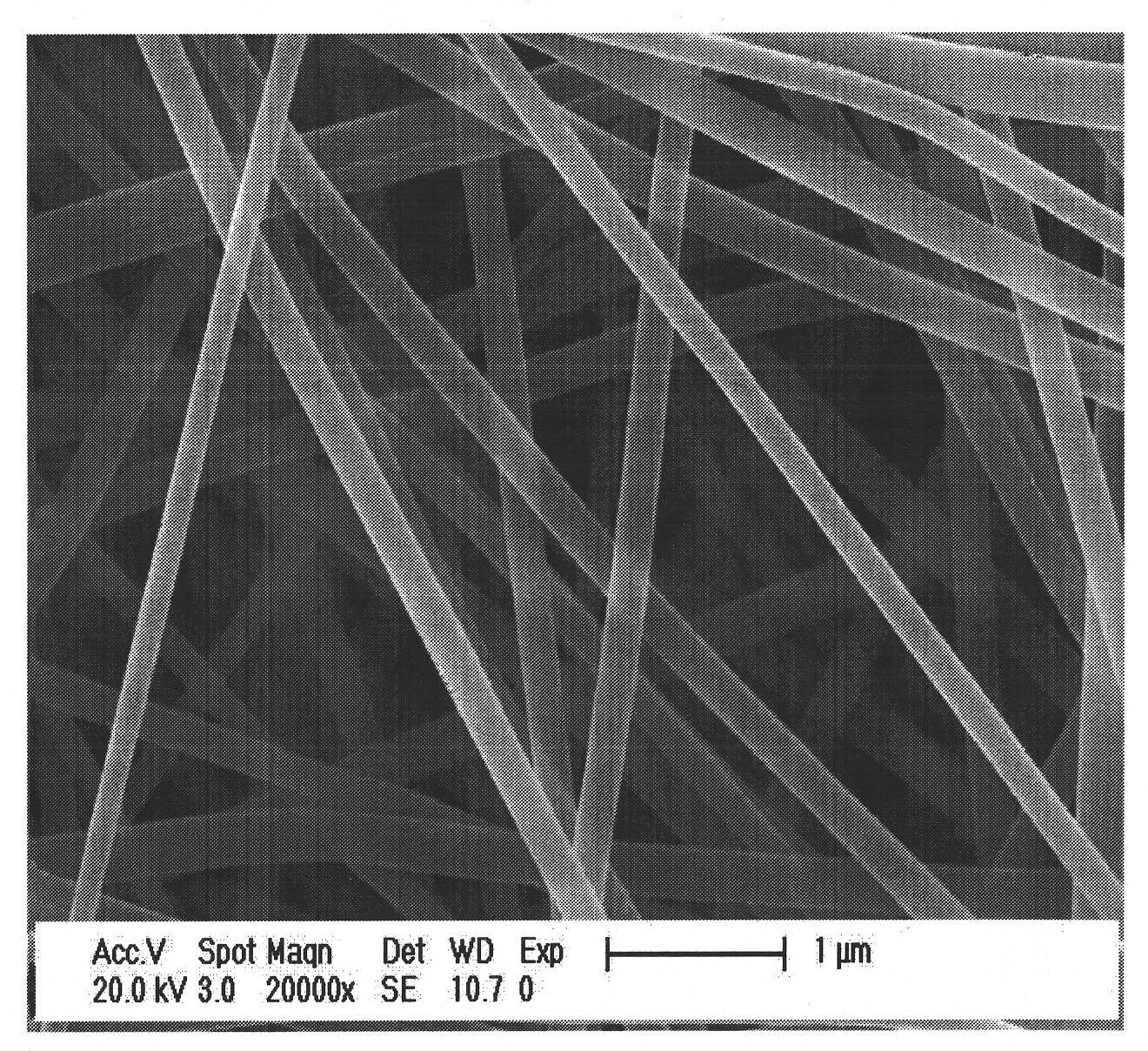
The invention relates to a method for preparing europium-doped yttrium fluoride nano fiber / polymer composite nano fiber, belonging to the technical field of nano material preparation. In the prior art, rare earth fluoride nano fiber and nanoribbon, rare earth fluoride nano particle / polymer composite nano fiber are prepared. The method comprises the following three steps of: (1) preparing Y2O3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber: preparing PVP / [Y(NO3)3+Eu(NO3)3] composite nano fiber by using the electrostatic spinning technology, and carrying out thermal treatment to obtain the Y2O3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber; (2) preparing YF3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber: fluoridizing the Y2O3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber by using the double crucible method to obtain the YF3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber; and (3) preparing YF3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber / PVP composite nano fiber: mixing the YF3:5%Eu<3+> nano fiber with PVP and DMF to obtain a spinning solution, and preparing the YF3:5%Eu3<3+> nano fiber / PVP composite nano fiber by using the electrostatic spinning technology. The diameter of the YF3:5%Eu<3+>nano fiber / PVP composite nano fiber is 276-362 nm, and the length is greater than 1 mm. The method is simple and feasible and has broad application prospect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Yttrium oxide-containing material, component of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and method of producing yttrium oxide-containing material
ActiveUS7833924B2Improve handlingImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCeramic shaping apparatusSemiconductorYTTRIUM FLUORIDE
There is provided an yttrium oxide-containing material with excellent mechanical characteristics. The yttrium oxide-containing material becomes strong by adding silicon carbide (SiC) and yttrium fluoride (YF3) to yttrium oxide (Y2O3). Accordingly, the yield, handling and reliability can be improved when this strengthened yttrium oxide-containing material is applied to and used for components of semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD +1
Mg-Gd-Y-Zr magnesium alloy refining flux and producing method thereof
The invention provides an Mg-Gd-Y-Zr magnesium alloy refining flux and a production method thereof. The chemical components of the flux are mixed according to the following mass percentages: potassium chloride of ranging from 30 to 50 percent, barium chloride of ranging from 5 to 20 percent, sodium chloride of ranging from 2 to 10 percent, calcium chloride of ranging from 10 to 20 percent, calcium fluoride of ranging from 2 to 8 percent, cryolite of ranging from 1 to 5 percent, gadolinium compound of ranging from 3 to 8 percent, yttrium compound of ranging from 3 to 8 percent, and zirconium compound of ranging from 2 to 8 percent, wherein, the gadolinium compound is gadolinium chloride, gadolinium carbonate or gadolinium fluoride, the yttrium compound is yttrium chloride, yttrium carbonate or yttrium fluoride, the zirconium compound is zirconium tetrachloride or potassium zirconium fluoride. The flux has good melting point, viscosity, wettability and the slag removing performance which is improved greatly. Because the flux does not contain magnesium chloride or react with the lanthanon such as gadolinium and yttrium, the chemical reaction loss of the lanthanon in the refining process is not caused, thereby being particularly suitable for the refining purifying process of the Mg-Gd-Y-Zr magnesium alloy and improving the refining effect of the magnesium fused mass.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Component For Plasma Processing Apparatus, And Manufacturing Method Therefor
Particle generation can be suppressed from a thermally sprayed film of yttrium fluoride. A component exposed to plasma in a plasma processing apparatus is provided. The component includes a base and a film. The base is made of aluminum or an aluminum alloy, and an alumite film may be formed on a surface of the base. The film is formed by thermally spraying yttrium fluoride on a surface of the base or on a surface of an underlying layer including a layer provided on the base. A porosity of the film is 4% or less, and an arithmetic mean roughness of a surface of the film is 4.5 [mu]m or less.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Visible near-infrared spectrum band reflection and infrared multispectral band transmission color separation filter and preparation method
The invention relates to a visible near-infrared spectrum band reflection and infrared multispectral band transmission color separation filter and a preparation method, and belongs to the field of surface technology. The color separation filter comprises a zinc selenide base and a film system on one side of the base; the structure of the film system is (0.3h 0.6l0.3 h) ^ 10 (0.38h 0.76 l0.38 h) ^ 10 (0.5 h l0.5 h) ^ 12, and the central wavelength is 890 nm, wherein h and l refer to zinc sulfide and yttrium fluoride film respectively; and the color separation filter is prepared through the following steps: heating the base in vacuum, using ion beam to bombard the base, using ion beam to assist electronic gun evaporation to deposit the film system on two sides of the base, and cooling. The reflectivity of the color separation filter is high at 0.43-0.90 micron; the transmittance of the color separation filter is high at 1.55-1.75 microns, 2.08-2.35 microns, 3.5-5.5 microns, 7.8-10 microns, and 11.08-12.55 microns; and the color separation filter meets beam split operating requirement of a remote sensing detection system.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
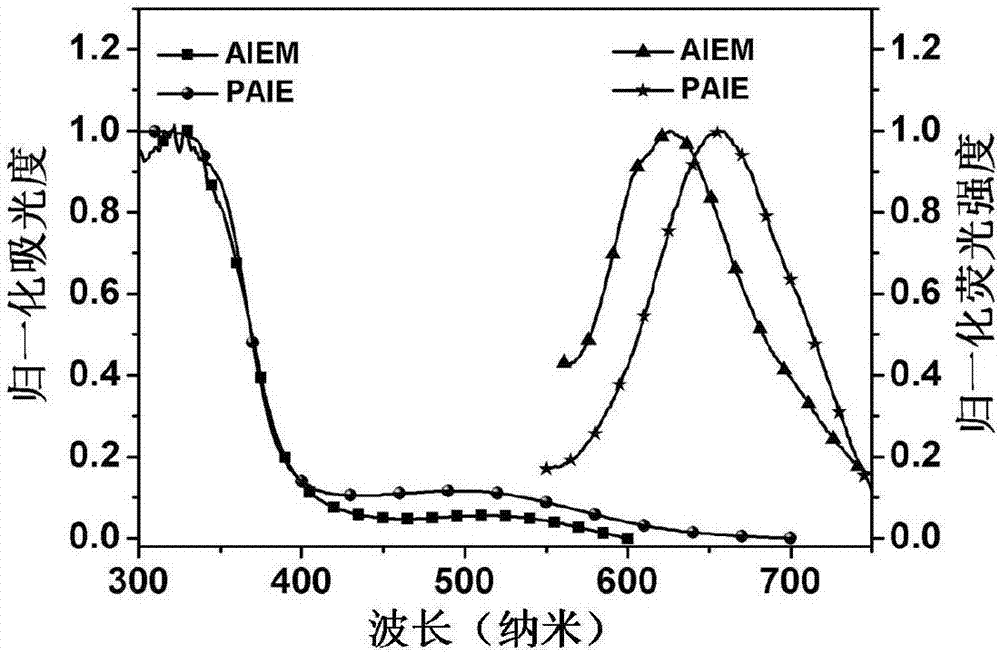
Near infrared laser-driven mitochondrial targeting fluorescent polymer and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107033283ALow optical damageGood optical damagePhotodynamic therapyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethacrylateAcrylonitrile
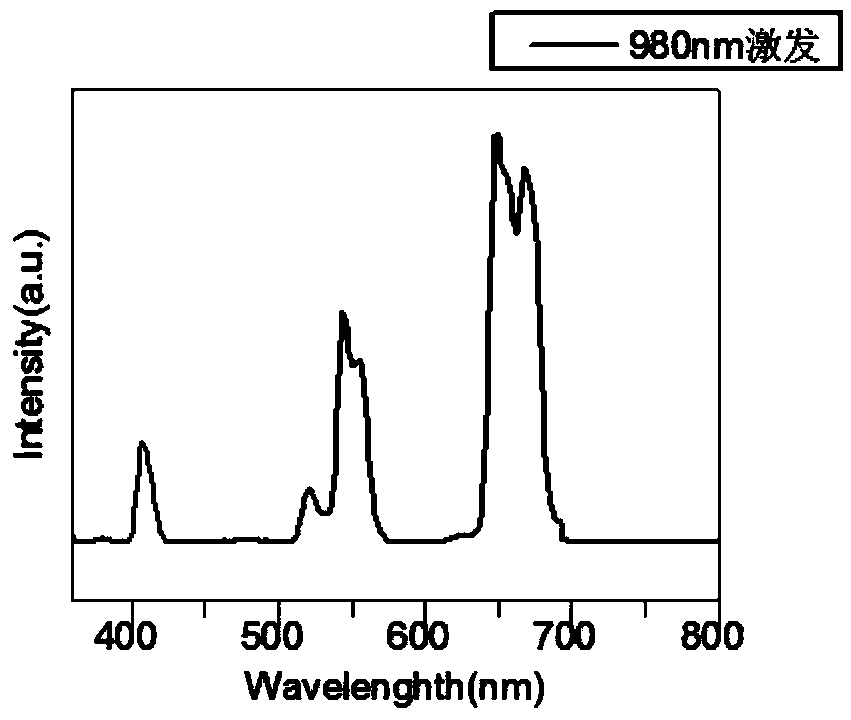
Disclosed is a near infrared laser-driven mitochondrial targeting fluorescent polymer and a preparation method and application thereof. A nano-scale photosensitizer, which is prepared from a polymer of poly-(2Z, 2'Z)-3,3'-(2, 5-bis(diphenylamino)-1, 4-phenyl) bis(2-(3, 5-bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl) acrylonitrile-copolymer (N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide)-copolymer (2-dimethylamino ethyl methacrylate) and an inorganic upconversion nano-scale particle of ytterbium and thulium codoped sodium yttrium fluoride in aqueous solution; when irradiated by laser of a wavelength of 980 nm, the nano-scale photosensitizer can produce reactive oxygen to effectively kill cells. The invention provides a novel and effective nano-scale photosensitive material for research and application of photodynamic therapy of tumor cells in the future.
Owner:深圳市丰用实业集团有限公司
Method for preparing rare earth magnesium alloy and yttrium-neodymium magnesium alloy
The invention relates to a method for preparing yttrium-neodymium magnesium alloy and the yttrium-neodymium magnesium alloy. A graphite block is adopted as an anode, a molybdenum rod serves as an inertia cathode, a molybdenum crucible serves as an alloy receiver, mixtures of yttrium oxide, neodymium oxide and magnesium oxide are added into a fluoride molten salt electrolyte system composed of yttrium fluoride, neodymium fluoride and lithium fluoride, then direct currents are guided for electrolysis and finally the yttrium-neodymium magnesium alloy is obtained; the mass ratio of the yttrium fluoride to the neodymium fluoride to the lithium fluoride in the fluoride molten salt electrolyte system is 5-20 to 70-90 to 5-10, the mass percent ratio of the neodymium oxide and the yttrium oxide to the magnesium oxide is 99-80 to 1-20, the mass percent ratio of the neodymium oxide to the yttrium oxide is 99-1 to 1-99, and the electrolysis temperature ranges from 1050 DEG C to 1150 DEG C. The method has the advantages that the technological process is simple, the cost is low, the product ingredients are stable, just carbon dioxide and little carbon monoxide are generated in the technological process, environmental pollution is small, and the process is friendly to environment and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:BAOTOU RES INST OF RARE EARTHS
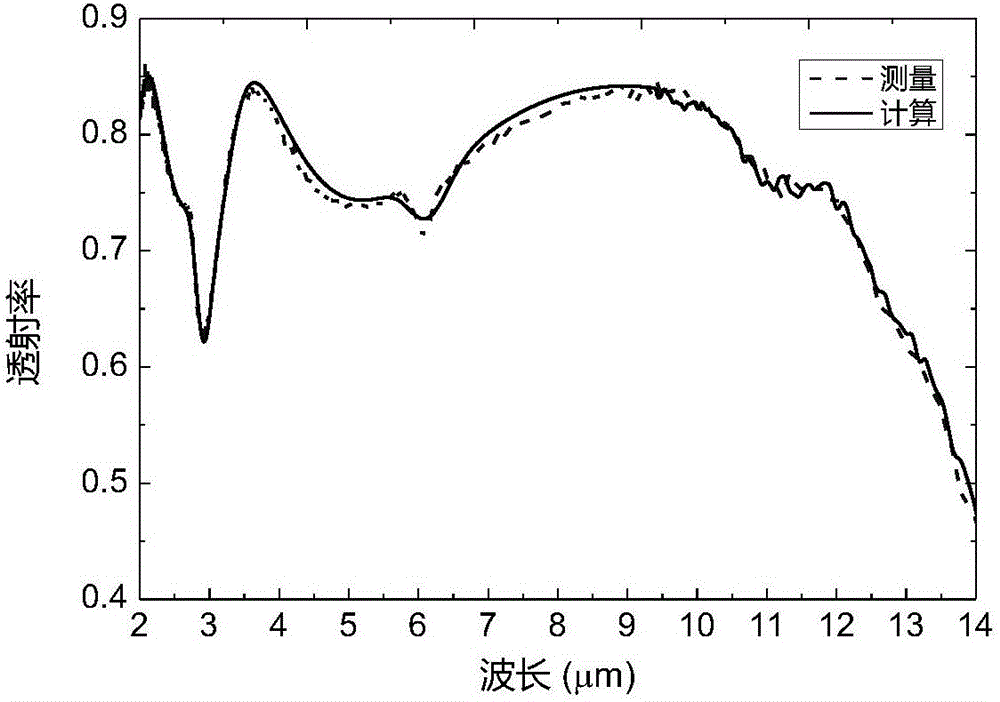
Infrared optical constant calculating method for yttrium fluoride optical thin film
The invention belongs to a field of optical thin films and specifically relates to an infrared optical constant calculating method for a yttrium fluoride optical thin film in an infrared band. According to the invention, through constructing a four-oscillator composite model of a dielectric constant of the yttrium fluoride optical thin film, measured substrate-film spectrum reflectivity and spectrum spectral transmittance are taken as a compound target and a substrate-film physical model is utilized for back calculation of a dielectric constant of the thin film and the optical constant of the thin film is calculated out through the dielectric constant. The method provided by the invention has universality in optical constant calculation of yttrium fluoride optical thin film material prepared in all the different deposition ways.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG INST OF TECH PHYSICS
Er-doped transparent glass ceramics containing nanometer sodium yttrium fluoride crystal and its prepn and use
InactiveCN101088946AHigh visible light up-conversion luminous efficiencyUp-conversion red regulationInfraredOptoelectronics
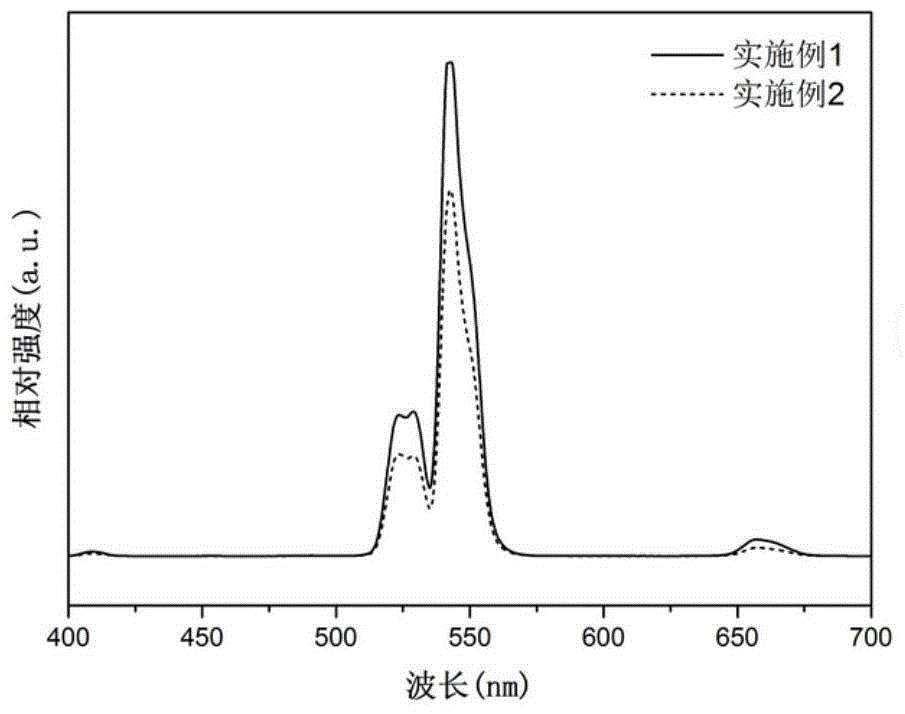
The present invention is Er-doped transparent glass ceramics containing nanometer sodium yttrium fluoride crystal and its preparation and use, and relates to light emitting material technology. The glass ceramics has the molar composition of 40SiO2-25Al2O3-xNa2CO3-10YF3-yNaF-zErF3, where x=15-20, y=25-x-z, and z=0.05-2.0. It is prepared through a melt chilling process. The glass ceramics may have the Er3+ doping amount altered to regulate the intensity ratio between the red light and the green light emitted under the excitation of infrared ray, near monochromic green light emitting corresponding to low doping concentration and near monochromic red light emitting corresponding to high doping concentration.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for growing large-sized rare-earth-doped barium yttrium fluoride single crystals
InactiveCN104562183ALimit heightImprove integrityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltRare earthPt element
The invention provides a method for growing large-sized rare-earth-doped barium yttrium fluoride single crystals. The method comprises the following steps: in a heating furnace, putting polycrystals of {xReF3+(1-x)YF3} and BaF2 into a crucible according to a mass ratio, vacuumizing, and introducing argon gas into the heating furnace successively, wherein the mass ratio of {xReF3+(1-x)YF3} to BaF2 is 2 to 1 and x is 0-100%; controlling the heating power by a temperature control instrument to melt the polycrystals, performing heat exchange by flowing of a liquid surface in the crucible and the gas in the furnace to form an axial temperature difference, and forming a radial temperature difference of temperature on a wall of the crucible and temperature in the center of the crucible to cause natural convection of a melt; fixing BaY2F8 seed crystals to a seed crystal rod by a platinum chuck, and lowering the seed crystals to be contacted with the melt for fluoride crystal growth; when fluoride crystals grow to have set sizes, annealing, cooling to the room temperature at a speed of 20 DEG C / hour, adjusting the rotary speed and the heating power, separating the crystals from the melt until the crystal growth is ended, and annealing in the crucible to obtain the large-sized fluoride crystals. The method solves the problems of negative growth factors of difficulty for crystal growth, a large amount of air bubbles in the crystals and the like caused by poor flowability of the fluoride melt.
Owner:SOUTH WEST INST OF TECHN PHYSICS
Conductive, plasma-resistant member
InactiveCN101135033APollution suppressionImprove toleranceMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingThermal sprayingDisplay device
An electrically conductive, plasma-resistant member adapted for exposure to a halogen-based gas plasma atmosphere includes a substrate having formed on at least part of a region thereof to be exposed to the plasma a thermal spray coating composed of yttrium metal or yttrium metal in admixture with yttrium oxide and / or yttrium fluoride so as to confer electrical conductivity. Because the member is conductive and has an improved erosion resistance to halogen-based corrosive gases or plasmas thereof, particle contamination due to plasma etching when used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment or flat panel display manufacturing equipment can be suppressed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Lithium yttrium fluoride nanocomposite material, its preparation method, and its application in photodynamic therapy
ActiveCN103980904ASensitization efficiency is highStrong Visible Upconversion EmissionEnergy modified materialsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellSinglet oxygen
The invention provides a photosensitizer coupled rare earth-doped LiAF4 nanocomposite material, its preparation method, and its application in the photodynamic therapy. The above photosensitizer coupled nanomaterial emits strong visible light under the irradiation of 980nm laser, and can sensitize the photosensitizer to generate singlet oxygen, so the nanomaterial can be used in the up-conversion photodynamic therapy. The method has the advantages of simplicity and high yield, the prepared nanomaterial has the advantages of good water solubility, excellent luminescence performance and high singlet oxygen yield, and the singlet oxygen can well kill cancer cells, so the nanomaterial can be applied in the diagnosis and treatment field of tumor diseases.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing rare-earth doped potassium yttrium fluoride up-conversion luminescence nano material
InactiveCN104327855AHigh crystallinityHigh luminous intensityLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldPotassium
The invention relates to a method for preparing a rare-earth doped potassium yttrium fluoride up-conversion luminescence nano material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) weighing yttrium oxide, sylvite and a fluorine source, adding in an oleic acid / oleylamine-containing solvent system, stirring and mixing, thus obtaining a first uniform solution; 2) weighing ytterbium fluoride and a rare-earth activator, adding in the oleic acid / oleylamine-containing solvent system, stirring and mixing, thus obtaining a second uniform solution; 3) rapidly heating the first uniform solution to a high temperature, and meanwhile rapidly filling the second uniform solution, and sufficiently stirring to react, thus obtaining a third uniform solution; and 4) cooling the obtained solution to room temperature, performing centrifugal separation, washing, and drying, thus obtaining the rare-earth doped potassium yttrium fluoride up-conversion luminescence nano material. The method has the beneficial effects that the preparation period of the material is effectively shortened, new ideas and ways are provided for preparing the up-conversion luminescence nano material, large-scale popularization and application are facilitated, and the purposes of controllable the monodisperse particle size, high quantum yield and the like are solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
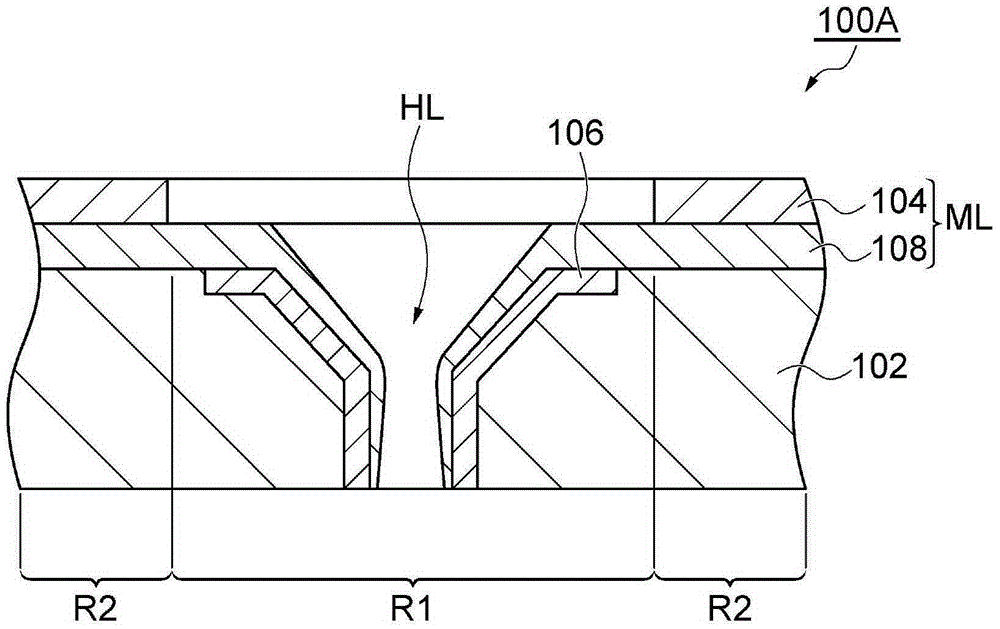
Plasma etching method
ActiveCN104347389AImprove surface qualityAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringCarbon ion
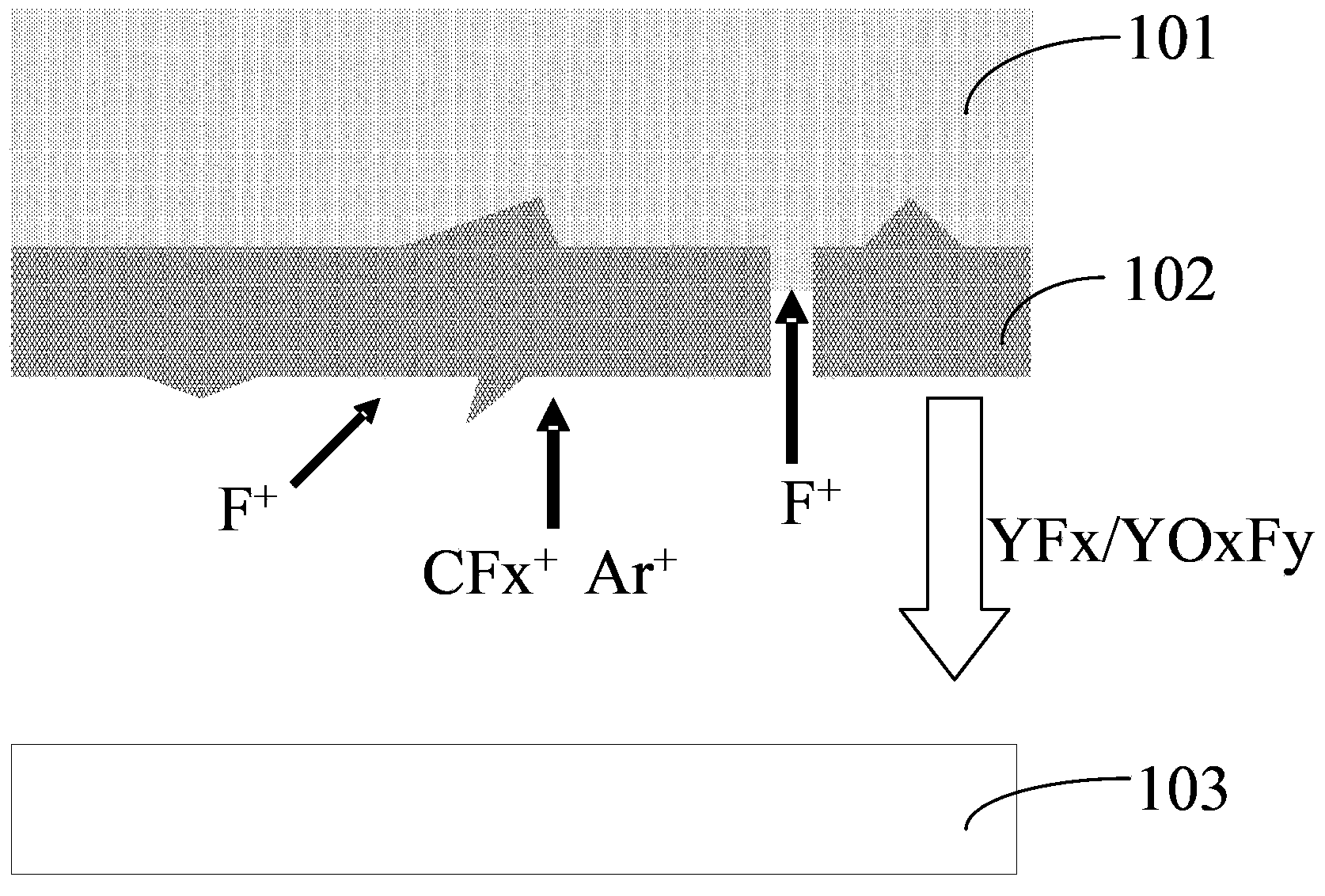
The invention relates to the technical field of a semiconductor, and discloses a plasma etching method. On the basis of a conventional fluorocarbon gas, Ar and O2, an N-containing gas is added to serve as an etching gas so as to react with carbon ions in plasma to generate a CN polymer depositing at the inner wall of a plasma etching cavity and the surface of a spray head, such that it is ensured that a yttrium oxide surface and yttrium fluoride generated through reaction are prevented from physical bombardment effect of the plasma, YFx sputtering is reduced, generation of yttrium-containing particles and residues are reduced, the residues brought when yttrium oxide covering the surface of the spray head is disposed at the surface of a semiconductor substrate to be etched during a plasma etching process is further decreased or even eliminated, and the surface quality of plasma etching is improved. Besides, the plasma etching method provided by the invention can also reduce damage caused by physical bombardment on the yttrium oxide covering the surface of the spray head during the plasma etching process and prolongs the service life of the spray head.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com