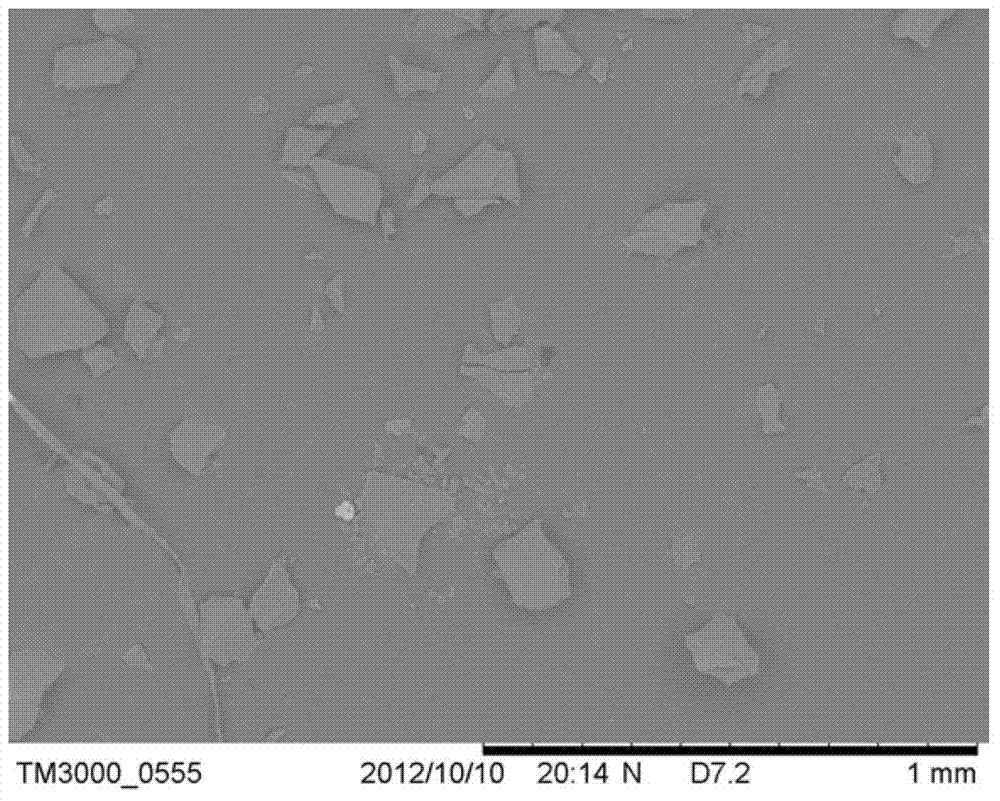
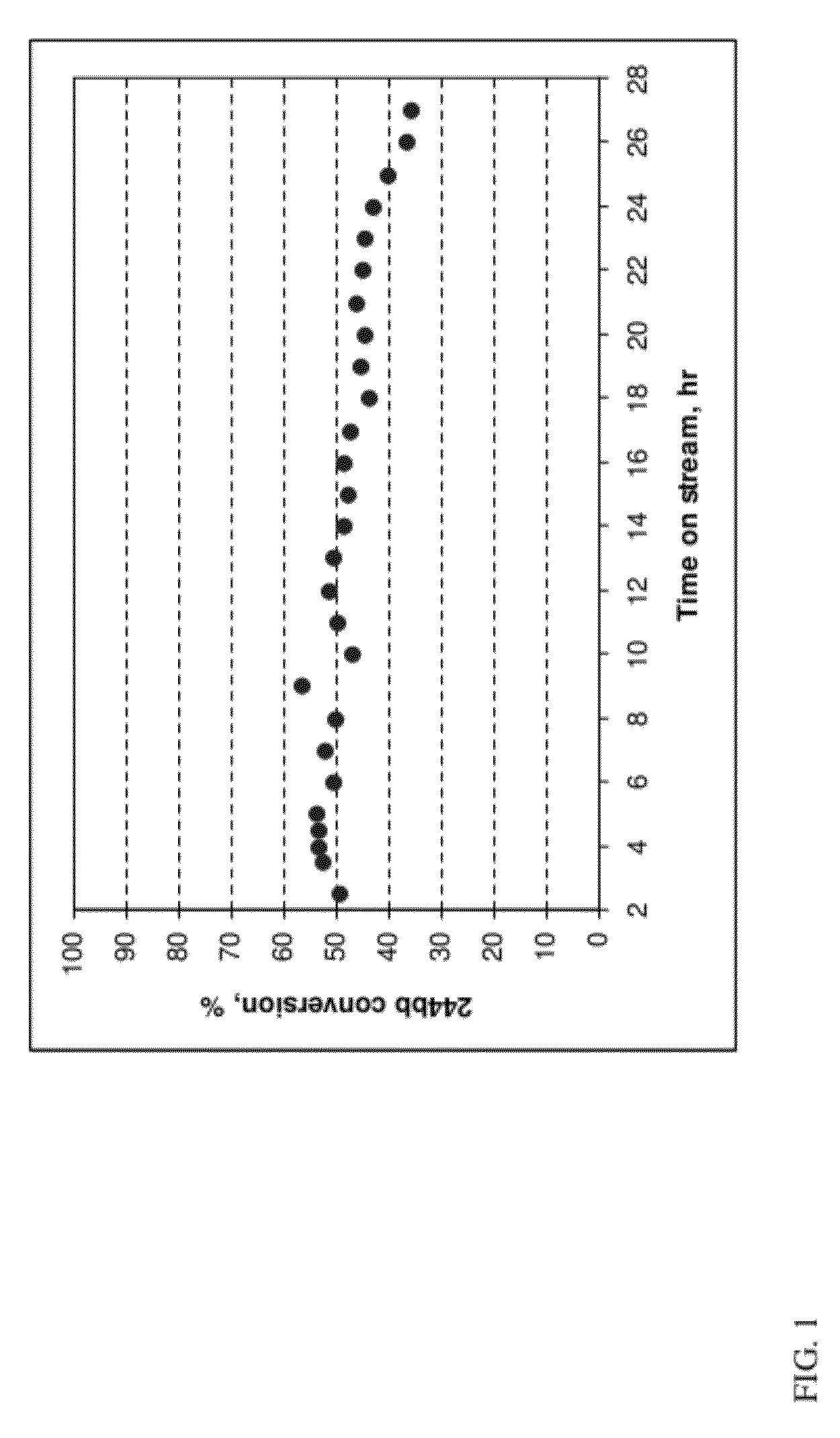
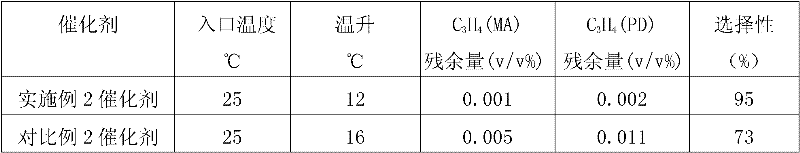
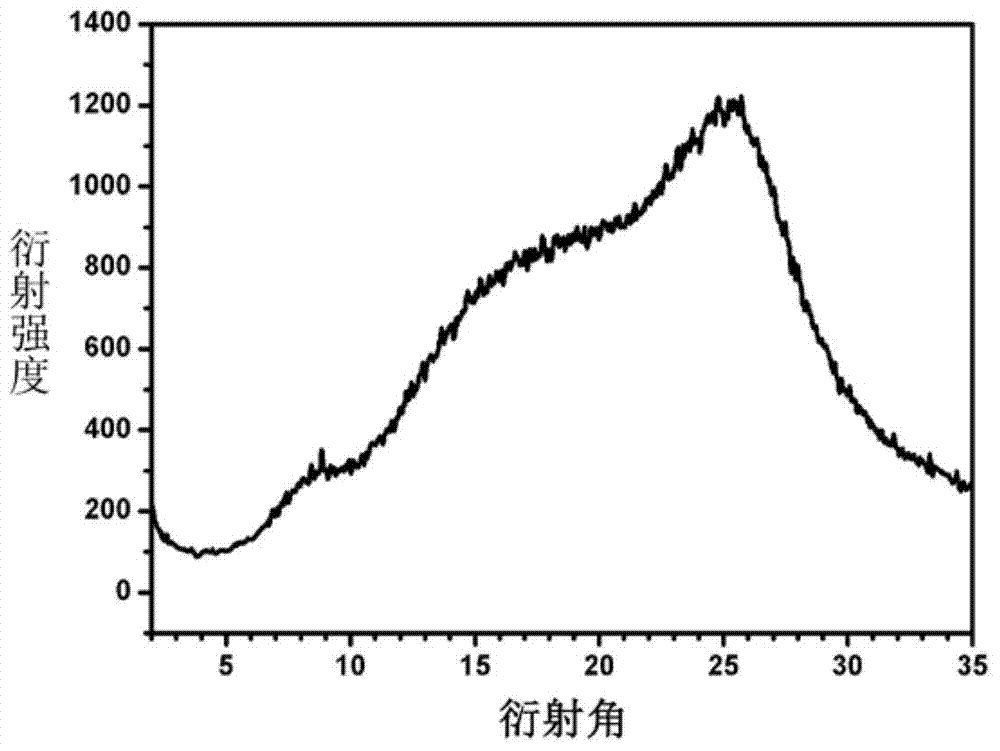
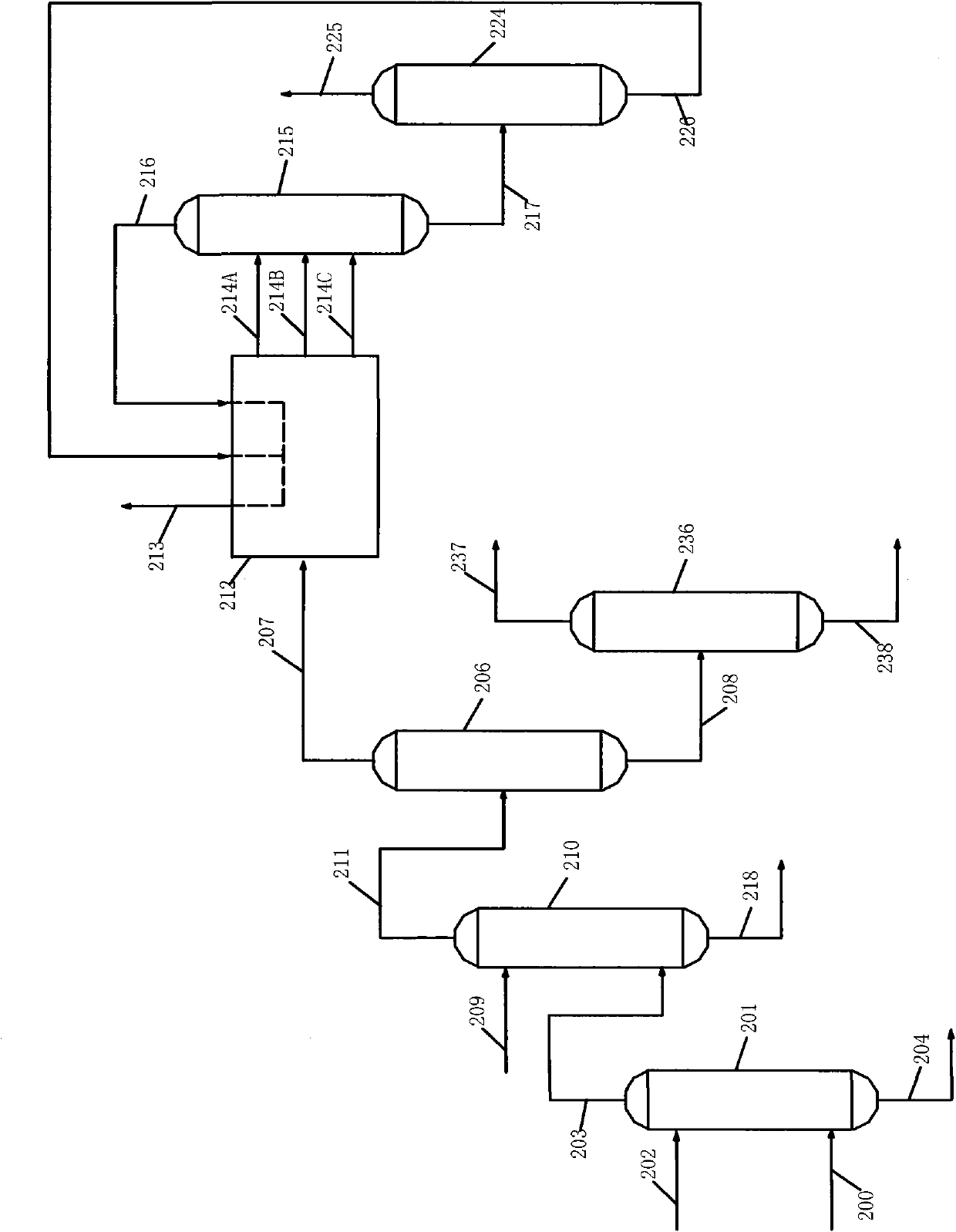
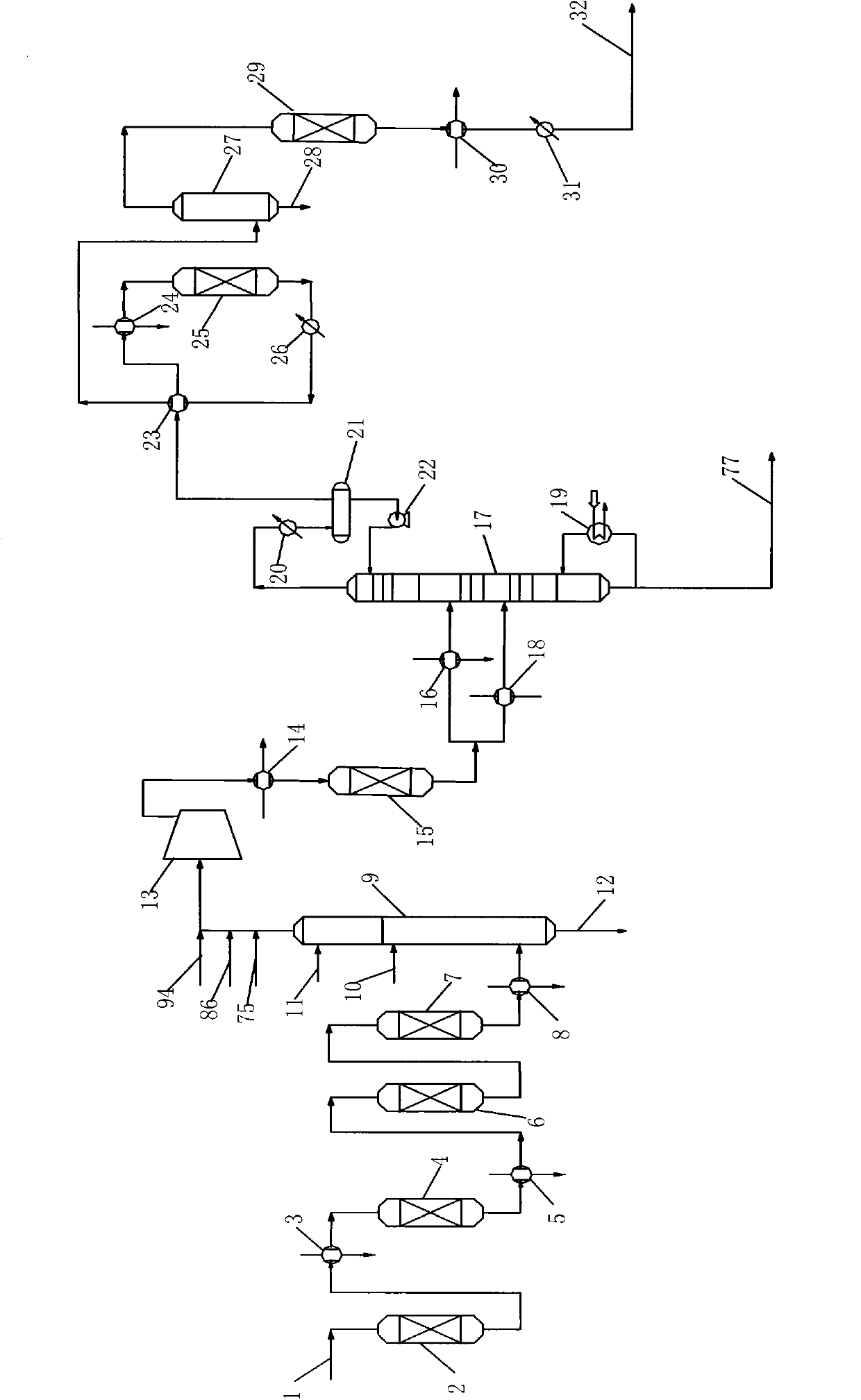
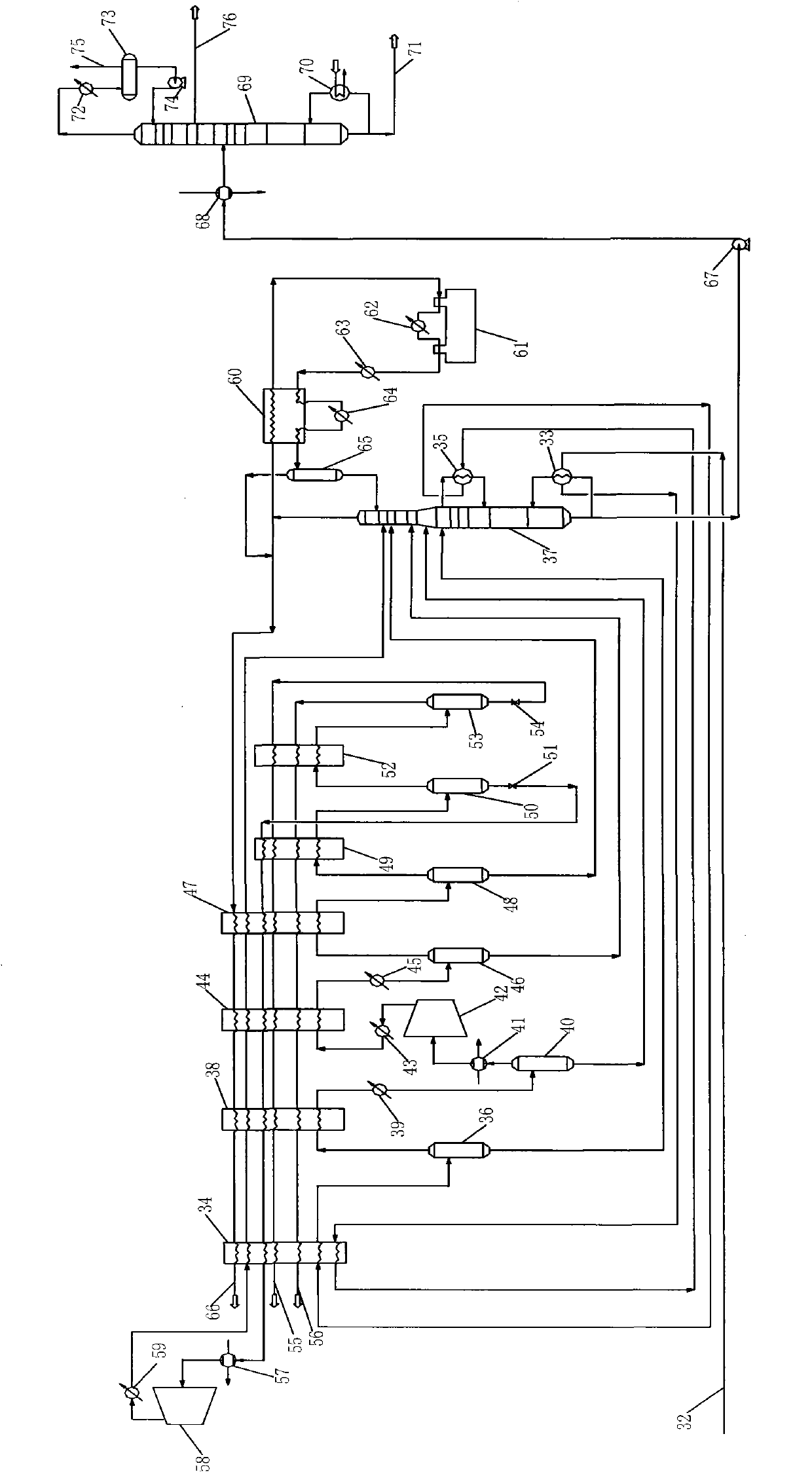
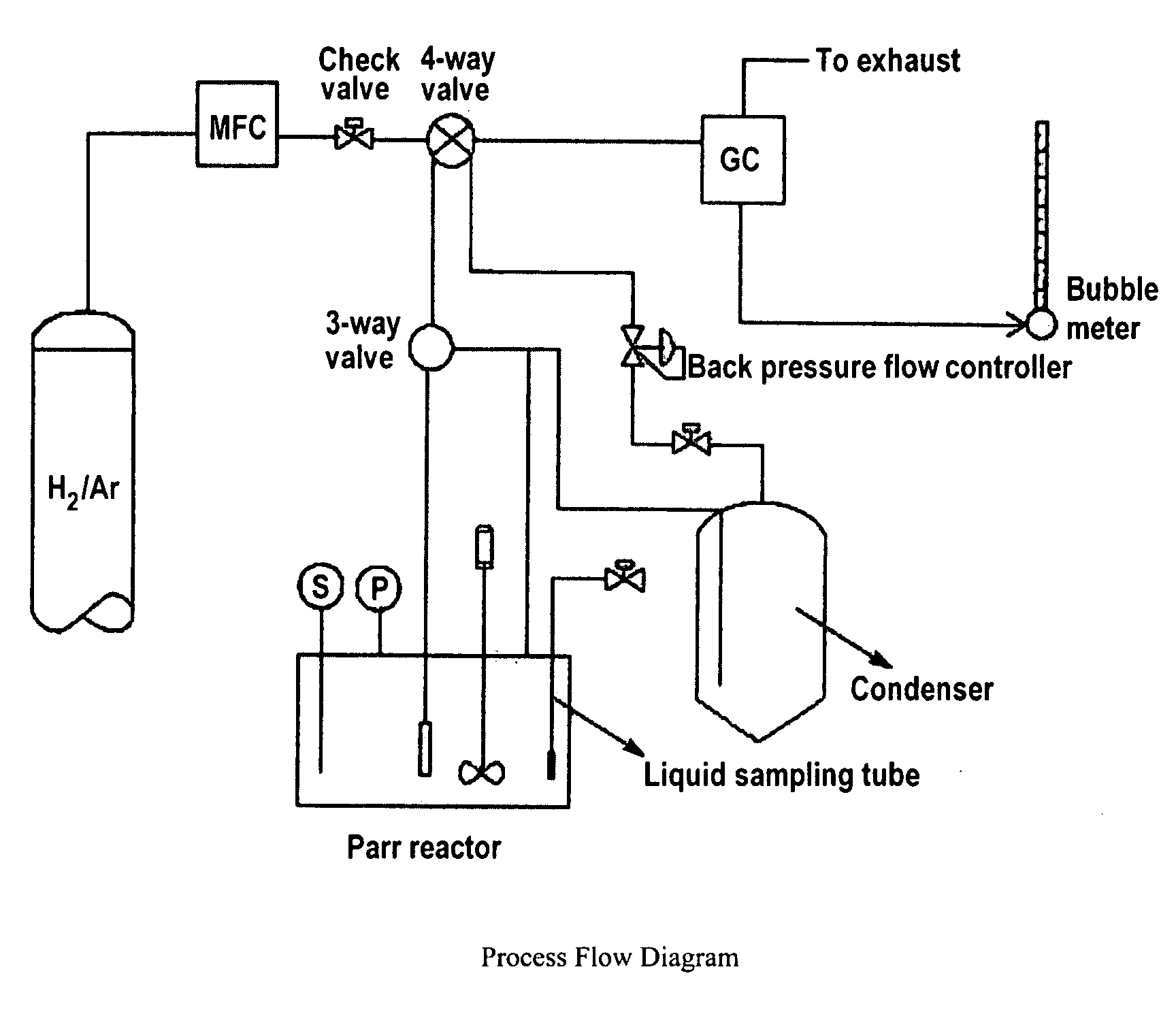
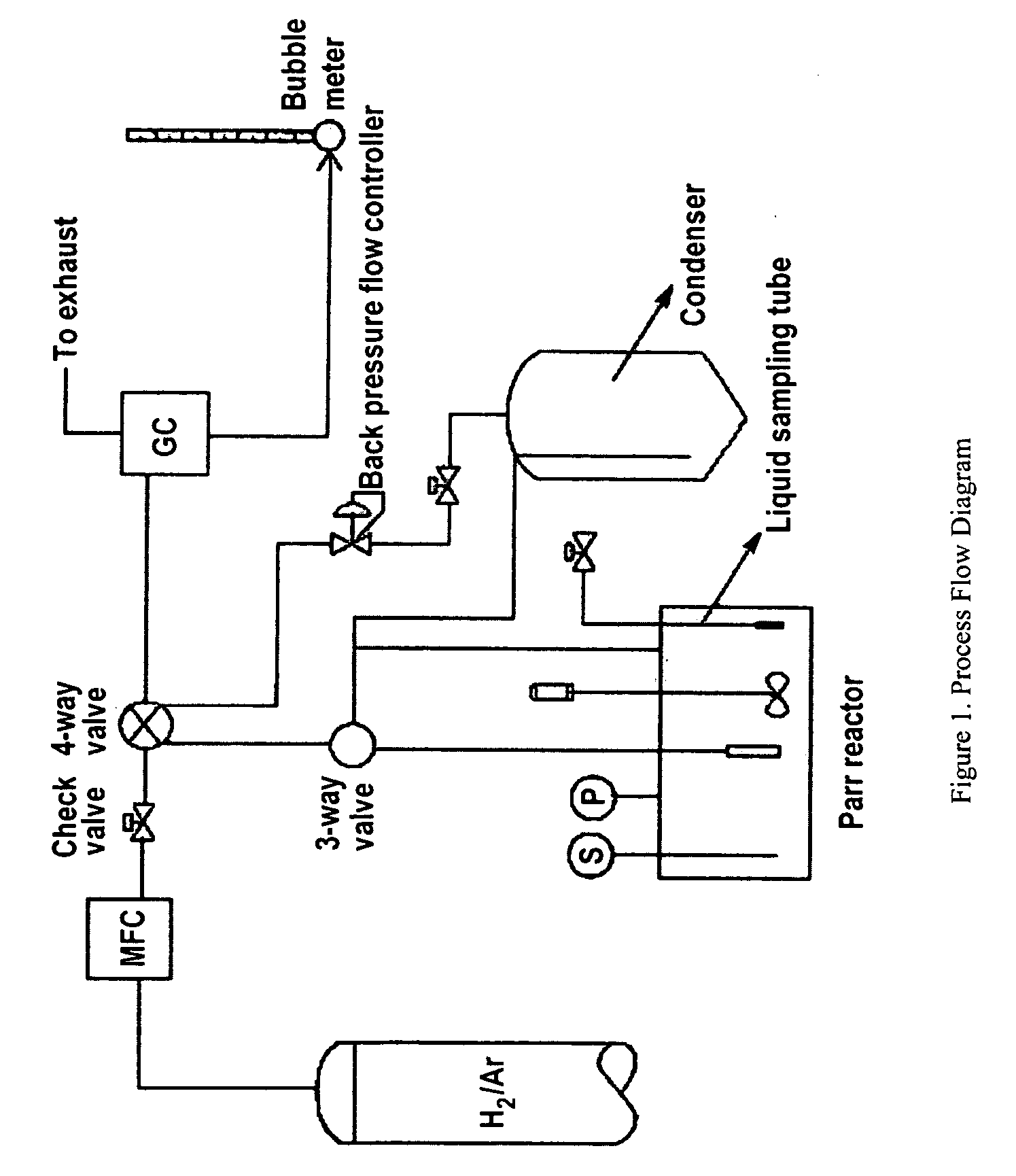
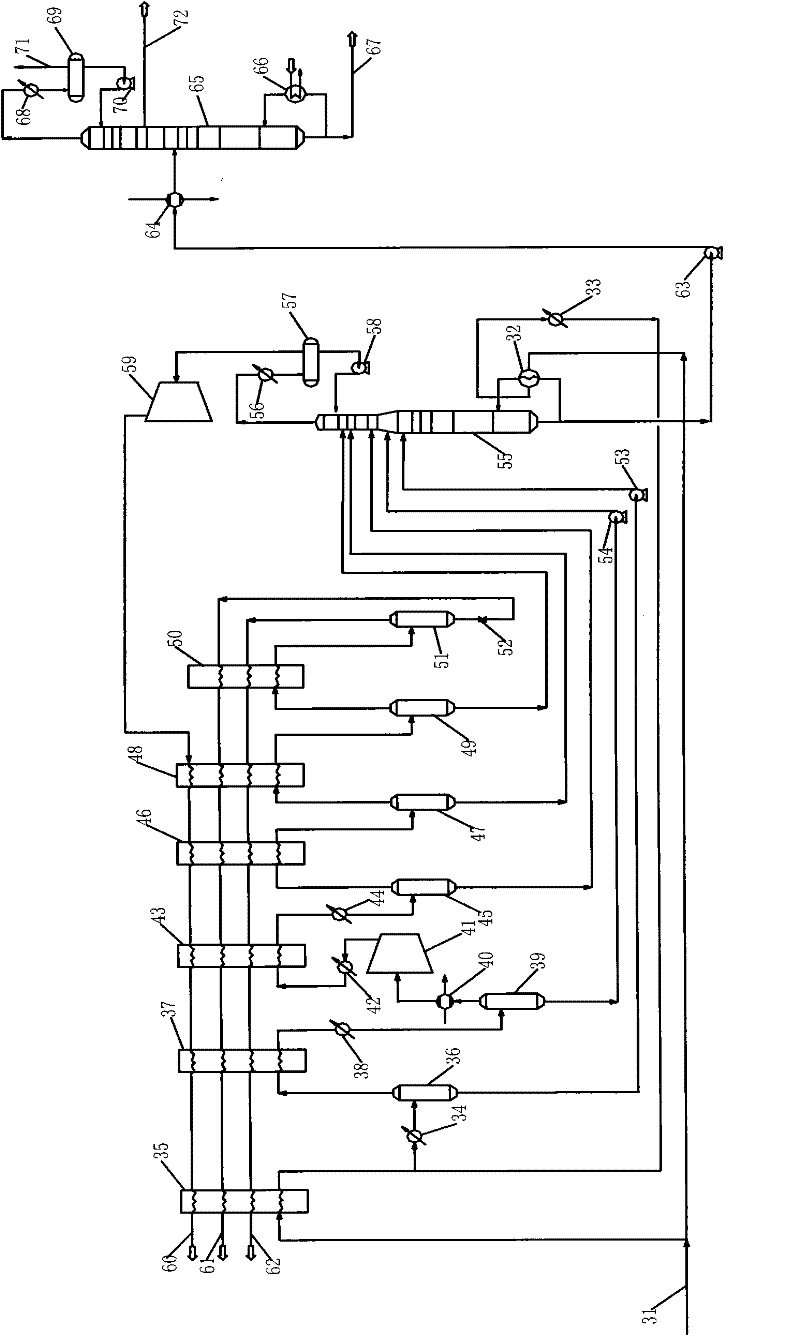
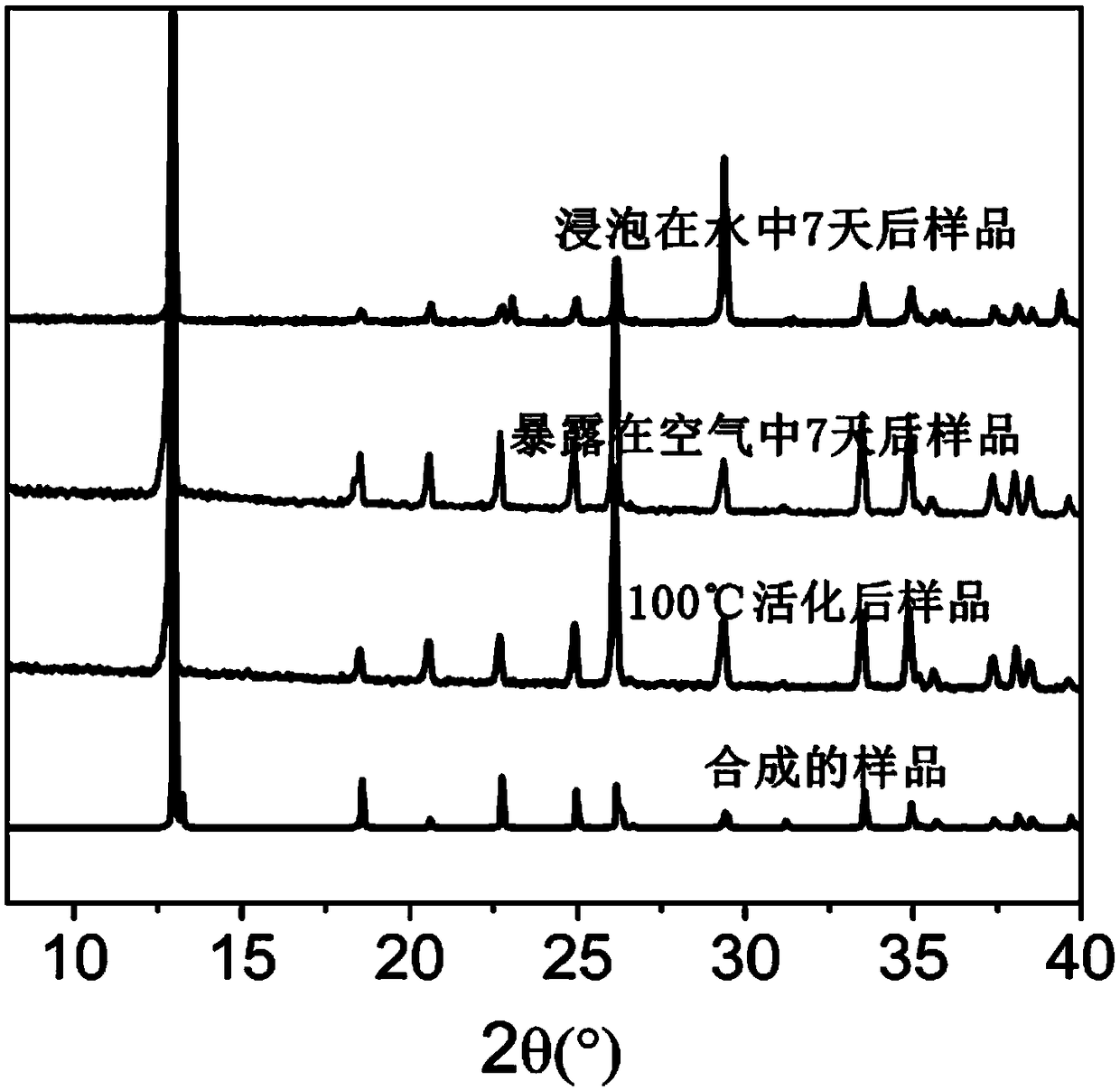
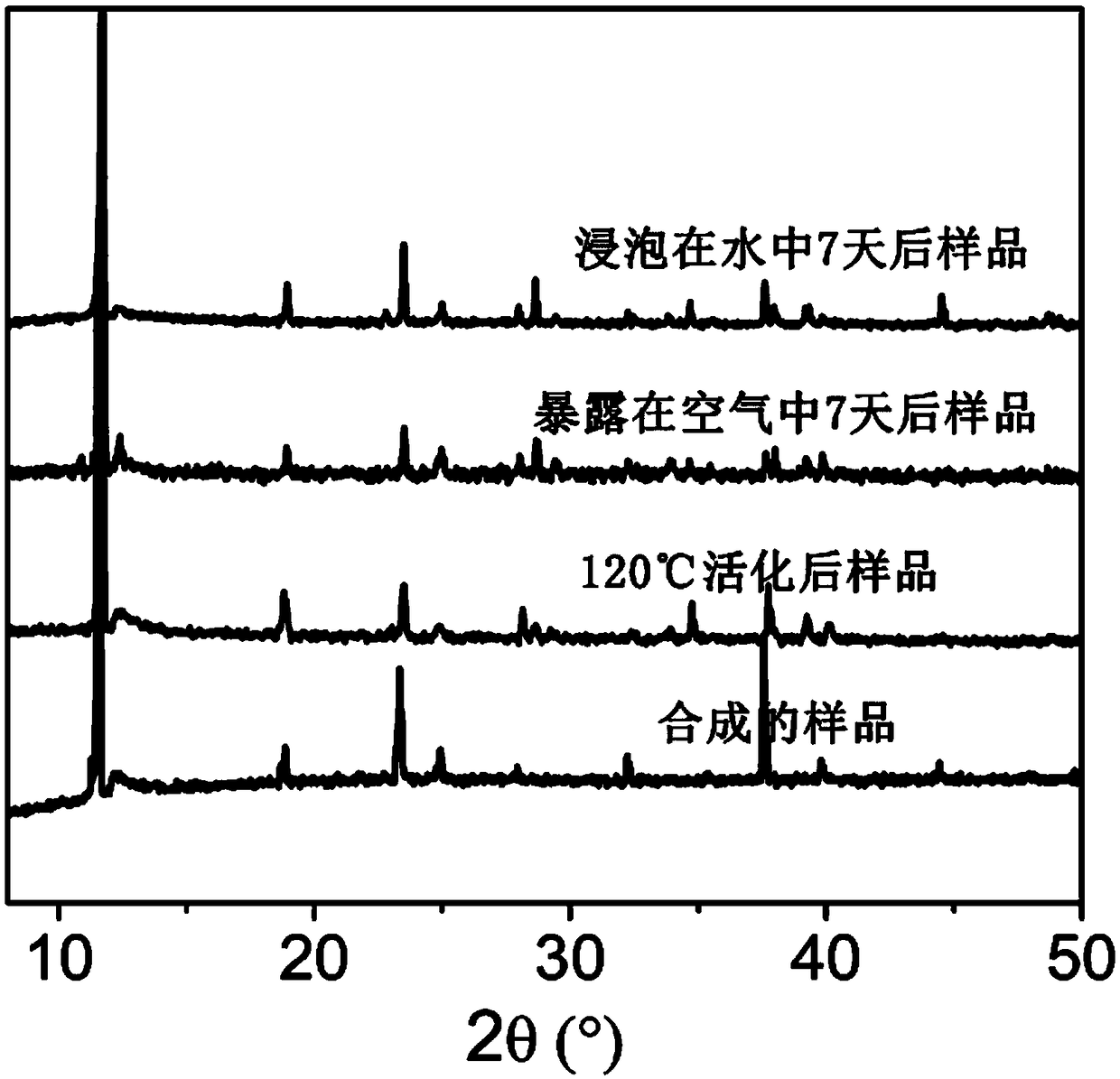
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
232 results about "Propyne" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Propyne (methylacetylene) is an alkyne with the chemical formula CH₃C≡CH. It was a component of MAPP gas—along with its isomer propadiene (allene), which was commonly used in gas welding. Unlike acetylene, propyne can be safely condensed.
Process for producing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene
ActiveUS8975454B2Increase productionPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationImpurityPropane
The instant invention relates to a process and method for manufacturing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene by dehydrohalogenating a reactant stream of 2-chloro-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoropropane that is substantially free from impurities, particularly halogenated propanes, propenes, and propynes.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
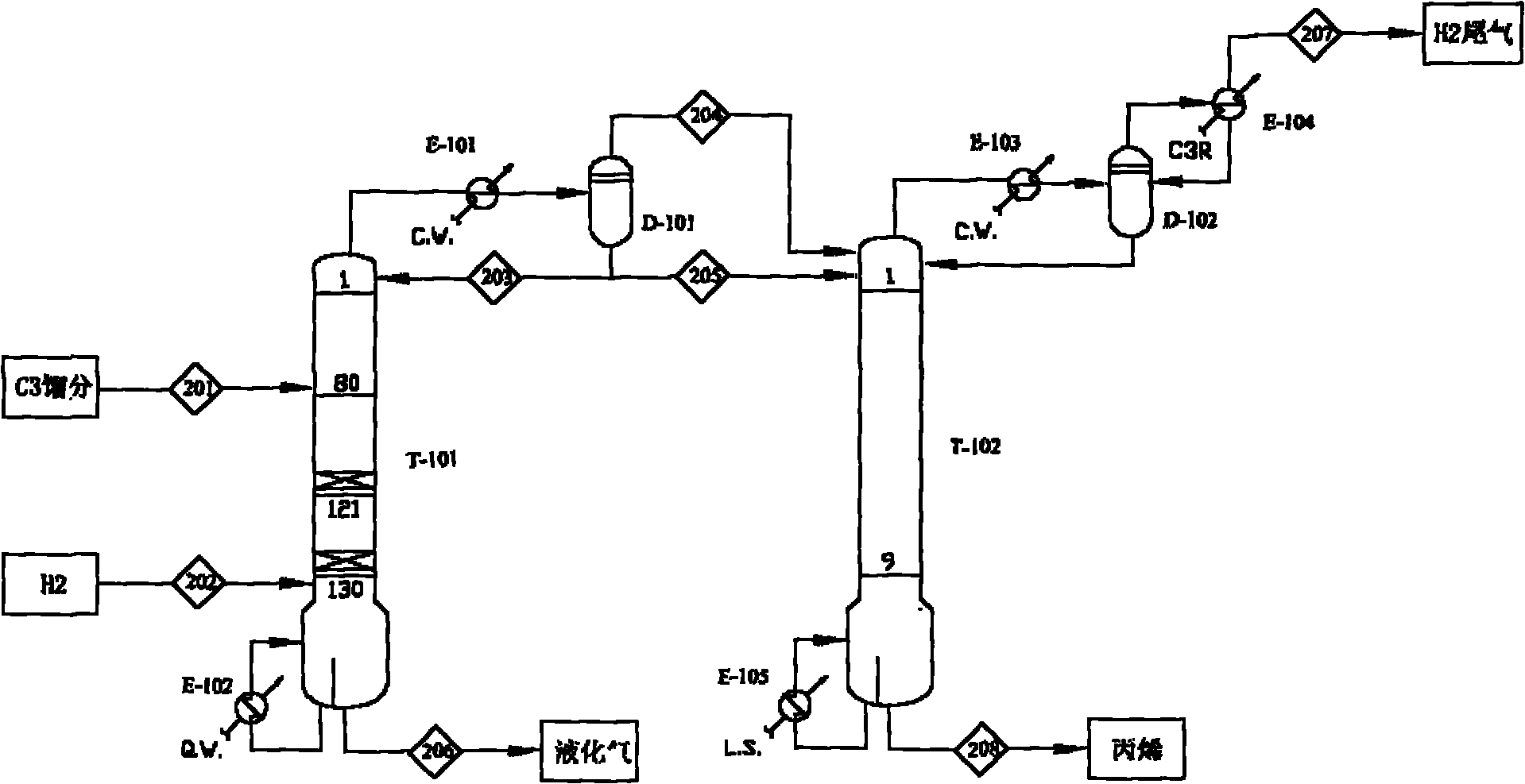
Selective hydrogenation method for C3 fraction
ActiveCN102206132ALower trend for deep hydrogenationEnhanced catalytic reaction selectivityHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsPolymer metalFixed bed
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method for a C3 fraction. The method is characterized in that: an adiabatic bed reactor is provided with a Pd-Ag catalyst, the Pd-Ag catalyst contains Al2O3 used as a carrier, 0.2-0.4% of Pd and preferable 0.05-0.2% of Ag based on 100wt% of the catalyst, the specific surface area of the catalyst is 15-100 m<2> / g, the pore volume of the catalyst is 0.3-0.6 mL / g, and the catalyst forms an organic polymer metal complex during preparation process; and the hydrogenation process conditions are as follows: the inlet temperature of the fixed bed reactor is 10-50 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 2.5-3.5 MPa, the liquid phase volume space velocity is 5-100 h<-1> and the mol ratio of hydrogen to propyne and propadiene is (1-5):1. The selective hydrogenation method provided by the invention improves the hydrogenation activity and selectivity, greatly broadens the reaction space velocity range, greatly improves the running safety and efficiency of an apparatus and greatly improves economical benefits of the apparatus.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Covalent triazine skeleton doped hybrid membrane preparation method
ActiveCN104722212AEasy and efficient preparationGood repeatabilitySemi-permeable membranesSilanesTriflic acid
A covalent triazine skeleton doped hybrid membrane preparation method comprises the steps of (1) preparation of a covalent triazine skeleton, to be more specific, the formula is organic monomer: a trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, wherein a = 5-50, the organic monomer and the trifluoromethanesulfonic acid are rapidly mixed in a microwave reactor for synthetic of CTFs material by microwave heating, the synthesis temperature is 100 to 150 DEG C, and the synthesis time is 10 to 60 minutes; (2) preparation of a hybrid membrane solution, to be more specific, the formula is b covalent triazine skeleton powder: organic matter, b = 1wt%-60wt%, the organic matter is polydimethylsiloxane, polymethylphenyl siloxane, polyimide, polysulfone and poly trimethyl silane-1-propyne; (3) preparation of the hybrid membrane on a porous carrier by a dipping method; and (4) drying of the hybrid membrane. The hybrid membrane prepared by the method has high liquid separation performance and certain gas separation performance, and the synthesis repeatability is good.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Technology for separating low carbon olefin gases
The invention discloses a technology for separating low carbon olefin gases, for solving the problems that hydrogen, methane, ethane and propane and other products with high purity can not be acquired and dimethyl ether and oxygen and carbon monoxide in impurities are not removed efficiently, etc. in the prior art. The technology is characterized in that a step of removing carbon monoxide and oxygen is added, methanol-to-olefin gas streams processed by removing carbon monoxide and oxygen enter into a deethanizing column, deethanizing column overhead streams successively pass through an ethene hydrogenation reactor, six separation pots, a low pressure demethanizing column and an ethene rectification column, etc. to separate to obtain ethene and ethane products, and deethanizing column bottom streams successively pass through a propyne hydrogenation reactor, a methane stripper and a propylene rectification column, etc. to separate to obtain propylene and propane products. According to the invention, polymer grade ethene and propylene products can be obtained, and hydrogen, methane, ethane and propane products, etc. with high purity can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Novel process and catalyst for carbon dioxide conversion to energy generating products
InactiveUS20080287555A1Simple processHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic compound preparationChemical reactionOxygen
A catalytic process and a nano material for the conversion of moist carbon dioxide into methanol, propyne and oxygen have been developed. In the process invented, hydrogen is produced from water in a catalytic reaction, when the moist carbon dioxide enters into the catalytic reactor, resulting in C—O and H—OH bond breakage at a relatively low temperature and at atmospheric pressure in a single step using a combination of catalytic materials comprising at least three metals dispersed on a catalyst support, preferably anatase form of titanium dioxide, to induce a multifunctional surface chemical reaction for the production of oxygenated products such as hydrocarbons of different chain lengths.
Owner:QUAID E AZAM UNIV
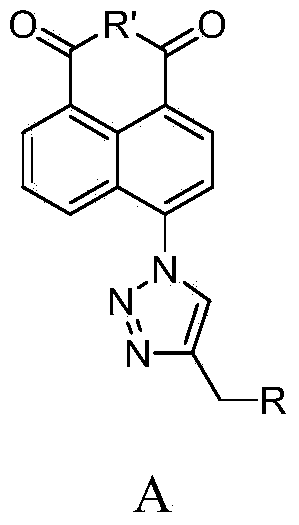
Synthesis of naphthalene nucleus 4-position 1,2,3-triazole containing naphthalimide derivative and application thereof
The invention relates to a synthesis of naphthalene nucleus 4-position 1,2,3-triazole containing naphthalimide derivative and application thereof, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The derivative has a compound in a general formula A structure; the preparation method of the derivative comprises the following steps: by using 4-bromo-1,8-anhydride naphthalene as raw material, amidating with the corresponding chain amine through azidation, finally reacting with an amido-propyne connected with cyclic amine; the obtained derivative is applied to a tumor cell inhibition drug.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Fourier transform infrared spectrum quantitative analysis-based transformer oil-immersed gas analysis system and analysis method thereof
InactiveCN101975761AAdvantages of Spectral AnalysisWon't happenSpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsGas analysisWater vapor
The invention discloses a Fourier transform infrared spectrum quantitative analysis-based transformer oil-immersed gas analysis system and an analysis method thereof. The system comprises a first transformer oil valve, a second transformer oil valve, an oil-gas separation device, a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer with an air chamber, a computer, an oil inlet pipe, a return oil pipe and a gas conveying pipeline. The analysis method comprises the following steps of: performing oil-gas separation on the transformer insulating oil, and then quantitatively analyzing the separated gas by using the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer to realize quick and quantitative analysis of the multi-component gas. The analyzed gas comprises iso-butane, n-butane, carbon monoxide, propylene, propyne, sulfur hexafluoride and water vapor besides methane, ethane, propane, ethylene, ethyne and carbon dioxide in conventional transformer oil-immersed gas analysis. Because of more categories of the analyzed gas, high speed, high resolution, low running cost, safety and reliability, the method is a transformer oil-immersed gas analysis method with broad application prospect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Boron fluoride dipyrrole fluorescent dye containing hydrophilic groups and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103865289ASimple reaction conditionsHigh yieldMethine/polymethine dyesLuminescent compositionsFluorescent spectraQuinone
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
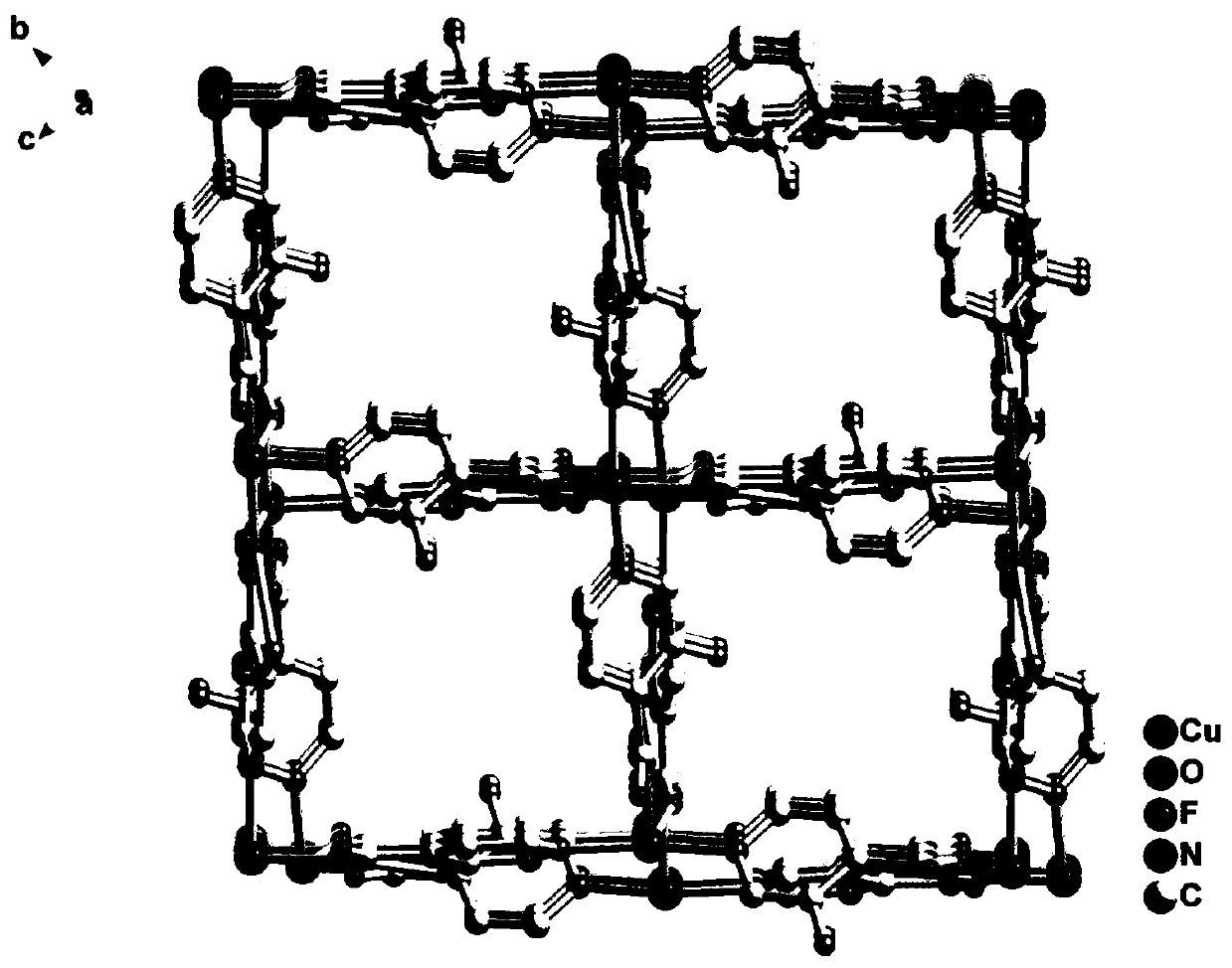
Two fluorinated metal organic framework materials and preparation and low-carbon hydrocarbon separation application thereof
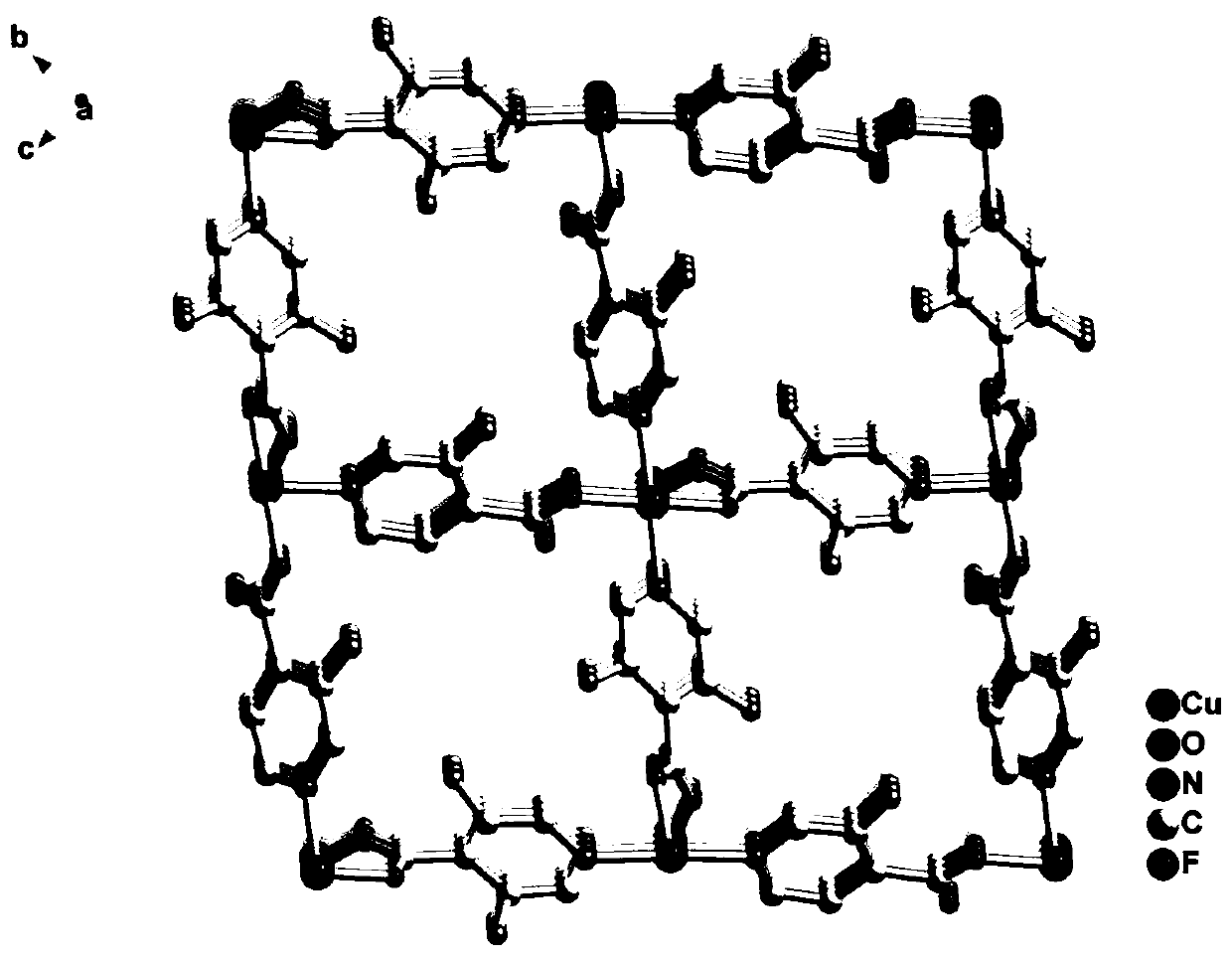
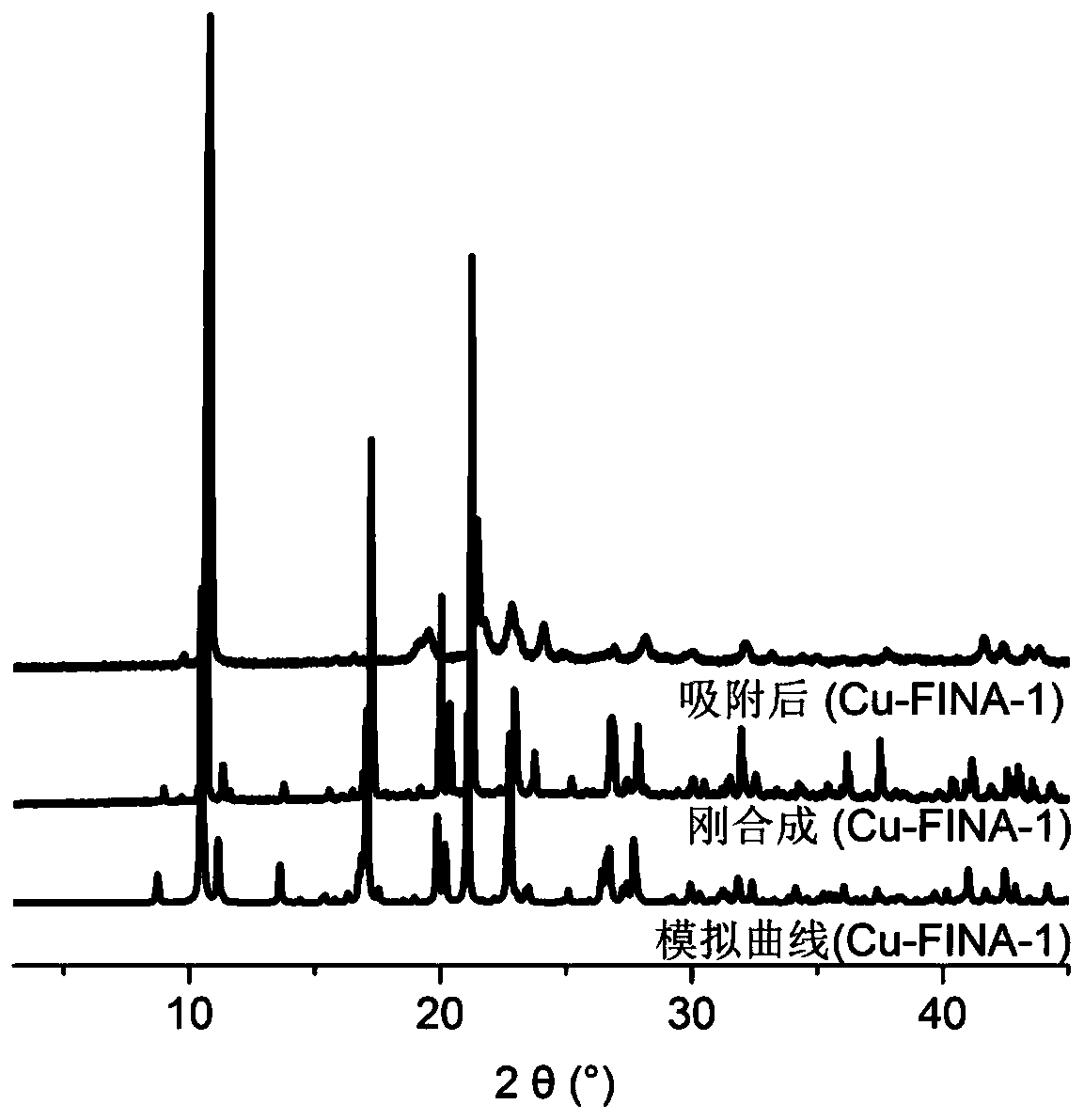
ActiveCN111072987ASimple structureLow priceOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationMetal-organic frameworkCopper nitrate
The invention discloses two fluorinated metal organic framework materials, preparation and low-carbon hydrocarbon separation application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of crystalline porous material preparation and gas separation. The two microporous copper-based MOF materials are formed by a cheap and easily available multi-coordination organic ligand 3-fluoroisonicotinic acid (FINA)and copper nitrate under different solvothermal conditions. The two MOF crystal structures have high porosity and have regular one-dimensional channels, the size of the channels is slightly larger than the molecular dynamics size of low-carbon hydrocarbon, and a structural basis is provided for adsorption separation of the low-carbon hydrocarbon gas molecules. Besides, hydrogen bond interaction sites exist in the pore channels, and alkyne molecules with smaller kinetic sizes can enter the pore channels easily after the pore channels are cut by fluorine atoms, and the acting force between alkyne gas molecules and the framework is enhanced so that the effect of preferentially adsorbing acetylene gas in acetylene-ethylene mixed gas and preferentially adsorbing propyne in propyne-propylene mixed gas is achieved, ethylene and propylene components in the mixed gas are purified, and the energy consumption in the separation process is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Separation method for preparing low-carbon olefin gas through methanol conversion
ActiveCN102675025AHigh purityReduce usageLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionAbsorption purification/separationOlefiant gasOxygen
The invention discloses a separation method for preparing low-carbon olefin gas through methanol conversion, and aims to solve the problems that products with high purity such as hydrogen, methane, ethane and propane which cannot be obtained in the prior art and oxygen, carbon oxide and the like in dimethyl enther and gas impurities cannot be effectively removed. According to the method, a step of removing the carbon oxide and the oxygen is increased, a methanol prepared olefin gas material flow from which the carbon oxide and the oxygen are removed enters a deethanizing column; the material flow on the top of the deethanizing column flows through an acetylene hydrogenation reactor, six separation tanks, a demethanizing column, an ethylene rectifying column and the like in sequence to separate to obtain ethylene and ethane products; and the material flow at the bottom of the deethanizing column flows through a propyne hydrogenation reactor, a methane stripping column, a propylene rectifying column and the like in sequence to separate to obtain propene and propane products. By using the separation method, polymer grade ethylene and propene products can be obtained, and products with high purity such as hydrogen, methane, ethane and propane can also be obtained.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Spiropyran photochromic compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104817528APhotochromic phenomenon is obviousReduce discolorationOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsAcetic anhydrideUltraviolet
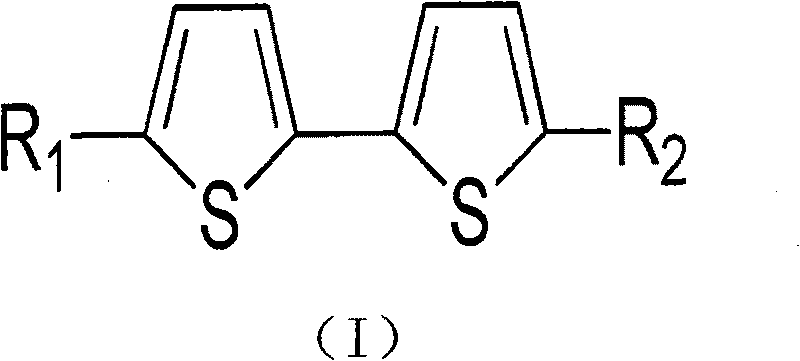
The invention relates to a spiropyran photochromic compound shown as formula I. The preparation method includes: subjecting 3, 4-dimethoxy benzophenone and butyric acid dimethyl ester to condensation reaction under an alkaline condition to obtain a compound s2, conducting acetic anhydride reflux cyclization to obtain 4-acetoxy-6, 7-dimethoxy-1-phenyl-2-naphthoic acid methyl ester, then performing alkaline hydrolysis to obtain 4-hydroxy-6, 7-dimethoxy-1-phenyl-2-naphthoic acid s4, subjecting the compound s4 to cyclization under an acidic condition to obtain an intermediate 5-hydroxy-2, 3-dimethoxy-7H-benzo[c]fluorine-7-one, then carrying out reaction with a methyl Grignard reagent to obtain 2, 3-dimethoxy-7-methyl-7H-benzo[c]fluorene-5, 7-diol, and finally under the catalysis of p-toluenesulfonic acid, reacting 2, 3-dimethoxy-7-methyl-7H-benzo[c]fluorene-5, 7-diol with 1, 1-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-propyne-1-ol to generate the compound shown as formula (I). The compound can change from colorless to green under ultraviolet irradiation, and can change from green to colorless after ultraviolet disappears.
Owner:JIANGSU SHIKEXINCAI CO LTD
Method for adsorption separation of propylene, propyne, propane and propadiene
ActiveCN109293467AStable structureImprove performanceGas treatmentOther chemical processesAlkaline earth metalSorbent
The invention discloses a method for separating propylene, propyne, propane and propadiene from a mixed gas. The method comprises: separating a mixed gas containing propylene, propyne, propane and propadiene by using a metal organic framework material as an adsorbent to obtain the gases of each single component, wherein the structural general formula of the metal organic framework material is [M(C4O4)(H2O)].1.5H2O, M is a metal ion, and transition metal ions or alkaline earth metal ions and squaric acid form a three-dimensional network structure through a coordination bond or intermolecular force. According to the present invention, the metal organic framework material has excellent adsorption separation selectivity to propylene, propyne, propane and propadiene, further has characteristicsof cheap and easily available raw materials, simple preparation process, low cost, good regeneration property and good repeatability, can maintain the original adsorption effect after vacuum or heating regeneration, and has broad industrial application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
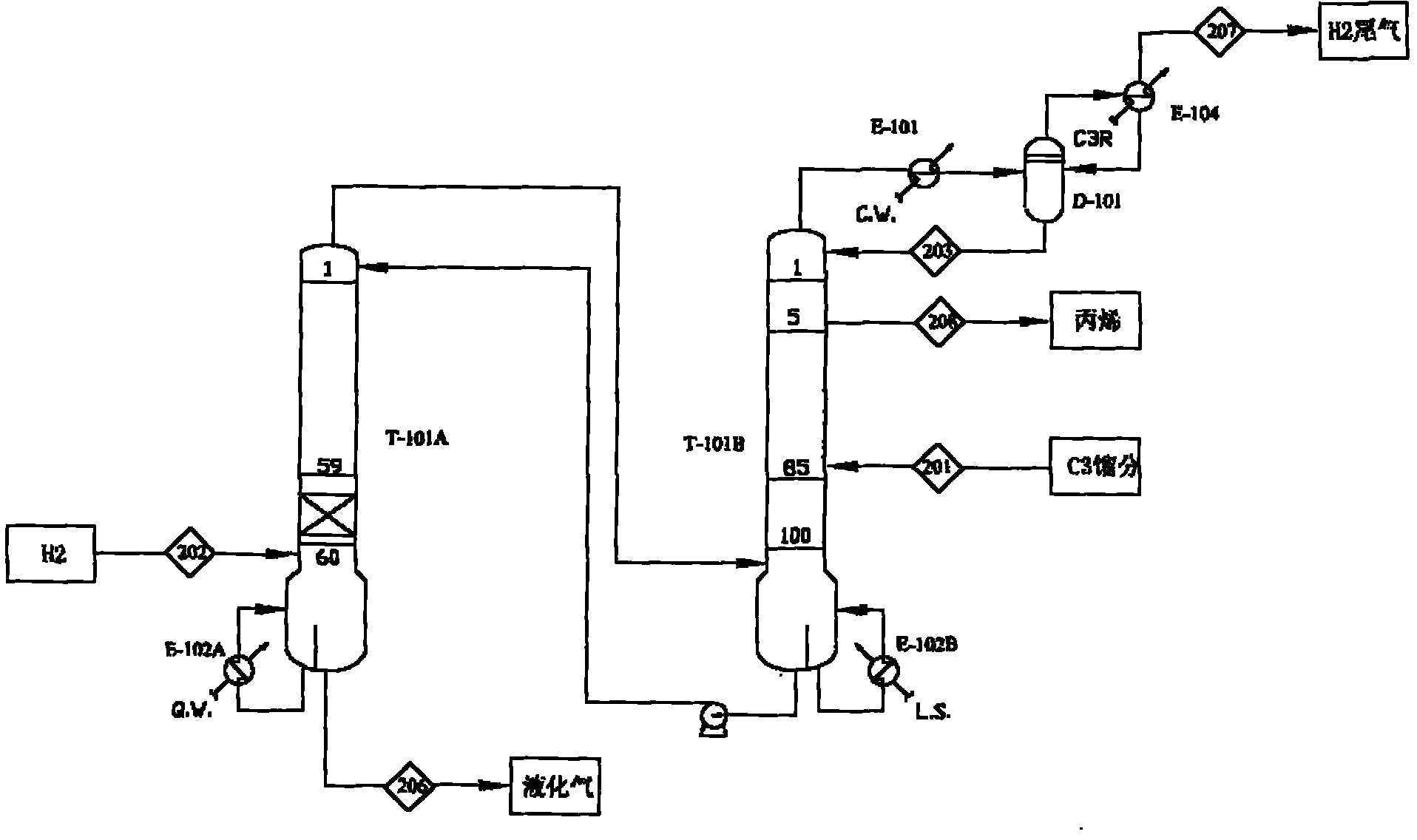
C3 fraction liquid phase selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN106608805ASimplify selective hydrogenation processImprove removal effectHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsHydrogenGas phase
The invention discloses a C3 fraction liquid phase selective hydrogenation method, wherein the method comprises the steps: mixing propargyl and / or allene-containing fresh C3 fraction a extracted from a depropanization tower in a propylene production process, a circular C3 material flow b and hydrogen gas c, then making the mixture contact with a selective hydrogenation catalyst, and carrying out selective hydrogenation; carrying out gas-liquid separation of the material obtained from the selective hydrogenation to obtain a gas phase material flow g containing propylene and propane and a liquid phase material flow h containing propylene and propane; dividing the liquid phase material flow h containing propylene and propane into a first part material flow i and a second part material flow j, and taking the first part material flow i as the circular C3 material flow b; and allowing the second part material flow j to return to the depropanization tower. The method provided by the invention not only effectively removes acetylene and / or allene in the C3 fraction but also reduces the energy consumption, and has incomparable superiority compared with the prior art.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Bithiophene compound and pharmaceutical composite and application thereof
InactiveCN101723940AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCombinatorial chemistryPropyne
The invention relates to bithiophene compounds shown in a general formula (I) and a preparation method and applications thereof, wherein the R1 is -H, -CHO, -COOH, -CHOHCH2OH, -CH2OH or -CH3 and R2 is -H, -1-propyne, -4-hydroxy-1-butyne, -3,4-dihydroxy-1-butyne or -COCH2CH2CH2OH.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalytic rectification method for removing MAPD by selective hydrogenation
ActiveCN102040446AHigh conversion selectivityLow inactivation effectHydrocarbon by hydrogenationGaseous fuelsHydrogenTower
The invention provides a catalytic rectification method for removing methyl acetylene and propadiene (MAPD) by selective hydrogenation. The method comprises the following steps of: placing a catalytic rectification member below a C3 fraction feeding position of a propylene rectification tower, introducing hydrogen into the tower from the lower part of the catalytic rectification member, and making the hydrogen upwards flow through the catalytic rectification member; and directly feeding the C3 fraction containing the MAPD into the propylene rectification tower or feeding the C3 fraction whichis pre-transformed through a first MAPD reactor into the propylene rectification tower to perform catalytic rectification and remove MAPD, directly recovering propylene meeting the polymerization level requirement from a lateral line, or recovering the material from the top of the tower, and removing light components to obtain polymerization level propylene, wherein the molar fraction of the MAPDin the tower can be directly reduced to below 0.1 to 2 percent. The method is characterized in that: by using the characteristic of low concentration of the propylene in the propylene rectification tower, the probability of side reaction of transforming the propylene into propane can be reduced, the selectivity of MAPD transformation is improved, and the purpose of high propylene yield is fulfilled.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
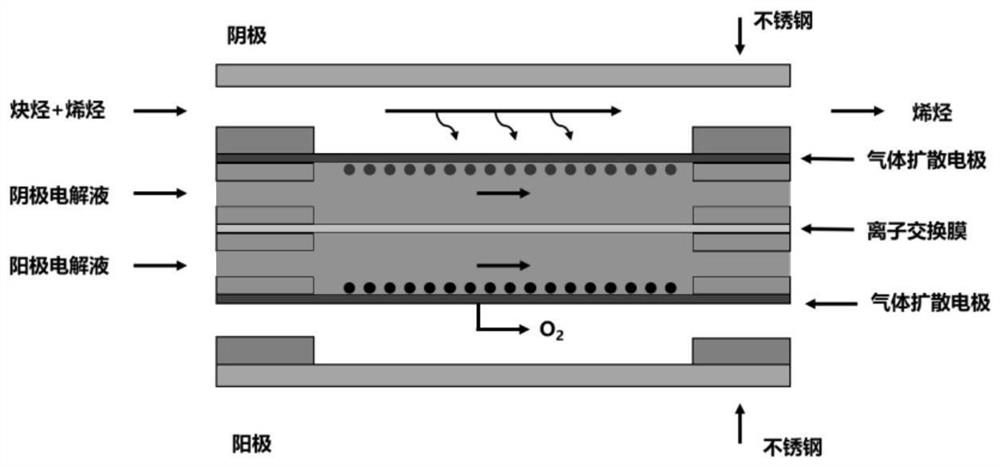
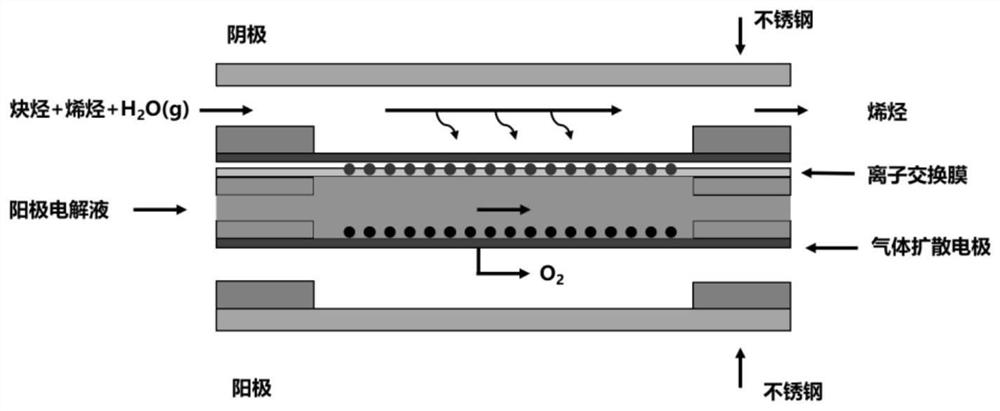
Method for electrocatalytically and selectively reducing alkyne impurities in olefin
PendingCN112301373AReduced residual concentrationReduce consumptionElectrolytic organic productionElectrodesPtru catalystAlkyne
The invention relates to a method for electrocatalytically and selectively reducing alkyne impurities in olefin, particularly to electrocatalytical and selective hydrogenation of acetylene, propargyl,butyne, phenylacetylene and the like. According to the invention, a gas diffusion electrode electrolytic tank is adopted, a catalyst is sprayed on a gas diffusion layer substrate (including conductive carbon paper and metal) to prepare a gas diffusion electrode, a cathode and an anode are isolated by an ion exchange membrane, and a three-electrode or two-electrode system constant voltage method is adopted to carry out electrochemical performance test, wherein the reaction gas olefin contains 1% of alkyne impurities; experimental results show that the residual concentration of olefin can be reduced to 5 ppm or below by regulating and controlling a proper voltage range; and compared with a traditional thermal catalysis technology, the method of the invention can selectively reduce alkyne impurities in olefin into olefin at normal temperature and normal pressure without hydrogen consumption, can greatly reduce energy consumption and potential risks in the process, better meets the requirements of green chemical engineering, and has great strategic significance.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Rigid tetracarboxyl hydrogen bond organic framework material as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN113201144ASimple preparation processLow costOther chemical processesAdsorption purification/separationCarboxyl radicalPhenyl group
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials, and particularly relates to a rigid tetracarboxyl hydrogen bond organic framework material and preparation and application thereof. The monomer molecule H4TPA of the rigid tetracarboxyl hydrogen bond organic framework material is N, N, N', N'-tetra (4-carboxyphenyl)-1, 4-phenylenediamine. The framework belongs to an orthorhombic system; the space group is Ibca; alpha = beta = gamma = 90 degrees; Z = 8; each tetrahedral H4TPA molecule is connected with four adjacent H4TPA molecules through four pairs of intermolecular -COOH... HOOC- hydrogen bonds; and the distance of O... O and the angle of O-H.... O are 2.6 angstroms and 171 degrees respectively. The rigid tetracarboxyl hydrogen bond organic framework material has the beneficial effects that the rigid tetracarboxyl hydrogen bond organic framework material is simple in preparation process and low in cost, is applied to selective separation and adsorption of propylene and propyne in C3H4 / C3H6 mixed gas, is easy to recycle and regenerate, and has good separation stability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Synthesis and application of novel vinyl boronizing reagent
ActiveCN104211723AImprove processing stabilitySimple and fast operationGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsHydrogen fluorideSynthesis methods
The invention relates to synthesis and application of a novel vinyl boronizing reagent, the reagent can be coupled with other organic boric acid to obtain trans potassium alkenyltrifluoroborate in various forms. The synthesis method is as below: slowly introducing propyne into a dichloromethane solution of boron tribromide at -10 to 0 DEG C; directly adding potassium fluoride aqueous solution or quenching under acidic conditions to obtain boric acid; then directly addingg potassium hydrogen fluoride to obtain a target boronizing reagent trans-bromoethenyl trifluoro borane potassium (1), which is a white flake solid, wherein the yield in the step is 71-82%. The boronizing reagents can be subjected to Suzuki coupling to be effectively applied in synthesis of trans potassium alkenyltrifluoroborate (3) in different forms. The invention has the advantages of high stereoselectivity and strong stability of the product, suitability for long time storage, and simple, fast and high yield synthesis method.
Owner:CANGZHOU PURUI DONGFANG SCI & TECH
Selective hydrogenation method for methanol to olefin product
InactiveCN108250010AModerate reactivityGreat operating flexibilityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalystsInorganic oxideMethanol
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method for a methanol to olefin product. An Fe-Co hydrogenation catalyst is employed for selective hydrogenation of a C2 and C3 mixture from a dryingtower bottom in an adiabatic bed reactor. The raw material composition includes, by volume, 1.2-1.5% of H2, 0.5-1.0% of N2, 0.005-0.015% of O2, 0.6-1.0% of CO, 0.2-0.6% of CO2, 0-0.0008% of H2S, 6-10% of methane, 1-2% of ethane, 0-0.01% of acetylene, 40-60% of ethylene, 1.5-3% of propane, 15-40% of propylene, 0-0.01% of propyne, 3-6% of C4, and 6-10% of C5 or above. The reaction conditions include: a temperature of 25DEG C-50DEG C, a pressure of 1.5-2.5MPa, and a space velocity of 2000-15000h<-1>. The hydrogenation catalyst carrier is a high temperature resistant inorganic oxide, and the active components at least contain Fe and Co, in terms of a 100% catalyst mass, the catalyst contains 2-6% of Fe and 0.5-1.0% of Co. The catalyst has mild hydrogenation activity and excellent ethylene selectivity, no ethylene loss, low "green oil" production, and much lower cost than a precious metal Pd catalyst.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Preparing method for parecoxib sodium
ActiveCN105418528AShort synthetic routeReaction raw materials are stable and easy to obtainOrganic chemistryChlorosulfuric acidPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the field of medicine chemical industry and particularly relates to a preparing method for parecoxib sodium. According to the method, benzaldoxime (compound I) and 1-phenyl-1-propyne (compound II) are subjected to an addition reaction under existence of a catalyst and an acid-binding agent to construct an isoxazole ring to obtain a parecoxib sodium intermediate (compound III); the compound III is subjected to a sulfonation and sulfonylation reaction to obtain a compound IV, and the compound IV and propionic anhydride react to form salt to obtain parecoxib sodium (compound V). According to the method, the dipole ring addition reaction is creatively adopted for preparing the compound III, common safe and low-toxicity reagents chlorosulfuric chlorosulfonic acid and ammonia water with relative stable nature are used to be subjected to the sulfonylation reaction, and the method has the advantages that the reaction condition is mild, operation is reasonable, selectivity is high, and product quality is high; raw and auxiliary materials in the reaction are low in price, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG LUOXIN PARMACEUTICAL GROUP STOCK CO LTD
Dimethyl ether fuel compositions and uses thereof
The present invention provides useful fuel compositions which may be produced substantially from renewable resources, such as biomass, to provide green fuel compositions, methods, and systems. In some embodiments, fuel compositions include dimethyl ether and one or more C2 or larger alcohol, such as ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 1-butanol, 2-butanol, isobutanol, or tert-butanol. In some embodiments, fuel compositions include dimethyl ether and one or more C2 or larger hydrocarbons, such as propane, propylene, propyne, and propadiene, n-butane, isobutane, isobutylene, 1-butene, 2-butene, or 1,3-butadiene. Methods of making these novel DME-based fuel compositions, particularly from biomass-derived syngas, are described. Various applications and methods of using the fuel compositions, such as portable cylinder fuels for camping, are disclosed. Additionally, principles of burner design for these fuel compositions are disclosed herein.
Owner:MAVERICK BIOFUELS
Synthetic method of propyne cellulose
The invention discloses a synthetic method of propyne cellulose. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) wetness-swelling: adding cellulose into N,N-dimethyl acetamide or N,N-dimethyl formamide for swelling; (2) dissolving: adding LiCl into a solution obtained in the step (1), continuously stirring, and fully dissolving cellulose; (3) reacting: cooling a solution obtained in the step (2) to the room temperature, and adding a catalyst and halogenated propyne for reacting; (4) precipitating: adding a solution obtained in the step (3) into a water-ethanol mixed solution for precipitating a reaction product; (5) purifying: washing a precipitate obtained in the step (4) with ethanol and water in sequence; and (6) drying. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of one-step homogeneous reaction, easiness, high synthesizing efficiency and uniform reaction.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Porous concrete waterproofing agent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a porous concrete waterproofing agent and a preparation method thereof. The waterproofing agent is prepared from, by weight, 25-40 parts of modified gel, 4-6 parts of an oxidizing agent, 5-9 parts of a cross-linking agent and 3-5 parts of a photoinitiator; the modified gel is prepared from, by weight, 30-40 parts of pretreated microspheres, 25-30 parts of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 15-20 parts of N-hydroxysuccinimide, 15-20 parts of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, 18-25 parts of sodium alginate and 10-14 parts of propyne. According to the porous concrete waterproofing agent and he preparation method thereof, process design is simple, and component proportion is reasonable; chitosan and sodium alginate are modified, and a Michael addition reaction and a chemical click reaction are used for forming a compact double-gel network, so the waterproof and seepage-proof performance of concrete can be effectively improved in use, meanwhile, the waterproofing agent can be self-repaired, and the waterproofing agent can be widely applied to concrete construction and has high practicability.
Owner:佛山市志必合材料有限公司
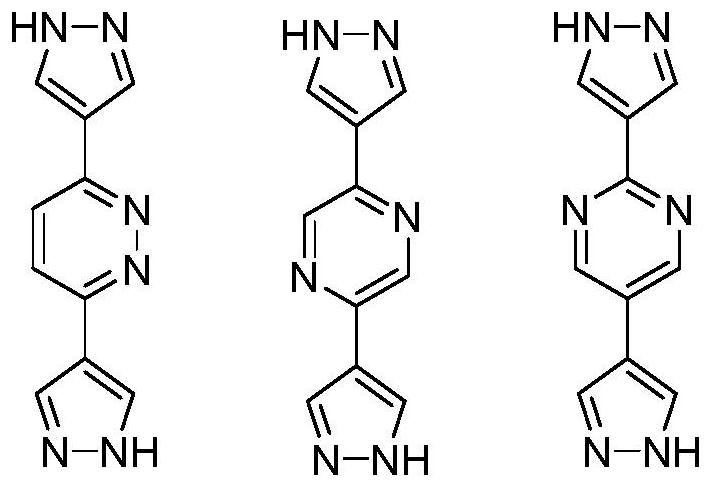
Polynuclear cobalt cluster metal organic framework material based on two-end pyrazole ligands and application
The invention discloses a polynuclear cobalt cluster metal organic framework material based on two-end pyrazole ligands and application, and belongs to the technical field of crystalline materials. The chemical formula is [Co8 (OH) 4 (OH2) 2 (BPZ-X) 6], H2BPZ-X is aryl di (1H-pyrazole), X represents an aromatic ring, and X = Pd, Pz and Pm, which are pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl and pyrimidinyl respectively. The synthesis conditions of the metal organic framework are as follows: in a closed environment, an organic ligand aryl di (1H-pyrazole) (H2BPZ-X) and cobalt nitrate are subjected to a solvothermal reaction in a mixed solution of N, N-dimethylformamide and water to obtain a crystal of a metal organic framework material; and the metal organic framework material shows separation performance onpropylene / propyne mixed gas.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
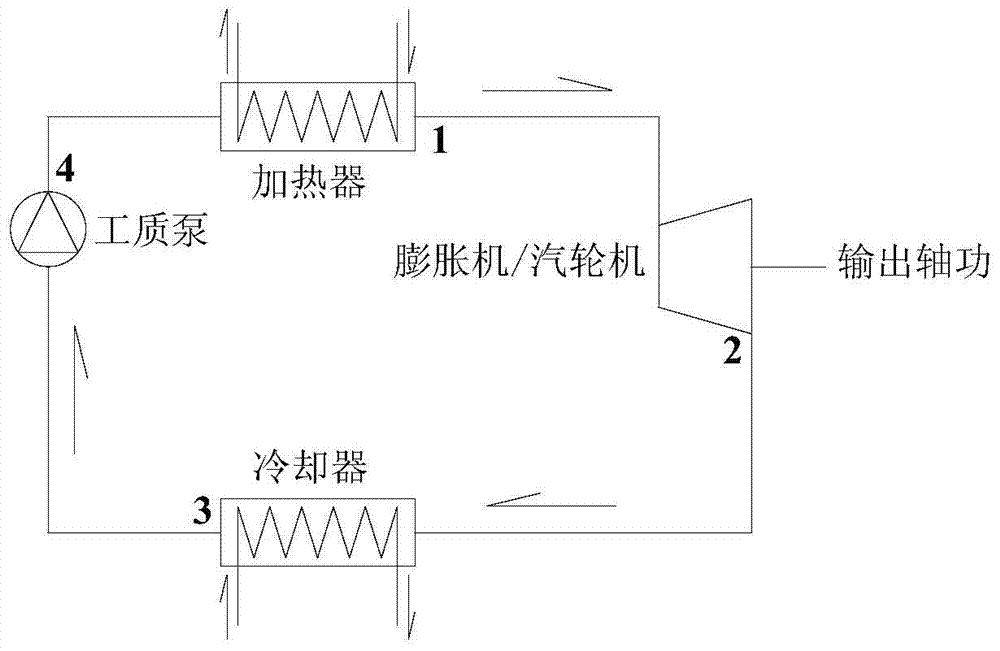
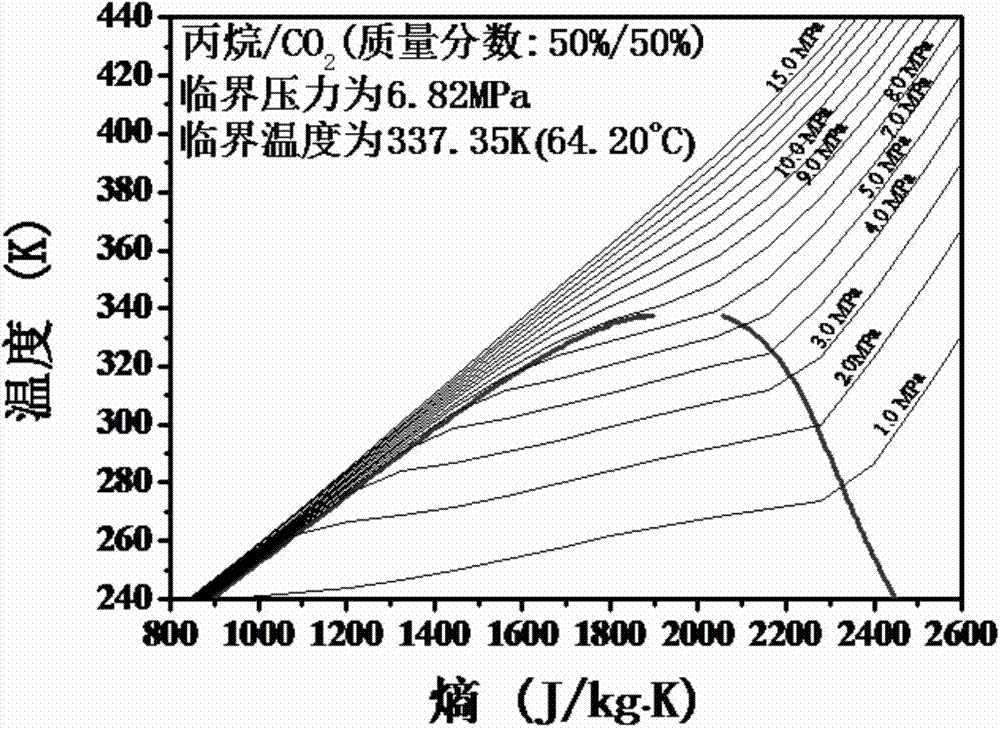
Novel power cycle mixed working medium taking CO2 as main component, as well as system and method thereof
ActiveCN103937459AHigh critical temperatureLow critical pressureHeat-exchange elementsButenePower cycle
The invention relates to the technical field of power machinery, and discloses a novel power cycle mixed working medium taking CO2 as a main component, as well as a system and a method thereof. The mixed working medium is prepared by physically mixing CO2 with one of propane, cyclopropane, propyne, butane, iso-butane, cis-butene, trans-butene and cyclopentane at certain proportion. The mixed working medium takes CO2 as a main component and one of propane, cyclopropane, propyne, butane, iso-butane, cis-butene, trans-butene and cyclopentane as a second component, so that the mixed working medium can be condensed by the conventional cooling water, and the working medium also has lower flammability. When being used for exchanging heat with a heat source fluid, the mixed working medium has better temperature matching, and the cycling has higher efficiency.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Selective hydrogenation method for allylene and allene in propylene material flow
ActiveCN102249836AGuaranteed reaction selectivityGuaranteed reactivityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrogenation reactionPalladium catalyst
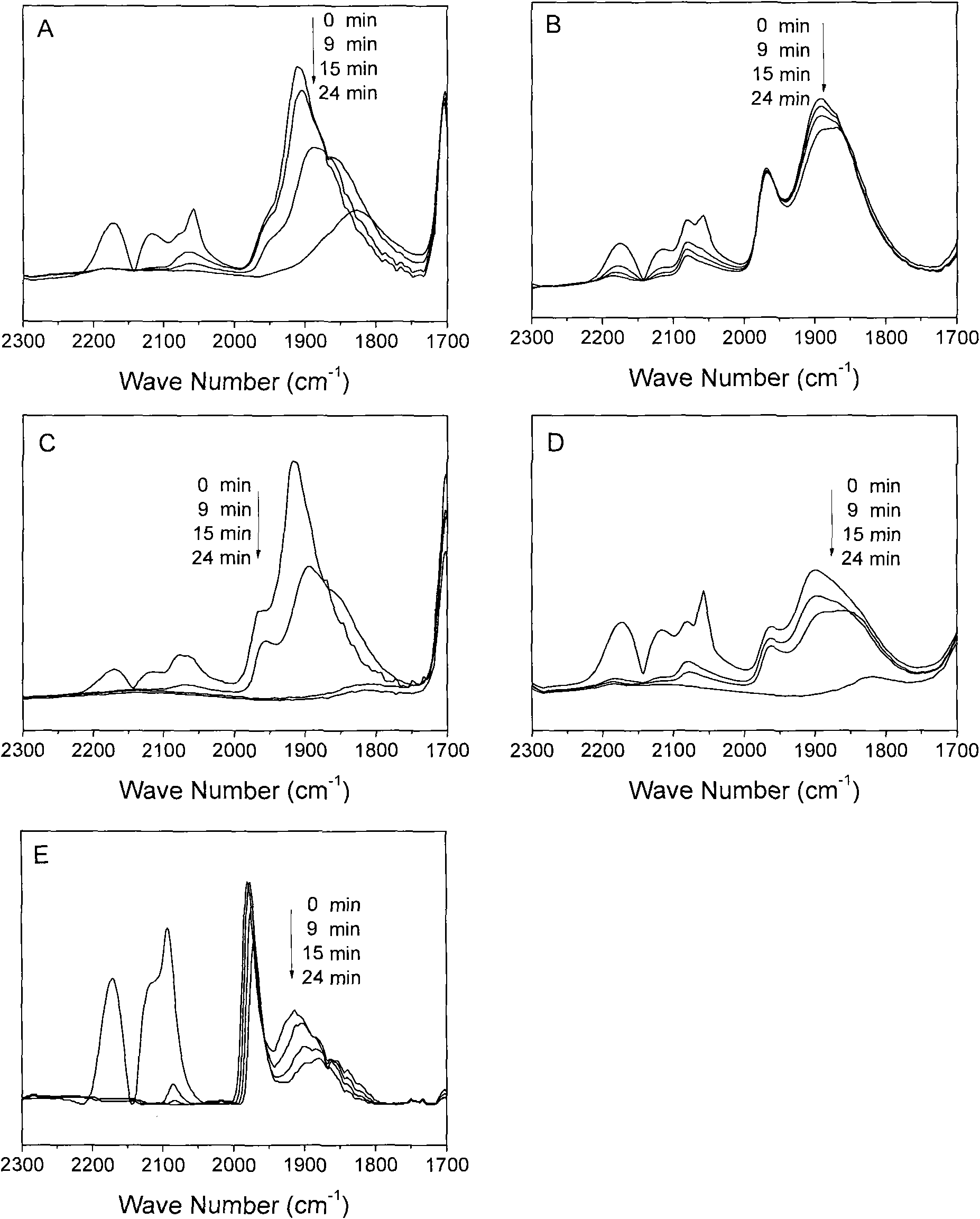
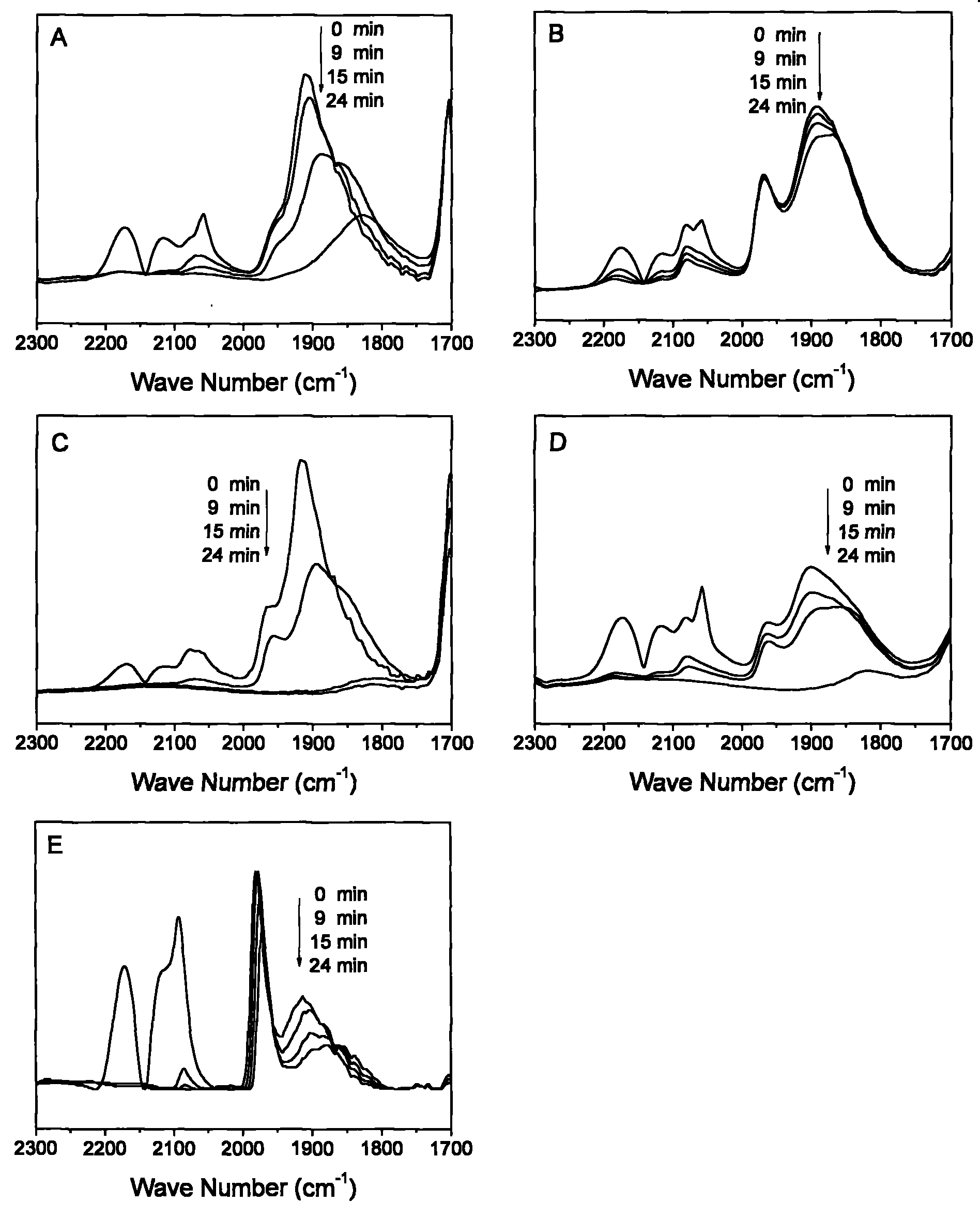
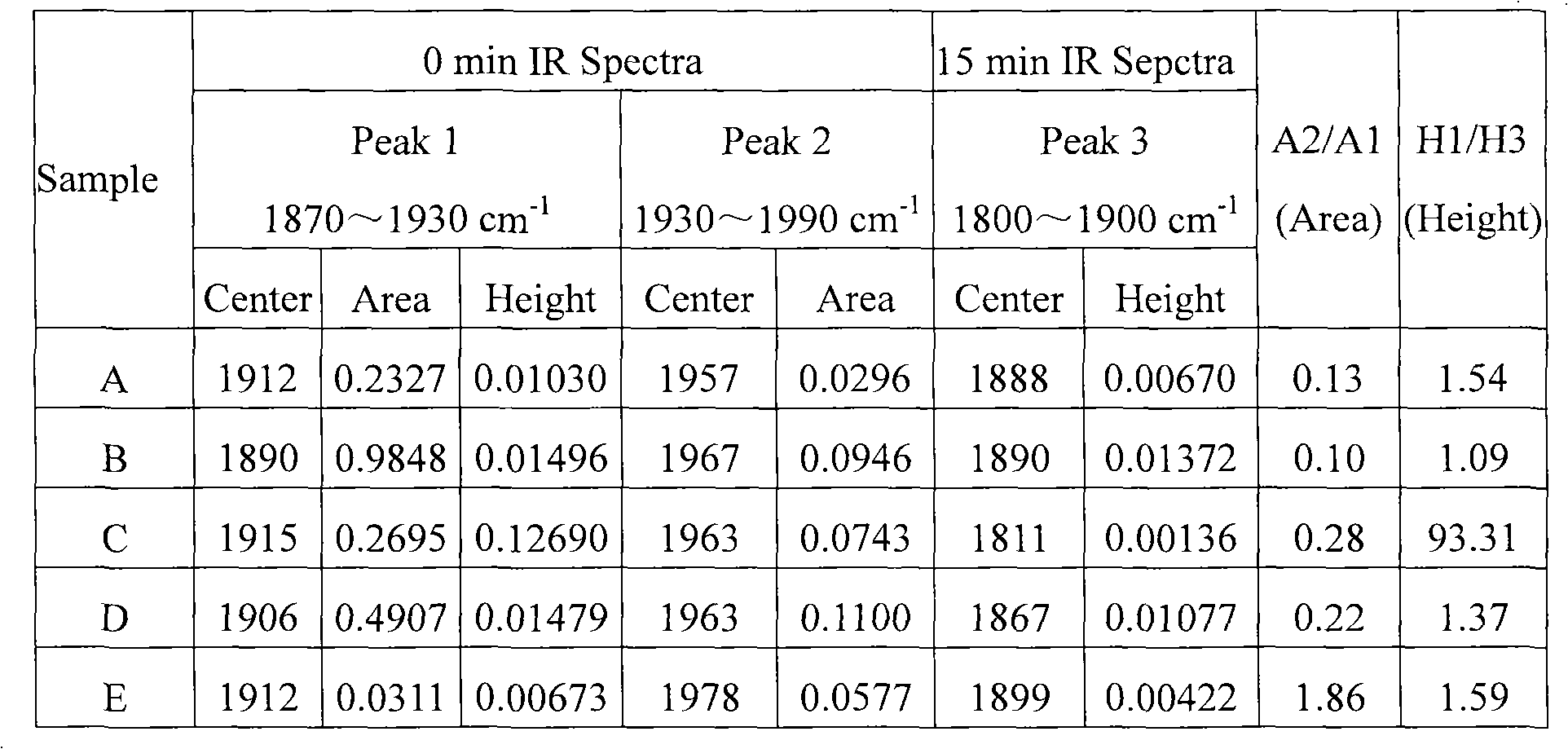
The invention provides a selective hydrogenation method for allylene and allene in propylene material flow. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing the propylene material flow containing 1-(methylamino)-2,3-propanediol (MAPD) and hydrogen into a hydrogenation reactor filled with a supported palladium catalyst, and performing selective hydrogenation on the MAPD in the propylene material flow at the inlet temperature of between 10 and 80 DEG C and a molar ratio of the hydrogen to the MAPD of 1-5 under the reaction pressure of 0.1-4Mpa, so that the MAPD becomes propylene and is removed, wherein the catalyst comprises a carrier, palladium and optional modifying components; and a carbon monoxide adsorption in situ infrared ray spectroscopy is used for testing the catalyst at 40DEG C, and an area ratio of a bridge absorption peak at a position of 1,930-1,990cm<-1> to a bridge absorption peak at a position of 1870-1,930cm<-1> in an infrared spectrum is less than 0.2 and preferably less than 0.15. By the method, the selective hydrogenation reaction for the allylene and allene in the propylene material flow has high selectivity, and can be stably performed for a long period.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst for preparing propylene through selective hydrogenation of propyne as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
PendingCN112452340AReduce loadGood dispersionHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalystsPtru catalystNon noble metal
The invention relates to a preparation method of a catalyst, in particular to a catalyst for preparing propylene through selective hydrogenation of propyne as well as a preparation method and application of the catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of organic chemistry. The catalyst for preparing propylene through selective hydrogenation of propyne is a supported noble metal catalyst, gamma-Al2O3 is used as a main component of a catalyst carrier of the catalyst, and MgO is attached to the surface of the carrier to form a composite metal oxide carrier; one or more of noble metals Ru, Pdand Pt are used as main active components, and the content of the noble metals is 0.1-3.0 wt% based on the weight content of the final catalyst; and one or more of non-noble metals Cu, Zn and Co are used as auxiliary metals to modify the noble metals, and the molar ratio of the noble metals to the non-noble metals is 1: 1-10.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SATELLITE ENERGY CO LTD
Preparation method of gas sensor array for detecting medicinal-flavor liquor
InactiveCN103424328AReduce the impactImprove resolutionWeighing by absorbing componentSensor arrayPolyvinyl alcohol
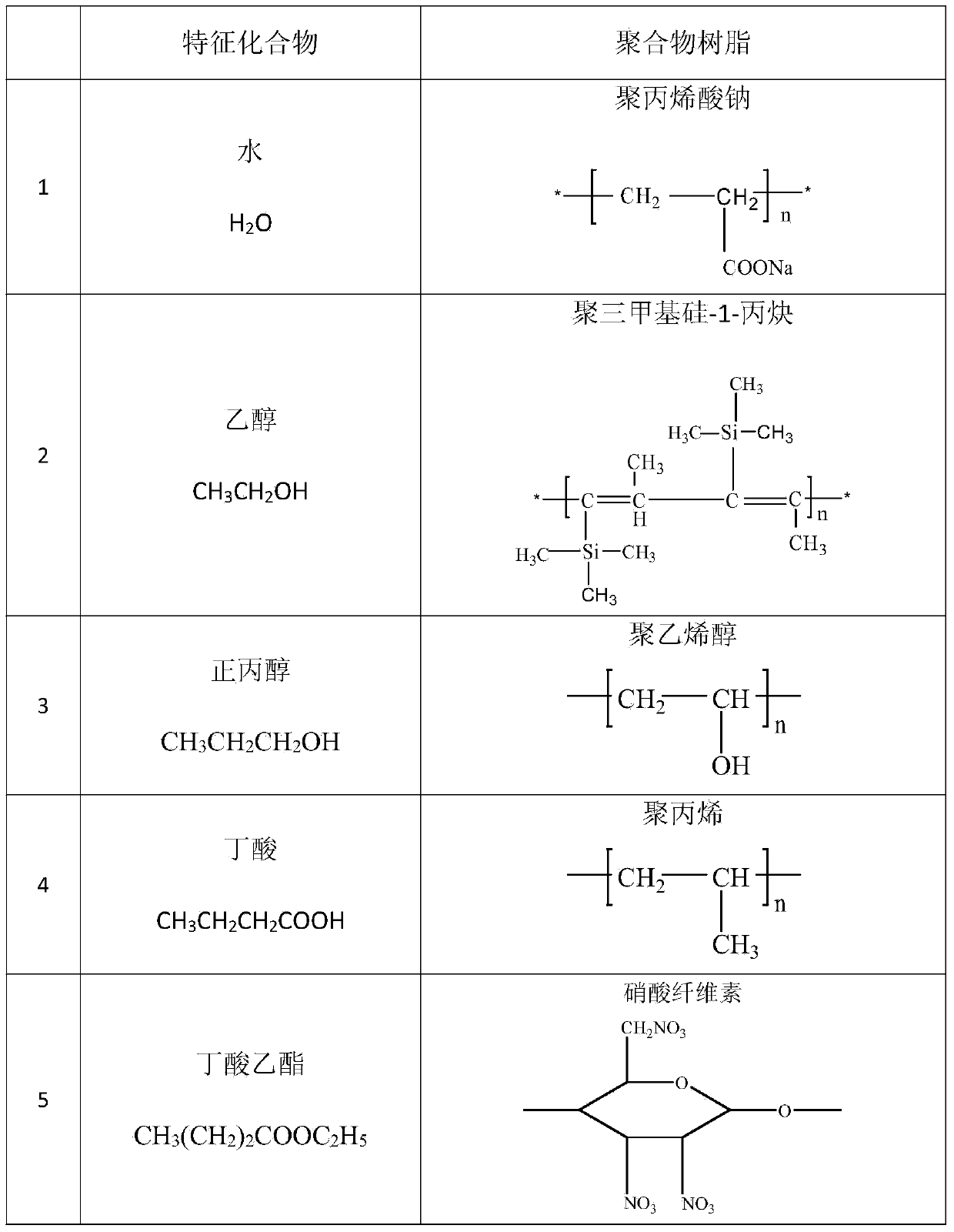
The invention provides a preparation method of a gas sensor array for detecting medicinal-flavor liquor. The method includes (1) evaporating sodium polypropylene, polyethylene trimethylsilyl-1-propyne, polystyrene, nylon-66 and nitrocellulose on different quartz substrates by a vacuum coating machine; (2) welding evaporated quartz substrates on a circuit board. The gas sensor array prepared by the method is small in size, low in cost, good in repeatability, small in affection produced by coexisting gases and high in resolution performance for gas mixture, and is capable of being operated for long time; an electronic nose system produced by combining the gas sensor array with a piezoelectric system is used, a pre-treatment process with tedious samples is omitted during detection of authenticity of the medicinal-flavor liquor, the detection can be performed directly, response speed is high, and accuracy is good.
Owner:中安高科检测科技(北京)有限公司
Dry Etching Agent and Dry Etching Method Using the Same
ActiveUS20120298911A1High GWPEasy to produceOrganic chemistrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess windowDry etching
A dry etching agent according to the present invention contains (A) a fluorinated propyne represented by the chemical formula: CF3CCX where X is H, F, Cl, Br, I, CH3, CFH2 or CF2H; and either of: (B) at least one kind of gas selected from the group consisting of O2, O3, CO, CO2, COCl2 and COF2; (C) at least one kind of gas selected from the group consisting of F2, NF3, Cl2, Br2, I2 and YFn where Y is Cl, Br or I; and n is an integer of 1 to 5; and (D) at least one kind of gas selected from the group consisting of CF4, CHF3, C2F6, C2F5H, C2F4H2, C3F8, C3F4H2, C3ClF3H and C4F8. This dry etching agent has a small environmental load and a wide process window and can be applied for high-aspect-ratio processing without special operations such as substrate excitation.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
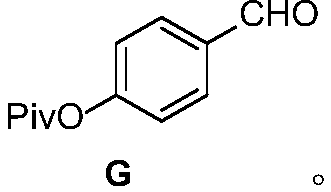
Method for synthesizing AMG837
ActiveCN110590767AMild reaction conditionsGood repeatabilityAsymmetric synthesesCombinatorial chemistryRepeatability
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a compound, in particular to a method for synthesizing AMG837. The method comprises the following steps: a step of preparing an intermediate D by a reaction of an intermediate E with propyne; a step of deprotecting the intermediate D to prepare an intermediate B; a step of preparing an intermediate A by a reaction of the intermediate B with an intermediate C; and a step of hydrolyzing the intermediate A. According to the method, a chiral C-C bond of the AMG837 is constructed by taking a Sonogashira C(sp)-C(sp<3>) asymmetric cross coupling reaction as a key step, so that the synthesis route is obviously shortened, and the total yield can reach 10%. The reaction condition is mild, repeatability is good, industrial expansion synthesis is easy, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com