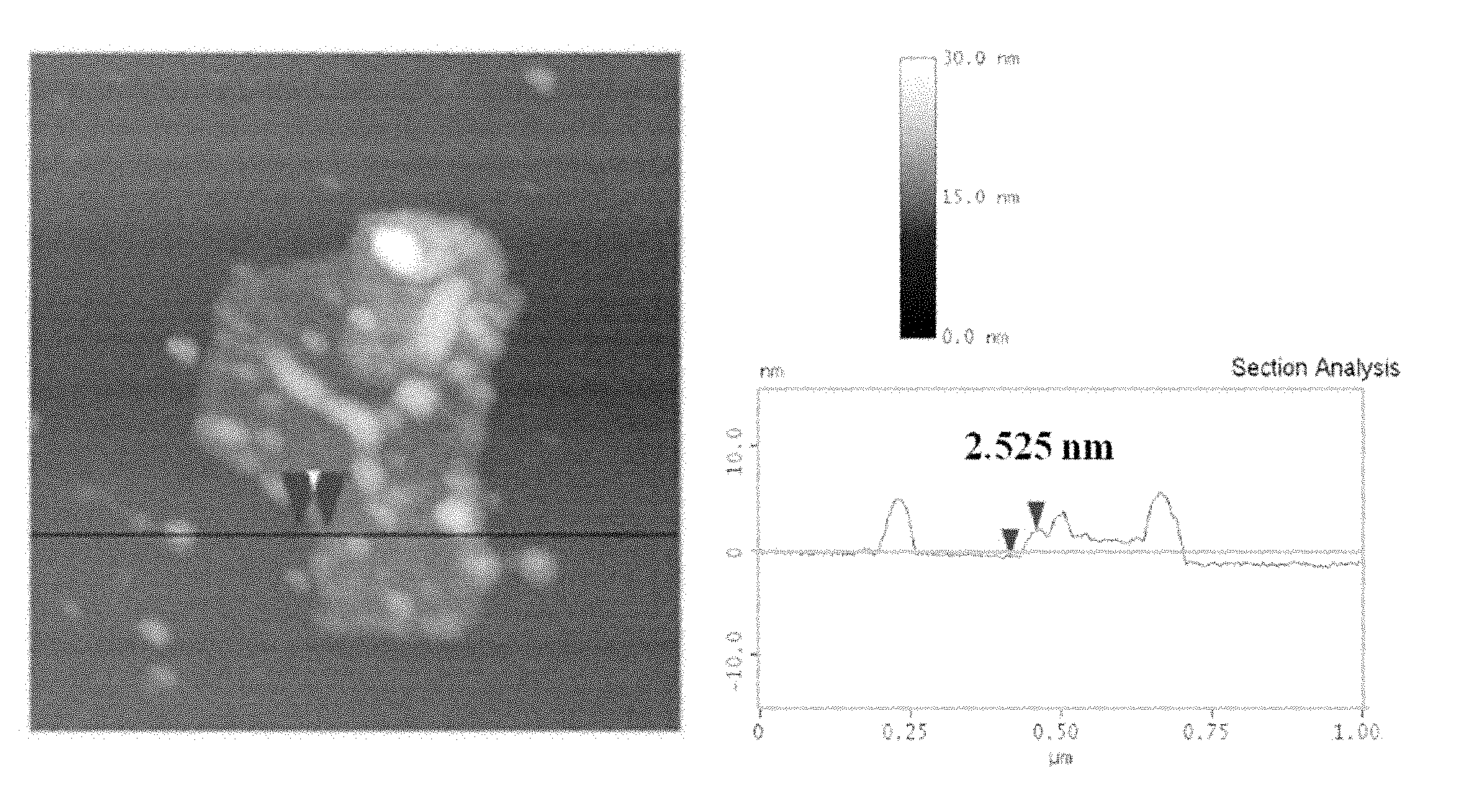
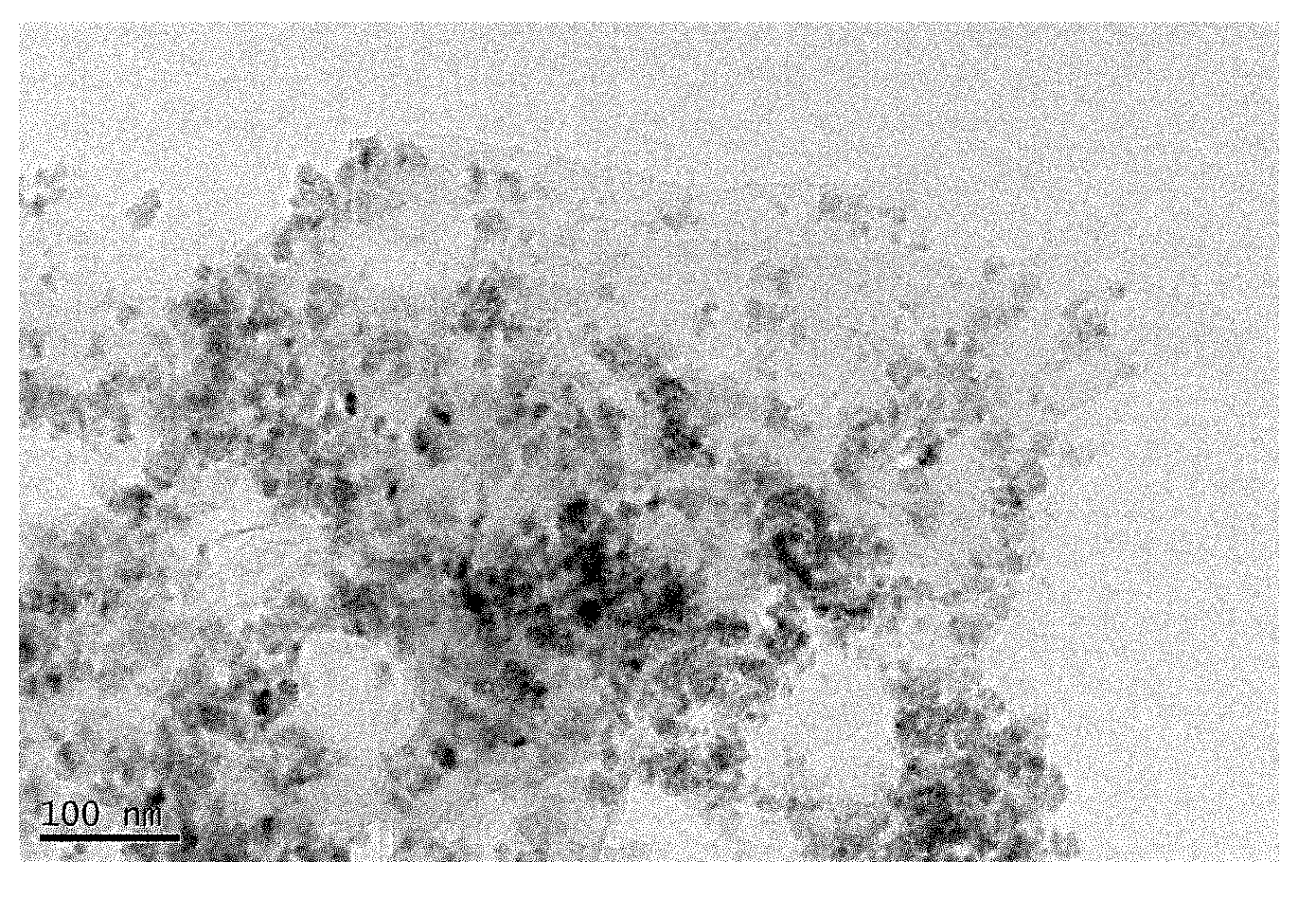
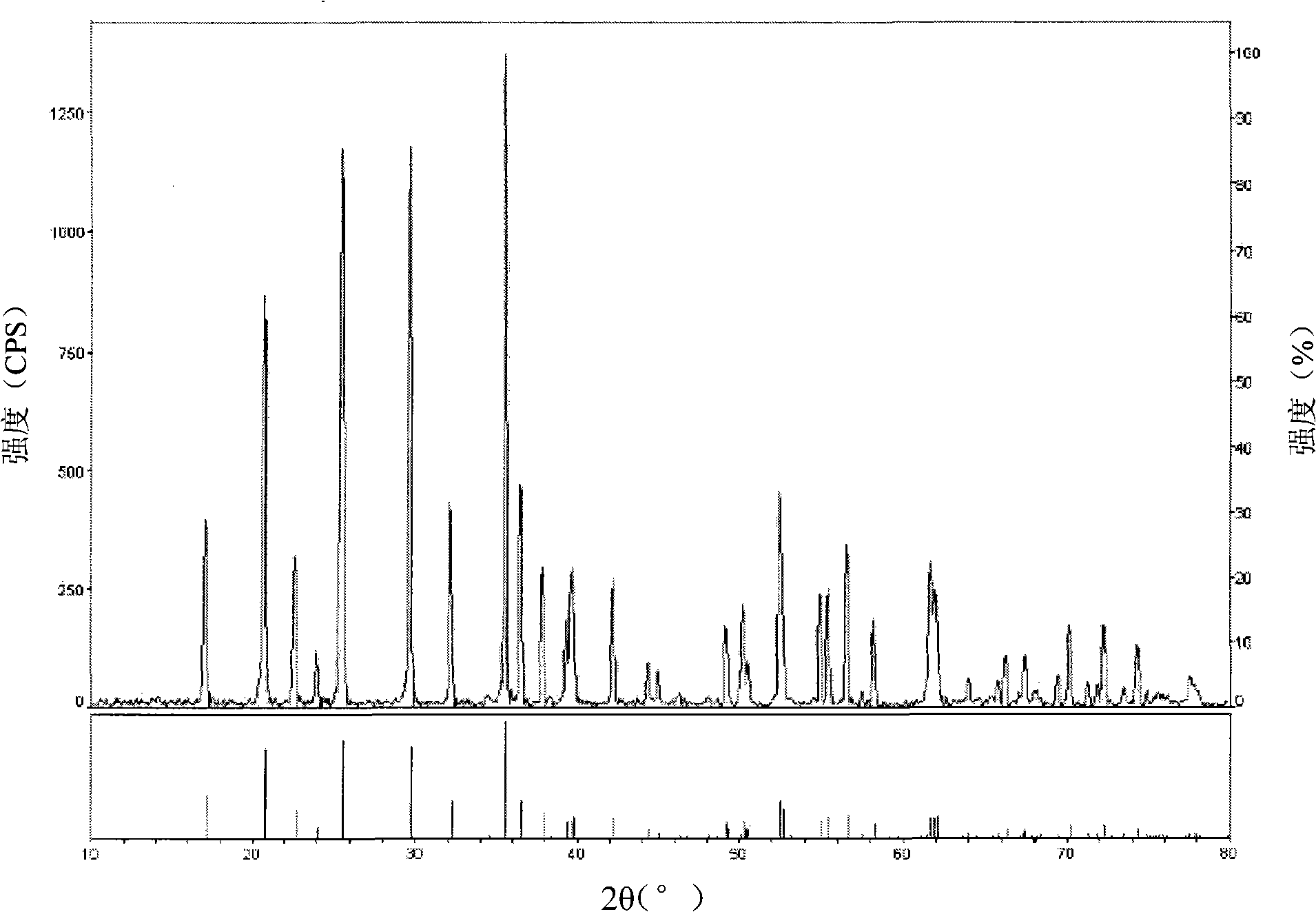
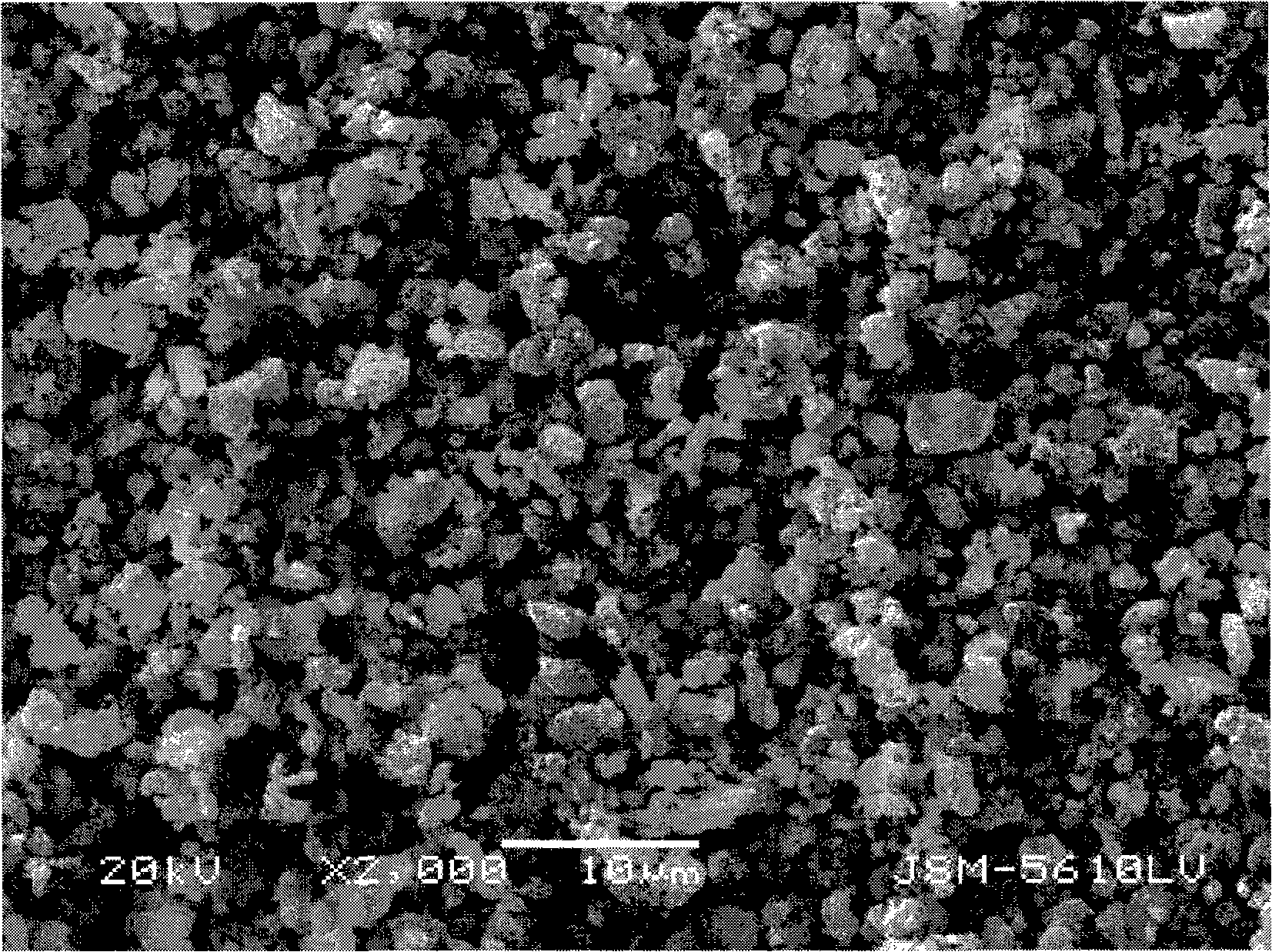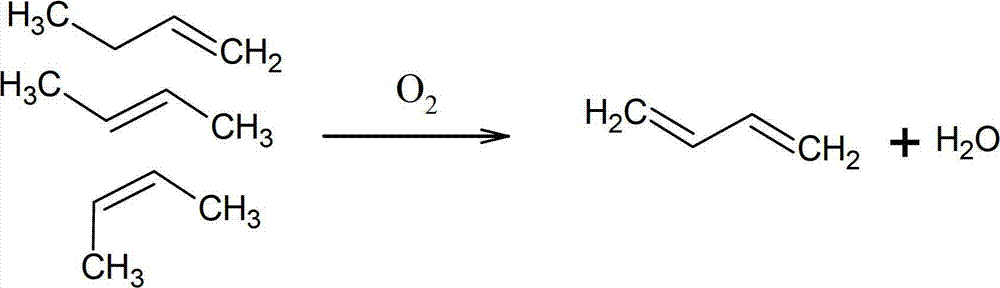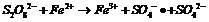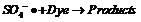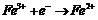Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2900 results about "Ferric salts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
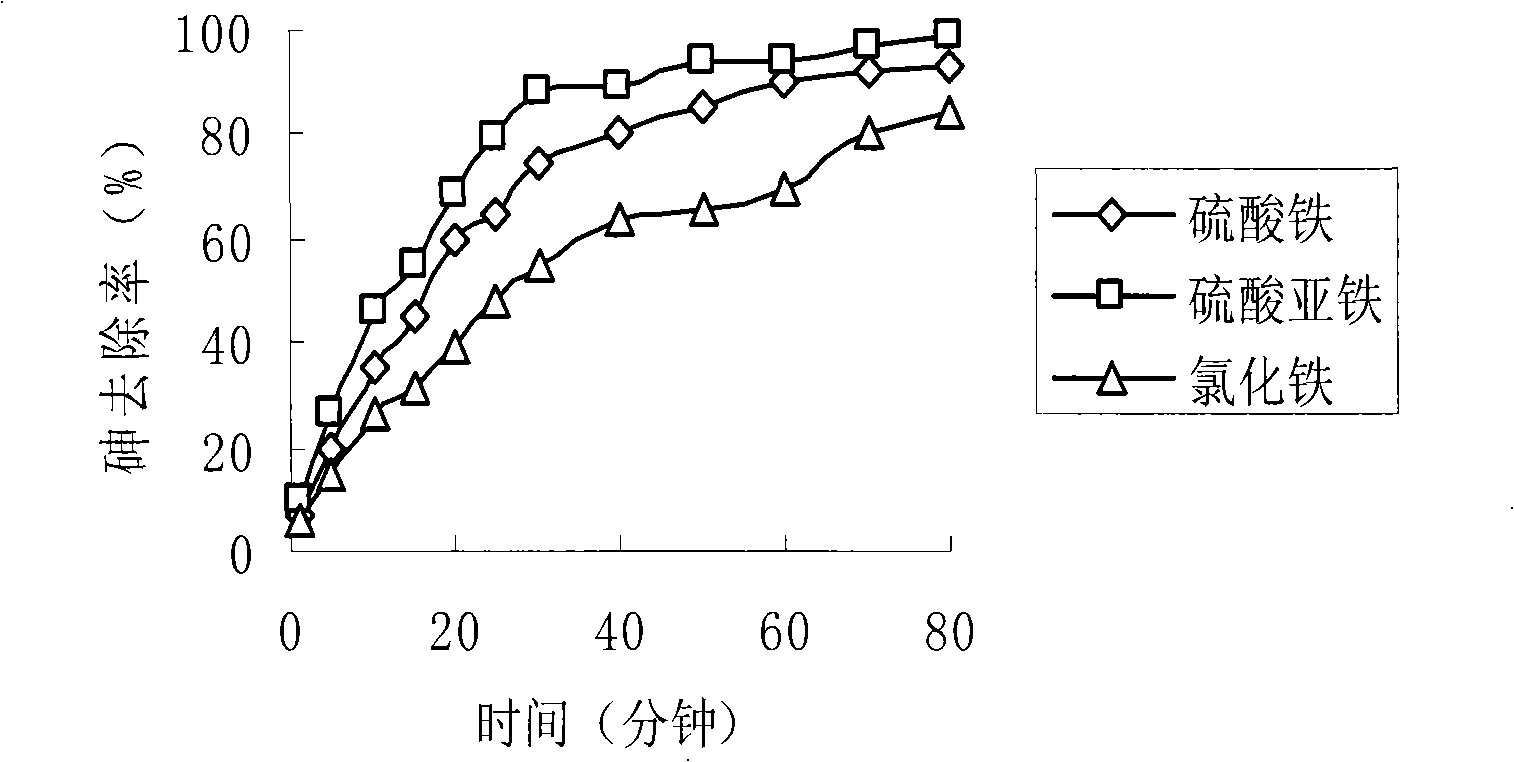
Iron Salt Properties and Dosing. Iron salts are supplied as liquid solutions containing 5-13% ferrous or ferric iron as either a chloride or sulfate salt. They are supplied in containers of 55 or 300 gallons, or in bulk shipments of 4,000 - 20,000 gallons.
Method for producing carbon coated nano stage lithium iron phosphate by precipitation
InactiveCN101393982AAvoid synthetic stepsEasy to controlElectrode manufacturing processesIron saltsPhosphate
The invention discloses a precipitation method for preparing nanometer level iron phosphate lithium coated with carbon. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, weighing iron salt, deionized water and a compound of metallic elements; after the stirring and the mixing are performed, adding a phosphorous compound and citric acid diluted with water to the mixture; after the stirring is performed again, adding a precipitation agent to the mixture and controlling to the neutrality; stirring to react in a container, and after the static placement, respectively adding the deionized water, a carbon source and lithium salt to mix uniformly after the precipitate is filtered and washed; stirring again to react, and drying the water at 30 to 160 DEG C and warming up at the heating rate under the protection of non-oxidized gas after a product is crashed; baking at a constant temperature of 450 to 850 DEG C, cooling down to a room temperature at a cooling rate or with a stove, and finally obtaining the nanometer level ferric phosphate lithium coated with the carbon after crashing is performed. The precipitation method has the advantage that the raw material cost and the processing cost are low because bivalent iron is taken as the raw material. The iron phosphate lithium prepared by using the process has the characteristics of good physical processing performance and good electrochemistry performance, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:南京海泰纳米材料有限公司
Method for preparing graphene loaded ferroferric oxide magnetic nanometer particle composite material
InactiveCN101941842AGood dispersionPromote crystallizationMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrodesHydrazine compoundNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene loaded ferroferric oxide magnetic nanometer particle composite material. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dispersing graphite oxide into deionized water, pouring into a vessel after ultrasonic and centrifuging, putting the vessel into an oil-bath pan, adding hydrazine hydrate and an anionic surfactant for heating, condensing and refluxing, and cooling and drying to obtain modified graphene; and (2) dispersing the graphene into aqueous solution, and ultrasonically stirring and centrifuging to obtain modified graphene dispersion liquid; and weighing a soluble trivalent ferric salt and divalent ferric salt, dissolving the salt into the deionized water, introducing nitrogen, pouring into the modified graphene dispersion liquid, dripping ammonia after uniform ultrasonic stirring, heating for reaction, washing and collecting a product, and drying the product. The method is simple and easy for industrial production; and the prepared composite material has the advantages of pure crystal phase, uniform distribution and excellent electrocatalytic activity.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for recycling lithium iron phosphate anode material from lithium ionic cell waste
ActiveCN101359756AHigh tap densityIncrease capacityWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingRecovery methodLithium iron phosphate
The invention relates to a method for recovering a lithium iron phosphate anode material in lithium ion battery scraps, comprising: roasting the scraps in the atmosphere of inert gases at a temperature of between 450 and 600 DEG C for 2 to 5 hours, wherein, the method also includes: adding the powdered products into an ethanol solution of soluble ferric salt for mixing, drying the mixture, then roasting the mixture in the atmosphere of inert gases at a temperature of between 300 and 500 DEG C for 2 to 5 hours, and obtaining the lithium iron phosphate anode material through recovery. The recovery method can be used to obtain the lithium iron phosphate anode material with rather high tap density, so the lithium ion secondary battery made by adopting the anode material has rather high capacity.
Owner:贵州中伟资源循环产业发展有限公司
Ferric phosphate lithium material for lithium ion powder cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101081696APromote crystallizationSingle structureElectrode manufacturing processesLithium compoundsCarbon layerLithium iron phosphate
The present invention discloses lithium iron phosphate material for lithium ion power cell and its preparation process, and dissolves the technological problem of raising the discharge power and safety performance. The lithium iron phosphate material is spherical or spheroid composite particle with one base body of lithium iron phosphate and doping and modifying agent and one coating carbon layer. Its preparation process includes wet ball milling the mixture comprising lithium salt, ferric salt, phosphoric acid, doping and modifying agent and dispersant, spraying to pelletize, heating for pre-treatment, maintaining temperature, cooling, pulverizing and shaping. Compared with available technology, the present invention has the features of high crystallization, single structure, average composite particle size of 5-60 microns, specific surface area of 8.0-15.0 sq m / g, bulk density of 1.4-1.7 g / cu cm, high specific capacity, high safety, etc.
Owner:BTR (TIANJIN) NANO MATERIAL MFG CO LTD
Hydro-thermal synthetic preparation method for lithium ion battery anode material lithium iron phosphate
InactiveCN101121509AImprove electrochemical performanceHigh purityCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsPhosphateInlet valve
The present invention relates to a hydrothermal synthesis preparation method of a lithium iron phosphate of an anode material used by a lithium ion battery, concerning a phosphate containing two metals. The step is that a lithium source and a phosphor source are solubilized into the water or mixed with the water and then put into a high pressure kettle. After the air in the kettle is blown out by an inert gas, the high pressure kettle is sealed and heated to a temperature between 40 DEG C and 50 DEG C from a room temperature after being stirred. An inlet valve and a vent valve are opened and then a prepared divalent ferric salt liquor is added in. The high pressure kettle is sealed and the reaction time lasts from 200 minutes to 480minutes at the temperature between 140 DEG C and 170 DEG C. At the time, the inner pressure corresponding to the system is from 0.36 MPa to 0.85 MPa. The mixture rate of the added substance is Li: Fe: P and the mol ratio is 3.0-3.15: 1: 1.0-1.15. When the reaction starts, the reactant concentration is from mol / L 0.2 to 1.0mol / L, computed according to the concentration of the ferrous ion and then the resultant is filtrated, cleaned, dried and coated with the carbon. Finally the lithium iron phosphate product can be obtained. The present invention has the advantages of simple technology, good batch stability, good electrochemical performance and even distribution. The purity quotient can be more than 99 percent and the grain diameter D50 is between1.5Mu m and 2Mum.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Liquid infusion method for producing linaloe on aquilaria sinensis trees
ActiveCN101755629AIncrease productionShorten the production cycleBiocidePlant growth regulatorsInfusion methodMedicine
The invention belongs to biological technical field, in particular to a liquid infusion method for producing linaloe on aquilaria sinensis trees. The method includes of drilling on the aquilaria sinensis trunk, gradually dropping a linaloe catalyst into the aquilaria sinensis tree body through the liquid infusion method; the operation is repeated every 2-3 months, after 6-12 months, the chocolatebrown oil-like material and the yellowish-brown discolored eaglewood formed in the trunk is cut and is dried to obtain the linaloe; the linaloe catalyst is mixed up by a phytohormone solution and a chemical reagent solution; the chemical reagent is ferric salt or sodium salt. The process of the invention has simple technique, convenient operation, can greatly increase production quantity of the linaloe and greatly shorten the production period of the linaloe through the inducing method, has good linaloe-forming effect, can effectively ease the contradiction between supply and demand for sinensis, is applicable to large-scale standardization and commercialization production, provides a new effective path for protecting, developing and utilizing the aquilaria sinensis tree resources, and has important economical, social and ecological benefits.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI HAINAN BRANCH
Methods for the preparation and use of ferric pyrophosphate citrate chelate compositions
A highly water soluble ferric pyrophosphate citrate chelate useful for treating iron deficiency contains 2% or less phosphate by weight. These chelate compositions are easily milled and / or processed into dosage forms using conventional techniques, and are expected to exhibit advantageous biocompatibility as compared to conventional soluble ferric pyrophosphates, ferric salts, ferric polysaccharide complexes and ferrous salts.
Owner:ROCKWELL MEDICAL INC
Preparation method of nano porous metal oxide/carbon lithium ion battery cathode material
ActiveCN104045116AImprove cycle performanceImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesHigh energyManganese oxide
The invention provides a preparation method of a nano porous metal oxide / carbon lithium ion battery cathode material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, weighting ferric salt or manganese salt and carboxylate organic ligands, and putting into a high-pressure reaction kettle; and after a polar solvent is added and dissolved, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction for 10-72h at 100-180 DEG C to generate a transition metal coordination polymer precursor; and after the transition metal coordination polymer precursor is washed and dried, decomposing the precursor for 0.5-6h at a temperature of 300-600 DEG C in an inert atmosphere in a tube furnace, thus obtaining a nano porous metal oxide / carbon lithium ion battery cathode material containing iron oxides or manganese oxides. According to the preparation method, since the transition metal coordination polymer precursor which is structurally designable and controllable is used as a template-type precursor, a nano porous metal oxide / carbon lithium ion battery cathode material is obtained by using an in-situ thermal decomposition method. The method is simple in process, and the obtained products have the advantages of high electrical conductivity, high specific capacity, good cycle stability, excellent high-ratio discharge performance and high energy density.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparing anode material of lithium ion battery in series of phosphate of olivine type
InactiveCN101049922AAchieve hybridEvenly distributedCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsAluminium-ion batteryPhosphate
This invention relates to a method for preparing olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material. The method comprises: mixing one or more of ferrous salt solution, cobalt salt solution and manganese salt solution with oxalic acid or oxalate (precipitating agent) aqueous solution to obtain composite oxalate precursor, uniformly mixing with lithium source and phosphorus source by ball milling, and reacting in inert or weak-reductive atmosphere to obtain olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material. The method utilizes co-precipitation method for metal ion doping, and realizes molecular level uniform mixing among different ions. The obtained olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material has uniform chemical and physical compositions. The average particle size can be controlled within 0.3-10 mu.m. The first charge and discharge cycle specific capacity can reach 150 mAh / g at 0.1 C rate and room temperature. The livine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material has such advantages as high cycle performance and high charge / discharge performance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of attapulgite-loaded nanometre iron material
InactiveCN102755883ANot easy to form agglomerationLess prone to autoxidationOther chemical processesAluminium silicatesAqueous solutionNanometre
The invention provides a preparation method of an attapulgite-loaded nanometre iron material. Acidized and modified attapulgite is taken as a load material, and KBH4, NaBH4, N2H4 and the like are taken as reducing agent under the protection of inert gases, so that ferric salt or ferrite can be reduced to be zero-valent iron; and the multi-duct characteristic of the attapulgite is utilized, so that nanometre iron particles are sufficiently dispersed and fixedly loaded on the attapulgite material. Compared with un-loaded nanometre iron, the attapulgite-loaded nanometre iron material prepared by the preparation method has better dispersibility and stability, is more uniform in particle size distribution, not easy to cause particle agglomeration and self-oxidization; and moreover, the attapulgite-loaded nanometre iron material has better suspension property and stability in aqueous solution, a stronger oxidative degradation ability to environmental pollutants, longer effective reaction time, and a better adsorption capacity. The material is expected to be extensively applied to environment pollution abatement and repair engineering, and fills a blank in the filed at home and abroad.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing magnetic nanometer ferroferric oxide-graphene composite catalyst
ActiveCN102553593AReduce usageNo pollution in the processWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMagnetic separationGraphite oxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnetic nanometer ferroferric oxide-graphene composite catalyst, which includes steps of: 1) dispersing graphite oxide in ethanol and water system; 2) respectively mixing soluble trivalent ferric salt and divalent ferric salt in ethanol; 3) mixing and stirring systems obtained in step 1) and step 2); 4) heating reaction system of 3) at temperature of 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C, and adjusting pH to be 9-11 for reaction by adding ammonia water; and 5) performing magnetic separation on products of step 4), washing through deionized water, and obtaining magnetic nanometer ferroferric oxide-graphene composite catalyst. The method provides a simple and practical coprecipitation method for preparing the nanometer ferroferric oxide-graphene composite catalyst which is uniform in particular sizes, even in dispersing and good in magnetism. The nanometer ferroferric oxide-graphene composite catalyst prepared by the method has excellent catalytic activity and is easy in preparing process and environment-friendly.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Method for preparing nano iron phosphate
InactiveCN101693531AReduce volumeReduce energy consumptionNanostructure manufacturePhosphorus compoundsPhosphateFerrous salts
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano iron phosphate, belonging to the technical field of the preparation of lithium ion battery cathode materials. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: inputting an alkaline aqueous solution and a mixed solution formed by one of phosphoric acid or a soluble phosphate solution, one of a water-soluble ferrous salt solution and an oxidant or a ferric salt solution and a water-soluble dispersing agent into a rotating packed bed layer by a metering pump at a certain feeding speed; regulating the rotating speed of the rotating packed bed and controlling the pH value of the reaction system by an alkaline solution; discharging nano iron phosphate particles generated by reaction crystallization from a discharge hole of the rotating packed bed along with the mixed solution; and filtering, washing and drying the nano iron phosphate particles to obtain nano iron phosphate (FePO4.2H2O) powder. The method is simple and has easy operation and high efficiency, and the prepared iron phosphate reaches the nano grade, has uniform particle size and narrow distribution range and is suitable for industrialized production. The nano iron phosphate is a good precursor material for preparing lithium iron phosphate which is used as a cathode material of high-power type lithium ion batteries.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
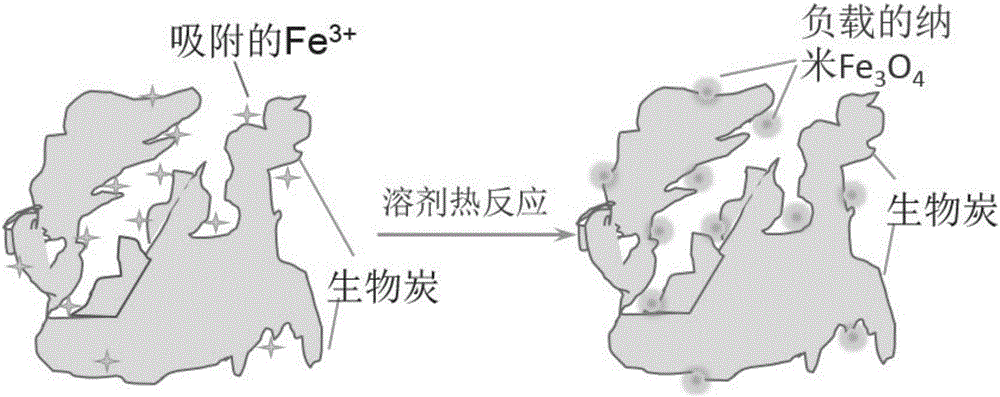
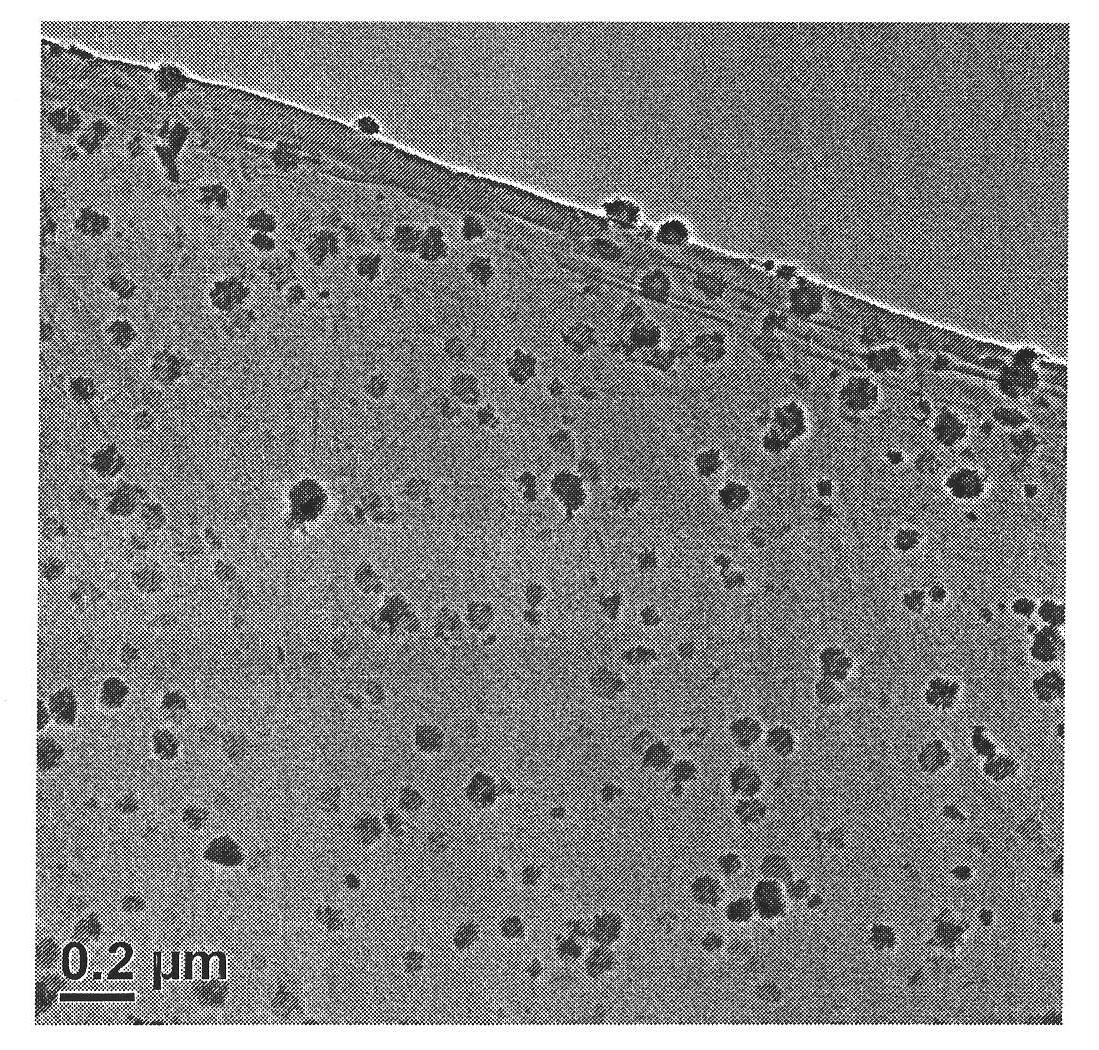
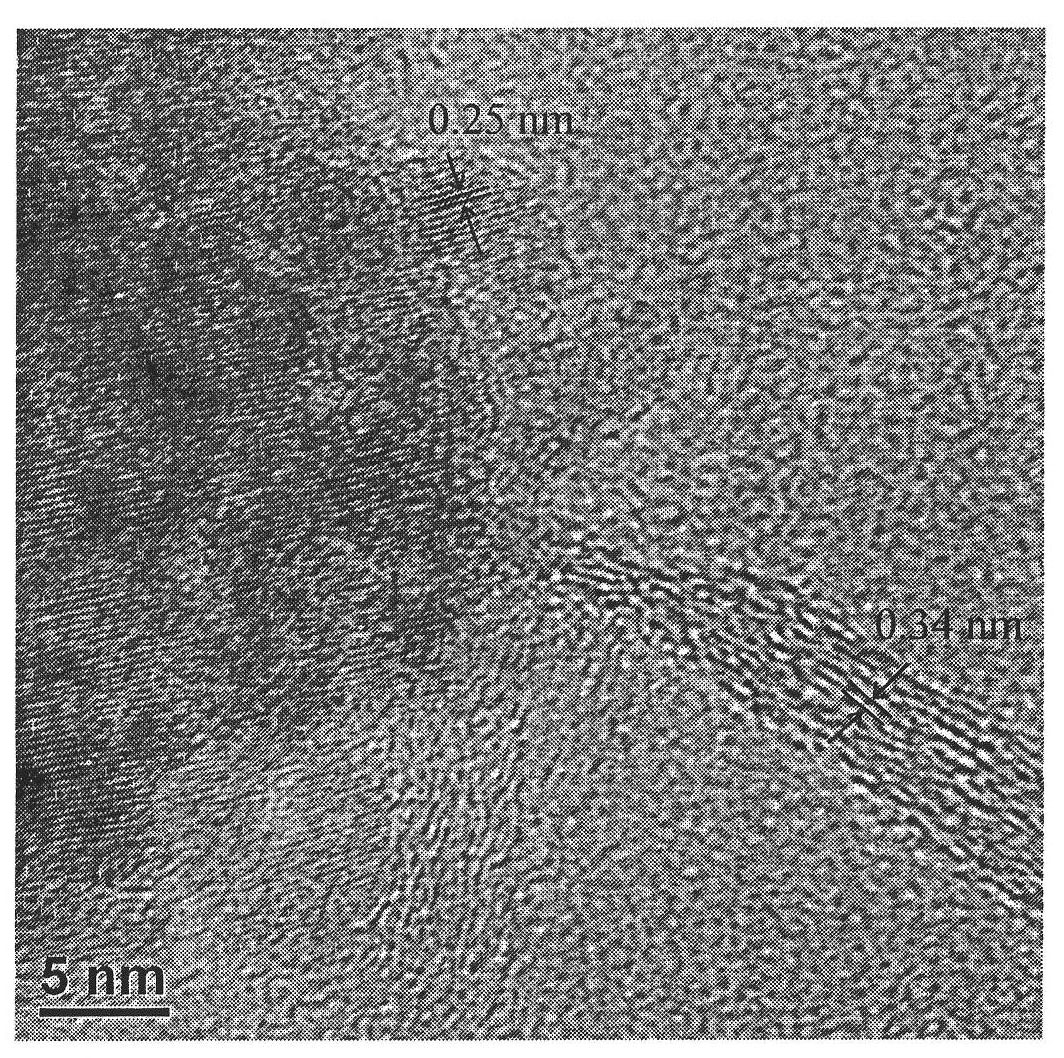
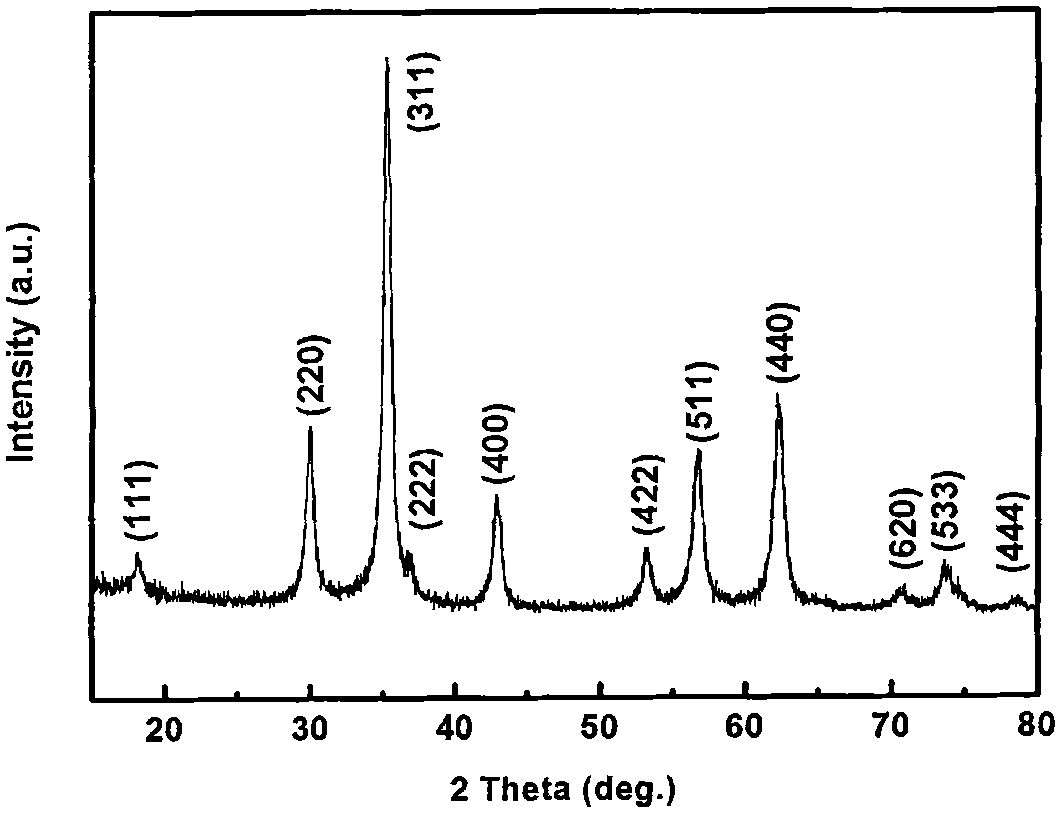
Magnetic biochar adsorbing material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106362690AGood lookingSimple structureOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSodium acetateSodium acetrizoate
The invention discloses a magnetic biochar adsorbing material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of biochar: by using powder obtained by treating plant biomass as a raw material, roasting under oxygen-free conditions to obtain porous biochar; (2) preparation of ferric iron precursor liquid: by using ethanediol as a dispersing agent, adding a solid-state ferric iron salt, continuing adding sodium acetate and a surfactant into the ethanediol, and stirring to form a disperse system which is the ferric iron precursor liquid; and (3) solvothermal reaction: uniformly mixing the biochar and ferric iron precursor solution to obtain a mixture, putting the mixture into a teflon hydrothermal reaction kettle, and carrying out solvothermal reaction to obtain the magnetic biochar adsorbing material. The pretreatment technique of the key biomass raw material and the specific conditions of solvothermal reaction in the preparation method are improved, thereby effectively solving the problem of poor connection stability between the magnetic biochar material magnetic particles and biomass.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing graphene/Fe3O4 composite powder by alcohol thermal method
InactiveCN101837971AEasy to prepareLow requirements for production equipmentFerroso-ferric oxidesAlcoholPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene / Fe3O4 composite powder by an alcohol thermal method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing oxidated graphite and ferric salt at room temperature, dispersing into a glycol solution, adding polyethylene glycol after dissolving completely, then adding anhydrous sodium acetate, stirring and forming reaction liquid; (2) putting into a reaction kettle, heating to the temperature of 180 to 220 DEG C and reacting for 8 to 16h; and (3) cooling to the room temperature, collecting a product by using a magnet, washing the product by deionized water and drying so as to obtain the graphene / Fe3O4 composite powder. In the invention, the preparation method is simple and is easy for industrialized production; and Fe3O4 in the prepared graphene / Fe3O4 composite powder has pure crystalline phase, little possibility of agglomeration, favorable compounding with graphene and good dispersibility at the surface of the graphene and in the layer of the graphene, and the composite powder has small resistivity and high magnetization intensity.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Compound phosphorus removing agent for phosphorus wastewater and application method of compound phosphorus removing agent
ActiveCN103626276AEfficient removalNo secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatmentWastewaterOrganic phosphorus
The invention relates to a compound phosphorus removing agent for phosphorus wastewater and an application method of the compound phosphorus removing agent. The compound phosphorus removing agent comprises the following components by mass: 10-50 percent of ferric salt, 10-40 percent of calcium salt, 5-40 percent of a mineral material, and 5-20 percent of a strong oxidant. The compound phosphorus removing agent is suitable for wastewater which can be either inorganic phosphorus wastewater or organic phosphorus wastewater. Through the combination of the physical method and the chemical method, phosphorus in the inorganic phosphorus wastewater or organic phosphorus wastewater can be removed effectively. The compound phosphorus removing agent and the application method have the advantages that the operation is simple and efficient, the operation cost is relatively low, and the secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:浙江一清环保工程有限公司
Catalyst and method used for preparing 1,3-butadiene by oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butene
ActiveCN102824914AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic selectivityHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMagnesium saltDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a catalyst and a method used for preparing 1,3-butadiene by oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butene. The catalyst is a cobalt and magnesium modified zinc ferrite catalyst which is obtained by proportioning a ferric salt, a zinc salt, a cobalt salt, a magnesium salt and a deionized water in a mole ratio, regulating pH value with ammonia water, concentrating, filtering, drying, roasting, cooling, grinding and screening. The method for preparing 1,3-butadiene by utilizing the catalyst comprises the following steps of: with C4 fraction produced by MTO (methanol to olefin) as a raw material, carrying out catalytic oxidative dehydrogenation reaction on a reaction mixture which is formed by the C4 fraction, air and vapour under the action of the cobalt and magnesium modified zinc ferrite catalyst so as to efficiently prepare1,3-butadiene, wherein the main ingredient of the C4 fraction is n-butene. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the C4 fraction is not required to be refined to remove impurities such as oxygenated chemicals, thus the method disclosed by the invention is a simple and efficient method for preparing a high-additional-value product by utilizing C4 resource of the MTO.
Owner:SHAANXI COAL & CHEM TECH INST
Repair medicament for compound heavy metal polluted soil as well as preparation and application method thereof
InactiveCN106244163AShort repair cycleLow costAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersPhosphateSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a repair medicament for compound heavy metal polluted soil. The repair medicament comprises the following components: phosphate compound, soluble ferric salt, magnesium oxide, inorganic clay, an organic chelating agent and silicon dioxide, wherein the phosphate compound adopts one or the combination of phosphate, hydrophosphate or dihydric phosphate. The repair medicament is applicable to compound heavy metal polluted farmland soil, compound heavy metal polluted industrial site soil and compound heavy metal polluted mine site soil. Stirring and mixing of the repair medicament and the heavy metal polluted soil belong to in-site stirring and mixing or off-site stirring and mixing. The repair medicament is short in repair cycle and low in cost, has wide spectrum, and is simple in technical operation.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
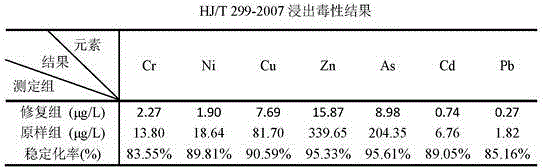
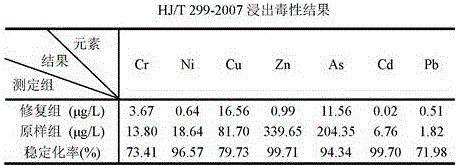
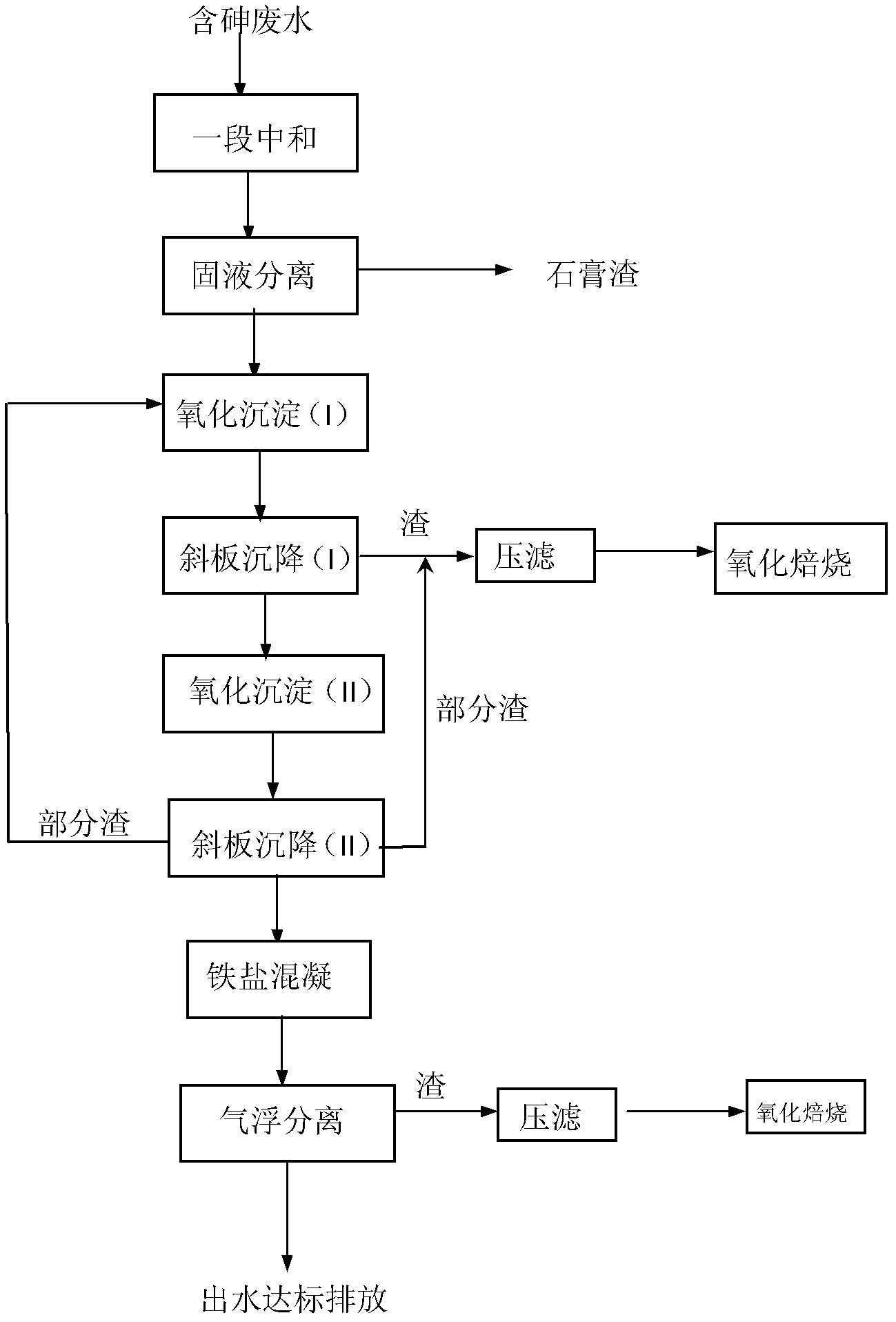
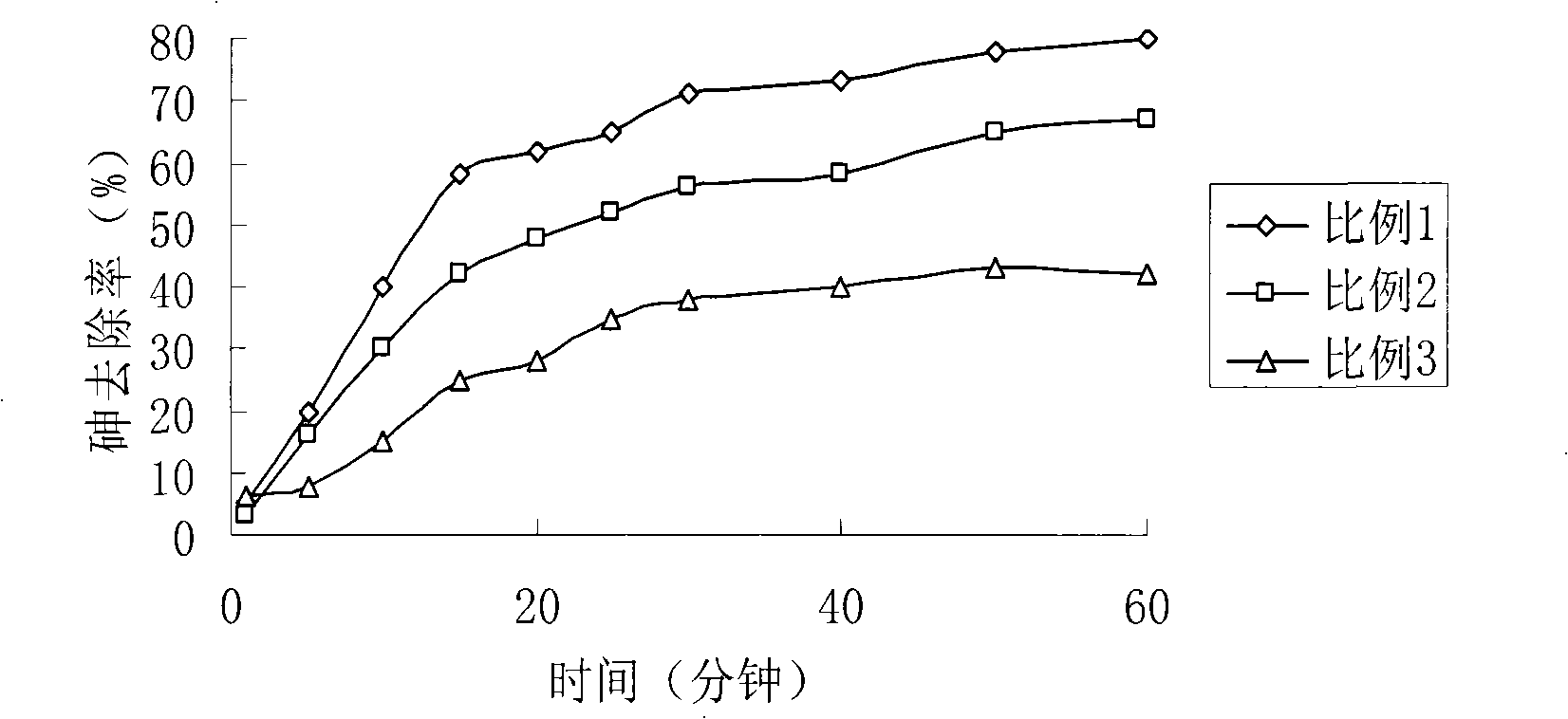
Treatment method for high-concentration arsenic waste water
ActiveCN103030233ARealize solid-liquid separationEfficient curingWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationFiltration
The invention discloses a treatment method for high-concentration arsenic waste water, and relates to the technical field of sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out pH neutralization adjustment, and executing solid-liquid separation after neutralization; 2, oxidizing sedimentation (I): treating the arsenic waste water with an alkaline coagulant, then, executing oxidization, and carrying out inclined plate settling to realize solid-liquid separation; 3, oxidizing sedimentation (II): adding lime or lime milk in the neutralized waste water, executing oxidization simultaneously, and carrying out inclined plate settling to realize solid-liquid separation; 4, ferric salt coagulation: adding an inorganic coagulant in water solution, stirring, and then, adding an organic flocculant; and 5, air floatation separation: adding a surface active agent, separating iron and arsenic slag, executing pressure filtration and drying, and carrying out oxidizing roasting. The method has the beneficial effect that the effluent As concentration of the treated waste water can meet the national emission standard; the As concentration of the leach liquor of the oxidized and roasted arsenic waste residue buried underground is far below the national stipulated limit, and arsenic is cured effectively.
Owner:深圳市明登科技有限公司
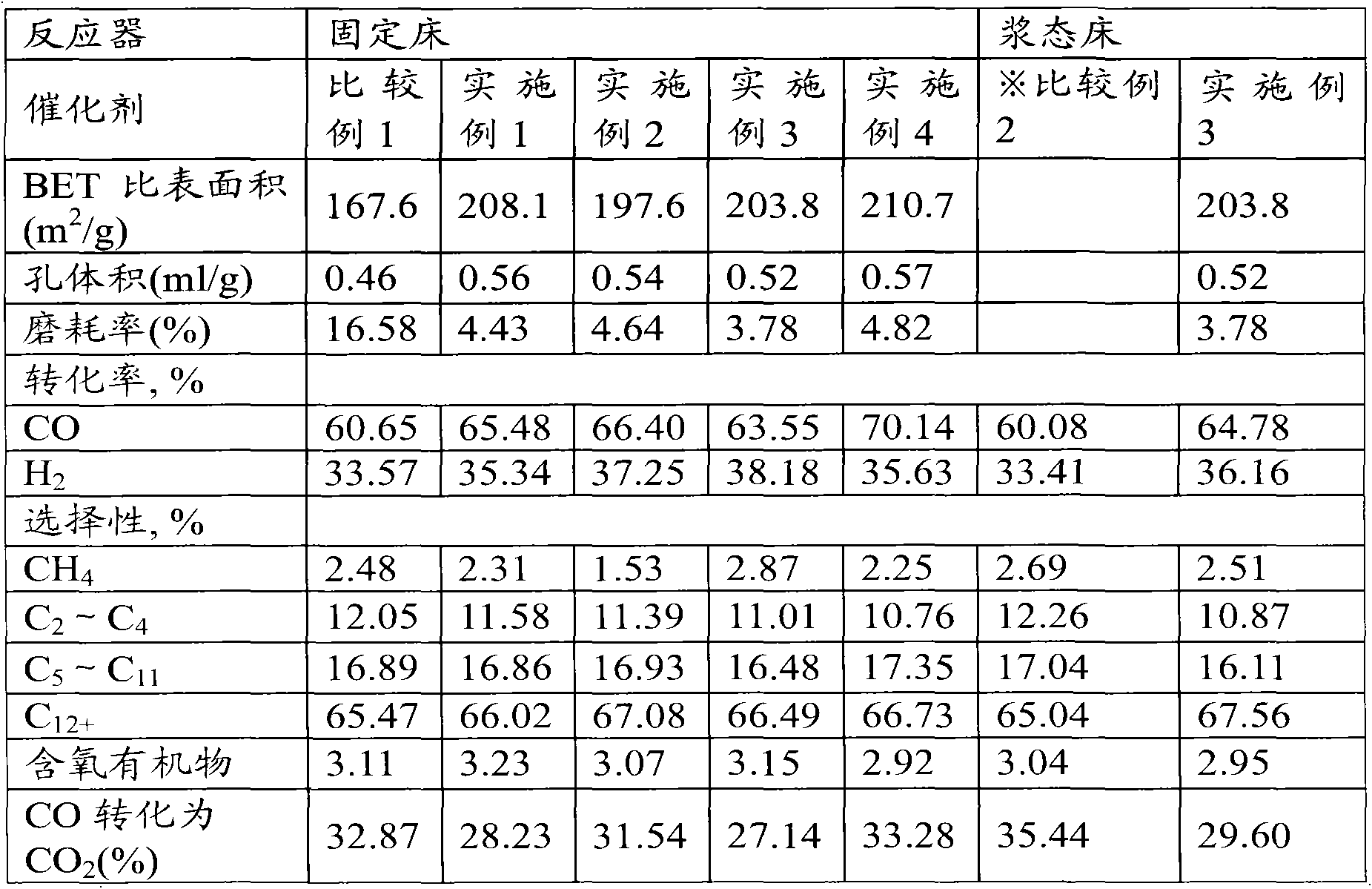
Precipitated iron catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101884926AHigh specific surface areaIncrease the areaCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionPrecipitationIon
The invention relates to a precipitated iron catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (a) feeding ferric salt solution, aid saline solution, the solution of precipitator and a small amount of solution of silicon compounds in a form of concurrent flow into a precipitation reactor; (b)performing coprecipitation reaction on the mixture under certain process conditions in the reactor, and fast cooling, filtering and rinsing pulp obtained after the precipitation reaction is finished;(c) adding a silicon compound binder into a filter cake obtained after the rinsing, adding a nitric acid into the filter cake to adjust pH and performing secondary filtration; (d) performing secondary pulping on the obtained filter cake with de-ionized water or the mixed solution of the de-ionized water and the required aid saline solution; and (e) performing spray-drying molding and baking on the obtained catalyst pulp. The catalyst prepared by the method of the invention has high specific surface area, proper pore volume, high wear strength, high sphericity and smooth surface.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
Preparation method of modified active carbon-based gasoline desulfurization adsorbent
InactiveCN103143322ACarrier is easy to getLow priceOther chemical processesHydrocarbon oils refiningSorbentAdsorption selectivity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a modified active carbon-based gasoline desulfurization adsorbent, and relates to a preparation method of a gasoline deep desulfurization adsorbent. The adsorbent is a Fe ion-loaded active carbon adsorbent; and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing cleaning pretreatment of the raw material of the adsorbent carrier particles; drying the pretreated carrier particles, mixing the carrier particles with a nitric acid solution, performing backflow and electromagnetic stirring; washing the oxidized carrier particles; drying the carrier particles; roasting to modify the dried particles; and steeping the carrier particles and a soluble ferric salt solution; drying the steeped carrier particles; and roasting to activate the dried particles. The preparation process is simple and easy to implement and realizes easy regeneration; the service life of the adsorbent is long; the adsorbent has high adsorption capacity and adsorption selectivity on thiophene and derivatives thereof in gasoline; the adsorption process is performed in a normal-temperature normal-pressure condition, and the operation cost is low; and no pollutant is generated in the adsorption process, good economic practicability is realized, and environmental protection requirements are met.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Process for solid phase synthesis of lithium iron phosphate anode materials under high pressure
InactiveCN1884053ALow reaction temperatureReduce manufacturing costCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsAir atmosphereLithium iron phosphate
The invention discloses a synthesizing method of anode material of high-pressure solid-phase ferric-lithium phosphate, which comprises the following steps: blending lithium salt, ferric salt and phosphate according to 1:1:1 proportion evenly; grinding the material into ball for 6-24 h to obtain priority; disposing priority for 2-10 h at 200-350 deg.c in the air environment; cooling naturally; grinding to obtain powder material; adding carbon material in the powder material with weight percentage of carbon material at 1-20 percent; grinding again for 6-24 h; disposing for 4-24 h at 450-1000 deg.c in the 1-15 Mpa inert environment; cooling naturally to obtain the product.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for treating organic waste water by using electrochemistry under assistance of persulfate
InactiveCN102249378AReduce dosageLess side effectsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationElectrochemical responseSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a method for treating organic waste water by using electrochemistry under the assistance of persulfate. The method comprises the following steps of: putting sulfate, a divalent or tervalent ferric salt and organic waste water into an electrochemical reactor consisting of a DSA (Dimensional Stable Anode) and an anti-corrosive cathode; adjusting the pH value of a reaction liquid to 3-9; stirring; and switching on a power supply for reacting. The method is characterized in that: special requirement on the ferric salt is not made, the ferric salt can be divalent or tervalent, generated free sulfate radicals can be used for effectively treating organic pollutants in water; meanwhile, in the electrochemical reactor, reutilization of divalent ferric ions can be realized under the reducing action of the cathode, so that the adding amount of the ferric salt is reduced, side reactions between an excessive amount of ferric salt and free sulfate radicals are reduced, ineffective consumption of free sulfate radicals is avoided, and the generation of iron sludge is reduced simultaneously.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Improved nanometer nulvalent iron particle and method for making same
The invention discloses a modified nanometer nulvalent ferric particle and preparing method with grain size at 20-50nm and even grain size at 30-40nm and specific surface at60-70m<2> / g, which comprises the following steps: allocating soluble ferric salt solution and NaBH4 or KBH4 alcohol-water composite solution with bulk rate at 1: 1-20, adding polyvinyl pyrrolidone in the soluble ferric salt solution according to rate, stirring evenly, adding NaBH4 or KBH4 alcohol-water composite solution in the soluble ferric salt solution, stirring continually until the solution becomes black, adopting magnetic method to select nanometer nulvalent ferric particle, washing through distilled water completely, washing through acetone or alcohol then, reserving in the acetone or alcohol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
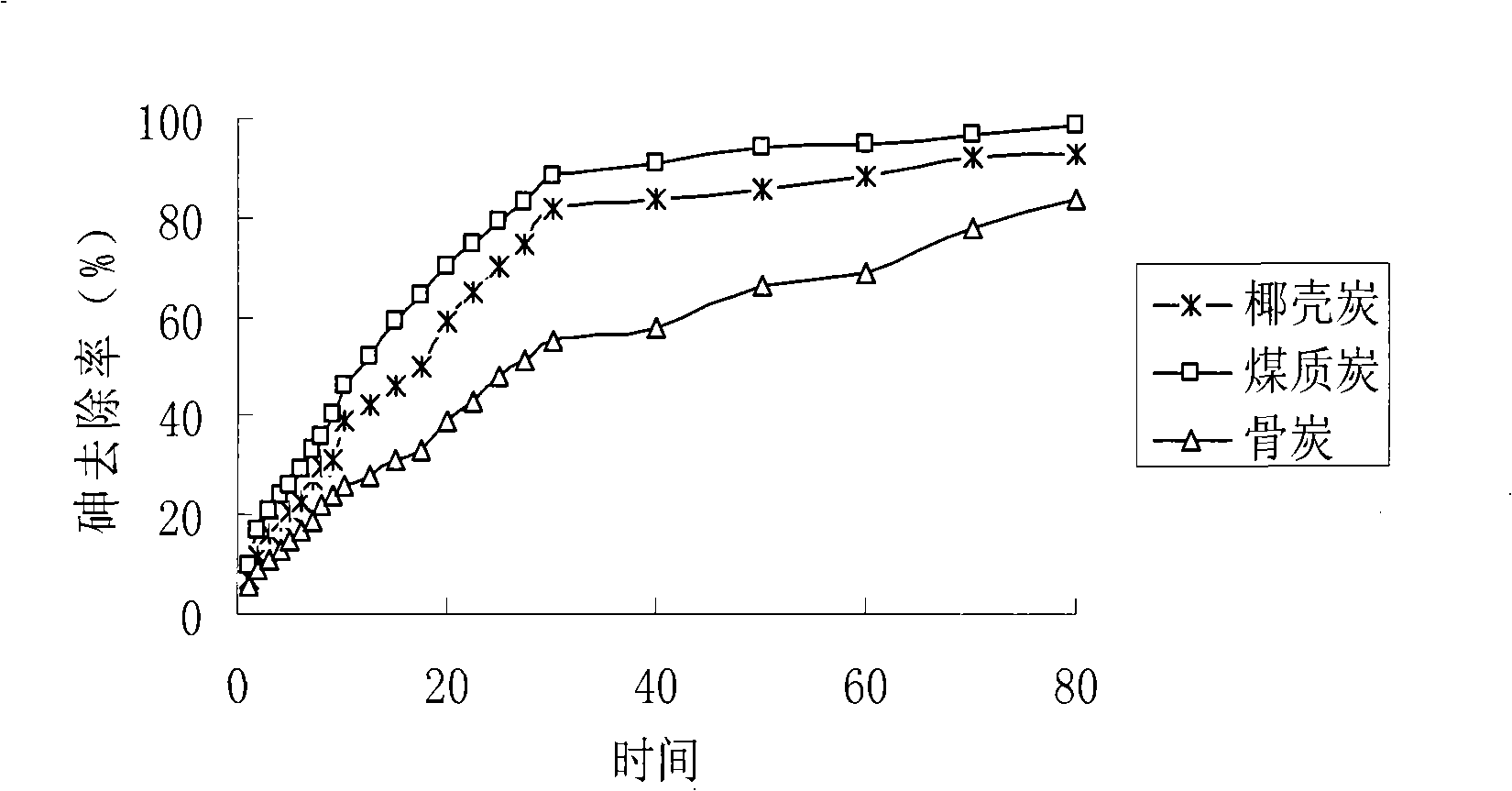
Method for preparing load type nano arsenic-removing sorbent for drinking water
InactiveCN101347717ALarge adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPotassium borohydrideSorbent
The invention relates to the elimination of the arsenic in drinking water, in particular to a preparation method of a supported type nano-adsorbent for removing arsenic from drinking water; the method includes the following steps: (1) activated carbon material with pore volume of 0.100-0.500cm<3> / g is selected for pretreatment; (2) soluble ferric salt solution is firstly used for soaking the activated carbon for 10-120 min; (3) alcoholic solution is taken as a dispersant to be added into the ferric salt solution; (4) under the protection of inert gases at room temperature, a strong reductant, potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride, is used for titrating the ferric salt, and agitation is carried out under the protection of inert gases; after the titration of potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride solution, agitation lasts for 10-120 min; (5) after agitation, centrifugation is carried out; oxygen-free water is firstly used for washing for 1-3 times, then organic solvent is adopted for washing for 1-3 times, and vacuum drying is done at 40-100 DEG C for 12-48h to obtain the product. The adsorbent of the invention has large adsorption capacity and small volume and is safe, stable and easy to store and transport.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing nanometer zero-valent iron grain using improved liquid phase reduction method
The invention discloses a method for preparing nanometer iron particle with a modified liquid phase reduction method. The main steps comprise: preparing soluble ferric salt solution and NaBH4 or KBH4 solution; adding polyethylene pyrrolidone into said soluble ferric salt solution according to a certain proportion, stirring evenly; adding NaBH4 or KBH4 solution into said soluble ferric salt solution under continuous stirring condition, stirring continuously until solution changes into black; selecting nanometer iron particle with magnetic method; washing with distilled water firstly, then washing with acetone or alcohol, storing in acetone or alcohol. The invention needs no nitrogen protective device, process is easy for operation, production cost is low; the distribution of got nanometer iron particle is homogenous (40-80nm), average particle size is 60 nm, specific surface area is 45-56m2 / g, and there is no ferric oxide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
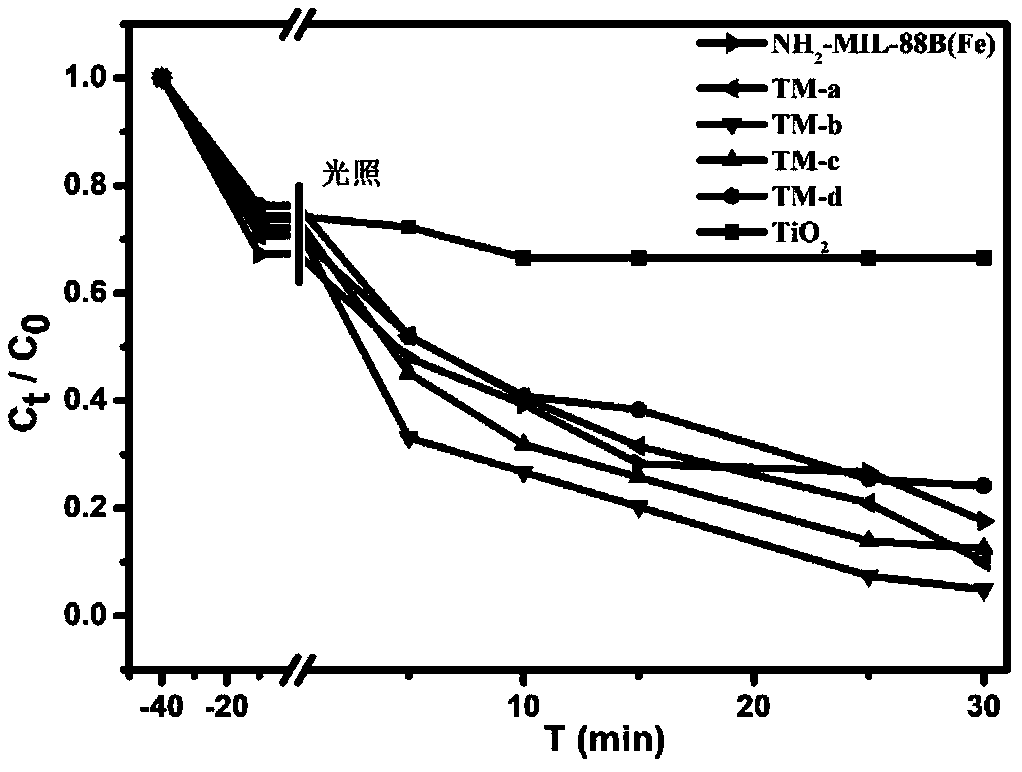
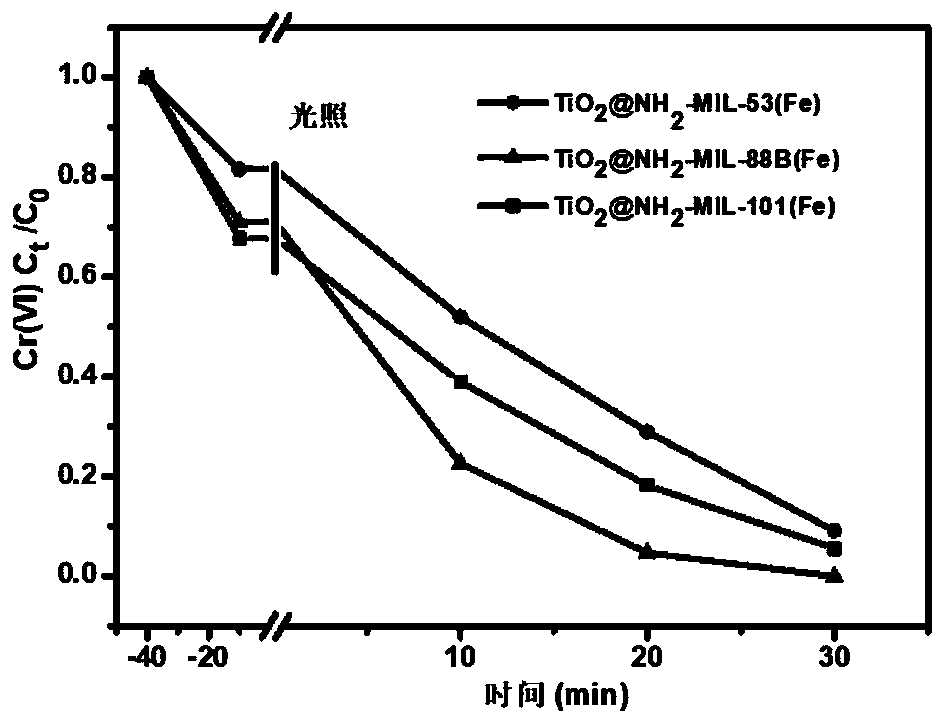
Preparation method and applications of nanometer titanium dioxide @ Fe-based MOF visible light composite catalyst
InactiveCN109289927AWide variety of sourcesLow priceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsWastewaterPollution
The invention belongs to the field of environment pollution treatment, and more specifically relates to a preparation method and applications of a nanometer titanium dioxide @ Fe-based MOF visible light composite catalyst. The preparation method comprises following steps: a ferric iron salt, 2-amino terephthalic acid, and nanometer TiO2 are added into N, N-dimethyl formamide, ultrasonic uniform dispersion treatment is carried out so as to obtain a precursor solution; the precursor solution is subjected to hydro-thermal reaction so as to obtain the nanometer titanium dioxide @ Fe-based MOF visible light composite catalyst. Under sun light effect, the nanometer titanium dioxide @ Fe-based MOF visible light composite catalyst is capable of realizing high efficiency reduction of Cr(VI) under mild neutral conditions, efficiency is high, energy consumption is low, and the nanometer titanium dioxide @ Fe-based MOF visible light composite catalyst is widely suitable for processing of a plurality of chromium containing waste water.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Carbon coated lithium manganese phosphate/lithium iron phosphate core-shell structure material as well as preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon coated lithium manganese phosphate / lithium iron phosphate core-shell structure material as well as a preparation method thereof. The constitutional general formula of the core-shell structure material is LiMnFe(1-x)PO4.a[LiFeyMn(1-y)PO4], wherein the constitutional general formula of a core material is LiMnxFe(1-x)PO4, and the constitutional general formula of a shell material is LiFeyMn(1-y)PO4, x is greater than or equal to 0.8 but less than or equal to 1, y is greater than or equal to 0.8 but less than or equal to 1, and a is greater than or equal to 0.2 but less than or equal to 0.5. Meanwhile, the core-shell structure material further comprises 0.2-50wt% of carbon element which is distributed in the shell. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out solid phase sintering of a lithium manganese phosphate / manganese phosphate material; and then, after ball-milling and mixing the material with ferric salt, phosphate, a lithium source and the like, sintering in a protective atmosphere to obtain a target product. The carbon coated lithium manganese phosphate / lithium iron phosphate core-shell structure material as an anode material for a lithium ion battery, disclosed by the invention, has higher volume and better cycling stability, is concise in process, easy to operate, high in efficiency, and beneficial to industrial production on a large scale.
Owner:中科致良新能源材料(浙江)有限公司
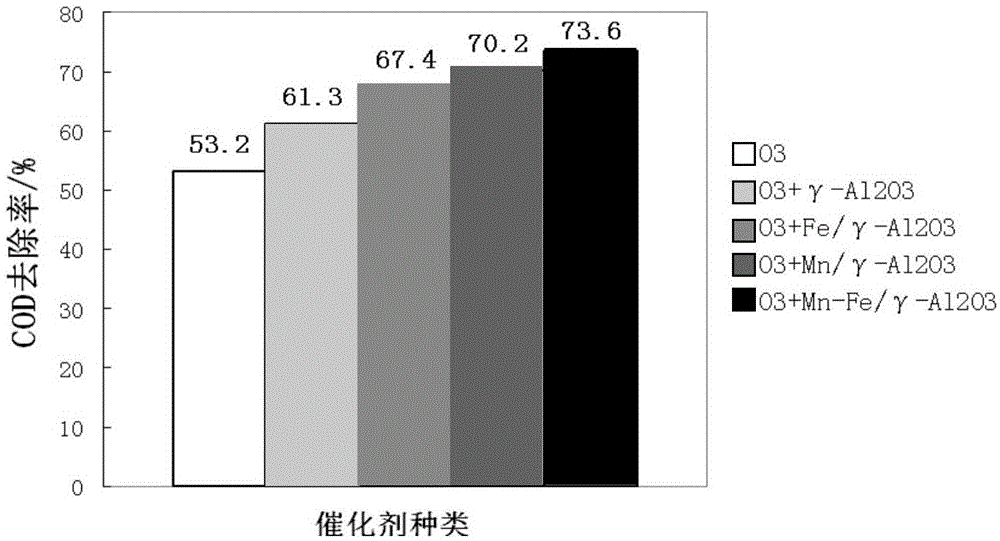
Loaded binary composite metal oxide catalytic ozonation catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105013504AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic performanceWaste water treatment from plant processingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMicrosphereActive component
The invention belongs to the field of catalysts and discloses a loaded binary composite metal oxide catalytic ozonation catalyst with gamma-Al2O3 microspheres as carriers and manganese oxide and ferric oxide as active components and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the loaded binary composite metal oxide catalytic ozonation catalyst comprises dipping gamma-Al2O3 microspheres in a mixed solution containing water-soluble manganese salt and water-soluble ferric salt, taking out the gamma-Al2O3 microspheres, carrying out drying and carrying out high temperature roasting to obtain the loaded binary composite metal oxide catalytic ozonation catalyst. The loaded binary composite metal oxide catalytic ozonation catalyst has significantly improved particle uniformity, good stability, good reusability and excellent catalytic activity. Compared with gamma-Al2O3 microsphere or manganese and iron single component-loaded catalysts, the loaded binary composite metal oxide catalytic ozonation catalyst significantly improves an organic removal rate by at most 38%, greatly reduces paper-making wastewater organic pollutant types and content and fully degrades difficultly biodegraded organics.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing drug carrier based on magnetic carbon quantum dot/chitosan composite microsphere
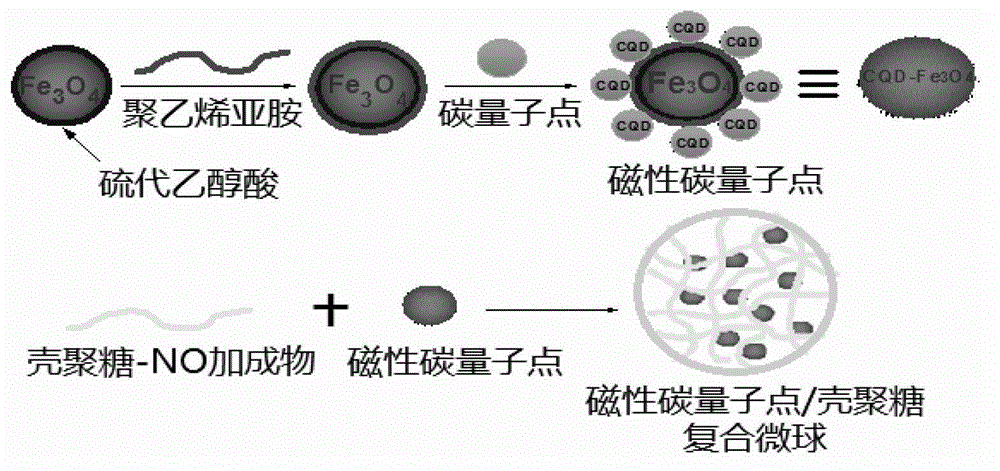
InactiveCN102973948ALow costSimple methodInorganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsSodium methoxideIron salts
The invention relates to a method for preparing a drug carrier based on a magnetic carbon quantum dot / chitosan composite microsphere. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out a coprecipitation reaction on bivalent and trivalent iron salts in an alkaline aqueous solution so as to prepare nano magnetic ferroferric oxide; (2) carrying out microwave radiation reaction on a glucose and polyethylene glycol mixed solution to prepare carbon quantum dots, and forming magnetic carbon quantum dot composite particles through electrostatic adsorption; (3) reacting the chitosan which is dissolved in a mixed solution of sodium methoxide / absolute methanol with nitric oxide in a high-pressure kettle, and forming a chitosan-nitric oxide addition product; and (4) dropwise adding the magnetic carbon quantum dots into the addition product, and forming the magnetic carbon quantum dot / chitosan composite microsphere through electrostatic adsorption. Compared with the prior art, the method is simple, rapid, low in cost, and the prepared product can be developed into the drug carrier which integrates magnetic targeting, fluorescence imaging or tracing, nitric oxide in-situ release and fluorescence detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of lithium ferric phosphate / grapheme composite positive electrode material
ActiveCN102169986AAchieving controllable equipmentUniform growthCell electrodesPhosphateNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a preparation method of a lithium ferric phosphate / grapheme composite positive electrode material. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a lithium ferric phosphate precursor, namely weighing raw materials such as a catalyst, lithium salt, ferric salt and phosphate, adding the raw materials into a dispersing agent, and ball-milling to obtain the lithium ferric phosphate precursor; and (2) growing grapheme on the lithium ferric phosphate precursor first, then closing carbon source gas and ammonia gas, introducing hydrogen into a reactor, adjusting the temperature of the interior of the reactor to be 600 to 800 DEG C at a speed of 10 to 20 DEG C per minute in the process of hydrogen introduction, keeping the temperature of the interior of the reactor constant for 24 to 48 hours, and then cooling a product which is obtained in the reactor in the nitrogen atmosphere to room temperature so as to prepare the lithium ferric phosphate / grapheme composite positive electrode material. The lithium ferric phosphate / grapheme composite positive electrode material which is prepared by the method is high in conducting performance and high in power multiplying performance.
Owner:JIANGSU LENENG BATTERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com