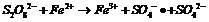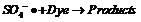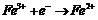Method for treating organic waste water by using electrochemistry under assistance of persulfate
A technology of organic wastewater and persulfate, applied in electrochemical water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve good practical application prospects, realize recycling, and reduce side reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: In this example, three systems of ferric ion-activated persulfate (1), separate electrolysis (2) and ferrous ion-activated persulfate (3) under electrochemical action are compared to orange yellow II The effect of decolorization efficiency. In the ferric ion-activated persulfate system, the decolorization rate of Orange II remained basically unchanged after 5 min of reaction, and the decolorization rate was limited. In the single electrolysis system, the decolorization rate of orange-yellow II increased with the progress of the reaction, and the decolorization rate of orange-yellow II reached 65.8% after the reaction for 60 min. In the system in which persulfate was activated by ferric ions under electric field conditions, the decolorization efficiency of Orange II was much greater than that of the former two systems. This example shows that the combined application of the first two systems has a synergistic effect, which can effectively improve the decolori...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: In this example, the effects of different valence iron ions on the decolorization efficiency of Orange II were compared. Ferric iron ions (1) and divalent iron ions (2) were put into the system as iron sources, respectively. This example shows that in the system adding ferric ions, the decolorization rate in the initial stage of the reaction is lower than the system adding ferrous ions. However, with the progress of the reaction, the ferric ions are reduced to ferrous iron at the cathode and the persulfate is activated. After 60 min of reaction, the system adding ferric ions as the iron source can also achieve better decolorization effect. Therefore, under electrochemical action, ferric ions can also act as iron sources to activate persulfate by reducing to ferrous ions. The detailed operating conditions and processing results are as follows:
[0057] 1. Operating conditions:
[0058] Anode: Titanium-based DSA flat electrode
[0059] Cathode: stainless st...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: In this example, the effects of different pH conditions on the decolorization efficiency of Orange II were compared. The decolorization efficiency of Orange II was investigated in acidic pH 3 (1) and alkaline pH 9 (2) systems, respectively. This example shows that the decolorization effect of Orange II under alkaline conditions is slightly lower than the decolorization effect of Orange II under acidic conditions, but it can also achieve a better treatment effect. The detailed operating conditions and processing results are as follows:
[0071] 1. Operating conditions:
[0072] Anode: Titanium-based DSA flat electrode
[0073] Cathode: stainless steel flat electrode
[0074] Electrode size: 5×11.9 cm
[0075] Orange II solution concentration: 44 mg / L
[0076] Dye waste water volume: 200 mL
[0077] Persulfate concentration: 4 mmol / L
[0078] Ferric ion dosage: 56 mg / L
[0079] Molar ratio of persulfate to ferrous ion: 4:1
[0080] Power supply: DC, 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com