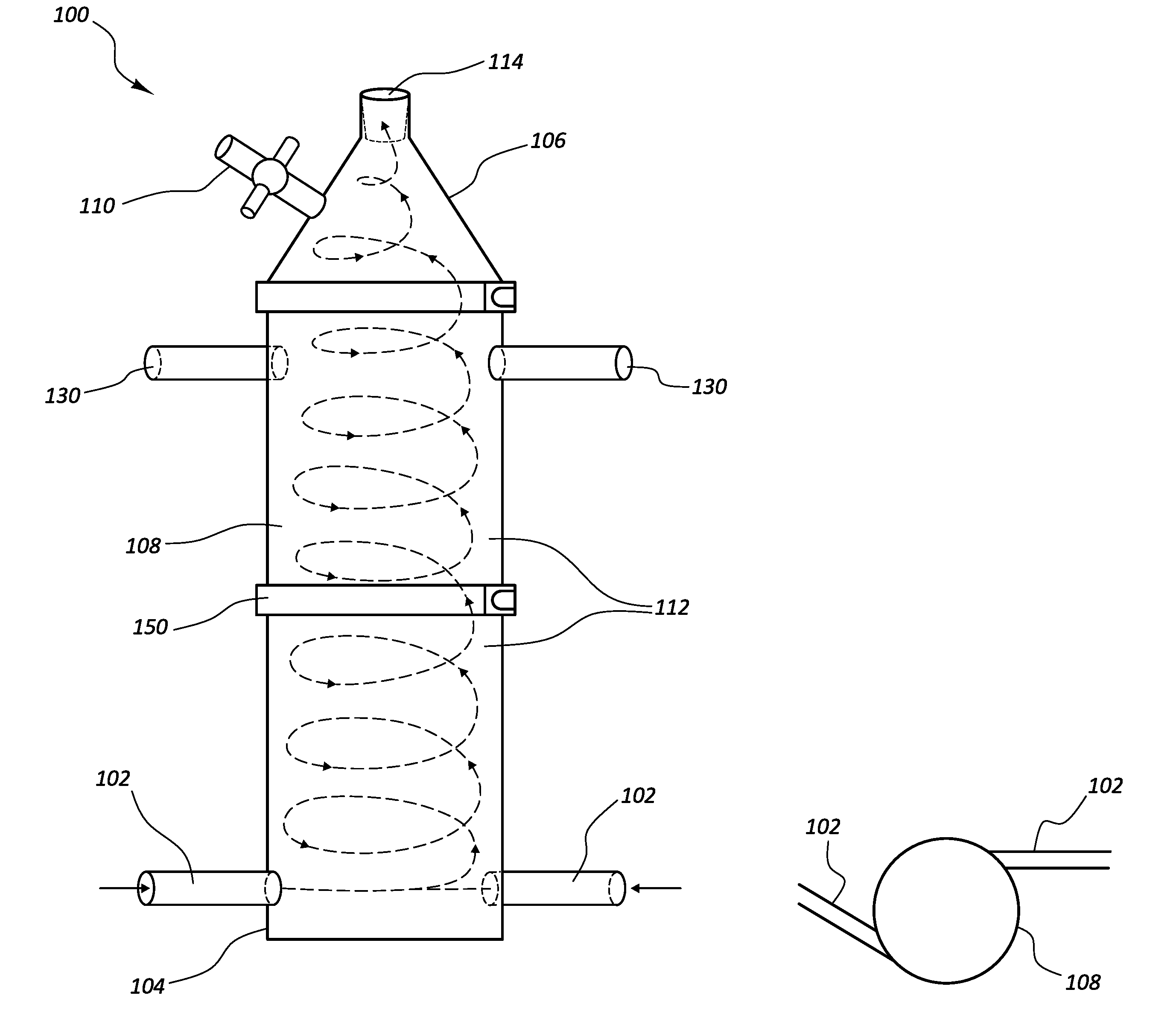
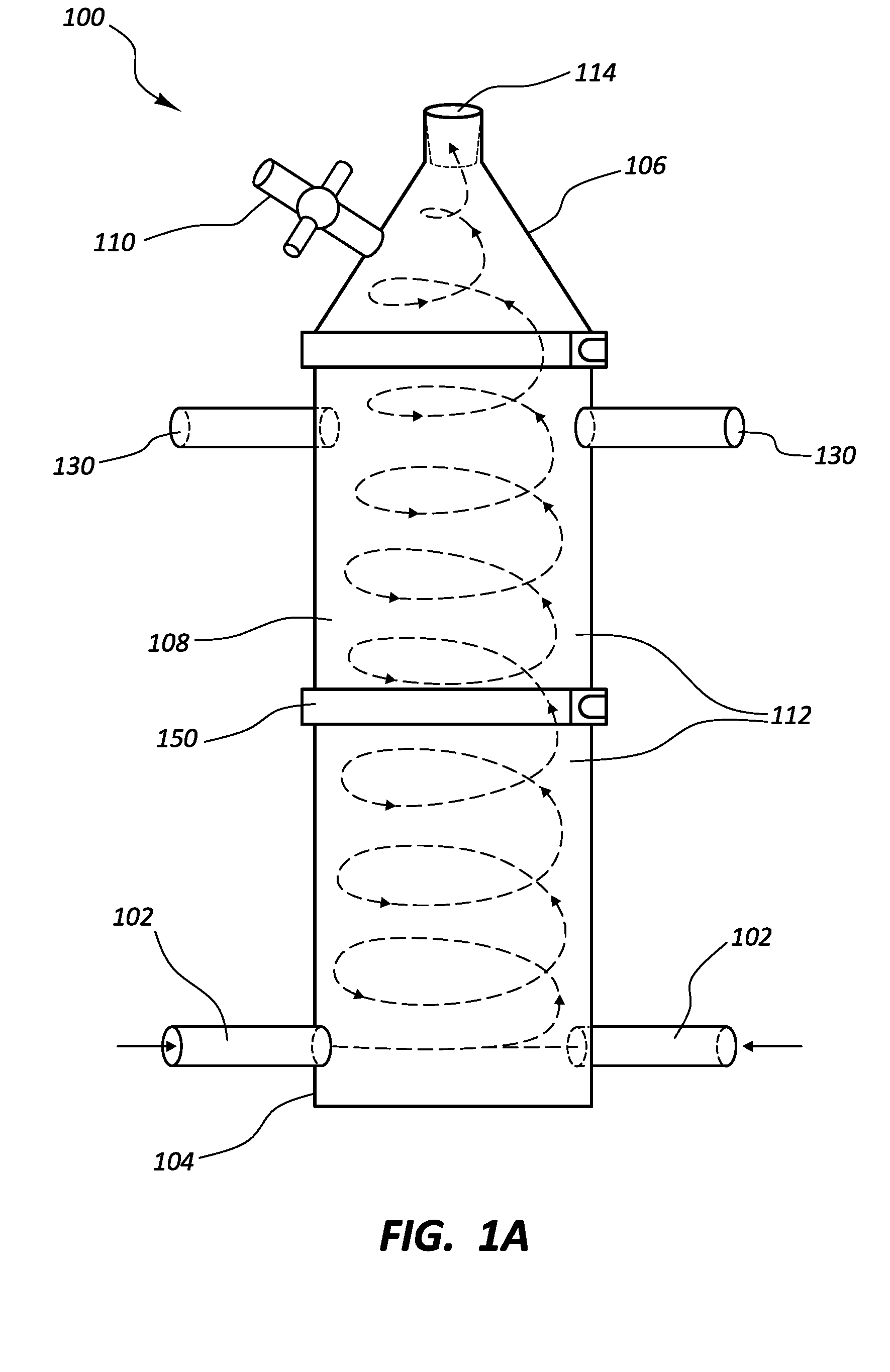
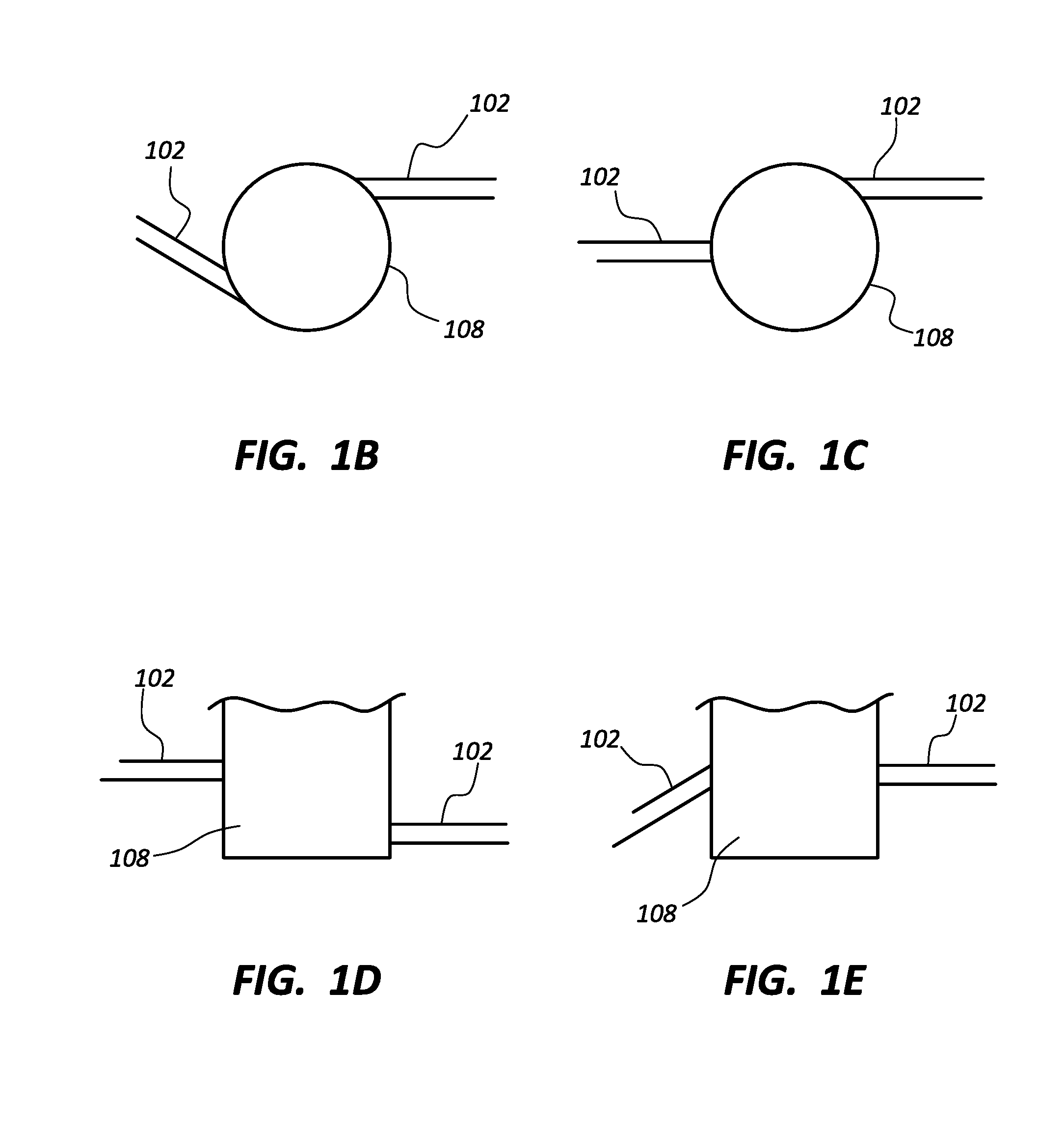
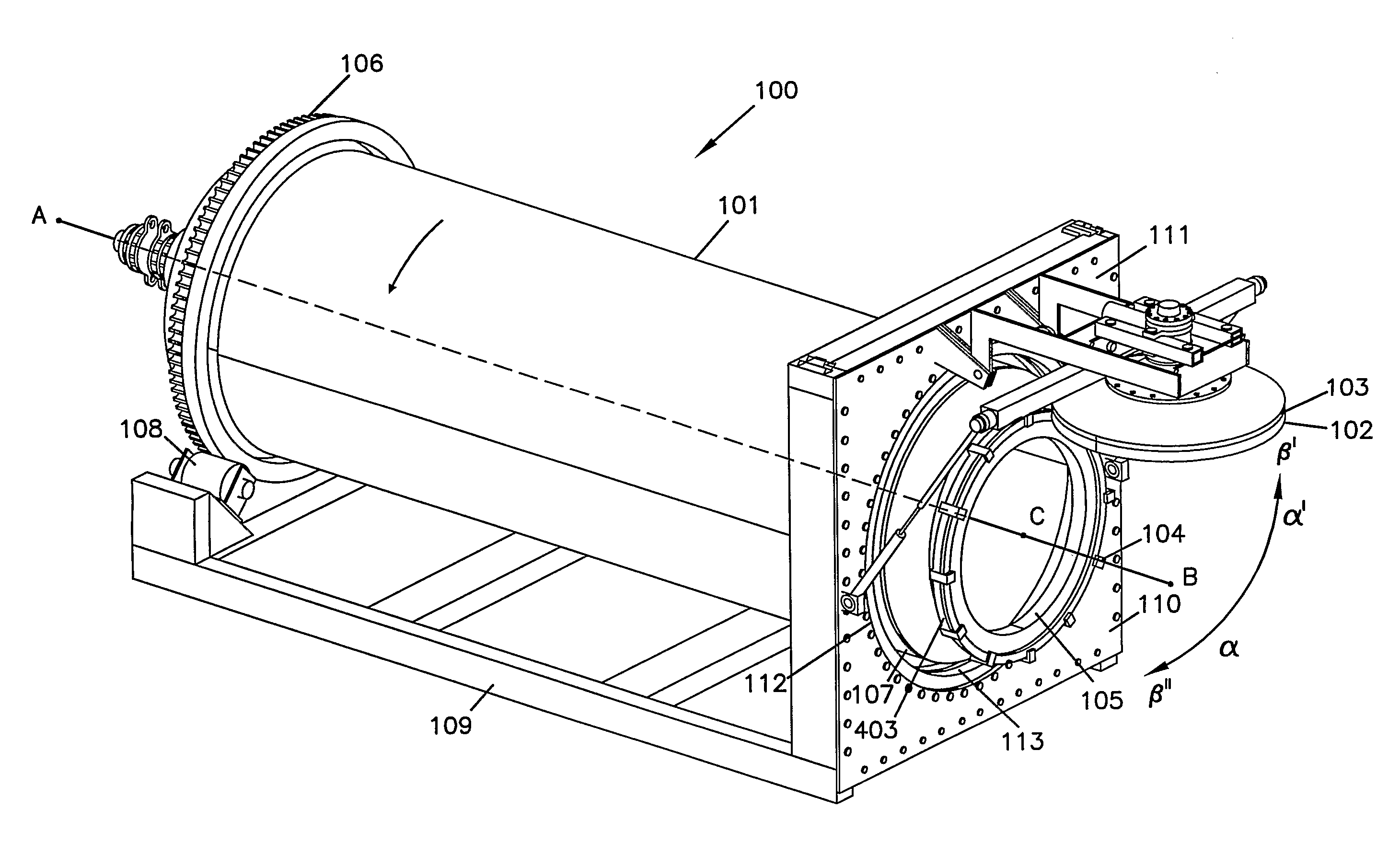
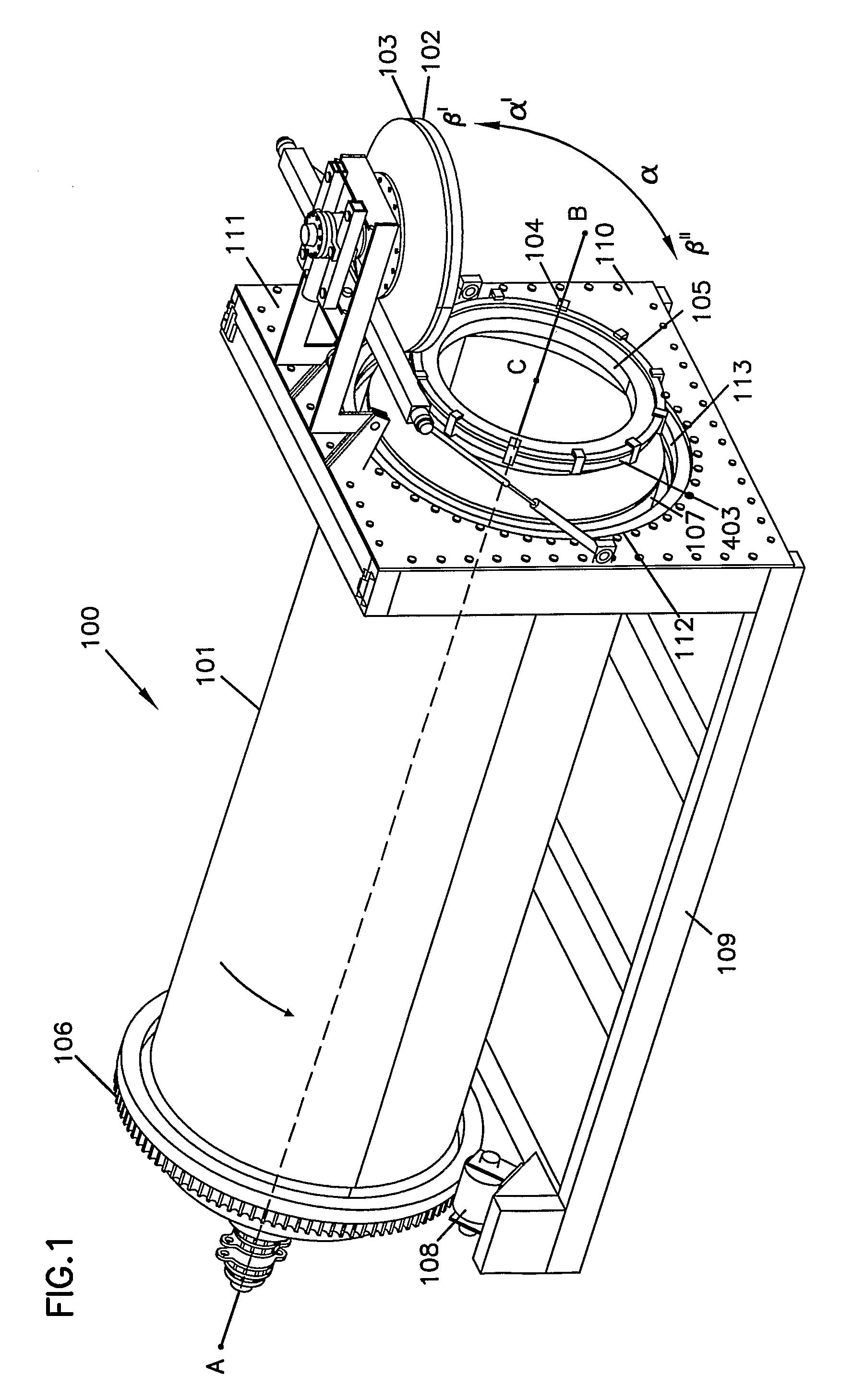
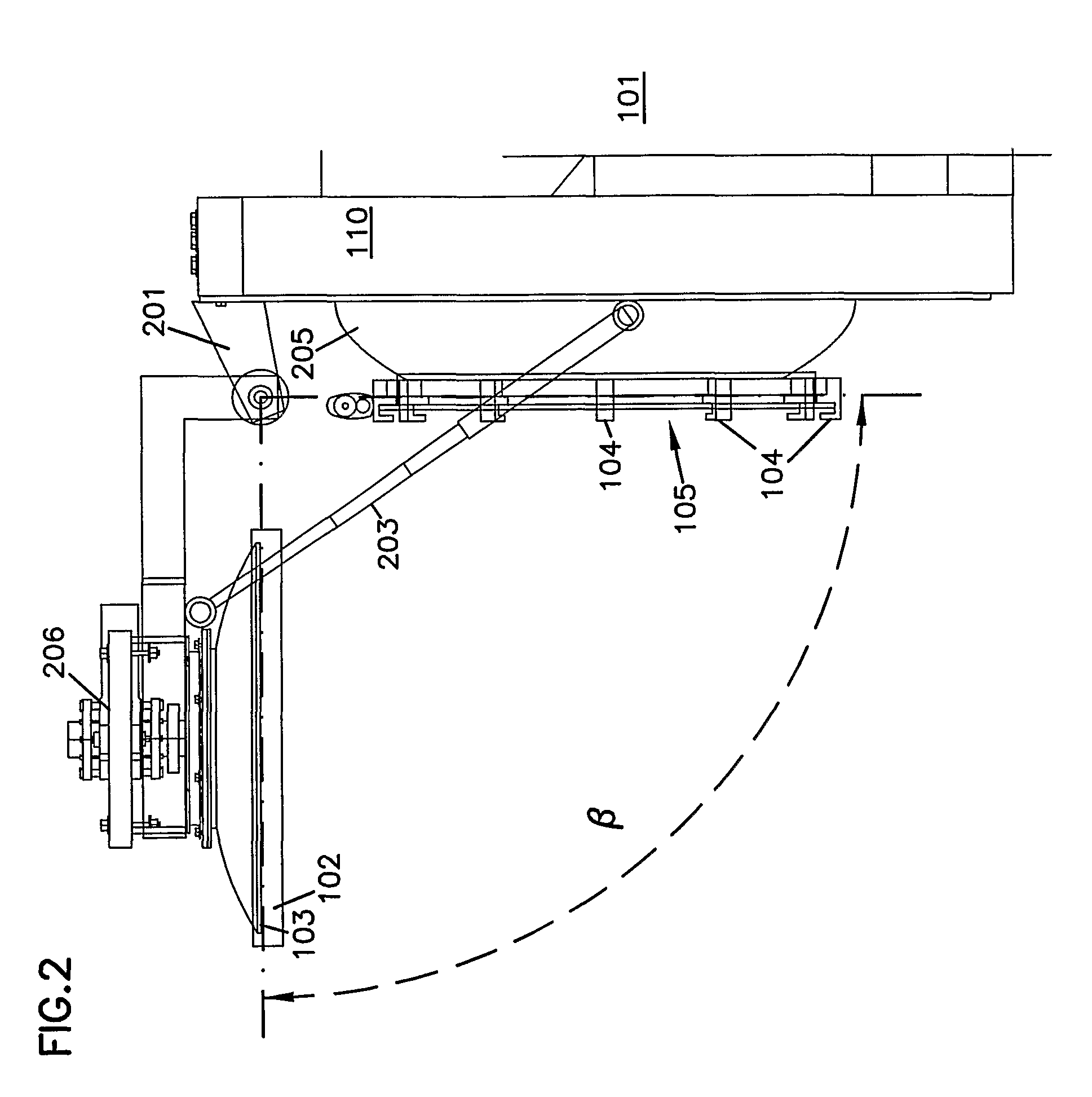
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
916results about "Chemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
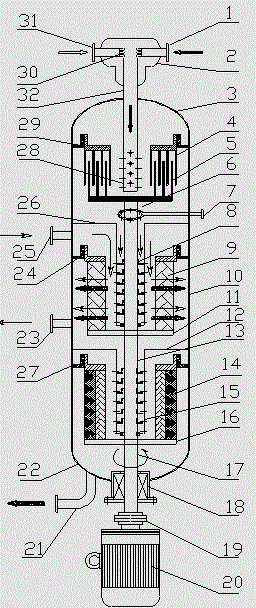
Catalytic reaction method
InactiveCN1507940AReduce dosageIncrease profitChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsPorous catalystMulti phase
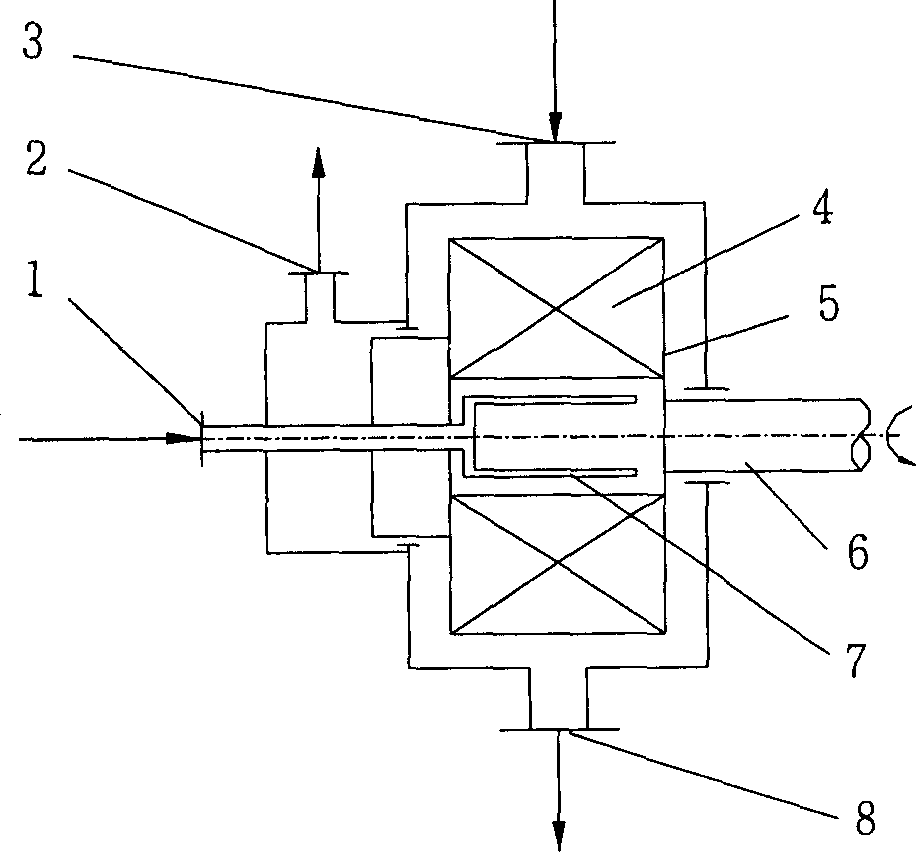
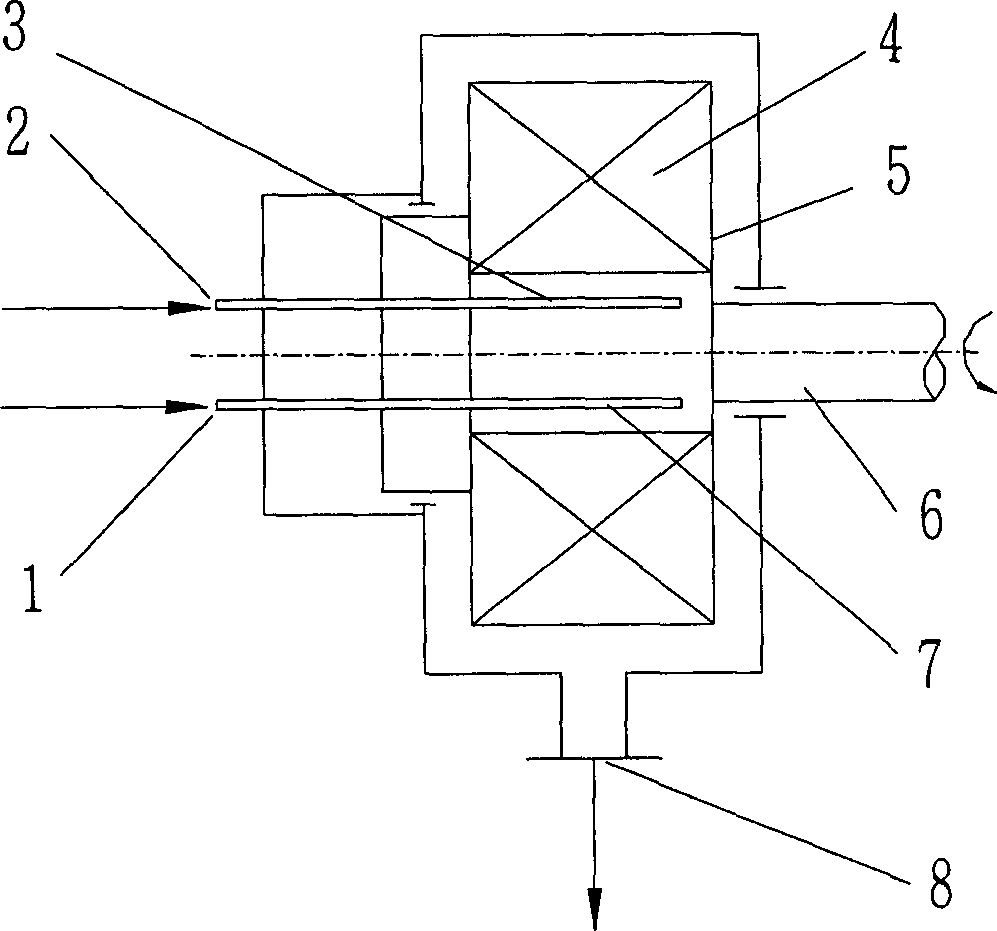
The present invention discloses a catalytic reaction method. Said method can make the catalytic reaction be implemented in the supergravitational field. Said method utilizes the rotary bed supergravitational field equipment as reactor, on the rotor of said rotary bed supergravitational field equipment a porous catalyst layer and / or a porous filler layer are fixed, and the described catalytic reaction is homogeneous reaction or heterogeneous reaction. Said invention cal reduce catalyst consumption, raise utilization rate of catalyst, raise stability of catalyst and can reduce denergy consumption, etc.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Chemical reactor with pressure swing adsorption
InactiveUS20070253872A1Improve energy efficiencyCompact machineryGas treatmentHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesChemical reactionChemical reactor
A chemical reaction is performed with separation of the product(s) and reactant(s) by pressure swing adsorption (PSA), using an apparatus having a plurality of adsorbers cooperating with first and second valve assemblies in a PSA module. The PSA cycle is characterized by multiple intermediate pressure levels between higher and lower pressures of the PSA cycle. Gas flows enter or exit the PSA module at the intermediate pressure levels as well as the higher and lower pressure levels, entering from compressor stage(s) or exiting into exhauster or expander stages, under substantially steady conditions of flow and pressure. The PSA module comprises a rotor containing the adsorbers and rotating within a stator, with ported valve faces between the rotor and stator to control the timing of the flows entering or exiting the adsorbers in the rotor. The reaction may be performed within a portion of the rotor containing a catalyst.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
High-pressure rotary bed gas-liquid mass-transferring and reaction equipment in superheavy force field
InactiveCN1428189AOvercome deficienciesOvercome defectsLiquid-gas reaction processesPressure/vacuum vesselsDrive shaftEngineering
The present invention relates to a gas-liquid mass transfer and reaction equiopment of high-pressure rotating bed in ultragravity force field. Said invention drive equipment is a magnetic drive equipment, including driving portion, driving magnetic stell protecting cover positioned on the exterior of the machine shell and driving magnetic steel and driving shaft which are placed in the protecting cover and driven portion, driven magnetic steel protecting cover positioned in the interior of the machine shell and driven magnetic steel and driven shaft which are placed in the driven magnetic steel protecting cover. The driving portion and driven portion are separatedy by means of magnetic isolation cover between both them. Said invention adopts band pressure design and measures of internal and internal magnetic steel protecting cover, magnetic steel cooling system, high-effective coating layer and others so as to raise mass transfer effect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Pulsating reactors
InactiveUS20050098497A1High densityTreatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingFlocculationLiquid medium
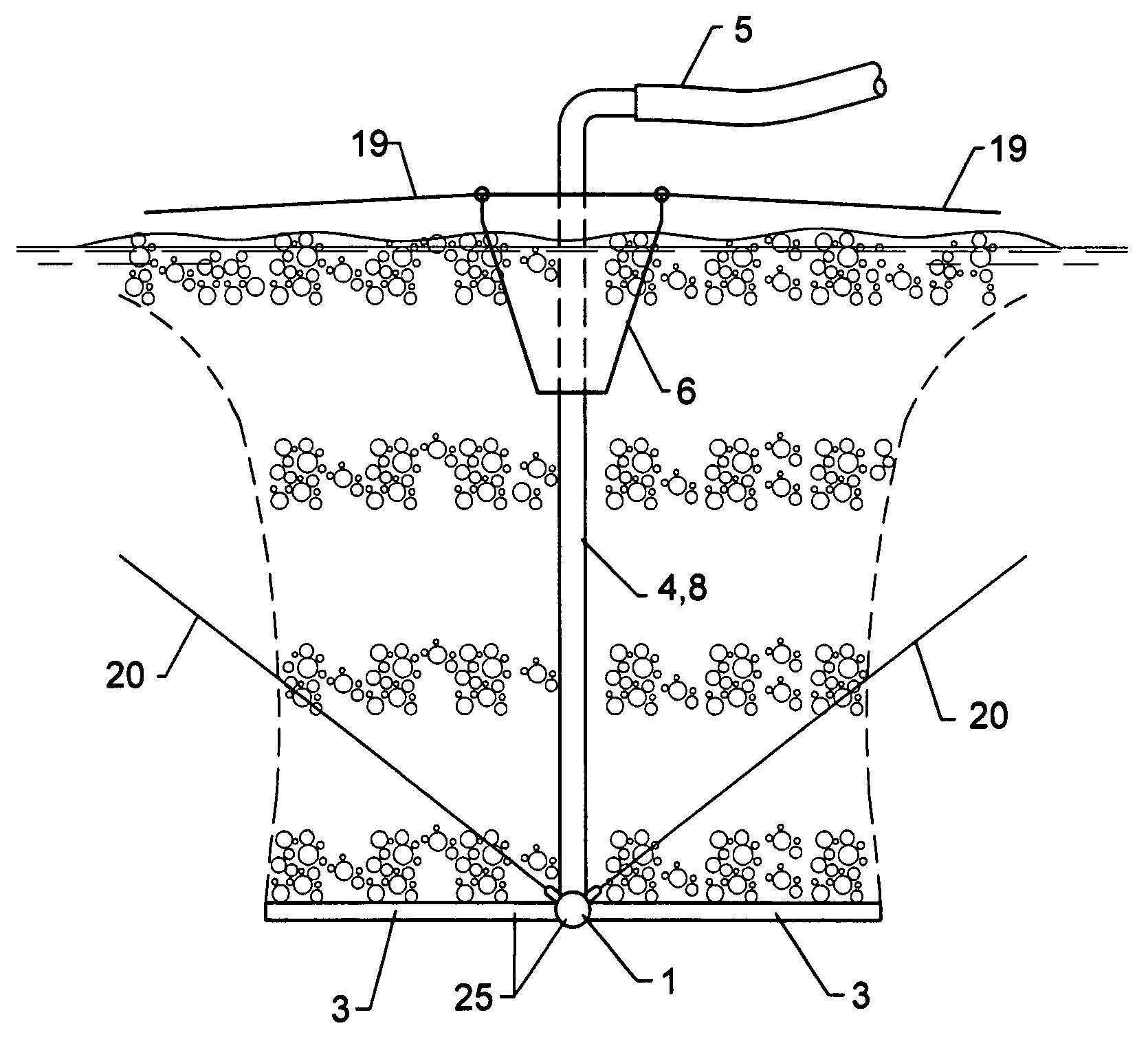
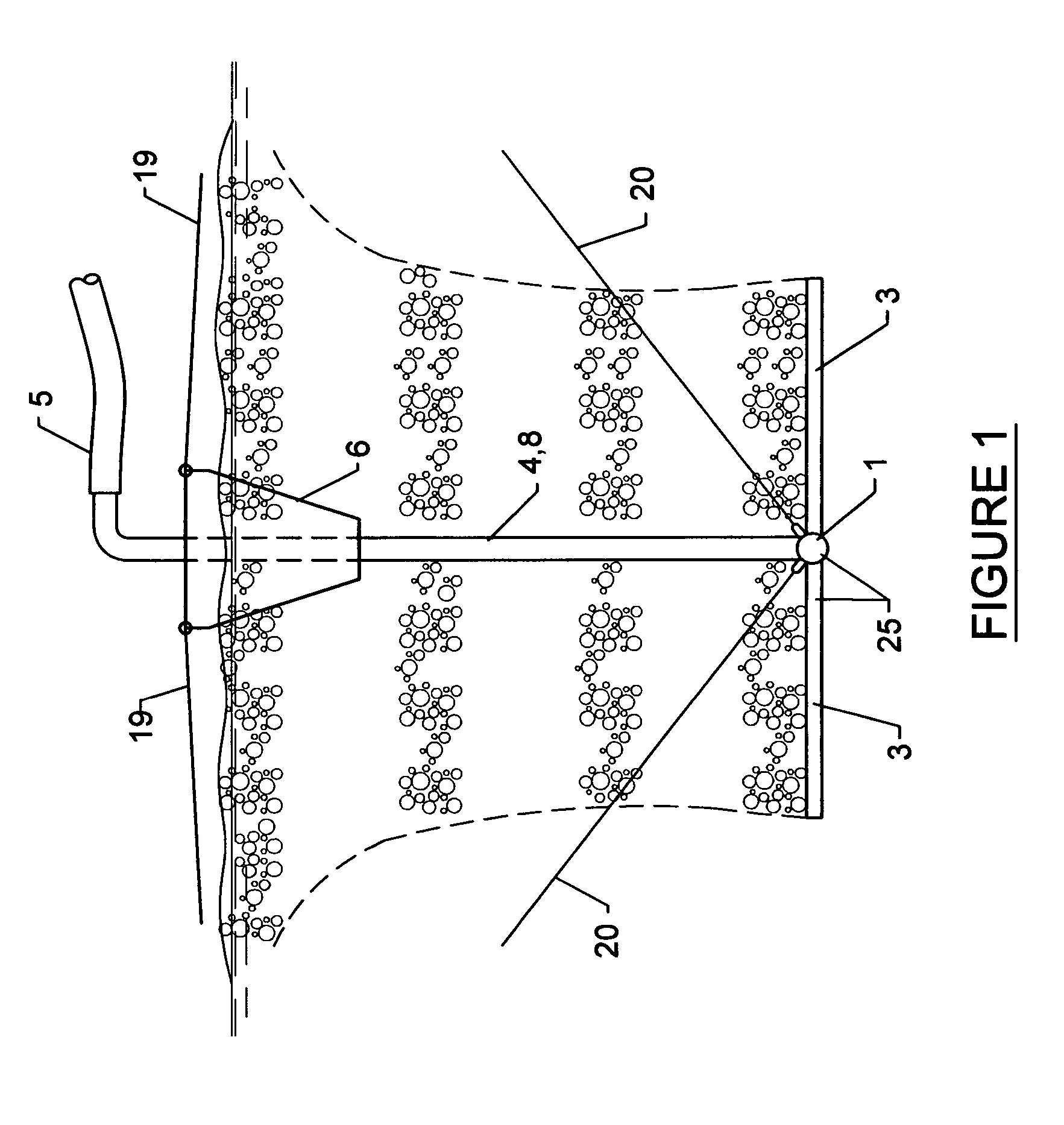
This is a method and apparatus for treatment of liquid media making use of at least one float positioned at the top of the liquid and at least one gas diffuser placed under the float and connected to this float by at least one brace, the diffuser is connected to a gas source by at least one flexible conduit. The gas emitted from the diffuser produces a mixture with liquid having density lower than the liquid and the float partially sinks in the liquid thus increasing the submergence of the diffuser and lowering the gas flow through the diffuser. At increased submergence, the gas flow is reduced, the mixture density increases, and the float rises. A repeatable motion up and down of the float-diffuser is established producing pulsations in the liquid. The method and apparatus can be used in a multitude of chemical, pharmaceutical, petrochemical, environmental and other industries for carrying out mass transfer, chemical and biological transformations, phase separations, thickening of suspensions, mixing, suspending of particles, washing, coagulation-flocculation, membrane filtration, filtration across particulate media, filtration across floating media, mass transfer across membrane, and other processes.
Owner:KHUDENKO BORIS MIKHAILOVICH
Ultragravity field rotary bed mass transfer and conversion unit
ActiveCN1611293ASmall sizeSmall footprintChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsFractional distillationLine tubingMetal
The present invention discloses an ultragravitational field rotation bed mass transfer and reaction equipment. Said equipment comprises machine shell, rotor, rotary foam-catching device and transmission device. The described machine shell comprises gas inlet end cover, straight cylinder section and gas outlet end cover; the described transmission device is formed from motor, transmission shaft, supporting bearing and seal system, and the described rotor is formed from dual rotors, and is consisted of two metal frames with shared bottom plate, two phases of gas and liquid can be parallelly-flowed and contacted on one rotor, and on another rotor they are counter-current-wise contacted, and the rotors are fixed on the shaft by means of shared bottom plate. Said invented equipment can be extensively used in the mass transfer and reaction process of multiphase material system of gas-liquid, gas-liquid-solid and gas-liquid-liquid.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Apparatus and process for treating waste
ActiveUS20130029394A1Easy to separateEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDigestionInternal combustion engine
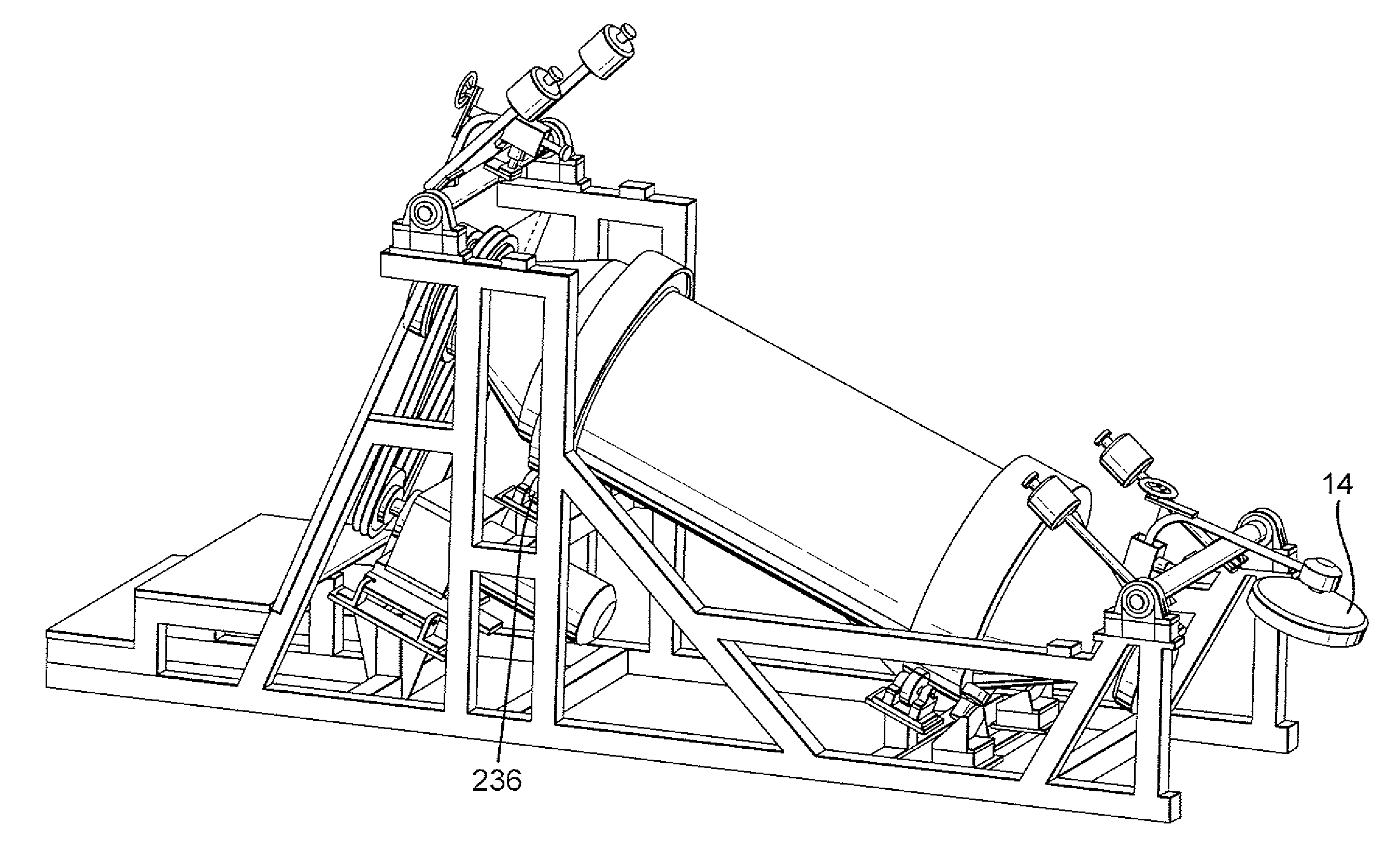
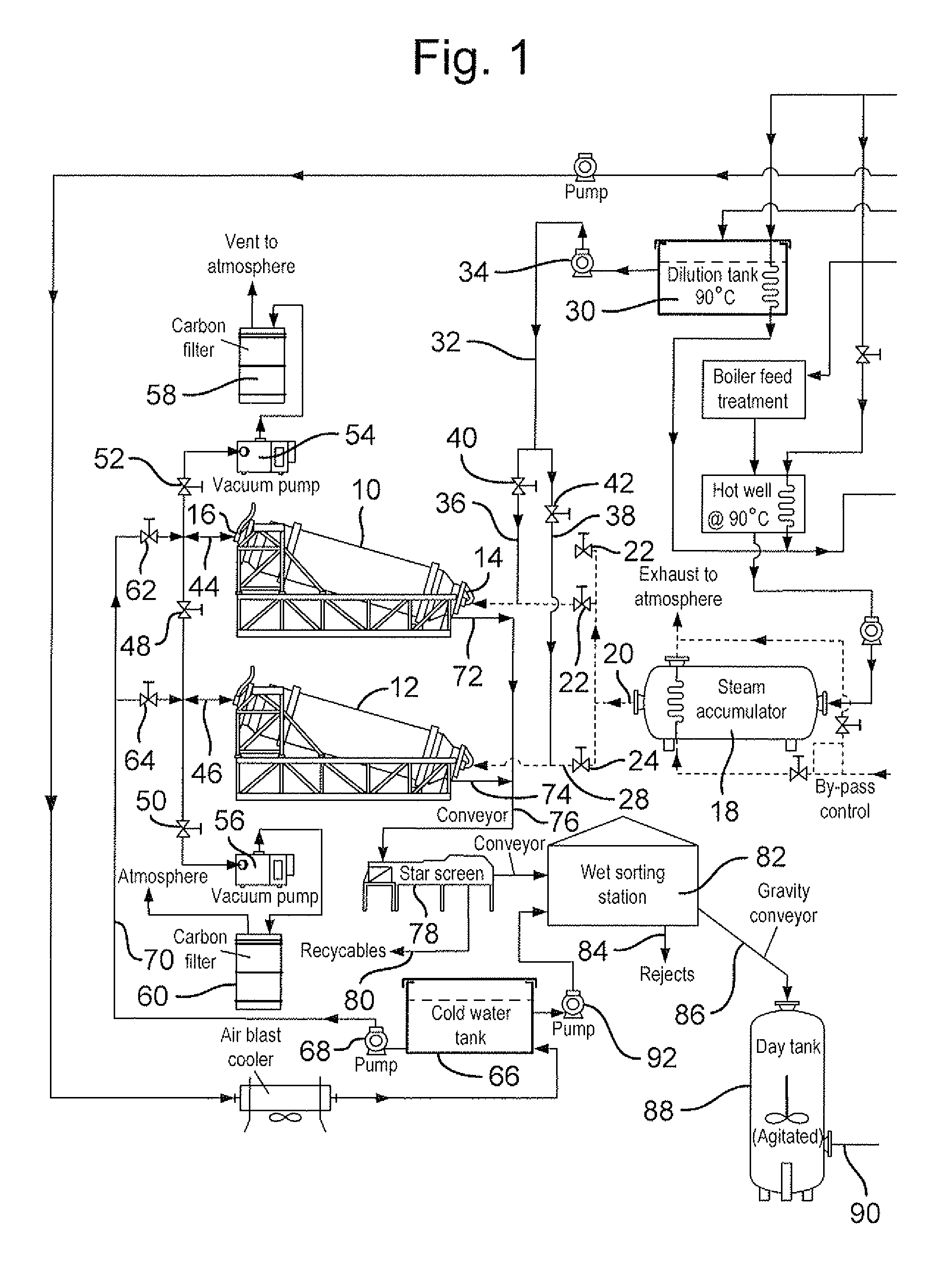
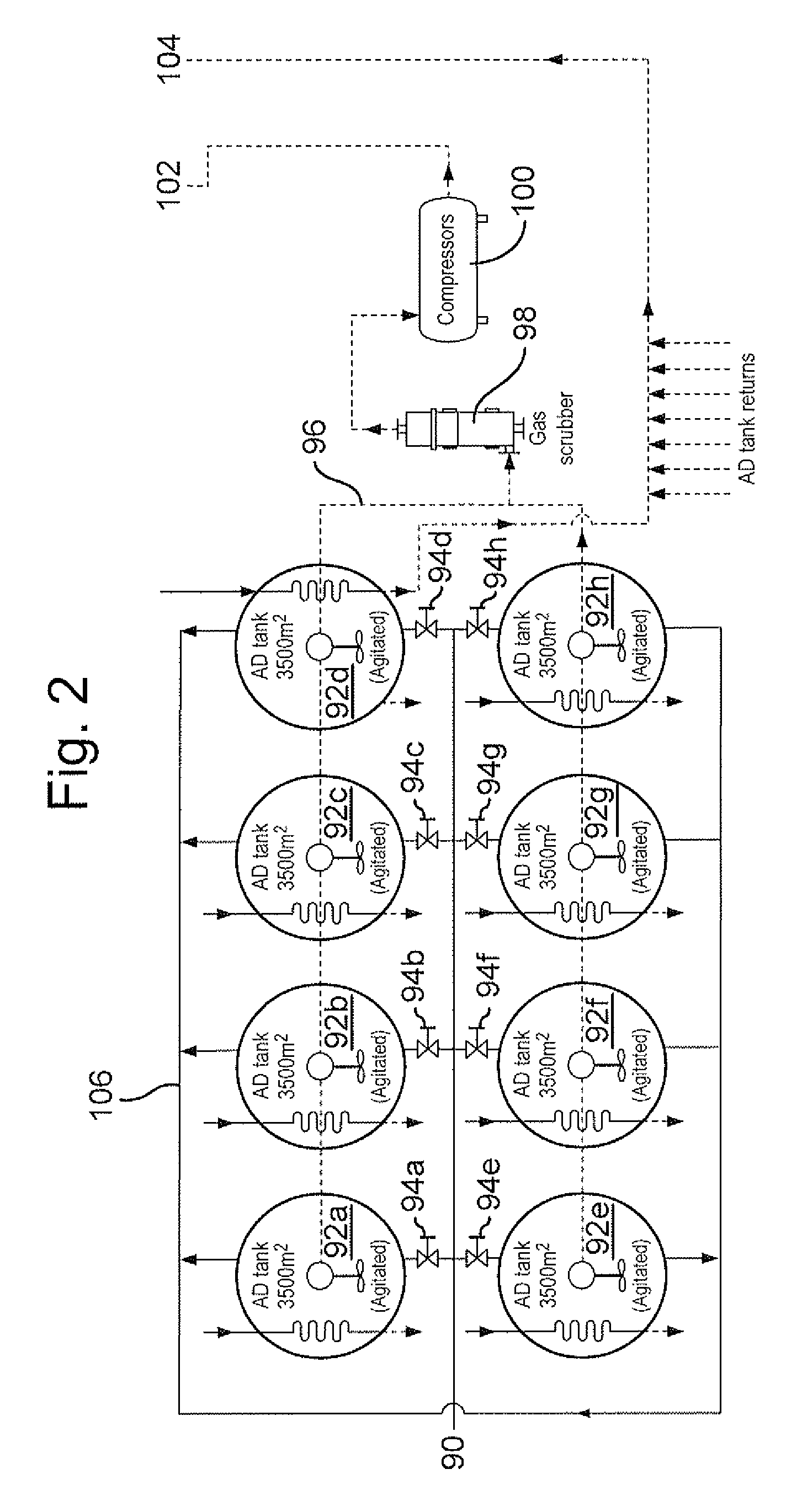
A method for treating municipal solid waste and other waste is provided which comprises: introducing said waste into a rotary autoclave which is downwardly inclined towards its discharge end and has a door at the discharge end; and injecting steam through said door into said autoclave to treat the load. A method is also provided for treating waste, comprising steam autoclaving the waste, anaerobically digesting an organic-rich fraction of the autoclaved waste, recovering methane-containing gas from anaerobic digestion, internally combusting the methane-containing gas to generate power and exhaust gas, and generating steam for autoclaving using the waste heat. A plant for treating the waste may comprise at least one autoclave for steam treating the waste, at least one anaerobic digestion tank for digesting an organic-rich fraction of the autoclaved waste, a recovery system for recovering methane-containing gas from the or each digestion tank, at least one internal combustion engine for combusting the methane-containing gas and generating power, and a steam generator fed with combustion gas from the internal combustion engine for generating and accumulating steam for supply to said at least one autoclave. Also provided is a method of treating waste material in a rotary autoclave, which comprises: loading the waste material into a top opening of the autoclave whilst rotating the autoclave in a first direction in which screw flights within the autoclave convey the waste forwardly along a downwardly inclined body of the autoclave towards a base of the autoclave; rotating the autoclave in a second direction opposite to the first direction so as to establish a circulation of the loaded material between the upper and lower ends of the autoclave to facilitate vacuum and / or steam treatment thereof; and monitoring the load imparted by the autoclave adjacent upper and lower ends thereof during the reverse rotation, increase of the load adjacent the upper end of the autoclave providing an indication of effective load circulation. A door structure for a commercial-scale autoclave based on a castellated door and a locking ring with lock blocks of inwardly facing U-structure is also provided.
Owner:AEROTHERMAL GROUP
Systems and methods for processing fluids
InactiveUS20160346758A1Promote generationReducing and eliminating cavitation-induced erosionShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSludge treatmentChemical effectsNuclear engineering
A vortex reactor includes a reactor body having first and second ends, with one or more inlet ports coupled to the first end. The reactor is configured to form one or more vortices in a fluid passed into the reactor. The inlet port(s) may be positioned to advance a reactor fluid into the reactor body at an angle tangential to an inner surface of the reactor body, forming a vortex that advances toward the second end along the inner surface of the reactor body. A vortex induction mechanism can be disposed within the reactor to induce or augment a vortex within the reactor. The reactor includes an ultrasound-imparting device configured to generate cavitation bubbles in the reactor fluid. The fluid flow within the reactor concentrates the cavitation bubbles within the vortex, thereby providing beneficial physical and / or chemical effects, while protecting the reactor walls and other reactor components from cavitational erosion.
Owner:CETAMAX VENTURES
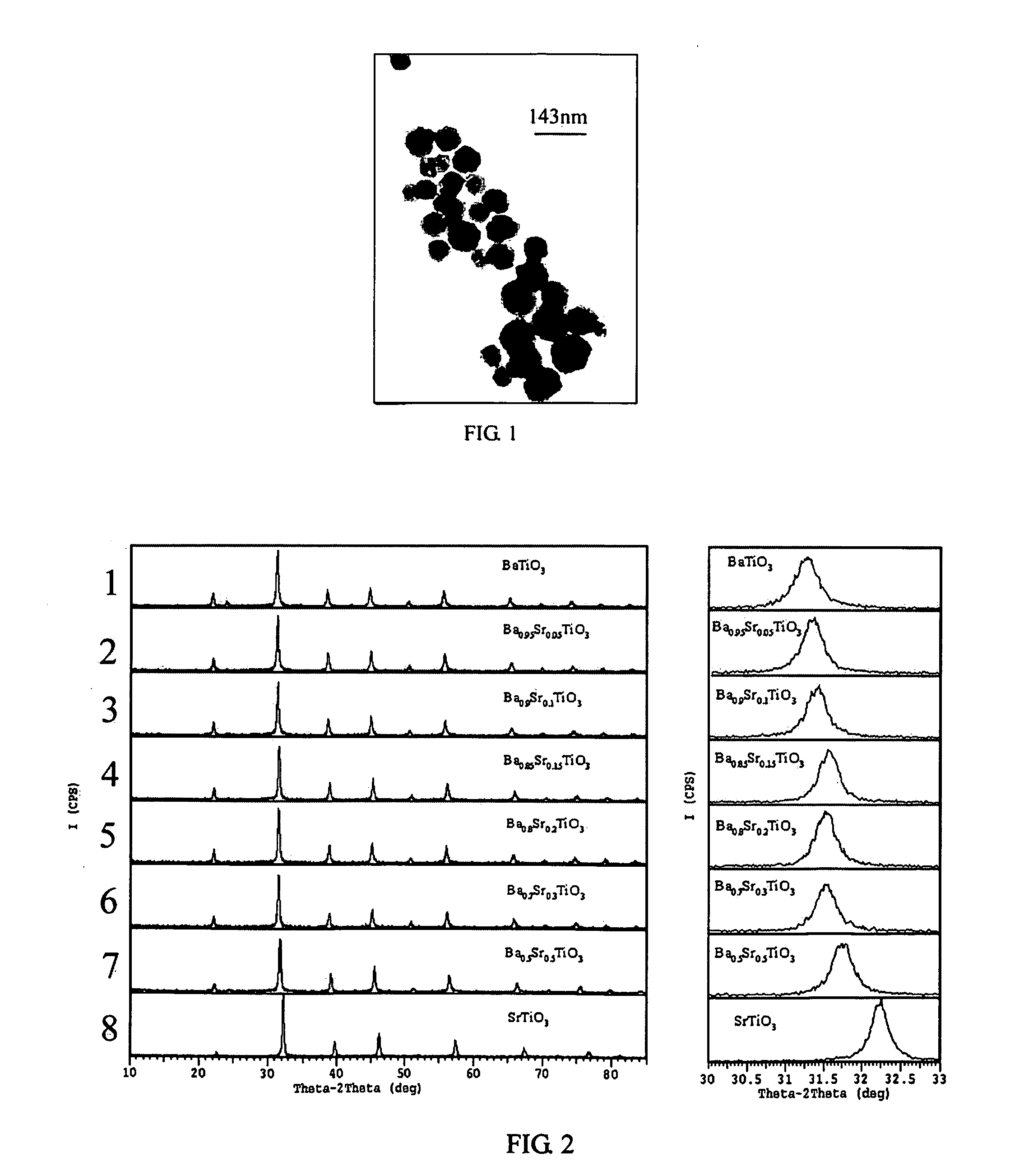
Process for preparing perovskite-type crystalline compound powders
InactiveUS20060045840A1Alkaline earth titanatesMaterial nanotechnologyRare earthParticle-size distribution
A process for preparing perovskite-type compound Ax(BO3)y powders involving reacting a solution containing A and a solution containing B, or a combined solution comprising A and B, with an alkaline solution in a high-gravity reactor at a temperature ranging from about 60° C. to about 100° C. A is one or more metal elements selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Pb, Sm, La, Nd, Bi, and other rare-earth metal elements. B is one or more metal elements selected from the group consisting of Ti, Zr, Sn, Hf, Nb, Ce, Al, Zn, Mn, Co, Ni, Fe, Cr, Y, Sc, W, Ta, and the like. The resulting mixture is then filtered, rinsed and dried to obtain the desired powders. The obtained perovskite-type compound Ax(BO3)y powders have a small average particle size with a narrow particle size distribution, a perfect crystal form and a uniform particle shape, and is suitable for use as raw material for making dielectric, piezoelectric, anti-ferroelectric, pyroelectric, pressure-resisting, sensing, microwave media, and other ceramics.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
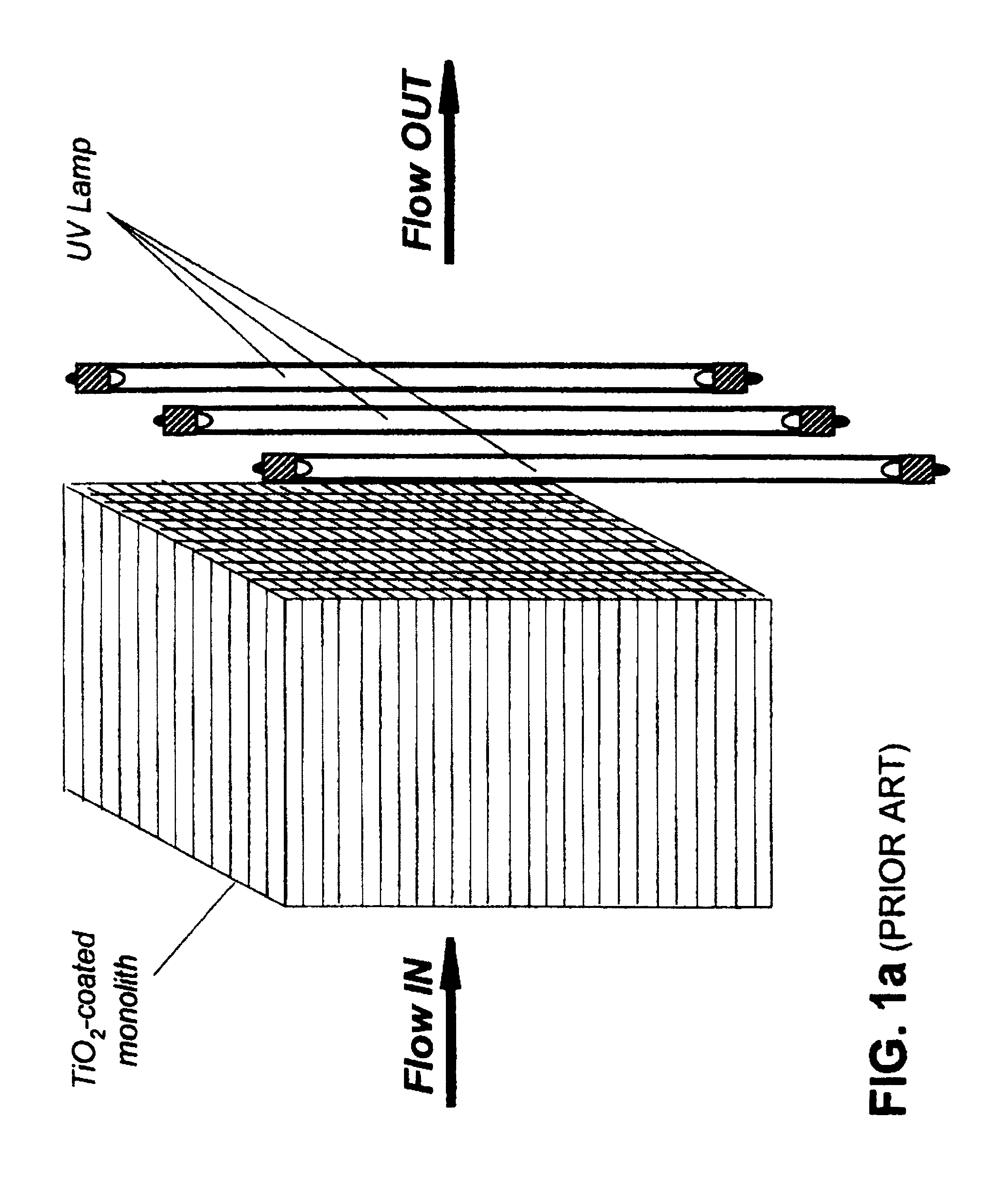
Apparatus for low flux photocatalytic pollution control
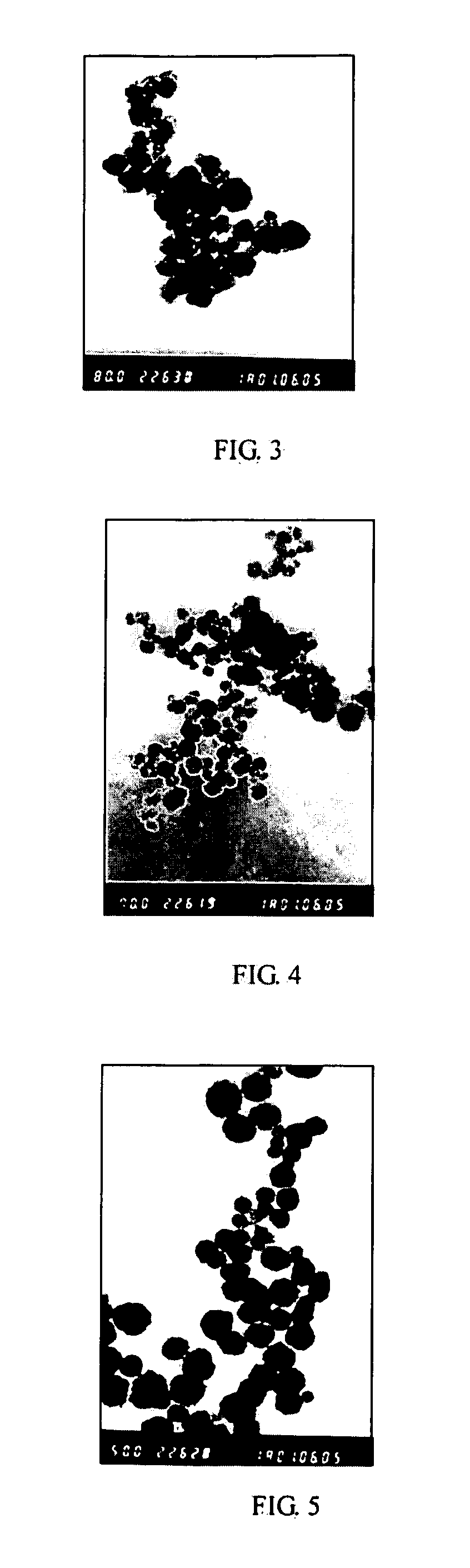
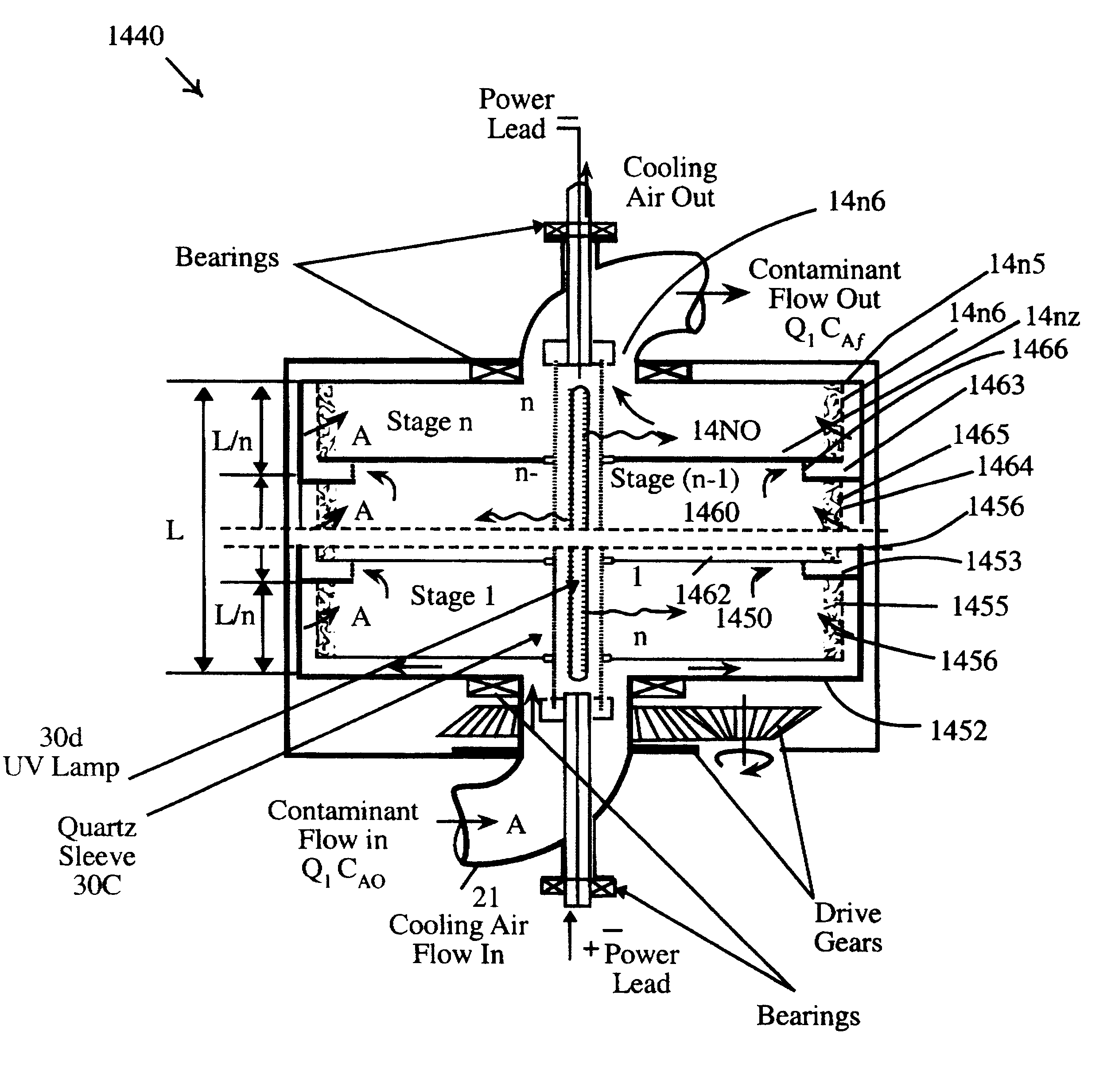
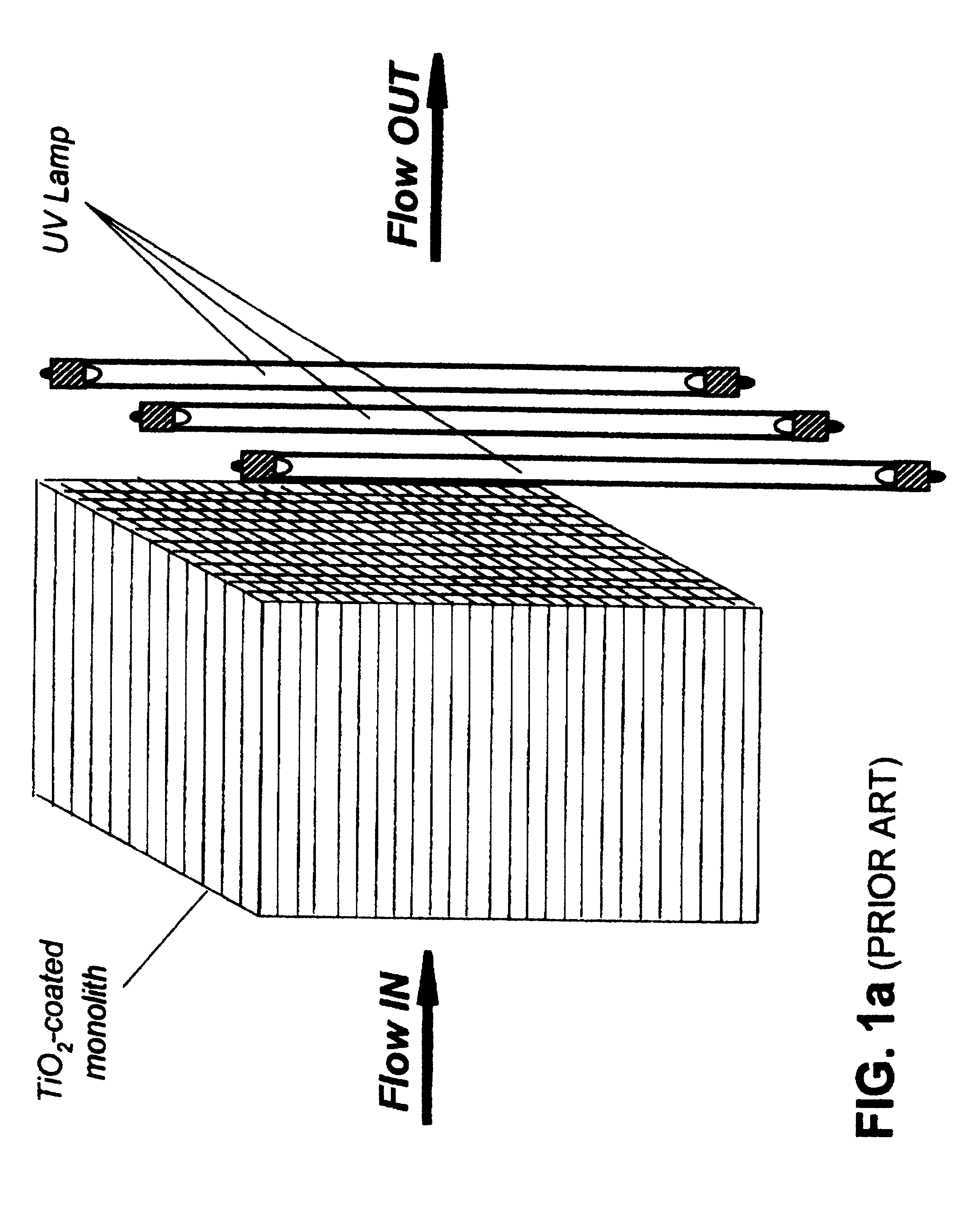
InactiveUS6309611B1Minimizes mass transfer intrusionOptimizationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationPhysical/chemical process catalystsEnergeticsNuclear engineering
A new apparatus for design and scale-up of photocatalytic and thermocatalytic processes is disclosed. The apparatus is based on optimizing photoprocess energetics by decoupling of the process energy efficiency from the DRE for target contaminants and is applicable to both low- and high-flux photoreactor design and scale-up. The low-flux apparatus is based on the implementation of natural biopolymeric and other low-pressure drop media support for titanium dioxide and other band-gap photocatalysts and is further based on the implementation of multifunctional metal oxide aerogels and other media in conjunction with a novel rotating fluidized particle bed reactor.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
Hybrid thermal process to separate and transform contaminated or uncontaminated hydrocarbon materials into useful products, uses of the process, manufacturing of the corresponding system and plant
ActiveUS20160053184A1Increase volumeReduce contentThermal non-catalytic crackingChemical/physical/physico-chemical reactor detailsChemical compoundWaste oil
Process for reclaiming useful products from a waste oil, comprising a thermal separation step performed in a vessel at conditions, of temperature and pressure, allowing to substantially avoid cracking of the waste oil and to assure the separation of said heated waste oil into a first heavy oil fraction and into a second light oil fraction having, in comparison with the waste oil, a low content in solids and / or in other contaminants that are different from water and from inert gas. The process is further characterized in that while, during the thermal separation treatment, the waste oil is heated to a temperature about the boiling temperature of the heavy oil fraction, and below the cracking temperature of the waste oil, and at a pressure that is preferably below the atmospheric pressure, the heavy oil fraction of the vapours existing the vessel, in contact with a cooler surface, condenses and falls back into the vessel, while the second fraction, in a gaseous state, is eventually submitted to at least one further separation treatment. When water is present in the waste oil, said water is used to improve the amount of recovered light oils; and / or when no water is present in the waste oil, water or at least one inert gas or at least one component that may become an inert gas by heating may be added to the waste oil or to the thermal separation unit. Uses of the process for environmental applications and for treating used oils and to prepare oil products. Systems for reclaiming useful products from waste oils comprising at least one rotating kiln and at least one self-refluxing condenser and / or at least one dephlegmator.
Owner:ENVIROLLEA
Method for conducting catalytic reaction in ultragravity field
ActiveCN1743064AEasy to prepareExtended regeneration cycleChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsEmulsionActive component
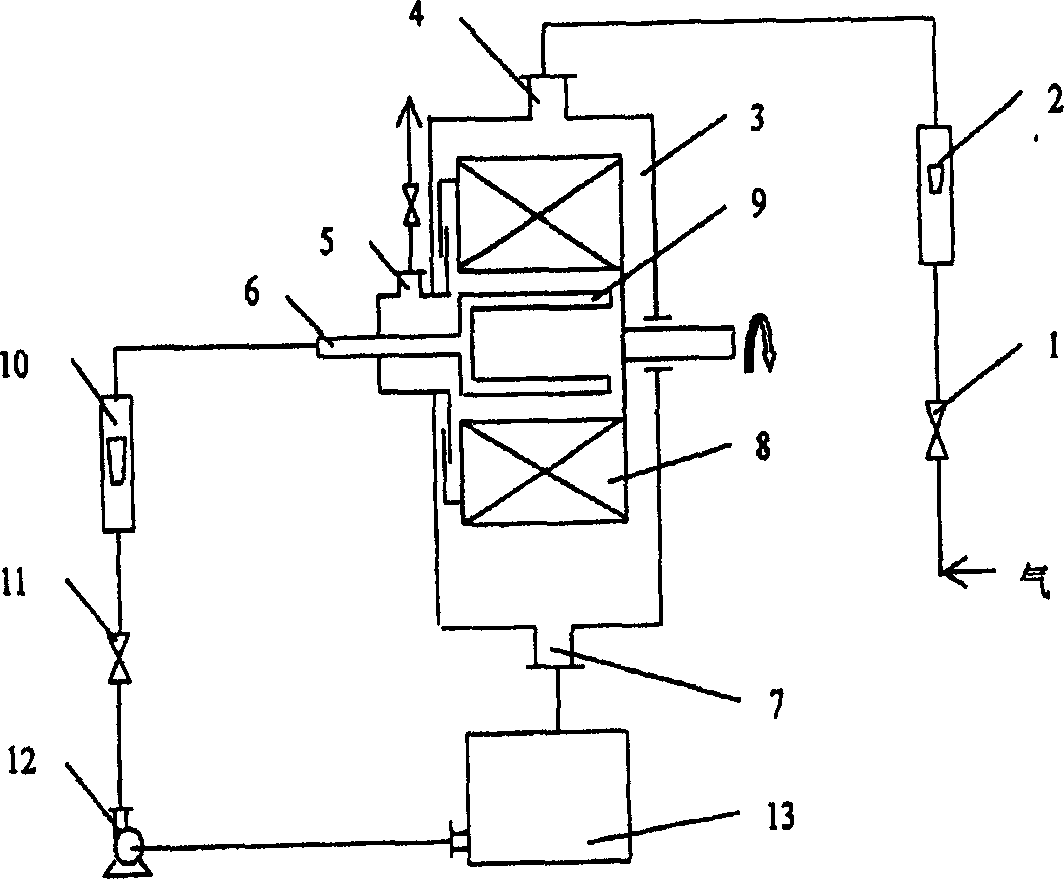
The present invention discloses a method for making catalytic reaction in supergravitational field. Said method includes the following steps: after the heterogeneous catalyst is formed into liquid phase, it can be used for making catalystic reaction, and said reaction is made in the supergravitational rotary bed reactor, in which the described liquid phase formation is characterized by that the active component of catalyst is dissolved in the liquid phase reaction material or solvent to form homogeneous mixture or dispersed in the liquid phase reaction material or solvent to form emulsion
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
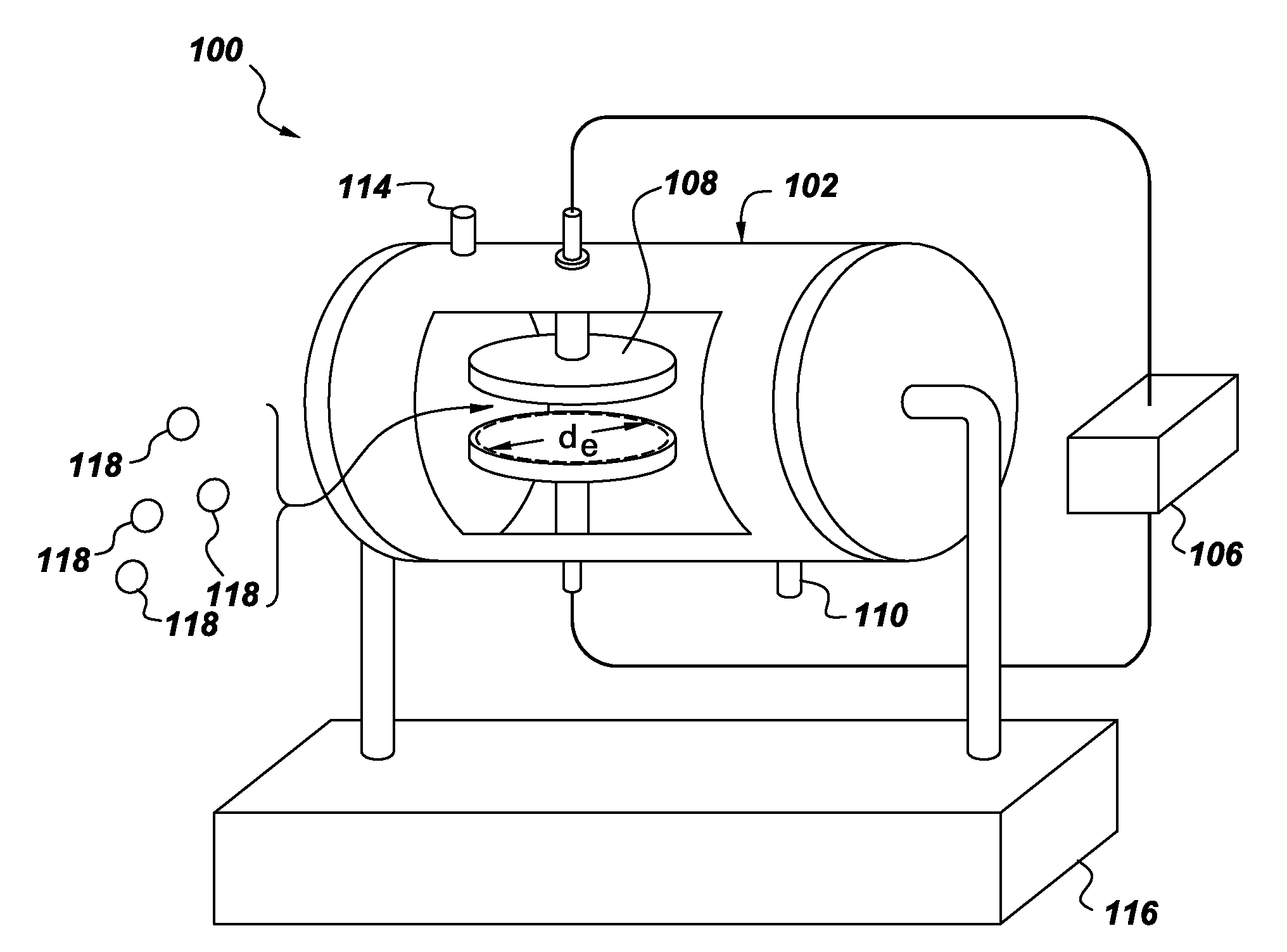
Reaction method, metal oxide nanoparticle or carbon carrying the nanoparticle, obtained by the method, electrode containing the carbon, and electrochemical device with the electrode
InactiveUS20100025627A1Increase surface areaImprove output characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentChemical reactionMetal oxide nanoparticles
The present invention aims at: providing an accelerated reaction in a liquid-phase reaction; forming, by way of the reaction, a metal oxide nanoparticle and carbon that carries the metal oxide nanoparticle in a highly dispersed state; and providing an electrode containing the carbon and an electrochemical device using the electrode. In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, shear stress and centrifugal force are applied to the reactant in the rotating reactor so that an accelerated chemical reaction is attained in the course of the reaction. Further, the carbon carrying a metal oxide nanoparticle in a highly dispersed state comprises: a metal oxide nanoparticle produced by the accelerated chemical reaction, wherein shear stress and centrifugal force are applied to a reactant in a rotating reactor in the course of the reaction; and carbon dispersed in the rotating reactor by applying shear stress and centrifugal force. An electrochemical device produced by using the carbon carrying the metal oxide nanoparticle as an electrode has high output and high capacity characteristics.
Owner:NIPPON CHIMI CON CORP
Chemical reactor with pressure swing adsorption
InactiveUS7250150B1Improve energy efficiencyCompact machineryOrganic chemistry methodsHydroxy compound preparationChemical reactionChemical reactor
A chemical reaction is performed with separation of the product(s) and reactant(s) by pressure swing adsorption (PSA), using an apparatus having a plurality of adsorbers cooperating with first and second valve assemblies in a PSA module. The PSA cycle is characterized by multiple intermediate pressure levels between higher and lower pressure of the PSA cycle. Gas flows enter or exit the PSA module at the intermediate pressure levels as well as the higher and lower pressure levels, entering from compressor stage(s) or exiting into exhauster or expander stages, under substantially steady conditions of flow and pressure. The PSA module comprises a rotor containing the adsorbers and rotating within a stator, with ported valve faces between the rotor and stator to control the timing of the flows entering or exiting the adsorbers in the rotor. The reaction may be performed within a portion of the rotor containing a catalyst.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
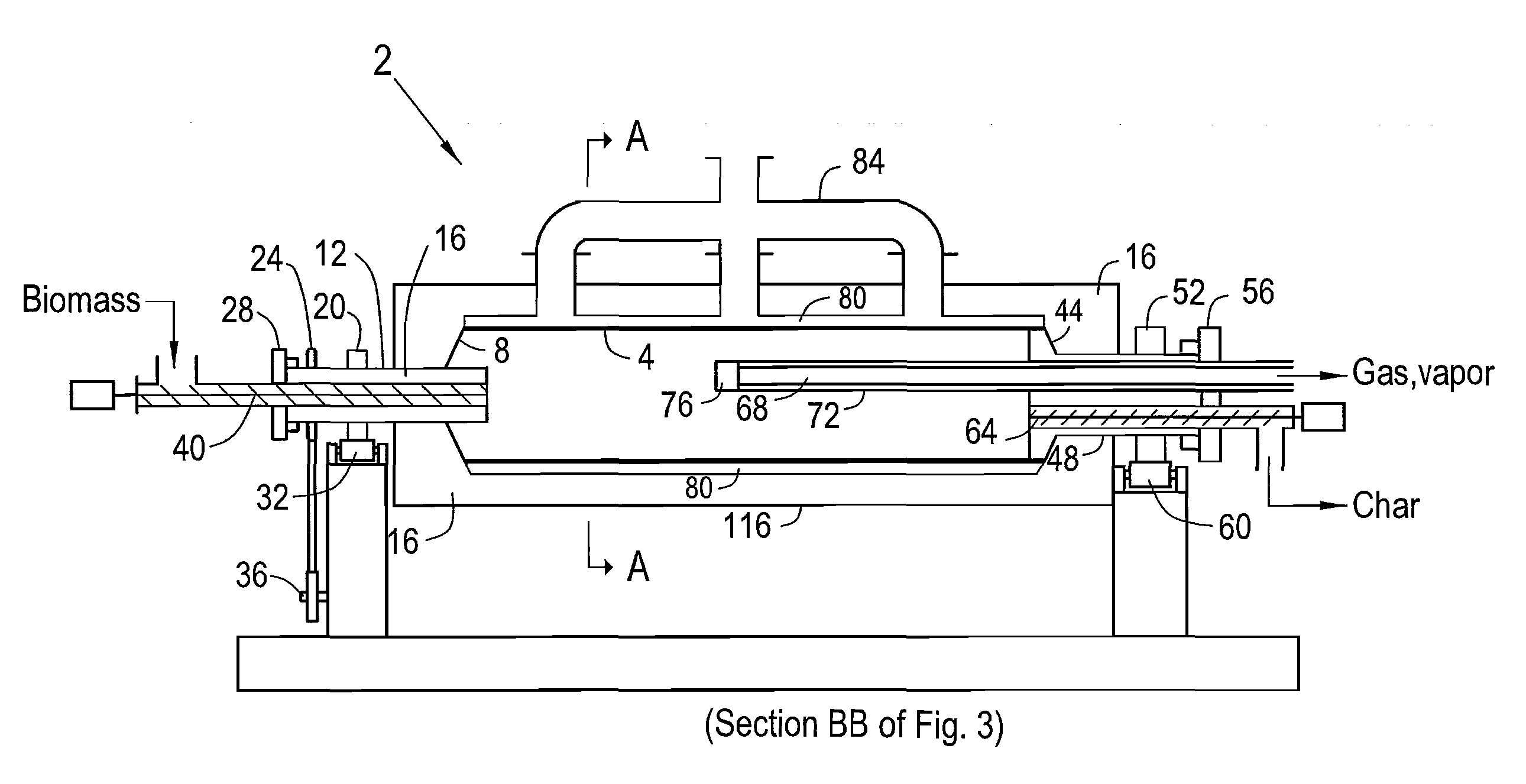
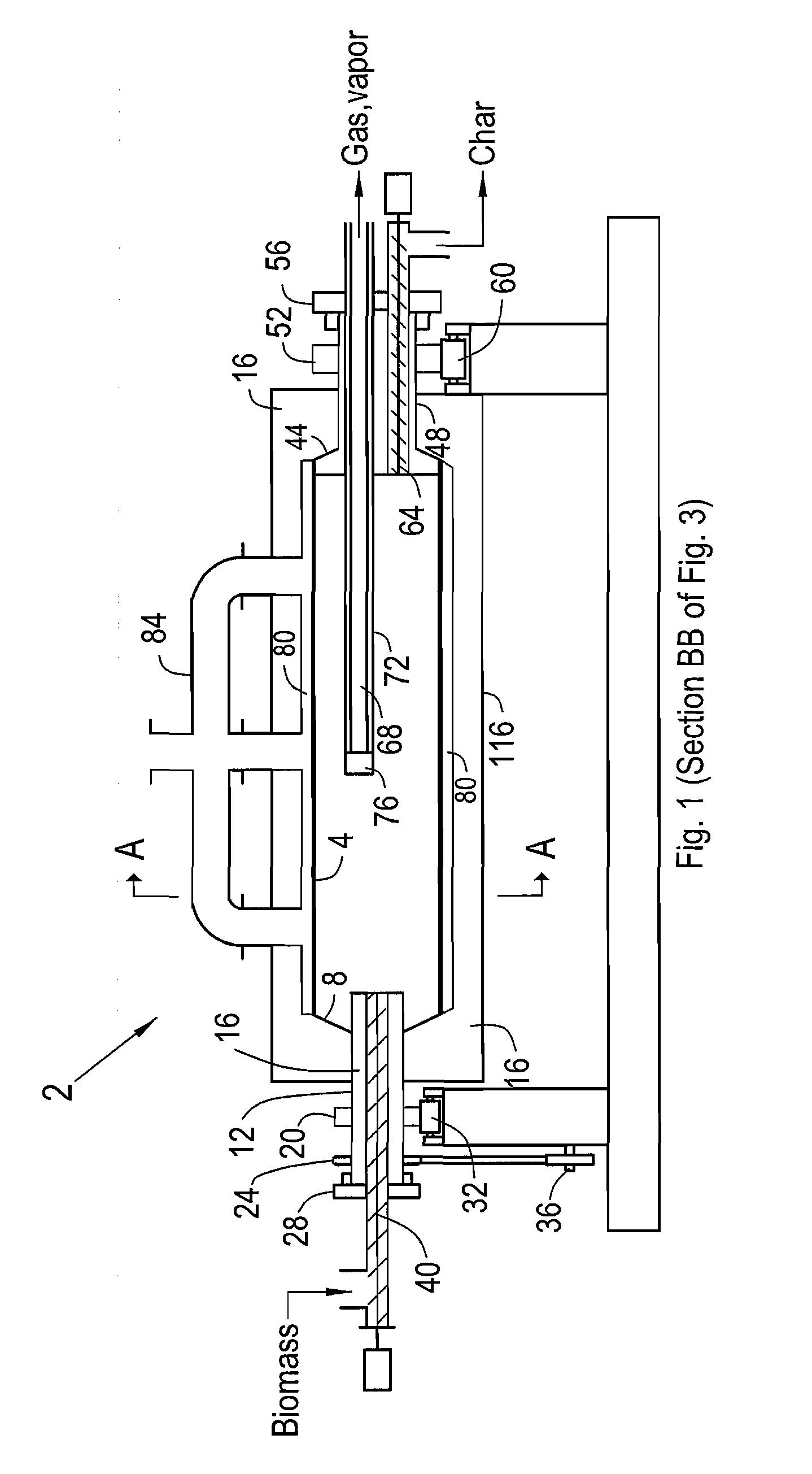
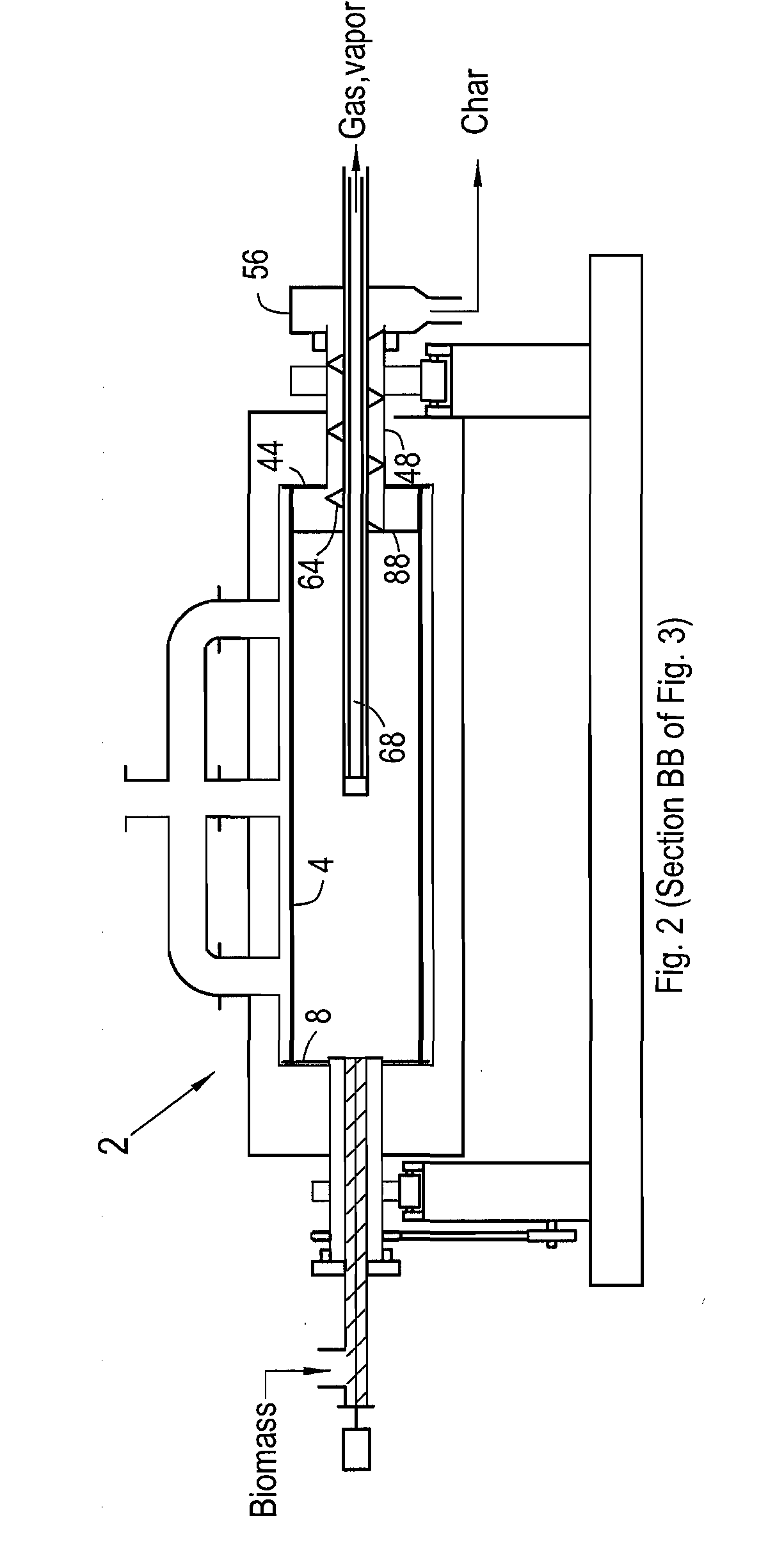
Method and apparatus for fast pyrolysis of biomass in rotary kilns
ActiveUS20120063965A1Fast heatingEliminate shut downPressurized chemical processGaseous chemical processesCombustorFlue gas
Described herein are systems and methods for achieving fast pyrolysis of wood and other carbonaceous solids in rotary reactors. Novel heating, feeding and condensing methods result in high oil yields near those currently achieved with more complicated fast pyrolysis systems. High intensity burners are arranged and controlled to produce high heating rates and uniform temperature of the rotating cylindrical walls of the reactors. The feeding system delays the onset of pyrolysis until the solids fall onto the heated kiln walls. The pyrolysis gases and vapors are rapidly withdrawn and quenched with recycled liquids. The first condenser incorporates a clean out nozzle. Char products are readily separated and discharged into a heat exchanger where heat is recovered and used together with heat from reactor flue gas to dry the solids prior to being fed to the reactor.
Owner:RALPH & MYRNA COATES TRUST
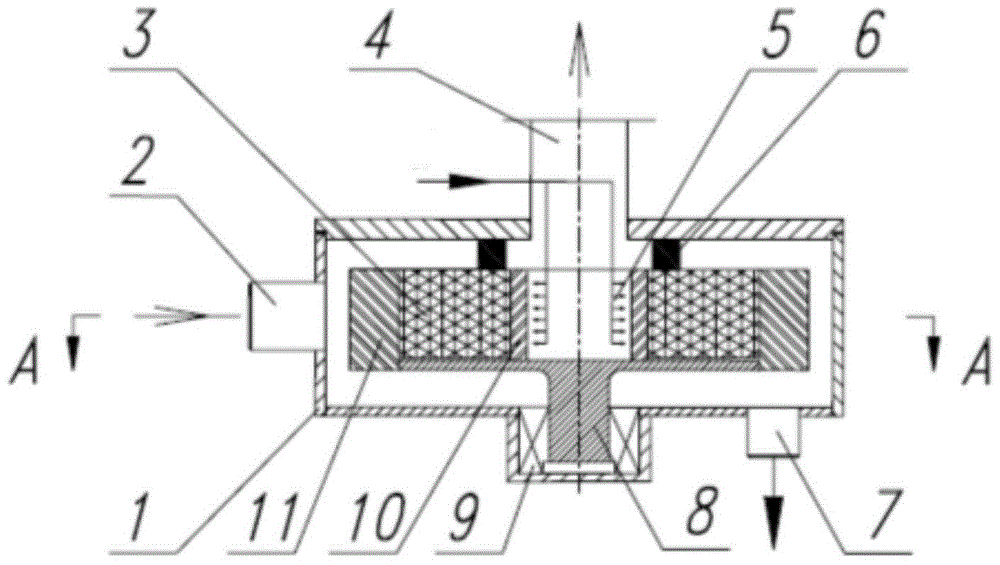
Novel passive super-gravity rotary bed device
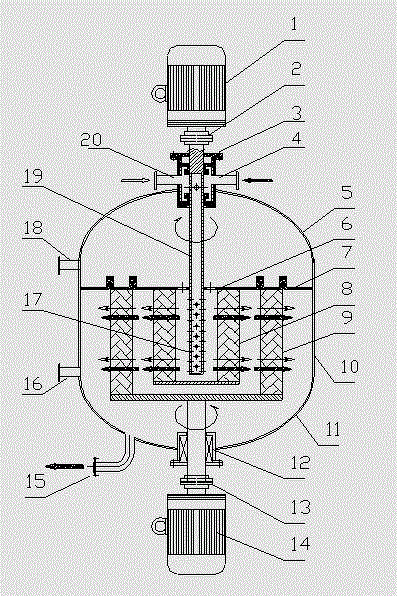
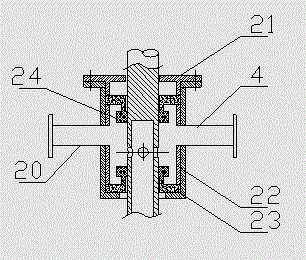
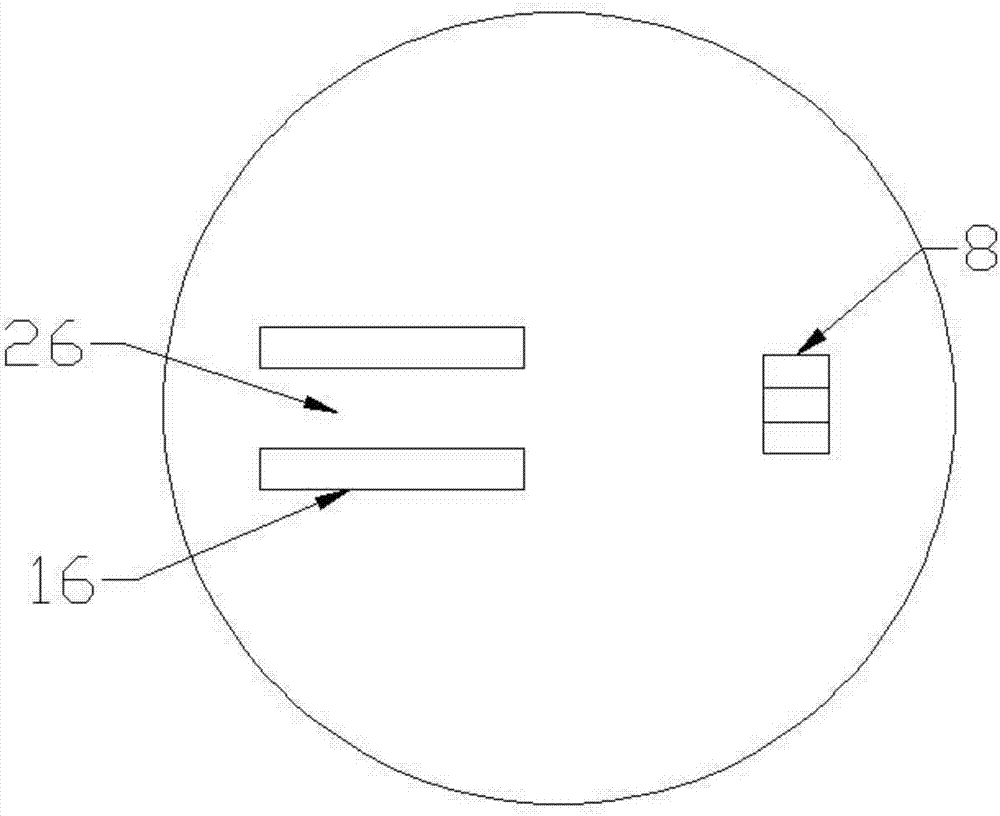
InactiveCN104549100AMeets the requirement to omit the motorReduce energy consumptionTransportation and packagingUsing liquid separation agentEngineeringHigh pressure
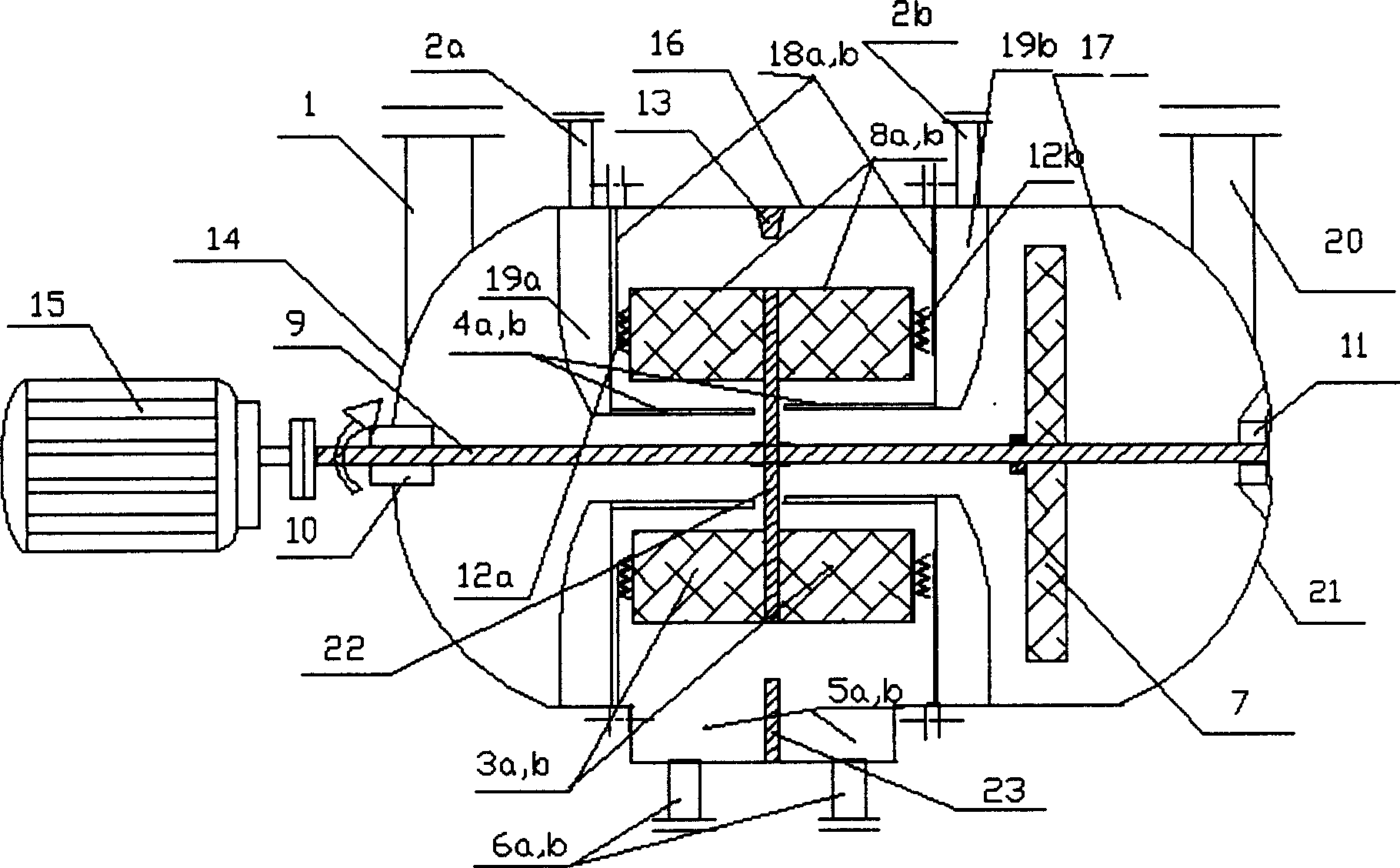
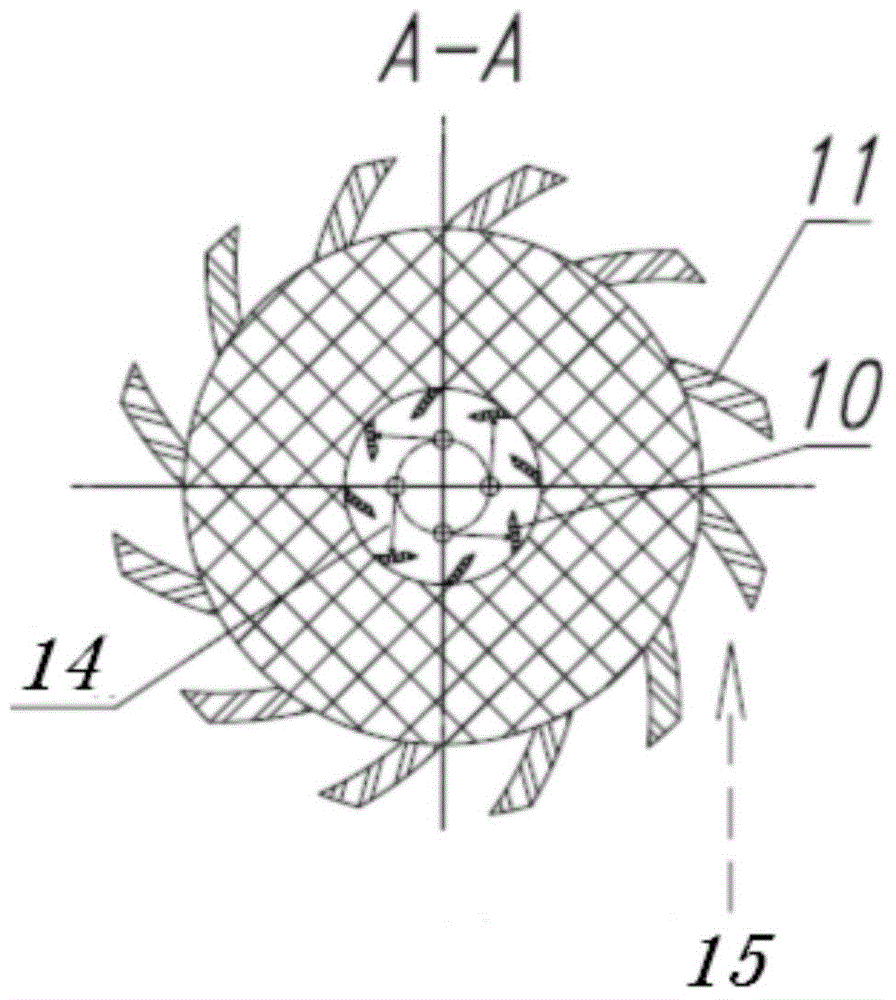
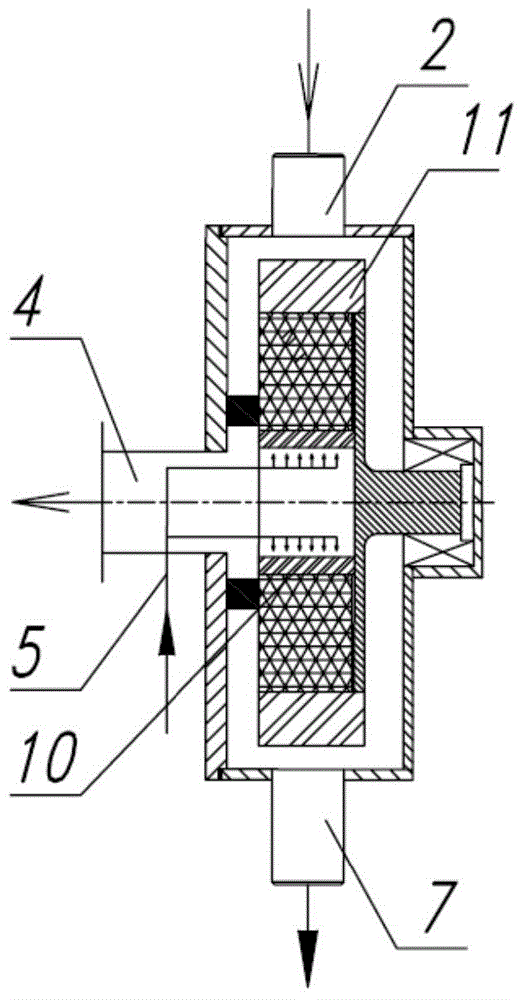
A passive supergravity rotating bed apparatus, comprising a housing (1), a rotor (3), a rotary shaft (8), a first gas conduit (2), a second gas conduit (4), liquid separators (5), and a liquid outlet (7). The rotor (3) is disposed within the housing (1) and is rotatably connected to the housing (1) by means of the rotary shaft (8). The first gas conduit (2), the second gas conduit (4), and the liquid outlet (7) are disposed on the housing (1). The liquid separators (5) are disposed at the inner edge of the rotor (3). Blades (10, 11) are provided on the inner edge of the rotor (3), the outer edge of the rotor (3), or on the inner and outer edges of the rotor (3). High-pressure fluid pushes the blades (10, 11), thereby driving the rotor (3) to rotate. Hence, no electric motor is required to drive the rotor.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Method for preparing ordered mesoporous aluminium oxide
InactiveCN101024503AGood dispersionUniform shapeAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium hydroxide preparationSalt solutionMaterials science
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for ordered medium aperture alumina that includes the following steps: adding surface activator into inorganic aluminum salt as template agent, making precipitant solution, adding inorganic aluminum salt solution into hypergravity reactor, adding precipitant, when the reacting solution reaching a certain pH value, the precursor sol would be gained; taking aging, filtering, washing, and drying to the precursor sol to gain precursor powder. The powder could be made into ordered medium aperture alumina after taking sintering. The invention has the advantages of simple technology, safe to operate, low cost, etc. The specific surface of the product reaches 250-300m2 / g, and the shape has certain orderliness. It has crucial application value in adsorption and catalyzing process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
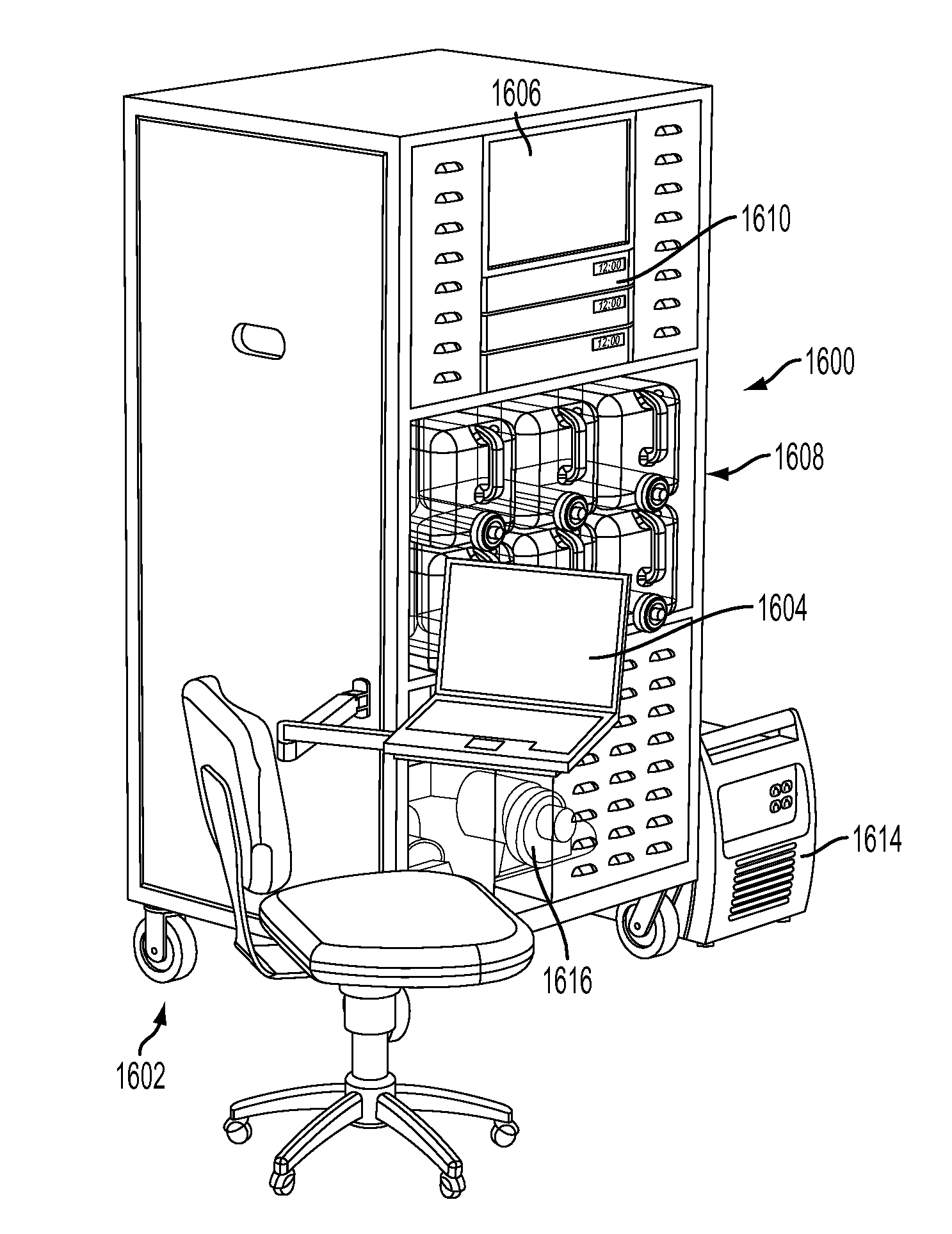
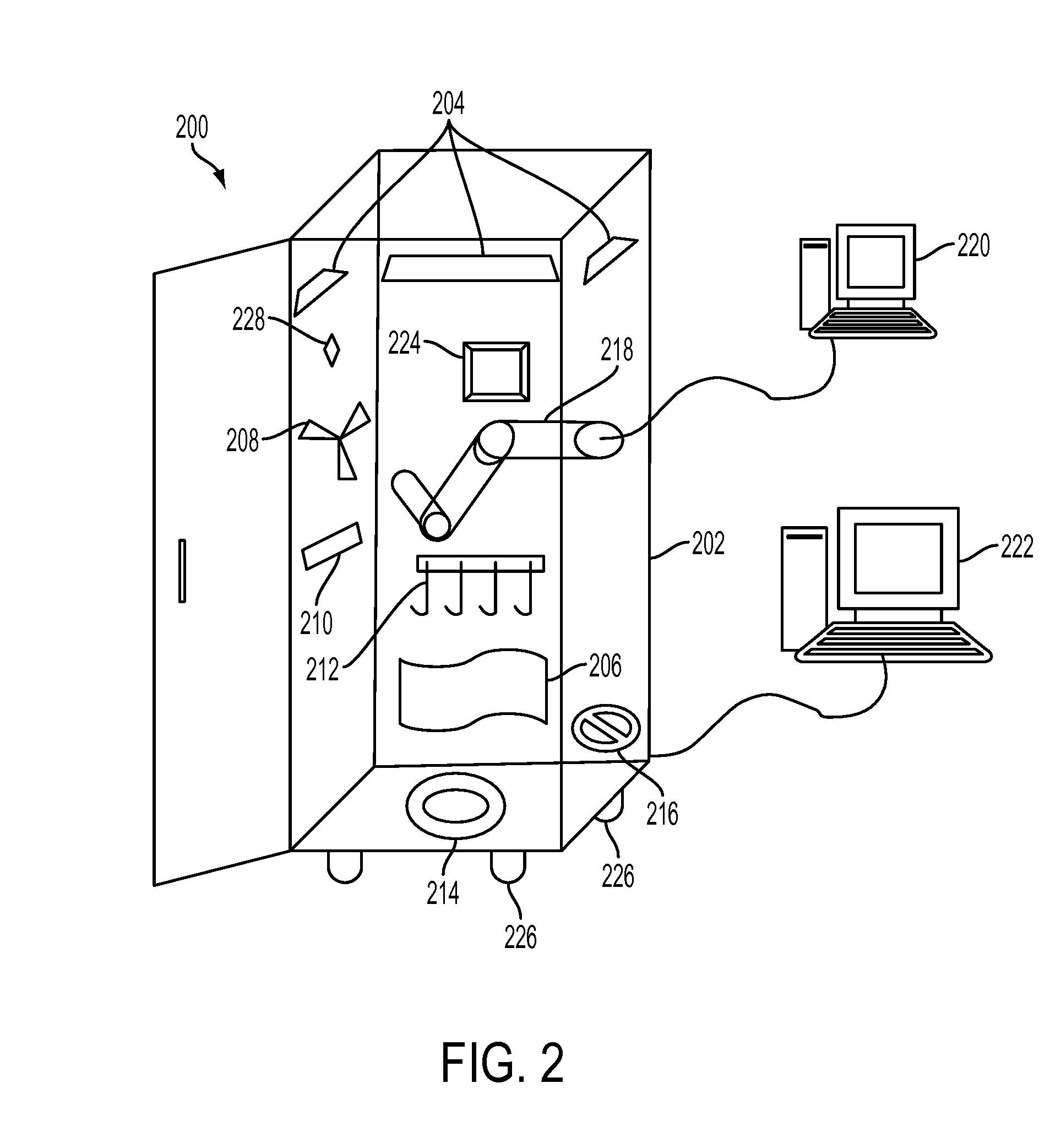
Decontamination apparatus
A decontamination apparatus is provided including an enclosure. A first and second decontamination system may be provided within the enclosure. The first and second decontamination systems may be arranged within the enclosure and configured to decontaminate the articles received in the enclosure. The first and second decontamination systems may rely on different methods of decontamination. The enclosure of the decontamination apparatus may be defined by a plurality of connected prefabricated modular walls. A mobile control and supply module may also be provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
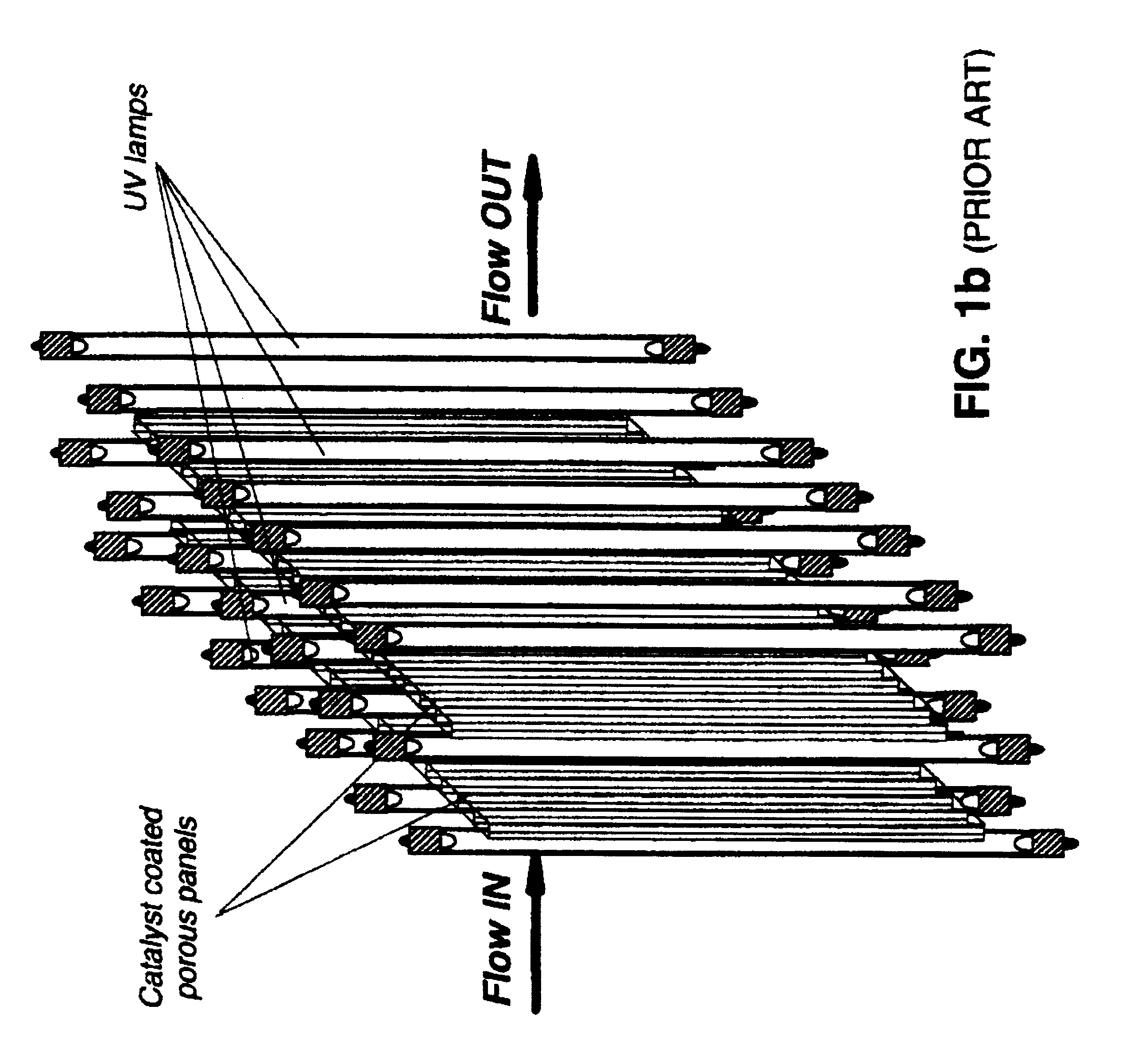
Method for high flux photocatalytic pollution control
InactiveUS6315870B1Efficient retentionMinimizes mass transfer intrusionNitrogen compoundsEnergy based wastewater treatmentEnergeticsPollution
A new method for design and scale-up of photocatalytic and thermocatalytic processes is disclosed. The method is based on optimizing photoprocess energetics by decoupling of the process energy efficiency from the DRE for target contaminants. The technique is applicable to both low- and high-flux photoreactor design and scale-up. The low-flux method is based on the implementation of natural biopolymeric and other low-pressure drop media support for titanium dioxide and other band-gap photocatalysts. The high-flux method is based on the implementation of multifunctional metal oxide aerogels and other media in conjunction with a novel rotating fluidized particle bed reactor.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
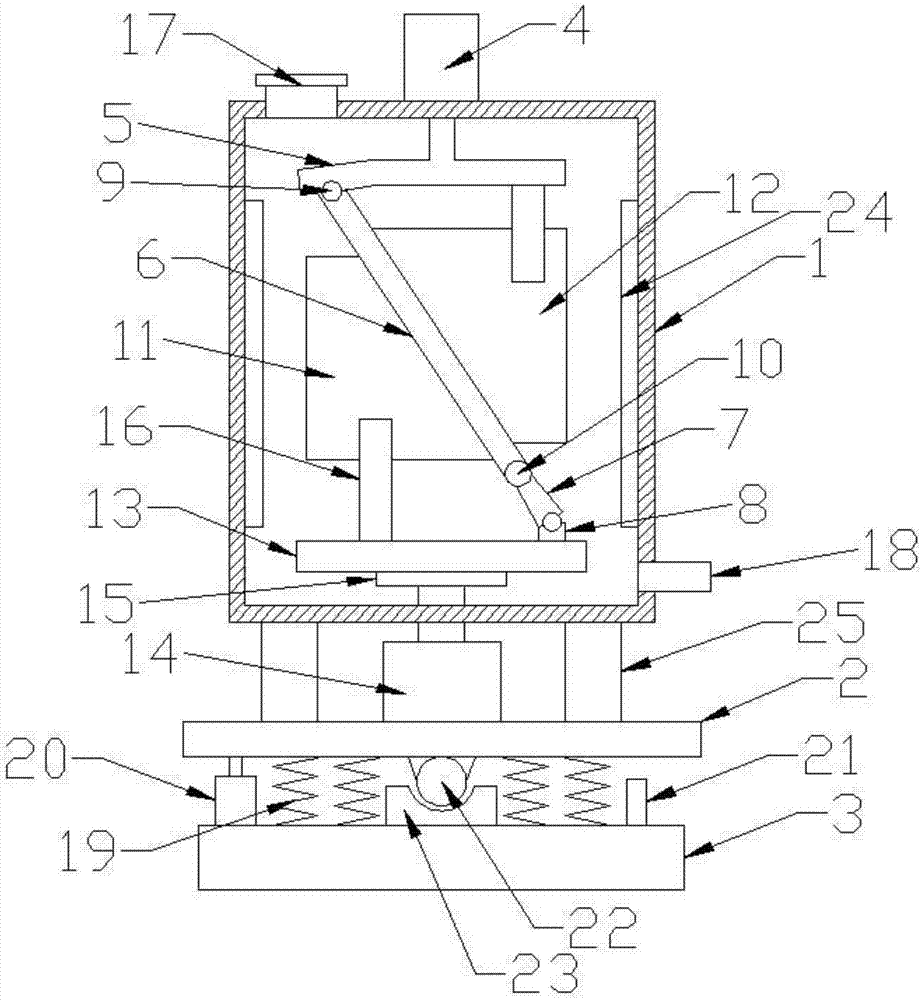
Movable stirring device of reaction kettle
InactiveCN107321290AGuaranteed uptimeUniform processingTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersArchitectural engineeringAir pump
Owner:武晓丹
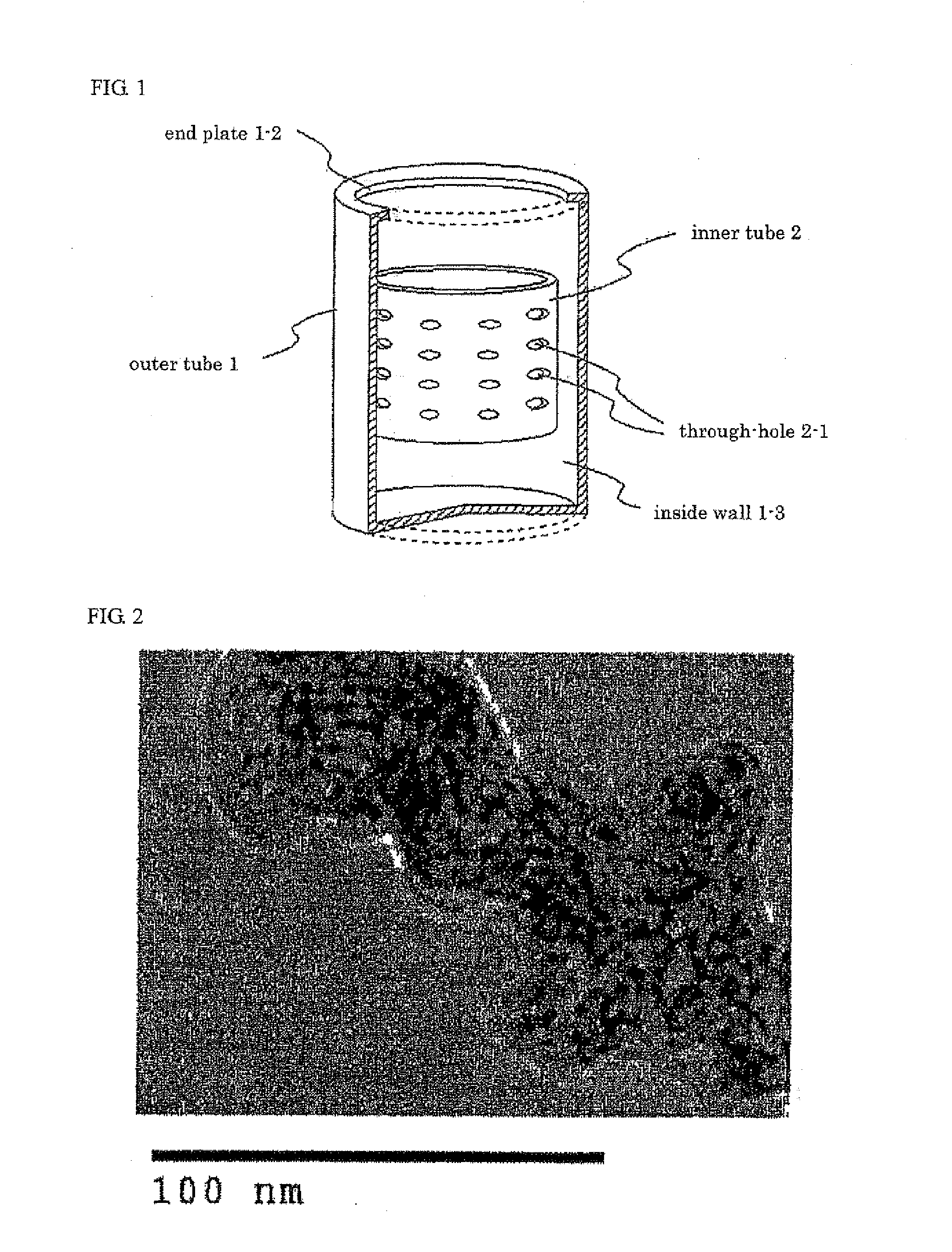
Concentric ring type cross current type hypergravity field swinging bed device
ActiveCN101234261AUniform cross sectionSimple structureChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsFractional distillationHypergravityEngineering
The invention relates to concentric cross-flow type rotating packed bed in high-gravity field , comprising a shell, a rotating disc, a rotating shaft and a liquid redistributor, the shell is provided with a medium a inlet pipe, a medium b outlet pipe, a medium d outlet pipe and a fluid bath, a concentric ring and the liquid redistributor are fixedly connected with the rotating disc, the center of which is in fixed connection with the rotating shaft, the end of labyrinth seal is in connection with the shell, the lower end is in connection with a guiding pipe which is inserted in the fluid bath, the labyrinth seal and the rotating disc divide the shell into an upper cavity and a lower cavity, the medium b outlet pipe is in communication with the upper cavity, the medium a inlet pipe and the medium d outlet pipe are separately in communication with the lower cavity, one end of a medium c inlet pipe is in communication with the upper end of a liquid distributor, while the other end surpasses the shell and is sealed together with the shell. The beneficial effect of the rotating packed bed is that the rotating packed bed of the invention has the simple and reasonable structure so as to be easily installed, the little gas resistance, the low equipment pressure drop, and the higher efficiency and the better effect of gas-liquid mass transfer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Pressure vessel door seal mechanism
Owner:BURCELL TECH INC
Optical networks
ActiveUS20120224850A1Control power consumptionRotary drum/kiln gasifiersCalcinationLength waveOptical transmitter
An optical network (10) comprising an optical network element (12) comprising a first optical transmitter (14), a first controller (16), an optical receiver (18), a second optical transmitter (22), a second controller (24) and optical receiver apparatus (26). Said first controller is arranged to control said first optical transmitter to generate and transmit a first optical signal in response no second optical signal being detected. Said first controller is arranged to iteratively generate and transmit said first optical signal at different wavelengths of a plurality of wavelengths until said second optical signal is detected, and is further arranged to subsequently maintain generation and transmission of said first optical signal at said wavelength at which said second optical signal is detected. Said second controller is arranged to control said second optical transmitter to generate and transmit said second optical signal following detection of said first optical signal by said optical receiver apparatus.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
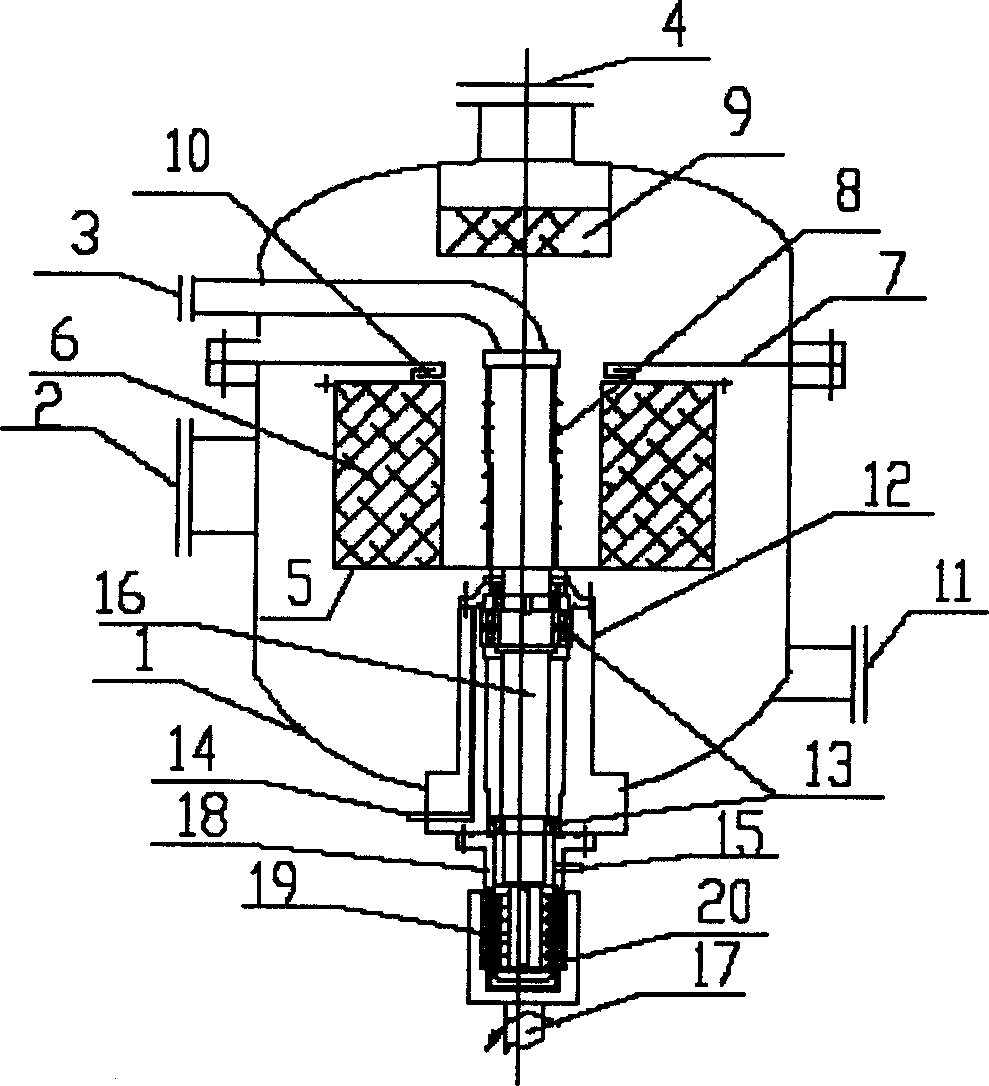
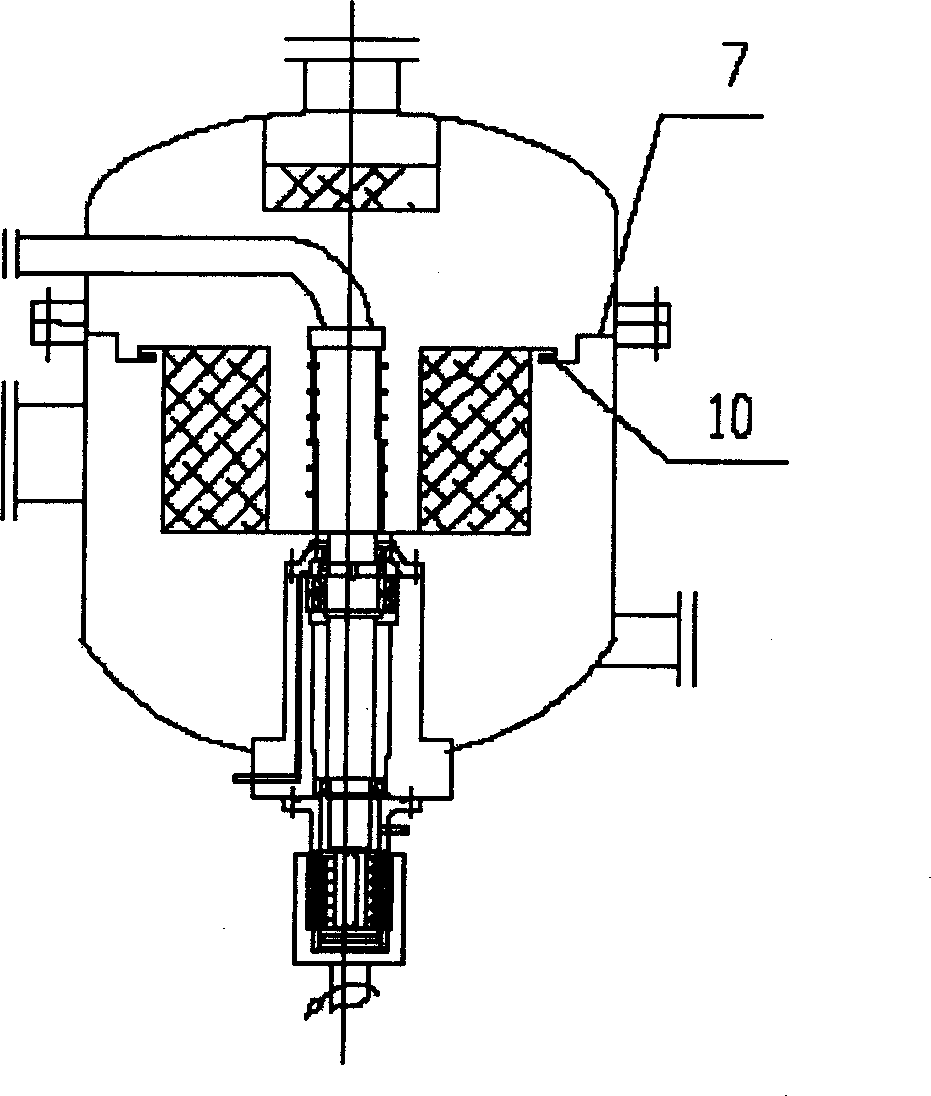
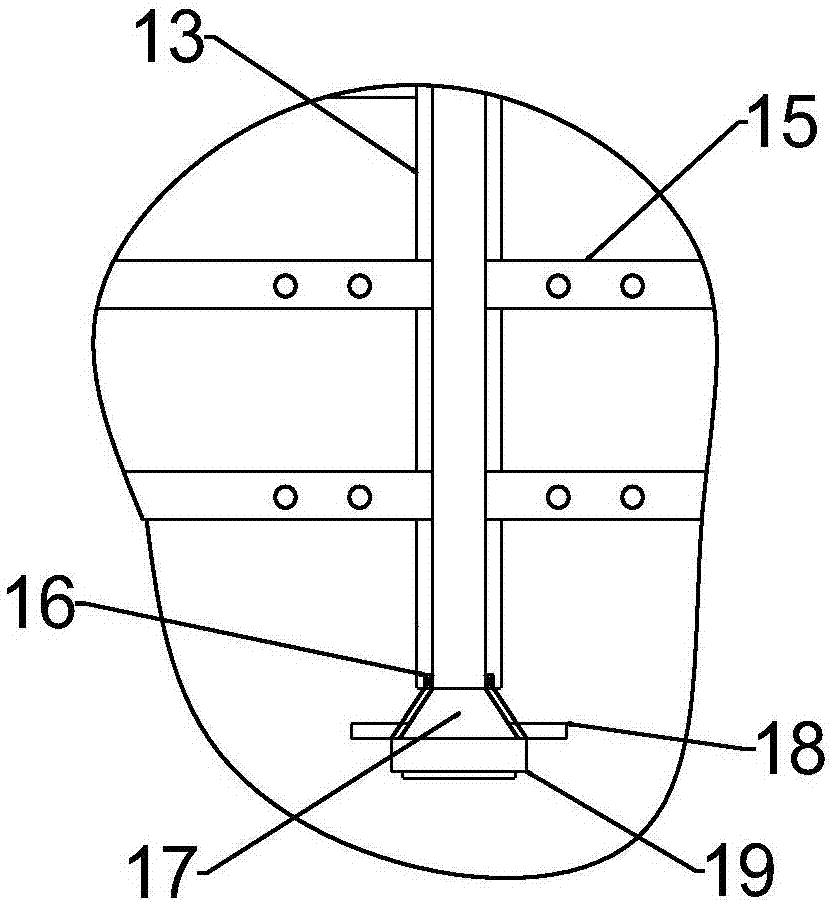
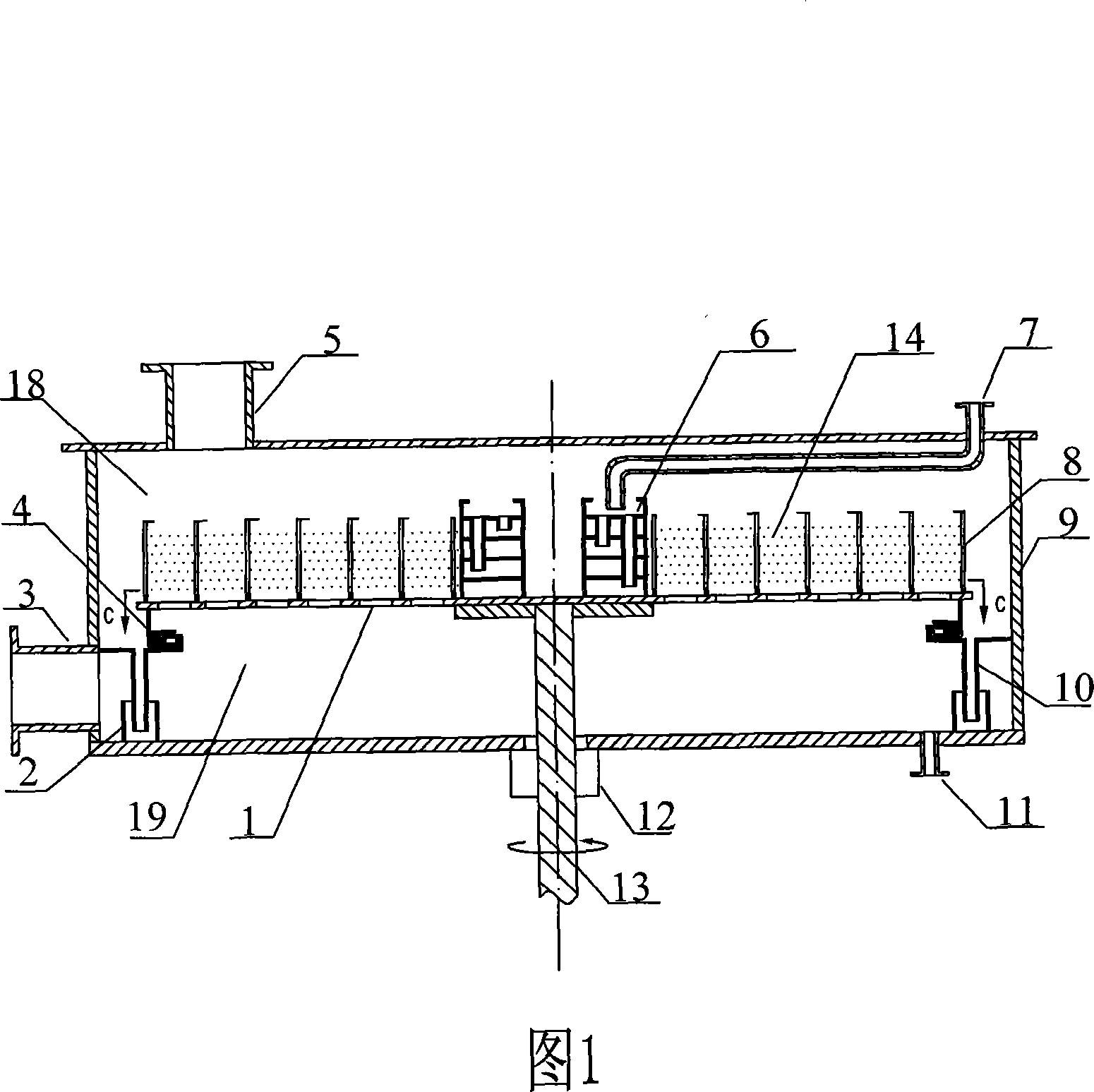
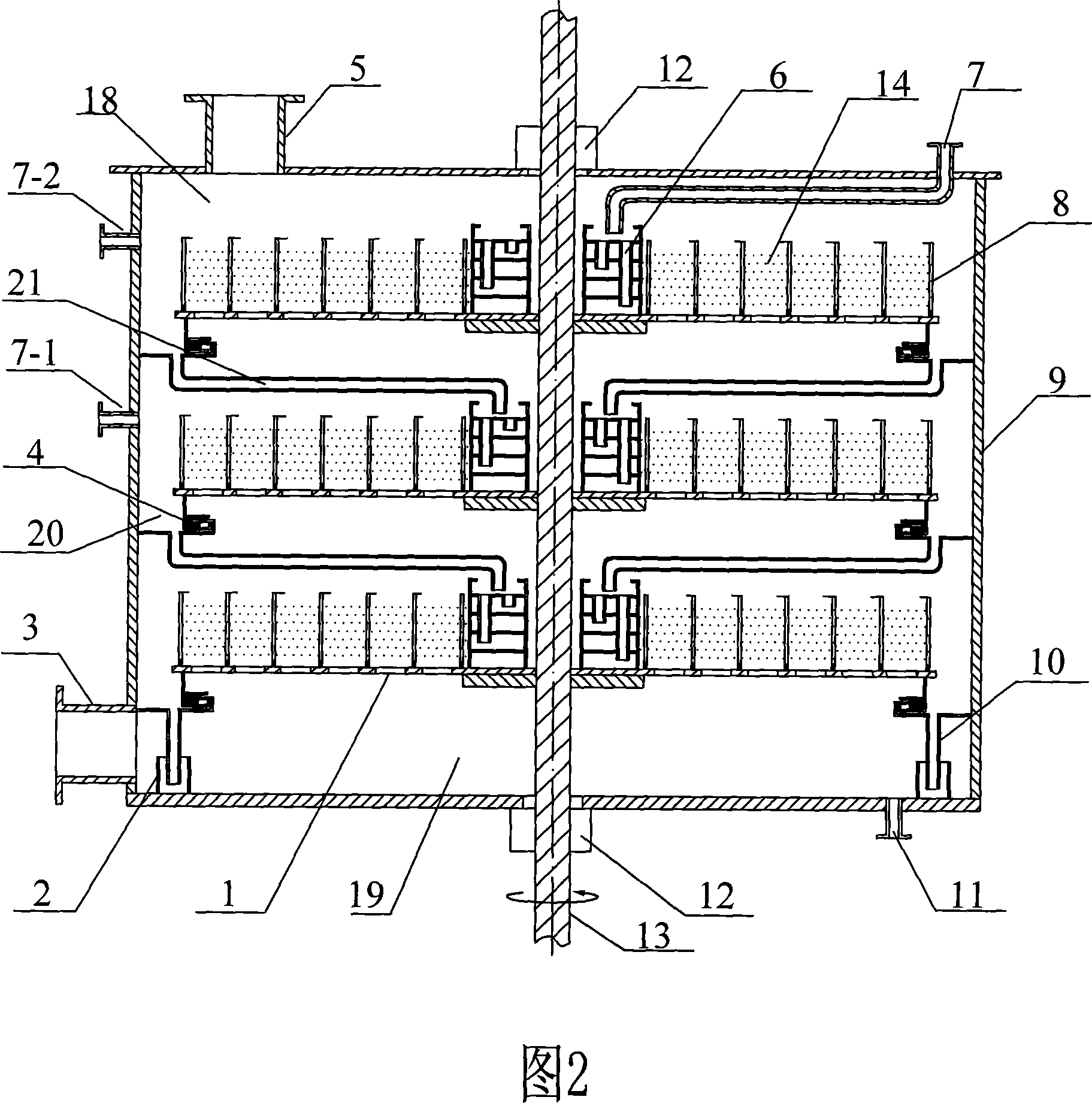
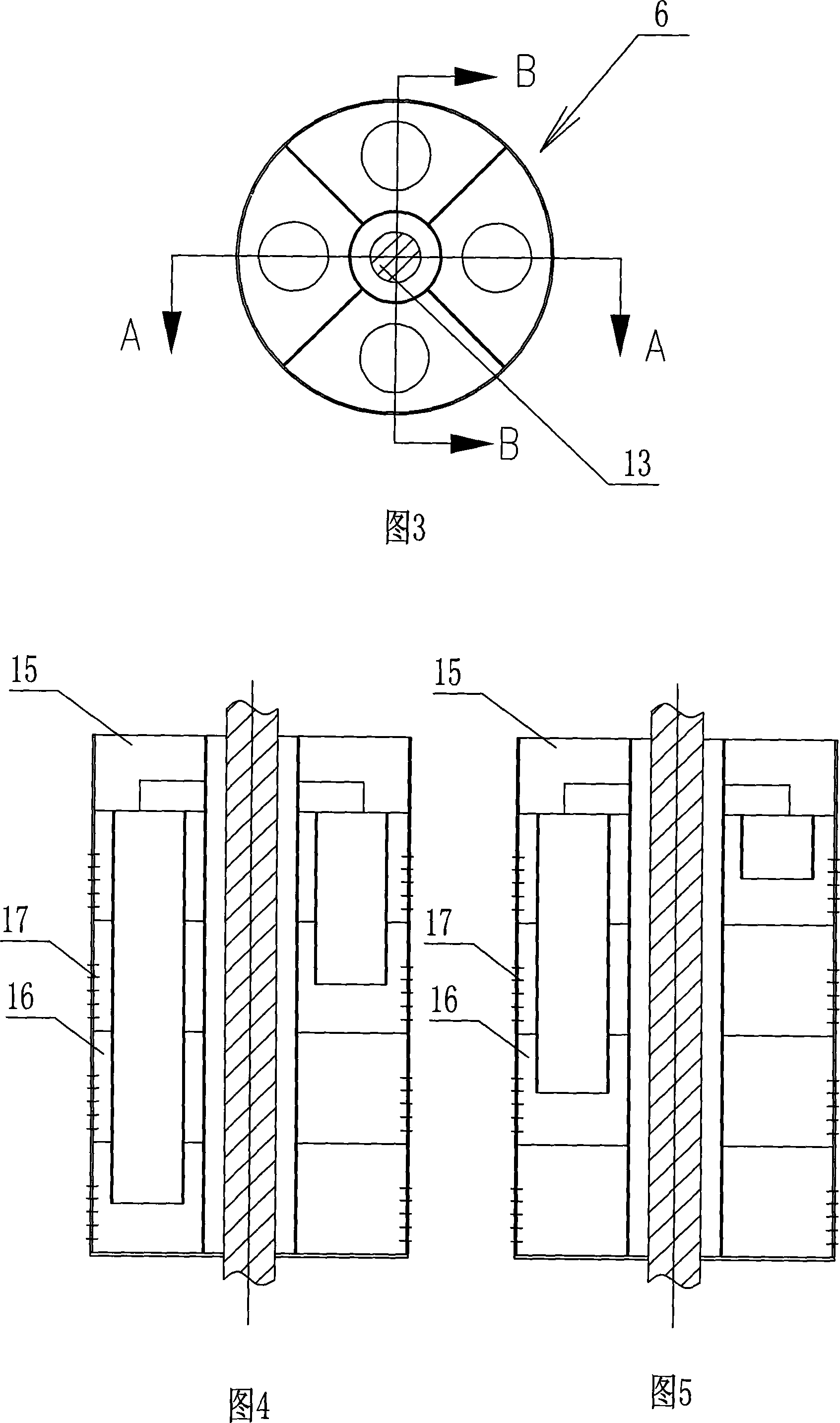
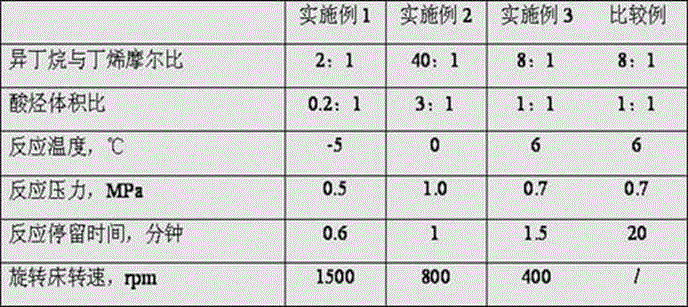
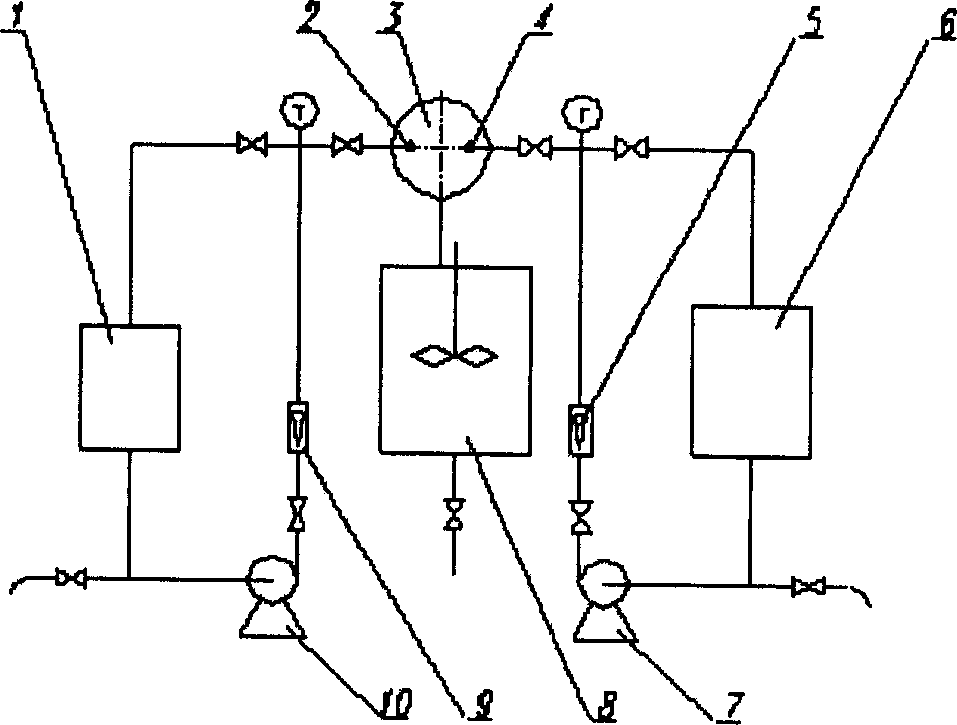
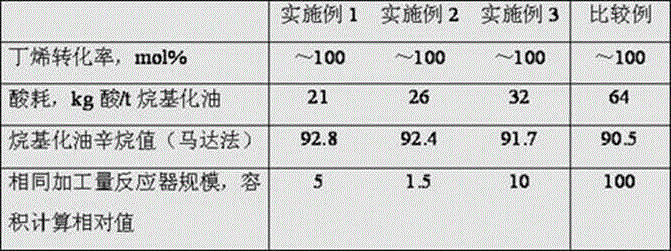
Novel alkylation reactor and alkylation reaction method
ActiveCN104549114AFully dispersedBoost octaneLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionChemical/physical/physico-chemical nozzle-type rreactorsPtru catalystAlkene
The invention discloses an alkylation reactor and an alkylation reaction method. The alkylation reactor comprises a reactor drum body, a sealing head, an inner rotating bed, an outer rotating bed, a feeding pipe, a fed material distributing pipe, a discharging opening, a circular cooling gas inlet and a circular cooling gas outlet, wherein the reactor drum body and the sealing head form a closed shell; the inner rotating bed is arranged in the middle in the shell; the fed material distributing pipe is arranged in a central hollow drum structure of the inner rotating bed and is communicated with the feeding pipe; a feeding mixer is arranged at the connecting position of the feeding pipe and the sealing head; the discharging opening is formed in the lower part of the shell; the inner rotating bed is connected with a driving device by the feeding pipe; the outer rotating bed is arranged at the outer side of the inner rotating bed; the upper end of the inner rotating bed and the fed material distributing pipe are connected into an integrated structure by a sealing member; the outer rotating bed and the shell are fixedly connected; and the outer rotating bed is connected with the driving device at the lower part by a rotating shaft. The alkylation reactor and the alkylation reaction method disclosed by the invention have the advantages that concentrated sulfuric acid is adopted as a catalyst, iso-butane and olefin are adopted as materials to carry out alkylation reaction, the reaction can be carried out under low temperature, the acid consumption is low and the quality of a product is high.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
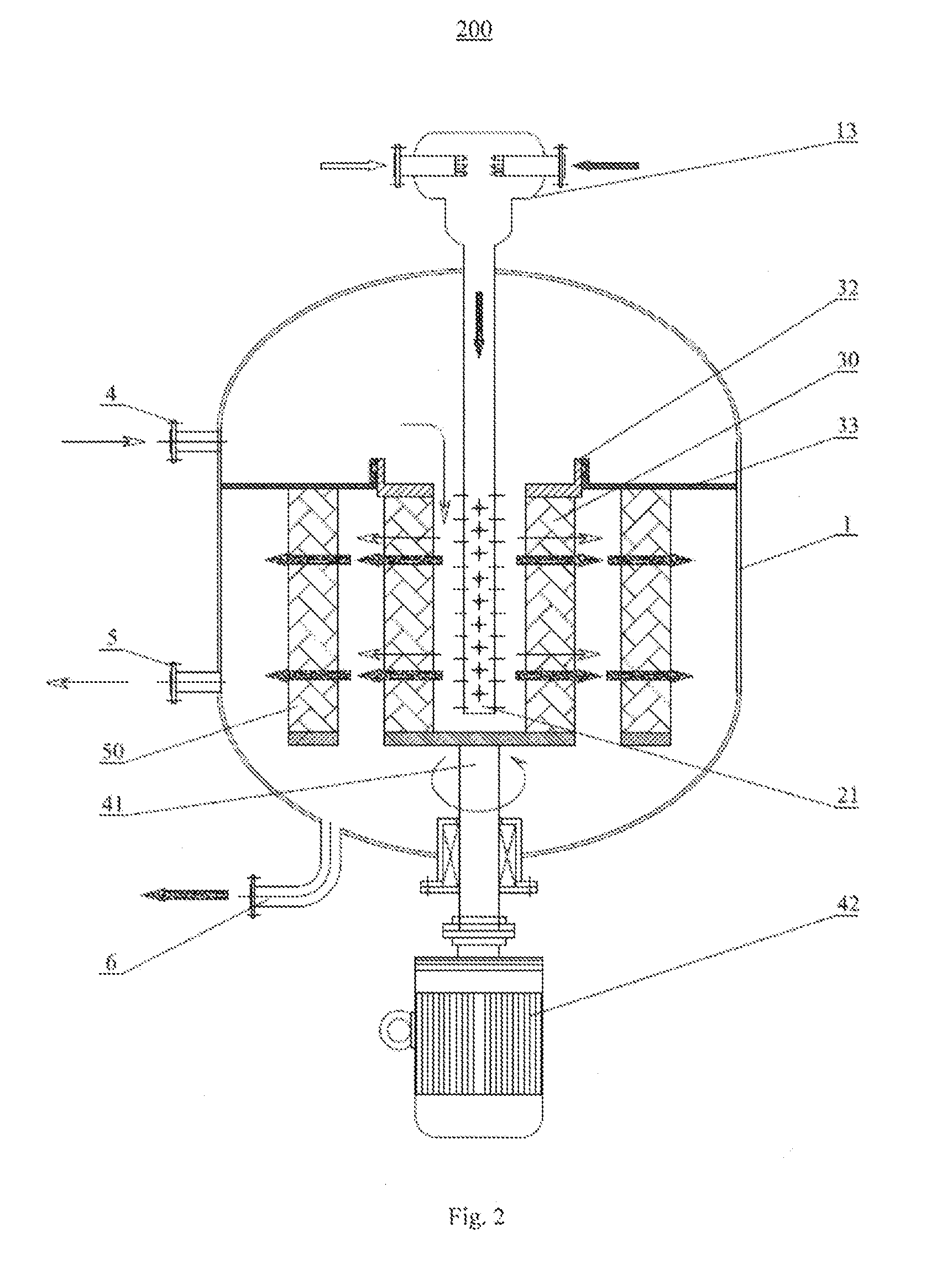
Reactor and Alkylation Process Using the Reactor
ActiveUS20140128654A1High catalytic efficiencyLower reaction temperatureHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionCatalystsAlkyl transferEngineering
The present disclosure provides a reactor for at least two liquid materials, comprising an enclosed reactor housing; a feeding tube having liquid material inlets for receiving corresponding liquid materials respectively; a distribution tube communicating with the feeding tube and extending into the reactor housing, the distribution tube being provided with a plurality of distribution holes in the region thereof extending into the reactor housing; a rotating bed in form of a hollow cylinder, which is disposed in the reactor housing via a fixing mechanism, thus dividing inner cavity of the reactor housing into a central area and an outer area, the rotating bed being capable of rotating driven by a driving mechanism; and a material outlet provided in a lower portion of the reactor housing for outputting product after reaction. The distribution tube extends into the central area spaced from inner surface of the rotating bed, so that materials can enter into the outer area from the central area through the rotating bed and can be output via the material outlet.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Reaction kettle with adjustable stirring
InactiveCN107096446AFully contactedSafe and stable operationShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingControl engineeringElectric machinery
Owner:HEFEI WISDOM DRAGON MACHINERY DESIGN CO LTD
Preparing method for nano titanium dioxide
InactiveCN1490249ASmall volumeEnhanced mass transferTitanium dioxideChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsDispersityGranularity
A process for preparing nano-class TiO2 by use of supergravitational rotating packed-bed reactor includes such steps as neutralizing-hydrolyzing reacting of TiCl4 or titanium oxygen sulfate to obtain hydrated TiO2, drying and calcining. Its advantages are uniform granularity, and high dispersity and productivity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
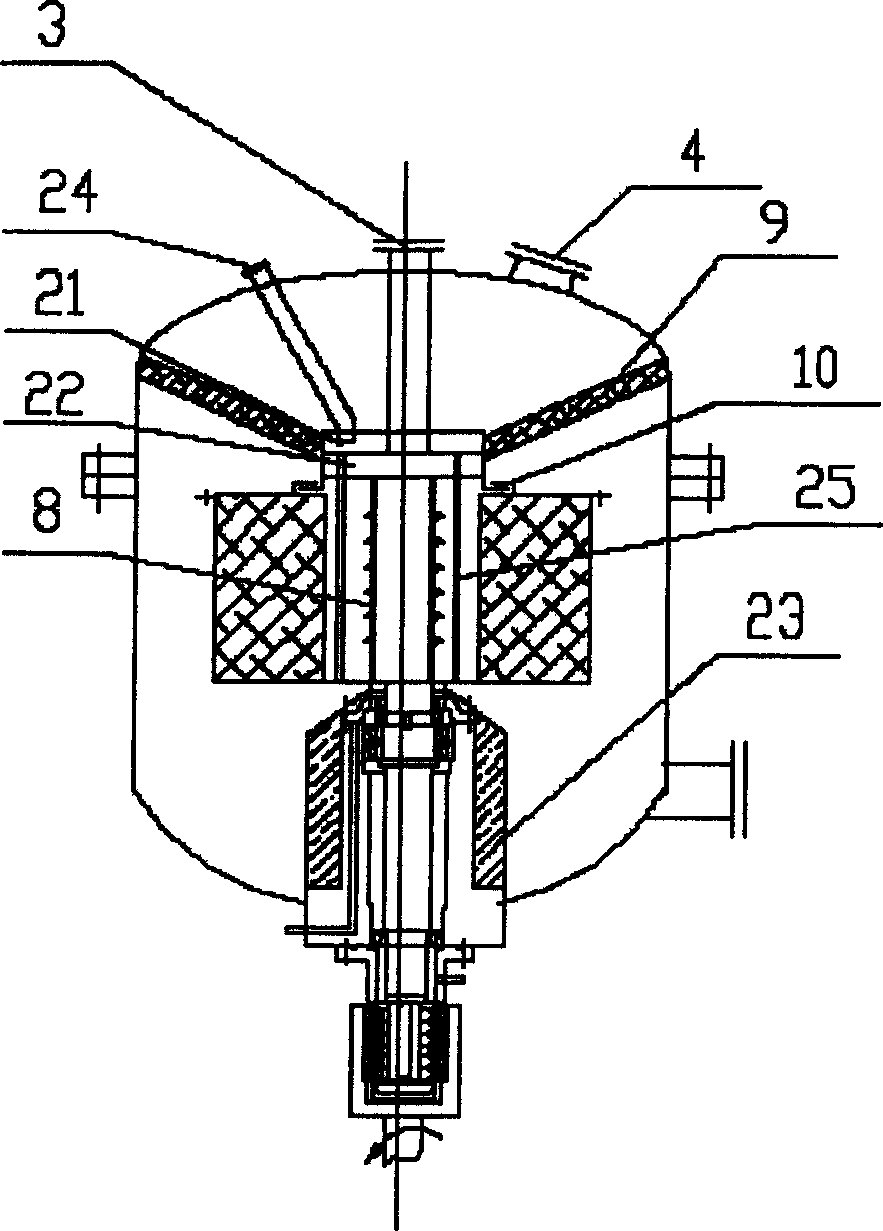
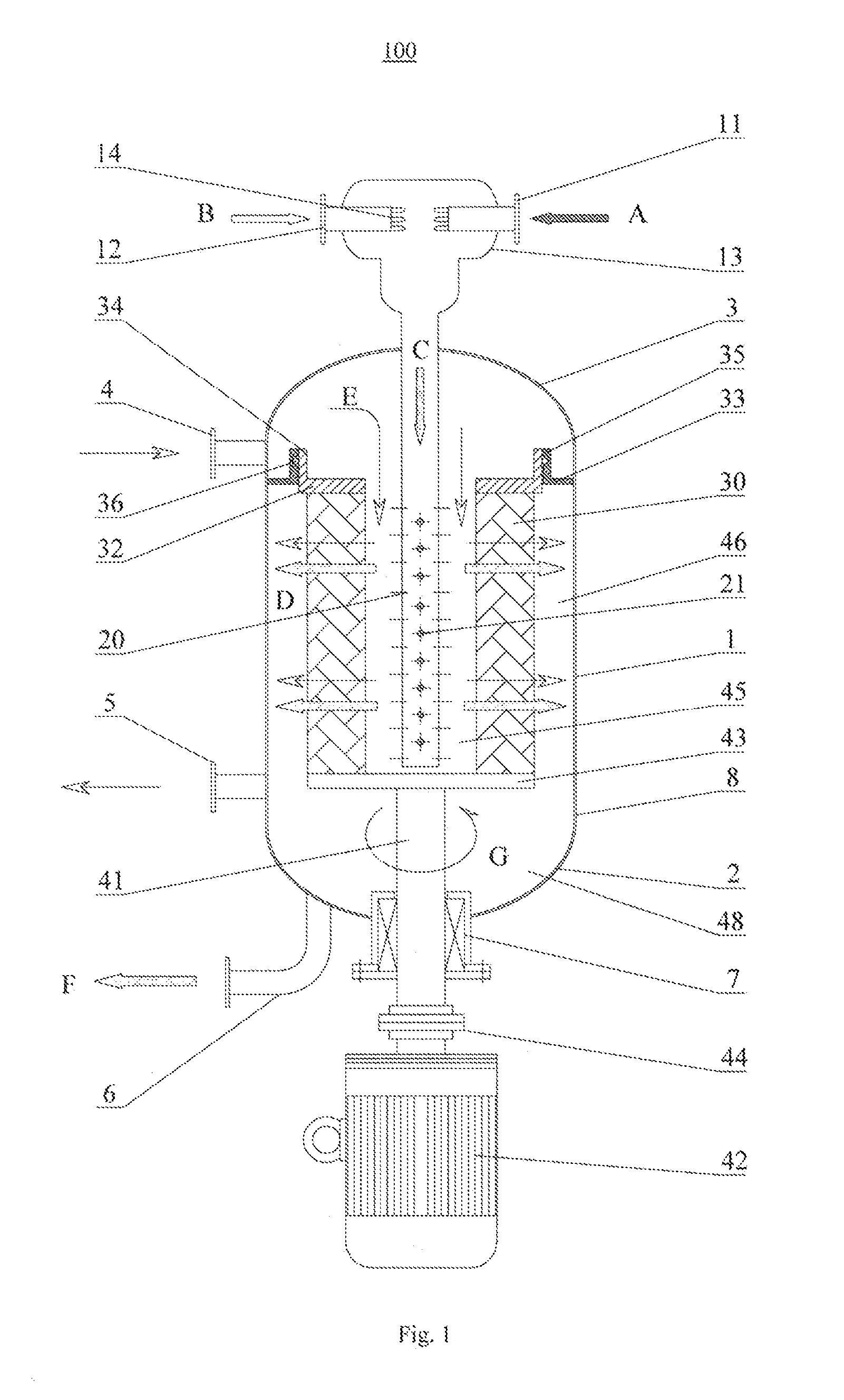
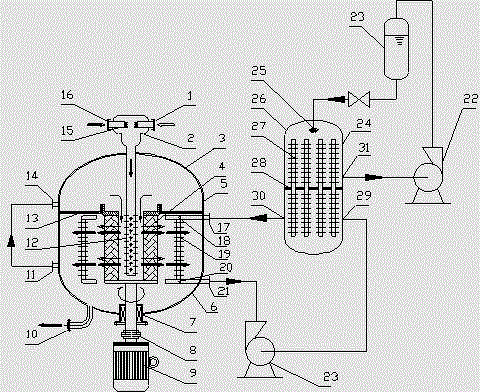
Sectional feed alkylation reactor and alkylation reaction technology
ActiveCN104549116AOvercoming wrapping forceAchieve surface renewalLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionChemical/physical/physico-chemical nozzle-type rreactorsEmulsionPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a sectional feed alkylation reactor and an alkylation reaction method. The reactor comprises a reactor cylinder, a sealing head, a partition plate, an upper bed layer, a rotating bed, a composite bed layer, a feed pipe, a feed distribution pipe, a rotating shaft, a material supply inlet, a discharge outlet, a circulating cooling gas inlet and a circulating cooling gas outlet. The invention further provides an alkylation reaction method, which comprises the following steps: by adopting the sectional feed alkylation reactor, iso-butane and concentrated sulfuric acid are firstly mixed to form acid hydrocarbon emulsion in the upper bed layer, then the hydrocarbon emulsion and mixed hydrocarbon, entering from the material supply inlet, enter the rotating bed for performing alkylation reaction, and the reacted material can realize the demulsification process of the emulsion in the composite bed layer.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Apparatus and method for producing plasma during milling for processing of material compositions
InactiveUS20110297532A1Energy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesPlasma techniqueEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
method for preparation of Sr titanate powder
A method of preparing strontium titanate powder comprises, a Ti4+solution, a Sr2+ Solution and an aqueous alkali, or a mixture containing Ti4+ and Sr2+ and an aqueous alkali are reacted in a G-force reactor at about 60degree C -100degree C. Strontium titanate powder of the invention has a small mean particle size with an uniform diameter, and is suitable for the raw material of dielectric, piezoelectric, sensitive ceramics and others. The method of preparing strontium titanate powder in a G-force reactor could produce continuously strontium titanate powder.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Alkylation reactor capable of intensifying mass transfer, and alkylation technology method
ActiveCN104549115ASuitable temperature environmentFully dispersedFlow mixersTransportation and packagingAlkyl transferProcess engineering
The invention discloses an alkylation reactor, and an alkylation technology method. The alkylation reactor comprises a reactor cylinder, a sealing head, a rotating bed, a feed pipe, a feed distribution pipe, a discharge outlet, a circulating cooling gas inlet, a circulating cooling gas outlet and a circulating cooling gas refrigeration system; the reactor cylinder and the sealing head form a sealed shell, the rotating bed is arranged in the middle of the shell, the feed distribution pipe is arranged at the center of the rotating bed, and communicated with the feed pipe, and the discharge outlet is formed in the lower part of the shell; and a fin assembly is arranged on the radial outer side of the rotating bed, the upper end and the lower end of the fin assembly are respectively communicated with the circulating cooling gas inlet and the circulating cooling gas outlet through an upper circulating cooling gas distribution pipe and a lower circulating cooling gas distribution pipe, the circulating cooling gas inlet and the circulating cooling gas outlet are formed in the shell, and the circulating cooling gas refrigeration system is arranged between the circulating cooling gas inlet and the circulating cooling gas outlet. The alkylation reaction method comprises the following steps: reacting by taking iso-butane and olefin as raw materials through taking the concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst. The reaction can be carried out at a low temperature, the acid consumption is low, the product quality is high and the equipment scale is small.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com