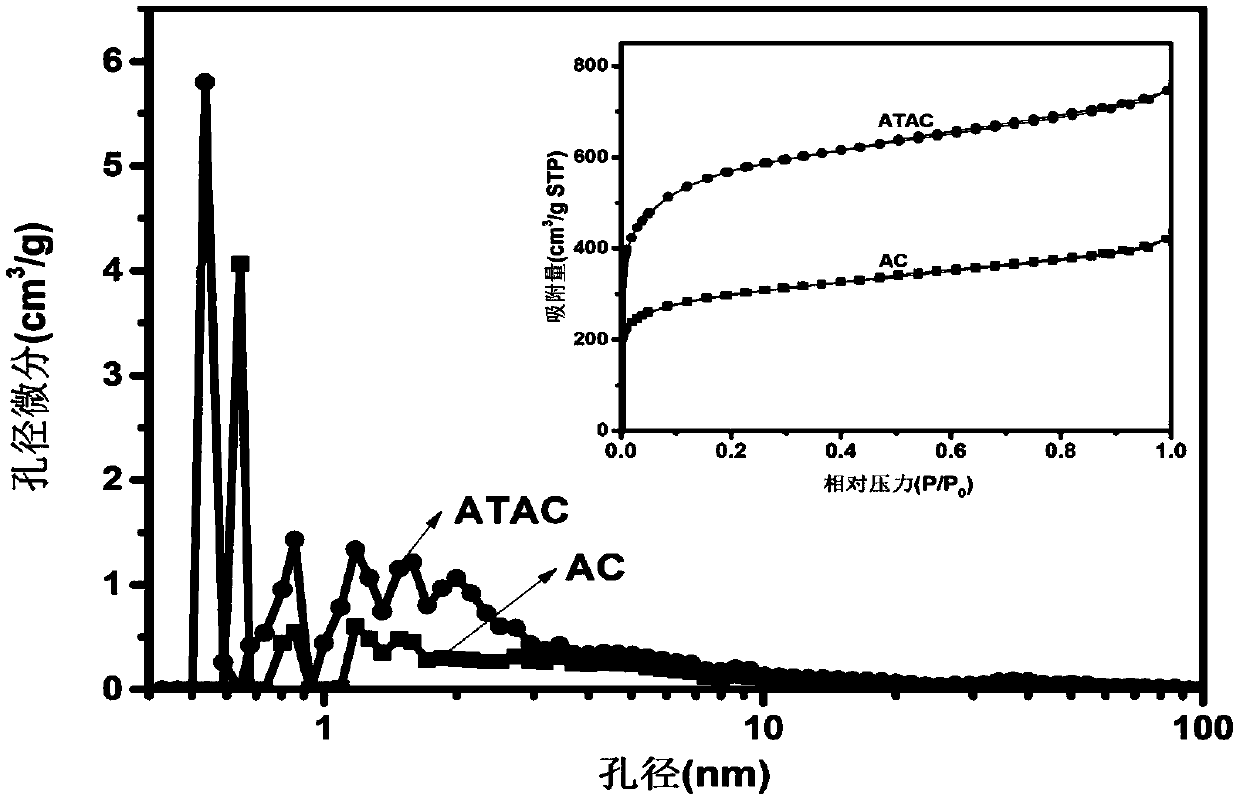
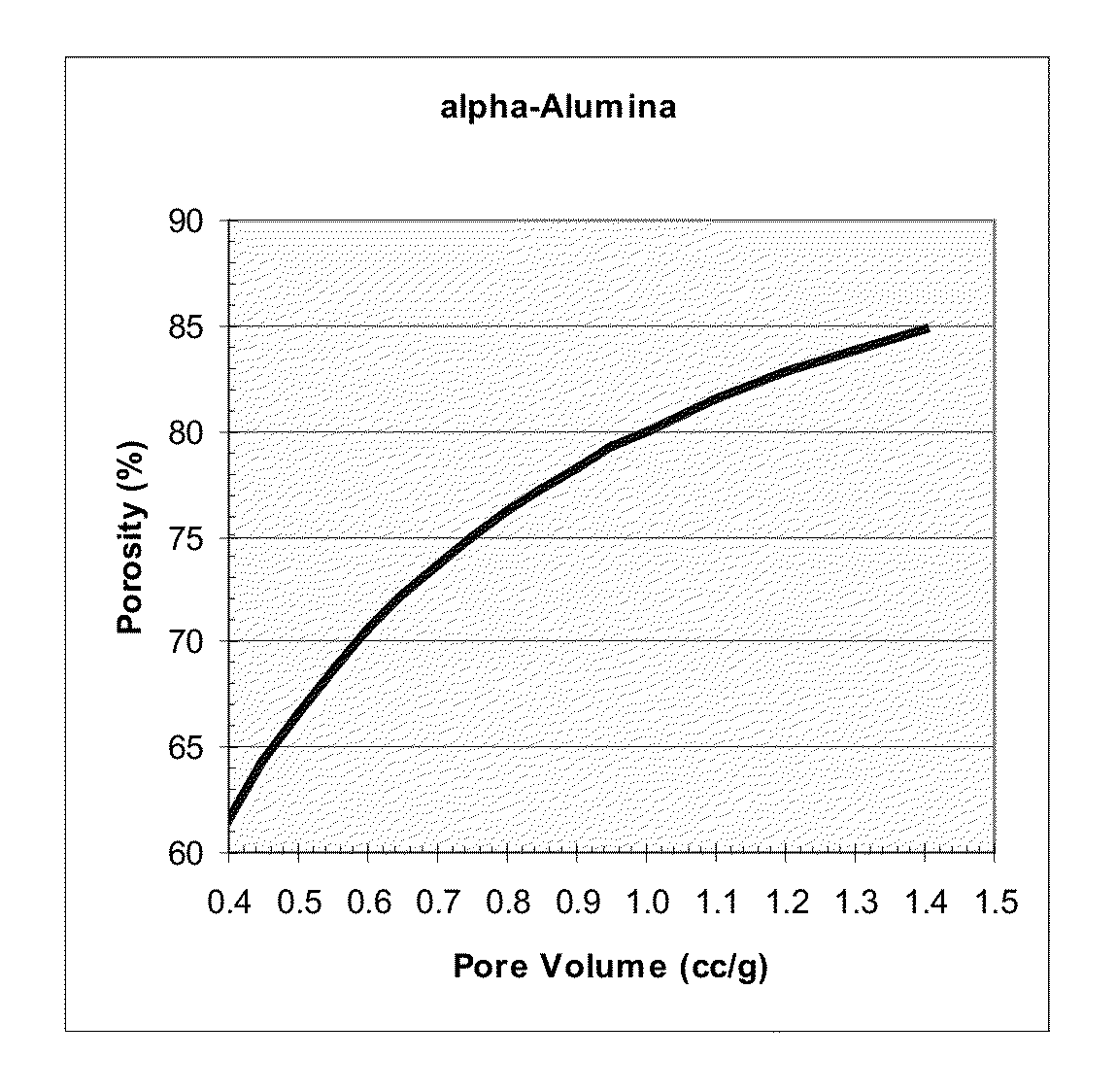
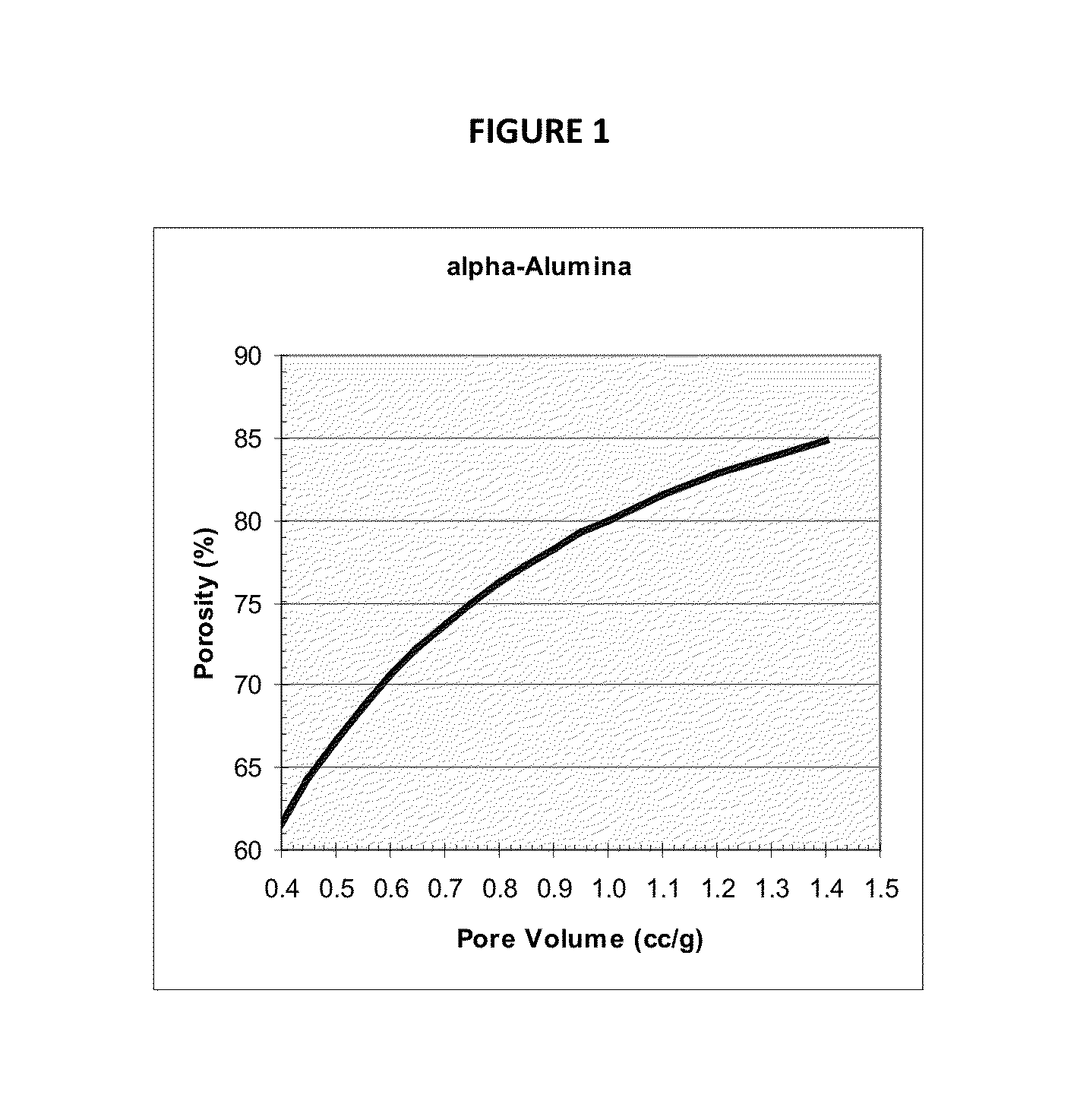
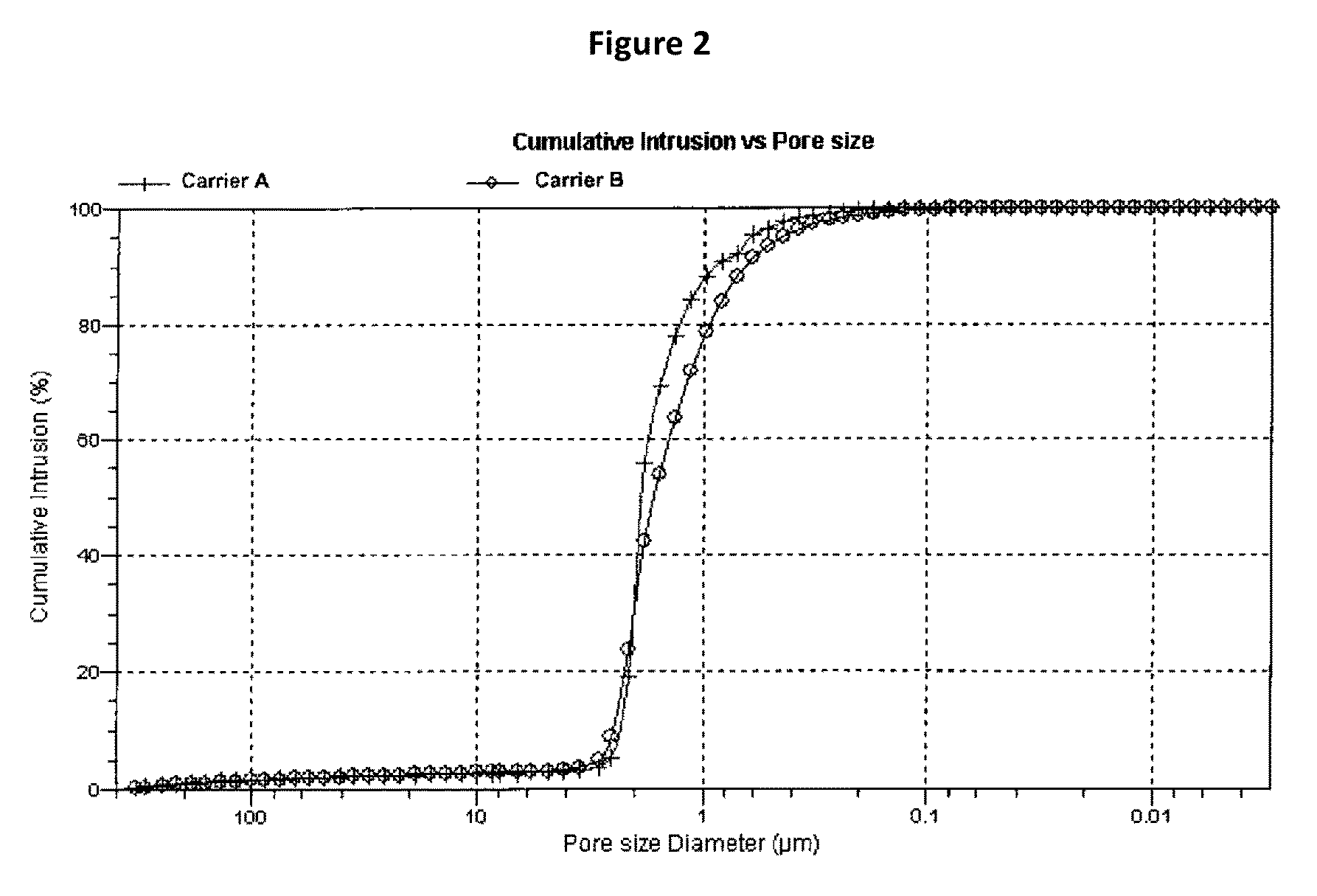
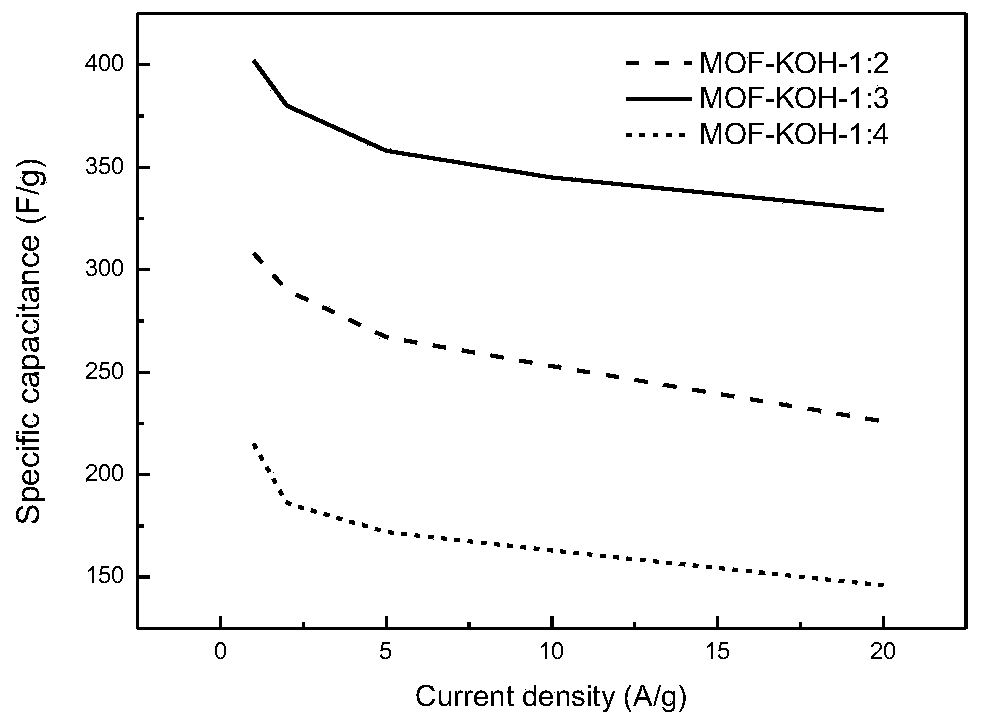
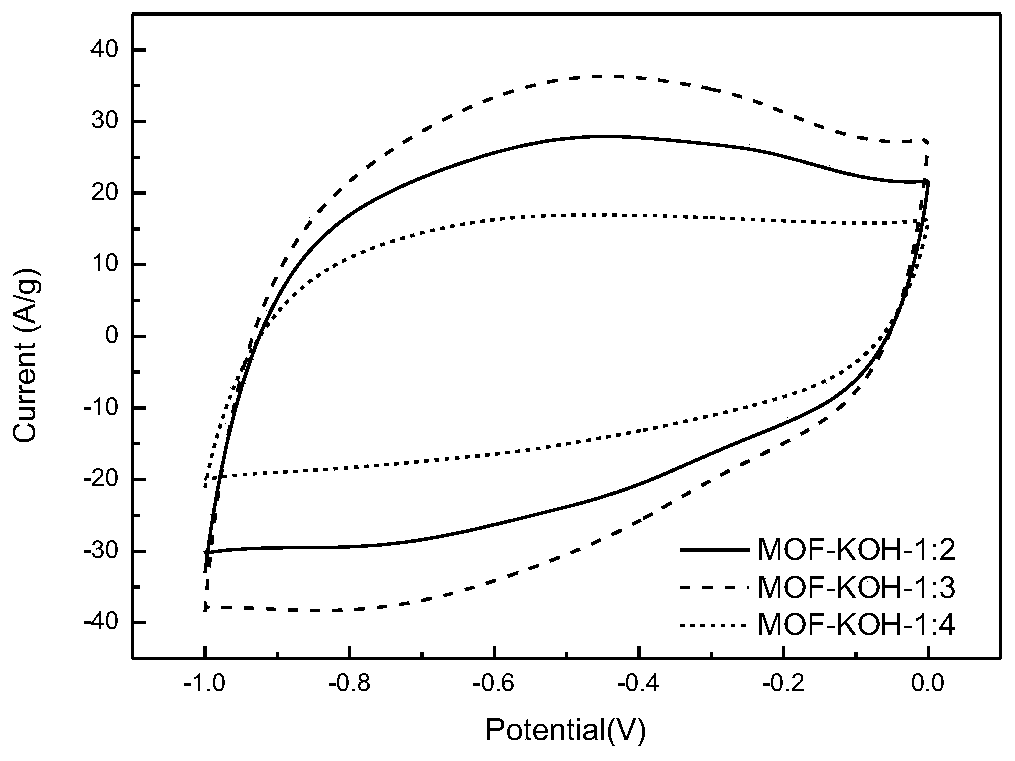
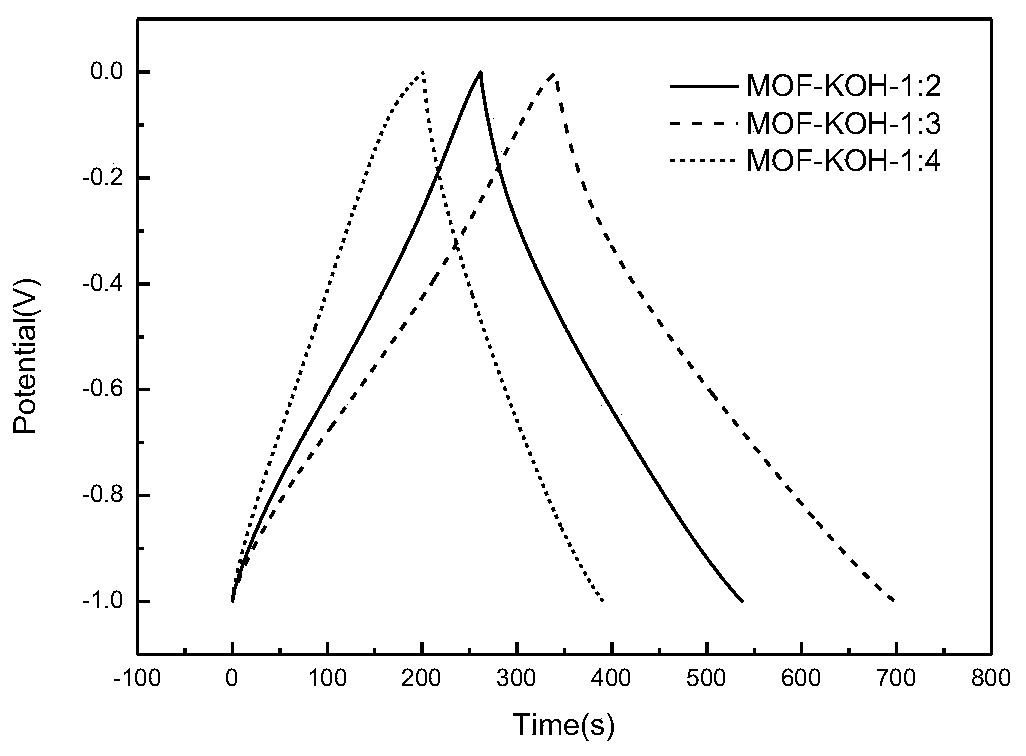
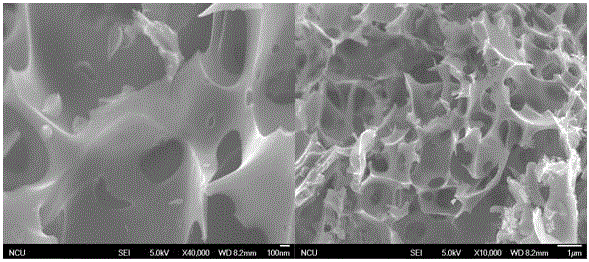
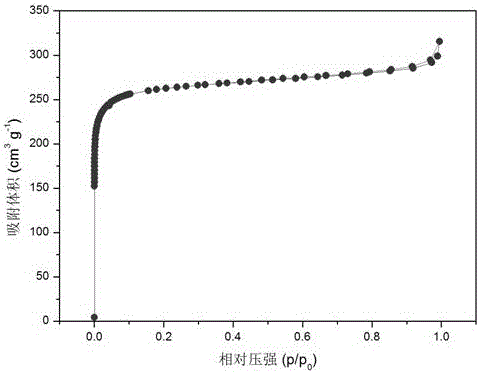
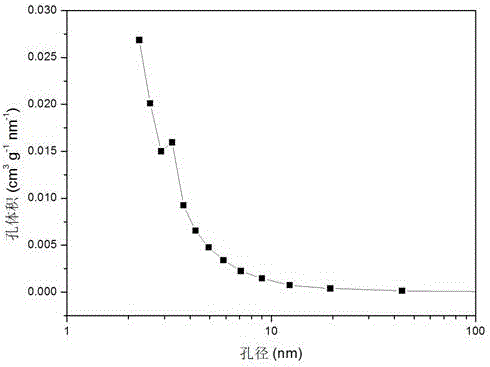
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
207results about How to "Improved pore size distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
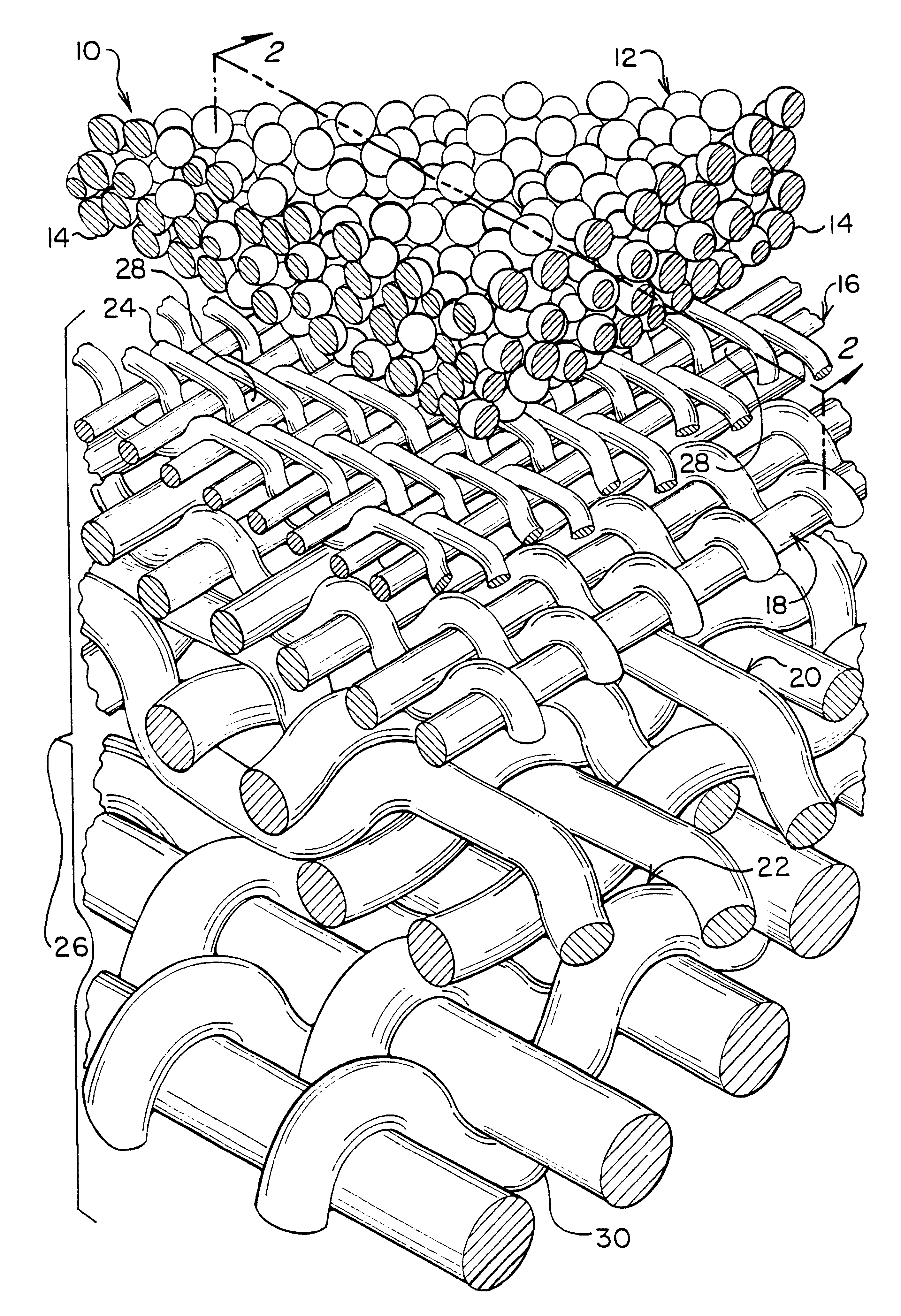
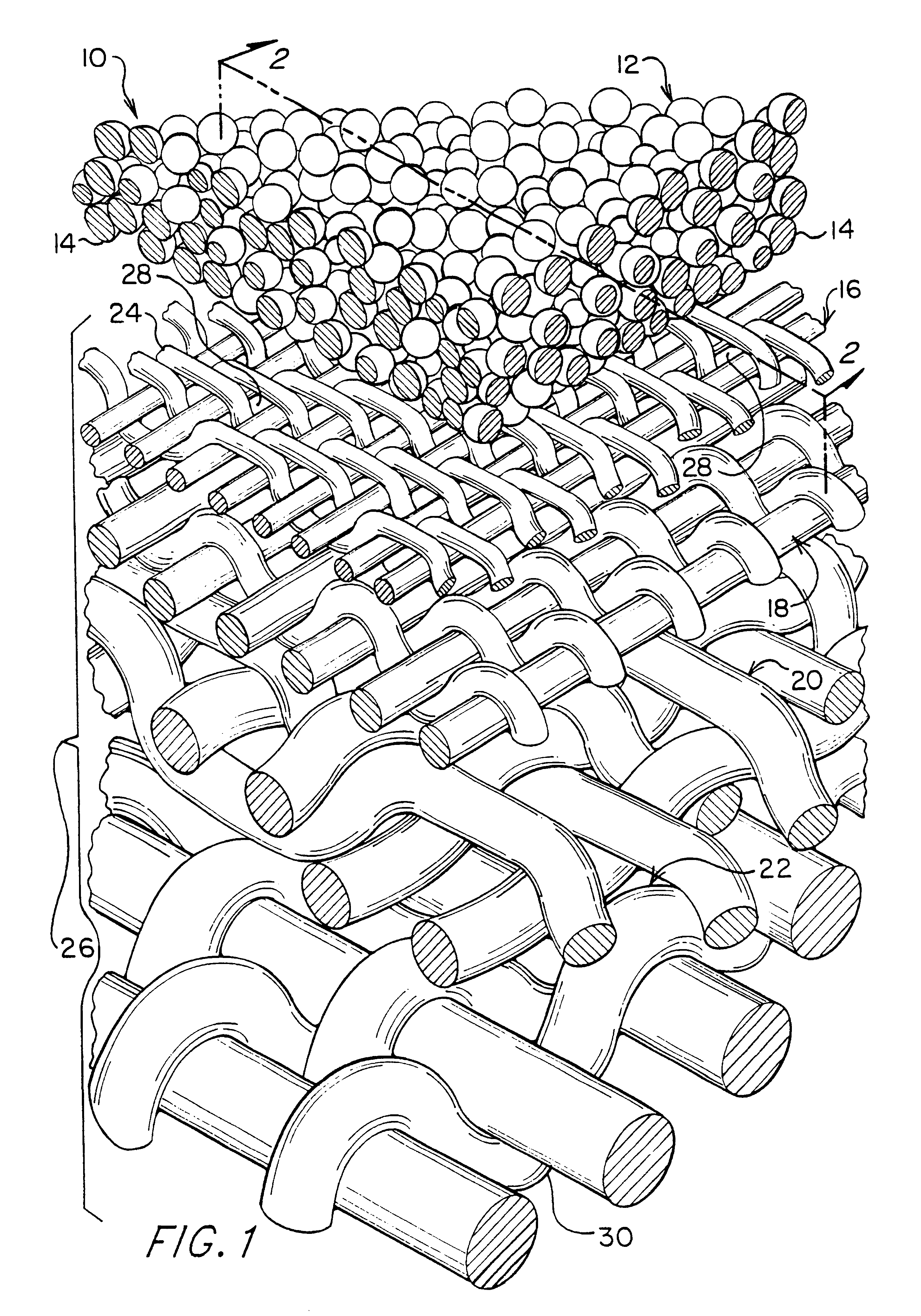
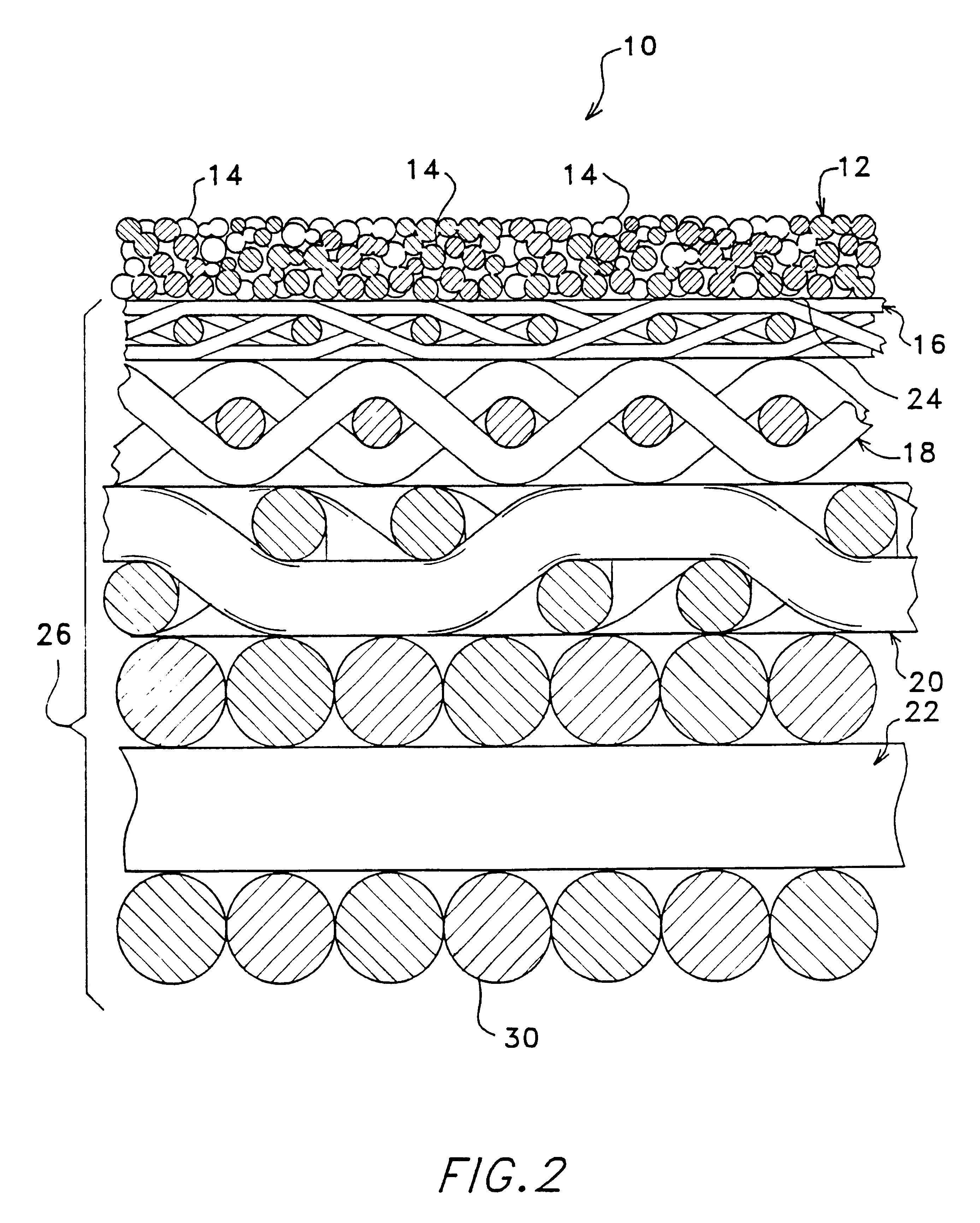
Micro and ultrafilters with controlled pore sizes and pore size distribution and methods for making
InactiveUS6309546B1High permeabilityMinimal pressure dropSemi-permeable membranesMembranesMicrometerPore diameter
A micro / ultrafiltering element (10) and method for making a filter element are provided. The filtering element comprises a multi-level support (26) having a filtering membrane layer (12) formed thereon comprising sintered particles (14) of uniform diameter. The filtering membrane preferably has an average pore size of from about 0.005-10 micrometers. The filter element is capable of being formed in a variety of geometrical shapes based on the shape of the porous support,
Owner:ELLIPSIS CORP
Preparation method of high-specific-surface-area porous nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial
ActiveCN103303912AAchieve preparationHigh degree of graphitizationMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonLow nitrogenPore diameter
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-specific-surface-area porous nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial, relating to a preparation method of a carbon material and aiming at solving the problems of small specific surface area, low nitrogen content, low productivity, poor graphitizing degree and high cost of the nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial prepared by the prior art. The preparation method comprises the steps of: I. preparing a complex; II. curing and carbonizing the complex; and III. carrying out acid leaching method treatment, and drying. Compared with an existing nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial, the prepared high-specific-surface-area porous nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial has the advantages that the graphitizing degree is improved, the nitrogen content is increased, and the specific surface area is obviously increased, and the high-specific-surface-area porous nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial has obvious pore diameter distribution. The preparation method is used for preparing the high-specific-surface-area porous nitrogen-doped graphitizing carbon nanomaterial.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Methods for spherically granulating and agglomerating metal particles, and the metal particles prepared thereby, anodes made from the metal particles
ActiveUS20070068341A1Improve liquidityImproved pore size distributionElectrolytic capacitorsTransportation and packagingCapacitanceNiobium
A method for spherically granulating and agglomerating metal particles such as tantalum and / or niobium powders is described in the present invention, which includes the steps of: a). comminuting the metal particles to form fine particles having D50 less than 50 μm; b). granulating the comminuted metal particles comprising volatile liquid, for example, tantalum and / or niobium particles comprising volatile liquid, to form wet spherical particles; c). still drying the wet spherical particles and removing volatile liquid to form flowable pre-agglomerated particles with increased bulk density; d). heat treating the pre-agglomerated particles; e). screening the heat treated powder to obtain the flowable agglomerated particles. The present invention provides a flowable spherical agglomerated metal particles, and especially tantalum and / or niobium particles having improved properties. The present agglomerated tantalum powder have a flow rate of at least about 2.0 g / sec, a BET surface area of from about 0.2 to about 6.0 m2 / g, a FSSS of at least 1.0 μm, a Scott bulk density of from about 1.2 g / cm3 to about 5.5 g / cm3. The present agglomerated niobium powder have a flow rate of at least about 1.0 g / sec, a BET surface area of from about 0.5 to about 8.0 m2 / g, a FSSS of at least 1.0 μm, a Scott bulk density of from about 0.7 g / cm3 to about 3.5 g / cm3. Said tantalum and / or niobium metal particles have improved pore size distribution of the sintered anodes and increased pellet crush strength. The present invention further provides an electrolytic capacitor anodes made from the tantalum and / or niobium particles according to the present invention having a capacitance of from about 5,000 μFV / g to about 300,000 μFV / g.
Owner:NINGXIA ORIENT TANTALUM IND
Battery positive electrode and preparation method thereof, and lithium ion secondary battery
ActiveCN103633289AIncrease energy densityHigh Aperture RatioSecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesHigh temperature storageLithium
The present invention provides a battery positive electrode and a preparation method thereof, and a lithium ion secondary battery. The positive electrode comprises a conductive substrate and a material layer coated on the conductive substrate surface, wherein the material layer comprises a first conductive material layer attached on the conductive substrate, a first active material layer attached on the first conductive material layer, a second conductive material layer attached on the first active material layer, and a second active material layer attached on the second conductive material layer, and the compact density of the second active material layer is lower than the compact density of the first active material layer. According to the present invention, characteristics of excellent pore size distribution, good electrolyte infiltration and material shedding resistance are provided, and the prepared battery has characteristics of good cycle performance, low internal resistance, excellent rate capability, excellent high temperature storage performance and high energy density.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method Of Making The Porous Carbon Material And Porous Carbon Materials Produced By The Method
InactiveUS20090117094A1Improved pore size distributionAdvanced sorption propertyBiocideCarbon compoundsPorous carbonCarbide
A method for making the microporous carbon with modified pore size distribution and advanced sorption behaviour. The carbon is derived from metal or metalloid carbides. The method employs the use of oxidant in reaction medium that during the carbide conversion into carbon widens small micropores, which otherwise would be hardly accessed by sorbing molecules or ions in practical applications. The microporous carbon obtained is free of impurities and possesses extremely narrow pore size distribution.
Owner:OU SKELETON TECH GRP
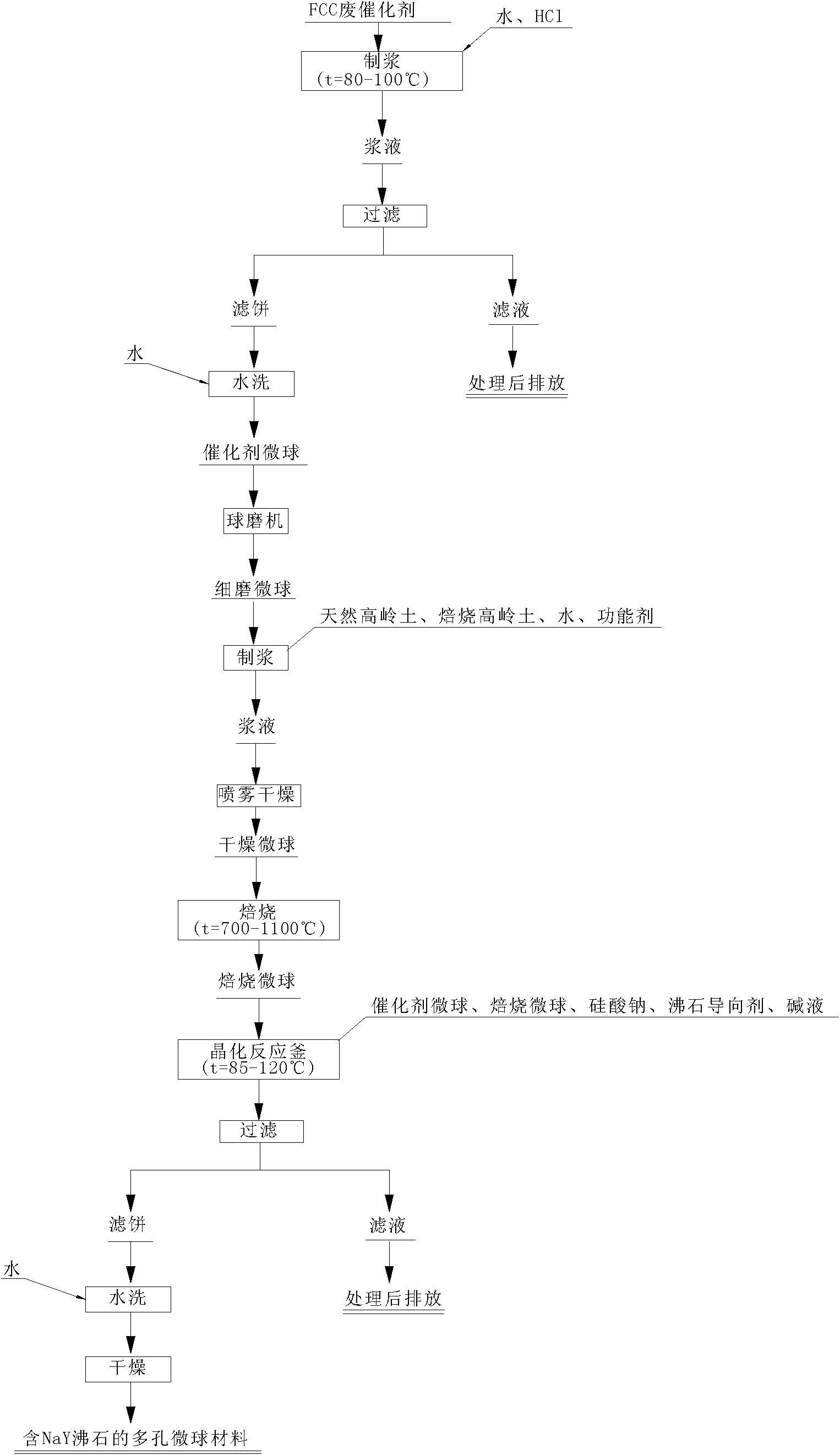
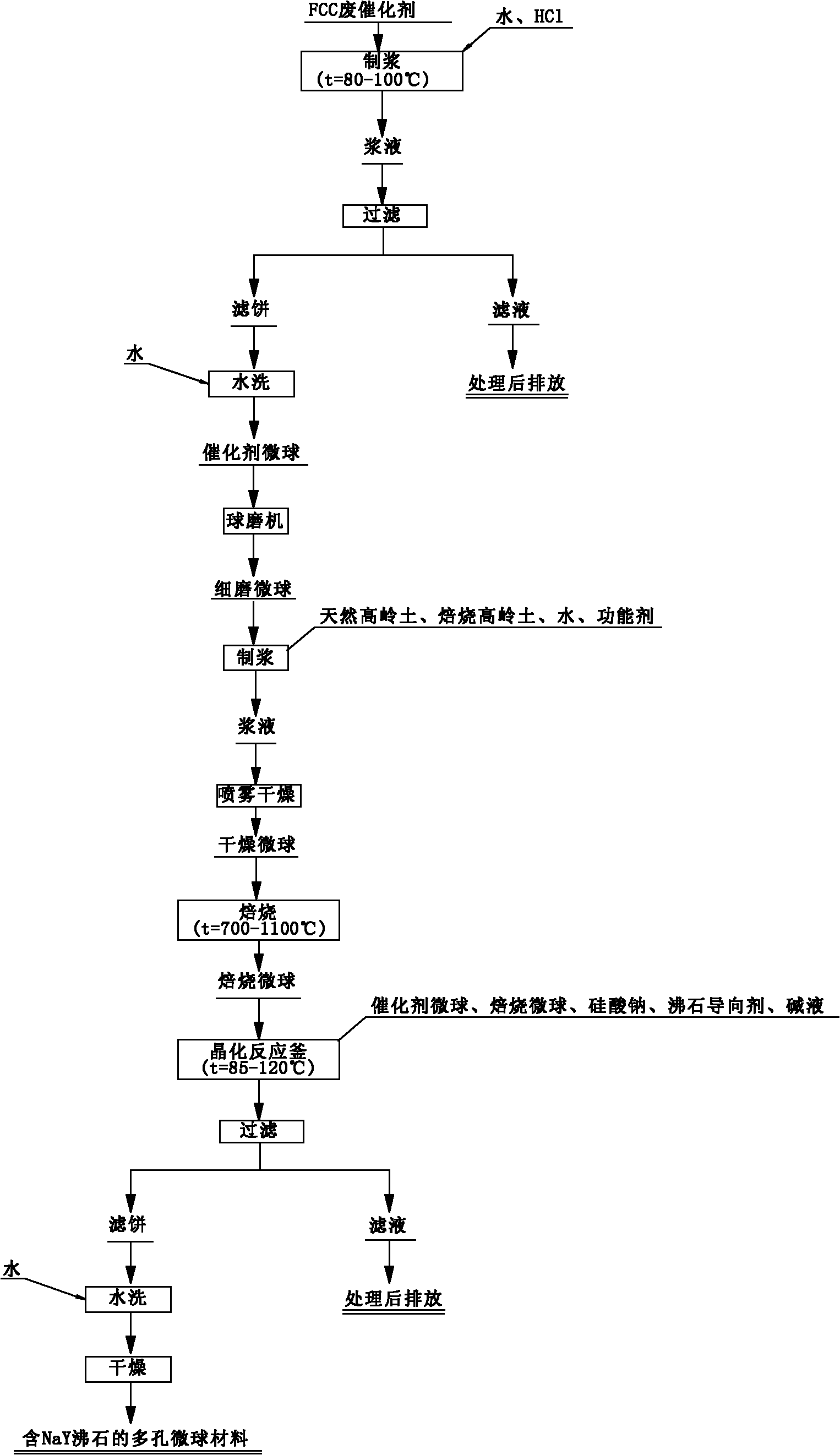
Method for synthesizing porous microsphere material containing NaY zeolite by waste FCC (fluid catalytic cracking) catalyst
ActiveCN102125872AReduce pollutionImprove performanceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsSlurrySodium silicate
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a porous microsphere material containing NaY zeolite by a waste FCC (fluid catalytic cracking) catalyst, which is a catalytic cracking process. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: A. adding water and hydrochloric acid to the waste FCC catalyst for mixing slurry and acidizing to obtain catalyst microspheres; B. mixing thecatalyst microspheres with one or a combination of natural kaolin and roasted kaolin, adding water to obtain slurry containing 30-50% of solid, adding a functional agent to the slurry and then forming dried microspheres through spray drying, and roasting the dried microspheres at the temperature of 700-1100 DEG C for 0.5-10 hours to obtain roasted microspheres; and C. adding sodium silicate, a zeolite directing agent and alkali liquor to the catalyst microspheres and / or the roasted microspheres, adding the obtained mixed solution to a crystallization reaction kettle, performing hydrothermal crystallization at the temperature of 85-120 DEG C for 10-30 hours, filtering out a mother liquid, washing the obtained filter cake with deionized water, and then drying to finally obtain the finished product. The method is mainly used for synthesizing the porous microsphere material containing the NaY zeolite.
Owner:HUNAN JULI CATALYST
Catalyst and process using the catalyst
InactiveUS20090177016A1High activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionParticulatesOxygen
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
In-situ pore generation in lead-acid battery separator
ActiveUS20110045339A1High strength mechanical propertiesLow in electricalCell component detailsLead-acid accumulators constructionIonic diffusionPorosity
A microporous polyethylene battery separator material (212), for use in a flooded-cell type lead-acid battery, benefits from increased porosity, enhanced wettability, and exceptionally low electrical resistance when an electrolyte-soluble pore former is employed in the manufacturing process. The pore former (210) is soluble in electrolytic fluid and therefore dissolves in-situ in sulfuric acid during battery assembly. The dissolution of the pore former leaves behind additional, larger voids (220) in the separator material and thereby enhances ionic diffusion and improves battery performance.
Owner:AMTEK RES INT
Composite non-woven fabric ceramic diaphragm for lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105304846AImprove stabilityImprove featuresSecondary cellsCell component detailsCeramic coatingSolvent
The invention discloses a composite non-woven fabric ceramic diaphragm for a lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The composite non-woven fabric ceramic diaphragm for the lithium ion battery comprises two layers of non-woven fabric base materials and a ceramic coating composited between the two layers of non-woven fabric base materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving macromolecule organic matter in a solvent to form macromolecular solution; (2) dispersing inorganic particles in the macromolecular solution to form organic and inorganic mixture; (3) first coating one side of one non-woven fabric base material evenly with the organic and inorganic mixture, and then pressing the other layer of non-woven fabric base material on a coating layer, and performing drying and rolling to form the composite diaphragm. The problems that the lithium ion battery diaphragm is poor in heat resistance, absorbs water easily, drops easily and is not high in mechanical strength are solved.
Owner:TIANNENG SAFT ENERGY JOINT CO
Preparation method of spherical hard carbon negative electrode material of high-capacity lithium ion battery
PendingCN106995210AOvercoming complexityOvercome costsCell electrodesSecondary cellsHigh rateCarbonization
The invention relates to the technical field of a lithium ion battery, in particular to a preparation method of a spherical hard carbon negative electrode material of a high-capacity lithium ion battery. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) material mixing; (2) precrosslinked polymerization reaction; (3) crushing and grading; (4) polymer powder pelletizing treatment; (5) oxidation stability treatment; (6) pre-carbonization treatment; (7) carbonization treatment. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the raw material sources are wide; the preparation process is simple; the structure and the processing performance of a precursor organic carbon source can be effectively improved through the precrosslinked polymerization reaction; the prepared spherical hard carbon has unique appearance and good pore diameter distribution, and also has the advantages of particle granularity distribution uniformity, high stacking density and the like; high capacity, high first coulombic efficiency, excellent high-rate performance and excellent circulation performance are also realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHANSHAN TECH CO LTD
Exhaust gas purification filter
ActiveUS20120317946A1Reduce the amount requiredIncreased pressure lossDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingPorosityHoneycomb structure
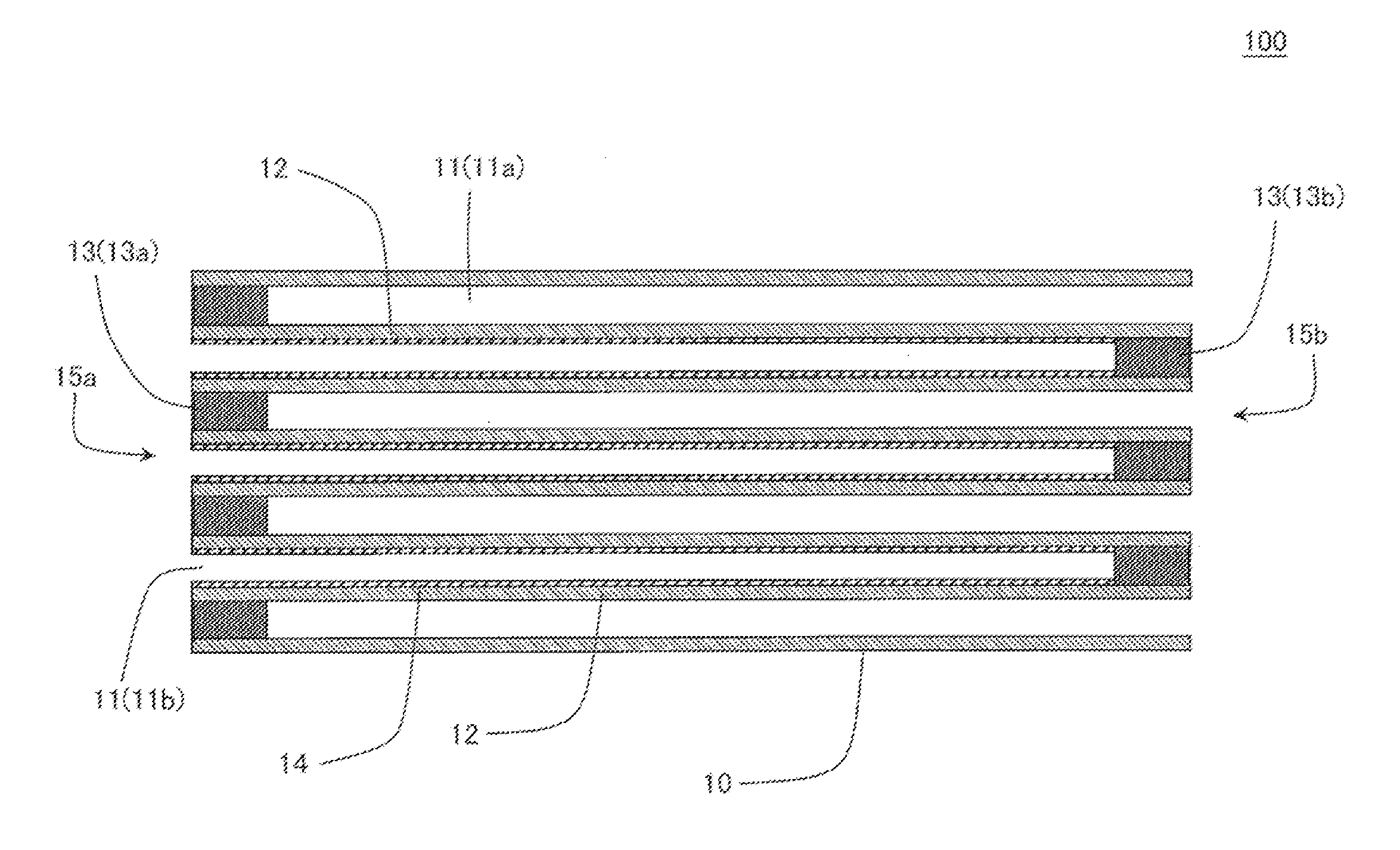
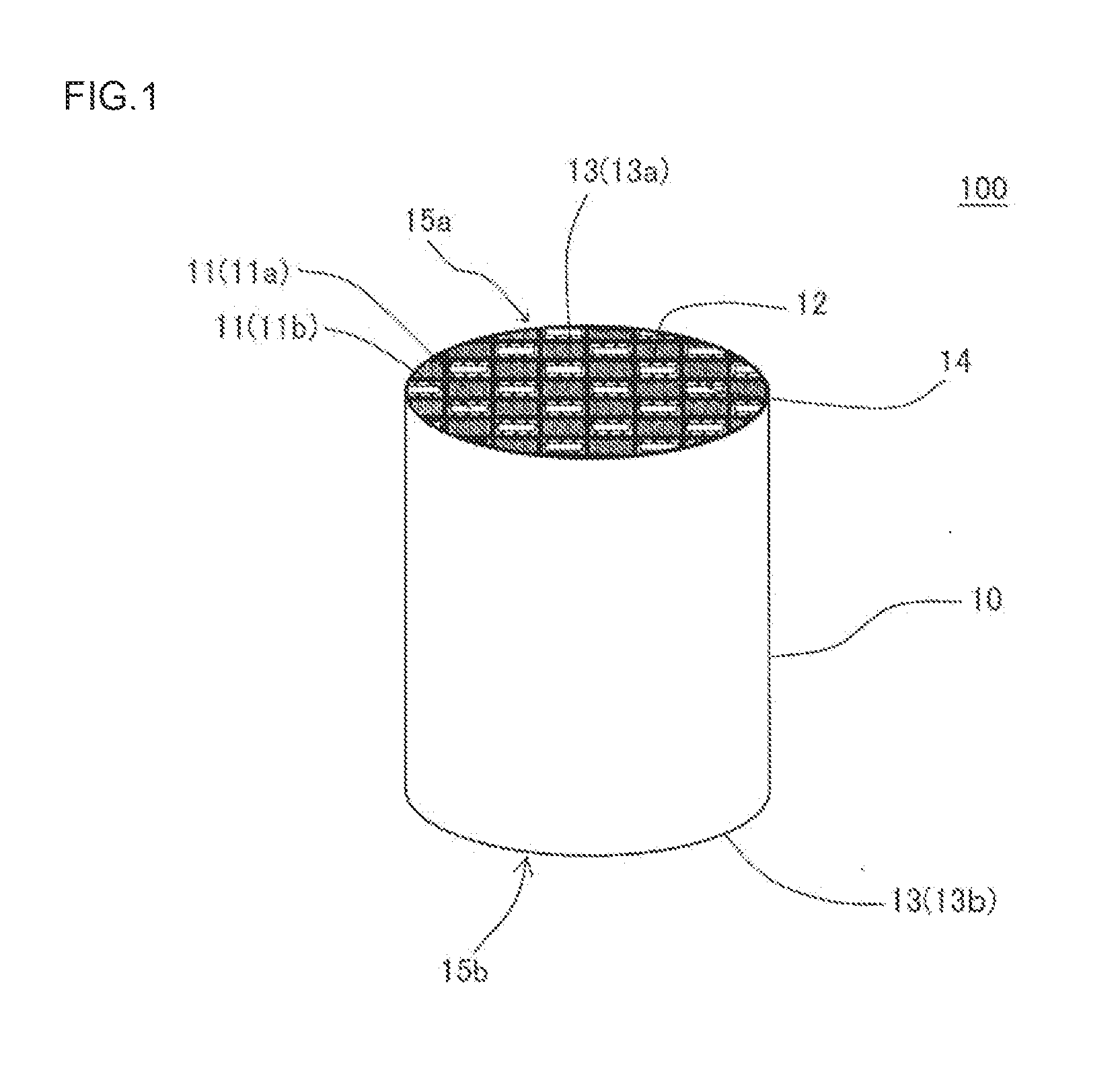
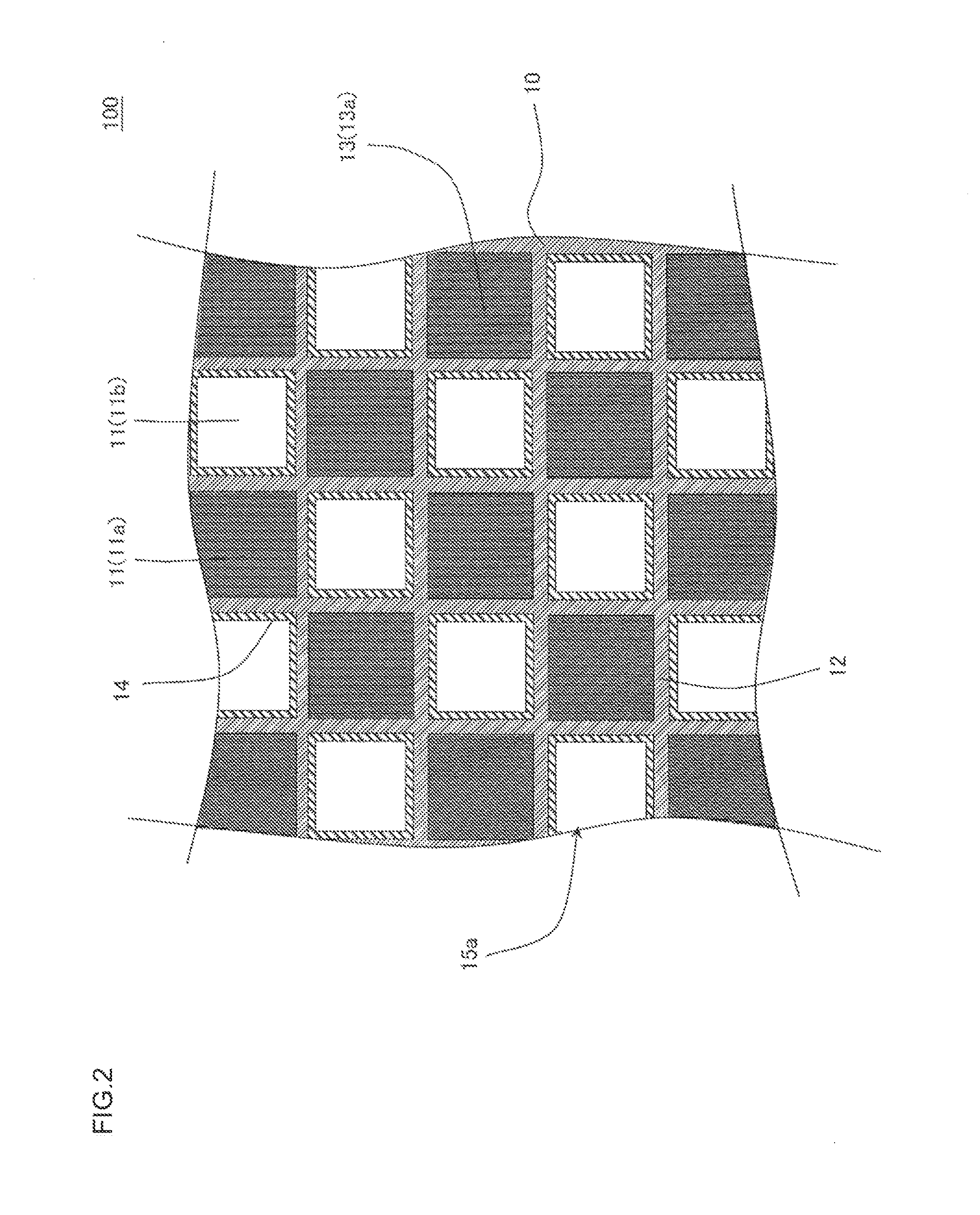
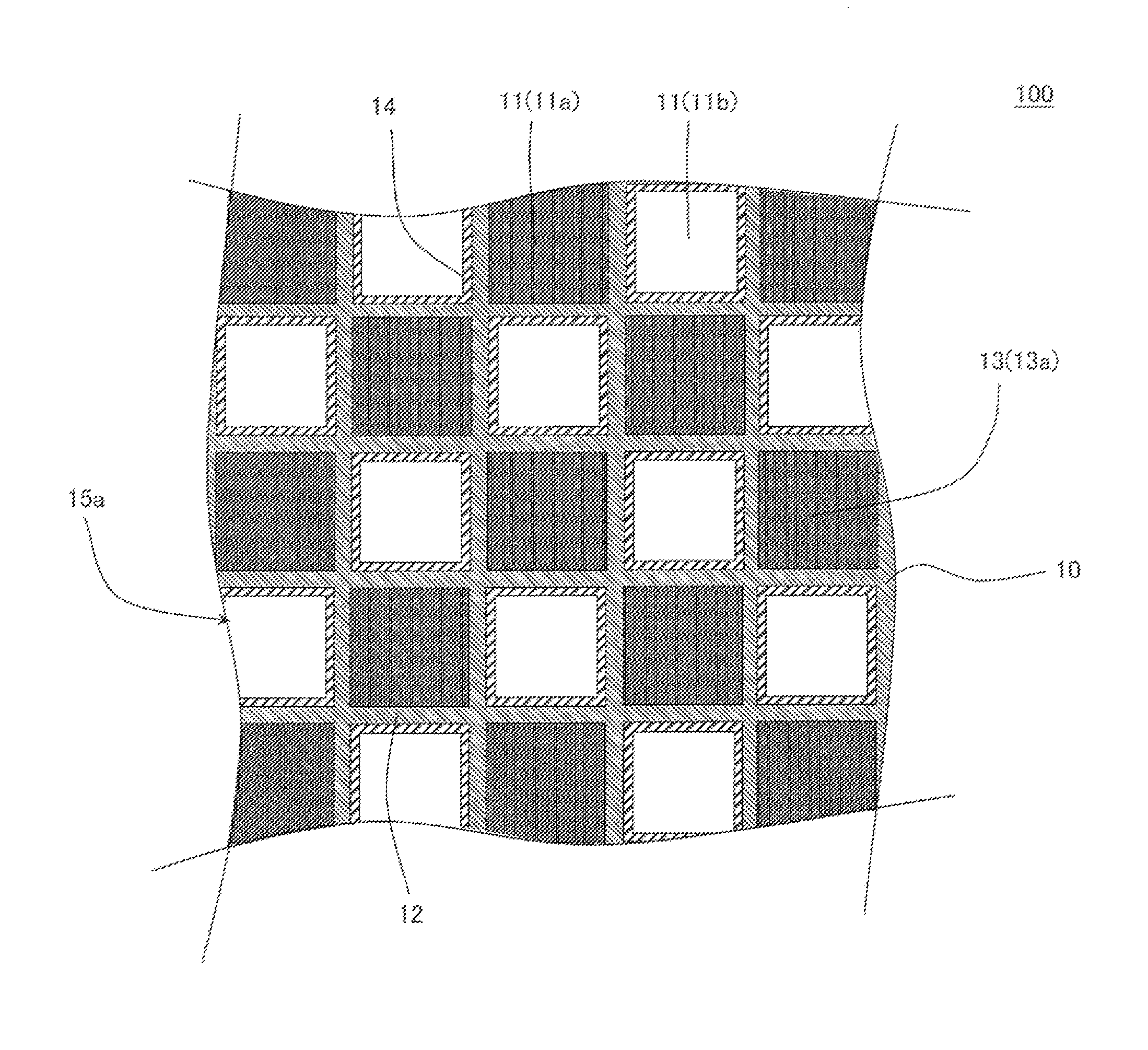
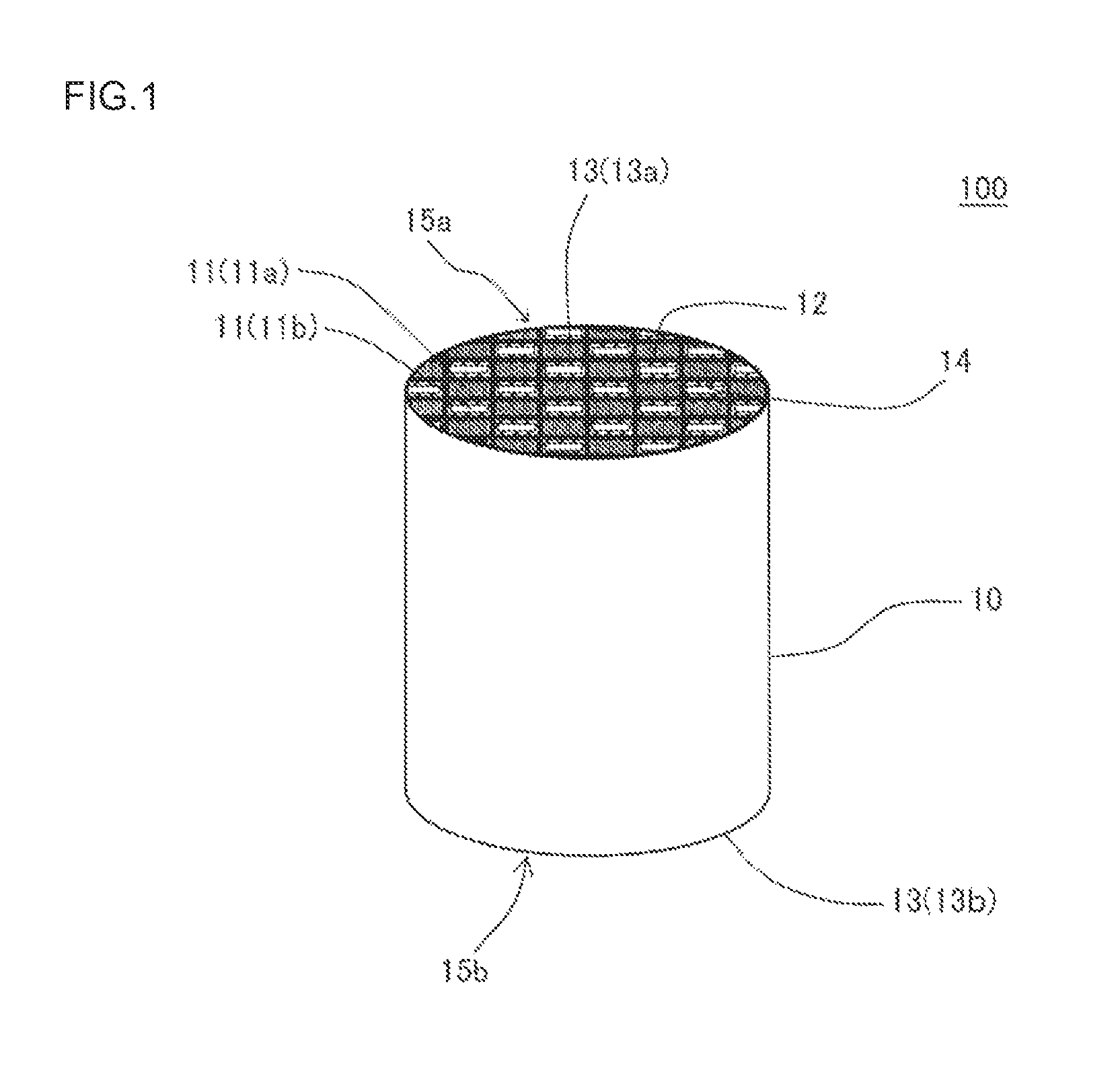
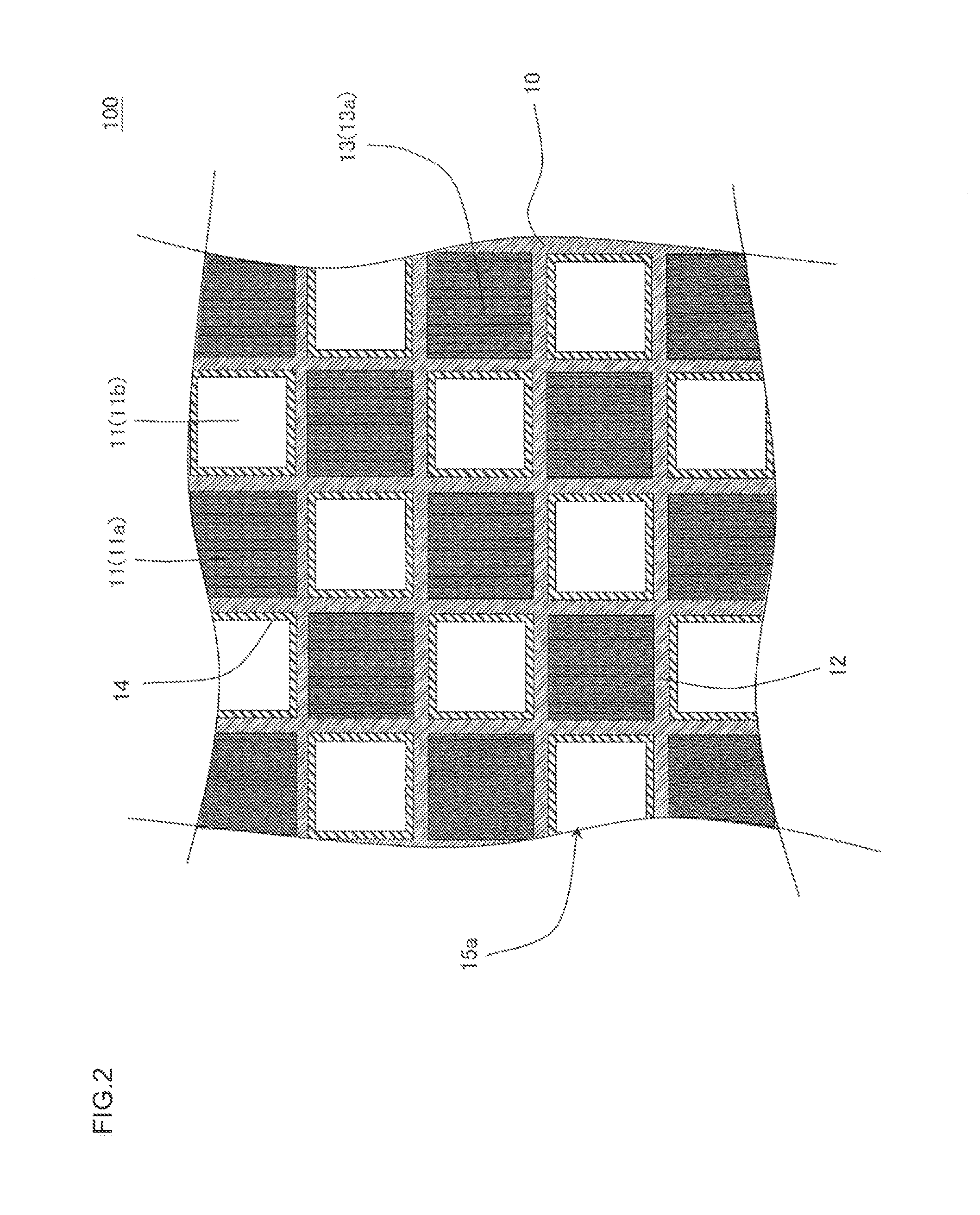
An exhaust gas purification filter 100 includes: a honeycomb structure 10 having partition walls 12, plugging portions 13, and a surface trapping layer 14 having an average pore size of 0.1 μm or more and 5 μm or less, a porosity of 50% or more and 80% or less, and a thickness of 1 μm or more and 50 μm or less. The partition walls 12 have a thickness of 0.05 mm or more and 0.18 mm or less and an average pore size of 10 or more and 18 μm or less, and the proportion of the volume of the pores having a size of twice the average pore size or more in the entire pore volume in a pore size distribution of the partition walls 12 is 5% or more and 40% or less.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Porous body precursors, shaped porous bodies, processes for making them, and end-use products based upon the same
InactiveUS20100280261A1Easy to controlHigh porosityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationProduct baseHeat treated
The present invention provides porous body precursors and shaped porous bodies. Also included are catalysts and other end-use products based upon the shaped porous bodies and thus the porous body precursors. Finally, processes for making these are provided. The porous body precursors are germanium doped and comprise a precursor alumina blend. It has now surprisingly been discovered that inclusion of germanium, alone or in combination with such a blend, in porous body precursors can provide control over, or improvements to, surface morphology, physical properties, and / or surface chemistry of shaped porous bodies based thereupon. Surprisingly and advantageously, heat treating the shaped porous bodies can result in additional morphological changes so that additional fine tuning of the shaped porous bodies is possible in subsequent steps.
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Preparation method of one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods
InactiveCN103011264AImproved pore size distributionLarge roughness factorMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium compoundsNanoparticleEthylene glycol
A preparation method of one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods relates to a preparation method of titanate nanorods, and mainly solves the problems that a titanate photocatalyst material prepared in the prior art has a relatively small specific surface area, a relatively low roughness factor and non-uniform size and shape. The preparation method of one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods comprises the following specific steps: 1, preparing a metal salt ethylene glycol solution; 2, adding a titanium source; 3, centrifuging and eluting; 4, drying; and 5, roasting to obtain the one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods. The preparation method has the advantages as follows: 1, the specific surface area of the prepared one-dimensional metal titanate nanorod photocatalyst is 2-43 times of the surface area of the titanate nanoparticle photocatalyst material prepared in the prior art; and 2, the prepared one-dimensional metal titanate nanorod photocatalyst has an apparent pore size distribution and a relatively large roughness factor. The preparation method is mainly applied to preparation of the one-dimensional titanate nanorods.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Porous carbon spheres-coated silicon/silicon dioxide nano-composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105789571AImproved pore size distributionLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPorous carbonElectric capacity
The invention provides a porous carbon spheres-coated silicon / silicon dioxide nano-composite material and a preparation method and an application thereof. The porous carbon spheres-coated silicon / silicon dioxide nano-composite material comprises a silicon / silicon dioxide nano-composite material and porous carbon spheres, wherein the porous carbon spheres coat the silicon / silicon dioxide nano-composite material and comprise micropores and mesopores. The porous carbon spheres-coated silicon / silicon dioxide nano-composite material can form physical and chemical adsorption on polysulfide when used as an anode material for a lithium-sulfur battery, is high in sulfur loading capacity and demonstrates excellent electric capacity and cycling stability; and active materials are not easy to lose.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Complex reservoir rock pore structure parameter extraction method
ActiveCN105654486AImproved pore size distributionAccurate Pore Size DistributionImage enhancementImage analysisRock coreData set
The invention discloses a complex reservoir rock pore structure parameter extraction method. The method includes the following steps that: 1) the three-dimensional image of the core of the pore structure of a complex reservoir rock is obtained, a three-dimensional digital core is established; 2) a pore network model with maximal ball clusters adopted as units is formed through using a maximal ball algorithm based on the three-dimensional digital core; 3) sectioning processing is performed on the pore network model obtained in the step 2), and sectioned sections are recorded; 4) as for the sectioned sections obtained in the step 3), rays are emitted from the center of the core at every one preset angle, the rays extend until reaching skeleton voxelsm, and the length of each ray is calculated, a data set of pore local spatial scale is established based on the length of each ray, and the optimal segmentation threshold value of the data set of the pore local spatial scale is determined; and 5) the pore diameter distribution of the complex reservoir rock can be obtained according to the optimal segmentation threshold value obtained in the step 4). With the method of the invention adopted, the pore diameter distribution of the complex reservoir rock can be extracted accurately.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material and preparation and application methods thereof
InactiveCN108529619AWidely distributedReduce wasteCarbon compoundsHybrid capacitor electrodesProtonationCapacitance
The invention discloses a nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material. The nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material is prepared by subjecting glucose, melamine, dimethyl sulfoxide andconcentrated sulfuric acid to protonation and performing operations such as heating reaction and calcined activation. According to the nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material, the range ofthe specific surface area is 1203.9-1932.1 m2 g-1, the mean pore size is uniform in distribution within a range of 1.421-3.627 nm. The preparation method of the nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material comprises 1) protonation of melamine, 2) preparation of a nitrogen and sulfur-containing precursor, 3) activation of the nitrogen and sulfur-containing precursor, and 4) aftertreatment ofthe nitrogen and sulfur-containing precursor. The invention also discloses application of the nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material as a supercapacitor electrode material, and when the electric current density is 1 A g-1, the range of the capacitance of the nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material is 180-293 F g-1. Protonation treatment of the concentrated sulfuric acid onthe melamine adjusts the electron structure of the melamine to produce the nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material high in content of nitrogen; the dimethyl sulfoxide is high in polarity and hydrophilicity and favorable to doping reaction with hydroxyl of the glucose. Therefore, the prepared nitrogen and sulfur codoped porous carbon material is excellent in electrochemical properties and has an application prospect in the field of supercapacitors.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Preparation method of high-specific-surface porous TiO2 nano-fiber
InactiveCN103741263AHigh photocatalytic activityHigh photocatalytic stability and chemical stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsFilament/thread formingSolventCalcium hydroxide
The invention relates to the field of photocatalytic materials, and in particular relates to a preparation method of a high-specific-surface porous TiO2 nano-fiber. According to the preparation method, the nano-fiber is obtained by dissolving out SiO2-phase nano-particles in a double-phase SiO2-TiO2 electrostatically-spun nano-fiber by adopting a solvent dissolution method, wherein the solvent is one of sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, barium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide or hydrofluoric acid. The preparation method disclosed by the invention regulates the dissolution rate of SiO2 in the double-phase SiO2-TiO2 nano-fiber by means of regulating the pH value, temperature, concentration and dissolution time of the solvent so as to regulate the appearance of a microstructure of the nano-fiber. The double-phase SiO2-TiO2 nano-fiber is prepared by mixing organism precursors of titanium and silicon, adding high polymer, performing electrostatic spinning, and then roasting by adopting a roasting method. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in process and low in preparation cost, the target product has high photocatalytic activity and porosity, and the pore size distribution is centralized.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing multi-level pore carbon from lignin degrading bacteria-modified lotus leaves and application of multi-level pore carbon
PendingCN108043359AEfficient use ofSimple preparation processGas treatmentOther chemical processesWater vaporSorbent
The invention belongs to the technical field of adsorbents, and discloses a method for preparing multi-level pore carbon from lignin degrading bacteria-modified lotus leaves and application of the multi-level pore carbon. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pretreating lotus leaves; (2) introducing the pretreated lotus leaves and suspension of lignin degrading bacterial spores into aliquid medium, performing oscillation at a constant temperature of 25-35 DEG C for 3-10 days for cultivation, and performing filtration, washing and drying to obtain microorganism-treated lotus leaves; and (3) performing carbonization treatment on the microorganism-treated lotus leaves at 600-1000 DEG C, and conducting activation treatment in an atmosphere of water vapor to obtain the multi-levelpore carbon. According to the method, the lotus leaves are adopted as a self-template material, so that the lotus leaves are utilized effectively; the method has a simple preparation process and low production cost, and is environmentally friendly, and compared with other activated carbon, the obtained multi-level pore carbon material has better pore size distribution, better selective adsorptionperformance and greater adsorption capacity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Surface graphene-coated high-capacity spherical hard carbon negative electrode material
ActiveCN107026262AWide variety of sourcesConvenient sourceCell electrodesGrapheneReduction treatmentMicrosphere
The invention relates to the technical field of a lithium ion battery, specifically to a surface graphene-coated high-capacity spherical hard carbon negative electrode material. The negative electrode material is characterized by comprising the following processing steps of (1) preparing a hard carbon precursor; (2) preparing polymer microspheres; (3) preparing spherical hard carbon; (4) preparing a graphite oxide coating body; and (5) performing carbonization and thermal reduction treatment. Compared with the prior art, the spherical hard carbon in the inner core has the advantages of unique appearance and good pore diameter distribution, uniform particle granularity distribution, high stacking density and the like; and the spherical hard carbon surface coating graphene forms the conductive network of the core-shell structure, so that ion and electron transmission can be facilitated, thereby improving the electrical conductivity of the negative electrode material.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHANSHAN TECH CO LTD
Porous carbon material with high specific surface area prepared by virtue of fungal pretreatment as well as method and application thereof
PendingCN109574007ASimple processLow equipment requirementsGas treatmentCarbon compoundsPre treatmentBiomass
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of porous carbon materials, and discloses a porous carbon material with a high specific surface area by virtue of fungal pretreatment as well as a method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) drying and crushing waste biomass to obtain crushed waste biomass; 2) carrying out the constant-temperature oscillation reaction for the crushed waste biomass and fungal spore suspension in a liquid culture medium, filtering, washing, and drying to obtain a carbonization precursor; carrying out the high-temperature carbonization treatment to obtain a primary carbonized substance; and 3) activating the primary carbonized substance and an activator in inert atmosphere to obtain the porous carbon material with ahigh specific surface area. According to the invention, the porous carbon material is prepared by virtue of the regulation of fungal treatment, so that the waste biomass is effectively utilized, the preparation process is simple, the production cost is low, and the method is environment-friendly; and the obtained porous carbon material is high in specific surface area and unique in aperture distribution and capable of obtaining micro-porous, mesoporous or micro-mesoporous carbon materials. The porous carbon material is applied to the field of adsorption.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Rhenium-promoted epoxidation catalysts and methods of making and using them
ActiveUS8546294B2Improved pore size distributionIncrease surface areaOxygen-containing compound preparationHydrocarbon by isomerisationRheniumPtru catalyst
The present invention provides rhenium-promoted epoxidation catalysts based upon shaped porous bodies comprising a minimized percentage of their total pore volume being present in pores having diameters of less than one micron, and a surface area of at least about 1.0 m2 / g. Processes of making the catalysts and using them in epoxidation processes are also provided.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
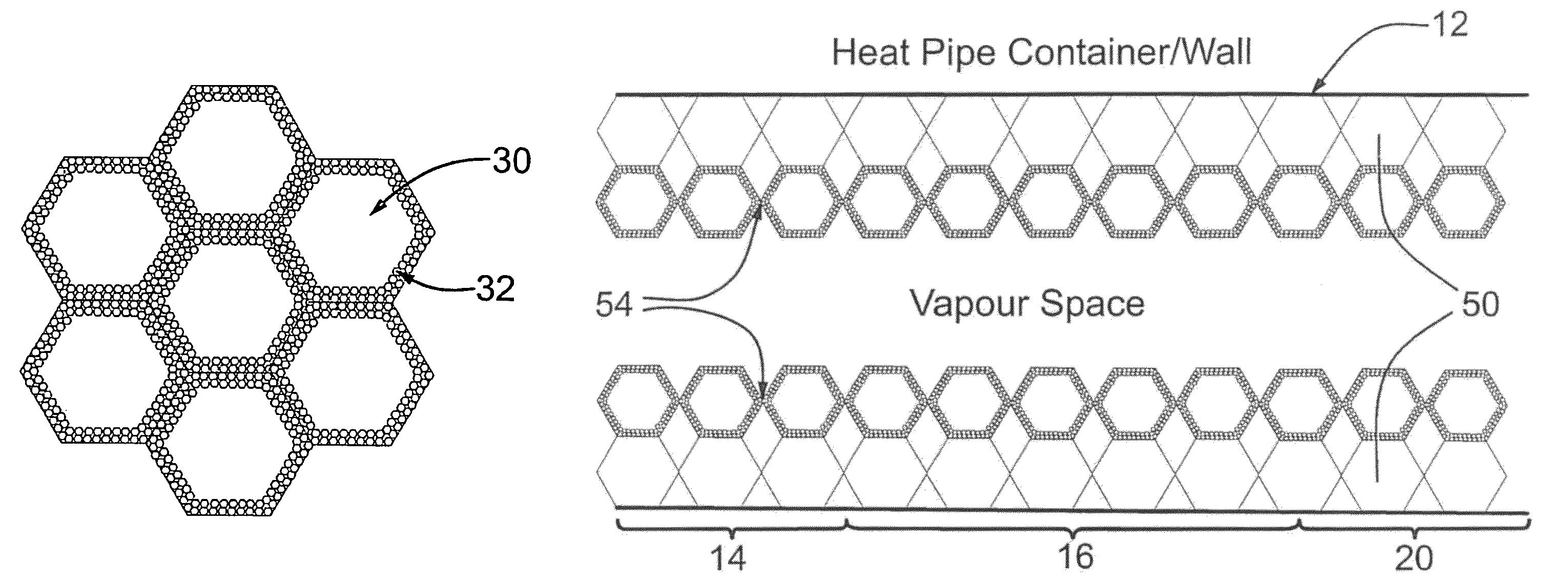
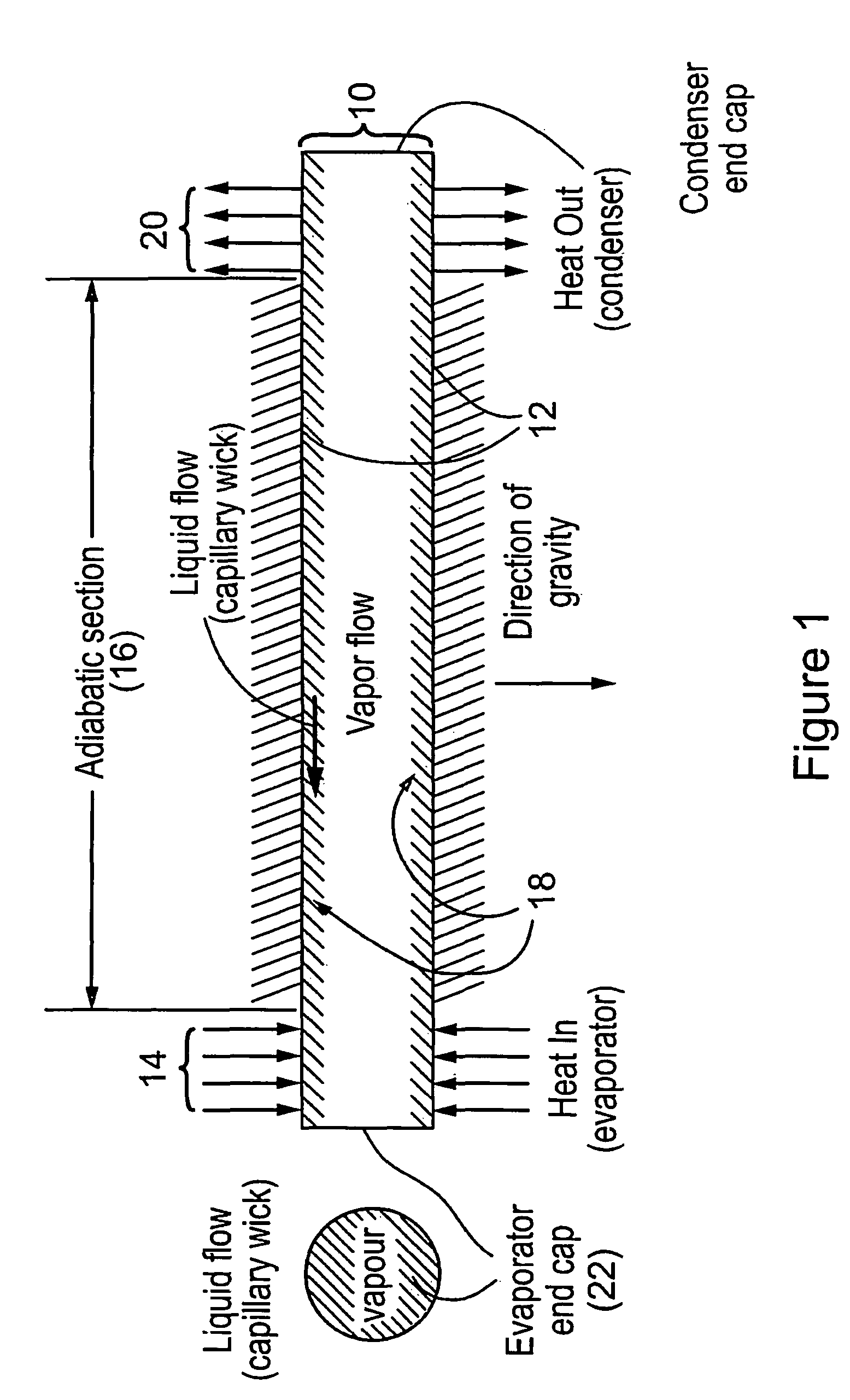
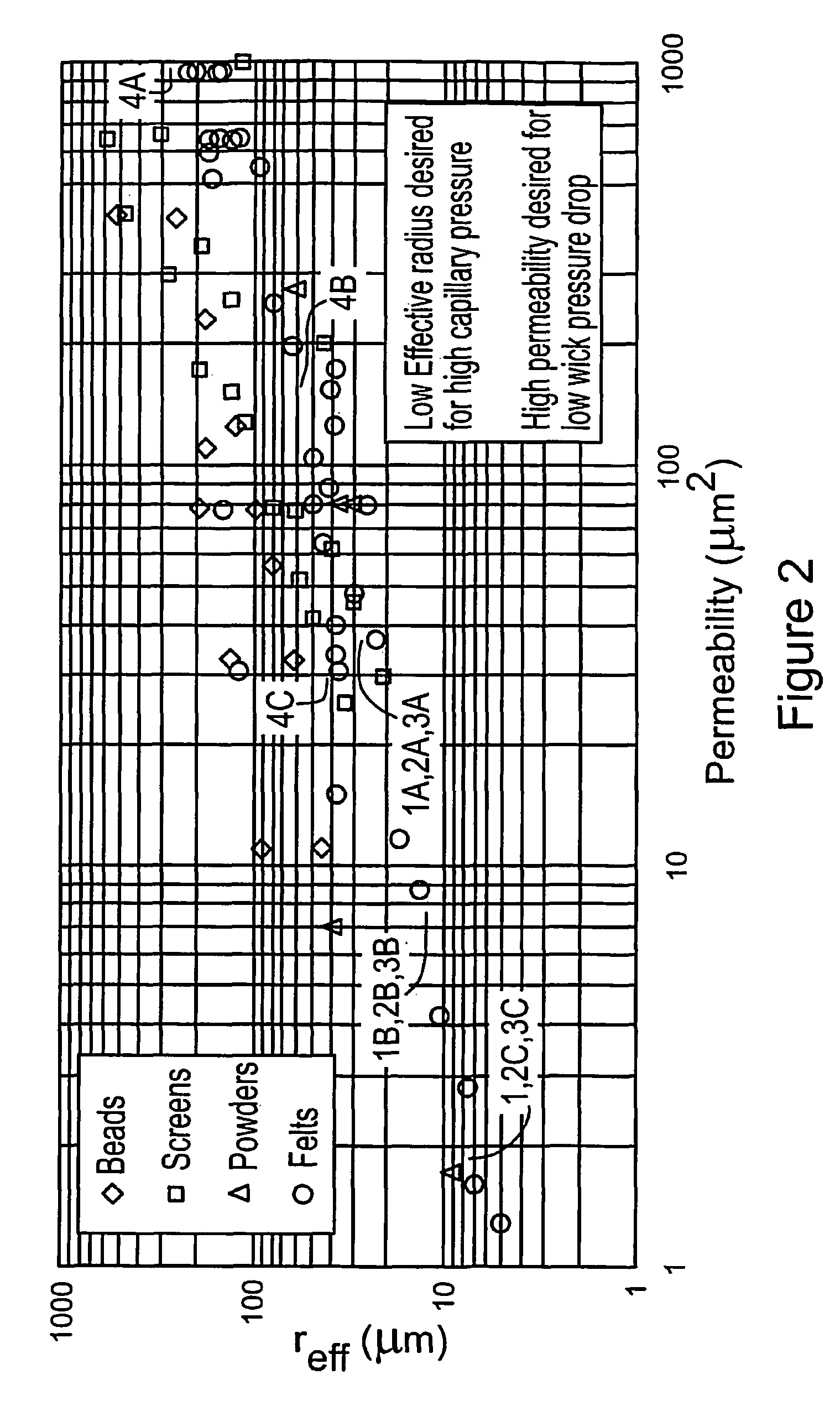
Hybrid wicking materials for use in high performance heat pipes
InactiveUS7828046B2Improve heat transfer performanceIncrease the differential pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNiobiumAlloy
Hybrid wicking materials are used in high performance heat pipes where a bi-modal distribution of pore sizes offers advantages over a homogeneous monolithic porous structure. This wick is comprised of sintered metal powder formed on a foam, felt, screen or mesh metal substrate. A fine pore structure is formed by the metal powder while the substrate is comprised of large pores. The large pores are several times, preferably five times to several orders of magnitude larger in size than the small pores. The sintered powder metal and the metal substrate may be made of nickel, copper, molybdenum, niobium, aluminum, iron, cobalt, titanium and alloys based on these metals. This provides a wicking material with axial and radial variations in pore size for optimized performance under both horizontal and against gravity orientations.
Owner:HUANG XIAO +1
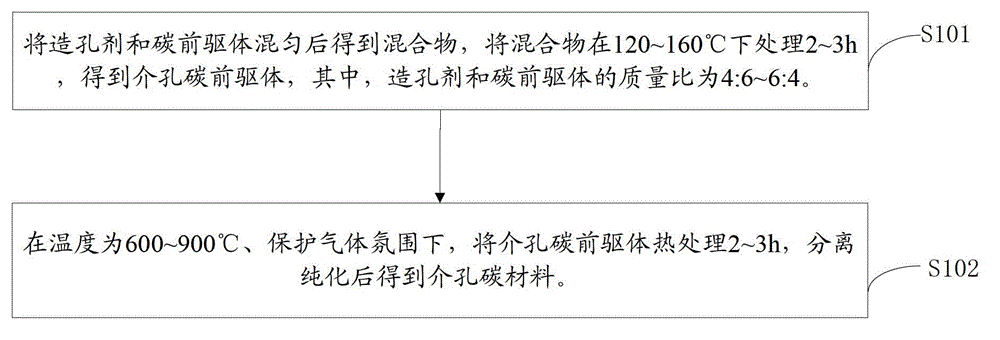
Mesoporous carbon material, elemental sulfur and preparation method for mesoporous carbon composite material
InactiveCN104157861AGood dispersionEasy to operateCell electrodesSecondary cellsShielding gasDissolution
Provided is a preparation method for a mesoporous carbon material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pore forming agents and carbon precursors are mixed uniformly and a mixture is obtained, the mixture is processed for 2-3h at the temperature of 120-160 DEG C, and mesoporous carbon precursors are obtained, and the mass ratio of the pore forming agents to the carbon precursors is 4:6-6:4; the mesoporous carbon precursors are subjected to heat treatment at the temperature of 600-900 DEG C and under protection gases, and the mesoporous carbon material is obtained after separation and purification. In the preparation method, a hard template method is employed for preparation of the mesoporous carbon material, the operation is simple, good pore size distribution is achieved, and the mesoporous carbon material facilitates high dispersion of sulfur. In addition, the strong adsorptivity of the material can inhibit dissolution and loss of polysulfides effectively, and the mesoporous carbon material is helpful to raise the utilization rate of active sulfur.
Owner:HYB BATTERY +1
Production process for spunlace composite high temperature-resisting and corrosion-resisting filtering material
ActiveCN102580400AGood strengthStrong chemical resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsNeedling machinesCorrosion resistantFilter material
The invention relates to a production process for a spunlace composite high temperature-resisting and corrosion-resisting filtering material and belongs to the technical field of a textile filtering material. The production process comprises the following steps that: taking polyphenylene sulfide fibers and fiberglass fabrics as raw materials; checking, weighing and charging the polyphenylene sulfide fibers; charging the polyphenylene sulfide fibers into a long curtain, a horizontal opener, a big-cabin cotton blending box and a refined opener successively; and then carding by using a carding machine I and a carding machine II in a layering mode; placing into a cross lapping machine I and a cross lapping machine II to lap; clamping the fiberglass fabrics between the raw materials delivered by the cross lapping machine I and the cross lapping machine II and performing superposition; and performing the processes of pre-wetting, hydroentangling, dehydrating, drying and taking-up. The production process for the spunlace composite high temperature-resisting and corrosion-resisting filtering material provided by the invention has the advantages of excellent mechanical performance, filtration performance, high temperature-resisting performance, and chemical corrosion-resisting performance and size stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BAOREN NONWOVEN CO LTD
Exhaust gas purification filter
ActiveUS8734558B2Reduce the amount requiredIncreased pressure lossCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationPorosityHoneycomb structure
An exhaust gas purification filter 100 includes: a honeycomb structure 10 having partition walls 12, plugging portions 13, and a surface trapping layer 14 having an average pore size of 0.1 μm or more and 5 μm or less, a porosity of 50% or more and 80% or less, and a thickness of 1 μm or more and 50 μm or less. The partition walls 12 have a thickness of 0.05 mm or more and 0.18 mm or less and an average pore size of 10 or more and 18 μm or less, and the proportion of the volume of the pores having a size of twice the average pore size or more in the entire pore volume in a pore size distribution of the partition walls 12 is 5% or more and 40% or less.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Application of ruthenium palladium/carbon catalyst
InactiveCN103709037AIncreased oxygen-containing functional groupsImprove surface propertiesOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationPalladium
The invention discloses application of a ruthenium palladium / carbon catalyst. A catalyst carrier is a carbon material; active components are Ru and Pd nano particles; the loading capacity of Ru is 0.5-8.0%; the loading capacity of Pd is 0.1-2.0%; the dispersity of ruthenium palladium can be up to 30-80%. The carrier is oxidized and pretreated by acid-base, so that an oxygen-containing functional group on the surface can be increased, the property of the ruthenium palladium at the surface of the carbon material is improved, the dispersity of the ruthenium palladium is improved, and the active components are firmly adsorbed on the foundational group, so that the catalyst displays high activity in the reaction process; the prepared catalyst is applied to hydrogenation preparation of cyclohexanedimethanol (DMCD) employing dimethyl terephthalate (DMT). The activity of the catalyst after being nested for 20 times is not reduced in a 5000ml of high-pressure kettle; the DMT transformation rate is 99.3-100%; the selectivity of the DMCD is 95.5-96.4%; the DMCD purity is greater than 99.5% by simple distillation and purification. Therefore, the ruthenium palladium / carbon catalyst is mild in technological condition, simple in equipment, free of three wastes emission, low in investment, low in energy consumption, and easy in achieving industrialization.
Owner:JIANGSU GOLD BRIDGE SALT & CHEM GRP +1
Preparation method of MOF-derived porous carbon electrode
InactiveCN109920655AImprove performanceOptimized areaHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitancePore distribution
The invention relates to a template-free two-dimensional MOF-derived carbon electrode material which is synthesized in one step at normal temperature and has high performance. According to the preparation method of the electrode material, Zn(NO3)2.6H2O, 2-methylimidazole and a surfactant are used as a raw materials, and the raw materials are synthesized in one step and then calcined to prepare anMOF-derived carbon electrode with a two-dimensional structure, wherein the 2-methylimidazole provides an N source, and the surfactant is added to increase the specific surface area. The MOF-derived carbon electrode is further activated to further control the pore structure, so that the structure of the prepared electrode structure is further optimized and then the electrode material with reasonable pore distribution and superior performance is formed. The prepared electrode material has reasonable pore size distribution, large specific surface area and high specific capacitance, is capable ofsolving the problem of adding a template and a toxic solvent in the process of synthesizing a two-dimensional MOF, is simple and convenient in preparation process and easy to get raw materials, accords with the needs of sustainable development, and is expected to achieve large-scale use in the field of supercapacitors and new energy materials.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Preparation method of spongy porous carbon material for supercapacitors
InactiveCN105836746AExcellent electrochemical performanceMild reaction conditionsHybrid capacitor electrodesIonNitrogen atmosphere
A method for preparing a spongy porous carbon material for a supercapacitor, comprising the following steps: cleaning the rice husk with deionized water to remove dust, and then dispersing the rice husk in an HF solution, and continuously stirring in a water bath to remove the dust from the rice husk. the ash content; filter and wash to obtain deashed rice husk; mix deashed rice husk with activator according to a certain mass ratio, then add water to make it evenly mixed, and obtain a mixture of rice husk and alkali after drying; mix the mixture in Carry out high-temperature activation treatment under the protection of nitrogen atmosphere, wash with deionized water, filter and dry to obtain a porous carbon material. The sponge-like porous carbon prepared by the invention has high specific surface area, good pore size distribution, and good electrochemical performance. The preparation has mild reaction conditions, low energy consumption, simple steps and easy operation, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Fibrous composite filtering materials of engine and preparing method thereof
A composite fibrous filter material for engine is prepared through adding dispersing assistant to water, ageing, adding plant fibres, inorganic fibres, and synthetic fibres, shaping with net, coating or dipping the reinforcing agent chosen from phenolic resin, epoxy resin, polyacrylic acid, and vinyl polyacetate, drying and solidifying. Its advantages are high filter accuracy and efficiency, low resistance, high physical strength and long service life.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
PVC battery separation plate production method and PVC battery separation plate
The present invention discloses a PVC battery separation plate production method and a PVC battery separation plate, wherein the method and the separation plate are used in the battery separation plate fields of the fields of lead-acid storage batteries and lead-acid gel storage batteries. According to the present invention, with the mixing and the extraction of the solvent and the combination of various process steps, the battery separation plate has high porosity zone and small and ideal pore size distribution; and with the matrix of the PVC polyvinyl chloride resin, the PVC polyvinyl chloride resin has characteristics of good penetration resistance, good resilience, good compressive strength, and good toughness.
Owner:ZHAOYUAN HAISI MICROPORE DIAPHRAGM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com