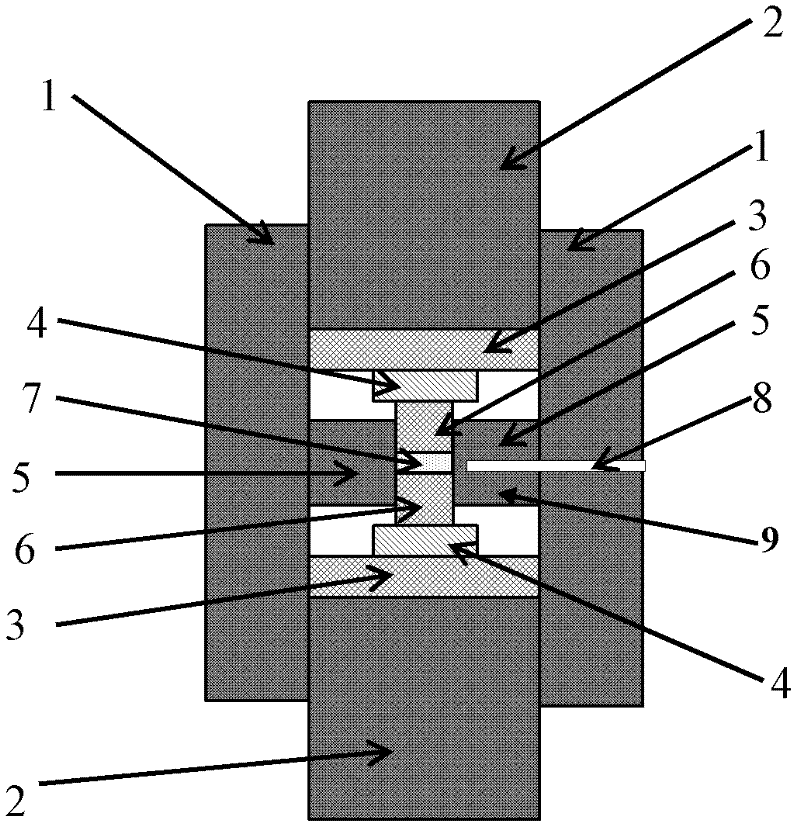
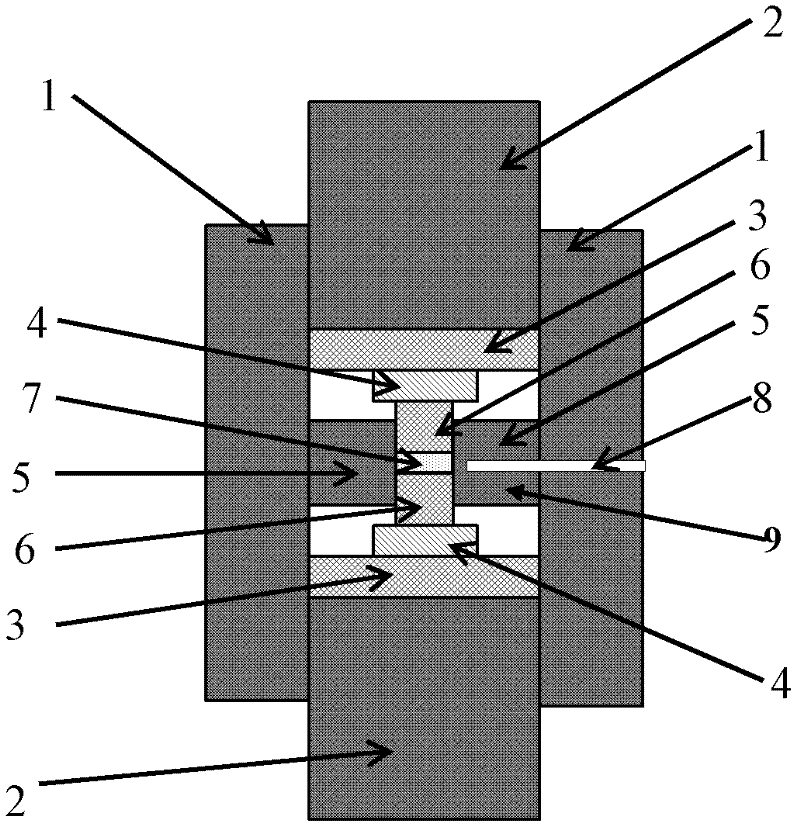
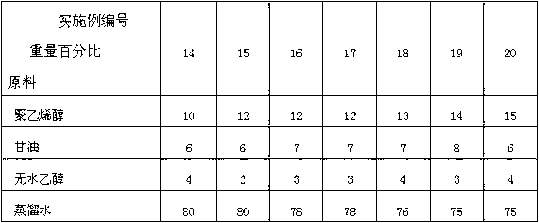
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58results about How to "Achieve densified sintering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aluminium nitride ceramics material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101386539ADoes not significantly affect colloidal propertiesGood dispersion propertiesAluminium acetylacetonateNano al2o3
The invention discloses an aluminium nitride ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The method is to add nano-alumina to raw materials in the prior preparation method for preparation according to the prior preparation process. In-situ growing nano-alumina can be obtained directly through adding the nano-alumina, or indirectly through adding organic aluminum, such as aluminium secondary butylate, aluminium isopropoxide or aluminium acetylacetonate, and by means of low-temperature decomposition of the organic alumina. The method can be applied to dry pressing and tape casting shaping, can obtain slurry with good dispersing characteristic and even mixing of the aluminium nitride and the nano-alumina by the ceramic preparation process, such as normal pressure, hot pressed sintering or the like, and is favorable for the improvement of sintering activity of materials, the reduction of sintering temperature, the improvement of luster uniformity, planeness and roughness for a ceramic substrate, and the reduction of production cost. The aluminium nitride ceramic material and the preparation method thereof can be widely applied to the field of aluminium nitride ceramic production.
Owner:无锡海古德新技术有限公司
Method for preparing large scale ceramic ball
InactiveCN101125755AHigh strength and structural uniformityAchieve densified sinteringHot isostatic pressingSilicon nitride
The invention relates to a preparation method of a large size ceramic ball, comprising the steps of material mixing, moulding and sintering. The method takes silicon nitride powder and additive as raw materials, of which the weight ratio is 100:15-5; certain amount of raw materials are weighted, evenly mixed by a ball milling method, dry pressed and then treated by cold isostatic pressure to get rough-body; the rough-body is hot isostatic pressure sintered under the protection of nitrogen and argon by adopting glass canning process; after a period of insulation and sintering, the temperature is reduced and the finished products are obtained. Compared with the prior art, the silicon nitride ceramic ball prepared by the invention has no stomata and gape on the surface, has even micro structure, 1500kg / mm2 of microhardness, above 5.4MPa.m1 / 2 of indentation and fracture toughness, and the invention can be widely applied to fields such as bearing ball, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MATERIAL
High-pressure sintering combined die and high-pressure rapid sintering method for preparing nanometer ceramic thereof
InactiveCN102390079AAchieve densified sinteringCeramic shaping apparatusInternal pressureHigh pressure
The invention discloses a high-pressure sintering combined die, which comprises a hollow cylindrical outer die, a hollow cylindrical inner die, one pair of cylindrical inner pressure heads, one pair of cylindrical metallic laminations, one pair of cylindrical ceramic laminations and one pair of cylindrical outer pressure heads, wherein the side face of the outer die is provided with a through hole into which a thermocouple is inserted; the hollow cylindrical inner die is arranged in the hollow cavity body of the outer die; the side face of the inner die is provided with a blind hole into which the thermocouple is inserted; the outer die and the inner die are in close fit, and the centre line of the through hole into which the thermocouple is inserted on the side face of the outer die and the centre line of the blind hole into which the thermocouple is inserted on the side face of the inner die coincide; the cylindrical inner pressure heads are half inserted into the upper end and the lower end of the hollow cavity body of the inner die; the inserted inner pressure heads and the hollow cavity body of the inner die form a die cavity; the cylindrical metallic laminations are arranged outside the inner pressure heads; the cylindrical ceramic laminations are arranged outside the cylindrical metallic laminations; the cylindrical outer pressure heads are arranged outside the cylindrical ceramic laminations; and the ceramic laminations and the outer pressure heads are in the close fit with the outer die. The invention also discloses a high-pressure rapid sintering method for preparing a nanometer ceramic by adopting the die. By adopting the die and the sintering method disclosed by the invention, the rapid low-temperature compact sintering can be realized on a nanometer ceramic material.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing radioactive waste solidified body
InactiveCN102930915AImprove performanceEasy to excludeRadioactive decontaminationHigh densityPolyvinyl alcohol
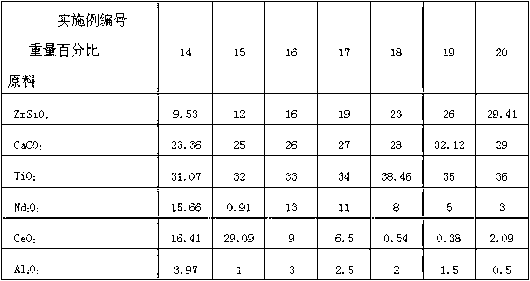
The invention discloses a method for preparing a radioactive waste solidified body. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: finely grinding a raw material which comprises 9.53 to 29.41 weight percent of ZrSiO4, 23.36 to 32.12 weight percent of CaCO3, 31.07 to 38.46 weight percent of TiO2, 0 to 15.66 weight percent of Nd2O3, 0 to 29.09 weight percent of CeO2 and 0 to 3.97 weight percent of Al2O3; drying the raw material; and adding polyvinyl alcohol sol, granulating, screening, molding, discharging the sol, performing vacuum hot-pressing sintering, and thus obtaining the radioactive waste solidified body. By adoption of the method, the raw material is low in cost, a high-purity and high-density perovskite acorite and titanite combined mineral solidified body is prepared at low temperature by using a simple and practical hot-pressing sintering technology, and foundation is laid for engineering application to artificial rock solidification treatment of high-level waste.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Metal ceramic inert anode for molten salt electrolysis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101255577AAchieve densified sinteringImplementing Continuously Incrementing DistributionsElectrodesRare earthAlloy
The invention relates to a raw material component of cermet inert anode having metallographic phase distributed in gradient from internal side to external side and preparation technology. The material is applied to extracting non-ferrous metal (Al, rare earths and metals with high-melting point) by fused salt electrolytic route. The component comprises the cermet formed by at least one Ca-Fe-Ni-O composite spinel oxide and at least one metallographic phase; wherein the anode material is composed of raw material with following mass prescription: 1% to 5% single metal or alloy, 1% to 99% spinel oxide, 0.1% to 10% other metal oxides; oxidizing the materials selectively in process of sintering the materials by adjusting oxygen content in whole atmosphere to form high strength, high tenacity, high conductivity inner layer (high content of metal) having anticorrosion outer layer (high content of oxides) functional gradient structure. The method of the invention is capable of effectively solving problems that the cermet inert anode is connected with the metal guide and the metallographic phase is dissolved and oxidized selectively in electrolytic process.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Titanium boride cathode material for aluminium electrolysis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101876079AAchieve densified sinteringAchieve homogeneous moldingAluminium electrolysisTitanium boride
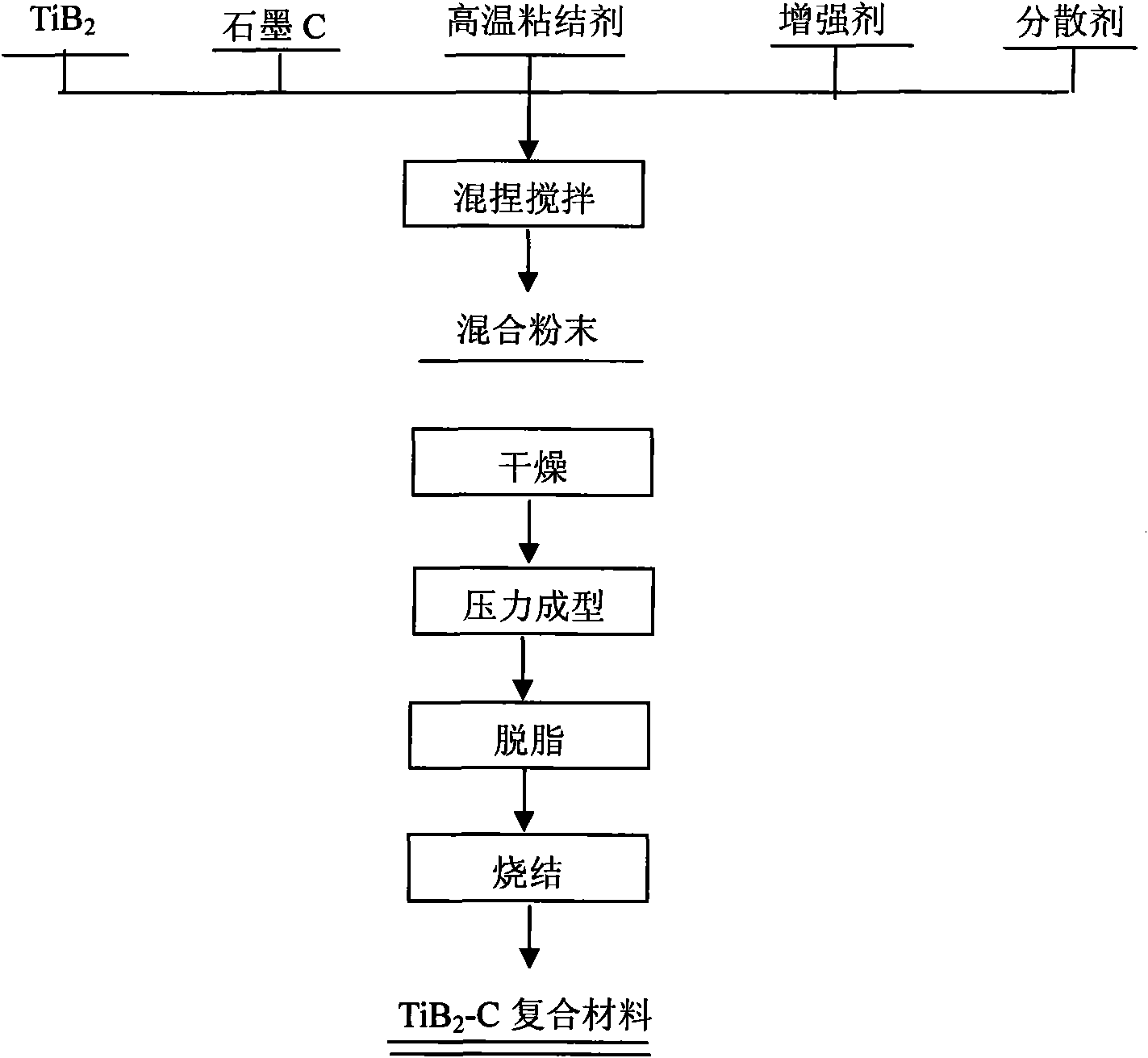
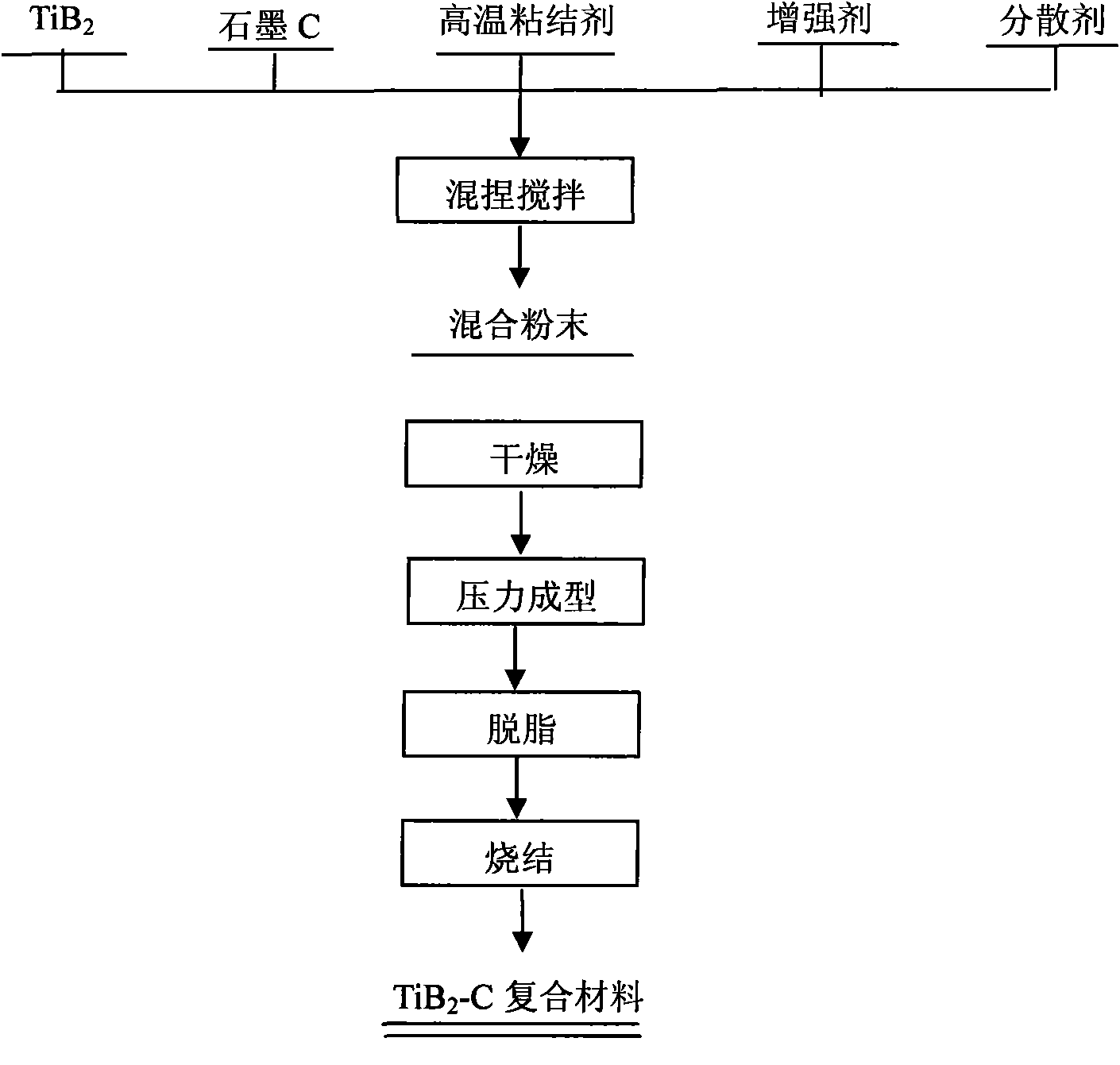
The invention discloses a titanium boride cathode material for aluminium electrolysis and a preparation method thereof and relates to a formula of an inert wettable cathode material for the aluminium electrolysis and the preparation method of the material. The titanium boride cathode material for aluminium electrolysis and the preparation method thereof are characterized in that: the cathode material comprises titanium diboride (TiB2), graphite, a high-temperature binding agent M and a reinforcing agent X. The preparation process comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing materials, namely, mixing, kneading and stirring the TiB2, graphite powder C, the high-temperature binding agent M and the reinforcing agent X according to theoretical ingredient volume and drying the mixture; (2) forming and degreasing, namely, performing pressure forming on the mixed raw materials to obtain green bodies and degreasing the green bodies under inert atmosphere; and (3) sintering, namely, sintering the degreased green bodies under the protective inert atmosphere or vacuum. A TiB2-C composite material for the aluminium electrolysis cell has the advantages of high wettability with aluminium liquid, high conductivity and high wear resistance, the realization of the sintering densification of the material and the homogeneous forming of the TiB2-C cathode material under the condition of normal pressure and low temperature, and the manufacturing cost which is far lower than that of a hot-pressing process.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Powder material for preparing high-strength high-toughness yttrium stabilized tetragonal polycrystal zirconia ceramics and preparation method of powder material
The invention discloses a powder material for preparing high-strength high-toughness yttrium stabilized tetragonal polycrystal zirconia ceramics. The powder material is prepared from zirconia and yttrium oxide, wherein the content of the yttrium oxide is 1.4-2.6mol% of the total amount of Zr<4+>; and the average grain size of raw crystal of the powder material is 50-110nm. Moreover, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the powder material. According to the zirconia powder material, the doping amount of yttrium is reduced, the tetragonal polycrystal ceramics prepared by using the powder are capable of realizing full tetragonal phase stable existence of zirconia at room temperature to guarantee the characteristic of high strength, activating the tetragonal phase in TZP (tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline), improving the transformation toughening performance and further optimizing the fracture toughness of TZP ceramics. The preparation method is safe and reliable, has the advantages of wide raw material source, low energy consumption and remarkable effect on energy conservation and emission reduction, is convenient for popularization and application, is suitable for industrial large-scale production, and can be used for effectively promoting application and development of zirconia materials.
Owner:江西赛瓷材料有限公司 +1
Magnesium/aluminum multi-layer composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110369709AAchieve high-quality connectionsAchieve densified sinteringTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusEconomic benefitsMetal
The invention relates to a powder metallurgy technology, in particular to a magnesium / aluminum multi-layer composite material and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims to solve the problemof bad connection property of magnesium / aluminum dissimilar materials caused by restriction of the prior art; meanwhile, by a compaction and connection integrated forming technology, significant economic benefit is created. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing laminating and powder paving on aluminum-containing powder and magnesium-containing powder in a mold, heating to 430 to 440 DEG C by a gradient heating mode, controlling the pressure to 20 to 45 MPa and performing spark plasma sintering to further obtain the well-connected magnesium / aluminum multi-layer composite material with a compact base body. The magnesium / aluminum multi-layer material prepared by the method has the advantages of few processes, short time and excellent combination property. The preparation method is suitable for preparation of a series of magnesium / aluminum based composite materials and can be extended to preparation of other dissimilar metal double-layer structure materials withapproximate sintering temperature. The preparation method is simple to operate, easy to control and convenient in industrialized application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Neodymium iron boron magnetic material with excellent magnetic performance
InactiveCN103617855AHigh energy productImprove remanenceInorganic material magnetismNiobiumDysprosium
The invention discloses a neodymium iron boron magnetic material with the excellent magnetic performance. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material with the excellent magnetic performance is formed by a main-phase alloy and a secondary-phase alloy through mixing. The main-phase alloy comprises, by weight, 64.5-68.5% of iron, 1.0-1.2% of boron, 30.2-34.3% of neodymium, 0.05-0.4% of niobium and 0.1-0.4% of aluminum. The secondary-phase alloy comprises, by weight, 50.8-54.2% of iron, 0.8-1.2% of boron, 18.9-21.1% of neodymium, 12.8-16.3% of praseodymium, 8.9-11.1% of dysprosium and 0.8-1.2% of copper. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material prepared with the method has the excellent magnetic performance and high intrinsic coercivity.
Owner:NINGBO STAR MATERIALS HI TECH
Preparation method of kularite ceramic solidifying body
InactiveCN103408304AThe process is simple and practicalGood for engineering applicationsHalf-lifeHigh-level waste
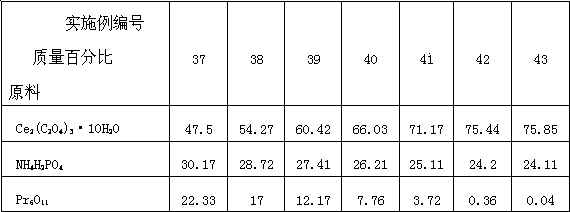
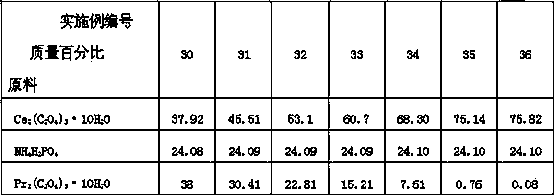
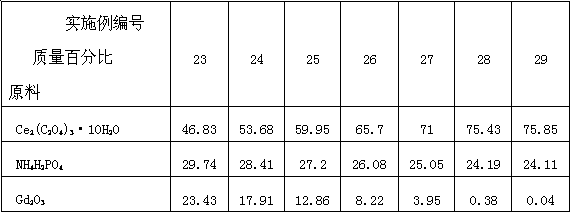
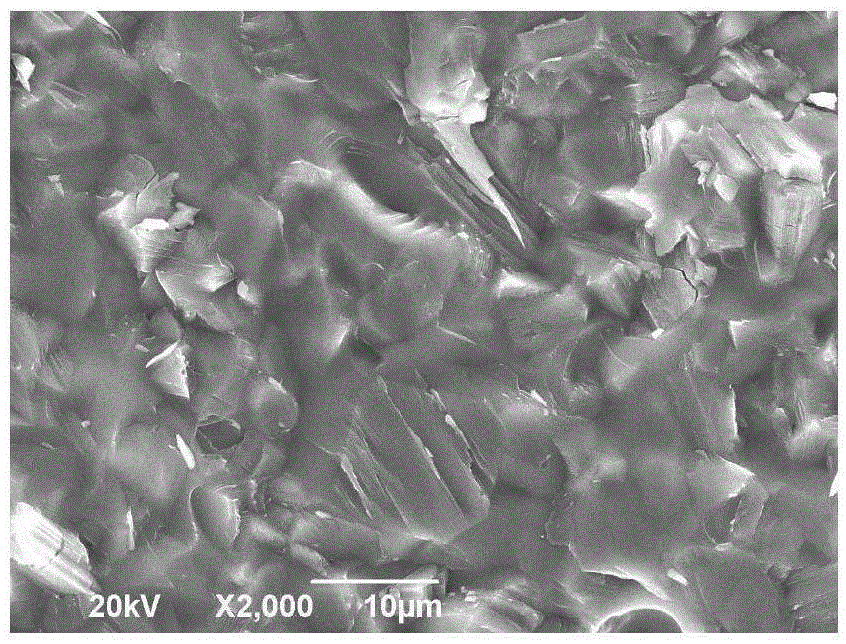
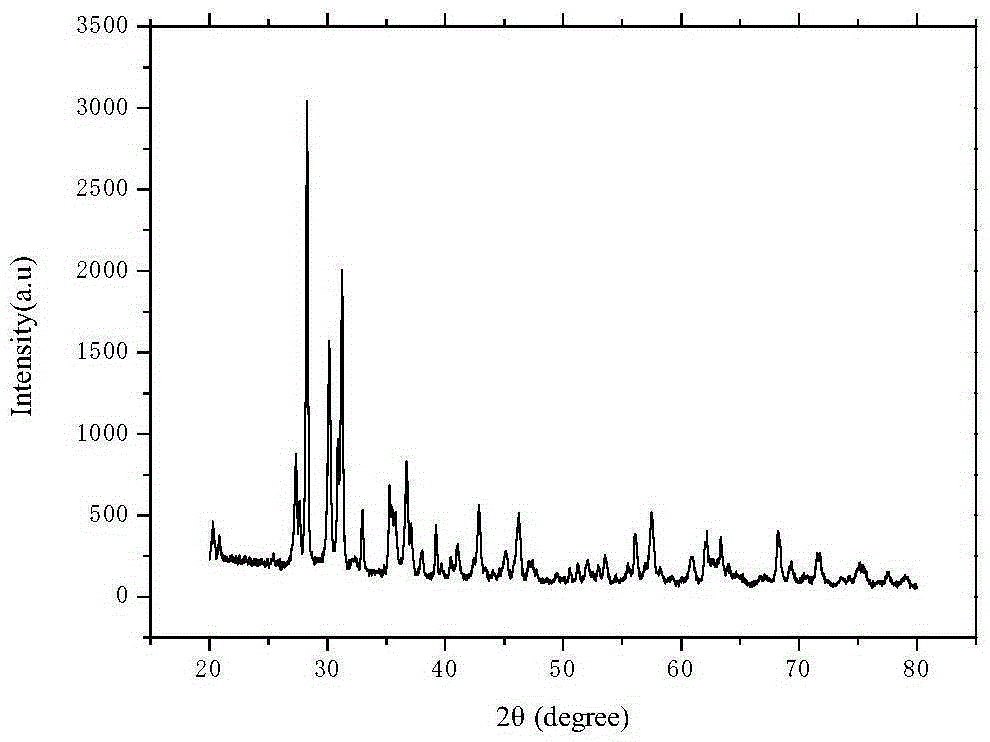
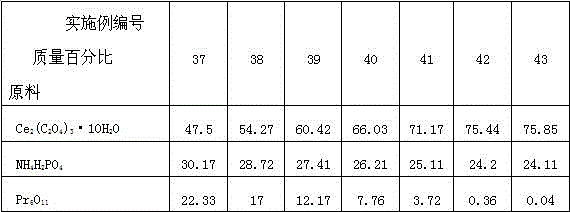
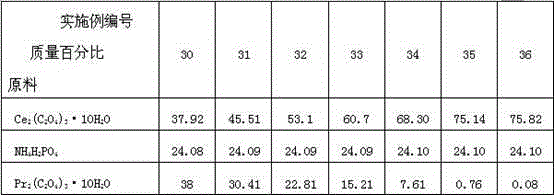
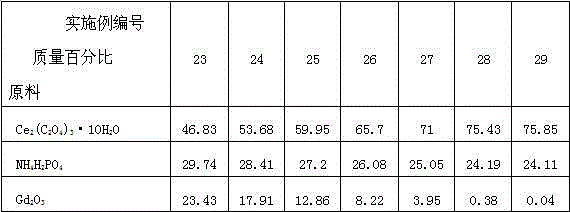
The invention discloses a preparation method of a kularite ceramic solidifying body. The preparation method is characterized in that Ce2(C2O4)3.10H2O, An2 (C2O4)3.10H2O / oxide of An (An=Gd, Pr and Eu) and NH4H2PO4 are taken as raw materials; the high-quality kularite ceramic solidifying body is prepared according to formulation designing and the steps such as fine grinding, drying, granulating, forming, adhesive removing and vacuum hot-pressing sintering at a lower temperature. The kularite ceramic solidifying body prepared according to the preparation method is high in heat stability, mechanical stability, chemical stability and anti-radiation stability, is applicable to the safe solidification treatment of high-level waste, particularly applicable to the safe solidification treatment of high-level minor actinides waste which is high in radioactivity and toxicity, and long in half life period, and also applicable to the engineering application of high-level waste ceramic solidification treatment needing remote operation.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Neodymium iron boron magnetic material strong in corrosion resistance
The invention relates to a neodymium iron boron magnetic material strong in corrosion resistance. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material strong in corrosion resistance is formed by a main-phase alloy and a secondary-phase alloy through mixing. The main-phase alloy comprises, by weight, 64.5-68.5% of iron, 1.0-1.2% of boron, 30.2-34.3% of neodymium, 0.05-0.4% of vanadium and 0.1-0.4% of aluminum. The secondary-phase alloy comprises, by weight, 50.8-54.2% of iron, 0.8-1.2% of boron, 18.9-21.1% of neodymium, 12.8-16.3% of tantalum, 8.9-11.1% of dysprosium and 0.8-1.2% of nickel. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material prepared with the method is excellent in corrosion resistance.
Owner:NINGBO STAR MATERIALS HI TECH
Preparation method of compact calcium hexaluminate-corundum composite ceramic
ActiveCN112125651ALow costAchieve densified sinteringCeramic materials productionPolyvinyl alcoholComposite ceramic
The invention relates to a preparation method of compact calcium hexaluminate-corundum composite ceramic, which comprises the following steps of: ball-milling, screening and dryingraw materials including 50-70% of ferrotitanium slag and 22%-38% of aluminum oxide, proportionally adding 8%-12% of zirconium oxide, uniformly mixing, adding PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) water solution, granulating, aging, carrying out compression molding in a mold, putting a formed blank into a drying oven for drying to form a green body, putting the green body into a silicon-molybdenum rod electric furnace for firing, and obtaining the compact calcium hexaluminate-corundum composite ceramic material at a proper firing temperature. The solid waste ferrotitanium slag is used as the main raw material, the solid waste utilization rate is high, the raw material cost is saved, the firing temperature is low, the fuel cost is reduced, and the prepared ceramic has high relative density.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
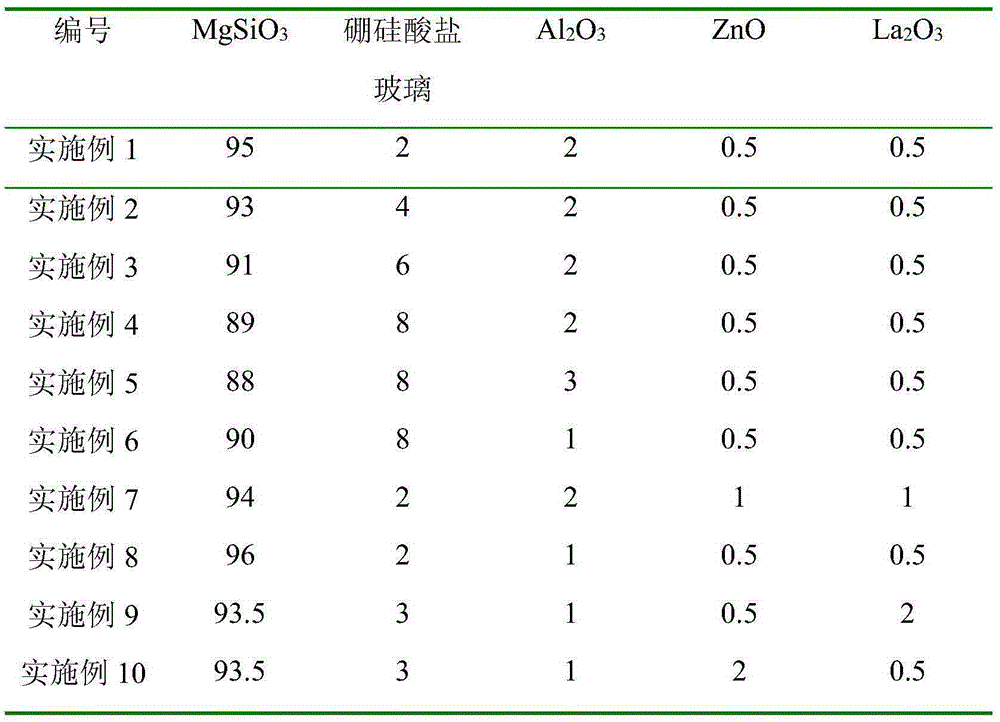
Ceramic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105384430AImprove densification performanceImprove flexural strengthGreek letter epsilonRepeatability
The invention discloses a ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of electronic functional materials and devices. The ceramic material is prepared by the following steps: mixing a main crystalline phase material and a doping phase material through ball milling, then subjecting the mixture to dry pressing and moulding, and finally sintering. The ceramic material comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 85 to 97% of MgSiO3, 1 to 8% of borosilicate glass, 1 to 3% of Al2O3, 0.5 to 2% of ZnO, and 0.5 to 2% of La2O3; wherein the MgSiO3 is the main crystalline phase, and the doping phase comprises borosilicate glass, Al2O3, ZnO, and La2O3. Compared with the similar ceramic material in the prior art, the provided ceramic material has excellent properties: the ceramic-forming density (rho) is larger than 2.7 g / cm3, the dielectric constant [epsilon]<r> is low (less than 7.0), and the flexure strength is high (higher than 150 MPa). The preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low price, and good production repeatability. The low-cost, massive, and stable production of MgSiO3 ceramic substrate material becomes possible.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for preparing oxide ceramic through furnace-free rapid sintering at room temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing oxide ceramic through furnace-free rapid sintering at room temperature, particularly a method for preparing metal oxide ceramic or oxide solid solutionceramic or composite oxide ceramic or complex oxide ceramic or oxide ceramic matrix or complex-phase oxide ceramic directly and rapidly through rapid sintering at room temperature through the currentheat effect without the need of a high-temperature heating furnace. Compared with an existing ceramic sintering technology, the method has the advantages that densified sintering of various oxide ceramic materials can be achieved without high-temperature furnace equipment or sample heating in advance, the sintering time is short, the efficiency is high, the hardware investment is small, the energyutilization rate is high, the application range is wide, the process is simple, the energy-saving effect is good, and the cost is low. The method is suitable for rapidly preparing oxide ceramic and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:陕西智航昱铠新材料有限责任公司
Li series microwave dielectric ceramic material as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN109534806AImprove dielectric constantImprove temperature characteristicsLow-k dielectricCeramic
The invention provides a Li series microwave dielectric ceramic material as well as a preparation method and use thereof. The Li series microwave dielectric ceramic material is prepared from main materials of Li2CO3, SiO2 and MgO, and substituted material NiO. The Li series microwave dielectric ceramic material has the excellent features of low dielectric constant, high quality factor, high relative density and low densification temperature. The preparation method of the Li series microwave dielectric ceramic material improves the sintering features, the micromorphology and the electric performance of Li2MgSiO4 microwave dielectric ceramic at the low sintering temperature of 1120 to 1160 DEG C; under the condition of adding a small quantity of sintering auxiliary agents, the sintering temperature lower than 961 DEG C can be realized.
Owner:工业和信息化部电子第五研究所华东分所
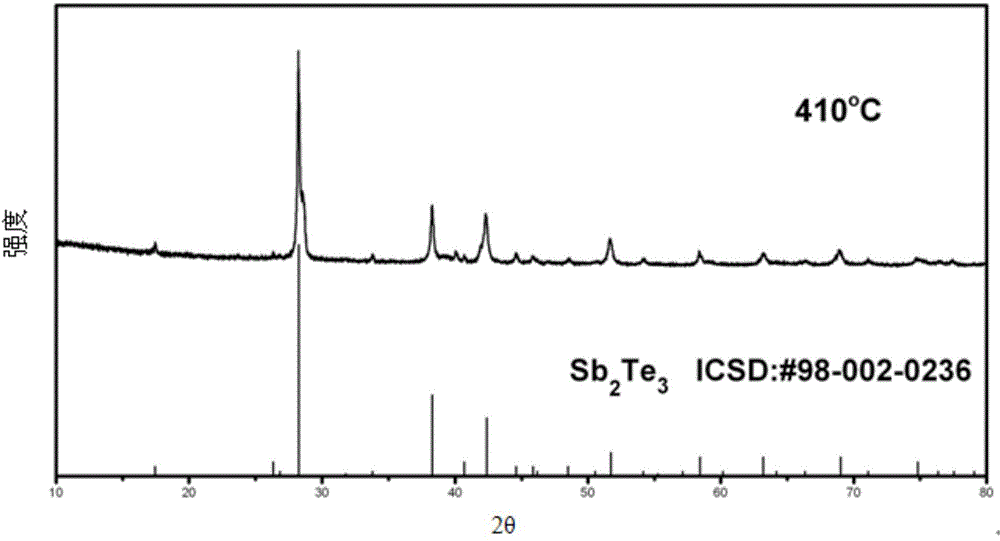
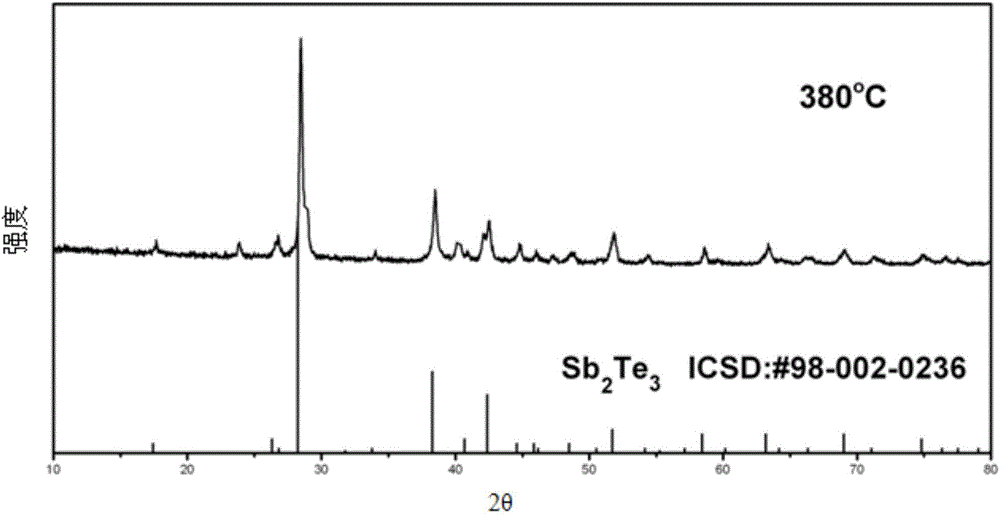
Method for quickly preparing antimony telluride thermoelectric material
ActiveCN106145062AQuick responseReduce energy consumptionBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsThermoelectric materialsReaction speed
The invention discloses a method for quickly preparing a Sb2Te3 thermoelectric material. The method comprises the following steps that 1, Sb powder and Te powder are weighed according to the stoichiometric ratio of all elements in Sb2Te3 and then ground and mixed to be uniform to obtain a mixed raw material; 2, discharging plasma activated sintering is conducted on the mixed raw material obtained in the step 1, and the compact single-phase Sb2Te3 thermoelectric material is obtained. The antimony telluride thermoelectric material has the advantages of being high in reaction speed, efficient, economical in energy, good in repeatability and the like and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Neodymium iron boron magnetic material with high coercivity
InactiveCN103617854AImprove intrinsic coercive forceImprove the characteristics of insufficient coercive forceMagnetic materialsCobaltBoron
The invention relates to a neodymium iron boron magnetic material with the high coercivity. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material with the high coercivity is formed by a main-phase alloy and a secondary-phase alloy through mixing. The main-phase alloy comprises, by weight, 64.5-68.5% of iron, 1.0-1.2% of boron, 30.2-34.3% of neodymium, 0.05-0.4% of molybdenum and 0.1-0.4% of gallium. The secondary-phase alloy comprises, by weight, 50.8-54.2% of iron, 0.8-1.2% of boron, 18.9-21.1% of neodymium, 12.8-16.3% of praseodymium, 8.9-11.1% of terbium, and 0.8-1.2% of cobalt. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material prepared with the method has high intrinsic coercivity.
Owner:NINGBO STAR MATERIALS HI TECH
Tungsten aluminum-nickel alloy sintered body and preparation thereof
The invention relates to a tungsten aluminum-nickel sintered body which is characterized by comprising tungsten aluminum powder and nickel powder; the expression formula of the tungsten aluminum powder is W1-xAlx, wherein, x is equal to 0.1 to 0.86; the mass proportion of the nickel powder in the sintered body is 5 percent to 80 percent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the tungsten aluminum powder and the nickel powder serve as raw materials, and are sintered under vacuum condition and through hot pressing, to prepare an alloy sintered body sample with high compaction and excellent performance. An alloy lump-shaped material with good crystal morphology and microstructure is synthesized by changing the mass percentage of nickel and controlling sintering temperature, pressure, time and other conditions. The mechanical properties of the alloy are as follows: the hardness is 5.13Gpa to 8.03Gpa, the bending strength is 1430Mpa to 1900Mpa, and the relative compaction of the sintered body is above 99 percent.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of Si-B-C-N (silicon-boron-carbon-nitrogen) ceramic with PBSZ (polyborosilazane) as additive
The invention provides a preparation method of Si-B-C-N (silicon-boron-carbon-nitrogen) ceramic with PBSZ (polyborosilazane) as an additive and belongs to the technical field of preparation methods of the Si-B-C-N ceramic. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, cubic silicon powder, hexagonal boron nitride powder, graphite powder and PBSZ are weighed in the mole ratio and in percentage by mass and taken as raw materials for standby use; S2, the raw materials weighed in S1 are put in a ball milling tank, high-energy ball milling is performed under the protection of the argon atmosphere, and ceramic powder containing amorphous Si-B-C-N is obtained; the ball-to-powder ratio of a ball material is (10-90):1, the ball milling diameter is 5-9 mm, and the ball milling time lasts 10-60 h; S3, the amorphous Si-B-C-N ceramic powder obtained in S2 is mixed with PBSZ, ball milling is performed under the protection of the argon atmosphere, and SiBCN compound powder is obtained; the ball-to-powder ratio is (1-20) :1, the ball milling diameter is 5-9 mm, and the ball milling time lasts 10-30 h; S4, the SiBCN obtained in S3 is subjected to spark plasma sintering, and the Si-B-C-N ceramic material with PBSZ as the additive is obtained.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Aluminium tungsten carbide hard alloy sintered body
The invention relates to a tungsten-cemented aluminium carbide sintered body, and the expression is(W1-xAlx)C-Co, in which x=0.1-0.86, which is alloy block-shaped material with good crystalline shape and fine texture. Proved by X-ray powder diffraction analysis and scanning electron microscope analysis, the tungsten-cemented aluminium carbide sintered body is of stable structure, improved crystallinity and higher degree of compactness. The tungsten-cemented aluminium carbide sintered body of this invention not only has glass hard and high-wearing feature of tungsten carbide, but also has lightweight, oxidation resistance and fine ductility of aluminium, which makes the alloy have high hardness, high bending strength and lower density and develop into new carbide alloy with high hardness, high strength, good workability and high oxidation-resistance temperature. The said material is hoped to be used in mechanical tool, glass-cutting, bolt die, broaching die, bowl, well drill, mine drill, cutting drill and electrical contact material.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Glass slurry, preparation method thereof and method for 3D printing of glass device
ActiveCN111825333AGood degreasingAvoid problems that affect printing accuracyGlass shaping apparatusGlass productionPhotoinitiatorGlycerol
The invention belongs to the technical field of glass device preparation, and particularly relates to glass slurry, a preparation method thereof and a method for 3D printing of a glass device. A high-temperature melting and casting process is adopted for preparing a macroscopic object through a traditional method, a chemical method is adopted for preparing a fine structure, the preparation processis dangerous, environmental pollution is large, energy consumption is high, and efficiency is low. The invention provides the glass slurry. The glass slurry comprises 600-1000 parts of silicon dioxide, 600-800 parts of acrylic resin, 1-13 parts of a light absorber, 1-15 parts of a photoinitiator, 1-15 parts of a polymerization inhibitor, 1-10 parts of glycerol, 1-18 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 1-18 parts of a defoaming agent and 1-15 parts of a sintering aid. By adding the sintering aid, the problem that high-viscosity slurry affects the printing precision is avoided, and a high-precision micro-lens glass device is obtained; through reasonable preparation of the glass slurry and the oxygen inhibition polymerization printing process, cracking is effectively inhibited, and the yield is increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of carborundum composite-phase ceramic
The invention discloses a producing method for carborundum complex phase ceram including a compound powder composed of carborundum and yttrium aluminitum garnet, firstly orderly doing a dry pressing and prepressing and cold isopressing, then sintering the disposed biscuit in vacuum without pressure; the weight percent proportion of the compound powder: 85-95% of carborundum and 5-15% of carborundum and yttrium aluminitum garnet; the preparing process including: 1) respectively adding the aluminum nitrate, yttrium nitrate into deionized water, then slowly adding methenamine solution, blending for 10-20 minutes at 35-80 DEG C to obtain transparent sol carborundum and yttrium aluminitum garnet; 2) adding carborundum fine powder, blending for 15-30 minutes in the water of 50-80 DEG C to obtain compound gel; 3) after the compound gel dry, heat processing for 2-6 hours at 900-920 DEG C to obtain compound powder. The produced carborundum complex phase ceram has a good mechanical property and a good thermal property.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microwave dielectric ceramic material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111807831ALow component complexityLow dielectric constantLow-k dielectricDielectric ceramics
The invention provides a microwave dielectric ceramic material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The microwave dielectric ceramic material comprises two materials, namely Zn3B2O6 and Mg3B2O6, the molar ratio of Zn3B2O6 to Mg3B2O6 is (1-x): x, and x is equal to 0.05-0.40. The microwave dielectric ceramic material is prepared from the following oxides in percentage by mole: 71.25-45.00% of a main material ZnO, 25.00% of a main material B2O3, and 3.75-30.00% of a substitute material MgO, wherein the sum of the molar percentages of the components is 100%, and the molar ratioof ZnO to MgO is (0.95: 0.05)-(0.60: 0.40). The microwave dielectric ceramic material has the excellent characteristics of low dielectric constant, high quality factor, high relative density, relatively stable temperature characteristic and low densification temperature.
Owner:YANCHUANG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH GANZHOU
Metal ceramic inert anode for molten salt electrolysis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101255577BAchieve densified sinteringImplementing Continuously Incrementing DistributionsElectrodesRare earthAlloy
The invention relates to a raw material component of cermet inert anode having metallographic phase distributed in gradient from internal side to external side and preparation technology. The material is applied to extracting non-ferrous metal (Al, rare earths and metals with high-melting point) by fused salt electrolytic route. The component comprises the cermet formed by at least one Ca-Fe-Ni-Ocomposite spinel oxide and at least one metallographic phase; wherein the anode material is composed of raw material with following mass prescription: 1% to 5% single metal or alloy, 1% to 99% spineloxide, 0.1% to 10% other metal oxides; oxidizing the materials selectively in process of sintering the materials by adjusting oxygen content in whole atmosphere to form high strength, high tenacity, high conductivity inner layer (high content of metal) having anticorrosion outer layer (high content of oxides) functional gradient structure. The method of the invention is capable of effectively solving problems that the cermet inert anode is connected with the metal guide and the metallographic phase is dissolved and oxidized selectively in electrolytic process.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Neodymium iron boron magnetic material suitable for motor
InactiveCN103632788AImprove degassing effectCrystallize fastMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsMagnetic materialsCeriumTitanium
The invention relates to a neodymium iron boron magnetic material suitable for a motor. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material is prepared by main phase alloy and auxiliary phase alloy in a mixed mode, the main phase alloy is prepared by, by weight, 64.5-68.5% of iron, 1.0-1.2% of boron, 30.2-34.3% of neodymium, 0.05-0.4% of stibium and 0.1-0.4% of gallium, and the auxiliary phase alloy is prepared by, by weight, 50.8-54.2% of iron, 0.8-1.2% of boron, 18.9-21.1% of neodymium, 12.8-16.3% of titanium, 8.9-11.1% of lanthanum and 0.8-1.2% of cerium. The neodymium iron boron magnetic material prepared according to the technical scheme has the advantages of having the mechanical property suitable for the motor and solving the problem that magnetic material of the motor are prone to being lost.
Owner:NINGBO STAR MATERIALS HI TECH
Aluminium tungsten carbide hard alloy sintered body
The invention relates to a tungsten-cemented aluminium carbide sintered body, and the expression is(W1-xAlx)C-Co, in which x=0.1-0.86, which is alloy block-shaped material with good crystalline shape and fine texture. Proved by X-ray powder diffraction analysis and scanning electron microscope analysis, the tungsten-cemented aluminium carbide sintered body is of stable structure, improved crystallinity and higher degree of compactness. The tungsten-cemented aluminium carbide sintered body of this invention not only has glass hard and high-wearing feature of tungsten carbide, but also has lightweight, oxidation resistance and fine ductility of aluminium, which makes the alloy have high hardness, high bending strength and lower density and develop into new carbide alloy with high hardness, high strength, good workability and high oxidation-resistance temperature. The said material is hoped to be used in mechanical tool, glass-cutting, bolt die, broaching die, bowl, well drill, mine drill, cutting drill and electrical contact material.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Tungsten aluminum-copper alloy sintered body and preparation thereof
The invention relates to a tungsten aluminum-copper alloy sintered body and a preparation method thereof; the tungsten aluminum-copper alloy sintered body is composed of tungsten aluminum powder and copper powder; the expression formula of the tungsten aluminum powder is W1-xAlx, wherein, x is equal to 0.1 to 0.86; the mass proportion of the copper powder in the sintered body is 5 percent to 80 percent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the tungsten aluminum powder and the copper powder serve as raw materials, and are sintered under vacuum condition and through hot pressing, to prepare an alloy sintered body sample with high compaction and excellent performance. An alloy lump-shaped material with good crystal morphology and microstructure is synthesized by changing the mass percentage of nickel and controlling sintering temperature, pressure, time and other conditions. The properties of the alloy are as follows: the electrical conductivity is 21.1MS / m<-1> to 29.4MS / m<-1>, the microhardness is 3.50 Gpa to 4.74Gpa, and the bending strength is 760Mpa to 1200Mpa.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Method for preparing apatite type composite solid electrolyte ceramic material by ultrasonic-assisted sol-gel method
ActiveCN109111228ANo impuritiesImprove sinterabilityFinal product manufactureElectrolytesApatiteSolid particle
The invention discloses a method for preparing apatite type composite solid electrolyte ceramic material by an ultrasonic-assisted sol-gel method, and relates to the technical field of preparation ofsolid electrolyte ceramic materials. The method comprises the following steps: weighing La(NO3)3.6H2O, Ba(NO3)2, C8H20O4Si, C16H36O4Ti, distilled water, citric acid and ethylene glycol; stirring to sufficiently dissolve the solid particles, and dropwise adding ammonia water to adjust the pH value; putting the blended solution in an ultrasonic cleaning machine to uniformly mix the solution under ultrasound, then transferring the solution onto a digital display heat collecting type magnetic stirrer, and stirring till a gel forms; taking out the stirred gel and drying in a drying oven; then taking out the dried gel, grinding and pre-sintering in a muffle furnace. Due to the doping of the metal elements barium and titanium, the sinterability of apatite electrolyte is improved, and densification sintering of the electrolyte can be realized at 1,500 DEG C.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
Preparation method of kularite ceramic solidifying body
InactiveCN103408304BGood chemical stabilityImprove mechanical stabilityRadioactive decontaminationRadiation stabilityHalf-life
The invention discloses a preparation method of a kularite ceramic solidifying body. The preparation method is characterized in that Ce2(C2O4)3.10H2O, An2 (C2O4)3.10H2O / oxide of An (An=Gd, Pr and Eu) and NH4H2PO4 are taken as raw materials; the high-quality kularite ceramic solidifying body is prepared according to formulation designing and the steps such as fine grinding, drying, granulating, forming, adhesive removing and vacuum hot-pressing sintering at a lower temperature. The kularite ceramic solidifying body prepared according to the preparation method is high in heat stability, mechanical stability, chemical stability and anti-radiation stability, is applicable to the safe solidification treatment of high-level waste, particularly applicable to the safe solidification treatment of high-level minor actinides waste which is high in radioactivity and toxicity, and long in half life period, and also applicable to the engineering application of high-level waste ceramic solidification treatment needing remote operation.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aluminium nitride ceramics material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101386539BDoes not significantly affect colloidal propertiesGood dispersion propertiesAluminium acetylacetonateNano al2o3
The invention discloses an aluminium nitride ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The method is to add nano-alumina to raw materials in the prior preparation method for preparation according to the prior preparation process. In-situ growing nano-alumina can be obtained directly through adding the nano-alumina, or indirectly through adding organic aluminum, such as aluminium secondary butylate, aluminium isopropoxide or aluminium acetylacetonate, and by means of low-temperature decomposition of the organic alumina. The method can be applied to dry pressing and tape casting shaping, can obtain slurry with good dispersing characteristic and even mixing of the aluminium nitride and the nano-alumina by the ceramic preparation process, such as normal pressure, hot pressed sintering or the like, and is favorable for the improvement of sintering activity of materials, the reduction of sintering temperature, the improvement of luster uniformity, planeness and roughness for a ceramic substrate, and the reduction of production cost. The aluminium nitride ceramic material and the preparation method thereof can be widely applied to the field of aluminium nitride ceramic production.
Owner:无锡海古德新技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com