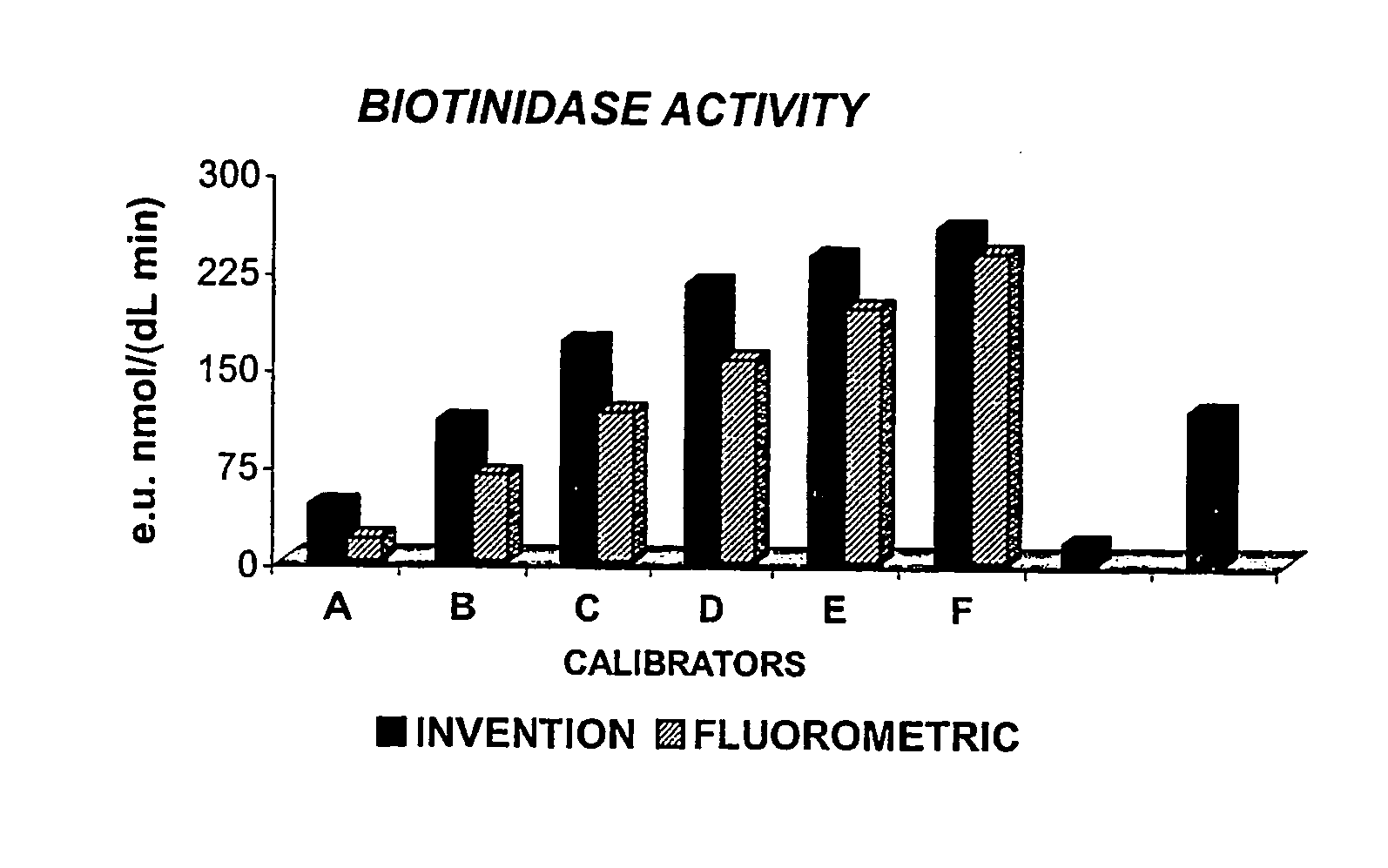
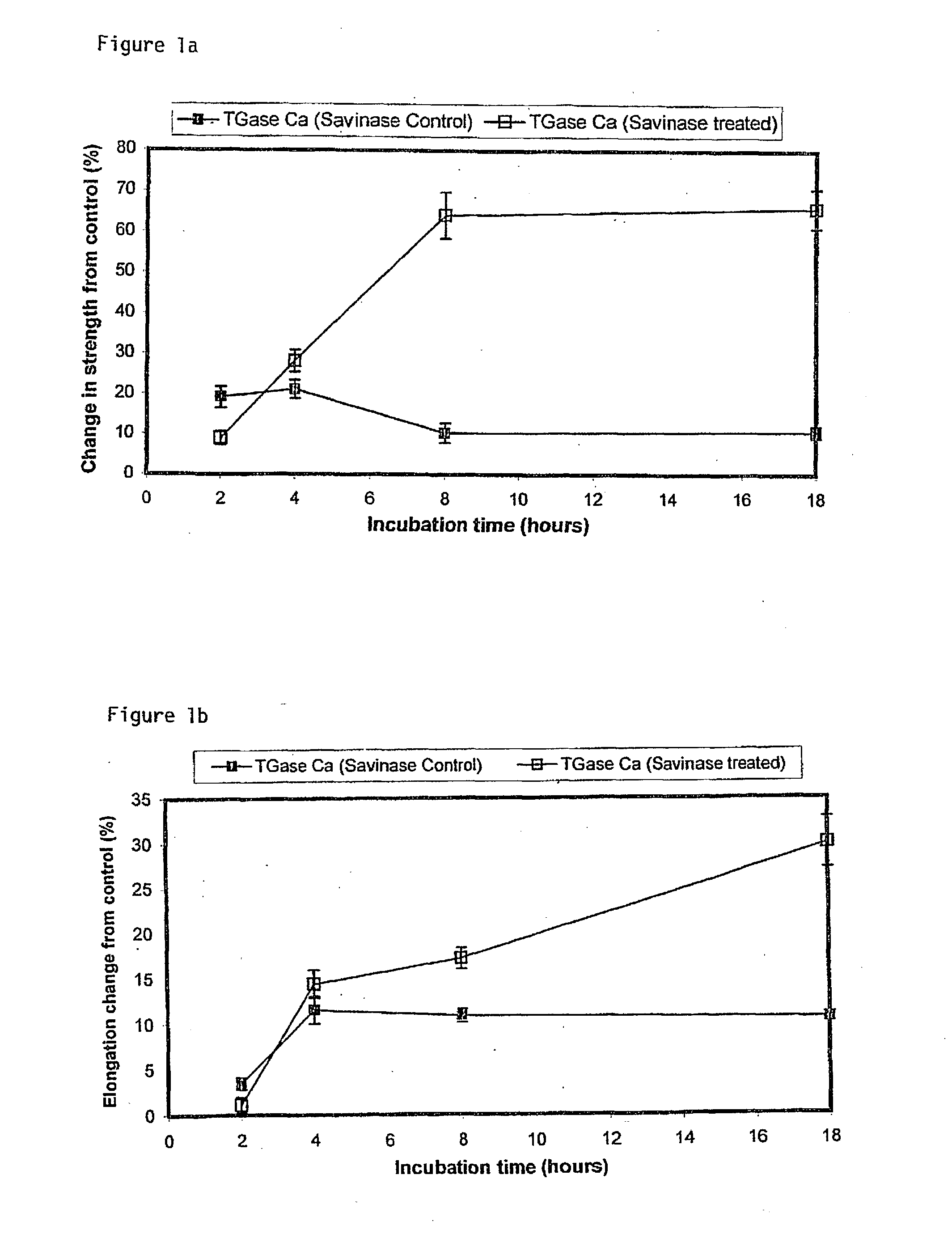
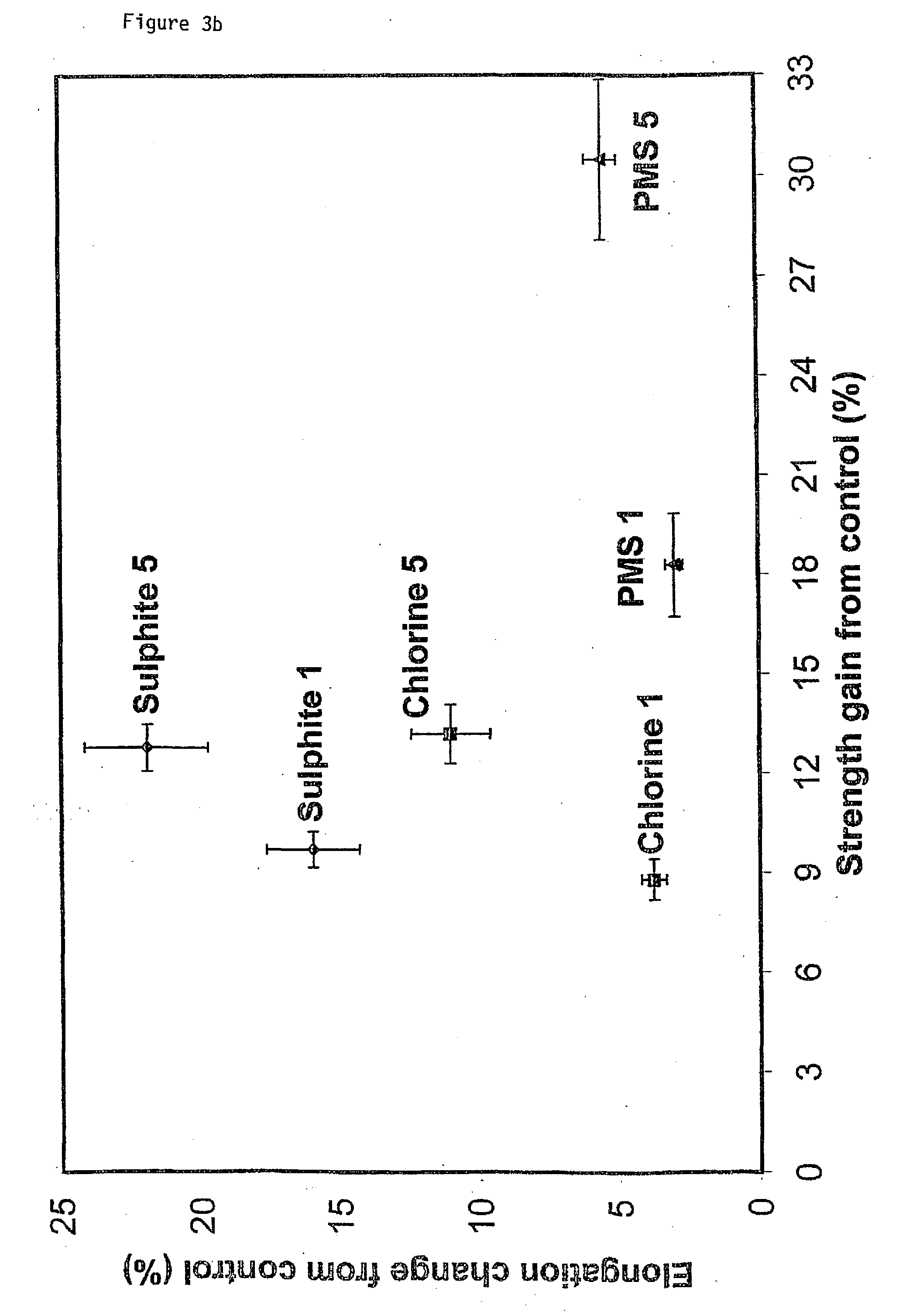
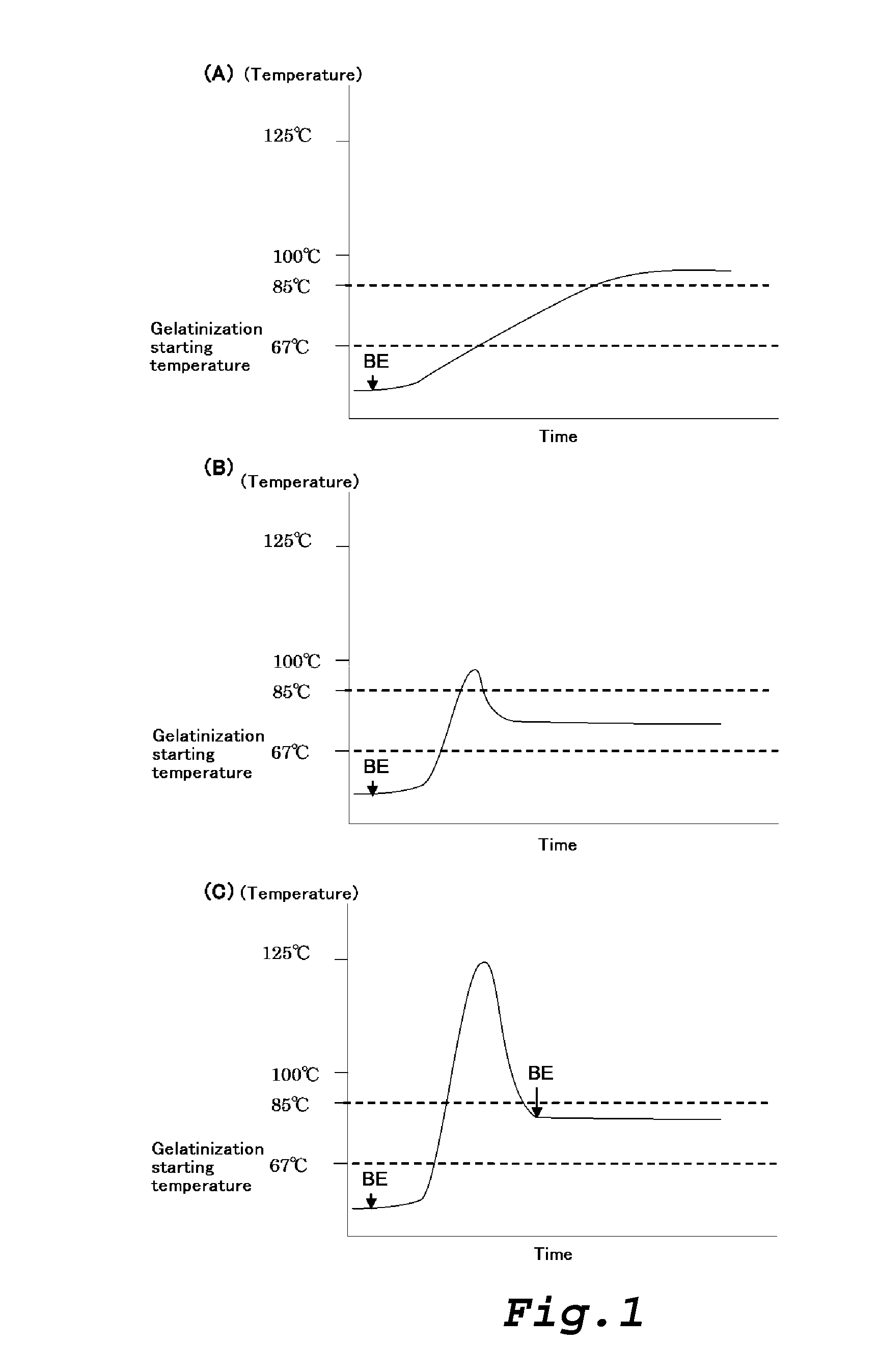
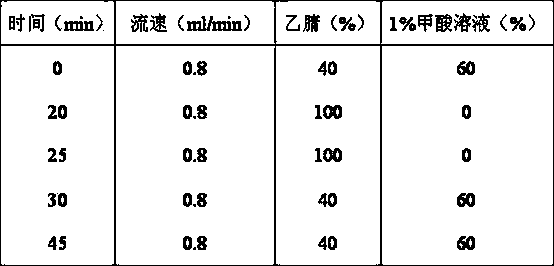
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Enzyme action" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The mechanism of enzymatic action. An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site, catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed, and then allows the products to dissociate (separate from the enzyme surface). The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the enzyme–substrate complex.
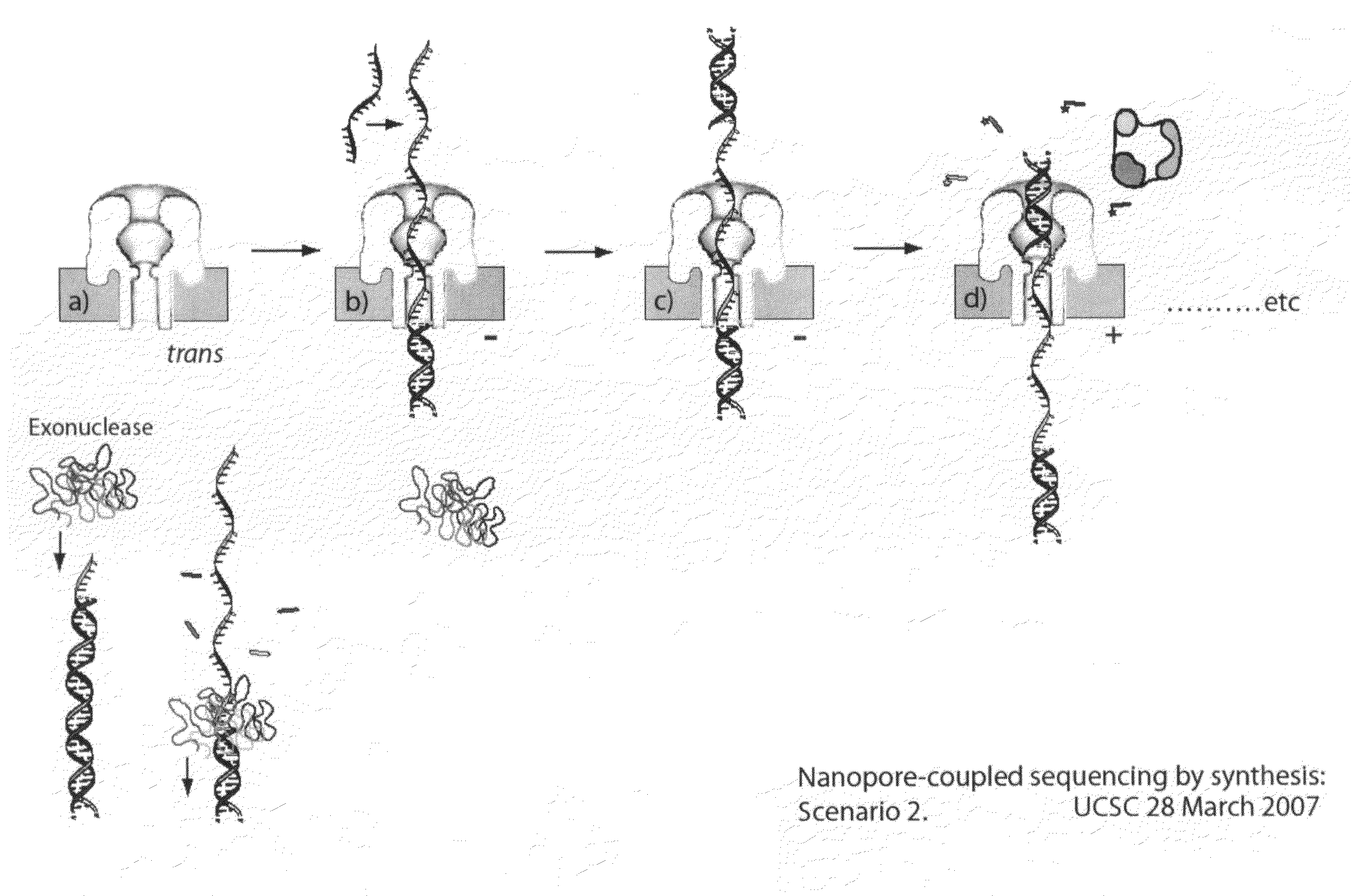
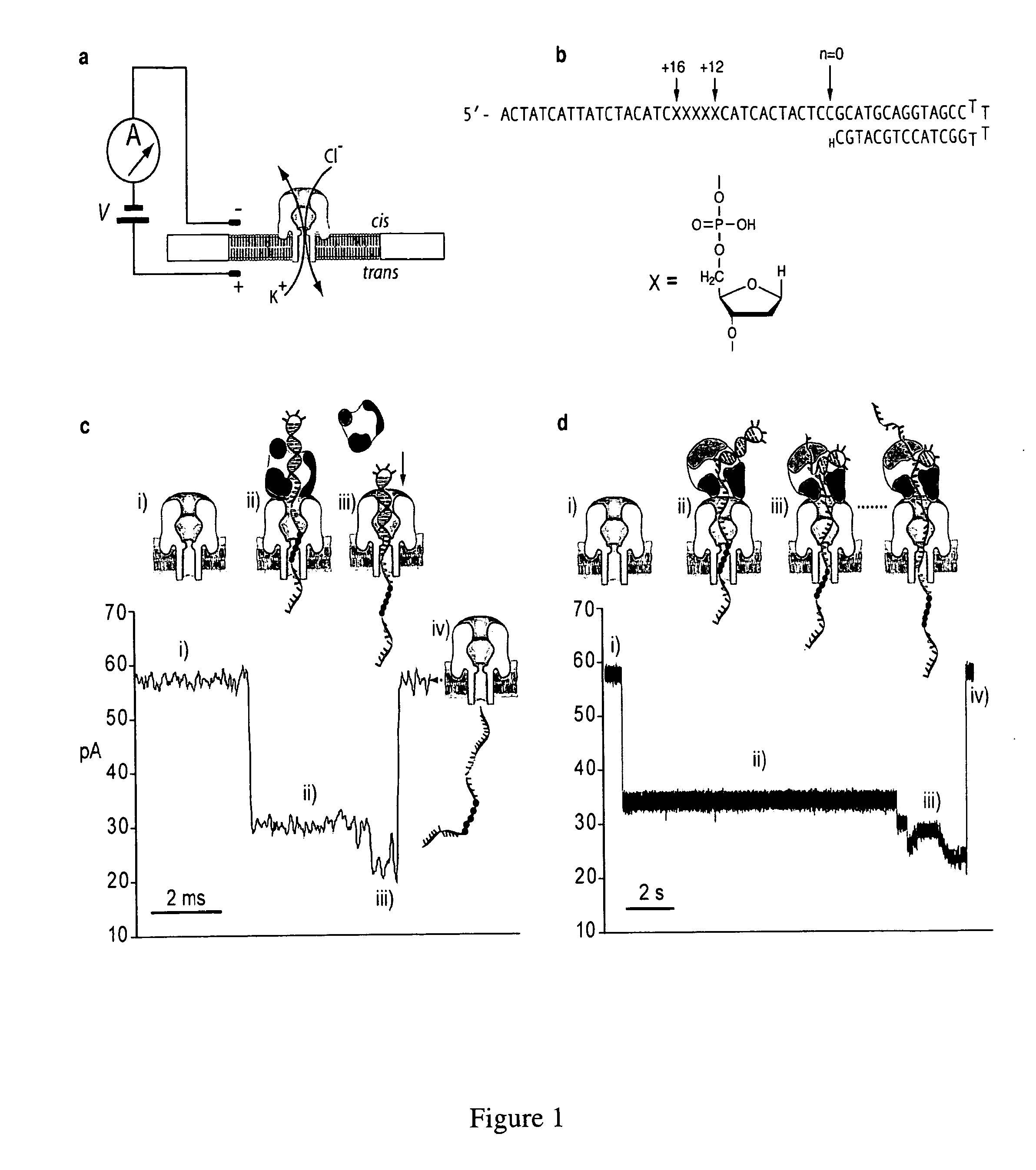
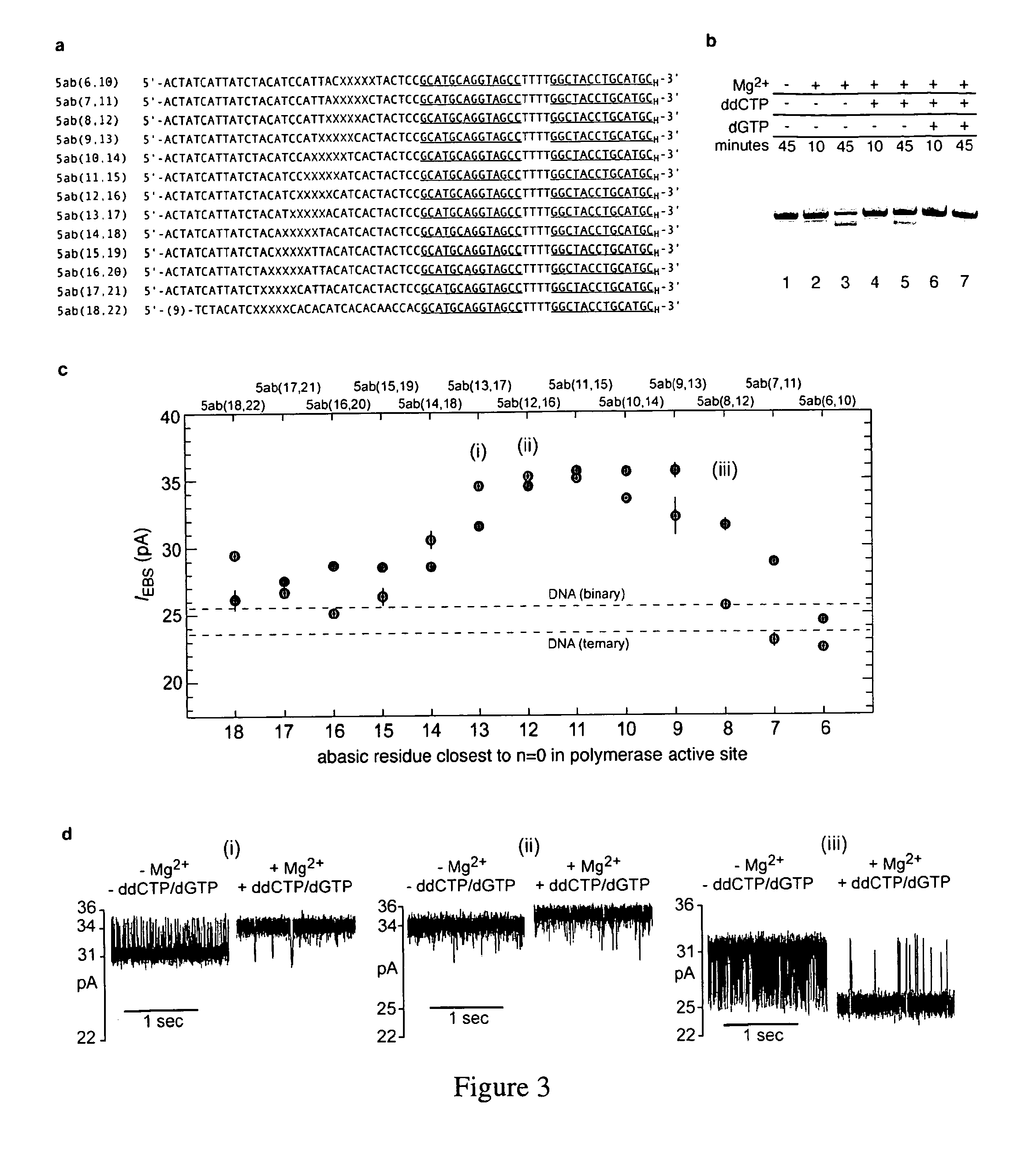
Compositions, devices, systems, for using a Nanopore
ActiveUS20100035260A1Low costRapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore in the absence of requiring a terminating nucleotide. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of drug discovery, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
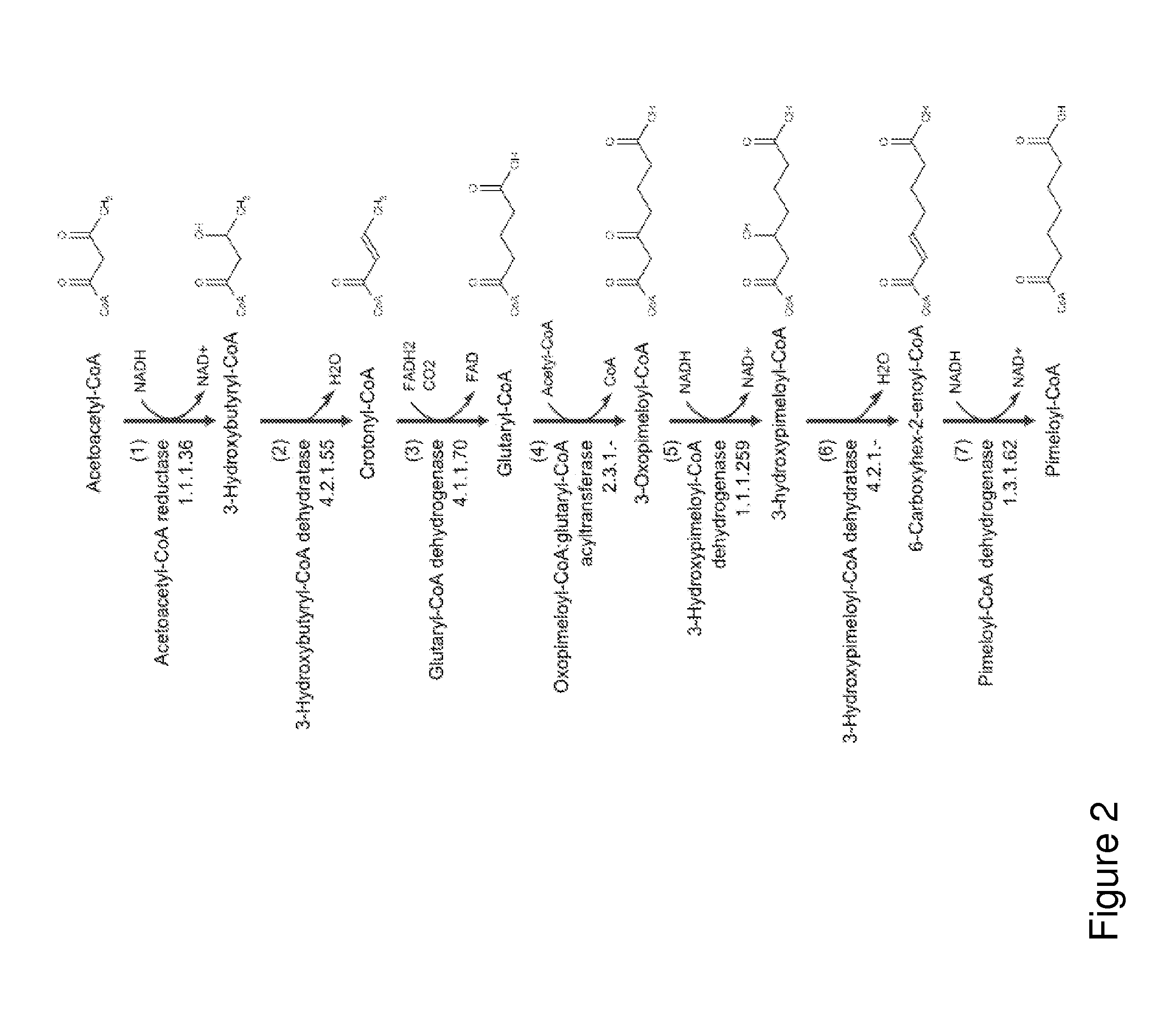
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has cyclohexanone pathways that include at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a cyclohexanone pathway enzyme. A pathway includes a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase and an enzyme selected from a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, and a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase. A pathway includes an enzyme selected from a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA reductase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate reductase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, and a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase. A pathway includes an adipate semialdehyde dehydratase, a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydrogenase, and a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydratase. A pathway includes a 3-oxopimelate decarboxylase, a 4-acetylbutyrate dehydratase, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase, a 2-cyclohexenone hydratase, a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase and an enzyme selected from a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA synthetase, a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), and a 3-oxopimeloyl-coA transferase. Each these pathways can include a PEP carboxykinase. A method for producing cyclohexanone includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
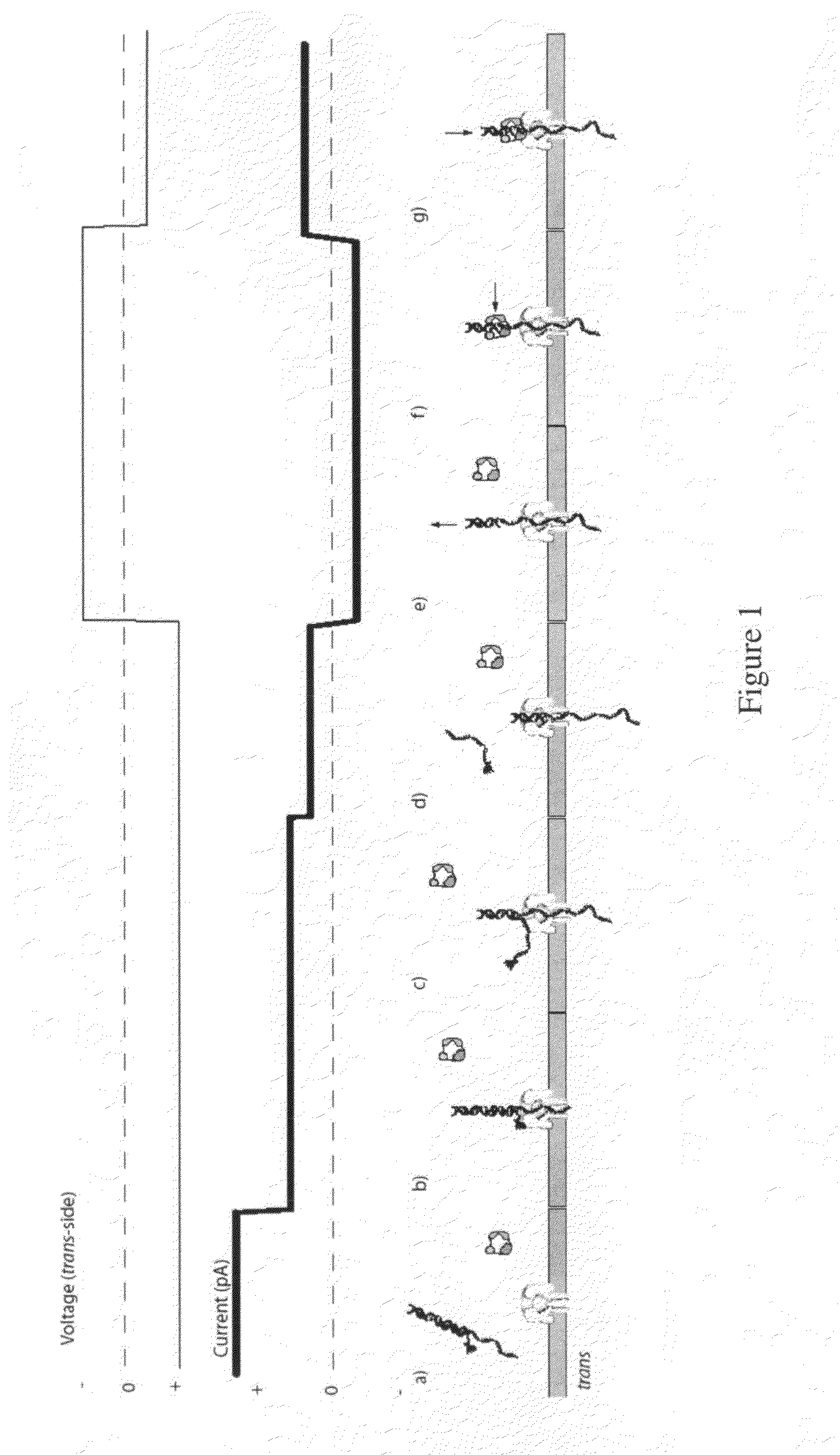
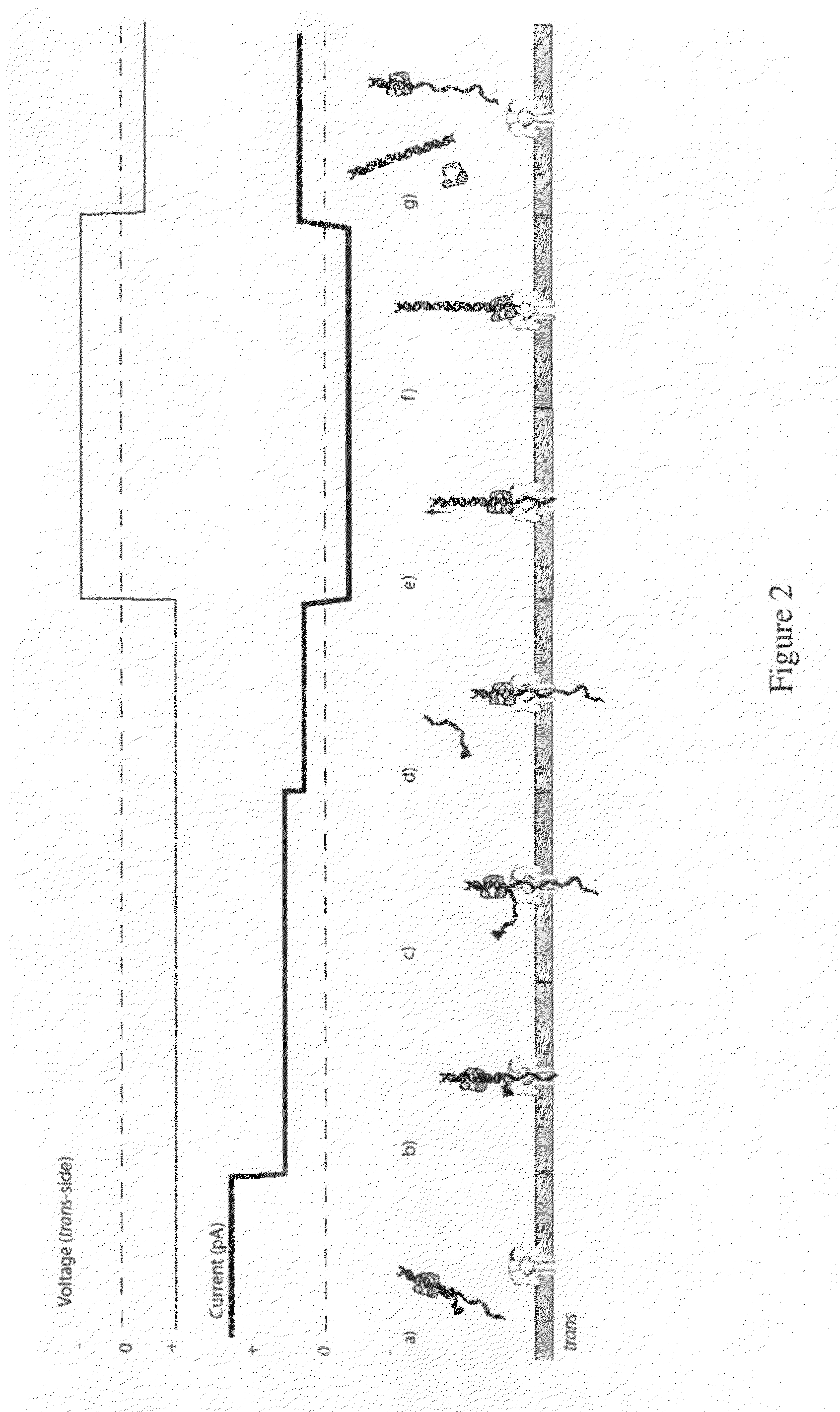
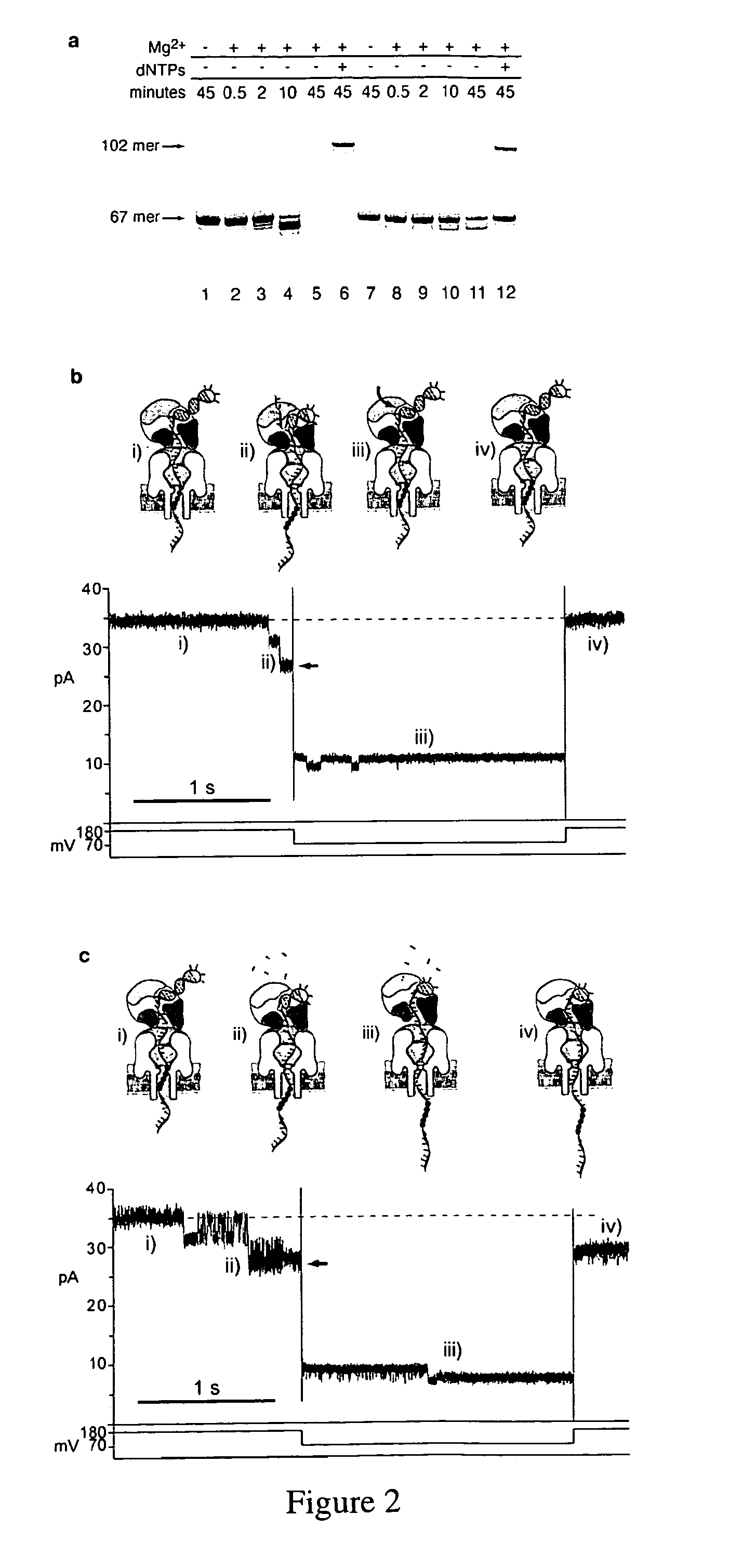
Control of DNA movement in a nanopore at one nucleotide precision by a processive enzyme
InactiveUS20140051068A1Improve the activity rateReduce decreaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore. Of particular note is the stability of the system in a saline medium and to detect individual nucleotide bases in a polynucleotide in real time and which may be used to sequence DNA for many hours without change of reagents. The invention is of particular use in the fields of forensic biology, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Binding Agents
The invention relates to binding agents which can be induced to aggregate in response to a specific stimulus. In preferred embodiments the binding agents comprise at least a binding member for a binding partner and the binding partner. At least one of the binding member and binding partner are reversibly masked such that a plurality of binding agents are not able to aggregate with one another until the masked moiety is unmasked. Preferred mechanisms to induce aggregation include irradiation and enzyme action. Applications of the invention include signal amplification in biochemical assays and provision of high local concentrations of therapeutic agents in vivo.
Owner:SELF COLIN
Chitin oligose preparing process
InactiveCN1847267AImprove efficiencySimple process routeOligosaccharidesFermentationBiotechnologyDegradative enzyme
The present invention relates to chitin oligose preparing process, and is especially enzyme generating fermentation process to degrade chitin colloid for preparing bioactive chitin oligose. The preparation process has simple technological path, effective inhibition of further degradation of bioactive chitin oligose, reuse of degrading enzyme and other advantages, and is suitable for industrial production. The preparation process includes: culturing Aeromonascaviae strain to obtain fermented liquid, centrifugally separating the fermented liquid to obtain enzyme supernatant; preparing chitin colloid; compounding chitin colloid buffer solution in an enzyme reactor and adding abacterial enzyme liquid for enzymolysis to obtain enzymolyzed chitin oligose liquid; four stages of membrane separation to obtain concentrate and spray drying to obtain bioactive chitin oligose product.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110343676AHigh substrate concentrationLow costOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringL-glutamate dehydrogenaseEnzyme action
The invention discloses an L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. The sequence of the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant comprises a sequence obtained by mutating amino acid residue Aat position 166 and / or amino acid residue V at position 376 in a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 into a basic, hydrophilic or small hindered amino acid residue. The application comprises the followingsteps: subjecting 2-oxo-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butanoate to amination reaction in the presence of an L-amino acid dehydrogenase mutant, an inorganic amino donor and a reduced coenzyme NADPH to obtain L-glufosinate salt; and further acidifying the obtained L-glufosinate salt to obtain L-glufosinate. Compared with wild-type L-glutamate dehydrogenase, the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant of theinvention has a higher catalyzed substrate concentration when used for preparing the L-glufosinate, thus the enzyme action efficiency is improved, the reaction cost is reduced, and industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIZHOU ZIYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Magnetic particle and single base extension based SNP automatic detection method
InactiveCN101445834AImprove accuracyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceEnzyme
The invention discloses a novel single nucleotide polymorphism detection method based on magnetic particles and single base extension technology. The detection method is characterized in that through extension primer of a detected locus marked with biotin, specific ddNTP marked with fluorescence is extended to the 3' end of the primer under the action of Taq enzyme, so as to amplify the genotype signal of the template through thermal cycle reaction including denaturation, annealing and extension. Then the extension primer is fixed to the surface of magnetic particles modified with avidin to detect the subtype signal of the specimen. The detection method has the advantages of simplicity, accuracy, low cost, high flux and high sensitivity, can realize automatic operation and has higher practicability than the traditional method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Pullulanase with high secretion capacity and application thereof
ActiveCN109628433AHigh extracellular secretion capacityEasy Fermentation PreparationFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses pullulanase with high secretion capacity and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering. The pullulanase has high extracellular secretion capacity, and escherichia coli carrying the pullulanase is fermented in a shake flask for 48 hours, the total enzyme activity in the fermentation liquor can reach 212.0 U mL<-1>, wherein the extracellular enzyme activity reaches 200.5 U mL<-1>, which accounts for 94.5% of the total enzyme activity; therefore, the pullulanase is easy to prepare through fermentation, and the control difficulty and cost of the fermentation process can be obviously reduced; the pullulanase has mild action condition, and can hydrolyze alpha-1, 6-glucosidic linkage at a condition with a temperature of 40-60 DEG C and a pH value of 6.0-7.5, therefore, the pullulanase can reduce the cost in industrial transformation, and has potential utilization value in industries such as food, starch sugar and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Potato anti-browning agent, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of anti-browning agents, and particularly relates to a potato anti-browning agent, and a preparation method and application thereof. The potato anti-browning agent is prepared by mixing ascorbic acid, cysteine, edible acidic pH regulator, chlorine additive, calcium additive, antioxidant and water according to a certain order. According to the invention, the potato anti-browning agent contains multiple components capable of inhibiting enzyme activity and changing enzyme action environment, such as citric acid, ascorbic acid, cysteine and malic acid; oxidation of a substrate can be prevented; sulfite is not contained, thereby avoiding injury of sulfate to a human body; the potato anti-browning agent is simple to operate and long in fresh-keeping time; and the browning degree can be kept basically unchanged in a preservation period of 30 days.
Owner:临沂星火知识产权服务有限公司
Mass spectrometry methods for simultaneous detection of metabolic enzyme activity and metabolite levels
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Fragrant black tea red-enriching technique
ActiveCN102726555AMellow tastePromote safe productionPre-extraction tea treatmentBiotechnologyTea consumption
The invention provides a fragrant black tea red-enriching technique. Combined with the traditional tea technology and black tea process, the technique provided by the invention has no added foreign substances in the producing process and promotes aromatic precursor, amino and sugars in the fresh leaves to be subjected to enzyme action to change and then form various aromatic substances by the processes such as sun withering, green making, rolling, red-enriching, and drying, so that the black tea has thicker fragrance; meanwhile, complex catechins such as ester type catechins which have strongbitter taste are subjected to oxidative condensation to generate theaflavin and thearubigins with thickened taste. With the adoption of the technique, the natural novel black tea products with various fragrance and mellow taste are produced without adding any flower and additive, so the production safety of tea is ensured and the industrial benefit is enhanced; the safe and healthy tea consumption concept is satisfied; the problems of single black product and way of summer and autumn are solved; and the economic benefit is improved by times than the traditional methods.
Owner:保山康源生物有限责任公司
Method for enzymatic treatment of textiles such as wool
InactiveUS20030154555A1Good dimensional stabilityImprove yarn strengthPhysical treatmentWrinkle resistant fibresFiberActive agent
The application provides a method of treating fibrous textile goods comprising treating the fibrous textile goods with an enzyme. This enzyme can be used to covalently link one or more active functional compounds to the fibres and / or to trap one or more acitve functional compound within an inter-fibre matrix and / or within an intra-fibre matrix formed by the action of the enzyme. Preferably, the enzyme is a traglutaminase, especially a calcium-dependent transglutaminase. The enzyme may be used to add primary-amine containing active agents to the textile goods and also for the addition of proteins or peptides that have functional groups linked to them.
Owner:NOTTINGHAM TRENT UNIVERSITY
Method for industrially producing cyclic-structure-containing branched glucan
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for industrially producing a branched glucan having a cyclic structure. The method for producing a branched glucan having a cyclic structure comprises the steps of: (1) preparing a mixed liquid which contains a branching enzyme in which starch granules are suspended at a concentration of 5% by weight or more and 50% by weight or less, and allowing the branching enzyme to act on starch in the starch granules, wherein a temperature of the mixed liquid at the time of preparation is 0° C. or higher and not higher than the gelatinization starting temperature of the starch granule; and (2) elevating the temperature of the mixed liquid to 85° C. or higher and 129° C. or lower, wherein in the method, none of α-amylase, β-amylase, amyloglucosidase and a transglucosidase is added to the mixed liquid.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Preparation method and application of pea protein peptide
InactiveCN106260498AHigh activityImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyFood ingredient as antioxidantVegetable proteins working-upNeutral proteaseFreeze-drying
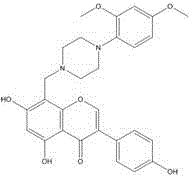
The invention belongs to the field of food processing, and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of pea protein peptide. The preparation method of the pea protein peptide includes the steps that pea protein powder is extruded and crushed, and an enzyme accelerant 8-((4-(2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-yl)methyl)-5,7-dyhydroxyl-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H- benzopyran-4-one and neutral protease are added into the extruded pea protein powder together to carry out enzymolysis on the pea protein powder to prepare pea protein polypeptide powder. As the pea protein powder is extruded, a spatial structure is changed into a chain structure beneficial to enzyme action, and the use level of the neutral protease is lowered; besides, the neutral protease accelerant improves the activity of the neutral protease, shortens enzymolysis time and improves enzymolysis efficiency. As the pea protein polypeptide powder is obtained after the pea protein powder is subjected to enzymolysis and then freeze-dried, the free radical scavenging efficiency is higher. Compared with pea protein polypeptide powder without any neutral protease accelerant added, the superoxide anion free radical scavenging rate is increased by 10.5-31.7%, and the pea protein polypeptide powder can be applied to development of anti-aging and anti-oxidation functional foods.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Agar-digesting enzyme and utilization thereof
An agar-digesting enzyme having the following properties. (1) Function: Hydrolyzing beta-1,4 bond of agarose to form neoagarooligosaccharides. (2) Substrate specificity: Acting at least on polysaccharides having a skeleton in which D-galactose units and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose units are bonded to each other alternately via beta-1,4 bond and alpha-1,3 bond (for example, agar and agarose) and oligosaccharides having the above skeleton to form agar-origin oligosaccharides. (3) Effect of temperature: Sustaining its activity even after heating to 54°C or higher for 30 minutes. Because of having a high activity at a high temperature compared with the existing agar-digesting enzymes, this enzyme can elevate the digestion speed of agar and thus is advantageously usable for industrial purposes.
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Refrigeration pretreatment production line for shrimps
ActiveCN103431495AWeaken the U-turn phenomenonCurb corruptionFood preservationQuick FreezeEngineering
The invention relates to a refrigeration pretreatment production line for shrimps. The production line is characterized in that: the production mainly comprises a conveying mesh belt, the conveying mesh belt is divided into a water spraying segment conveying mesh belt, a water draining segment conveying mesh belt and a freezing segment conveying mesh belt from the front to the rear according to technological requirements; the water spraying segment conveying mesh belt and the water draining segment conveying mesh belt are provided with a salt brine spraying, cooling and water draining device; the freezing segment conveying mesh belt is provided with a fast freezing device; the discharging end of the freezing segment conveying mesh belt is provided with a vibration ice coating device; and thus the refrigeration pretreatment production line for the shrimps is formed, and the whole refrigeration pretreatment on the shrimps in the production line is realized, the treatment efficiency on the shrimps is substantially improved, and the health status of the shrimps is improved. Also, the salt brine sprayed on the surface of the shrimps helps to inhibit corrosion caused by biological action and enzyme action, weaken the generation conditions of large ice crystal in the freezing segment, reduce possibility of damages to shrimp tissues and guarantee the quality of the shrimps; and the shrimps do not need secondary freezing because of vibration ice coating, and thus energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:NANTONG SINROFREEZE EQUIP
Composition & methods of screening
ActiveUS20160263144A1Strong specificityWell mixedCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningMicroorganismBiotechnology
The present invention relates to a prebiotic composition comprising a microbially produced oligosaccharide, wherein the oligosaccharide is characterised by being selective for a pre-determined probiotic bacterial strain and also capable of being produced by the pre-determined probiotic bacteria by reverse enzyme action. The present invention also relates to methods of screening a composition suitable for use as a prebiotic and methods for screening of prebiotics for incorporation into synbiotic formulations.
Owner:OPTIBIOTIX
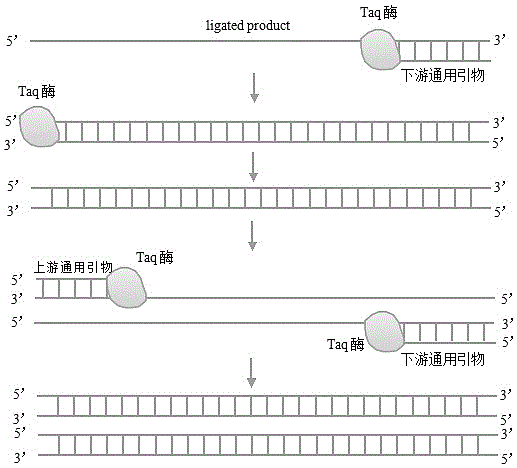
Method and kit for detecting high-risk HPV (human papillomavirus) E6/E7 mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) by ligase
InactiveCN105112564AEliminate the tedious steps of extractionReduce cumbersome stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman papillomavirusComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a method and a kit for detecting high-risk HPV (human papillomavirus) E6 / E7 mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) by ligase. The method is characterized in that specific connection primers are connected into a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment complementary with a target sequence of the HPV E6 / E7 mRNA under the action of the ligase, and the successfully connected cDNA fragment can be amplified by a pair of universal primers in a later fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system, in other words, eighteen high-risk HPVs capable of causing cervical cancer can be detected in the same amplification system by the single fluorescent PCR technology, so that the problems, such as low amplification efficiency and sensitiveness, caused by excessive primers are solved effectively. The aim of HPV E6 / E7 mRNA detection is to screen out high-risk groups in HPV-infected people groups, so that the method has more significance in clinical diagnosis as compared with existing HPV genome L1 distinguishing type detection methods.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HEAS BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for producing stock solution from sea cucumber by using ultrasonic glycolysis
The invention relates to a method for producing stock solution from sea cucumber by using ultrasonic glycolysis. Using fresh sea cucumbers as raw materials, the stock solution is prepared by the following processing steps: cutting intestines, cleaning, mincing, refining, conducting ultrasonic glycolysis, and decoloring and deodorizing and the like. The product can be further processed into food or drug with all kinds of characters and dosage forms, such as capsules, tablets, and granules and the like. Besides, with the aid of enzyme action of fresh sea cucumbers and auxiliary addition of accompanying batches of sea cucumber intestines, the sea cucumbers are colloid-refined and then beer yeast is added. Then the ultrasonic glycolysis is conducted without adding acid, alkali or enzyme, thus leading to a high yield of hydrolysate, good product taste, easy absorption by human body, simple production process, low production cost and shortened manufacturing time.
Owner:威海健方医药研究所
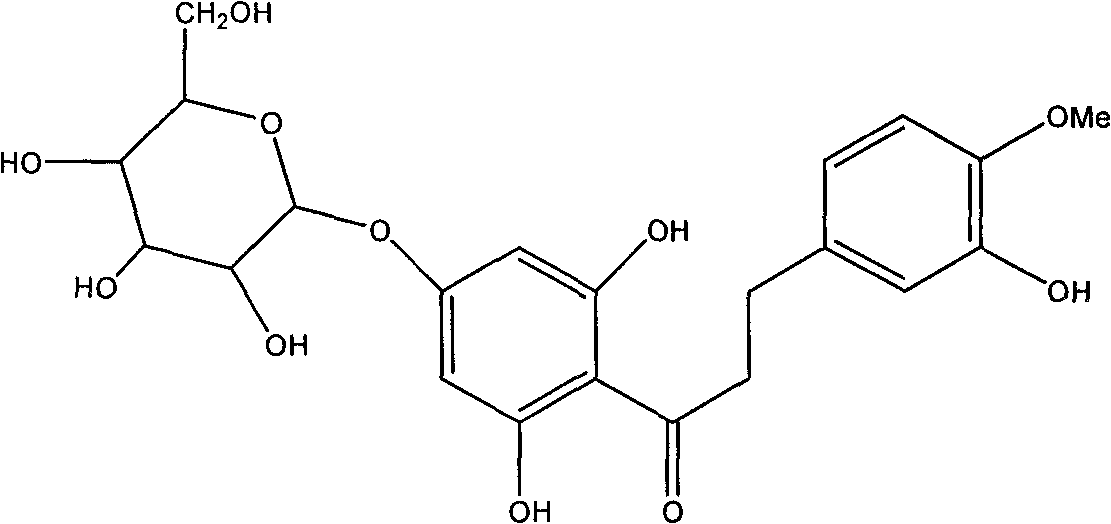
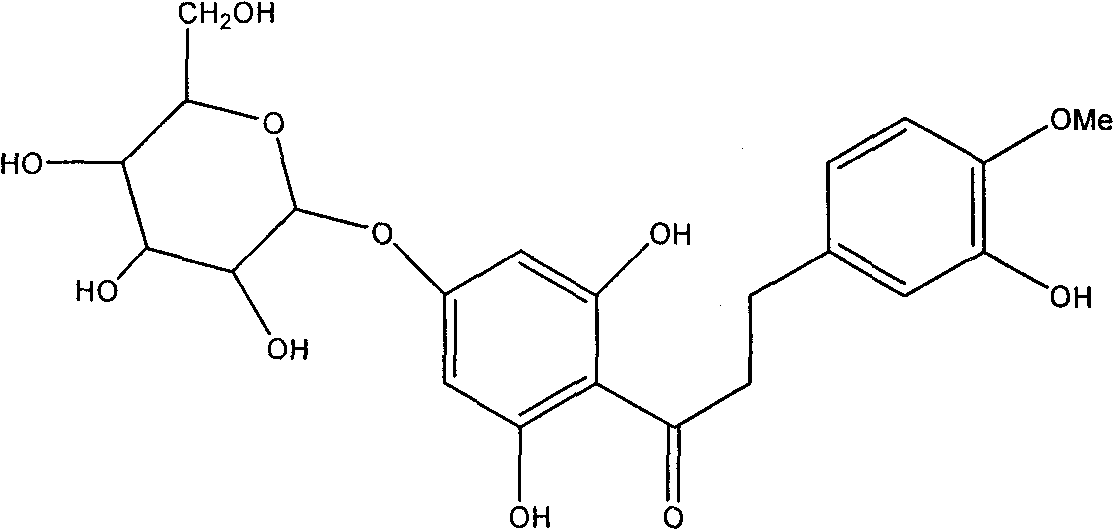
Hesperetin dihydrochalcone-7-O-glucoside and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101787062AImprove sweetness qualitySugar derivativesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a hesperetin dihydrochalcone-7-O-glucoside, wherein the compound is obtained by generating a rhamnose deglycosylation reaction of new hesperidin dihydrochalcone in water or a water and organic solvent system under an enzyme action. The sweetness multiple of the hesperetin dihydrochalcone-7-O-glucoside prepared by the invention is about 1800 times of sucrose, and the hesperetin dihydrochalcone-7-O-glucoside can be widely used for industries of foods, medicines, feed, daily use chemicals and the like and used as a sweetening agent, a flavoring agent, a flavor enhancer and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG FOOD IND INST +1
High-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase
ActiveCN103865903AHigh specific vitalityIncrease vitalityPulp bleachingMicroorganism based processesSubmerged fermentationEnzyme action
The invention discloses high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase and belongs to the technical field of preparation of enzymic preparations. The high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase is prepared by taking bacillus thermophilus 701 for producing the high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase as an original strain and performing liquid submerged fermentation. The specific activity of the high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase is 350-420IU / ml, the applicable temperature range is 40-75 DEG C, the optimal reaction temperature is 65 DEG C, the enzyme activity at the temperature of 75 DEG C is completely stable, the applicable reaction pH value ranges from 5.0 to 11.0, the enzyme activity at the pH value of 11.0 is completely stable, and the optimal reaction pH value is 10.0. Compared with the conventional high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase, the high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase in the invention is high in enzyme activity, high in temperature resistance, high in alkali resistance and wide in enzyme action optimal pH value range and is particularly suitable for industrial requirements in the fields of papermaking, foods and feed.
Owner:HUNAN HONGYING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Preparation method and new application of lupulus natural pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN104189086AClear ingredientsChemical Composition FeaturesMetabolism disorderKetone active ingredientsMoraceaePharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a composition which is extracted from moraceae lupulus and takes xanthohumol, isoxanthohumol, 8-isopentenyl naringenin, 6-isopentenyl naringenin, alpha-acid and beta-acid as main ingredients. An in-vivo experiment initially proves that the composition disclosed by the invention has activity of inhibiting lipase, so that the composition disclosed by the invention has new application in preparation of a medicine with a lipase inhibiting effect.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for preparing pea protein polypeptide powder
InactiveCN106011211AHigh activityImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyFermentationFood ingredient functionsFreeze-dryingChain structure
The invention belongs to the food processing field and relates to a method for preparing pea protein polypeptide powder. The method comprises extruding and crushing a pea protein, adding a papain promoter and a papain into the pea protein powder, and carrying out enzymolysis and enzyme deactivation on the pea protein powder to obtain the pea protein polypeptide powder. The space structure of the pea protein powder becomes a chain structure conducive to enzyme action after extrusion so that the use amount of papain is reduced. The papain promoter improves the activity of papain, shortens enzymolysis time and improves the efficiency of enzymolysis. After the pea protein powder enzymolysis, the pea protein polypeptide powder is obtained by freeze drying so that free radical removal efficiency is high. Compared with pea protein polypeptide powder without the papain promoter, the pea protein polypeptide powder provided by the invention improves a hydroxyl radical removal rate by 22.3%-51.1%. The pea protein polypeptide powder can be used in the development of functional foods for resisting aging and oxidation.
Owner:YANTAI SHUANGTA FOOD
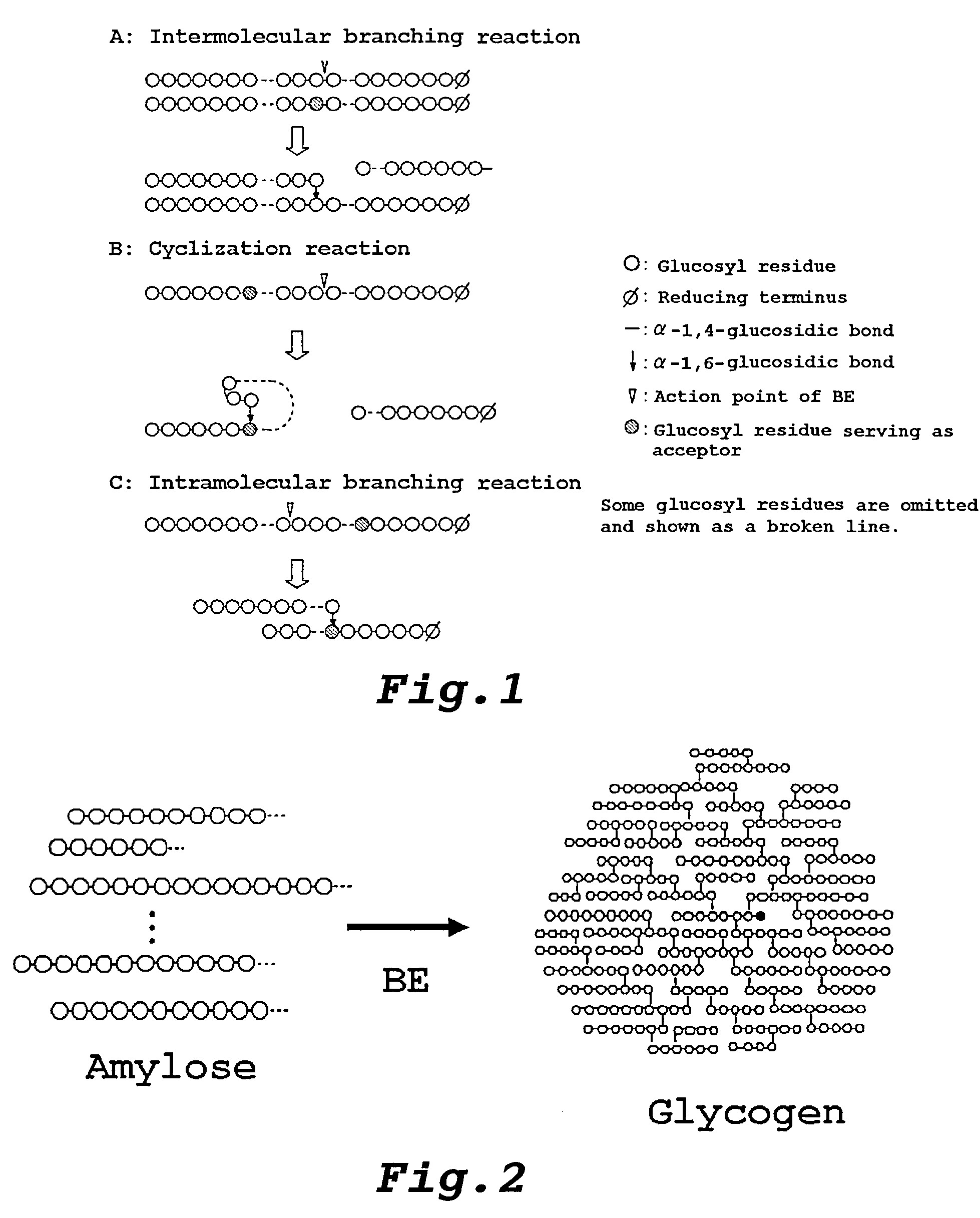
Method of producing glycogen
A method of producing glycogen comprising a step of: allowing a branching enzyme having the ability to synthesize glycogen to act on a substrate in a solution to produce a glycogen, wherein the substrate is an α-glucan being linked mainly with α-1,4-glucosidic bonds and having a degree of polymerization of 4 or more, and the number-average molecular weight of saccharides in the solution before initiation of the reaction is more than 180 but not more than 150,000. (The branching enzyme activity of the branching enzyme) / (the molecular-weight-decreasing activity of the branching enzyme) can be 500 or less. The branching enzyme can be a thermostable branching enzyme.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Enzyme silk noodle preparation method, wherein alum is replaced by starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes
The invention discloses an enzyme silk noodle preparation method, wherein alum is replaced by starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes, and belongs to the technical of food engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the enzyme silk noodle preparation method, plant starch is taken as a raw material; based on a traditional silk noodle preparation method, a starch branched chain hydrolytic enzyme action period is increased after starch gelatinization period in silk noodle preparation, wherein after starch gelatinization, the temperature of an obtained starch gelatinization liquid is reduced to a temperature suitable for the action of the starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes, and pullulanase, isoamylase, and the like, which are capable of hydrolyzing starch branched chain alpha-1,6 glucosidic bonds are added, and appropriate thermal insulation is carried out; or the starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes can be added before gelatinization, and after starch gelatinization, the obtained starch gelatinization liquid is subjected to appropriate thermal insulation at the temperature suitable for the action of the starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes. The other steps are the same as that of the traditional silk noodle preparation method. The enzyme silk noodle preparation method without using alum is provided, food safety of the added starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes is higher than that of alum, and using amount is less, and compared with the prior art, application of food additives can be reduced, and enlarged production is convenient to realize.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
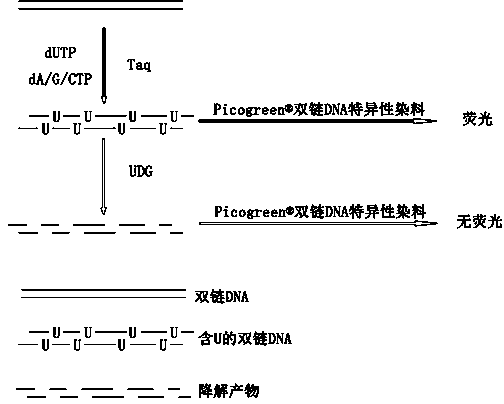
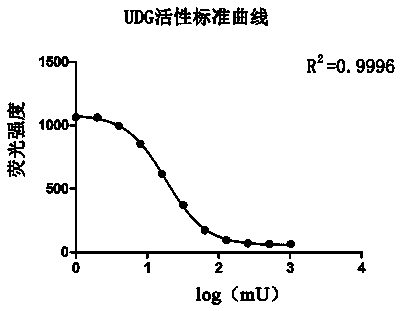
Uracil-DNA glycosylase activity measurement method
InactiveCN104293927AEasy to operateImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LUracil-DNA glycosylase
The invention discloses a uracil-DNA glycosylase activity measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out PCR amplified reaction; with a double-chain DNA as a template, carrying out polymerization reaction by using polymerase in the presence of a dU / A / G / CTP mixture and a primer, and carrying out amplification to generate amplification product UDNA double chains containing dU; secondly, carrying out uracil-DNA glycosylase reaction, and forming a lot of DNA chains in base deletion from the amplification product through the uracil-DNA glycosylase action; and finally, measuring the relative quantity of a single-chain DNA product or UDNA double chains in the reaction system, and deriving the uracil-DNA glycosylase activity degree according to the measurement result, wherein the uracil-DNA glycosylase activity degree is inversely proportional to the quantity of the DUNA double chains in the reaction system, and is directly proportional to the quantity of the single-chain DNA product. The method disclosed by the invention is free of radioactive pollution, simple and rapid in operation, high in sensitivity, and stable, and quantitative determination can be carried out.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
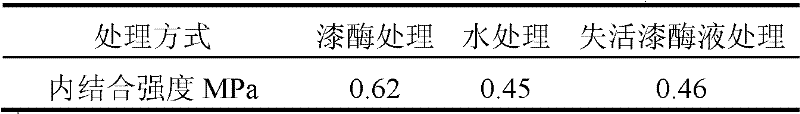
Wood raw material pre-treatment method
InactiveCN102514061APromote softeningReduce water consumptionWood impregnation detailsPretreatment methodAdhesive
The invention discloses a wood raw material pre-treatment method, belonging to the technical field of wood processing. The wood raw material pre-treatment method comprises the following concrete treatment processes: soaking wood raw material into a soak solution, regulating pH of the soak solution, controlling temperature of the soak solution, adding laccase, and taking out the wood raw material and drying the wood raw material after the wood raw material is under enzyme action for a while. The wood raw material pre-treatment method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that performances of the pretreated wood raw material are changed, namely a surface shell-shaped covering layer of the wood raw material is obviously loose, and partial surface shell-shaped covering layer is removed to form a hole structure; and surface wetting property is obviously improved. During wood processing, the changes of the performances can reduce water consumption and energy consumption in a softening stage, and spreading and penetration of glue solution on the surface of the wood raw material are improved and condensation adhesive and penetration adhesive properties of the glue solution are enhanced, thus the internal bonding strength of a wood product is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of mediated-heparin intracellular delivery crosslinking nanometer carrier
InactiveCN104524591AAvoid degradationEfficient releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityNano composites
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicines, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a mediated-heparin intracellular delivery crosslinking nanometer carrier. PEG-modified PEI is adopted; and heparin is entrapped by using cation performance of PET, so that the cell endocytosis ability is increased; the water solubility, the stability and the blood metabolic capability of a carrier and nano composites are improved by PEG molecules; removal of combination of composites and protein is avoided; meanwhile, degradation of the heparin caused by heparin enzyme action is avoided; in addition, effective release of the heparin in cells is achieved; and a disulfide bond is introduced through a crosslinking agent on the basis, so that nanoparticles are degraded to release the heparin, thus the heparin plays a biological effect in the cells.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Alpha-L-fucosidase detection kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105238848AAvoid interferenceReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementStabilizing AgentsChemistry
The invention discloses an alpha-L-fucosidase detection kit consists of an independent reagent 1 and an independent reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 consists of components of a buffer agent, a preservative, a metal ion chelating agent, a stabilizing agent and water; and the reagent 2 consists of components of a buffer agent, a preservative, an enzyme action substrate, a surfactant, a stabilizing agent and water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing the reagent 1: dissolving the various components in distilled water or double distilled water, uniformly mixing, regulating pH to 6.5-8.5, and setting a constant volume; (2) preparing the reagent 2: dissolving various components in distilled water or double distilled water, uniformly mixing, regulating pH to 6.5-8.5, and setting a constant volume; and (3) independently sub-packaging the reagent 1 and the reagent 2, and sealing. The detection kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good stability, high precision, broad linear test range, good repeatability, strong anti-interference performance and the like.
Owner:WUHAN LIFE ORIGIN BIOTECH LTD
MRNA targeting molecule based on combination of N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and preparation method of mRNA targeting molecule
ActiveCN111041025AImprove efficacySolve the technical challenges of targeted deliveryGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemGeneticsA-DNA
The invention provides an mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) targeting molecule based on N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and a preparation method of the mRNA targeting molecule. A plasmid vector containing a DNA fragment formed by sequentially connecting a promoter, a target gene, a specific protease cleavage sequence and a polypeptide GBD sequence capable of being combined with N-acetylgalactosamine is transcribed to obtain mRNA, the mRNA is connected with a DNA-puromycin connector under the action of T4 ligase, through protein translation and shearing with a specific protease, an mRNA-puromycin-GBD compound is obtained, and the mRNA-puromycin-GBD compound is combined with the GBD protein sequence under the action of N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase to form an mRNA-puromycin-GBD-GalNAccompound to complete the GalNAc modification of the mRNA; in the mRNA drug delivery process, the purpose of accurate drug delivery is achieved, and the drug effect of mRNA drug molecules is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN RHEGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com