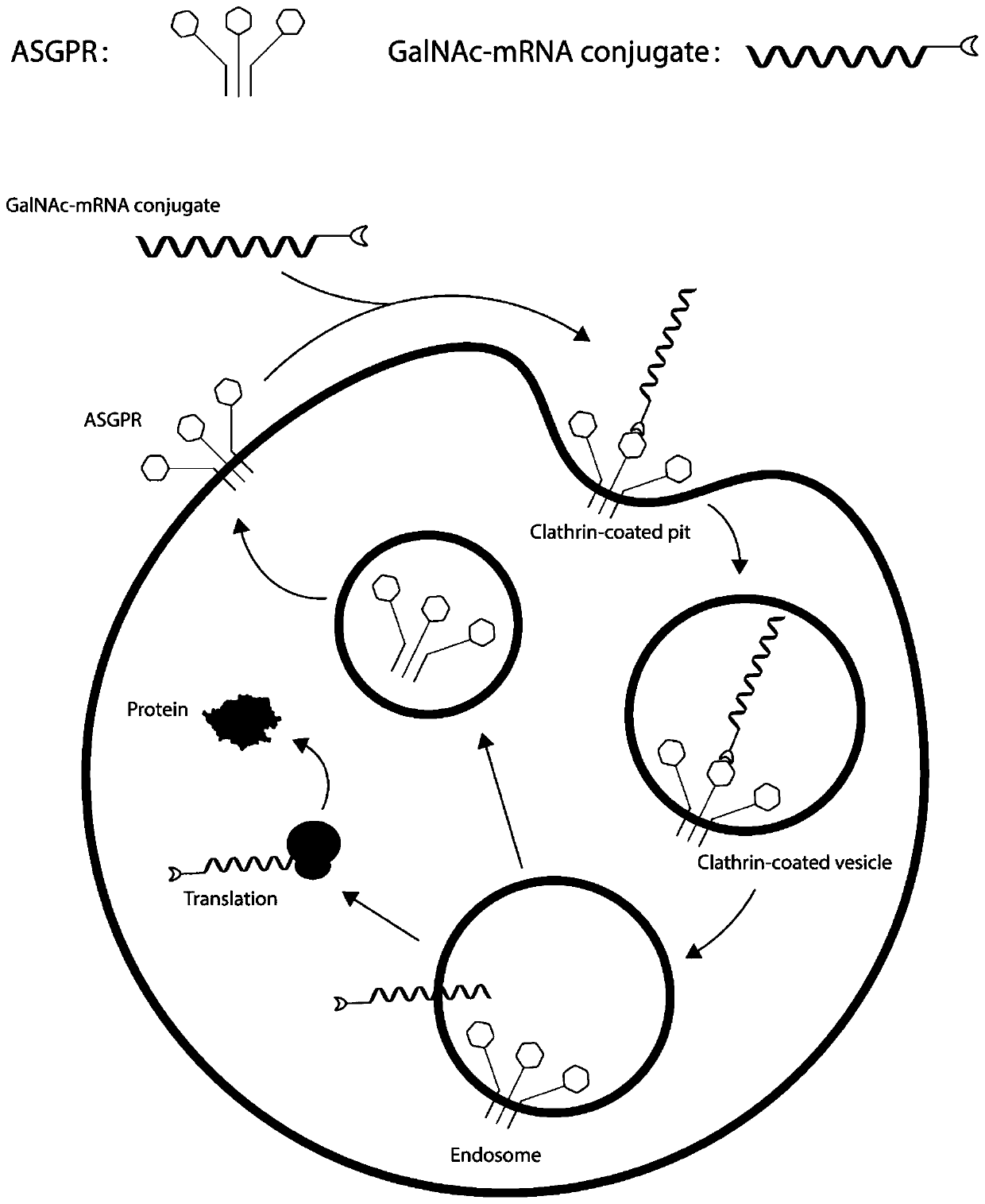
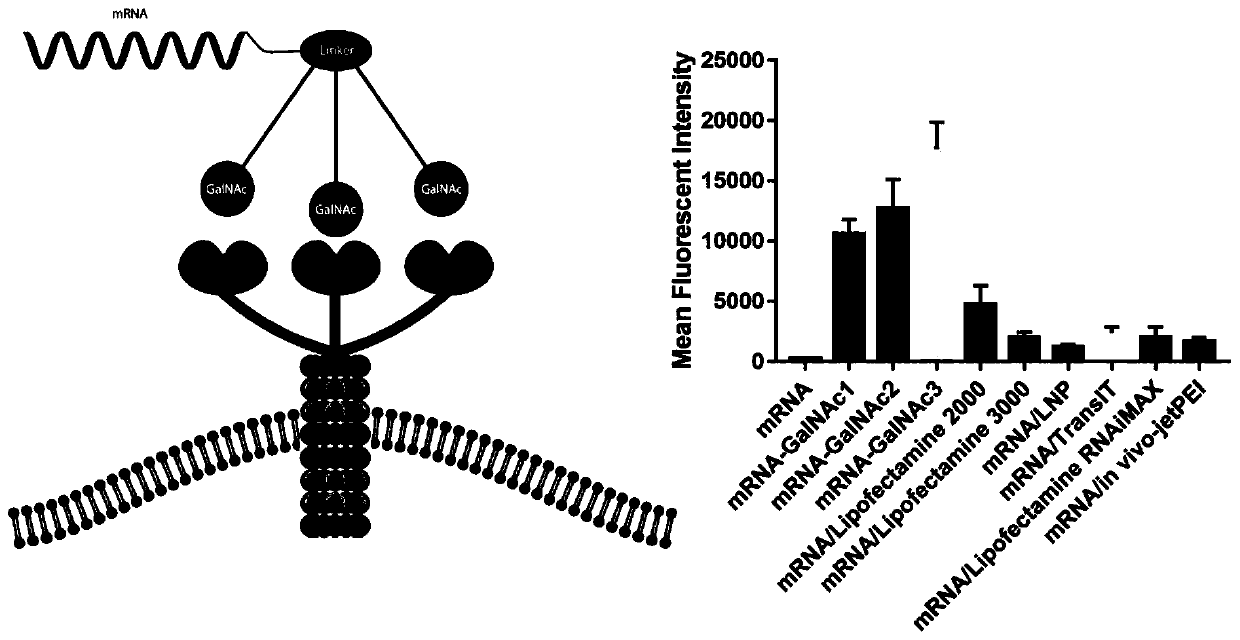
MRNA targeting molecule based on combination of N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and preparation method of mRNA targeting molecule
An acetylgalactosamine, targeting molecule technology, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, hybrid peptides, etc., can solve the problem of cytotoxicity, difficulty in clinical transformation, and inability to achieve effective coupling between mRNA and GalNAc and other problems to achieve the effect of solving targeted delivery and increasing drug efficacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] An mRNA targeting molecule based on binding N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide, which is a new type of mRNA drug with liver cell-specific binding ability. Wherein, the GalNAc modification of the mRNA molecule is combined with the GBD protein sequence of the mRNA-puromycin-GBD molecule through N-acetylgalactosamine transferase to form an mRNA-puromycin-GBD-GalNAc molecule. Puromycin is linked to the GBD polypeptide sequence; the mRNA molecule is obtained by in vitro transcription using a plasmid containing the above-mentioned DNA fragment, and the sequence of the mRNA molecule includes a 5' cap, a target gene sequence, a specific protease cleavage sequence, and a binding The polypeptide GBD sequence of N-acetylgalactosamine, the GBD polypeptide is obtained through ribosome translation of the GBD sequence, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0068] Step S1, according to the delivery tissue is liver cells, the target gene is selected as green fluorescent protein mWa...
Embodiment 2
[0098] An mRNA targeting molecule based on binding N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0099] Step S1, according to the delivery tissue is liver cells, select the target gene as luciferase (Luc), and design a polypeptide sequence (GBD) that can bind N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), and clone related cloning elements into the pCDNA3.1 plasmid vector. Wherein, the DNA fragment in the plasmid DNA includes a promoter, a target gene, a specific protease cleavage sequence, and a polypeptide GBD sequence capable of binding N-acetylgalactosamine and is sequentially connected.
[0100] In this embodiment, the GBD sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2 is used as the GBD sequence.
[0101] The sequence of the target gene is shown in SEQ ID No.7.
[0102] SEQ ID No.7
[0103] GTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAGACCACAATGGGCGTAATCAAGCCCGACATGAAGATCAAGCTGAAGATGGAGGGCAACGTGAATGGCCACGCCTTCGTGATCGAGGGCGAGGGCGAGGGCAAGCCCTACGACGGCACCAACACCATCAACCTGGAGGTGAAGGAGGGAGCCCCCCTGCC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com