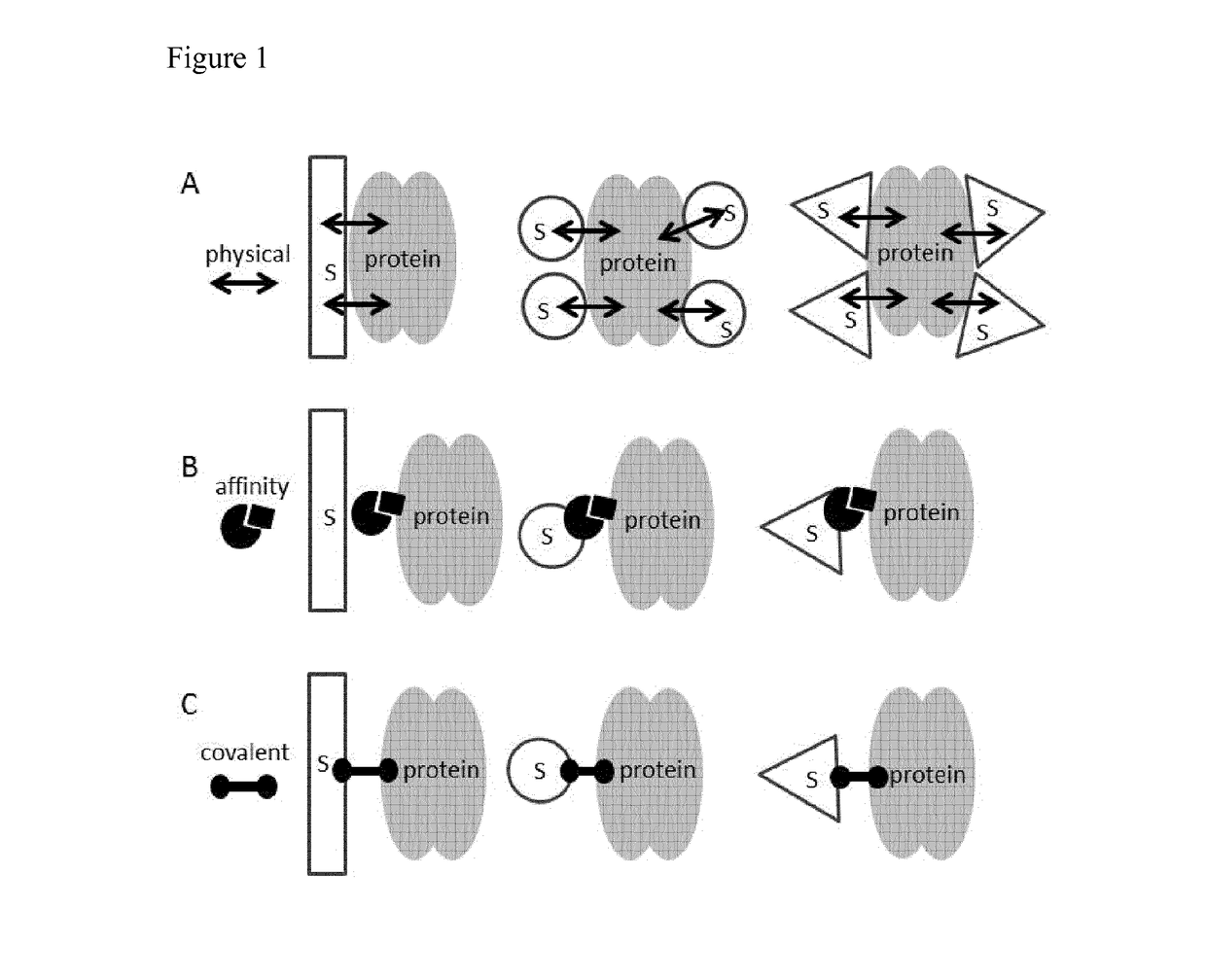
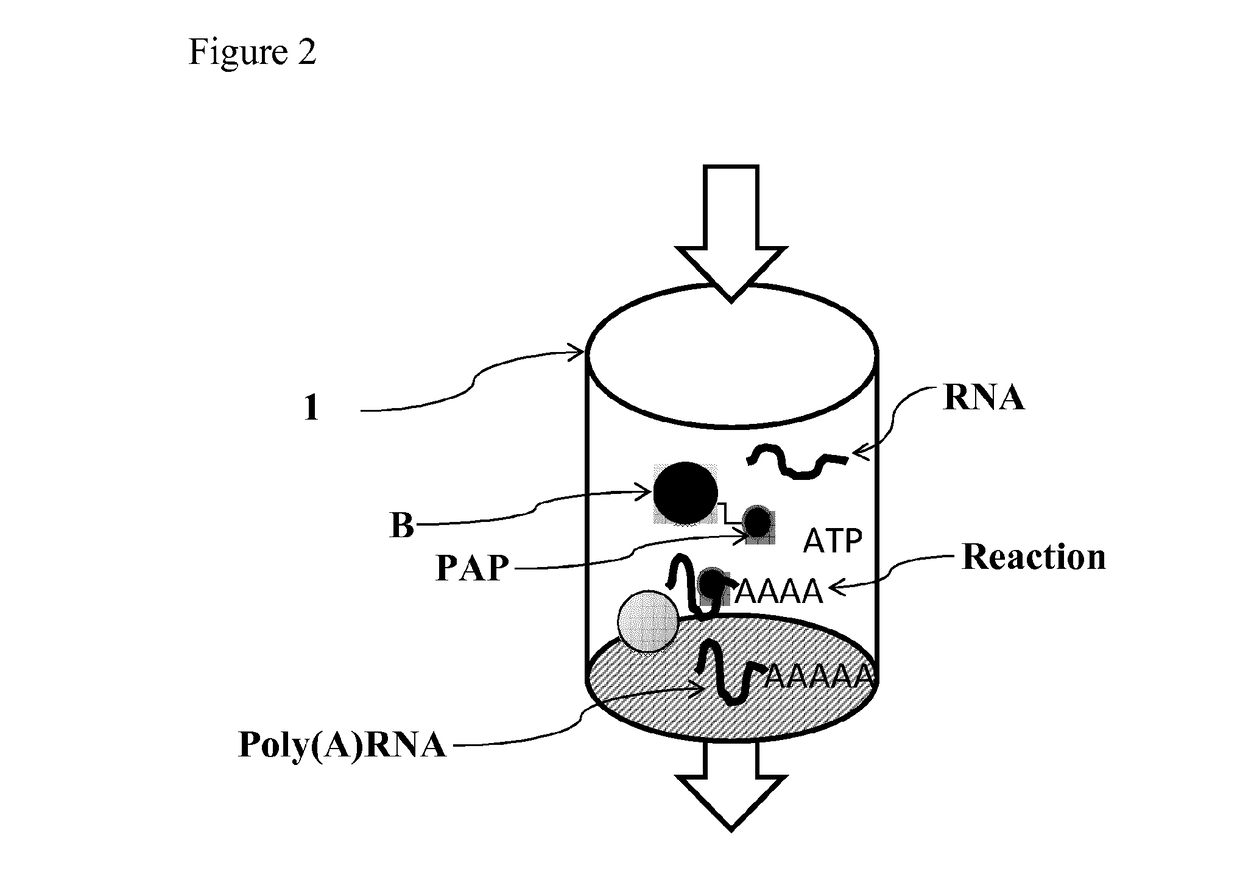
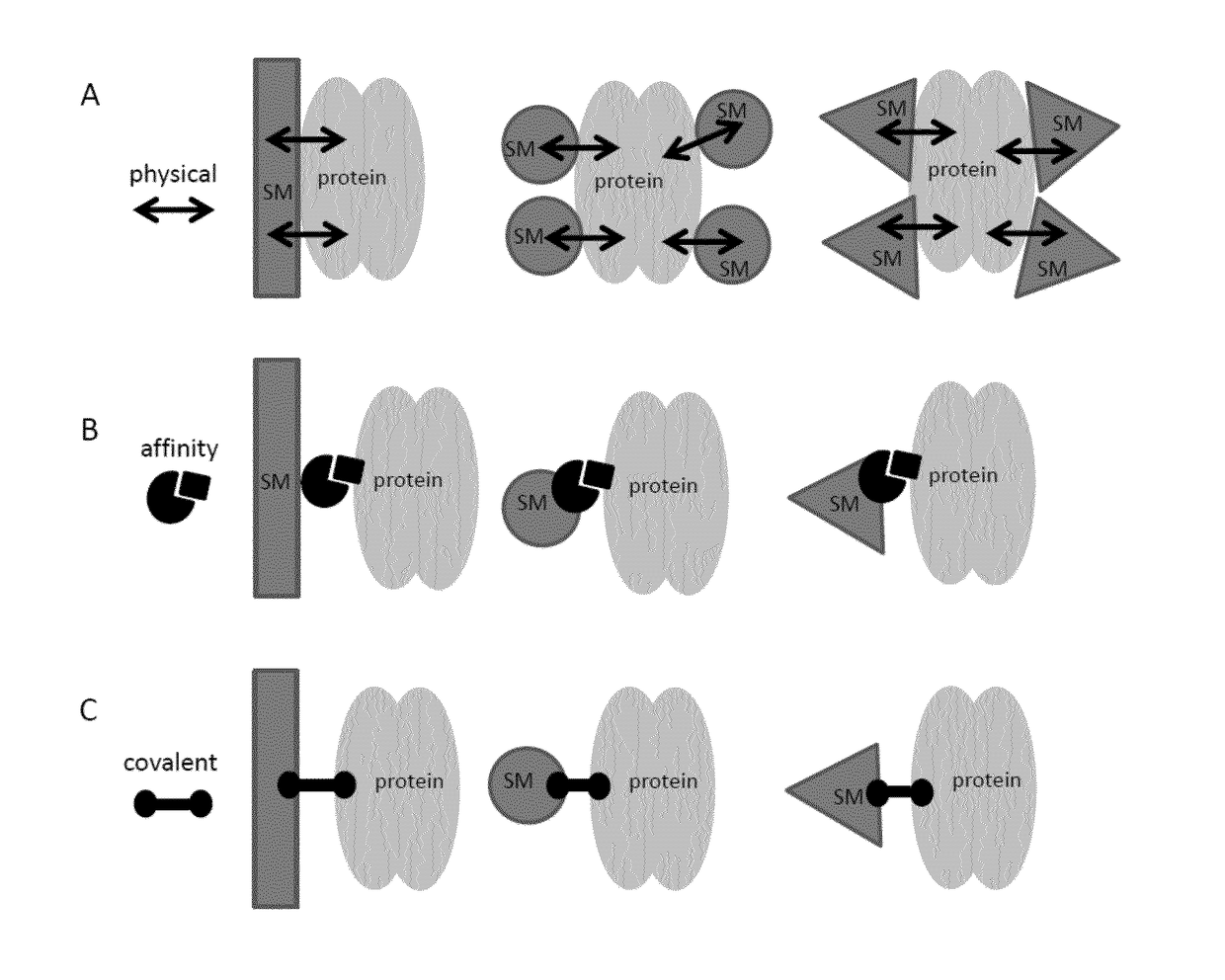
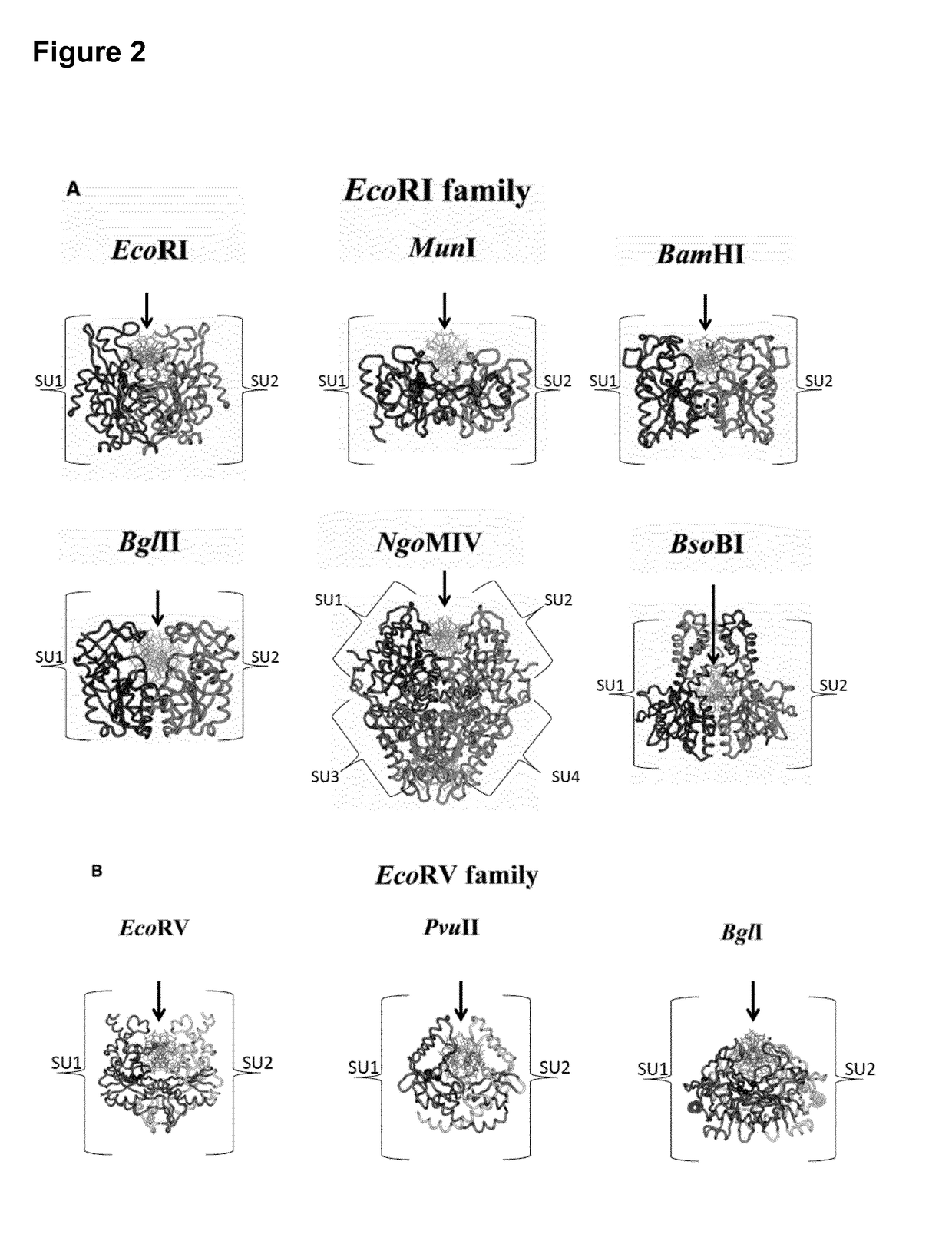
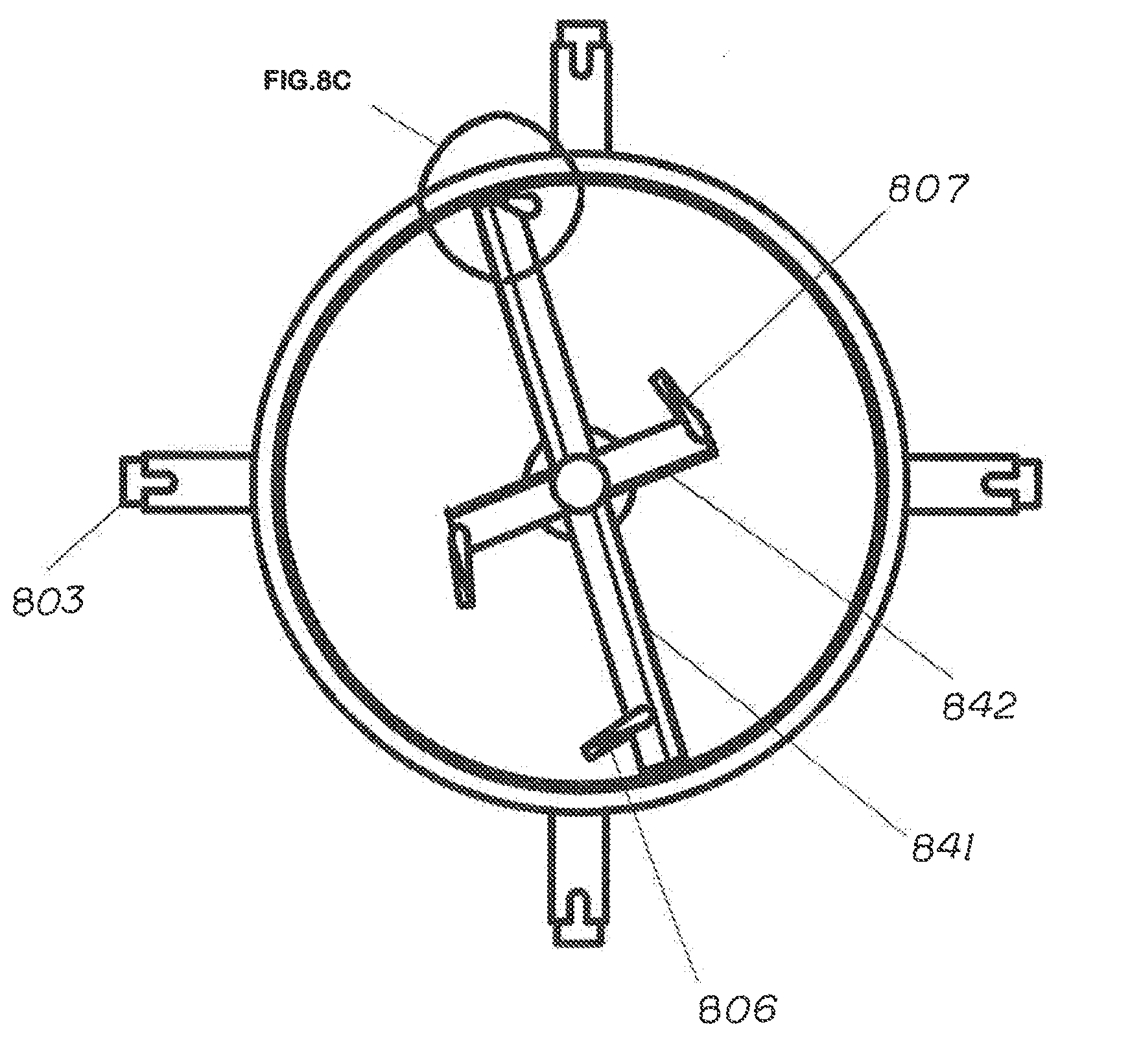
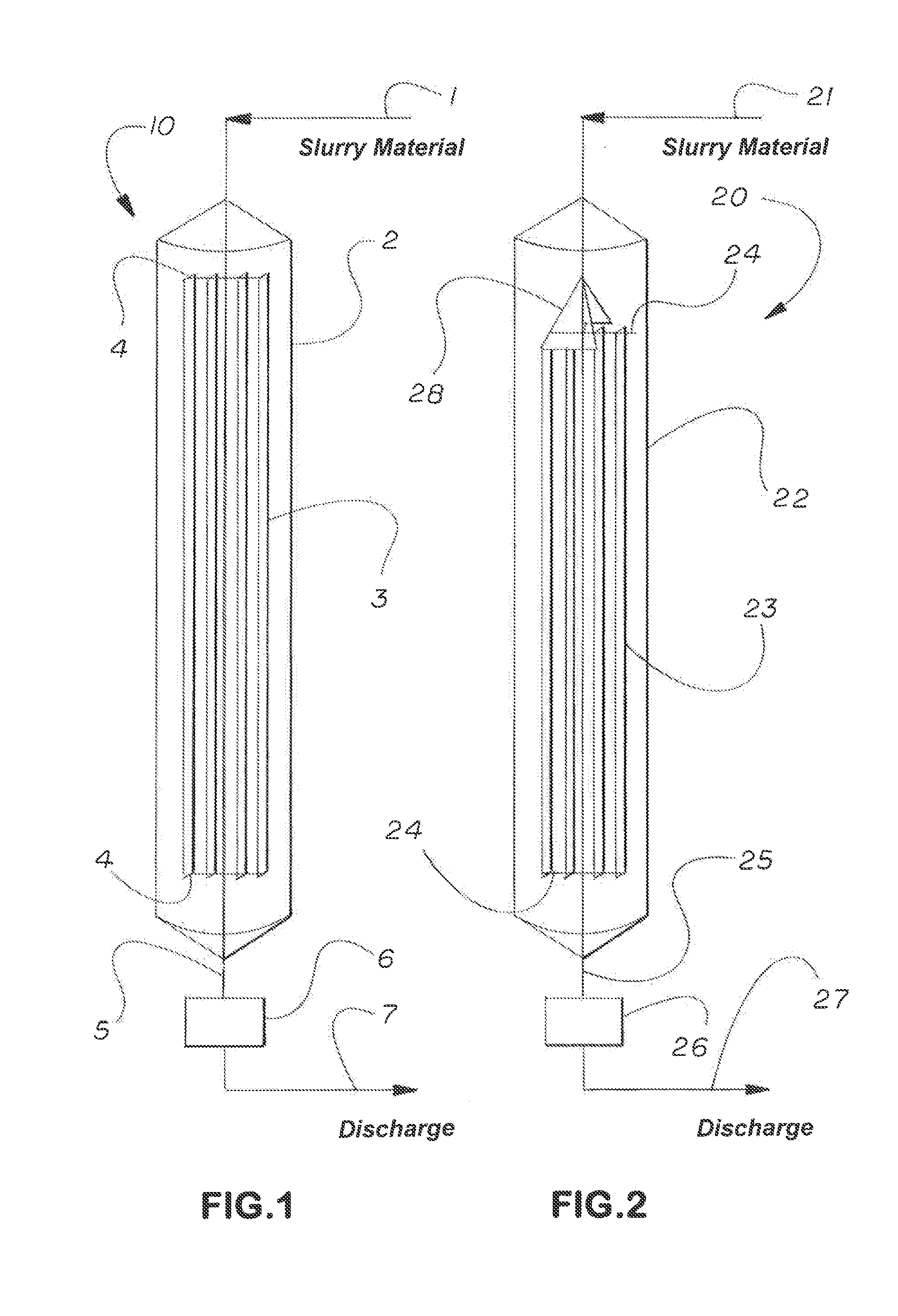
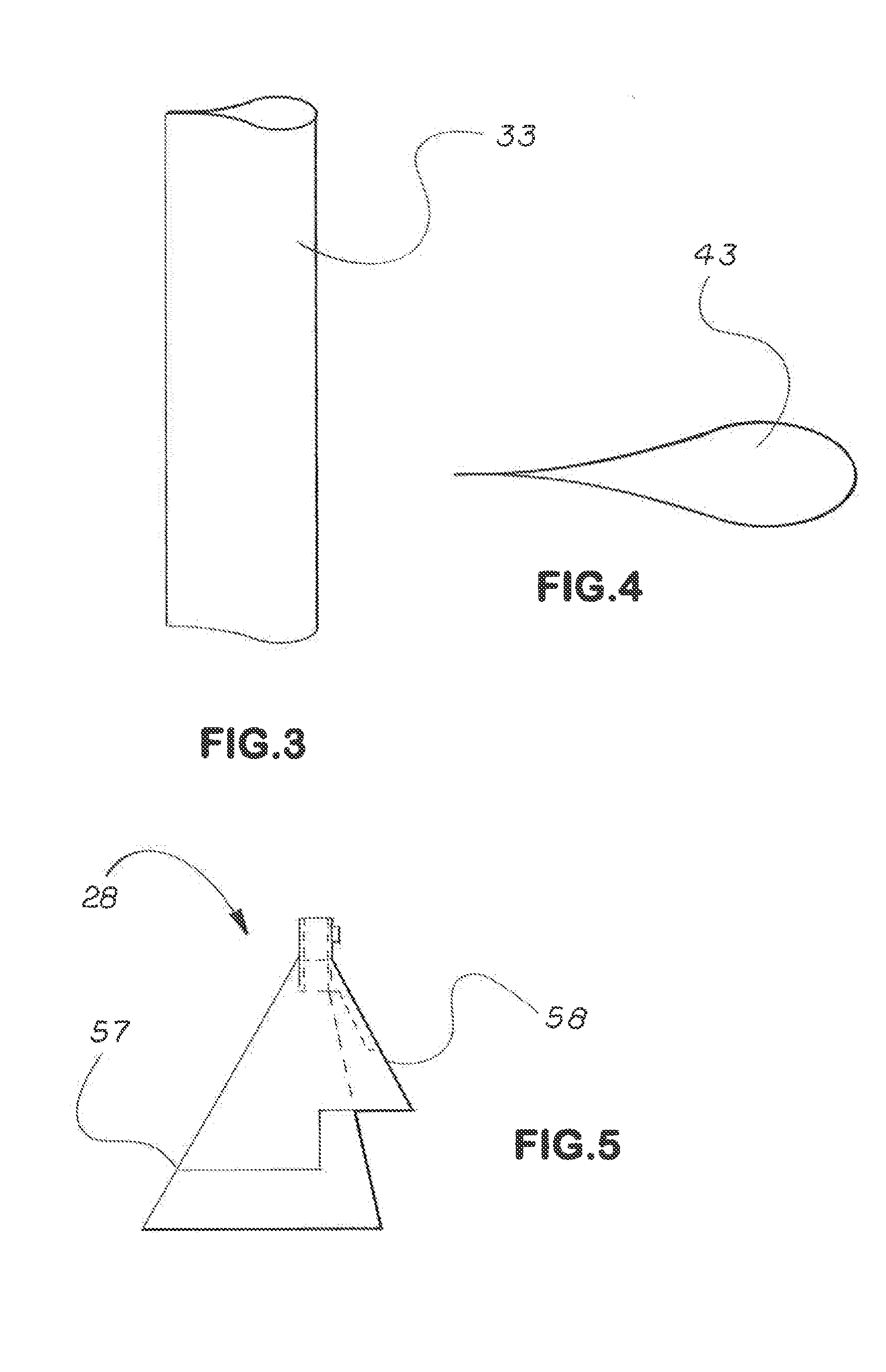
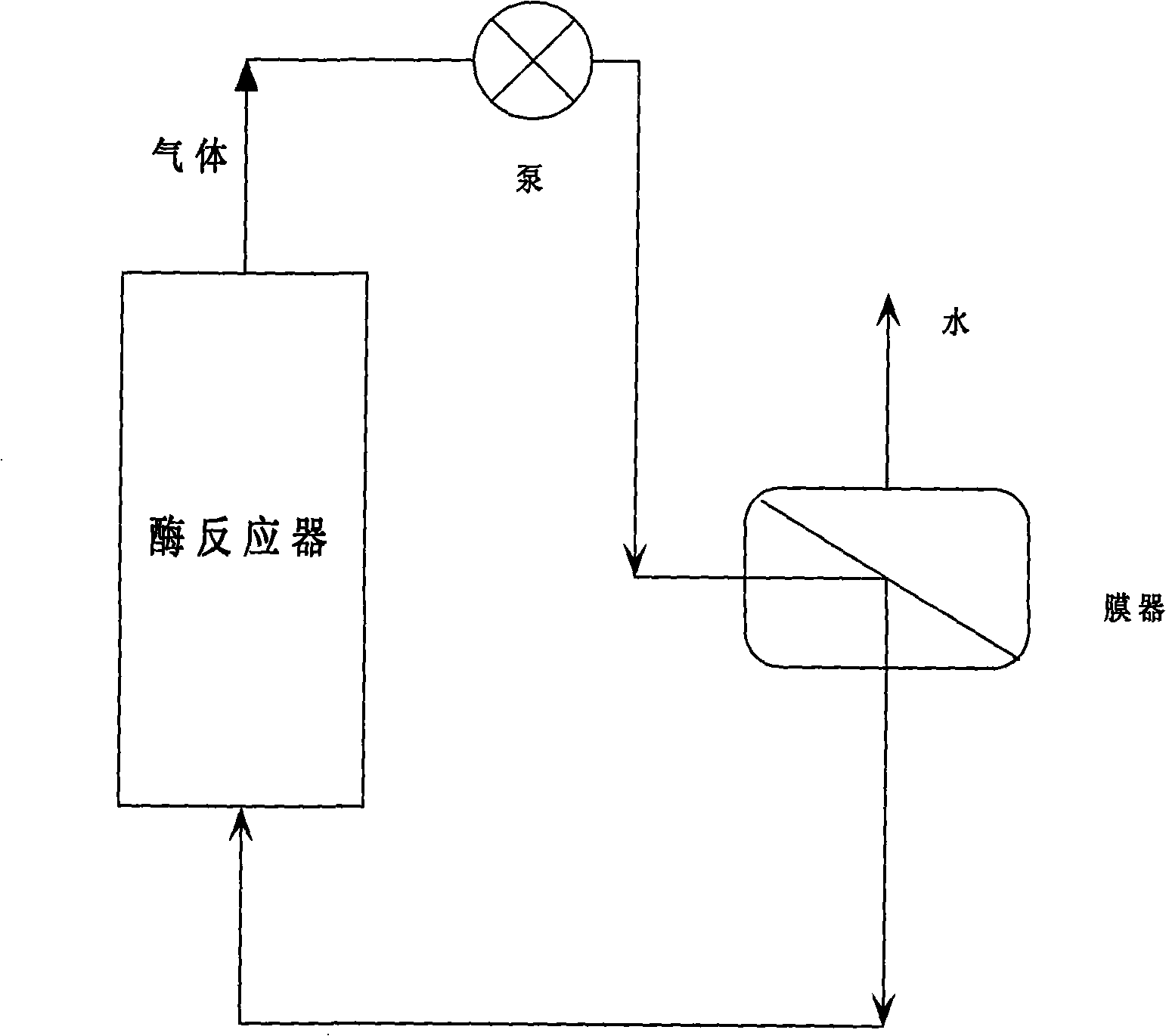
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
201 results about "Enzyme reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
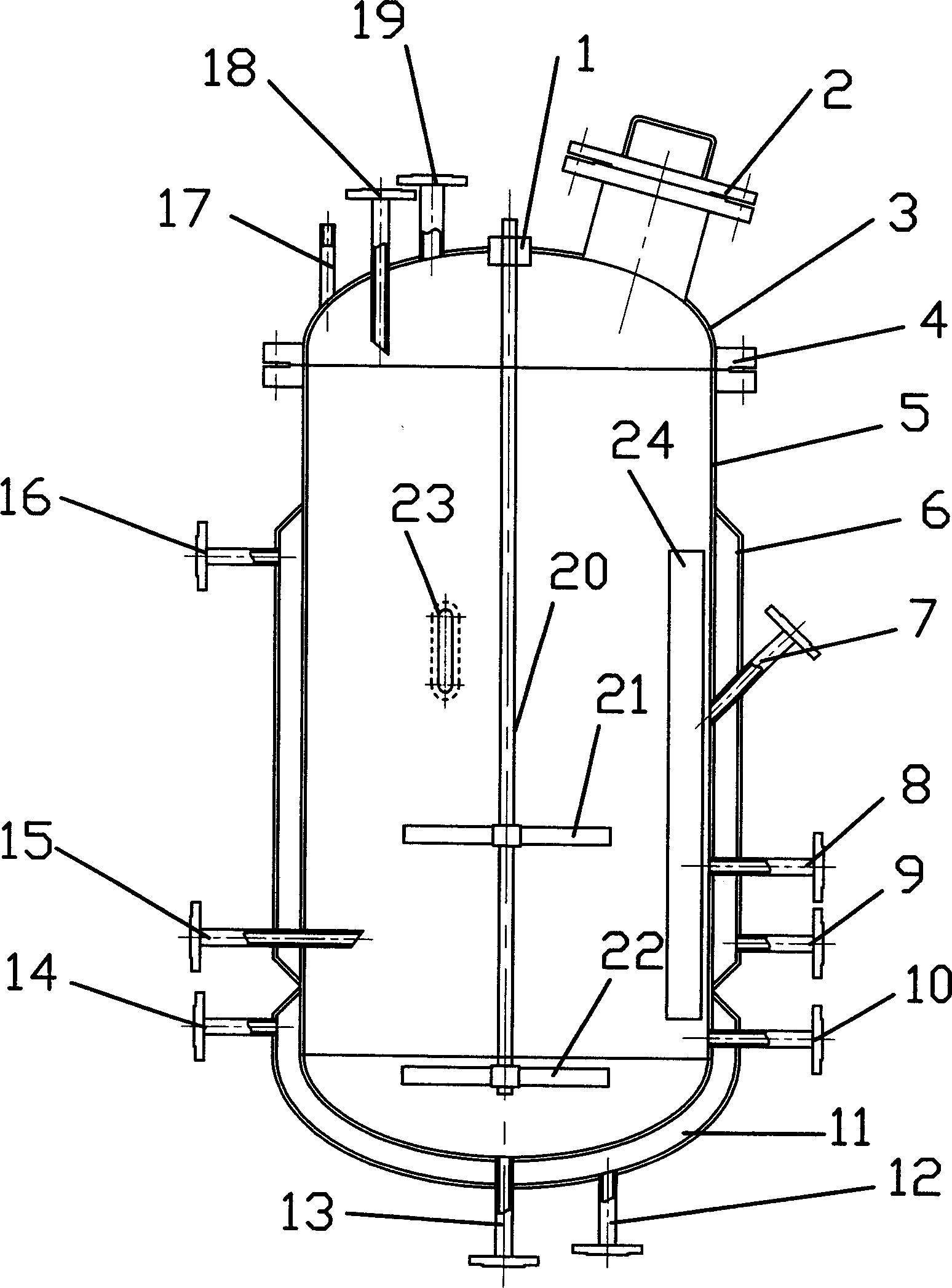
Enzyme reactors. An enzyme reactor consists of a vessel, or series of vessels, used to perform a desired conversion by enzymic means. A number of important types of such reactor are shown diagrammatically in Figure 5.1. There are several important factors that determine the choice of reactor for a particular process.
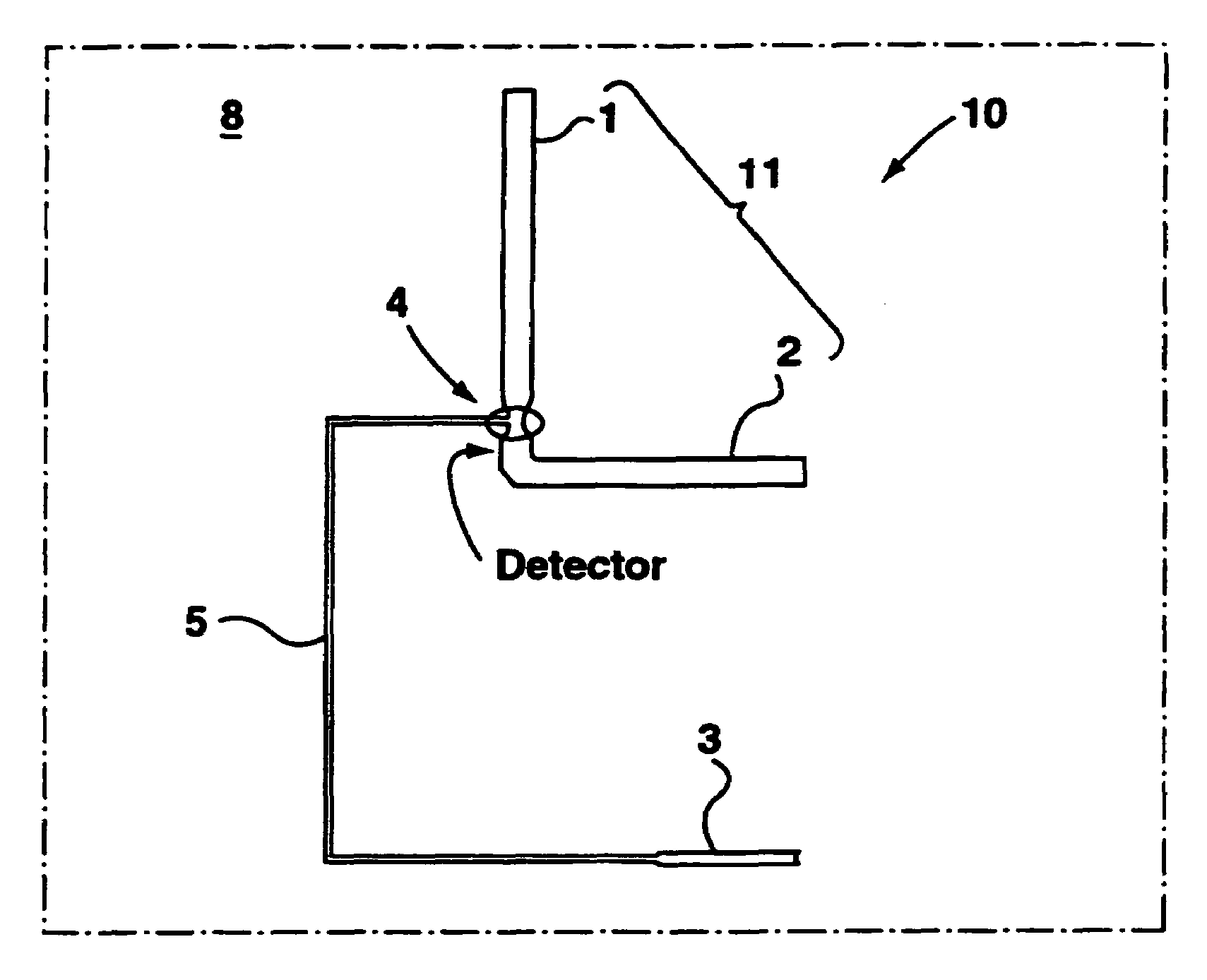
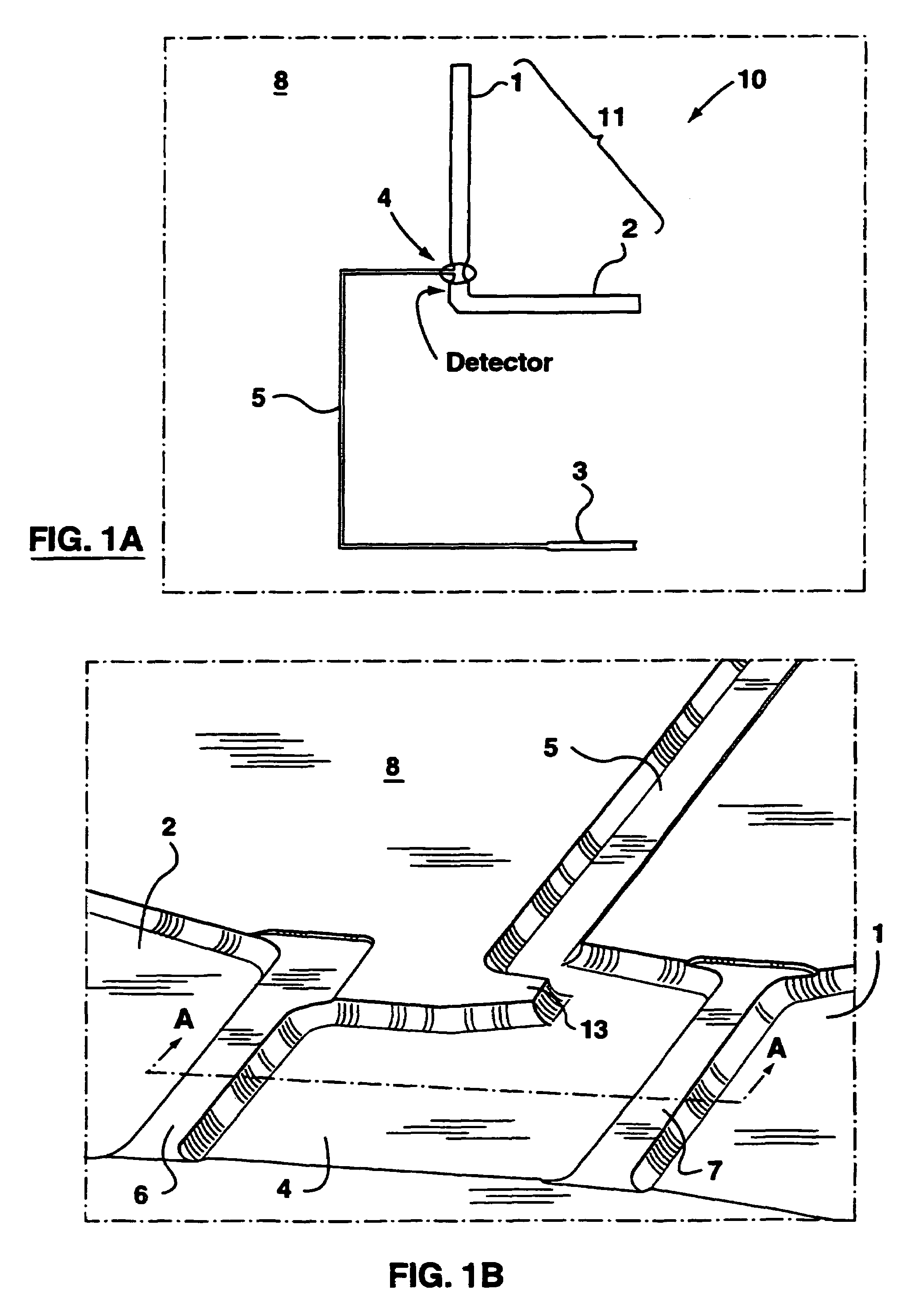
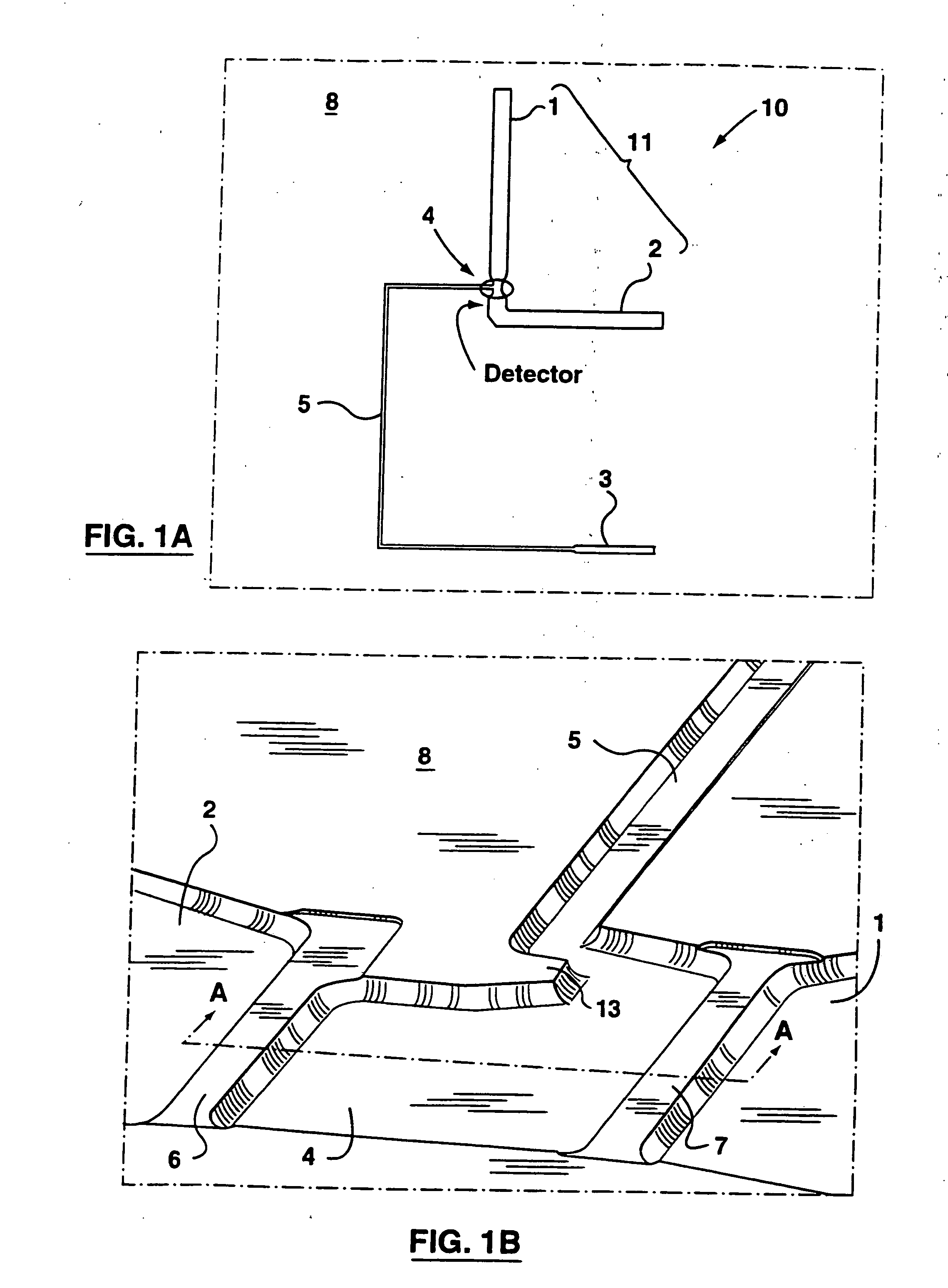
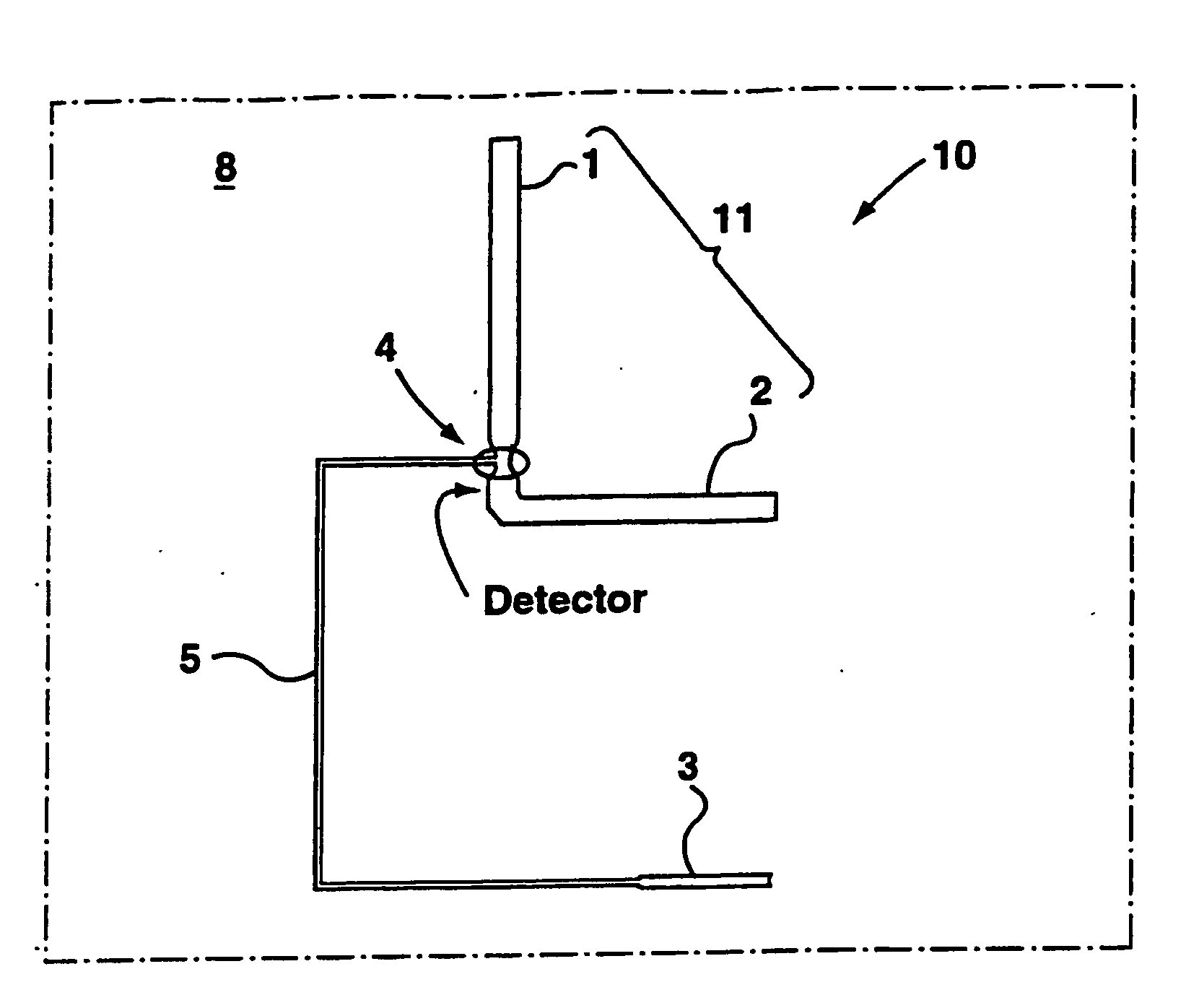
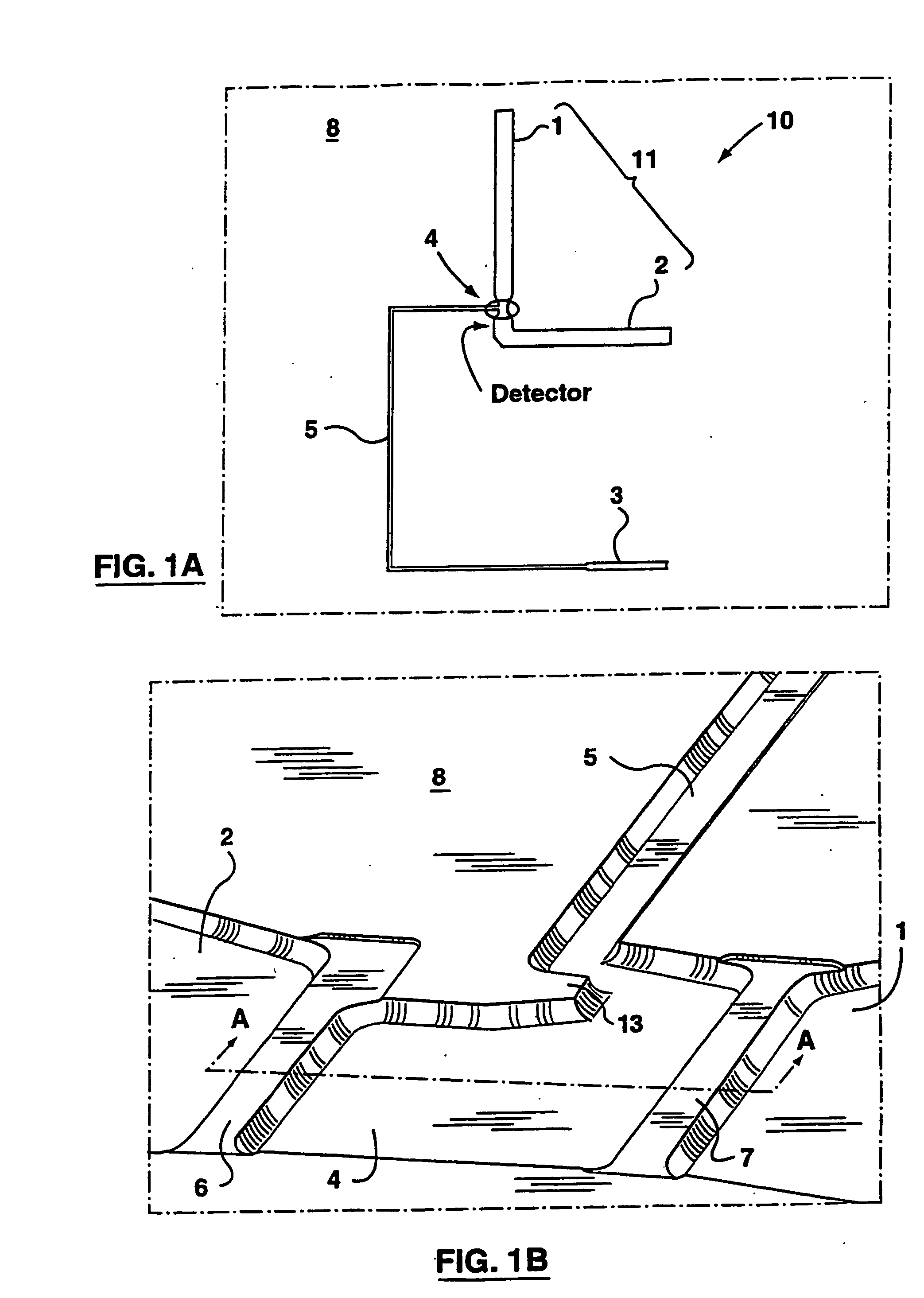
Apparatus and method for trapping bead based reagents within microfluidic analysis systems
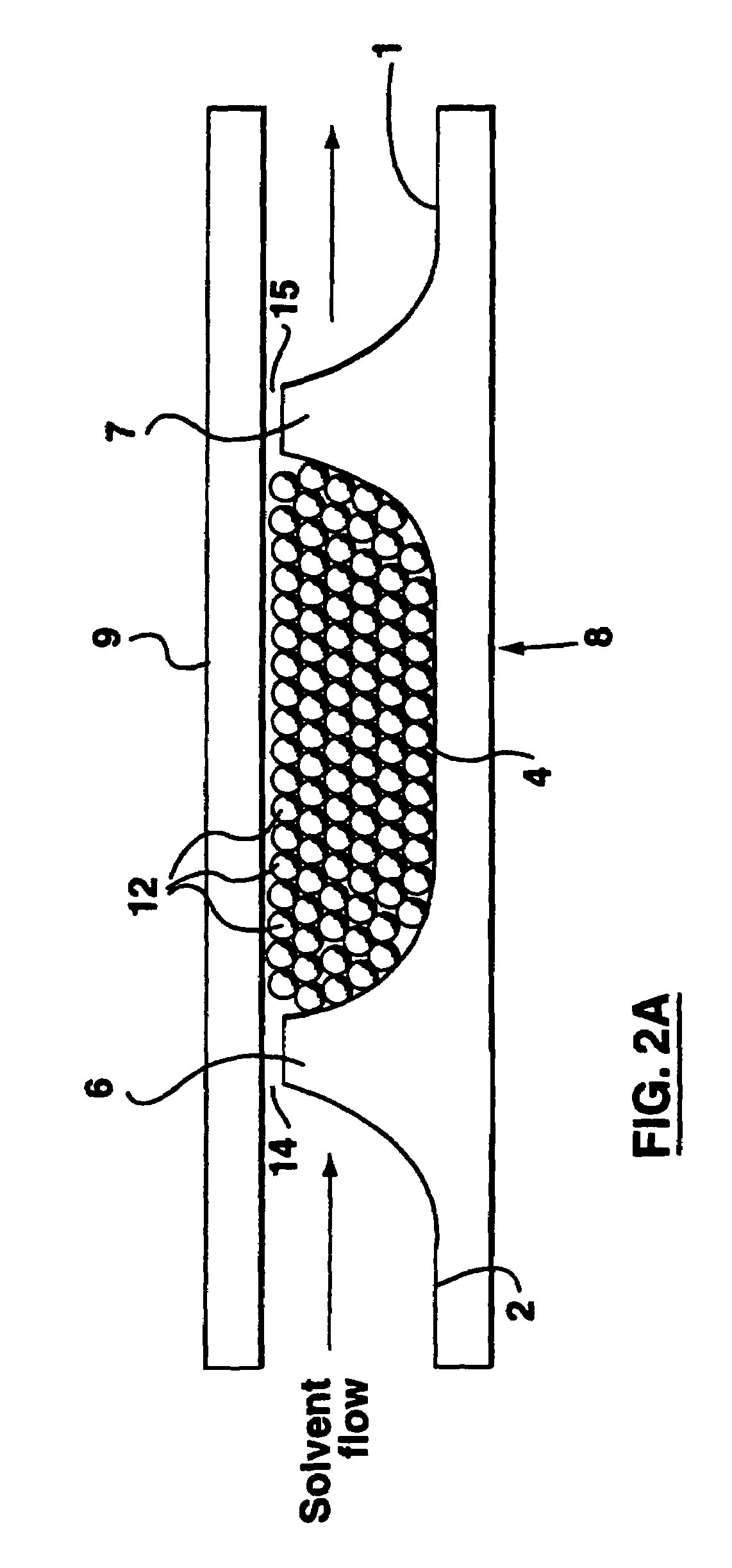
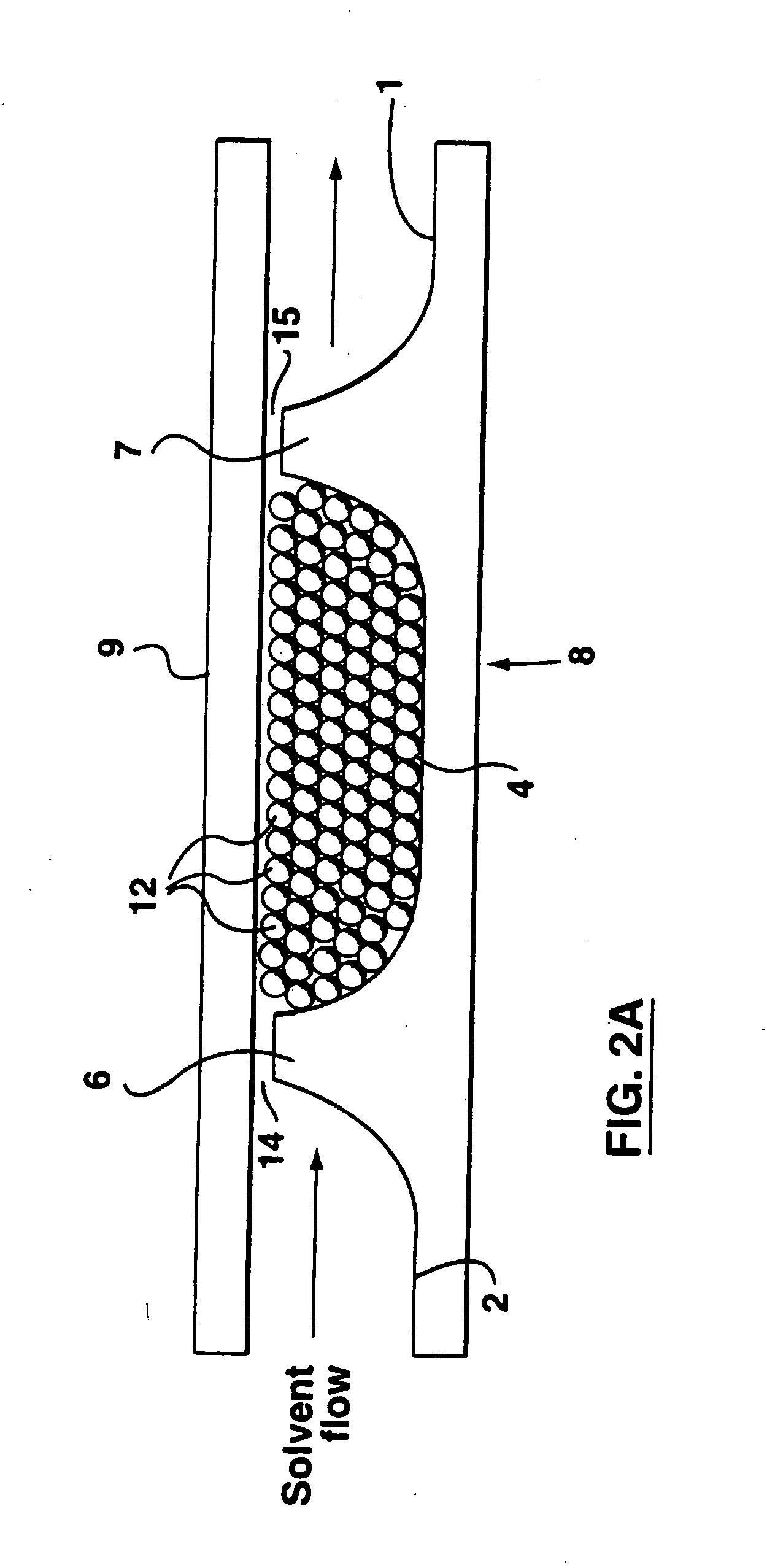
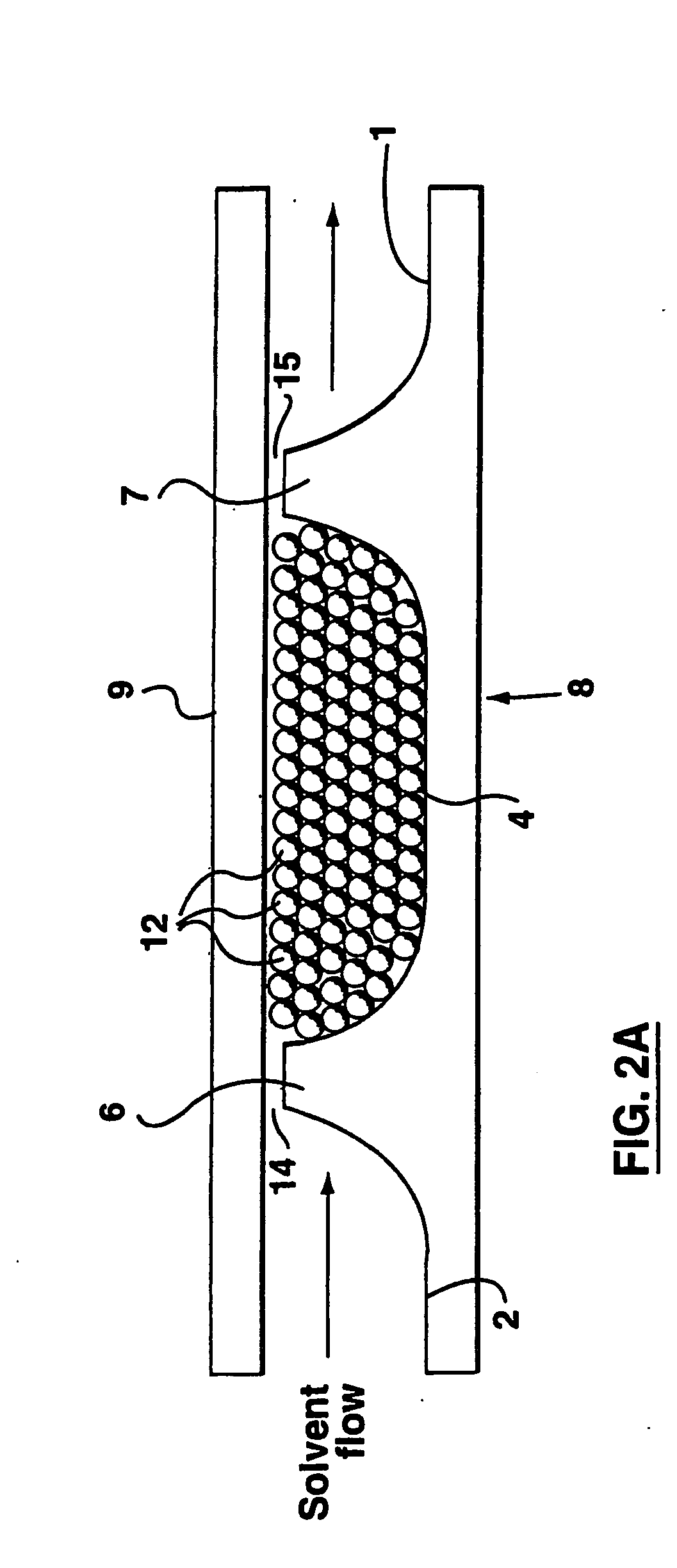
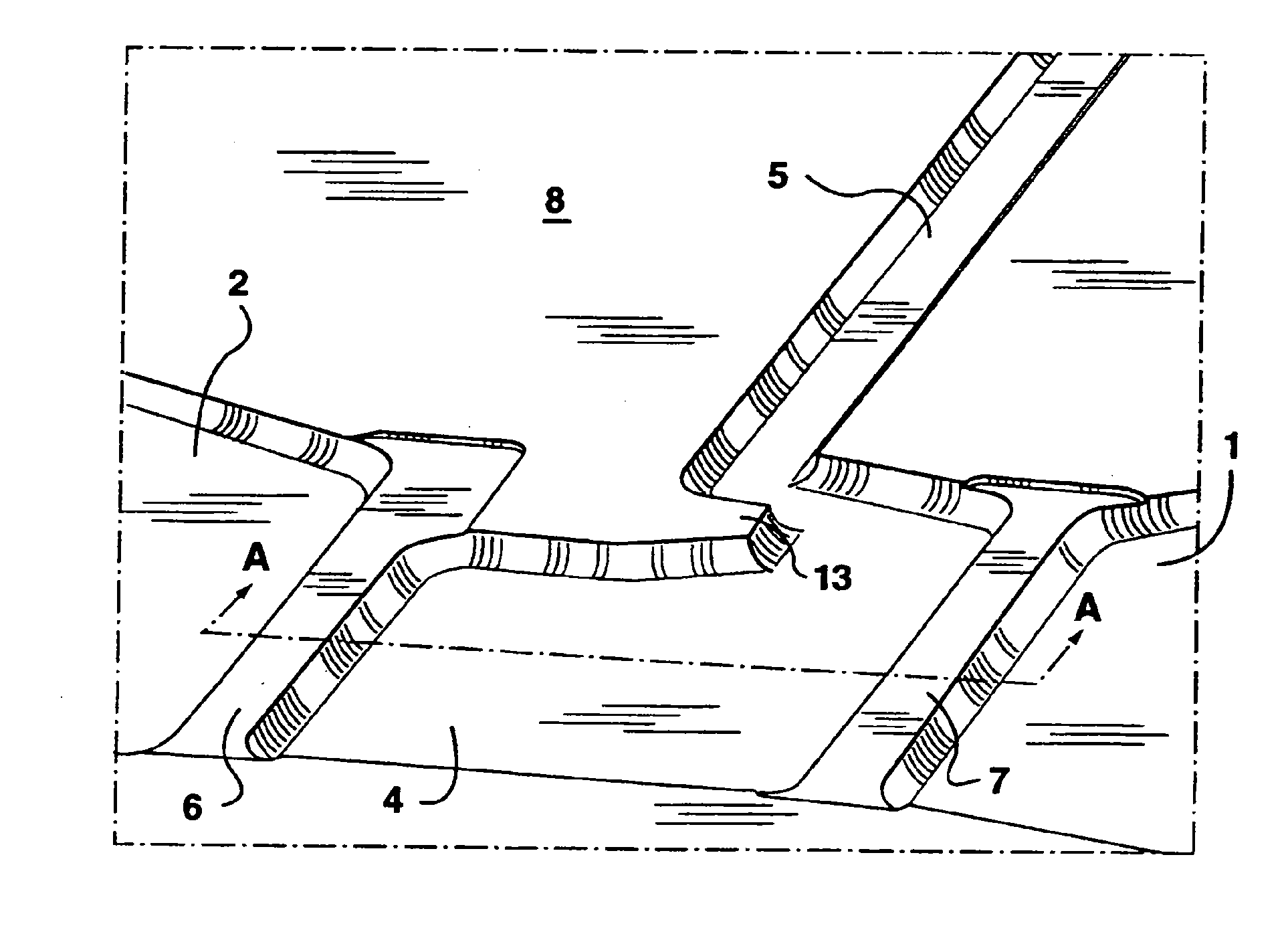
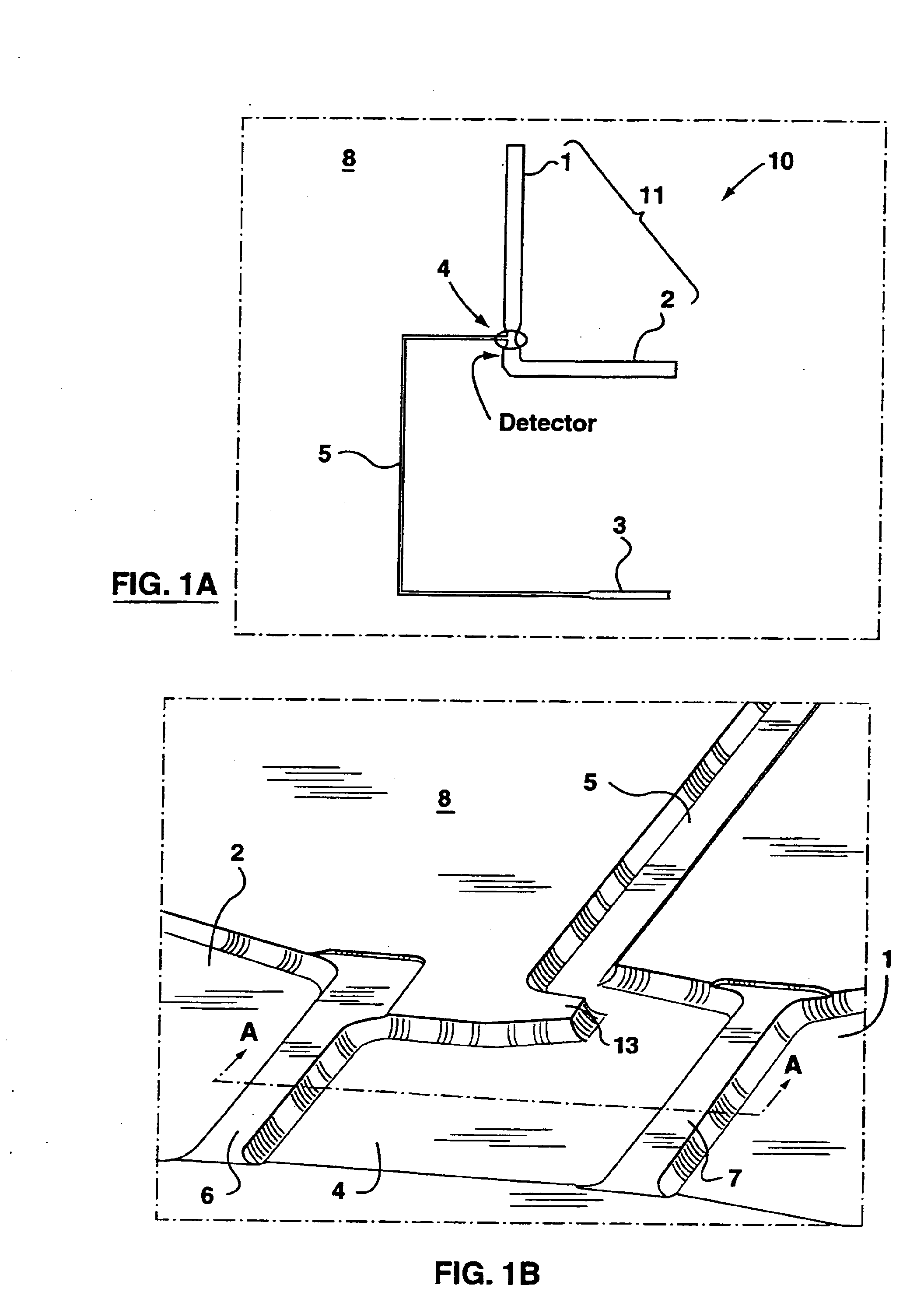
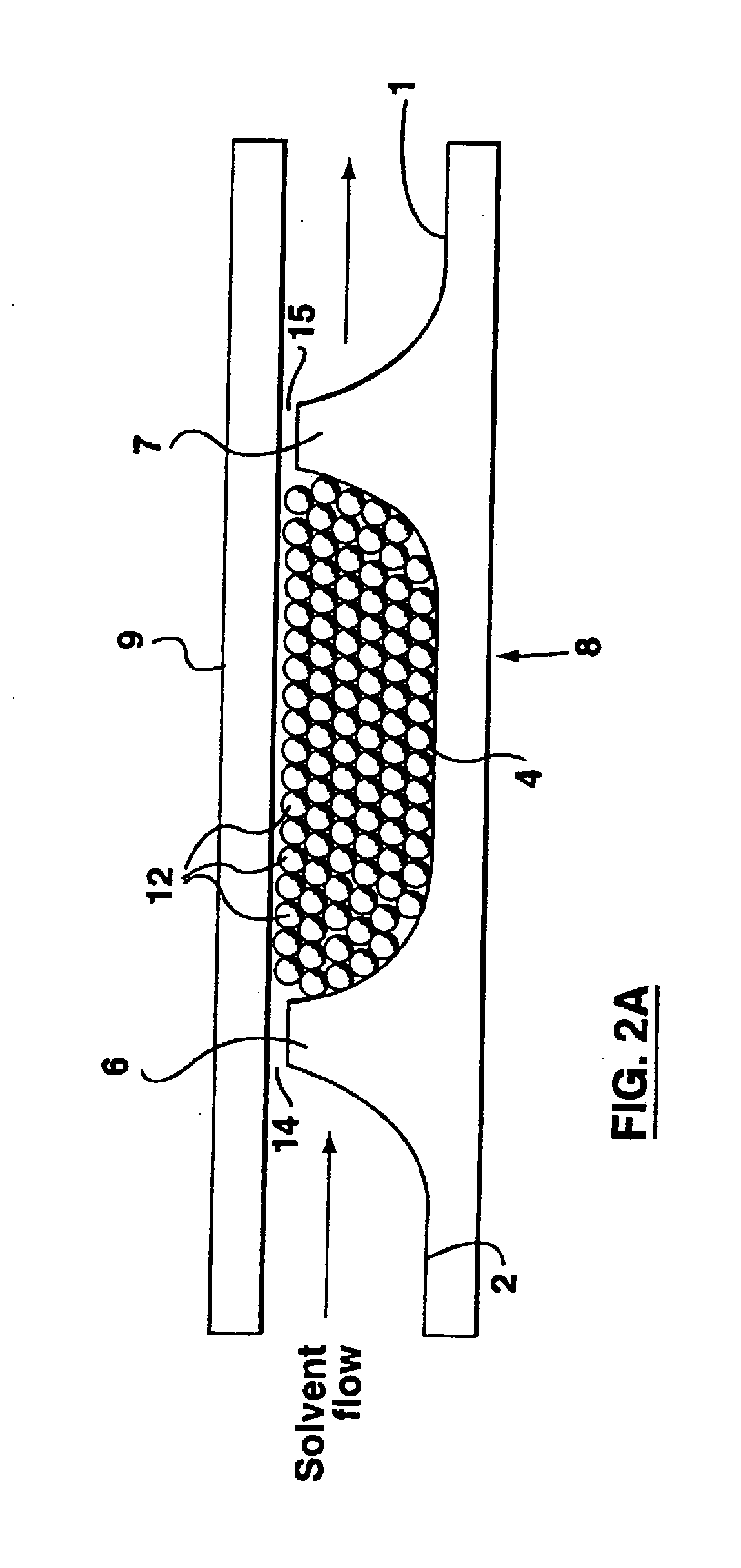
The present invention provides an on-chip packed reactor bed design that allows for an effective exchange of packing materials such as beads at a miniaturized level. In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a method of concentrating an analyte within a microfluidic analysis system, comprising the steps of: a) providing a main channel having a trapping zone suitable for trapping packing material; b) providing a slurry of a reagent treated packing material prepared in a solution having a predetermined composition of a solvent; c) inducing a flow of said packing material into said trapping zone through a flow channel connected to said trapping zone so as to load said trapping zone and form a packed bed of said packing material; d) and flowing a sample containing analytes through said packed bed, said reagent acting to concentrate at least some of said analytes within said trapping zone. The present invention extends the function of microfluidic analysis systems to new applications including on-chip solid phase extraction (SPE) and on-chip capillary electrochromatography (CEC). The design can be further extended to include integrated packed bed immuno- or enzyme reactors.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Apparatus and method for trapping bead based reagents within microfluidic analysis systems
InactiveUS20060027456A1Separation efficiency can be improvedAccelerated programBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityCapillary electrochromatography
The present invention provides an on-chip packed reactor bed design that allows for an effective exchange of packing materials such as beads at a miniaturized level. The present invention extends the function of microfluidic analysis systems to new applications including on-chip solid phase extraction (SPE) and on-chip capillary electrochromatography (CEC). The design can be further extended to include integrated packed bed immuno- or enzyme reactors.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Apparatus and method for trapping bead based reagents within microfluidic analysis systems
InactiveUS20050224352A1Reduce lightSeparation efficiency can be improvedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSludge treatmentElectricityCapillary electrochromatography
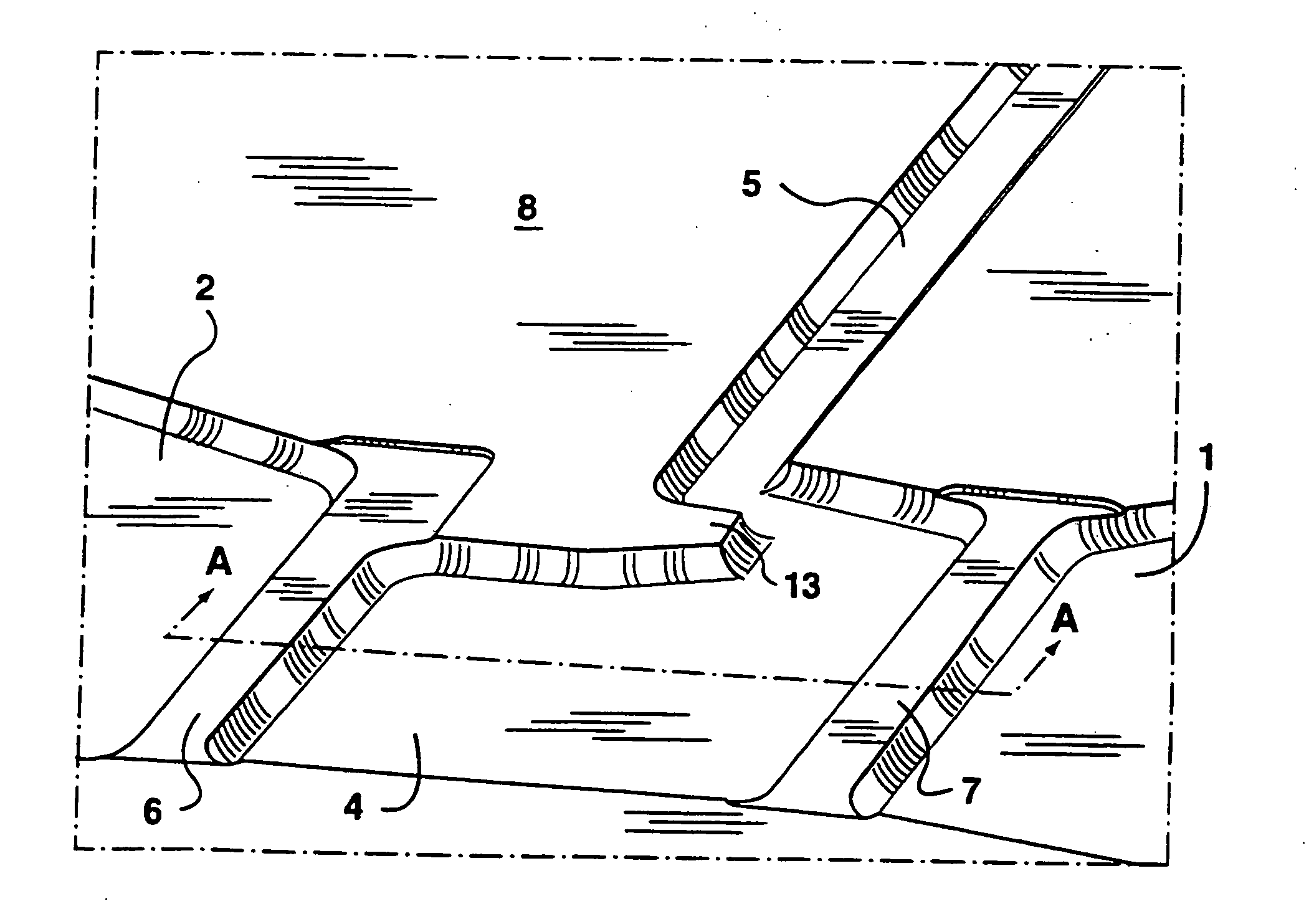
The present invention provides an on-chip packed reactor bed design that allows for an effective exchange of packing materials such as beads at a miniaturized level. The present invention extends the function of microfluidic analysis systems to new applications including on-chip solid phase extraction (SPE) and on-chip capillary electrochromatography (CEC). The design can be further extended to include integrated packed bed immuno- or enzyme reactors. The system comprises two weirs (6, 7) in a channel to trap packing material (12). The packing material might be introduced through a side channel to the chamber formed between the two weirs (6, 7). A plug is positioned in the side channel to close it.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Apparatus and method for trapping bead based reagents within microfluidic analysis systems
An on-chip packed reactor bed design is disclosed that allows for an effective exchange of packing materials such as beads at a miniaturized level. Also disclosed is a method of treating a sample within a microfluidic analysis system, comprising: providing a main channel having a trapping zone; providing a slurry of a reagent treated packing material; inducing a flow of said packing material into said trapping zone through a flow channel connected to said trapping zone to load said trapping zone and form a packed bed of said packing material; and flowing a sample containing analytes through said packed bed, said reagent treating the sample. The present invention extends the function of microfluidic analysis systems to new applications including on-chip solid phase extraction (SPE) and on-chip capillary electrochromatography (CEC). The design can be further extended to include integrated packed bed immuno- or enzyme reactors.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Method for preparing collagen peptide from fish scales
The invention discloses a method for preparing collagen peptide from fish scales, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, taking the fish scales and immersing hydrochloric acid to remove calcium; washing to be neutral, drying and crushing; 2, adding the calcium-removed, dried and crushed fish scales obtained by the step 1 into an enzyme reactor; adding water and mixed protease to extract the collagen peptide; after the extraction, carrying out enzyme deactivation and centrifuging to obtain an enzymolysis solution, wherein the mixed protease is a mixture of neutral protease, papain and flavored protease; and 3, carrying out film concentration on the enzymolysis solution obtained by the step 2; and freezing and drying a concentrated solution to obtain fish scale collagen peptide powder. According to the fish scale collagen peptide obtained by the invention, the neutral protease, the papain and the flavored protease are used for extracting the fish scale collagen peptide by an enzymic method at one step, so that not only can the enzymolysis time (9 hours)be reduced, but also the extracting rate (72.72%) of the collagen peptide is improved, and solves the special flavor problem of bitter taste of the collagen peptide and the like.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Immobilized poly(n)polymerase
ActiveUS20180142275A1Improve stabilityMore time-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical industryVaccinationRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The present invention relates to an immobilized poly(N)polymerase (PNP), methods of producing said PNP and uses thereof. Further disclosed is an enzyme reactor and kit comprising the PNP for producing polynucleotidylated ribonucleic acid poly(N)RNA)molecules which are useful in gene therapy, immunotherapy, protein replacement therapy and / or vaccination.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Chitin oligose preparing process
InactiveCN1847267AImprove efficiencySimple process routeOligosaccharidesFermentationBiotechnologyDegradative enzyme
The present invention relates to chitin oligose preparing process, and is especially enzyme generating fermentation process to degrade chitin colloid for preparing bioactive chitin oligose. The preparation process has simple technological path, effective inhibition of further degradation of bioactive chitin oligose, reuse of degrading enzyme and other advantages, and is suitable for industrial production. The preparation process includes: culturing Aeromonascaviae strain to obtain fermented liquid, centrifugally separating the fermented liquid to obtain enzyme supernatant; preparing chitin colloid; compounding chitin colloid buffer solution in an enzyme reactor and adding abacterial enzyme liquid for enzymolysis to obtain enzymolyzed chitin oligose liquid; four stages of membrane separation to obtain concentrate and spray drying to obtain bioactive chitin oligose product.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Method for in vitro transcription using an immobilized restriction enzyme
InactiveUS20180208957A1Enhancing and improving linearizationLow costHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierDNA EndonucleaseRestriction enzyme
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro transcription of a linear template DNA which is produced using an immobilized restriction endonuclease. The invention also relates to mutated restriction enzymes which are suitable for immobilization and a solid support to which these restriction enzymes are immobilized. Further, the present invention relates to an enzyme reactor containing said immobilized restriction endonuclease which enzyme reactor can be used for preparing linearized template DNA. Finally, the present invention relates to the use of said enzyme reactor for preparing a linear template DNA for in vitro transcription. In addition, the present invention relates to a kit comprising the immobilized restriction endonuclease.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Multifunctional post-extraction tank for extracting biological reaction product
InactiveCN1843612ASave investmentSave floor spaceSolvent extractionRotary stirring mixersFlocculationIon exchange
The invention relates to a multifunctional back extraction pot for extracting biological reaction product. It is formed by a pot, a jacket, a mixing axle, a mixing ores, materials and apparatus. Wherein, the mixing speed, the types, number, and positions of mixing ores can be adjusted; the jacket has several layers which can be used lonely or together; the kinds, number and position of contain interfaces can meet the demands of several back extractions. Said invention integrates the functions of several back extraction device into one device, as crystallizer, flocculation pot, evaporator, dynamic ion exchange and adsorb pot, pretreatment pot of fermentation liquor, extraction pot, depositing pot, and enzyme reactor, etc. It has the advantages that it can reduce the cost and area of back extraction device with increased functions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for trapping bead based reagents within microfluidic analysis systems
InactiveUSRE43122E1Efficient exchangeVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsCapillary electrochromatographyEngineering
The present invention provides an on-chip packed reactor bed design that allows for an effective exchange of packing materials such as beads at a miniaturized level. The present invention extends the function of microfluidic analysis systems to new applications including on-chip solid phase extraction (SPE) and on-chip capillary electrochromatography (CEC). The design can be further extended to include integrated packed bed immuno- or enzyme reactors.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Production method for coproducing unsaturated monoglyceride by using diglyceride enzyme method
ActiveCN103361387ASolve the acid value problemEasy to operateFermentationGeneration rateMonoglyceride
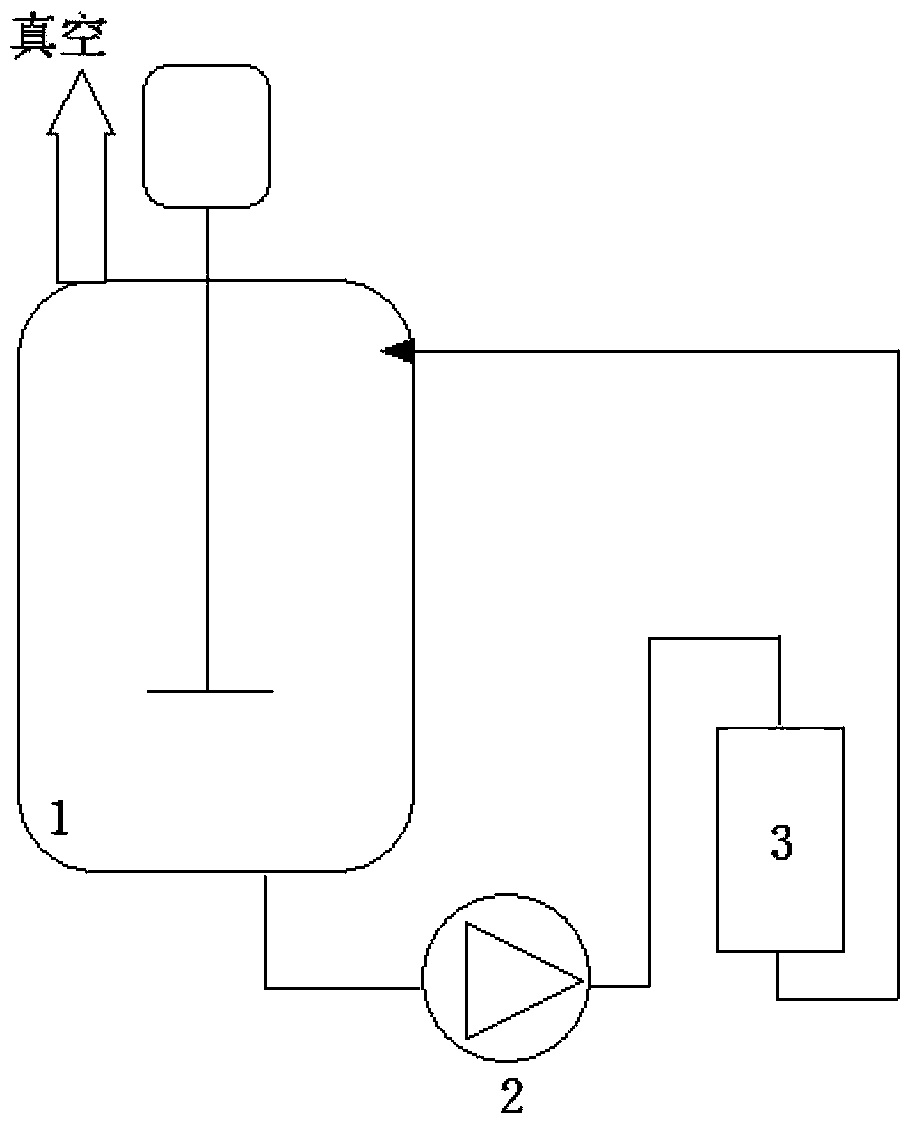
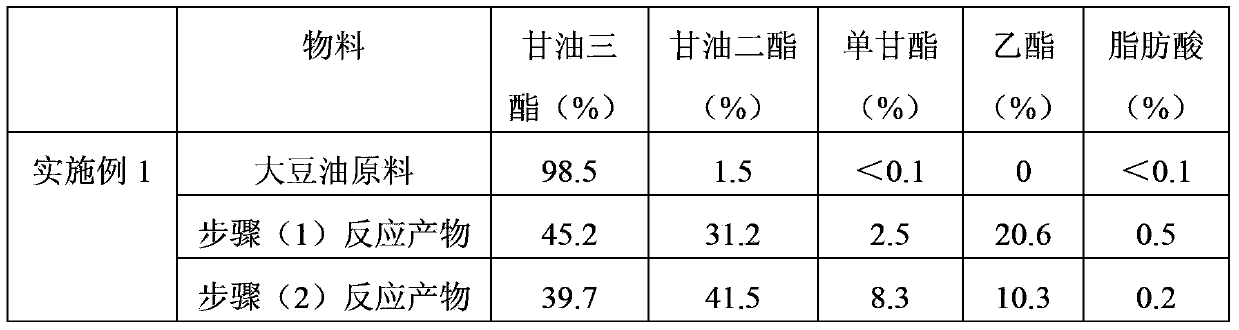
The invention discloses a production method for coproducing unsaturated monoglyceride by using a diglyceride enzyme method. The method comprises: (1)adding absolute ethyl alcohol into a natural grease, carrying out an alcoholysis reaction under catalysis of immobilized lipase, making the generation rate of fatty acid ethyl ester to be 5-40%w / w, and removing the residual alcohol to obtain an alcoholysis product; (2) adding 5-15%w / w of glycerin into the alcoholysis product of step (1), then reacting the above mixed substrates in a packed-bed enzyme reactor filled with immobilized lipase under a vacuum condition; and (3) performing molecular distillation on the reaction product of step (2), and separating to obtain a high-temperature fraction which is a diglyceride-containing product and a low-temperature fraction which mainly comprises monoglyceride. The reaction system of the invention needs no water, therefore the problem of product acid value is solved, and then coproduction of monoglyceride is realized; and the glycerin does not need preadsorption processing, and therefore the production operation is simplified.
Owner:YHSN TECH LTD
Method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase
ActiveCN101861909AOvercome hydrolysisOvercoming the problem of partial denaturation of proteinsVegetable proteins working-upFreeze-dryingReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase, which comprises the following steps: adding the rice protein or oryzenin into a constant-temperature enzyme reactor with phosphate buffer solution while stirring to obtain protein dispersion solution with a certain substrate concentration; adding protein glutaminase to obtain a system with a certain proportion of enzyme and substrate, wherein the temperature of enzymatic reaction is 36-38 DEG C, the time of the enzymatic reaction is 0.1-48 hour(s), and the pH value of the enzymatic reaction is maintained 7.0; adding dialysis solution, i.e. acetic acid solution of 0.10mol / L, wherein the dialysis time is about 8 hours; and carrying out vacuum freeze-drying, thereby obtaining the product. The invention can improve the protein solubility of the rice protein or the oryzenin, and can also enhance the emulsification, foaming performance, gelation and other functional properties of the rice protein or the oryzenin.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Biologically catalystic process of converting fat into ester to produce biological diesel oil
InactiveCN1453332AReduce pollutionSave energyLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockOil and greaseBiodiesel
In the biologically catalytic process, 3 or 4 stages of fixed bed enzyme reactors are used for continuous ester converting reaction. Raw material oil and grease and methanol in the methanol / oil molar ratio of 0.5-1 are added into the first fixed bed enzyme reactor, and the product effluent is separated to obtain coarse glycerine and other product to be passed through the subsequent reactors successively. The said process is repeated and ultimate product is separated to obtain biological diesel oil. Cheap oil and grease or even waste can be used to reduce the production cost of biological diesel oil. The present invention uses lipase and microbe cell as catalyst, and this can simplify material treatment and product collection, reduce reaction temperature, avoid the pollution of catalyst to glycerine as side product and eliminate pollutant exhaust.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method for rose extract and cosmetic
The invention relates to a preparation method for rose extract. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (a) mixing dry roseleaves or enzyme-inactivated fresh roseleaves with deionized water; regulating potential of hydrogen (pH) to 4.5-5.5; and grinding to obtain feed liquid; (b) adding the feed liquid obtained in the step (a) to an enzyme reactor; adding cellulase accounting for 0.02-0.05 percent of the weight of the feed liquid and pectinase accounting for 0.02-0.04 percent of the weight of the feed liquid; performing enzymolysis for 0.5-1.5 hours at the temperature of 45-50 DEG C at the pH of 4.5-5.5; and then, inactivating enzymes to obtain mixed feed liquid; (c) centrifuging the mixed feed liquid obtained in the step (b), and fetching supernate; (d) filtering the supernate by using a membrane to obtain filtrate; and (e) adding tea polyphenol to the filtrate, sterilizing and packaging. According to the preparation method for the rose extract, cell walls of the roses are broken by adopting the enzymolysis technology to enable active principles to be released from the cells, and moreover, the rose color and flavor are kept. Meanwhile, polysaccharide generated by proper enzymolysis also has a certain cosmetic effect. Moreover, the invention provides a cosmetic containing roseleaf and rose extracts and the tea polyphenol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RIDGEPOLE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Digestion tolerant starch and its preparation method and uses
ActiveCN1546678AExtensive resourcesEasy BiocompatibilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFermentationDrugChemistry
The invention discloses an alimentary resistant starch, the process for preparing the starch, and the use of the starch in preparing oral administration colon targeting medicament control release vectors, wherein the starch preparing process comprises the steps of, (1) mixing the starch with water, (2) heavy pressure modifying the starch or starch milk, (3) reacting in a reactor, (4) subjecting the enzymolysis product yield to centrifugation, scouring, filtering, drying and disintegration.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic immobilized cross-linked lipase aggregate and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102505008AIncrease vitalityImprove the problem of poor operabilityOn/in organic carrierEnzyme reactorCross-linked enzyme aggregate
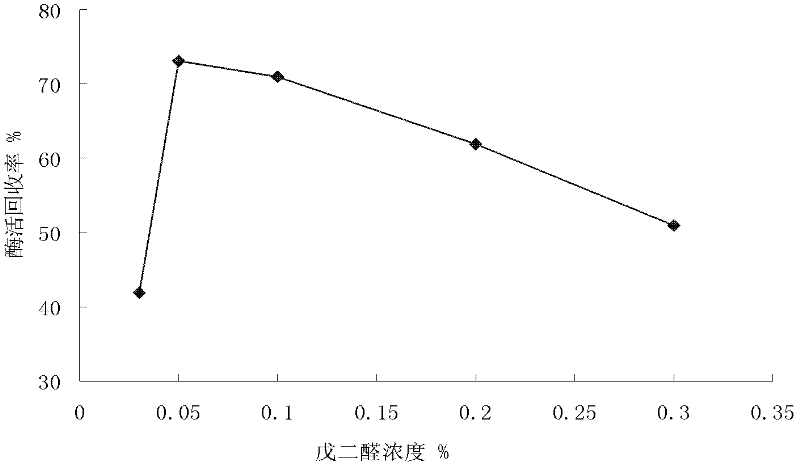
The invention discloses a magnetic immobilized cross-linked lipase aggregate and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: putting a cross-linked lipase aggregate into phosphate buffer, and fully oscillating to ensure that the cross-linked lipase aggregate is uniformly distributed in the phosphate buffer; adding a glutaraldehyde activated magnetic immobilized cross-linked lipase aggregate, and cross-linking; and separating liquid from a solid, washing the solid, and performing vacuum freeze drying to obtain the magnetic immobilized cross-linked lipase aggregate with the relative enzyme activity of over 80 percent. The preparation method is low in cost and easy to operate. A magnetic immobilized enzyme technology is organically combined with a cross-linked enzyme aggregate (CLEA) technology, so that the activity of a magnetic immobilized enzyme is improved, the problem of low operating performance of CLEAs is solved, and the obtained magnetic immobilized cross-linked lipase aggregate with high enzyme activity and operating performance is stable in property, can be used as a bio-enzyme catalyst to be widely applied, and is particularly suitable for a large-scale enzyme reactor.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High solids enzyme reactor mixer with vertical paddle and method
InactiveUS20140127756A1Speed up the flowReduce rotationBiological substance pretreatmentsRotary stirring mixersNuclear engineeringMixing chamber
A reactor vessel including: a mixing chamber having a vertical length, an upper inlet, and a lower outlet; and a vertically oriented paddle within the mixing chamber and having a cross-sectional shape of a hydrofoil, wherein the paddle moves with respect to the mixing chamber.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Bio diesel oil preparation technique using enzyme method of membrane on-line dehydration
ActiveCN101358216AImprove reaction efficiencyHigh yieldBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionChemical synthesisOil and grease
A process for preparing biodiesel by utilizing the enzymatic method of membrane online dehydration belongs to the field of biological and chemical synthesis. During the reaction of preparing the biodiesel by enzymatic grease with tertiary butyl alcohol as the reaction medium, volatilizable gases in the reaction system are directly used as the circulation dynamic force of the liquid in a reactor; the by-product water produced during the reaction is carried out from the enzyme reactor by the volatilizable gas and passes through a water-permselective membrane device so as to realize the online separation of the by-product water; the volatilizable gases such as the tertiary butyl alcohol and short chain alcohol still return to the enzyme reactor after passing through the membrane device and the circulation continues. The transmission of the membrane to water is more than 90 percent; the transmission of the membrane to the tertiary butyl alcohol is below 5 percent. The process for preparing biodiesel by utilizing the enzymatic method of membrane online dehydration has the advantage that the enzymatic reaction efficiency as well as the yield of the biodiesel are greatly improved, and is significant for the continuous production of preparing the biodiesel by the industrial enzymatic method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Fast organic waste recycling hot enzyme aerobic treatment technology
ActiveCN103304281AEfficient enzymatic fermentationEfficient and environmentally friendly processFertiliser formsOrganic fertilisersEvery HourDecomposition
The invention discloses a fast organic waste recycling hot enzyme aerobic treatment technology. The fast organic waste recycling hot enzyme aerobic treatment technology comprises the steps of: according to the proportion of (6-8):(2-4), respectively placing organic wastes and crop straw or wood chips into a hot enzyme reactor for stirring for 5-10min, respectively adding 0.05%-0.2% of heat-resistant enzyme and 0.05%-0.3% of thermophilic bacteria according to the weight percentage of the organic wastes and crop straw or wood chips, carrying out primary enzymatic fermentation, thorough decomposition and exhausting through the reactor, controlling the temperature of materials at 70-80 DEG C, controlling the humidity of the materials in the reactor to be 60%-70%, wherein the first-time exhausting amount is 100-500m<3> of per tonnage per hour, the exhausting time is 16-18 hours, and the rotating speed of stirring blade of the reactor is 1-20r / min; 16-18 hours later, finely adjusting the parameters of the hot enzyme reactor automatically, carrying out secondary enzymatic fermentation, thorough decomposition and exhausting, controlling the temperature of the materials to be 80-95 DEG C, the rotating speed of the stirring blade of the reactor to be 1-20r / min for 6-8 hours, wherein the second-time exhausting amount is 150-750m<3> of per tonnage per hour, and the exhausting time lasts for 6-8 hours; and then cooling and sieving, or further pelletizing or embedding to obtain the finished product.
Owner:BIOMAX ECOLOGICAL ENG
Magnetic immobilized cross-linking cellulase aggregates (CLEAs), preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102392013AIncrease vitalityImprove the problem of poor operabilityOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierEnzyme reactorChemistry
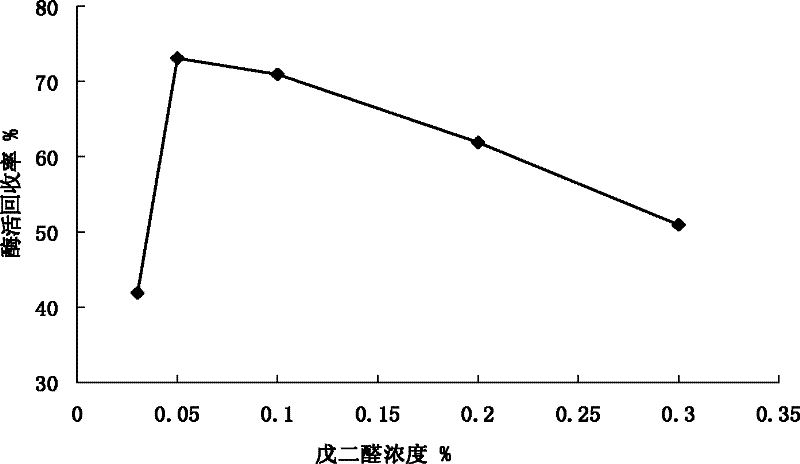
The invention discloses magnetic immobilized cross-linking cellulase aggregates (CLEAs), a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: first, fully swelling magnetic chitosan composite microspheres by using phosphate buffer, adding a cellulase solution, and adsorbing for 1 to 5 hours at the temperature of 10 to 25 DEG C; then, precipitating 0.5 to 2 hours at the temperature of 4 to 25 DEG C by adding a precipitating agent; and finally, adding a glutaric dialdehyde solution into a precipitated system, and performing a cross-linking reaction for 3 to 15 h at the temperature of 25 to 40 DEG C, thus obtaining the magnetic immobilized CLEAs. The preparation method provided by the invention is low in cost and is easy to operate. In the preparation method, a magnetic immobilized enzyme technology and a cross-linking enzyme aggregate technology are combined organically, not only the activity of the magnetic immobilized enzyme is improved, but also the problem of poor operating performance of the CLEAs is solved. The obtained magnetic immobilized CLEAs which have high enzyme activity and high operating performance have stable characteristics, can be widely applied by serving as biological enzyme catalysts, and are particularly suitable for a large-scale enzyme reactor.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Amphipathic block polymer, polymersome, and preparation method and application of polymersome
ActiveCN103588940AStimulus Modulation of Biocatalytic ActivityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOn/in organic carrierPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an amphipathic block polymer, a polymersome consisting of the amphipathic block polymer, and a preparation method and application of the polymersome. More specifically, the amphipathic block polymer is obtained from a hydrophilic chain segment and a hydrophobic chain segment by a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization method, wherein the hydrophilic chain segment is polyethylene glycol with the terminal group modified by tri-thioester and the molecular weight of the hydrophilic chain segment is 1,000 to 20,000 Da; the constitution of the hydrophobic chain segment is as shown in the following formula, m is equal to 1 to 11 and n is equal to 1 to 11. By adoption of the amphipathic block polymer, controllable and synchronous release of polymersome-loaded hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules is realized, and the biological catalytic activity of a polymersome-loaded enzyme reactor is regulated and controlled through stimulation. In addition, in the processing of triggering crosslinking by stimulation, the permeability of a sieve-shaped hydrophilic channel generated in a double-layer membrane of the polymersome and the membrane can be controlled by the duration time of stimulation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
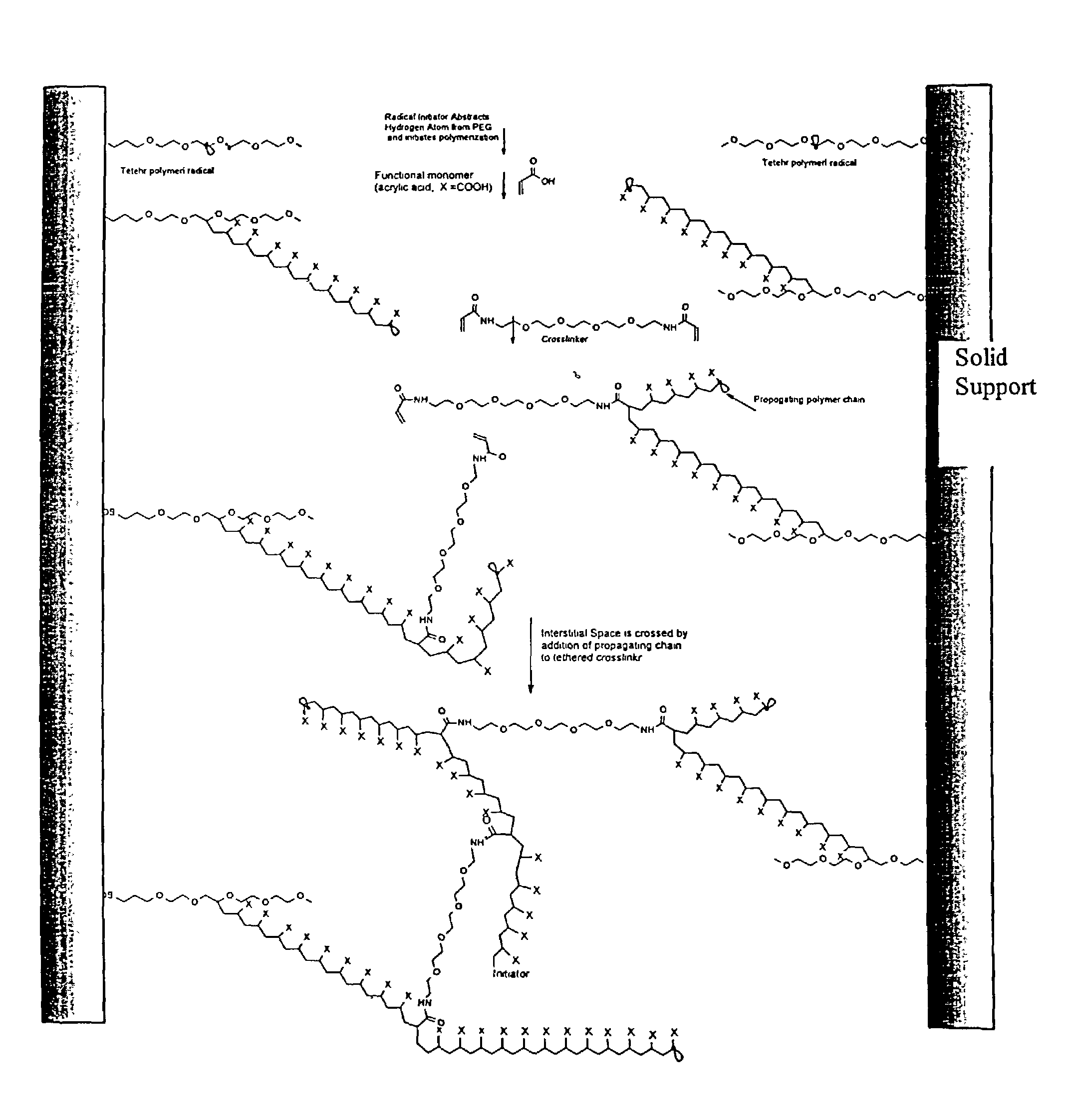
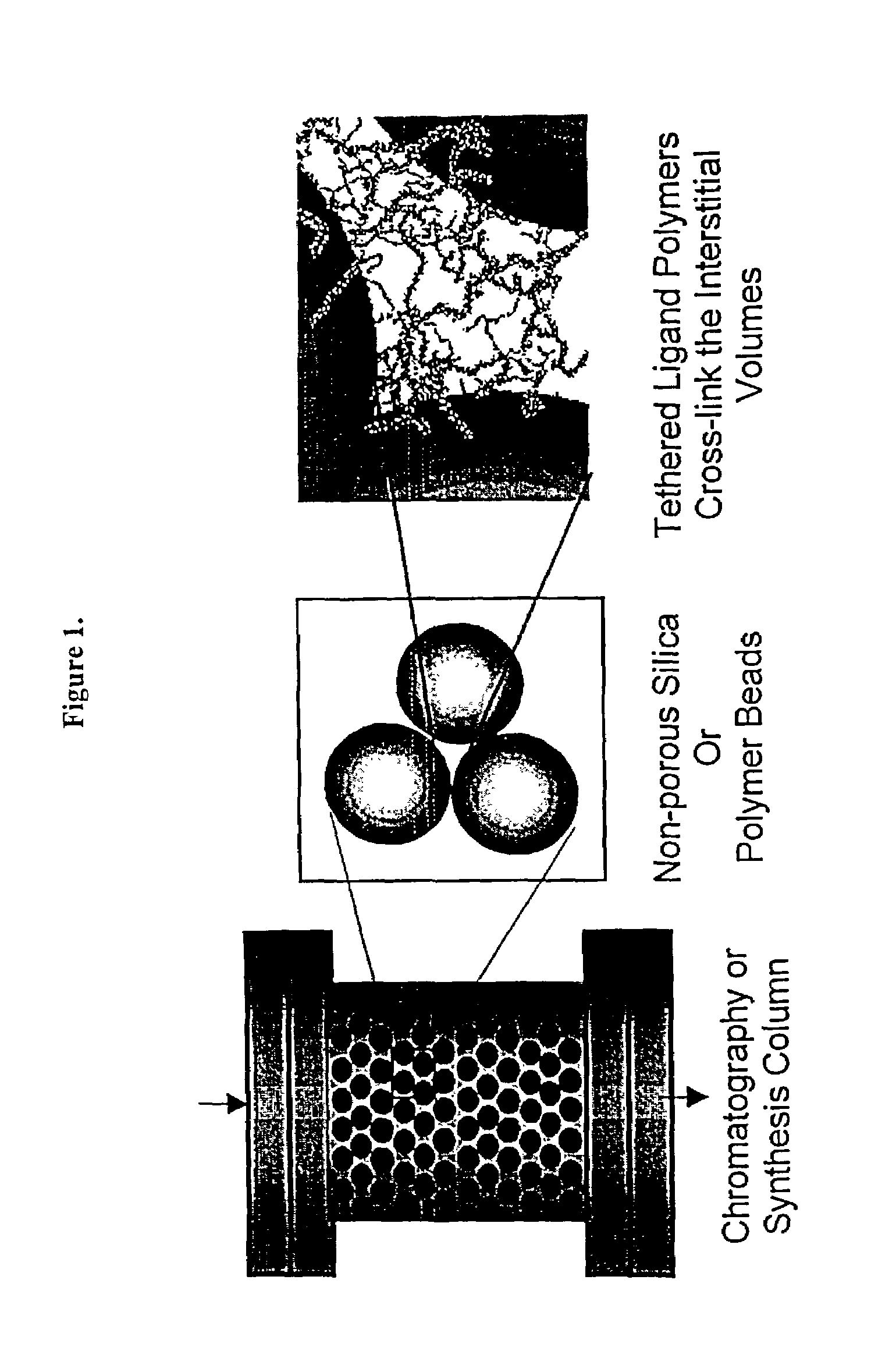
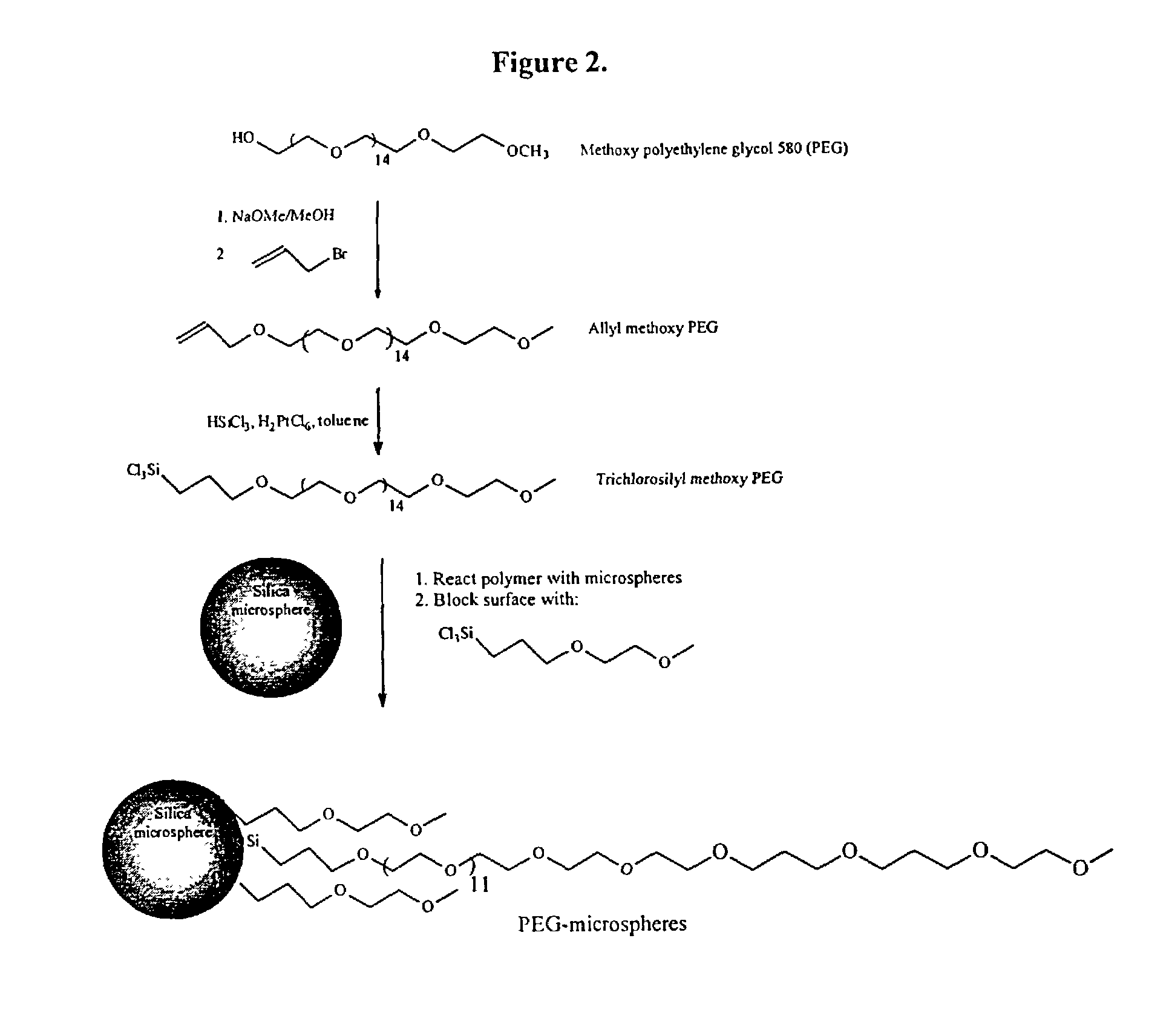
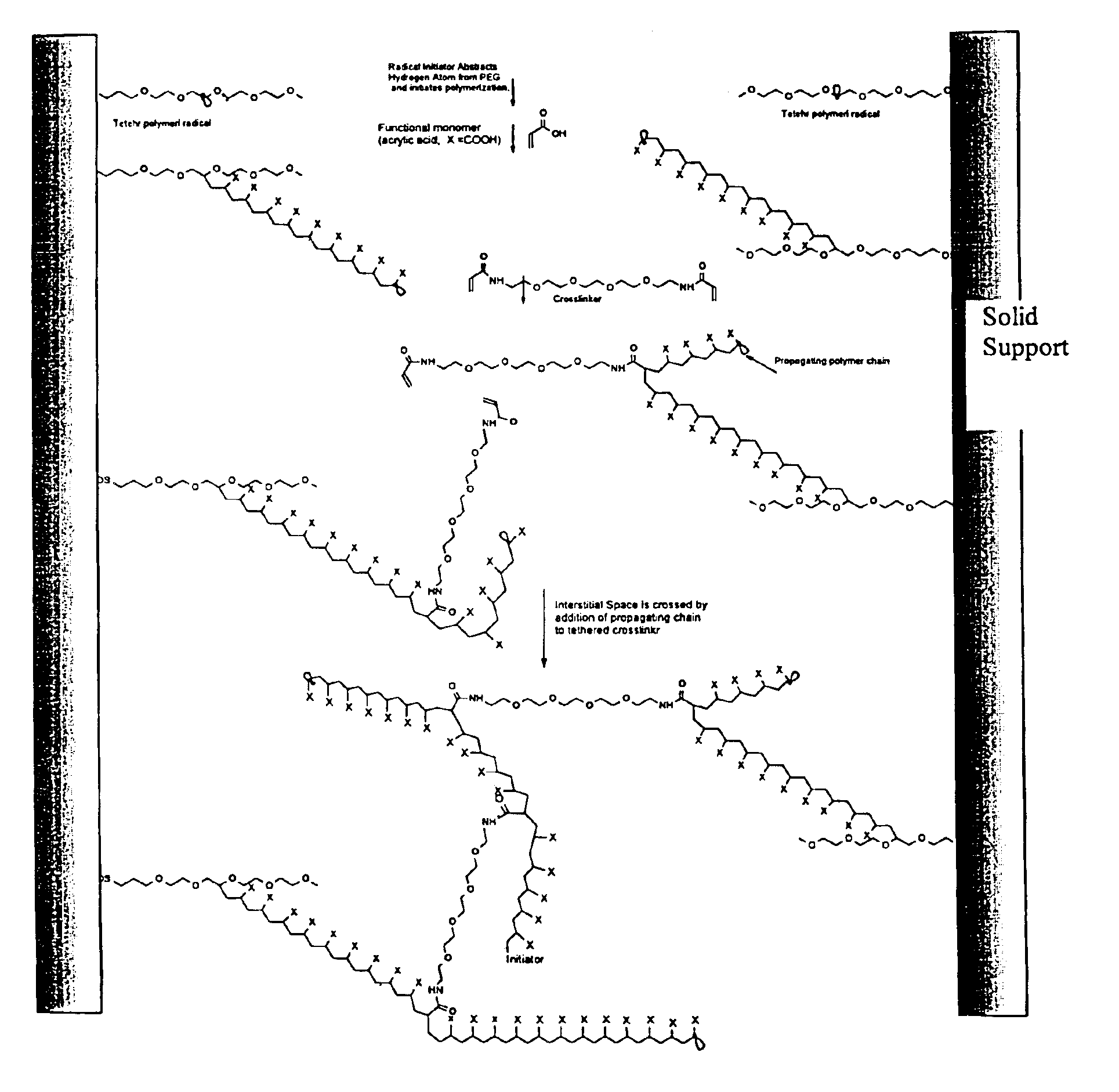
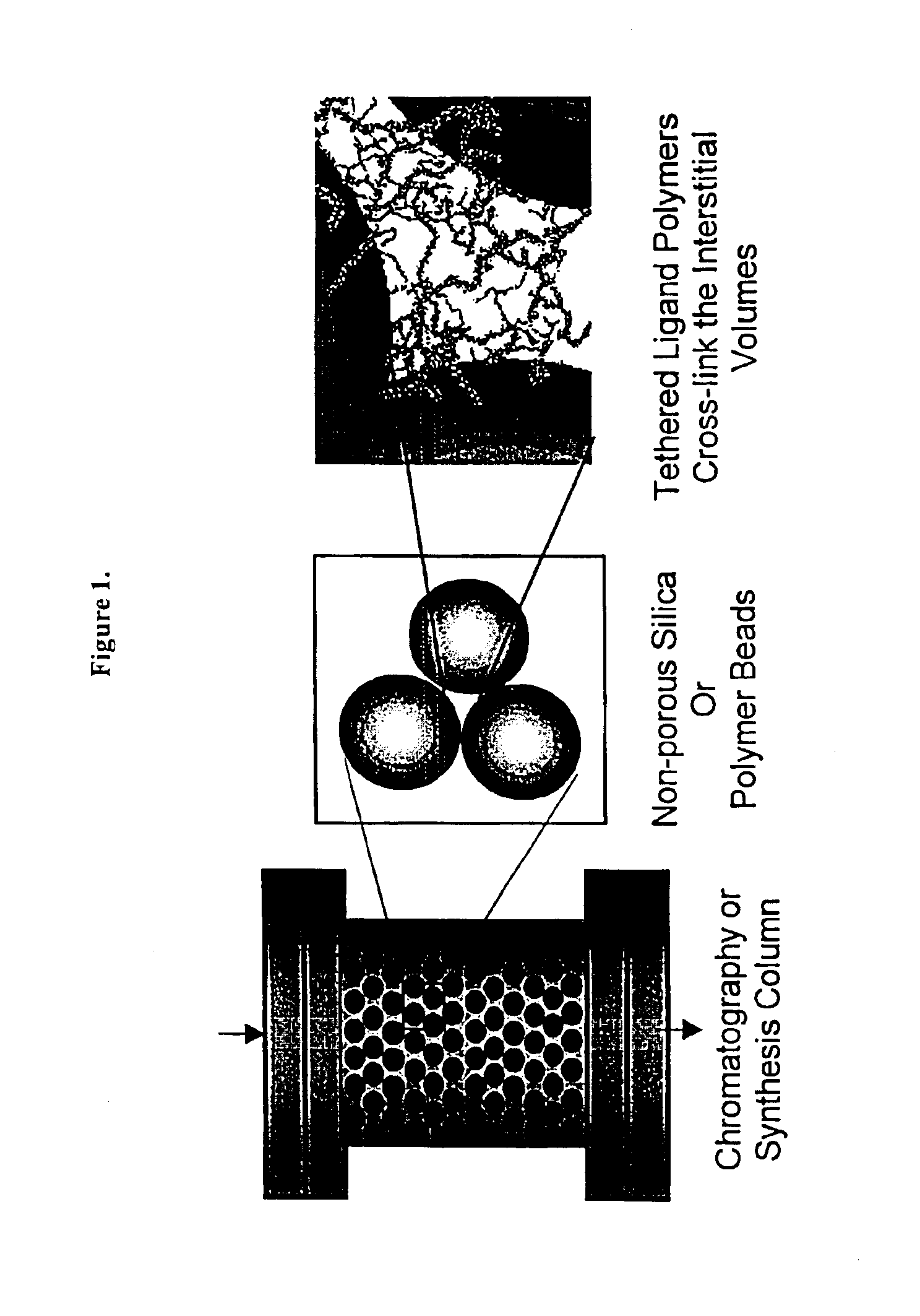
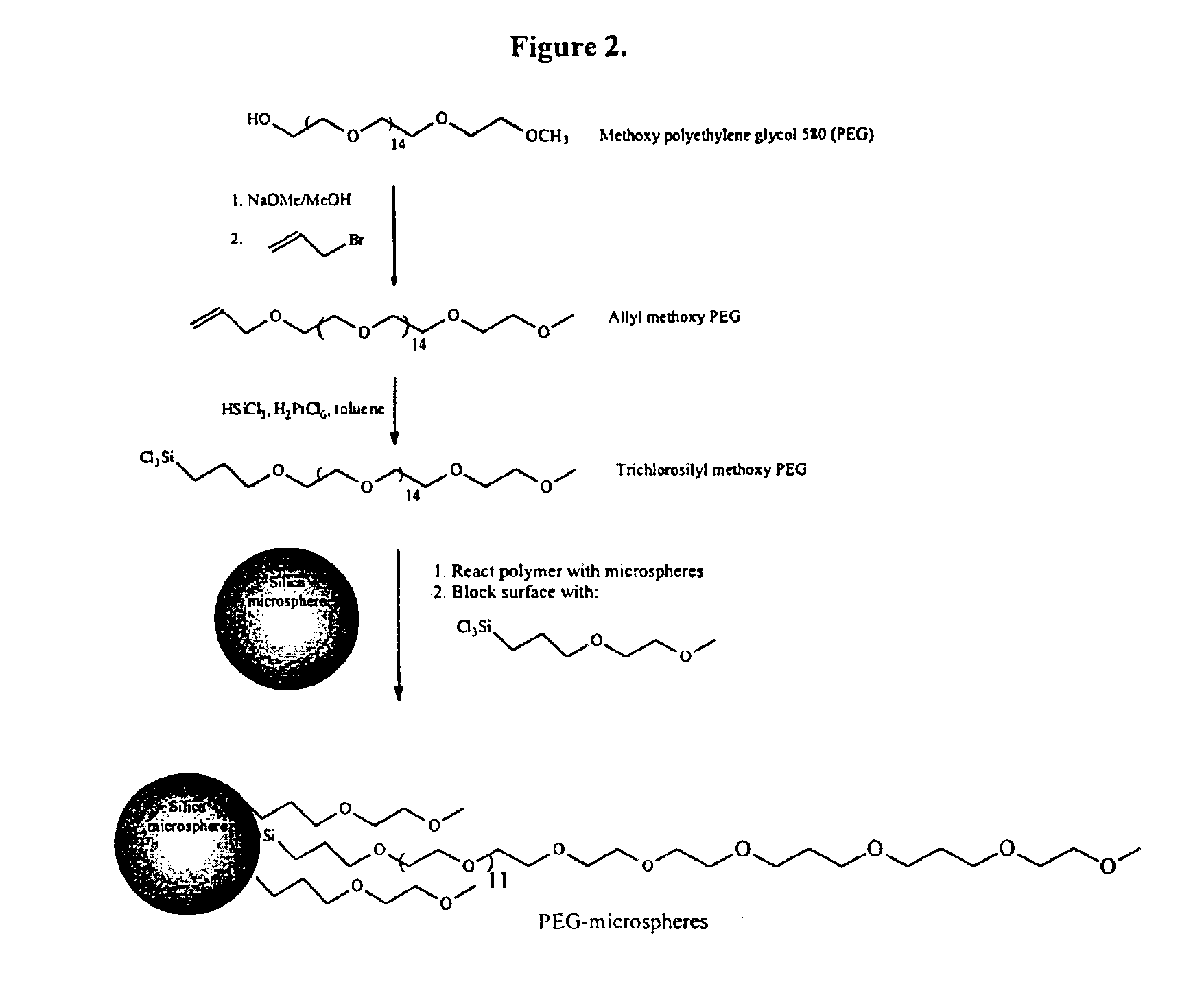
Composite matrices with interstital polymer networks
InactiveUS7201844B1High throughput screening separationMinimal flow resistanceIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesChemical reactionPolymer network
The present invention relates in general to the preparation and use of matrices having solid spaces, interstitial spaces and interstitial polymer networks. In particular, the interstitial polymer networks have utility in chemical and biochemical separations, solid phase synthesis, catalysis of chemical reactions, and immobilized enzyme reactors. The interstitial polymer networks in one embodiment comprise crosslinked polymers suspended in the interstitial spaces from and / or between solid particles. The matrices are characterized by high ligand and functional group density and by reversible high sorptive and binding capacity, and are substantially accompanied by a very low nonspecific adsorption or interaction with molecules such as proteins. Moreover, the matrices of the invention exhibit other characteristics highly desirable in chromatographic and catalytic applications, such as high physical rigidity, high ligand density, chemical stability, high ligand reactivity, and rapid exchange and reaction kinetics.
Owner:HAMMEN CORP
Composite matrices with interstitial polymer networks
InactiveUS6946070B2High throughput screening separationMinimal flow resistanceChromatographic cation exchangersSequential/parallel process reactionsPolymer scienceChemical reaction
The present invention relates in general to the preparation and use of matrices having solid spaces, interstitial spaces and interstitial polymer networks. In particular, the interstitial polymer networks have utility in chemical and biochemical separations, solid phase synthesis, catalysis of chemical reactions, and immobilized enzyme reactors. The interstitial polymer networks in one embodiment comprise crosslinked polymers suspended in the interstitial spaces from and / or between solid particles. The matrices are characterized by high ligand and functional group density and by reversible high sorptive and binding capacity, and are substantially accompanied by a very low nonspecific adsorption or interaction with molecules such as proteins. Moreover, the matrices of the invention exhibit other characteristics highly desirable in chromatographic and catalytic applications, such as high physical rigidity, high ligand density, chemical stability, high ligand reactivity, and rapid exchange and reaction kinetics.
Owner:HAMMEN CORP
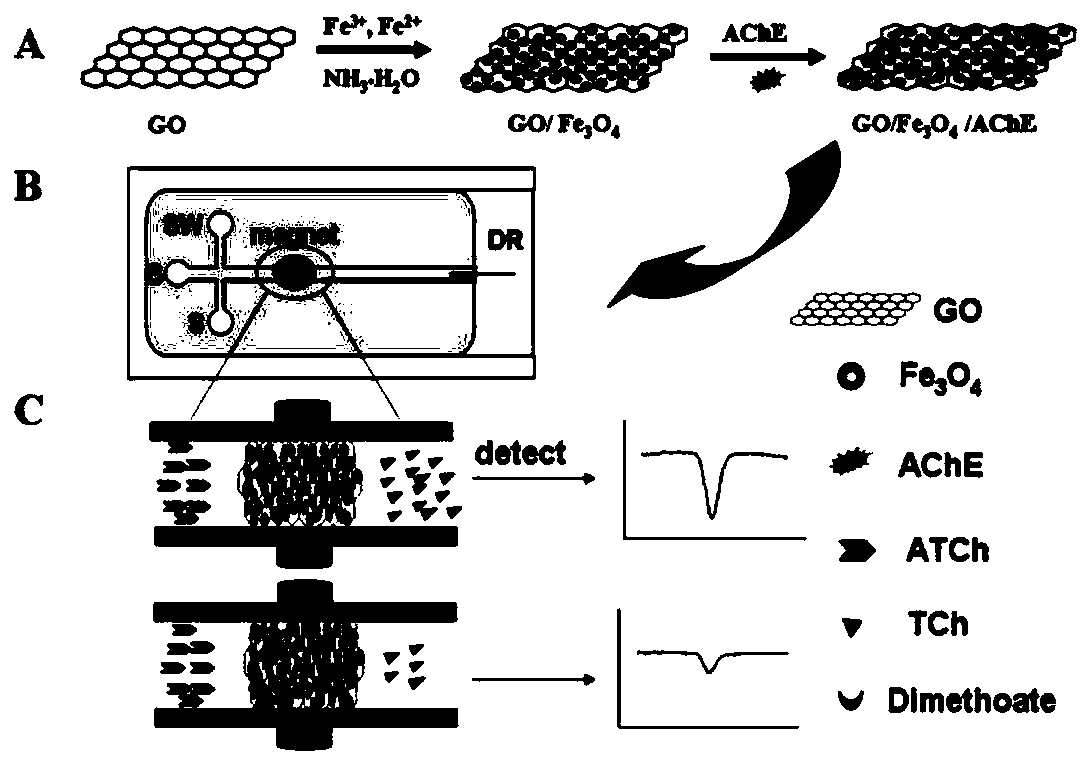
Preparation method and application of micro-enzyme reactor based on magnetic functionalized graphene oxide
InactiveCN103361267AIncrease loadHigh reuse rateMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme production/based bioreactorsAcetylhomocholineNanocomposite
The invention discloses a preparation method of a micro-enzyme reactor based on magnetic functionalized graphene oxide, and application of the micro-enzyme reactor in pesticide detection, belonging to the technical field of micro-fluidic control chips. The micro-enzyme reactor which can be applied to pesticide detection is prepared by firstly, loading Fe3O4 magnetic nano particles on the surface of graphene oxide by using a one-step in-situ synthesis method, so as to prepare a graphene oxide / Fe3O4 nano composite material with both good magnetism and biocompatibility, secondly, fixing acetyl choline esterase on the surface of the graphene oxide / Fe3O4 through action of pi-pi, hydrogen bonds and water repelling and the like, and fixing a graphene oxide / Fe3O4 / acetyl choline esterase compound inside a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) micro chip channel through the action of an external magnetic field. Based on the inhibition principle of pesticide to acetyl choline esterase, the rapid quantitative detection on dimethoate is realized. The micro-enzyme reactor which is prepared based on a graphene oxide / Fe3O4 / acetyl choline esterase composite material is rapid in action, simple to operate and good in reproducibility, and an effective means is provided for rapid and sensitive detection on pesticide.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Preparation of high-purity fructo oligosaccharides
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-purity low fructosan, which belongs to the technical field of purifying low fructosan by organically integrating barrier separation and enzyme reaction. In the invention, common low fructosan serves as the raw material; enzyme reaction and barrier separation are conducted in a barrier and enzyme reactor, the content of monosaccharide and sucrose is reduced to obtain the high-purity low fructosan. The content of the low fructosan obtained through the method is above 95 percent; the method has the advantages of convenient operation, stable quality, safety and reliability, and is applicable to industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Synthetic method of beta-alanine
InactiveCN104531796AImprove conversion efficiencyIncrease production capacityFermentationFiltrationL-Aspartate
The invention discloses a synthetic method of beta-alanine. The method comprises the steps: a) preparation of a substrate: filling 5g / L-80g / L L-aspartic acid substrate solutions into an enzyme reactor, and regulating pH into 5.0-8.5 by using alkalizers; b) enzymic catalytic reaction: adding enzyme-containing bacterium solutions into the substrate solutions for performing catalytic reaction, adding a proper amount of L-aspartic acid in batch during reaction to regulate pH of a reactant to 5.0-9.0, and performing fermentation culture, condensation and pulverization on the enzyme-containing bacterium solutions by utilizing engineering bacteria of high-yield L-aspartic acid alpha-decarboxylase; and c) filtration, decoloring and crystallizing treatment of the reactant in the enzyme reactor to obtain beta-alanine. L-aspartic acid is further catalyzed by using the enzyme-containing bacterium solutions and converted into beta-alanine, and the beta-alanine is mild in production condition, simple in process, low in environment pollution, high in quality of products and convenient to extract at the downstream; the purity reaches 99.0 percent, and the conversion rate of beta-alanine reaches 99.5 percent.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Dried maize flour noodle containing lysine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1669445ADelicate tasteImprove gluten qualityDough treatmentFood preparationNutritive valuesCorn flour
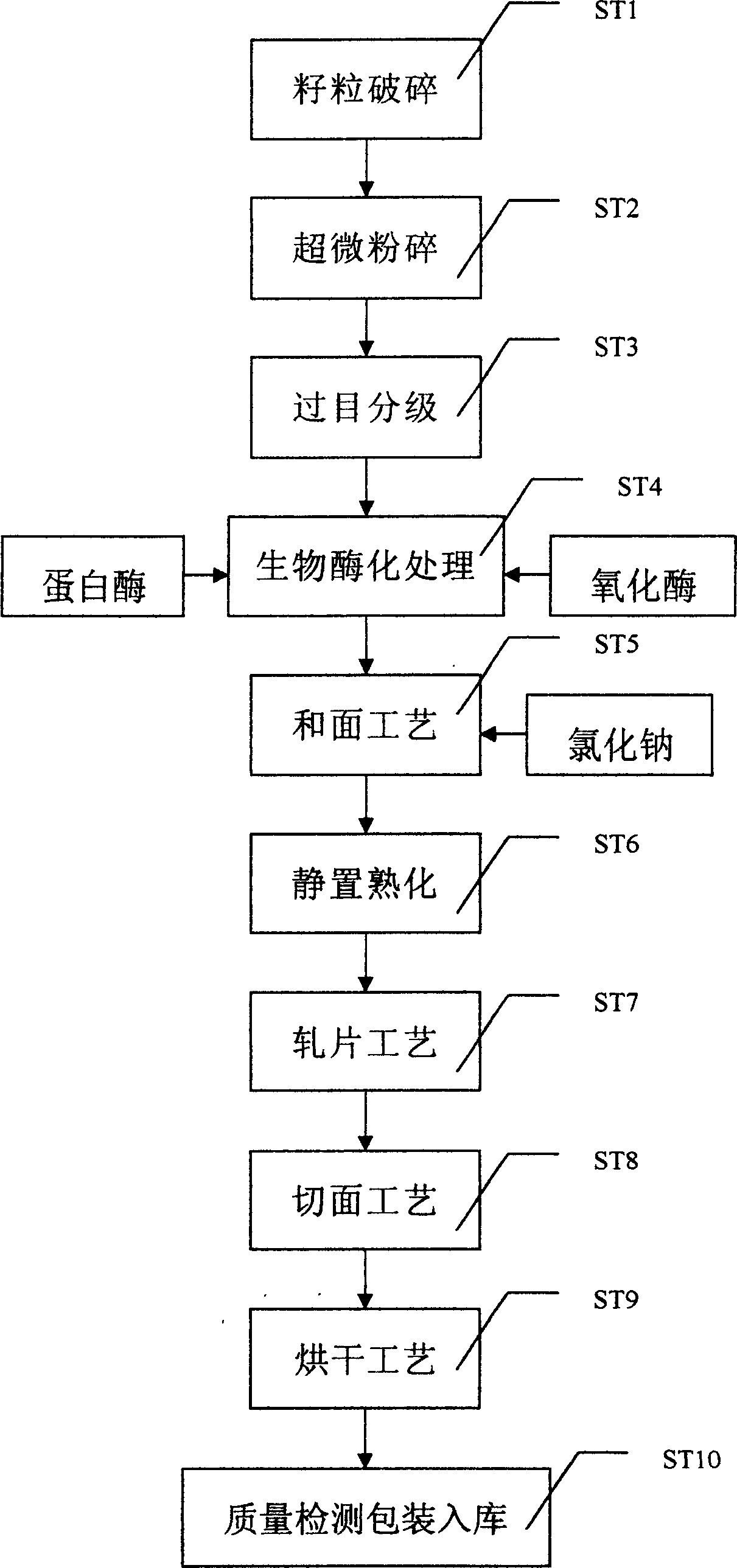
The invention discloses a lycine maize flour which contains 0.05percent to 1pencent weight of prolease, 0.0005percent to 0.01 percent weight of oxidase, and the left are the lycine corn. The preparing method includes the following steps:(1)microdisintegrate the lycine kernel corn, to make the silty reach 90order to 150order; (2)send the disintegrated maize flour into the biology enzyme reactor, matched with proteinase and oxidase, and mix them to react; (3)send the biological enzymed treatment powder into the dough mixing machine, and agitate it with water; (4)stewing maturation, sheeting, cut noodles and drying, then we gain the lycine maize flour. The invention relies on the high-lysine corn, improves the glutinous by microdisintegration and biological enzyme process, and makes the high-lysine corn noodle. The noodle is ate very deliciously, and it has great nutrition value, so it is the ideal health food for the current people.
Owner:四川美洛斯林生物科技有限公司
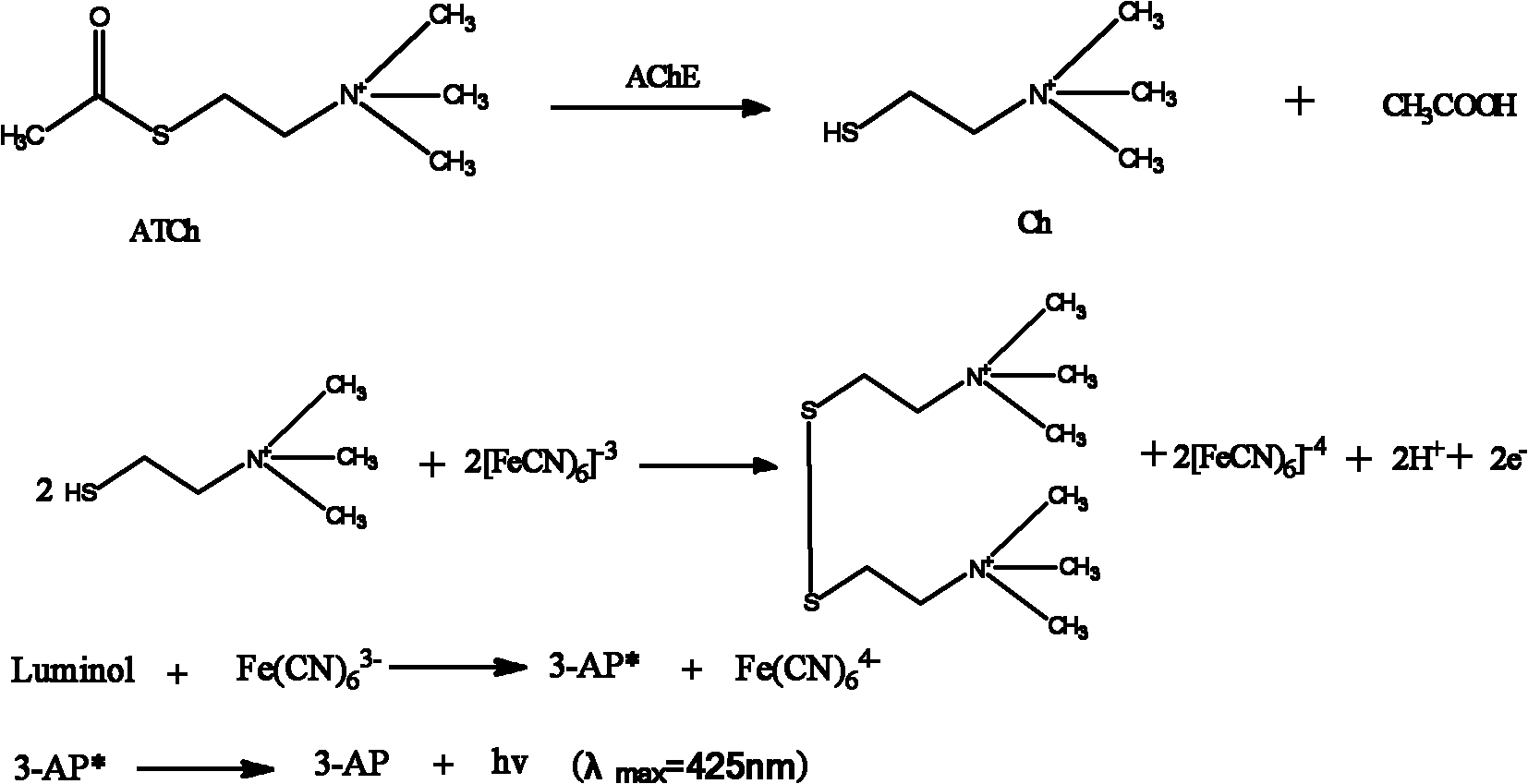
Acetylcholinesterase chemiluminescence bioreactor, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101968448AIncrease enzyme activityHigh recovery rateMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCarbamatePesticide residue
The invention discloses an acetylcholinesterase chemiluminescence bioreactor, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of analysis of pesticide residues and biotechnology. The reactor is a glass tube of which the two ends are sealed by 300-mesh bolting silk, wherein immobilized acetylcholinesterase is held in the glass tube; and the immobilized acetylcholinesterase is purified crucian muscle acetylcholinesterase which is immobilized on cyanogen bromide-activated (CNBr) sepharose 4B. The application of the reactor is characterized by comprising the following steps of: establishing the acetylcholinesterase chemiluminescence bioreactor; and detecting organic phosphorus and carbamate type pesticides. The crucian muscle acetylcholinesterase (AChE) extracted in the invention has high enzyme activity, obvious purification effect and high immobilized enzyme activity recovery rate; the detection limit of the organic phosphorus type pesticides and the carbamate type pesticides is low; the analysis time is short; and the enzyme reactor can be repeatedly used.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Protein doped organic-inorganic hybridized flower-shaped nano material
InactiveCN103289985ALow priceEasy to operateCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesOn/in inorganic carrierPhosphateInorganic compound
The invention discloses a protein doped organic-inorganic hybridized flower-shaped nano material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of organic-inorganic compound materials. The material is of a three-dimensional flower-shaped nano structure. The organic-inorganic hybridized flower-shaped nano material which is 5-50 mu m in diameter is obtained by taking protein, phosphate and soluble bivalent copper ion salt as raw materials in an aqueous liquor by reaction at 0-50 DEG C. The material provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low raw material cost, environmental friendliness and the like. The protein doped organic-inorganic hybridized flower-shaped nano material prepared by the invention has good using value and application prospect in the fields of biosensors, enzyme reactors and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Technique of enzyme method for treating organic wastewater and matched equipment
InactiveCN1686874AImprove stabilityImprove utilization efficiencyMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationTemperature controlFiltration
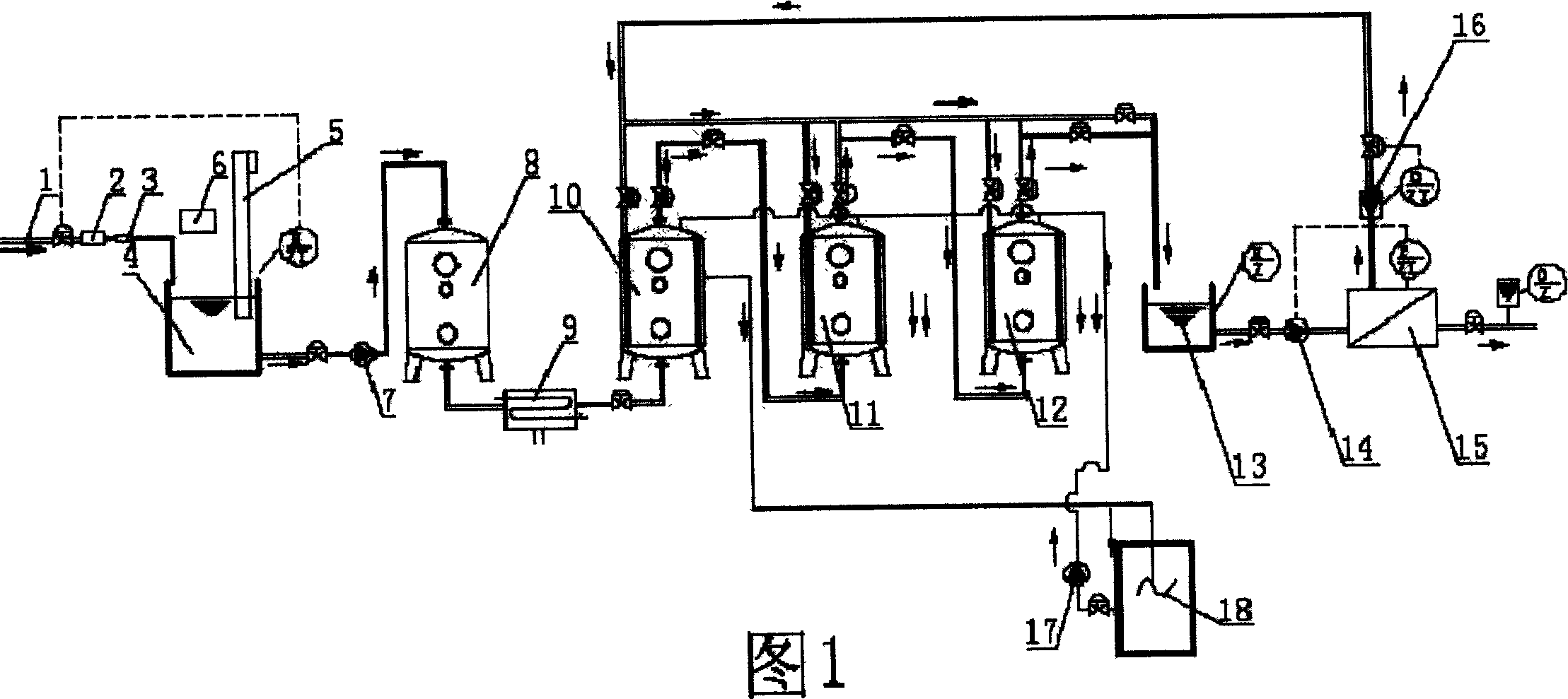
The present invention relates to a process for treating organic waste water by utilizing enzyme method. Said process is implemented by making organic waste water successively by passed through the water storage tank or precipitation tank, pH regulating tank, pretreatment device, temperature control device, enzyme reactor and filtration device. It is characterized by that the waste water is fed into the immobilized enzyme reactor from its bottom portion, and undergone the process of one-stage or multistage treatment to implement enzyme catalytic degradation so as to make discharged water meet discharge standard.
Owner:江苏晨翔环境科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com