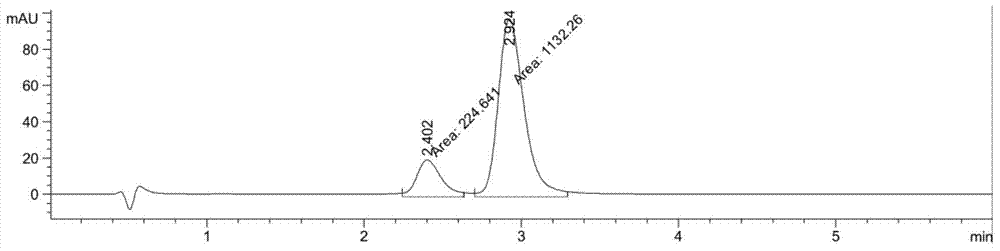
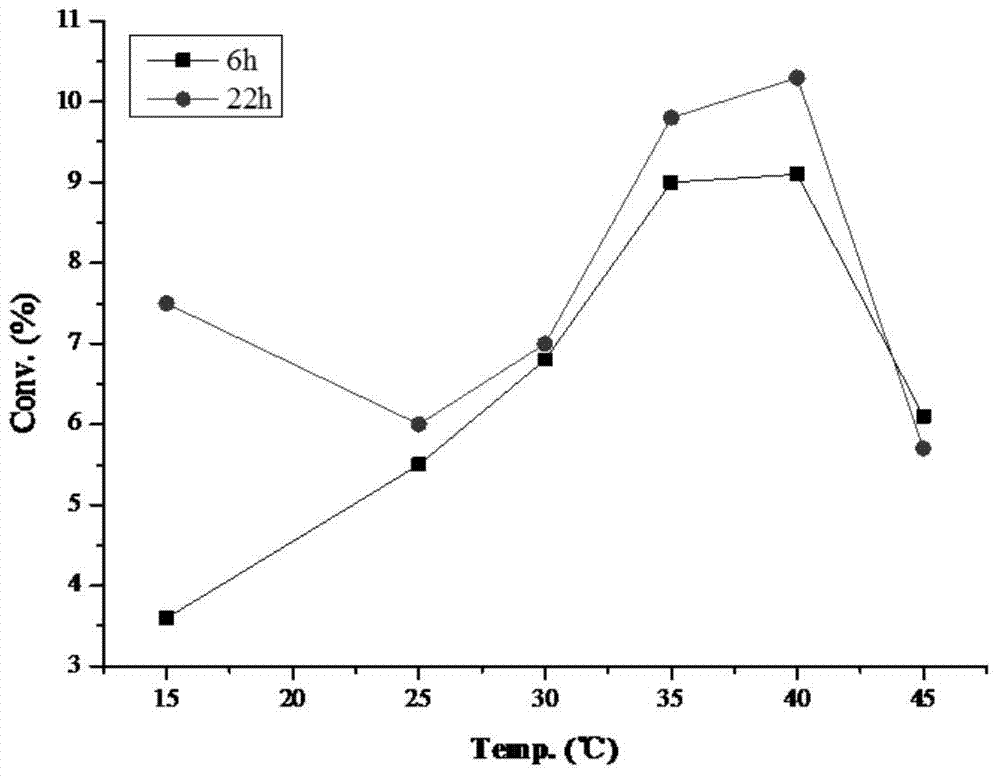
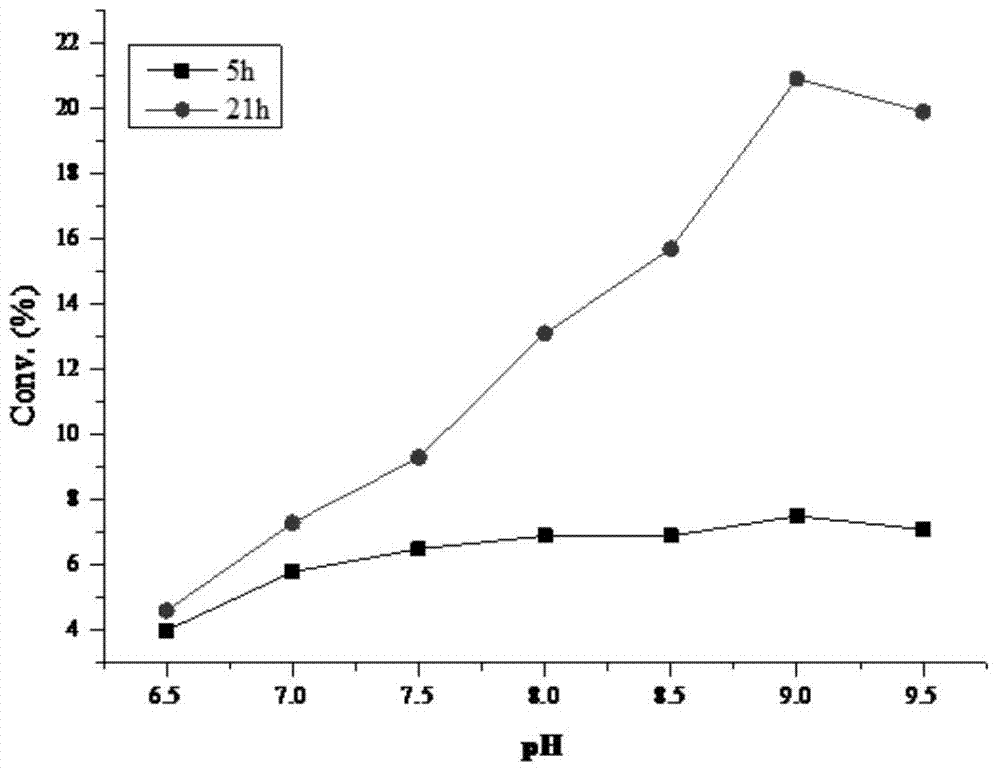
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102results about How to "High substrate concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
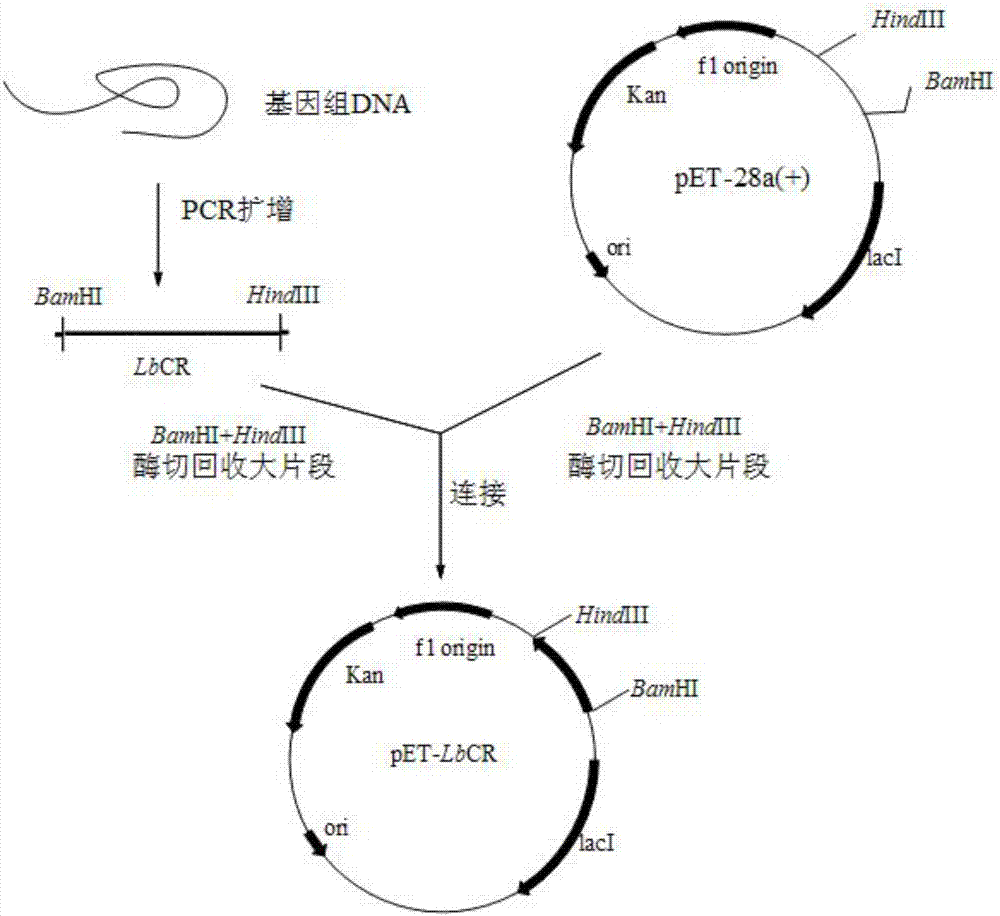
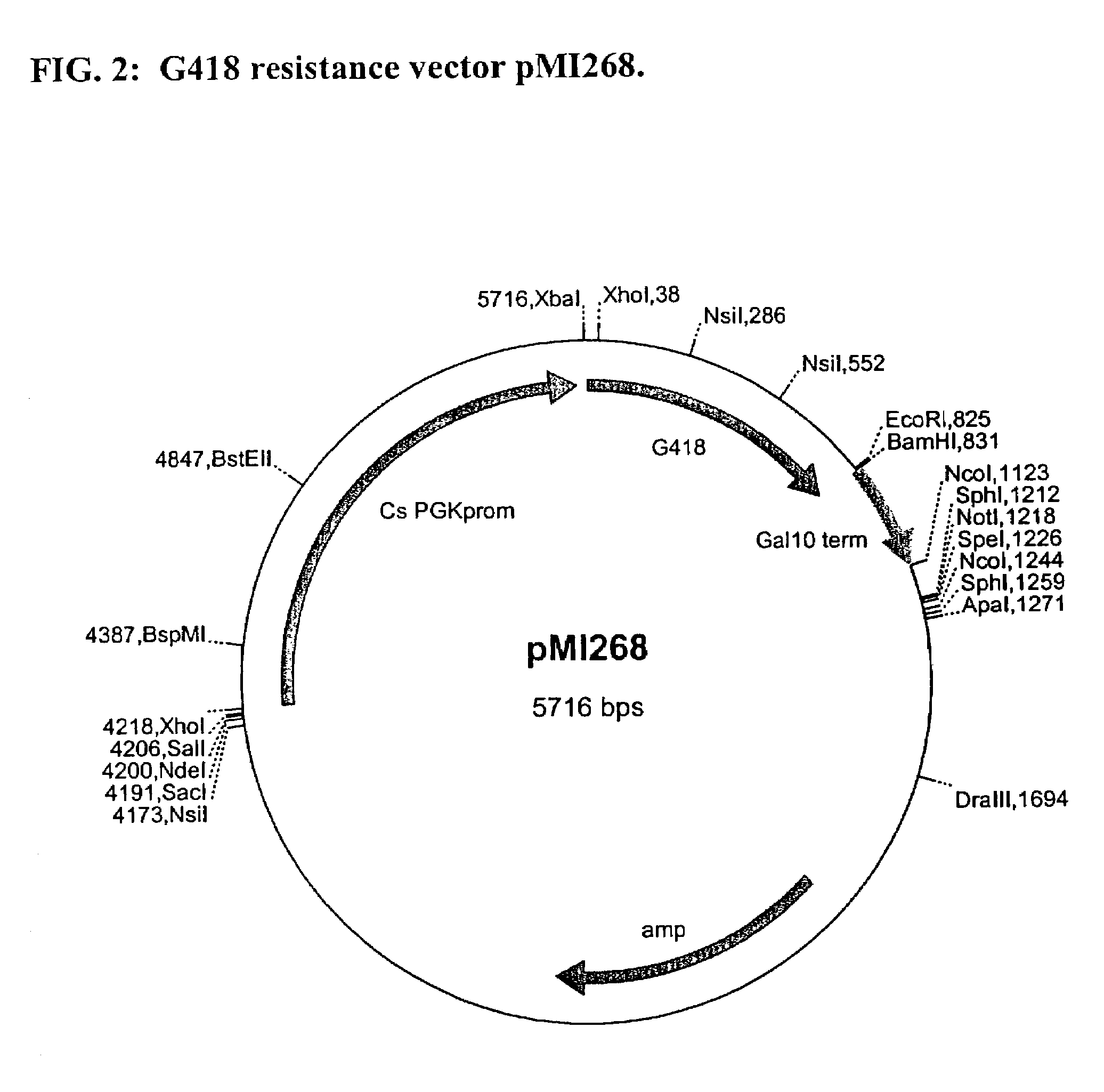
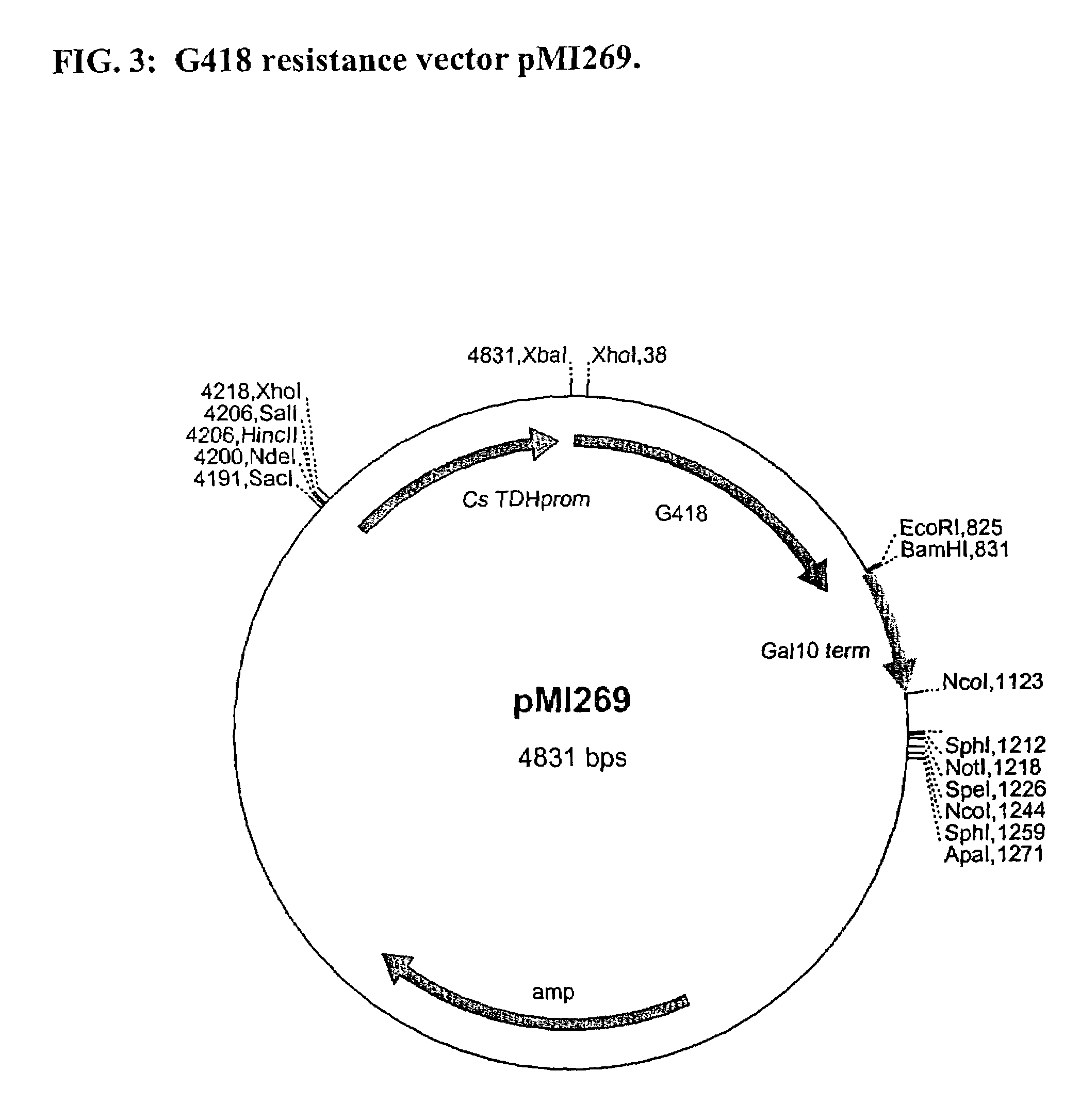
Methods and materials for the production of organic products in cells of Candida species
InactiveUS7141410B2Good conditionUse in synthesisSugar derivativesMicroorganismsHeterologousBiotechnology
The present invention relates to biocatalysts that are cells, optimally of the Crabtree-negative phenotype, comprising expression vectors encoding genes heterologous to the cell that enable increased production of organic products. More specifically, the invention relates to genetically modified Candida cells, methods for making the Candida cells, and their use in production of organic products, particularly lactic acid.
Owner:CARGILL INC
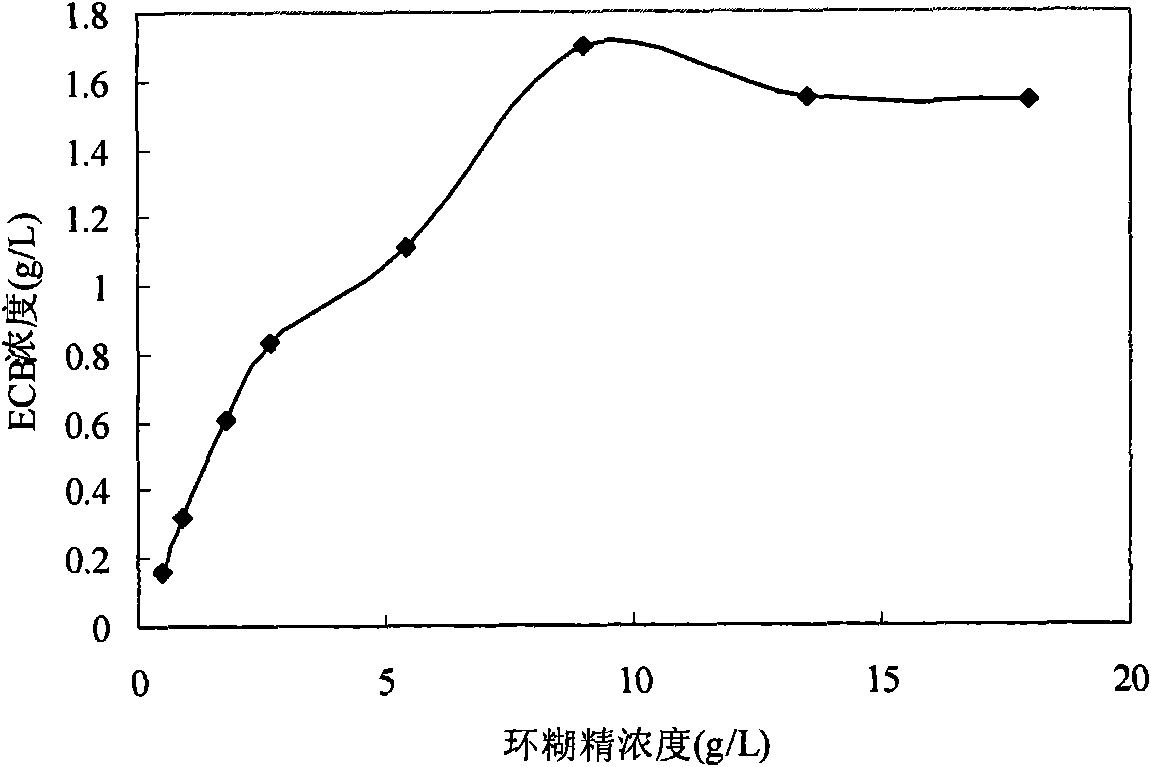
Biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its application
InactiveCN101020919AImprove solubilityPromote biotransformationMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolubilityMicroorganism
The present invention belongs to the field of biological sterol transforming technology, and is especially biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its derivative and its preparation. In a transforming system, cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain amount is added, or substrate and cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain ratio are made to form inclusion compound, so as to facilitate transformation. The process of the present invention is especially suitable for microbial transformation of hydrophobic compound, and can raise the solubility of reaction substrate in water solution, raise the substrate utilizing rate and reaction rate, release substrate and product inhibition and raise product converting rate. When the substrate concentration is 3-20g / L, the present invention has conversion period shorted to 3-4 days, conversion rate of 50-95 % and high industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
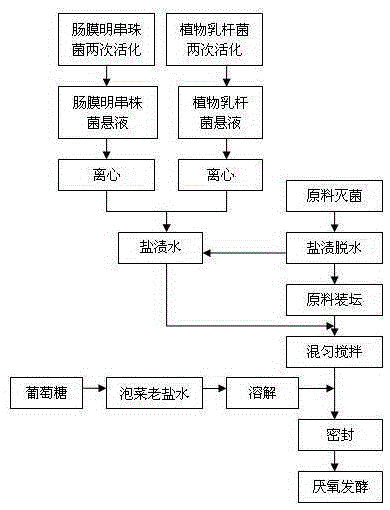
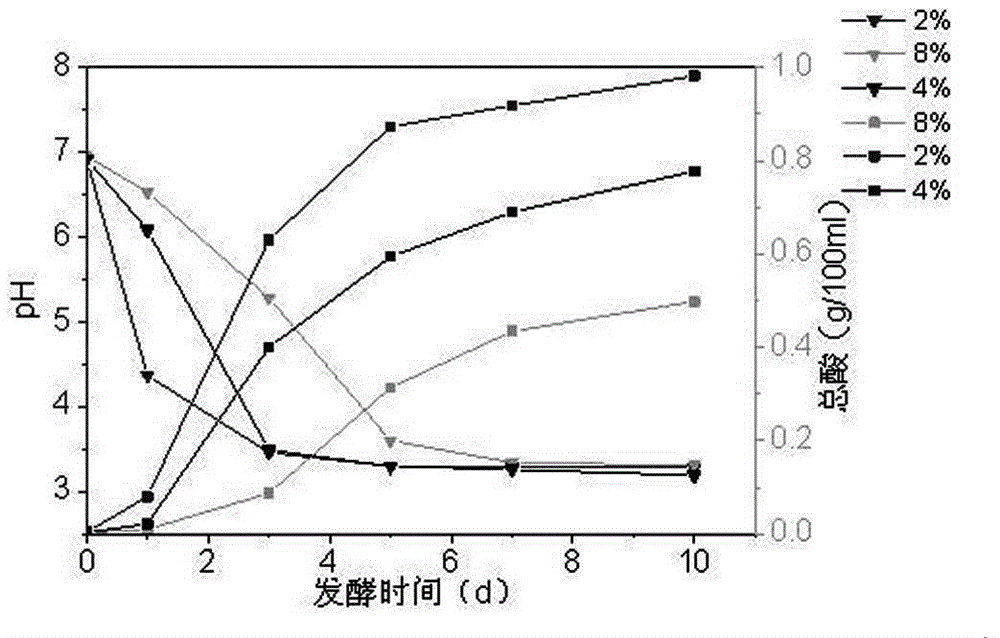
Manufacturing method of novel semisolid quick-fermentation pickle
PendingCN105394669AIncrease concentrationFull of nutritionClimate change adaptationLactobacillusLeuconostoc mesenteroidesSludge
The invention belongs to the field of food processing, and in particular discloses a manufacturing method of a novel semisolid quick-fermentation pickle. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating raw materials; (2) performing disinfection treatment on a pickle jar; (3) salting and dehydrating a pickle; (4) preparing lactobacillus plantarum and leuconostoc mesenteroide bacterial sludge; (5) adding auxiliary materials and a culture; (6) adding pickle old brine and glucose; (7) laying vegetable in the jar flat, adding a layer of film at the opening of the pickle jar, filling up the pickle jar edge water groove with water, thus achieving a double-layer sealing effect, and fermenting under normal temperature. According to the method, the pickle raw materials are firstly salted and dehydrated, and then leuconostoc mesenteroide and the lactobacillus plantarum are added into the pickle jar, so that an obtained pickle substrate is high in concentration, rich in nutrition, and short in fermentation period, and also has the characteristics of preventing pickle mildew, improving pickle taste, and improving pickle quality and safety, and the problem of high cost caused by great salt consumption and water consumption in pickle industrialization can be solved.
Owner:SICHUAN DONGPO CHINESE PAOCAI IND TECH RES INST
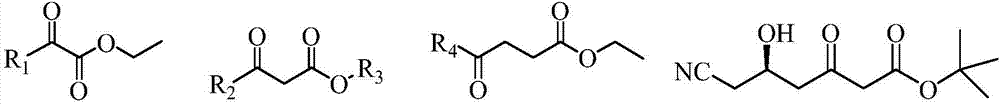
L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110343676AHigh substrate concentrationLow costOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringL-glutamate dehydrogenaseEnzyme action
The invention discloses an L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. The sequence of the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant comprises a sequence obtained by mutating amino acid residue Aat position 166 and / or amino acid residue V at position 376 in a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 into a basic, hydrophilic or small hindered amino acid residue. The application comprises the followingsteps: subjecting 2-oxo-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butanoate to amination reaction in the presence of an L-amino acid dehydrogenase mutant, an inorganic amino donor and a reduced coenzyme NADPH to obtain L-glufosinate salt; and further acidifying the obtained L-glufosinate salt to obtain L-glufosinate. Compared with wild-type L-glutamate dehydrogenase, the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant of theinvention has a higher catalyzed substrate concentration when used for preparing the L-glufosinate, thus the enzyme action efficiency is improved, the reaction cost is reduced, and industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIZHOU ZIYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for hydrolyzing chitosan and chitin
InactiveCN101723989ALow costFast hydrolysisSugar derivativesOligosaccharidesChitin formationReaction speed
The invention relates to a method for hydrolyzing chitosan and chitin to prepare monosaccharide and oligosaccharide by using ionic liquid as a reaction medium and using protonic acid as a catalyst under the condition of heating. Particularly, the method comprises the following steps: dissolving the chitosan or the chitin into the ionic liquid, adding acid and water into the solution, and heating the solution to perform reaction so as to obtain a hydrolysis product of which the yield reaches up to 70 percent based on total reducing sugar. The method has the advantages of mild operation condition, high reaction speed, reusability of the ionic liquid, low cost, simple process, environmental friendliness and the like, provides a new method for efficiently degrading the chitosan and the chitin, and develops a new path for preparing general oceanic chemicals and medicinal health-care products in large scale.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 and application thereof in preparation of chiral alcohol
ActiveCN103849574AHigh optical purityHigh substrate concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAlcohol
The invention discloses a novel strain, namely candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 and application thereof in preparation of high optical purity (5S)-(4-fluobenzene)-5-hydroxyvalerate by virtue of microbial catalytic asymmetric reduction of a 5-(4-fluobenzene)-5-keto pentanoic acid. The e.e value of a target product (5S)-(4-fluobenzene)-5-hydroxyvalerate achieves 99.9% and the yield achieves 95.37% when the concentration of a substrate is 47.62mmol / L and the final concentration of cosubstrate glucose is 100g / L by virtue of chiral biocatalysis of adopting the candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 cell as a catalyst.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
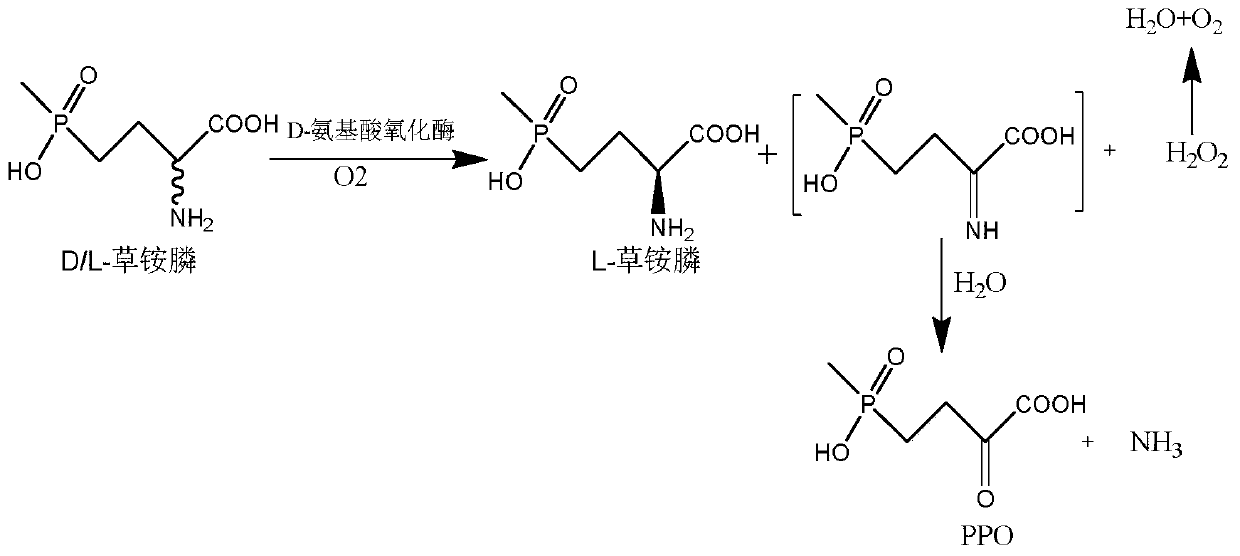
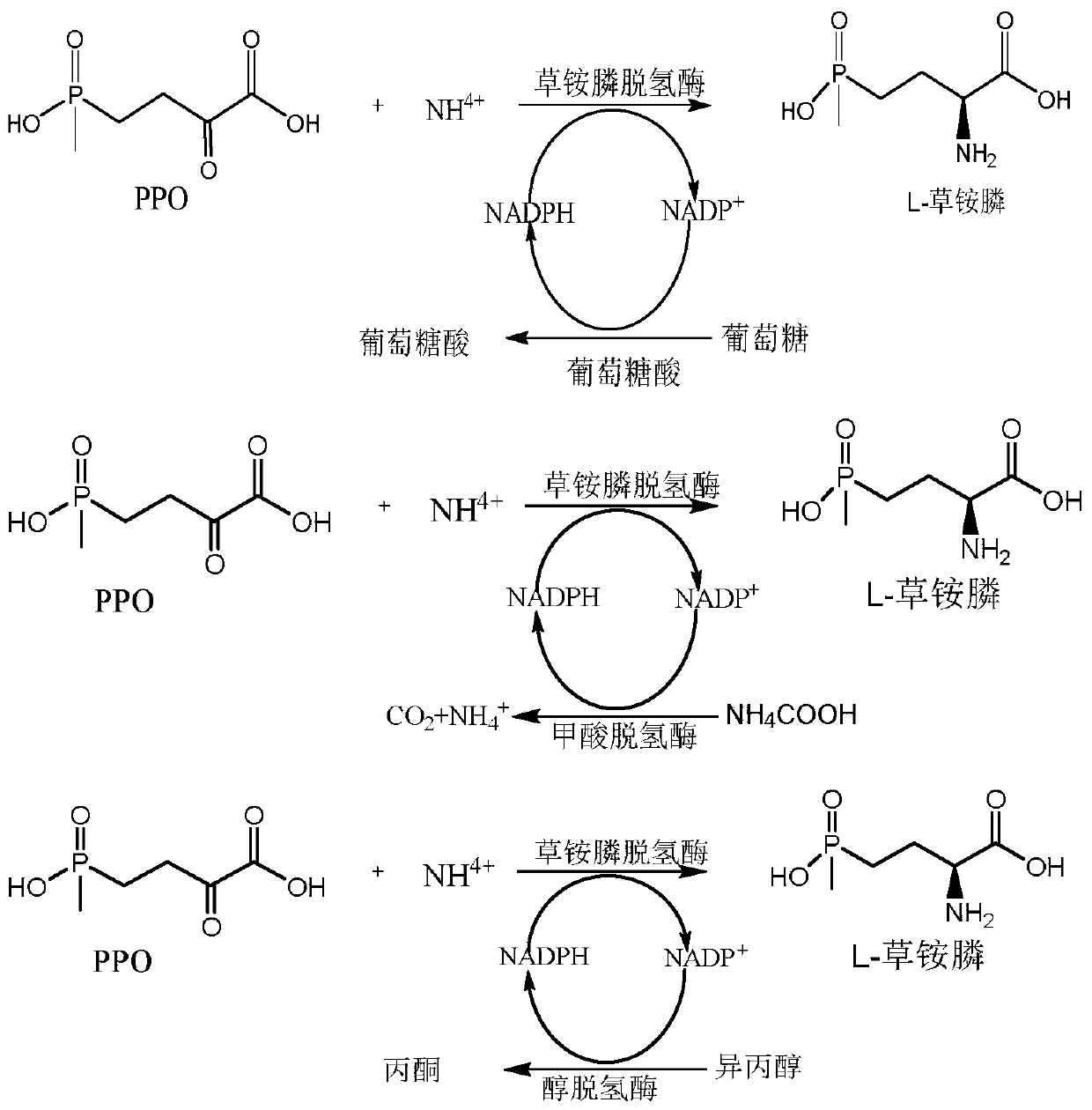
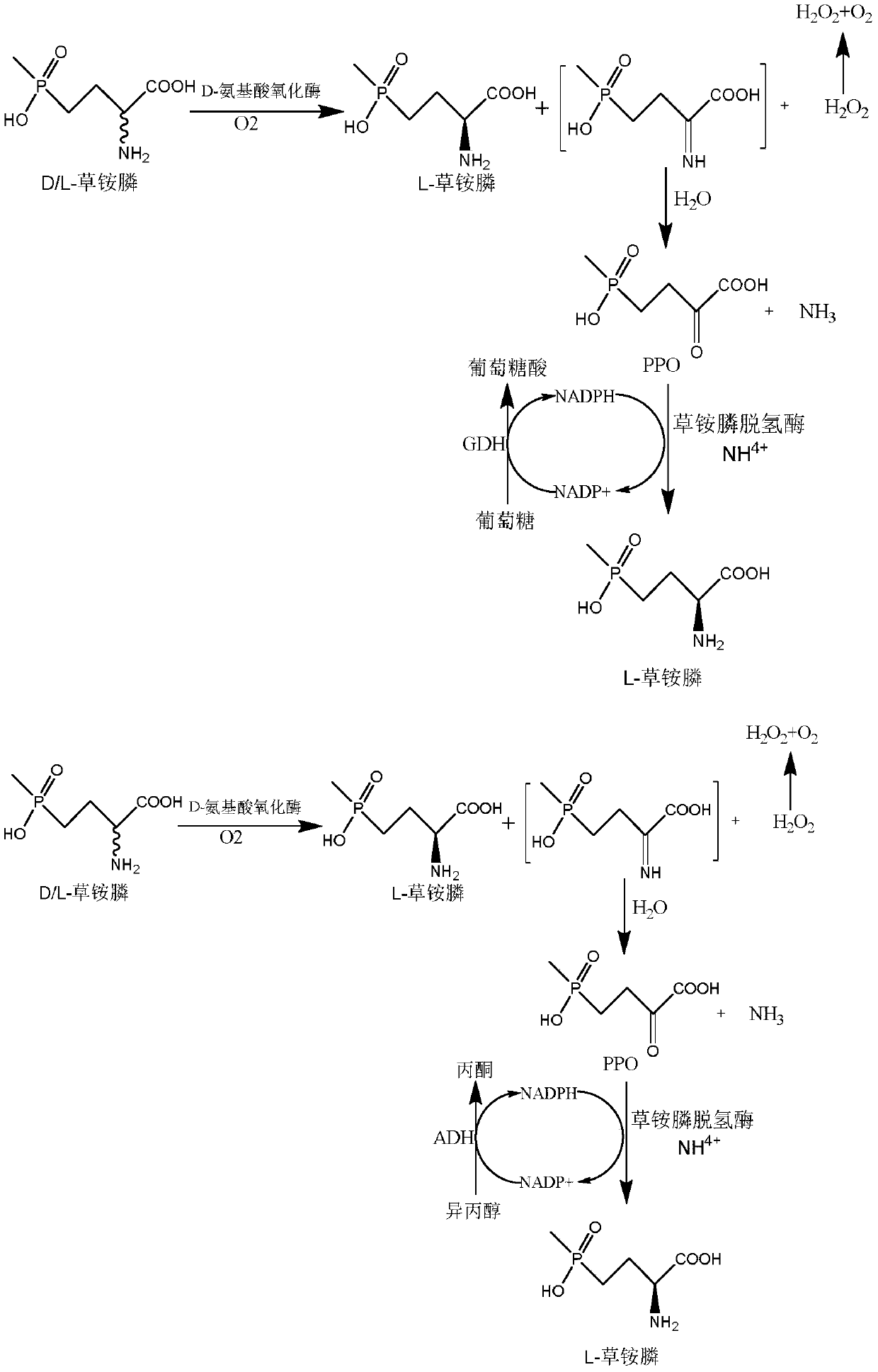
Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to production of L-glufosinate-ammonium through oxidation-reduction of multienzymes
InactiveCN110592036AHigh catalytic activityHigh substrate concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutantSubstrate concentration
The invention discloses a glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof to production of L-glufosinate-ammonium through oxidation-reduction of multienzymes. According to the method, a method for preparing an L-glufosinate-ammonium precursor through D-amino acid oxidase is utilized, D, L-glufosinate-ammonium or D-glufosinate-ammonium is used as substrate, and in aerobic environment or under the situation that catalase exists, through excised D-amino acid oxidase or in vitro expression of cells of D-amino acid oxidase, the D-glufosinate-ammonium is catalyzed to obtain 4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-2-oxobutanoic; and under the action of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, the 4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-2-oxobutanoic is catalyzed to generate the L-glufosinate-ammonium, the activity of a catalyst is improved by about 10 times, and the concentration of the substrate is increased by 5 times. The method is high in raw material conversion rate and high in yield, and products are easy to separate and purify.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
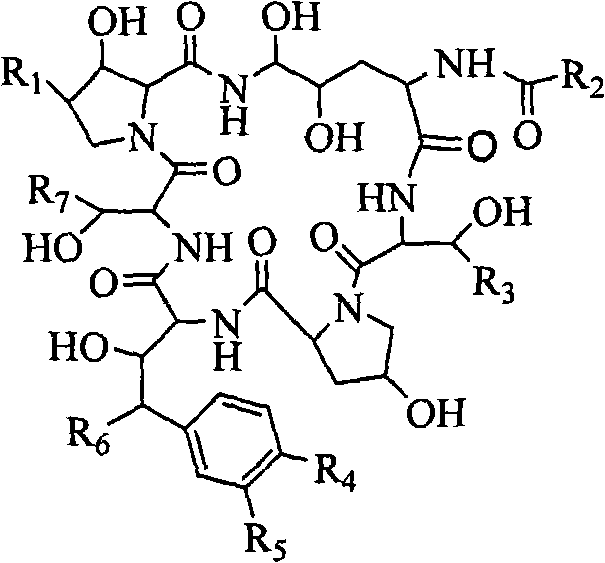
Echinocandin biotransformation method
ActiveCN102618606AAvoid steps such as separation and purificationReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationEchinocandinSolubility
The invention discloses an echinocandin biotransformation method using an actinomycete whole cell or fermentation broth as a catalyst. The invention also provides an echinocandin biotransformation method using cyclodextrin and its derivative or other cosolvents. A transformation system involved in the invention is characterized in that the system can effectively improve the solubility of echinocandin compounds in an aqueous solution, improve the utilization rate and the reaction rate of substrates, and improve the transformation rate of products. Actinoplanes involved in the invention and their mutant strains are in a nutritional medium containing an assimilable carbon and nitrogen source and can generate whole-cell deacylated enzymes under ventilation conditions, and the whole cell deacylated enzymes can be used for the echinocandin biotransformation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Production method and applications of cyclic carbonate
ActiveCN108440485AGood swelling propertiesImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEpoxyPhosphonium salt
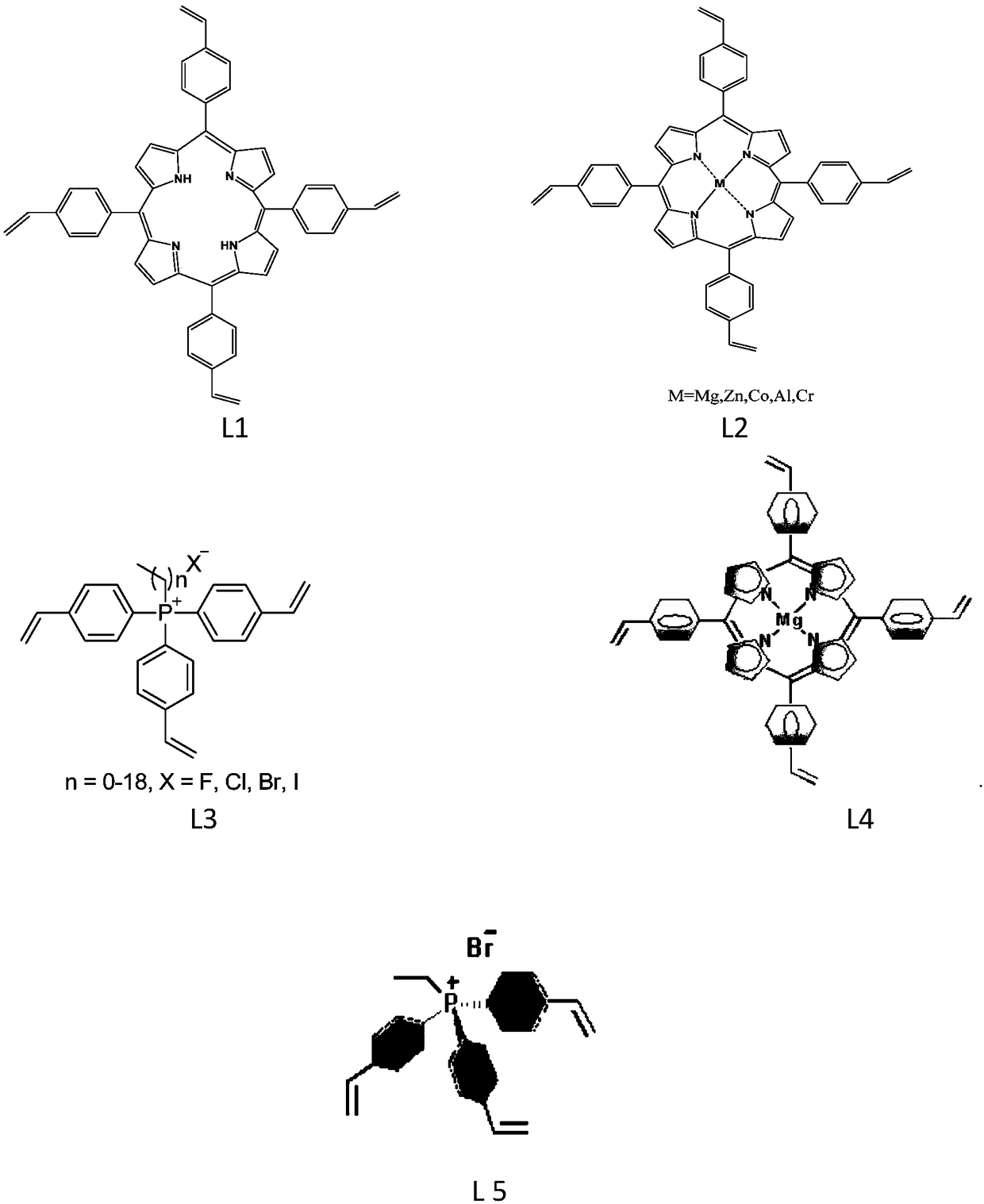
The invention relates to a production method and applications of cyclic carbonate. According to the present invention, the used catalyst is a multifunctional biomimetic heterogeneous catalyst formed by an organic porous copolymer based on metalloporphyrin and a quaternary phosphonium salt, the catalyst carrier is formed by carrying out mixed polymerization on alkylene-functionalized metalloporphyrin and a quaternary phosphonium salt, and the active component of the catalyst comprises metalloporphyrin (as a Lewis acid activation epoxy compound) and a quaternary phosphonium salt (as a ring-opening nucleophilic reagent) functional group; the obtained multifunctional biomimetic heterogeneous catalyst can be used for fixed beds, slurry beds, kettle type reactors, trickle beds and other reactors; the obtained multifunctional biomimetic heterogeneous catalyst has good performance, extremely high activity (2000-6000 h<-1>), good selectivity (more than 99%) of the formed cyclic carbonate and strong substrate applicability in the cyclic carbonate production reaction between the epoxy compound and the carbon dioxide, further has good stability, and can be simply and efficiently separated fromthe substrate and the product.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
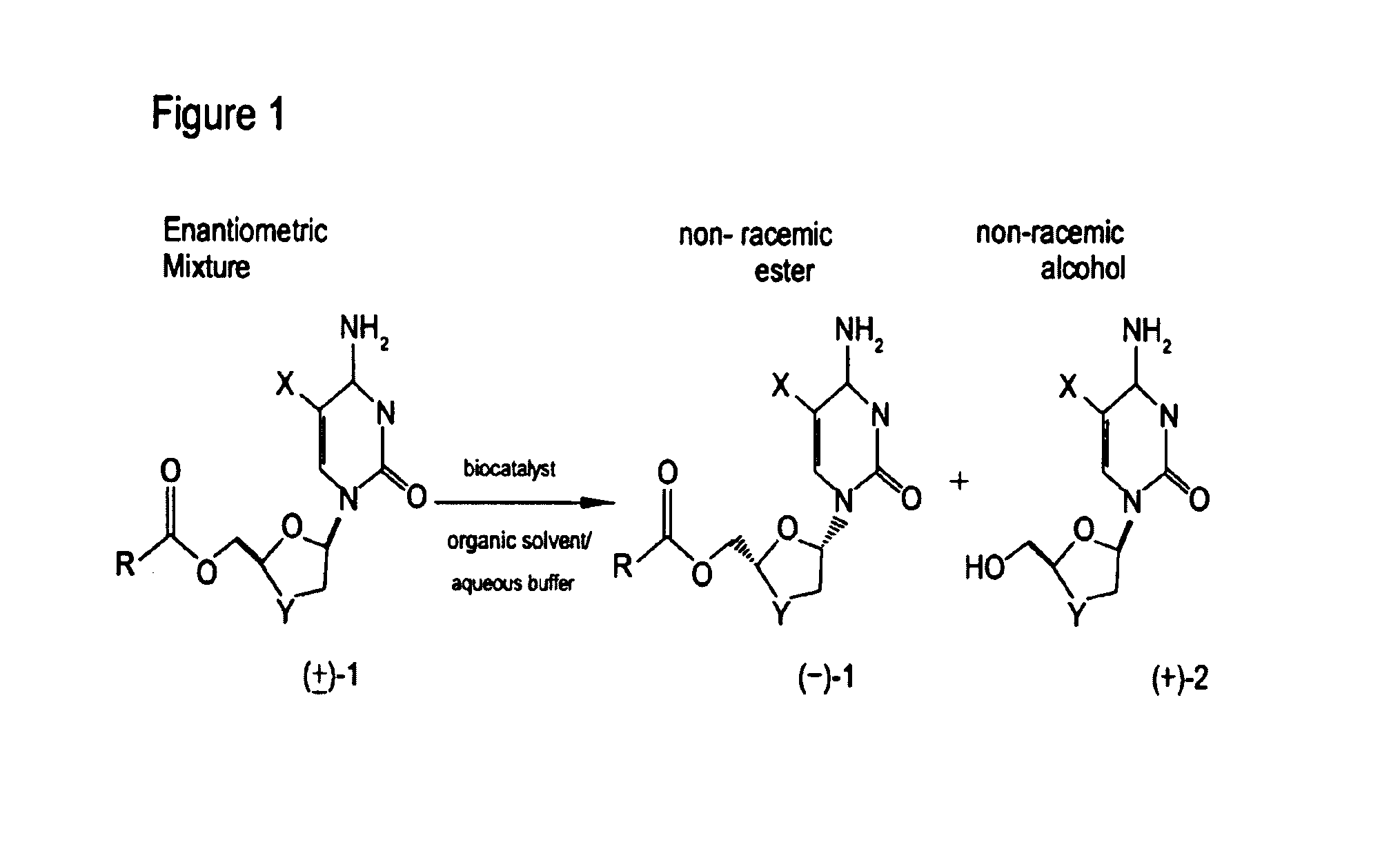
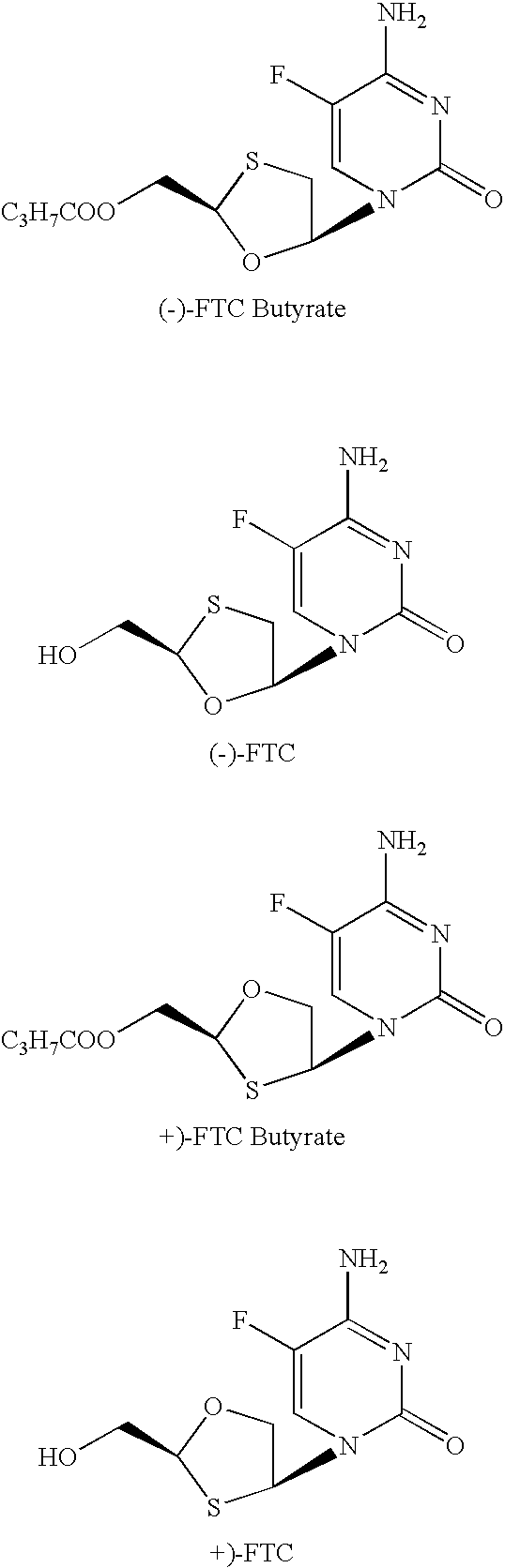
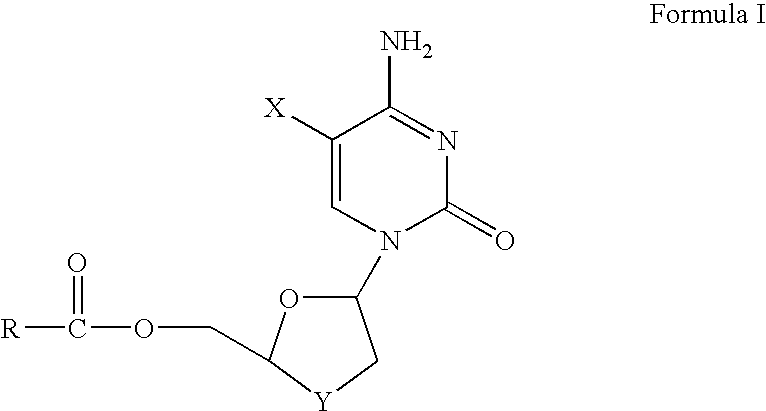
Non-homogeneous systems for the resolution of enantiomeric mixtures
InactiveUS6979561B1High substrate loadingReduce the amount requiredFermentationReaction systemEnzyme
The present invention relates to a process for the biocatalyst-mediated enantioselective conversion of enantiomeric mixtures of hydrophobic esters uing a biphasic solvent system. More particularly, the present invention relates to the enzyme-mediated enantioselective synthesis of anti-viral compounds, such as 2-hydroxymethyl-5-(5-flurocytosin-1-yl)-1,3-oxathiolane (FTC) and its analogues, in a non-homogenous reaction system.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Method of producing derivatives of lactosamine
InactiveUS6653109B1Improve solubilityPromote recoverySugar derivativesHydrolasesGlycosideOrganic group
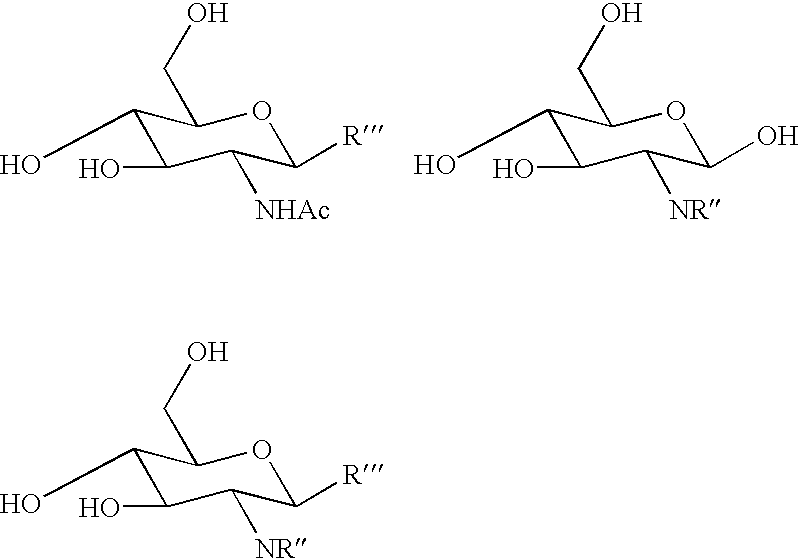
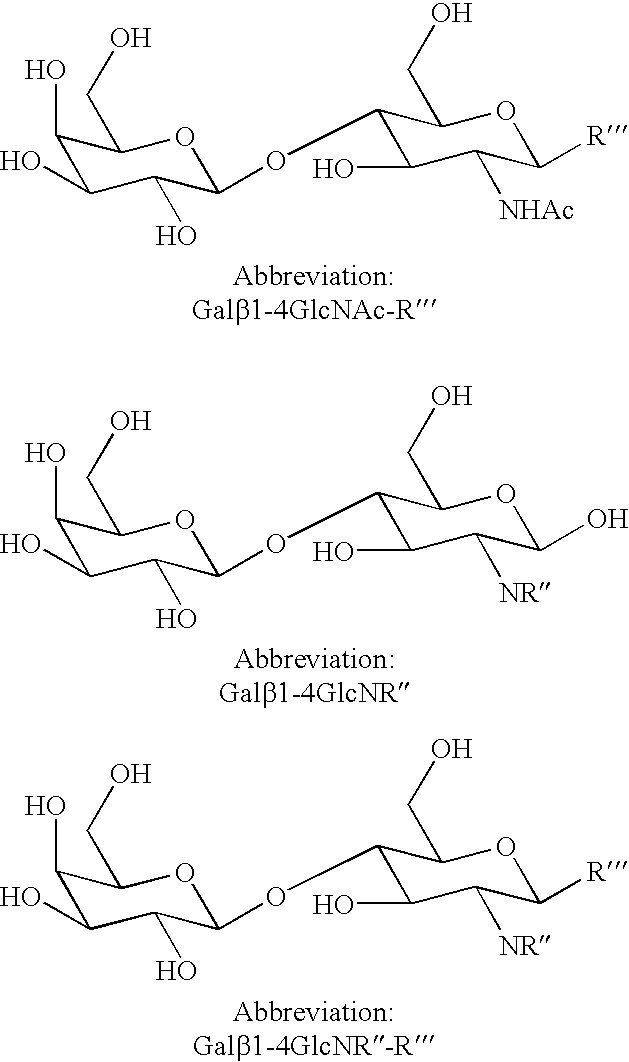
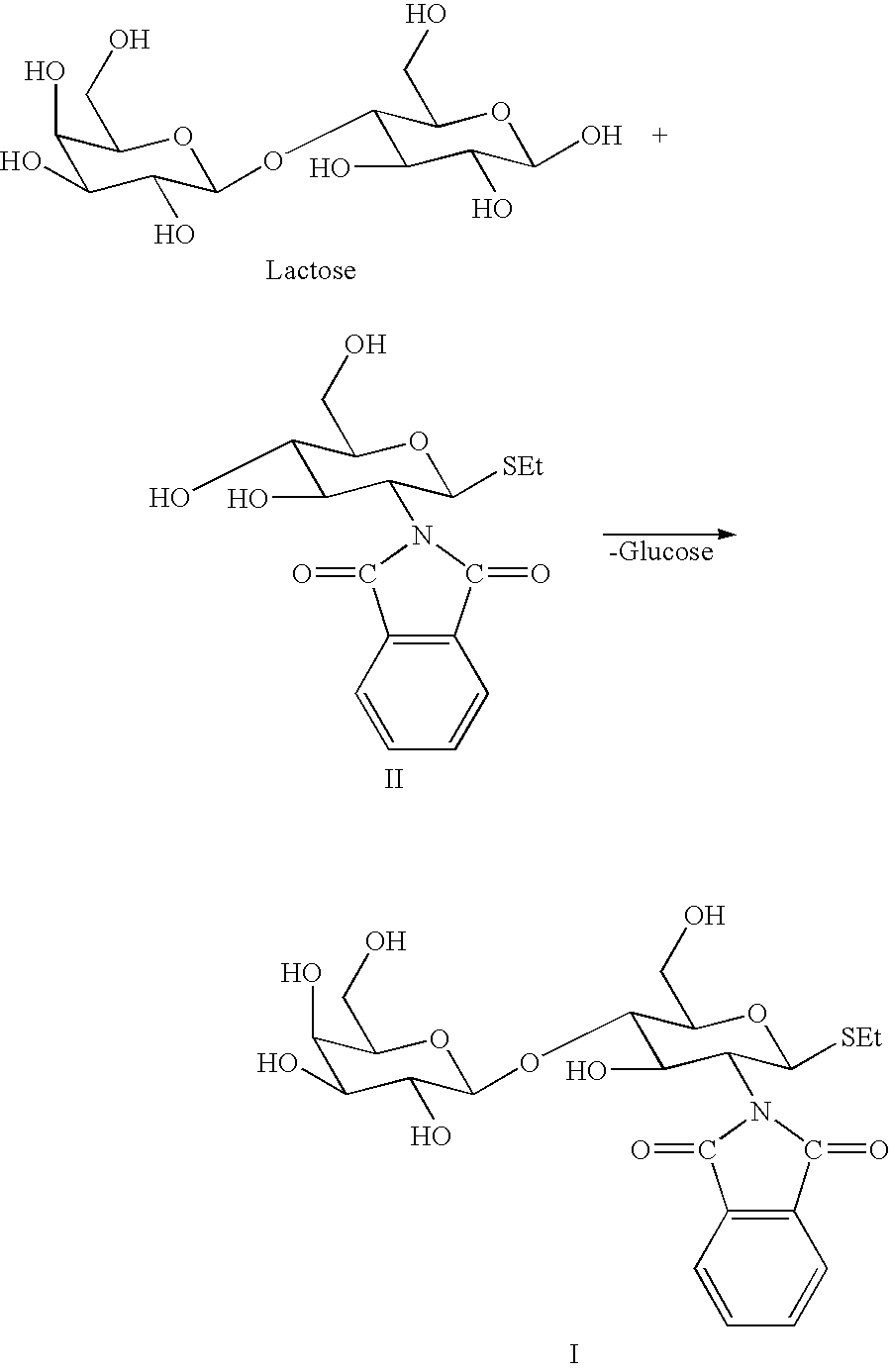
Disclosed is a method of producing a compound with beta1-4 linkage which contains the lactosamine structure involving reacting at least one donor substance GalbetaOR where R is an organic group, and at least one acceptor substance which is a glucopyranosamino derivative having the formula GlcNR''-R''', wherein NR'' is an azido, 2-N-acetyl-, 2-N-phtalimido, or an organic group bound to the 2-N-group of glucosamine, wherein R''' is a glycosidically bound fluoro or is an O-, C-, N- or S-glycosidically bound aliphatic or aromatic compound, with the proviso that if NR'' is NHAc then R''' is not OH and if NR'' is not NHAc then R''' may be OH, in the presence of Bullera singularis or an E.C. group 3.2 glycosidase of essentially the same structure as an E.C. Group 3.2 glycosidase obtained from Bullera singularis to form the lactosamine derivative; and optionally isolating the compound with beta1-4 linkage which contains the lactosamine structure.
Owner:GLYCOREX TRANSPLANTATION AB PUBL
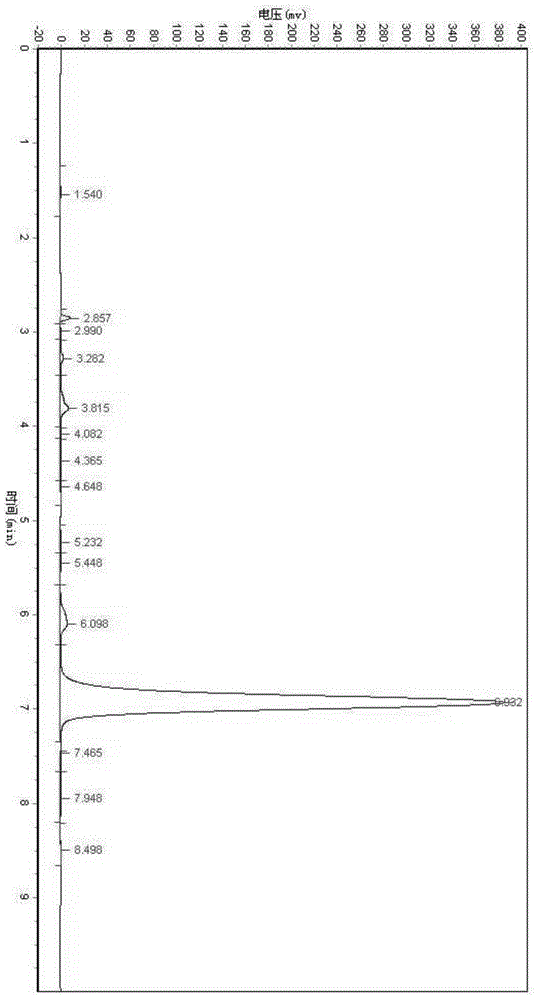
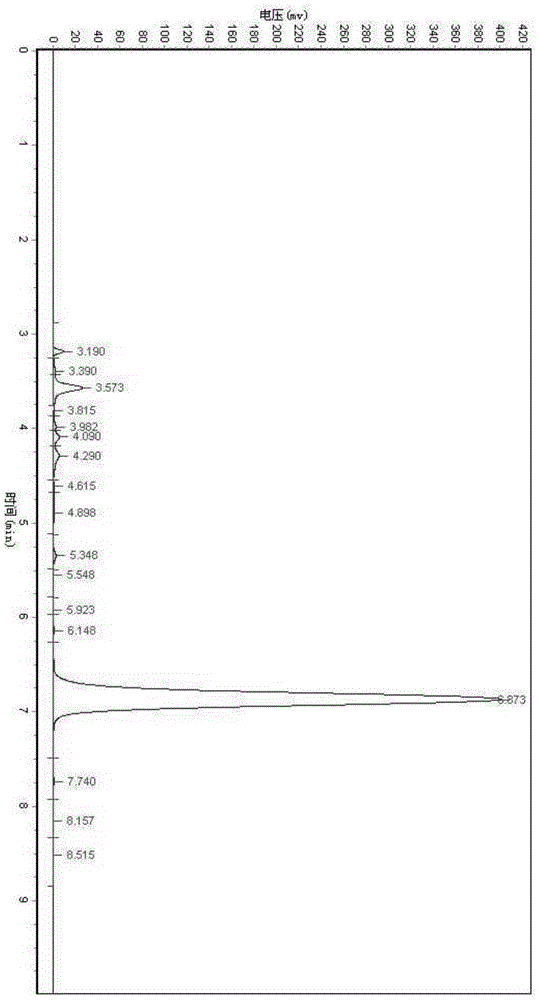
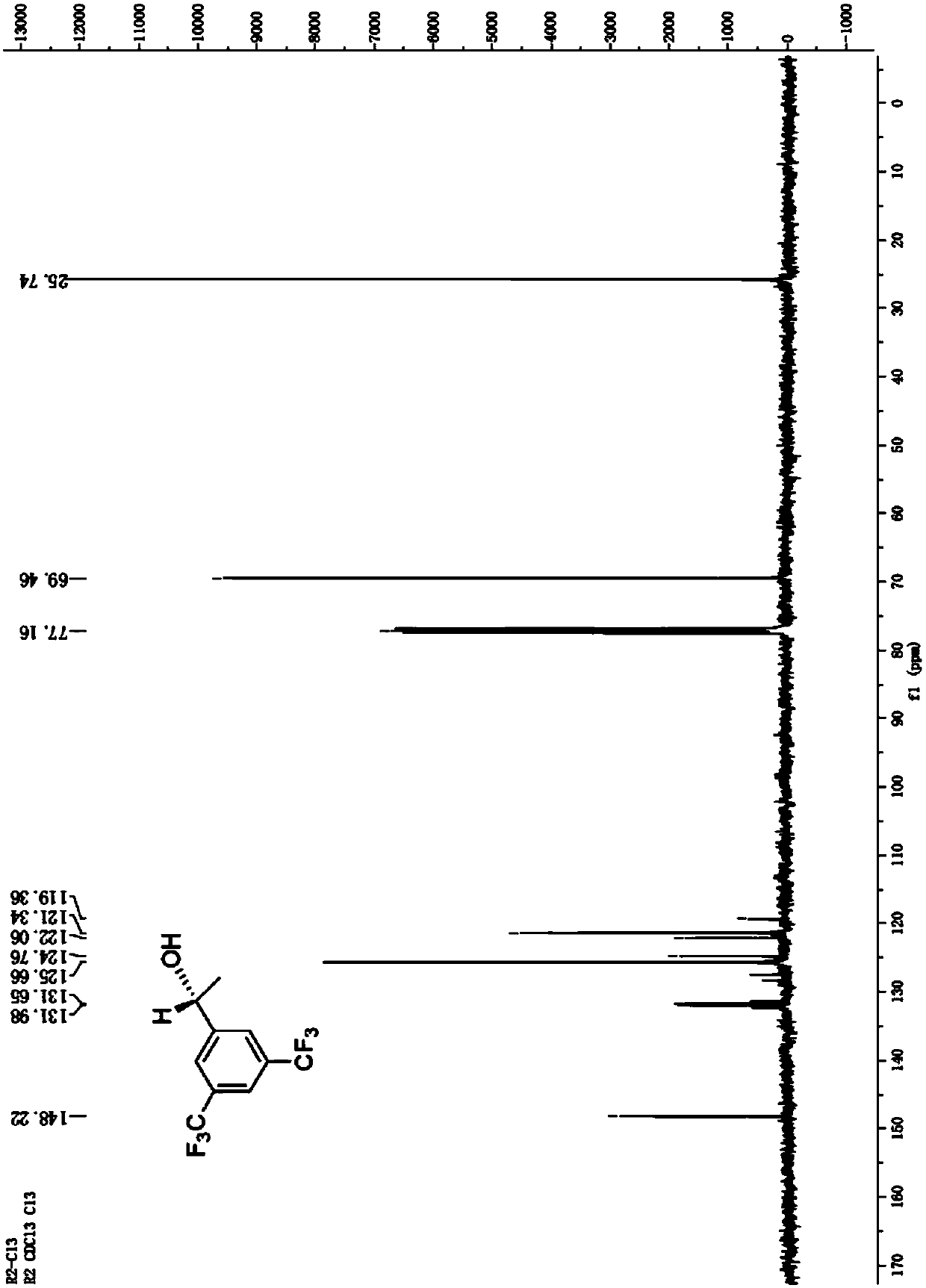
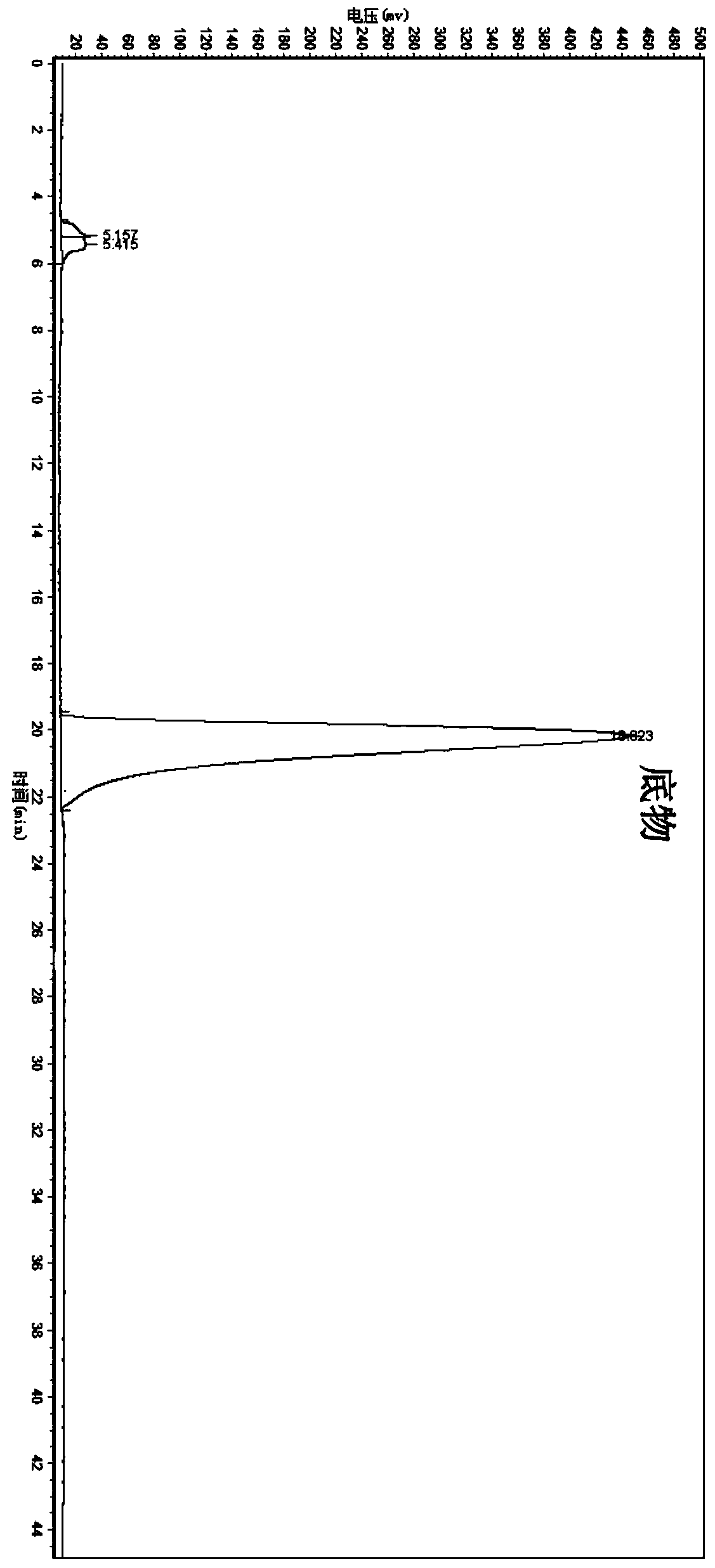
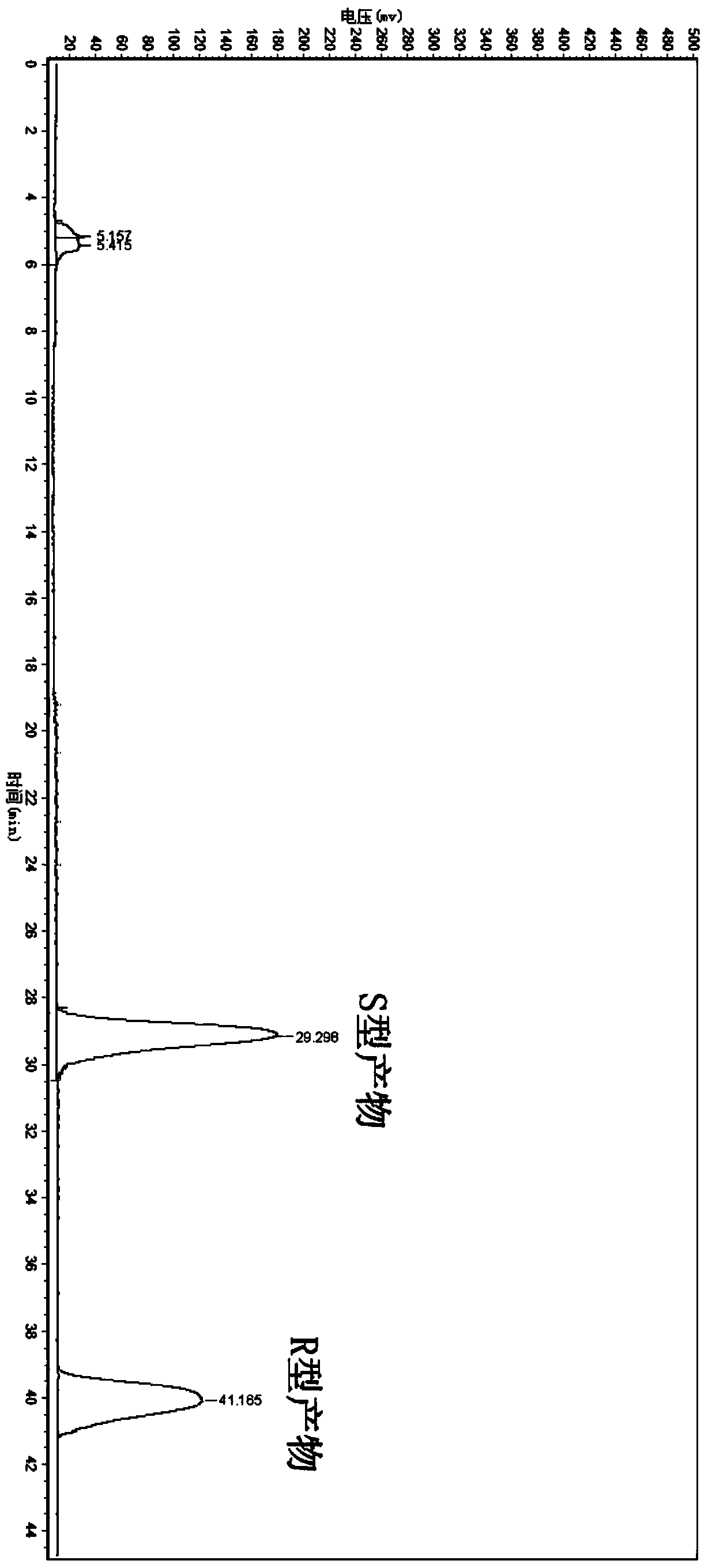
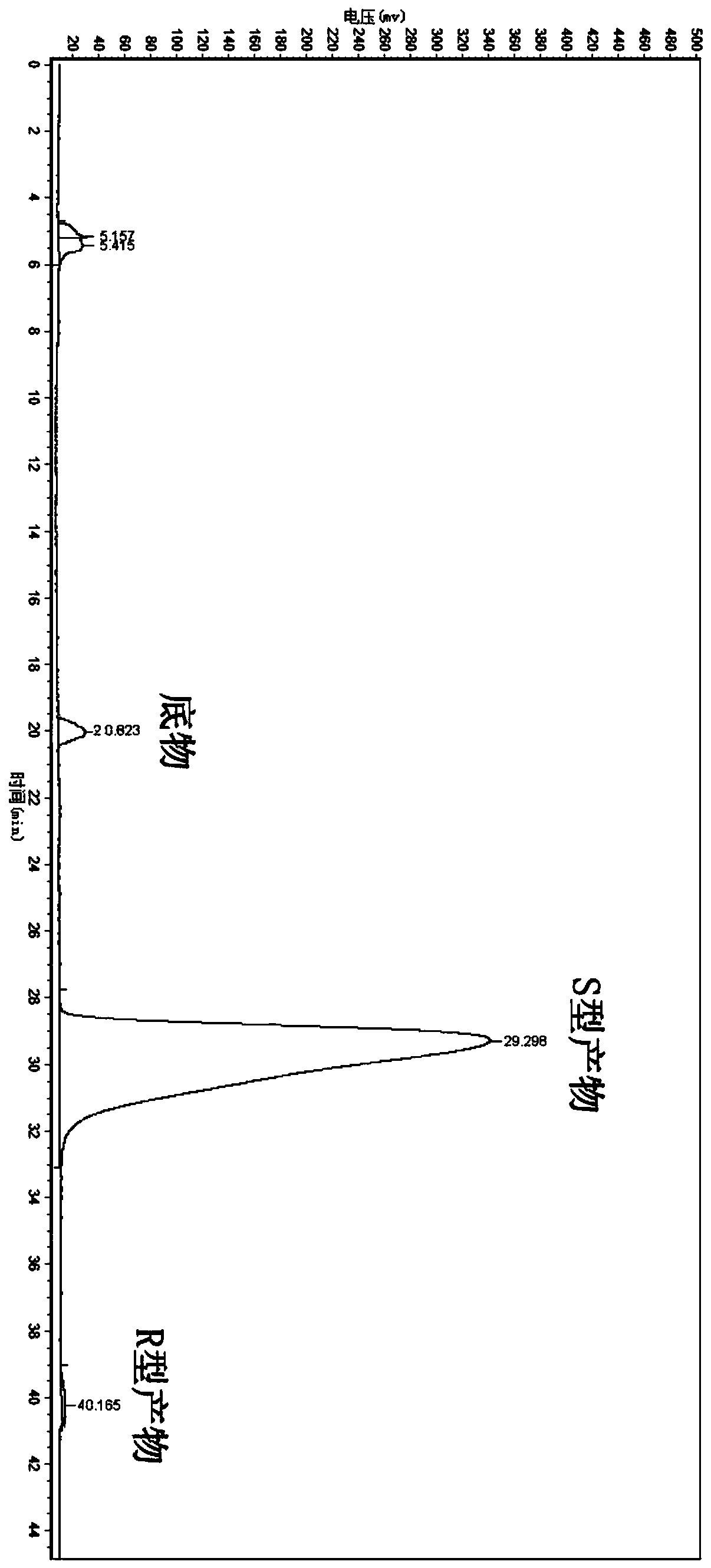
Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol
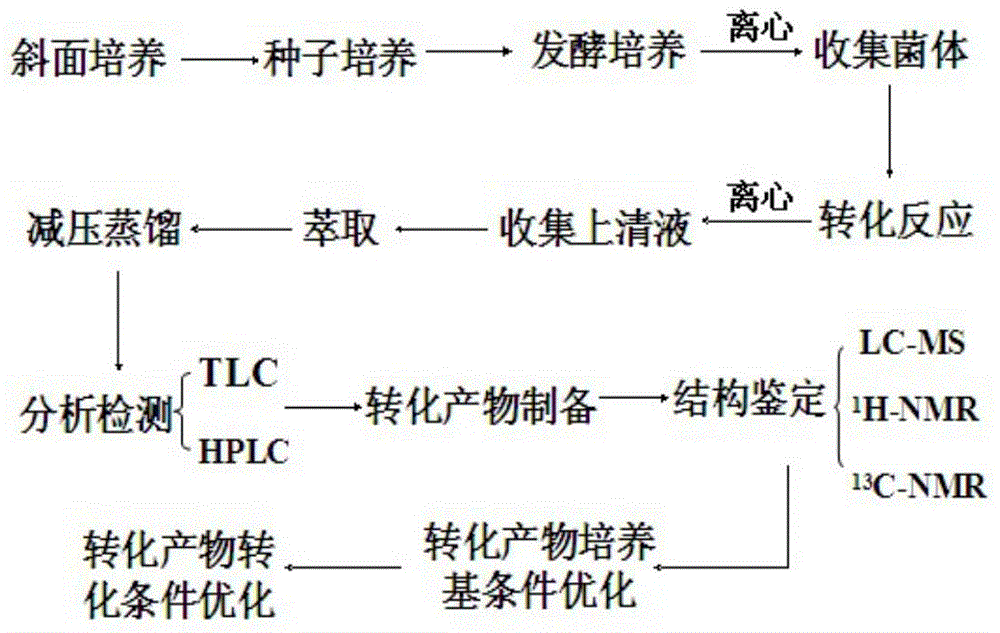
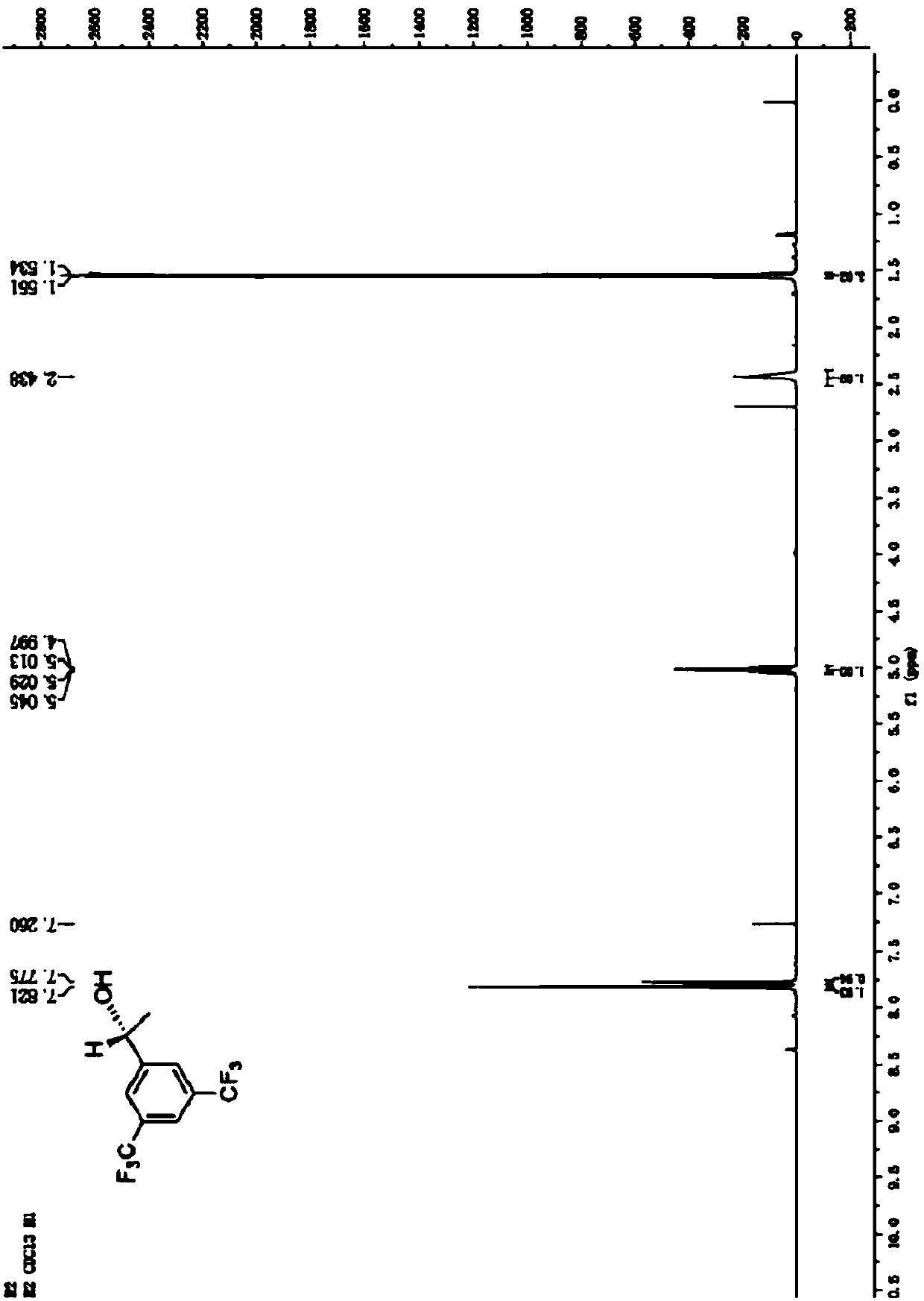
ActiveCN102102087AHigh substrate concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSubstrate concentrationPhotochemistry
The invention provides Leifsonia xyli which is a new strain that can be used in the preparation of high-optical purity (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol by asymmetric reduction of [3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone in presence of a microbe catalyst, and use thereof. The Leifsonia xyli HS0904 was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection located in Wuhan University (postcode:430072) in Wuhan, China on September 21, 2010, with a collection number CCTCC No.M2010241. The use of the new strain in the catalytic preparation of the optically pure (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol has the advantages of high substrate concentration, high stereoselectivity, high optical purity of product and the like. The strain is different from microbes reported in researches of the same kind, for the concentration of the substrate to be converted catalytically and the yield are both higher than those reported in documents. Thus, a beneficial reference is provided for the research on the preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol which is a key chiral intermediate of an Aprepitant medicine by a microbial catalysis process.
Owner:特康药业集团有限公司
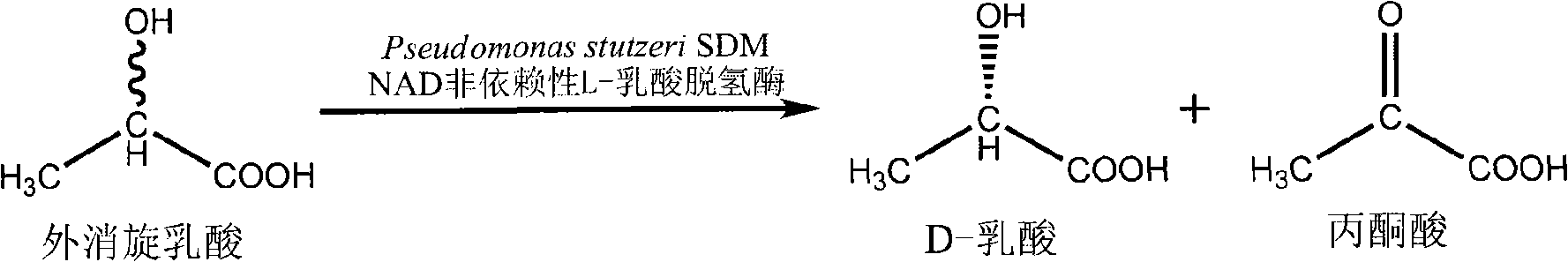
Method for producing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid
ActiveCN101974603AShorten the growth cycleLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationThermal denaturationHydroxybutyric acid
The invention discloses a method for producing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing complete cell suspension containing NAD independent hydroxy acid dehydrogenase or coarse enzyme liquid thereof with pseudomonas; (2) carrying out thermotropy on the complete cell suspension or the coarse enzyme liquid thereof prepared by the thermal denaturation step (1) to deactivate the NAD independent D-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase so as to obtain a biocatalyst only containing the NAD independent L-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase activity; (3) separating the racemic alpha-hydroxybutyric acid by the biocatalyst prepared in the step (2) to obtain the conversion fluid containing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid sodium salt and alpha-ketobutyric acid sodium salt; (4) pre-treating the conversion fluid; (5) acidifying the pre-treated conversion fluid; (6) separating the D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid form the alpha ketobutyric acid; and (7) refining the D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid. The method of the invention has the characteristics of simple components of culture medium, short growth period, low cost, easy subsequent separation and extraction, high enantiomeric excess of the product D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid and the like and lays a foundation for efficient production of the D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Carbonyl reductase, mutant and application of carbonyl reductase to preparation of statin synthetic intermediate
ActiveCN106929490AHigh optical purityHigh substrate concentrationOxidoreductasesFermentationSide chainSubstrate concentration
The invention relates to carbonyl reductase derived from lactobacillus brevis CGMCC 1.3258, an activity-improved mutant of the carbonyl reductase, a gene of the carbonyl reductase, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant containing the gene, as well as application of the recombinant carbonyl reductase or the recombinant expression transformant serving as a catalyst to catalysis of asymmetric reduction preparation of a chiral hydroxyl compound, particularly application in biological catalytic synthesis aspect of an atorvastatin chiral intermediate 6-cyan-(3R,5R)-dihydroxyhexanoate. Compared with other methods for performing asymmetric reduction preparation on the 6-cyan-(3R,5R)-dihydroxyhexanoate, the invention has the advantages of high substrate concentration, mild reaction condition, environmental friendliness, high yield, high optical purity of products and the like, so good application prospect in the industrialized production of atorvastatin chiral side chains is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
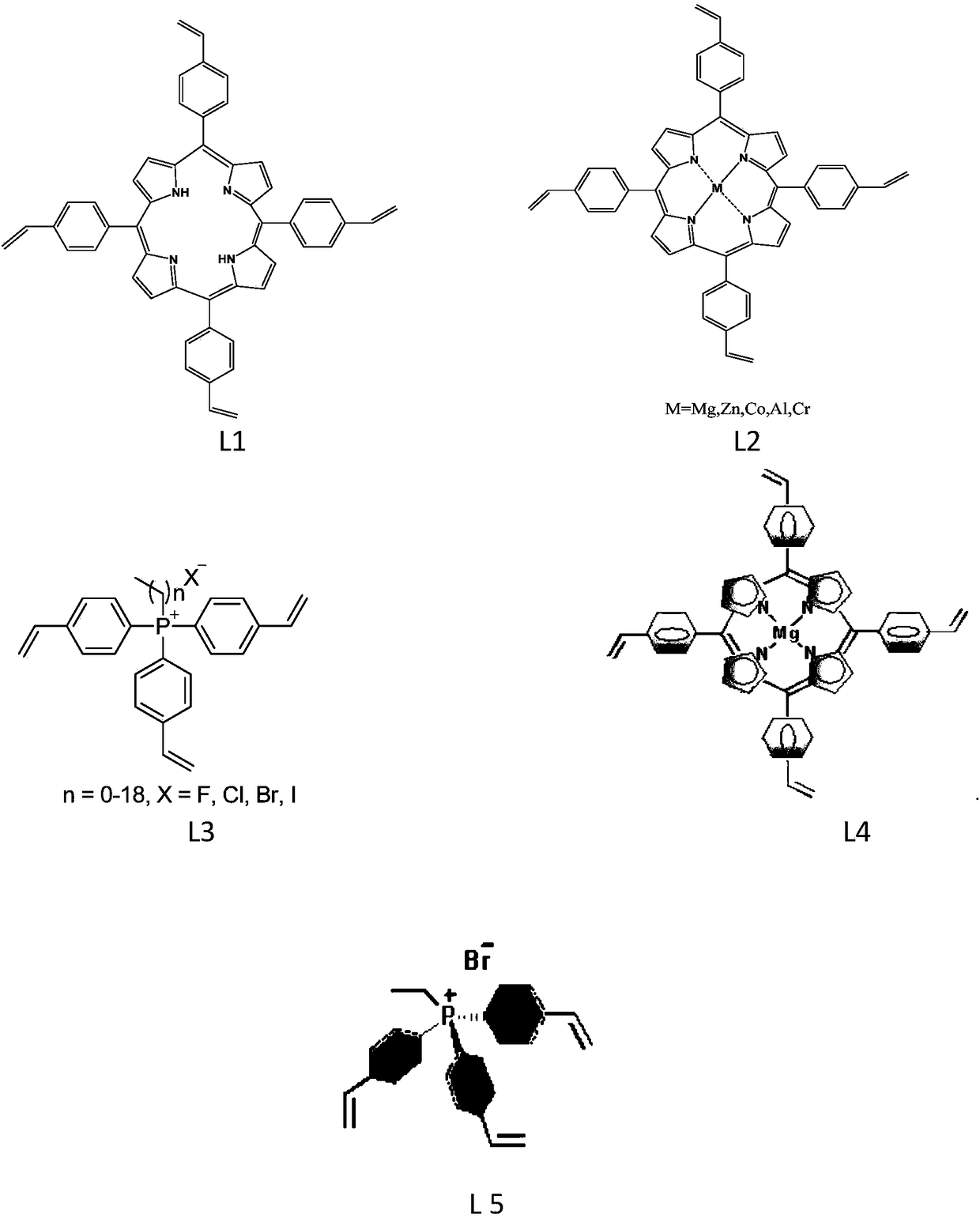
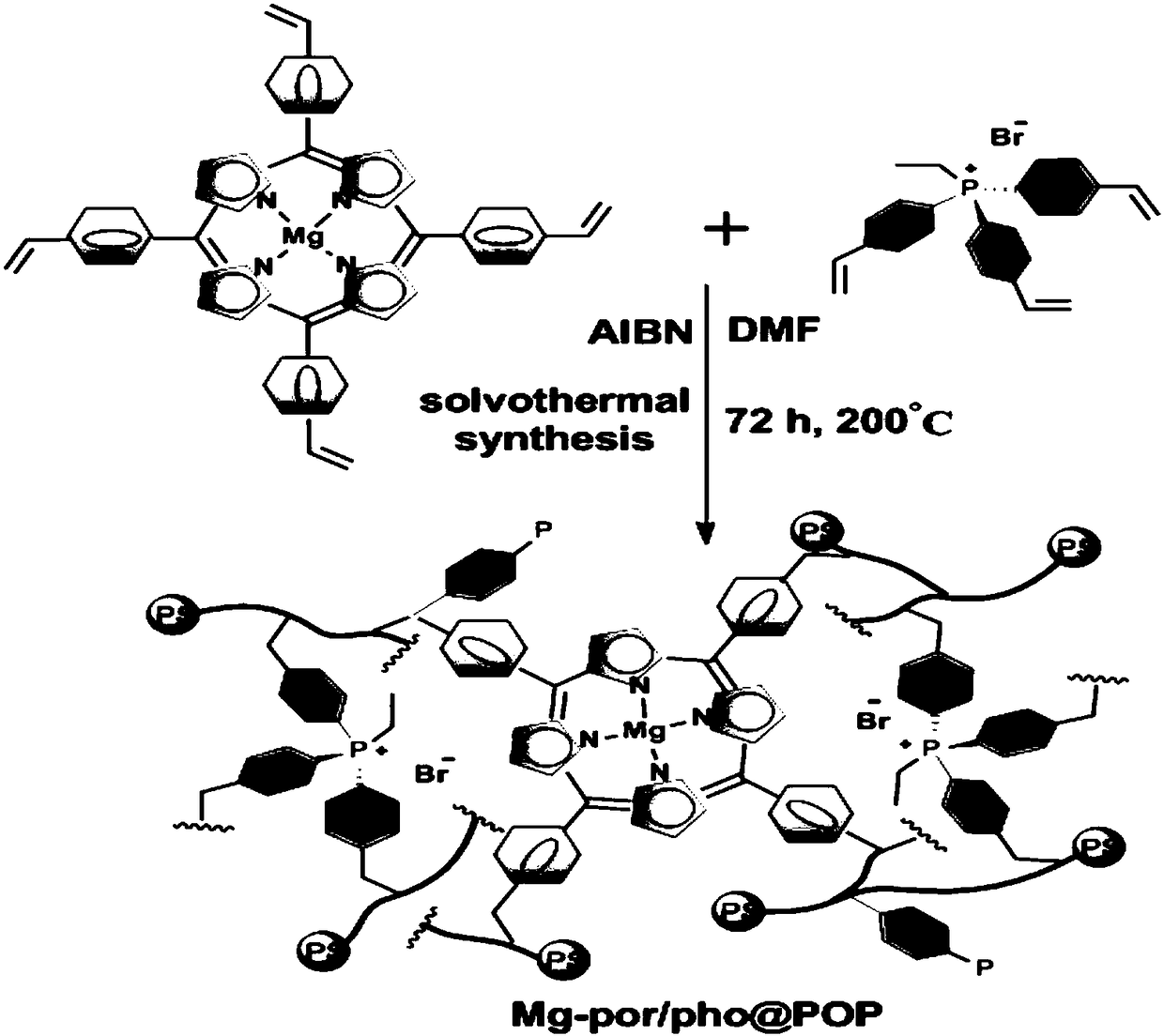
Organic porous copolymer multifunctional biomimetic heterogeneous catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108440488AGood swelling propertiesImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhosphoniumPhosphonium salt
The invention relates to a multifunctional biomimetic heterogeneous catalyst formed by an organic porous copolymer based on metalloporphyrin and a quaternary phosphonium salt, and a preparation methodthereof, wherein the metalloporphyrin and the quaternary phosphonium salt functional group are used as the main active component of the heterogeneous catalyst, the metalloporphyrin group is used as aLewis acid, the halogen ion in the quaternary phosphonium salt is used as a nucleophilic reagent, and the organic porous copolymer carrier containing metalloporphyrin and a quaternary phosphonium group is formed by carrying out co-polymerization on alkylene-functionalized metalloporphyrin and a quaternary phosphonium salt monomer. According to the present invention, the heterogeneous catalyst isused for the coupling reaction process of epoxy compounds and carbon dioxide, wherein the abundant N and P atoms in the polymer skeleton can increase the adsorption of CO2; and the porous organic polymer material can seal and limit the reaction substrate in the nano-scale pores and increase the concentration of the substrate at the catalytic site, such that the catalyst has double advantages of extremely high activity and extremely high stability.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biological transformation method by utilizing hydrophobic compound of cyclodextrin
InactiveCN101168765AImprove conversion rateIncrease the rate of conversion reactionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismReaction rate
The invention discloses a bioconversion method by using cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof, belongs to the bioconversion technical field, in particular relates to the bioconversion method by using the cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof, and provides the bioconversion method by using the cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof. The method of the invention is particularly suitable for the microbial conversion of hydrophobic compounds, can effectively improve the dissolubility of reaction substrate in aqueous solution, improve the utilization rate and the reaction rate of the substrate, release the inhibition of the substrate and the product to a certain extent, and improve the conversion rate of the product. The invention adopts a conversion system including the cyclodextrin, the special structure of the cyclodextrin ensures the cyclodextrin to have a certain solubilizing power, and strengthens the bioavailability of the substrate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing 11A, 17A-dihydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione by enzymatic method
The invention relates to a method for preparing 11A, 17A-dihydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione by an enzymatic method. The method is characterized by adding a substrate 11A, 17A-dihydroxy-pregna-1-ene-3,20-dione, 3-sterone-1-dehydrogenase, menadione and a cosolvent to an aqueous phase buffer solution with a pH value of 8-11 and stirring to react at a temperature of 30-50 DEG C to obtain 11A, 17A-dihydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, wherein the concentration of the substrate is 5-10g / l in an initial reaction system; the feeding amount of 3-sterone-1-dehydrogenase is 0.5-4 times the mass of the substrate; the cosolvent is selected from one of or a composite of more of dimethyl sulfoxide, polyethylene glycol-400 and Tween-60. The method has the advantages that the concentration of the reactive substrate can be 10g / L and the conversion rate within 3 hours can be 99% at most; the product has high yield and good quality; the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Processing method of mulberry leaf black tea
InactiveCN107518117AHigh substrate concentrationFully fermentedPre-extraction tea treatmentBlack teaRoom temperature
The invention discloses a processing method of mulberry leaf black tea. The processing method comprises the following steps of withering fresh mulberry leaves and fresh tea leaves so as to obtain withered mulberry leaves and withered tea leaves; uniformly mixing the withered mulberry leaves with the withered tea leaves in the proportion of the withered mulberry leaves to the withered tea leaves being (5-10) to 1, and performing twisting until the leaves are bent to form strips; and placing the twisted leaves under the condition that the temperature is 25-30 DEG C, and the humidity is greater than or equal to 90%, and performing fermentation for 2-4h; baking the fermented leaves, performing drying, and performing spreading for cooling to room temperature so as to obtain the mulberry leaf black tea. The processing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that an appropriate quantity of tea leaves are added to the mulberry leaves, so that the concentration of substrates and polyphenol oxidase are increased, fermentation can be guaranteed to be performed sufficiently, and green odor and green and astringent taste of the mulberry leaves are removed; the tea leaves are added, so that a certain quantity of flavored substances and fragrance substances are added, the organoleptic quality of the mulberry leaf black tea is greatly improved, and besides, the nutrient component and the health-care efficacy of the mulberry leaf black tea are also improved. The technology is simple to operate, the production cost is low, and the product quality is good.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
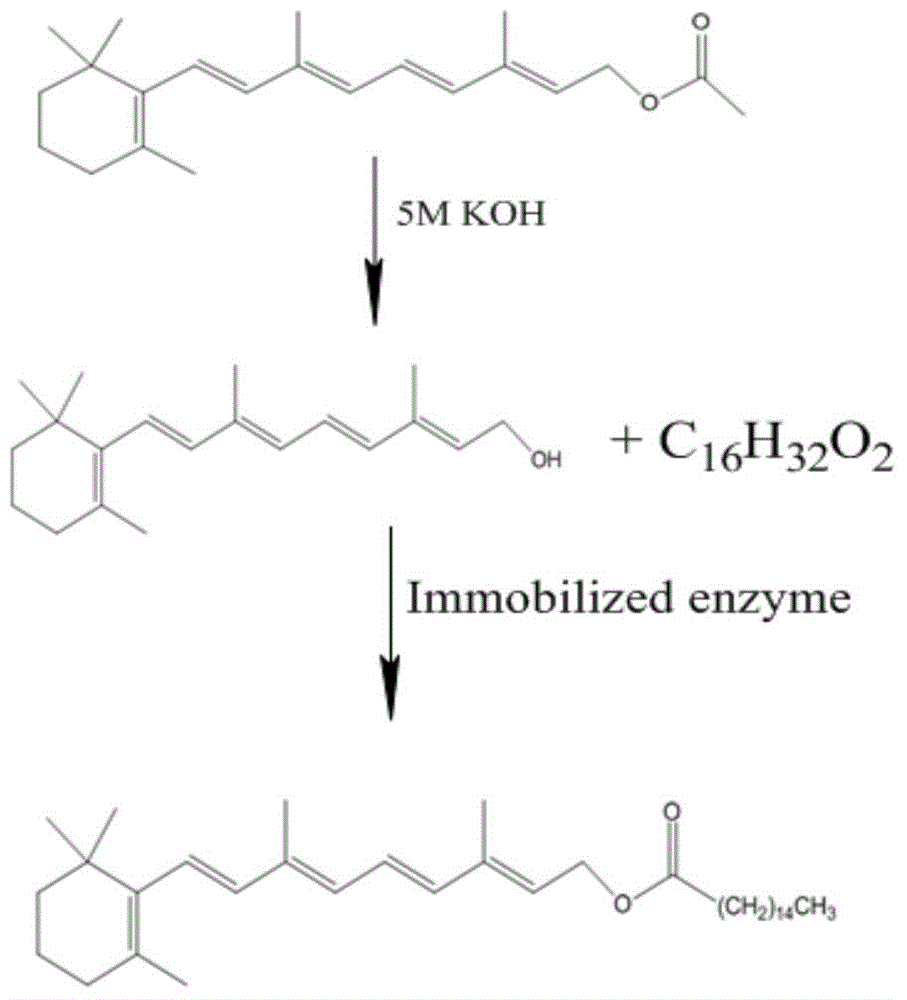
Synthetic method of vitamin A palmitate
InactiveCN105441521AImprove temperature stabilityReduce dosageHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierOrganic solventVitamin A Alcohol
The invention relates to a synthetic method of vitamin A palmitate. The vitamin A palmitate is synthesized through a chemical enzyme technology, and the method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, hydrolyzing vitamin A acetate by using an alkali solution with an organic solvent as a cosolvent to generate vitamin A alcohol; and 2, extracting the vitamin A alcohol by using an organic solvent, washing the obtained extract liquid with water to remove the cosolvent reacting with palmitic acid, and reacting the vitamin A alcohol with the palmitic acid in a non-aqueous system under the catalysis of immobilized lipase to generate the vitamin A palmitate. The synthetic method provided by the invention adopts the vitamin A alcohol to substitute vitamin A acetate as a substrate in the biological catalysis process, and the vitamin A palmitate to be synthesized through esterification, so the substrate concentration is improved, the conversion rate is high, the reaction time is shortened, the molar ratio of the substrate is reduced, the service life of the immobilized lipase is prolonged, the cost is reduced, industrial production requirements are met, and the gap in the enzyme production of the vitamin A palmitate in the current market is filled.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
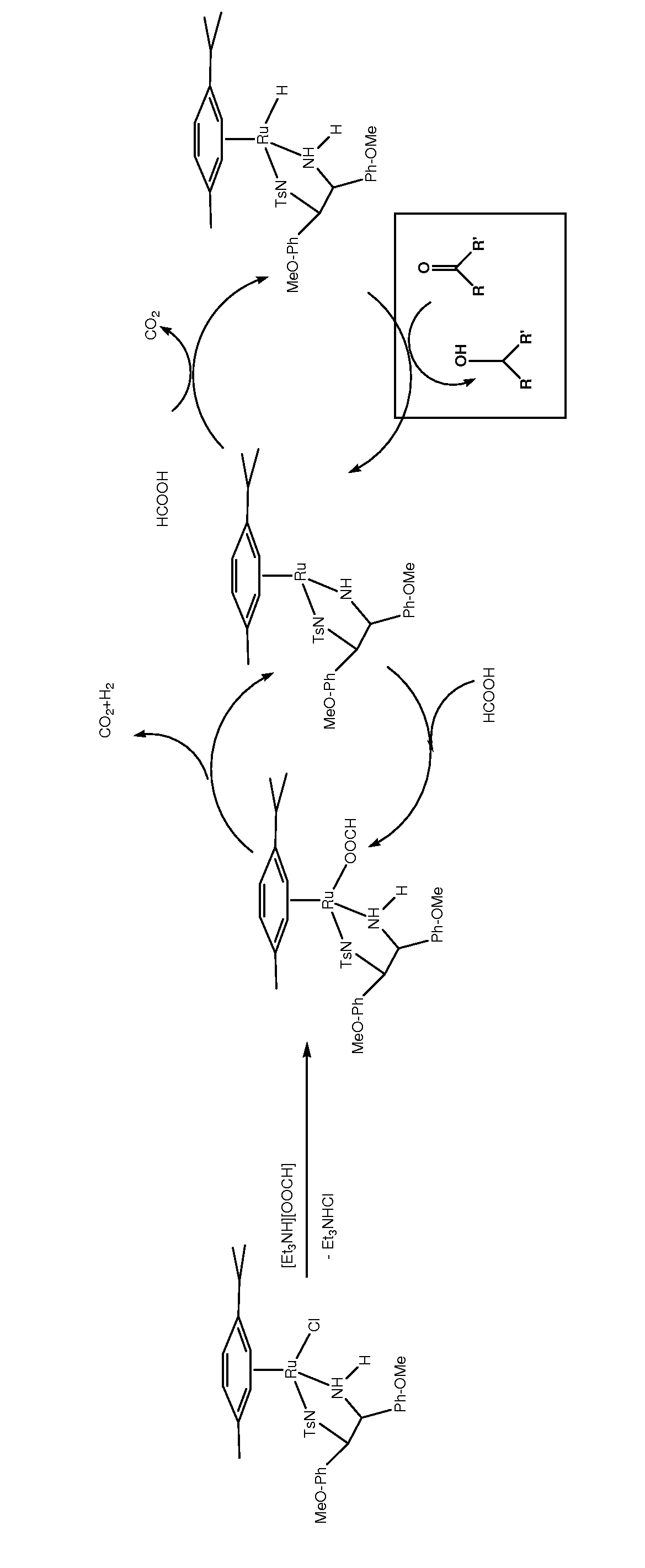
Asymmetric catalytic reduction of oxcarbazepine
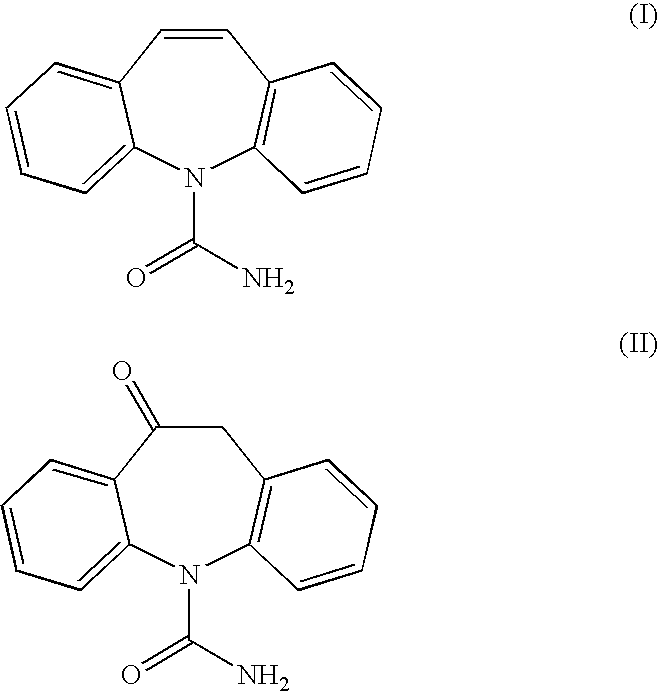
ActiveUS8288532B2High substrate concentrationOptimize volumeAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderHydrogenAlkaline earth metal
A process for preparing (S)-(+)-10,11-dihydro-10-hydroxy-5H-dibenz / b,f / azepine-5-carboxamide or (R)-(−)-10,11-dihydro-10-hydroxy-5H-dibenz / b,f / azepine-5-carboxamide, by reduction of oxcarbazepine in the presence of a catalyst and a hydride source is disclosed. The catalyst is prepared from a combination of [RuX2(L)]2 wherein X is chlorine, bromine or iodine, and L is an aryl or aryl-aliphatic ligand, with a ligand of formula (A) or formula (B):wherein R1 is chosen from C1-6 alkoxy and C1-6 alkyl, n is a number from 0 to 5, and when n is a number from 2 to 5, R1 can be the same or different, and R2 is alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, alkaryl or substituted alkaryl. The hydride source is either NR3R4R5 and formic acid, [R3R4R5NH][OOCH] and optionally formic acid, or [M][OOCH]x and formic acid, wherein R3, R4 and R5 are C1-6 alkyl, M is an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal and x is 1 or 2. A pH from 6.5 to 8 is maintained during the process.
Owner:BIAL PORTELA & CA SA
Biological preparation method of 6-cyano-(3R, 5R)-dihydroxyhexanoate
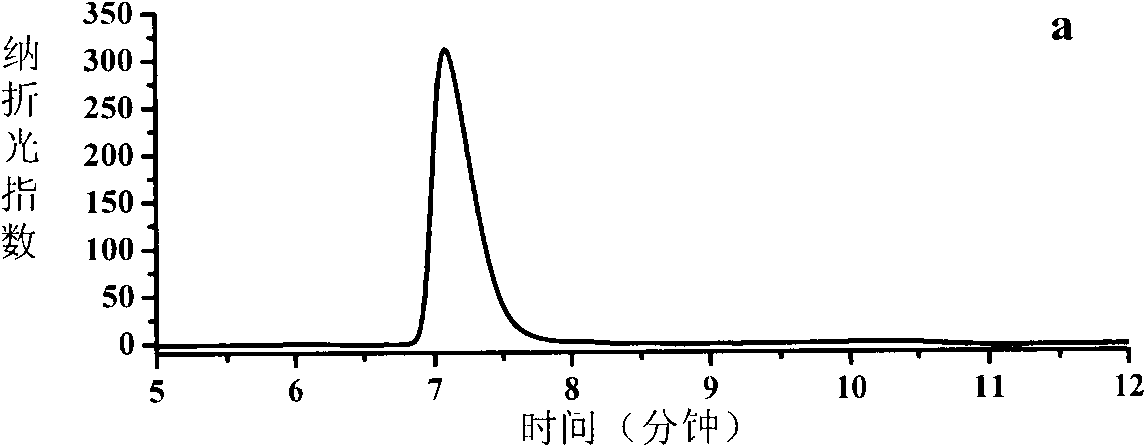
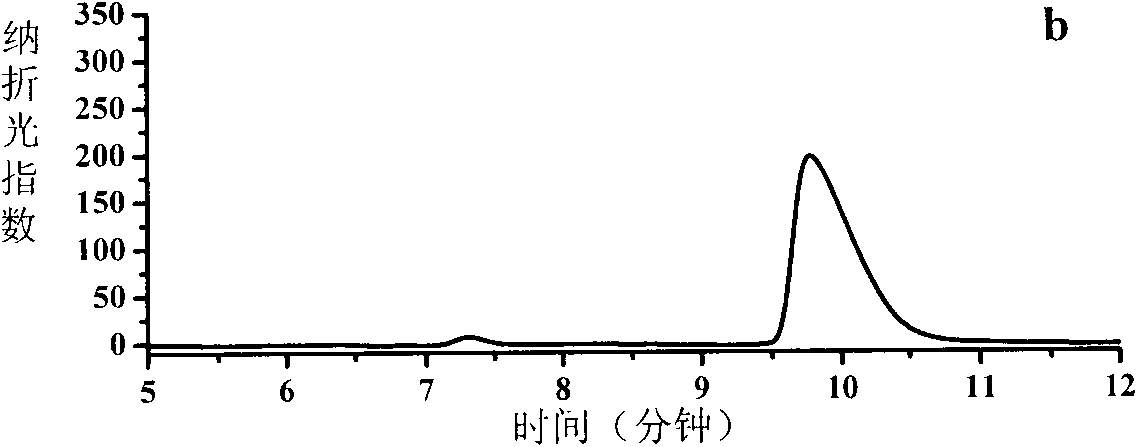
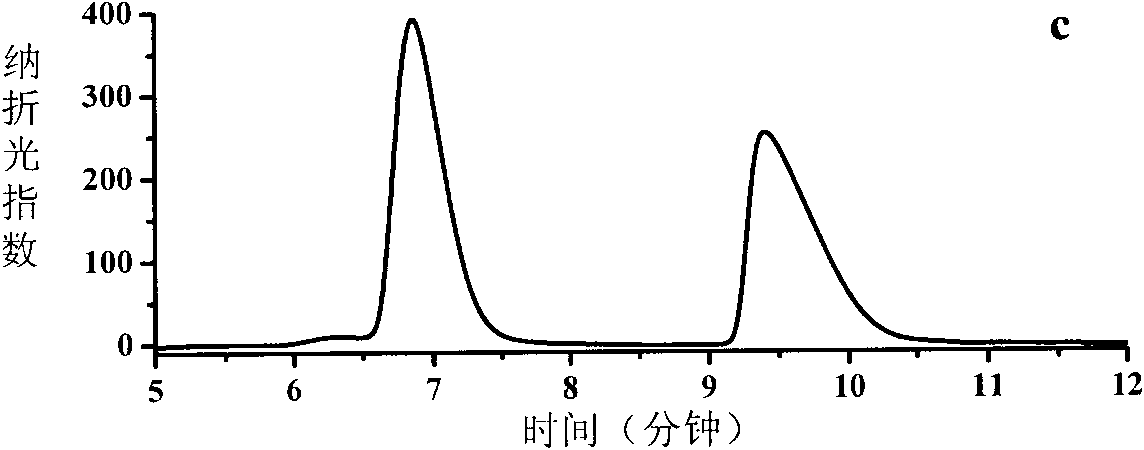
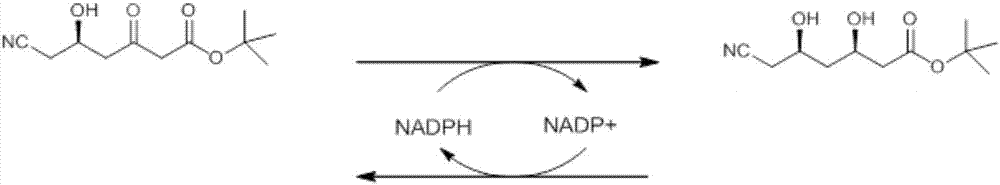
ActiveCN103014080AOptimizing Process ConditionsHigh substrate concentrationChemical recyclingFermentationSubstrate concentrationBiotransformation
The invention relates to a biological preparation method of 6-cyano-(3R, 5R)-dihydroxyhexanoate. According to the biological preparation method, 6-cyano-(6R)-hydroxyl-3-oxo-tertiary butyl hydroperoxide is used as a substrate; under the condition that a biocatalyst, a cofactor and a cofactor regeneration system exist, the substrate performs the reduction reaction to generate 6-cyano-(3R, 5R)-dihydroxyhexanoate; and the reduction reaction is carried out in water-phase buffer solution with pH of 6 to 8. According to the invention, by optimizing the process condition and mainly optimizing the pH of the reduction reaction, the concentration of the substrate is improved and the enzyme dosage is reduced, so that production cost is reduced and the high-efficiency biological conversion process is realized.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Method for preparing functional active peptide by glutamic acid fermentation solid residues
InactiveCN106978461ALittle effect on propertiesEnsure safetyNitrogenous fertilisersFermentationDPPHOxidation resistant
The invention relates to a method for preparing functional active peptide by glutamic acid fermentation solid residues. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) selecting and pretreatment of a raw material; (2) crushing and separating of slurry and residues; (3) removing of impurities (besides protein) by a chemical and physical combining method; (4) directional hydrolyzing reaction of two types of protease; (5) concentrating and drying of an enzyme hydrolyzing material, so as to obtain the finished active peptide. The molecular weight distribution ratio of active peptide at 500 to 1500 Da is greater than 60%; by measuring the ability of removing DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl) free radical, the anti-oxidizing activity is 50% to 70%. The active peptide can be used as a protein nutrient supplementing agent in food or reach the anti-oxidizing function, and can be used as an organic nitrogen source in organic fertilizer for plants to directly absorb and utilize, or be combed with some metal elements in soil to improve soil quality.
Owner:WUXI JINNONG BIOTECH CO LTD
Curcumin derivative preparing method
ActiveCN104894173AImprove pharmacological activityImprove biological activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationResting CellBacterial strain
The invention discloses a curcumin derivative preparing method. The curcumin derivative preparing method includes the steps that a conversion reaction is conducted in a phosphate buffer solution with pH value of 5.4-8.0 under the conditions of 25-35 DEG C and 150-250 rpm with wet cells obtained through fermentation cultivation of rhodococcus ZJPH1003 as an enzyme source and curcumin as a substrate, conversion reaction liquid is subjected to postprocessing after the conversion reaction is ended, and curcumin derivatives are obtained. A rhodococcus ZJPH1003 bacterial strain resting cell conversion method is utilized for conducting structural modification on the curcumin, and then the corresponding curcumin derivatives are obtained. The pharmacological or biological activity of the modified curcumin derivatives is improved to different extents compared with the unmodified curcumin substrate, and development of new medicinal preparations is facilitated. The technological process of adopting the microbial conversion method to obtain the curcumin derivatives is simple and environmentally friendly; biocatalyst is made of microbial cells, can be fermented and prepared automatically and has a stable quality and low cost.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
Synthetic method for L-carnitine
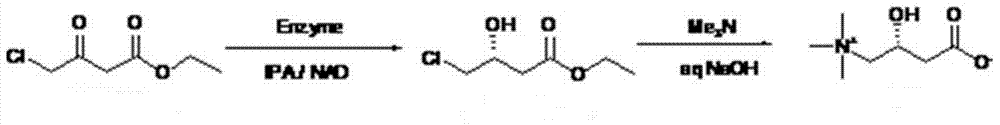
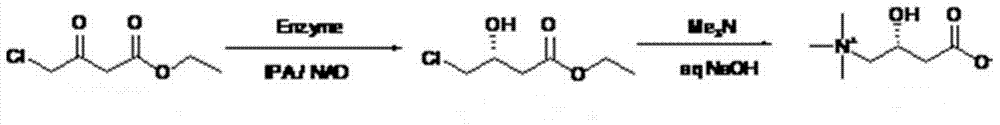
ActiveCN103709058AReduce production stepsHigh substrate concentrationOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationSubstrate concentrationHydroxy compound
The invention relates to a synthetic method for L-carnitine. L-carnitine is obtained by the steps of dissolving a substrate 4-chloracetyl acetidin in a phosphate buffer at a temperature of 25-35 DEG C; reacting the substrate for 20-50 hours at a pH of 6-7 under the effects of a ketoreductase, a co-enzyme and isopropanol to form (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyl-ethyl butyrate; dissolving sodium hydroxide in a trimethylamine aqueous solution with a mass ration of 25% to form a mixed solution; then dropwise adding the mixed solution in (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyl-ethyl butyrate slowly at a temperature ranging from -5 DEG C to 5 DEG C; reacting for 20-30 hours at the temperature ranging from -5 DEG C to 5 DEG C; stopping the reaction; adjusting a pH value to 5-7; and the purifying by centrifugation, ultra filtration and resin purification. The synthetic method improves a production flow, increases substrate concentration, reduces dosage of enzyme, reduces production cost and increases market competitiveness of products.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
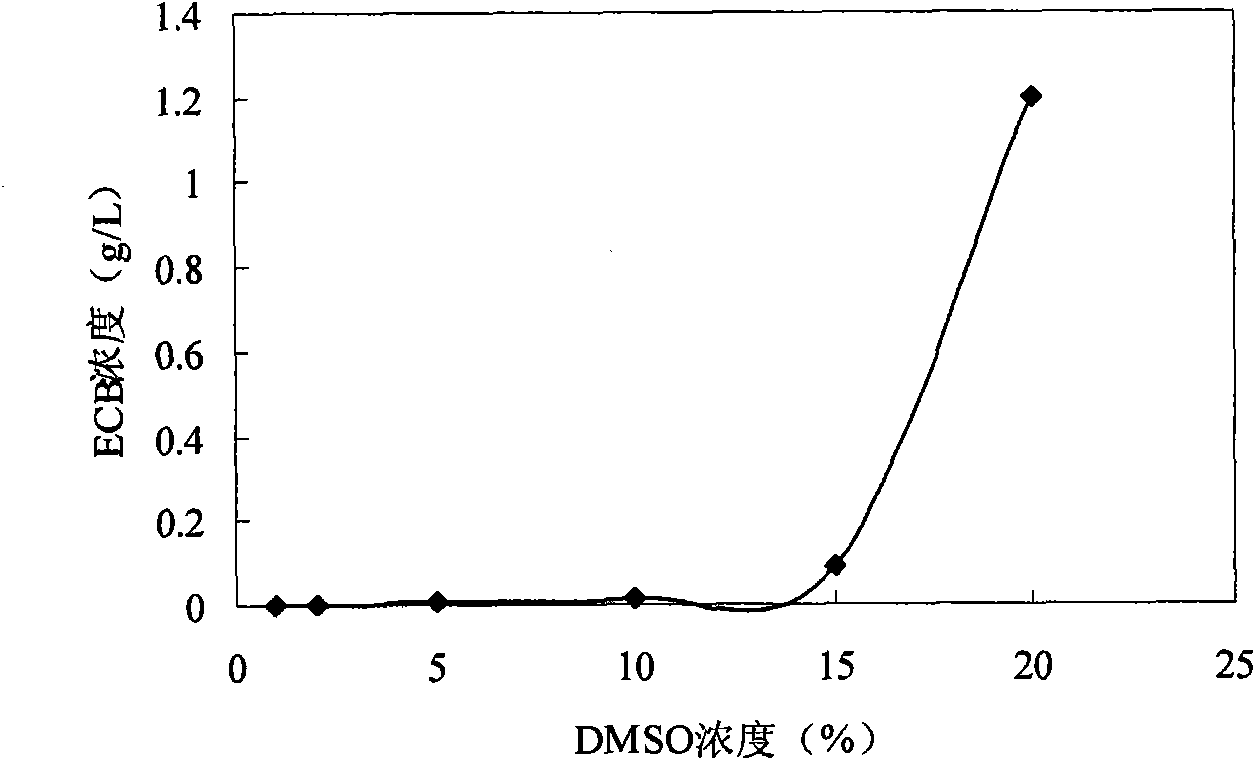
Method for preparing (R)-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenethyl alcohol in ionic liquid-containing cosolvent medium
ActiveCN104212841AImprove solubilityImprove permeabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolubilityCell membrane
The invention provides a method for preparing (R)-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenethyl alcohol in an ionic liquid-containing cosolvent system. The method is characterized in that an ionic liquid is added to a reaction system during asymmetric reduction of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)acetophenone by use of genetically engineered recombinant bacteria; the permeability of the cytomembrane is improved and a substrate is solubilized so that the solubility of the substrate can be effectively improved and the inhibition effect of the substrate and the product on the reaction can be reduced; as a result, the substrate concentration and the reaction efficiency of the reaction are improved; the substrate concentration of the reaction is increased to 1200mM from 50mM; besides, when the substrate concentration is 1200mM, the yield is increased to 93.8% from 70.4% of water phase reduction; the yield is increased by 33.2%; the ee value is greater than 99%.
Owner:南陵县建设投资有限责任公司
Method for producing D-lactic acid by enzyme resolution of D,L-lactic Acid
InactiveCN101333554AShorten the growth cycleLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationThermal denaturationD-lactic acid dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a method for producing D-lactic acid by splitting racemized lactic acid by adopting an enzyme method, comprising steps of: (1) preparation of an intact cell suspension or a crude enzyme liquid containing NAD independent lactic acid dehydrogenase, (2) inactivating the NAD independent D-lactic acid dehydrogenase by a thermal denaturation method, (3) splitting the racemized lactic acid, (4) preprocessing of transformation liquid, (5) separation of D-lactic acid and pyruvic acid, (6) refining the D-lactic acid and the pyruvic acid, etc. The method has advantages of simple culture medium, short growth cycle, low cost, low expenses of the follow-up separation and extraction, high substrate concentration resistance and high enantiomeric excess value of the product D-lactic acid, and lays the foundation for the development and application of low-priced racemized lactic acid and the high-efficient production of D-lactic acid.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
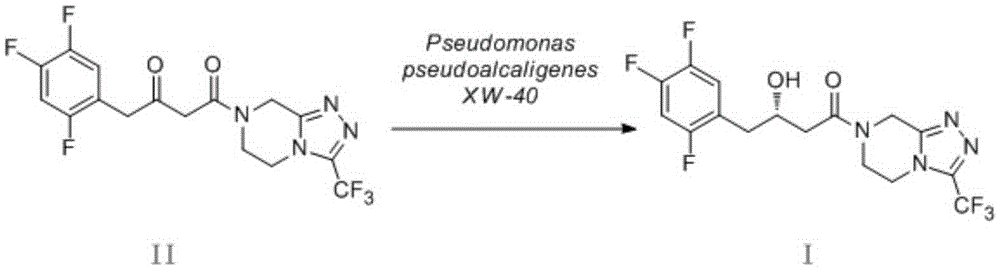
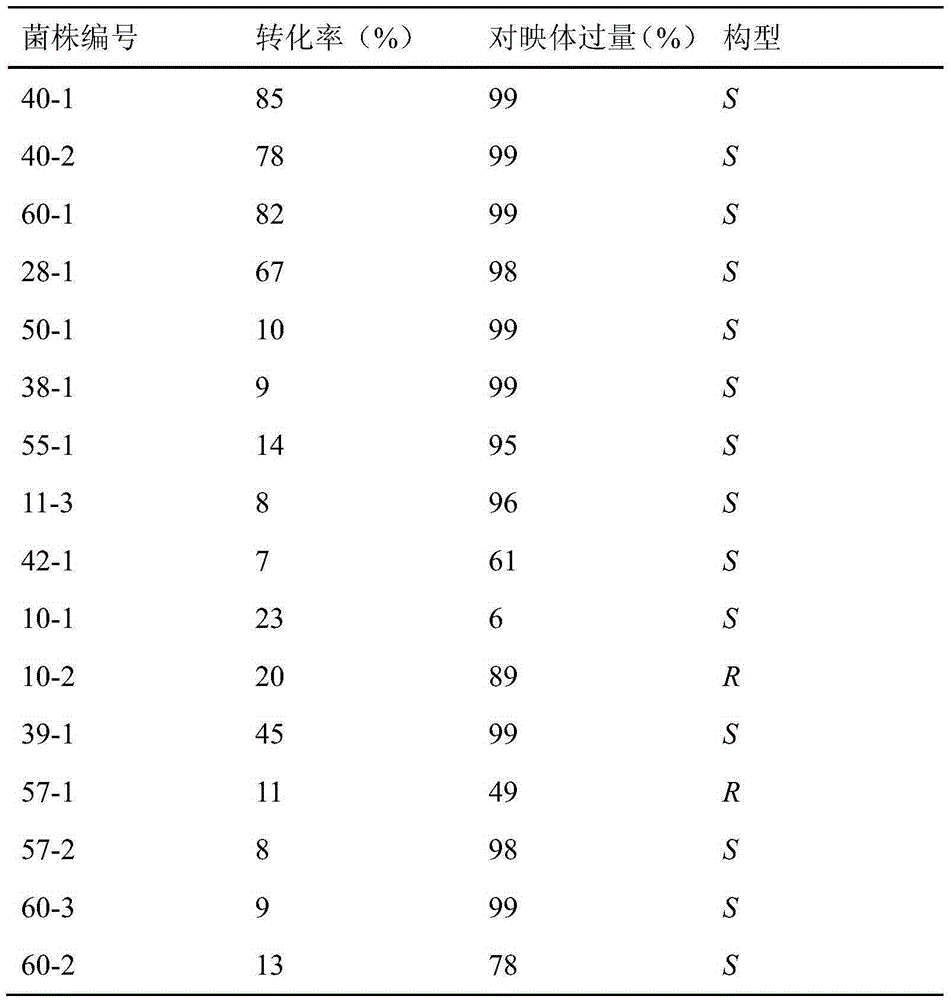
Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes and application of pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes to preparation of sitagliptin intermediate
The invention discloses pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes and application of the pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes to preparation of a sitagliptin intermediate. A colony of the pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes XW-40 is flat and round in surface morphology, smooth and neat in edge, moist, milk white and opaque and is about 1.9mm in diameter. The pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes is capable of effectively catalyzing 4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazine-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5)-trifluorophenyl)-butan-2-one to be reduced into a sitagliptin chiral intermediate; in optimal reaction conditions, the pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes can be tolerant to 10 g / L of high substrate concentration while keeps high selectivity, and is weak in substrate inhibition effect, so that high-substrate-concentration biological catalysis can be achieved; the pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes is recyclable and removes inhibition effect of a substrate and a product on cells as compared with fed-batch, so that catalytic activity of the pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes is used maximally.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Recombinant lipase mutant, engineering bacteria and application of recombinant lipase mutant
ActiveCN109182298AMild reaction conditionsHigh substrate concentrationBacteriaHydrolasesChemistryDecane
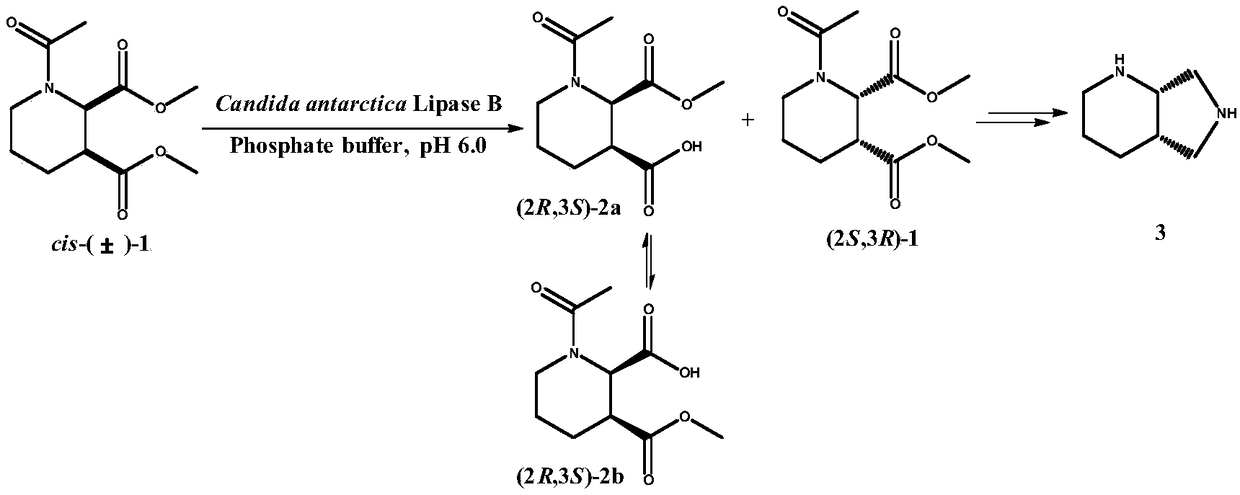
The invention discloses a recombinant lipase mutant, engineering bacteria and application of the recombinant lipase mutant in the preparation of (2S,3R)-N-acetyl-piperidine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester. The mutant is prepared by the step of carrying out single mutation or combined mutation on a site 140, a site 141, a site144, a site 189 and a site 190 of an amino acid sequence representedby SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with wild enzyme, the mutant has the advantages that the catalytic activity and the substrate tolerance are greatly improved, and the time consumed in the reaction progress is obviously shortened. Compared with (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]decane prepared by virtue of a chemical method, the produced prepared by virtue of the technique provided by the invention has the advantages of high stereoselectivity, relatively mild reaction condition, low facility request and environmental friendliness, and the reaction cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A microbial enzymatic conversion method for echinocandin B
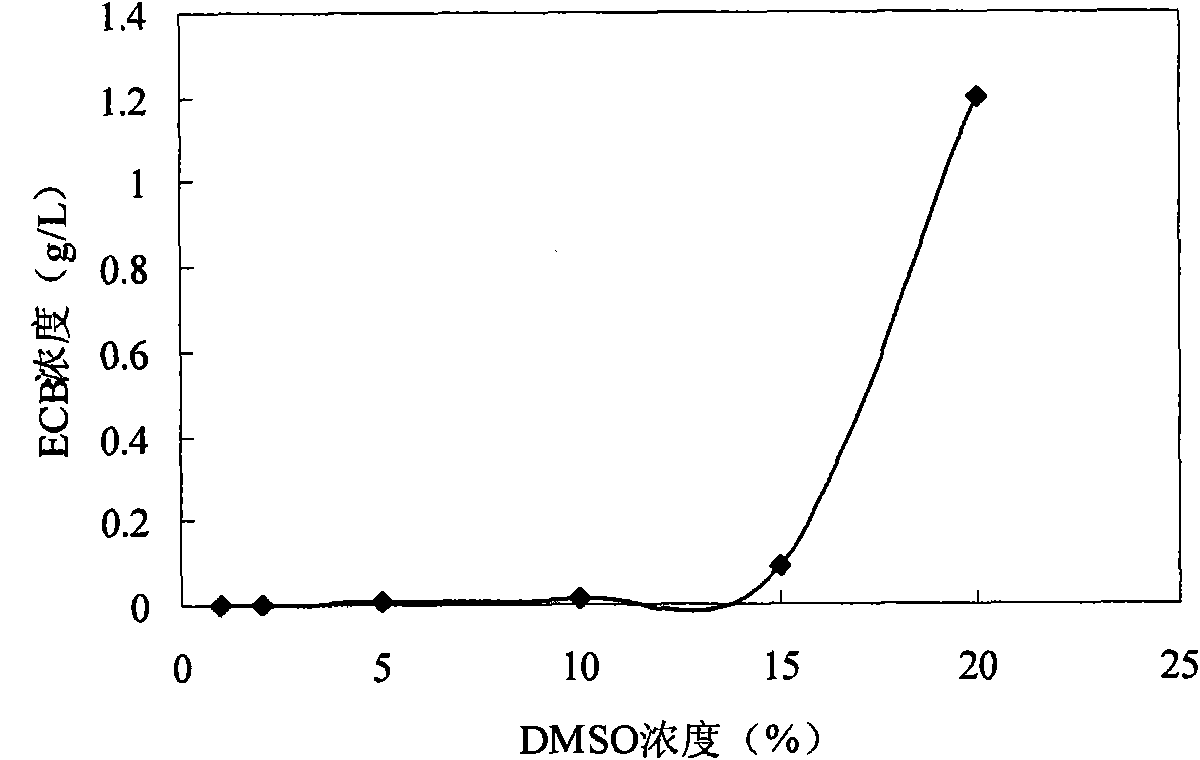
ActiveCN105648000AImprove solubilityEasy to extractMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingBiotechnologyEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a microbial enzymatic conversion method for echinocandin B, and particularly relates to a method of converting the echinocandin B into an echinocandin B nucleus. The method includes performing microbial fermentation to produce echinocandin B deacylase, extracting to obtain crude enzyme, and converting through adding the crude enzyme and the echinocandin B in a batch manner. The method is high in mole conversion ratio, high in product concentration, and beneficial to separation and purification. An echinocandin B substrate can be recovered and reutilized, thus reducing a production cost.
Owner:CHONGQING QIANTAI BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE +1
Echinocandin biotransformation method
ActiveCN102618606BAvoid steps such as separation and purificationReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolubilityEchinocandin
The invention discloses an echinocandin biotransformation method using an actinomycete whole cell or fermentation broth as a catalyst. The invention also provides an echinocandin biotransformation method using cyclodextrin and its derivative or other cosolvents. A transformation system involved in the invention is characterized in that the system can effectively improve the solubility of echinocandin compounds in an aqueous solution, improve the utilization rate and the reaction rate of substrates, and improve the transformation rate of products. Actinoplanes involved in the invention and their mutant strains are in a nutritional medium containing an assimilable carbon and nitrogen source and can generate whole-cell deacylated enzymes under ventilation conditions, and the whole cell deacylated enzymes can be used for the echinocandin biotransformation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f1859212-51b8-40ec-8270-6fdbed17b9a6/HDA0000029873840000011.PNG)
![Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f1859212-51b8-40ec-8270-6fdbed17b9a6/HDA0000029873840000012.PNG)
![Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol Leifsonia xyli and use thereof in preparation of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f1859212-51b8-40ec-8270-6fdbed17b9a6/HDA0000029873840000021.PNG)