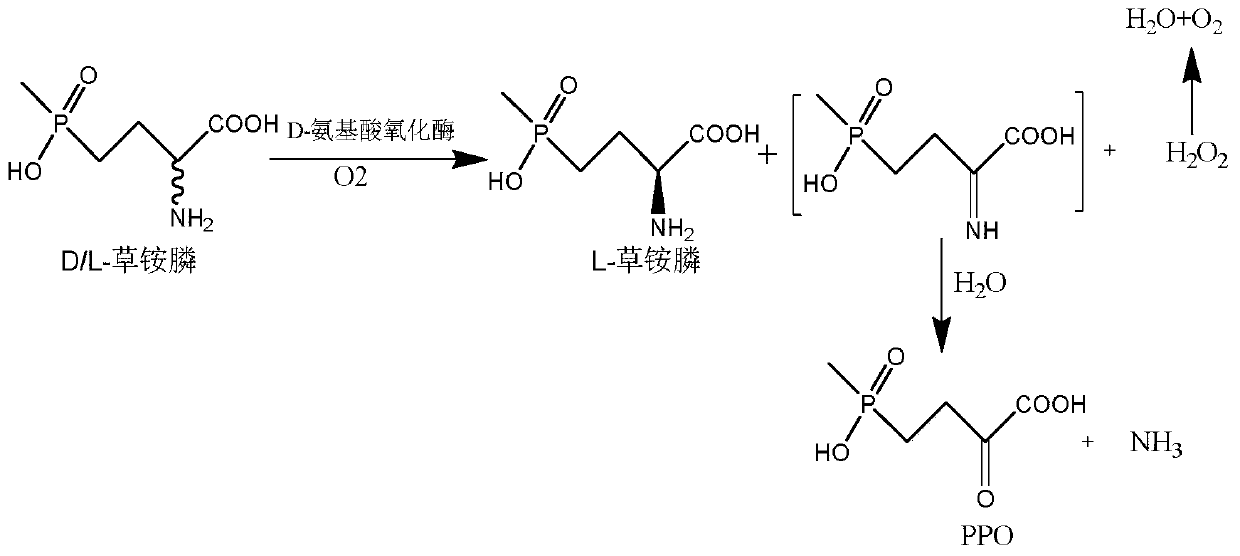
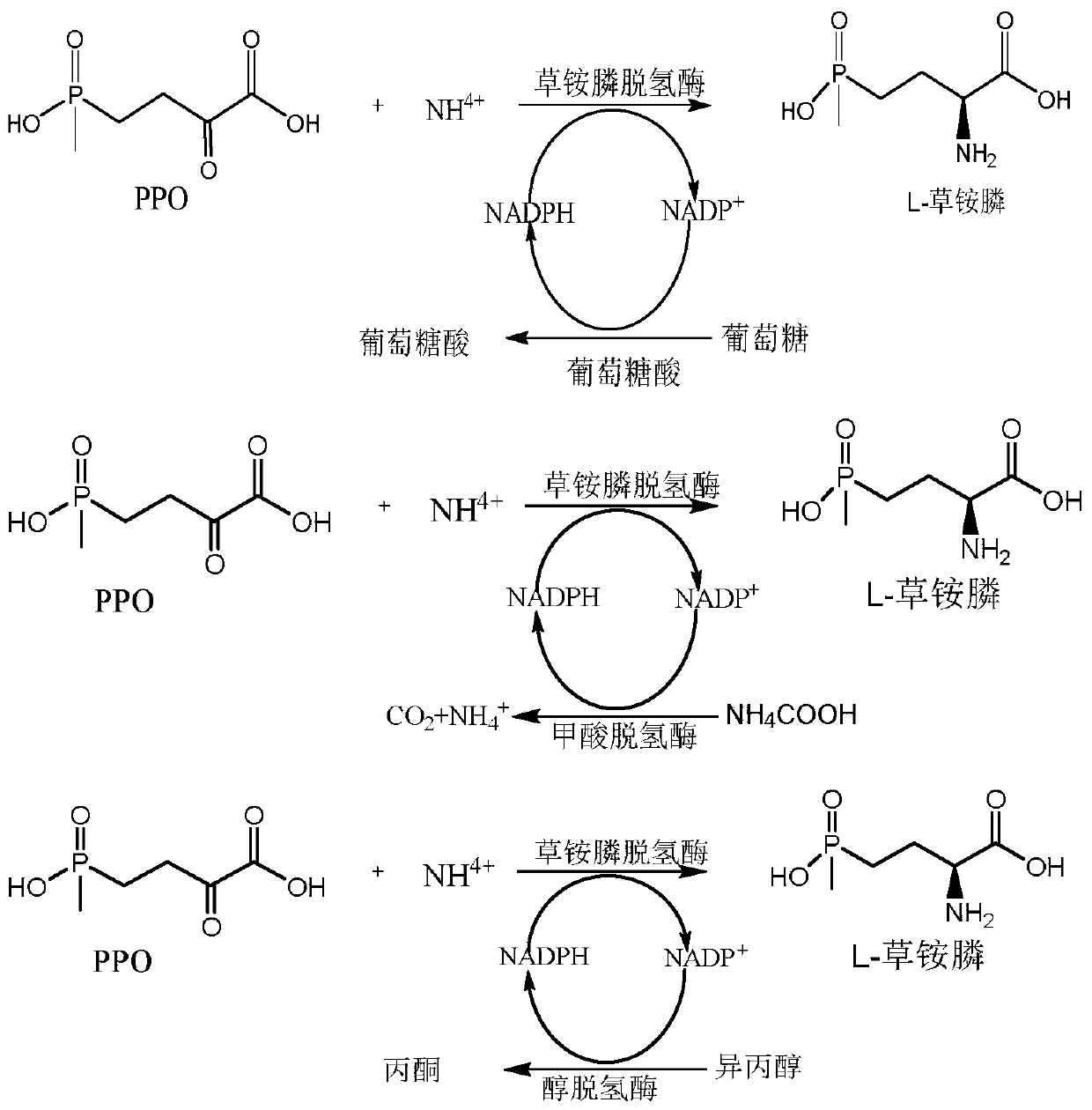
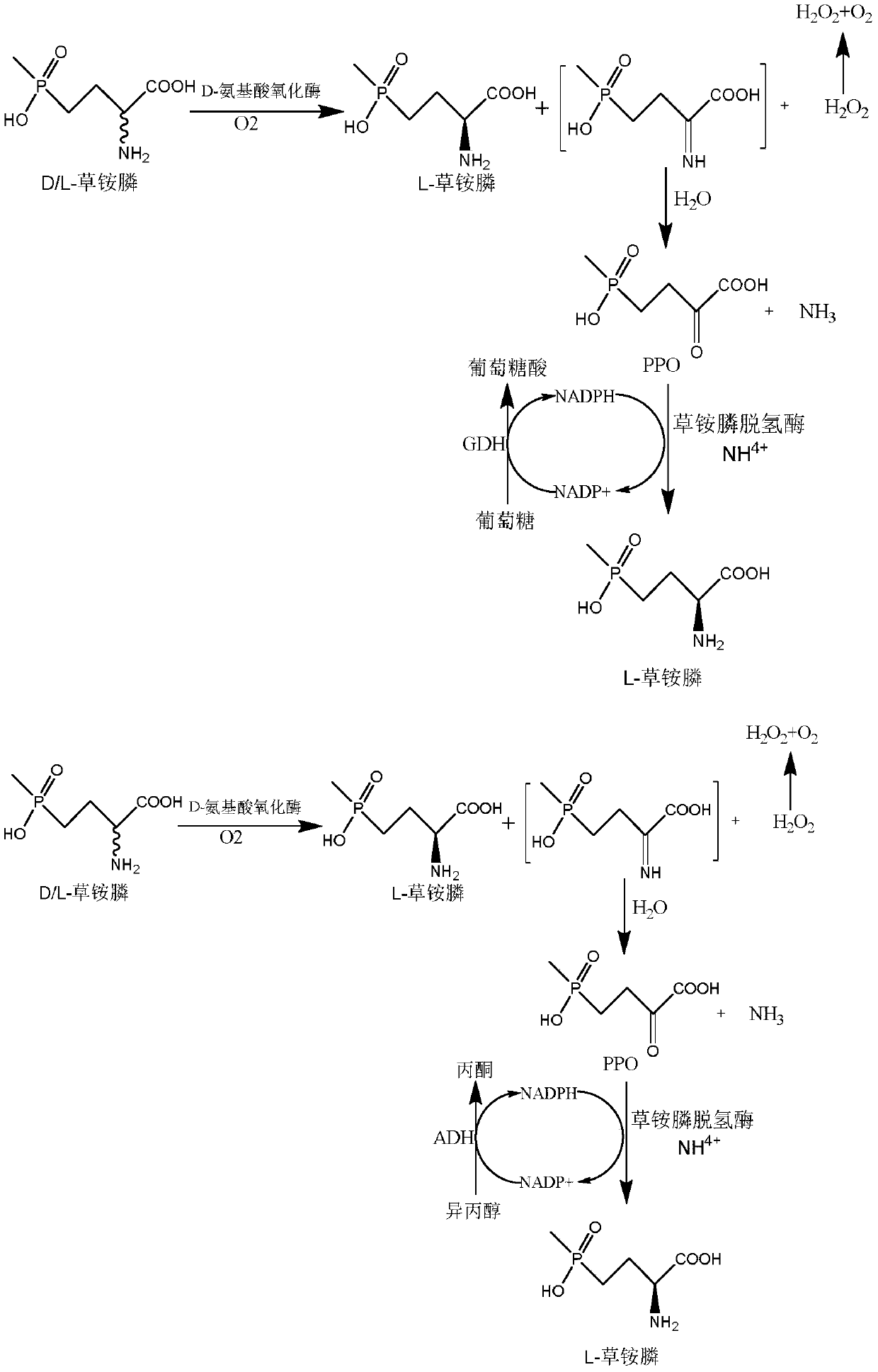
Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to production of L-glufosinate-ammonium through oxidation-reduction of multienzymes
A mutant, glufosinate-ammonium technology, applied in the production field of chiral pure L-glufosinate-ammonium, can solve the problems of insufficient activity and limited industrial application, and achieve improved catalytic activity, easy separation and purification, and high yield Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The construction of embodiment 1 expression vector and engineering bacterium
[0044] (1) Recombinant Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH
[0045] Through literature reports and gene sequence homology, a glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase strain derived from Pseudomonasmoorei was selected in the NCBI database, and the NCBI accession number was WP_090325311.1, and the whole gene was synthesized. The nucleotide sequence is shown in Figure SEQ Shown in ID NO.1, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.
[0046] Primers were designed according to the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and Sac I and NotI restriction enzyme sites were introduced in the primers respectively:
[0047] Upstream primer: 5'-GAGCTCATGATTGAGAGCGTCGAGTCT-3';
[0048] Downstream primer: 5'-GCGGCCGCTTAGACGACCCCCTGTGCC-3';
[0049] Using the pETDuet-1 plasmid as the expression vector, construct E. coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH:
[0050]Construction of the expres...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Glucose dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase, alcohol dehydrogenase were recombined with glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli E. coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH-GDH, E. coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH-ADH, E. coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH-FDH.
[0061] 1. Glucose dehydrogenase (NCBI accession number: KM817194.1), formate dehydrogenase (NCBI accession number: WP_013726924.1), and alcohol dehydrogenase (NCBI accession number: CAD66648.1) were respectively cloned by one-step cloning method To the second multiple cloning site of plasmid pETDuet-1:
[0062] Acquisition of glucose dehydrogenase gene, formate dehydrogenase gene and alcohol dehydrogenase gene with homologous sequences: each 15-20bp sequence at the beginning and end of the linearized vector pETDuet-1 is used as a homologous sequence to E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28b-GDH, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28b-FDH and E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28b-ADH (according to NCBI accession number, usi...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3: Induced expression of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase-glucose dehydrogenase or alcohol dehydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase recombinant bacteria, D-amino acid oxidase
[0083] 1. Wet thallus containing glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene-glucose dehydrogenase gene or alcohol dehydrogenase gene or formate dehydrogenase gene: the recombinant Escherichia coli E.coli BL21 (DE3) obtained in Example 1 was respectively / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH-GDH, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH-ADH, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDH-FDH, inoculated to contain 50μg / mL ampicillin The resistant LB liquid medium was cultured at 37°C for 12 hours at 200rpm, and then inoculated into fresh LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL ampicillin resistance with a 1% (v / v) inoculation amount, and incubated at 37°C , Cultivated to OD of the bacteria at 150rpm 600After reaching 0.6-0.8, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1mM, induce culture at 18°C for 16h, centrifuge at 8000rpm at 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com