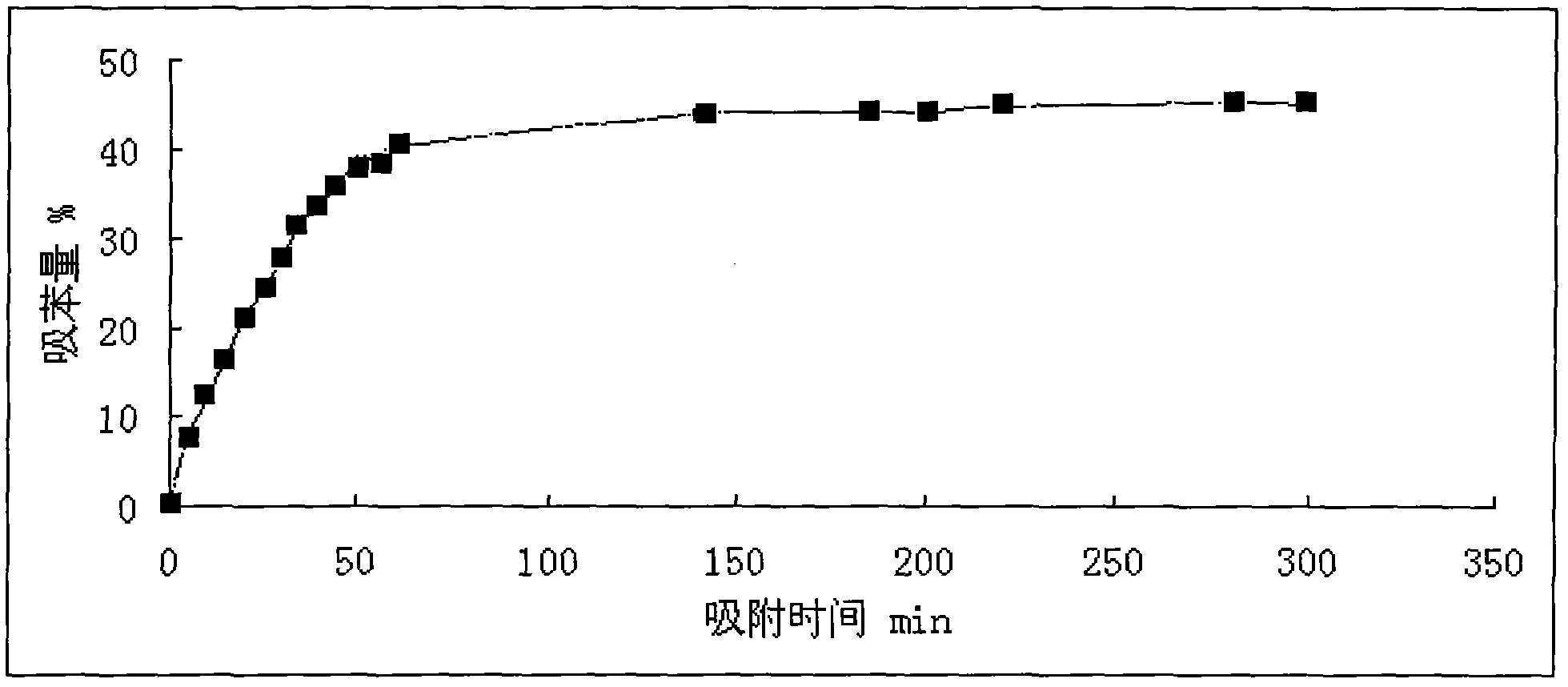
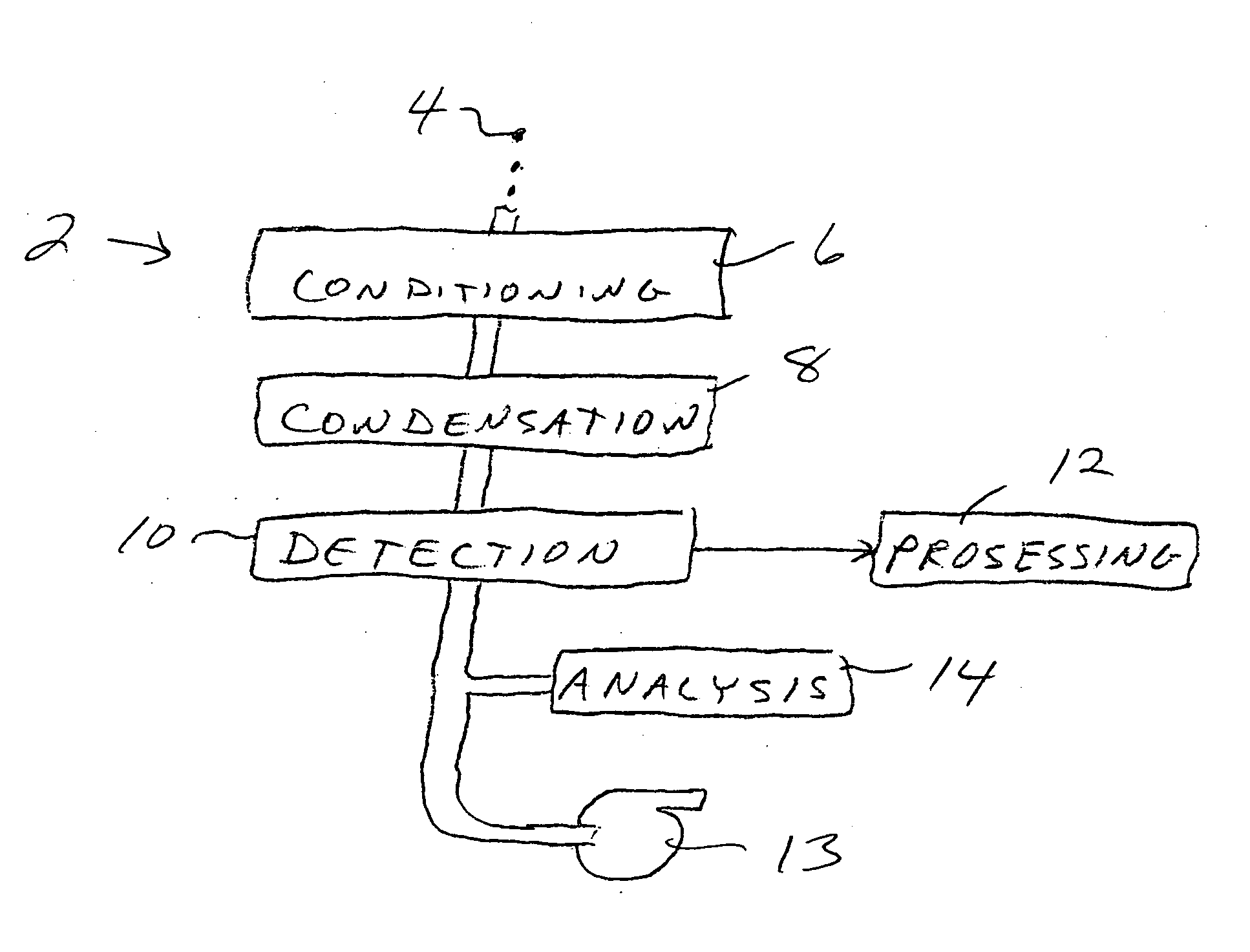
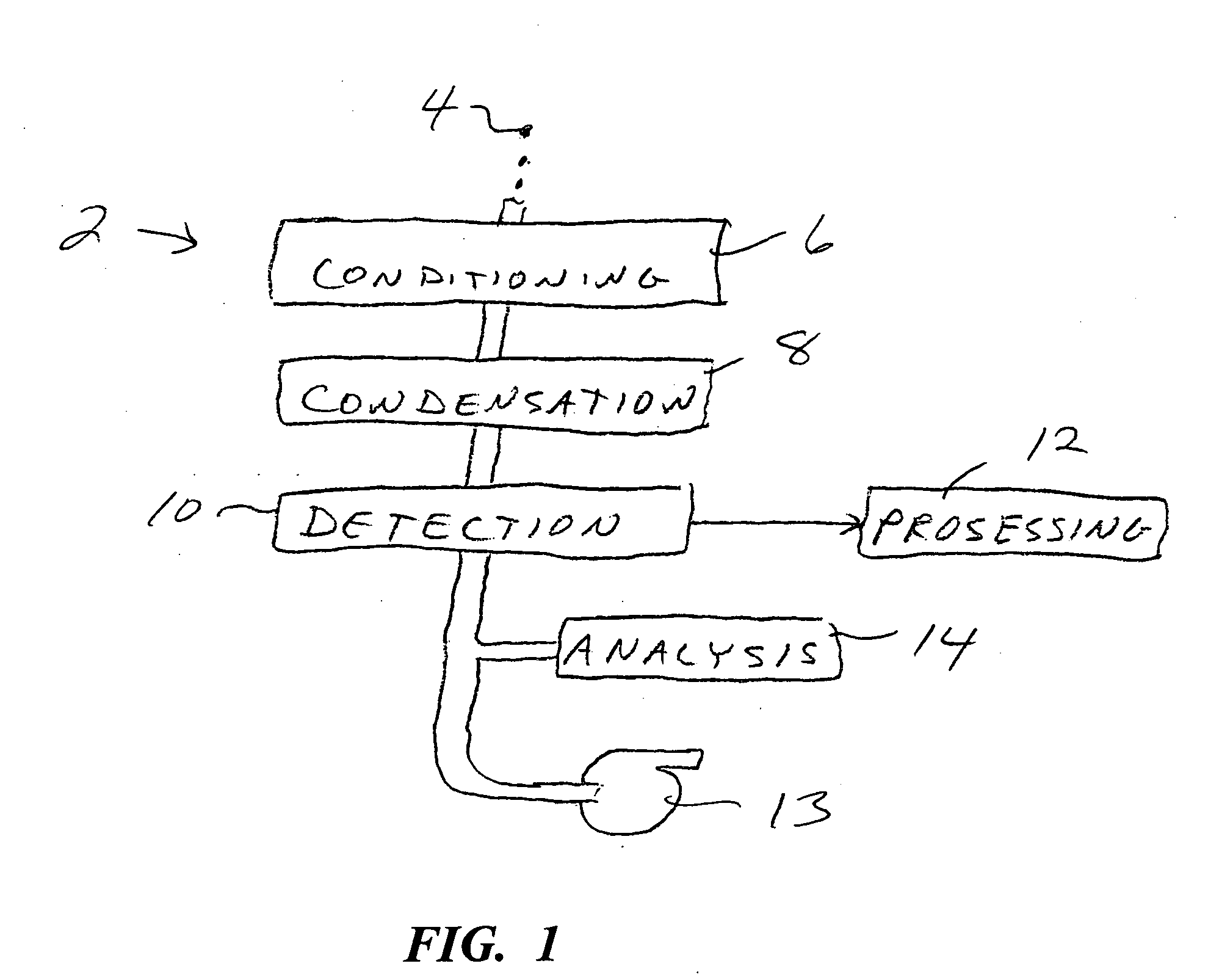
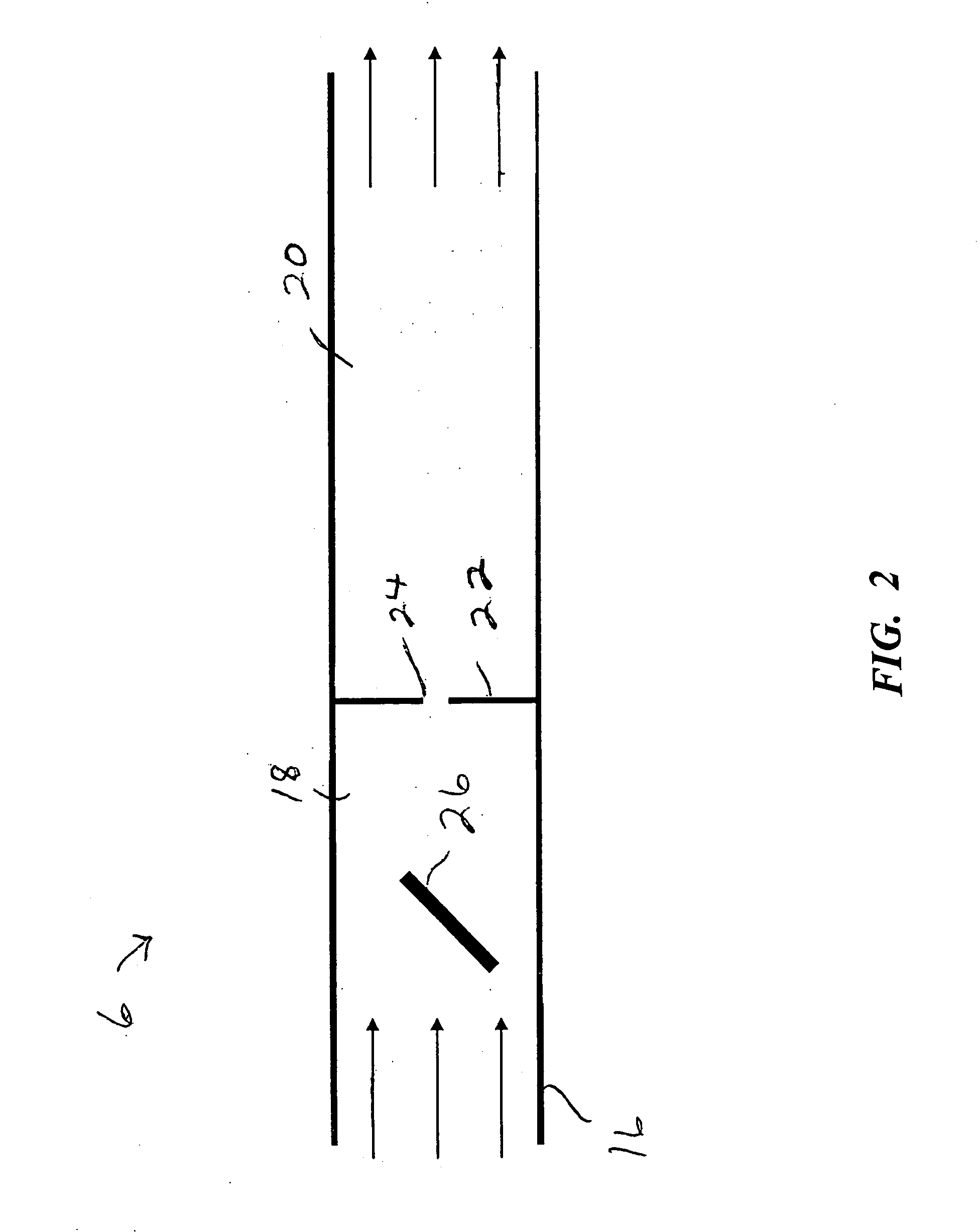
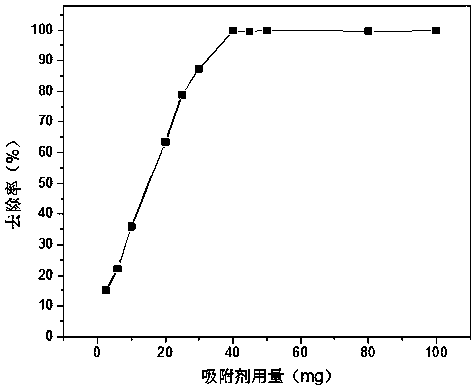
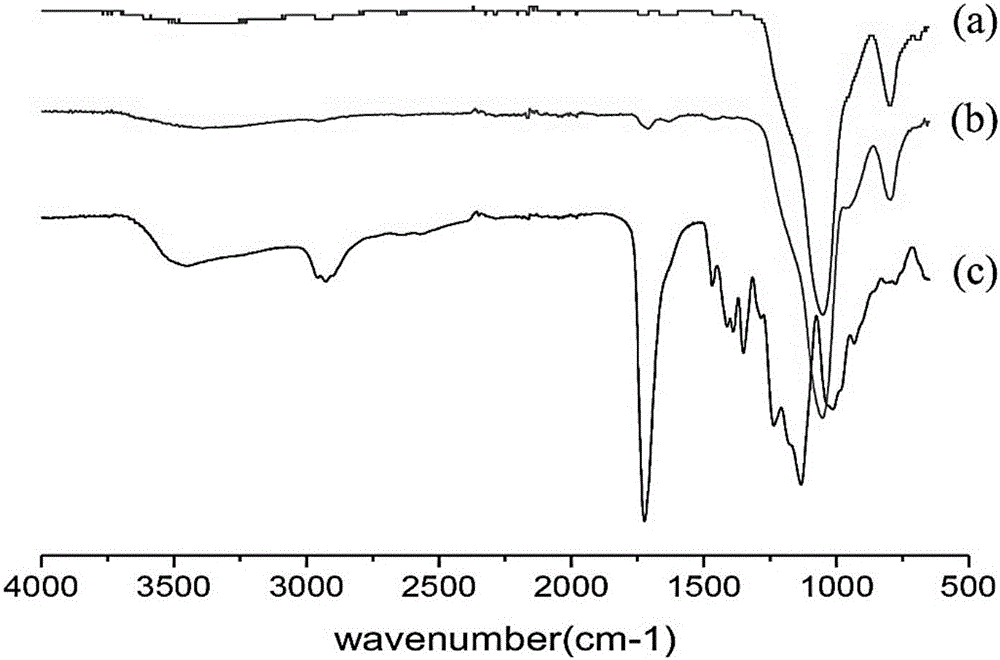
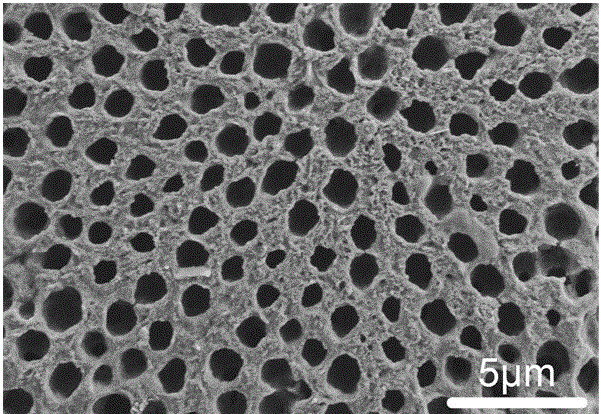
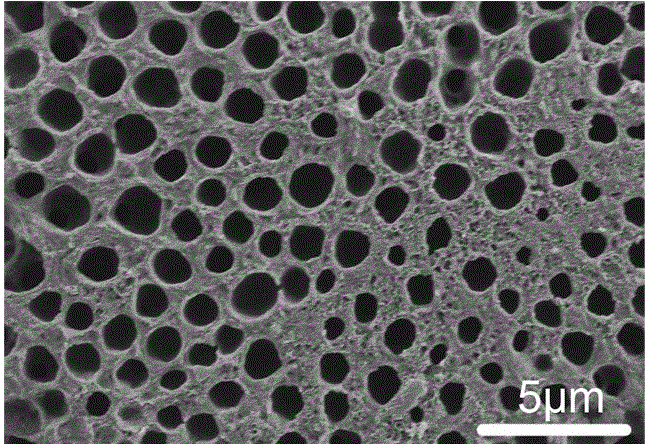
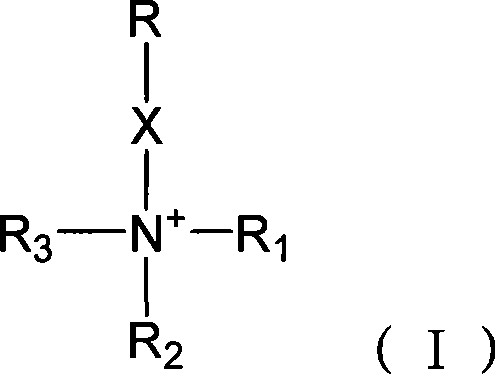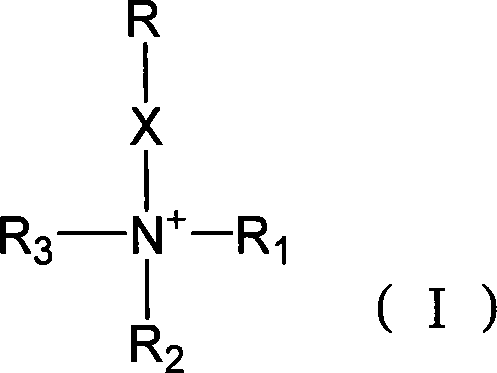Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Molecule adsorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adsorption refers to the collecting of molecules by the external surface or internal surface (walls of capillaries or crevices) of solids or by the surface of liquids. Absorption, with which it is often confused, refers to processes in which a substance penetrates into the actual interior of crystals, of blocks of amorphous solids, or of liquids.
Method for preparing high-quality graphene in large scale by intercalation stripping of graphite by chemical method
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-quality graphene in large scale by intercalation stripping of graphite by chemical method. The main principle and approach are as follows: inserting some reagent into graphite intercalation by chemical method, then adding energy or some reagent to make intercalation material rapidly and violently react to release air and stripping graphite into graphene. The specific embodiment proposal comprises means of liquid phase stripping, solid phase stripping and two-step liquid phase and solid phase combined stripping. The prepared graphene has high single intercalation quality and few detects since it does not go through oxidation and reduction processes. The oxygen content is only 1.63% and is the lowest in known graphene preparation method by graphite. There is no impurity or molecule absorbed on the graphene surface. The invention has low cost, high yield, simple and feasible preparation method and low energy consumption and is suitable for large scale generation.
Owner:深圳市长宜景鑫投资有限公司
Methods of using natural products as dewatering aids for fine particles
InactiveUS6526675B1Reduce moistureImprove hydrophobicityPigmenting treatmentDrying using combination processesLipid formationSlurry
A method of dewatering fine particulate materials is disclosed. In this method, an aqueous slurry of fine particles is treated with appropriate hydrophobizing reagents so that the particulate material becomes moderately hydrophobic. A lipid of vegetable or animal origin is then added to the slurry in solutions of light hydrocarbon oils and short-chain alcohols, so that the hydrophobic lipid molecules adsorb on the moderately hydrophobic surface and, thereby, greatly enhance its hydrophobicity. By virtue of the enhanced hydrophobicty, the water molecules adhering to the surface are destabilized and more readily removed during the process of mechanical dewatering. The moisture reduction can be further improved using appropriate electrolytes in conjunction with the lipids, spraying surface tension lowering reagents onto the filter cake, subjecting the cake to a suitable vibratory means, and using combinations thereof.
Owner:YOON ROE HOAN
Plastic surfaces and apparatuses for reduced adsorption of solutes and methods of preparing the same
InactiveUS20090148348A1Less likely to adsorbMore hydrophilicAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPreparing sample for investigationWater vaporProduct gas
A method of treating a plastic surface with fluorine gas to decrease adsorption of hydrophobic solute molecules to the surface is provided. The method can include treating a surface with a first gas comprising fluorine gas and a second gas comprising oxygen gas, water vapor, or both oxygen gas and water vapor. Plastics treated using the method provide useful drug discovery and biochemical tools for the testing, handling, and storage of solutions containing low concentrations of hydrophobic solutes. Microfluidic devices containing treated plastic interior surfaces and methods of using such devices to make concentration-dependent measurements are also described.
Owner:SCIEX
Arrays of electrodes coated with molecules and their production
InactiveUS20060151324A1High purityHigh resolutionMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsDesorptionElectrochemistry
The present invention provides a method of forming coatings of at least two different coating molecules on at least two electrodes, the method comprising: (a) providing an array of at least two individually-addressable electrodes, (b) allowing a layer of a masking molecule to adsorb onto all electrodes, (c) inducing electrochemical desorption of the masking molecule from at least one but not all electrodes to expose a first set of exposed electrodes, (d) allowing a first coating molecule to adsorb onto the first set of exposed electrodes, (e) exposing all electrodes to a masking molecule to allow adsorption of the masking molecule onto all electrodes, (f) inducing electrochemical desorption of masking molecule from a second set of electrodes to expose a second set of exposed electrodes, (g) allowing a second coating molecule to adsorb onto the second set of exposed electrodes.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD
Surface plasmon resonance detection with high angular resolution and fast response time
InactiveUS6784999B1Scattering properties measurementsElectron transfer reactionsDifferential signaling
A device and method of detecting surface plasmon resonance for sensing molecules or conformational changes in molecules with high resolution and fast response time is disclosed. Light from a light source (14) is focused through a prism onto a metal thin film (15) on which sample molecules to be detected are adsorbed. The total internal reflection of the laser / incident light is collected with a differential position or intensity sensitive photo-detecting device instead of a single cell or an array of photo-detectors (12) that are widely used in previous works. The ratio of the differential signal to the sum signal of the differential position or intensity sensitive photo-detecting device (12) provides an accurate measurement of the shift in the surface plasmon resonance angle caused by the adsorption of molecules onto the metal films (15) or by conformational changes in the adsorbed molecules. The present invention requires no numerical fitting to determine the resonant angle and the setup is compact and immune to background light, The methods and sensors of this invention can be used in numerous biological, biochemical, and chemical applications such as measuring subtle conformational changes in molecules and electron transfer reactions can be studied.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
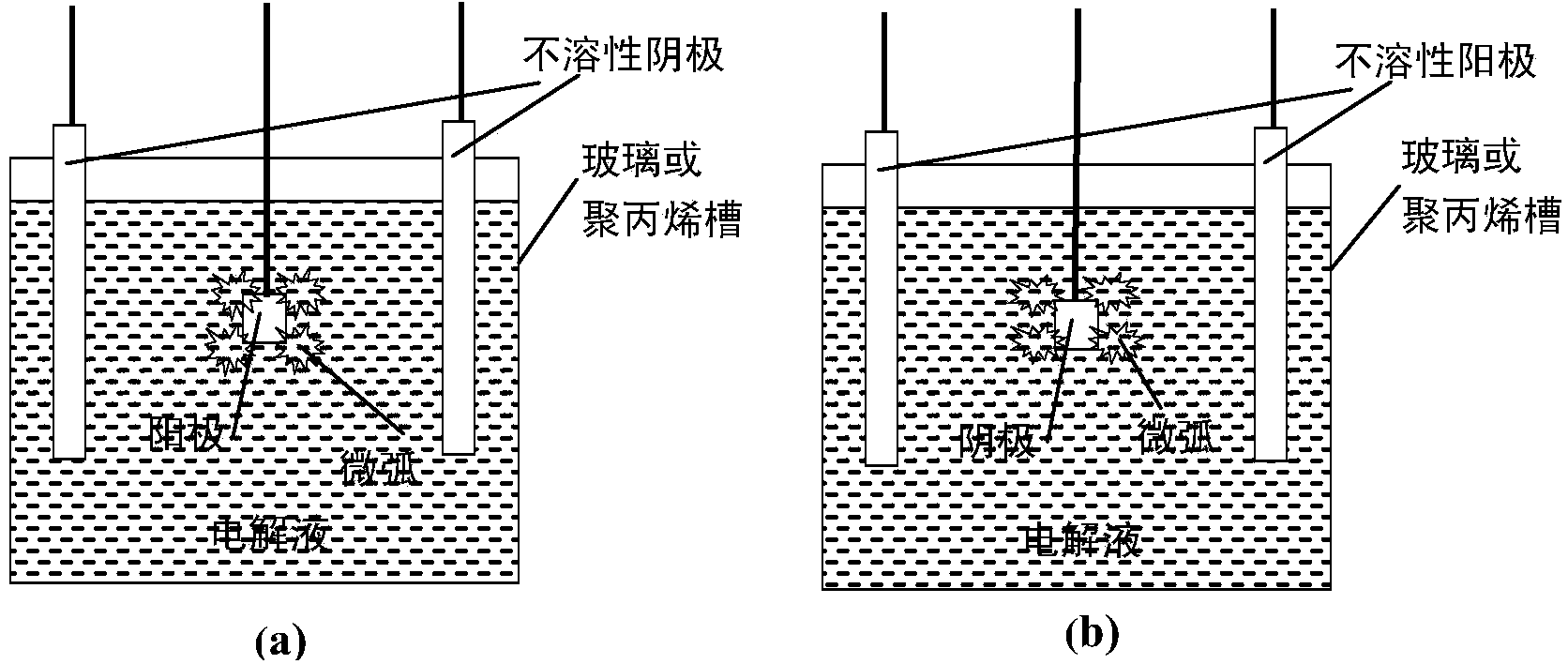
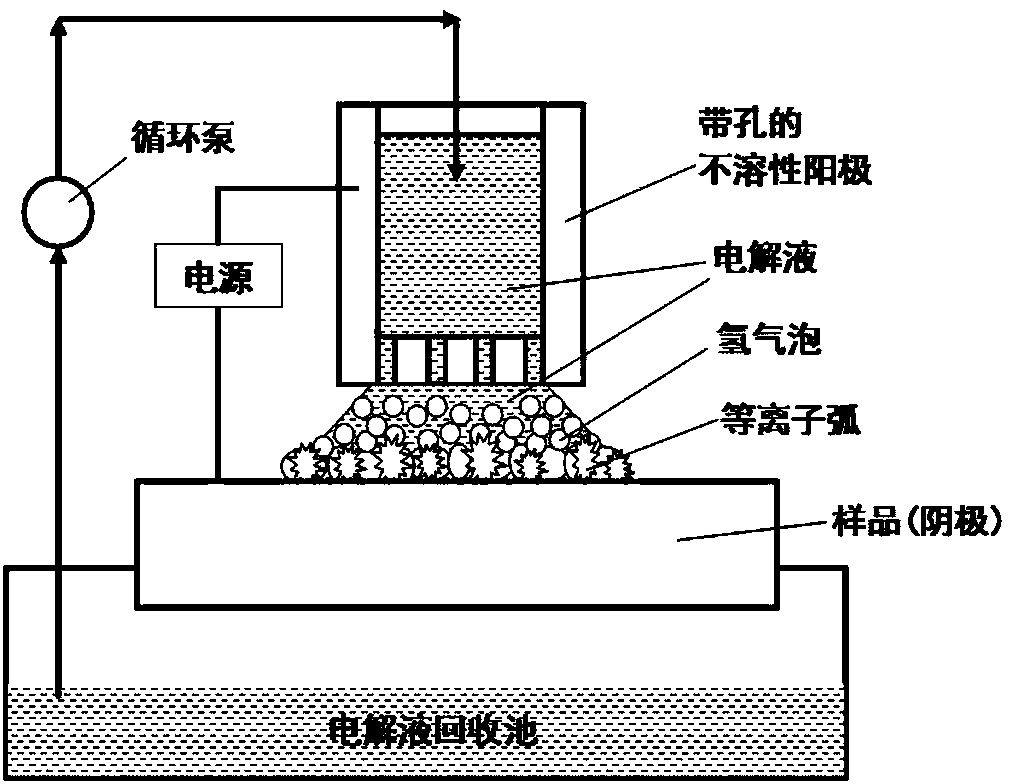
Method for large-area deposition of coating and surface modification by cathodic plasma electrolysis
InactiveCN104164690ALess investmentEasy to operateElectrolytic inorganic material coatingBorideElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for large-area deposition of a coating and surface modification by cathodic plasma electrolysis. A non-ionic water-soluble polymer is added in an electrolyte, and the cathodic plasma electrolysis is carried out by adopting a conventional electrolytic tank or an electrolytic tank that sprays the electrolyte and has an anode and a cathode that moves relatively. A certain direct current voltage or impulse voltage is applied to the electrolytic tank; and the non-ionic water-soluble polymer is absorbed on the surface of a cathode material to induce uniform and continuous large-area cathodic plasma high energy micro-arc discharge, thereby deposing oxide, carbide, nitride, boride and a compound ceramic coating in large area in an electrolyte with different components, deposing a compound coating of oxide and dispersed noble metal particles in large area , and cleaning the surface of the material in the large area and realizing surface nanocrystallization of the material. The method endows materials with novel characteristics such as optics, electrics, magnetics, chemistry, electrochemistry, mechanics and biology, and has wide application in various industrial fields.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Warmth retaining fiber structure
InactiveUS20030068949A1Effective coolingMinimizing chilly feelGarment special featuresOrnamental textile articlesMoisture permeabilityEngineering
The present invention relates to a heat-retaining fiber structure comprising a cloth layer having a moisture / heat release control capability laminated with a cloth layer having water molecule adsorption / heat release capability, wherein said cloth layer having the moisture / heat release control capability has a moisture permeability of 3000-12000 g / m<2>.24 hr and said cloth layer having water molecule adsorption / heat release capability has an exothermic energy index of 5 or larger and a contact thermal sensation factor (qmax) of 0.1 W / cm<2 >or less. This constitution makes it possible to provide clothing having high heat-retaining performance achieved by water molecule adsorption capability.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate based on carbon nanometer pipe arrays and metal nanometer particles
InactiveCN102530828AAdsorbed substances have a large surface areaIncrease surface areaDecorative surface effectsRaman scatteringCarbon nanotubeUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a method for realizing a surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate based on carbon nanometer pipe arrays and metal nanometer particles. The method includes: utilizing the carbon nanometer pipe arrays arranged perpendicularly as nanometer metal structural carriers with large superficial area, depositing precious metal nanometer particles on the nanometer pipe carriers to form a surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate, attaching molecules to be detected onto the surface of rough metal, and irradiating the surfaces of the molecules to be detected by excitation light to enhance Raman scattering signals of the molecules evidently. The surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate is simple in manufacturing process, low in cost and free of pollution, the superficial area of the carbon nanometer pipe arrays is large, packing effect of metal nanometer particles is effectively improved, thereby the sectional area of Raman scattering is enlarged and the enhanced intensity of the Raman scattering signals is higher.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
High-molecule adsorption material
InactiveCN102553546ARapid enrichment and getteringRapid decontaminationOther chemical processesHazardous substanceAlkylation
The invention relates to a high-molecule adsorption material, which is a polymer with a novel resin structure and is greatly different from the conventional phenylethylene crosslinked high-molecule adsorption resin. A main body structure of the high-molecule adsorption material is a network structural system consisting of an aromatic benzene ring and a methylene structure which are connected with each other. A preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing continuous pay-gram alkylation polymerization reaction on a derivative such as benzene-type aromatic hydrocarbon and the like and a precursor dichlorine methyl-type rigid cross-linking agent; and synthesizing a novel non-combustible adsorption material and non-phenylethylene type adsorption resin material. The material is high in polymerization reaction yield, and can be applied to fields of air purification, such as leakage treatment for dangerous chemical substances, adsorption and elimination of industrial poisonous and harmful substances, treatment for tail gas from a factory, effective and quick absorption and removal of oil pollution on a water surface and the like, research and development on relevant protection materials of personal safety protection devices and the like.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA
Particle surface treatment for promoting condensation
ActiveUS20050248750A1Reduce the overall diameterIncrease capacityCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentWorking fluidPhysical chemistry
A system is disclosed for condensation particle counting in conjunction with modifying an aerosol to enhance the formation and growth of droplets of a selected working fluid, preferably water. Before saturation with the working fluid, the aerosol is exposed to an aerosol modifying component, preferably a vapor including molecules that are adsorbed onto surfaces of the particles or other elements suspended in the aerosol. Adsorption alters the surface character of the suspended elements towards increased affinity for the vapor of the working fluid, to promote the formation and growth of working fluid droplets. The droplets are optically detected to indicate numbers and concentrations of the suspended elements.
Owner:TSI INC +1
Thin film-like polymer structure and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20100062258A1Lamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer thin filmsSolvent
A thin film polymer structure having a functional substance on the face (A surface) and reverse face (B surface) of the film, obtained by the steps of(a) causing polyfunctional molecules to adsorb to an area of an arbitrary shape in an interface between a substrate body and a liquid phase;(b) polymerizing and / or crosslinking the adsorbing polyfunctional molecules to form a polymer thin film;(c) bonding a functional substance to the A surface of the formed thin film and then(d) forming a soluble support film thereon; exfoliating the thin film and the soluble support film from the substrate body;(e) bonding to the B surface of the thin film a functional substance identical to or different from the abovementioned functional substance and then dissolving the soluble support film with a solvent.A method for preparing a thin film molecular structure having a functional substance on the face (A surface) and reverse face (B surface) of the film is offered through the above process.
Owner:TAKEOKA SHINJI +2
Water-soluble cationic polymer adsorption material and applications thereof
InactiveCN101224413AGood compatibilityAvoid non-specific adsorptionOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesChemical synthesisBlood plasma
The invention relates to a water soluble cationic polymer adsorption material in the biomedical material field and the application thereof, which contains the quaterisation reaction synthesis of natural polysaccharides with amino groups and hydroxyls and the derivatives thereof or chemosynthetic polymers. The invention is characterized in that the molecule of the polymer adsorption material has a structure in formula I: in the formula, R is selected from the natural polysaccharides with amino groups and hydroxyls and the derivatives thereof or the chemosynthetic polymers, the molecular weight of which is from 6 KD to 500 KD; X is selected from a C0 to C6 paraffinic chain with O atoms, N atoms or OH groups; R1, R2 and R3 are selected from a C1 to C4 alkyl group. After the adsorption material is dissolved in a medical dialysis solution, the material can be applied to a blood purification treatment for severe hepatitis patients. The invention has the advantages of removing protein-bound toxin and water soluble toxin molecule at the same time, low cost which is only about one tenth of that of a molecular adsorbent recirculating system and little nonspecific adsorption to plasma protein.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Thin-Filmy Polymeric Structure and Method of Preparing the Same
A thin film polymer structure obtained by the steps of:(a) causing polyfunctional molecules to adsorb to an area of an arbitrary shape in an interface between a substrate body and a liquid phase;(b) polymerizing and / or crosslinking the adsorbing polyfunctional molecules to form a polymer thin film; and(c) exfoliating the formed thin film from the substrate body.
Owner:TAKEOKA SHINJI
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105277526AEasy to manufactureEfficient enrichmentRaman scatteringGas phaseSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
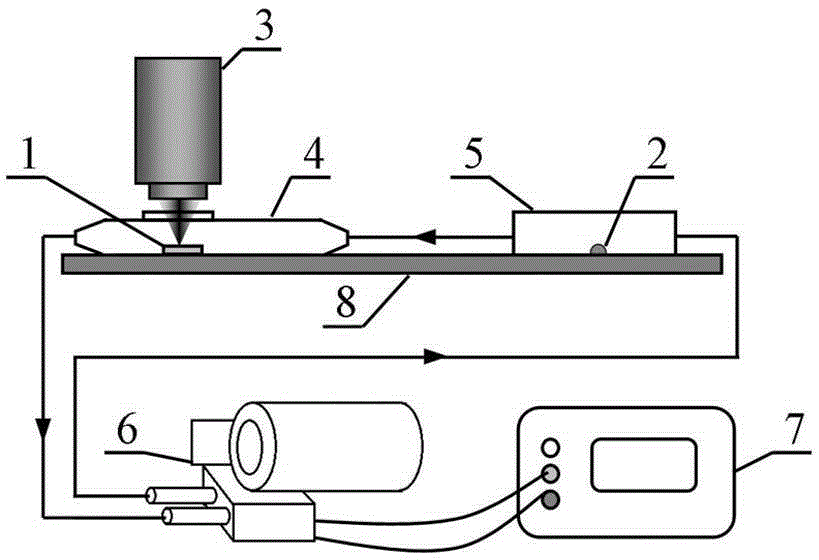
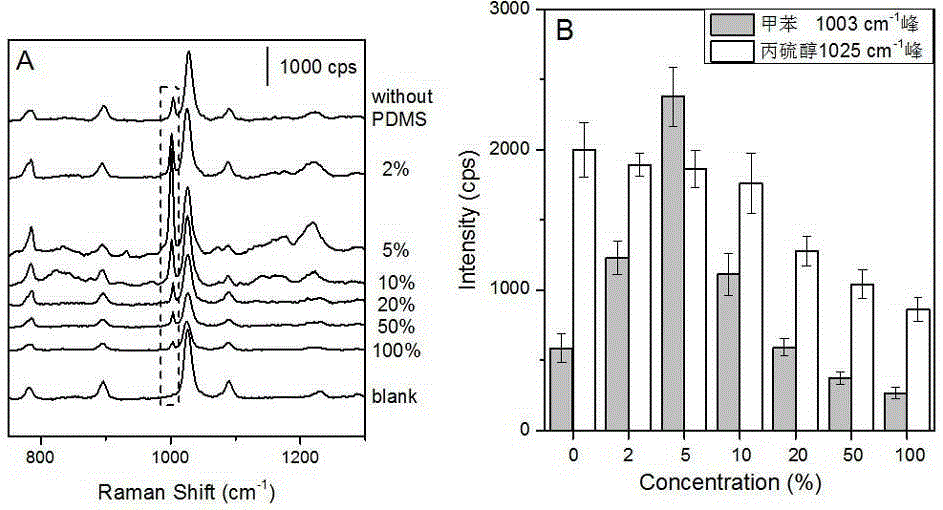
The invention discloses a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate material, a preparation method and an application thereof. The substrate material is a three-layer composite structure: the lower layer is an Au (at) Ag nanoparticle monofilm; the middle layer is a propanethiol molecular layer modified on the Au (at) Ag film; and the upper layer is a polydimethylsiloxane film of 200-400 nm thick. According to the three-layer composite structural substrate material, the polydimethylsiloxane film enriches mononuclear aromatics gaseous molecules in flowing gas through physical action, propanethiol adsorbs the molecules onto the surface of the Au (at) Ag film to carry out enhanced detection. Thus, toxic atmospheric pollutants can be effectively enriched, fixed and detected. Especially for detection of methylbenzene, benzene and xylene in a flowing gaseous phase, detection signal intensity is enhanced by more than 50 times. The invention provides a more sensitive new method for detection of relevant pollutants in industrial waste gas and in the atmospheric environment.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Graphene molecule sensor based on localized surface plasma resonance
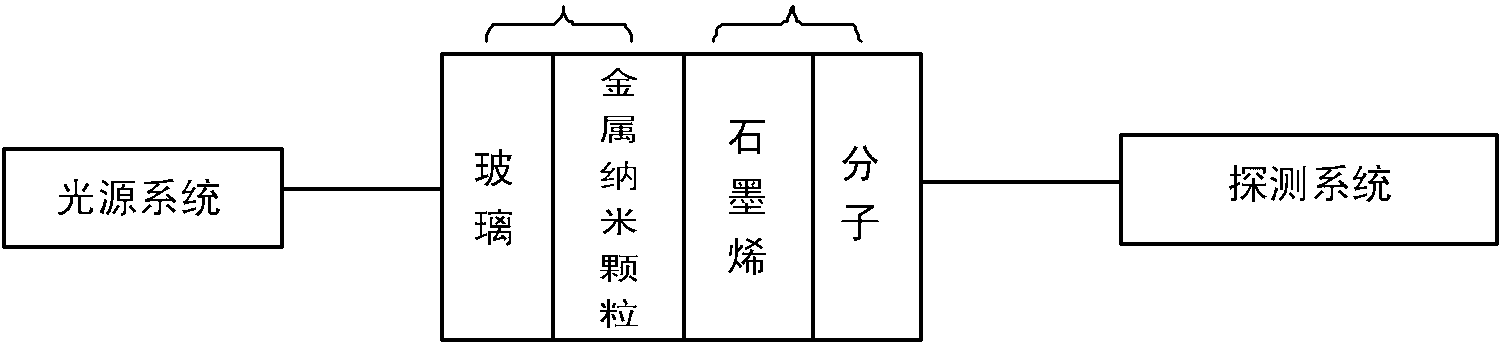
InactiveCN103063619ASimple preparation processLow costTransmissivity measurementsDielectricChemical reaction
The invention relates to a graphene molecule sensor based on localized surface plasma resonance. The sensor comprises a light source system, a transparent metal nanoparticle film system, a graphene molecule adsorbing system and a detection system. After molecules are adsorbed on the surface of graphene, the carrier concentration and the dielectric constant in the graphene are changed, so that the localized surface plasma resonance frequency of the transparent metal nanoparticle film system is influenced, and the type and the concentration of the molecules are detected. The sensor has the characteristics that the preparation process is simple, the cost is low and the operation is convenient; besides, the graphene can be effectively protected from being corroded or inactivated, and the service life of the system is guaranteed; and moreover, toxic or related chemical reaction resulted by the contact between the metal and the molecule can be prevented, the stability of the system is good, and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:泰州巨纳新能源有限公司
Magnetic porous adsorbent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109529780AHigh surface areaImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCross-linkSorbent
The invention discloses a magnetic porous macromolecular adsorbent and a preparation method thereof. The method includes: taking melamine resin, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, chitosan and ferroferric oxide as the main raw materials, firstly subjecting melamine resin, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and ferroferric oxide to cross-linking reaction under an acidic condition to prepare a magneticfunctional compound, then adding chitosan and a cross-linking agent for deep cross-linking reaction to form a cross-linked porous compound, and then conducting drying and ethanol reflux to obtain thechitosan modified melamine resin magnetic porous adsorbent. The adsorbent has good adsorption effect, can achieve a removal rate on new coccine dye in wastewater up to 99%, also has simple and fast magnetic separation function, is beneficial to simplification of the time-consuming and energy-consuming centrifugation and settlement process commonly used in wastewater treatment, and has good application prospects in sewage treatment field.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of molecularly imprinted polymer based on click chemistry
ActiveCN106008856AImprove adsorption capacityHigh selectivityOther chemical processesCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molecularly imprinted polymer based on the click chemistry. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing silicon dioxide pellets with grafted double bonds; dissolving a template molecule and a functional monomer in a solvent, performing self assembly, and sufficiently shaking up the solution; adding the silicon oxide microspheres with the grafted double bonds, a cross-linking agent containing sulfhydryls, an initiator and a dispersant into the self-assembled solution, and performing polymerization reaction, thereby obtaining a molecularly imprinted polymer coated with template molecules on the surface; and washing the molecularly imprinted polymer coated with template molecules on the surface, removing the template molecules which coat the surface, and drying, thereby obtaining the molecularly imprinted polymer. According to the preparation method of the molecularly imprinted polymer based on click chemistry, during a preparation process, the cross-linking agent containing the sulfhydryls is used, and a sulfhydryl-alkenyl click chemistry and molecular imprinting combination technology is utilized, so that reaction conditions are mild, reaction is rapid, and the template molecule adsorption capacity and template molecule selection performance of the molecularly imprinted polymer prepared by the preparation method are greatly improved.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of stereocomplex polylactic acid porous membrane material
ActiveCN106496613AUniform pore size distributionOptimal Control StructureHeat resistancePorous membrane
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymeric materials and particularly relates to a preparation method of a stereocomplex polylactic acid porous membrane material. Stereocomplex polylactic acid membrane materials with different thickness (stereocomplex polylactic acid is prepared by blending or copolymerizing poly-L-lactic acid and poly-D-lactic acid) are prepared by using solution casting film-forming method; prepared stereocomplex polylactic acid membrane samples are added to a degrading liquid and are degraded in a thermostatic oven, sapling is carried out in different time, and the porous-structure stereocomplex polylactic acid membrane material is prepared. The porous membrane material prepared herein has uniform pore size distribution, has good heat resistance and biodegradability, is widely applicable to biomolecular separation, fuel molecule adsorption, battery diaphragm materials and the like, and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing high-specific-surface-area graphene under conditions of normal pressure and low temperature
ActiveCN102424382ALarge specific surface areaFacilitate strippingNanotechnologyCvd grapheneAtmosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene under the conditions of normal pressure and low temperature, which comprises the following steps that: firstly, volatile acid is used for treating graphite oxide so that volatile acid molecules are adsorbed between sheet layers of the graphite oxide, acidized graphite oxide is obtained, then, a heat treatment expansion method is adopted for preparing the graphene, experiments prove that the acidized graphite oxide generates a large amount of acid gas in the heat expansion process, and the peeling of the graphite oxide is prompted, so thegraphite oxide can generate the expansion peeling in the normal-pressure and low-temperature atmosphere, the graphene can be obtained, and in addition, the obtained graphene has high specific surfacearea. Therefore, the preparation method provided by the invention is simple, is easy to implement and overcomes the defect of vacuum or low-pressure condition limitation required during the graphene preparation in the prior art, the assurance is provided for the large-scale production of the graphene, and wide market application prospects are realized.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of cellular starch-based porous carbon material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cellular starch-based porous carbon material. Starch is pre-treated under a certain atmosphere condition so that the starch swells and produces holes, and the pre-treated starch is subjected to charing treatment by a conventional method so that the cellular starch-based porous carbon material is obtained. The preparation method has simple processes, a wide raw material source and a low production cost, realizes industrial production, is suitable for fields of macro-molecule adsorption, catalysis and gas separation and can be used as a microbe propagation and motion carrier.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing corrosion-resistance surface of bearing by laser texturing
InactiveCN106925894ALow corrosion rateRealize self-lubricationShaftsBearing componentsMachined surfaceRelative motion
The invention discloses a method for preparing a corrosion-resistance surface of a bearing by laser texturing. Firstly, a laser marking machine is adopted to machine micropit or microgroove structures on relative motion surfaces of a rolling bearing or a slide bearing, and the area occupancy of the micropit or microgroove structures is 10-30%; then, the machined surface of the bearing is polished to remove surface burrs; and finally, the surface of the bearing is immersed in a stearic acid ethanol solution to form a monomolecular absorption layer on the whole surface to reduce the surface energy. Through the laser texturing technology, on the one hand, air can be trapped in microholes, so that corrosion ions of the bearing have difficulty in making contact with the surface of a substrate in sea and other strong corrosion working environments, and the corrosion rate of the bearing is reduced; and on the other hand, after the surface of the bearing is microporous, a certain quantity of lubricating grease can be stored in the microholes beforehand, so that the bearing realizes self-lubrication during working, the antifriction wear resistance and the corrosion resistance of the bearing are improved, and the capability of the bearing adapting to bad working environments is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Raman enhanced chemical sensor and production method thereof
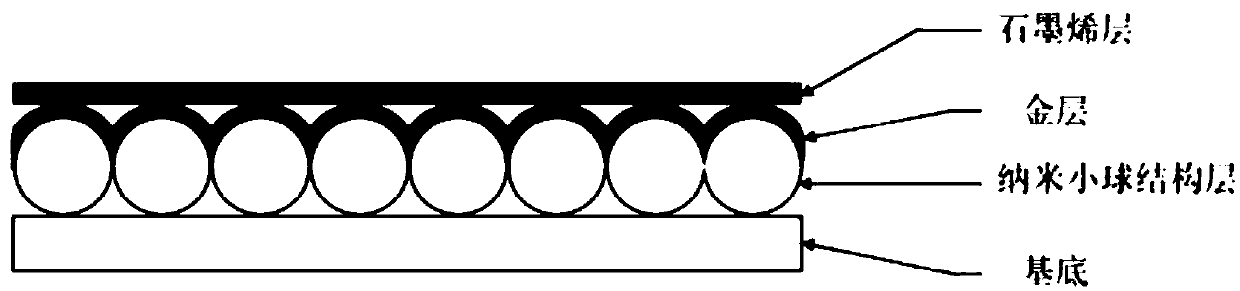
The invention relates to a Raman enhanced chemical sensor and a production method thereof, which belong to the field of a semiconductor micro nano device for detecting chemical molecules. The chemicalsensor comprises a four-layer structure, which is a glass substrate, a nano spheres structural layer, a metal layer, and a single layer graphene layer from up to down. The nano spheres structural layer formed by polystyrene is used for forming a surface arraying structure for enhancing scattering of Raman light, the metal layer is used for realizing Raman electromagnetic enhancement, and the single layer graphene layer is capable of absorbing molecules and realizing chemical enhancement; the Raman enhanced chemical sensor uses precious metal to realize electromagnetic enhancement, and uses the single layer graphene layer for realizing chemical enhancement, so that a Raman signal is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation of copper complexing natural polymer adsorbing material
InactiveCN101279245ALarge adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCelluloseOrganic fluid
The invention discloses a method for preparing copper complex natural polymer adsorption material, which consists of the following steps: 1) cupric salt is dissolved into ammonia water to prepare cuprammonium solution; 2) fibrin is dissolved into the cuprammonium solution and then is added with lignin; 3) the mixture is stirred for 6-48 hours at the constant temperature of 20-80 DEG C for centrifugal filtration and then washed twice to three times with distilled water; 4) filtrated solid product is dried at the temperature of 50-105 DEG C; 5) dried activation product is grinded and passes 100 mesh sieve to acquire the copper complex natural polymer adsorption material. The copper complex natural polymer adsorption material prepared by the invention has strong adsorption capacity of organic contamination in water and large adsorption capacity and can be popularized and used in the treatment of difficult degradable organic waste water and the adsorption and fixation treatment for sudden discharging of large quantity of organic liquid, at the same time natural polymer waste materials such as the lignin, the fibrin, etc. produced in the process of paper making, etc. can be recycled.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Graphene polypyrrole based electrode material for pseudocapacitive supercapacitor
The invention discloses a graphene polypyrrole based electrode material for a pseudocapacitive supercapacitor. The electrode material is prepared according to the following steps of; carrying ultrasonic dispersion on graphite oxide in distilled water for 0.5 to 1 hour, adding sodium polystyrene sulfonate and reacting for 1 to 2 hours at 60-80 DEG C, cooling, filtering, adding hydrazine hydrate and reacting for 1 hour at 100 DEG C, and cooling, filtering and washing to obtain graphene nano slices; and enabling pyrrole to be adsorbed onto the graphene nano slices by using a molecule adsorption method, dispersing the adsorbed pyrrole into an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, dropwise adding ferric chloride solution and reacting for 4 to 6 hours at 0-4 DEG C, and washing and drying to obtain the graphene polypyrrole based electrode material for the pseudocapacitive supercapacitor. The electrode material for the pseudocapacitive supercapacitor, prepared by the invention, simultaneously has high conductivity, large specific surface and high chemical stability, and is also endowed with excellent capacitance performance.
Owner:西安岳达生物科技股份有限公司
Separation method for obtaining plenty of high-purity semiconductor single-walled carbon nanotubes
InactiveCN102963878AEasy to operateEasy to operate and controlCarbon nanotubesNanotechnologyCarbon nanotubeControllability
The invention belongs to the technical field of carbon nanotubes, and particularly discloses a separation method for obtaining plenty of high-purity semiconductor single-walled carbon nanotubes. The method comprises the following steps of: evenly mixing a right amount of single-walled carbon nanotubes with lauryl sodium sulfate, ultrasonically centrifuging to obtain carbon tubes which independently suspend in a water solution, causing relatively large difference between metal and semiconductor carbon tubes and sepharose gel by utilizing different surfactant molecule adsorption capacities of the metal and semiconductor carbon tubes, and adjusting the voltage and electrophoresis time of an external electric field to realize the massive gathering of semiconductor carbon tubes. The method has the advantage of obtaining the semiconductor sing-walled carbon nanotubes with purity higher than 99% without damaging the structures of the carbon tubes. The method has the characteristics of simplicity and easiness in operation, high purity, low cost, controllability, good repeatability, easiness in amplification and the like, is capable of realizing large-scale production and has favorable industrial application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing fibrous macromolecule adsorption material
ActiveCN103301818AGuaranteed StrengthFast adsorptionOther chemical processesFilament/thread formingFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for preparing a fibrous macromolecule adsorption material. The method comprises the following specific steps of: preparing polymer silk from linear polymers, of which the molecular weight is 15,000-20,000, by a melting and spinning method; and then putting the polymer silk into a cross-linking agent and pore-forming agent solution at the temperature of 130-150 DEG C for 25-35 seconds to obtain the fibrous macromolecule adsorption material. The method adopts a novel preparation technology; a cross-linking layer is formed on the surface of a fiber through quick cross-linking, so that the strength of the fiber is guaranteed; the bonding force of the fiber on adsorbed molecules is improved through a pore-forming agent, the adsorption speed of the fiber is enhanced, and the adsorption capacity of the fiber is improved; the obtained fibrous macromolecule adsorption material meets the requirement on large adsorption capacity and long service life for industrial waste liquid treatment and quick response and high treatment speed for emergency accidents; therefore, the application field and the industrial application value of the fibrous adsorption material are expanded and improved.
Owner:SUZHOU TIMELYBLUE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Magnetic cyclodextrin-based crosslinked polymer adsorption material and preparation method thereof
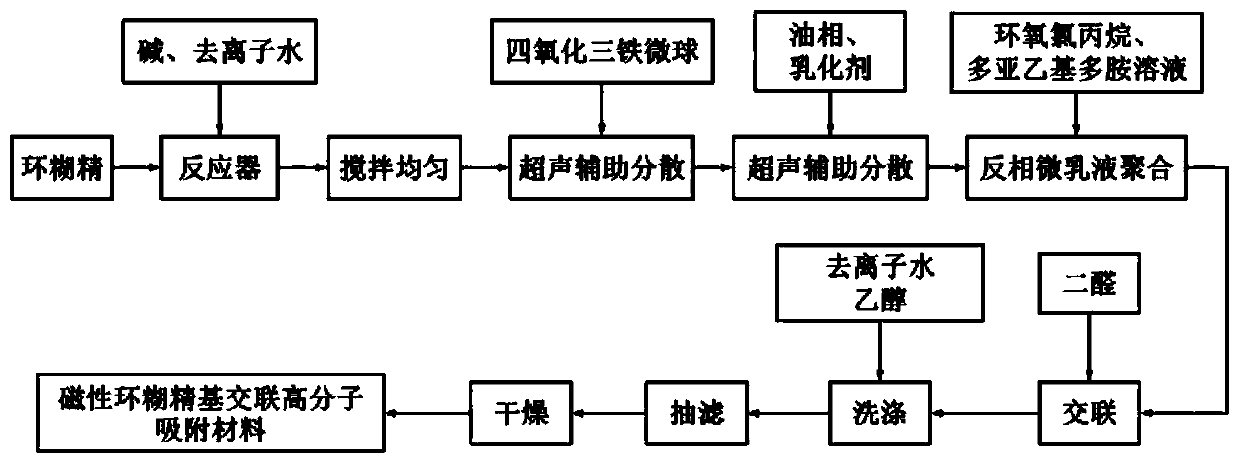
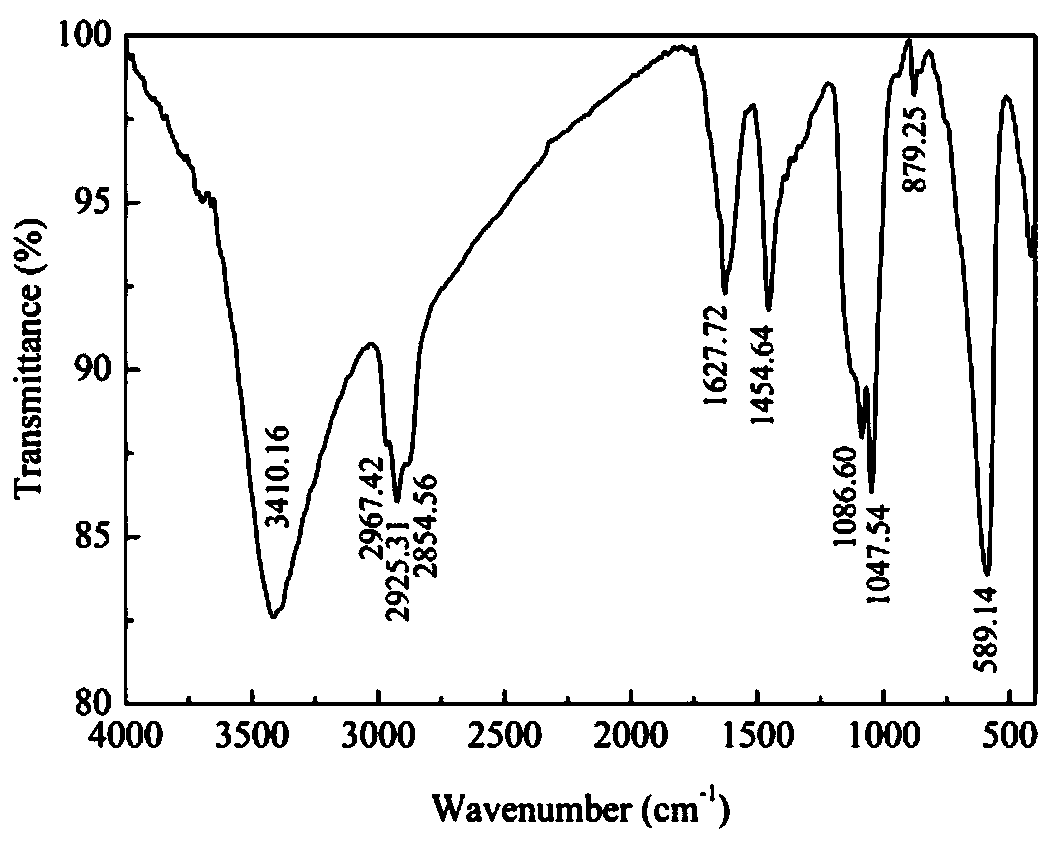
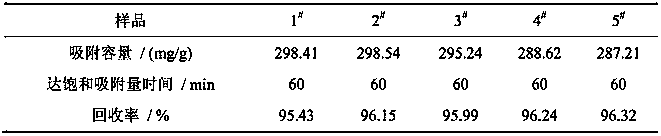
ActiveCN110115984AImprove adsorption capacityEase of industrial applicationOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAutomatic controlSorbent
The invention discloses a magnetic cyclodextrin-based crosslinked polymer adsorption material and a preparation method thereof. According to the material, magnetic ferroferric oxide microspheres are used as inner cores, cyclodextrin, epichlorohydrin and polyethylene polyamine are used as raw materials, dialdehyde is used as a crosslinking agent, and core-shell magnetic adsorption polymer microspheres are prepared by using crosslinking active polymer layers for coating online through a reversed-phase microemulsion method. The obtained adsorption material contains not only abundant active groupssuch as amino groups, imine groups and hydroxyl groups but also ferroferric oxide microsphere inner cores with strong magnetism and cyclodextrin units capable of forming clathrate compounds with organic pollutants. The material solves the problems that traditional adsorbents are poor in heavy metal-organic matter composite pollutant disposal effect, low in efficiency and high in cost, heavy metaland organic pollutants in wastewater cannot be removed synchronously, particularly, the separation and recovery of the adsorbents after disposal are difficult, and it is difficult to automatically control the operation and achieve continuity. The adsorption material is suitable for disposing different kinds of wastewater containing heavy metal, organic matter and heavy metal-organic matter composite pollutants.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
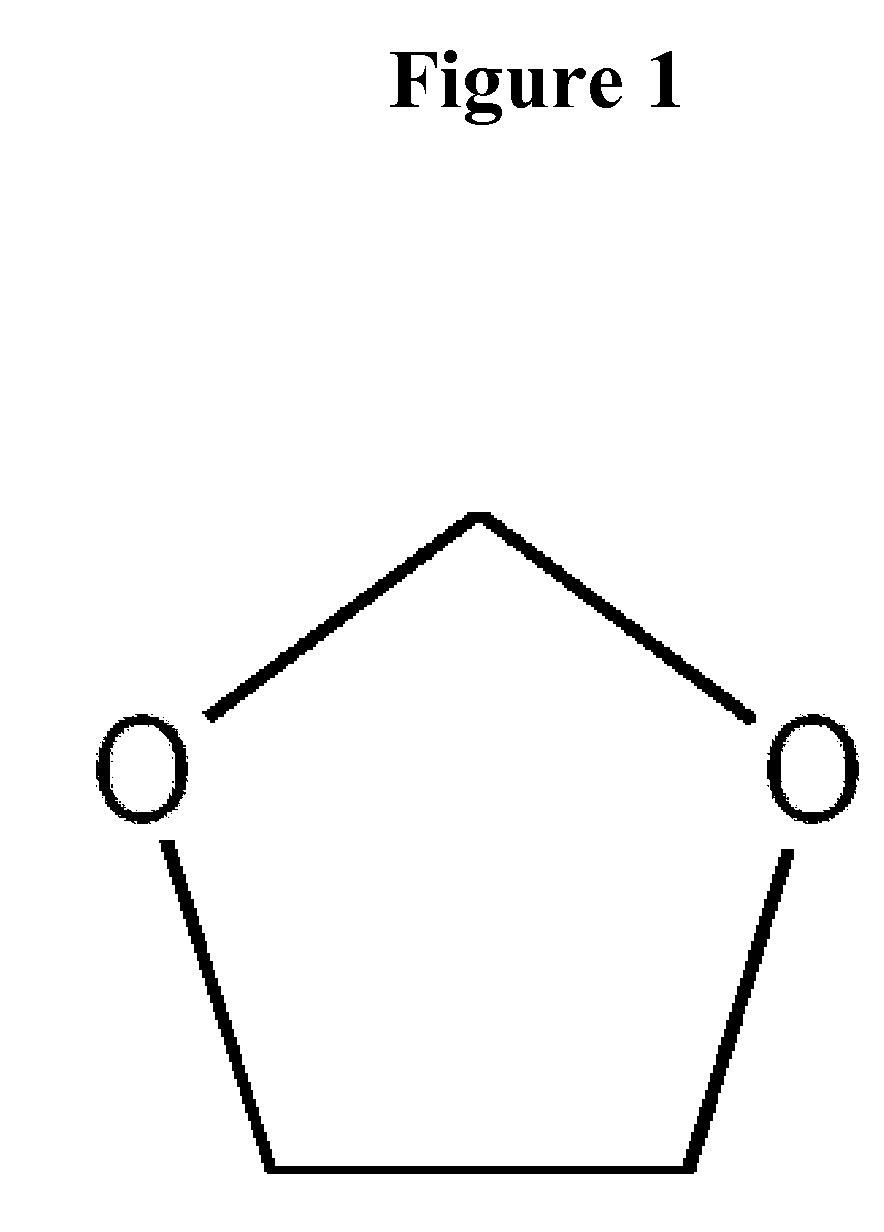
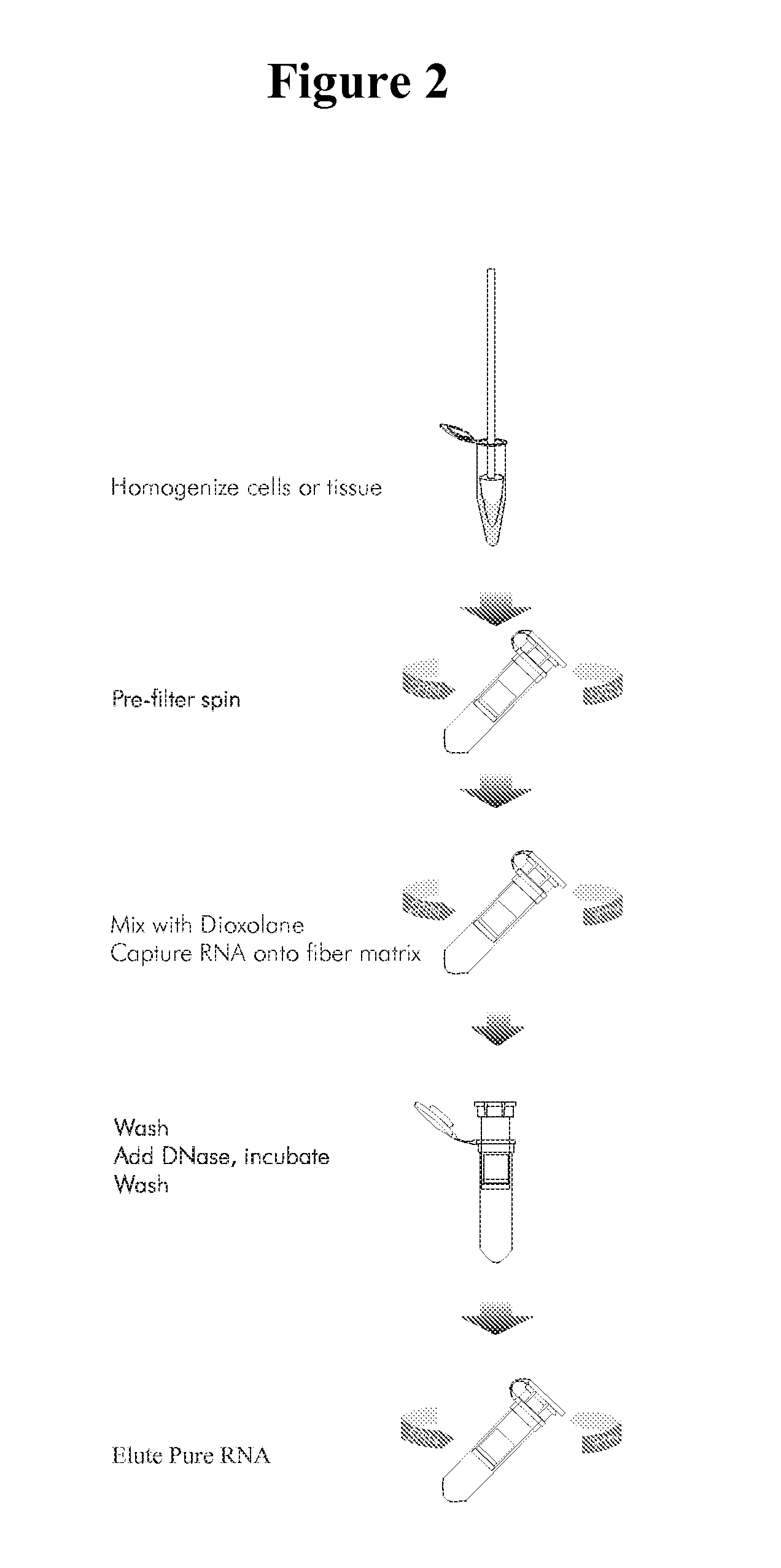
Methods for the separation of biological molecules using dioxolane
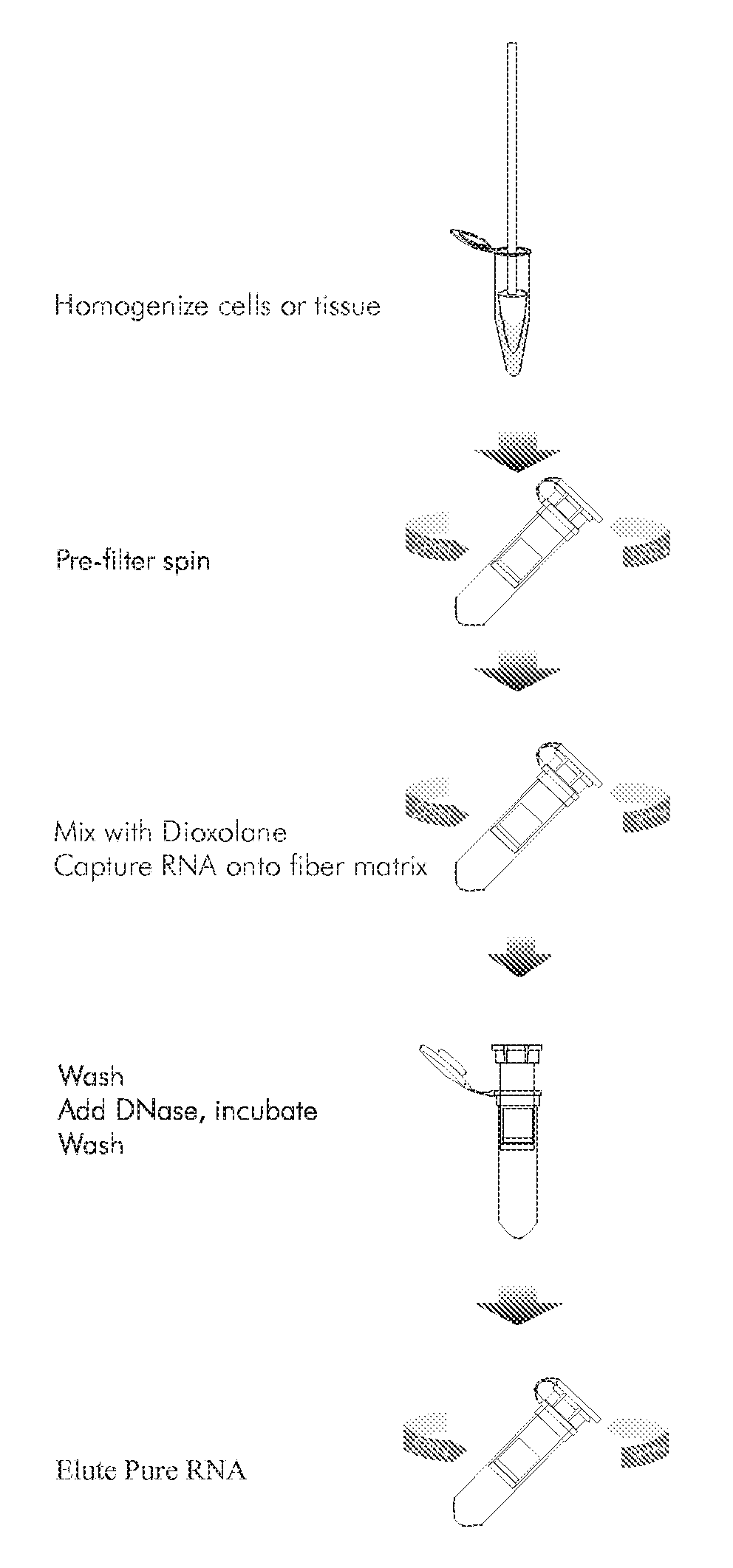
InactiveUS20080146789A1Eliminates organic solvent extractionHigh yieldSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesMolecule adsorptionDioxolane
The present invention provides a method for the isolation of biological molecules by the adsorption of the molecules onto a mineral substrate in the presence of an appropriate mixture of salts and dioxolane. Preferably, the biological molecules are nucleic acids. Compositions and kits for performing the process according to the invention are also provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for in-situ preparation of porous structure zinc oxide nanometer rod array
ActiveCN105836789AImprove adsorption capacityHigh purityMaterial nanotechnologyZinc oxides/hydroxidesZinc Acetate DihydrateZinc oxide nanorod
The invention discloses a method for in-situ preparation of a porous structure zinc oxide nanometer rod array. The method comprises preparing a zinc oxide precursor solution from a zinc acetate dihydrate, methanol and ammonium acetate, cleaning a substrate, dipping the substrate in the zinc oxide precursor solution, carrying out multiple drawing film formation, carrying out drying and annealing treatment to obtain a high purity zinc oxide film crystal seed layer, carrying out crystal seed layer growth in a growth solution of a zinc acetate dehydrate, cadmium sulfate, deionized water and ethene diamine multiple times, and carrying out cleaning and annealing treatment to obtain a directionally arranged porous structure zinc oxide nanometer rod array. The porous structure zinc oxide nanometer rod array has a large specific surface area and provides more spaces for molecule adsorption. The method has a low cost and low equipment requirements and is suitable for a large-area substrate.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Giant electrorheological fluid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108300555ASmall particle sizeImprove stabilityAdditivesComposite nanoparticlesMaterials science
The invention provides a giant electrorheological fluid and a reparation method thereof. The giant electrorheological fluid is prepared from urea coated metal salt composite nanoparticles, a dispersing agent and an insulation base fluid, wherein each molecule of the dispersing agent contains a hydrophilic end and an oleophilic end; the metal salt composite nanoparticles are suspended in the insulation base fluid, the molecules of the dispersing agent are adsorbed on a solid liquid interface formed by the metal salt composite nanoparticles and the insulation base fluid, the hydrophilic ends tend to be adsorbed on the surfaces of the metal salt composite nanoparticles, and the oleophilic ends tend to extend to the insulation base fluid. By adding the amphiphilic dispersing agent, size of theagglomerated particles is reduced remarkably, settlement resistance is further improved, hardening of the nanoparticles is prevented effectively, so that stability of the giant electrorheological fluid is improved, and breakdown resistance of the giant electrorheological fluid is improved effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com