Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "D-Glucaric Acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Saccharic acid, also called glucaric acid, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H10O8. It is derived by oxidizing a sugar such as glucose with nitric acid.
Method for preparing activated carbon for biomass-based super capacitor
The invention discloses a method for preparing activated carbon for a biomass-based super capacitor, in particular relates to a new method for preparing activated carbon with high specific surface area and high specific capacitance by the steps of hydrolysis of biomass with concentrated acid, in-situ polycondensation and carbonization of saccharic acid solution and activation under certain conditions. The method comprises the following specific steps of: firstly, hydrolyzing biomasses with inorganic acid with a certain concentration, and filtering to obtain a saccharic acid solution and filter residues; adjusting the concentration of the saccharic acid solution, performing polycondensation and carbonization to prepare hydrothermal carbon; mixing the hydrothermal carbon with an activating agent in a certain mass ratio for activating to finally obtain the activated carbon for the super capacitor. The method for preparing activated carbon for the super capacitor by using biomasses is a pollution-free process route meeting the requirement of sustainable development.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of biomass-based colloidal carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method of biomass-based colloidal carbon and in particular relates to a colloidal carbon ball using xylose or glucose as a precursor. The colloidal carbon ball is prepared by hydrolyzing biomass by using dilute acid or concentrated acid respectively to obtain saccharic acid solution of xylose and glucose and performing in-situ polycondensation and carbonization on the saccharic acid solution. The preparation method particular comprises the following steps of: hydrolyzing the biomass by using dilute acid at a certain concentration; filtering to obtain xylosic acid solution and filter residues; adjusting the concentration of the saccharic acid solution and performing polycondensation and carbonization to prepare the colloidal carbon ball with grain size of 160 to 1,800 nm; performing alkali boiling on the residues to remove lignin; performing hydrolysis reaction on the residues and the concentrated sulfuric acid; filtering to obtain acid solution of the glucose; and performing in-situ polycondensation and carbonization to prepare the colloidal carbon ball with grain size of 180 to 2,000 nm. The method for preparing the colloidal carbon from the biomass is a green production route of sustainable development.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Jujube-acetic acid beverage and processing technic thereof
InactiveCN101869333AIncrease the juice yieldReduce manufacturing costFood scienceSaccharic acidUltra high pressure
The invention discloses jujube-acetic acid beverage and a processing technic thereof. The processing technic comprises the following steps: pretreatment of raw materials, pulp preparation, ultra-high-pressure enzymolysis, saccharic acid adjustment, vaccination, alcohol fermentation, acetic acid fermentation, clarification, sterilization, mixng and bottling. Based on the traditional process, the invention adopts a new technique and the ultra-high-pressure assisted enzymolysis, thereby not only improving the yield of jujube juice, but also reducing the working time; and due to the liquid-state shaker fermentation, the method shortens the fermentation time, facilitates the reduction of the production cost of the enterprise, and improves the economic efficiency. In addition, with the optimized mixing scheme, the invention solves the problem of single taste. The jujube-acetic acid beverage produced in the invention has the advantages of good taste, moderate and refreshing sweetness and sourness, high clarity and transparency, fruity palate and delicate flavor.
Owner:北京中食德源投资管理有限公司
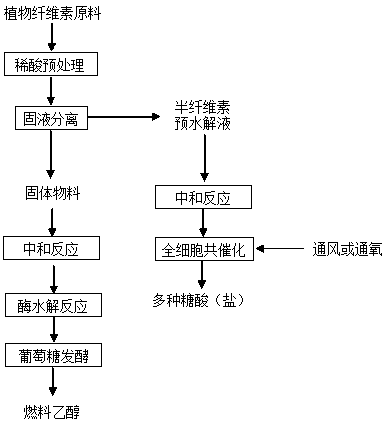
Method for co-producing plurality of saccharic acids from cellulose fuel ethanol
InactiveCN103627735ARelieve stressIncrease profitBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidFiber
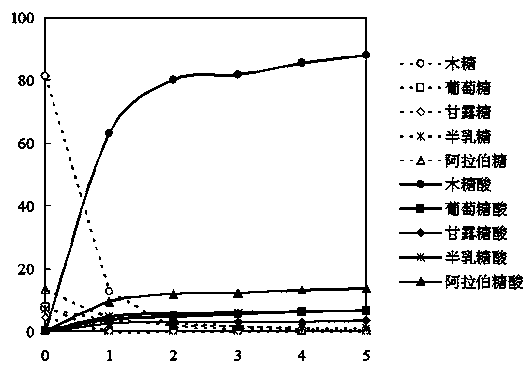
The invention discloses a method for co-producing a plurality of saccharic acids from cellulose fuel ethanol. The method comprises the following steps: performing dilute acid hydrolysis pretreatment or dilute acid steam explosion pretreatment on plant fiber raw materials to obtain a hemicellulose pre-hydrolysate and cellulose-enriched solid material through solid-liquid separation, wherein an enzyme hydrolysate is obtained by neutralizing and performing cellulose enzyme hydrolysis on the solid material, and fuel ethanol is produced by anaerobically fermenting the enzyme hydrolysate through saccharomyces cerevisiae or zymomonas mobilis; and a plurality of saccharic acids are produced by whole-cell co-catalyzing through gluconobacter oxydans or pseudomonas fragi under an aerobiotic condition after the hemicellulose pre-hydrolysate is concentrated and neutralized. The plurality of saccharic acids can be co-produced from fuel ethanol prepared from the plant fiber raw materials, the inhibiting effect of hemicellulose pre-hydrolysate sugar fermentation can be effectively overcome, the utilization efficiency of various carbohydrate substances in the plant fiber raw material can be obviously improved, the pollution load in industrial wastewater is effectively reduced, thereby improving the economic benefit of bio-refinery of the plant fiber raw materials. The utilization rate of total carbohydrate in the raw materials is over 80%, and the carbohydrate conversion rate is more than 90%.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
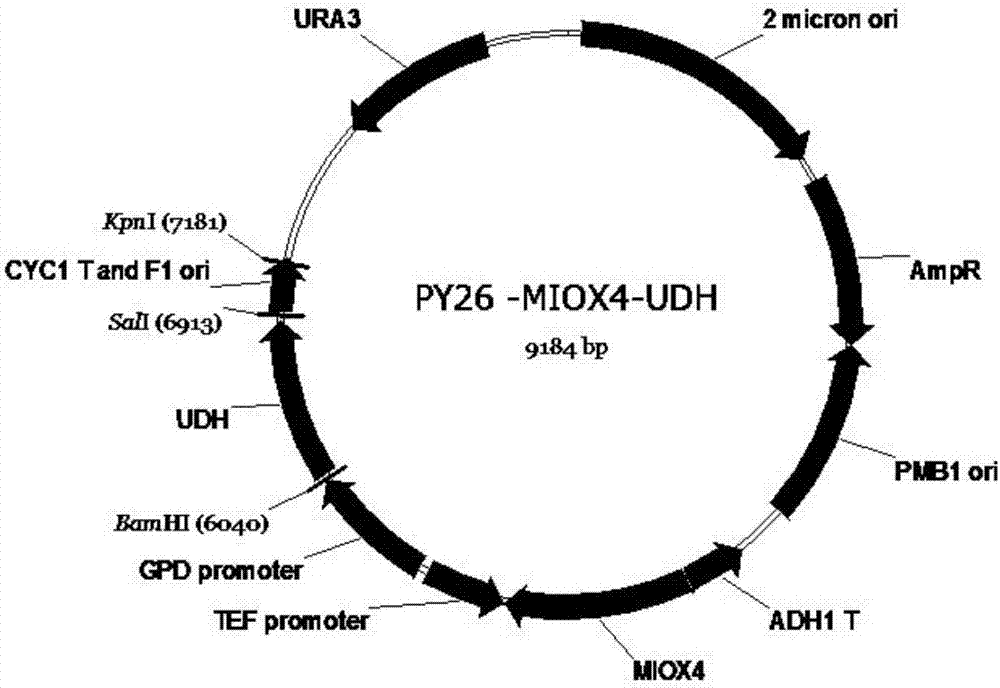
Method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and fermenting
ActiveCN107164255AAvoid non-selectiveImprove energy performanceFungiHydrolasesHigh energyInositol monophosphatase
The invention discloses a method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and fermenting and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out an OPI gene of saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741; introducing myo inositol-1-phosphate synthase and inositol monophosphatase from the saccharomyces cerevisiae, inositol from arabidopsis thaliana and uronic acid dehydrogenase from pseudomonas syringae into the saccharomyces cerevisiae through constitutive plasmid pY26-GPD-TEF, and realizing approach construction of the saccharomyces cerevisiae from glucose to the glucaric acid. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by use of a constructed metabolic pathway, non-selectivity, high energy consumption property and high cost performance of a chemical oxidation method are avoided; the low-priced glucose is directly transformed into D-glucaric acid with high added value by fermentation culture of engineering bacteria; the method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high transformation rate and fewer byproducts; production cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition for the management of tumors
InactiveUS20060281793A1Reduce generationAvoid developmentBiocideAnimal repellantsAbnormal tissue growthPositive control
The present invention relates to the effect of naturally occurring compounds on tumor development. As an example of proof, we used low; non-toxic doses of three compound e.g. Calcium D-glucarate, a naturally occurring Ca++ salt of D-glucaric acid; Nicotinamide (NA), a naturally occurring vitamin and butyric acid (BA), a naturally occurring saturated short chain fatty acid. 7,12 dimethylbenzanthracene (DMBA), which is a very potent skin carcinogen and is an environmental pollutant, was used for skin tumor development. Experiment was performed upto 30 weeks. All the above-mentioned compounds were used either alone or concomitantly any two or all the three. In the positive control group 100% tumorigenesis was attained in 28 weeks, use of single compound led to the inhibition of DMBA induced tumorigenesis between 33 to 47%, use of two compounds resulted in the 73 to 80% reduction in tumorigenesis but the concomitant use of three compounds resulted into 100% inhibition of tumor development at the end of 30 weeks. This led us to conclude that the concomitant use of Cag, NA and BA in combination of two is useful for preventing skin tumor develoment for a sort or long period of time. But the concomitant use of all the three compounds, as described, exhibited the perfect synergistic effect in preventing the tumor development completely. This strategy should be equally effective in the management of benign and possibly malignant tumor in any organ caused by any mean.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Bacillus coagulans used to preparing L-lactic acid and application method thereof
ActiveCN102690764ARaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidHigh concentration
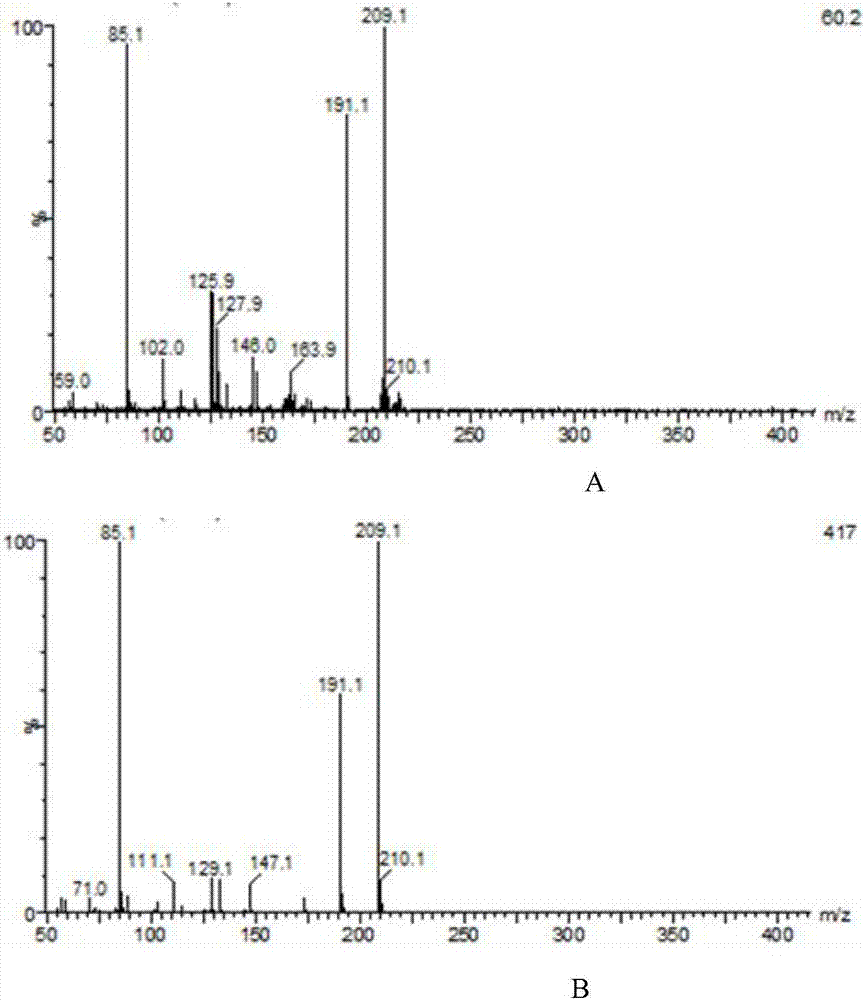
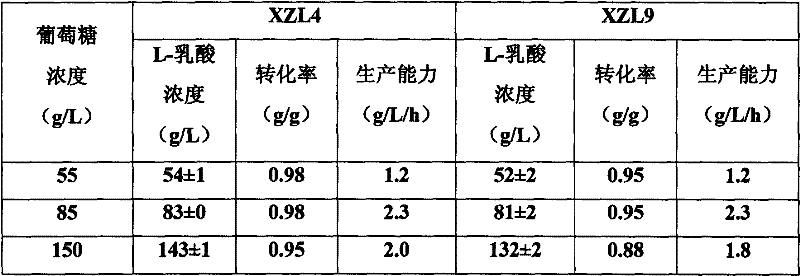
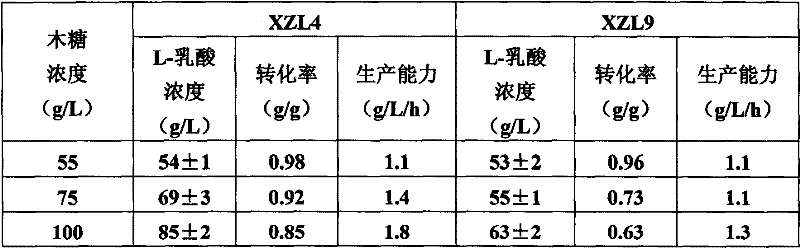
The invention pertains to the technical field of lactic acid preparation, and relates to a bacillus coagulans used to preparing L-lactic acid and application methods thereof. Pentose or hexose is taken as raw material, or agricultural and industrial wastes containing the pentose, the hexose or combinations thereof are taken as raw materials. Ferment is performed on the raw materials to obtain theL-lactic acid. By applying the method of the invention, the highest yield can reach 195g / L, optical purity is greater than 99%, the highest conversion rate of saccharic acid can reach 0.98, and throughput of the ferment process is 2.7g / L / h. By using the bacillus coagulans XZL4(DSM No.23183) and the bacillus coagulans XZL9(DSM No.23184) provided in the invention, high concentration of L-lactic acid can be produced by directly fermenting various reducing sugar in by-products produced in xylitol productions. According to the invention, low cost is achieved, and production efficiency is improved at the same time. The bacillus coagulans and the methods are applicable to popularization and application in industrial productions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of azithromycin intermediate
ActiveCN102127064AHigh yieldReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistrySaccharic acidChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a preparation method of azithromycin intermediate, in particular to a preparation method of azithromycin intermediate 9- deoxidation-alpha- heterocyclic nitrogen-9a-erythromycin A, belonging to the field of pharmaceutical chemical synthesis. The preparation method comprises the steps of: in acid aqueous solution, under the action of potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride, carrying out reduction reaction on erythromycin A 6, 9-imine ether, adding organic saccharic acid for hydrolysis reaction, and obtaining the 9-deoxidation-alpha-heterocyclic nitrogen-9a-erythromycin A. By adopting the method, the hydrolysis of boric acid ester is thorough, the products of acid degradation are less, the yield is high, the production cost of azithromycin is remarkably reduced, and the industrialized production can be very smoothly carried out.
Owner:KAIFENG PHARMA GRP +1
Fermentation production method for citric acid
ActiveCN102250971AImprove automationReduce occupancyMicroorganism based processesFermentationSaccharic acidContinuous fermentation
The invention discloses a fermentation production method for citric acid, and in particular relates to a continuous fermentation production method for citric acid. A citric acid continuous fermentation system consists of a culture medium storage tank, a seed culture tank, two or more serially connected fermentation tanks and a fermentation mash storage tank. By the citric acid continuous fermentation system, a fermentation period can be saved, the conversion rate of saccharic acid and the utilization rate of the fermentation tanks are improved, and stages such as growth and development and saccharification effects of aspergillus niger on citric acid production bacteria, fermentation and acid production and the like are controllable sectionally.
Owner:RIZHAO JINHE BOYUAN BIOCHEM
Method for producing polymer grade L-lactic acid by bacillus by utilizing hydrolysate of maize straws
InactiveCN102643874AStrong ability to produce L-lactic acidAvoid pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSaccharic acidHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for producing polymer grade L-lactic acid. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating bacillus sp. into a fermentation culture medium taking maize straw hydrolysate as an only carbon source for fermentation culturing to obtain the L-lactic acid; the mass ratio of glucose, xylose and arabinose in the maize straw hydrolysate is (27-29): (8-10):1; and the bacillus sp. is bacillus coagulans XZL4DSM No.23183. With adoption of the method, the glucose in the maize straw hydrolysate can be efficiently utilized; the xylose also can be utilized; the yield of the L-lactic acid can reach 80g / liter; the conversion rate of saccharic acid can reach 94-98%; the condition that D-lactic acid exists in a fermentation liquid cannot be detected; and the optical purity can reach 100%; and in addition, the method also can lower the cost of the fermenting the raw materials and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and method for producing L-threonine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106867952AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to an escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and a method for producing L-threonine by using the escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium. The gene engineering bacterium is characterized in that a promoter P<ppc> of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) of an initial strain is replaced into a promoter P<zwf> of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf), so that the goal of regulating the L-threonine production capacity by glycine betaine is achieved. In the fermentation process, the glycine betaine is added, so that the L-threonine yield through shaking flask fermentation can reach 50 to 55g / L; the 5L fermentation tank yield reaches 120 to 150g / L; the saccharic acid conversion rate reaches 59 to 61 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
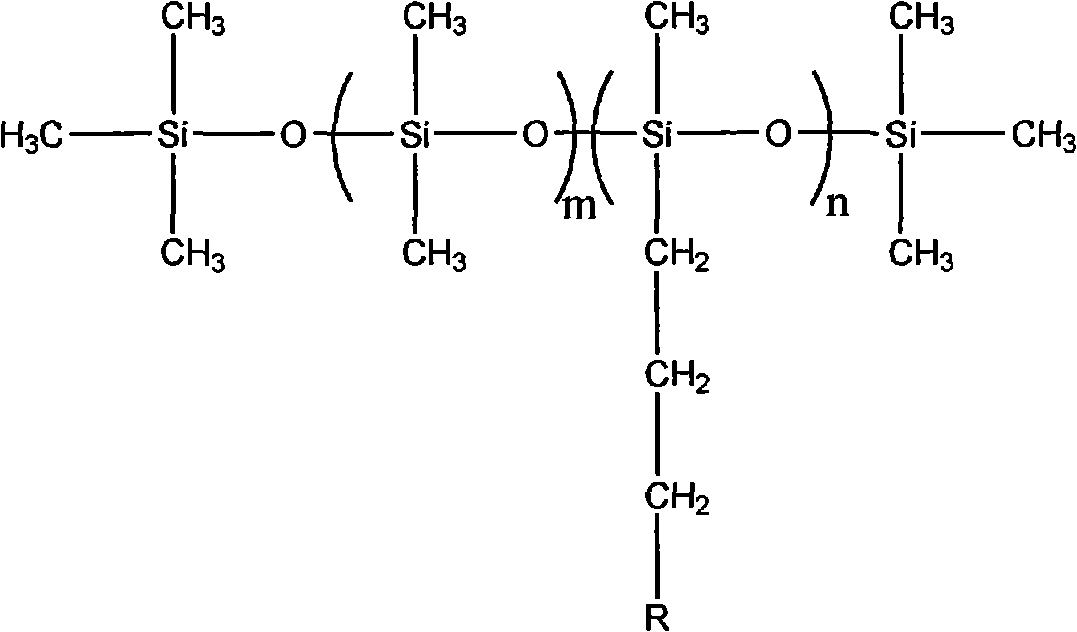
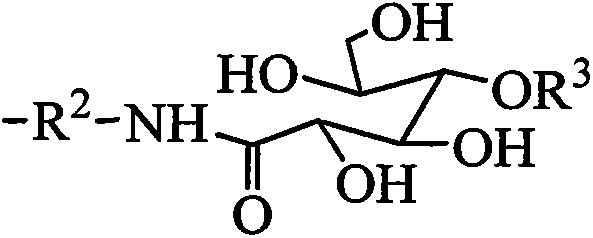
Method for preparing glycosyl amide modified polysiloxane
ActiveCN101942097AToxicAvoid the hydrosilylation reaction stepPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSaccharic acidAlcohol
The invention discloses a method for preparing glycosyl amide modified polysiloxane. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting cyclosiloxane, hexamethyldisiloxane and aminosilane serving as raw materials under the action of a catalyst at the temperature of between 30 and 220 DEG C for 4 to 8 hours, wherein the molar ratio of the cyclosiloxane to the aminosilane to the hexamethyldisiloxane is 0.25-2.25:3-5:1; the molar ratio of the catalyst to the sum of the cyclosiloxane, the aminosilane and the hexamethyldisiloxane is 0.1 to 1; inactivating the catalyst after the reaction is finished; performing reduced pressure distillation to obtain the amino-polysiloxane; reacting the amino-polysiloxane and glycosyl lactone or saccharic acid in low-carbon alcohol serving as a solvent at the temperature of between 30 and 200 DEG C for 5 to 10 hours, wherein the molar ratio of primary amine of the amino-polysiloxane to the glycosyl lactone or saccharic acid is 1-5:1; and evaporating off the solvent to obtain the glycosyl amide modified polysiloxane after the reaction is finished. The method has the advantages of low cost, no toxicity and large-scale industrialization.
Owner:CHINA RES INST OF DAILY CHEM IND
L-lysine fermenting method
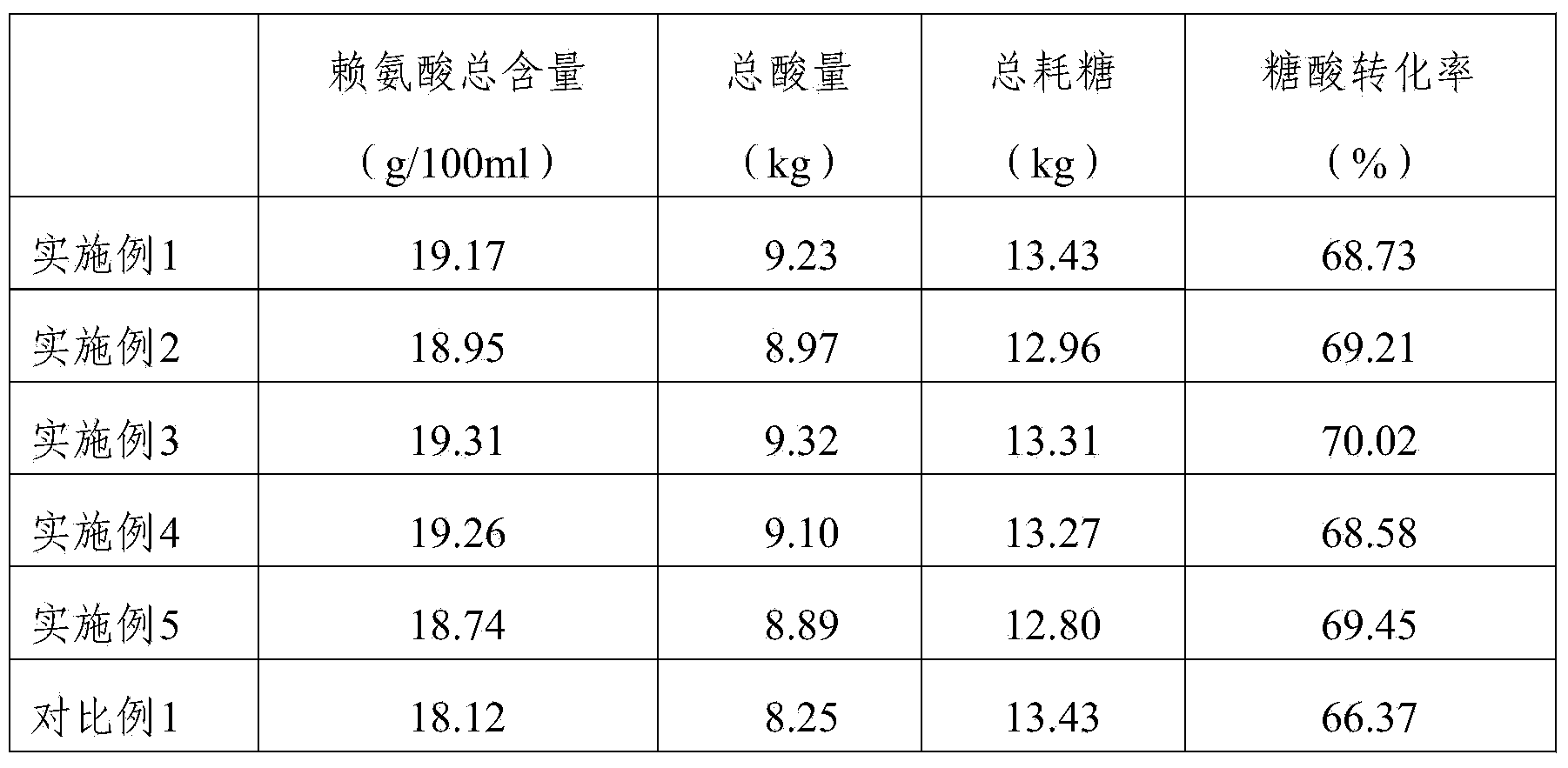
InactiveCN104250659AIncrease end-point lysine contentIncrease acidityMicroorganism based processesFermentationSaccharic acidD-Glucaric Acid
The invention relates to the field of fermentation, in particular to an L-lysine fermenting method. The L-lysine fermenting method comprises the following steps: inoculating a lysine first stage seed medium with a lysine shake flask seed, culturing the seed till the seed is mature, then, inoculating the seed in a lysine second stage seed medium for culturing till the seed reaches a mature standard of a lysine second stage seed, inoculating a lysine fermenting medium with the second stage seed, and under conditions of a fed-batch carbon source and a fed-batch nitrogen source, performing fermentation culture till the end of fermentation, wherein the nitrogen source in the lysine primary seed medium, the lysine secondary seed medium and the lysine fermenting medium is ammonium chloride, and during fermentation culture, the fed-batch nitrogen source is an ammonium chloride solution. By the L-lysine fermenting method, the final content of lysine, the total acid amount and the conversion ratio of saccharic acid can be significantly increased.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Black and red Chinese wolfberry fruit compound fermented beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109619352AImprove stabilitySolve difficult to recycleFood scienceEscherichia coliSaccharic acid
The invention discloses a novel black and red Chinese wolfberry fruit compound fermented beverage and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the processing field of microbial fermentation technologies of foods. The preparation method mainly comprises the steps of pretreatment of raw materials, juicing, ultrasonic assisted chitosan immobilized complex enzyme treatment, filtration, pasteurization, primary fermentation of a lactic acid bacterium composite leavening agent, secondary fermentation with active dry yeast and acetic acid bacteria, saccharic acid blending, centrifugation, pasteurization, filling and finished beverage. The preparation method is simple in process and low in processing cost, the prepared beverage has the flavor of Chinese wolfberry fruits and also has the smell produced through Chinese wolfberry fruit, a pleasant mellow aroma and soft sour, so that the beverage has more delicate taste, has no bad odor, homogeneous color and luster and good nutritional health-care functions; the total acid of the beverage is 2.83%, pH is 3.70, the aqueous protein of plants is 2.83g / L, the total phenol is 38.17mg / L, the carotenoid is 35.67ug / L, the alcoholic strength is 1% or below, and bacteria and escherichia coli are not detected out.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Method for fermenting L-lysine
The invention relates to the field of fermentation, and particularly provides a method for fermenting L-lysine. Acetate is added into lysine primary seed culture media, lysine secondary seed culture media and lysine fermentation culture media, and formulas and fermentation processes for the various culture media are optimized. The method has the advantages that growth of lysine producing thalli and synthesis of lysine can be promoted, accordingly, the endpoint lysine content, the total acid content and the saccharic acid conversion rate can be obviously increased, and the fermentation periods can be obviously shortened.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Method for increasing yield of L-arginine synthesized from corynebacterium crenatum
ActiveCN109370975AIncrease productionOptimizing Fermentation ConditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidArginine
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of L-arginine synthesized from corynebacterium crenatum, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. By means of the method, recombinant corynebacterium crenatum of which a nitrogen transcriptional regulation factor AmtR is knocked out and ammonium transport protein is over-expressed is successfully constructed. By adopting a strategy of batch fermentation by a 5-L fermentation tank and optimizing fermentation conditions, finally the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum Cc5-5 / pXMJ19-amtB is fermented for 96 h, the L-arginine yield of the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum reaches 60.9+ / -1.31 g / L, the yield is increased by 30.56% compared with an original strain of corynebacterium crenatum original strain SYPA5-5, the production intensity reaches 0.634 g / L.h, and the saccharic acid conversion rate is 0.36+ / -0.018 g / g, so that high yield of the L-arginine is realized. Meanwhile, utilization of NH4+ is increased in therecombinant corynebacterium crenatum, so that it is shown that knockout of the nitrogen transcriptional regulation factor and overexpression of the ammonium transport protein have a remarkable effecton the yield of the L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Technique for glycosylated degradation of white spirit waste lees to prepare fermentalbe sugar
InactiveCN101775446AIncrease sugar yieldReduce separation costsGlucose productionSaccharic acidSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a technique for glycosylated degradation of white spirit waste lees to prepare fermentalbe sugar, which includes the procedures of drying and grinding of the white spirit waste lees, glycosylated degradation, the separation of saccharic acid, and the like. The technique is as follows: mixing ground waste lees with hydrogen chloride with mass fraction of 2% according to mass per unit volume of 1:10 for glycosylated degradation and collecting the filtrate; letting the filtrate pass through a chromatographic column which is filled with anionic resin, eluting through distilled water and collecting the eluate by step; and combining the eluates with sugar content equal to or more than 0.5 to be recovered sugar liquid. The recovered sugar liquid can be used as material for alcohol fermentation or other fermentations after being concentrated, and the used anionic exchange resin can be regenerated through NaOH. The concentration of the reducing sugar in the recovered sugar liquid prepared through the technique is equal to or more than 1%, wherein the content of dextrose is 55%, the content of xylose is 35% and the content of others is 10%; and the separation and recovery rate of the saccharic acid is more than 75%. The saccharic acid separation process is low in cost and no harmful impurities such as sulfate radical and the like are left behind, so the fermentalbe sugar has little effect to the subsequent alcohol fermentation or other fermentations. Therefore, the fermentalbe sugar is ideal material for alcohol fermentation and other fermentations.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Fermentation method for increasing yield of L-valine
InactiveCN103215322AImprove fermentation yieldImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationD-Glucaric AcidProtein synthetics
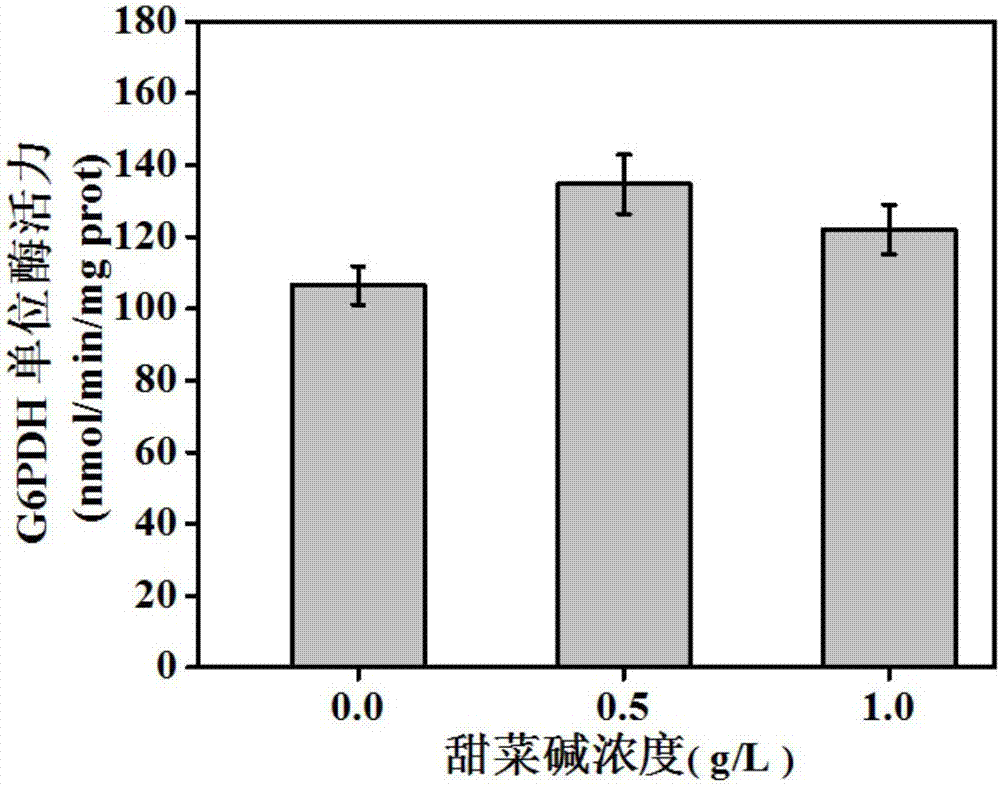
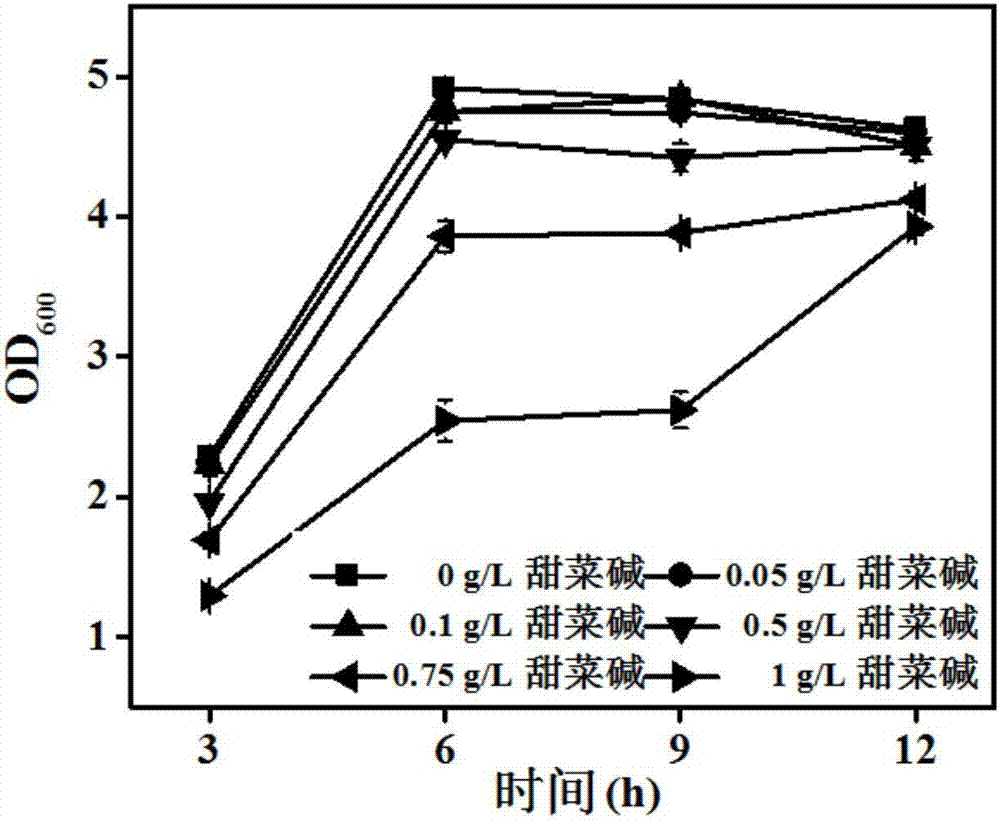
The invention discloses a fermentation method for increasing the yield of L-valine. A valine producing strain is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium containing glycine betaine to ferment to obtain the L-valine, wherein the fermentation culture medium contains 0.1-10g / L of the glycine betaine. The glycine betaine can be used as a methyl doner of the valine producing strain and used for adjusting the osmotic pressure inside cells, promoting fat metabolism and protein synthesis, also simulating the growth of the strain and promoting to produce acid; the fermentation culture medium in which the glycine betaine is added has high L-valine yield up to 67.3g / L and high saccharic acid conversion rate up to 27.5% which are respectively increased by 8.5% and 6.2% than those of a fermentation culture medium in which no glycine betaine is added.
Owner:北京轻发生物技术中心 +2
Escherichia coli capable of producing L-alanine through fermentation and application of escherichia coli
ActiveCN108060114AImprove transportation capacityClear genetic backgroundCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaSaccharic acidEscherichia coli
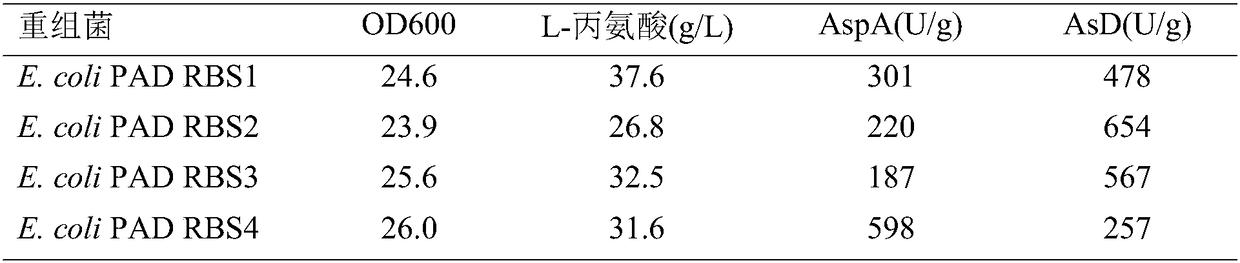
The invention discloses escherichia coli capable of producing L-alanine through fermentation and application of the escherichia coli and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the escherichia coli, aspartase AspA and L-aspartic acid-beta-decarboxylase AsD are introduced into the escherichia coli capable of producing fumaric acid through the fermentation; furthermore, a YgaW gene is over-expressed to strengthen the transport ability of the L-alanine in recombinant bacteria, so that a novel strain capable of fermenting glucose to produce the L-alanine is constructed; when the recombinant strain is fermented in a fermentation tank for 45h, the yield of the L-alanine reaches 147g / L and the saccharic acid conversion rate is 79.0 percent.
Owner:金华利家园生物工程有限公司 +1
Actinobacillus succinogenes capable of producing succinic acid
ActiveCN102533622AReduce manufacturing costIncrease production intensityBacteriaMutant preparationSaccharic acidD-Glucaric Acid
The invention discloses actinobacillus succionogenes capable of producing succinic acid with high yield and a method for screening and producing the succinic acid by a fermentation method. The actinobacillus succinogenes takes CGMCC1593 as the original strain and is obtained by blending a plurality of turns of protoplast in a progressive way through a method of '96-pore plate culture, HPLC concentration detection and then anaerobic bottle re-screening'. The actinobacillus succinogenes has already been preserved on February 26, 2012 in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2012036. The actinobacillus succinogenes adopts fed-batch culture in a 5 to 15 L fermentation tank, 95.6 g / L succinic acid is produced in 48 hours, the production intensity is 1.99 g / (L.h), and the saccharic acid transformation rate is 0.71 g / g. Compared with other bacterial strains at home and abroad, the actinobacillus succinogenes has the advantages of high yield and lowerproduction cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium-glutamicum recombinant strain for increasing conversion rate of L-phenylalanine saccharic acid
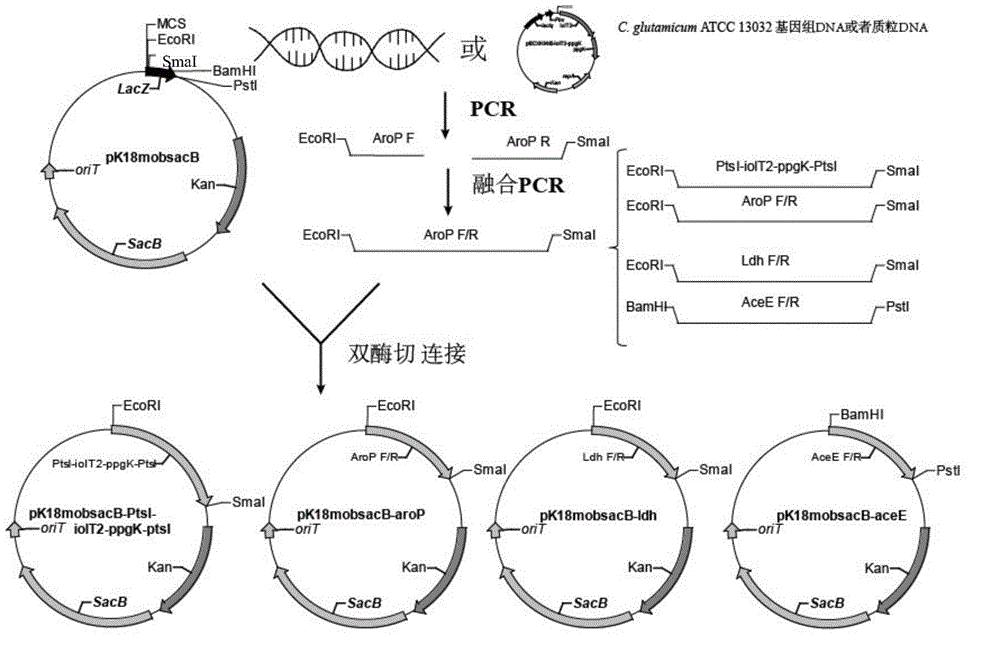
InactiveCN104560852ABlock formationBlock formation pathwayBacteriaTransferasesSaccharic acidMetabolite
The invention discloses a corynebacterium-glutamicum recombinant strain for increasing the conversion rate of L-phenylalanine saccharic acid and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. The recombinant strain is characterized in that genes such as aroP, aceE, ldh and pstI are deficient, iolT2-ppgk gene is integrated on the original pstI site, and simultaneously regulatory expression plasmid containing eight key enzymes in the L-Phe synthesis path is transferred. The corynebacterium-glutamicum recombinant strain disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the accumulated amount of PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) of an L-Phe intermediate product, the yield of the L-Phe and the conversion rate of the L-Phe for saccharic acid of glucose are obviously increased, the flowing direction of a carbon source is changed to reduce or block accumulation of side products, and the means of the metabolic engineering can be applied in synthesis of other metabolites adopting PEP as a precursor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for improving saccharic acid conversion rate in L-tryptophan fermentation process
InactiveCN103409477AImprove sugar-acid conversion rateIncrease biomassMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologySaccharic acid
The invention relates to an improved method for preparing L-tryptophan through a fermentation process, and concretely relates to a method for improving the saccharic acid conversion rate in an L-tryptophan fermentation process. In the invention, the content of acetic acid in the fermentation process is substantially reduced by controlling the dissolved oxygen level, the initial glucose concentration, the glucose limited feeding, the specific thallus growth rate and the like according to a cellar metabolic flux distribution regulating principle, so the thallus biomass, the L-tryptophan output and the saccharic acid conversion rate are substantially improved. The method effectively increases the conversion rate in the L-tryptophan fermentation process and substantially improves the L-tryptophan output without adding extra apparatuses or manpower investment, and is suitable for the industrialized production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving gluconobacter oxydans for producing 2-keto-L-gulconic acid
InactiveCN104673736AImprove heat resistanceConducive to continuous catalytic reactionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidCross-link
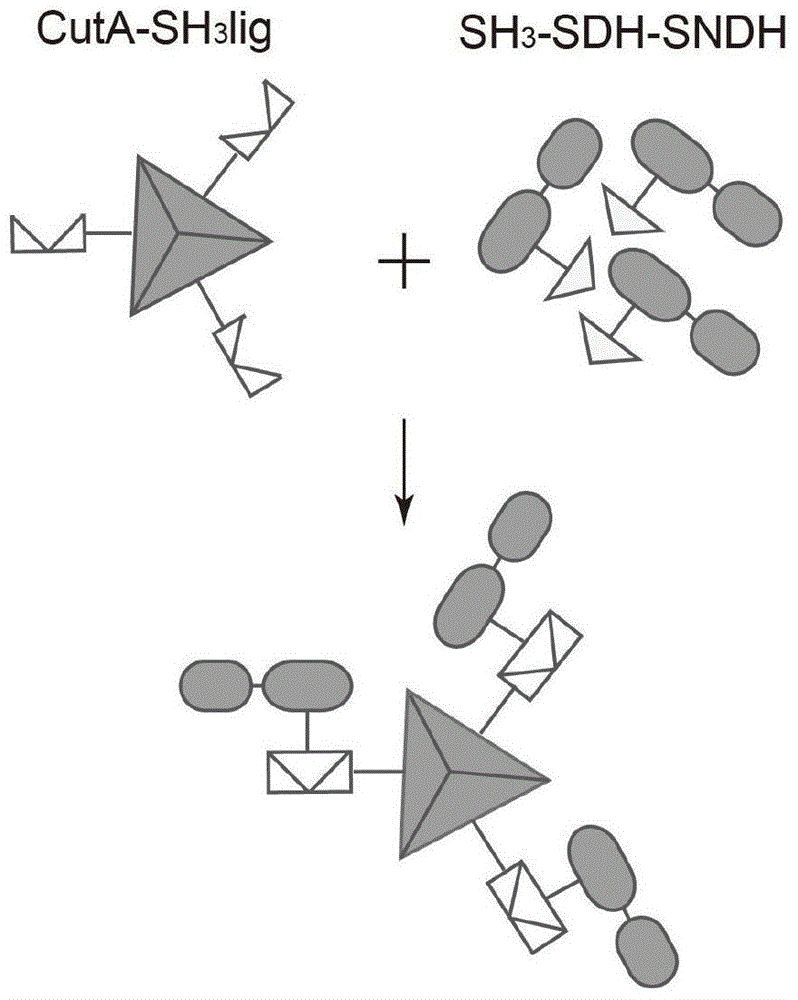
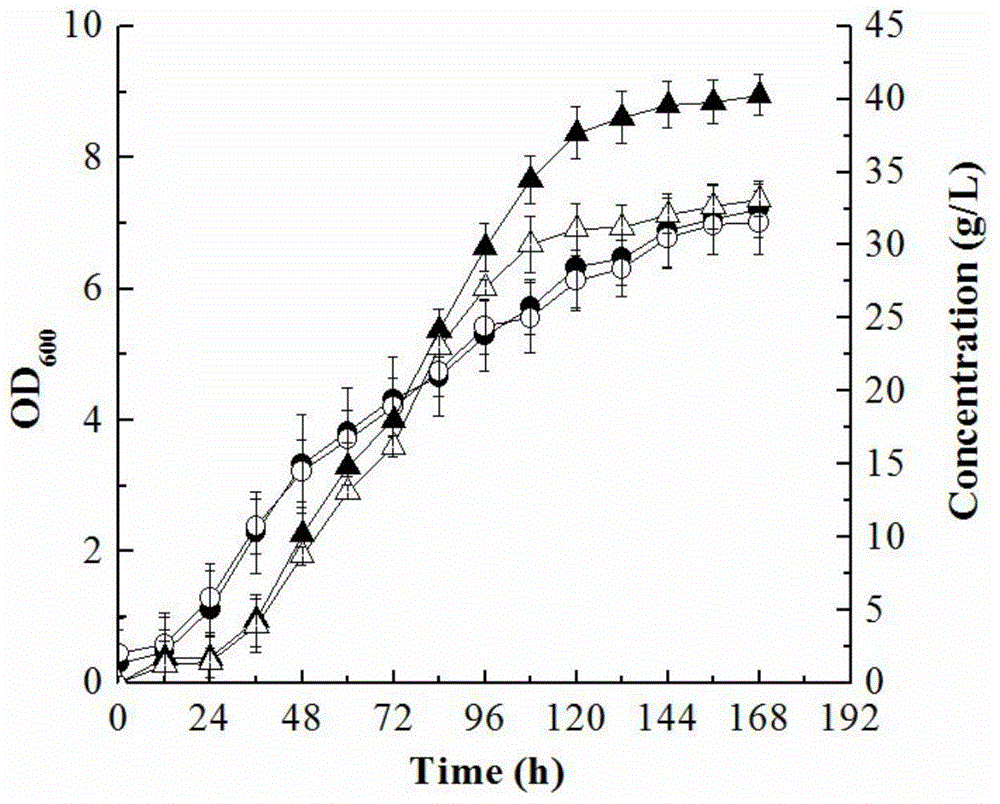
The invention discloses a method for improving gluconobacter oxydans for producing 2-keto-L-gulconic acid, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. On the basis of genetic engineering transformation, adaptor protein SH3 and ligand protein SH3lig of the adaptor protein, a CutA gene and a key enzyme gene in saccharic acid transformation are subjected to fusion expression, and G.oxydans is transformed to produce 2-KLG in a one-step fermentation manner, so that the yield of 2-KLG is finally increased to be 40.3 g / L, that is, the yield is increased by 24.4% when being compared with that of a one-step engineering bacterium of which CutA is not expressed; in addition, due to the thermal resistance of foreign protein, the thermal resistance of the engineering bacterium is further improved. Enzyme cross-linking inside cells can be achieved by expressing the foreign protein CutA, continuous catalytic reaction of a plurality of enzymes can be facilitated, and the method has significance in is one-step fermentation production of vitamin C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of co-catalytically synthesizing various saccharic acids by virtue of synergism of metal ions and selective regulation whole-cell
InactiveCN105132476ADeter and reduce utilizationEfficient synthesisFermentationSaccharic acidCellulose
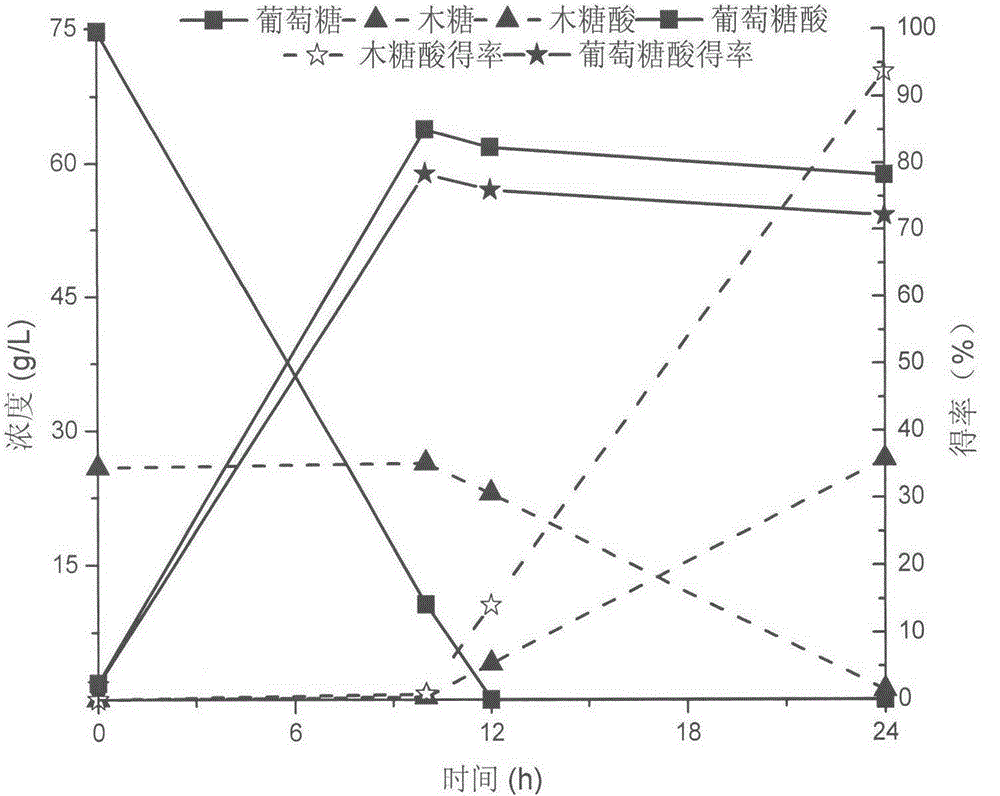
The invention discloses a method of co-catalytically synthesizing various saccharic acids by virtue of the synergism of metal ions and a selective regulation whole-cell, and relates to the technical field of synthesizing the saccharic acids by biologically catalyzing sugar. The method is mainly characterized in that in a mixed sugar solution or lignocelluloses hydrolysate containing glucose and xylose, 1g / L to 10g / L of gluconobacter oxydans is used as a biological catalyst to co-catalyze the glucose and the xylose under an oxygen-supply condition so as to synthesize the saccharic acids. Metal salt of a given concentration containing zinc ions and trivalent iron ions is added so as to selectively inhibit the catabolism of a cell on the gluconic acid, but a dehydrogenation catalytic reaction of the xylose and the glucose is hardly affected, thus an effect of the cell for co-catalyzing and high-efficiently synthesizing a gluconic acid (salt) and xylonic acid (salt) product can be further achieved, and the reaction time is effectively shortened. By adopting the method, the utilization rate of the glucose and the xylose reaches 100 percent, and the yield of the gluconic acid is more than 70 percent, and the yield of the xylonic acid is more than 92 percent, and the total concentration (mass concentration) of the product gluconic acid (salt) and xylonic acid (salt) can be more than 30 percent.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for producing L-tryptophan
ActiveCN101914584AIncreased acid production levelsImprove conversion rateOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidGLUCOSE LIQUID
The invention discloses a method for producing L-tryptophan, which comprises the following steps of: performing primary culture and shaking culture on corynebacterium glutamicum strains to obtain shaking liquid strains; preparing glucose liquid from corn serving as a raw material by steps of soaking, pulping, liquefying, saccharifying and the like, wherein the glucose liquid is used as a carbon source of a culture medium and adds sugar for fermentation flow; performing secondary culture on the shaking liquid strains to obtain secondary strains, and performing fermentation culture on the secondary strains to obtain L-tryptophan fermentation liquid; and extracting and refining the L-tryptophan fermentation liquid to obtain the L-tryptophan. The acid yield of the strains can reach 40g / L at most by controlling the composition of the culture medium and the fermentation conditions; the glucose liquid is produced by using the corn, so the production cost is low; the fluctuation of the glucose content of the culture medium is low and the saccharic acid conversion rate of a fermentation acid production level box is improved by continuously adding the glucose liquid; and the extracting and refining process flows are reasonable, the purity of the L-tryptophan product can reach over 99 percent, and the yield reaches over 75 percent.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing piglet syrup feed without fish meal and plasma proteins
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed processing, particularly relates to a method for preparing a piglet syrup feed without fish meal and plasma proteins. After insoluble constituents are subjected to coarse grinding, water, chicken egg pulp or duck egg pulp, lactic acid and other constituents are added to be stirred, mixed and evenly prepared, and wet process superfine grinding and pulp grinding are performed through a ball grinding mill or a colloid mill to prepare starch proteolipid pulp. Soluble constituents are added into the water to prepare saccharic acid calcium micro-water pulp. The saccharic acid calcium micro-water pulp and starch proteolipid pulp are mixed, coarse residues are removed through filter pressing of a plate frame, emulsified liquid is prepared through homogeneity and emulsification of a high-pressure homogenizer and directly packed into a paste or liquid feed, or is manufactured into a powder feed through absorption of extruded corns and drying of a tube bundle dryer, or is manufactured into a small-pellet feed through the drying of a spray dryer after tempering is performed by adding the water. The feed does not contain the fish meal and the plasma proteins, has the advantages of being high in nutrition, easy to digest, good in palatability, low in antinutritional factor content and the like, and can remarkably increase food consumption of piglets and stimulate the growth of the piglets.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINXINNONG FEED
Method for producing kiwi fruit wine with immobilized yeast
InactiveCN102978074AImprove fermentation effectHigh ethanol production efficiencyAlcoholic beverage preparationOn/in organic carrierSaccharic acidAlcohol content
The invention provides a method for producing kiwi fruit wine with immobilized yeast. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing juice; preparing suspension and immobilized yeast beads; and fermenting the kiwi fruit wine, specifically, carrying out low temperature centrifugation and sterilization on the kiwi juice obtained in the step 1 after regulating the kiwi juice with saccharic acid, then pumping the kiwi juice into a fermentation tank, inoculating the immobilized yeast beads to ferment the kiwi juice at 18-22 DEG C, transferring the kiwi juice to after fermentation when the alcohol content of the fermentation liquor no long rises and filtering the kiwi juice after adopting natural clarification, thus obtaining the kiwi fruit wine. The method has the beneficial effects that the prepared immobilized kiwi fruit wine yeast has SO2 tolerated concentration of 160-180mg / L, high fermentation capacity, high alcohol production efficiency and high aroma producing capacity; and the made raw wine is clear and transparent, has light yellow color and has VC content of 80-130mg / L, alcoholic strength of 12-15 degrees (v / v), strong aroma and strong typicality.
Owner:SICHUAN NONGXINGYUAN AGRI DEV
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
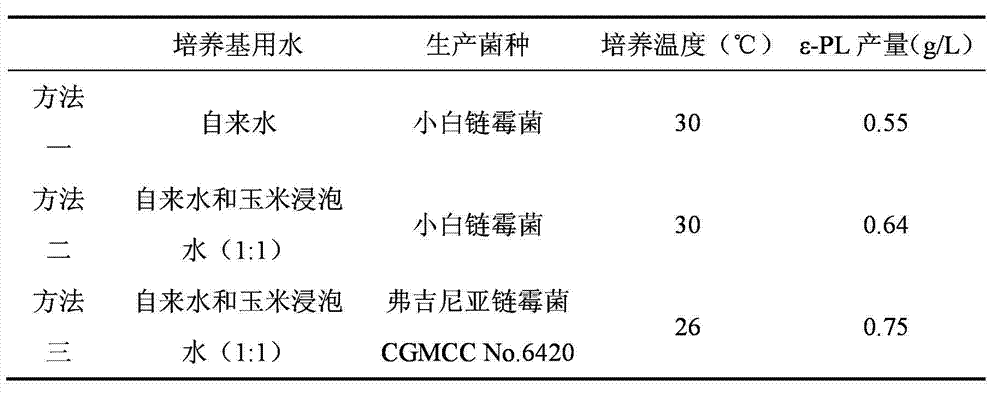
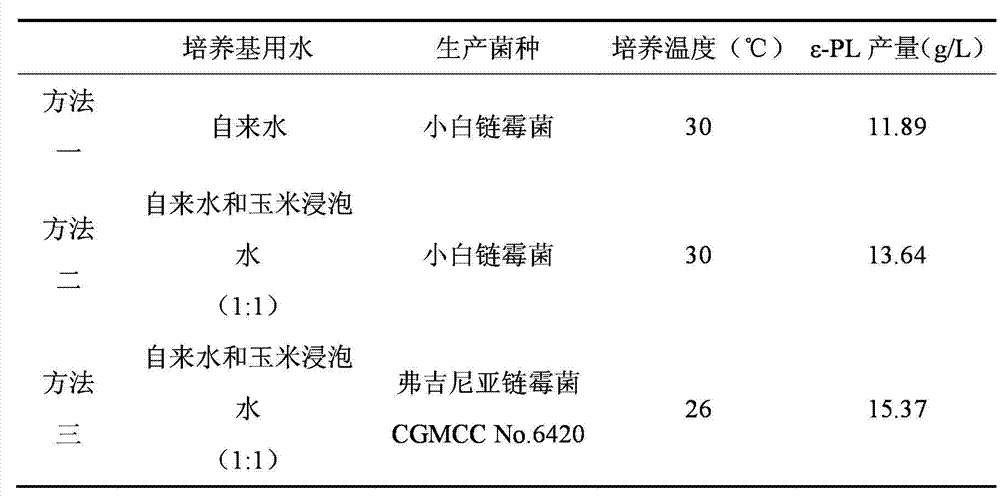
Method for fermentation production of epsilon-polylysine by corn soaking water
InactiveCN102827889AImprove protectionIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSaccharic acidAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method for fermentation production of epsilon-polylysine by corn soaking water and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. The corn soaking water is used for replacing partial ingredient water and yeast cream, streptomyces virginiae obtained through screening in the soil is adopted for fermentation production of epsilon-polylysine. The process operation is convenient, the ingredient water can be saved, the energy consumption during concentration of the corn soaking water can also be saved, and meanwhile, the problem of environment pollution generated during the original corn soaking water treatment is also solved. In addition, the acid production rate and the saccharic acid conversion rate are also improved, and the method can be used for industrial-scale fermentation.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM
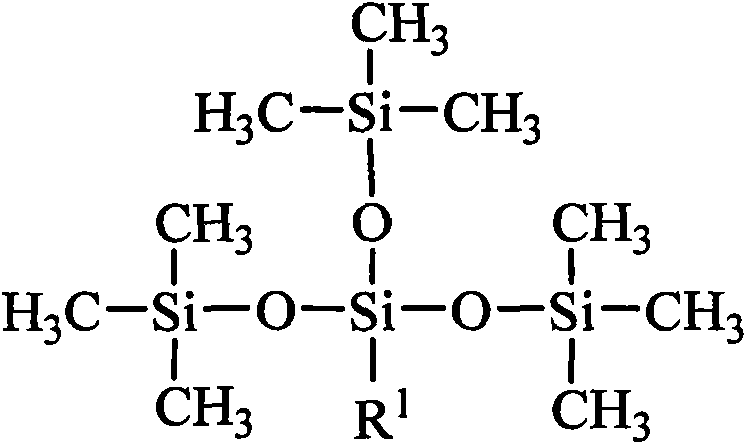
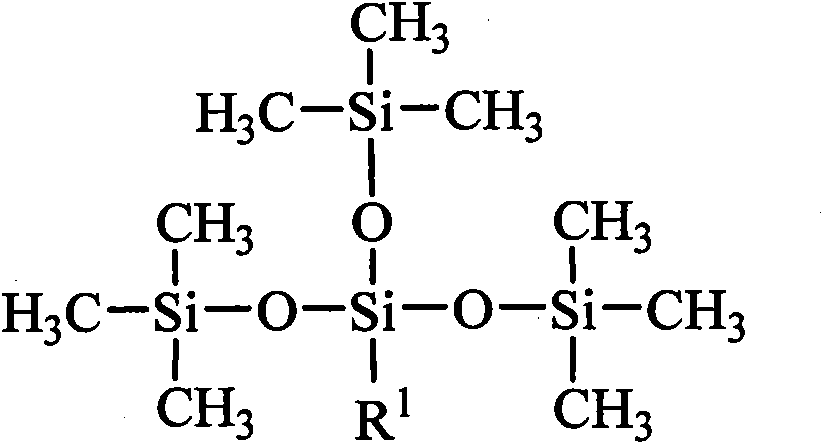
Tetrasiloxane containing sugar acylamino and preparation method
InactiveCN104072563AImprove adsorption capacityNot easy to hydrolyzeBiocideSugar derivativesSaccharic acidSilanes
The invention provides tetrasiloxane containing sugar acylamino and a preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of organic compound composition. The tetrasiloxane containing sugar acylamino is a compound obtained in a bonding reaction through silicone, oxygen, nitrogen or carbon in molecules; the preparation method comprises the following steps: propyl chloride tetrasiloxane is prepared by hexamethyldisiloxane and chloride propyl silane at presence of an acid catalyst; N-Beta-ammonia alkyl-Gamma-aminopropyl tetrasiloxane is prepared by propyl chloride tetrasiloxane and alkyl diamine; the tetrasiloxane containing sugar acylamino is prepared by the N-Beta-ammonia alkyl-Gamma-aminopropyl tetrasiloxane and saccharic acid or saccharic acid internal ester in a lower alcohol solvent; the tetrasiloxane containing sugar acylamino cannot be hydrolyzed in the water within 30 days and can be widely applied in the fields of pesticides and the like.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com