Method for producing polymer grade L-lactic acid by bacillus by utilizing hydrolysate of maize straws
A technology of corn stalks and bacillus, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of unfavorable lactic acid production cost and high price, and achieve the effects of strong ability, avoiding bacterial contamination, and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
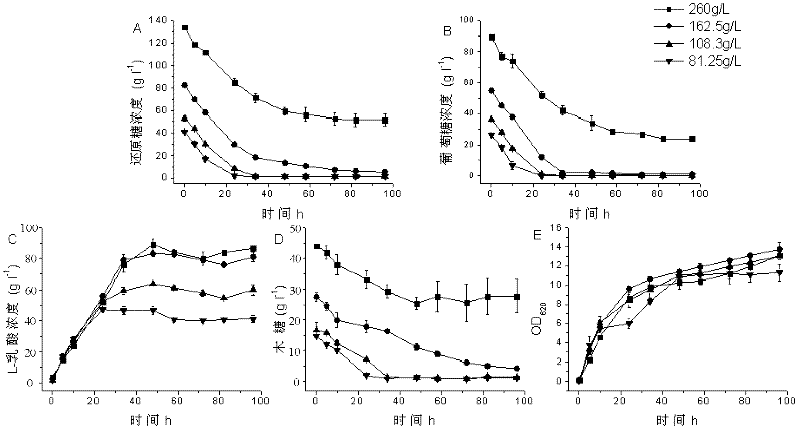
[0034] Example 1. Determination of the optimum corn stalk hydrolyzate concentration for efficient production of L-lactic acid
[0035] The fermentation medium used in this example is based on the different concentrations of corn stalk hydrolyzate, and there are four kinds in total. Any part of the solution, the final concentration of total reducing sugar (total reducing sugar is the sum of glucose, xylose and arabinose) is 41.0g / L, 52.9g / L, 82.53g / L and 133.7g / L respectively (the above four concentrations refer to the addition of corn stalk hydrolyzate in the fermentation medium, such as 81.25g / L refers to the addition of 81.25g corn hydrolyzate in every liter of fermentation medium, under this condition, the total The final concentration of reducing sugar in fermentation medium is 41.0g / L); Final concentration is the yeast powder of 10g / L; Content is the calcium carbonate of total reducing sugar quality 60% in fermentation medium; Surplus is water; pH6. 5. The yeast powder ...
Embodiment 2
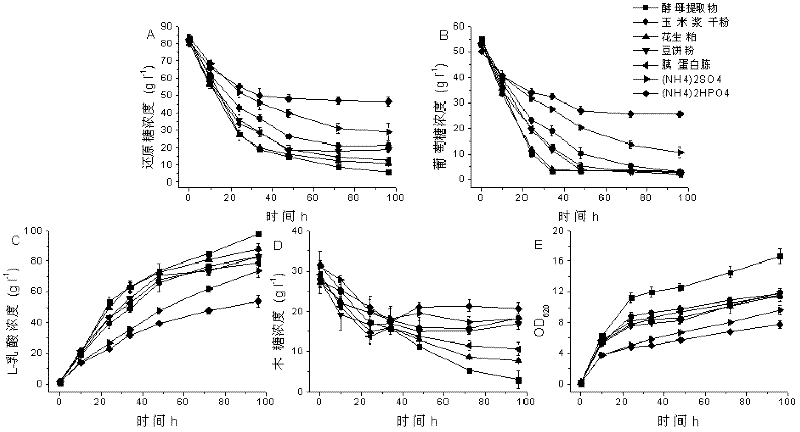
[0040] Example 2, Determination of cheap nitrogen source for efficient production of L-lactic acid
[0041] The fermentation medium used in this embodiment is based on the different types of nitrogen sources, and there are seven kinds in total. conditions, the final concentration of total reducing sugars in the fermentation medium was 82.53g / L, of which glucose was 69.4g / L, xylose was 21.7g / L, and arabinose was 2.5g / L); nitrogen sources were yeast extract, peanut meal, tryptone, corn steep liquor dry powder, bean cake powder, ammonium sulfate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate, the nitrogen content of each nitrogen source (that is, the mass percentage of nitrogen element in each corresponding nitrogen source) is 9.8 %, 7.6%, 13.5%, 4.02%, 8%, 21% and 21%, corresponding to the final concentration of each nitrogen source added to the fermentation medium is 5g / L, 6.45g / L, 3.63g / L, 12.19g / L, 6.13g / L, 2.33g / L and 2.33g / L, the uniform nitrogen content (i.e. the mass percentage of n...
Embodiment 3
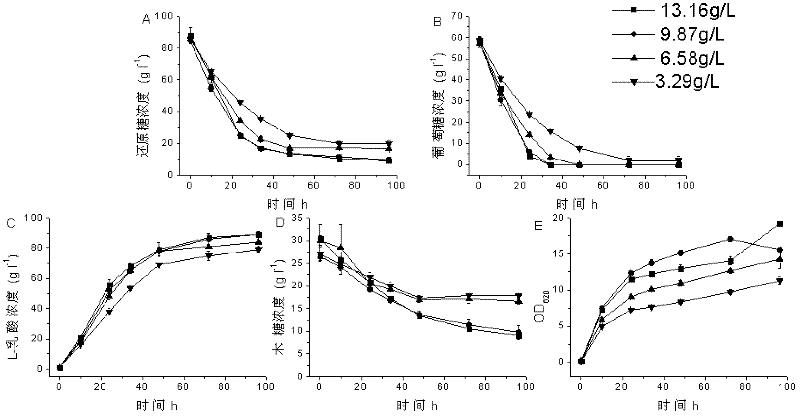
[0046] Example 3. Determination of the concentration of peanut meal, a cheap nitrogen source for efficient production of L-lactic acid
[0047] The fermentation medium used in this embodiment is based on the difference in the concentration of cheap nitrogen source peanut meal, and there are four kinds in total. / L, of which glucose is 69.4g / L, xylose is 21.7g / L, and arabinose is 2.5g / L); the nitrogen source is peanut meal, and the final concentrations are 3.29g / L, 6.58g / L, and 9.87g respectively / L and 13.16g / L, the final concentration of neutral protease is 0.3g / L (60000U / L); the final concentration of calcium carbonate is 50g / L; the balance is water; pH6.5.
[0048] The specific steps to determine the optimal concentration of peanut meal as an inexpensive nitrogen source for the production of L-lactic acid are as follows:
[0049] 1) Seed fungus culture: under sterile conditions, put the Bacillus coagulans (Bacillus coagulans) XZL4DSM No.23183 stored in the LB slant into 30...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com