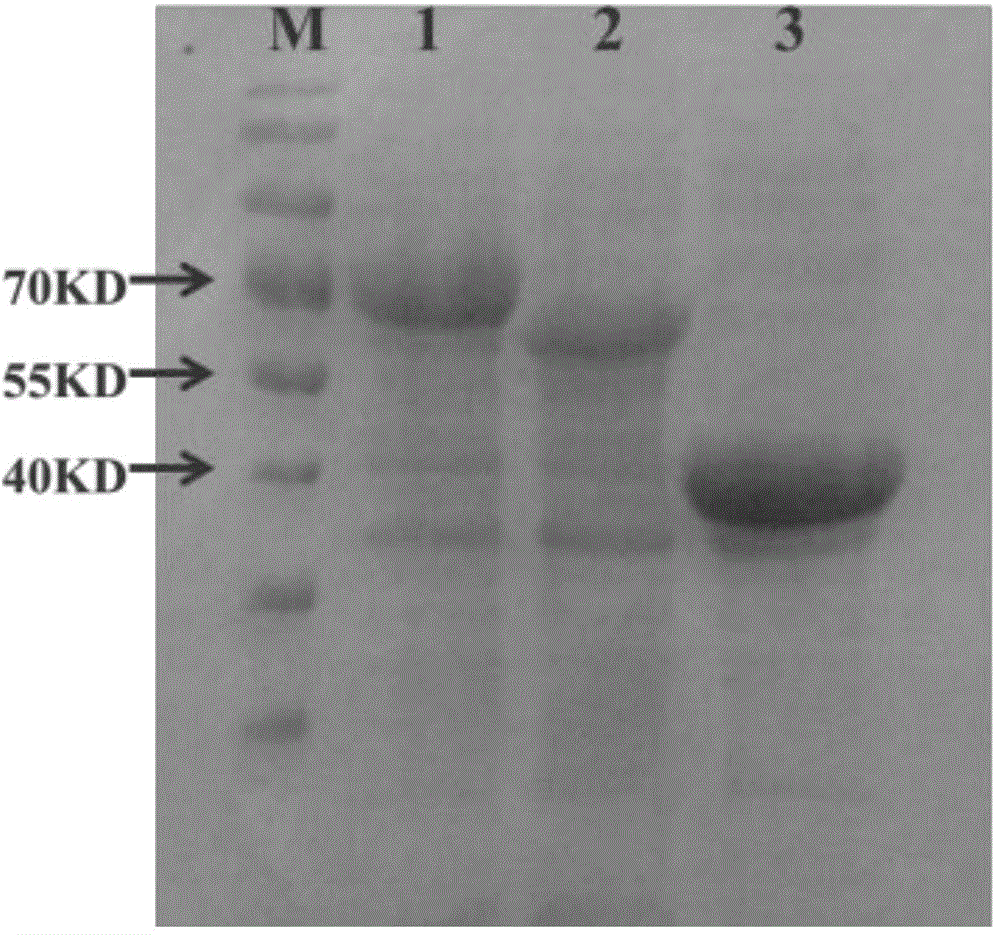
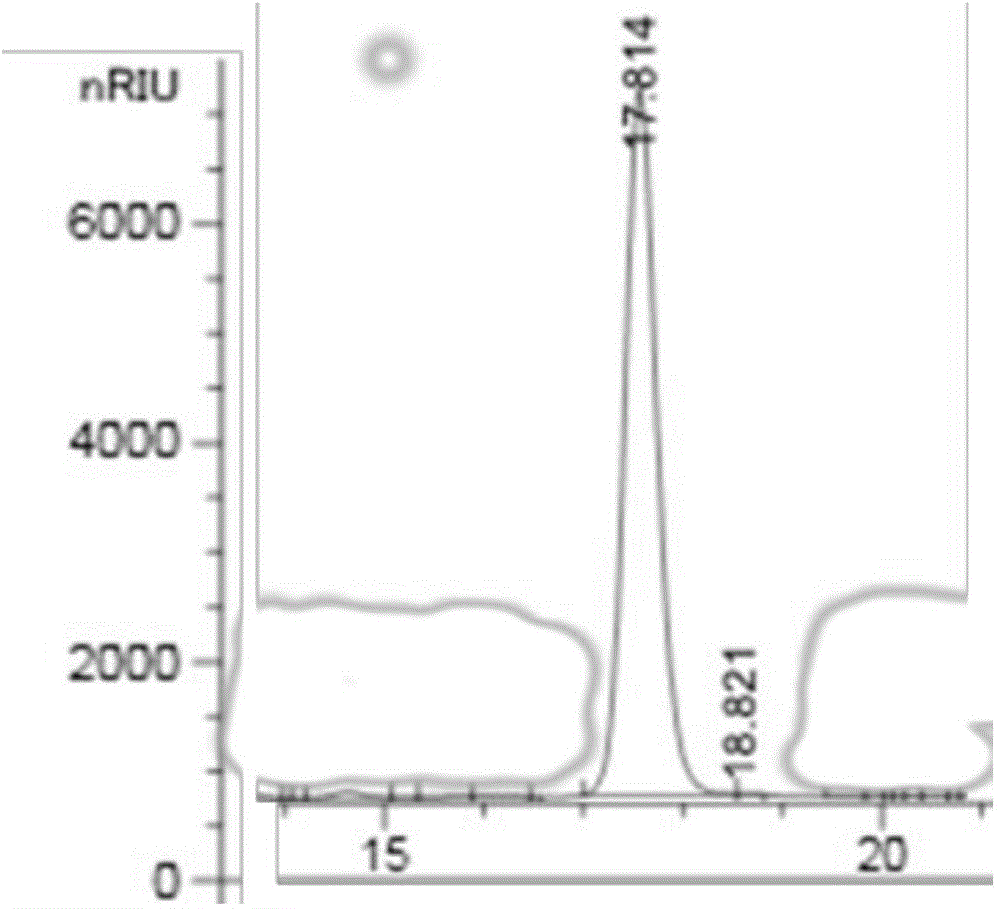
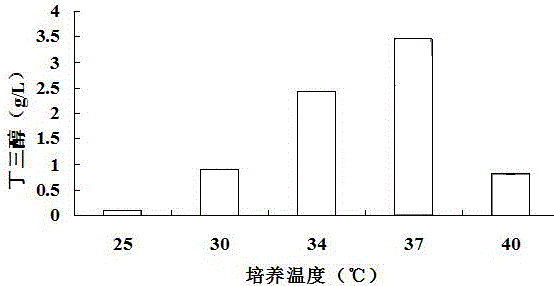
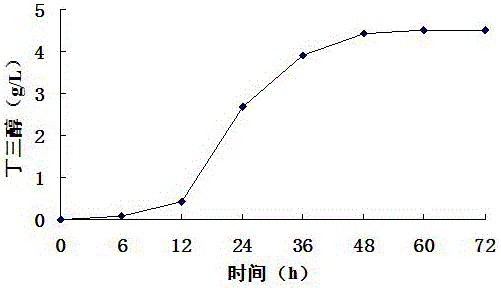
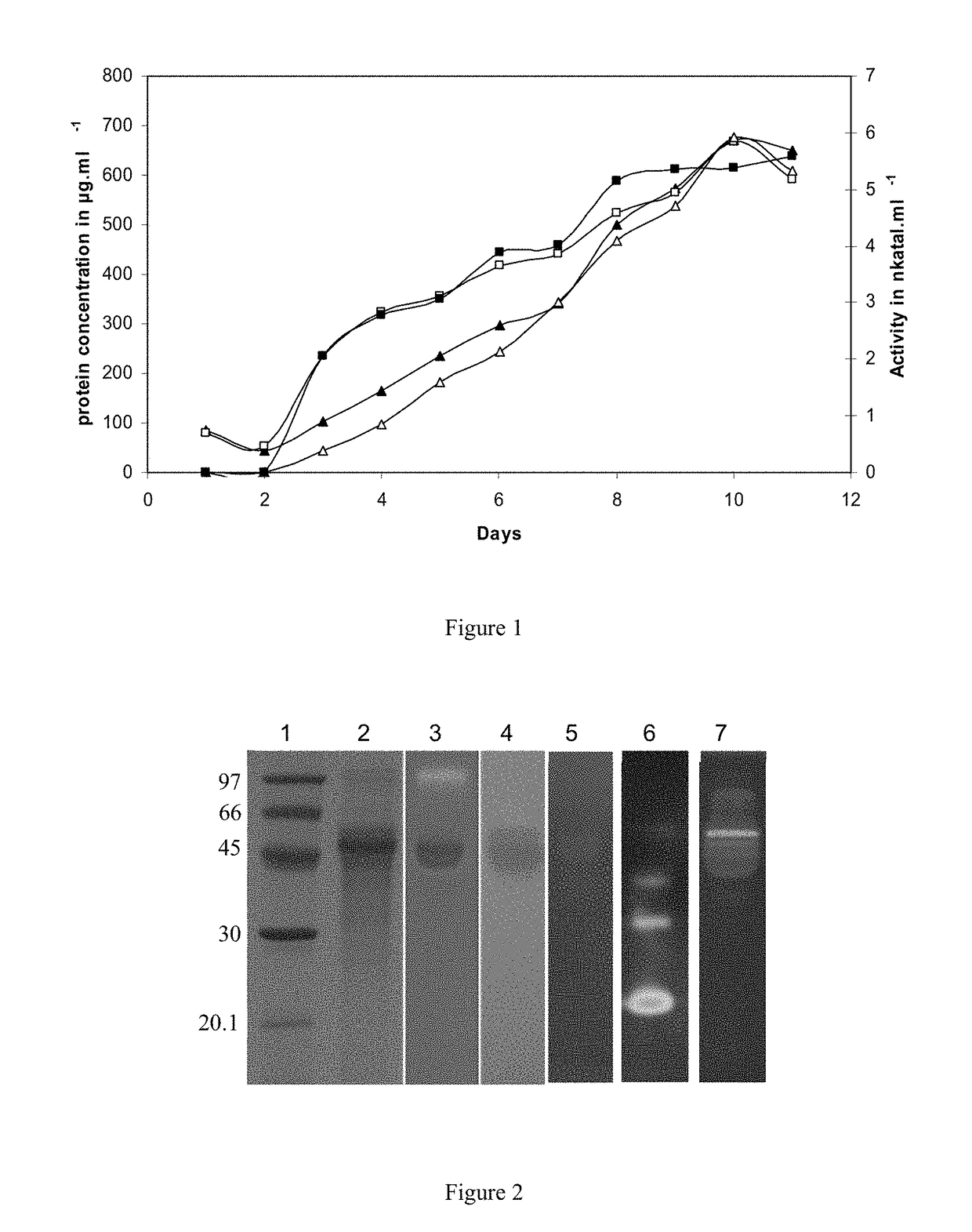
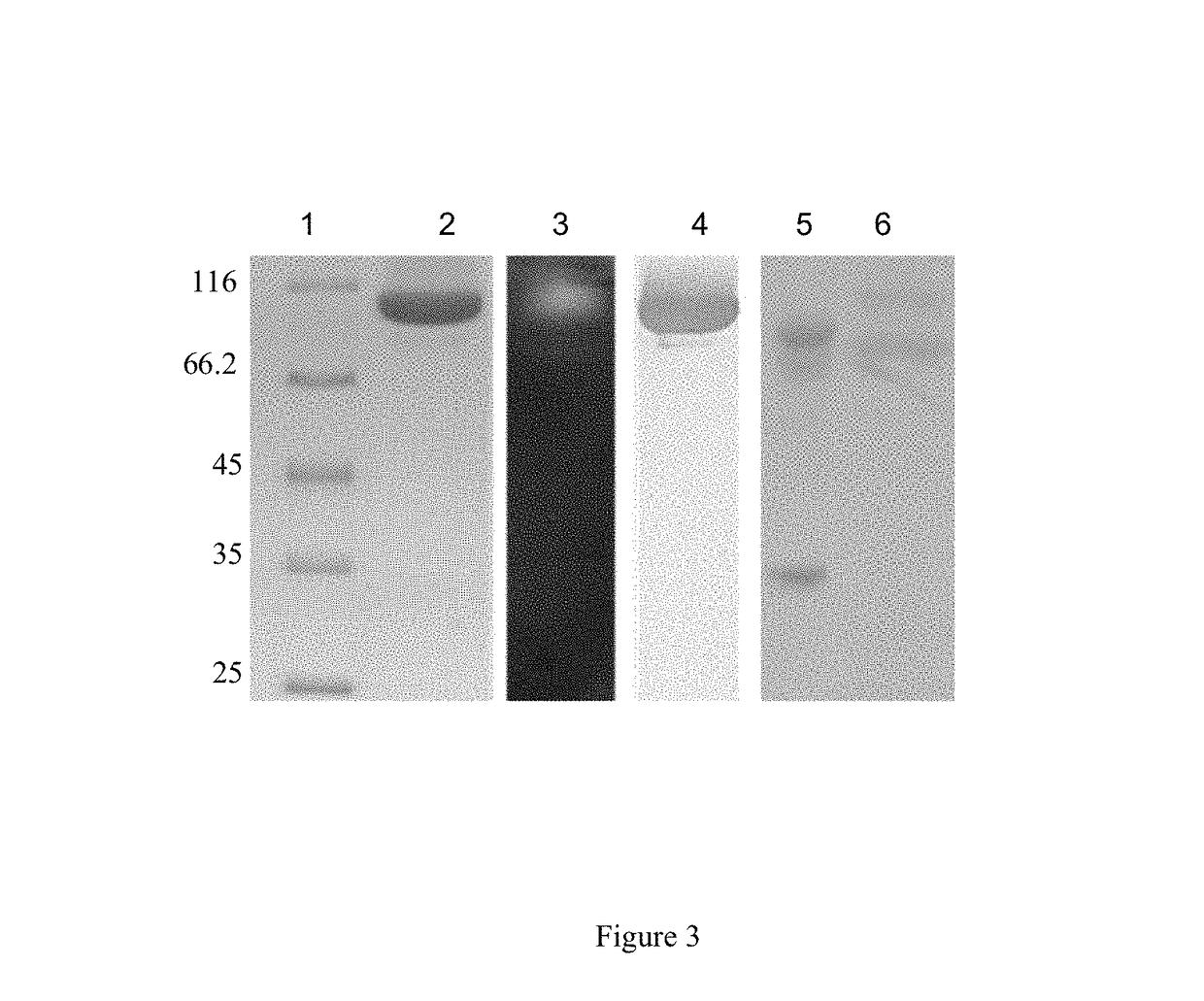
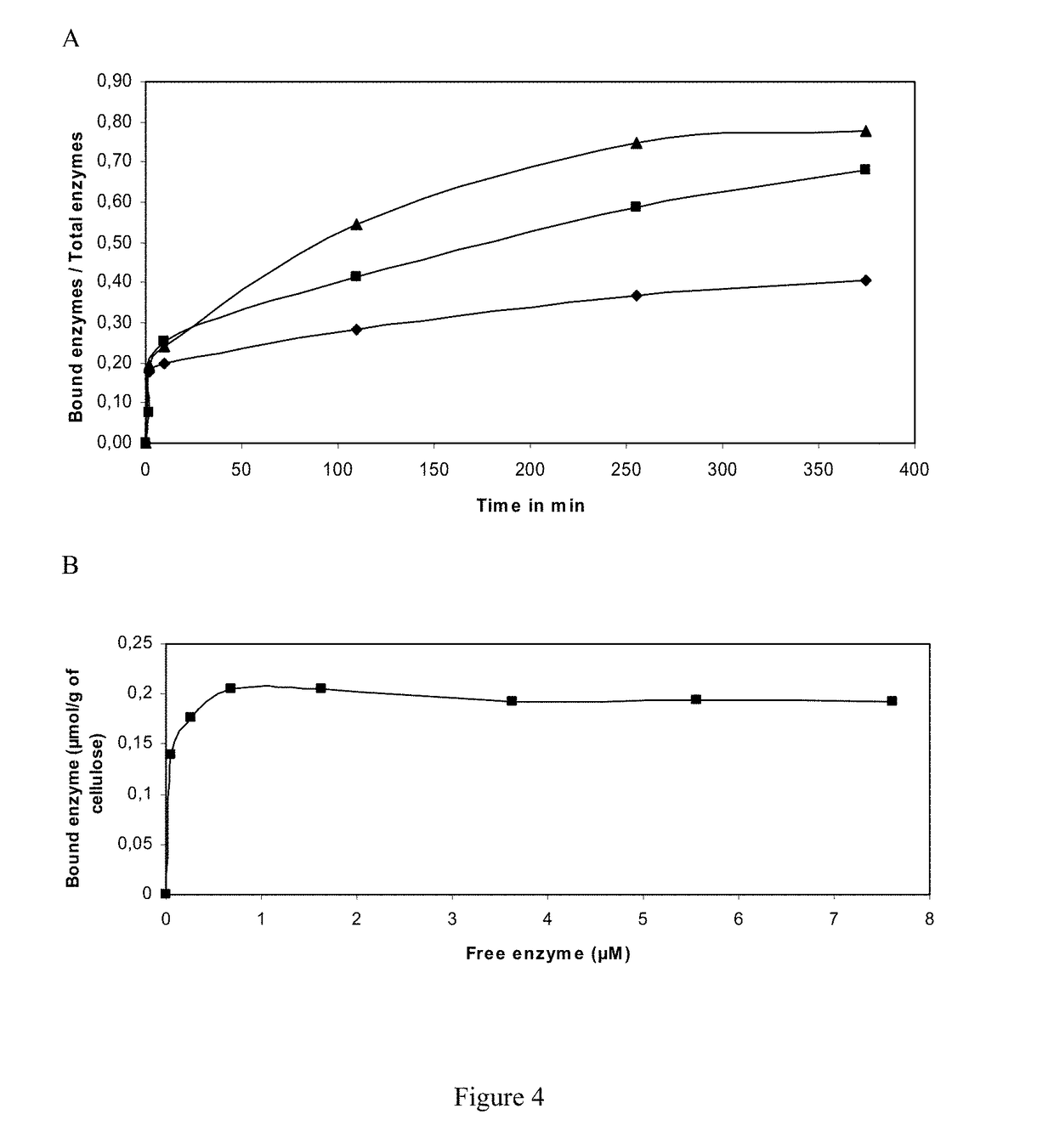
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Xylonic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xylonic acid is a sugar acid that can be obtained by the complete oxidation of xylose (a primary alcohol).
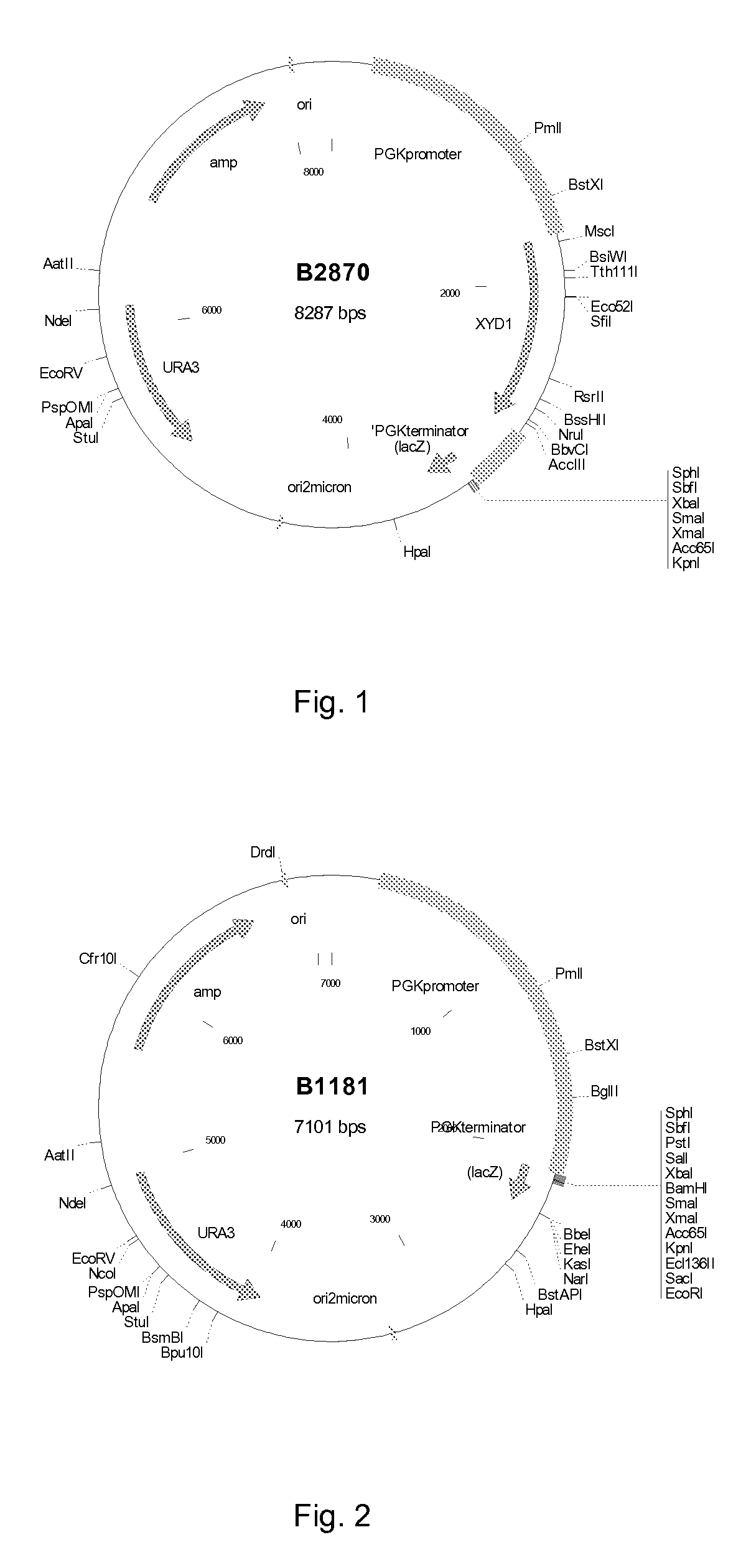
Method of generating 1,2,4-butantriol by in vitro enzyme reaction and application thereof
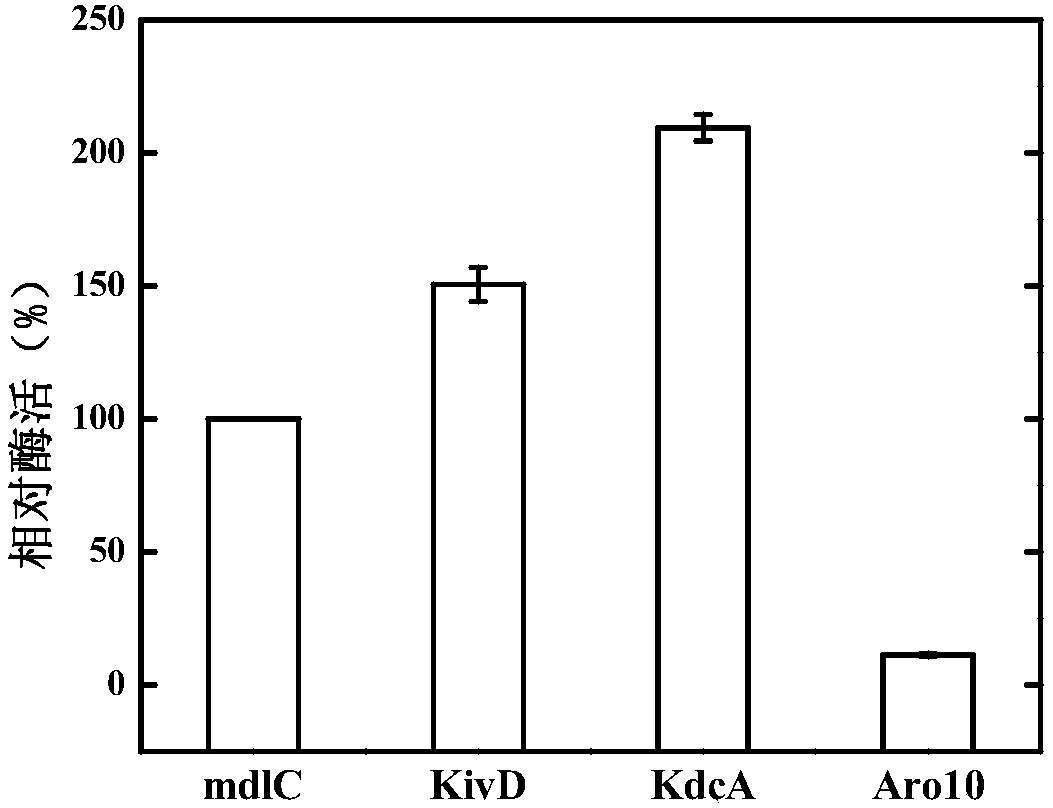
ActiveCN104450798AAchieve synthesisPrecise control of dosageOxidoreductasesFermentationKetoacid decarboxylase1,2,4-Butanetriol
The invention discloses a method of generating 1,2,4-butantriol by the in vitro enzyme reaction and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: respectively constructing genetically-engineered bacteria of over-expressed D-xylonic acid anhydrase genes, 2-keto acid decarboxylase genes and alcohol dehydrogenase genes; after carrying out fermentation cultivation on the obtained genetically-engineered bacteria, crushing thalli by ultraviolet waves; collecting crude enzyme fluid; and after carrying out mixed adjustment on concentration of D-xylonic acid anhydrase, 2-keto acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase, adding a reaction substrate to synthesize 1,2,4-butantriol. The method provided by the invention realizes synthesis of 1,2,4-butantriol in vitro by controlling the enzyme reaction and using D-xylonic acid as the raw material and has the characteristic of good convenience for enlarging production; and the enlarged yield can reach 5.98g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing D-1,2,4-butantriol through bio-converting cellulosic hydrolyzate
ActiveCN106148429AHigh purityReduce branch pathwaysMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesCelluloseXylonic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing D-1,2,4-butantriol through bio-converting cellulosic hydrolyzate. The method comprises the steps of constructing genes for cloning and expressing 2-keto acid decarboxylase, D-xylitol dehydrogenase, D-xylonic acid dehydrase and D-alcohol dehydrogenase, shifting the constructed genes into cells of host bacteria for knocking out xylose isomerase so as to obtain genetic engineering strains, culturing the genetic engineering strains, inoculating the genetic engineering strains to the cellulosic hydrolyzate, and carrying out fermentation so as to produce the D-1,2,4-butantriol. The method disclosed by the invention is easy and feasible, is high in yield and is applicable to industrialization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for Producing a Target Substance by Fermentation
ActiveUS20130295621A1Efficient productionEfficiently assimilateHydrolasesOxidoreductases2-ketoglutaric acidXylonic acid
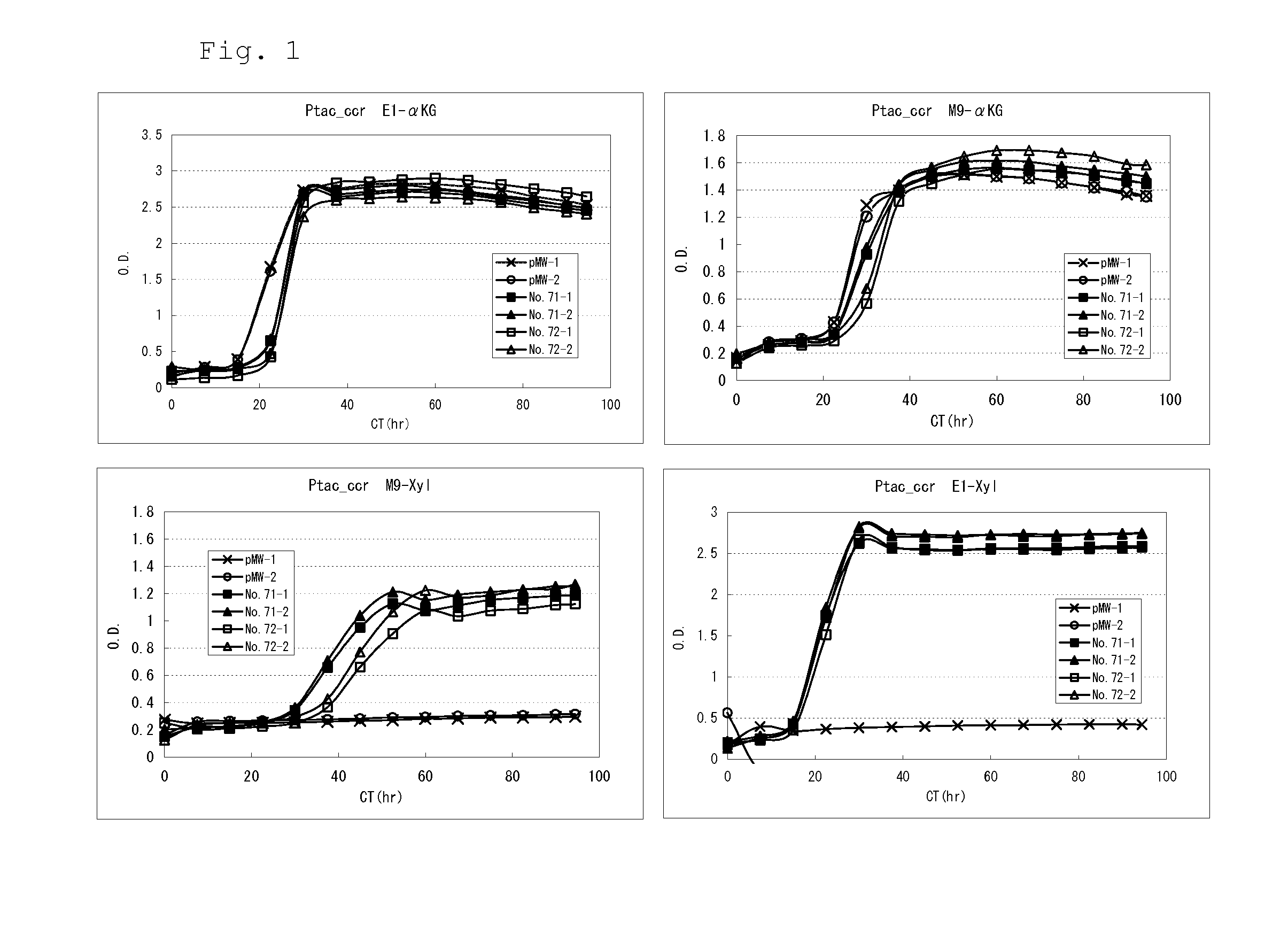
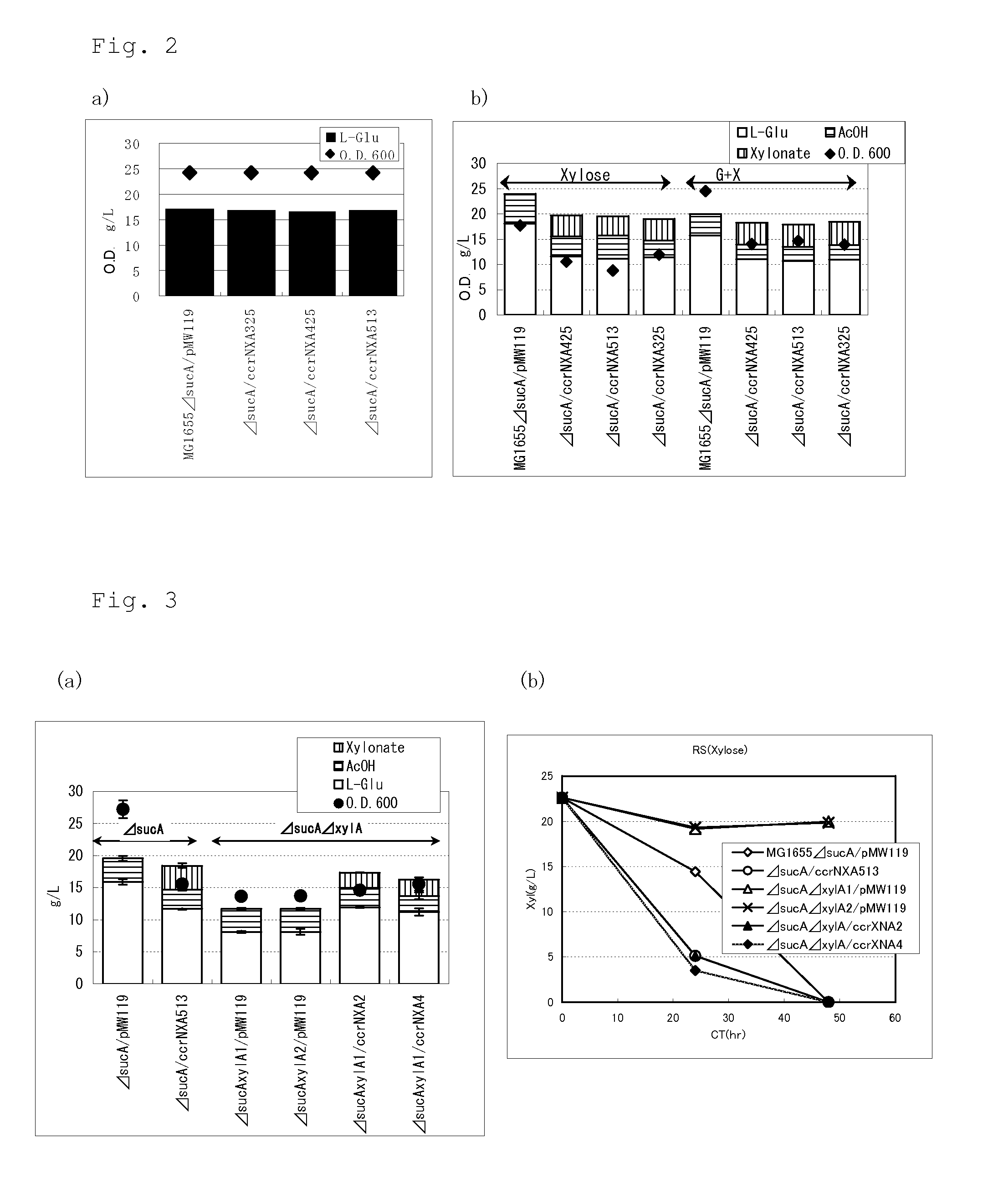
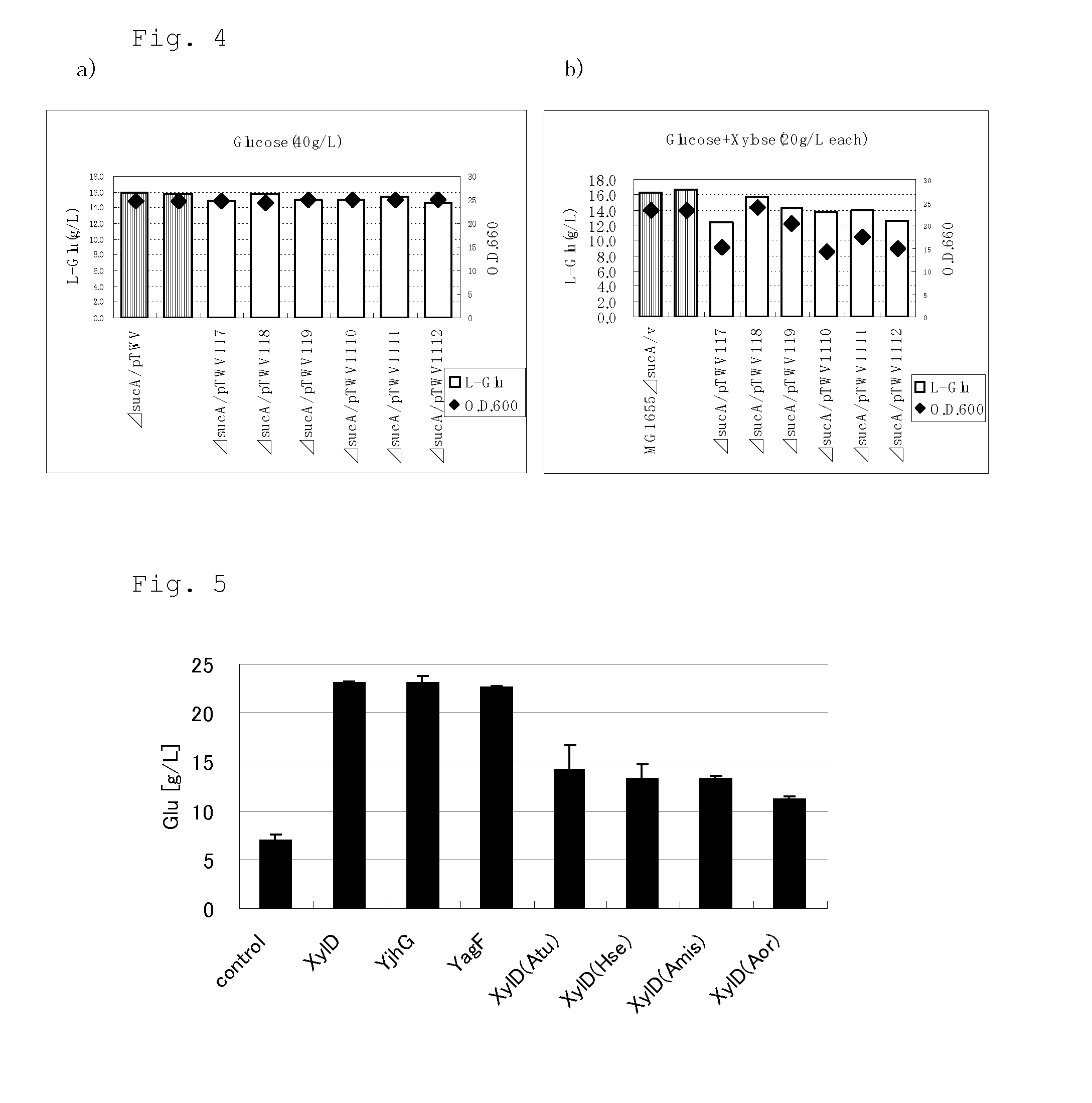
A target substance can be produced by culturing a bacterium having an ability to produce 2-ketoglutaric acid or a derivative thereof, and an ability to produce xylonic acid from xylose, which is imparted with xylonate dehydratase activity, 2-keto-3-deoxyxylonate dehydratase activity and 2-ketoglutaric semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity, or in which these activities are enhanced, in a medium containing xylose as a carbon source to produce and accumulate the target substance in the medium, and collecting the target substance from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and building method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and a building method and application of the recombinant bacteria and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The xylose dehydrogenase gene, xylonic acid lactonase gene, xylonic acid dehydratase gene, 3-deoxygenation-D-glycerin ketopentose acid aldolase gene and glycolic aldehyde dehydrogenase gene in the recombinant bacteria using the xylose to produce the glycollic acid are overexpressed. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method of the recombinant bacteria and a method using the recombinant bacteria to produce the glycollic acid. By the recombinant bacteria, the biological synthesizing path using D-xylose as the carbon source to form the glycollic acid through glycolic aldehyde conversion is achieved for the first time.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of BT (D-1,2,4-butanetriol)
ActiveCN107699536AIncrease productionOptimization pathBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyKetoacid decarboxylase
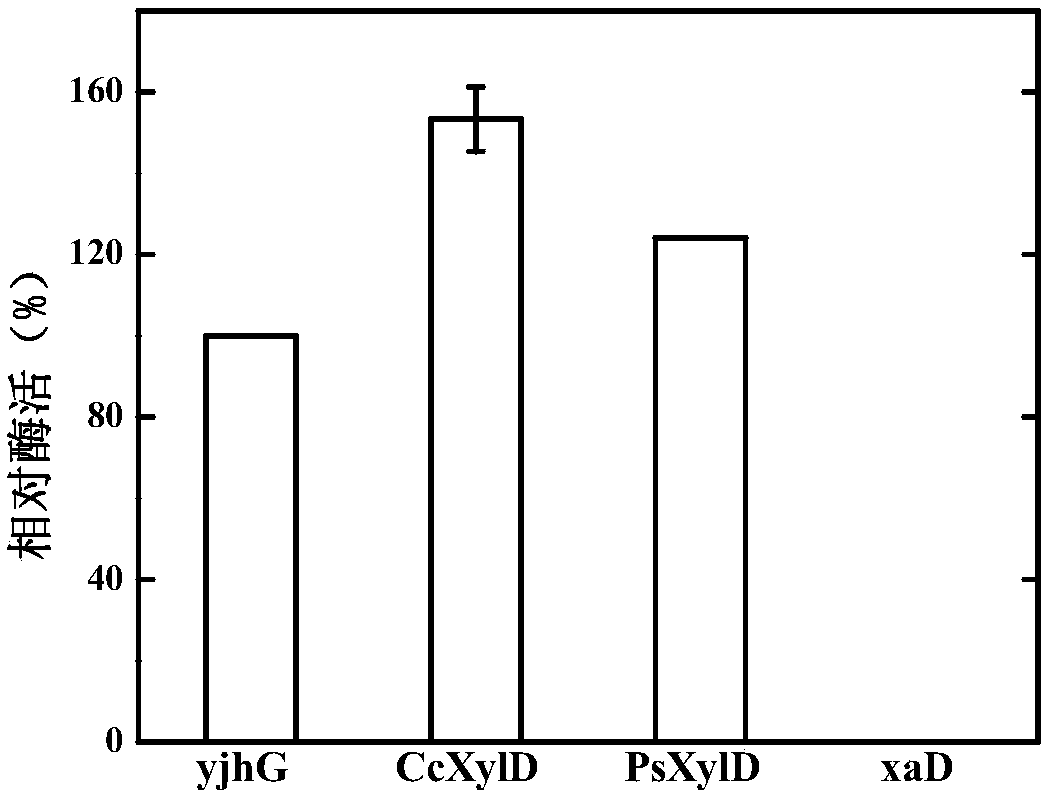
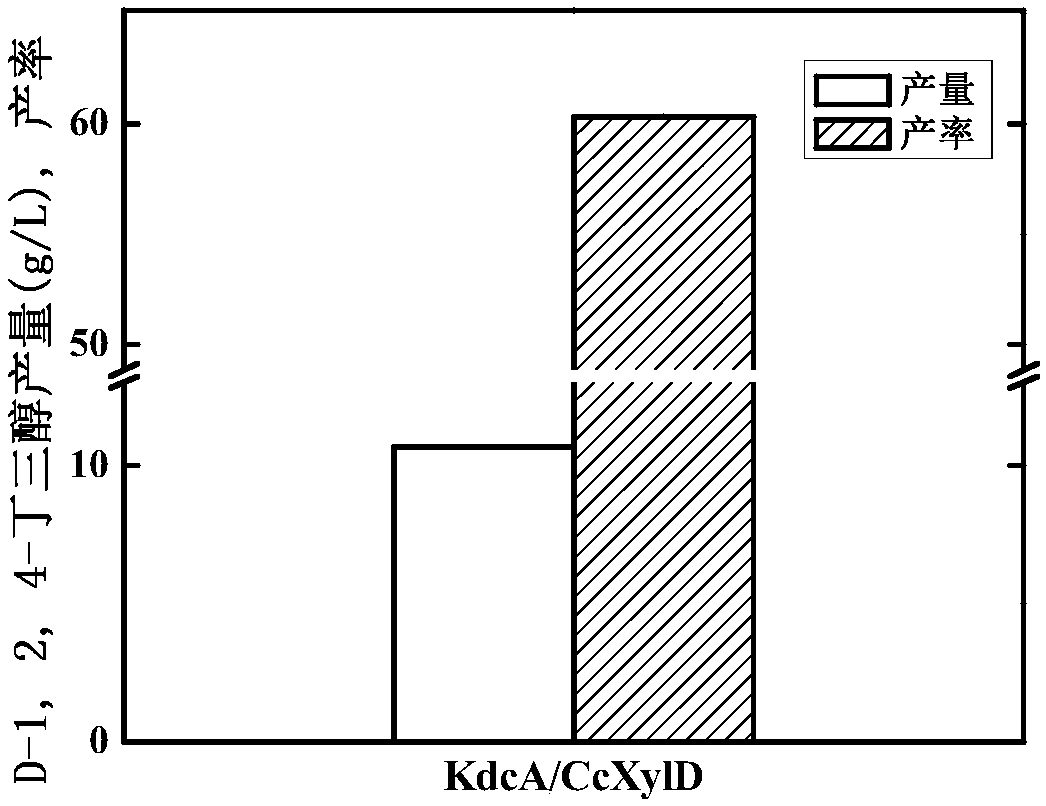
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria and an application thereof in production of BT (D-1,2,4-butanetriol). The genetically engineered bacteria are novel genetically engineered bacteria which are obtained as follows: a 2-keto acid decarboxylase gene MalC, an xylose dehydrogenase gene XylB, an xylonic acid dehydratase gene YjhG and an alcohol dehydrogenase gene YqhD are constructed, cloned and expressed, the genes are transferred into cells of host bacteria BL21(DE3), genetically engineered bacteria BL21-02 are obtained, and new xylonic acid dehydratase is screened on the basis of the genetically engineered bacteria; the genetically engineered bacteria are subjected to fermenting culture for production of BT. The capability of synthesizing BT from D-xylose can be improvedby screening the provided xylonic acid dehydratase gene CcXylD. The optimal xylonic acid dehydratase gene CcXylD and alpha-keto acid decarboxylase gene KdcA from lactococcus lactis are applied to theproduction process of BT, the optimal strain BL21-15 is obtained, and finally, the BT yield can reach 10.66 g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method of co-catalytically synthesizing various saccharic acids by virtue of synergism of metal ions and selective regulation whole-cell
InactiveCN105132476ADeter and reduce utilizationEfficient synthesisFermentationSaccharic acidCellulose
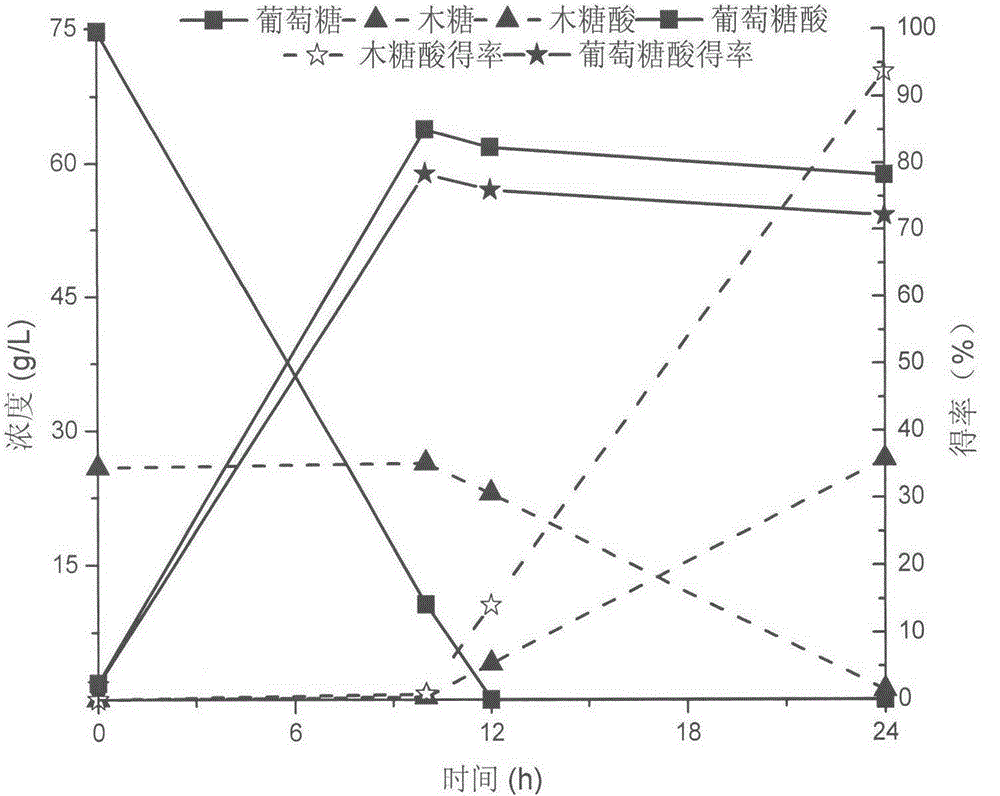
The invention discloses a method of co-catalytically synthesizing various saccharic acids by virtue of the synergism of metal ions and a selective regulation whole-cell, and relates to the technical field of synthesizing the saccharic acids by biologically catalyzing sugar. The method is mainly characterized in that in a mixed sugar solution or lignocelluloses hydrolysate containing glucose and xylose, 1g / L to 10g / L of gluconobacter oxydans is used as a biological catalyst to co-catalyze the glucose and the xylose under an oxygen-supply condition so as to synthesize the saccharic acids. Metal salt of a given concentration containing zinc ions and trivalent iron ions is added so as to selectively inhibit the catabolism of a cell on the gluconic acid, but a dehydrogenation catalytic reaction of the xylose and the glucose is hardly affected, thus an effect of the cell for co-catalyzing and high-efficiently synthesizing a gluconic acid (salt) and xylonic acid (salt) product can be further achieved, and the reaction time is effectively shortened. By adopting the method, the utilization rate of the glucose and the xylose reaches 100 percent, and the yield of the gluconic acid is more than 70 percent, and the yield of the xylonic acid is more than 92 percent, and the total concentration (mass concentration) of the product gluconic acid (salt) and xylonic acid (salt) can be more than 30 percent.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Two-dimensional composite photocatalyst namely h-BN/Ti3C2/TiO2, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110433847AEasy to makeReaction conditions are easy to controlPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationPhoto catalyticPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a two-dimensional composite photocatalyst namely h-BN / Ti3C2 / TiO2, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The catalyst has a two-dimensional composite structure, wherein wafer-shaped h-BN is loaded on a Ti3C2 nanosheet; meanwhile, a TiO2 particle obtained by oxidation of Ti3C2 is located between the wafer-shaped h-BN and the Ti3C2 nanosheet. The preparation method for the catalyst provided by the invention is simple and highly-efficient and has easily-controllable reaction conditions. The catalyst provided by the invention has the advantages of high catalytic activity, good thermal stability, recyclability and the like, realizes simple and highly-efficient catalytic synthesis of xylosic acid, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
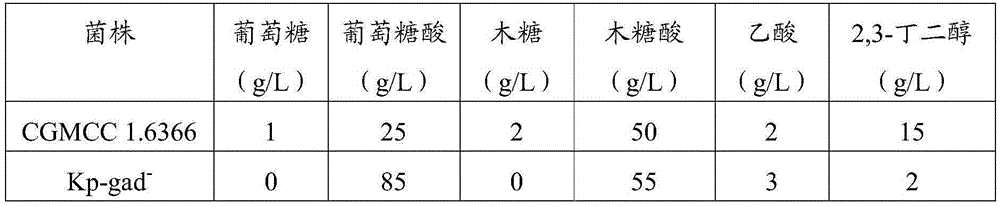
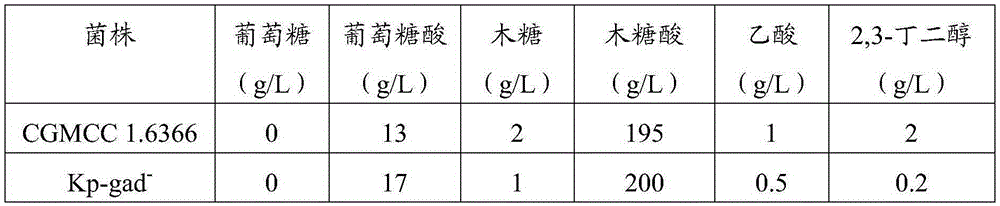
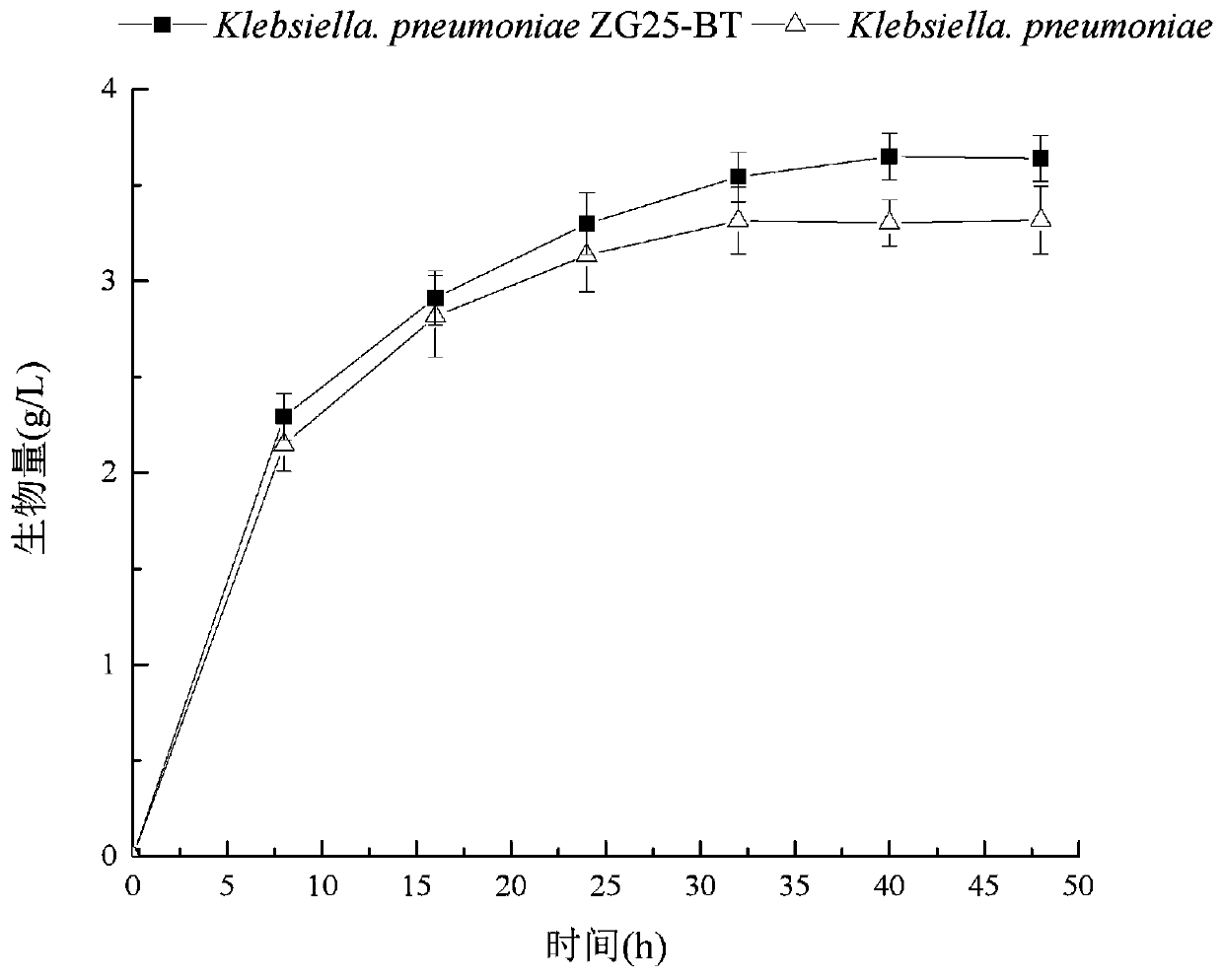
Method using klebsiella pneumoniae to produce xylonic acid
ActiveCN106701844AMaximum final concentrationHigh final concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationNeutral phHydrogen
The invention discloses a method using klebsiella pneumoniae to produce xylonic acid. The method comprises the following steps of using xylose as raw material, and enabling the klebsiella pneumoniae to convert the xylose into xylonic acid under the aerobiotic condition; furthermore, utilizing the klebsiella pneumoniae with deactivation of gluconate dehydrogenase to convert the xylose into the xylonic acid, so as to improve the conversion rate from xylose into xylonic acid; furthermore, utilizing a two-step fermenting method, enabling a fermenting liquid to maintain the neutral pH (potential of hydrogen) condition in the first fermenting phase, enabling the fermenting liquid to maintain the acid fermenting condition in the second fermenting phase, and fermenting to produce the xylonic acid. The method has the advantages that the primer conversion rate is higher, the production intensity is higher, and the product final concentration is higher; by using the glucose and xylose mixture as the raw material, the gluconic acid and the xylonic acid can be simultaneously produced.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
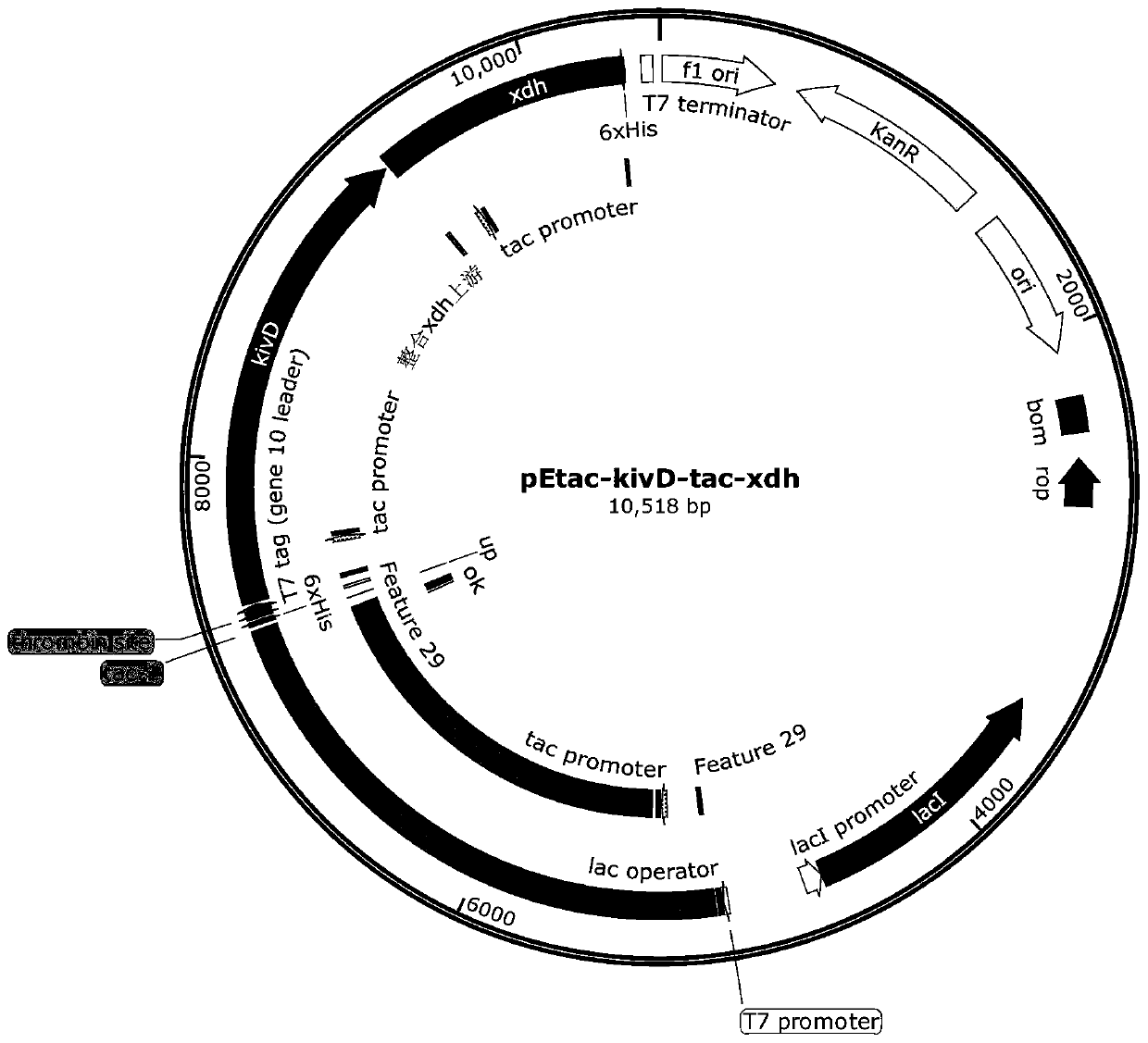
Method for co-production of 1,3-propanediol and D-1,2,4-butanetriol
ActiveCN111593014AImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlycerolXylonic acid
The invention discloses a method for co-production of 1,3-propanediol and D-1,2,4-butanetriol, belongs to the technical field of fermentation and the technical field of biology and provides a recombinant klebsiella capable of efficiently transforming glycerol and xylose to co-produce 1,3-propanediol and D-1,2,4-butanetriol. The recombinant klebsiella takes a klebsiella as a host and expresses a gene xdh of encoding xylose dehydrogenase, a gene kivD of encoding 2-ketoisovalerate decarboxylase and a gene yjhG of encoding xylonic acid dehydratase, and the recombinant klebsiella is inoculated intoa fermentation medium containing the glycerol and the xylose for fermentation for 48 h, so that the yield of the 1,3-propanediol in a fermentation liquid can reach 18.1 g / L, and the yield of the D-1,2,4-butanetriol can reach 3.3 g / L; and meanwhile, the transformation rate of the glycerol in the fermentation liquid can reach 45.3% and the transformation rate of the xylose can reach 12.3%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
NiTi nanoflower hydrotalcite photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111408377ASpecial nanoflower structureImprove apparent quantum efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationNickel saltPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a NiTi hydrotalcite photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The catalyst is three-dimensional NiTi nanometer, and the diameter of the nanoflower is 6-7 [mu] m. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving titanium salt, nickel salt and urotropine in water, and stirring the solution until the solution is transparent; heating the reaction system for a reaction; and cooling and drying after heating to obtain the nickel-titanium nano-flower hydrotalcite photocatalyst, wherein the nickel-titanium nano-flower hydrotalcitephotocatalyst can be used for catalyzing xylose to be converted into xylonic acid. The catalyst is very simple and convenient to synthesize in the aspect of catalyst preparation, high-temperature heating is not needed, and the synthesized catalyst can be directly used for catalytic reaction without subsequent treatment. The catalyst provided by the invention has industrial potential, is low in catalytic process cost, is different from traditional thermal catalysis, is green and environment-friendly in process, and does not generate harmful byproducts.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
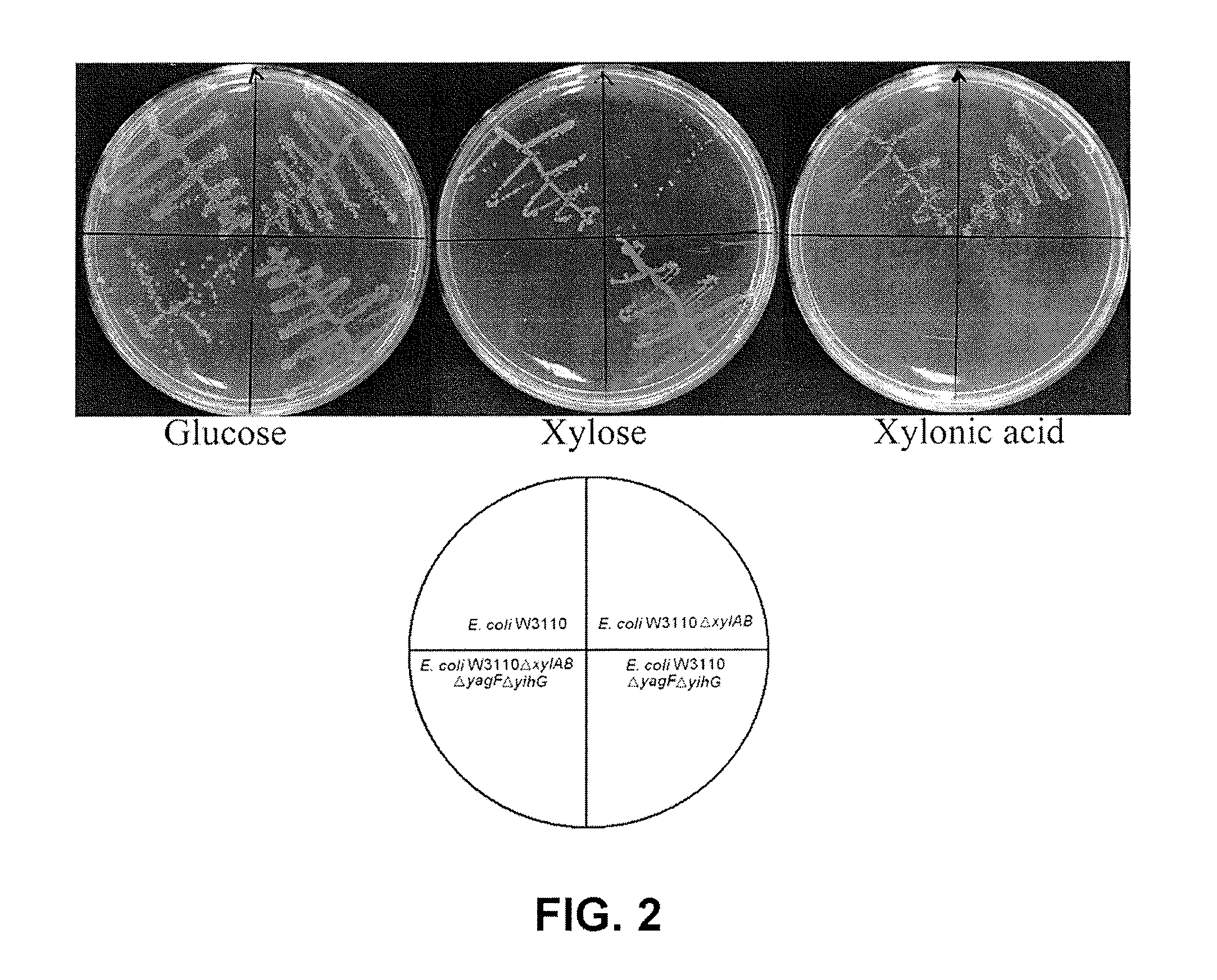
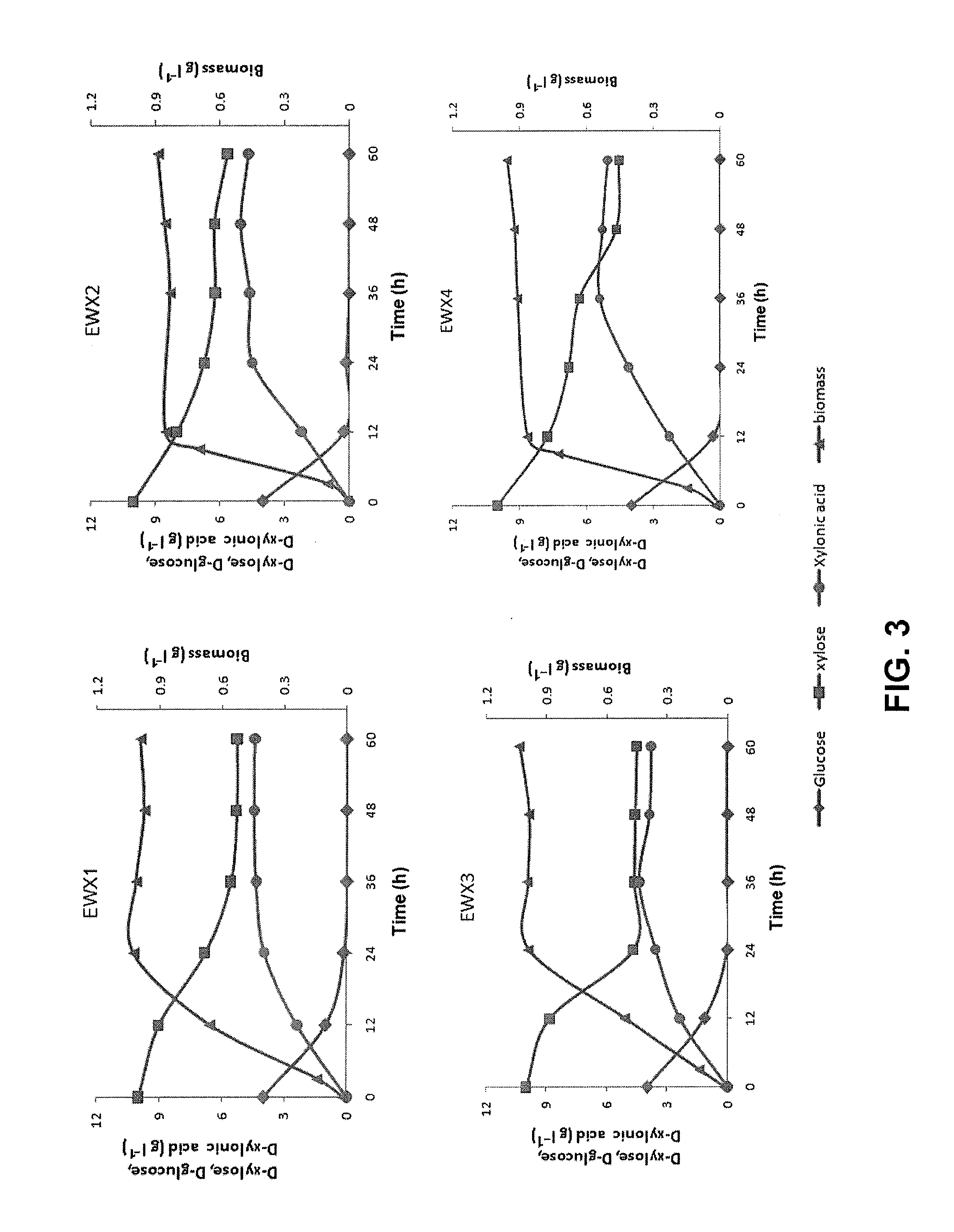
Recombinant Escherichia coli producing D-xylonic acid from D-xylose and method for producing D-xylonic acid using the same
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
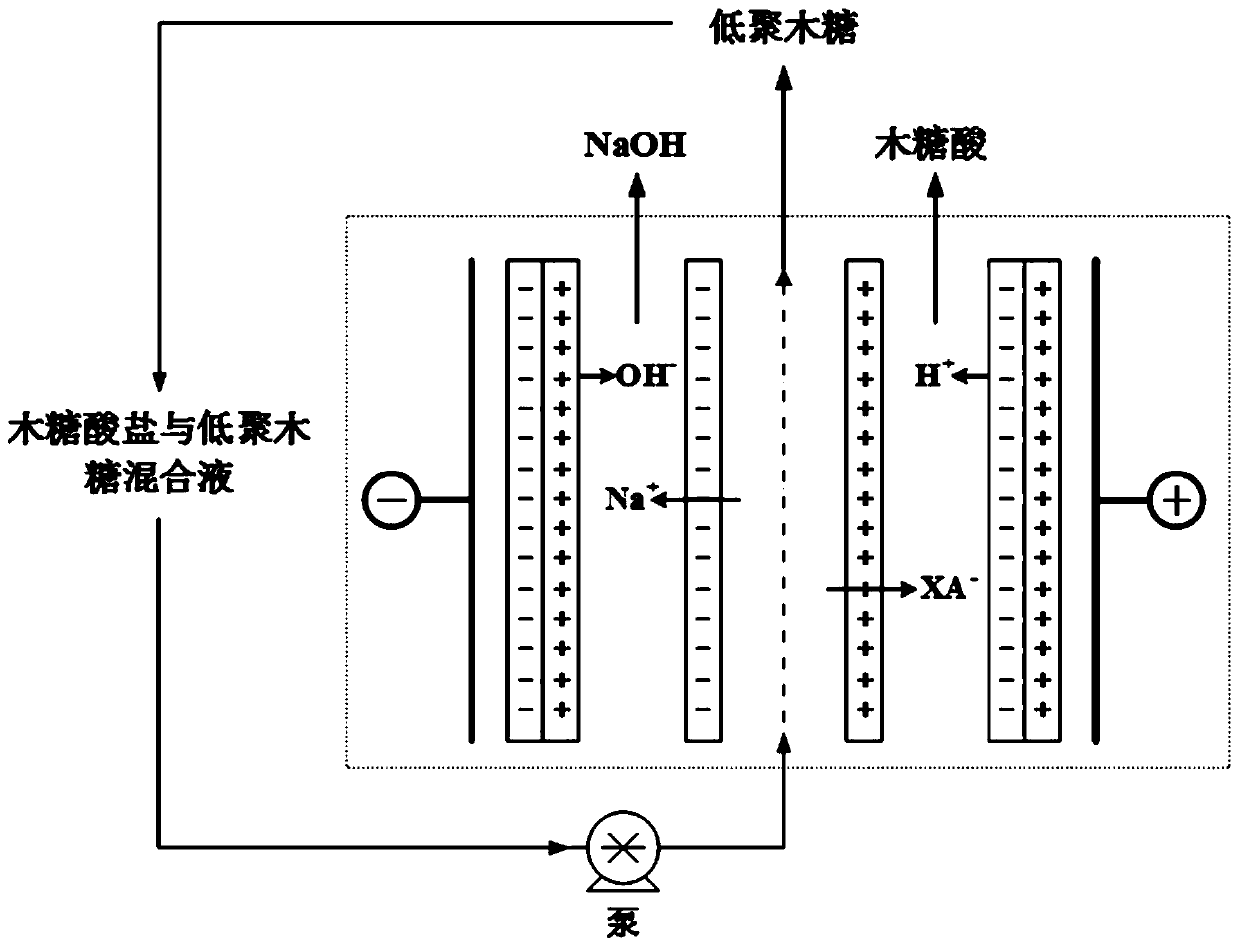
Method for preparing xylose acid through electrodialysis desalination and acid transformation by one-step method
InactiveCN106187731APreparation from carboxylic acid saltsCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPotassiumXylonic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylose acid through electrodialysis desalination and acid transformation by a one-step method. The method comprises the following steps of treating xylose acid salts by bipolar membrane electrodialysis, and using an electric field as driving force to realize dialysis desalination and electrolyze the xylose acid salts at the same time so as to generate the xylose acid; and therefore, the effect of completing desalination and acid transformation by the one-step method so as to prepare the xylose acid is realized. The xylose acid salts (sodium, potassium and zinc) are used as raw liquid, after impurities of colloid and the like are removed through adsorption, bipolar membrane electrodialysis is adopted, and deionized water of which the resistivity is higher than 18 megohms is added to an acid chamber and an alkali chamber, and 0.1mol / L-0.5mol / L sodium sulphate is used as a conducting medium between a connecting film group and a film electrode; and xylose acid salt liquid is treated under the condition that the voltage is 15-20V, and the electric current is 0-10A, until the electrical conductivity of product liquid is reduced to 300ms / cm or below, and falls down no longer, the xylose acid product liquid is obtained. The desalinization ratio of the xylose acid salt raw liquid is higher than 99%, the conversion rate of sugar acid is higher than 97%, and the effect of preparing the xylose acid by the one-step method is realized. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple to operate, high in production efficiency and low in cost.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
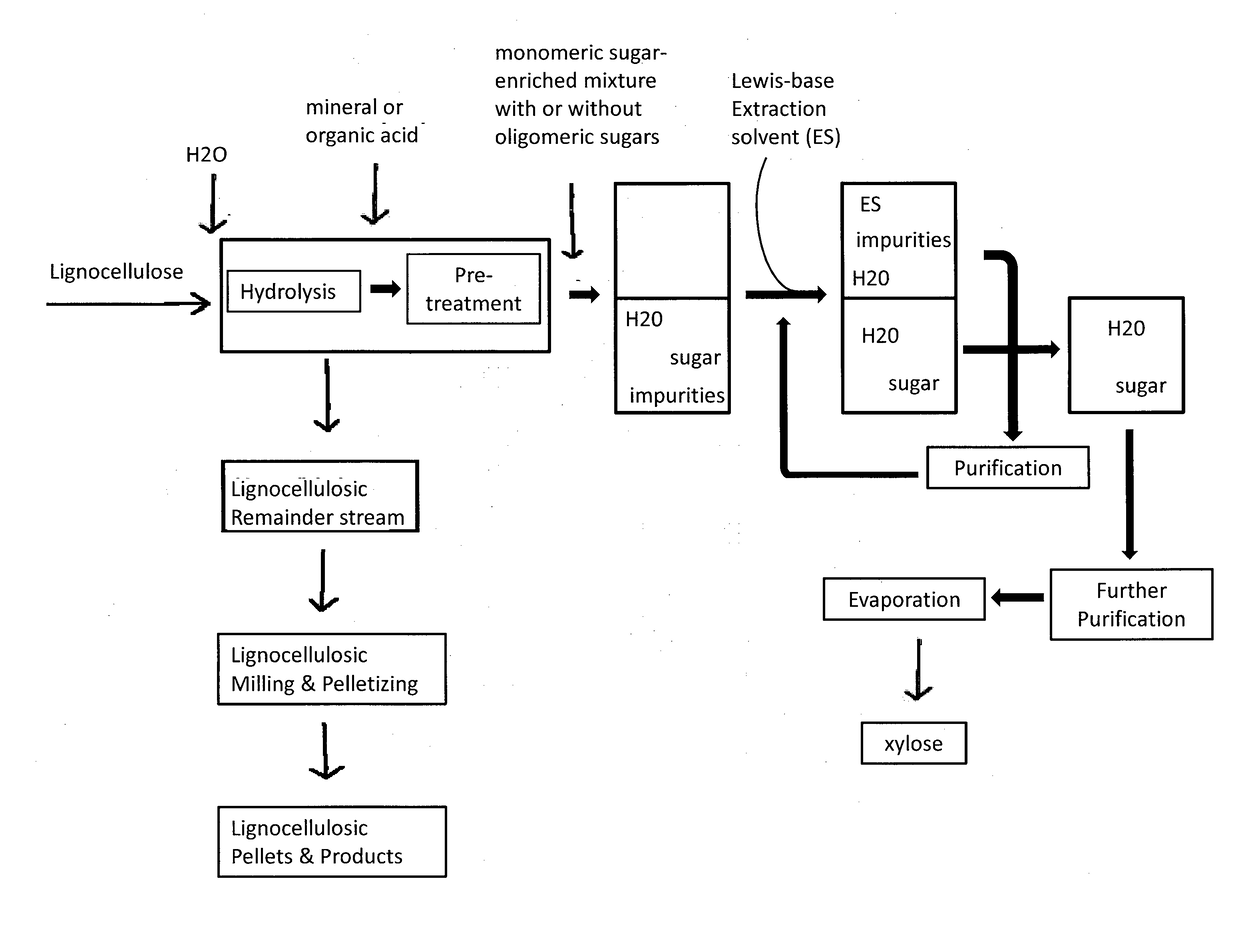
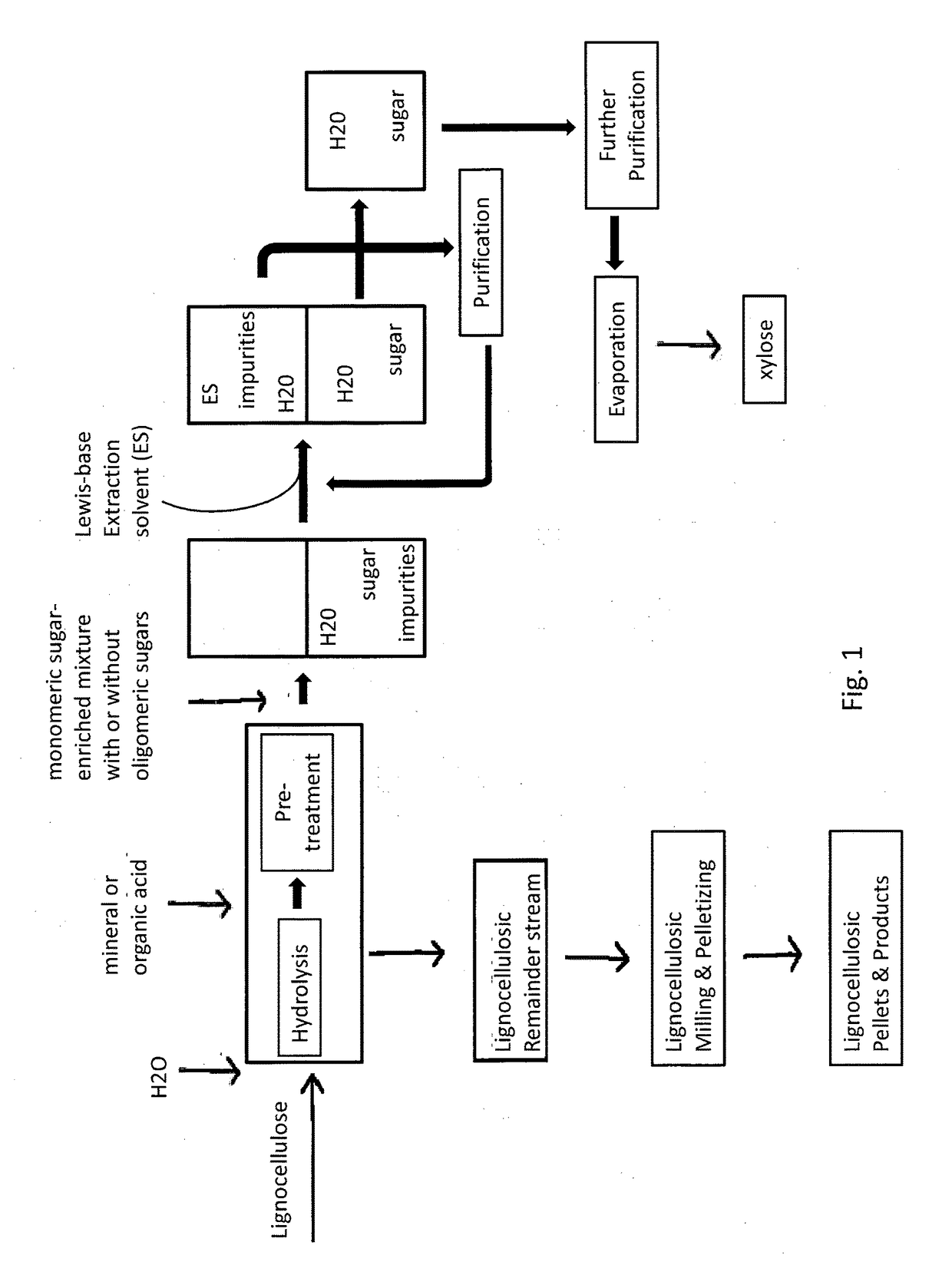
Method for treating lignocellulosic materials
A method of generating a refined sugar stream that comprises xylose from a biomass hydrolysis solution including contacting a biomass hydrolysis solution that includes a population of mixed sugars comprising xylose, an acid, and impurities, with an extraction solvent to form an extraction mixture; and separating from said extraction mixture a first stream that includes the acid and a second, refined sugar stream that includes the extraction solvent and xylose. The extraction solvent is a tri-alkyl phosphine oxide, a dialkylsulfoxide, or a dialkylphosphite, or any combination thereof.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
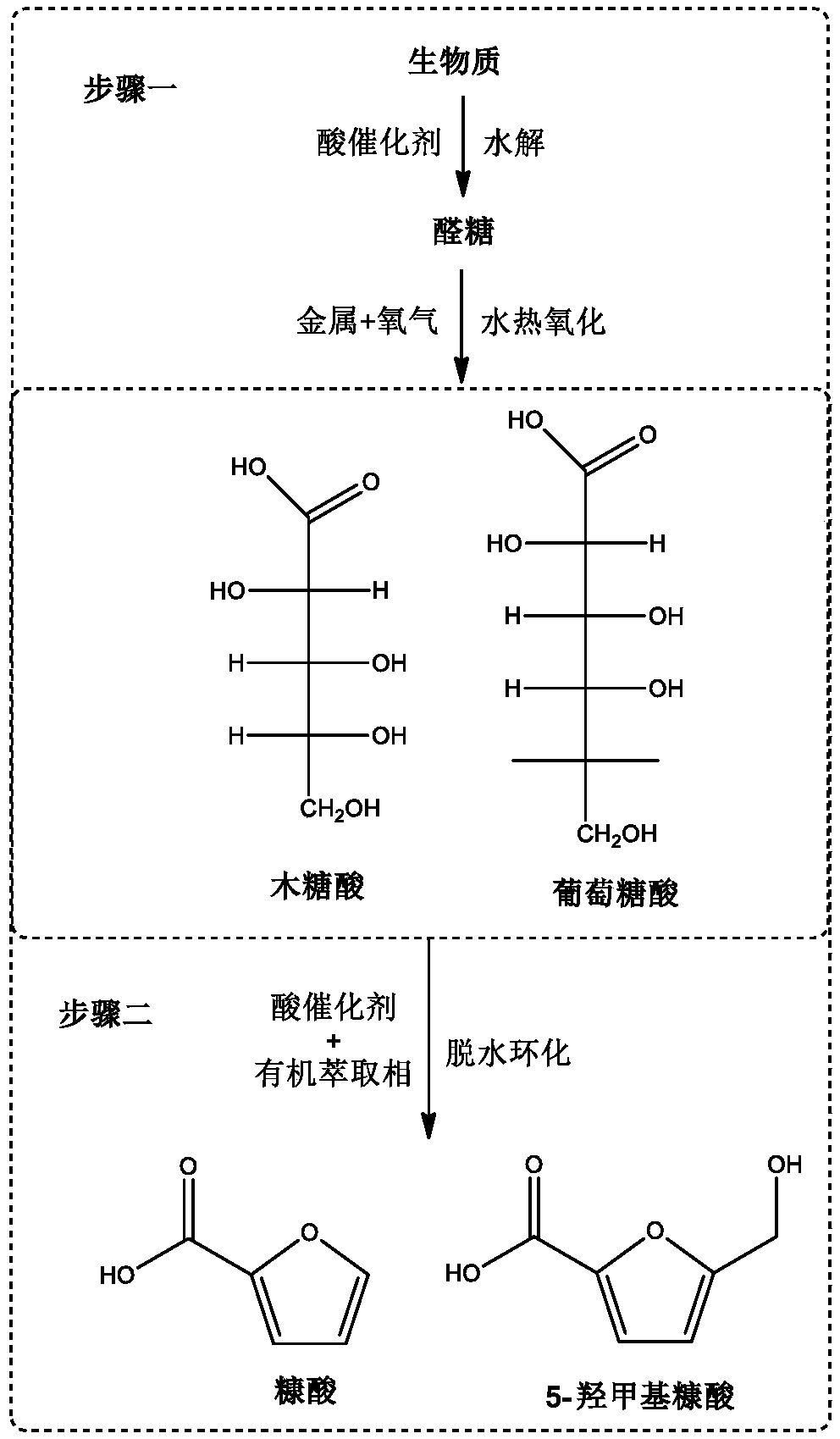
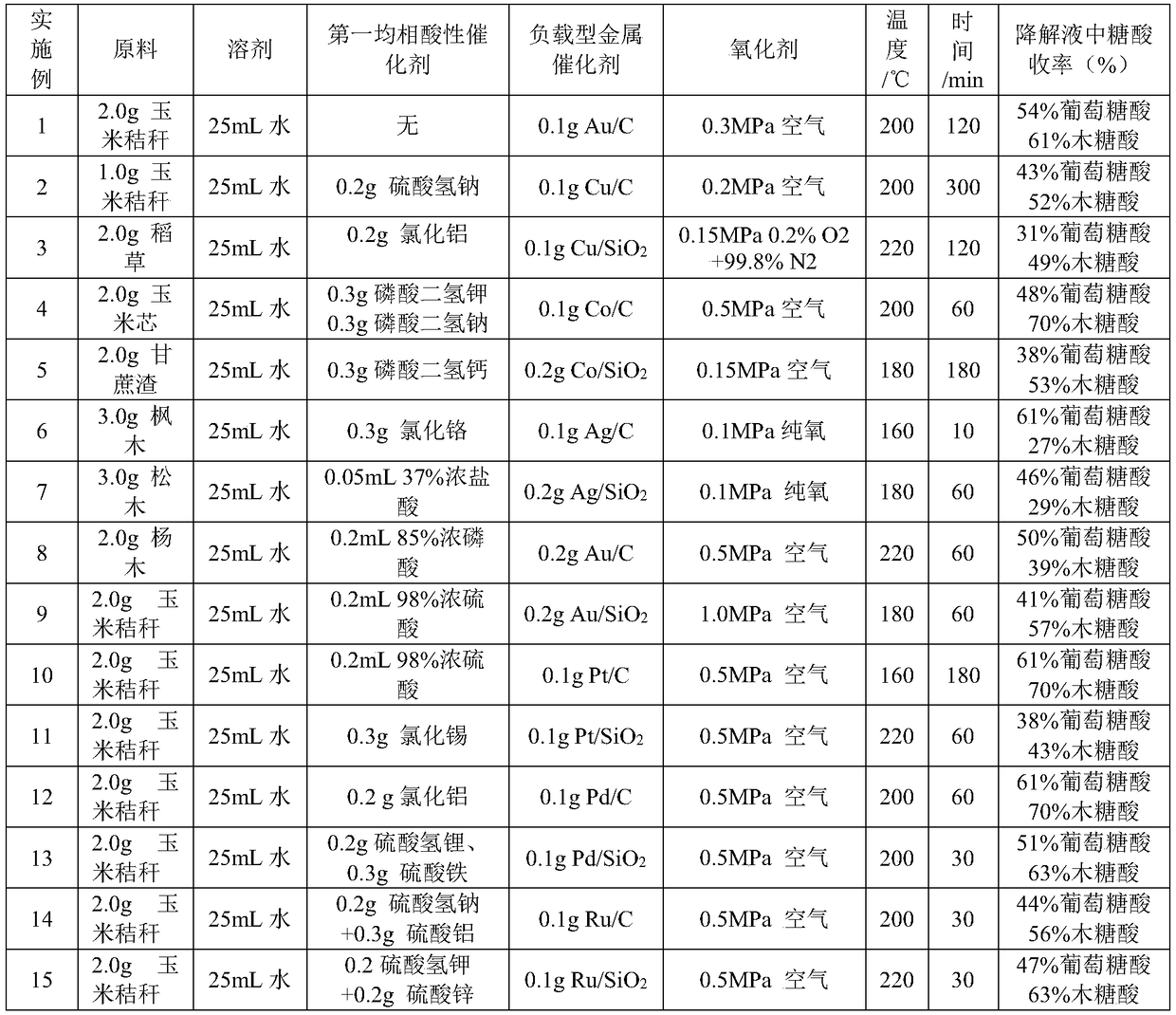
Method for preparing furoic acid and 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid by biomasses
The invention discloses a method for preparing furoic acid and 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid by biomasses. The method includes the steps: (1) taking oxygen-containing gas as an oxidizing agent, and converting the biomasses into degradation liquid containing gluconic acid and xylonic acid under hydrothermal reaction conditions through combined actions of a first homogeneous acid catalyst and a supported metal catalyst; (2) placing the degradation liquid containing the gluconic acid and the xylonic acid into an inert atmosphere, sequentially adding an organic solvent and a second homogeneous acidcatalyst to obtain mixed liquid, performing reaction on the mixed liquid to obtain the furoic acid and the 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid. According to the method, a small amount of solid residue is generated in the whole reaction process, and the method avoids the problems of low target products, carbon deposition on device wall surface, pipeline blockage and the like caused by a lot of solid residue generated in traditional biomass degradation process.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF TECH
Brewing yeast strain capable of metabolizing xylose
InactiveCN102604850AGrow fastShort metabolic pathwayFungiMicroorganism based processesGlycerolCarboxylic acid
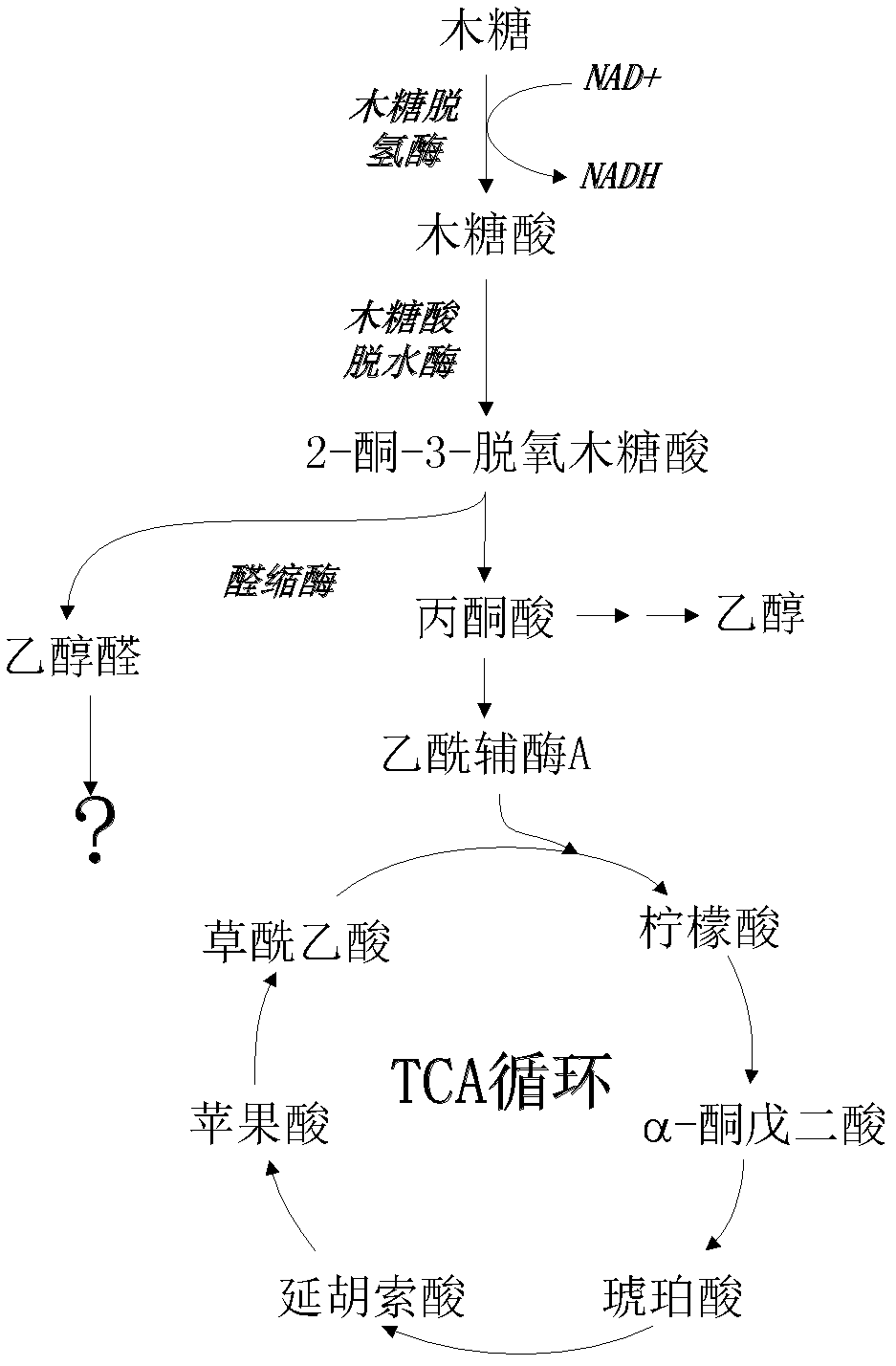
The invention discloses a brewing yeast strain capable of metabolizing xylose. The strain is a brewing yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) BSHH02B, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Feb. 8th, 2012, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC No. 5747. The strain carries a unique xylose metabolizing way, i.e. a molecular xylose generates a molecular pyruvic acid and a molecular glycolaldehyde through two mesostate, i.e. xylonic acid and 3-deoxyl-D-glycerol-ketopentose acid. By the xylose metabolizing way, the brewing yeast BSHH02B can quickly grow by using the xylose under an aerobic condition, and can be applied to the production of chemical products by using xylose-containing raw materials, wherein the chemical products include ethanol, glycol, carboxylic acid and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for producing a target substance by fermentation
ActiveUS9045789B2Efficient productionEfficiently assimilateHydrolasesOxidoreductases2-ketoglutaric acidXylonic acid
A target substance can be produced by culturing a bacterium having an ability to produce 2-ketoglutaric acid or a derivative thereof, and an ability to produce xylonic acid from xylose, which is imparted with xylonate dehydratase activity, 2-keto-3-deoxyxylonate dehydratase activity and 2-ketoglutaric semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity, or in which these activities are enhanced, in a medium containing xylose as a carbon source to produce and accumulate the target substance in the medium, and collecting the target substance from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Compositions comprising cellobiose dehydrogenase from Pycnoporus cinnabarinus and their use for the degradation of lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS9688966B2Speed up the processPromote degradationHydrolasesBiofuelsGlycosideGluconic acid
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +2
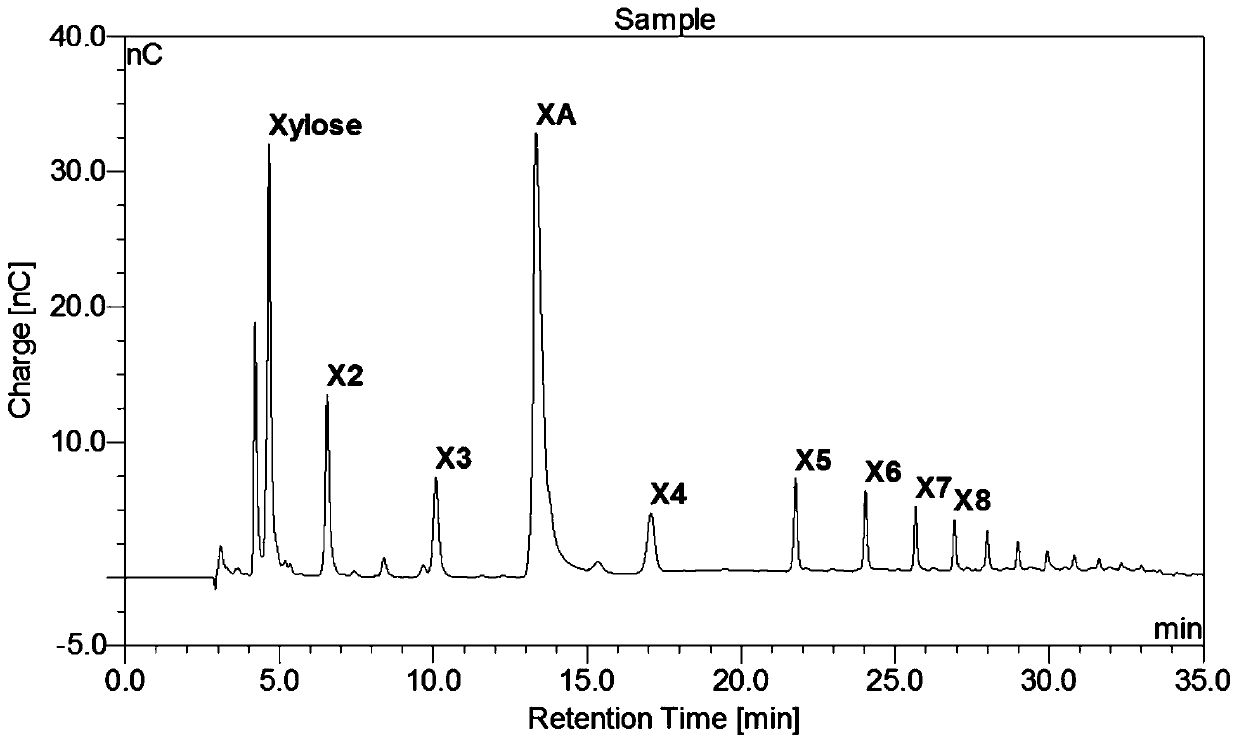
Method for producing xylooligosaccharide under catalysis of xylonic acid
ActiveCN110616238AHigh yieldLess xylose furfuralMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing xylooligosaccharide under catalysis of xylonic acid. The method for producing the xylooligosaccharide under catalysis of the xylonic acid comprises the following steps: mixing 1 part by mass of a xylan raw material and 5-12 parts by mass of the xylonic acid, and performing heating and stirring. Preferentially, the method for producing the xylooligosaccharide by fermentation under catalysis comprises the following steps: mixing xylose and bacteria, adjusting the pH, and performing stirring at low temperature; and adding the xylan raw material, andperforming heating and stirring. The method utilizes the reaction of microbial whole cell biological oxidation of the xylose to the xylonic acid, and uses the produced xylonic acid as a catalyst, andcompared with a product prepared by using acetic acid and other inorganic acids, the produced glycan prepared by using the xylonic acid is not easily excessively degraded, and has a high yield and less by-product xylose furfural.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Vegetable color protection preservative
InactiveCN107518066AEasy to keep freshGood color protectionFruit and vegetables preservationSodium acetateCarboxymethyl cellulose
The invention provides a vegetable color-protecting and fresh-keeping agent, which is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-5 parts of ligninic acid, 8-10 parts of sodium chloride, 0.5-1 part of L-cysteine, citric acid 5-8 parts, 1-2 parts of sodium deoxyacetate, 1-2 parts of Eucommia chlorogenic acid, 2-3 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. The vegetable color-preserving and preservative can well preserve the freshness of the vegetables, inhibit their respiration, slow down the nutrient consumption and chlorosis of the vegetables, and meanwhile have good color-protecting effect, is non-toxic and harmless, and is made of green materials.
Owner:成都三跨蔬菜农场
Synthetic method for xylonic acid
InactiveCN107337597ALow costWill not be deactivatedOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationActivated carbonOxygen
The invention relates to the field of xylonic acid production, and especially relates to a synthetic method for xylonic acid. The xylonic acid is obtained by using a d-xylose solution as a reaction liquid and activated carbon as a catalyst, introducing oxygen, adjusting the pH of the reaction liquid to 8-10, performing reaction, and performing separation and purification after the reaction is finished. According to the synthetic method for the xylonic acid provided in the invention, xylose is taken as a raw material, the activated carbon is taken as the catalyst, when the pH is 8-10, oxidation is conducted by the oxygen, and separation and purification are conducted after the oxidation is finished, so that the xylonic acid is obtained. According to the invention, the activated carbon is used as the catalyst of the synthetic method, so that the catalyst costs are lower than that of conventional heavy metals and the catalyst cannot be inactivated, and the catalyst can be used repeatedly; the speed of an oxidation reaction by using the oxygen is rapid, and the efficiency is high, so that the production costs are effectively reduced; and the purity of the xylonic acid crystal is equal to or more than 99%, the product quality is improved, resources are saved, and the effects are improved.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Highly efficient green agricultural and forestry waste pretreatment method
InactiveCN108660171AReduce processing costsReduce concentrationXylose productionFermentationPretreatment methodHigh energy
The invention belongs to the field of biomass resources, and particularly relates to a highly efficient green agricultural and forestry waste pretreatment method. The method comprises the following steps: (a) agricultural and forestry waste is mixed with the aqueous solution of acidic co-solvent to react, so that reaction liquid and solid residue are obtained; the agricultural and forestry waste contains hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin; and the acidic co-solvent is prepared from a sulfonic acid group and a hydrophobic group; (b) the concentration of the acidic co-solvent in the reaction liquid is decreased, so that lignin precipitate and xylose-containing acid liquor are obtained; and the solid residue is hydrolyzed under the existence of cellulase, so that glucose is obtained. The method uses the acidic co-solvent to treat agricultural and forestry waste, lignin in the agricultural and forestry waste can be removed under relatively mild reaction conditions, the defects of conventional treatment methods, such as high energy consumption, harsh reaction and sugar degradation, are overcome, the agricultural and forestry waste treatment cost can be reduced, and the yield of glucoseand xylose are increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
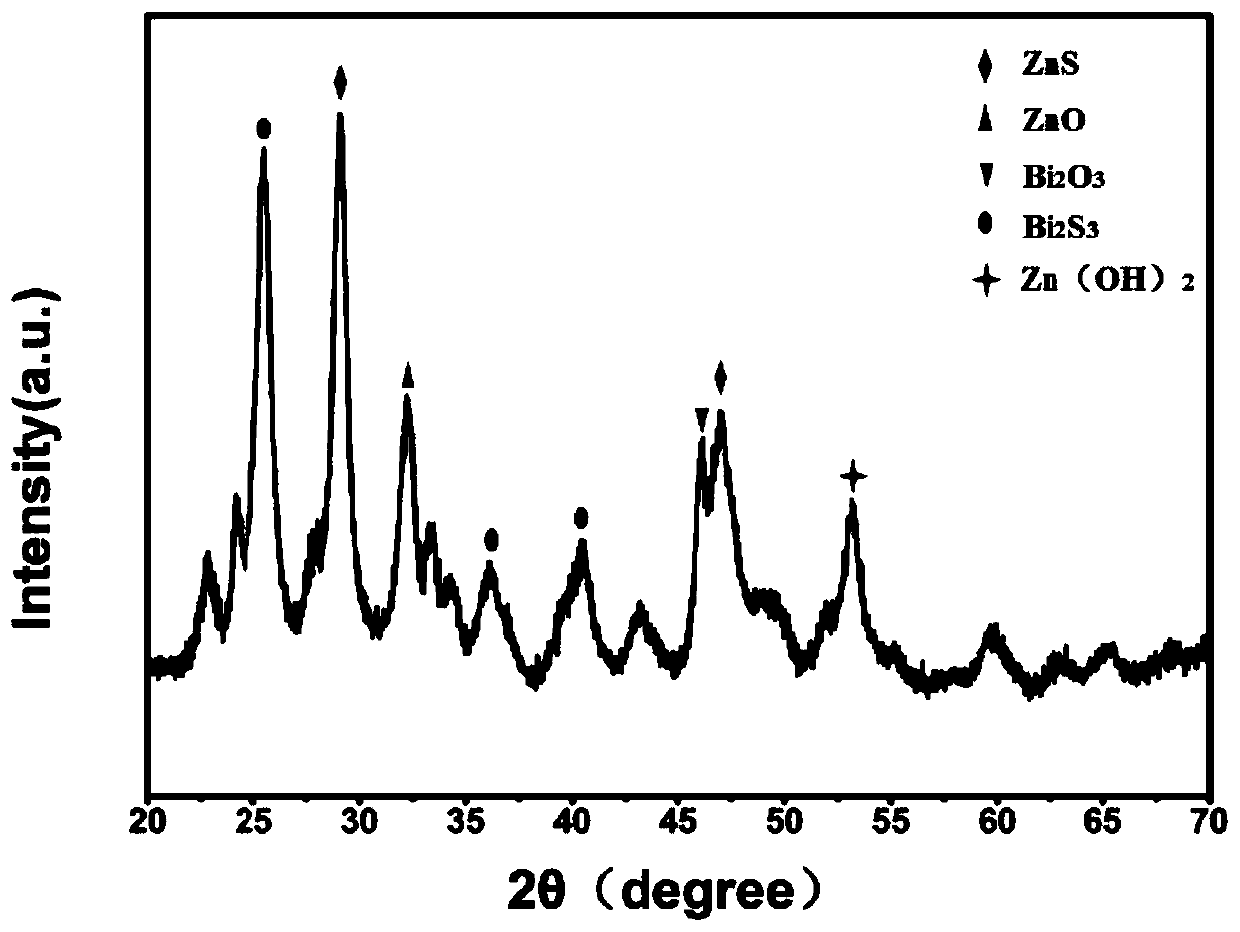
BiZn hydrotalcite photocatalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110433793ATypical two-dimensional sheet structureEasy to cleanOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationPhotocatalytic reactionFiltration
The invention discloses a BiZn hydrotalcite photocatalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof. The photocatalyst is two-dimensional ultra-thin BiZn nanosheets having a thickness of 5-10nm. The method includes (1) mixing a surfactant, ethylene glycol and water, then adding n-butanol, and stirring the solution until the solution is transparent; (2) adding a zinc salt and a bismuth salt, stirring the mixture, then adding thiourea or urea to obtain a mixture solution, and heating the solution for reaction; and (3) after heating is finished, performing cooling, filtration and dryingto obtain the BiZn hydrotalcite photocatalyst. The photocatalyst can be used for catalyzing xylose conversion to prepare xylonic acid. The method has advantages of low reaction condition requirements,low raw material costs, simple and feasible synthesis, and a reduced production cost so that the method has an industrial production potential. A photocatalytic reaction system different from the traditional thermal catalytic processes is energy-saving, safe and environmentally friendly.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
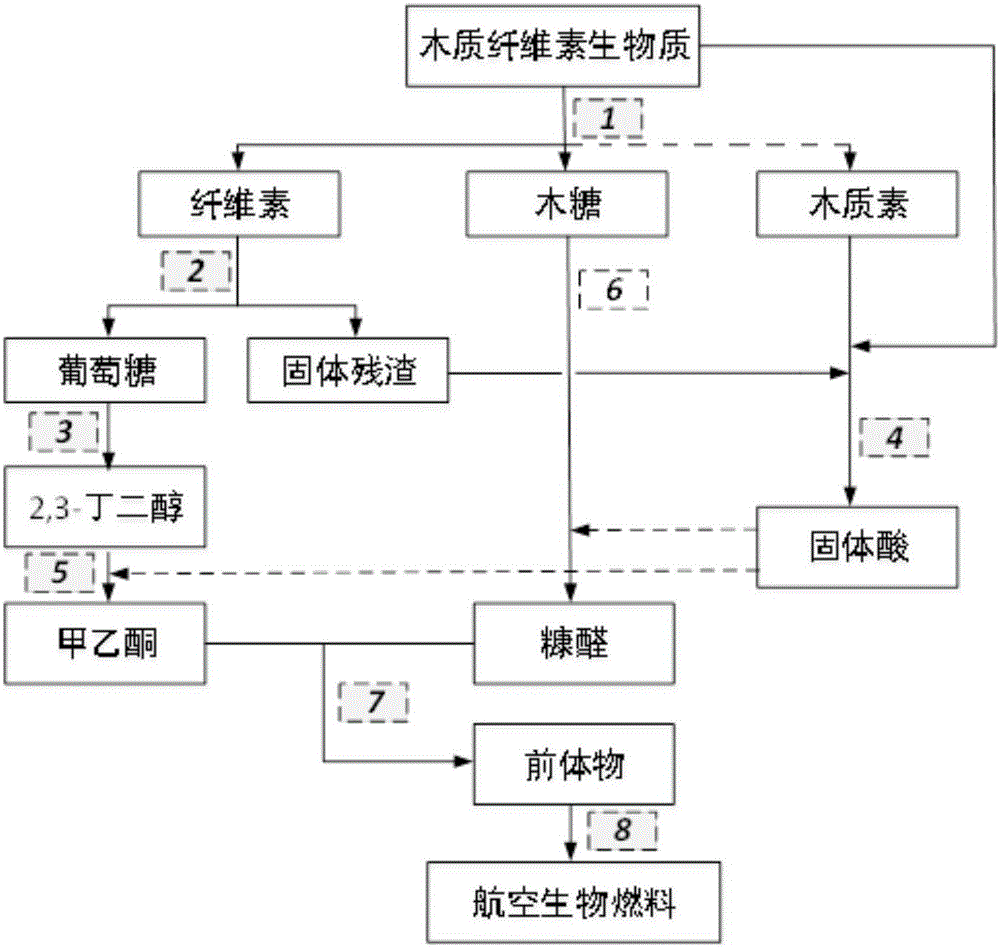
Method for preparing whole biomass base aviation biofuel
The invention provides a method for preparing whole biomass base aviation biofuel. The method includes the steps that raw materials are pretreated, cellulase catalytic hydrolysis is conducted, glucose is biologically fermented and converted into 2,3-butanediol, at least one of lignocellulose biomass, a lignin solid and solid enzymolysis residue is carbonized and sulfonated, xylonic acid is catalytically dehydrated and degraded into furfural, the 2,3-butanediol is subjected to acid catalysis dehydration and converted into methyl ethyl ketone, an aldol reaction happens to the furfural and the methyl ethyl ketone, and oxygen-containing precursor hydrodeoxygenation treatment is conducted. By the utilization of the method, the whole biomass base aviation biofuel with the main raw materials and catalysts coming from lignocellulose can be prepared, the raw materials are renewable, cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the lignocellulose are comprehensively used, atom economy and environmental friendliness are achieved, and the net emission of carbon dioxide is remarkably reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High performance building cast-in-place concrete and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a high performance building cast-in-place concrete and a preparing method thereof. The high performance building cast-in-place concrete is prepared from, by weight, 85-100 parts of sulphoaluminate concrete clinker, 20-30 parts of doped materials, 15-35 parts of granular river sand, 10-15 parts of botanical xylonic acid, 18-25 parts of perlite, 10-20 parts of rubber particles, 20-25 parts of aluminum silicate ceramic fiber, 10-15 parts of anhydrite, 10-20 parts of zeolite powder, 6-9 parts of admixture, 3-7 parts of modifier, 8-15 parts of early strength agent and 10-15 parts of grinding aid. According to the high performance building cast-in-place concrete and the preparing method thereof, effective matching of the sulphoaluminate concrete clinker, the doped materials, the granular river sand, botanical xylonic acid, perlite, the rubber particles, the aluminum silicate ceramic fiber, anhydrite, the zeolite powder, the early strength agent and the grinding aid is adopted, the prepared concrete is strong in crushing resistance and good in crushing resistant effect, qualitative change cannot occur, the production cost is low, the environment pollution can be reduced, and mineral resources are saved; the price is low, the production technology is simple, and the concrete is suitable for scale production.
Owner:芜湖浩权建筑工程有限公司
Method for preparing immobilized D-xylonic acid dehydratase
InactiveCN112063609AEfficient packagingKeep aliveOn/in inorganic carrierCarbon-oxygen lyasesPtru catalystMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for preparing immobilized D-xylonic acid dehydratase. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing the buffer solution of D-xylonic acid dehydratase with ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles modified by polydopamine to obtain mixed liquid; and (2) adding dopamine into the mixed liquid, standing, and carrying out centrifugation, wherein an obtained precipitate is the immobilized D-xylonic acid dehydratase. By use of the method disclosed by the invention, a magnetic nanometer material of a nuclear shell structure is used for efficiently packaging the D-xylonic acid dehydratase, and an obtained enzyme catalyst has convenient magnet recovery performance, long-acting catalysis service life, good enzyme activity stability and higher enzyme catalysis activity. A whole preparation process does not need expensive equipment and complex preparation technologies, a nano-enzyme preparation synthesis step is simplified, and the activity of the enzyme in the preparation process can be guaranteed to a maximum extent.
Owner:南京凯诺生物科技有限公司
Super-hydrophobic bean dreg nano-cellulose film and clean preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112411230APreparation Process GreenThe preparation process is simple and environmentally friendlyCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesRaw material divisionBiotechnologyPullulan
The invention discloses a preparation process of a super-hydrophobic bean dreg nano-cellulose film. The preparation process comprises the following steps: sieving bean dregs to obtain bean dreg powderwith a size of 20-100 meshes; adding 1-10% lipase to process the bean dreg powder to obtain pure bean dregs; mixing choline chloride and oxalic acid according to a molar ratio of 1: 1-1: 3, and adding xylonic acid to obtain homogeneous transparent liquid, so as to obtain a ternary eutectic solvent DES; adding DES into pure bean dregs according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1: 10-1: 40, adding a catalyst, and stirring and heating at 40-100 DEG C for 20-60 minutes to obtain a bean dreg cellulose solution; carrying out microwave treatment for 1-5 minutes, then carrying out 5-20 KHz ultrasonic treatment for 2-6 minutes, adding water to carry out reverse separation, and carrying out centrifugal separation to obtain pure bean dreg nano cellulose; adding 5-15% of pullulan and 0.05-2% of bee waxinto the bean dreg nano cellulose, the super-hydrophobic bean dreg nano-cellulose film is obtained through a coating method, the water contact angle can reach 150 degrees or above, and certain glycerin resistance is achieved.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A special fertilizer synergist for walnut trees
ActiveCN104163720BSignificant synergyReasonable ratioFertilizer mixturesMinor elementSodium Bentonite
The invention discloses a special fertilizer synergist for walnut trees, which is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10-16 parts of minor element, 20-30 parts of xylonic acid, 5-15 parts of zeolite powder, 1-10 parts of bentonite, 3-8 parts of composite amino acid, 0.1-2 parts of urease inhibitor, 4-10 parts of traditional Chinese medicine component, 0.5-1.5 parts of microbial inoculant, 1-3 parts of pesticide and 0.3-0.8 part of biological growth promoter. The synergist enhances the utilization ratio of the special fertilizer for walnut trees, supplements nutrient elements which can be easily deficient, inhibits harmful bacteria in the soil from propagation, and lays foundation for improving the soil.
Owner:吉林省新展望肥业有限公司
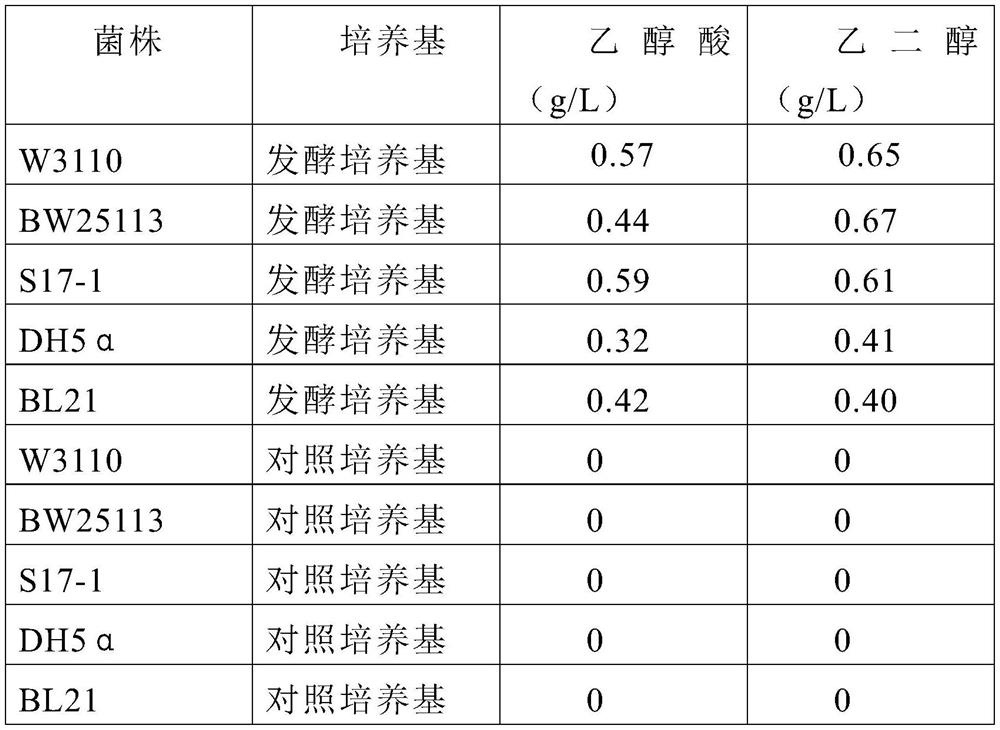
Method for producing ethylene glycol and glycolic acid by using escherichia coli and genetically engineered bacteria
InactiveCN112779197AImprove conversion rateIncrease production intensityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAldehyde oxidase
The invention discloses a method for producing ethylene glycol and glycolic acid by using escherichia coli and genetically engineered bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out fermenting by using the escherichia coli or the escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria by taking xylonic acid as a carbon source to produce the ethylene glycol and / or the glycolic acid, wherein the escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria are obtained by inactivating an aldehyde oxidase gene aldA or an alcohol dehydrogenase gene yqhD by the escherichia coli, or are obtained by over-expressing the aldehyde oxidase gene aldA or the alcohol dehydrogenase gene yqhD by the escherichia coli. According to the method disclosed by the invention, when the escherichia coli is used and the xylonic acid is used as the carbon source to carry out fermentation culture, the xylonic acid is metabolized in cells to generate the glycolic acid and / or the ethylene glycol and is accumulated in fermentation liquid, so that the conversion rate is relatively high and the production strength is high. Furthermore, the escherichia coli is subjected to inactivation or over-expression of the aldehyde oxidase gene aldA and the alcohol dehydrogenase gene yqhD, so that the conversion rate and the production strength of the glycolic acid and / or the ethylene glycol can be further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
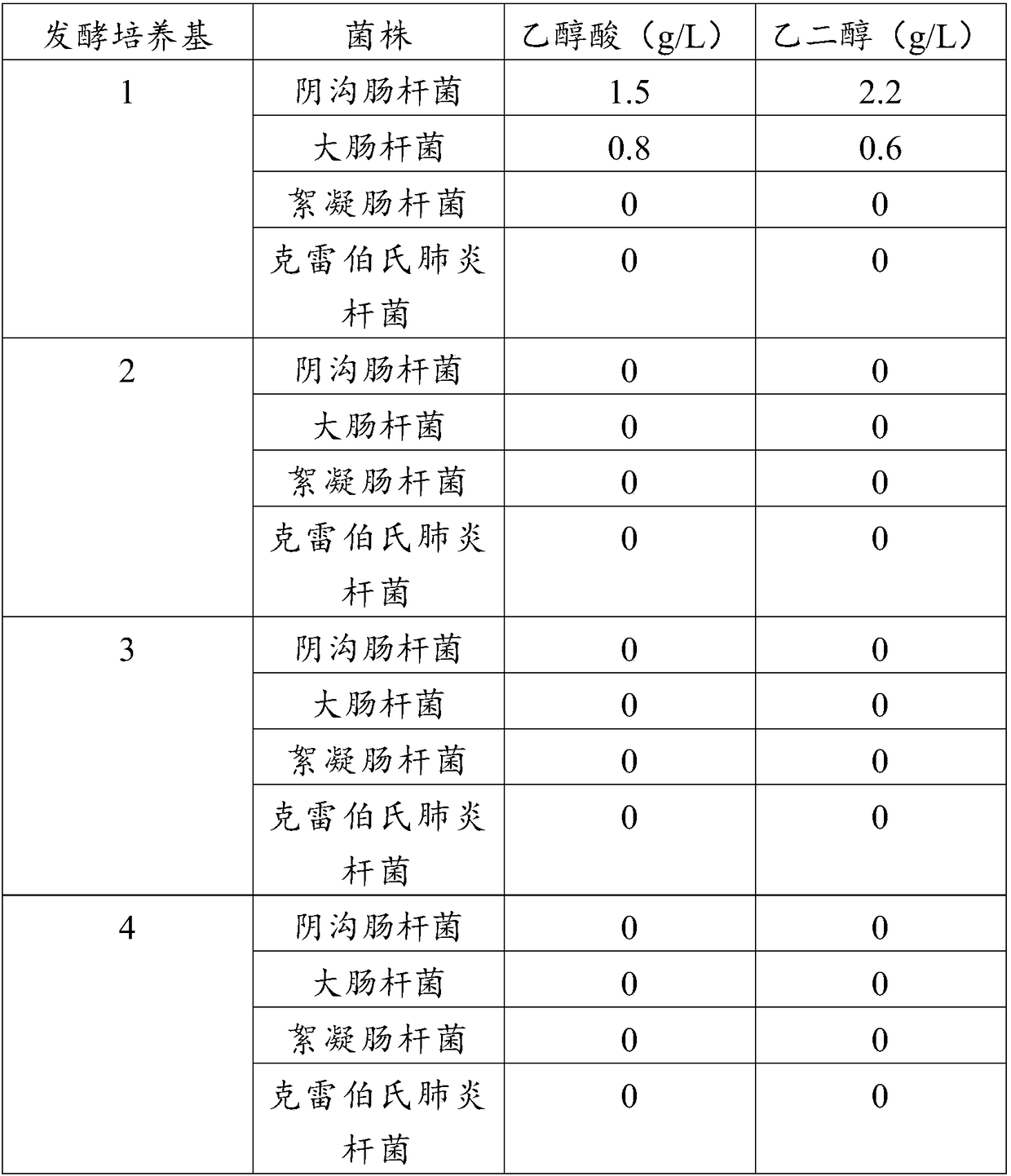
Method for producing glycol and glycollic acid by using xylose as raw material
ActiveCN109022505AHigh genetic stabilityTenacious growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliGluconic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing glycol and glycollic acid by using xylose as a raw material. In the method, xylose is used as a raw material and undergoes enzymatic conversion or fermentable conversion to generate xylosic acid; by using enterobacter cloacae and escherichia coli, xylosic acid is used as a substrate to undergo fermentation for production of glycollic acid and glycol under the neutral pH and aerobic conditions. The two production strains of the invention are wild-type strains, and have high genetic stability and strong growing power. The two strains for productionof glycollic acid and glycol have advantages of simple production process, high substrate conversion rate, low content of by-product and the like. The method of the invention has good application value and economic benefit.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Manufacture of xylonic acid
Provided is a method for producing xylonic acid from xylose with a recombinant fungal strain that is genetically modified to express a xylose dehydrogenase gene, which is able to convert xylose to xylonolactone, which is spontaneously or enzymatically hydrolyzed to xylonic acid. The xylonic acid is excreted outside the host cell. Xylonate production may be coupled with xylitol production. Alternatively, if xylitol production is not desired, its production is reduced by removing the aldose reductase (or specific xylose reductase) enzyme, which converts xylose to xylitol. Expression of a heterologous lactonase encoding gene may result in higher acid concentrations. The method is suitable for producing xylonic acid from a hemicellulose hydrolysate such as hydrolyzed lignocellulosic plant biomass.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com