Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Catechuic Acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for processing tea
ActiveCN101233880ASolve temperature problemsFix stability issuesPre-extraction tea treatmentTea flavoringPolyphenolChlorophyll
The invention pertains to a method for processing tea, in particular to a method for processing gyokurocha tea. The invention aims at providing a processing technique for producing a tea with excellent look, smell and taste to overcome the shortages of complex operation, high labor intensity, low production efficiency, small-scale production, low annual output and failing to meet the market demand in the traditional processing technique. The technical proposal of the invention is the method for processing the tea, which is characterized in that: the processing method comprises the following steps: (a) fresh tea spreading, (b) steaming the tea into green color and dewatering, (c) kneading, (d) drying for the second time, (e) stripping, (f) form regulation, (g) glazing, (h) adding fragrance, (i) selection. The tea processing method of the invention has the advantages of even and regular shape compared with the traditional technique, fragrance, tea water color, taste, color of the leaf bottom and higher content of chlorophyll, tea polyphenols, catechuic acid and theine better than the product produced by the traditional technique.
Owner:恩施市润邦国际富硒茶业有限公司
Acorus gramineus total phenylpropanoid extraction and total phenols extraction and method for preparing simultaneously
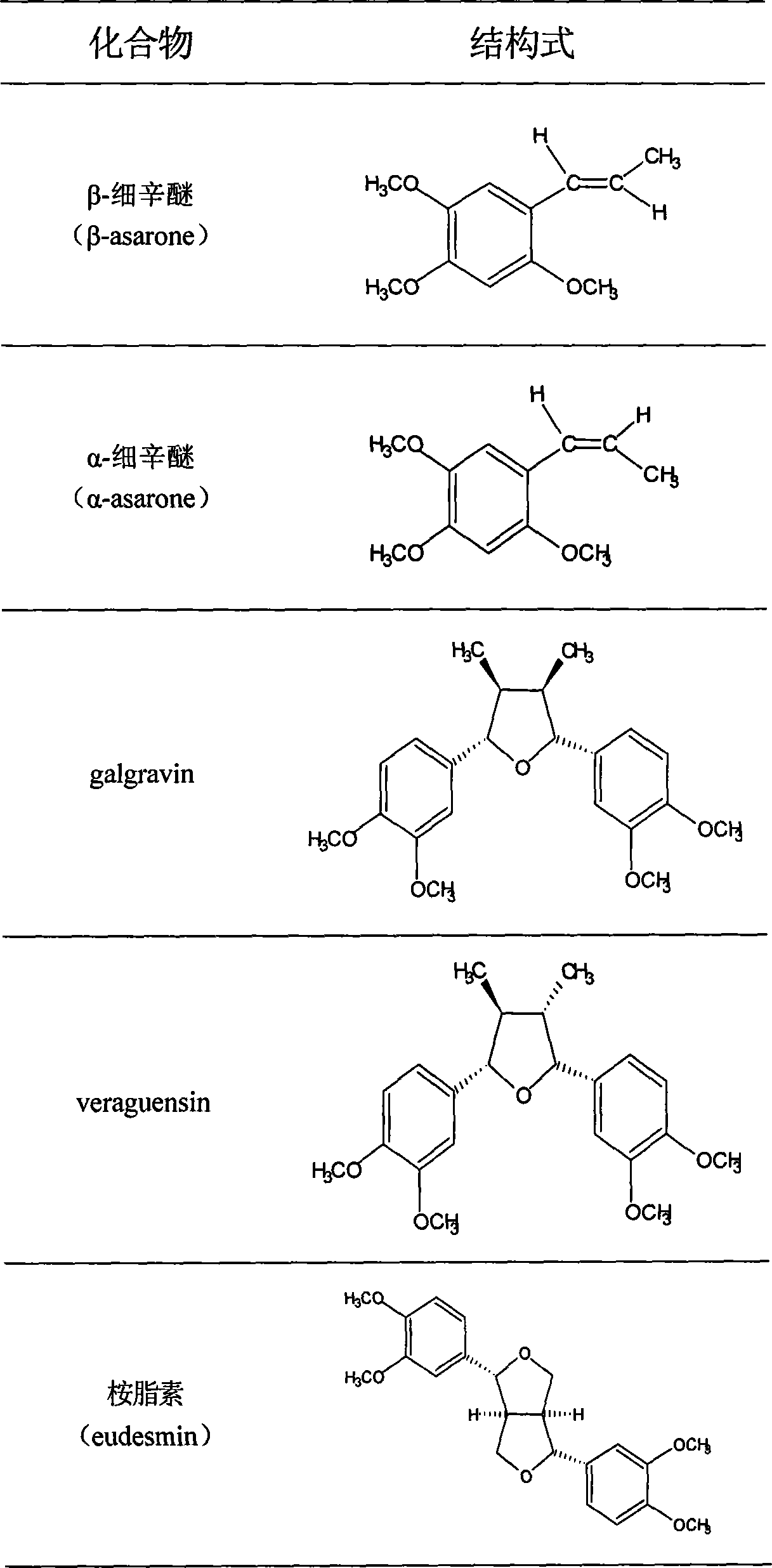
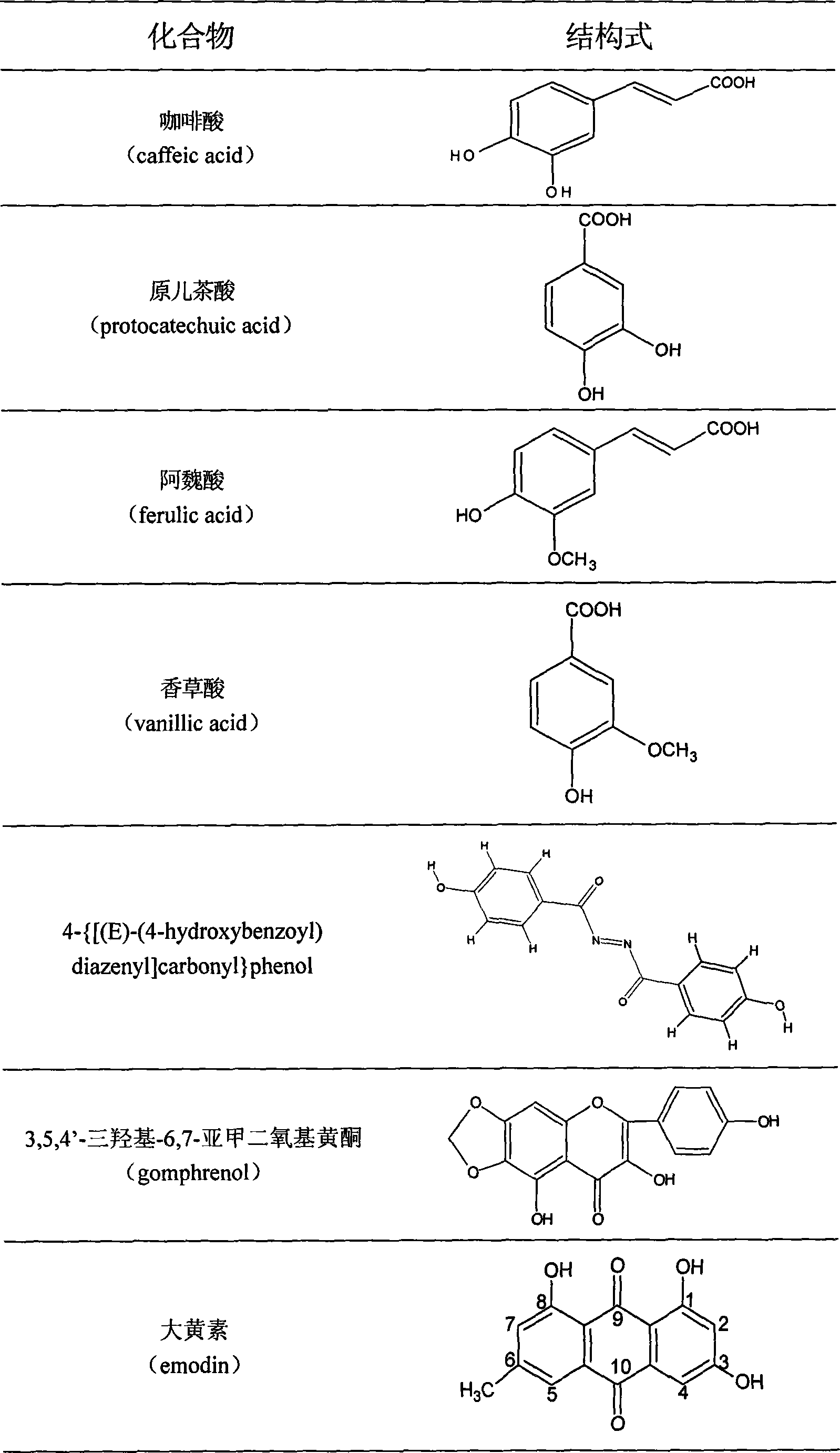
The invention discloses total phenyl propanoid extract and total phenol extract extracted from grassleaved sweetflag rhizome and its preparation method. Total phenyl propanoid extract mainly comprises beta -asaricin, alpha -asaricin, eudesmin, galgravin, veraguensin and other derivant with veraguensin as mother nuclide. Total phenol extract mainly comprises caffeic acid, protocatechuic acid, ferulic acid, vanillic acid and glucosides with vanillic acid as mother nuclide and other derivants. Total phenyl propanoid extract and total phenol extract of grassleaved sweetflag rhizome can be extracted through one or more of methods of solvent-extraction, solvent extraction, precipitation method, macroporous adsorbent resin, extraction by supercritical fluid, column chromatography, and liquid-liquid countercurrent distribution chromatography. Total percentage content of phenyl propanoids in the obtained total phenyl propanoid extract of Grassleaved sweetflag rhizome is 5-100% (w / w), wherein content of beta -asaricin and alpha -asaricin occupy 5-100% (w / w).Total percentage content of phenols in total phenol extract of grassleaved sweetflag rhizome is 5-100% (w / w), wherein content of caffeic acid and protocatechuic acid occupy 5-100% (w / w).
Owner:石任兵 +1
Electrostatic atomization apparatus
InactiveCN101314151ACause adverse effectsGet deodorizedElectrostatic spraying apparatusHigh pressureAir purifier
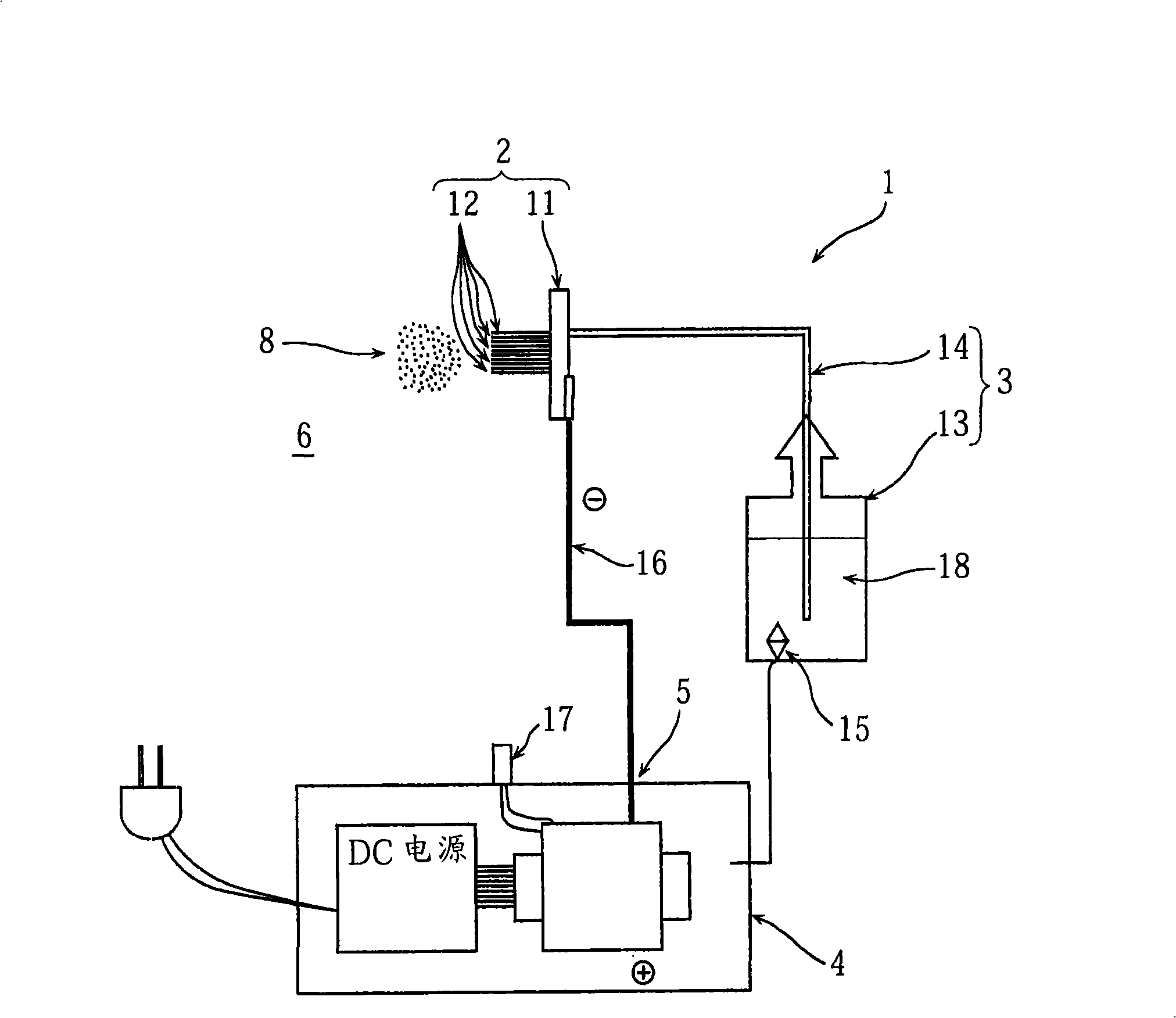
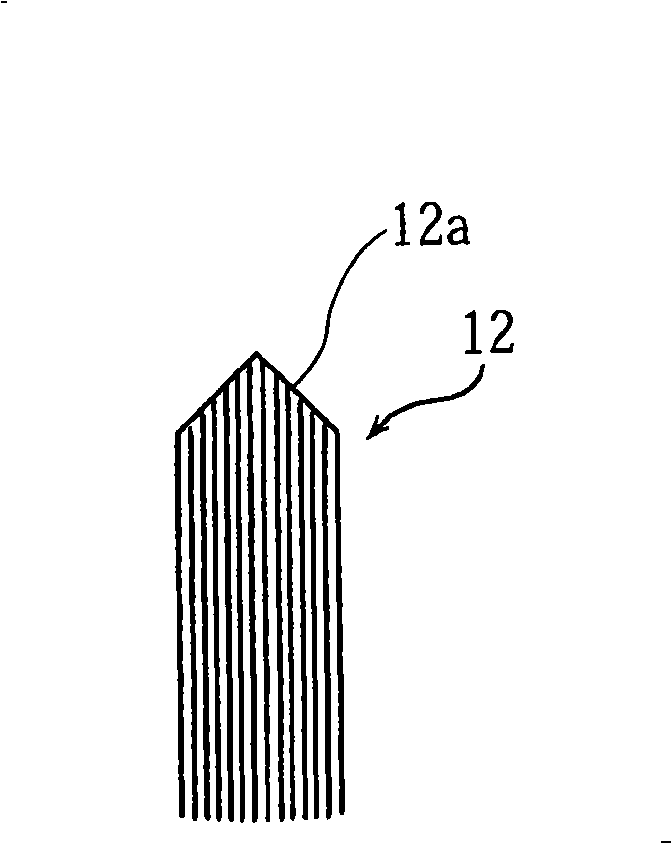
The invention provides an electrostatic atomization device which releases a large amount of ultrafine fog with nanometer dimensions from cold storages, air conditioners, air purifiers, humidifiers, cosmetic instruments and so on, to play the effects of deodorization, sterilization, preservation and so on, in rooms or the cold storages in order to improve indoor environment or the environment in the cold storages. The invention also provides an electrostatic atomization device which releases functional components such as vitamins or catechuic acid without volatility and so on, to the air in the form of the ultrafine fog with the nanometer dimensions. The electrostatic atomization device comprises that: a porous water retaining component (11) is protrudingly provided with a porous release pin component (12) to form a porous shaped body (2) with water absorptivity, water retention property and updraught characteristic, and the porous shaped body (2) is connected with a negative pole (5) to ensure that the porous shaped body (2) is electrified into a direct current high voltage power supply (4) with negative polarity. Moreover, an antipode of positive polarity corresponding to the negative polarity formed by electrifying the porous shaped body (2) does not exist.
Owner:TECHNO FRONTIER +1
Feed additive capable of improving anti-stress and immunity of ruminants and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106509415AMeet needsEnhance non-specific immunityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffEcological environmentPhosphate
The invention discloses a feed additive capable of improving anti-stress and immunity of ruminants and a preparation method thereof. The feed additive capable of improving the anti-stress capability and immunity of ruminants is prepared from the following raw materials: bacillus subtilis powder, lactobacillus plantarum powder, saccharomycete powder, catechuic acid, xylooligosaccharide, calcium fatty acids, chromium nicotinate, medical stone, vitamin C, vitamin B1, nicotinic acid, pine pollen, tricalcium phosphate, manganese sulfate, soy isoflavone, berberine, soya bean meal, versioolor swallowwort root, herba ephedra, futokadsura stem, herba potentillae chinensis, ford manglietia fruit, ciliate desert-grass, ajuga decumbens, tangerine leaves, cow soapwortseed and table salt. The feed additive capable of improving the anti-stress capability and immunity of ruminants contains multiplex vitamins, trace elements and Chinese medicinal herb ingredients, and all the ingredients achieve a synergistic effect, so that the intestinal micro-ecological environments of ruminants can be effectively improved, the quantity of pathogens is reduced, stress reaction is reduced to a great extent, the immunity is improved and thus the disease incidence of ruminants.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANYUAN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Pawpaw total phenolic acid extract and use thereof
InactiveCN101450127AEasy to prepareGood anti-inflammatory activityAntipyreticAnalgesicsChlorogenic acidAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a pawpaw total phenolic acid exact and its application for preparing anti-inflammatory medicament and food belonging to the medicine technology field. The exact prepared from pawpaw fruit of the invention is called pawpaw total phenolic acid exact because composition analysis shows that: its main component contains catechuic acid 30-35%, chlorogenic acid 20-25, and phenolic acid compounds 50-60%. Animal experiments shows that: the pawpaw total phenolic acid exact achieves substantial anti-inflammatory activity, consequently, can be used for preparing anti-inflammatory medicament or food. The invention provides a new approach for new anti-inflammatory medicament.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Sunscreen containing catechuic acid acetylated derivative
InactiveCN102784075AIncrease fat solubilityImprove bioavailabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBenzoic acidFormate
The invention provides sunscreen containing a catechuic acid acetylated derivative. The sunscreen is prepared from raw materials including water, propylene glycol, caprylic / capric triglyceride, catechuic acid EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) acetylated derivative, titanium dioxide, methoxycinnamic acid phthalic acid ester, C12-15 alkanol benzene formate, mineral oil, ethylhexyl salicylate, cetostearyl alcohol, steareth-2, methylparaben and essence. The sunscreen contains the catechuic acid EGCG acetylated derivative, ultraviolet absorptivity of catechuic acid EGCG molecules is used, lipid solubility of the sunscreen is improved by means of acetylation, bioavailability of the catechuic acid EGCG molecules in skin superficial cells is effectively enhanced, and accordingly, sun protection and ultraviolet injury repair effects are improved.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for protecting living body in radialization of UV-B using catechuic acid
Disclosed is a method for protecting living body in radialization of UV-B using catechuic acid, wherein catechuic acid is employed to preventing living body from radialization damage of UV-B, or recovering the living body damaged by UV-B. The content of [(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate(EGCG)] in the catechin is not lower than 40%, the content of ECG is not lower than 15%, the content of caffeine is no less than 2.5%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Synthesis and application of epoxy resin based on catechuic acid
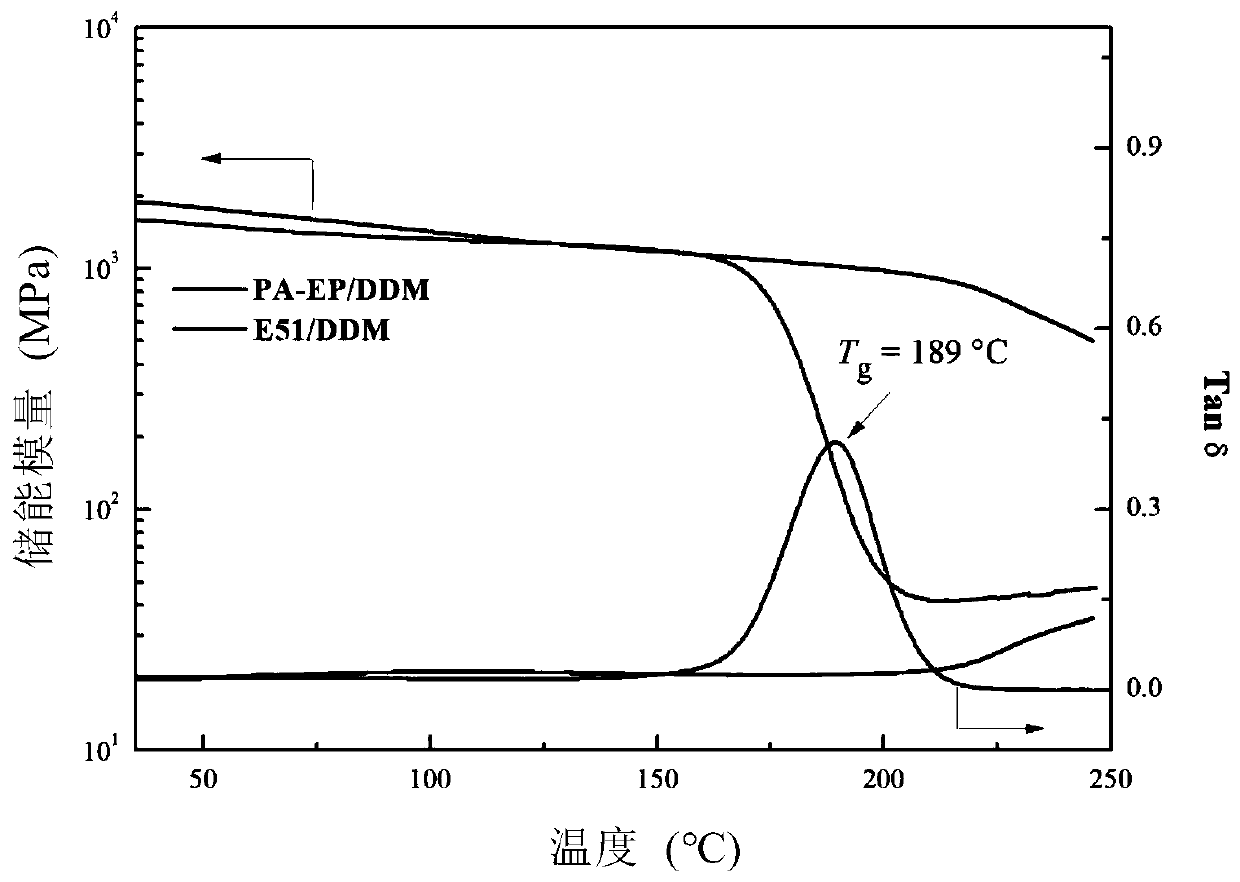
The invention provides synthesis and application of epoxy resin based on catechuic acid, and particularly provides a catechuic acid epoxidation monomer. The catechuic acid epoxidation monomer has a structure represented by formula I in the specification. The monomer can be cured to form catechuic acid epoxy resin, so that the catechuic acid epoxy resin is used for preparing aerospace special materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
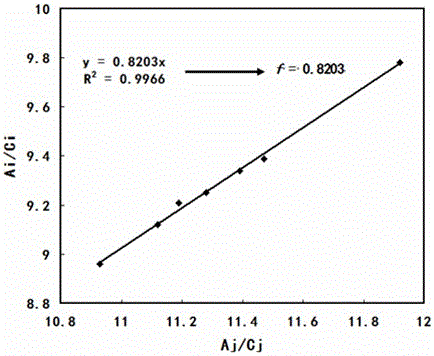
Method for determining content of catechuic acid in tea and tea products
ActiveCN104568930AStable in natureEasy to manufactureMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorbanceTea leaf
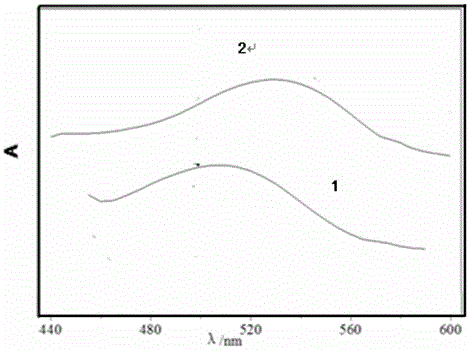
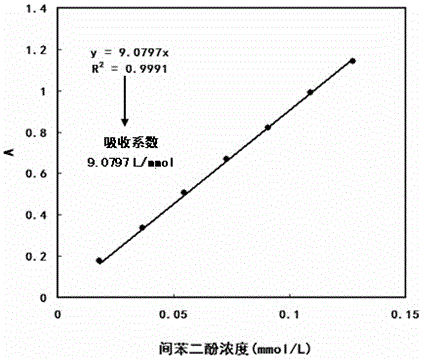
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of catechuic acid in tea and tea products. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a gradient standard solution by adopting resorcinol instead of catechuic acid reference substance, preparing a to-be-tested solution from tea or tea products, determining the absorbance of the gradient standard solution through a hydrochloric acid-vanillin developing system under the wavelength of 510nm, establishing a standard curve taking molarity as an x-coordinate and establishing a regression equation and then determining the absorbance of the to-be-tested solution, resolving the unit concentration of resorcinol in the to-be-tested solution from the regression equation, then calculating the content of catechuic acid in tea and tea products according to the dilution factor, resorcinol unit number contained in the unit relative molecular mass of the catechuic acid reference substance, and correction factor. The resorcinol used is stable in property, easily available and low in price, the problems that the resorcinol reference substance is limited in sources, expensive in price and high in determination cost can be solved, and the method is simple to operate, accurate in results and good in repeatability.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Heat-processed products having altered monomer profiles and processes for controlling the epimerization of (-)-epicatechin and (+)-catechin in the products
InactiveCN101218221AOrganic chemistryFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingIsomerizationHeating time
A method for controlling the isomerization of (-)-epicatechin to (-)-catechin in an epicatechin-containing product, preferably an edible product, which method comprises the step of heating the product at a temperature of up to about 190 DEG C. and at a pH of up to about 8. A method for controlling the isomerization of (+)-catechin to (+)-epicatechin in a catechin-containing product, preferably an edible product, which method comprises the step of heating the product, at a temperature of up to about 190 DEG C. and at a pH of up to about 8. Preferably, the temperature is from about 72 DEG C. to about 125 DEG C., the pH is from about 4 to about 7, and the time is at least about 15 seconds. Under either method, the isomerization may be carried out in an open food processor in a reduced oxygen atmosphere or in a closed food processor. The edible product may be pasteurized, boiled or sterilized during the isomerization. The isomerization is minimized by lowering the heating temperature, by lowering the pH, and / or by lowering the heating time. Conversely, the isomerization is maximized by increasing the heating temperature, by increasing the pH, and / or by increasing the heating time. The edible product may contain or be a fruit product, a vegetable product, a cereal product, a bean product, a nut product, or a spice product.
Owner:MARS INC
Processing method of green tea
InactiveCN108552335AStrong Green FlavorRich nutritional structurePre-extraction tea treatmentMaterials preparationOrganic acid
The invention belongs to the field of tea process and specifically relates to a processing method of green tea. The processing method comprises the following steps: material preparation, withering, rolling, fixation, secondary withering, hot rolling, drying and rewetting. According to the processing method of the green tea, by adjusting the processing steps, a green taste of the tea fully gives off and a flower fragrance is increased; fixation is performed after rolling, so catechuic acid, caffeine, amino acids, protein, organic acids and saccharides in the tea sufficiently interact with eachother to generate esters and other aromatic substances, so the nutrient structure of the tea is richer, aromatic components are increased and a bitter and astringent taste is reduced; and the green tea prepared by the processing method has light bitter and astringent taste and green taste, strong subtle fragrance, green and yellowish but not turbid tea liquor and good mouthfeel.
Owner:思南梵众白茶开发经营有限公司
A method for determining catechin content in tea leaves and tea products
ActiveCN104568930BStable in natureEasy to manufactureMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsLength waveAbsorbance
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of catechuic acid in tea and tea products. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a gradient standard solution by adopting resorcinol instead of catechuic acid reference substance, preparing a to-be-tested solution from tea or tea products, determining the absorbance of the gradient standard solution through a hydrochloric acid-vanillin developing system under the wavelength of 510nm, establishing a standard curve taking molarity as an x-coordinate and establishing a regression equation and then determining the absorbance of the to-be-tested solution, resolving the unit concentration of resorcinol in the to-be-tested solution from the regression equation, then calculating the content of catechuic acid in tea and tea products according to the dilution factor, resorcinol unit number contained in the unit relative molecular mass of the catechuic acid reference substance, and correction factor. The resorcinol used is stable in property, easily available and low in price, the problems that the resorcinol reference substance is limited in sources, expensive in price and high in determination cost can be solved, and the method is simple to operate, accurate in results and good in repeatability.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for simultaneously determining four components in herba cynomorii
InactiveCN107290442AGuaranteed separation effectAccurate methodComponent separationGallic acid esterGradient elution
The invention provides a method for simultaneously determining four components in a herba cynomorii-containing sample, in particular to a method for simultaneously determining gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, catechin and phlorizin in the herba cynomorii-containing sample by using a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). According to the method, a standard product solution and a sample solution are determined by using the HPLC, and multi-gradient elution is carried out by using acetonitrile and 0.05% of a glacial acetic acid solution as mobile phases, so that the four components can be determined. Compared with the chemical composition determination method in the prior art, the method provided by the invention is simple in operation process, good in repeatability and high in accuracy, avoids the consumption of time and cost, can be used as an effective method for quantitatively controlling the quality of herba cynomorii, and is also used for detecting herba cynomorii-related effective components in Chinese patent medicines.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI +1
Bacillus megatherium-containing desilting agent and application thereof in salt eliminating underground pipe
InactiveCN106010809AReduce plugging rateImprove dredging effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAdhesiveOxygen
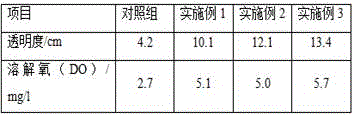
The invention provides a bacillus megatherium-containing desilting agent which comprises a biocatalyst, a nonionic surfactant, centella extract, ginger extract, liquorice extract, a bio-enzyme activator, ammonium molybdate, malic acid, protocatechuic acid, a vitamin complex, a matrix, a porous sodium activated zeolite powder carrier, halophilic bacteria, bacillus megatherium and an adhesive. The invention also provides an application of the bacillus megatherium-containing desilting agent in a salt eliminating underground pipe. By adopting the desilting agent provided by the invention, the chroma of water in the salt eliminating underground pipe is reduced that the residual chroma is reduced to 5.2-6.1 degrees after treatment; the salt content of water in the salt eliminating underground pipe is reduced that the salt content of water at an exit of the salt eliminating underground pipe is reduced to 0.47-0.49%; the hole blocking rate of the salt eliminating underground pipe is reduced that the hole blocking rate of water in the salt eliminating underground pipe is reduced to 10.0-11.2%; the desilting effect is good; and after one year of desilting, the dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water is as high as 5.0-5.7mg / l.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Use of protocatechuic acid and composition containing protocatechuic acid
InactiveCN111000838APrevent and/or ameliorate symptoms caused by high energy dietary intakeSmall toxicityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyLiver functions
The invention relates to a use of protocatechuic acid and a composition containing the protocatechuic acid, in particular to a use of protocatechuic acid in preparation of products for preventing and / or improving symptoms caused by high-energy diet intake, and the symptoms comprise obesity, metabolic diseases caused by excessive fat, impaired liver functions and intestinal flora disorder. Protocatechuic acid has a wide application prospect in the fields of medicines, foods and feeds. When protocatechuic acid is applied to high-fat feed, intestinal tract micro-ecological environment disturbanceand liver metabolism burden and damage caused by high-fat daily ration can be effectively eliminated, so that the utilization rate of nutrient substances by animals is increased, the immunity of theanimals is improved, and the production performance of the animals is improved.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Beautifying and restoring cream containing catechuic acid and preparation method of beautifying and restoring cream
InactiveCN106344455AGood at scavenging free radicalsPrevent excessive agingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAntioxidantPotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to the field of cosmetics, in particular to beautifying and restoring cream containing catechuic acid and a preparation method of the beautifying and restoring cream. The beautifying and restoring cream is mainly prepared from 5-9 parts of an antioxidant, 0.5-2 parts of an anti-allergy agent, 2.5-6 parts of a skin lightener, 2-12 parts of a humectant, 7-24 parts of an emollient, 0.03-0.2 part of potassium hydroxide, 0.1-0.3 part of a thickening agent, 1.5-5.8 parts of an emulsifying agent and 0.2-1 part of a preservative. The beautifying and restoring cream has the beneficial effects of delaying skin aging, increasing the skin elasticity and improving the skin color, as well as beautifying and whitening skin after being used for a long time.
Owner:FOSHAN JUCHENG BIOCHEM TECH RES & DEV CO LTD
Paracoccus-pantotropha-containing desilting agent and application thereof in salt drainage concealed pipes
InactiveCN106007305AIncrease the speed of sludge treatment in saline-alkali landImprove clearanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlkali soilAdhesive
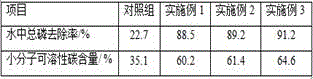
The invention provides a dredging agent containing pantotrophic paracoccus, which comprises biocatalyst, nonionic surfactant, extract of purslane, extract of peach leaf, extract of cactus, biological enzyme active agent, EDTA chelated boron , lactic acid, epicatechin, multivitamin, substrate, porous sodium-type activated zeolite powder carrier, halophilic bacteria, pantotrophic paracoccus, adhesive; the present invention also provides a desilting agent containing pantotrophic paracoccus Application in the salt-discharging hidden pipe; the dredging agent of the present invention has improved the speed of processing the saline-alkali land silt, and the time required for processing the saline-alkali land silt with a thickness of 8cm is 12-16 days; the mud removal rate per unit time has been improved, and within 1 year The sludge removal rate was 80.9‑82.6%; the dredging effect was good. After one year of dredging, the total phosphorus removal rate was 88.5‑91.2%, compared with 22.7% in the control group; the small molecule soluble carbon content was 60.2‑64.6%.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Transformant, and method for producing protocatechuic acid or salt thereof using same
Provided is a microorganism that is able to efficiently produce protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof by using a saccharide as a raw material, and a method of efficiently producing protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof by using the microorganism. Provided is a transformant having protocatechuic acid producing ability, subjected to modifications of enhancement of 3-dehydroshikimate dehydratase activity; enhancement of chorismate pyruvate lyase activity; and enhancement of 4-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase activity. Also provided is a method of producing protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof, including the step of culturing the transformant in a reaction solution containing a saccharide so as to cause the transformant to produce protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
Preparation method of catechin-chitosan loose nanofiltration membrane based on PAN-support
InactiveCN108816045AHigh Dye RetentionGood inorganic salt permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesWater contaminantsVitamin CCongo red
A preparation method of a catechin-chitosan loose nanofiltration membrane based on PAN-support, belongs to the technical field of a membrane. The invention allows two water-soluble natural substancesincluding catechin and chitosan to be blended at a certain ratio, and uses vitamin C and hydrogen peroxide as initiators, to adjust the pH value of the reaction, and to deposit chitosan modified by catechin on a PAN substrate. The obtained composite nanofiltration membrane has a relatively loose separation layer. The permeability of NaCl and Na2SO4 is 87.5% and 95.2% respectively, the rejection rate of the dyes including Congo red, magenta and crystal violet is 99. 6%, 98.7% and 98.5% respectively, and the permeate flux reaches 72L m<-2>h<-1>MPa<-1>.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A method and application of using microbial whole cells to catalyze the conversion of natural anthocyanins into protocatechuic acid
ActiveCN107058409BStable in natureEnsure safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFermentationCatechuic Acid
The invention discloses a method for converting natural anthocyanins into protocatechuic acid by using microbial whole cells to catalyze. The method uses complete cells of specific probiotics as biocatalysts, weakly acidic phosphate buffer as a medium, and natural anthocyanin extracts as a substrate to form a biotransformation anthocyanin system. The method of the invention has mild conditions, specific substrates and products, and significantly simplifies the subsequent purification process. It is a simple strategy for using microorganisms to bioconvert protocatechuic acid to anthocyanins, and no other organic matter is added during the fermentation process, which reduces the impact on the environment. possible contamination. The content of protocatechuic acid converted into the target product can reach up to 33mg / L. The invention is of great significance for in vitro research on the mechanism of microbial metabolic conversion of anthocyanin, and also provides a theoretical basis for the direct application of natural anthocyanin conversion products to probiotic fermented food.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Modified protocatechuic acid liposome for preservation and fresh keeping of shrimps and crabs, and preparation method and application of modified protocatechuic acid liposome
ActiveCN112136874AGood chemical stabilityAvoid breedingFood ingredient as antioxidantFood freezingCholesterolCitrus Pectin
The invention relates to the technical field of processing and fresh-keeping of aquatic products, and discloses a modified protocatechuic acid liposome for preservation and fresh keeping of shrimps and crabs, and a preparation method and application of the modified protocatechuic acid liposome. The modified protocatechuic acid liposome comprises the following three layers of structures from insideto outside: a protocatechuic acid core part, a soybean lecithin / cholesterol / vitamin E composite layer and a citrus pectin / aminated bacterial cellulose composite layer. According to the modified protocatechuic acid lipidosome, the protocatechuic acid lipidosome is coated with the citrus pectin / aminated bacterial cellulose composite layer, so that the viscosity of the lipidosome can be improved, the lipidosome has higher stability, and the functions of slowly releasing protocatechuic acid and retaining water can be better exerted.
Owner:OCEAN RES CENT OF ZHOUSHAN ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compound microemulsion fresh-keeping agent for fish as well as preparation method and application of compound microemulsion fresh-keeping agent
InactiveCN109122817AInhibit color deteriorationGood storage stabilityFood ingredient as antioxidantMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsAdditive ingredientGlycerol
The invention discloses a compound microemulsion fresh-keeping agent for a fish as well as a preparation method of the compound microemulsion fresh-keeping agent. The compound microemulsion fresh-keeping agent for the fish, which is prepared by dispersion phase preparation, continuous phase preparation, mixing and homogenization, comprises the following ingredients by weight percentage: 6-12% of asurfactant, 0.2-0.5% of food grade absolute ethyl alcohol, 1-2% of chitosan, 0.5-2% of succinic acid, 1-3% of catechuic acid, 1-2% of acetic acid, 0.5-1.5% of glycerol, 0.5-1.5% of thyme essential oil and 75.5-89.3% of water. The compound microemulsion fresh-keeping agent for the fish prepared by the invention is used for fresh keeping of the fish, can inhibit activity change of fish endogenous protease, a protein degradation process caused by a microbial spoilage effect and color deterioration due to fish lipid oxidization, slows down fish texture and color deterioration, and improves the storage stability of a fish product.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Multi-component content detection of ginkgo armillaria mellea oral solution and construction of a fingerprint spectrum method of the ginkgo armillaria mellea oral solution
The invention relates to multi-component content detection of a ginkgo armillaria mellea oral solution and construction of a fingerprint spectrum method of the ginkgo armillaria mellea oral solution. The content detection analysis method established by the invention is good in precision, reproducibility, stability and sample recovery rate. Therefore, the content detection method is simple and convenient to operate, accurate and reliable, and can be used for determining the content of the gingko armillaria mellea oral solution. According to the fingerprint spectrum detection method, 19 characteristic fingerprint peaks in the gingko armillaria mellea oral solution can be detected at the same time, and 15 fingerprint peaks, namely uridine, adenosine, guanosine, acesulfame potassium, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, sodium benzoate, rutin, isoquercitrin and the like, are identified through a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology and comparison of a reference substance. The detection method can be used for controlling the quality of the gingko armillaria mellea oral solution.
Owner:QIONGLAI TIANYIN PHARM CO LTD
Composition for relieving vomitoxin poisoning of pigs, feed additive, feed and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113966788AProductivity declineAlleviate and repair damageFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention relates to a composition for relieving vomitoxin poisoning of pigs, a feed additive, a feed and a preparation method thereof. The composition for relieving vomitoxin poisoning of pigs comprises quercetin, protocatechuic acid, a schisandra chinensis extract and cardamine hirsute. The invention further provides a feed additive or feed prepared from the composition for relieving pig vomitoxin poisoning and a preparation method of the feed additive or feed. According to the composition, the feed additive and the feed for relieving vomitoxin poisoning of the pigs, the reduction of the production performance of the pigs caused by vomitoxin can be remarkably relieved, and the intestinal tract structure, the digestion function and the barrier function are remarkably improved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Alcaligenes family aerobic new bacterium T-4 and application thereof
ActiveCN113652375AEfficient degradationWill not cause secondary pollutionTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaBiotechnologyBenzoic acid
The invention discloses an aerobiotic bacterium T-4 of alcaligenes family and application thereof. The alcaligenes aerobic bacterium T-4 is preserved in CGMCC, the preservation date is September 11, 2019, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.18488. According to the invention, a single strain T-4 is adopted for aerobic culture at 50 DEG C to effectively degrade terephthalic acid, and the degradation rate reaches 100% when the initial concentration does not exceed 50mM. The strain can be used for treating terephthalic acid wastewater, can also be used for completely degrading biodegradable plastics containing terephthalic acid groups in compost or soil environment, and can also be used for other important phenyl compounds, e.g. degradation of m-phthalic acid, protocatechuic acid, benzoic acid, m-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-formylbenzoic acid, bisphenol A and 4,4-diaminodiphenylmethane. The strain does not cause secondary pollution, and has wide application prospects in the environmental restoration aspect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and application thereof in preparation of protocatechuic acid
ActiveCN113201466ASolve the use problemRealize high-value utilizationFungiTransferasesGenetic engineeringMethyl palmoxirate
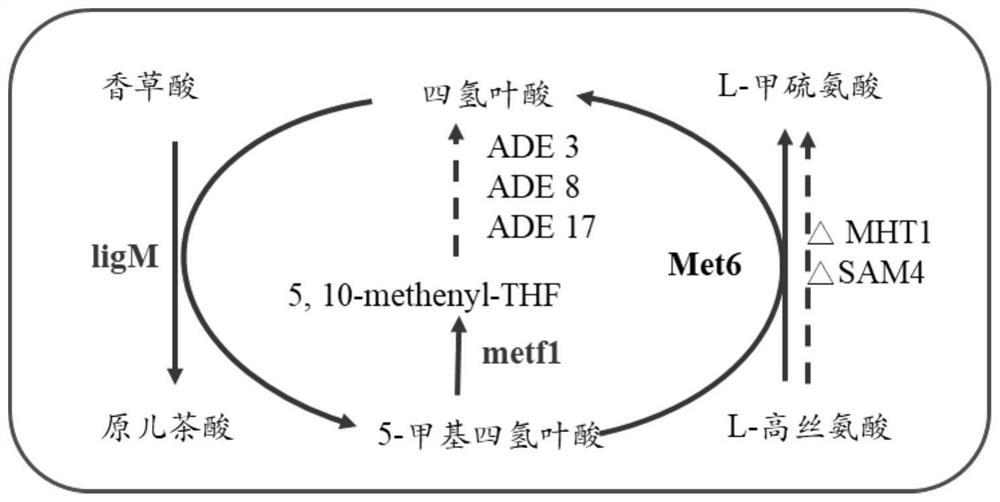
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular to saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and application thereof in preparation of protocatechuic acid. According to the invention, on the basis of saccharomyces cerevisiae without ADH6, ADH7 and BDH2 genes, at least one of exogenous genes 4CL, ECH, vdh, vanA, vanB, metf1 and ligM is transferred; an endogenous gene MET6 is over-expressed; and / or at least one of endogenous genes MHT1 and SAM4 is knocked out, a new lignin bioconversion path is constructed in the yeast body, the path regulates and controls the demethylation of tetrahydrofolate metabolism intensified strains through the modification of the genes to promote the conversion of vanillic acid to synthesize protocatechuic acid, and the purpose of synthesizing protocatechuic acid by using lignin monomers and lignin is achieved. Not only can the utilization problem of the lignin be solved, but also the protocatechuic acid which is an important chemical raw material can be generated, and high-value utilization of the lignin is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for improving the color and texture quality of vacuum freeze-dried reconstituted strawberry chips
ActiveCN112544919BImprove stabilityLimited dissociationFood freezingFood homogenisationFreeze-dryingGlucoside
The invention discloses a method for improving the color and texture quality of vacuum freeze-dried recombined strawberry chips, which comprises the following steps: step 1, crushing strawberries to obtain strawberry pulp, mixing the strawberry pulp with pectin and protocatechuic acid evenly, And adjust pH to 3.0~3.8 to obtain material A; Wherein, the mass ratio of strawberry pulp and pectin is 1:0.02~0.08, the mass concentration of protocatechuic acid in material A is 0.1~1.0g / kg; Step 2, the material A is poured into a mold tray, placed in a freezer at -18°C for freeze-thaw processing to obtain block material B; step 3, coating a layer of chitosan on the surface of material B to obtain material C; step 4, placing material C in Dry in a vacuum freeze-drying box, and then pack with nitrogen filling to obtain strawberry crisps. The invention creates a brand-new recombined strawberry crisp, which effectively solves the problems of unstable storage period of the product geranium-3-glucoside and low hardness and brittleness of the product.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for increasing polyphenol content in tartary buckwheat by high-pressure coupling germination
ActiveCN112492918AReduced germinationIncrease health functionSeed and root treatmentVanillic acidHypericin
The invention discloses a method for increasing polyphenol content in tartary buckwheat by high-pressure coupling germination. The method comprises the following steps of (1) putting tartary buckwheatseeds into a vacuum bag, and conducting vacuumizing and sealing; (2) putting the tartary buckwheat seeds into ultrahigh-pressure equipment for high-pressure treatment; (3) soaking the tartary buckwheat seeds in a sodium hypochlorite solution with the mass concentration of 1%; (4) washing to be neutral, and then adding hot water for heat treatment; and (5) cooling the tartary buckwheat seeds to room temperature after heat treatment, then sprouting under a constant temperature condition, and watering and supplementing water in the sprouting process. The method has the advantages that the content of vanillic acid, hypericin, aromadendrin, catechin, acetosyringone and catechuic acid can be remarkably increased under the stress action of 20 MP-30 MP ultrahigh pressure, and the health-care function of the tartary buckwheat in the aspect of oxidation resistance is improved.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV +1
Phytoceutical compositions for pets
This invention comprises applying phytoceutical compositions to pets, which given their sedentary life and nutrition, are susceptible to a higher prevalence of cancer and degenerative diseases. The compounds contained in said compositions frequently have anti-oxidizing properties acting to inhibit harmful reactions of free radicals; and free radicals are often a cause of cancer. Said compositions comprise extracts or concentrates obtained from the enzymatic or alkaline hydrolysis of several plant sources, containing effective concentrations of two or more phenolic compounds, such as ferulic acid, coumaric acid, caffeic acid, protocathecoic acid, and vanillic acid.
Owner:BIOKAB S A DE
A method for the simultaneous determination of 22 flavonoids and phenolic acids in citrus fruits
ActiveCN108490094BSimple and fast operationImprove accuracyComponent separationBenzoic acidChlorogenic acid
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining twenty-two flavones and phenolic acids in citrus fruits by adopting high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-fluorescence detector (HPLC-DAD-FLD). The method is capable of simultaneously determining twenty-two phenolic compounds in citrus fruits such as gallic acid, synephrine, chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid,caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, rhamnosylvitexin, eriocitrin, ferulic acid, rutin, benzoic acid, narirutin, naringin, hesperidin, diosmin, neohesperidin, quercetin, naringenin, kaempferol, nobiletin,hesperetin, acacetin and the like, derivatization is not needed, and the method is high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and excellent in repeatability.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com