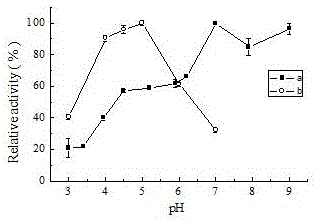
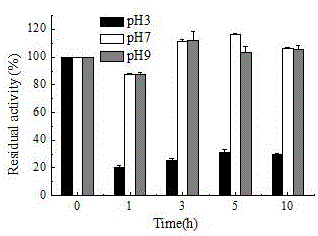
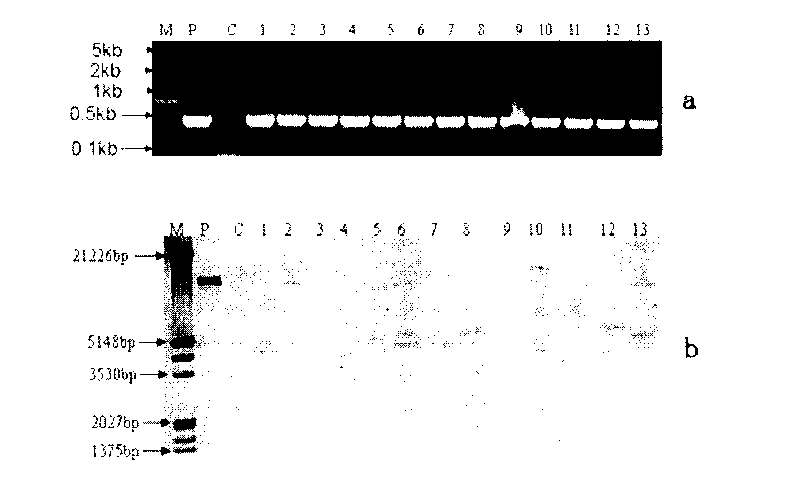
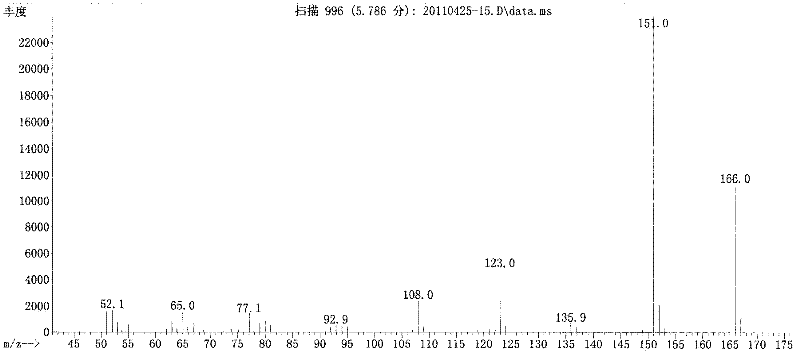
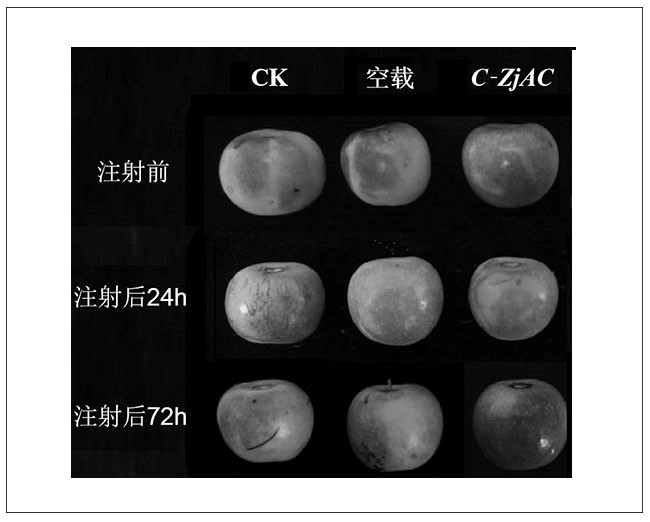
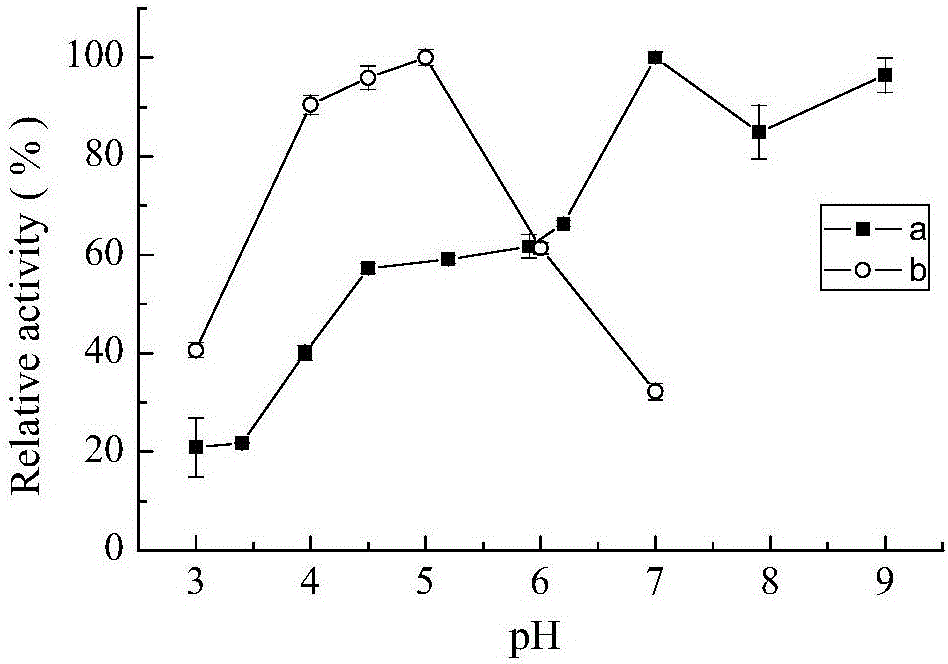
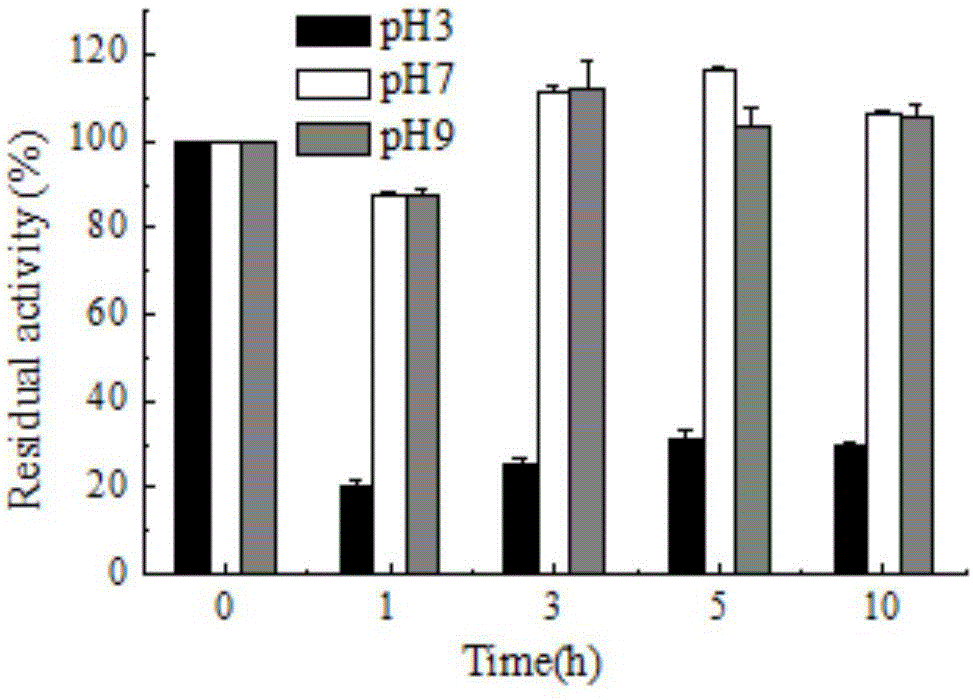
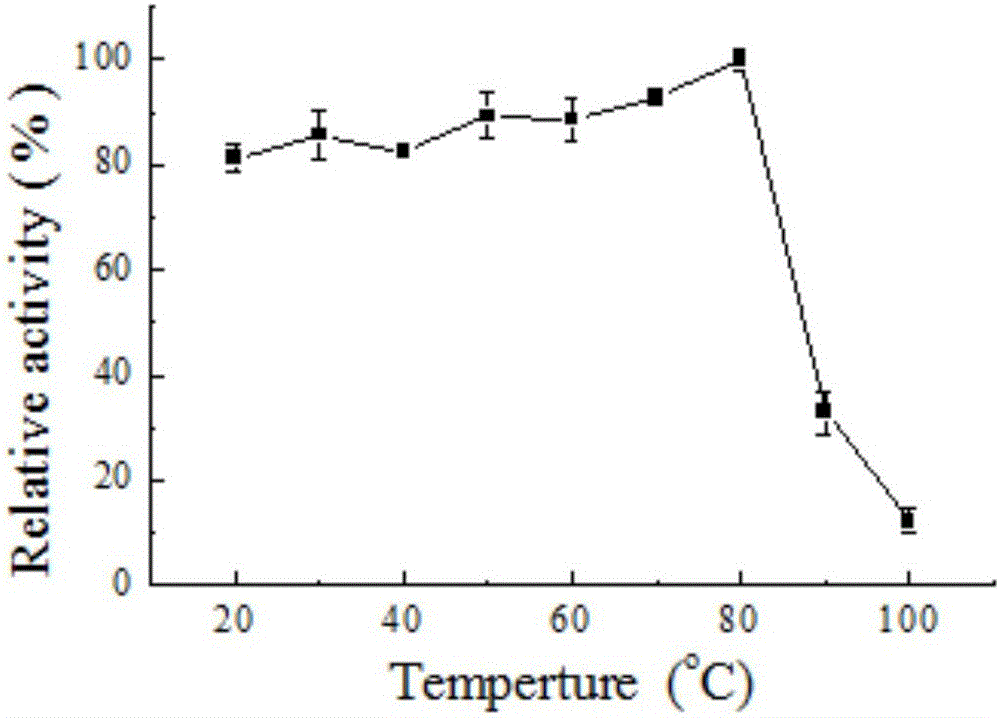
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Acetosyringone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
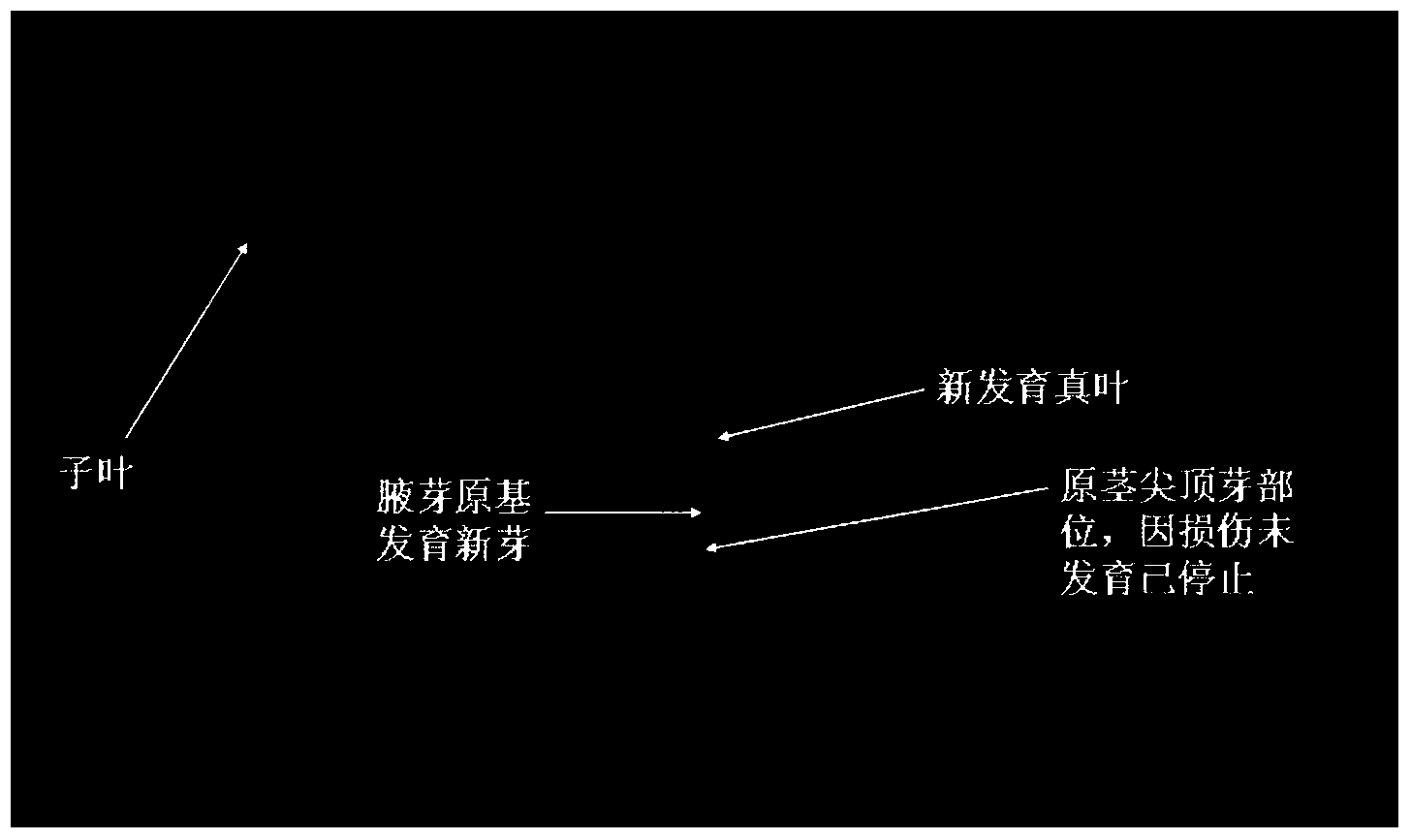
Acetosyringone is a phenolic natural product, and is a chemical compound related to acetophenone and 2,6-dimethoxyphenol. It was first described in relation to lignan/phenylpropanoid-type phytochemicals, with isolation from a variety of plant sources, in particular, in relation to wounding and other physiologic changes.
Efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink
InactiveCN105296535ASolving questions about gene functionGenetic engineeringFermentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses an efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink. A specific primer is designed according to a coding gene sequence of PDS (phytoene desaturase), and about 500bp cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments are amplified in the Chinese pink through RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction). Obtained PDS cDNA fragments are connected to TRV2, and acetosyringone concentration, seedling age and preculture temperature after infection as well as light conditions for plants after preculture are integrated in an assorted manner by optimizing an agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silence system according to photobleaching frequency, bleached leaf area and bleached conditions of the plants, so that the rapid efficient virus-induced silence system is established, virus-induced gene silence character can be obtained, and further, the problem that Chinese pink gene functions are verified effectively is solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Laccase CotA and application thereof
InactiveCN106047827AIncrease alkalinityImprove stabilityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesChemical structureHigh concentration
The invention discloses laccase CotA and application thereof. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequences of the laccase CotA are shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and amino acid sequences of the laccase CotA are shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The laccase CotA and the application have the advantages that the prepared laccase CotA is mature in operation, easy and convenient to operate, high in enzyme activity and wide in pH (potential of hydrogen) and temperature catalysis range, is good in stability in high-salinity and high-concentration organic solvents under alkaline and high-temperature conditions and is high in applicability as compared with fungal laccase; synthetic dye with different chemical structures can be effectively decolorized by the laccase CotA under the condition of participation of acetosyringone which is a mediator substance, excellent decolorization effects still can be kept under alkaline conditions, and accordingly the laccase CotA has an excellent application prospect in the aspect of treatment on industrial dye wastewater.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Agrobacterium-mediated cotton transgenic method independent of tissue culture
InactiveCN101691583ASimple transformation systemAvoiding Somaclonal VariationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTransformation systemsMoisture
The invention relates to an agrobacterium-mediated cotton transgenic method independent of tissue culture, belonging to the biotechnology field. The method comprises the following steps: dispensing agrobacterium-sucrose solution with 0.05% of surfactant Silwet L-77 and 40mg of 1-1acetosyringone on stylus in the afternoon of cotton fertilization or in the morning on the next day; preserving moisture for two days; harvesting seeds and performing resistance authentication; extracting DNA and performing PCR and Southern blot detection; and obtaining transgenic plants by multiple treatments. The transformation ratio ranges from 0.05% to 0.65%, thus proving the repeatability and reliability of transformation systems of agrobacterium-dipped cotton stylus. Compared with the traditional transgenic method dependent on tissue culture, the transformation method of the agrobacterium-dipped cotton stylus is simpler, more convenient, more economical and efficient, and simultaneously can avoid problems of limitation by cotton genetype and easy occurrence of somaclonal variation and the like in the process of tissue culture.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing acetosyringone and vanillyl ethyl ketone by oxidizing lignin
InactiveCN102295547AEfficient use ofHarm reductionCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationGas liquid chromatographicNitrobenzene
The invention discloses a method for preparing acetovanillone and acetosyringone (AS) through oxidation of lignin by using an oxidizing agent. According to the method, an oxidizing agent reacts with the lignin in an alkaline solution; the resulting reaction solution is subjected to acidification, extraction and concentration to obtain the crude product after completing the reaction; the treatments of recrystallization and rectification are performed to obtain the acetovanillone and the AS. The oxidizing agent is the one selected from p-nitrobenzoic acid, 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid, 3-nitrosalicylic acid, 5-nitrosalicylic acid or 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid. According to the present invention, the oxidizing agent has low toxicity, such that the harm to the environment can be reduced; the post-treatment steps are simplified, and the uses of the organic solvents are reduced, such that the secondary pollution to the environment is reduced; the yield is relatively high, the purities of the products are respectively 97.3% and 98.2% through the gas chromatography analysis; the two important chemical raw materials of guaiacol and lilac alcohol can be synchronously obtained when preparing the acetovanillone and the AS.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Transgenic method of agrobacterium-mediated rape field
InactiveCN101748148AReduced transforming activitySimplify the collection processGenetic engineeringFermentationSucroseBud
The invention discloses a transgenic method of an agrobacterium-mediated rape field. The method comprises the following steps: eluting an agrobacterium on a YEB solid plate with 1 / 2 MS fluid nutrient media which comprises 5% of sucrose, 0.05-0.1% of Silwet-77, 0.2-0.4% of acetosyringone and 0.0001-0.0002% of 6-BAP by concentration; removing blooming flowers from a main inflorescence and each branched inflorescence and only leaving buds when the buds of a principal branch and part of lateral branches of the rape and a plurality of flowers bloom before the conversion; bundling the inflorescences immediately after soaking in eluted conversion bacterium liquid for 30 seconds; continuously dip-dyeing one inflorescence for 3 times with an interval of 2-3 days; and removing a parchment bag on the inflorescence and the flowers and buds at the top end of the inflorescence. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, high transgenic efficiency and no genotype dependence, thereby having excellent potential application in the aspects of culturing rapes of new species by utilizing the gene engineering means and establishing rape mutant libraries.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated explants genetic transformation method
InactiveCN105238813ANot too much growthNot overgrownFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyTransformation efficiency
The invneiton discloses an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated explants genetic transformation method, which comprises agrobacterium activation, agrobacterium infection explants, cocultivation of agrobacterium and explants, induction, screening differentiation of explants, wherein the operations of the cocultivation of the agrobacterium and the explants are that sterilization filter paper is placed on a solid co-culture medium, and a bacterial liquid which is arranged on the surfaces of the explants which are infected by the agrobacterium is placed on the sterilization filter paper to culture for 3-4 days after being sucked clean. A method for preparing the solid co-culture medium is that 0.7% (W / V) agar powder is added into distilled water, and is added with 200 uM acetosyringone after being sterilized in high voltage. The agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated explants genetic transformation method enables the agrobacterium to be capable of fully contacting with the explants not to grow overly when the agrobacterium and the explants are co-cultivated during the genetic transformation process, improves transformation efficiency, and can reduce pollution probability by simplifying culture mediums.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Method for preparing acetovanillone and acetosyringone by catalytically saponifying lignin
ActiveCN107286006AEfficient degradationEnvironmentally friendlyOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationLiquid productHeating time
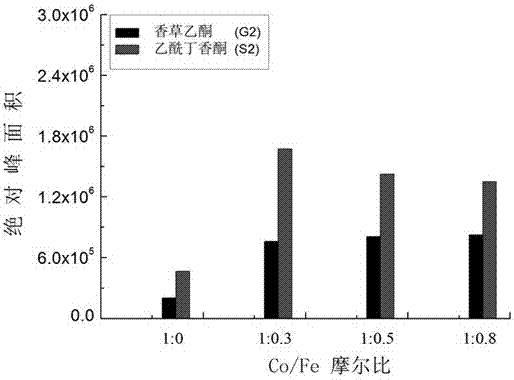
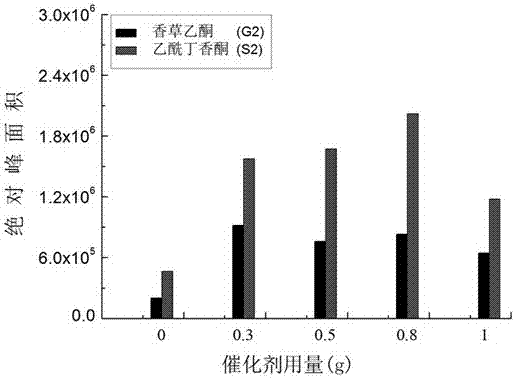
The invention discloses a method for preparing acetovanillone and acetosyringone by catalytically saponifying lignin. The method comprises the following steps: by taking lignin as a raw material, performing microwave alcoholysis in an alcohols solvent containing a loaded metal catalyst; cooling, filtering and washing, thereby acquiring a liquid product containing acetovanillone and acetosyringone as primary components. The loaded metal catalyst is formed by active center Co and carrier. The invention provides an environment-friendly and low-cost loaded metal catalyst by modifying the traditional method for degrading lignin; two compounds in high yield, namely, acetovanillone and acetosyringone, are prepared by efficiently degrading the lignin under a microwave heating condition; the method is characterized by mild reaction condition, short heating time and higher reaction efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Non tissue culture gene transferring method by using half of peanut seed as acceptor
InactiveCN102191269AEasy to operateShort experiment cycleGenetic engineeringFermentationNutrient solutionGenotype
The invention discloses a non tissue culture gene transferring method by using half of a peanut seed as an acceptor, the method comprises: (1) shelling the peanut seed, flushing and soaking by distilled water; then disinfecting, shelling, cutting the seed, taking half of a seed containing embryo, cutting embryo along cotyledon nodes of the embryo to obtain an explant; (2) inoculating Agrobacterium to a YEP liquid nutrient solution and cultivating overnight; centrifuging to collect Agrobacterium thalline, hanging in a liquid MS medium containing acetosyringone to obtain an invasion, (3) immerging the explant into the invasion; taking out of the explant and laying in a co-culturing medium, culturing for 2 to 3 days in the dark; culturing for 7 to 10 days with light irradiation to obtain a co-culturing explant, (4) removing the co-cultured explant to disinfection sandy soil, culturing and acclimatizing, moving into a greenhouse for breeding. The method of the present invention has the advantages of short experimental period, high conversion efficiency and survival rate. The conversing effect is stable among the different genotype peanuts; the strict tissue culture technique required by a traditional co-culturing method can be avoided.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for introducing RNA (ribonucleic acid) interfering gene resistant to root-knot nematode into cucumber
InactiveCN102634539ARaise the ratioReduce false positive rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureScreening methodTransgenic technology
The invention relates to a method for introducing a RNA (ribonucleic acid) interfering gene resistant to root-knot nematodes into cucumber, which relates to the technology of cucumber transgene and is characterized in that by means of an exogenous gene contained gene pCAGC1341-dsMiMpkl, 100mg / L lipoic acid and 50mg / L acetosyringone are added in each neutral co-culture medium of Agrobacterium Tumefaciens suspension to increase conversion rate of Agrobacterium Tumefaciens. In addition, the invention further provides a hygromycin gradient screening method and corresponding medium schemes, so that the efficiency of obtaining cucumber positive transformants is increased further.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for producing transgenic plants
InactiveUS20090038032A1Other foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureSucroseGold particles
A method for producing transgenic plants, including treating a target tissue using plasmolying media (PM) which contains 4% to 10% of sucrose and 100 μM to 300 μM of Acetosyringone (AS) and gold particles. The target tissue is infected by a bacterial suspension using a suitable strain and a suitable transformation vector. A PM containing 4% to 10% sucrose and 100 μM to 300 μM AS is treated for a period between 1 to 3 days. Cultivation is performed in a cultivation media in a dark condition at a temperature between 25° C. to 30° C. A non-selection media with an antibiotic is introduced. A selection media containing an active ingredient phosphinothricin (PPT) is introduced in a light condition at a temperature of between 25° C. to 30° C. in a sub culture for a period of between 3 weeks to 1 month. The putative transformant is regenerated and the number of copies of the transgenes is analyzed.
Owner:MALASIAN PALM OIL BOARD
Method for acquiring transgene cotton
InactiveCN101831459AImprove transgenic efficiencyEasy accessVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceHypocotyl
The invention discloses a method for acquiring transgene cottons. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) cutting cotyledons, leaf stalks and a part of hypocotyl of cotton cotyledon seedlings and keeping r 1-3 cm of the hypocoty to obtain tissues to be infected at 25-30 DEG C and with the relative humidity 40-60%, and culturing for 2-3 days under dark environment; (2) scratching double surfaces from the top of a stem tip to the base part of the hypocotyl with the cut of 0.8-1.2 mm in depth; (3) dip-dyeing for 15-45 min in solution A which contains a recombination agrobacterium carrying exogenous genes; (4) co-culturing for 2-4 days and then carrying out resistance screening to obtain the resistant cotton seedling; and (5) grafting the resistant cotton seedling on a cotton rootstock to obtain the transgene cotton. The invention improves the conversion efficiency through adjusting the growth states of the stem tip, determining the appropriate depth of the agrobacterium-converted stem tip infection, adding acetosyringone and adjusting the proper pH value. Transgene plants can be quickly obtained by using the method, and the higher transgene efficiency is higher.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for agrobacterium-induced genetic transformation of Ustilaginoidea virens
InactiveCN103834681AShorten the timeImprove conversion rateFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BLoss rate
The invention discloses a method for agrobacterium-induced genetic transformation of Ustilaginoidea virens. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out pre-induction culture on agrobacterium containing a hygromycin B gene and a marker gene, mixing an Ustilaginoidea virens spore liquid and the pre-induced agrobacterium liquid according to a volume ratio of 1: 1 to obtain a mixed bacterium liquid, uniformly coating the mixed bacterium liquid on an acetosyringone-containing modified AIM solid medium flat plate of which the surface is coated with a filter paper, a PVDF film or a nitrocellulose film, carrying out co-culture in the dark at a temperature of 20-24 DEG C for 36-48h, shearing the co-cultured film into small slices, paving the small slices on a modified selective medium CM, and carrying out culture at a temperature of 26 DEG C for 4-5 days to obtain hygromycin B gene-containing Ustilaginoidea virens. The method shortens converter time by 4-5d and has a conversion rate of 91.3%. The transgenic Ustilaginoidea virens has stable offspring, a low gene loss rate and converter stability of 95%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Tomato transformation method of agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation
InactiveCN106148400AImprove conversion efficiencyGood repeatabilityFermentationGenetic engineeringKanamycinMicrobiology
The invention provides a tomato transformation method of agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation. Cotyledon explants (the seedling age is 8 days) are precultured for one day in an MSB5 culture medium with 2.0 mg / L of zeatin and 0.1mg / L of IAA, and are then infected by EHA105 agrobacterium for 20 minutes; the concentration of OD600 is 0.2 to 0.6; after the culture is performed for 3 days on a co-culture medium, the co-culture is performed for one day on a culture medium of 500mg / L of cephalosporin; the screening is performed for 6 to 8 weeks on the culture medium containing 100mg / L of kanamycin and 500mg / L of carbenicillin. The method has the advantages that the conversion efficiency is high; feeder layer cells, acetosyringone and bleeding sap are not needed; the conversion efficiency reaches 20 percent or higher; simplicity and high repeatability are realized.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for efficiently and rapidly stabilizing gene transformation for tomatoes
ActiveCN105200080AImprove transgenic efficiencyReduce concentrationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiological activationBiology
The invention discloses a method for efficiently and rapidly stabilizing gene transformation for tomatoes. The method comprises the steps that 1, activation of stains is conducted; 2, preparation of plant materials is conducted; 3, infection is conducted; 4, screening and culturing are conducted. According to the method, the tomato transgenic efficiency is increased, and the transformation rate can reach over 30 percent. The concentration of bacterial liquid is reduced, the infection time is prolonged, and on one hand, agrobacterium pollution is avoided; on the other hand, the infection efficiency is increased. The infection bacterial liquid is not added with drugs for assisting in infection, so that damage to tomato leaves is reduced, the survival rate and the regeneration rate of leaf culture are increased; in a traditional method, drugs such as acetosyringone which assists in infection are usually added, damage is caused to leaves, and the regeneration capacity of the leaves is reduced. By means of carriers carrying strong expressed reporter genes, transgenic plants can be obtained directly by screening through observation, and tedious work in traditional detection is avoided. The cycle of transgenes is shortened.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Method for obtaining hairy roots of broccoli
InactiveCN105063084AShort infection timeHigh induction rateVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiotechnologyBroccoli raab
The invention relates to a method for obtaining hairy roots of broccoli. The method comprises the step (1) of clipping explants of aseptic seedlings of rapid propagation of the same batch, putting the explants on sterile filter paper, using a sterile needle head to prick 2-8 wounds on the surfaces of the explants, inoculating the explants in an MS culture medium and performing preincubate in the dark to obtain the oreincubate sterile seedling explants; step (2) of using agrobacterium rhizogenes to infect the sterile seedling explants to be cultured, using the sterile filter paper to soak up residual bacterial liquid on the surfaces, inoculating the explants to an MS culture medium adding acetosyringone to culture the explants together in the dark to obtain receptor explants cultured together; and step (3) of transferring the receptor explants cultured together to an MS culture medium adding Carbencillin Disodium to be cultured in the dark, transferring the receptor explants once every 5 days and obtaining the aseptic hairy roots after the explants are transferred from 2 to 5 times. The method is simple and efficient and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Laccase composite dielectric body and decolorization method
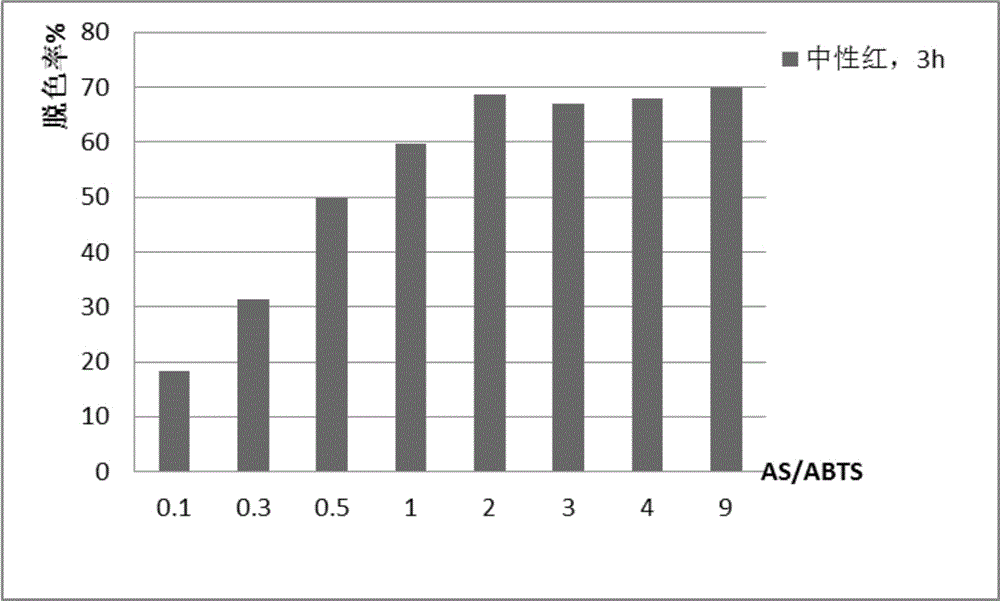
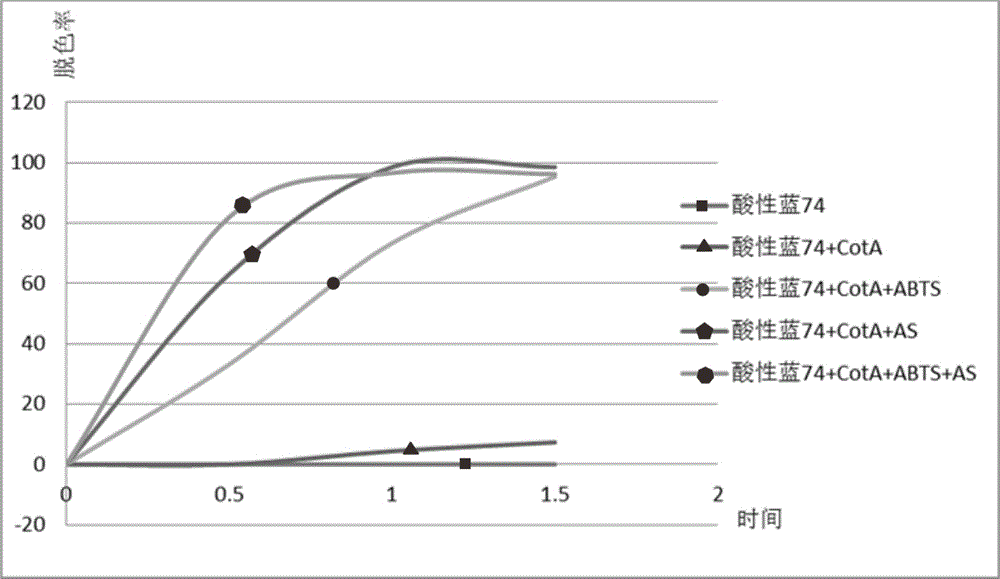
InactiveCN105776567AHigh speedHigh decolorization rateWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsABTSMaterials science
The invention discloses a laccase composite dielectric body composed of two dielectric bodies: acetosyringone AS and 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) ABTS, wherein the AS / ABTS molar ratio is (0.1-9) to 1. The composite dielectric body is formed from the acetosyringone AS and the 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) ABTS; in a decolorization process, the 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) ABTS can be subjected to concerted reaction with the acetosyringone, so as to improve the decolorization speed and decolorization rate of laccase.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method for preparing genetically modified cotton from axillary bud of cotton cotyledon
InactiveCN103667342AAvoid genotype-limited problems of culture regenerationShort conversion cycleFermentationGenetic engineeringAxillary budTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a method for preparing genetically modified cotton from an axillary bud of a cotton cotyledon. An infection reagent disclosed by the invention comprises a solvent and a solute, wherein the solvent is a 1 / 2MS culture medium, and the solute includes SILWET L-77, cane sugar, acetosyringone and KT. The method has the following advantages: 1, infection is conducted directly in the special stage of the cotyledon period of a cotton seedling to avoid the problem that the culture and regeneration of a cotton tissue is restricted by genotype, so that all cotton types can be transformed; 2, the transformation period is short, a genetically modified cotton plant can be obtained within only one cotton growth period of about four months; 3, the transformation efficiency is as high as 30%.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
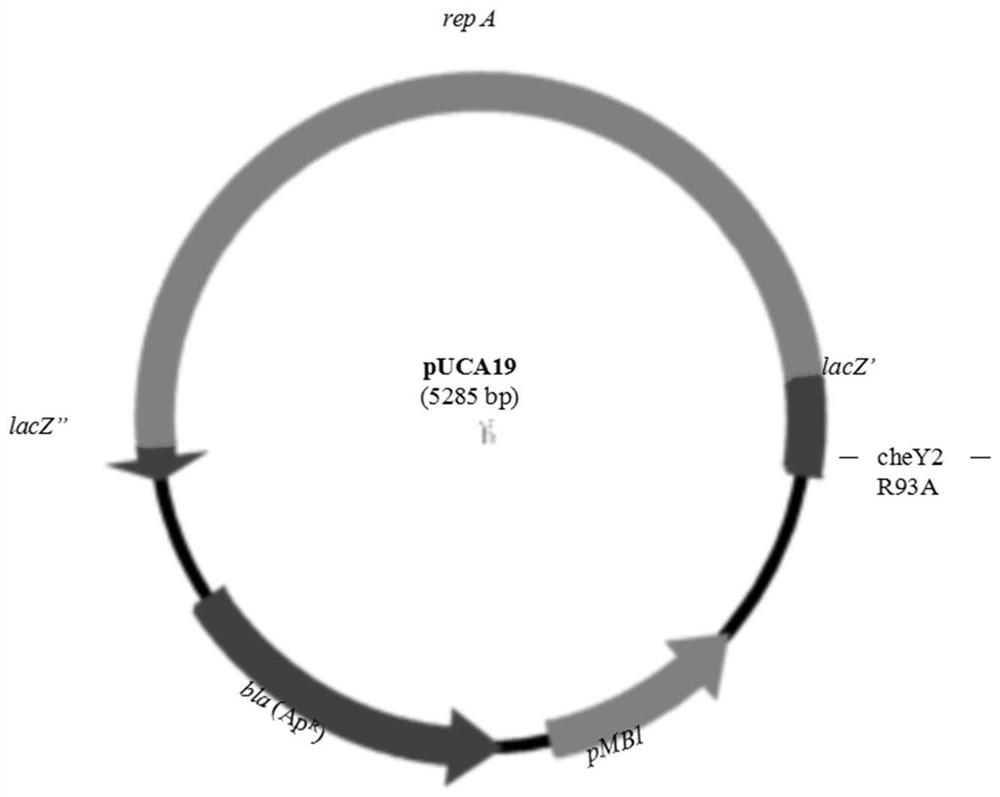
CheY2 mutant protein and application thereof
ActiveCN111793118AEnhance Chemotactic ResponsivenessBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutated proteinMutant protein
The invention discloses a CheY2 mutant protein and application thereof. Specifically, at least one of amino acids, located in the 93rd position, 96th position, 107th position, 109th position and 123rdposition of a wild chemotactic response regulatory protein, of the CheY2 mutant protein mutates. Compared with a wild CheY2 protein, the CheY2 mutant protein can remarkably improve swimming capacityof agrobacteria on a swimming flat plate, remarkably improve chemotactic capacity for a single substance acetosyringone (AS), but not limited to AS, in capillary tubes, and remarkably improve bindingcapacity of the CheY2 protein and FliM protein in the flagellar motor regulating area.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Agrobacterium-mediated dendrocalamus latiflorus transformation method
ActiveCN107190019AOvercoming barriers to applicationImprove conversion efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyBasic research
The invention discloses an agrobacterium-mediated dendrocalamus latiflorus transformation method which comprises the steps of preparing explants, preparing an agrobacterium infected bacteria solution, infecting, screening, inducing of adventive buds, and inducting and rooting. agrobacterium is utilized to infect explant at stem apex of dendrocalamus latiflorus, co-culture is performed in a NB culture medium containing 2 mg / L, 2,4-D and 200 mu M acetosyringone, and steps such as screening are performed to finally obtain transgenic dendrocalamus latiflorus. The agrobacterium-mediated dendrocalamus latiflorus transformation method utilizes an agrobacterium-mediated efficient transformation system to firstly establish a transgenic system, which takes dendrocalamus latiflorus nutritive organs as start, of dendrocalamus latiflorus, and the system can overcome the obstacle that the conventional breeding method cannot be applied to bamboo, and provides premise for molecular breeding of dendrocalamus latiflorus through the transgenic technology. Through the method, technical support is provided for researching genetic functions of bamboos in the basic research field.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
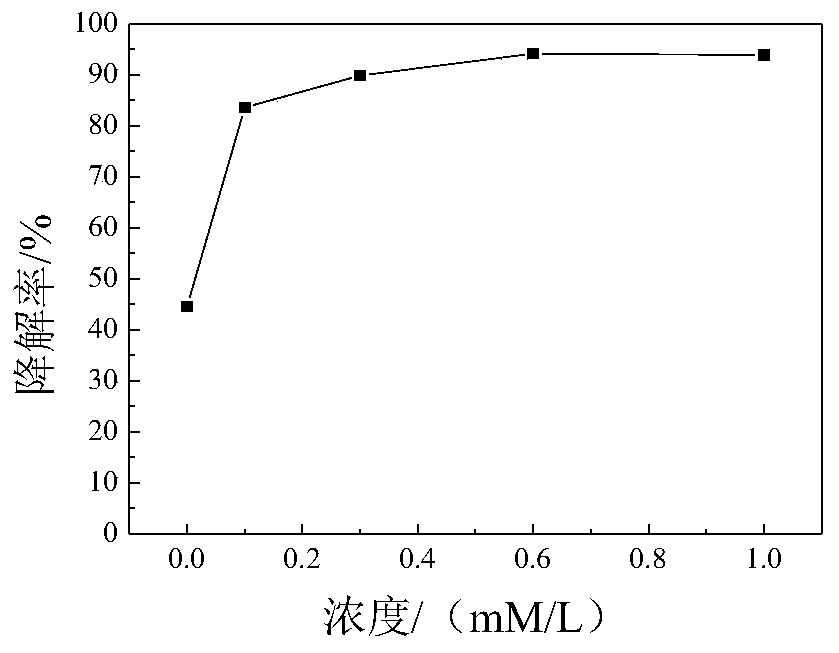
Method for improving degradation rate of laccase for degrading diethylstilbestrol by using acetosyringone, and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for improving the degradation rate of laccase for degrading diethylstilbestrol by using acetosyringone, and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical fieldof environmental pollution treatment. The method comprises the following steps: forming an acetosyringone-laccase medium buffer solution from acetosyringone and laccase, mixing the acetosyringone-laccase medium buffer solution with a diethylstilbestrol solution, performing a reaction in a shaking incubator, and quenching the reaction by using ethyl acetate to realize the degradation of the diethylstilbestrol. The acetosyringone is used as a redox medium for electron shuttle between laccase and a substrate, so that the steric hindrance of laccase is overcome, thereby the laccase can be well combined with the diethylstilbestrol, and the degradation efficiency of the laccase is remarkably improved. The method is simple and efficient to operate, and has extremely high application values in environmental pollution treatment.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for obtaining transgenic cotton through agrobacterium-mediated living immature embryo transformation
InactiveCN104726489AImprove adsorption capacityPromote infectionGenetic engineeringFermentationTransformation efficiencyEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for obtaining transgenic cotton through agrobacterium-mediated living immature embryo transformation. The method comprises the steps of stripping of a sterile embryo, preparation of a transformation liquid, oscillation infection, preparation of the transgenic cotton and identification of a transgenic plant. In the step of stripping of the sterile embryo, 30 percent hydrogen peroxide and sterile water are mixed to form a disinfection liquid; cotton seeds are detinted and put into the disinfection liquid to be soaked for 24 hours at the temperature of 25 DEG C; the seeds are taken out and put in a culture dish; seed peels and 1 / 3-1 / 2 of cotyledons are cut off; the surplus cotton embryos are put into the culture dish including a basic culture medium to enable the cotton embryos to be damaged; in the step of preparation of the transformation liquid, an inducing liquid is prepared from acetosyringone and magnesium sulfate, the acetosyringone can be used for inducing an agrobacterium Vir gene to be activated so as to improve the integration efficiency of an exogenous gene; and in the step of oscillation infection, Silwet L-77 and MS liquid culture media are added into the transformation liquid to ensure that the agrobacterium covers the cotton embryos in a large range. The method has the advantages of easiness for screening and operation, short growth period of the cotton, high transformation efficiency and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Efficient genetic transformation method of agrobacterium-mediated dendrobium candidum
ActiveCN107227313AIncrease temperatureExtension of timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCulture mediumsLiquid culture
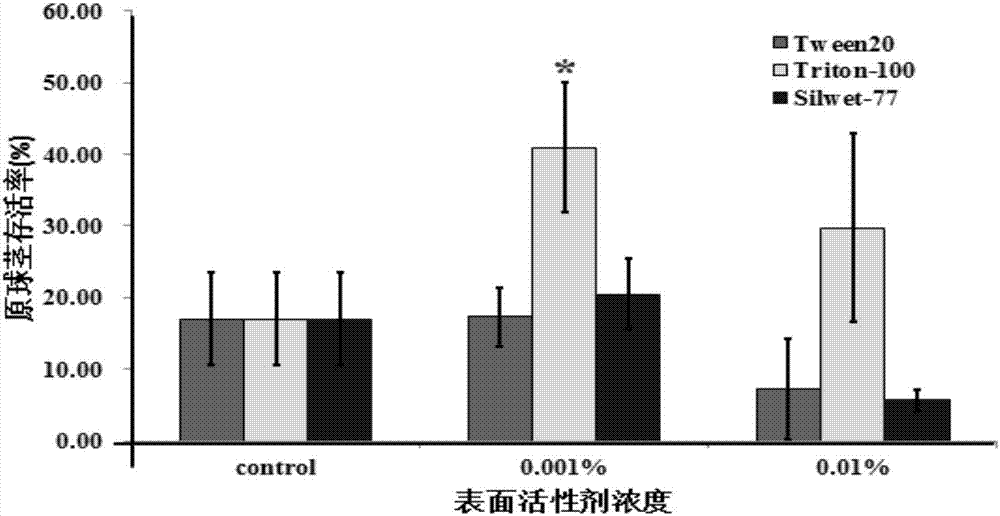
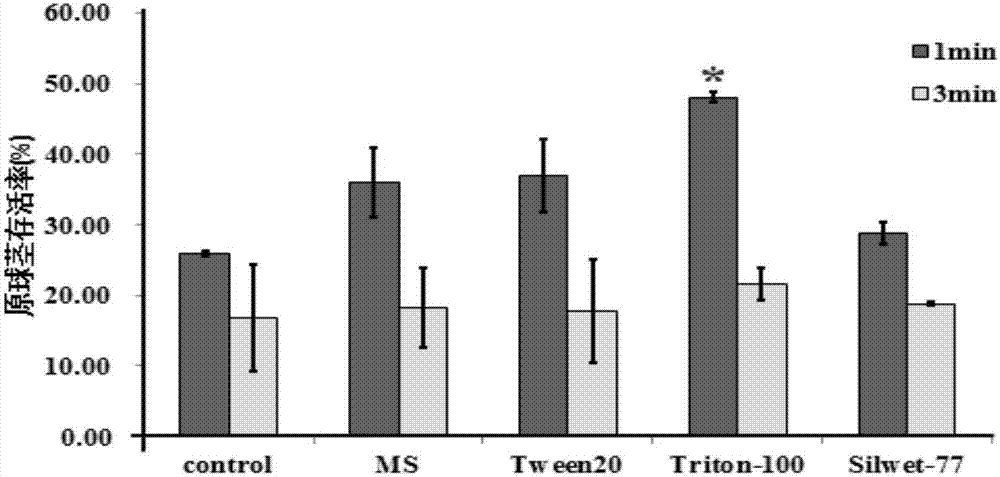
The invention provides an efficient genetic transformation method of agrobacterium-mediated dendrobium candidum. The efficient genetic transformation method comprises the following steps: (1) performing activating culture on agrobacteria; (2) performing a dip dyeing liquid: adding the agrobacteria obtained in the step (1) into an MS liquid culture medium, putting on ice so as to enable the agrobacteria to be completely dissolved in the culture medium, adjusting bacterial liquid by using the MS liquid culture medium till OD600 is 0.4-0.8, then adding 100[mu]mol / L of acetosyringone(AS) and 0.001-0.01% of Triton-100, and uniformly shaking; (3) performing ultrasonic treatment and dip dyeing: under the conditions of 280-320W and 36-45KHz, performing ultrasonic treatment for 1-3min; (4) performing co-culture; (5) screening; (6) performing plant regeneration. A transformation system is complete; the survival rate of protocorms of dendrobium candidum is high; through optimization of the steps and parameters, plants with excellent resistance are obtained through transformation; the transformation rate is high, and the positive transformation rate is as high as 69.7%.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Inducing method and proliferation method of red clover hairy roots
InactiveCN110972954AImprove conversion rateImprove survival rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyRed Clover
The invention discloses an inducing method and proliferation method of red clover hairy roots, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The inducing method comprises the following steps of firstly, performing disinfection and cleaning treatment on red clover seeds, placing the treated red clover seeds in MS liquid culture mediums, and performing culture so as to obtain red clover bacteria-free seedlings; with the red clover bacteria-free seedlings as infestation materials, and injecting agrobacterium rhizogenes infestation liquid into the infestation materials; and then inoculating the MS culture mediums containing acetosyringone, with the infestation materials to which the agrobacterium rhizogenes infestation liquid is injected, performing co-culture treatment, then transferring theco-cultured MS culture mediums into MS culture mediums containing cefotaxime sodium, and performing bacteriostasis culture treatment so as to obtain induced converted hairy roots. According to the inducing method disclosed by the invention, through screening appropriate explants and improving a bacterial liquid infestation manner, besides, through controlling the addition concentration of the acetosyringone and the cefotaxime sodium and controlling co-culture time, the inducing conversion rate and the survival rate of the hairy roots can be greatly increased.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV FOR THE NATITIES
Agrolbacterium-mediated method for transforming lily from exogenous gene
InactiveCN1563392ASimple methodWith characteristicsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureKanamycinShoot
This invention relates to a method for transforming lily with agricillin mediaed ex-source function gene applying a way of transforming lily bulb with agricillins, and applying liquid Ms added by acety1 syringone activation mycelium to get the effect of setting up agricillin mediaed lily gene genetic transformation system and increasing its transformation rate. First of all, the lily bulb is disinfected and cut to small blocks and cultivated on a fix MS culture medium, unpolluted lepises are selected to be cut to form new wounds on the edge, an explant is infected by the resuspended agricillin to be cultivated on a co-culture medium to be selectively cultivated on a screen medium with kantlex to induce resistant adrentitious buds finally to be induced on a rooting medium and to be shift to get regeneration shoots and transformed lily plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Genetic transformation method for mung beans
The invention discloses a genetic transformation method for mung beans. The genetic transformation method comprises the steps: taking a hypocotyl segment containing cotyledonary nodes as explants to carry out infection and co-culture on the explants by an agrobacterium-mediated method, and inducing and regenerating transgenic plants after the infection is finished, wherein the infection liquid isan MSB liquid culture medium containing agrobacterium, 0.15-0.25 mg / L of 6-BA and 100-200 mg / L of acetosyringone, and OD is 0.5-0.6; during co-culturing, the co-culture medium is an MSB solid culturemedium containing 0.15-0.25 mg / L of 6-BA and 100-200 mg / L of acetosyringone. A technical system for genetic mung bean transformation is established, and the genetic transformation method can be used for genetic improvement of mung beans and innovative cultivation of new germplasms and provides a basis for functional gene verification and genome editing character improvement of the mung beans.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for efficiently screening out non-transgenic mutants in agrobacterium tumefacien mediated gene editing
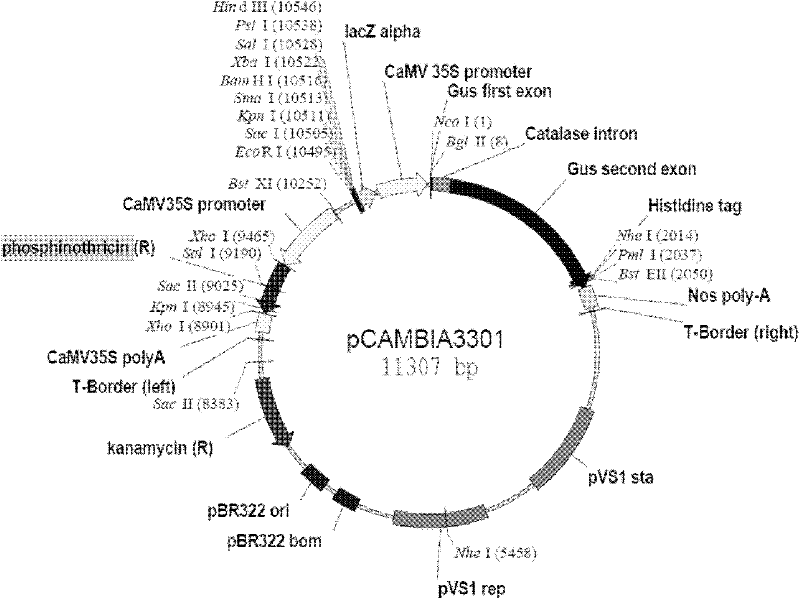
ActiveCN110632157ASolve the requestSolve efficiency problemsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNicotiana tabacumBud
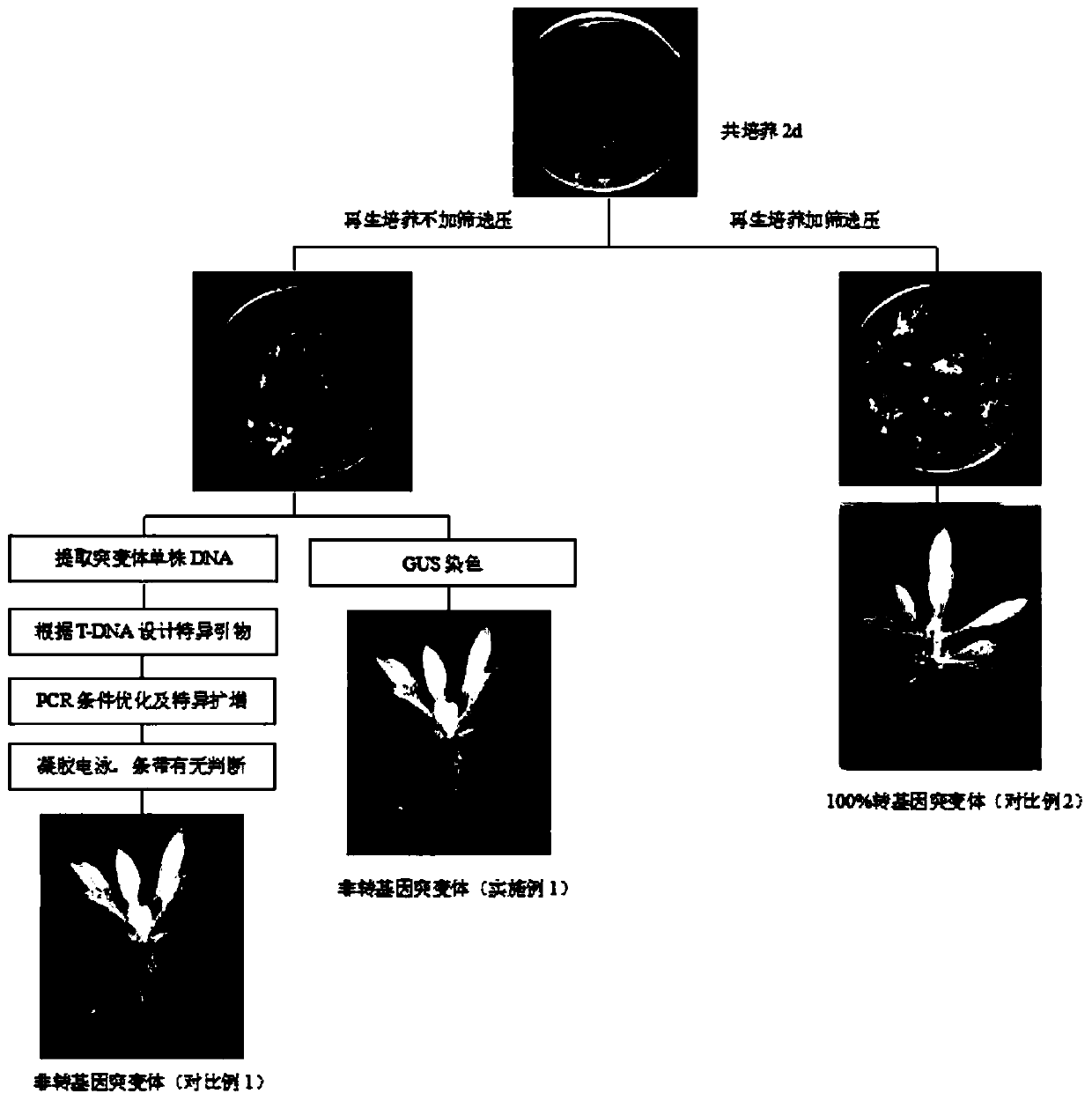
The invention discloses a method for efficiently screening out non-transgenic mutants in agrobacterium tumefacien mediated gene editing, which comprises the following steps: (1) connecting a CaMV 35Spromoter started GUS reporter gene to a traditional gene editing vector, and transferring the vector into an agrobacterium tumefacien EH105; (2) infecting common tobacco leaves with the agrobacteriumtumefacien EH105 transferred into the vector by using a leaf disc method, inoculating the infected leaves onto an MS solid culture medium containing acetosyringone, and co-culturing the leaves for 2 days at 25 DEG C in a dark environment; (3) inoculating a co-cultured explant onto a regeneration culture medium without screening pressure, and replacing the regeneration culture medium with a same fresh regeneration culture medium every 20 days; and (4) inoculating regenerated albino buds onto an MS culture medium containing Timentin, and carrying out sampling for GUS dyeing when albino seedlingsgrow to 3-4 leaves, wherein the albino seedlings without GUS signals are candidate non-transgenic mutants. According to the invention, transgenic mutants can be removed and non-transgenic mutant canbe obtained rapidly, and the method is rapid, convenient, simpler and more practical.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Gene transient expression method with in-vivo jujube fruits as materials
ActiveCN111621516AOvercome the difficult problem of gene function verificationAvoid many problems of stable genetic transformation systemMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a gene transient expression method with in-vivo jujube fruits as materials. The method comprises the following steps of performing homologous cloning according to sequence information in an NCBI database to obtain a target gene, integrating the target gene into a plant overexpression plasmid vector through enzyme digestion-connection, and transferring a recombinant plant vector into agrobacterium GV3101; carrying out shake culture on the agrobacterium in an LB culture medium at 28 DEG C until OD600 reaches 1.0-1.2, centrifuging and collecting bacteria, pouring out theLB culture medium, and resuspending thalli by using a penetrating fluid containing MgCl2, MES and acetosyringone for later use; injecting the agrobacterium penetrating fluid into the in-vivo jujube fruits in the half-red period by using a medical injector; and verifying the function of the target gene by observing the phenotypic changes of the jujube fruits and detecting the expression quantity ofthe target gene and the content of related metabolites. The method avoids the problems of poor repeatability, low conversion rate, long time and the like of stable genetic transformation of ziziphusjujuba mill, can verify the gene function in a short time, is simple and quick, and saves the cost.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Bacillus subtilis cjp3 for producing CotA laccase as well as CotA laccase and application thereof
PendingCN106754519AMature and easy to operateIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChemical structure
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis cjp3 for producing CotA laccase as well as CotA laccase and application thereof. The CotA laccase producing bacterium is named as Bacillus subtilis, collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection with number CCTCC No: M 2016408 on July 21, 2016 in Wuhan University of China. The DNA sequence of the CotA laccase is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The operation on the CotA laccase is mature and convenient, the obtained laccase has high activity, and the prepared CotA laccase has a wide pH and temperature catalysis range, high stability under alkali and high-temperature conditions in the presence of high salt and high-concentration organic solvents, and stronger practicability than fungal laccase. Under the participation of an acetosyringone mediator, the CotA laccase can be used for effectively decolorizing synthetic dyes of different chemical structures, still keeps a good decolorizing effect under the alkali condition, and has a good application prospect on treatment of industrial dye wastewater.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation method for toona ciliata
ActiveCN113215191AAchieve genetic transformationPromote the development of industrializationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLotus japonicus
The invention relates to an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation method for toona ciliata. The method comprises the following steps: taking leaves of toona ciliata as an explant, infecting the explant with a bacterial solution of agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying a plant expression vector; inoculating the infected explant into a co-culture medium, and carrying out co-culture; and carrying out induction culture on the co-cultured explant, wherein the induction culture comprises induction culture of callus, induction culture of adventitious buds, induction culture of buds and induction culture of roots; the bacterial solution contains acetosyringone, and the co-culture medium contains acetosyringone. By adopting the method, agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated toona ciliata genetic transformation is successfully realized, genetic transformation rate is kept at about 10%, and the method is good in repeatability and stability, suitable for batch seedling culture and beneficial to agricultural industrialization development.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Agrobacterium-mediated Leptosphaeria biglobosa genetic transformation method
ActiveCN110195078ARealize the genetic transformation systemGenetic stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionLiquid mediumTransformation efficiency
The invention provides an Agrobacterium-mediated leptosphaeria biglobosa genetic transformation method, which belongs to the technical field of genetic transformation of plant pathogenic fungi. The method comprises the following steps: 1) inoculating agrobacterium containing plasmid pCHs-GFP in a LB liquid medium for culture, and then transferring the agrobacterium into a CM liquid medium containing 150-250 [mu]g / mL acetosyringone to obtain agrobacterium bacterial fluid; 2) collecting the conidiospore of the leptosphaeria biglobosa, and mixing the conidiospore with sterile water to prepare a conidiospore suspension having a concentration of (0.5-9)*10<6> / mL; and 3) mixing the agrobacteriumbacteria liquid with the conidiospore suspension, co-cultivating the material for 3-4 days, transferring the material to a screening medium, and screening and culturing the material for 7-15 days to obtain a transformant; The method has high transformation efficiency, low copy and genetic stability.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com