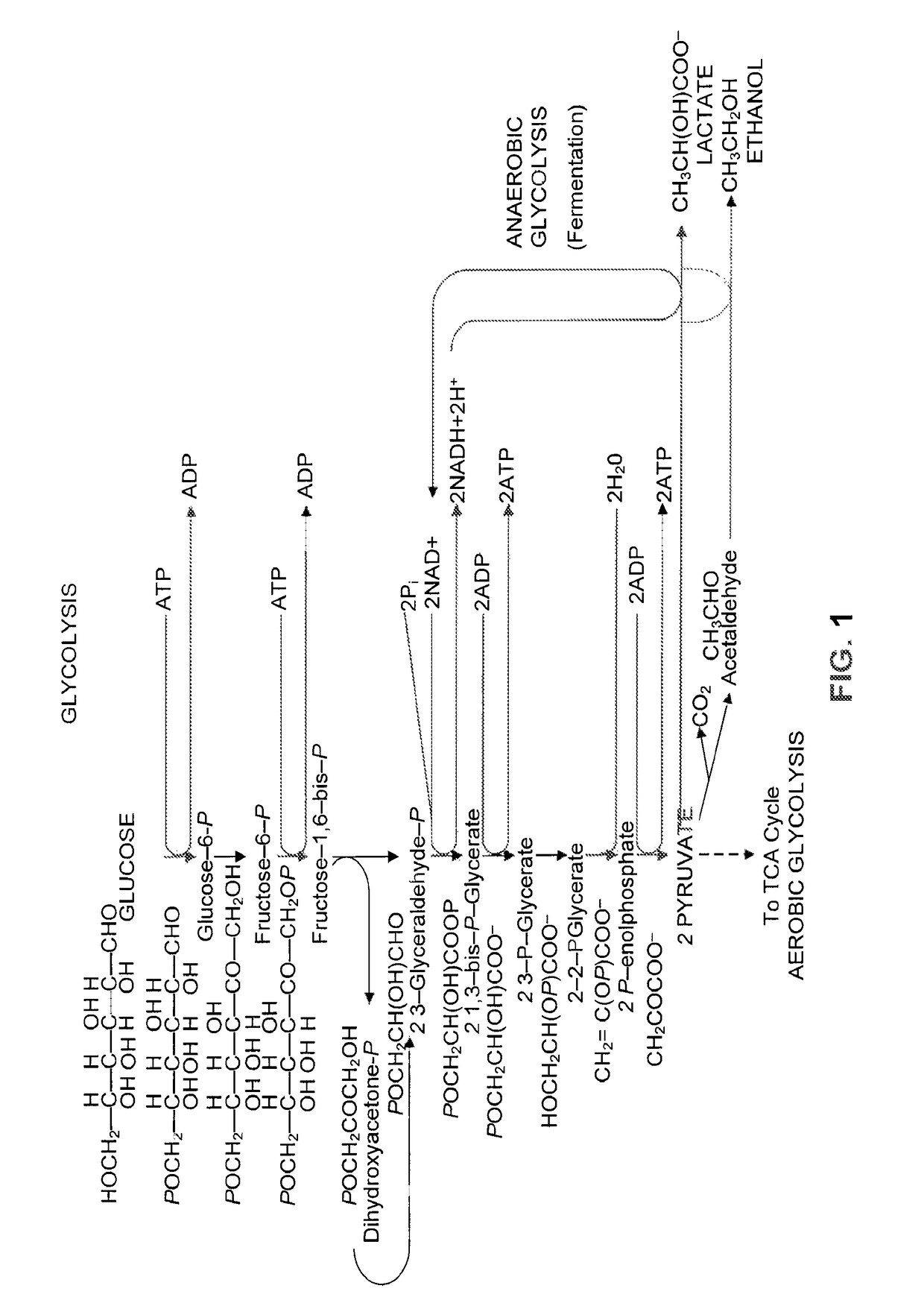
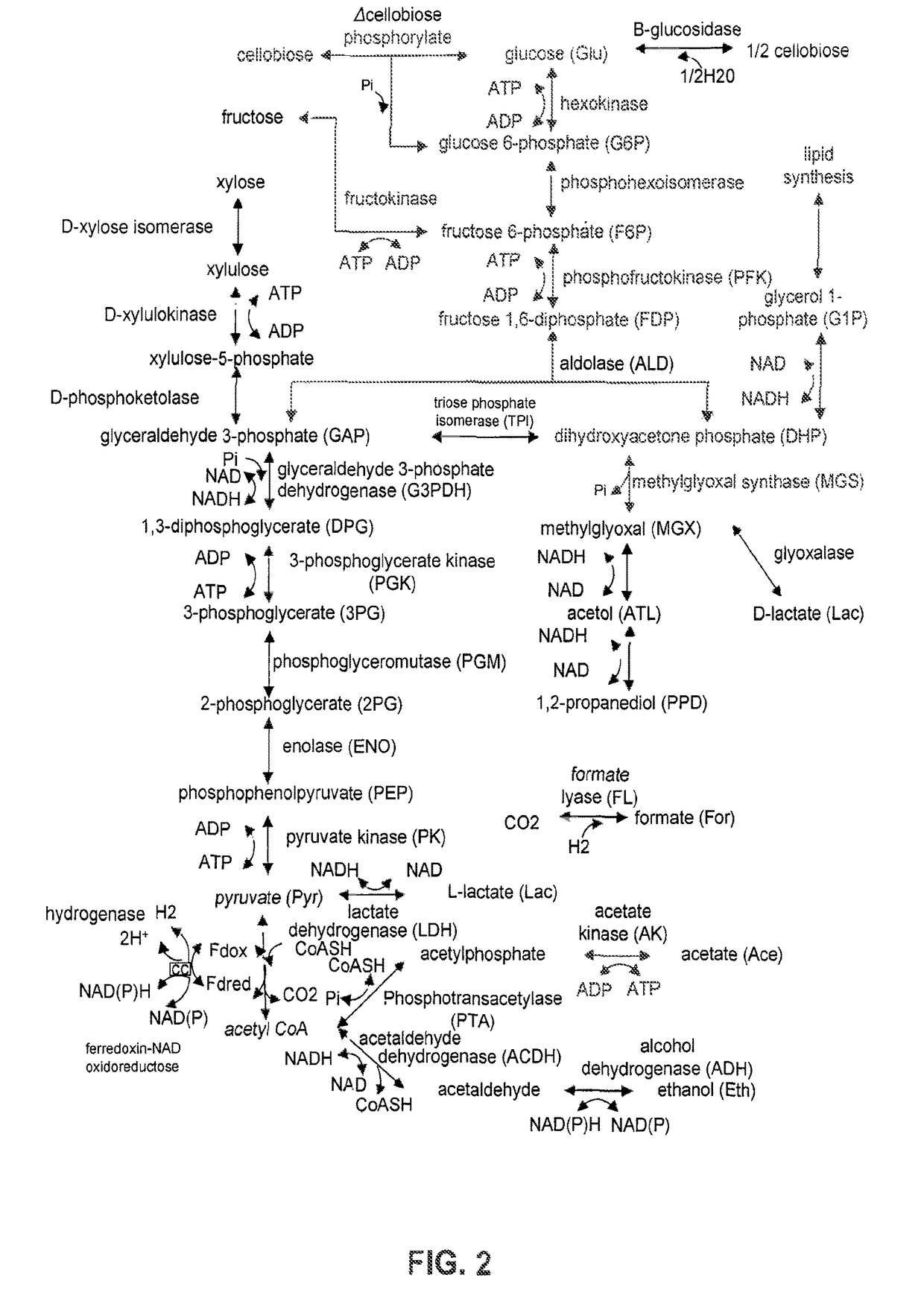
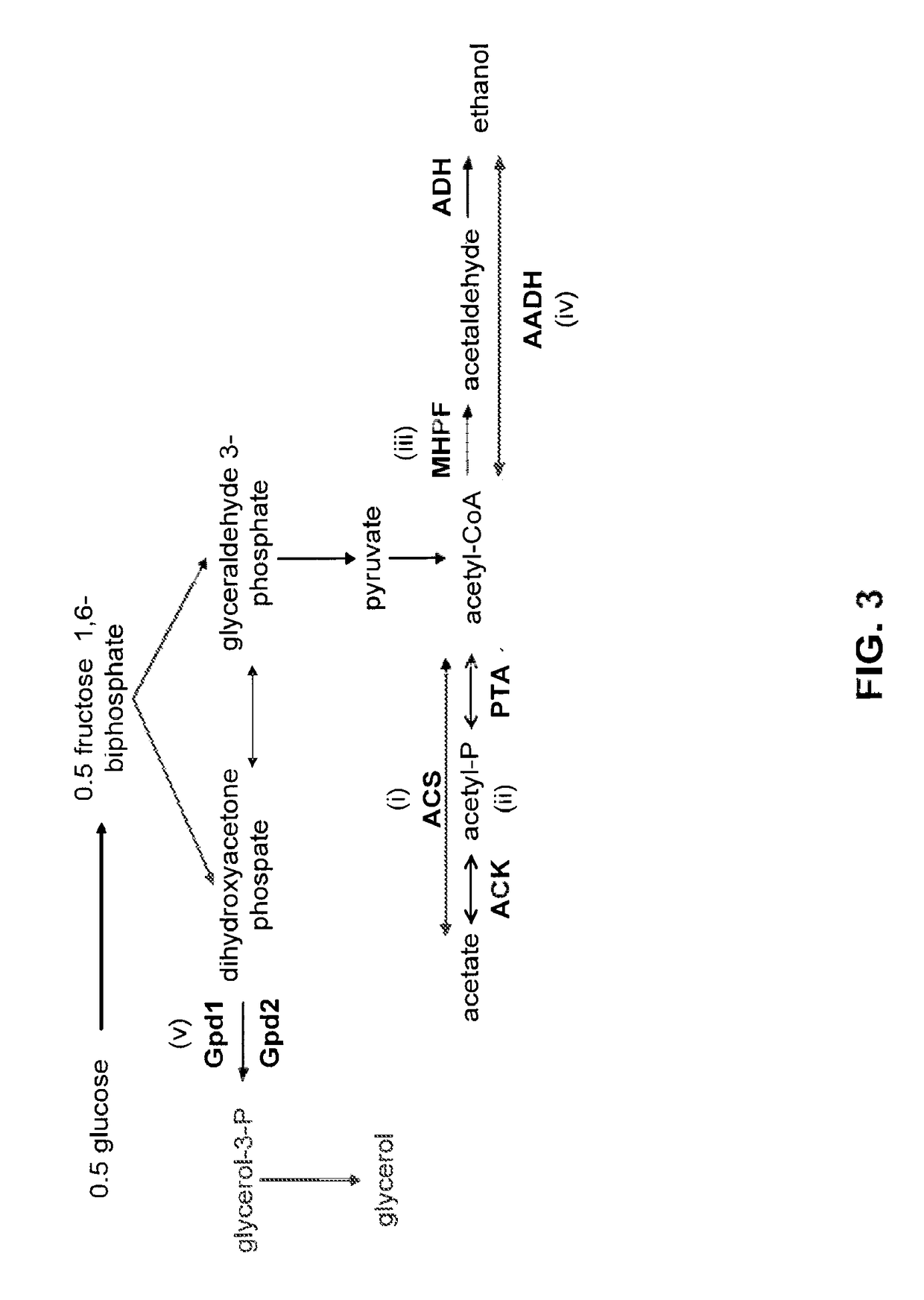
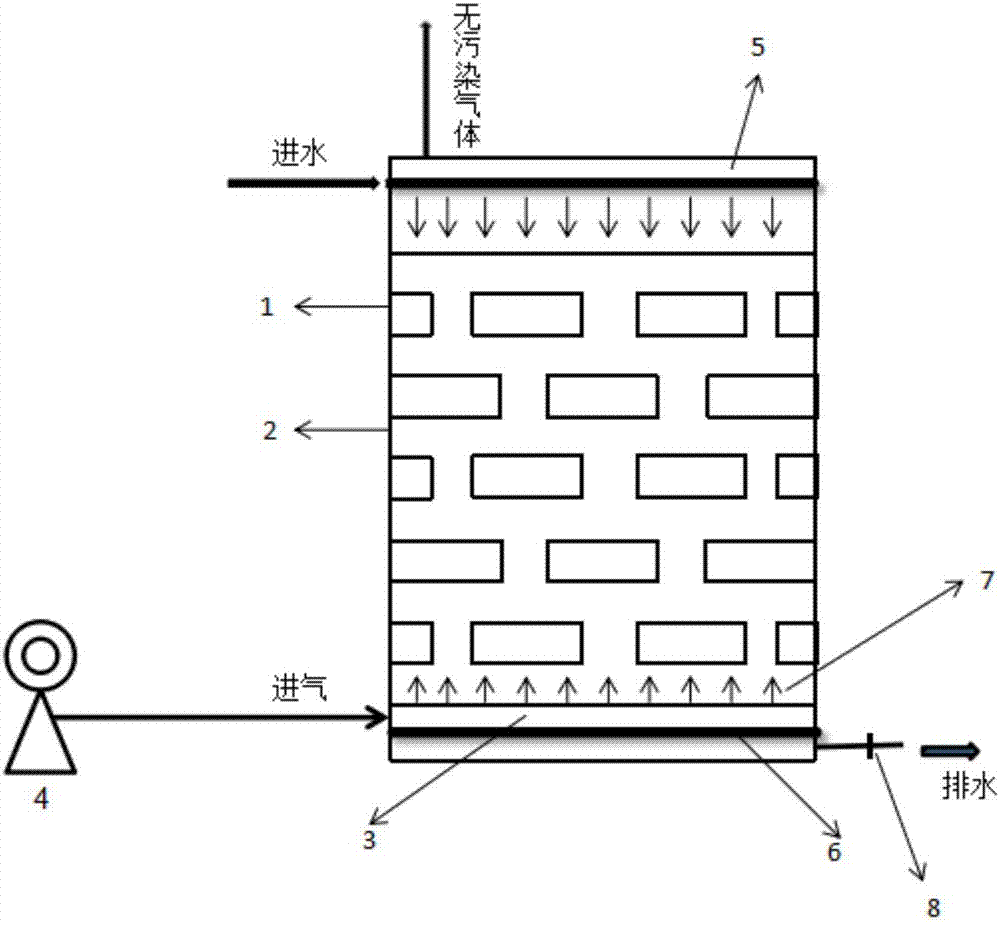
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Metabolic conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
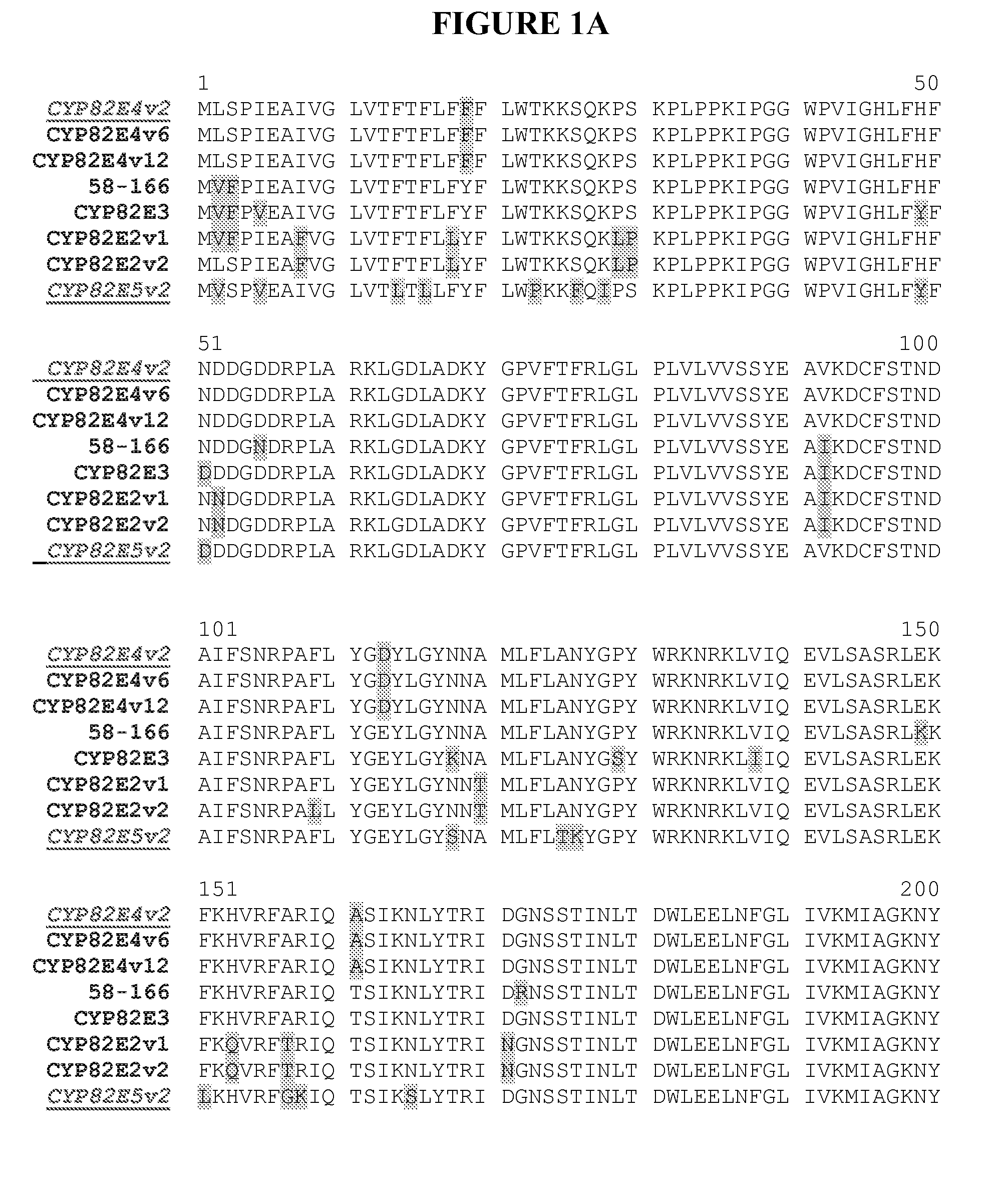
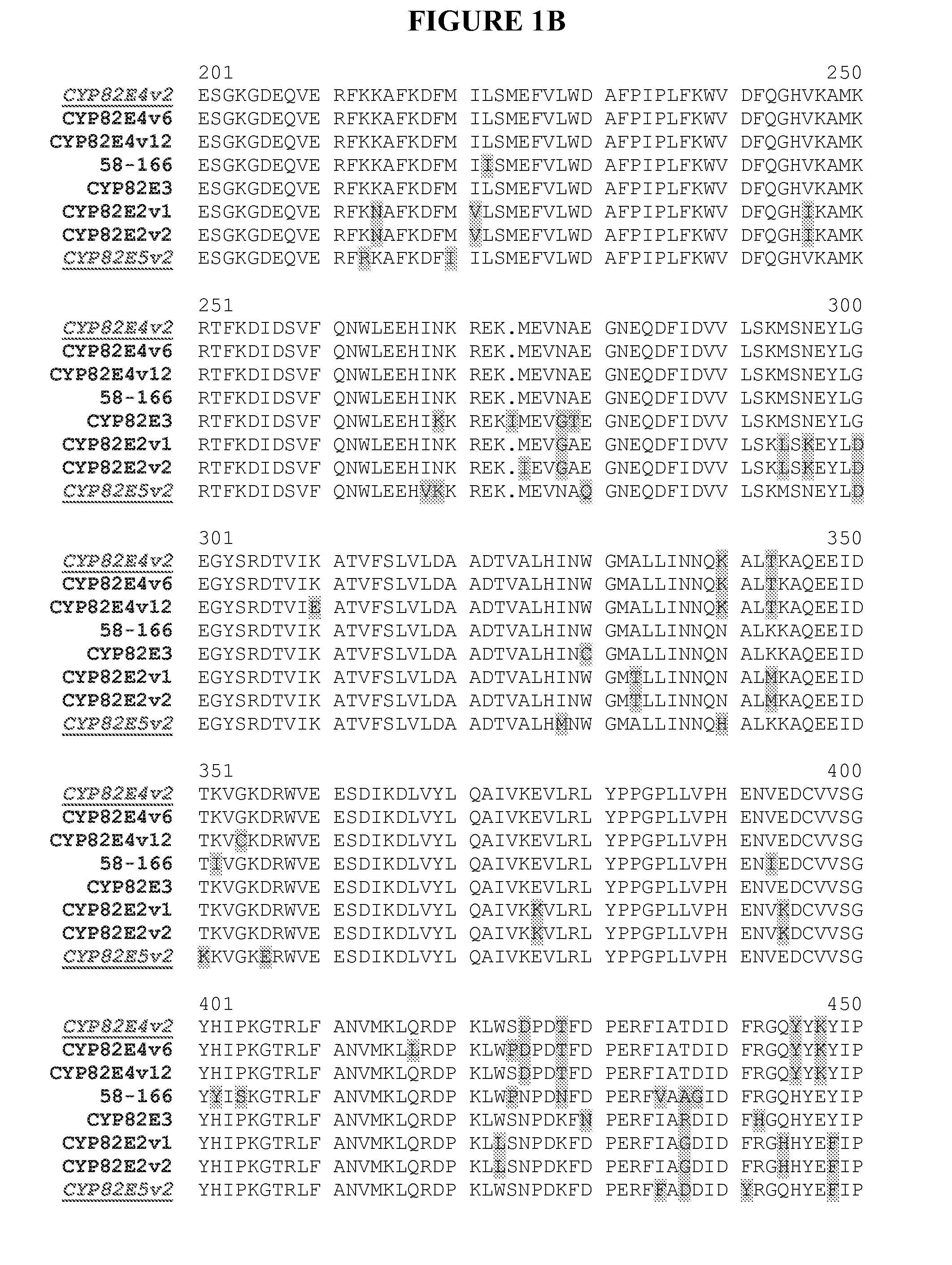
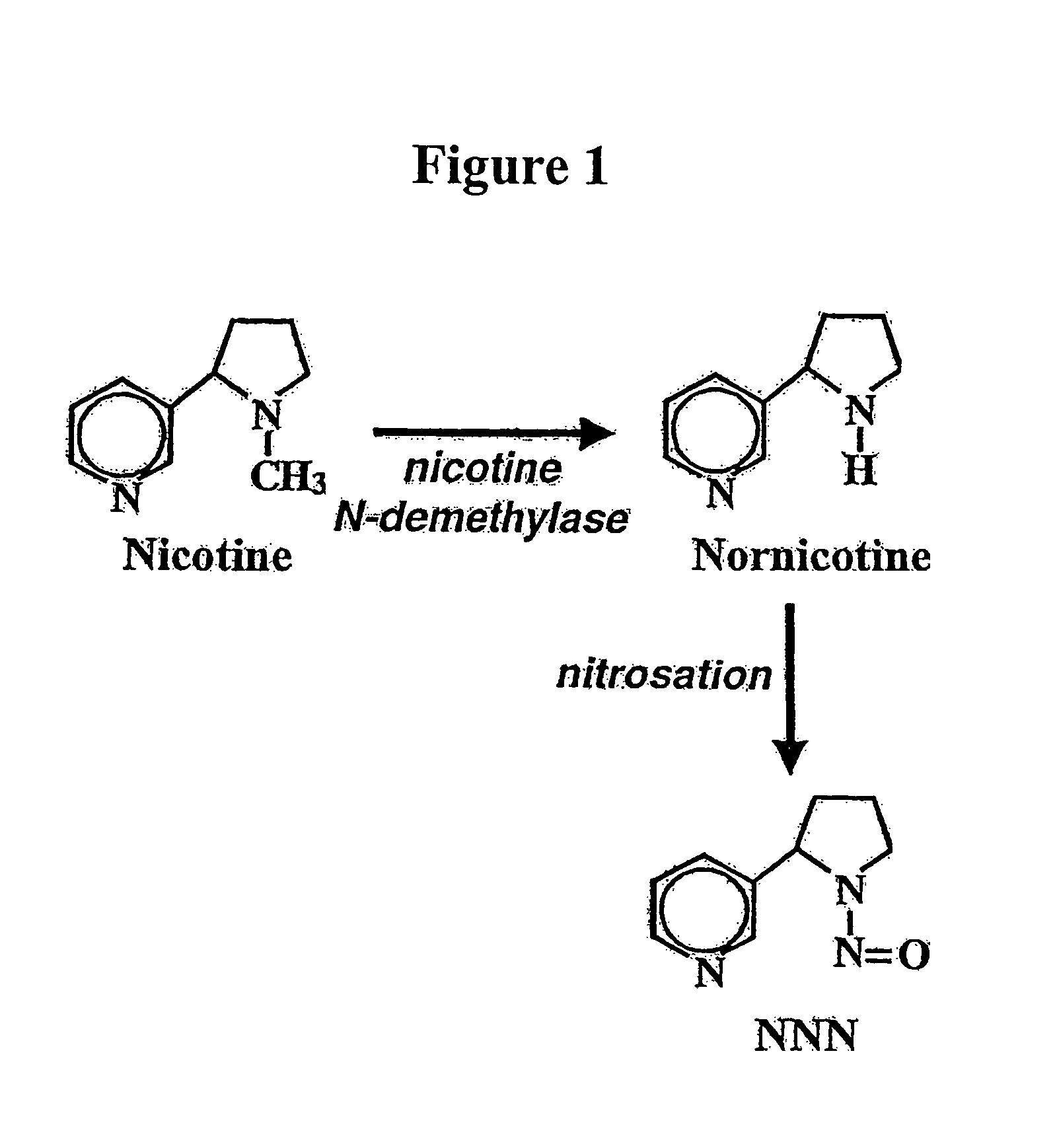
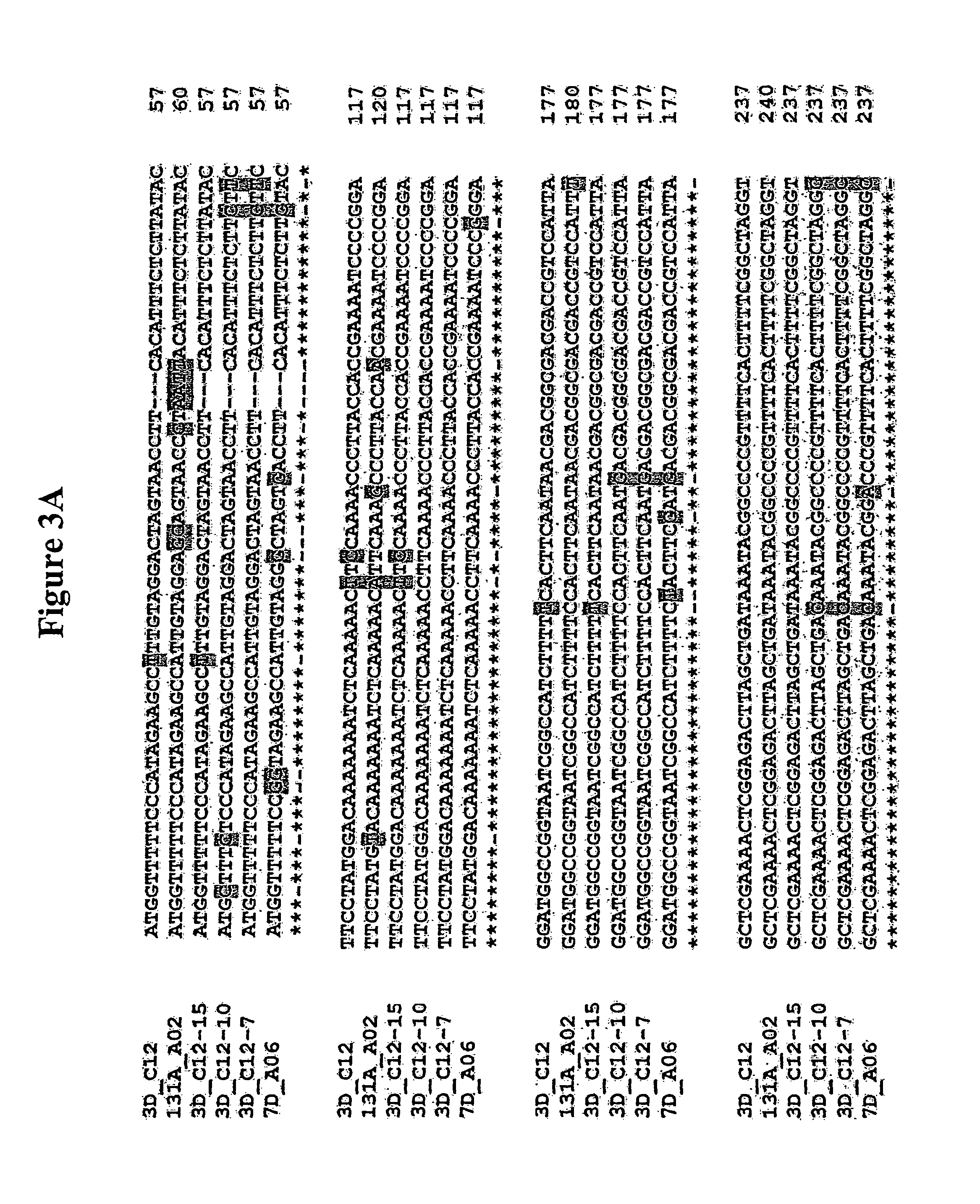
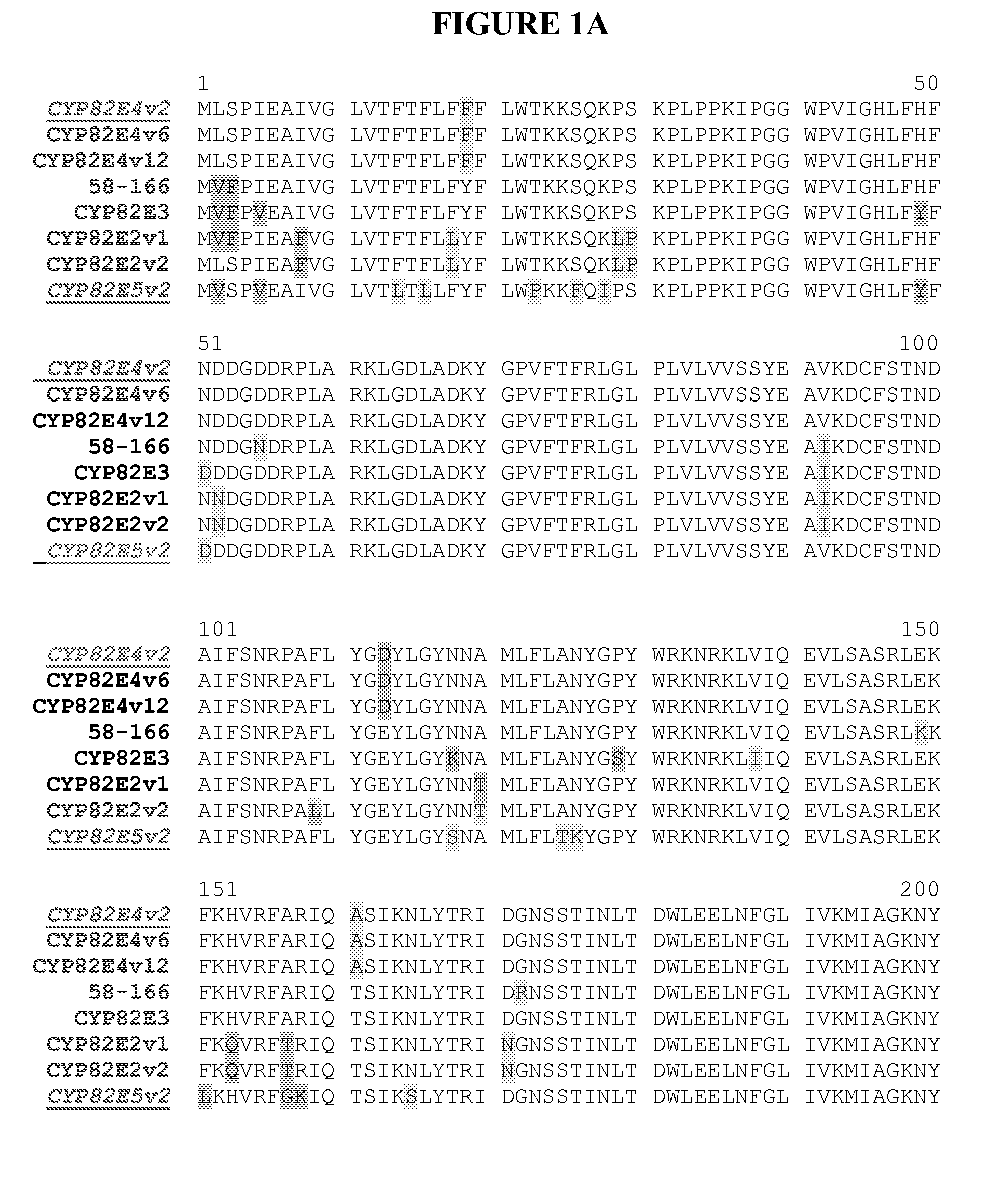
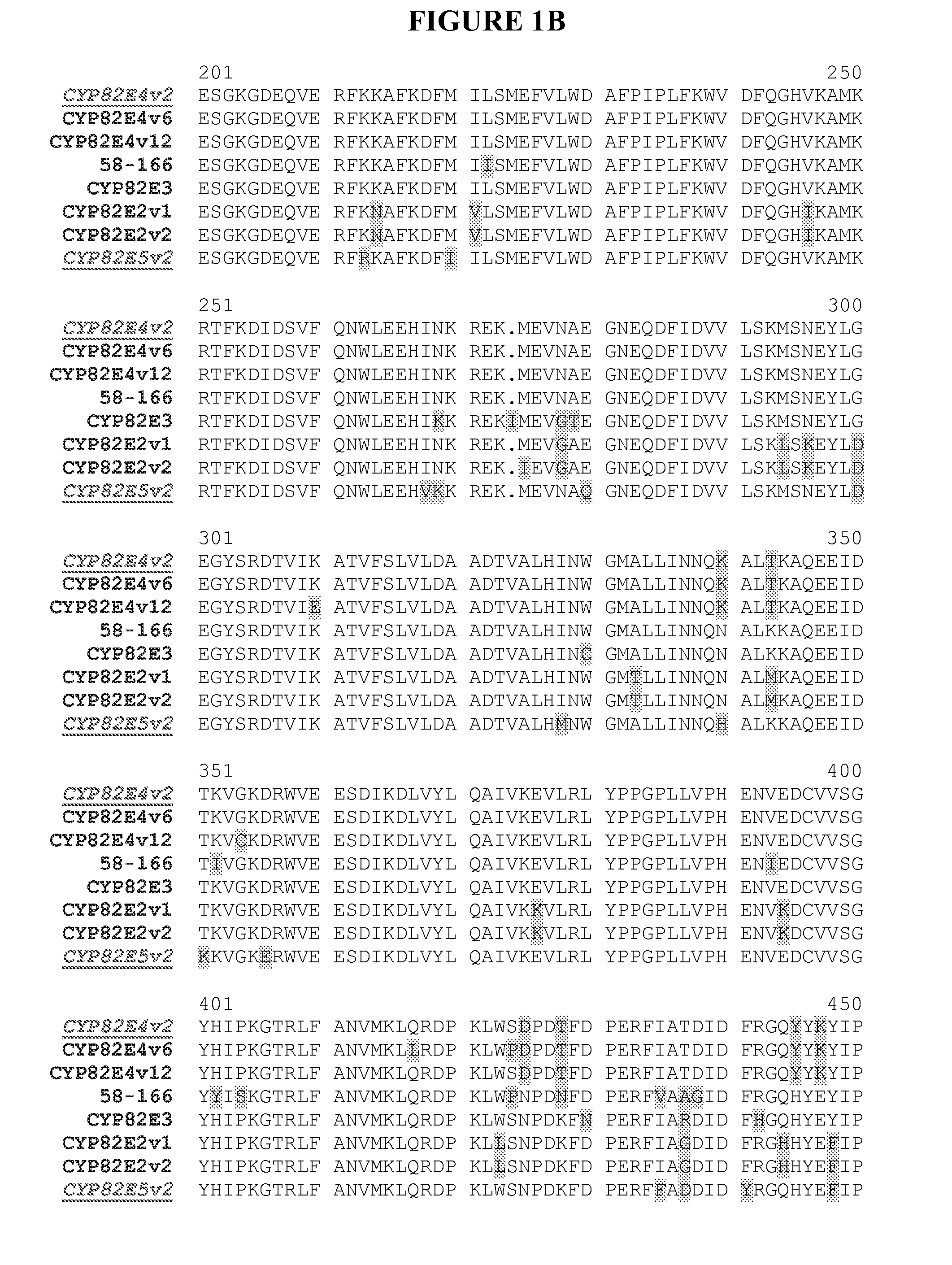
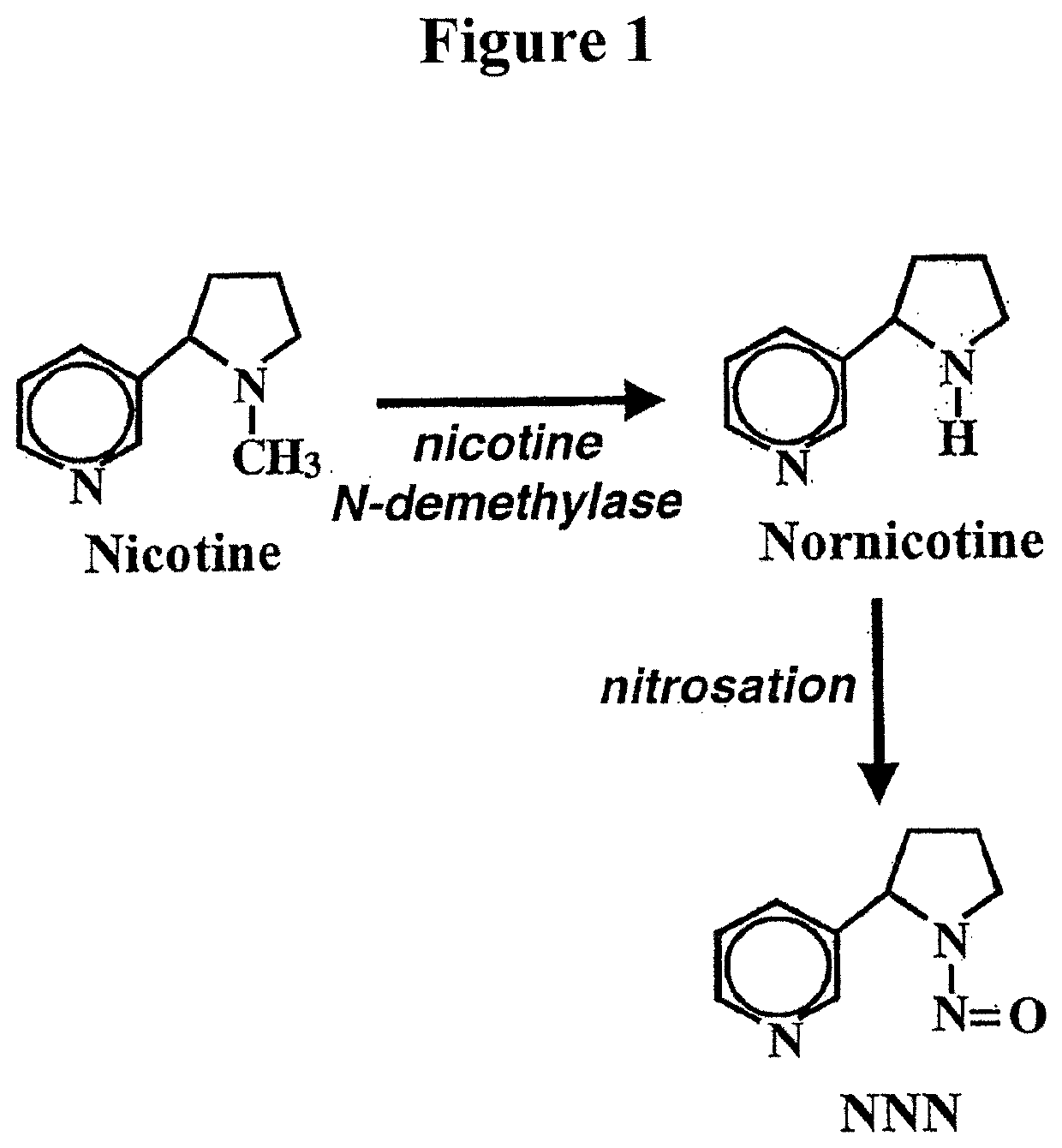
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
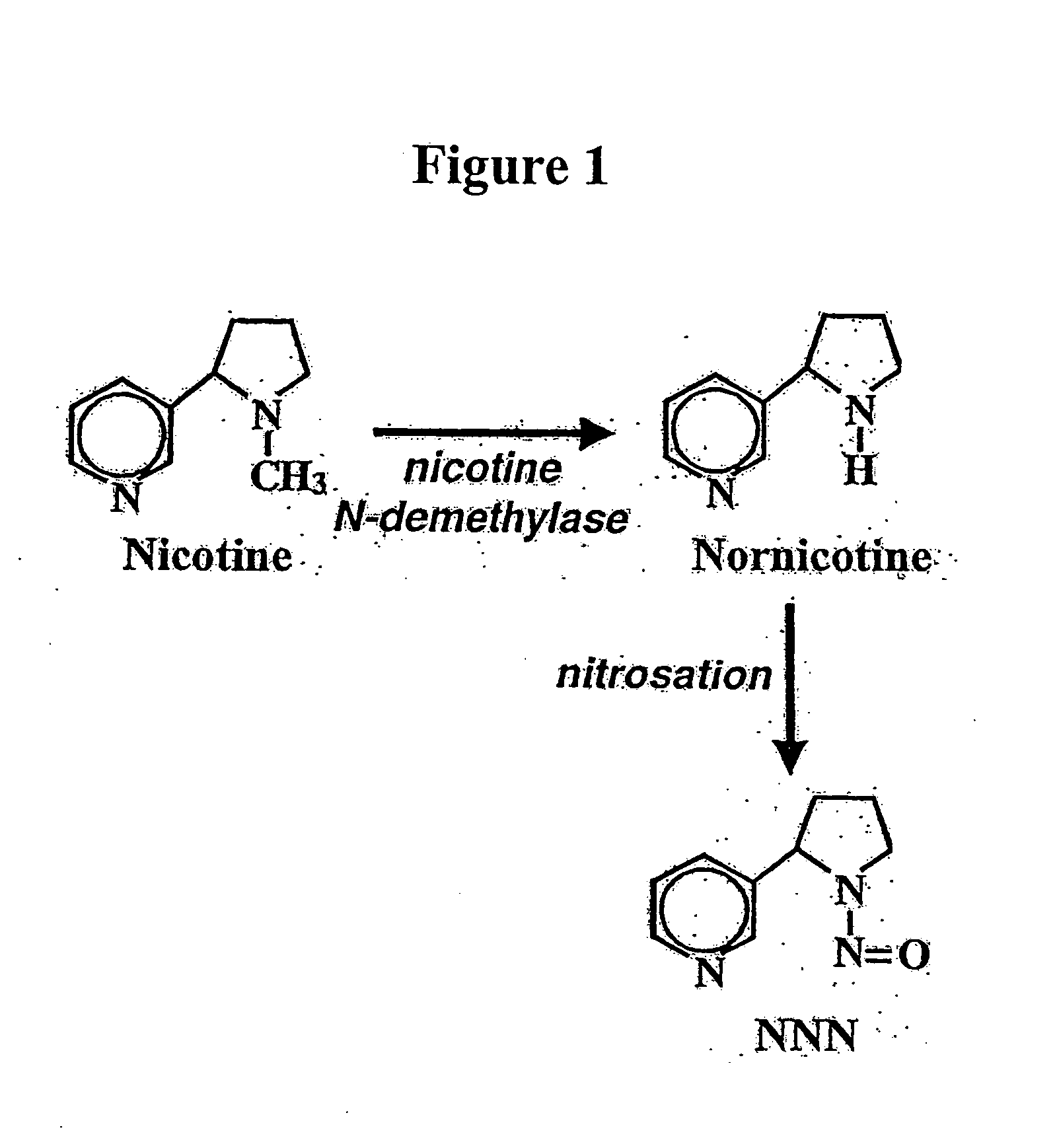
ActiveUS8124851B2Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS7884263B2Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsTobacco treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Compositions and methods for minimizing nornicotine synthesis in tobacco
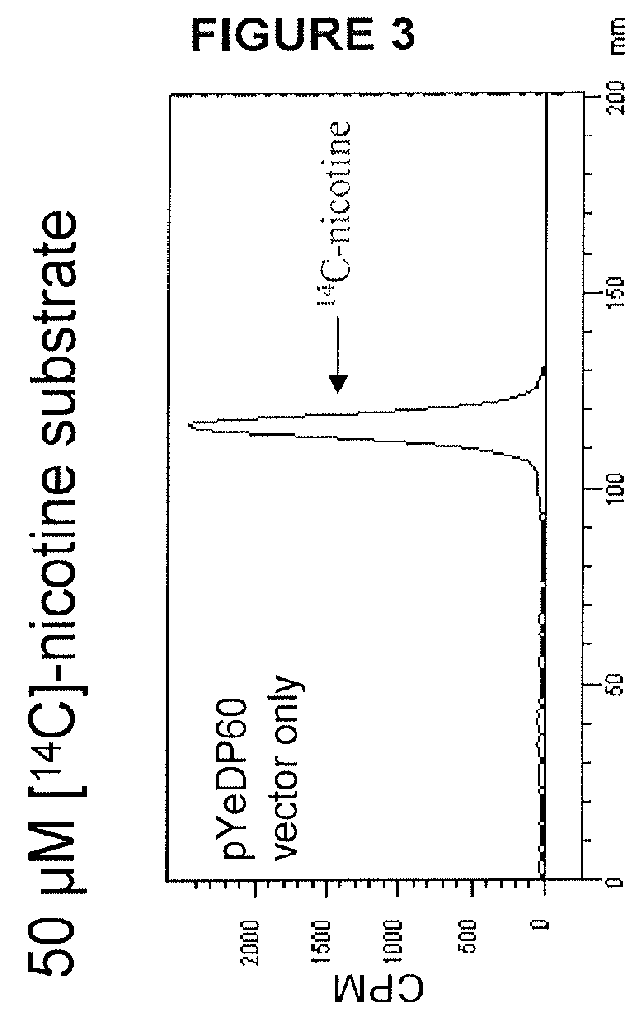
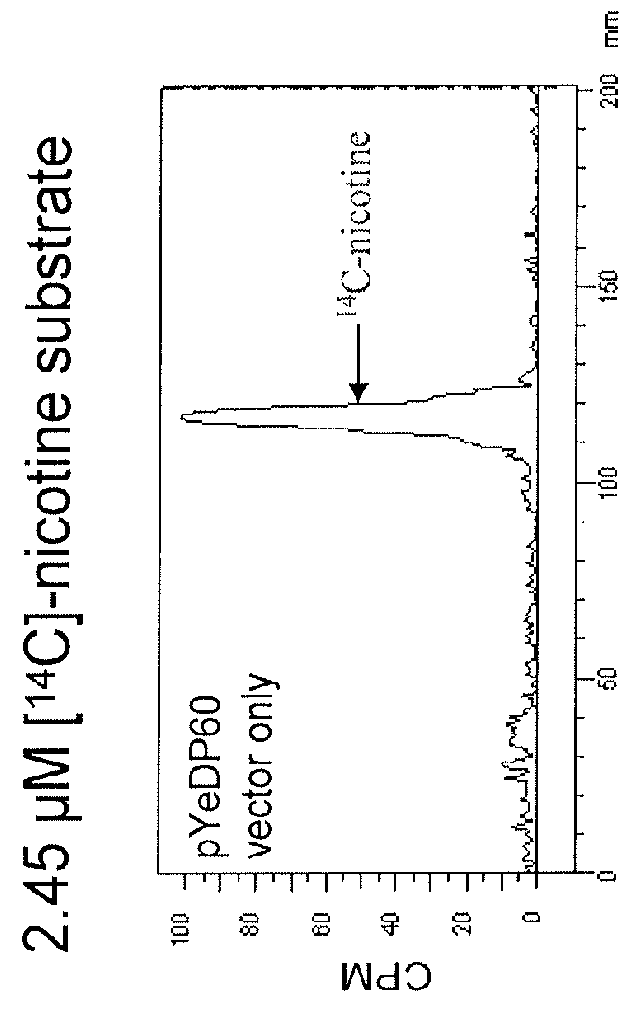
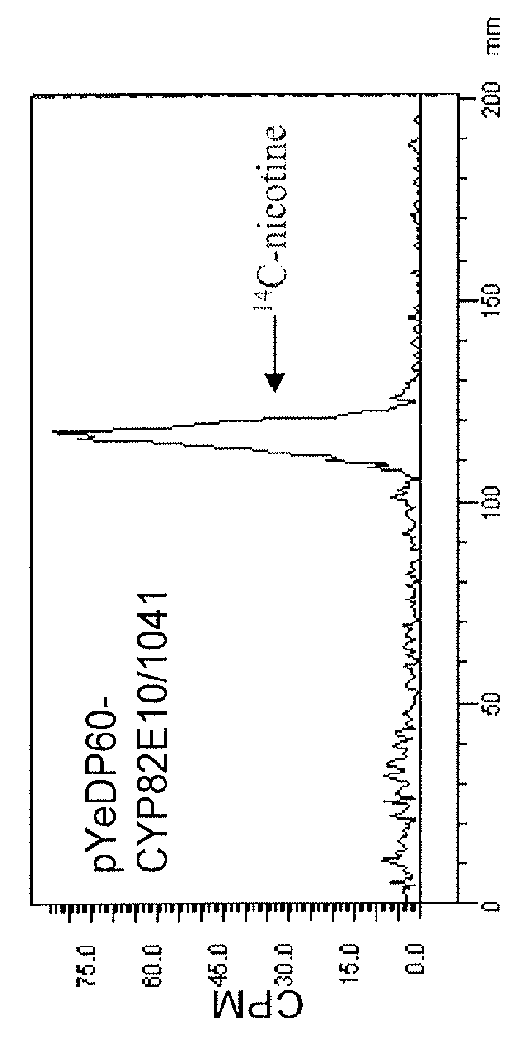
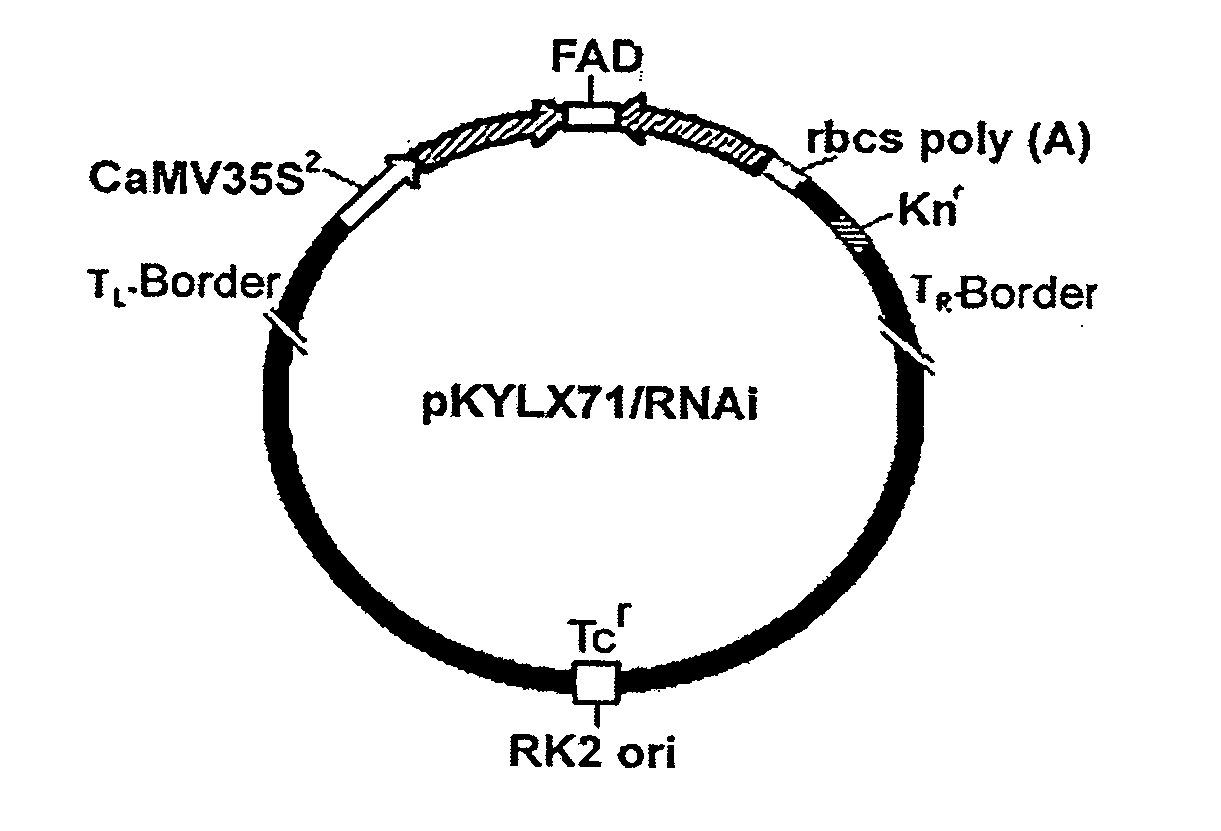
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in tobacco plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for a root-specific nicotine demethylases, CYP82E10, and variants thereof, that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Compositions of the invention also include tobacco plants, or plant parts thereof, comprising a mutation in a gene encoding a CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase, wherein the mutation results in reduced expression or function of the CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase. Seed of these tobacco plants, or progeny thereof, and tobacco products prepared from the tobacco plants of the invention, or from plant parts or progeny thereof, are also provided. Methods for reducing the level of nornicotine, or reducing the rate of conversion of nicotine to nornicotine, in a tobacco plant, or plant part thereof are also provided. The methods comprise introducing into the genome of a tobacco plant a mutation within at least one allele of each of at least three nicotine demethylase genes, wherein the mutation reduces expression of the nicotine demethylase gene, and wherein a first of these nicotine demethylase genes encodes a root-specific nicotine demethylase involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in a tobacco plant or a plant part thereof. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome p450 genes
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in Nicotiana plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for cytochrome P450s that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Expression cassettes, vectors, plants, and plant parts thereof comprising inhibitory sequences that target expression or function of the disclosed cytochrome P450 polypeptides are also provided. Methods for the use of these novel sequences to inhibit expression or function of cytochrome P450 polypeptides involved in this metabolic conversion are also provided. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS20080202541A1Lower Level RequirementsReducing nornicotine levelTobacco treatmentTobacco devicesMetaboliteNornicotine
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in Nicotiana plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for cytochrome P450s that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Expression cassettes, vectors, plants, and plant parts thereof comprising inhibitory sequences that target expression or function of the disclosed cytochrome P450 polypeptides are also provided. Methods for the use of these novel sequences to inhibit expression or function of cytochrome P450 polypeptides involved in this metabolic conversion are also provided. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Quick and intensive straw management method based on ecological conversion via housefly metabolism
ActiveCN102805053ANo pollution in the processPollution controlFood processingSolid waste disposalMaggotFiltration
The invention discloses a quick and intensive straw management method based on ecological conversion via housefly metabolism. The method comprises the following steps of: housefly species collection and clean breeding and acclimatization, induction and stabilization of straw conversion adaptation housefly strains, breeding of cellulose high expression housefly strains, pretreatment of straw housefly maggot bioconversion, stabilization of industrialized straw conversion housefly strains, and production of industrialized housefly maggot products. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that biotechnologies are adopted for functional induction and filtration of seed maggot straw ecological conversion, passage and engineered cultivation, a machinery crushing method and a biofermentation technology are adopted, and a modernized engineering means is adopted, so that intensive straw management based on microbe fermentation and insect metabolic conversion is realized. Compared with other methods, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high ecological degree, high bioavailability, short rotten period, high product quality, high extra-value output of resources, non-environmental pollution, and scientific proportion and high fertilizer efficiency.
Owner:GUIZHOU BOKANG BIOENG
Treatment for dry eye syndrome
InactiveUS20060088600A1Inhibits cyclooxygenaseImprove inflammatory responseBiocideSenses disorderEssential fatty acidNutrient
Owner:BIOSYNTRX
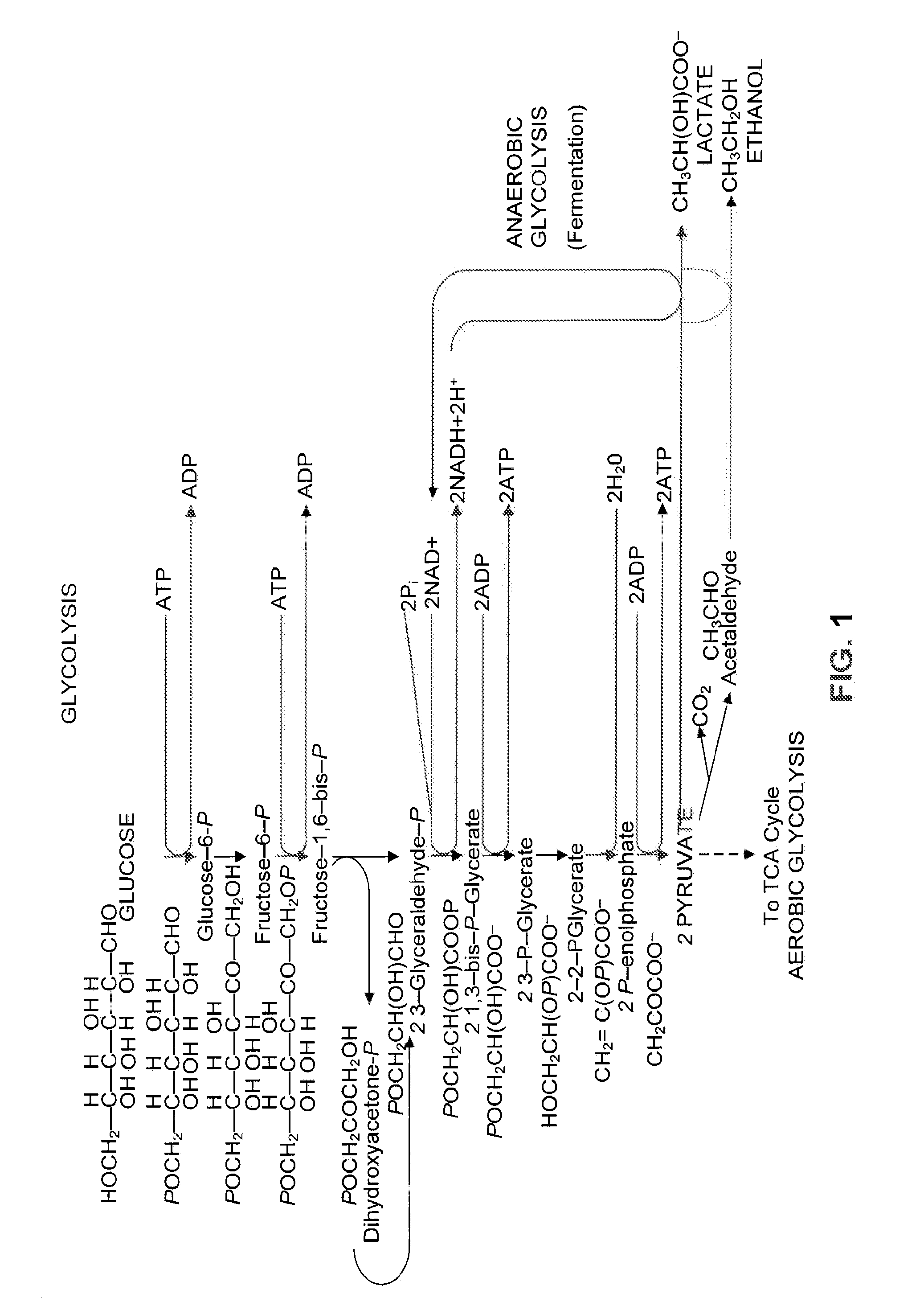
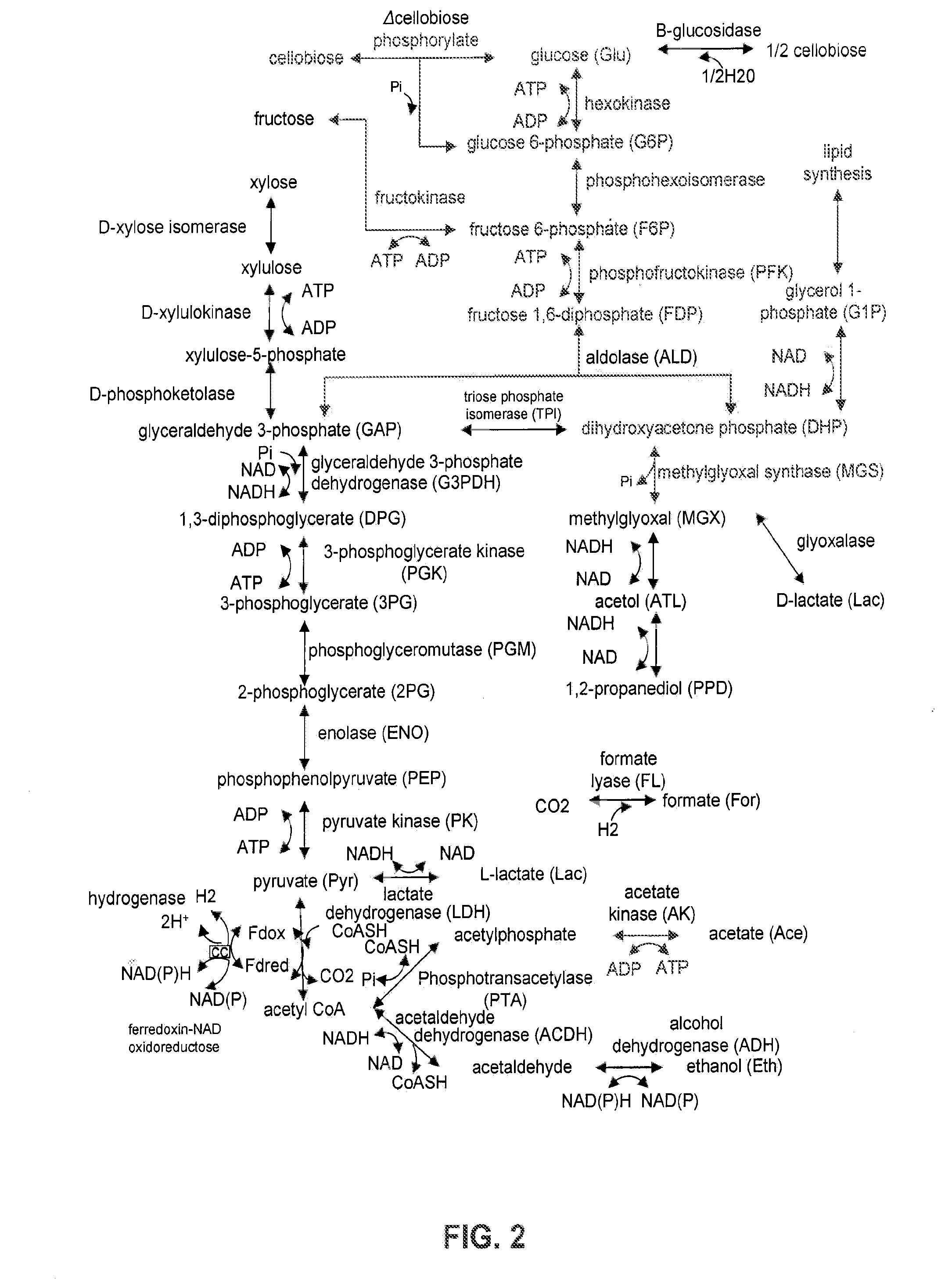
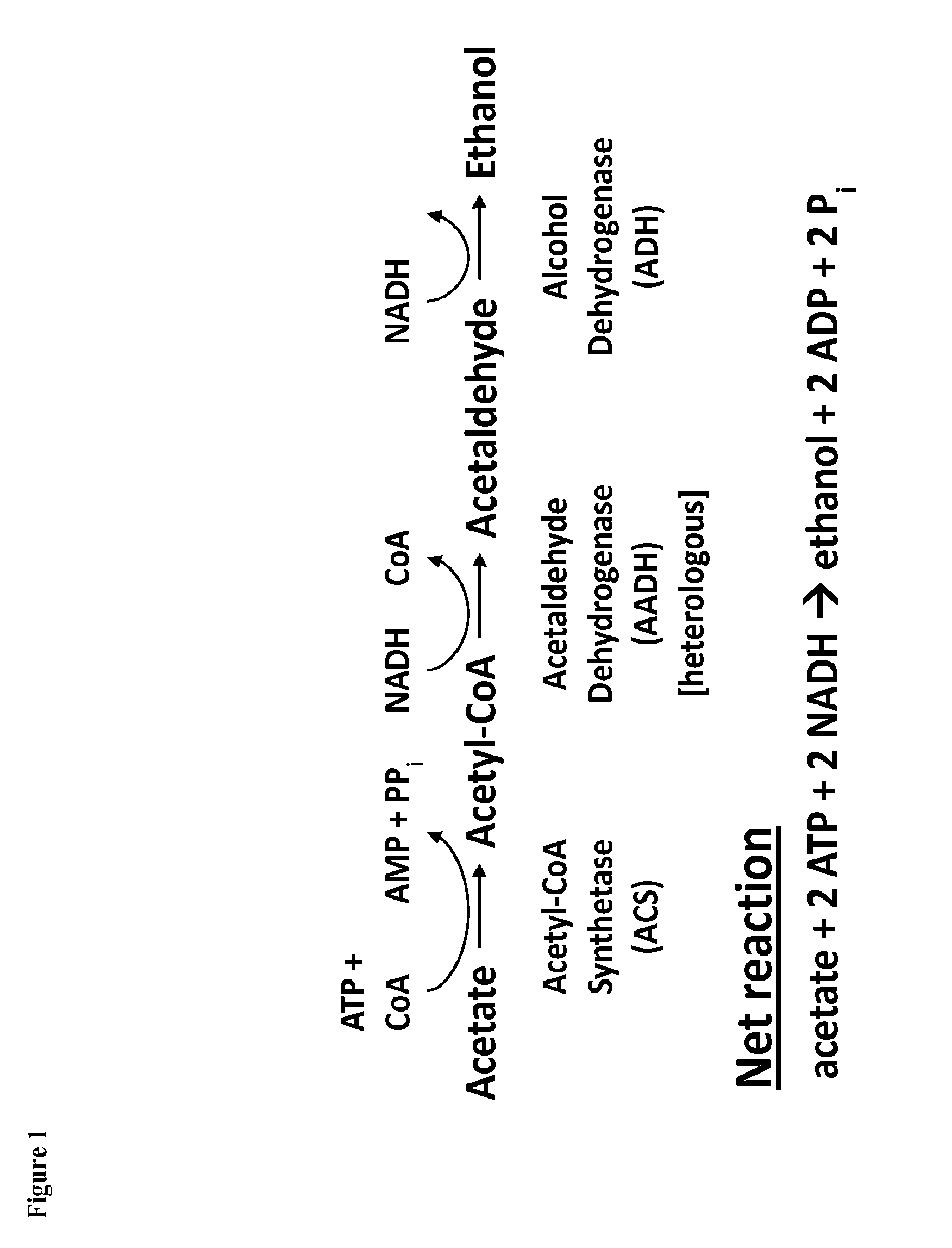
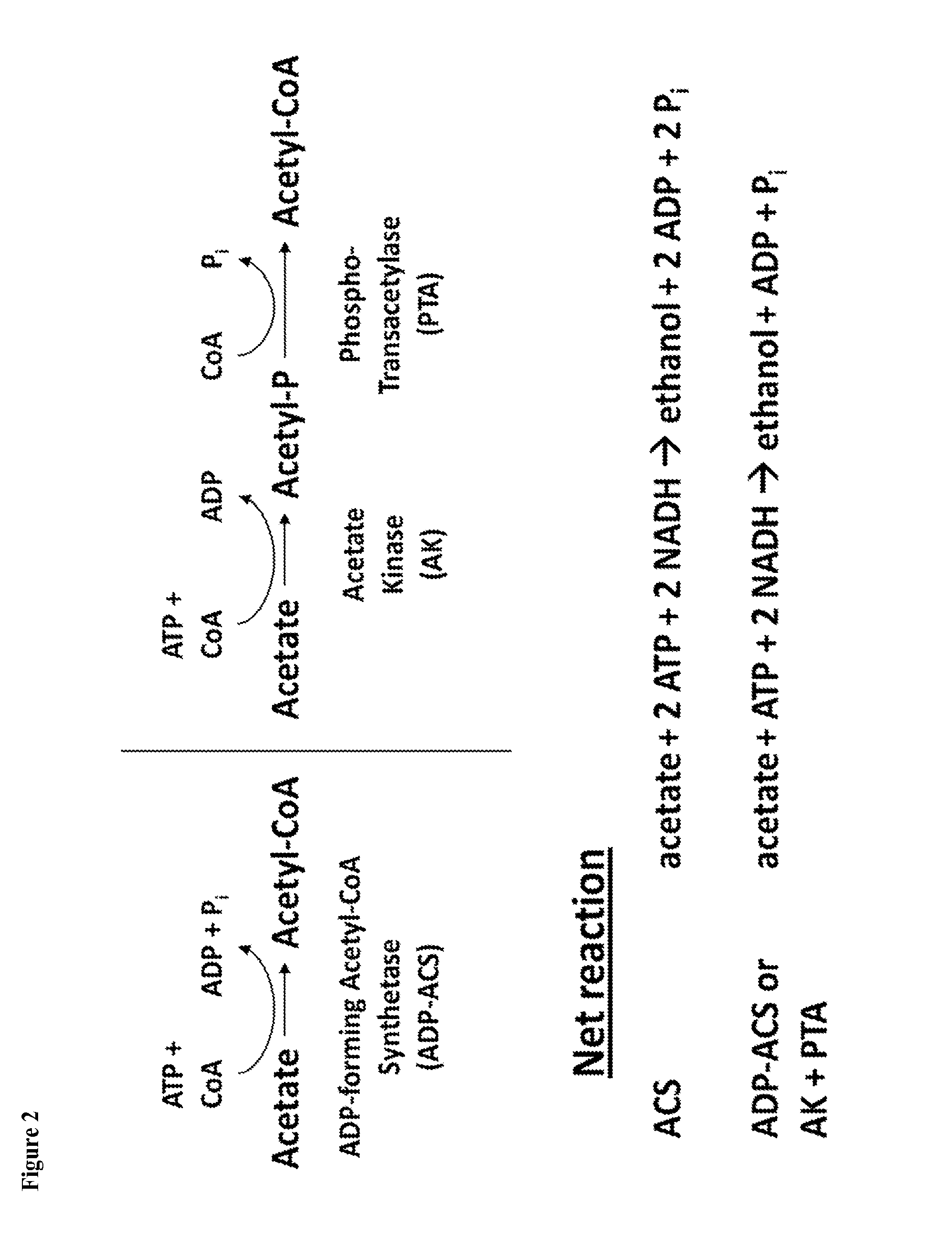
Method for Acetate Consumption During Ethanolic Fermentaion of Cellulosic Feedstocks
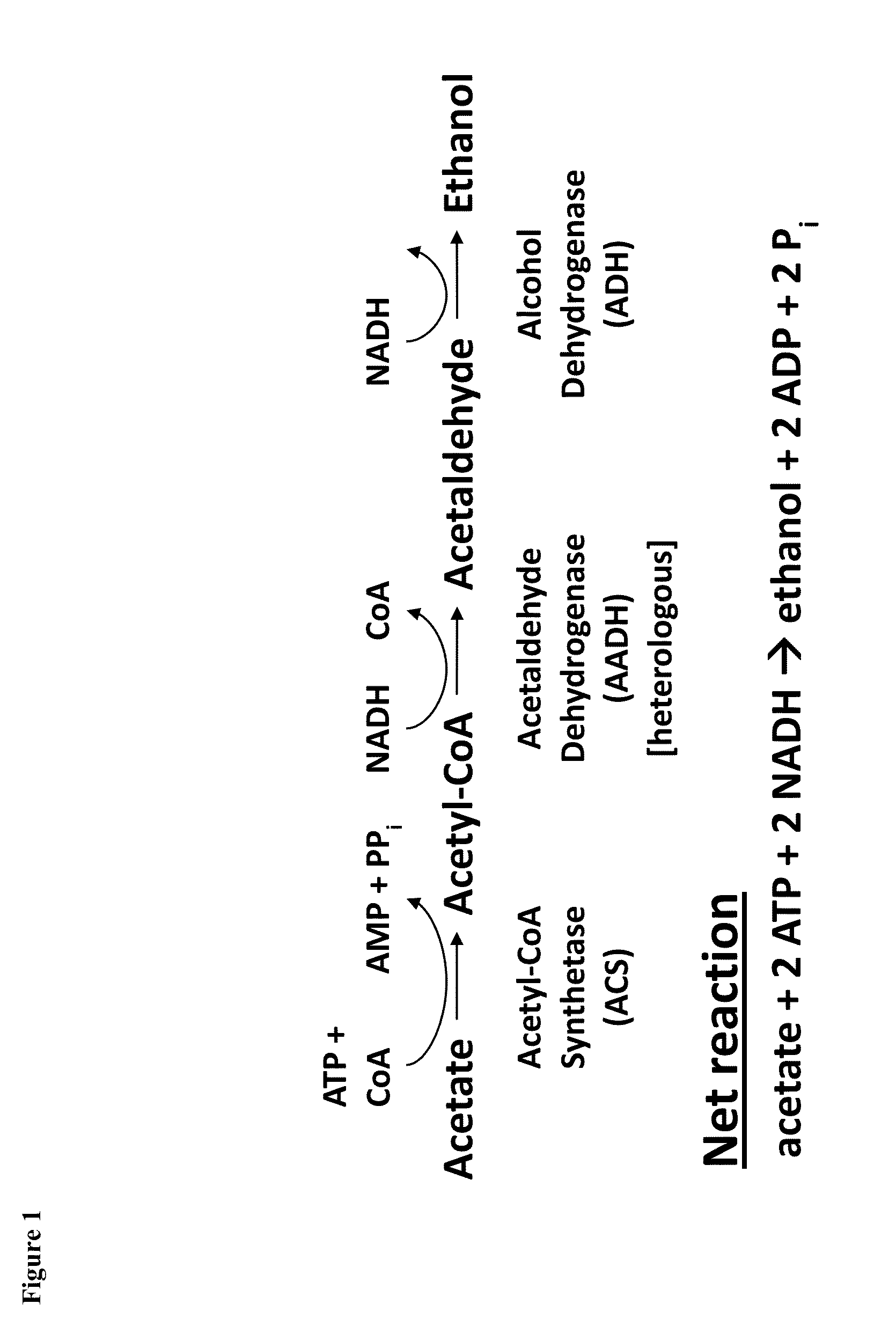
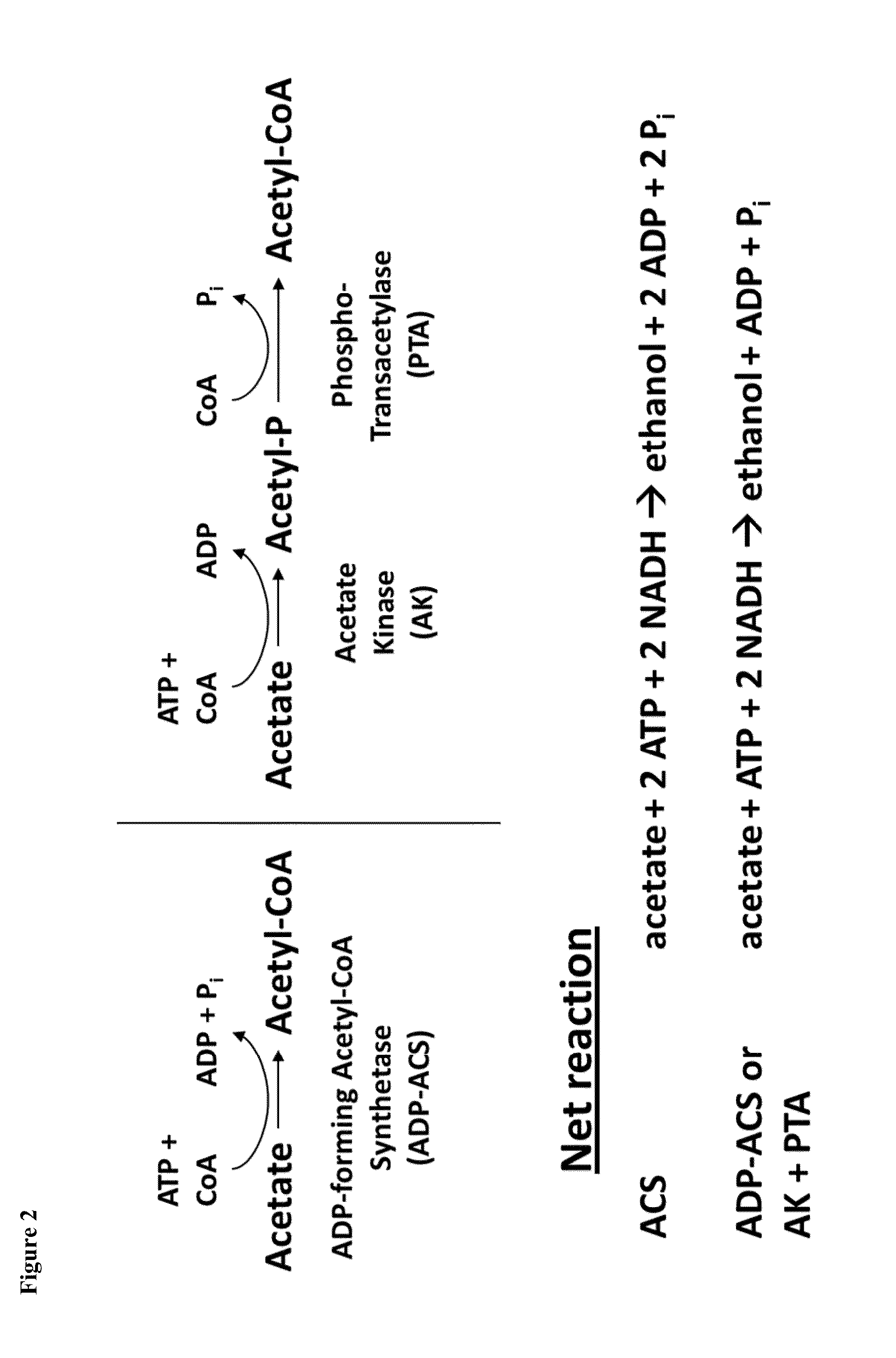
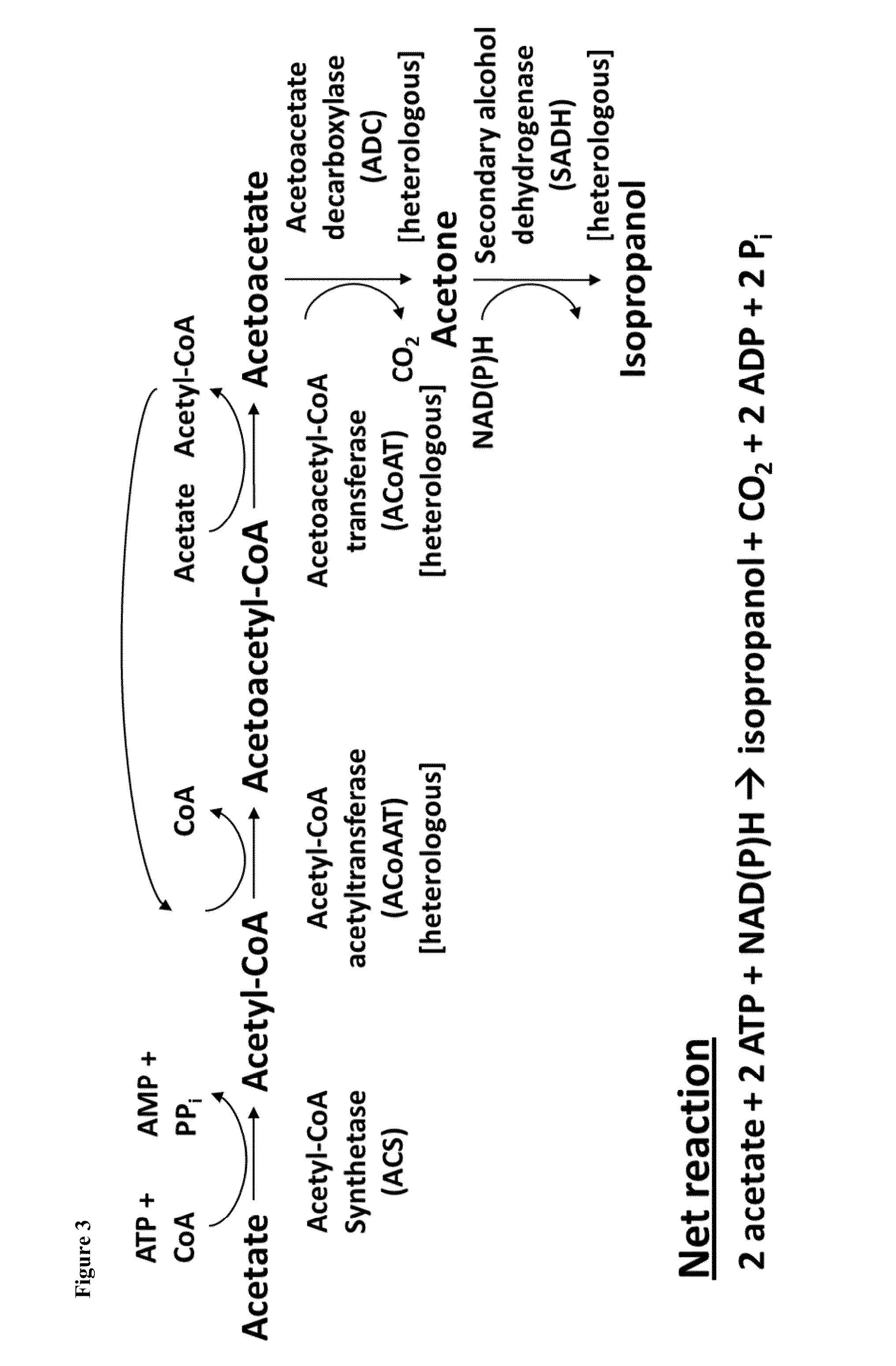
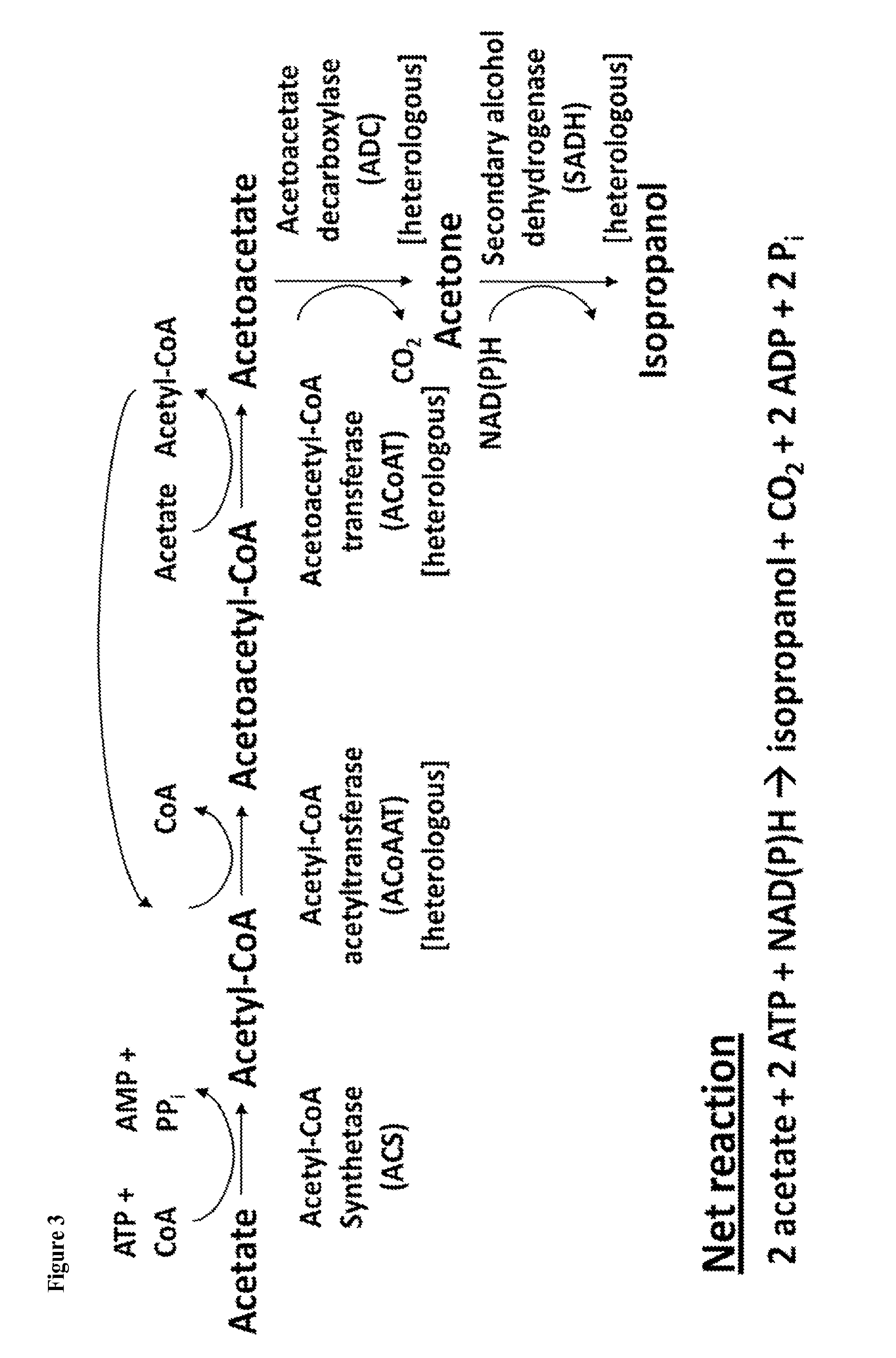
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to detoxify biomass-derived acetate via metabolic conversion to ethanol, acetone, or isopropanol. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more first engineered metabolic pathways to achieve: (1) conversion of acetate to ethanol; (2) conversion of acetate to acetone; or (3) conversion of acetate to isopropanol; and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more second engineered metabolic pathways to produce an electron donor used in the conversion of acetate to less inhibitory compounds; wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Detoxification of Biomass Derived Acetate Via Metabolic Conversion to Ethanol, Acetone, Isopropanol, or Ethyl Acetate
One aspect of the invention relates to a genetically modified thermophilic or mesophilic microorganism, wherein a first native gene is partially, substantially, or completely deleted, silenced, inactivated, or down-regulated, which first native gene encodes a first native enzyme involved in the metabolic production of an organic acid or a salt thereof, thereby increasing the native ability of said thermophilic or mesophilic microorganism to produce lactate or acetate as a fermentation product. In certain embodiments, the aforementioned microorganism further comprises a first non-native gene, which first non-native gene encodes a first non-native enzyme involved in the metabolic production of lactate or acetate. Another aspect of the invention relates to a process for converting lignocellulosic biomass to lactate or acetate, comprising contacting lignocellulosic biomass with a genetically modified thermophilic or mesophilic microorganism.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Method for Acetate Consumption During Ethanolic Fermentation of Cellulosic Feedstocks
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to detoxify biomass-derived acetate via metabolic conversion to ethanol, acetone, or isopropanol. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more first engineered metabolic pathways to achieve: (1) conversion of acetate to ethanol; (2) conversion of acetate to acetone; or (3) conversion of acetate to isopropanol; and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more second engineered metabolic pathways to produce an electron donor used in the conversion of acetate to less inhibitory compounds; wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, unregulated, or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Treatment for dry eye syndrome
InactiveUS7029712B1Speed up the conversion processInhibit productionBiocideSenses disorderEssential fatty acidNutrient
A novel formulation for the treatment of the many underlying inflammatory processes that cause dry eye syndrome. In particular, the formulation, which is orally administered includes the optimal blend of omega-3 and omega-6 essential fatty acids, and nutrient cofactors necessary to enhance the metabolic conversion associated with the tear-specific series E-one anti-inflammatory prostaglandin (PGE1). As used herein, the term “nutrient cofactor” refers to a compound that supports and enhances the conversion of linoleic acid to gamma-linolenic acid. Additionally, the formulation inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory compounds, as well as the growth of viral and bacterial pathogens of the three-layer tear film.
Owner:BIOSYNTRX
Integrated process for dual biocatalytic conversion of co2 gas into bio-products by enzyme enhanced hydration and biological culture
InactiveUS20150024453A1Improve scalabilityImprove processing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydration reactionPower station
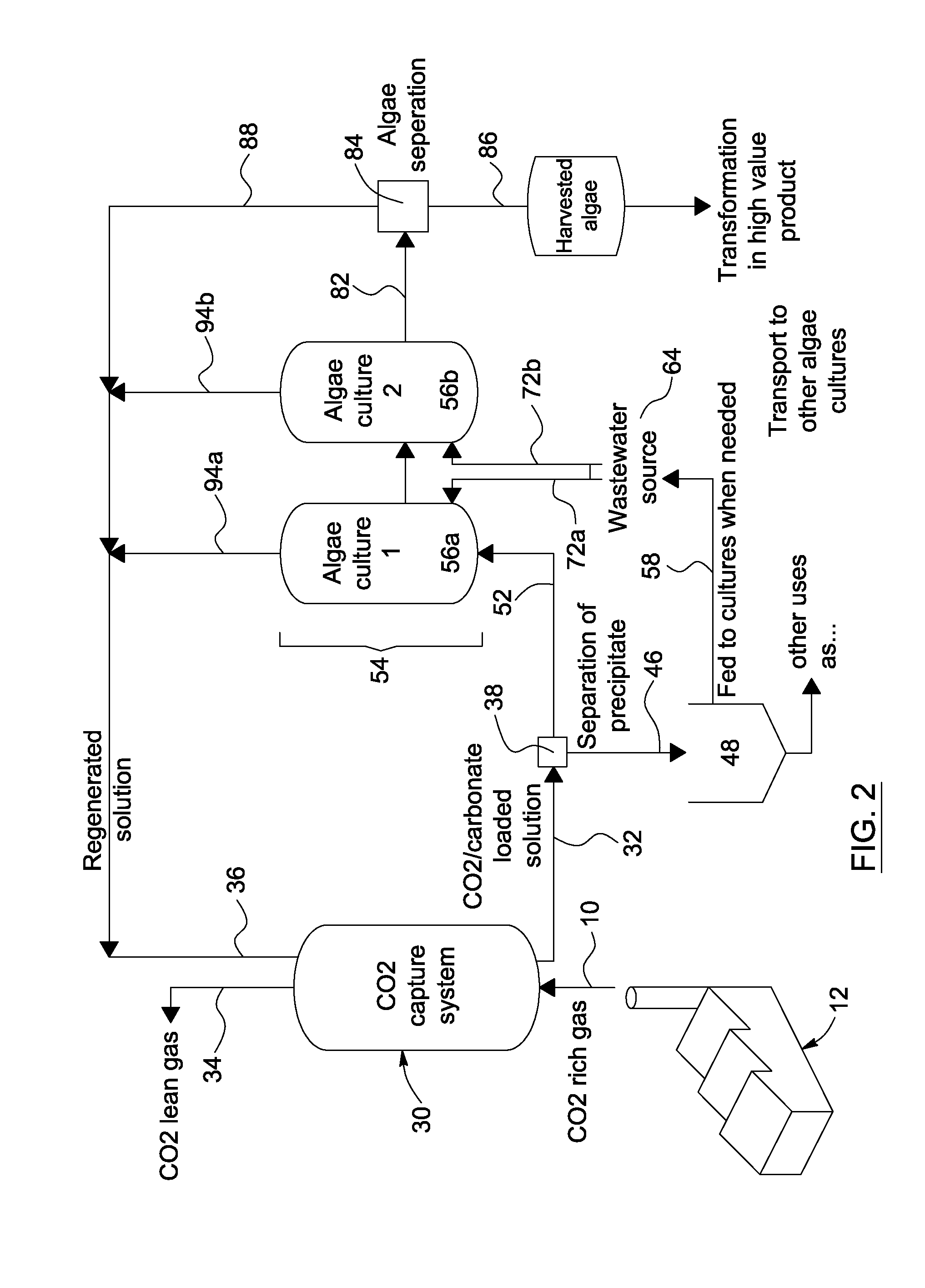
A method, process, apparatus, use and formulation for dual biocatalytic conversion of CO2 containing gas into carbon containing bio-products by enzymatic hydration of CO2 into bicarbonate ions in the presence of carbonic anhydrase and metabolic conversion of the bicarbonate ions into carbon containing bio-products in a biological culture. The dual biocatalytic conversion may be relatively constant with controlling a feeding of the bicarbonate ions to the biological culture in accordance with demands of the biological culture by retaining over-production of bicarbonate ions and feeding part of the over-production to the biological culture in accordance with nutrient demands of the biological culture. Bicarbonate ions may also be reconverted to generate a pure CO2 gas stream. The CO2 containing gas may be derived from operations of a power plant which receives a carbon-containing fuel for combustion, and the biological culture may be an algae culture.
Owner:CO2 SOLUTION
Compositions and methods for minimizing nornicotine synthesis in tobacco
ActiveUS20130037040A1Reducing nornicotine levelLower conversion rateTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMetaboliteNornicotine
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in tobacco plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for a root-specific nicotine demethylases, CYP82E10, and variants thereof, that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Compositions of the invention also include tobacco plants, or plant parts thereof, comprising a mutation in a gene encoding a CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase, wherein the mutation results in reduced expression or function of the CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase. Seed of these tobacco plants, or progeny thereof, and tobacco products prepared from the tobacco plants of the invention, or from plant parts or progeny thereof, are also provided. Methods for reducing the level of nornicotine, or reducing the rate of conversion of nicotine to nornicotine, in a tobacco plant, or plant part thereof are also provided. The methods comprise introducing into the genome of a tobacco plant a mutation within at least one allele of each of at least three nicotine demethylase genes, wherein the mutation reduces expression of the nicotine demethylase gene, and wherein a first of these nicotine demethylase genes encodes a root-specific nicotine demethylase involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in a tobacco plant or a plant part thereof. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Microbes, methods, and devices for redox-imbalanced metabolism
InactiveUS20140004578A1High activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRedoxCarbon flux
The invention generally relates to methods, devices, and microbes involved in performing redox imbalanced fermentations. In one aspect, the invention provides a device that generally includes an electrode and at least one microbe in electron communication with the electrode. The microbe generally can exhibit increased activity of at least one enzyme involved in converting a substrate to a redox imbalanced product. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for performing redox imbalanced fermentation. Generally, the method includes providing a substrate to a microbe under conditions effective for the microbe to metabolize the substrate to a redox imbalanced product. At least one microbe may be in contact with an electrode. In some cases, metabolic conversion of the substrate to the redox imbalanced product can include transferring electrons between the electrode and the microbe. In other cases, metabolic conversion of the substrate to the redox imbalanced product exhibits a carbon flux from organic substrate to organic product of at least 80%. In another aspect, the invention provides a genetically modified Shewanella oneidensis microbe.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
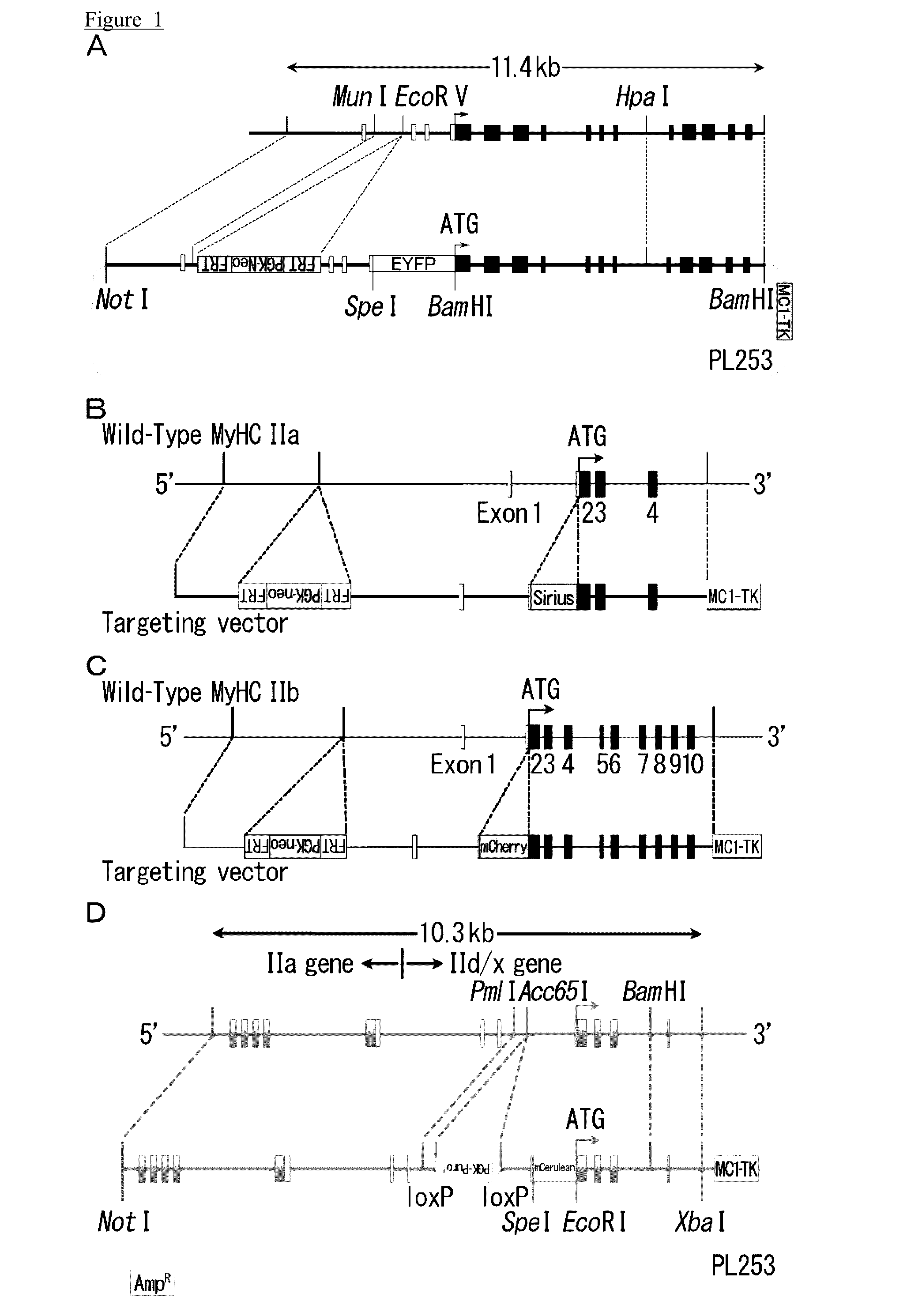
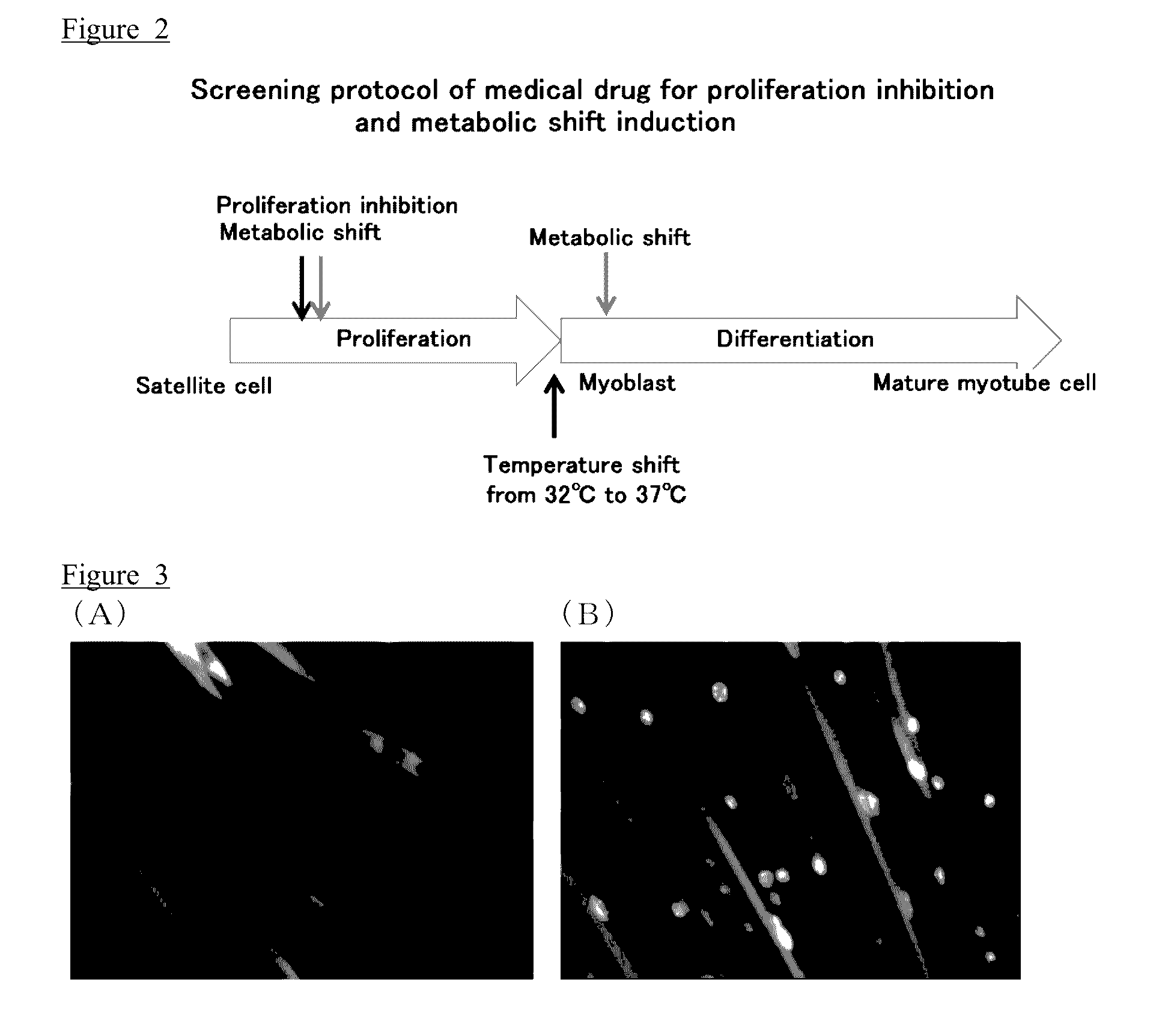
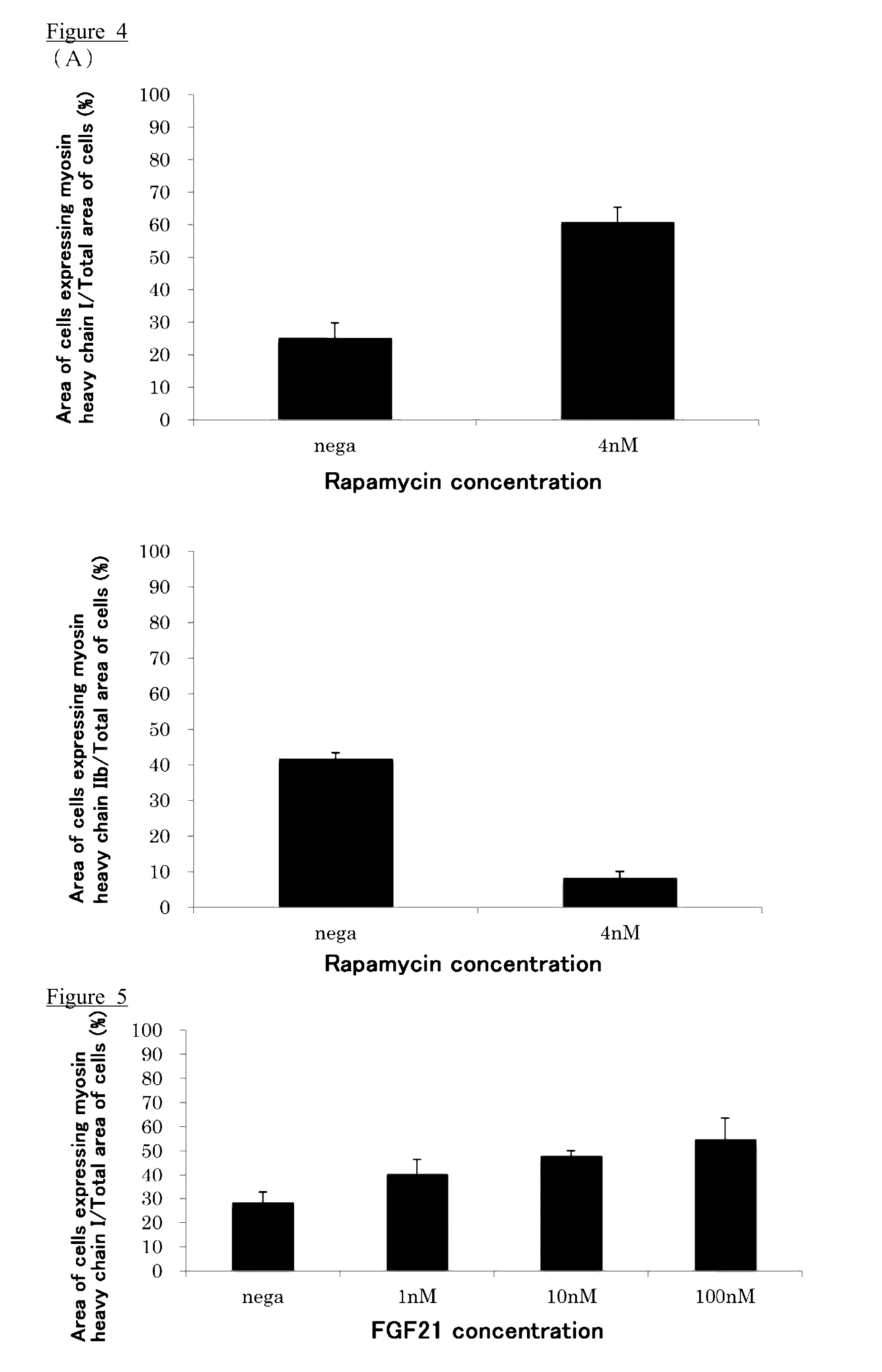
Muscle stem cell or myoblast, method for screening substances that participate in metabolic conversion using same, and pharmaceutical composition comprising substance obtained from said screening method
ActiveUS20160305933A1Treat and prevent skeletal muscle weaknessCompound screeningNervous disorderHeavy chainScreening method
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for screening a substance involved in a metabolic shift of skeletal muscle, and a kit for screening a substance involved in a metabolic shift of skeletal muscle.The object can be solved by a muscle stem cell or myoblast comprising at least one myosin-heavy chain fusion gene selected from the group consisting of a myosin-heavy chain I fusion gene wherein a myosin-heavy chain I gene and a fluorescent protein or photoprotein gene are fused, a myosin-heavy chain IIa fusion gene wherein a myosin-heavy chain IIa gene and a fluorescent protein or photoprotein gene are fused, a myosin-heavy chain IId / x fusion gene wherein a myosin-heavy chain IId / x gene and a fluorescent protein or photoprotein gene are fused, and a myosin-heavy chain IIb fusion gene wherein a myosin-heavy chain IIb gene and a fluorescent protein or photoprotein gene are fused.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN GERIATRIC HOSPITAL & INST GERONTOLOGY
Production method of purely natural DHA (docosa hexaenoic acid) raw milk and application of production method
The invention belongs to the technical field of the production of dairy products, and particularly relates to a production method of purely natural DHA (docosa hexaenoic acid) raw milk and an application of the production method. According to the production method of purely natural DHA raw milk, a ration with schizochytrium limacinum powder is fed to cows at the lactation period, so that the content of DHA ingested by the cows is increased; and through autologous metabolism of the cows, natural DHA fresh raw milk stable in production state is transformed. The raw milk has processing characteristics of normal raw milk, and besides, contains certain natural DHA components, in the processing course of subsequent dairy products, later-stage addition of DHA nutrient components is not needed, the problems that peculiar smell is easy to produce in the addition course of product ingredients and the processing technology is complex are solved, and a novel way is opened up for production of purely natural DHA raw milk and dairy products.
Owner:内蒙古圣牧高科牧业有限公司
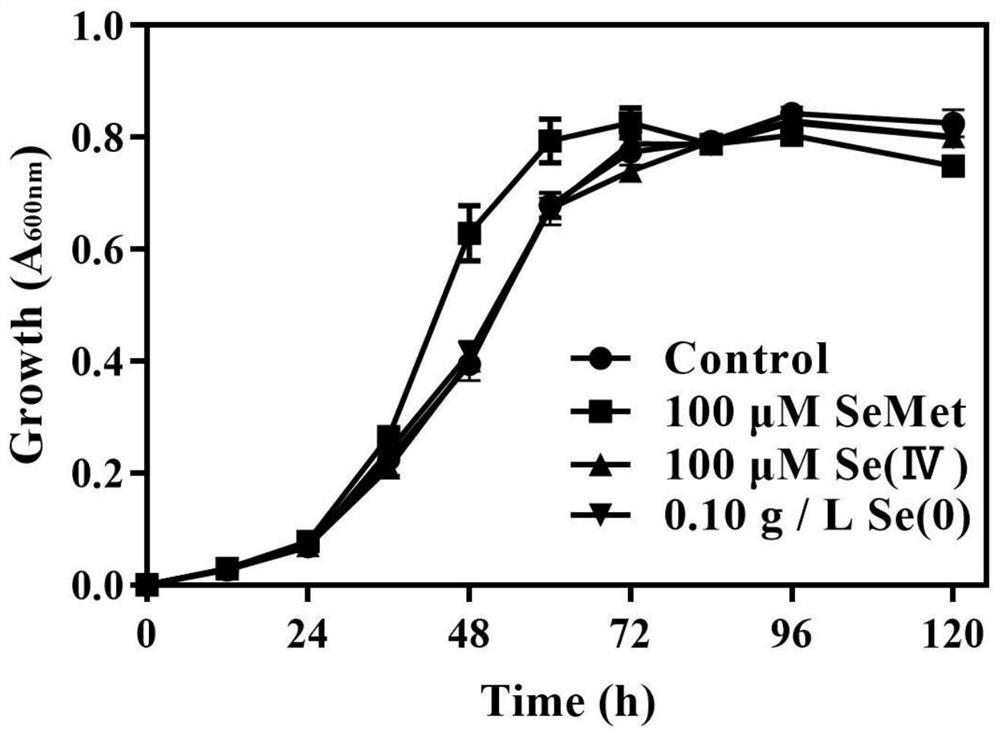
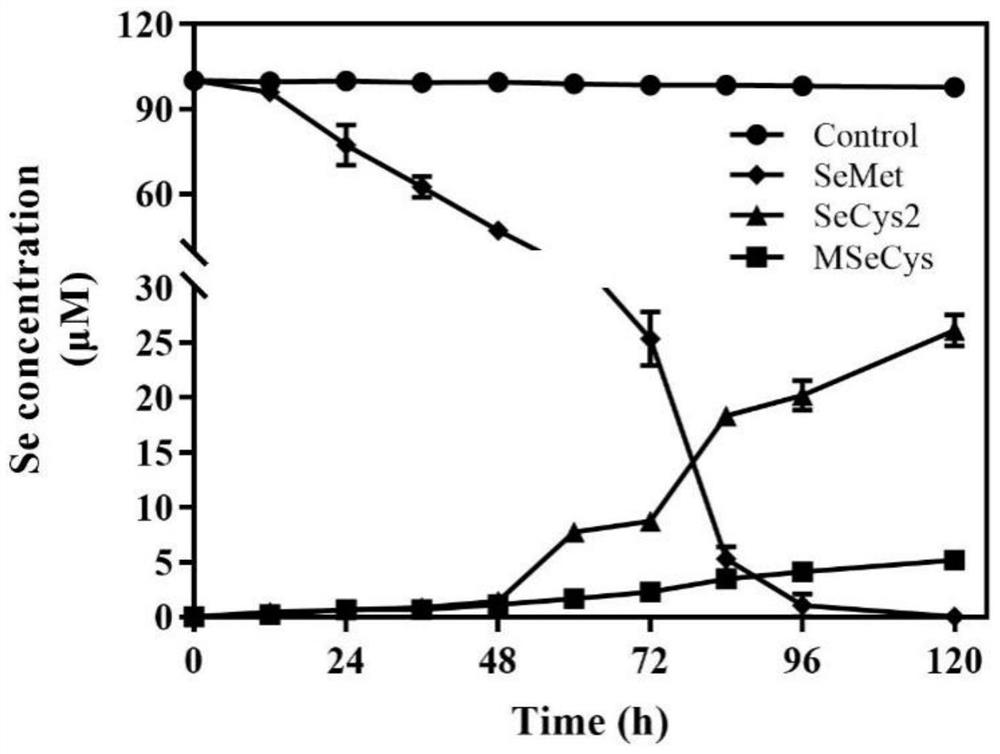
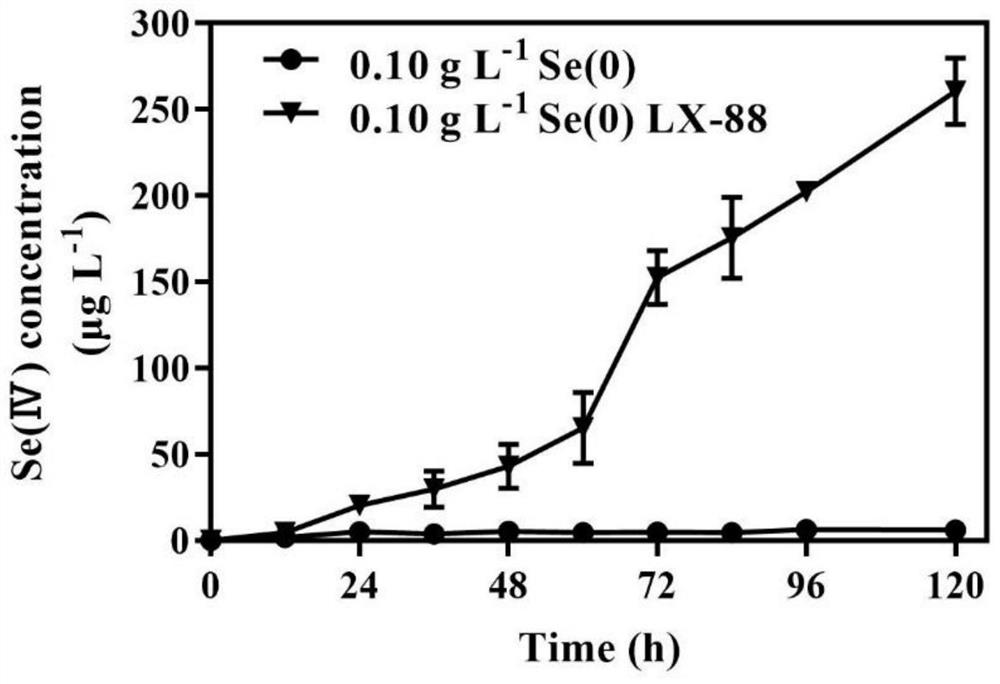
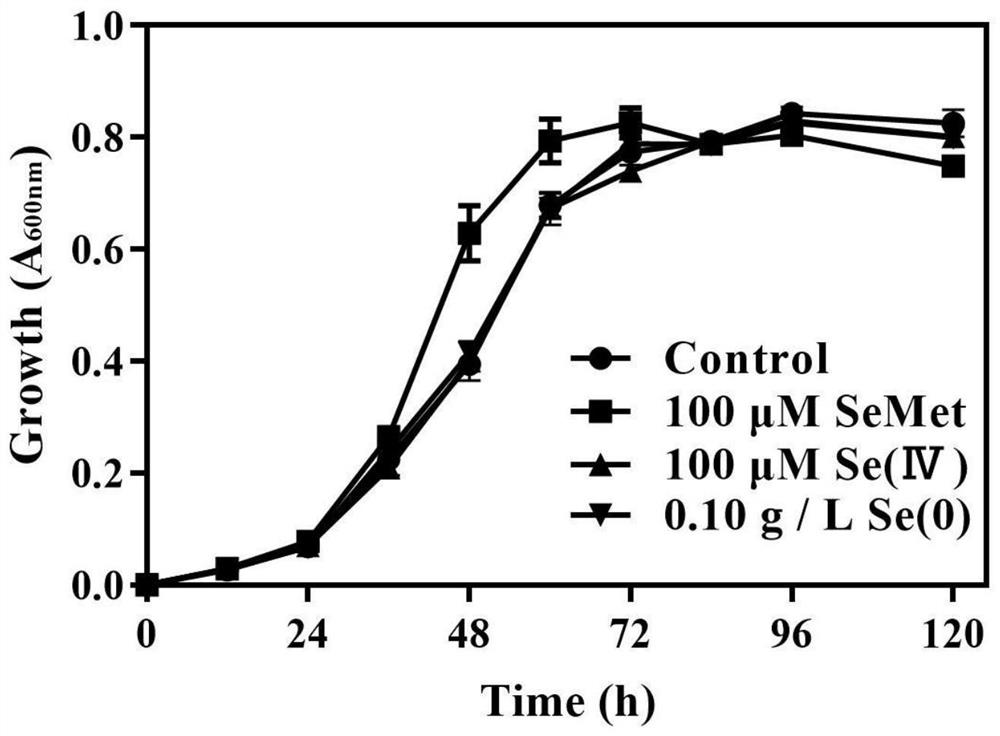
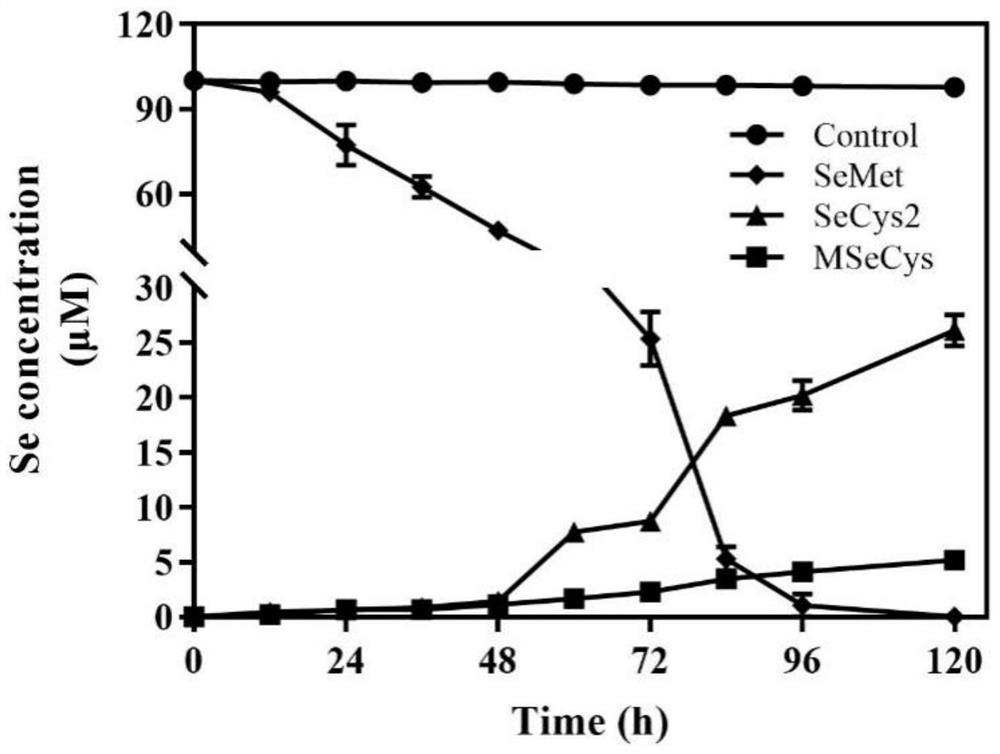
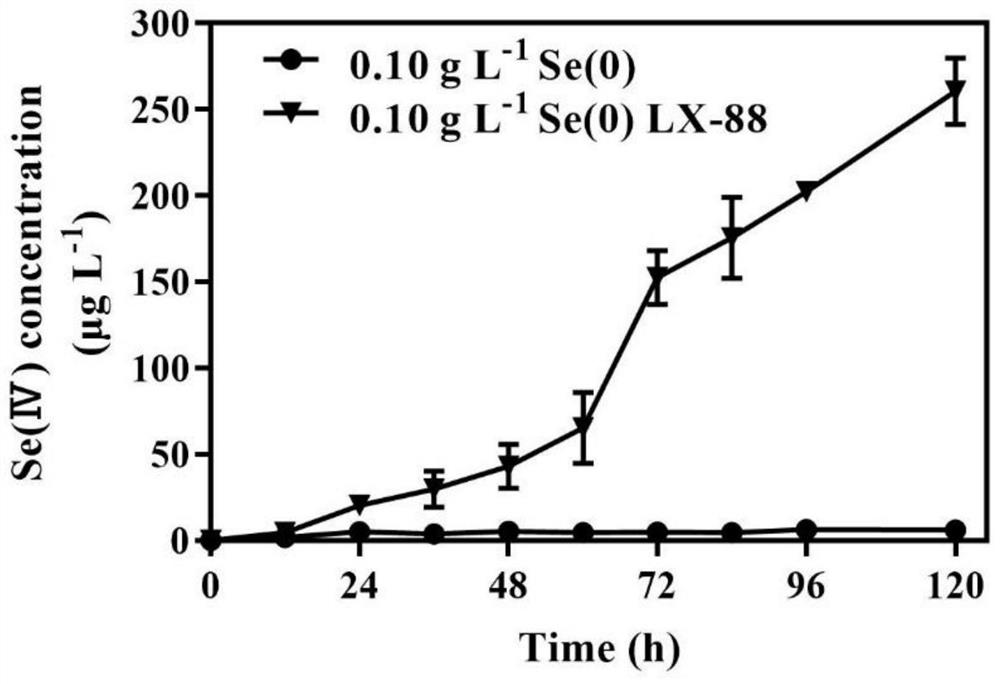
LX-88 strain with good selenium conversion and Se (0) oxidation capacities and application of LX-88 strain
ActiveCN113322211APromote selenium enrichmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses an LX-88 strain with good selenium conversion and Se (0) oxidation capacity and application of the LX-88 strain, and the preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M2021542. The strain can convert SeMet into selenocystine (SeCys2), methyl selenocysteine (MSeCys) and the like and has an oxidation effect on elemental selenium, and the strain LX-88 can be used for reducing Se (IV) and can be used for reducing the Se (IV) into red nano-selenium (SeNPs), SeCys2 and MSeCys. Therefore, the strain LX-88 can be used as an industrial microorganism and is applied to production and preparation of SeCys2 and MSeCys; the strain can be used as a model microorganism for research on metabolic transformation of organic selenium and Se (IV); the plant selenium-rich microbial inoculum can be prepared and can be used as a microorganism for Se (0) oxidation research.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for promoting starting of anaerobic digestor and accelerating conversion of propionic acid into methane
InactiveCN106350567AImprove degradation rateShorten the timeWaste based fuelFermentationPropanoic acidMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for promoting the starting of an anaerobic digestor and accelerating the conversion of propionic acid into methane. The method comprises the steps of preparing compound bacteria, adding a solid carrier into the compound bacteria in a mass percentage of 1%-20%, inoculating the compound bacteria into a sterile anaerobic BCTY culture medium containing 1500ppm-10000ppm of sodium propionate, and carrying out anaerobic standing culturing at 40 DEG C, wherein the pH value of the sterile anaerobic BCTY culture medium is 7.5-8.5. By virtue of the method, the degradation rate of propionic acid can be substantially increased, and the time required for the complete degradation of propionic acid can be substantially shortened; the operation efficiency of the metabolic conversion of propionic acid into methane is remarkably promoted; and the transport metabolism of H2 in an anaerobic digestion system can be effectively promoted, so that the anaerobic digestion system is maintained at a relatively low hydrogen partial pressure state, is relatively stable and has relatively strong inversion resistance, and the operation load is substantially improved.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Detoxification of biomass derived acetate via metabolic conversion to ethanol, acetone, isopropanol, or ethyl acetate
One aspect of the invention relates to a genetically modified thermophilic or mesophilic microorganism, wherein a first native gene is partially, substantially, or completely deleted, silenced, inactivated, or down-regulated, which first native gene encodes a first native enzyme involved in the metabolic production of an organic acid or a salt thereof, thereby increasing the native ability of said thermophilic or mesophilic microorganism to produce lactate or acetate as a fermentation product. In certain embodiments, the aforementioned microorganism further comprises a first non-native gene, which first non-native gene encodes a first non-native enzyme involved in the metabolic production of lactate or acetate. Another aspect of the invention relates to a process for converting lignocellulosic biomass to lactate or acetate, comprising contacting lignocellulosic biomass with a genetically modified thermophilic or mesophilic microorganism.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Smelly-gas treatment system based on combination of multiple filter material media and method
InactiveCN107469613ASmall footprintImprove processing efficiencyDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementWater dischargeProduct gas
The invention discloses a smelly-gas treatment system based on combination of multiple filter material media in the field of biological material smelly-gas treatment and a method. The system is mainly composed of soil mixed layers, inorganic filler layers, a large-particle zeolite layer, a draught fan, a water distribution pipe, a gas distribution pipe, a grille board and a water discharging valve; and the grille board is located between one inorganic filler layer and the large-particle zeolite layer, the water distribution pipe is located at the top of the system, and the water discharging valve is located at the bottom of the system. Gases sequentially enter the large-particle zeolite layer, the inorganic filler layer and the soil mixed layer through conveying by the draught fan, are adsorbed by volcanic rock and then are subjected to metabolic conversion by microorganisms, so that the smelly gases are treated effectively. Compared with a smelly-gas treatment system which simply utilizes an inorganic filler or an organic filler, the system provided by the invention has the advantages that the system can effectively adsorb and treat the smelly gases for a long time, the microorganisms in a filler can be recycled, and the system is not easy to block.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Preparation method of spiced beef jerky
InactiveCN108902754AHigh in nutrientsGreat tasteFood ultrasonic treatmentFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentFiberCooking & baking
The invention discloses a preparation method of spiced beef jerky, and belongs to the technical field of beef processing. According to the present invention, the pretreatment of the spiced beef preparation is performed by combining ultrasonic soaking and pulse magnetic field; the ultrasonic soaking respectively adopts a CaCl2 solution and a starch solution, wherein the Ca<2+> is a triggering agentfor protein metabolism and biological enzymes, can promote the metabolic conversion of proteins into amino acids, and can easily improve the nutrients and the taste of beef, the starch solution can easily maintain the freshness, the tenderness and the smoothness of beef, the mechanical effect of the ultrasound can easily reduce the shearing force of beef, and the cavitation effect of the ultrasound can easily achieve the small-sheet beef fiber and improve the tenderness of beef; and finally the special beef aroma is formed by using the variable temperature baking technology through the degradation of various fats, proteins and saccharides and the complex chemical reaction among the products during the baking of beef, and the different temperatures are adopted at different stages, such that the water content and the tenderness of beef are easily maintained, the taste can be improved, and the quality uniformity of beef can be easily improved.
Owner:ANHUI WANLI FOODS CO LTD
Brush polymer modified graphene oxide-immobilized capture receptor compound and application thereof in enrichment of monoclonal antibodies
InactiveCN113030284AIncrease loadHigh enrichment efficiencyComponent separationAntiendomysial antibodiesAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention relates to a brush polymer modified graphene oxide-immobilized capture receptor compound and application thereof in enrichment of monoclonal antibodies. The preparation method of the brush polymer modified graphene oxide compound comprises the following steps of: 1) modifying an initiator on the surface of graphene oxide; and (2) performing surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization on the product obtained in the step 1) and acrylic acid in the presence of CuCl, CuCl2 and N, N, N',N'',N''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine to obtain the compound. According to the invention, specific enrichment of immobilized capture receptors and high-sensitivity detection of LC-MS are combined, so that accurate pharmacokinetic parameters and metabolic transformation process of monoclonal antibody drugs in vivo are expected to be obtained. According to the preparation method of the present invention, the efficient enrichment detection of different antibody drugs or protein drugs can be achieved by replacing a capture receptor, such that the efficient specific enrichment detection method can be popularized to the analysis detection and the pharmacokinetic research of other protein drugs so as to further guide the drug research and development, the mechanism research, the clinical medication and the like.
Owner:BEIJING SHIJITAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIVERSTY
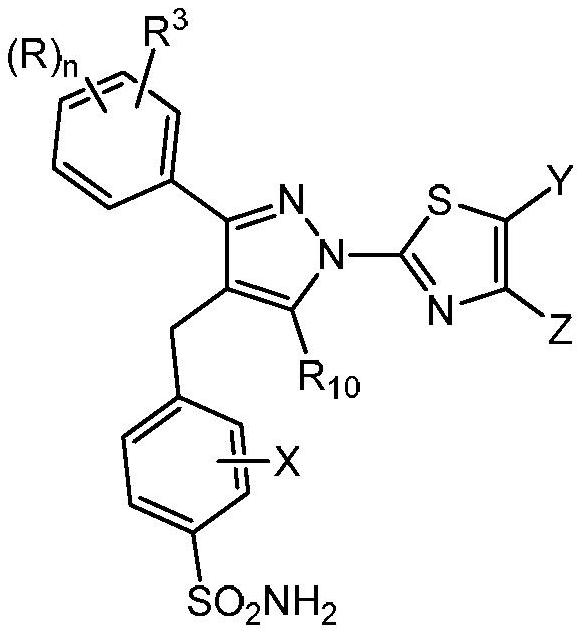
1h-pyrazol-1-yl-thiazoles as inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase and methods of use thereof
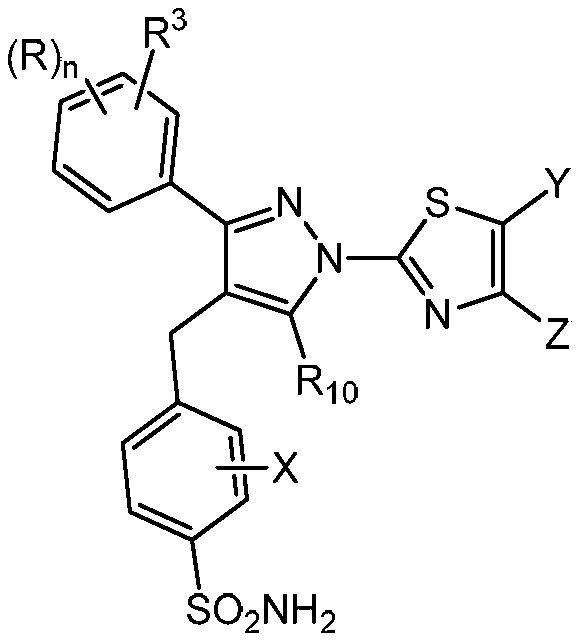
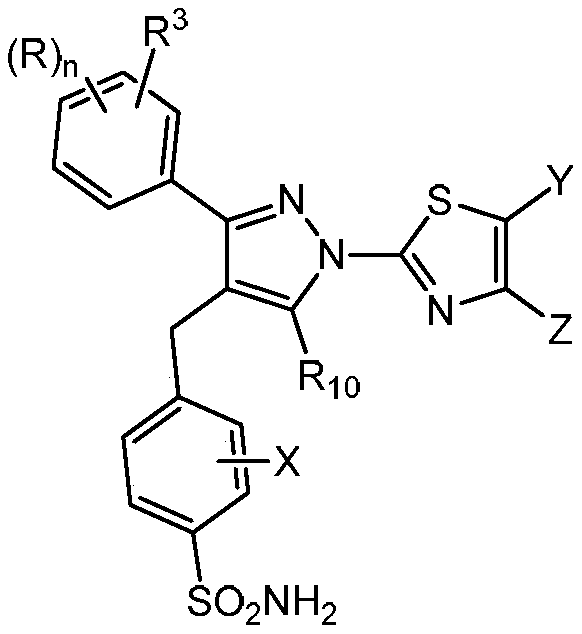
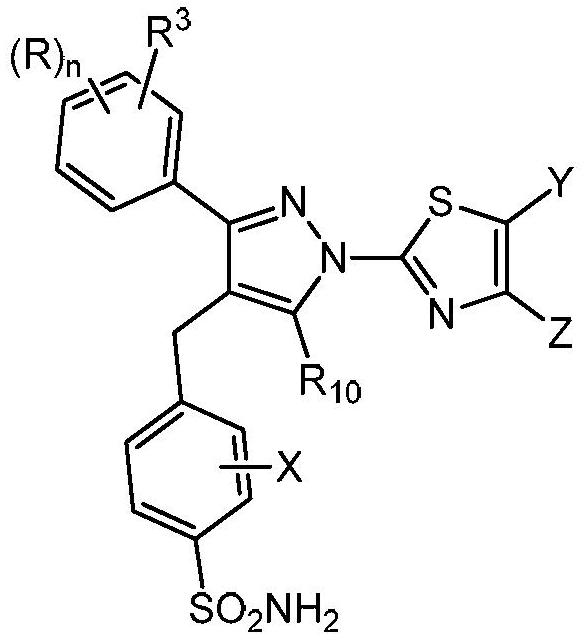
The invention provides a compound of the formula (II) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The variables, e.g. n, R, R3, R10, X, Y, and Z are defined herein. These compounds act as lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors and are useful for treating cancer and fibrosis. The compounds may be particularly useful for treating forms of cancer in which a metabolic switch from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis has occurred. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing a compound of this formula and a method for treating patients having cancer, fibrosis, or other conditions in which a metabolic switch from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis has occurred.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +3
Improved specificity in treatment of diseases
A drug is modified by covalently coupling a blocking group to the drug via a nitrogen atom in the blocking group. The blocking group in the modified drug prevents metabolic conversion and sequestration of the drug in non-target cells, and the blocking group is enzymatically removed in the target cell. Particularly contemplated advantages of presented compounds and methods include reduction of cytotoxicity by inhibition of metabolic conversion to potentially cytotoxic metabolites, reduction of dosages of drugs by reduction of sequestration into non-target cells, and increase of selectivity of a drug.
Owner:RIBAPHARM
Muscle stem cell or myoblast, method for screening substances that participate in metabolic conversion using same, and pharmaceutical composition comprising substance obtained from said screening method
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN GERIATRIC HOSPITAL & INST GERONTOLOGY
A lx-88 strain with good selenium transformation and se(0) oxidation ability and its application
ActiveCN113322211BPromote selenium enrichmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and specifically discloses a LX-88 bacterium with good selenium conversion and Se(0) oxidation capabilities and its application. The preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M2021542. The strain can convert SeMet into selenocysteine (SeCys2) and methylselenocysteine (MSeCys), etc., and has oxidation effect on elemental selenium. The strain LX‑88 can reduce Se(IV), and can convert Se (IV) Reduction to red nanoselenium (SeNPs), SeCys2 and MSeCys. Therefore, the bacterial strain LX‑88 can be used as an industrial microorganism for the production and preparation of SeCys2 and MSeCys; it can be used as a model microorganism for the study of organic selenium and Se(IV) metabolic transformation; Microorganisms for the study of oxidation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome p450 genes
PendingUS20220000055A1Lower Level RequirementsReducing nornicotine levelTobacco treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrosoNornicotine
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in Nicotiana plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for cytochrome P450s that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Expression cassettes, vectors, plants, and plant parts thereof comprising inhibitory sequences that target expression or function of the disclosed cytochrome P450 polypeptides are also provided. Methods for the use of these novel sequences to inhibit expression or function of cytochrome P450 polypeptides involved in this metabolic conversion are also provided. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND +1
1h-pyrazol-1-yl-thiazole as an inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase and methods of using the same
The present disclosure provides compounds of formula (II) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Variables such as n, R, R 3 , R 10 , X, Y and Z are defined herein. These compounds act as inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase and are used in the treatment of cancer and fibrosis. The compounds may be particularly useful in the treatment of forms of cancer in which metabolic transformation from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis occurs. The present disclosure also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of this formula and methods for treating patients with cancer, fibrosis, or other disorders in which the metabolic transition from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis occurs.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +3
High productivity methane fermentation processes
ActiveUS10934566B2Improve productivityHigh densityBy-product recoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementCo2 removalMicroorganism
Processes are provided for enhancing the productivity of fermenters during the metabolic conversion of methane-containing gases to products containing polyhydroxyalkanoate, which products can be used to make, for instance, animal feed or biodegradable, polymeric articles. The processes involve one or both of attenuating the heat generated to grow a population of microorganisms and removal of heat during the fermentation by removal of carbon dioxide.
Owner:MANGO MATERIALS INC
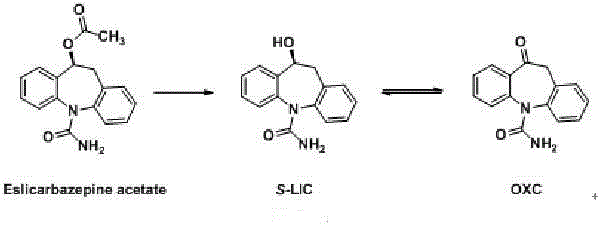
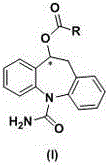
Brain-targeting eslicarbazepine ester prodrug and application thereof
ActiveCN106588773AImprove the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB)Improve Brain UptakeNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAdjuvantEster prodrug
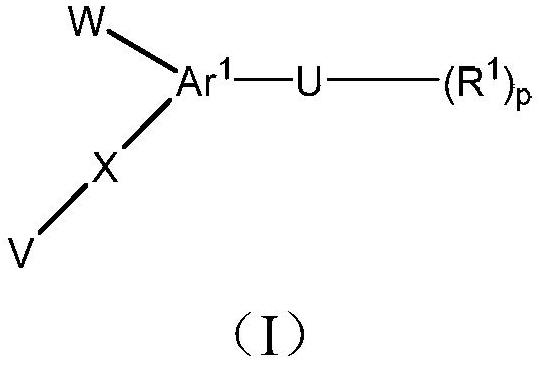
The invention relates to an eslicarbazepine ester prodrug and an application thereof, wherein the prodrug is a compound represented by the formula (I) or optical isomers or physiologically acceptable salts of the compound represented by the formula (I), wherein R represents a lipophilic substituent. The compound represented by the formula (I) is the eslicarbazepine ester prodrug containing the lipophilic substituent, is converted into eslicarbazepine through metabolism in vivo to play pharmacological effects, and can be applied in preparation of drugs for treatment, prevention or adjuvant treatment of central nervous system diseases, such as epilepsy and the like.
Owner:北京现代药物代谢研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com