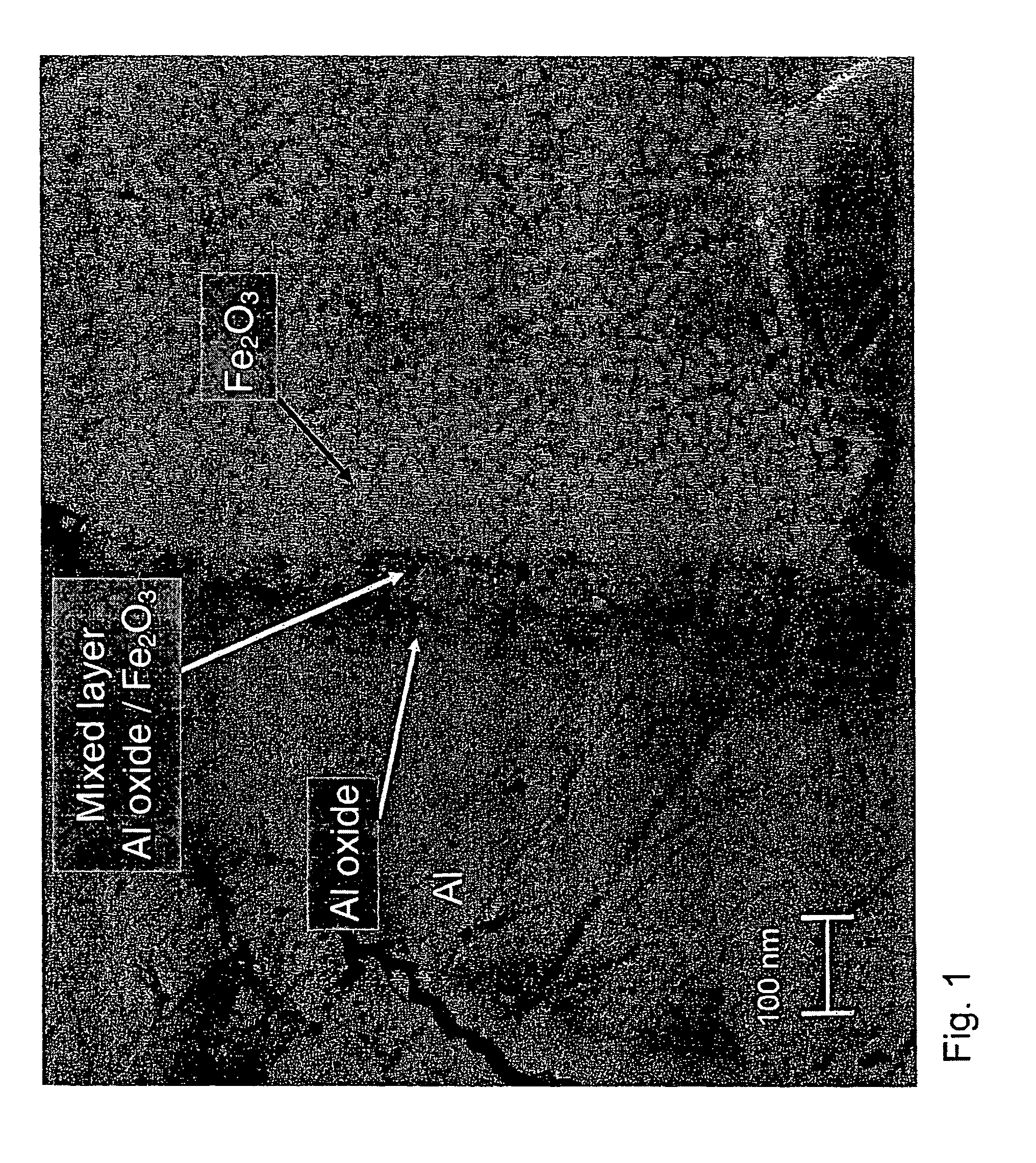
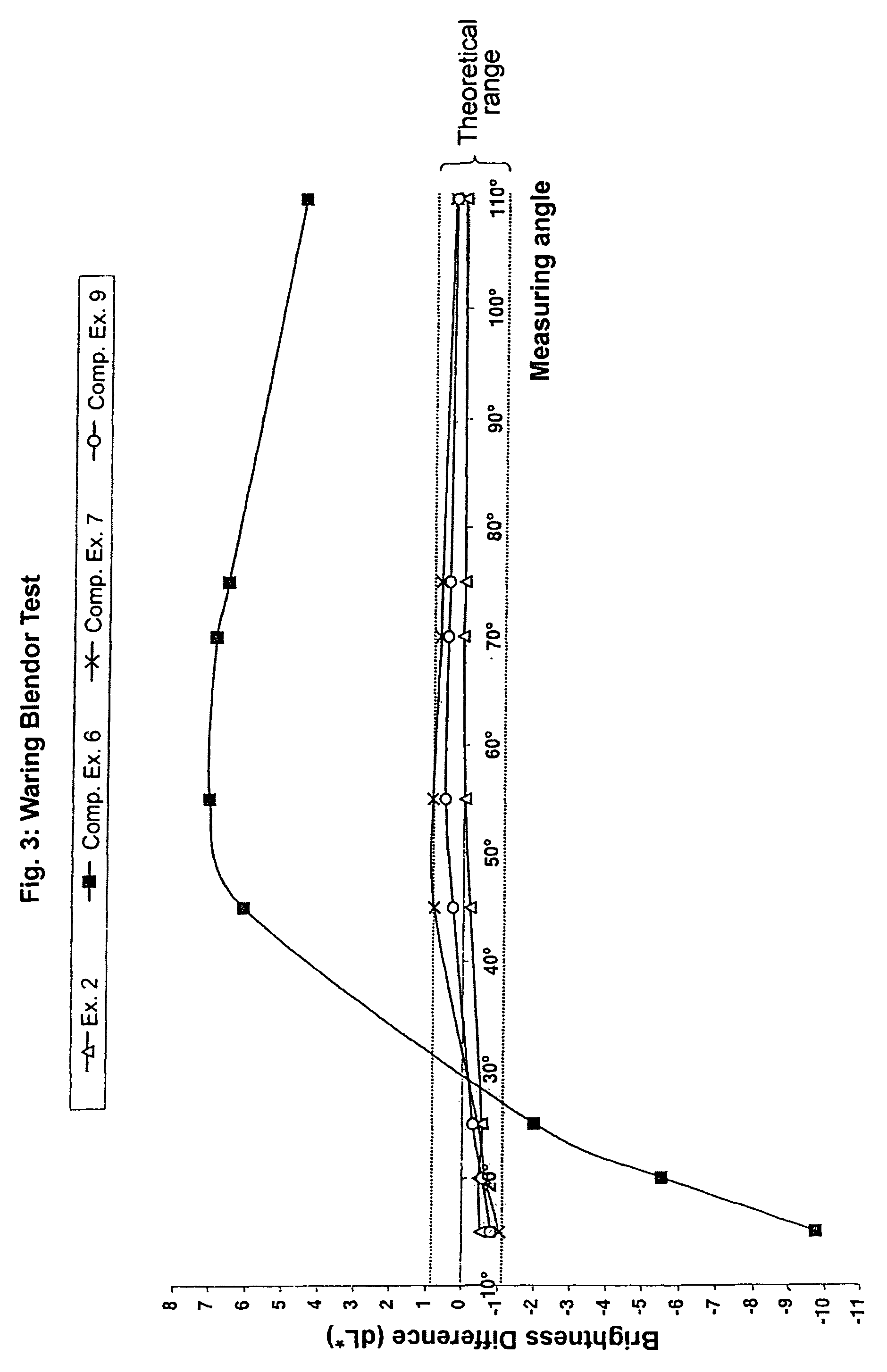
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
844 results about "Mixed layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity. The atmospheric mixed layer is a zone having nearly constant potential temperature and specific humidity with height. The depth of the atmospheric mixed layer is known as the mixing height. Turbulence typically plays a role in the formation of fluid mixed layers.
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20050084712A1Lower energy barrierLow voltage driveDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic structureSimple Organic Compounds
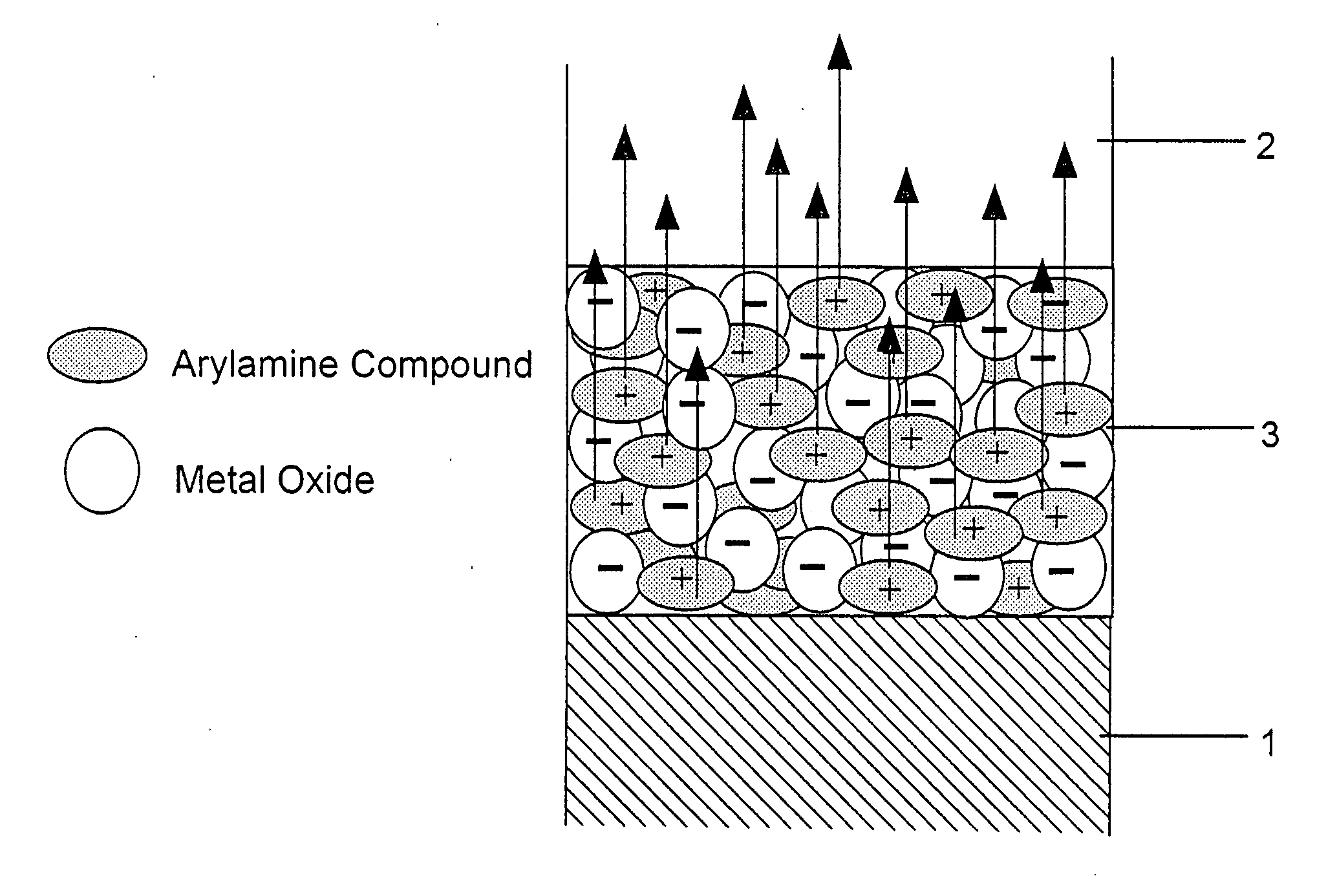
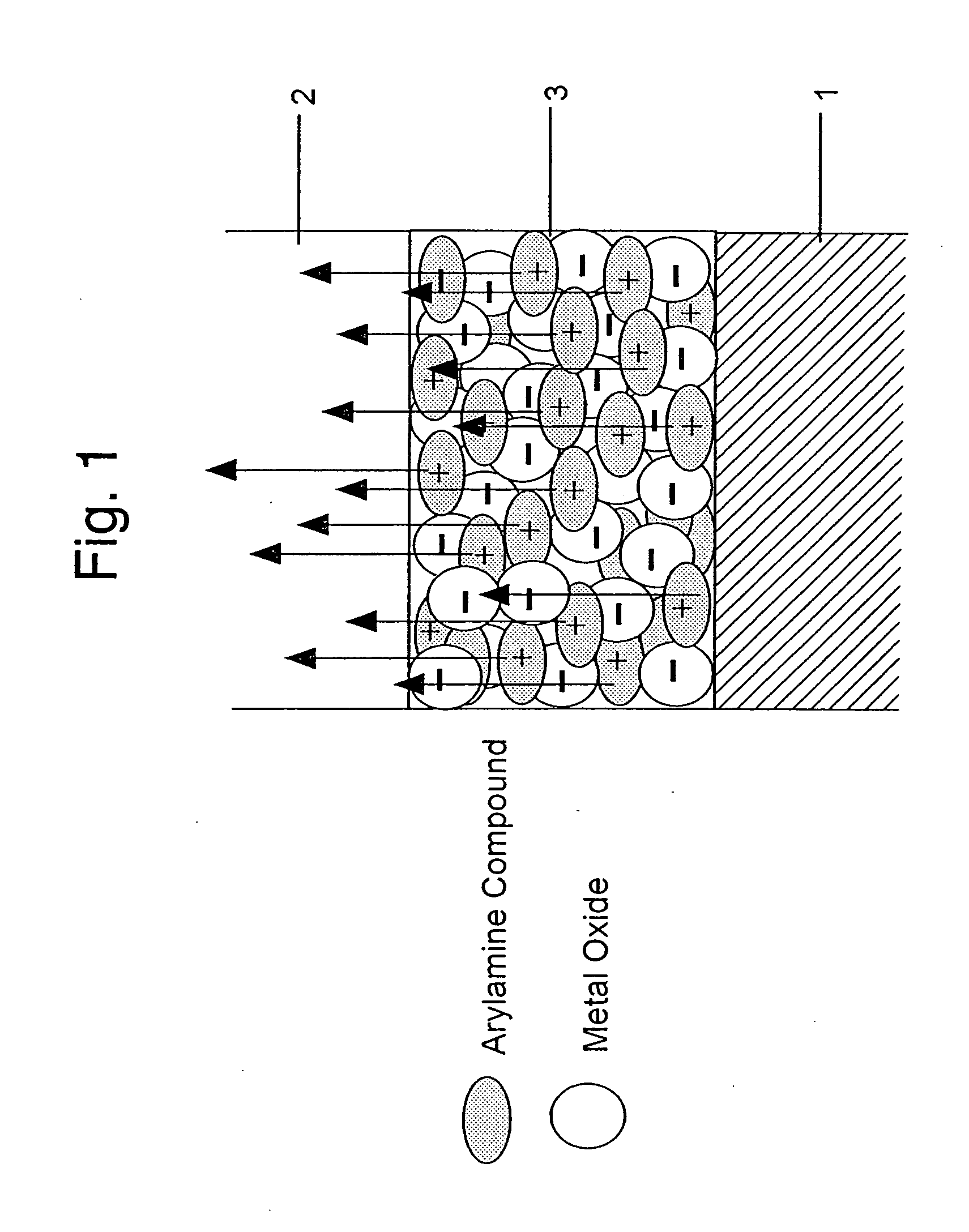
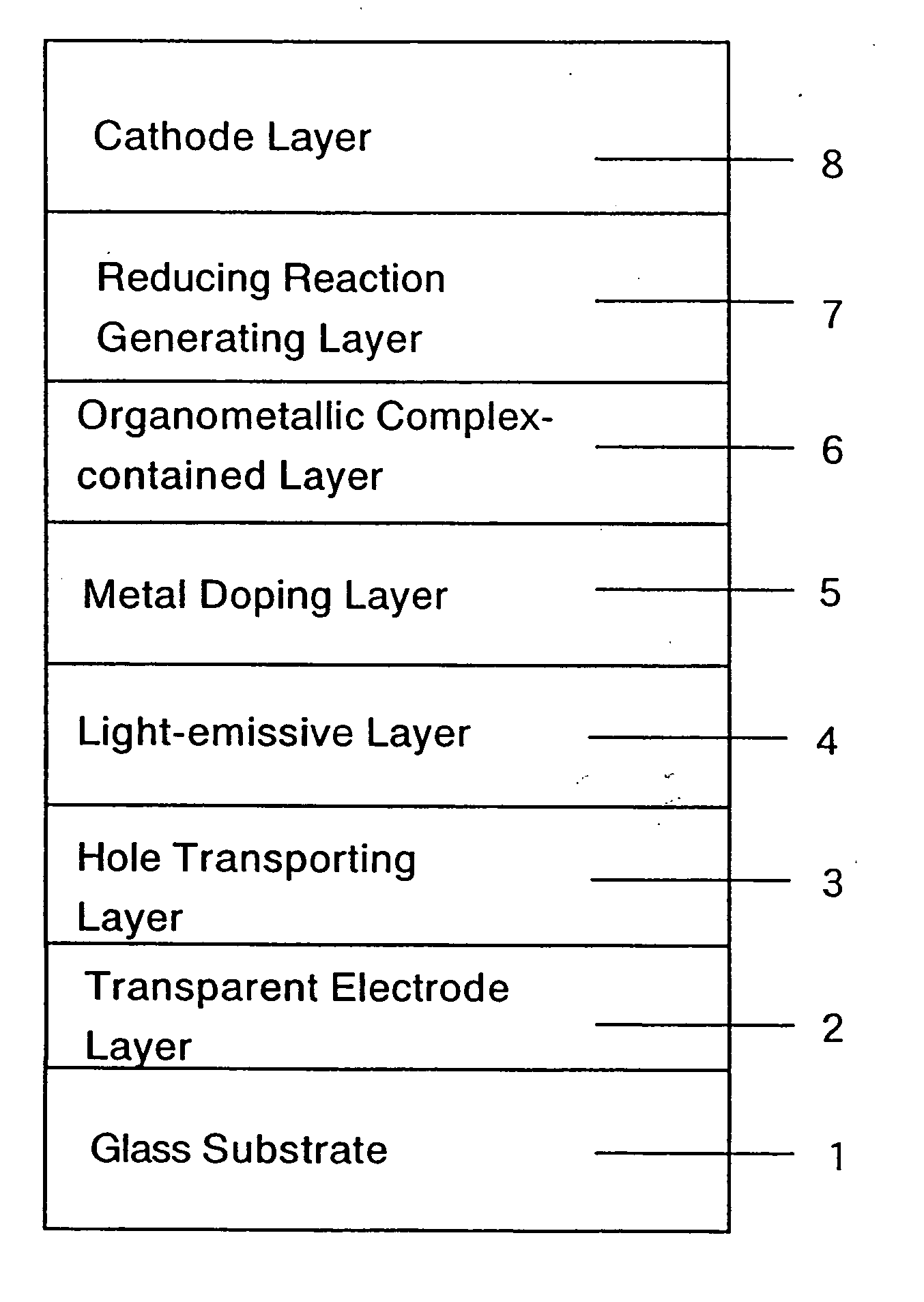
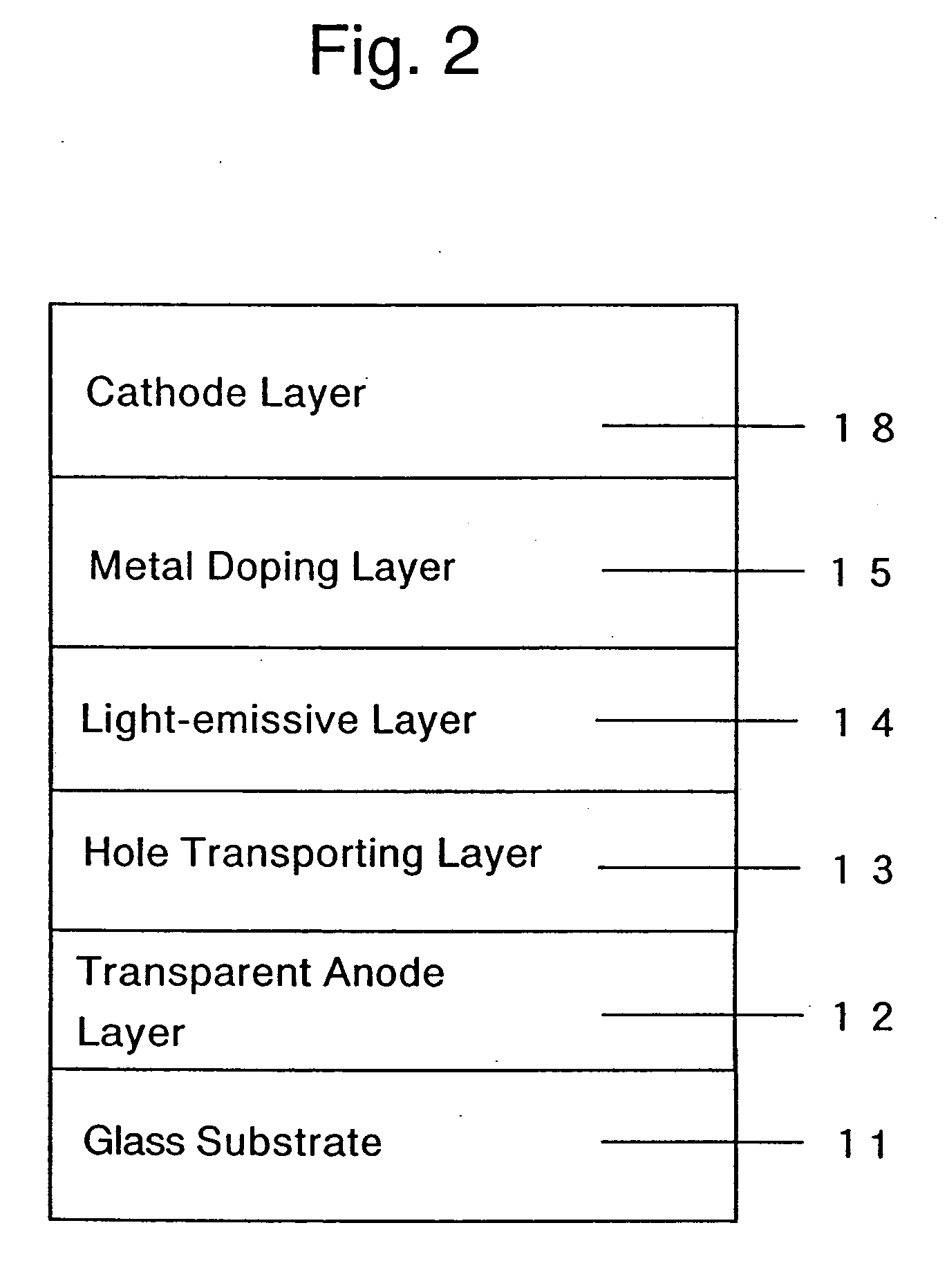
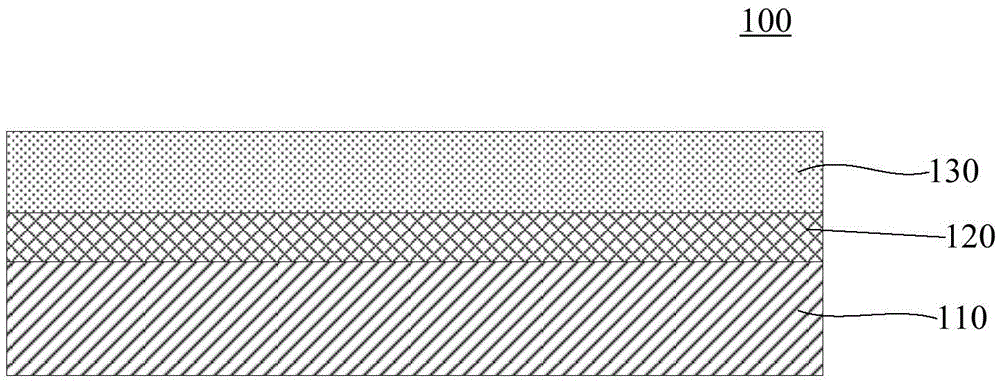
An organic electroluminescent device includes an anode electrode layer; a cathode electrode layer opposed to the anode electrode layer; a hole injection layer provided adjacent to the anode electrode layer an organic structure including at least one light-emissive layer_or at least one light-emissive unit having at least one light-emissive layer; between the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer. At least one of the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer is transparent. The hole injection layer includes a mixed layer of a metal oxide and an organic compound. The mixed layer is formed upon co-deposition of the metal oxide and the organic compound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
Organic electroluminescent device and production process thereof
ActiveUS20050084713A1Stable device propertyIncrease the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic structureAlkaline earth metal
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
Light emitting device and electronic appliance using the same
InactiveUS20060292394A1Easy to changeDistanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesVanadium oxideOrganic compound
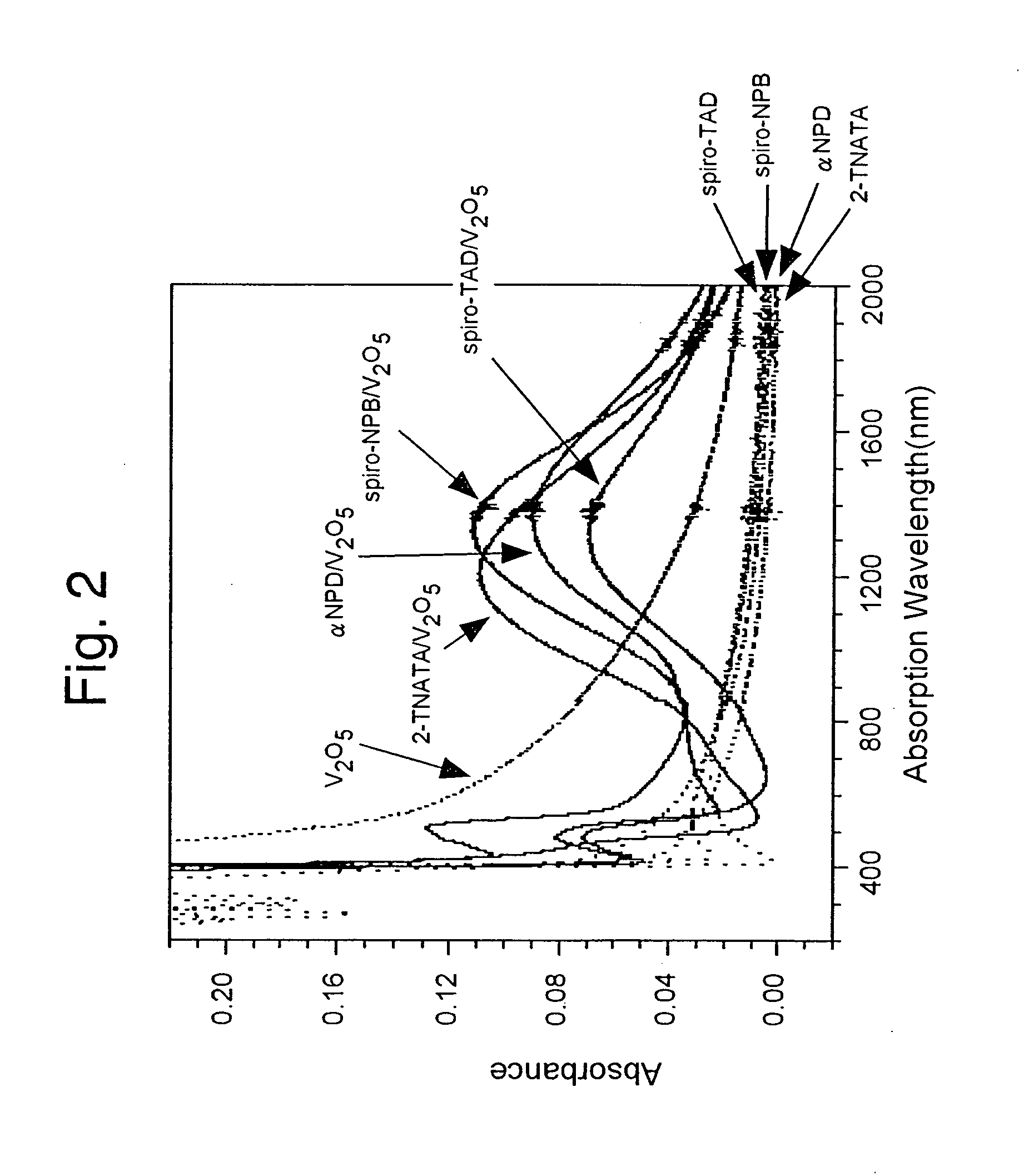
A light emitting device comprises a pair of electrodes and a mixed layer provided between the pair of electrodes. The mixed layer contains an organic compound which contains no nitrogen atoms, i.e., an organic compound which dose not have an arylamine skeleton, and a metal oxide. As the organic compound, an aromatic hydrocarbon having an anthracene skeleton is preferably used. As such an aromatic hydrocarbon, t-BuDNA, DPAnth, DPPA, DNA, DMNA, t-BuDBA, and the like are listed. As the metal oxide, molybdenum oxide, vanadium oxide, ruthenium oxide, rhenium oxide, and the like are preferably used. Further, the mixed layer preferably shows absorbance per 1 μm of 1 or less or does not show a distinct absorption peak in a spectrum of 450 to 650 nm when an absorption spectrum is measured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Devices with multiple organic-metal mixed layers
InactiveUS20030234609A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceMaterials science
A display device composed of: (a) a cathode; (b) an anode; (c) a luminescent region between the cathode and the anode; and (d) an optional region adjacent to the cathode or the anode, wherein the device includes a plurality of metal-organic mixed layers disposed at one or more of the cathode, the anode, the luminescent region and the optional region, wherein each of the metal-organic mixed layers includes: (i) an inorganic metal containing material, and (ii) an organic material.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Display devices with organic-metal mixed layer
InactiveUS6841932B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceInorganic materials
A display device composed of: (a) a cathode; (b) an anode; (c) a luminescent region between the cathode and the anode; and an optional region adjacent one of the electrodes, wherein at least one of the cathode, the anode, the luminescent region, and the optional region includes a metal-organic mixed layer composed of: (i) an inorganic metal containing material, (ii) an organic material, and (iii) optionally, at least one component selected from the group consisting of metals, organic materials, and inorganic materials.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes mixed with particles
InactiveUS20040070326A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
The present invention is directed toward cathodes and cathode materials comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and particles. The present invention is also directed toward field emission devices comprising a cathode of the present invention, as well as methods for making these cathodes. In some embodiments, the cathode of the present invention is used in a field emission display. The invention also comprises a method of depositing a layer of CNTs and particles onto a substrate to form a cathode of the present invention, as well as a method of controlling the density of CNTs used in this mixed layer in an effort to optimize the field emission properties of the resulting layer for field emission display applications.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electric-controlled light-regulating medium
ActiveCN101415280A"Multi-stable" characteristics are goodNo electromagnetic radiationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityControl area
The invention discloses an electronic control dimming medium which comprises two substrate layers. A mixed layer is arranged between two substrate layers and is made by mixing smectic phase liquid crystal and additives. A conductive electrode layer is arranged at the sides of two substrate layers towards the mixed layer, and the conductive electrode layer is connected with a circuit drive control apparatus. Two substrate layers can be made of glass, or two substrate layers can be made of plastic, or one substrate layer is made of the glass, and the other substrate layer is made of the plastic. When an electric signal which is applied to the conductive electrode layer is controlled, smectic phase liquid crystal molecules can be characterized by different arrangement states, and the arrangement states are the same in the electroless case, so as to ensure that the medium can be switched between a vaporific shielding state and a full transparent state and even can be switched among various gradual progress states of different gray scales. The electronic control dimming medium can be widely applied to the fields of building decoration and fitment, privacy control area, automobile electronics, electronic bulletin board, etc.
Owner:重庆汉朗精工科技有限公司
Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes mixed with particles
InactiveUS6798127B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp incadescent bodiesField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
The present invention is directed toward cathodes and cathode materials comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and particles. The present invention is also directed toward field emission devices comprising a cathode of the present invention, as well as methods for making these cathodes. In some embodiments, the cathode of the present invention is used in a field emission display. The invention also comprises a method of depositing a layer of CNTs and particles onto a substrate to form a cathode of the present invention, as well as a method of controlling the density of CNTs used in this mixed layer in an effort to optimize the field emission properties of the resulting layer for field emission display applications.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
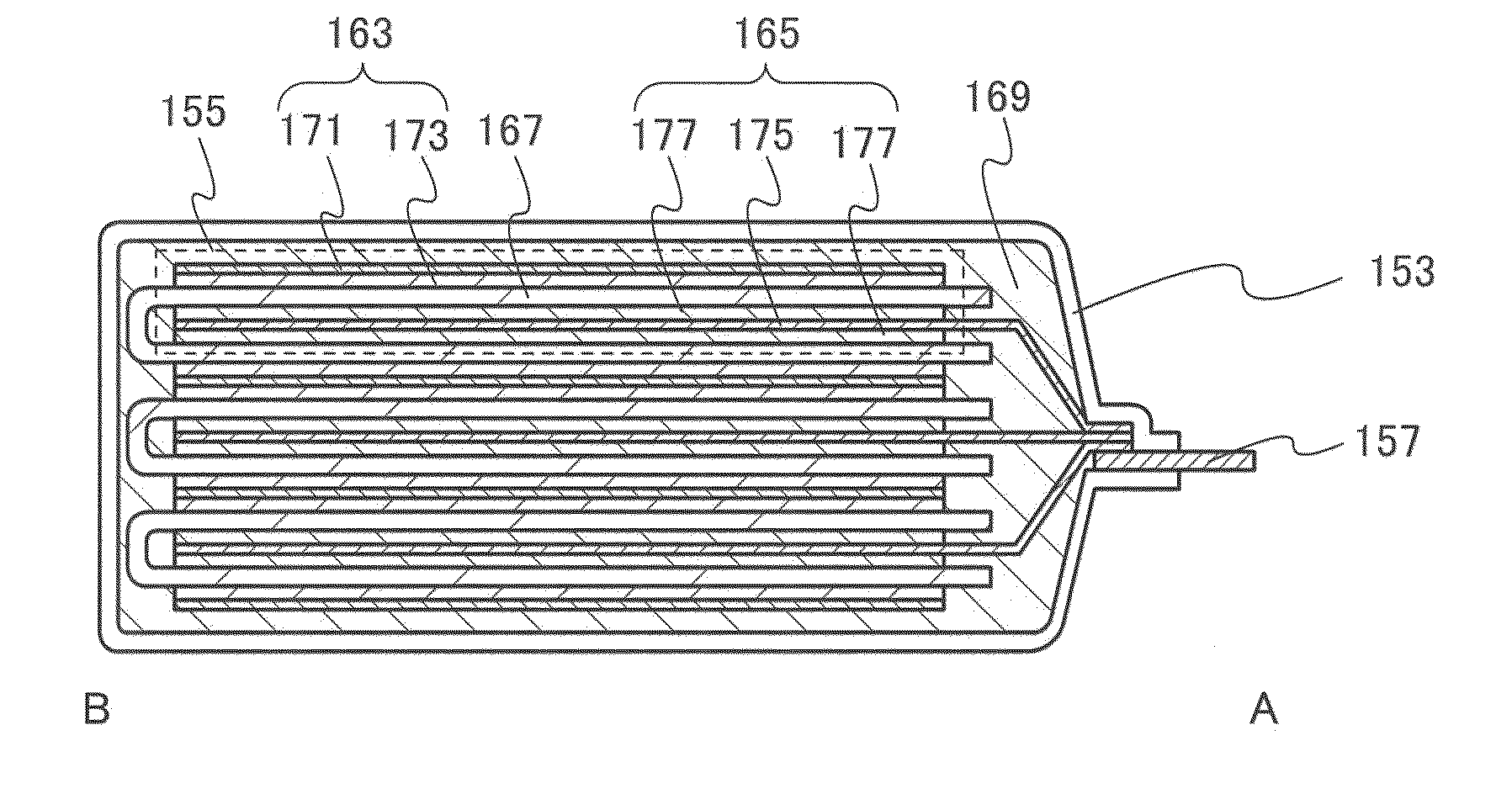
Power storage device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110266654A1Improving interface characteristicResistanceFuel and secondary cellsFinal product manufactureEngineeringWhiskers
Provided is a method for manufacturing a power storage device in which a crystalline silicon layer including a whisker-like crystalline silicon region is formed as an active material layer over a current collector by a low-pressure CVD method in which heating is performed using a deposition gas containing silicon. The power storage device includes the current collector, a mixed layer formed over the current collector, and the crystalline silicon layer functioning as the active material layer formed over the mixed layer. The crystalline silicon layer includes a crystalline silicon region and a whisker-like crystalline silicon region including a plurality of protrusions which project over the crystalline silicon region. With the protrusions, the surface area of the crystalline silicon layer functioning as the active material layer can be increased.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
All-solid-state lithium secondary battery and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20140162113A1Increase energy densityLow melting pointElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureAll solid stateClose contact
An all-solid-state lithium secondary battery includes a positive electrode; a negative electrode; and a solid electrolyte arranged between the positive and negative electrodes, to conduct lithium ions. In the all-solid-state lithium secondary battery, a mixed layer is in close contact with a surface of the solid electrolyte adjacent to the positive electrode, the mixed layer containing the positive-electrode active material and (Lix(1−α), Mxα / β)γ+(B1−y, Ay)z+O2−δ (wherein in the formula, M and A each represent at least one or more elements selected from C, Al, Si, Ga, Ge, In, and Sn, α satisfies 0≦α<1, β represents the valence of M, γ represents the average valence of (Li+x(1−α), Mα), y satisfies 0≦y<1, z represents the average valence of (B1−y, Ay) and x, α, β, γ, z, and γ satisfy the relational expression (x(1−α)+xα / β)γ+z=2δ) serving as a matrix.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Composite floor board and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101487336AWith natural textureWith comfortWood working apparatusFlooringThermoplasticSolid wood
The invention relates to a composite floor and a preparation method thereof. Thermoplastic plastics and wood powder are mixed and extruded to obtain a mixed layer, and then the mixed layer is mixed with thermofusible resin and extruded to obtain a profile which is taken as basic material of the floor, a decorating layer and an exterior wear-resisting layer are laid on the surface of the basic material of floor in sequence to obtain a floor blank, finally, after processes like conventional gouging and the like, an end product of composite floor is obtained. The obtained composite floor has the natural grain and the amenity of the solid wood floor, and overcomes the shortcomings of non-watertight, being easy to rot, easy to be deformed and low wear resistance of the conventional wood floor. The preparation method of the composite floor is simple and feasible and has low cost.
Owner:来安县扬子地板有限公司
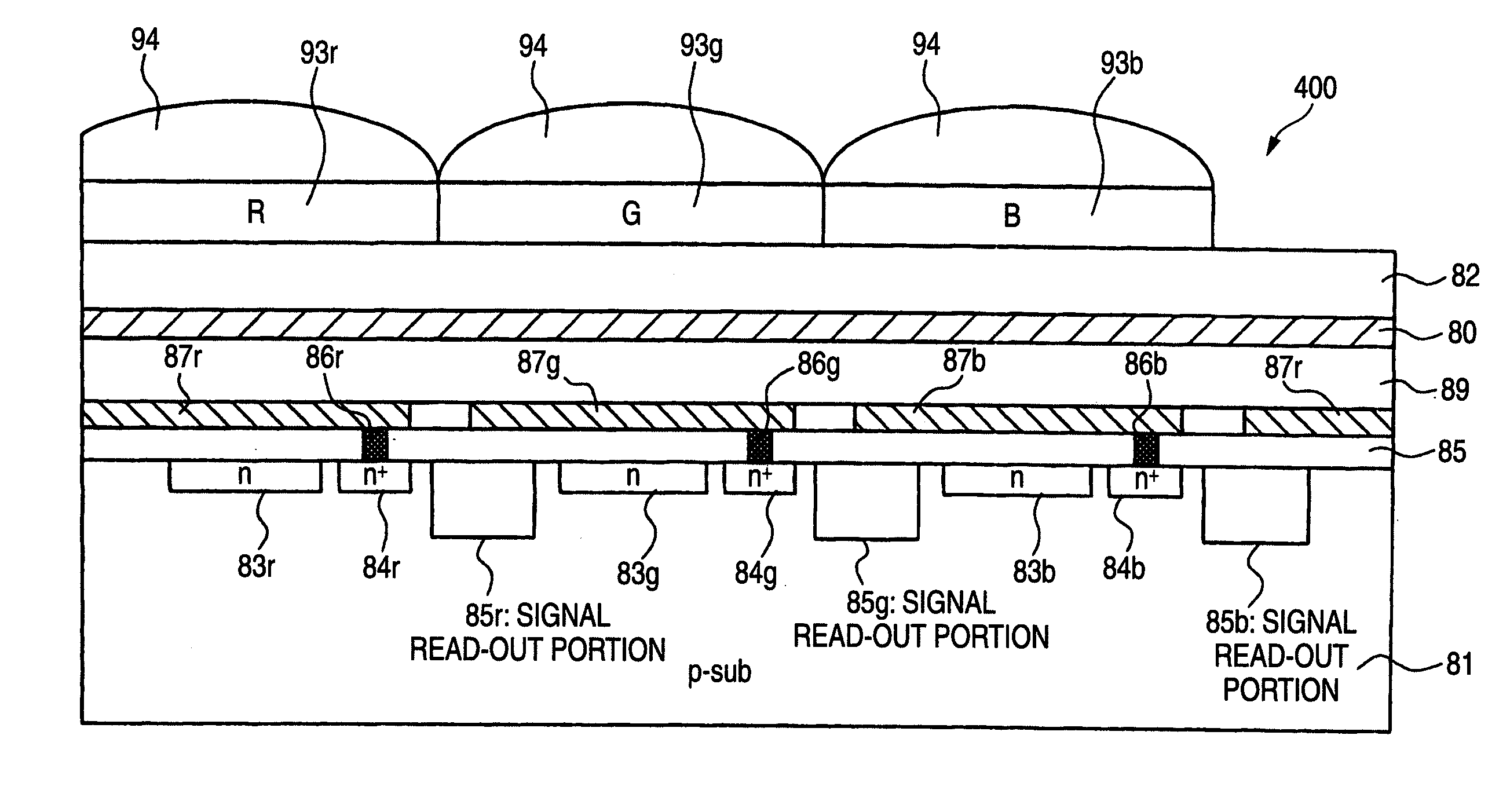
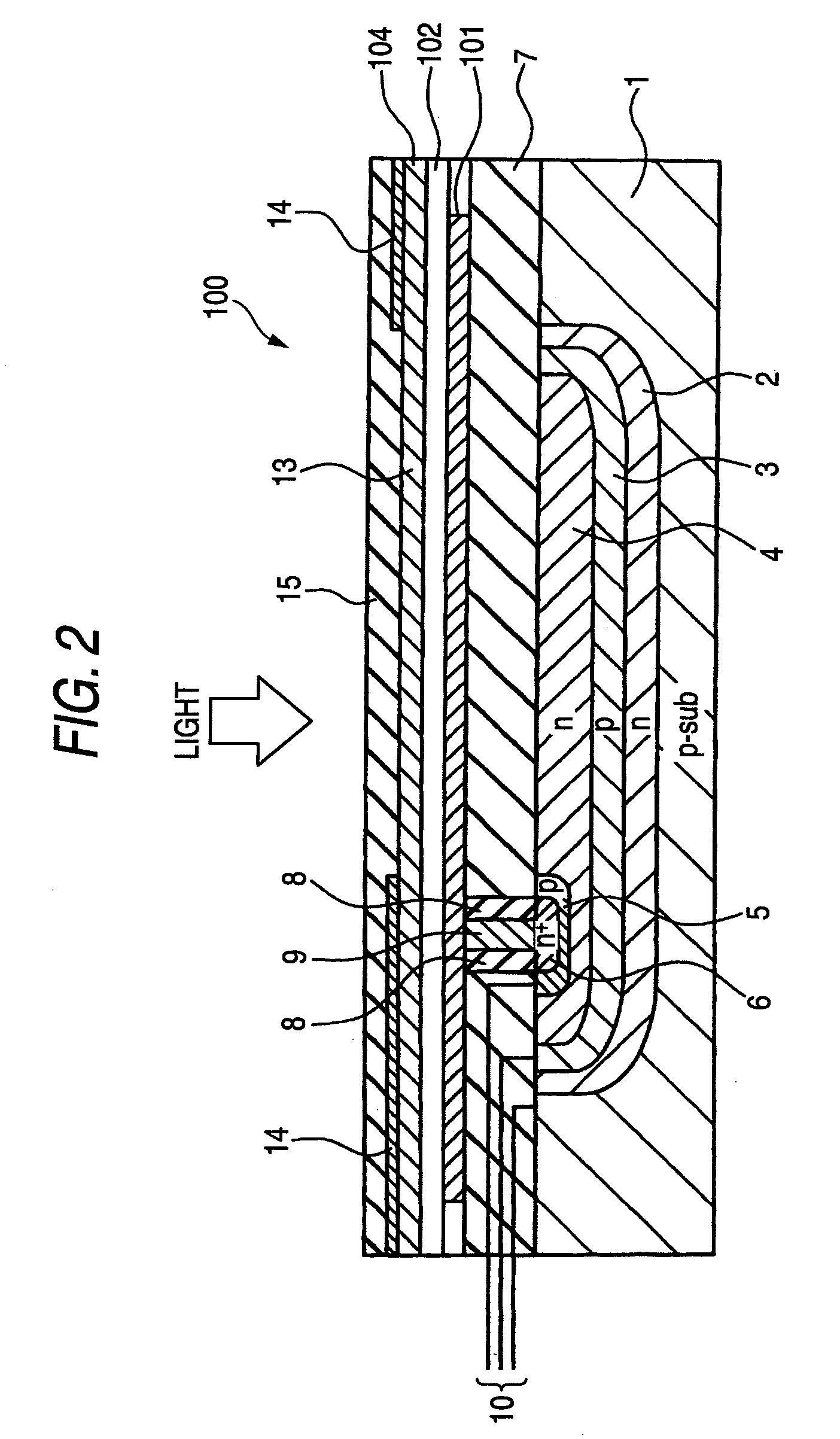
Photoelectric conversion element, method for producing photoelectric conversion element, and solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS20090050881A1Suppress generationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyTelevision system detailsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes a photoelectric conversion portion. The photoelectric conversion portion includes: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion layer between the pair of electrodes, and at least part of the photoelectric conversion layer includes a mixed layer of a p-type organic semiconductor and a fullerene, and a mixing ratio of the fullerene to the p-type organic semiconductor in terms of thickness ratio is less than 1:1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Light emitting device having organic light emitting material with mixed layer
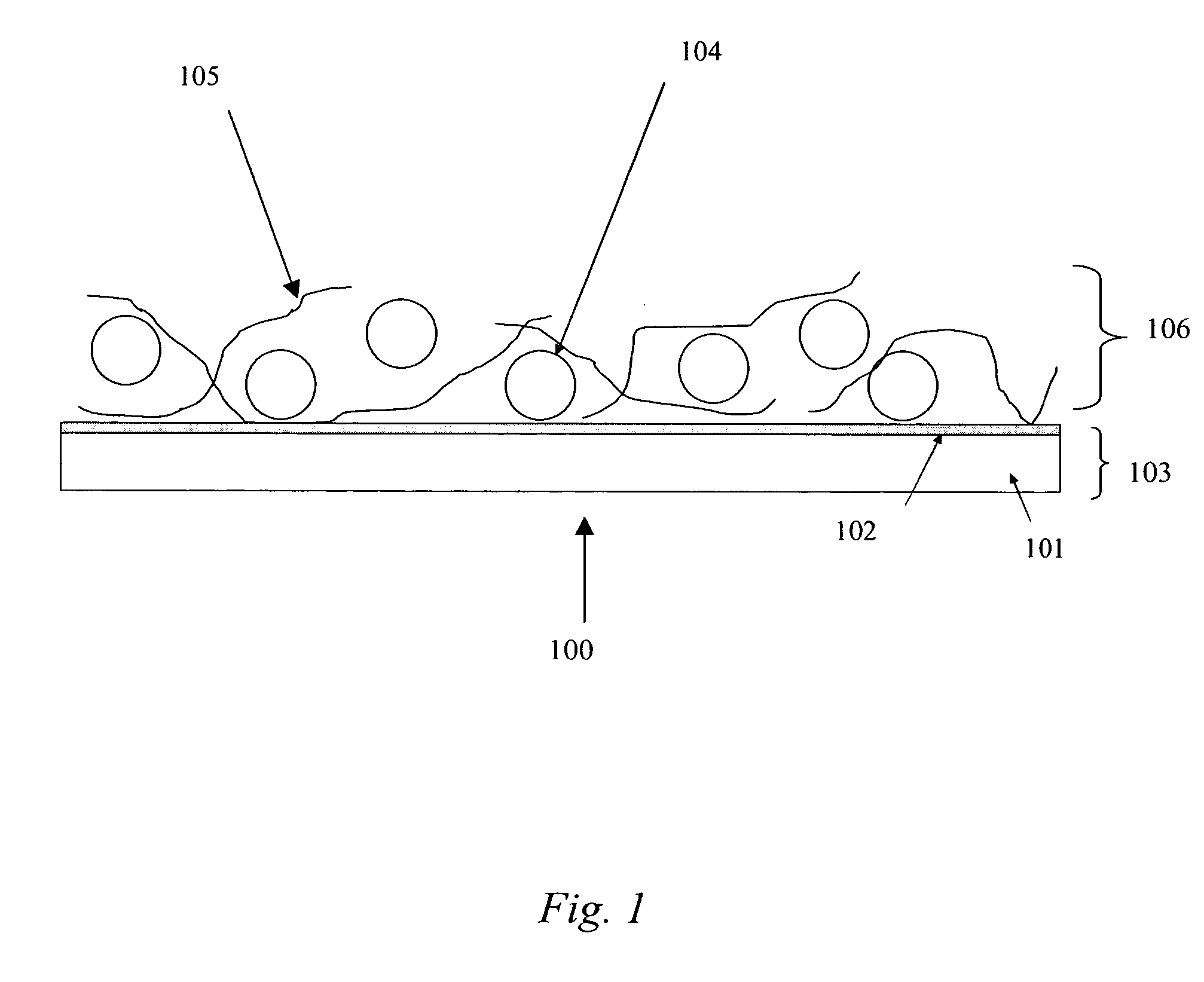
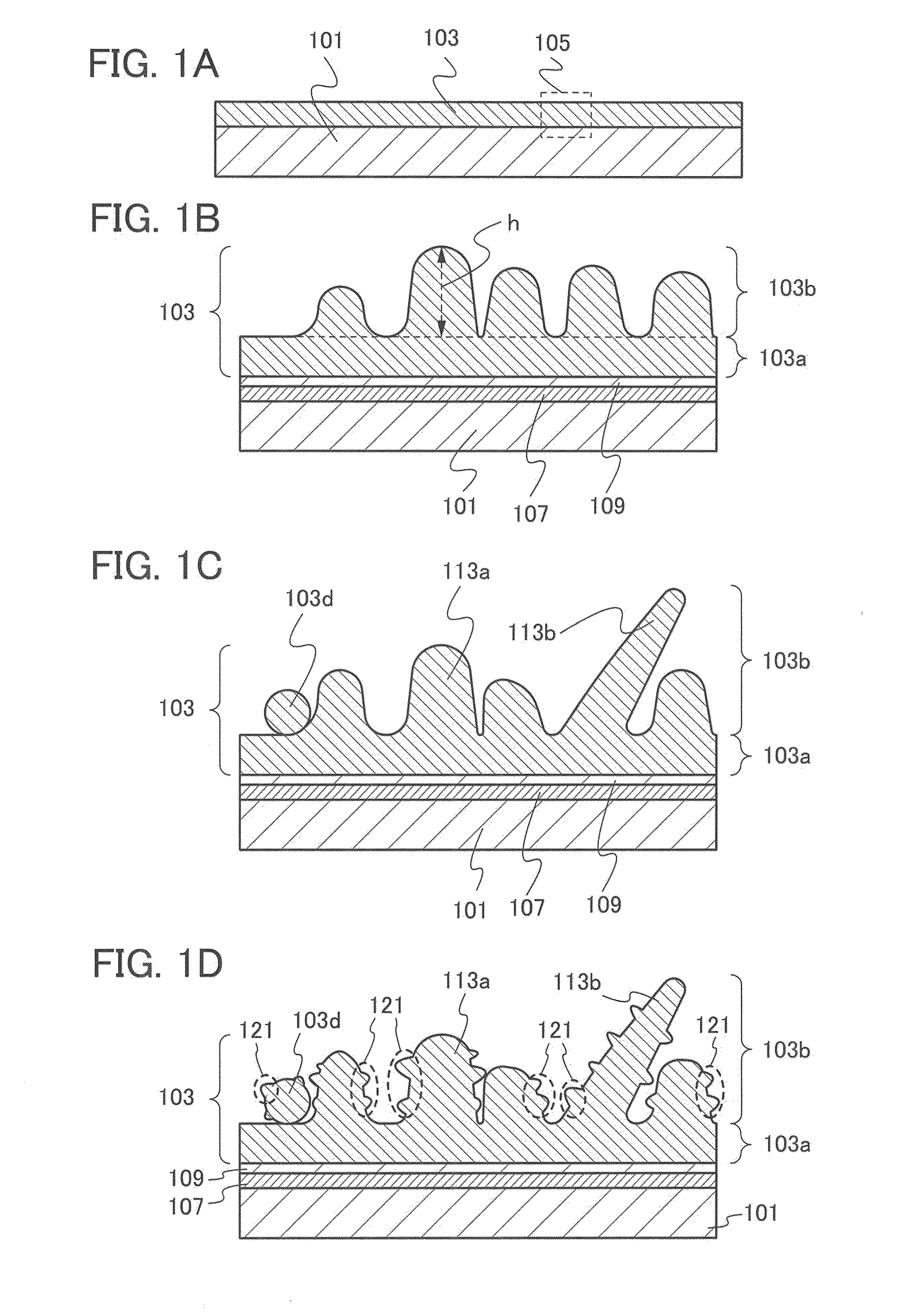
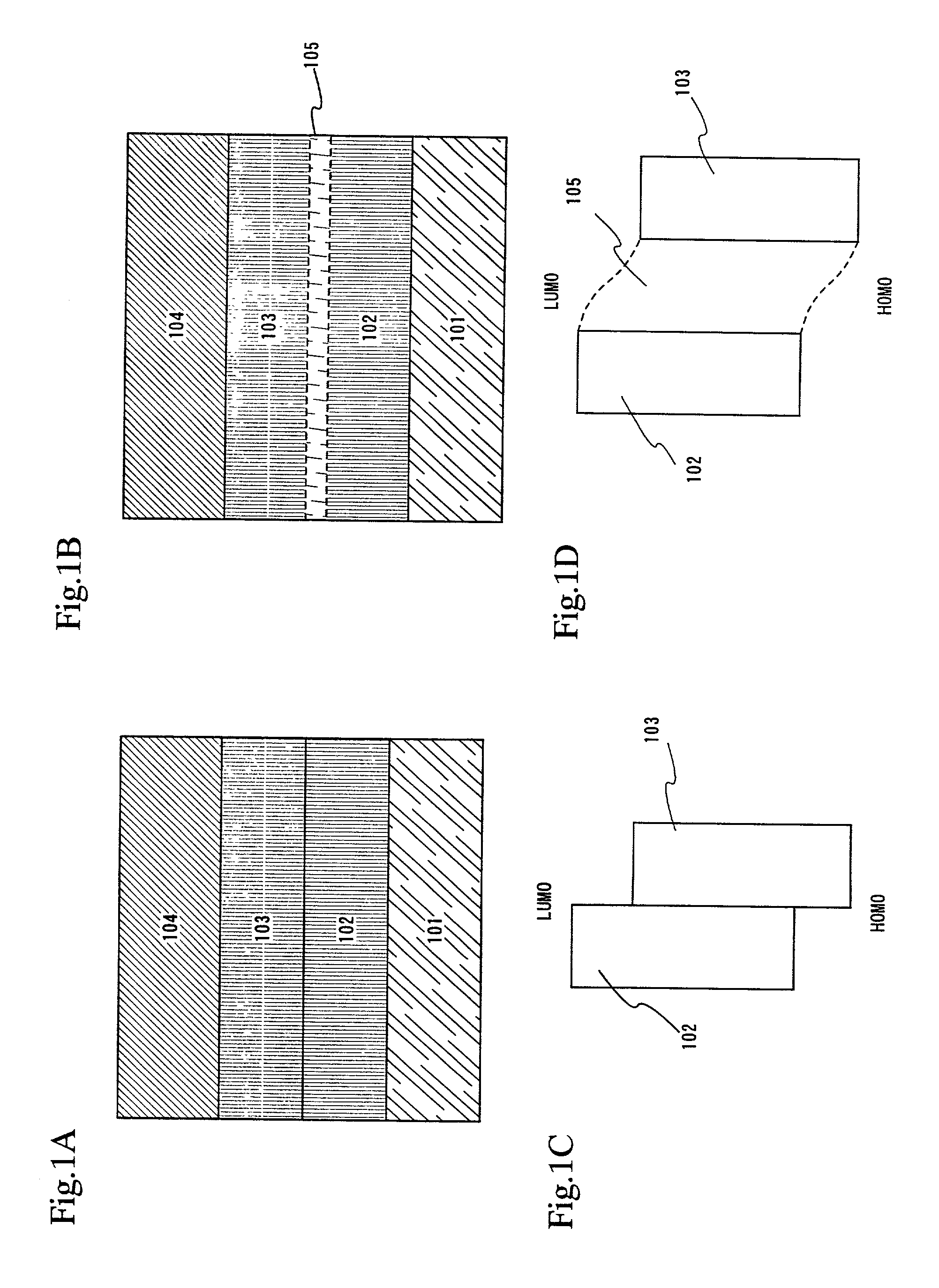
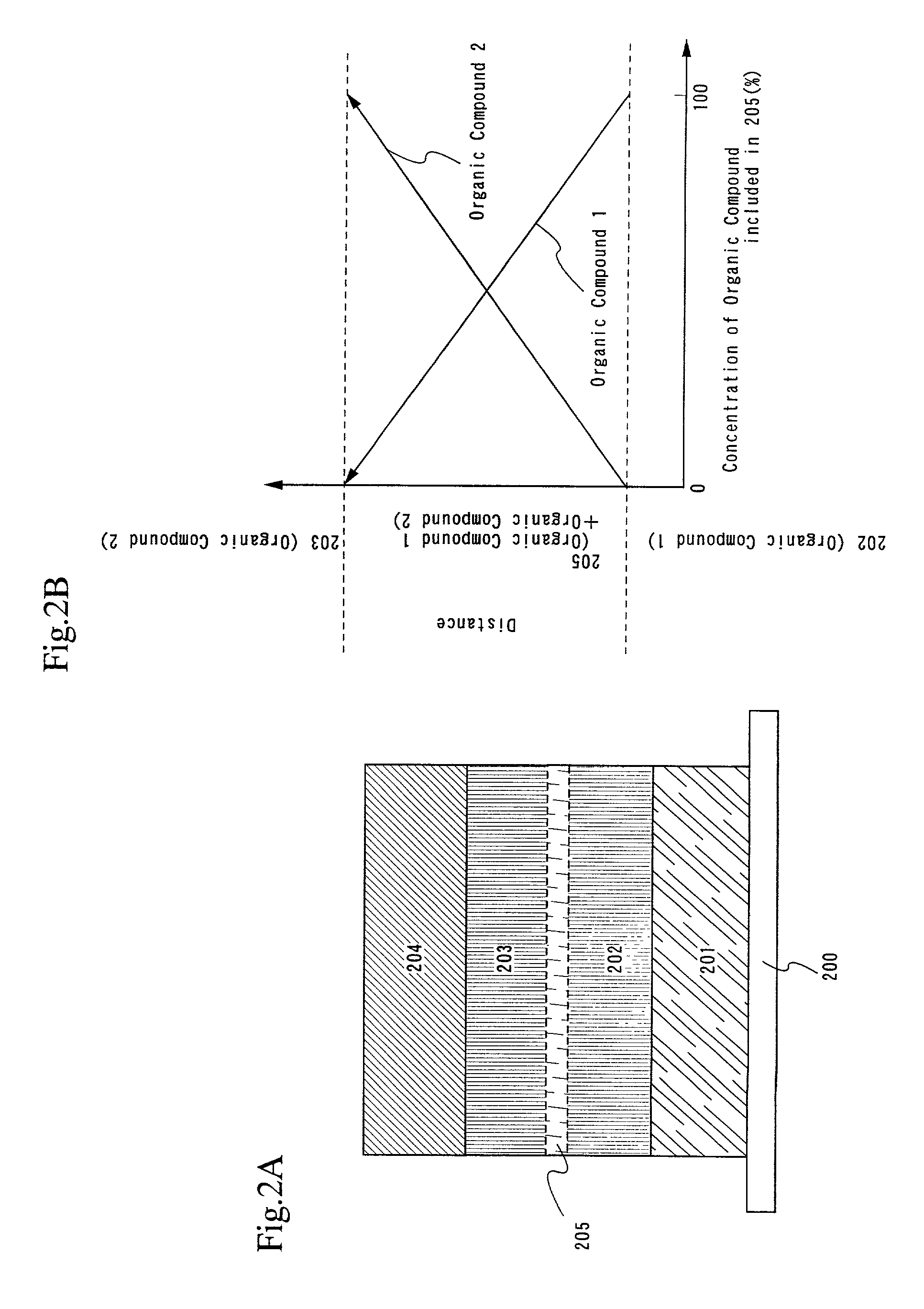
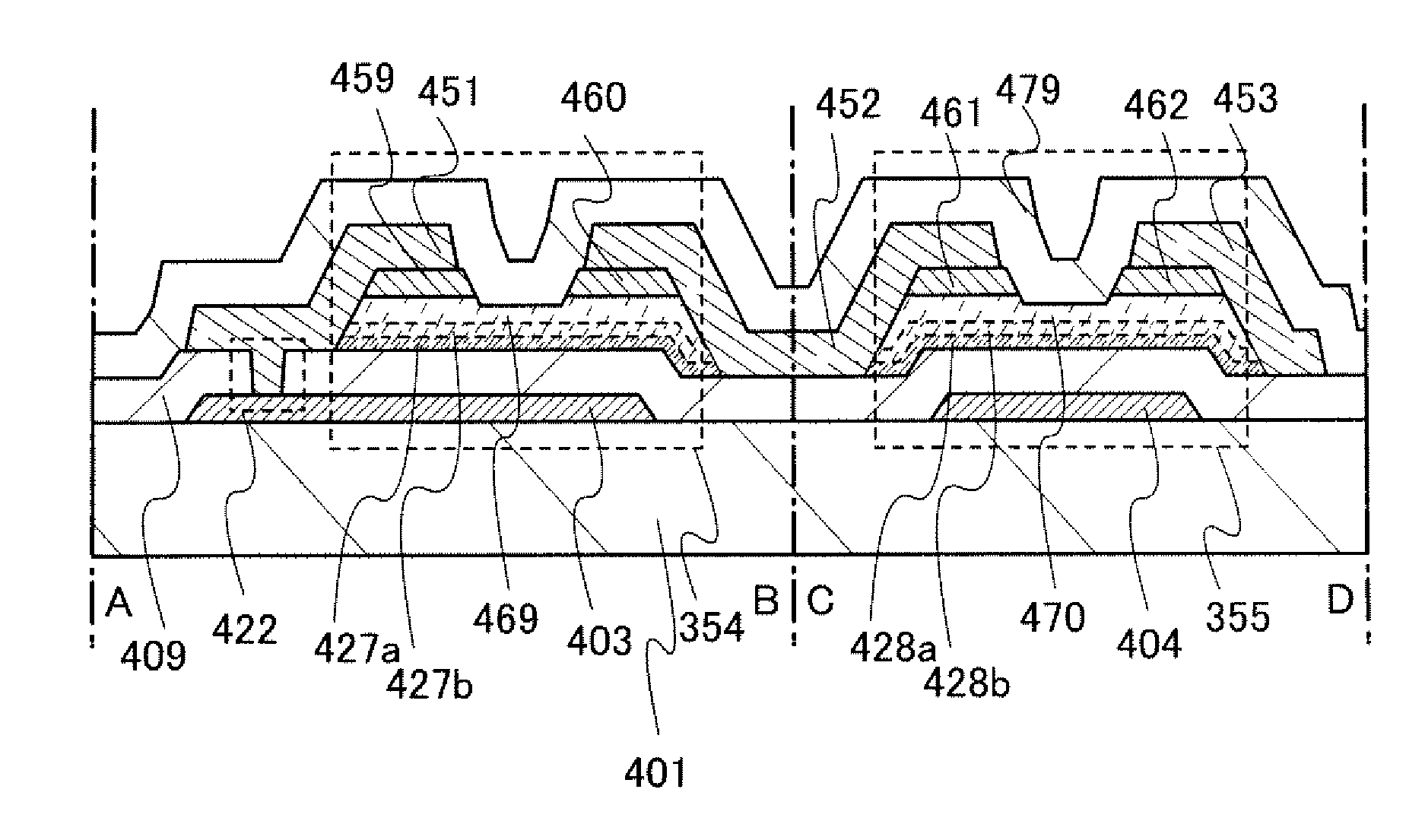
InactiveUS7342355B2Reduce the driving voltageLonger heating element lifetimeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic compoundLight emitting device
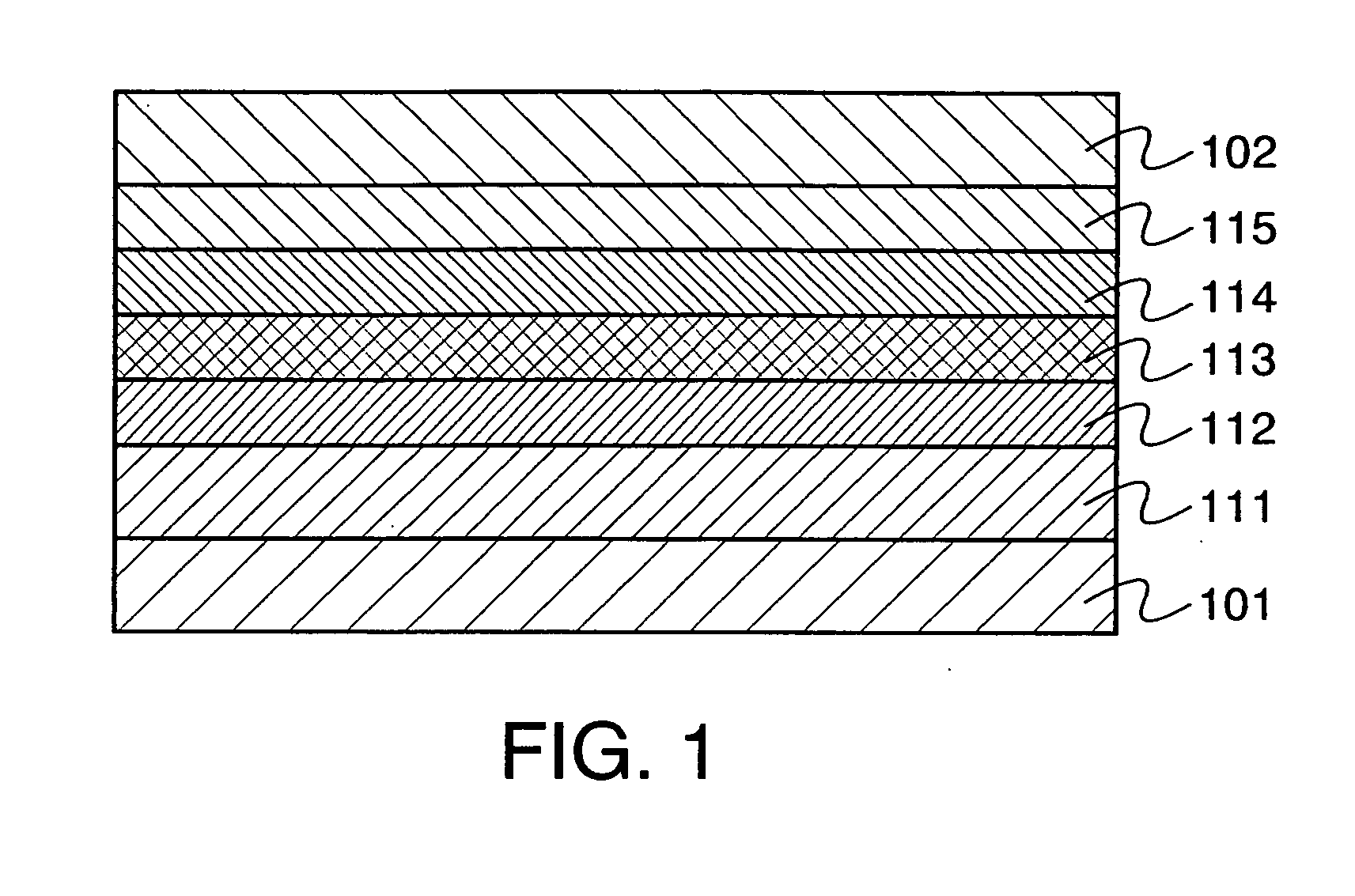
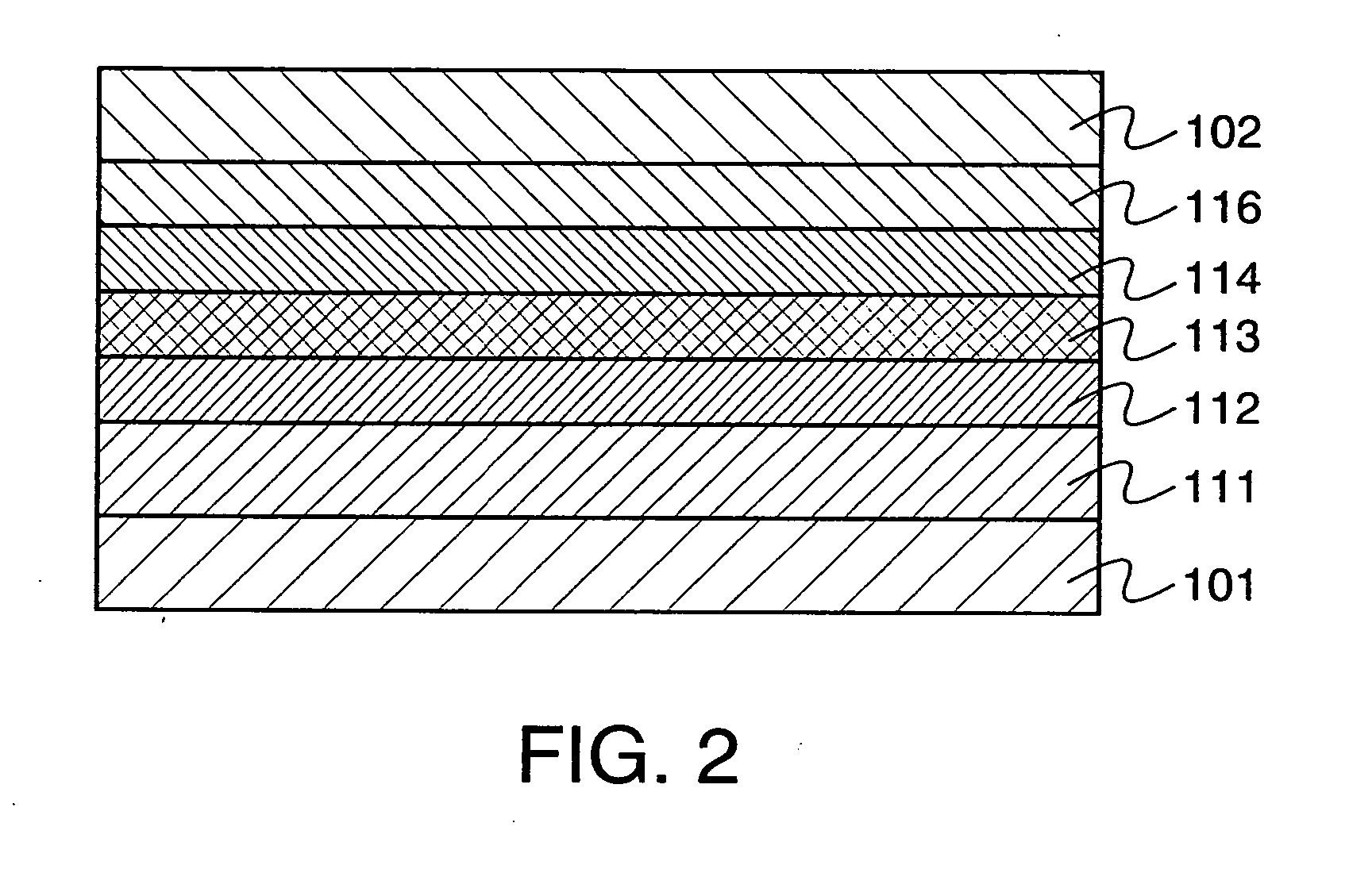
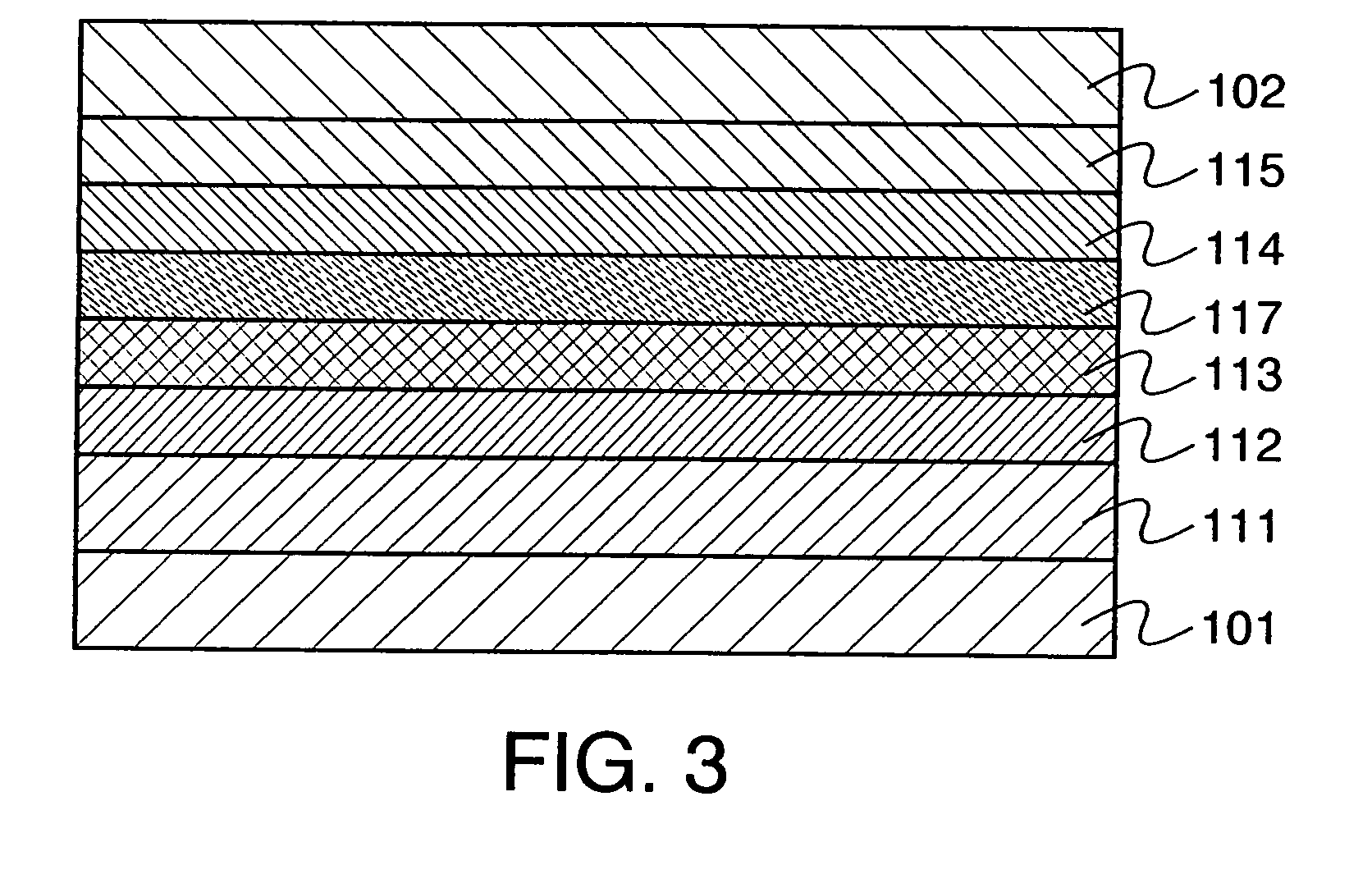
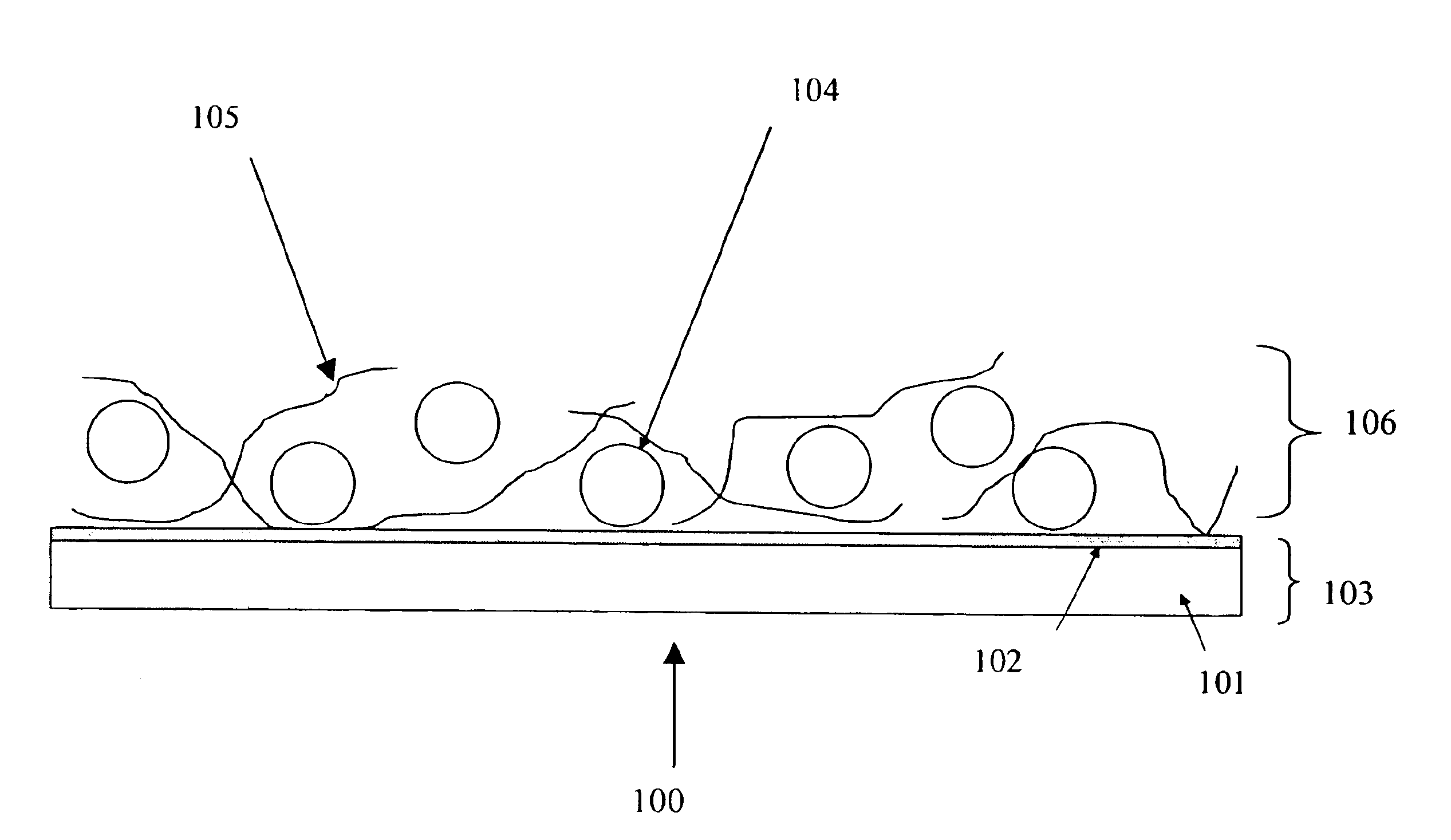
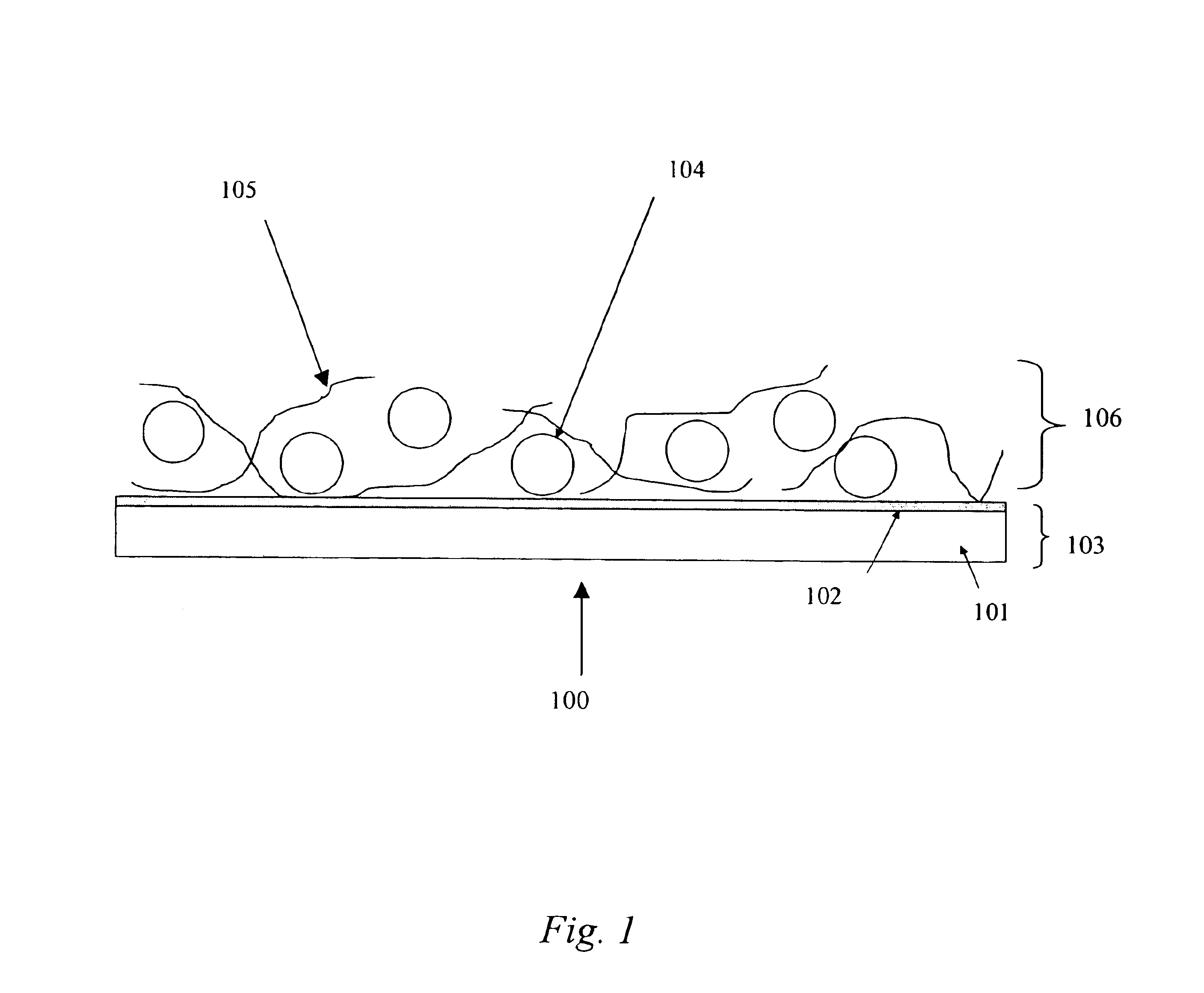
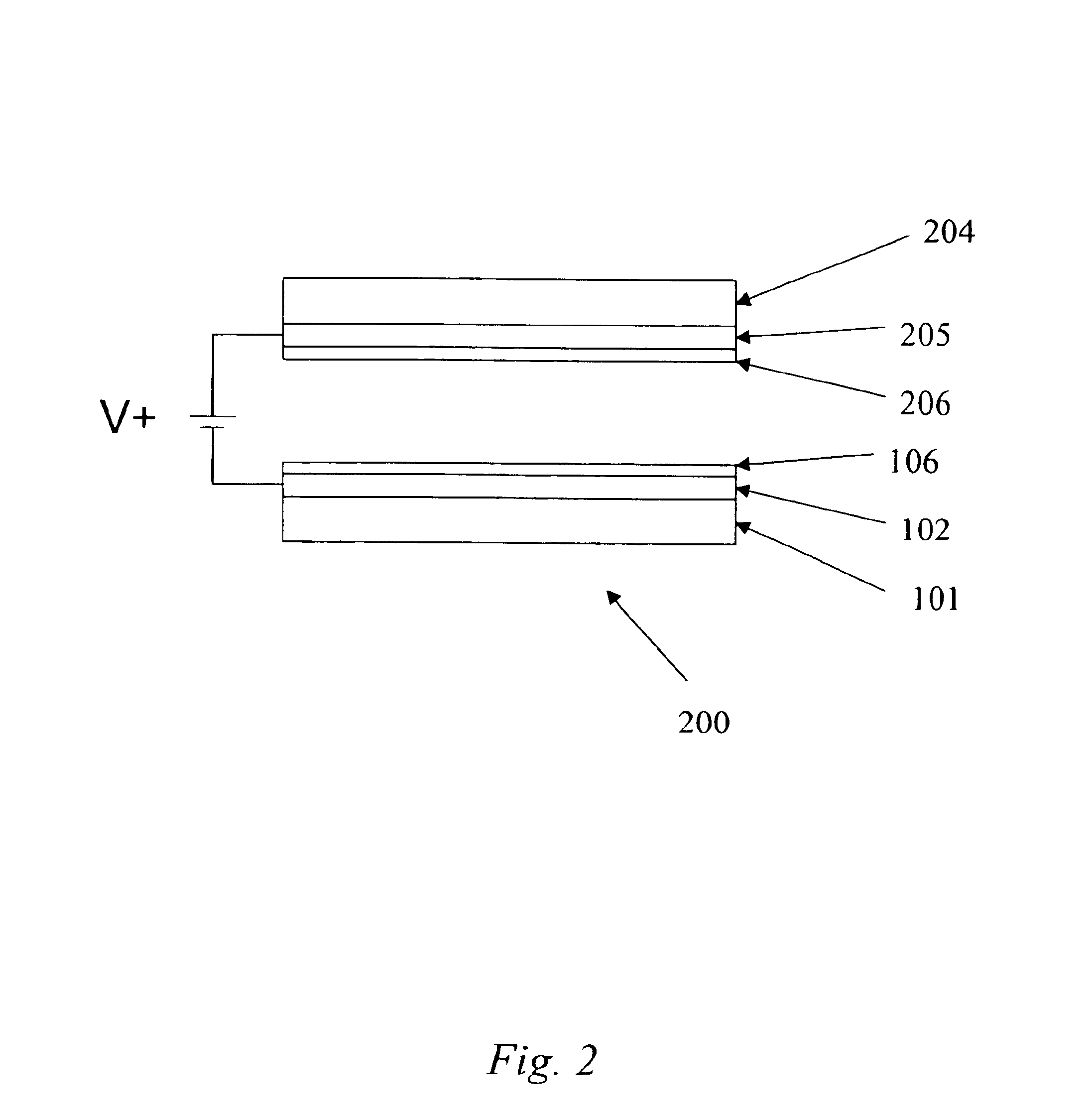
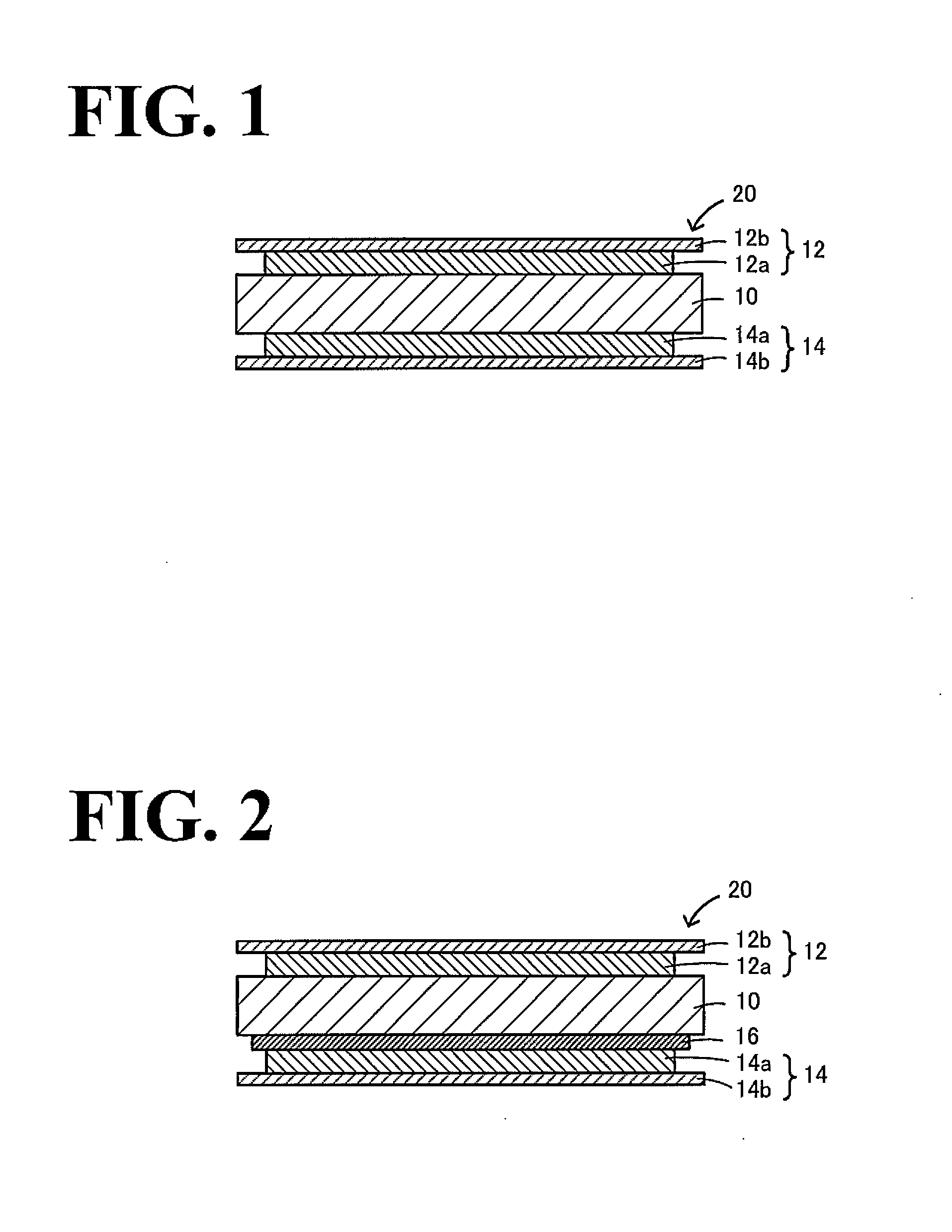
A light emitting device is provided which has a structure for lowering energy barriers at interfaces between layers of a laminate organic compound layer. A mixed layer (105) composed of a material that constitutes an organic compound layer (1) (102) and a material that constitutes an organic compound layer (2) (103) is formed at the interface between the organic compound layer (1) (102) and the organic compound layer (2) (103). The energy barrier formed between the organic compound layer (1) (102) and the organic compound layer (2) (103) thus can be lowered.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
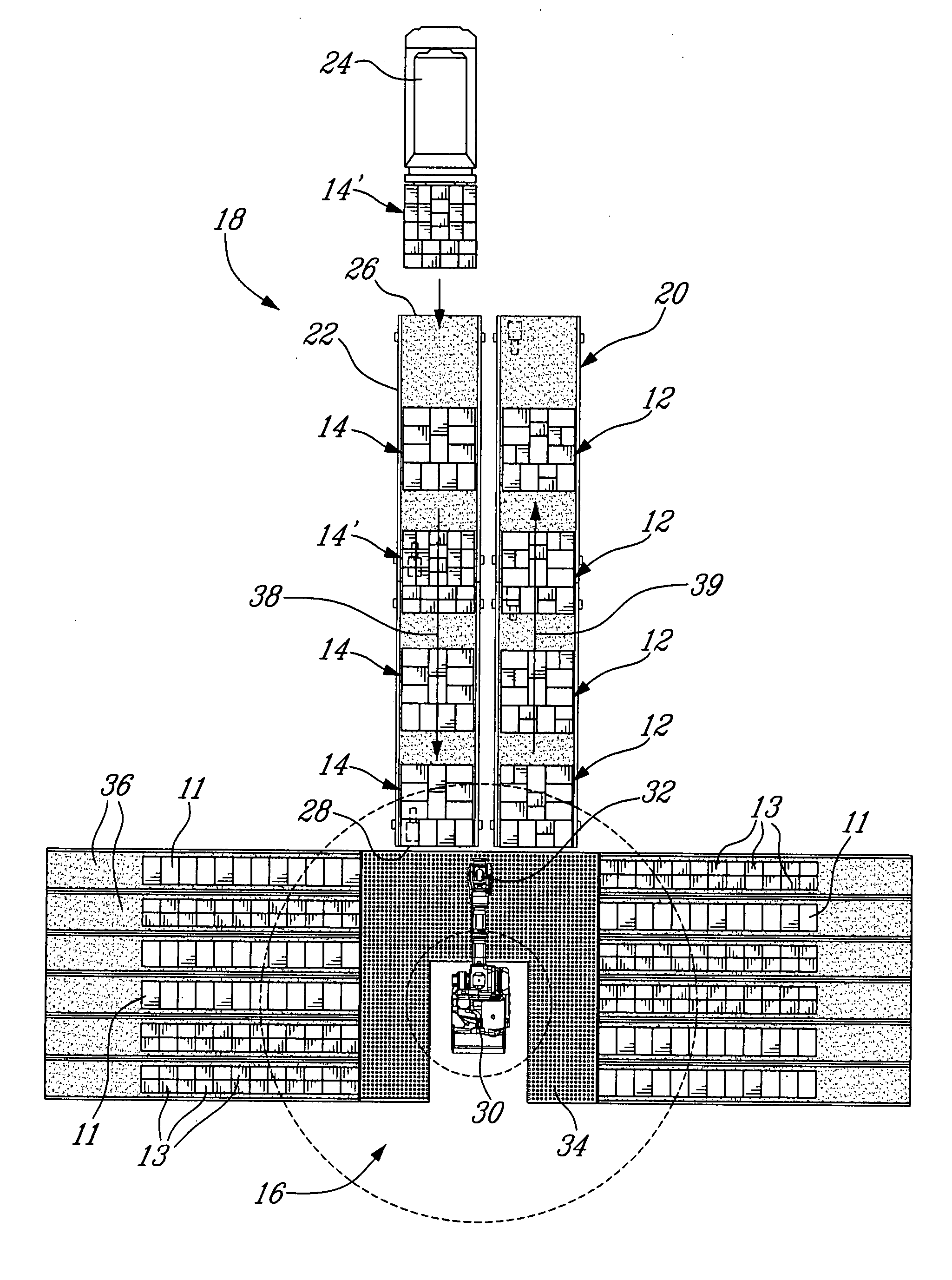
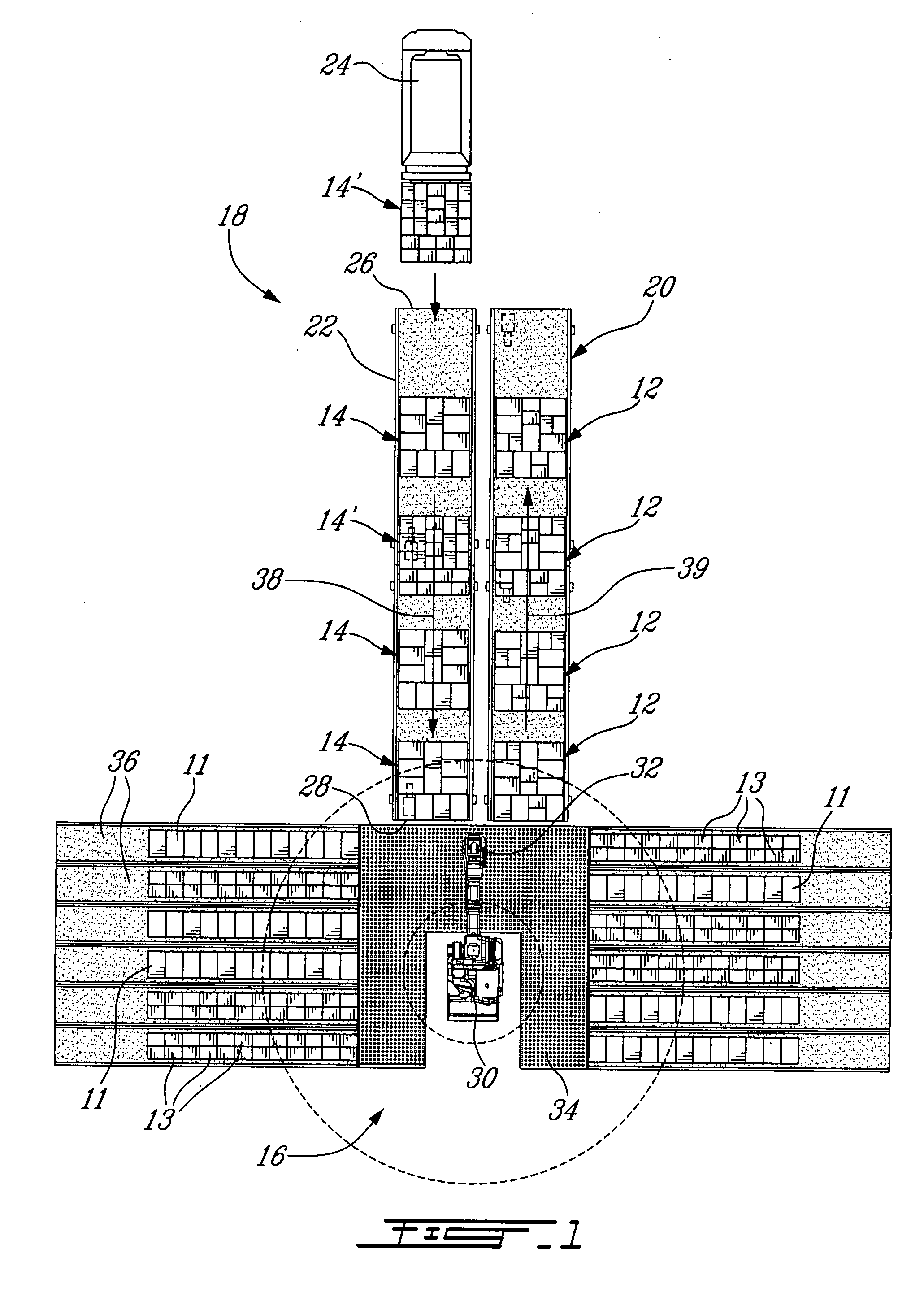
System and method to build mixed pallet layers from full pallet layers
A method and system to build mixed pallet layers from full pallet layers comprises a palletizing / de-palletizing system, a feeding system for feeding the full pallet layers to the palletizing / de-palletizing system; and a mixed pallet output system for receiving the mixed pallet layers from the palletizing / de-palletizing system. The palletizing / de-palletizing system includes a ball table to receive and support the full pallet layers of products and to support the mixed pallet layers; a plurality of product accumulating rows located adjacent the ball table for receiving and accumulating identical products from the full pallet layers and a robot, provided with a tool, to pick products from one of the full pallet layers on the table, to store the products in a selected one of the accumulating rows, and to form a mixed pallet layer on the table by picking selected products in the accumulating rows and by positioning the selected products according to a mixed layer pattern.
Owner:AXIUM
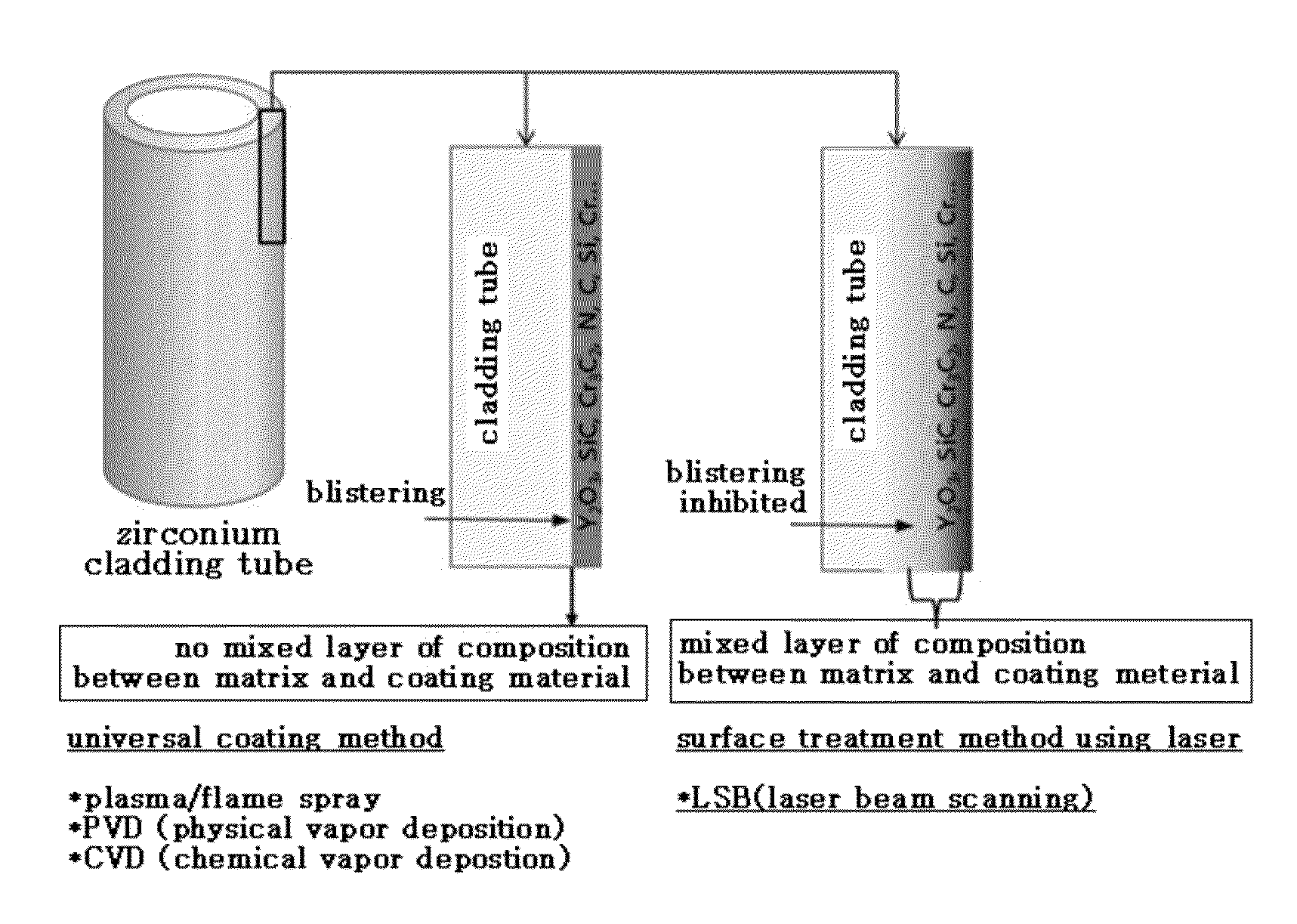
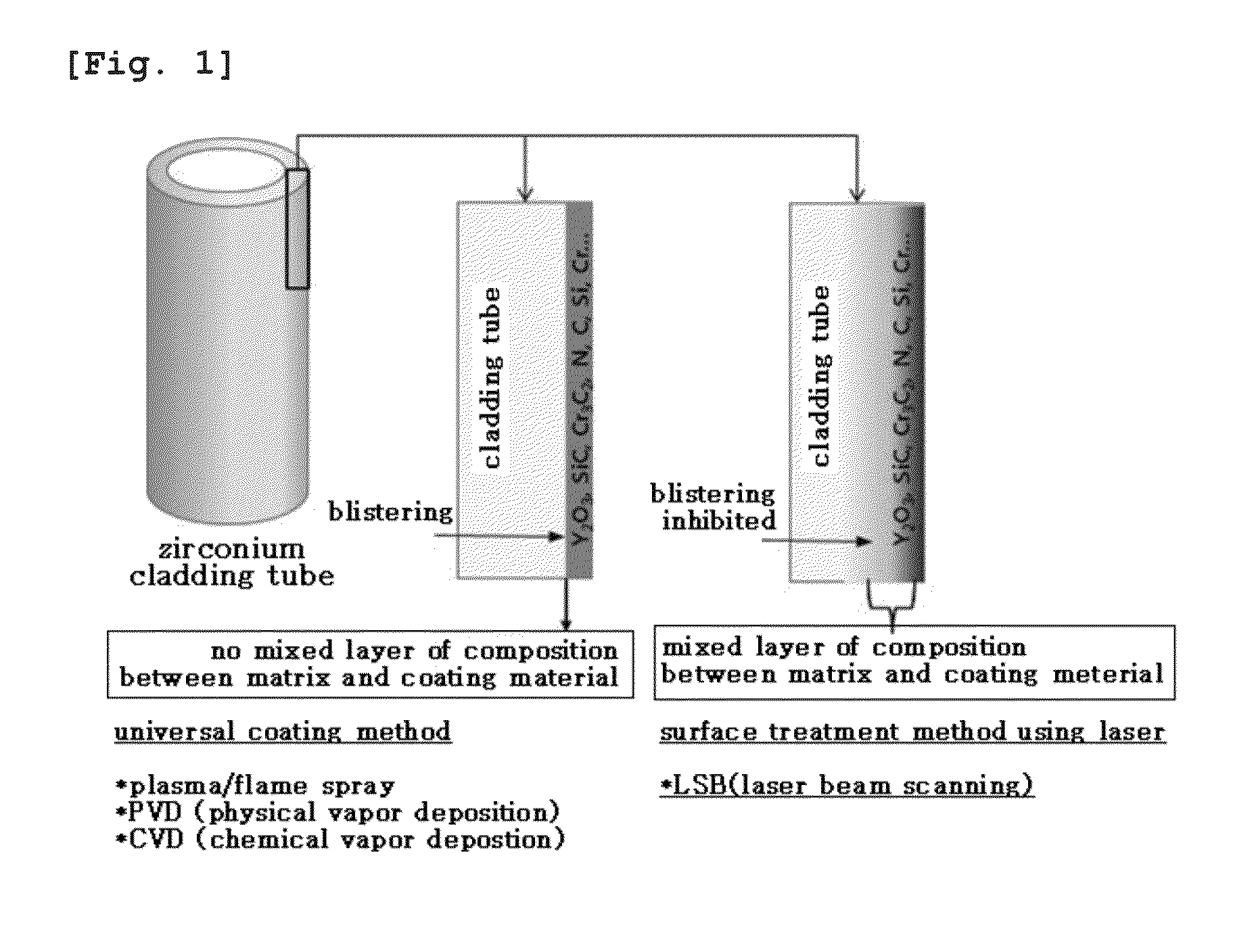
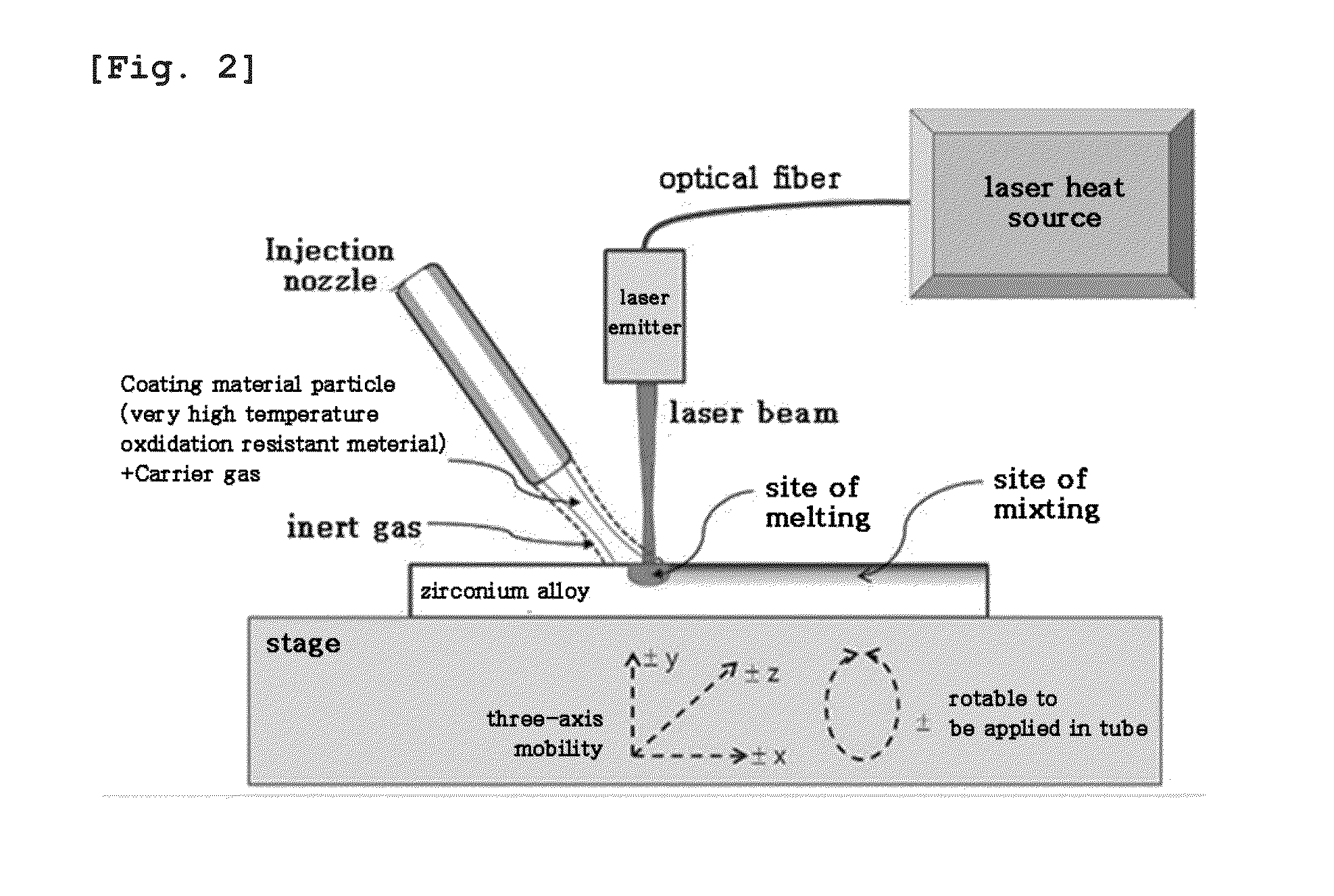
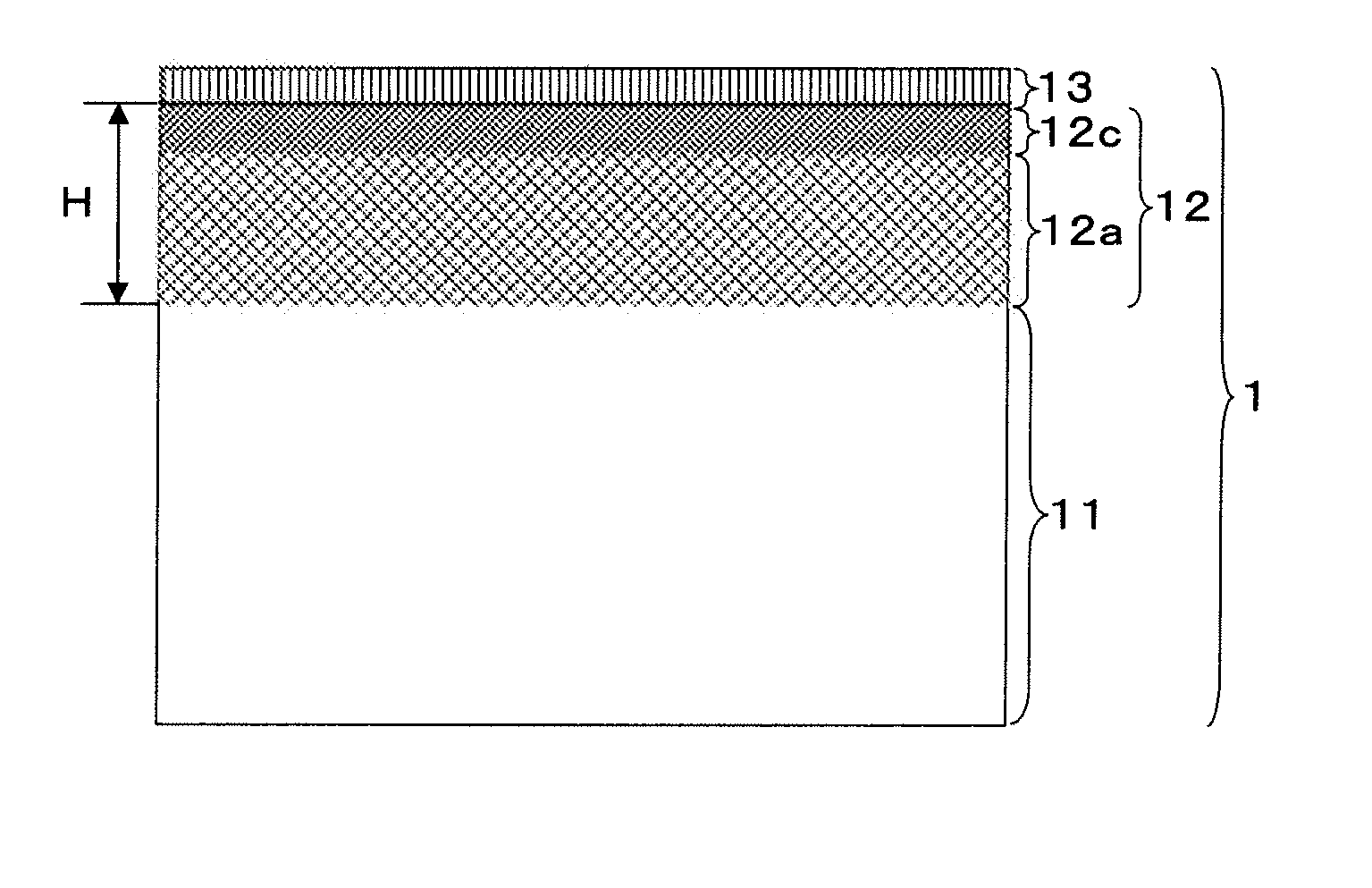
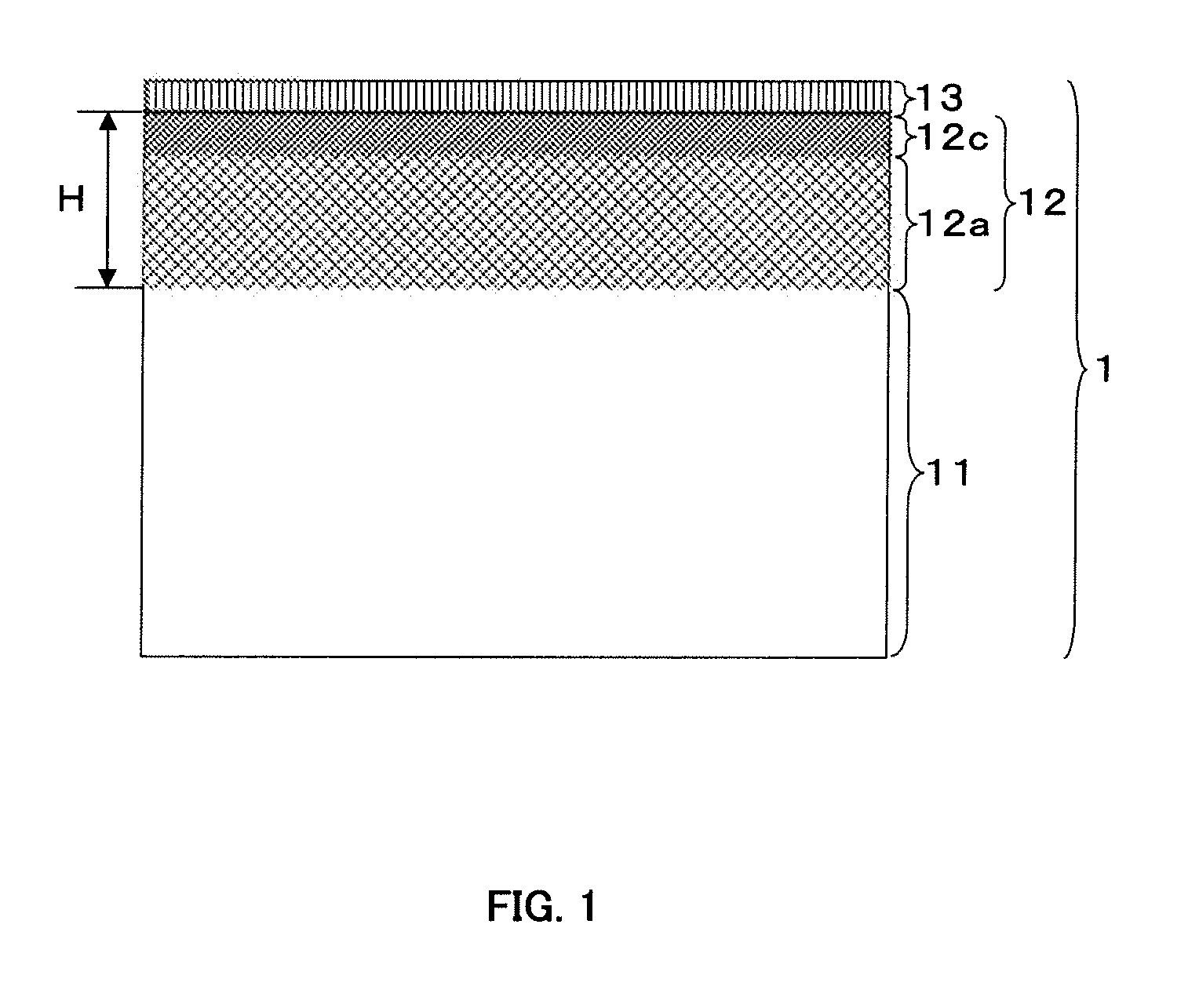
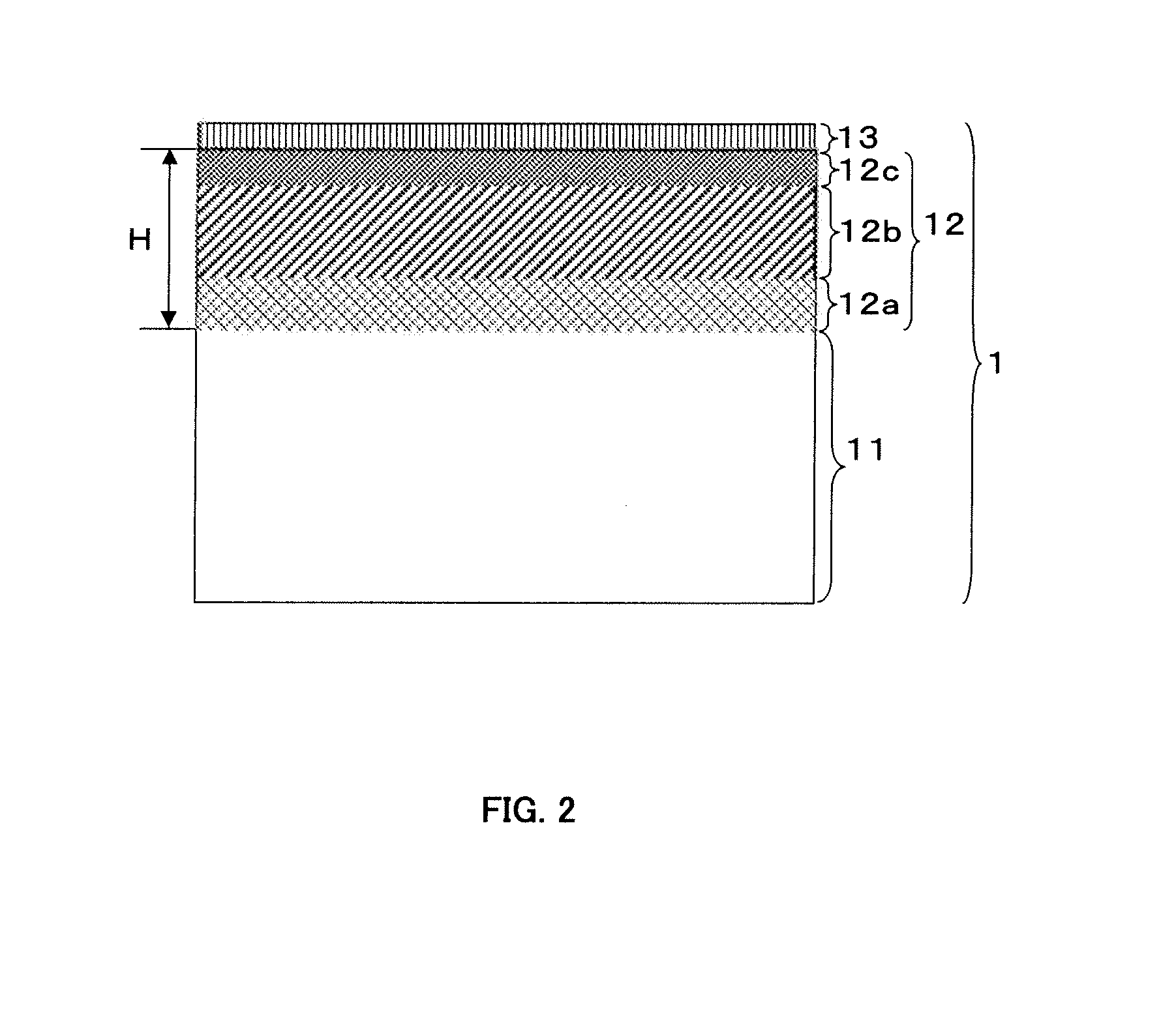
Zirconium alloy with coating layer containing mixed layer formed on surface, and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20130344348A1High-temperature anticorrosiveAvoid physical damageAdditive manufacturingPretreated surfacesOxidation resistantZirconium alloy
A zirconium alloy with a coating layer formed on a surface comprising a mixed layer, the mixed layer comprises one or more very high temperature oxidation resistant material and zirconium alloy parent material selected from the group consisting of Y2O3, SiO2, ZrO2, Cr2O3, Al2O3, Cr3C2, SiC, ZrC, ZrN, Si and Cr, and in a vertical direction on a boundary between the mixed layer and the zirconium alloy parent material is formed a gradient of compositions between the very high temperature oxidation resistance material and the zirconium alloy parent material.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Anti-Reflection Film And Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20100208350A1Good optical performanceLow refractive indexLayered productsPolarising elementsOptical propertyRefractive index
The present invention provides an anti-reflection film which has not only sufficient anti-reflection properties and antistatic properties but also excellent optical properties. The anti-reflection film of the present invention includes an antistatic hard coat layer and a low refractive index layer on a transparent substrate, the antistatic hard coat layer containing conductive particles and a binder matrix, the antistatic hard coat layer including a mixed layer in which the transparent substrate component and the binder matrix blend together with a gradient and a localized layer, the mixed layer being optically indistinguishable and the localized layer being optically distinguishable, and the localized layer having an optical thickness in the range of 50-400 nm.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Photovoltaic devices using semiconducting nanotube layers
InactiveUS20110203632A1Improve light absorptionPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSchottky barrierMetal insulator
Photovoltaic (PV) devices employing layers of semiconducting carbon nanotubes as light absorption elements are disclosed. In one aspect a layer of p-type carbon nanotubes and a layer of n-type carbon nanotubes are used to form a p-n junction PV device. In another aspect a mixed layer of p-type and n-type carbon nanotubes are used to form a bulk hetero-junction PV device. In another aspect a metal such as a low work function metal electrode is formed adjacent to a layer of semiconducting nanotubes to form a Schottky barrier PV device. In another aspect various material deposition techniques well suited to working with nanotube layers are employed to realize a practical metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) PV device. In another aspect layers of metallic nanotubes are used to provide flexible electrode elements for PV devices. In another aspect layers of metallic nanotubes are used to provide transparent electrode elements for PV devices.
Owner:NANTERO
Display device
InactiveUS20100148177A1Improve display characteristicsLower display costsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A display device including an inverter circuit and a switch is provided. The inverter circuit includes a first thin film transistor and a second thin film transistor which have the same conductivity type. The first thin film transistor and the second thin film transistor each include: a gate insulating layer in contact with a gate electrode; a microcrystalline semiconductor layer in contact with the gate insulating layer; a mixed layer in contact with the microcrystalline semiconductor layer; a layer which includes an amorphous semiconductor and is in contact with the mixed layer; and a wiring. A conical or pyramidal microcrystalline semiconductor region and an amorphous semiconductor region filling a space except the conical or pyramidal microcrystalline semiconductor region are included in the mixed layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for manufacturing light emitting device
InactiveUS20060102910A1Little initial deteriorationInitial deterioration is reducedStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsDisplay device
An object of the present invention is to provide a new light emitting element with little initial deterioration, and a display device in which initial deterioration is reduced and variation in deterioration over time is reduced by a new method for driving a display device having the light emitting element. One feature of the invention is that a display device comprising a light emitting element including a first electrode, a second electrode opposed to the first electrode, and a mixed layer of metal oxide and an organic compound provided between the first electrode and the second electrode is subjected to aging drive.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Photoelectric conversion element, solar battery, and photo sensor
InactiveUS20060118166A1Improve energy conversion efficiencyImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSimple Organic CompoundsHigh energy
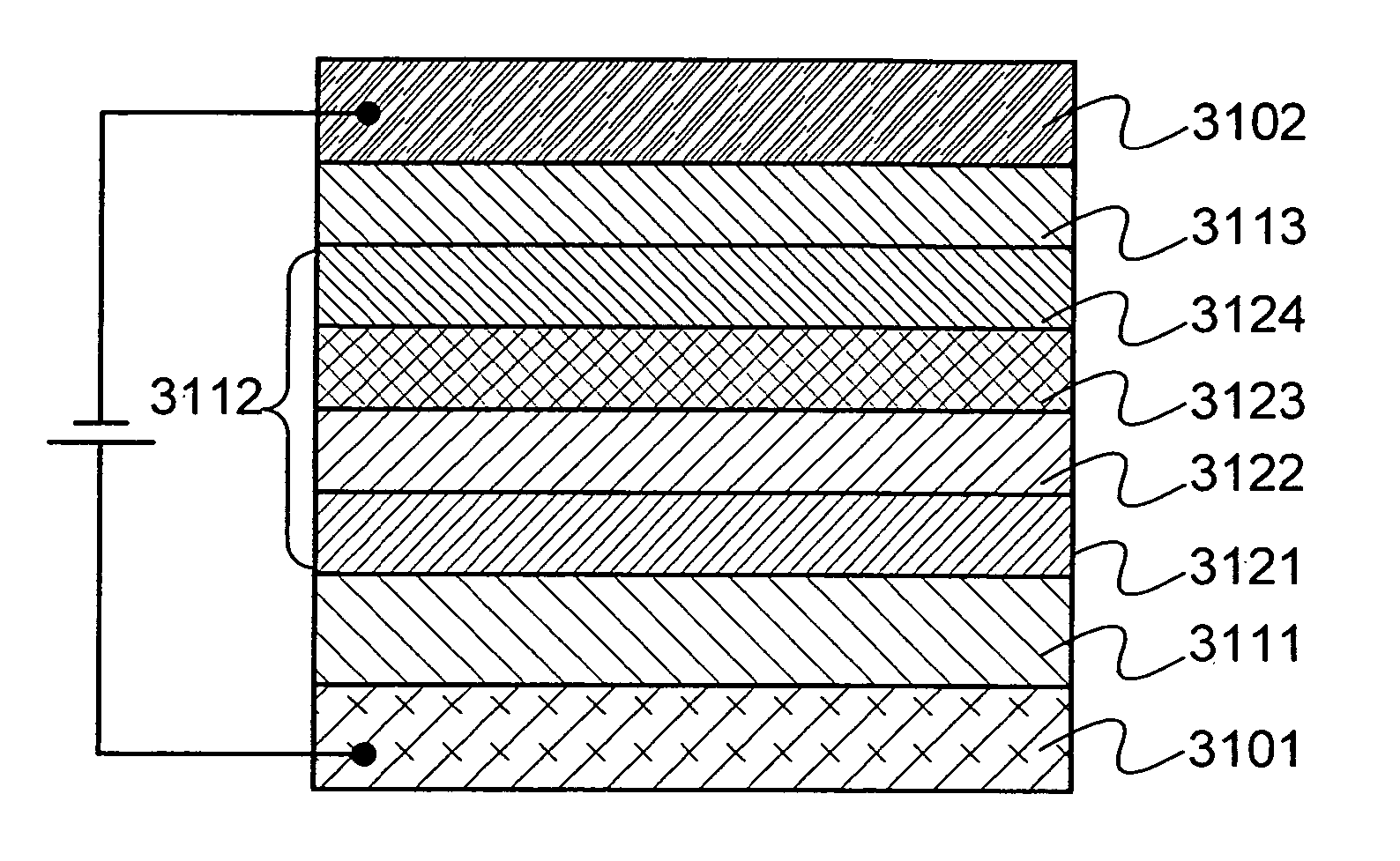
The invention provides a photoelectric conversion element and a solar battery having the photoelectric conversion element each of which has a structure with a high carrier generating rate. Further, the invention provides a photoelectric conversion element and a solar battery having the photoelectric conversion element of which high energy converting efficiency. According to the invention, the photoelectric conversion element and the solar battery having the photoelectric conversion element are characterized in that a pair of electrodes sandwich a mixed layer including a charge generating layer and a charge acceptor layer. The charge generating layer is formed of a first organic compound and an inorganic compound. The charge acceptor layer is formed of a second organic compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Encryption method for network and information security
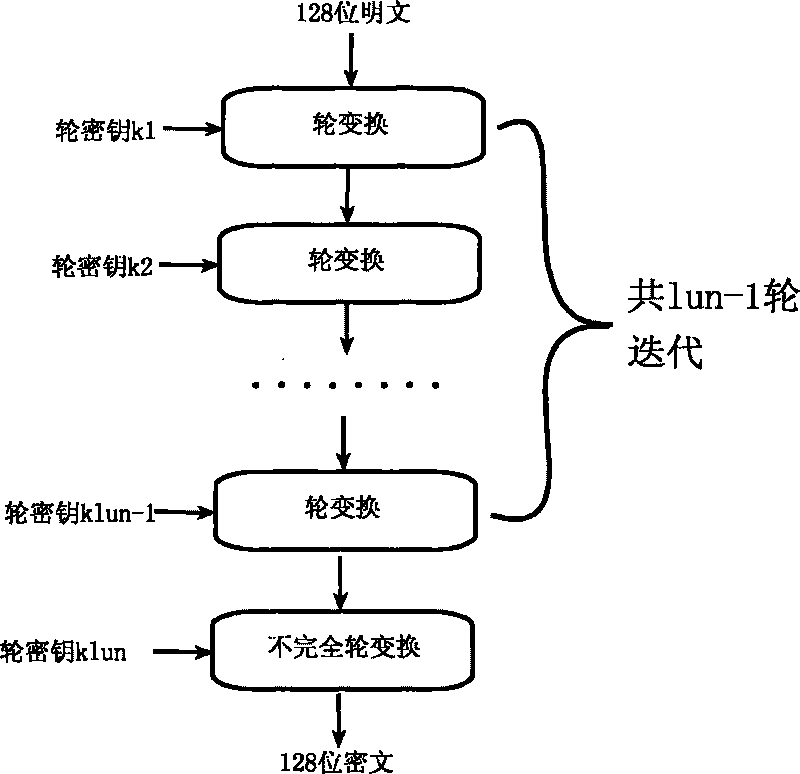
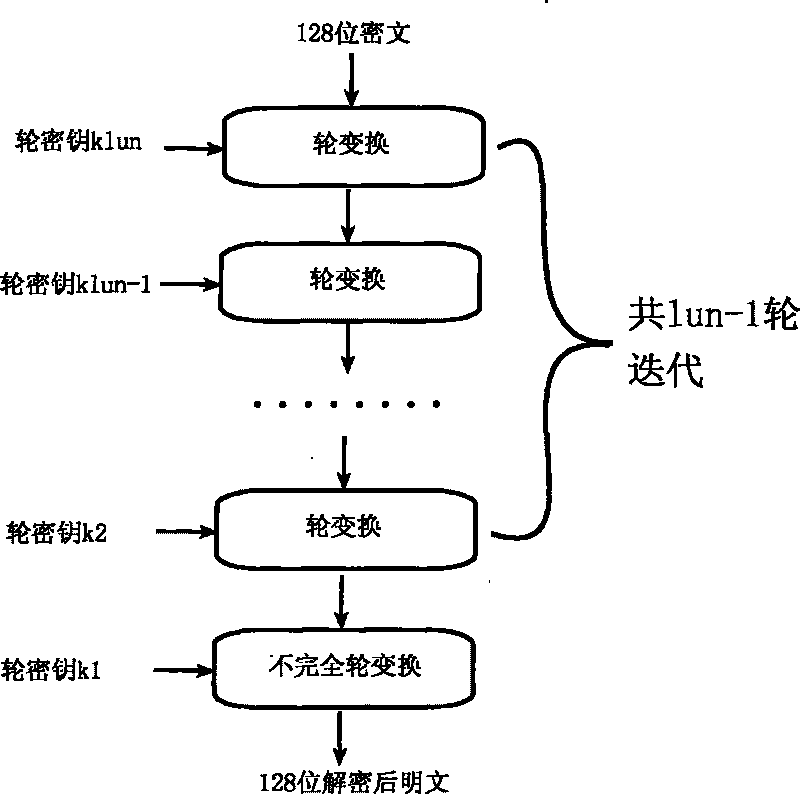
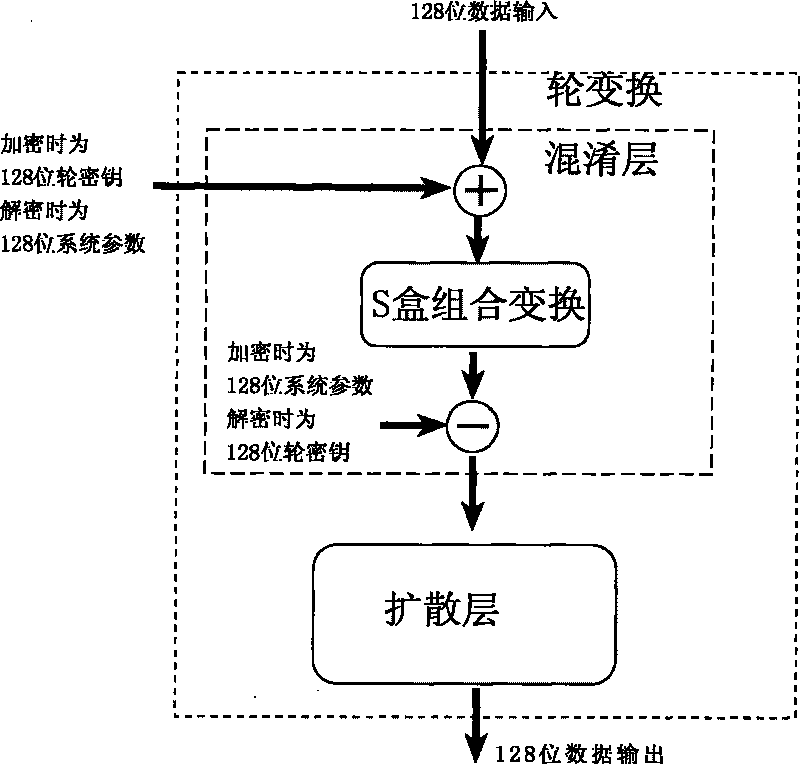
ActiveCN101764686AHigh speedDiffusion is fastKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareKey size
The invention relates to an encryption method for network and information security; the adopted packet length and key length are 128 bits, and a 128-bit system parameter is added; encryption algorithm comprises a plurality of rounds of round transform iteration consisting of mixed layers and diffusion layers, wherein the last round is incomplete round transformation, and the incomplete round transformation consists of the mixed layer; the mixed layer comprises key plus, S box portfolio transform and system parameter minus; the S box portfolio transform comprises 8-input 8-output reversible S box transform and inverse S box transform in the same number which are output by parity exchange; the diffusion layer can construct linear transformation with a reversible re-model polynomial matrix; an encryption round key is generated by an encryption key through encryption round transformation; and decryption algorithm is the inverse transformation of encryption algorithm. The encryption methodfor network and information security has the advantages of high diffusion speed, good security strength, hardware resource saving, and very high speed when being realized by hardware and on a software platform.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS HEBEI ACADEMY OF SCI
Electronic product case and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to an electronic product case and a manufacturing method thereof. The electronic product case comprises a metal or alloy body layer and a flashing effect layer arranged on the metal or alloy body layer. The flashing effect layer is a coating layer doped with flashing particles, or the flashing effect layer is an overlaying structure formed by a flashing particle layer and the coating layer that is outside, or the flashing effect layer is a mixed layer overlaid by the coating layer doped with flashing particles and the overlaying structure. The electronic product case has a flashing effect, can make the product more fashionable, and improves the user experience. According to the manufacturing method, the coating layer is sprayed and prepared on the metal or alloy case material, so that the appearance of the product is effectively protected and is less likely to wear.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Absorbent Core For Use In Absorbent Articles
An absorbent core for use in an absorbent article, the absorbent core including a first absorbent layer comprising a first substrate, a layer of first superabsorbent polymer particles deposited on the first substrate on a deposition area and a fibrous layer of thermoplastic adhesive material covering the layer of first superabsorbent polymer particles, and a second absorbent layer comprising a second substrate and a mixed layer comprising a mixture of second superabsorbent particles and cellulosic fibers deposited on the second substrate. The first and second absorbent layers are combined together such that at least a portion of the fibrous thermoplastic adhesive material of the first absorbent layer contacts at least a portion of the mixed layer of the second absorbent layer.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
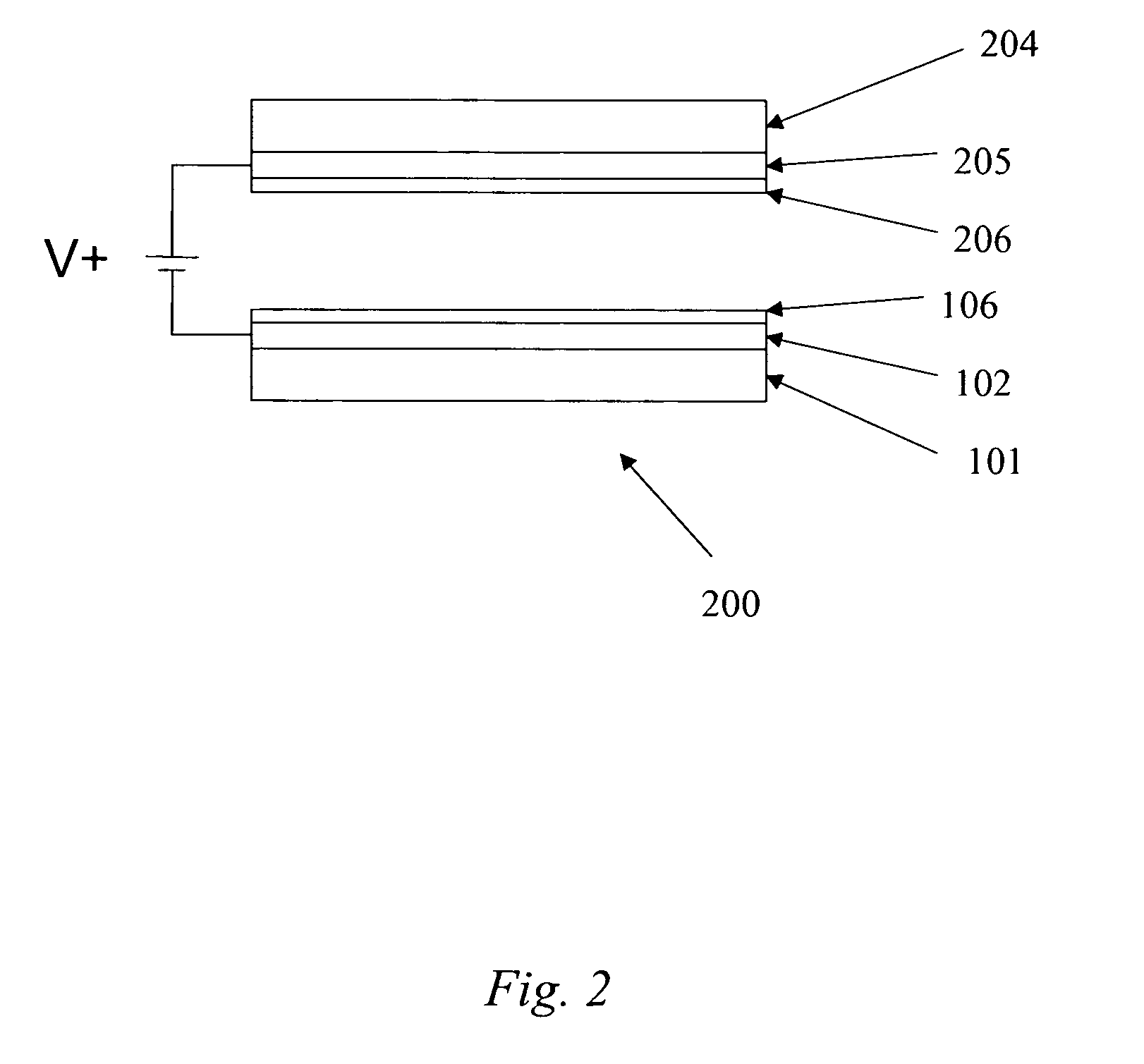
Display device with metal-organic mixed layer anodes
ActiveUS20060263628A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A display device comprises an anode, a cathode, and a luminescent region disposed between the anode and the cathode, wherein the anode comprises a metal-organic mixed layer operatively combined with an electron-accepting material. An anode may comprise a mixture of a metal-organic mixed layer and an electron-accepting material within a single layer of the anode. Alternatively, the anode may have a multilayer configuration comprising a metal-organic mixed layer and a buffer layer adjacent the metal-organic mixed layer, wherein the buffer layer comprises an electron-accepting material and optionally a hole transport material.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Substrate with antimicrobial properties and process for obtaining such substrate
InactiveUS20090162695A1Easy to useLow production costVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringDiamond-like carbon
A process for the production of a substrate having antimicrobial properties, including depositing a mixed layer on a substrate by sputtering under vacuum, the mixed layer containing at least one antimicrobial agent and a binder material selected from metal oxides, oxynitrides, oxycarbides, carbides, diamond like carbon and nitrides, where mixed targets are used for depositing the mixed layer. Substrates with mixed layers. Substrates made by the invention processes.
Owner:AGC FLAT GLASS EUROPE SA
Nonwoven composite material with oriented water guide function, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105369476AGood orientationRealize directional water guideNon-woven fabricsFiberHydrophobic effect
The invention provides a nonwoven composite material with an oriented water guide function, and a manufacturing method thereof. The nonwoven composite material with an oriented water guide function is characterized by comprising a hydrophilic layer, a water repellent layer, and a mixed layer between the hydrophilic layer and the water repellent layer. The hydrophilic layer is formed by hydrophilic fibers. The water repellent layer is formed by hydrophobic fibers. The mixed layer is formed by the hydrophilic fibers and the hydrophobic fibers. Part or all hydrophilic fibers in the hydrophilic layer and part or all hydrophobic fibers in the water repellent layer are arranged along a certain direction, and arraying directions of the hydrophilic fibers and the hydrophobic fibers are the same. A horizontal surface and a vertical surface have the oriented water guide function at the same time, and oriented water guide effect is excellent.
Owner:南京锦琪昶新材料有限公司
Devices with multiple organic-metal mixed layers
InactiveUS7288887B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A display device composed of:(a) a cathode;(b) an anode;(c) a luminescent region between the cathode and the anode; and(d) an optional region adjacent to the cathode or the anode, wherein the device includes a plurality of metal-organic mixed layers disposed at one or more of the cathode, the anode, the luminescent region and the optional region, wherein each of the metal-organic mixed layers includes:(i) an inorganic metal containing material, and(ii) an organic material.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Effect pigments having an aluminum or an aluminum aloy core, process for the production thereof and use thereof
ActiveUS7828890B2Minimal thicknessEasy to useCosmetic preparationsPigmenting treatmentMetallic aluminumRefractive index
The invention relates to effect pigments having an aluminum core or aluminum alloy core and an aluminum oxide-containing or aluminum oxide / hydroxide-containing layer enveloping said aluminum core or aluminum alloy core, obtained by chemical wet-process oxidation of lamellar aluminum pigments or aluminum alloy pigments, the content of metallic aluminum in the aluminum core or aluminum alloy core being not more than 90% by weight, based on the total weight of the pigment, wherein the oxidized aluminum pigments or aluminum alloy pigments exhibit at least one highly refractive metal chalcogenide layer having a refractive index of >1.95, and a mixed layer is formed between the highly refractive metal chalcogenide layer and the enveloping aluminum oxide-containing or aluminum oxide / hydroxide-containing layer. The invention further relates to a process for the production of such effect pigments and to the use thereof.
Owner:ECKART GMBH & CO KG
Sea electric power cable
ActiveCN101807450ASolve the problem of induced potentialSolve the circulation problemPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSubmarine cablesOcean bottomState of art
The invention relates to a sea electric power cable which comprises a conductor (1), semi-conduction layer (2), insulation layer (3), a buffer layer (4), a lead casing (5), an inner jacket layer (6), an armor layer (7) and an armored outer protective layer (8) which are arranged from inside to outside. The invention is characterized in that the inner jacket layer (6) is a mixed layer formed by the end-to-end connection of the semi-conduction layer and the insulation layer in series. Compared with the prior art, the armored inner jacket layer adopted by the invention is the mixed layer formed by the end-to-end connection of semi-conduction layer and insulation layer in series. Such design has the advantage that the underwater portion and the onshore portion of the sea electric power cable comprise different inner jacket layers, wherein the underwater portion is an anticorrosive semi-conduction layer, thereby effectively solving the problem of induced potential, and further solving the problem of circular current; and the onshore portion is an insulation layer which is the same structure as the common electric power cable, thereby realizing cross interconnection, and further achieving the purposes of reducing loss and raising current capacity.
Owner:浙江省电力公司舟山电力局
Fiber grating liquid flow sensor with temperature compensation
InactiveCN102095451AImprove protectionAccurate measurementSurveyVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectChemical industryFiber
The invention relates to a fiber grating sensor, in particular to a fiber grating liquid flow sensor with temperature compensation or for eliminating the influence of temperature change on a measurement value. The sensor has high data acquisition precision and long service life, can work under the environment of high temperature (over 300 DEG C) and high pressure (over 40MPa) and acquire effective data, and is not affected by the adverse conditions of electric field, magnetic field, explosiveness, flammability and the like; the service life of the sensor is nearly semi-permanent; and the sensor has small volume, is easy to install, has high measurement precision, and can adapt to flow measurement of complex, layered and mixed layers. Particularly in the petroleum extraction process, the requirement of measurement of liquid yield is more prominent; and particularly, the sensor can be applied in the places where the temperature sensors of other forms are not competent, and particularly has great application prospect in the fields of nuclear power plants, oil fields, spaceflight, chemical industry, mining industry, energy conservation, emission reduction and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN METALWORKING MACHINERY & EQUIP MFG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com