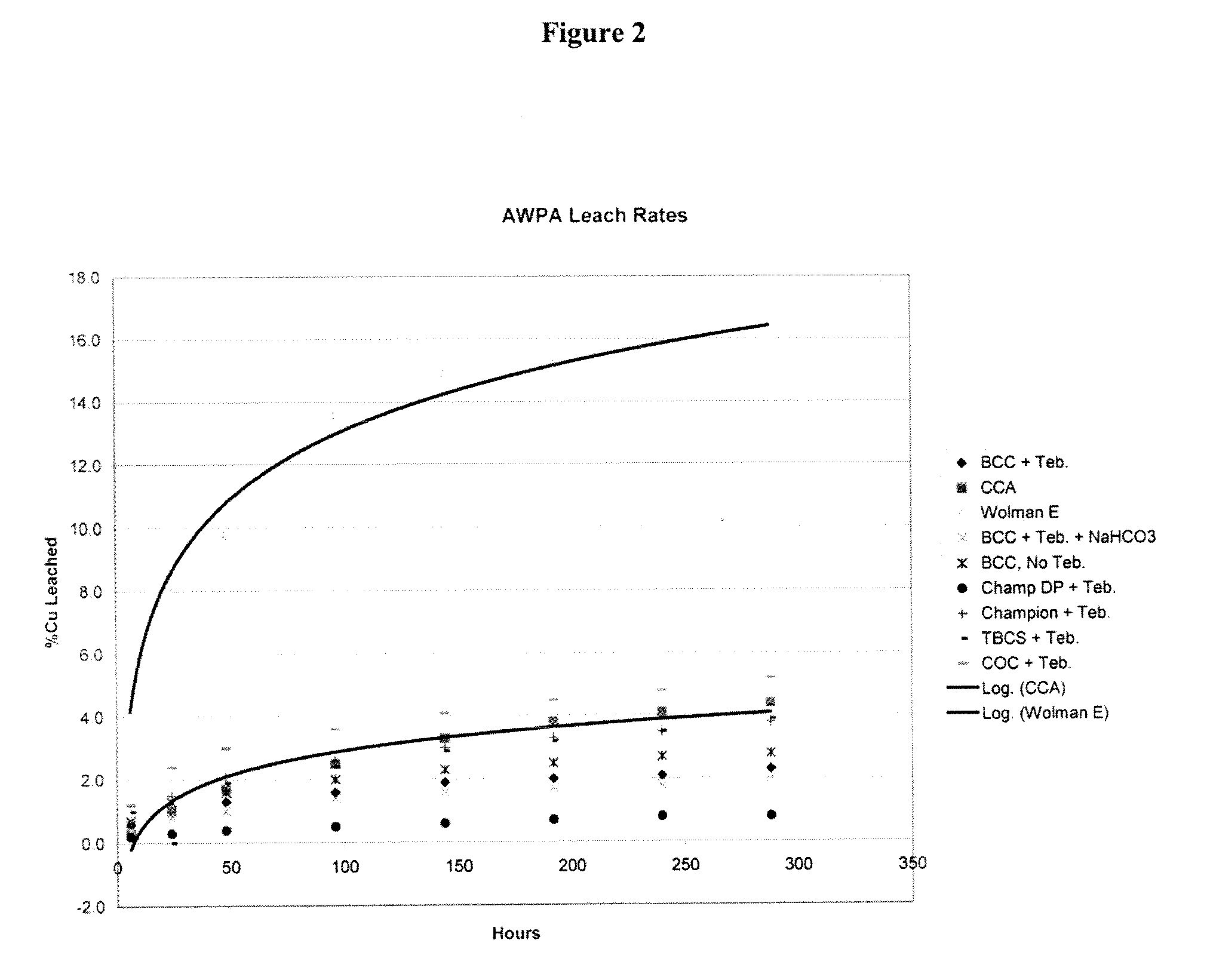
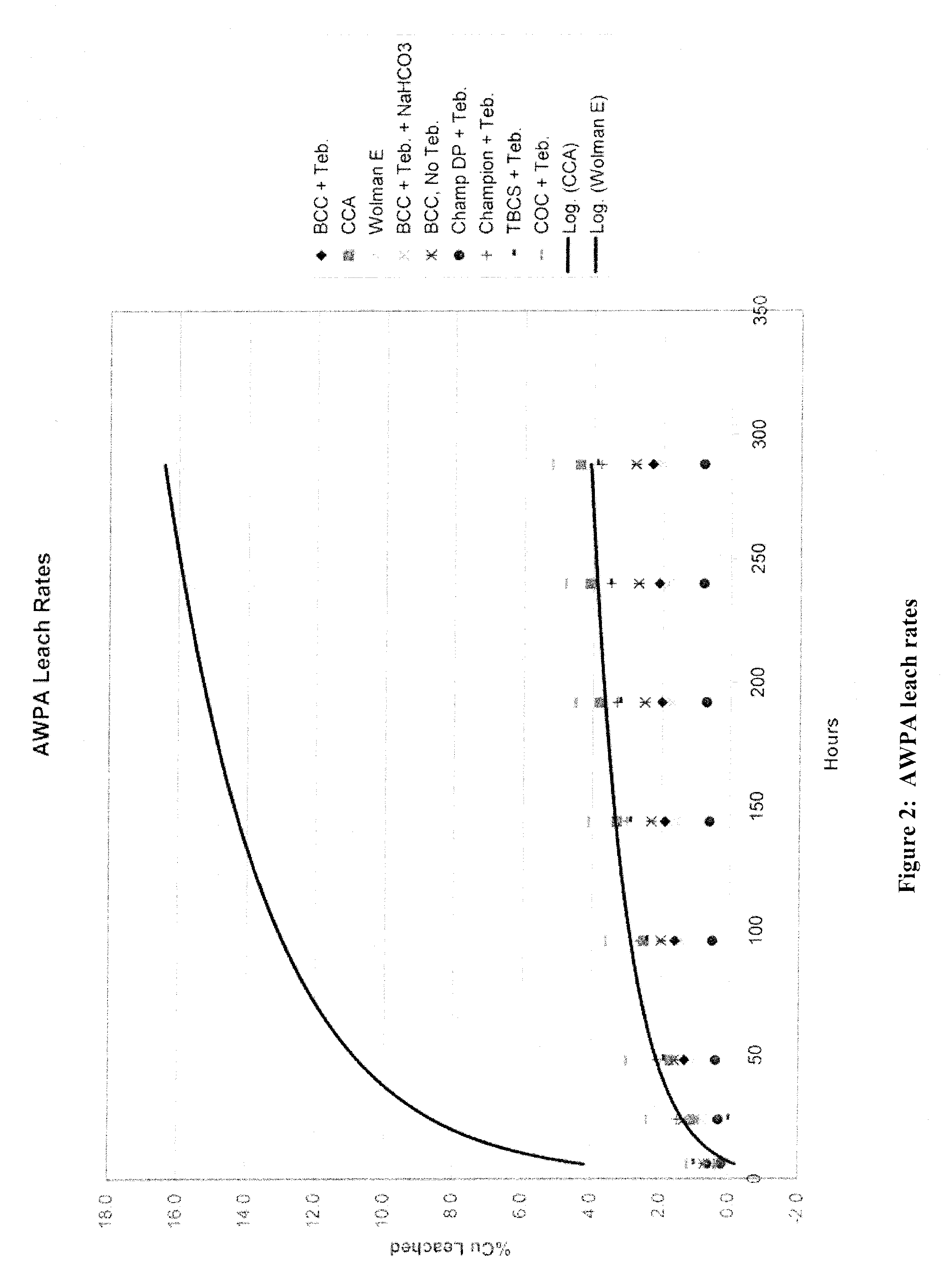
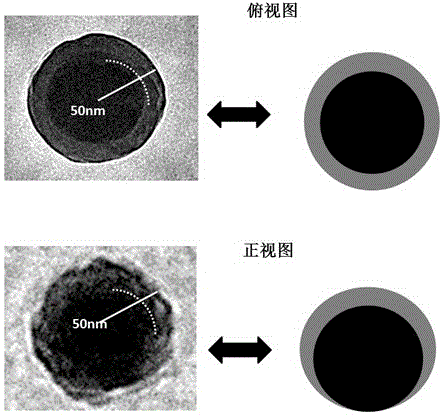
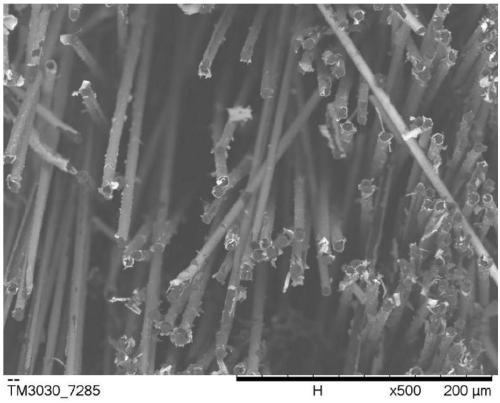
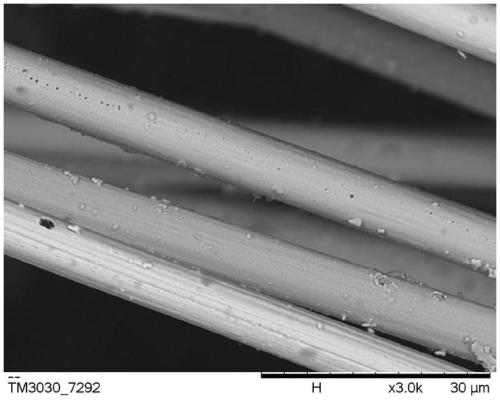
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "BASIC COPPER SULFATE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
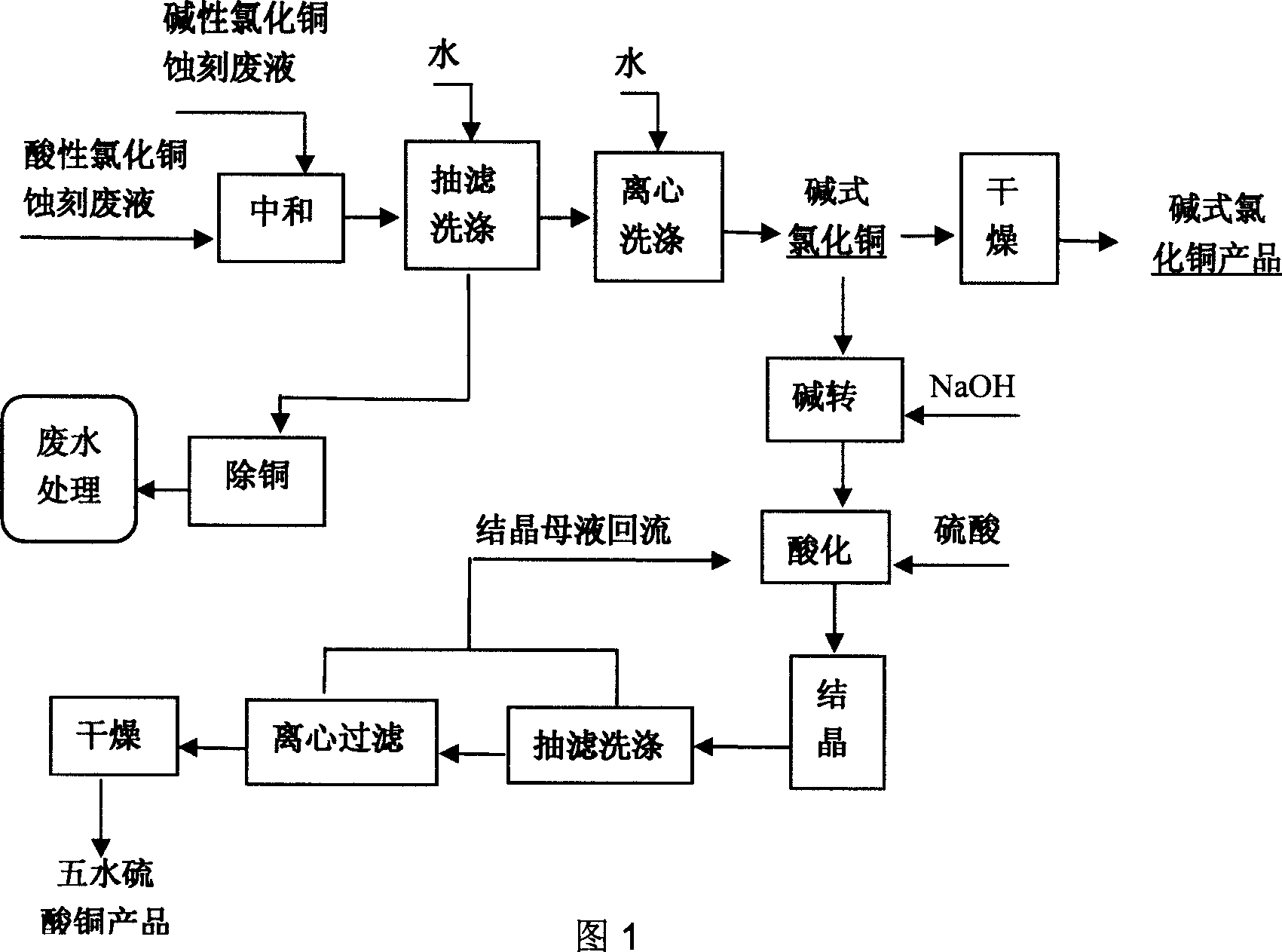
Method for producing basic copper chloride, cupric sulfate pentahydrate from copper-containing etching waste liquid
ActiveCN101391800AEfficient removalImprove product qualityCopper chloridesMultistage water/sewage treatmentCopper chlorideSulfate
The invention relates to a method for producing copper chloride hydroxide and blue vitriod by using cupriferous etching wastewater; the method comprises the following steps: acidic copper chloride etching wastewater and alkaline copper chloride etching wastewater are neutralized and crystallized to get acidic copper chloride crystal under the condition of strictly controlling filling liquid and the Ph range of a reaction kettle, and then pumped and filtrated, and centrifugated; part of the obtained alkaline copper chloride crystal is dried to obtain finished products while the other is added with NaOH solution for alkali conversion to obtain copper oxide, and then is acidulated by sulphuric acid, crystallized, washed, centrifugated, and dried to obtain blue vitriod products. The method for producing blue vitriod by directly using sulphuric acid-oxyful etching wastewater includes the following steps: sulphuric acid-oxyful etching wastewater and composition brass wasterwater in a PCB manufacture are blended together and added with NaOH to form cupric hydroxide precipitation which filtrated, washed, and then acidulated by sulphuric acid to obtain copper sulphate solution; after the copper sulphate solution is cooled, crystallized, centrifugated and dried, and the blue vitriod is obtained.
Owner:HUIZHOU DONGJIANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
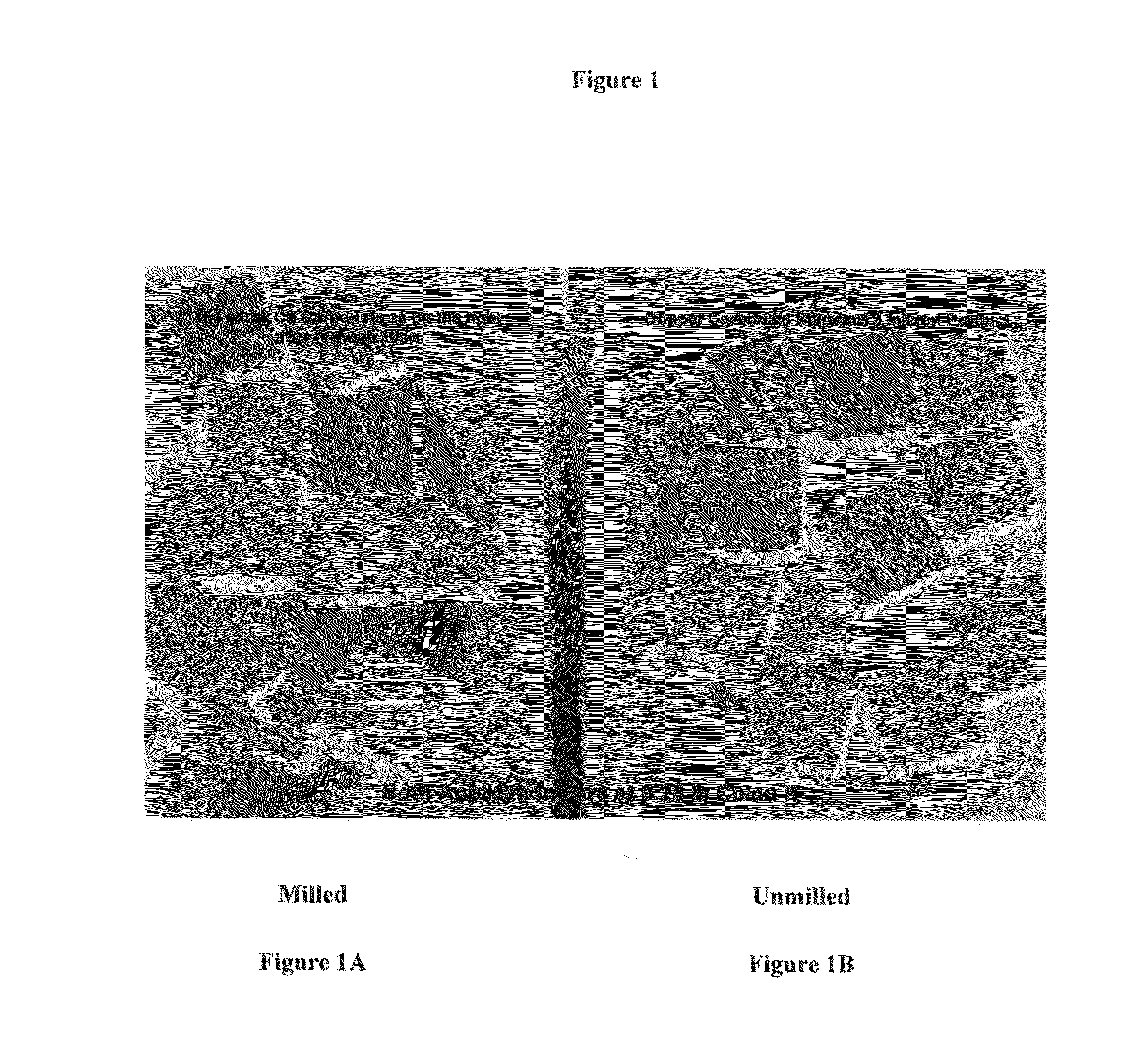
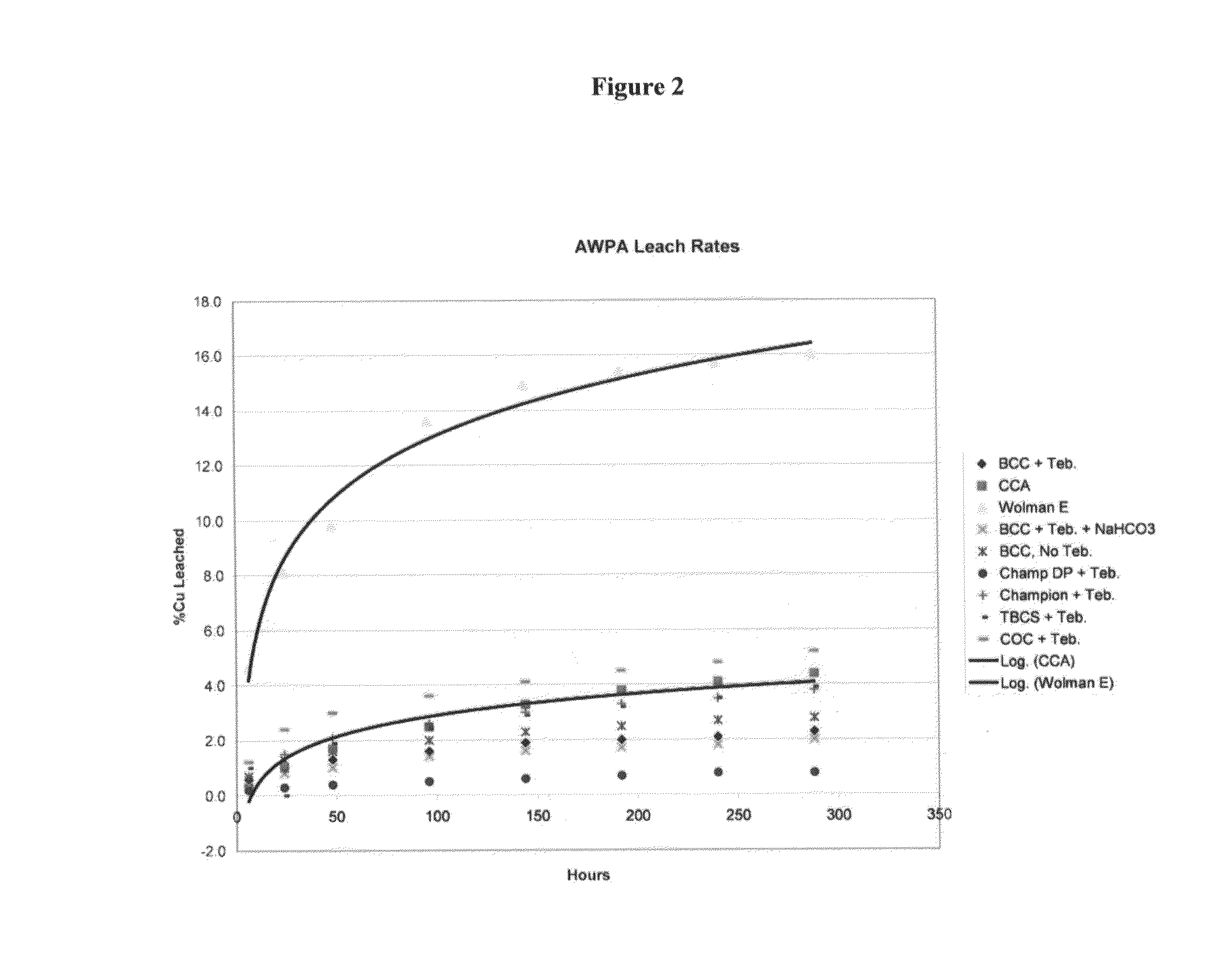
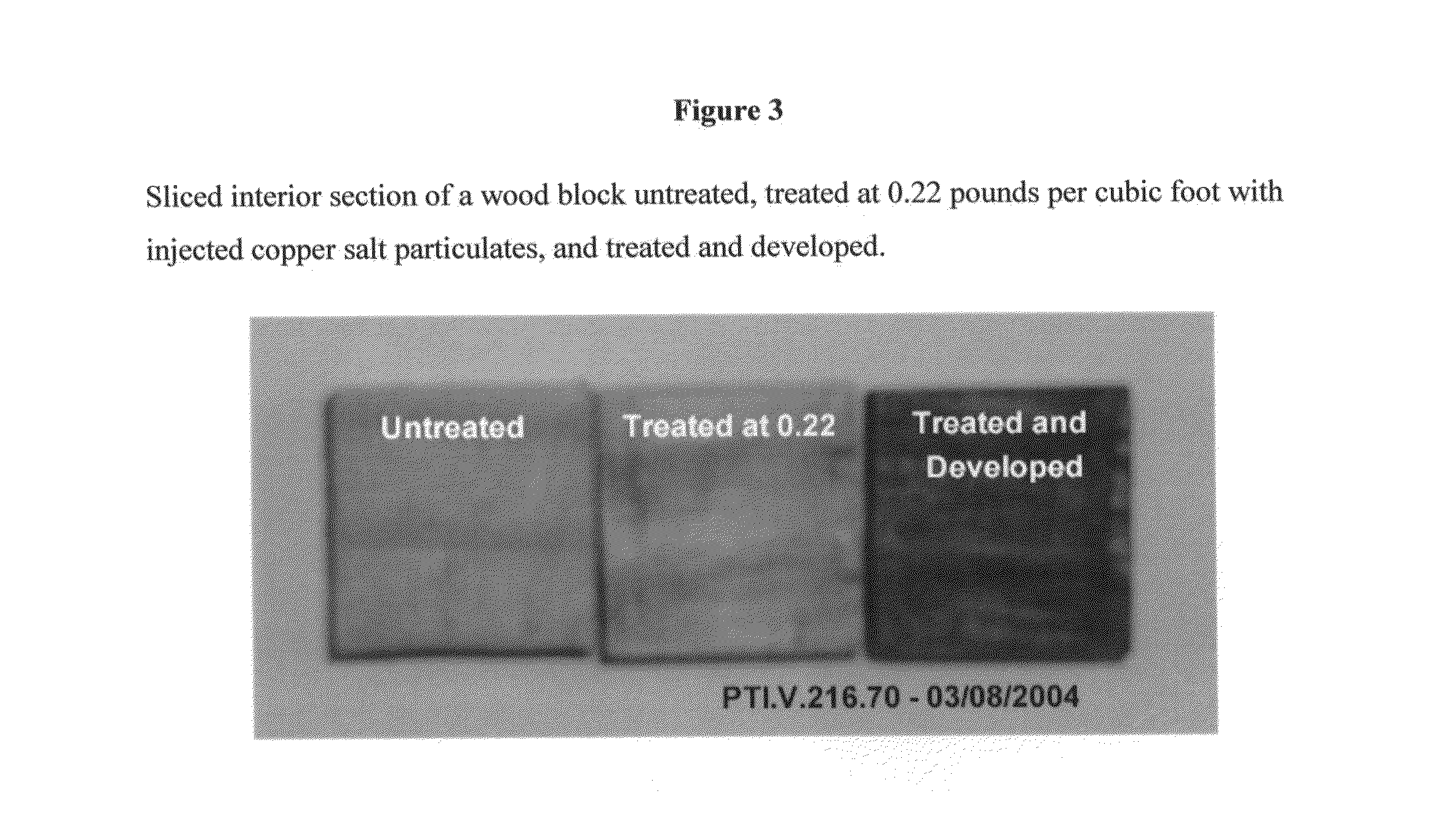
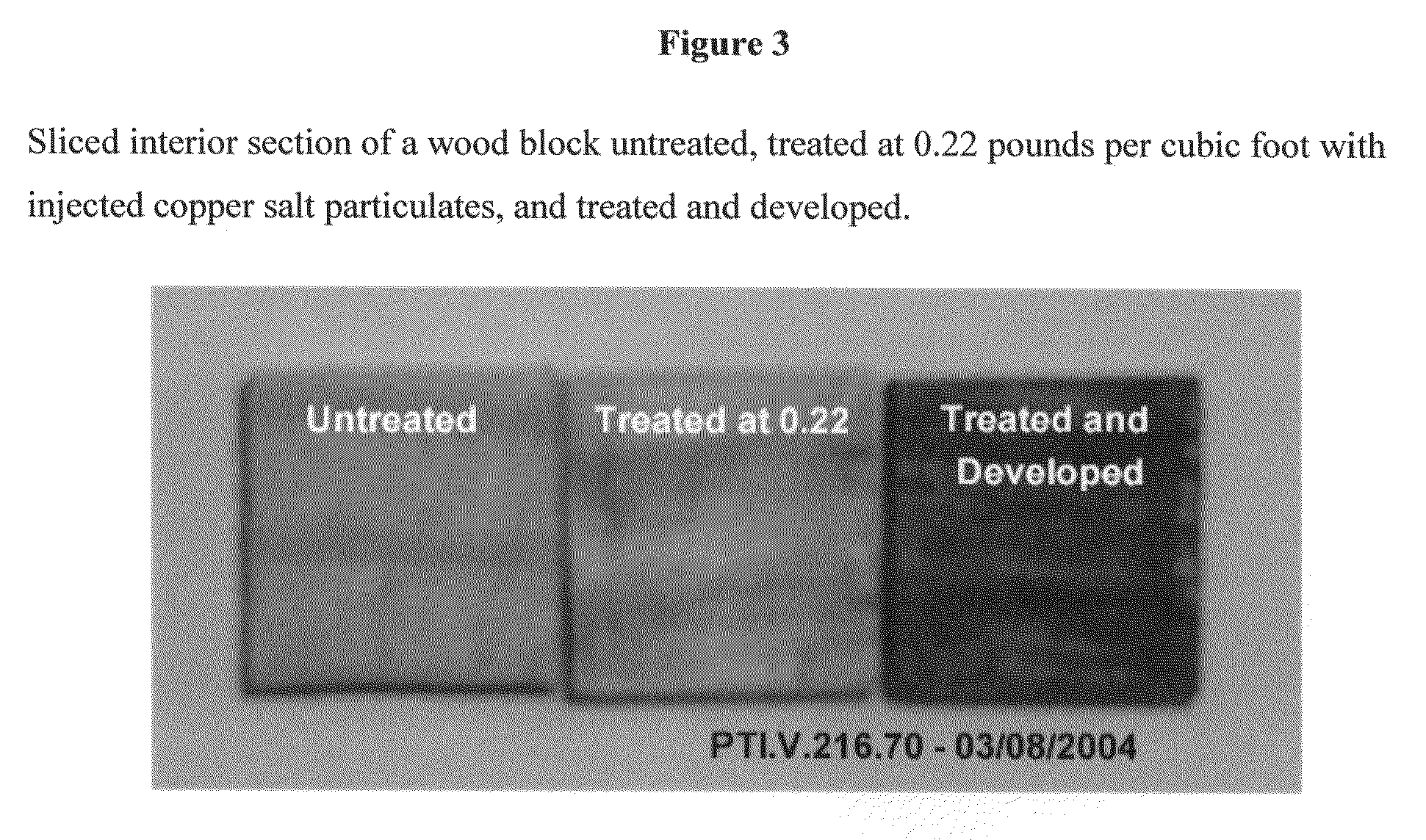
Use of sub-micron copper salt particles in wood preservation
InactiveUS20060062926A1Little dangerSmall particle sizeBiocideLiquid surface applicatorsPhosphateCopper nitrate
A method for preserving wood by injecting into the wood a slurry having: particles of a sparingly soluble copper salt, copper hydroxide, or both, wherein the weight average diameter d50 of the particles in the slurry is between 0.1 microns and 0.7 microns and the d98 of the particles in the slurry is less than about 1 micron; a dispersant; and water. The dispersant is anionic or a mix of anionic and non-ionic. Advantageously, less than 20% by weight of the particles have a diameter less than 20 nanometers. Useful copper salts include basic copper carbonate, tri-basic copper sulfate, copper oxychloride, basic copper nitrate, basic copper borate, copper borate, basic copper phosphate, or copper silicate. The slurry most preferably includes copper hydroxide particles. The slurry further advantageously includes at least one organic biocide, wherein at least a portion of the organic biocide is coated on the particles.
Owner:OSMOSE
Particulate wood preservative and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050252408A1Reduce the amount requiredWide particle size distributionBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsCopper(II) hydroxideBasic copper carbonate
A wood preservative includes injectable particles comprising one or more sparingly soluble copper salts. The copper-based particles are sufficiently insoluble so as to not be easily removed by leaching but are sufficiently soluble to exhibit toxicity to primary organisms primarily responsible for the decay of the wood. Exemplary particles contain for example copper hydroxide, basic copper carbonate, copper carbonate, basic copper sulfates including particularly tribasic copper sulfate, basic copper nitrates, copper oxychlorides, copper borates, basic copper borates, and mixtures thereof. The particles typically have a size distribution in which at least 50% of particles have a diameter smaller than 0.25 μm, 0.2 μm, or 0.15 μm. At least about 20% and even more than 75% of the weight of the particles may be composed of the substantially crystalline copper salt. Wood or a wood product may be impregnated with copper-based particles of the invention.
Owner:OSMOSE
Non-cyanide alkaline copper plating bath, preparation and use method thereof
The present invention is a new non-cyanide alkaline copper plating bath, preparation and use method thereof. In the copper plating bath, using copper sulfate or basic copper carbonate as main salt, using hydroxy-ethylidene diphosphonic acid as main complexant, using trisodium citrate, potassium citrate or potassium sodium tartrate as auxiliary complexant, using sodium nitrate or potassium nitrate as conductive salt, using sodium hydroxide or potassium hydrate as pH value regulator; the operation conditions are: cathode current density is 0.5-3.0 A / dm [2], pH of plating bath controlled between 12 and 13, plating bath temperature is 50-70 DEG. Comparing with the prior known technology, the invention has following advantages or positive effects: simple plating bath formula, easy control and operation, wide temperature range of plating bath using, high current efficiency, fine crystallization coating, good appearance color, stable plating bath, strong uniform plating and covering ability, low cost, easy wastewater treatment. The invention can be used for pre copper plating or direct electro-coppering instead of virulent cyaniding electro-coppering process.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
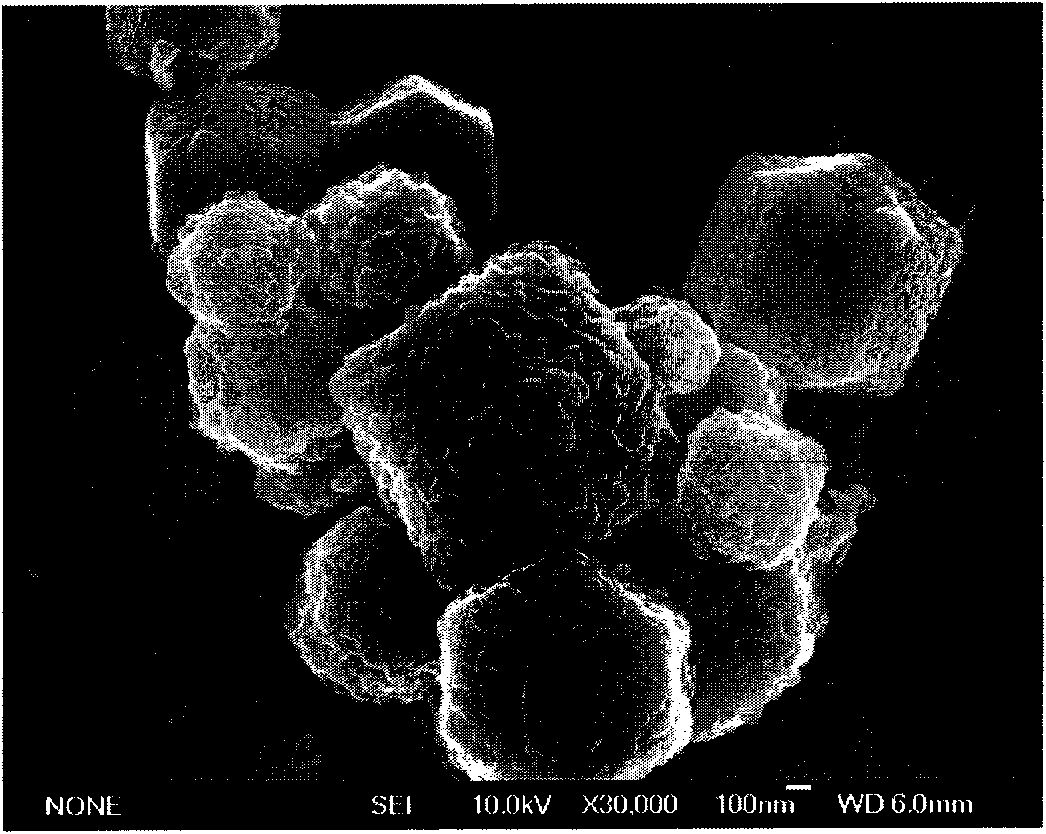
Preparation method of metal organic framework coated phase-change material microcapsule
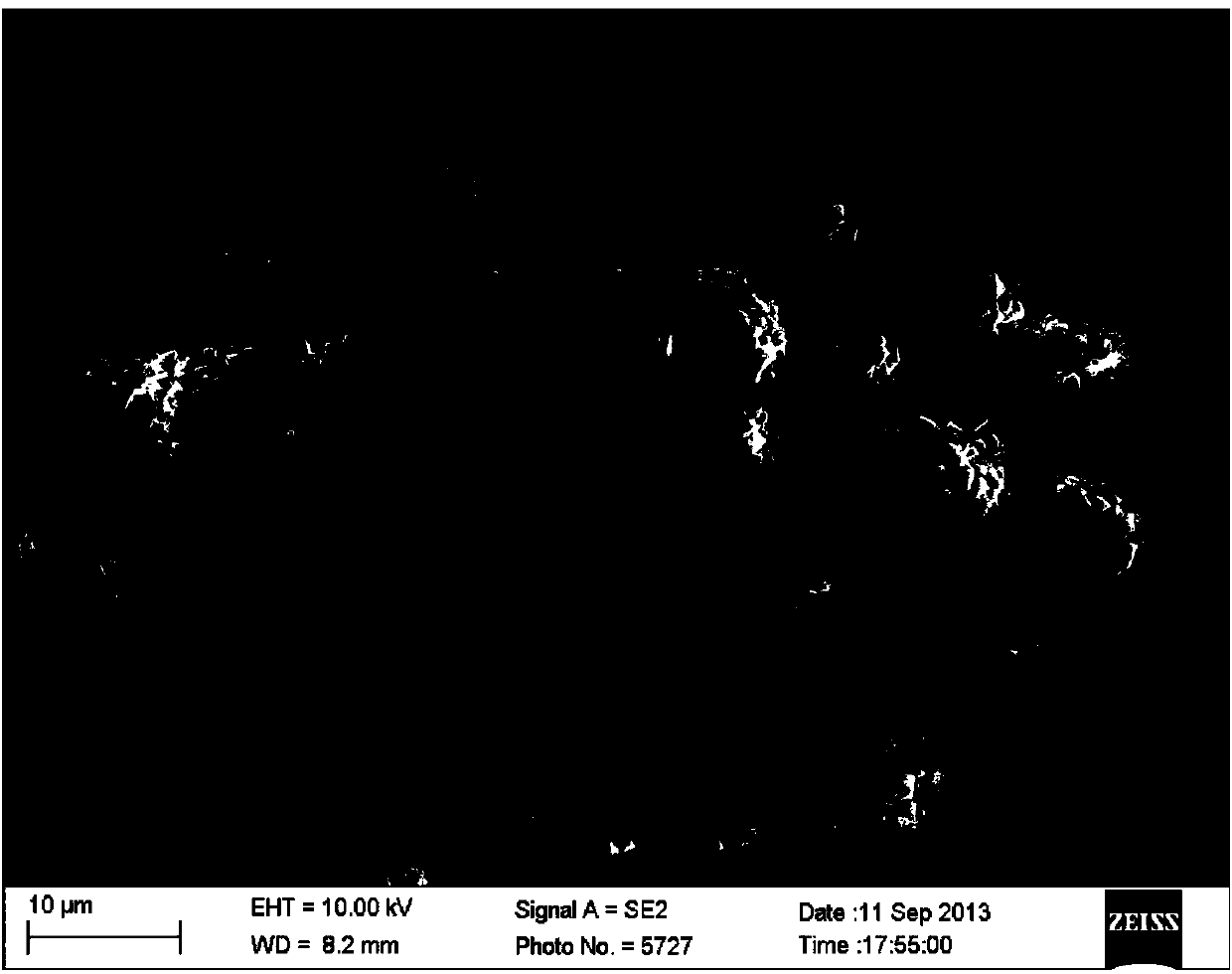
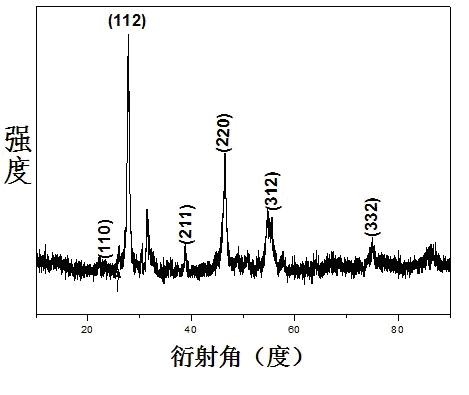
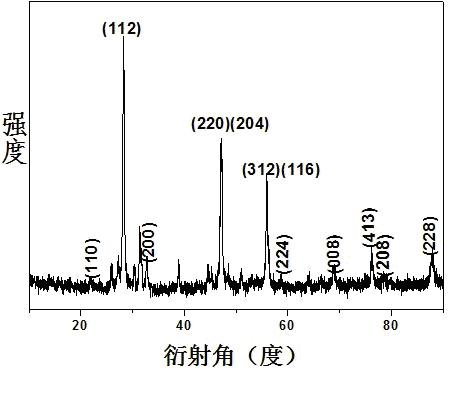
The invention relates to a preparation method of a metal organic framework coated phase-change material microcapsule. The method comprises the steps that a basic copper sulfate microsphere in a hollow structure or a yolk / shell structure is prepared; a shell layer of the basic copper sulfate microsphere is assembled by nano sheets; a gap is formed between every two nano sheets; a phase-change material can enter the microsphere through the gaps of the shell layer of the basic copper sulfate microsphere; the shell layer is converted into a metal organic framework material in situ; a dense metal organic framework material shell layer is formed; the phase-change material is encapsulated and dried; and then the metal organic framework coated phase-change material microcapsule is prepared. The method has the advantages that 1) a novel metal organic framework coated phase-change material microcapsule is developed; 2) the prepared metal organic framework coated phase-change material microcapsule can effectively avoid leakage, corrosion and the like, and improve the heat conductivity of a composite; and 3) the method is mild in reaction condition, simple in technology and short in period, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A multipurpose bactericial composition for farm crop
InactiveCN101156597APromote growthThe formula is scientific and reasonableBiocideFungicidesDiseaseAdipic acid
The invention provides a multi-purpose sterilizing combination for crops. The constituents has weight percentages that: constituent A is 1-50 percent, constituent B is 5-63 percent, constituent C is 0.1-5 percent, common carrier is 25-88 percent, and common assistant is 5.0-25 percent. The constituent A is any one of difenoconazole, prochloraz, prochloraz manganic salt, or metalaxyl-m. The constituent B is any one of basic copper sulfate, bluestone, copper hydroxide, copperchloride, cuprous oxide, copper acetate, cuaminosulfate, amber glue copper adipic acid, or copper rosinate. The constituent C is any one of diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate, sodium nitrophenolate, naphthyl acetic acid, gibberellins, or brassinosteroids lactone. The invention not only can multiply the expansion of the preventing spectrum on the crop disease, can delay the produce of the drug-resistance; can lower the dosage of each agent in the combination, can obviously improve the medical effect of the constituents when being used separately, can prevent and cure the disease, can facilitate the growth of the crop, and can increase the yield and the harvest of the crop.
Owner:湖南万家丰科技有限公司
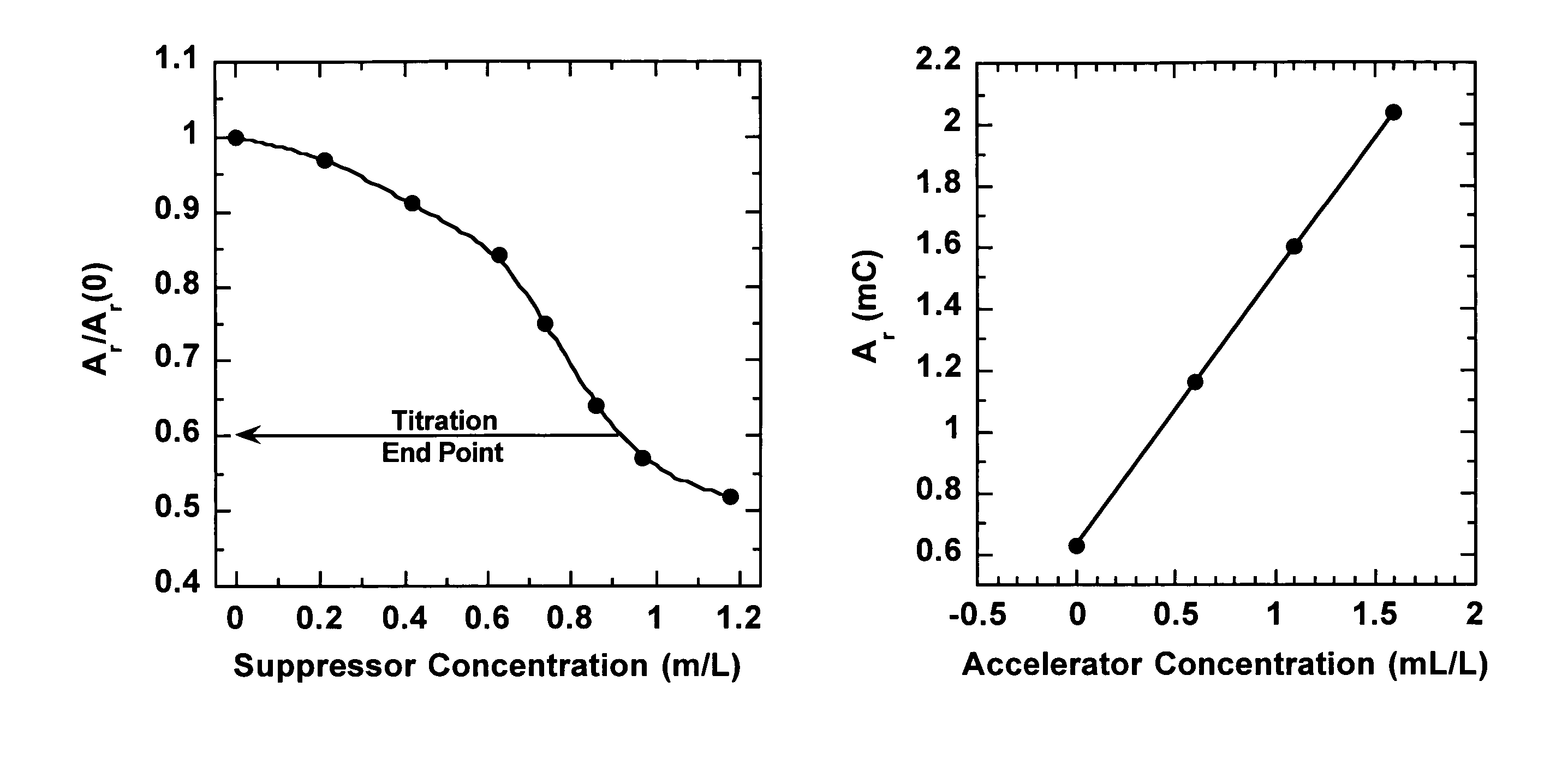
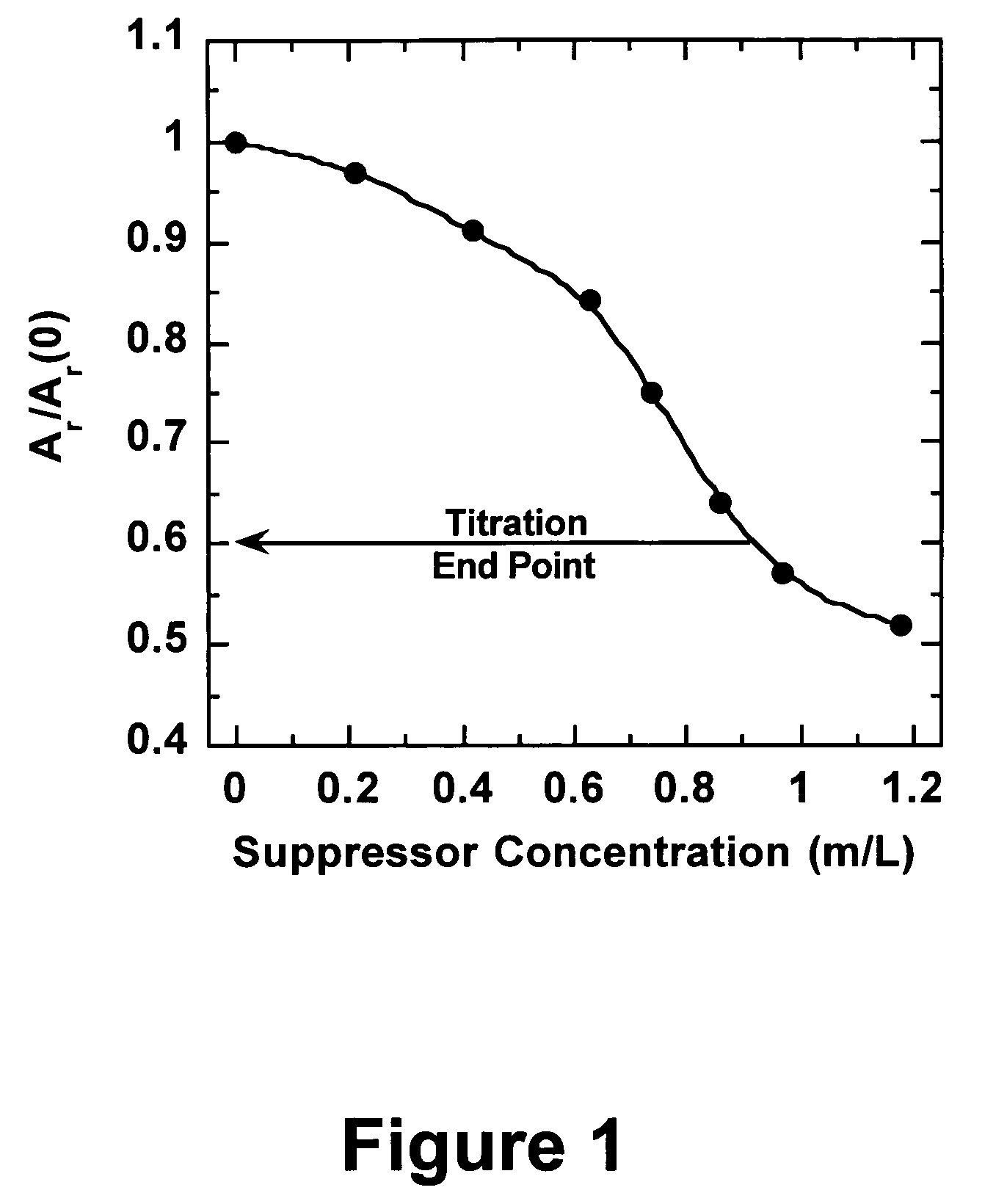
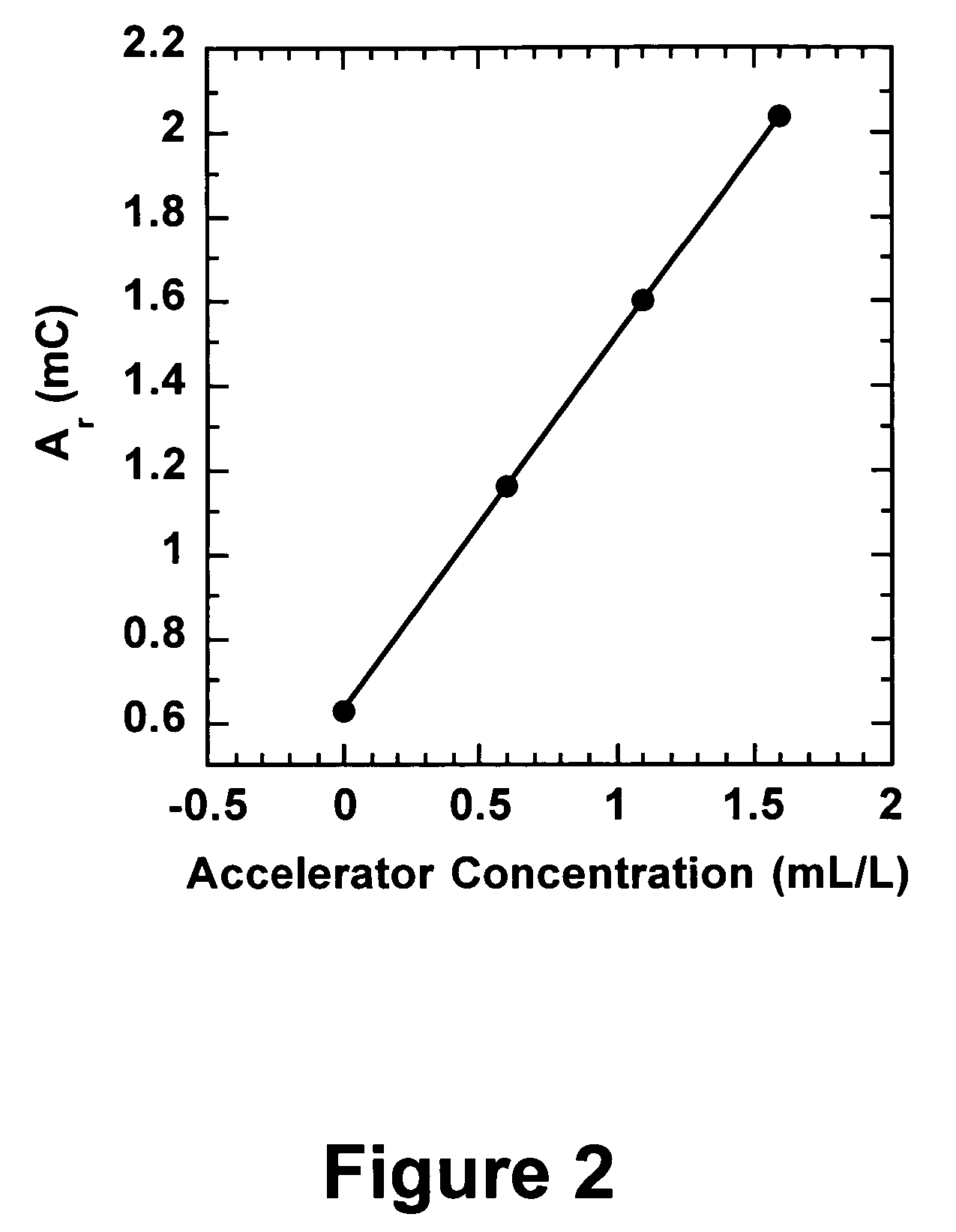
Efficient analysis of organic additives in an acid copper plating bath
InactiveUS7186326B2Consumption of of wasteQuantity of wasteCellsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCopper platingSuppressor
Owner:KLA CORP
Production method for health food rich in multiple trace elements and used for rehabilitation of coronary heart disease
InactiveCN103355607AOvercome absorbencyOvercome the disadvantages of side effects caused by direct administrationFood preparationChromium(III) chlorideBASIC COPPER SULFATE
The invention relates to a production method for health food rich in multiple trace elements and used for rehabilitation of a coronary heart disease. The production method comprises the following steps: filling 10 kg of grains into a square container and weighing 29 to 31 g of chromium chloride, 248 to 252 g of zinc chloride, 2.5 to 2.8 g of nickel chloride, 6 to 7 g of sodium selenite, 0.6 to 0.7 g of sodium metavanadate, 88 to 89 g of germanium tetrachloride, 155 to 160 g of copper sulphate, 140 to 145 g of manganese chloride, 288 to 292 g of iron chloride, 10 to 14 g of lithium chloride, 7 to 8 g of sodium molybdate, 0.6 to 0.7 g of cobalt chloride, 605 to 607 g of sodium silicate, 82 to 85 g of strontium sulfate and 65 to 68 g of sodium fluoride; mixing above-mentioned salts, adding water for dilution of the salts until 6 to 6.5 kg of a mixed salt solution is obtained and allowing the salt solution to be completely absorbed by the grains; and drying and crushing the grains so as to obtain the health food. The health food provided by the invention has a plurality of trace elements needed by a human body, and the trace elements and amino acids are compounded to form a plurality of amino acid salts which can be easily absorbed by the human body; the health food can maintain balance of trace elements in the human body, prevent and correct metabolic disorders of inorganic salts and trace elements, prevent and restore incomplete cells and regenerate new cells, enables blood vessels to be unblocked and rehabilitation of the coronary heart disease to be realized and has prevention and health care effects on the coronary heart disease.
Owner:买世禄 +1
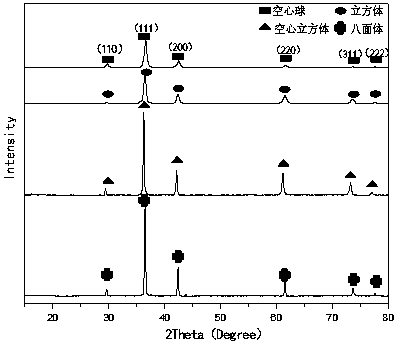
Method of preparing cuprous oxide rhombic dodecahedron and low-temperature reduction reaction
InactiveCN101549883AFlexible production processSave raw materialsCopper oxides/halidesSolventMicrometer
The invention provides a method of preparing cuprous oxide rhombic dodecahedron and low-temperature reduction reaction; the method is characterized by taking blue vitriod as copper source, taking glucose as surfactant, using mixed solvents of water and ethanol, and using sodium hydroxide to cause the whole solvent to keep alkalinity, carrying out reduction reaction under 60 to 120 degrees centigrade to obtain the cuprous oxide rhombic dodecahedron. The produced cuprous oxide rhombic dodecahedron has high photocatalytic activity. In the past, various methods are used to prepare cuprous oxide nanometer / micrometer cubes and octahedral, but the invention prepares the cuprous oxide rhombic dodecahedron formed by 12 congruent (110) crystal faces; and the method provided by the invention has simple processing equipment, low production cost and is suitable for commercial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Particulate wood preservative and method for producing the same
ActiveUS8409627B2Effective, long-lasting, environmentally responsible, non-staining/coloringLow dissolution ratePowder deliveryBiocideCopper(II) hydroxideCopper nitrate
A wood preservative includes injectable particles comprising one or more sparingly soluble copper salts. The copper-based particles are sufficiently insoluble so as to not be easily removed by leaching but are sufficiently soluble to exhibit toxicity to primary organisms primarily responsible for the decay of the wood. Exemplary particles contain for example copper hydroxide, basic copper carbonate, copper carbonate, basic copper sulfates including particularly tribasic copper sulfate, basic copper nitrates, copper oxychlorides, copper borates, basic copper borates, and mixtures thereof. The particles typically have a size distribution in which at least 50% of particles have a diameter smaller than 0.25 μm, 0.2 μm, or 0.15 μm. At least about 20% and even more than 75% of the weight of the particles may be composed of the substantially crystalline copper salt. Wood or a wood product may be impregnated with copper based particles of the invention.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
Particulate wood preservative and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090280185A1Low dissolution rateEasy to characterizePowder deliveryBiocideCopper nitrateTribasic copper sulfate
A wood preservative includes injectable particles comprising one or more sparingly soluble copper salts. The copper-based particles are sufficiently insoluble so as to not be easily removed by leaching but are sufficiently soluble to exhibit toxicity to primary organisms primarily responsible for the decay of the wood. Exemplary particles contain for example copper hydroxide, basic copper carbonate, copper carbonate, basic copper sulfates including particularly tribasic copper sulfate, basic copper nitrates, copper oxychlorides, copper borates, basic copper borates, and mixtures thereof. The particles typically have a size distribution in which at least 50% of particles have a diameter smaller than 0.25 μm, 0.2 μm, or 0.15 μm. At least about 20% and even more than 75% of the weight of the particles may be composed of the substantially crystalline copper salt. Wood or a wood product may be impregnated with copper based particles of the invention.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
Direct synthesis of copper carbonate
ActiveUS20070269362A1High purityEasy to convertGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsCopper ammonia complexesOxygenCopper carbonate
A basic copper salt selected from basic copper carbonate, basic copper sulfate, basic copper acetate, basic copper citrate, and basic copper nitrate is manufactured by contacting copper metal with an aqueous solution having ammonia; an acid selected from carbonic acid, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, or citric acid; and oxygen, under conditions where the copper metal is converted to the basic copper salt; and then recovering the basic copper salt. The most economical embodiment is where the ammonia is present in the aqueous solution is in an amount between about 6.7 g / l and about 15 g / l calculated as NH3, and the pH of the composition is between 8 and 10, and the temperature of the composition is between 25° C. and 100° C. The method is particularly useful if the basic copper salt is basic copper carbonate. The basic copper carbonate produced has the formula: (CuCO3)x(Cu(OH2)y, where y is 1 and x is between 0.1 to less than 1; or where y is 1 and x is 1, or where y is 1 and x is between 0.5 to less than about 0.95, or where y is 1 and x greater than 1.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
Particulate Wood Preservative and Method for Producing Same
ActiveUS20090123505A1Reduce the amount requiredWide particle size distributionBiocideLiquid surface applicatorsCopper nitrateTribasic copper sulfate
A wood preservative includes injectable particles comprising one or more sparingly soluble copper salts. The copper-based particles are sufficiently insoluble so as to not be easily removed by leaching but are sufficiently soluble to exhibit toxicity to primary organisms primarily responsible for the decay of the wood. Exemplary particles contain for example copper hydroxide, basic copper carbonate, copper carbonate, basic copper sulfates including particularly tribasic copper sulfate, basic copper nitrates, copper oxychlorides, copper borates, basic copper borates, and mixtures thereof. The particles typically have a size distribution in which at least 50% of particles have a diameter smaller than 0.25 μm, 0.2 μm, or 0.15 μm. At least about 20% and even more than 75% of the weight of the particles may be composed of the substantially crystalline copper salt. Wood or a wood product may be impregnated with copper-based particles of the invention.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
Use of Sub-Micron Copper Salt Particles in Wood Preservation
InactiveUS20090223408A1Little dangerSmall particle sizeFireproof paintsBiocideCopper(II) hydroxidePhosphate
A method for preserving wood by injecting into the wood a slurry having: particles of a sparingly soluble copper salt, copper hydroxide, or both, wherein the weight average diameter d50 of the particles in the slurry is between 0.1 microns and 0.7 microns and the d98 of the particles in the slurry is less than about 1 micron; a dispersant; and water. The dispersant is anionic or a mix of anionic and non-ionic. Advantageously, less than 20% by weight of the particles have a diameter less than 20 nanometers. Useful copper salts include basic copper carbonate, tri-basic copper sulfate, copper oxychloride, basic copper nitrate, basic copper borate, copper borate, basic copper phosphate, or copper silicate. The slurry most preferably includes copper hydroxide particles. The slurry further advantageously includes at least one organic biocide, wherein at least a portion of the organic biocide is coated on the particles.
Owner:OSMOSE
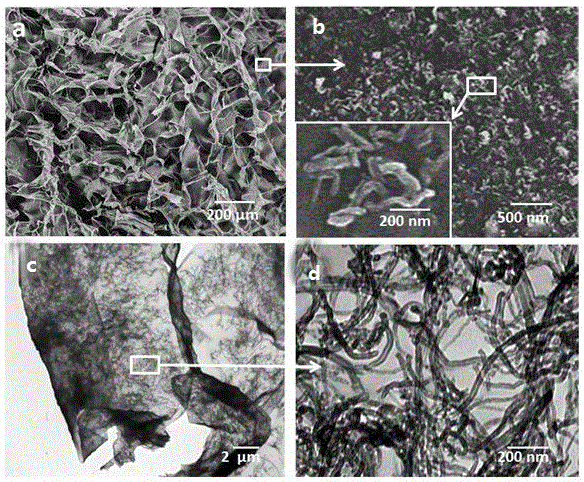
Preparation method of basic copper sulfate/metal organic framework core-shell microsphere
InactiveCN103752240AMild reaction conditionsSimple processMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMicrosphereRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a basic copper sulfate / metal organic framework core-shell microsphere, and belongs to the technical field of advanced nano composite preparation. The preparation method of the basic copper sulfate / metal organic framework core-shell microsphere comprises the steps that a basic copper sulfate microsphere in a core-shell structure is prepared; a shell layer of the basic copper sulfate microsphere is converted into a metal organic framework material in situ; and the basic copper sulfate / metal organic framework core-shell microsphere is prepared. The preparation method has the advantages that 1) the basic copper sulfate / metal organic framework core-shell microsphere is prepared by a simple two-step method at a room temperature; 2) different metal organic framework shell layers can be prepared by adjusting the kind of added organic ligands by using the basic copper sulfate microsphere prepared by the method; and 3) the method is mild in reaction condition, simple in technology and short in period, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Comprehensive utilization method of waste liquor in production of basic cupric carbonate
ActiveCN103449501AAchieve reuseRealize recycling of resourcesCopper chloridesCopper nitratesSulfate radicalsIndustrial waste water
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization method of waste liquor in the production of basic cupric carbonate and relates to the field of treatment methods of industrial wastewater. The invention aims at providing a comprehensive utilization method of waste liquor in the production of basic cupric carbonate, and in particular relates to a method for reusing sodium bicarbonate in the waste liquor. The waste liquor in the production of the basic cupric carbonate is the waste liquor generated after the basic cupric carbonate is produced by a reaction between an acidic copper chloride solution or an acidic copper sulfate solution and a sodium carbonate solution. The comprehensive utilization method of the waste liquor in the production of the basic cupric carbonate mainly comprises the following steps: adding a little distilled water into a reaction kettle as a base solution; when the reaction temperature rises to 35-90 DEG C, starting a stirring device, and adding the waste liquor containing sulfate radicals or chlorine and the acidic copper solution into the reaction kettle for reaction, wherein the pH value during the addition of the solutions is controlled to be 3-6; and filtering, washing, drying and sieving reaction products to obtain the basic copper salt. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, easy to control reaction conditions, and widely applicable to the recycling and reusing of the waste liquor in the production of basic cupric carbonate.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENTOU ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
Direct synthesis of copper carbonate
ActiveUS7411080B2High purityEasy to convertNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsCopper organic compoundsCopper nitrateOxygen
A basic copper salt selected from basic copper carbonate, basic copper sulfate, basic copper acetate, basic copper citrate, and basic copper nitrate is manufactured by contacting copper metal with an aqueous solution having ammonia; an acid selected from carbonic acid, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, or citric acid; and oxygen, under conditions where the copper metal is converted to the basic copper salt; and then recovering the basic copper salt. The most economical embodiment is where the ammonia is present in the aqueous solution is in an amount between about 6.7 g / l and about 15 g / l calculated as NH3, and the pH of the composition is between 8 and 10, and the temperature of the composition is between 25° C. and 100° C. The method is particularly useful if the basic copper salt is basic copper carbonate. The basic copper carbonate produced has the formula: (CuCO3)x(Cu(OH2)y, where y is 1 and x is between 0.1 to less than 1; or where y is 1 and x is 1, or where y is 1 and x is between 0.5 to less than about 0.95, or where y is 1 and x greater than 1.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
Soluble fine-denier PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) fiber and purpose thereof
ActiveCN107287674ALow densityGood dispersionMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentDrilling compositionDispersityCross-link
The invention discloses a soluble fine-denier PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) fiber. The PVA fiber has the single-fiber linear density of 0.1dtex to 1.0dtex and the dry break strength which is greater than or equal to 4cN / detx, and has the property of being dissolved in water at 20 to 100 DEG C; the PVA fiber is made through the steps of the preparation of a spinning stock solution, the preparation of a nascent fiber and post treatment by adopting PVA with the polymerization degree of 1,000 to 2,500 and the alcoholysis degree of 88.0(mol)% to 99.9(mol)% as a raw material; the preparation of the spinning stock solution comprises the following steps of agitating and mixing the PVA with a cross-linking agent, then dissolving in the water, and confecting to be the spinning stock solution; the cross-linking agent is one or multiple of boric acid, borax, aluminum chloride, aluminum sulfate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, copper chloride and titanium chloride; the mass concentration, in the spinning stock solution, of the PVA is 10 percent to 20 percent; the addition amount of the cross-linking agent is 0.8 percent to 2.0 percent of the mass of the PVA. The PVA fiber provided by the invention is low in linear density and good in dispersity which can reach a grade 1; when being used in the fracturing of oil and gas fields, the fracturing temporary plugging of the oil and gas fields and the well cementation of the oil and gas fields, the fiber can be more uniformly dispersed in base fluid, so as to improve the fracturing, temporary plugging and well cementing performance of the soluble fine-denier PVA fiber.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
The water bath preparation method of cu2znsns4 or cu2cdsns4 nanocrystalline film
InactiveCN102275980AEasy to prepareSynthesis temperature is lowTin compoundsWater chlorinationTin(II) chloride
The invention discloses a low-temperature preparation method of a Cu2ZnSnS4 or Cu2CdSnS4 nanocrystalline film with low cost and high quality, comprising the following steps of: firstly adding a certain amount of copper sulphate, zinc chloride or cadmium chloride, stannous chloride and thioacetamide into a beaker with deionized water, letting glass which undergoes ultrasonic cleaning by the use ofalcohol, acetone and deionized water vertically suspend inside the beaker; adding dropwisely a diluted hydrochloric acid solution into the beaker to adjust the pH value and make the solution to stay in the acid condition; heating up and reacting for a certain time at a certain stirring rate, carrying out annealing treatment on the glass, on which the Cu2ZnSnS4 or Cu2CdSnS4 nanocrystalline film grows, in Ar and H2S(5%) atmospheres to finally obtain the high-quality Cu2ZnSnS4 or Cu2CdSnS4 nanocrystalline film. The invention has the following advantages: the nanocrystalline preparation method issimple; the synthesis temperature is low; the cost of precursor materials is low; and the nanocrystalline film prepared is uniform and compact. The Cu2ZnSnS4 or Cu2CdSnS4 nanocrystalline film prepared in the invention can be used as an absorbed layer for photovoltaic devices or a good thermoelectric material.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Trace element premixed feed
The present invention discloses a trace element premixed feed. The trace element premixed feed is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 8 to 12 parts of methionine manganese, 4 to 6 parts of zinc sulfate monohydrate, 12 to 18 parts of ferrous sulfate monohydrate, 12 to 16 parts of amino acids chelated zinc, 4 to 6 parts of amino acid chelated magnesium, 5 to 8 parts of selenomethionine, 0.5 to 1 part of phytase, 3 to 6 parts of basic copper sulfate, 0.05 to 0.08 part of chromium picolinate, 0.2 to 0.4 part of calcium iodate, 4 to 6 parts of lysine, 0.05 to 0.08 part of hexamminecobalt (III) chloride, 0.5 to 1 part of germanium protein, 4 to 6 parts of yeast iodine, 2 to 5 parts of ionic ligand and the balance of a premixed feed carrier. A rational use of the trace element component in the trace element premixed feed not only reduces an incidence rate of diarrhea, but also reduces pollution on environmental and soil. The trace element premixed feed is rich in various trace elements for livestock growth, and can be easily absorbed by livestock.
Owner:雷红
Preparation method of cubic cuprous oxide nano material
InactiveCN104030339AHigh purityMild method conditionsMaterial nanotechnologyCopper oxides/halidesBlue VitriolFluid phase
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cubic cuprous oxide nano material. The method is characterized by successfully obtaining the cubic cuprous oxide material by using blue vitriol as a copper source and glucose as a reducing agent and using a liquid phase reduction method and a hydrothermal method. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the raw materials needed for preparation are rich, are low in costs and do not produce wastes; the preparation process is simple and has good repeatability; the prepared cubic cuprous oxide nano material is widely applied to photocatalysis, gas sensitive materials, antibacterial materials and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Tempered glass
The invention relates to a tempered glass which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 6-10 parts of waste glass, 5-10 parts of calcite, 5-7 parts of borax, 3-8 parts of clarifier, 7-10 parts of bauxite, 4-10 parts of titanium dioxide, 3-9 parts of chromic nitrate, 6-11 parts of potassium permanganate, 4-9 parts of chalcanthite, 3-6 parts of barium hydroxide, 4-11 parts of potassium silicate, 5-10 parts of silicon dioxide, 7-9 parts of aluminum oxide and 4-9 parts of bismuth oxide. The tempered glass has the advantages of favorable strength, favorable hardness and low possibility of spontaneous explosion, and can not hurt the human body.
Owner:QINGDAO ZHIGU INNOVATION TECH
Laser carving powder applied to laser marking and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses laser carving powder applied to laser marking. The laser carving powder comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: polypropylene resin, C5 petroleum resin, barium sulfate, a nucleating agent, an antioxidant, toner, a lubricant, silicon oxide, titanium dioxide, zinc sulfide, chromium sesquioxide, neodymium oxide, bismuth oxide, tin oxide, zinc molybdate, ammonium molybdate, basic copper phosphate, copper oxide, copper chromite black, copper carbonate, copper sulfate, copper chloride, copper chromite, copper thiocyanate, spinel, tin dioxide, tin ash, sodiumstannate, potassium stannate, zinc sulfate, antimony trioxide, antimony pentoxide, sodium antimonate, potassium carbonate, syndiotactic polystyrene and polyhexamethylene adipamide; according to the preparation process of the laser carving powder applied to laser marking, the laser carving powder applied to laser marking is prepared, and the preparation process comprises the following steps: S1, grinding; S2, performing crushing; S3, performing mixing; S4, adding a chemical agent; S5, drying; and S6, crushing.
Owner:东莞市烁康新材料科技有限公司
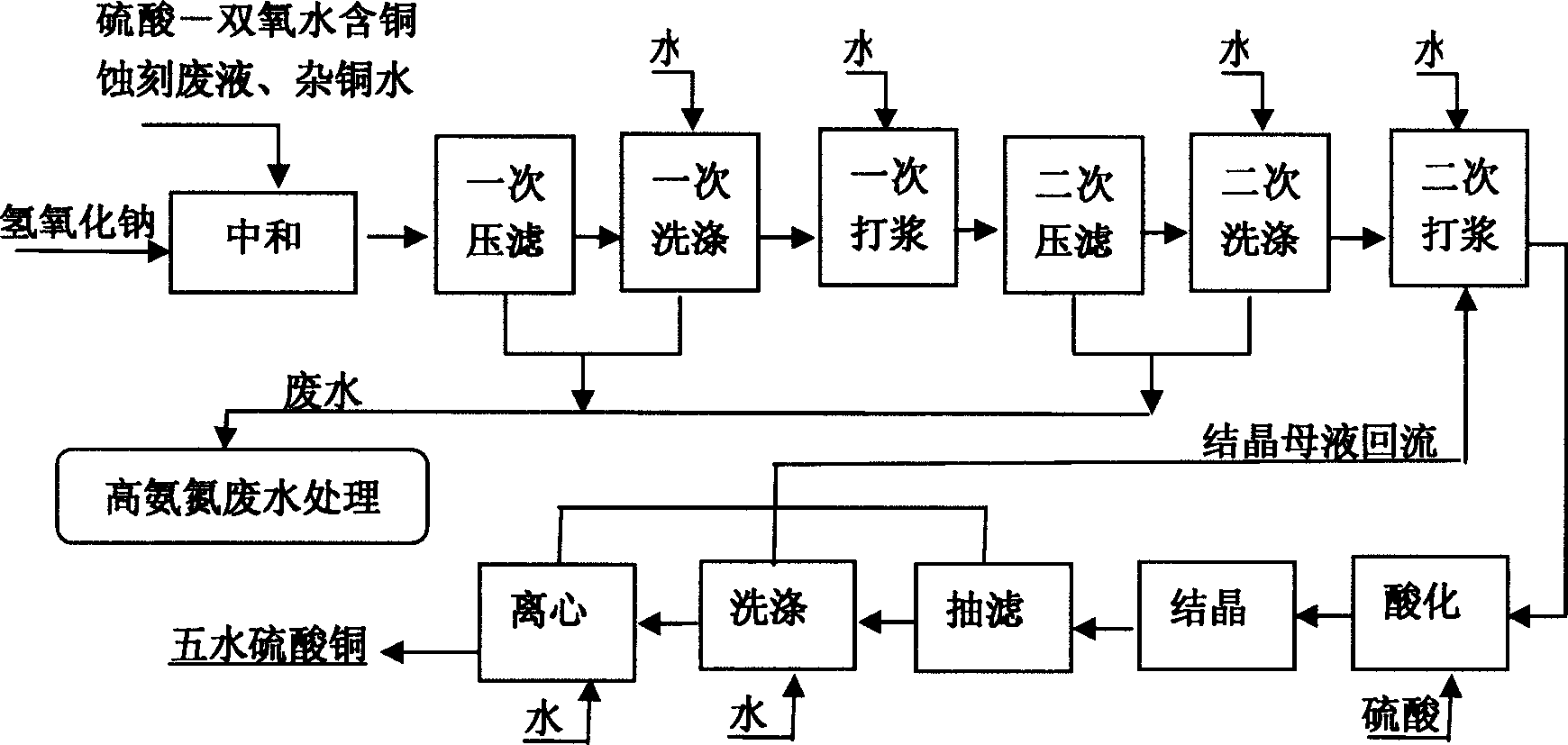
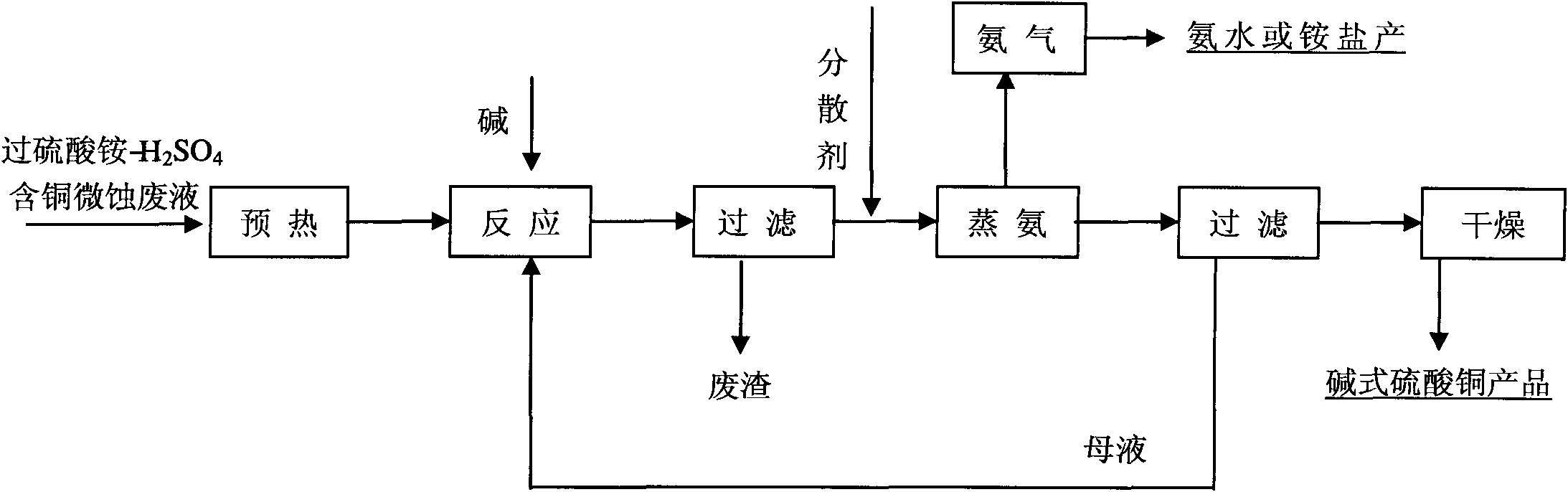
Method for preparing basic bluestone by utilizing PCB ammonium persulfate-H2SO4 micro-etched waste liquid
ActiveCN101780972AReduce the concentration of ammonia nitrogenReduce the burden onMultistage water/sewage treatmentCopper sulfatesLiquid wasteProcess equipment
The invention discloses a method for preparing basic bluestone by utilizing PCB ammonium persulfate-H2SO4 micro-etched waste liquid. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preheating ammonium persulfate-H2SO4 micro-etched waste liquid and basic solution to the temperature of between 50 and 100 DEG C respectively, and adding the preheated micro-etched waste liquid into a neutralizing reaction kettle with a stirring device; (2) gradually adding the basic solution into the micro-etched waste liquid with the stirring for neutralization reaction, and controlling the pH value in the neutralizing reaction kettle to be between 8.0 and 13.0; (3) after filtering precipitate, adding dispersant into filtrate; (4) transferring the filtrate of which the pH value is regulated to an ammonia evaporation reaction kettle for atmospheric distillation to ensure that ammonia escapes from the reaction kettle till the pH value is reduced to be between 7.5 and 8.5, and completing ammonia evaporation; and (5) filtering, washing, drying and sifting basic bluestone precipitate in the material to obtain a crystal-type basic bluestone product. The method has the advantages of efficiently recycling copper resource and contributing to generating high-purity basic bluestone, along with simple whole process equipment, easily controlled operating conditions, and less equipment investment.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KECHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Milk cattle feedstuff and manufacturing technique
InactiveCN101081062AIncrease milk productionImprove absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsSodium bicarbonateVegetable oil
The present invention discloses one kind of milk cow feed. Pre-mixed material is first produced with zinc sulfate, ferrous sulfate, anhydrous cupric sulfate, potassium iodide, sodium selenite, cobalt chloride, manganese sulfate, molybdenum chloride, vitamin A, vitamin D3 and vitamin E and through mixing; and then mixed with slow released non-protein nitrogen, calcium biphosphate, feather powder, cotton seed dregs, tree leaf powder, calcium carbonate, table salt, anhydrous sodium sulfate, sodium bicarbonate, yeast and vegetable oil through stirring homogeneously to produce the milk cow feed. The milk cow feed has balanced nutrients, protein capable of being decomposed directly in the rumen of milk cow, high absorption rate and capacity of raising milk yield.
Owner:齐庆文
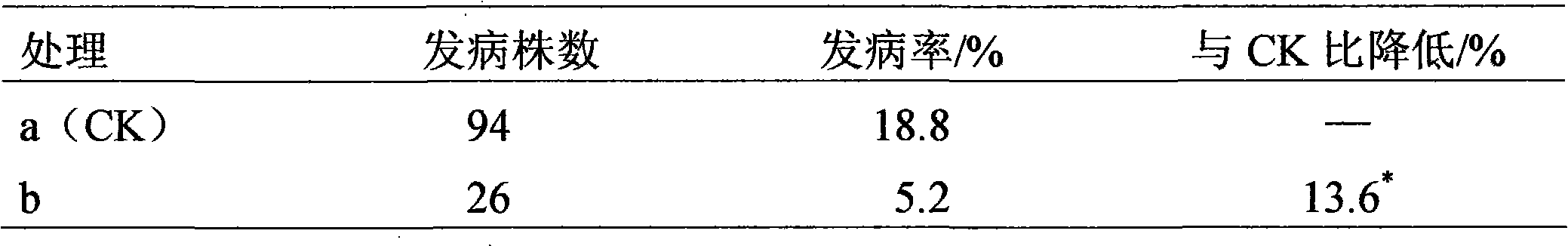
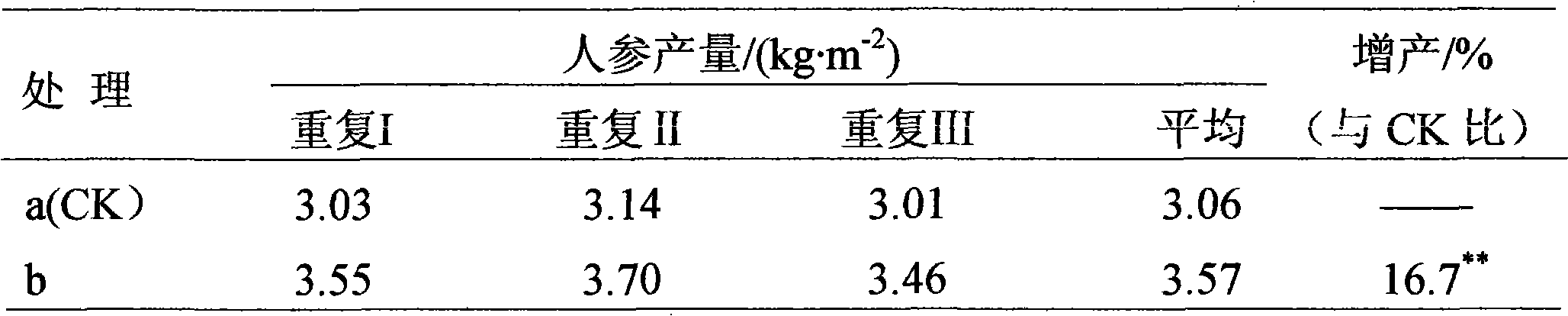
Method for preventing and curing ginseng diseases by mixing carbendazim with basic copper sulfate
The invention provides a method for preventing and curing ginseng diseases by mixing carbendazim with basic copper sulfate, belonging to the field of the modernization of the traditional Chinese medicines, and aiming at solving the problems that the carbendazim is easy to generate drug resistance to the pathogenic bacteria and is bad in a disease-resistant effect when the carbendazim is independently taken as the bactericide. The method for sterilizing the ginseng soil comprises the steps of: taking the smashed plant straw, the turfy soil or the fine bed soil as a carrier, evenly mixing the carbendazim and the basic copper sulfate with the carrier, splashing the mixture on the surface of the ginseng bed soil before transplanting, evenly mixing with the bed soil, and transplanting. The method for sterilizing the bed surface before the ginseng is sprouted comprises the steps of: mixing the carbendazim with the basic copper sulfate to prepare mixed water solution, and spraying the water solution onto the surface of the bed before the ginseng is sprouted. The method for preventing and curing the disease after the ginseng is sprouted comprises the steps of: mixing carbendazim with basic copper sulfate to prepare mixed water solution, and irrigating the mixed water solution onto the surface of the bed after the ginseng is sprouted. The method is used for preventing and curing the melasma, the rust corrosion disease and the sclerotiniose of the ginseng.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Special fertilizer for rice seedling raising
InactiveCN104788192AStrong stress resistanceGood regulationFertilizer mixturesPlant growthFermentation
The invention discloses special fertilizer for rice seedling raising. The special fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60-70 parts of organic fermentation substances, 15-20 parts of fucoidin, 8-12 parts of amino acid chelate manganese, 4-6 parts of basic zinc sulfate, 12-18 parts of amino acid chelate iron, 12-16 parts of ammonium molybdate, 5-8 parts of selenomethionine, 0.5-1 part of humic acid, 3-6 parts of basic copper sulfate, 0.05-0.08 part of biochemical fulvic acid, 0.02-0.04 part of amino acid chelate calcium; 4-6 parts of lysine, 0.05-0.08 part of chitin, 4-6 parts of iodine yeast, 0.2-0.5 part of fungus polysaccharide, 0.5-1 part of S-abscisic acid, and 6-12 parts of a bacterium solution obtained by mixing azotobacter, cellulose decomposition bacteria and root nodule bacteria. The stress resistance of the special fertilizer adopting the formula to a plant is very high, so that the plant growth can be regulated, and the cold resistance, the disease resistance, the drought resistance and the water-logging resistance of the plant can be enhanced.
Owner:中国科学院北方粳稻分子育种联合研究中心
Hydroponic vegetable nutrient solution and preparation method and use method thereof
InactiveCN107500864ANutritional balanceImprove absorption and utilizationMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserNutritionMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a hydroponic vegetable nutrient solution. The hydroponic vegetable nutrient solution comprises a fertilizer A, a fertilizer B and a fertilizer C, wherein the fertilizer A comprises 0.1-0.5 mol / L ammonium nitrate, 0.2-0.8 mol / L calcium nitrate and 0.5-1.0 mol / L potassium nitrate; the fertilizer B comprises 0.2-0.8 mol / L potassium sulfate, 0.1-0.6 mol / L magnesium sulfate and 0.1-1.0 mol / L monopotassium phosphate; the fertilizer C comprises 50-1,000 mmol / L chelated iron, 50-80 mmol / L cupric sulfate, 30-80 mmol / L zinc sulfate, 50-200 mmol / L manganese sulfate, 100-300 mmol / L boric acid, 10-50 mmol / L ammonium molybdate and 20-100 mmol / L cytex. The prepared hydroponic vegetable nutrient solution is balanced in nutrition and high in crop absorption and utilization ratio, can effectively promote crop growth and development, improves the crop yield and quality, and is good in stability and strong in buffering capability.
Owner:珠海市绿之宝农业有限公司
Cu2O@CuO semi-core-shell structure nano composite material and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN105116030AEffective use of electrochemical detectionEvenly dispersedMaterial electrochemical variablesCrosslinked chitosanPorous carbon
The invention discloses a Cu2O@CuO semi-core-shell structure nano composite material and a preparation method therefor. The structure comprises porous carbon sponge and Cu2O@CuO semi-core-shell structure nanoparticles absorbed on the sponge. The carbon sponge employs crosslinked chitosan as a framework and CNTs are embedded into the crosslinked chitosan. The Cu2O@CuO semi-core-shell structure nanoparticles comprise a Cu2O core at the inner layer and a CuO shell at the outer layer. The CuO shell at the outer layer is a semi-shell structure formed on the surface of the carbon sponge. The preparation method is as follows: carbon sponge is prepared through an ice template method; copper sulphate is absorbed by the carbon sponge; the copper sulphate is subjected to in-situ reduction by sodium borohydride; further oxidation in the air is carried out; cleaning and drying are carried out. The method is advantaged by simple technology, mild reaction conditions, low preparation cost and good stability. In the prepared composite material, the CS plays a support role, the embedded CNTs play a role in electron conduction, the Cu2O@CuO semi-core-shell structure has advantages compared with a complete core-shell structure, namely, CuO at the outer layer play a main catalysis role, and the lower part of Cu2O at the inner layer contacts with the surface of the carbon sponge directly and plays a role in auxiliary catalysis and electron conduction. The composite material can be widely applied in the biosensor field.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for chemically plating copper on carbon fiber surface by utilizing sodium hypophosphite as reducing agent
ActiveCN109680269ASolve problems in the plating process such as instability and side reactionsSolve pollutionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a method for chemically plating copper on a carbon fiber surface by utilizing sodium hypophosphite as a reducing agent. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing, namely, sequentially carrying out oil removing, roughening, neutralizing, sensitizing, activating and reducing on carbon fibers; (2) preparing a plating solution, namely, treating deionized water as a solvent to prepare the following components: cupric sulfate pentahydrate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium citrate, boric acid, nickel sulfate, thiourea and sodium hydroxide; (3) chemically platingand coating the preprocessed carbon fibers in a prepared plating solution; and (4) flushing the plated and coated copper plated carbon fibers through deionized water; drying in a vacuum drying box; moving out from the vacuum drying box; and sealing and storing. The method overcomes the damage that formaldehyde is treated as the reducing agent in a traditional chemical copper plating solution of the carbon fiber surface; and the method is a novel nontoxic, environmentally-friendly and stable technology for chemically plating copper on the carbon fiber surface.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com