Method for producing basic copper chloride, cupric sulfate pentahydrate from copper-containing etching waste liquid
A technology of copper sulfate pentahydrate and etching waste liquid, which is applied in the direction of copper sulfate, copper chloride, chemical instruments and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
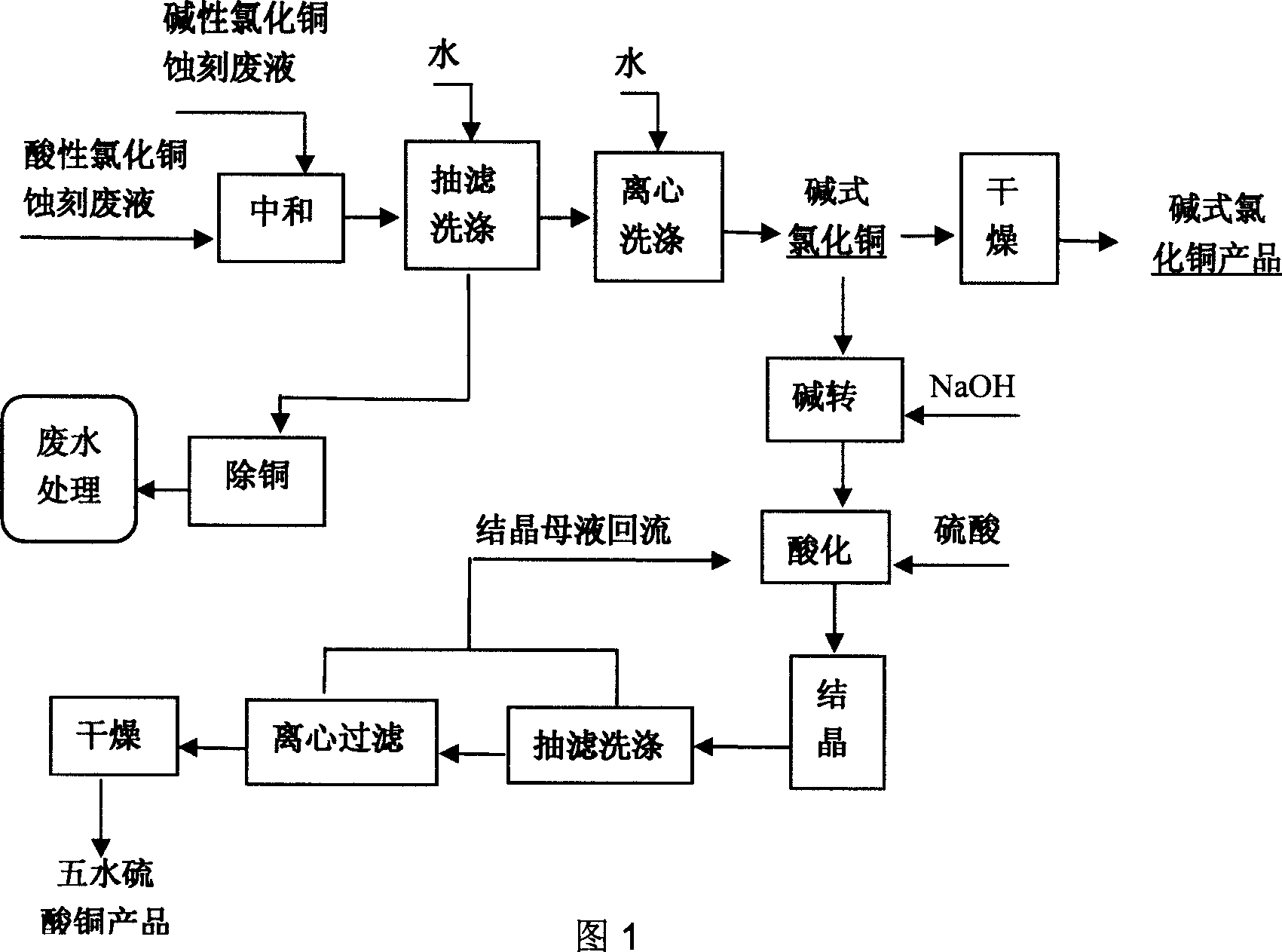
[0057] Production of basic copper chloride by using acidic and alkaline etching waste liquid.
[0058] The alkaline copper chloride etching waste liquid comes from circuit board factory A, and its phase analysis is shown in Table 5. The acidic copper chloride etching waste liquid comes from circuit board factory B, and its phase analysis is shown in Table 6.
[0059] Phase name NH 3 Cu 2+ Cl - other additives Content g / l 120 90 78 6.5
[0060] table 5
[0061] Phase name HCl CuCl 2 CuCl NaCl NH 4 Cl other additives Content g / l 60 180 15 110 8.6 5.4
[0062] Table 6
[0063] The above materials are pretreated in their respective pretreatment tanks, that is, hydrogen peroxide, magnesium chloride, and polyferric are added successively to oxidize cuprous ions into divalent copper, and precipitate arsenate and arsenite ions. After this pretreatment, copper in the material exists in the state of divalent ions, ...
example 2
[0066] Copper sulfate is produced from basic copper chloride.
[0067] A company produces copper sulfate pentahydrate by alkali conversion reaction of basic copper chloride to obtain copper oxide, and then acidifies with sulfuric acid. Feeding amount: 2 tons of basic copper chloride, 3m 3 Crystallization mother liquor, 1 ton of tap water, 1.3 tons of sulfuric acid, the volume after reaction is about 5m 3 ; After crystallization, discharge at 45°C to obtain 2.6 tons of copper sulfate product. The crystallization rate of copper in copper sulfate is 60%. The obtained copper sulfate pentahydrate product reaches feed grade. The volume of mother liquor after crystallization is 4.5m 3 , the copper content is 120g / l, circulated to the acidification tank 3m 3 , back to the raw material pool 1.5m 3 ,Continuous production.
[0068] In the process of alkali conversion to produce copper oxide, the pH in the alkali conversion reactor is controlled between 9.0 and 10.5, and when the c...
example 3
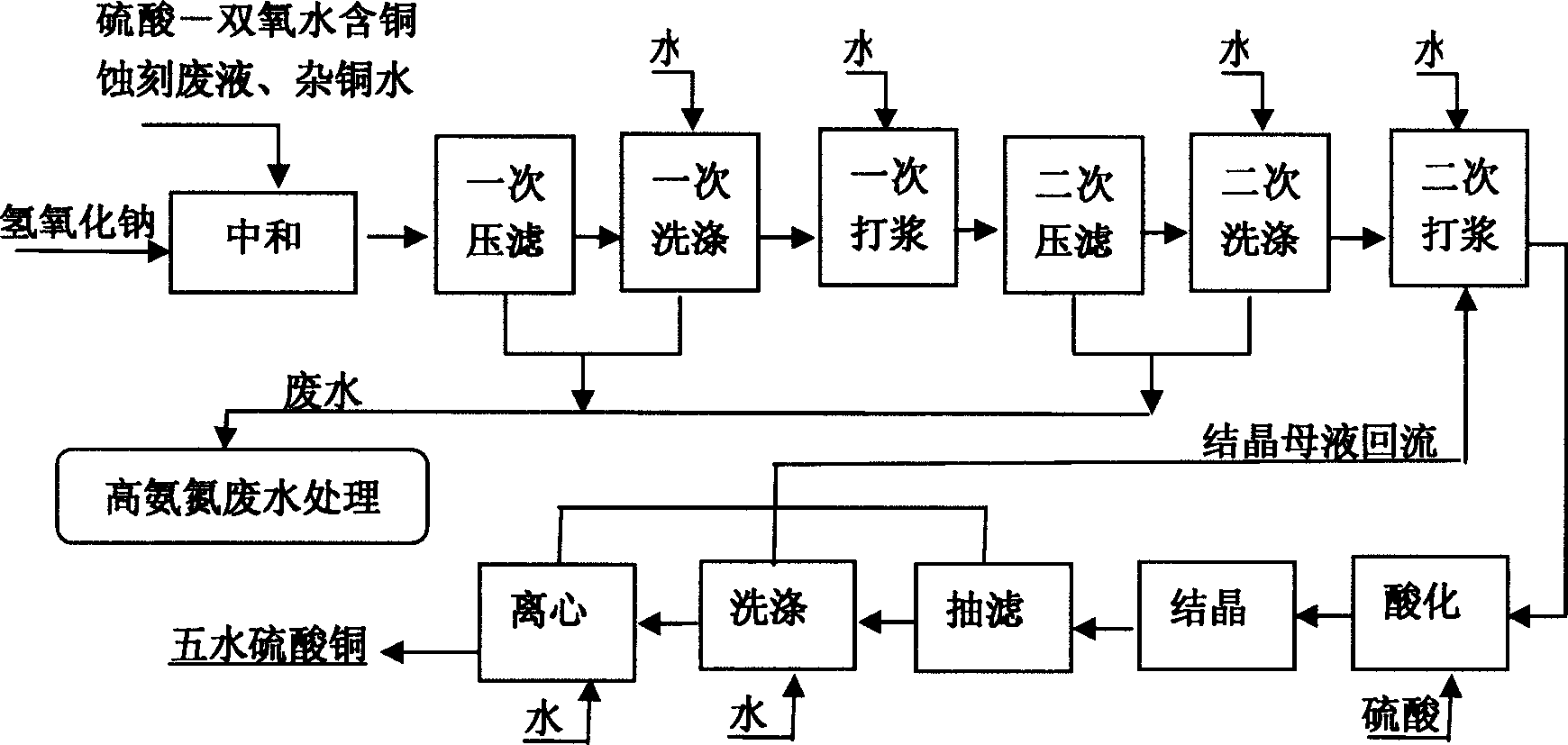
[0070] Production of copper sulfate pentahydrate from sulfuric acid-hydrogen peroxide etching waste liquid.
[0071] A sulfuric acid-hydrogen peroxide etching waste solution from circuit board factory C, its phase analysis is shown in Table 7.
[0072] Phase name H + SO 4 2- Cu 2+ other additives Content g / l 1.5 260.0 48.5 6.5
[0073] Table 7
[0074] First add hydrogen peroxide, magnesium chloride, and polyiron to the pretreatment tank for pretreatment to remove cuprous ions and arsenic, then pump the material into the alkali conversion reaction kettle, add sodium hydroxide solution for neutralization reaction, and use pH electrode Control the respective flows, and the pH range is controlled between 9.0 and 10.0. After the reaction is completed, copper hydroxide precipitates are formed, press-filtered, washed, the filtrate is sent to the filtrate storage tank, and the filter cake is sent to the slurry tank, where water is added and washed. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com