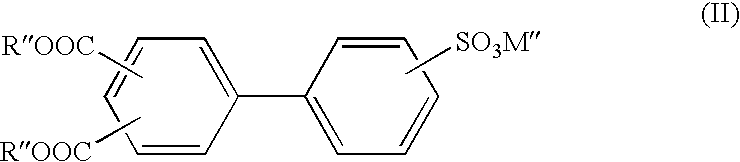
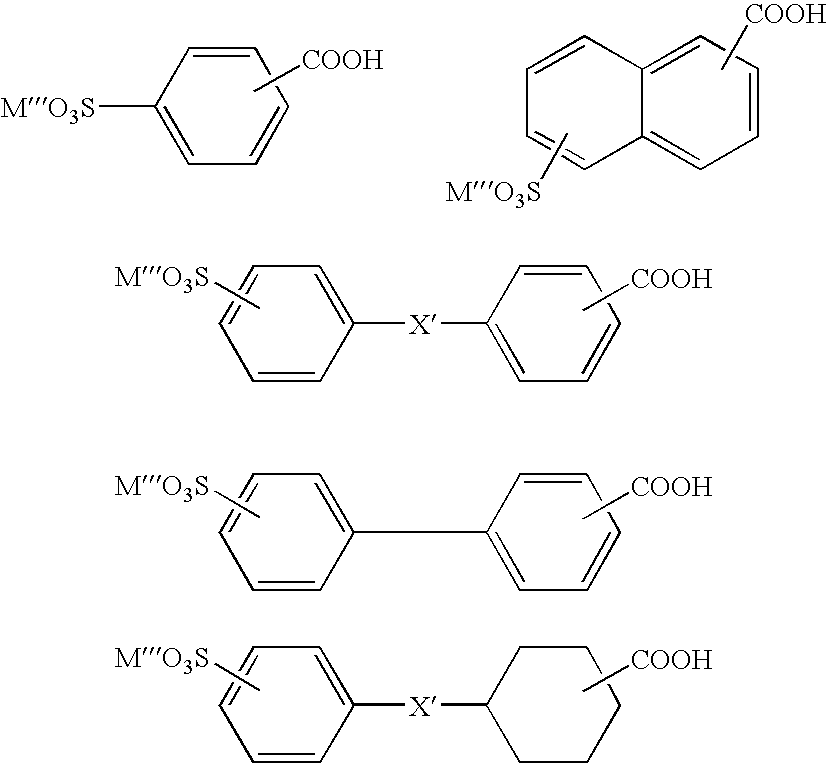
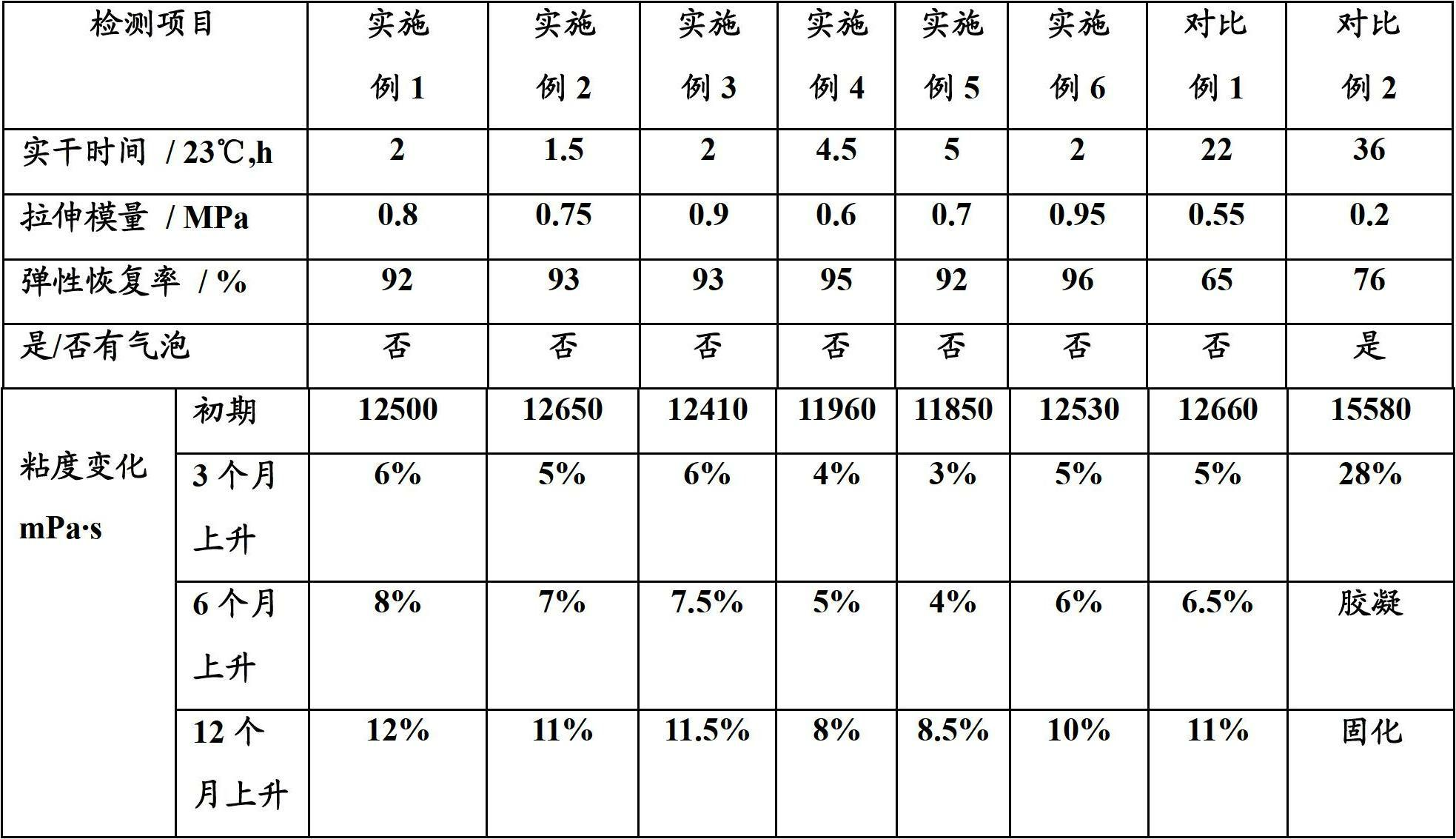
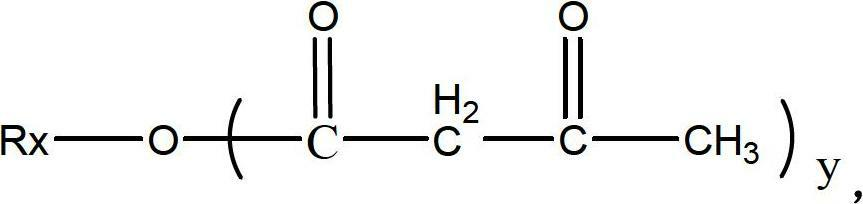
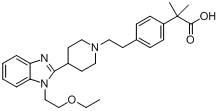
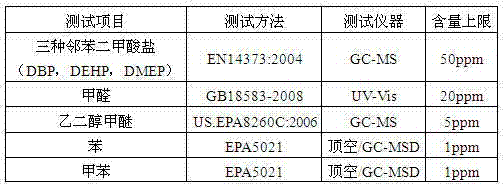
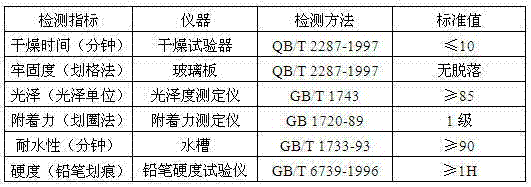
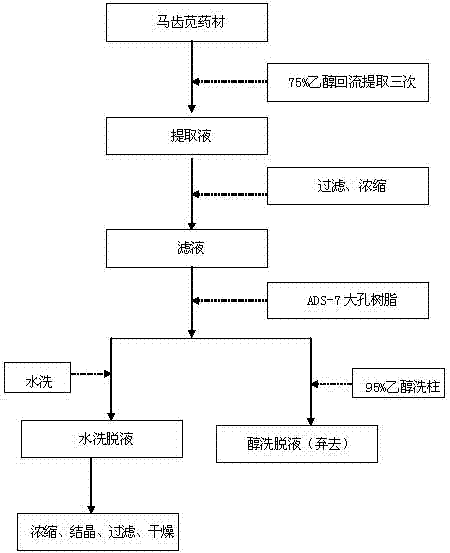
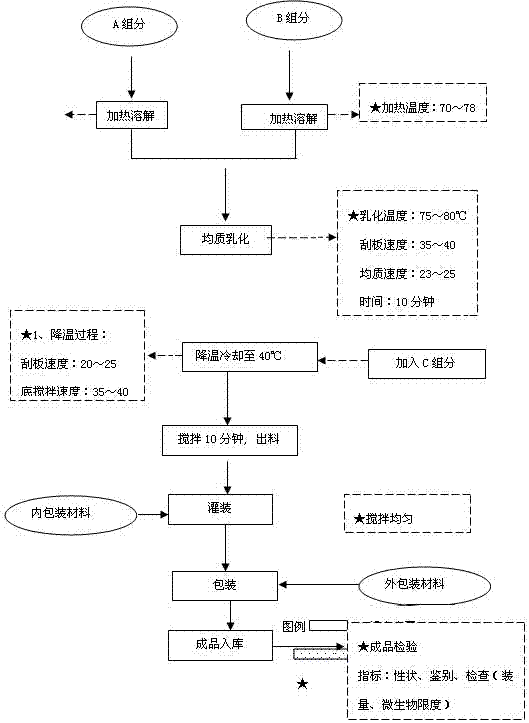
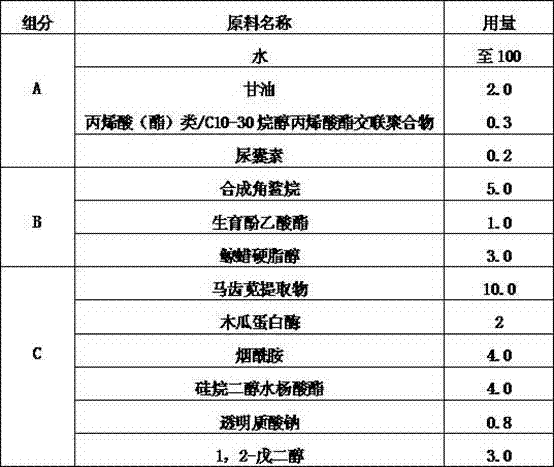
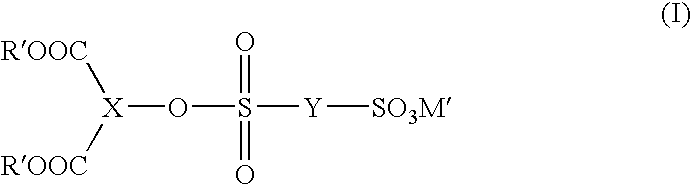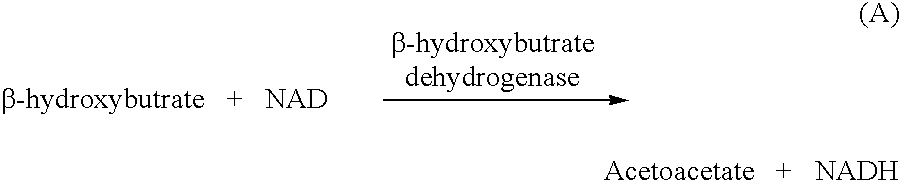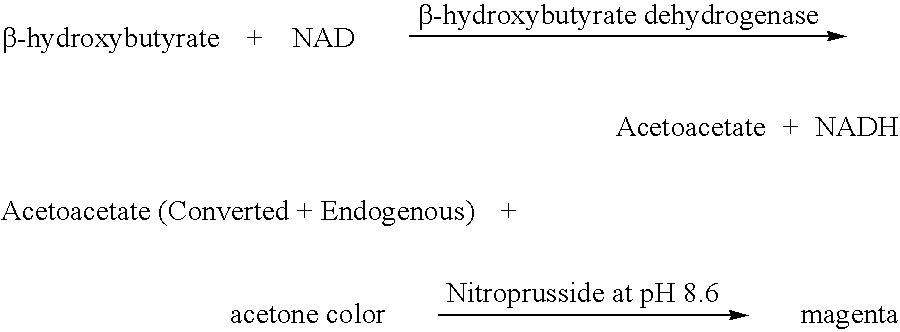Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
880 results about "Acetic Acid Esters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
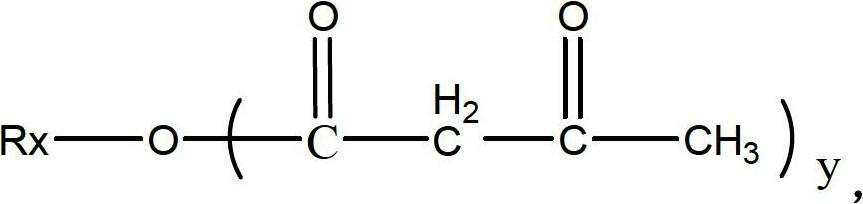
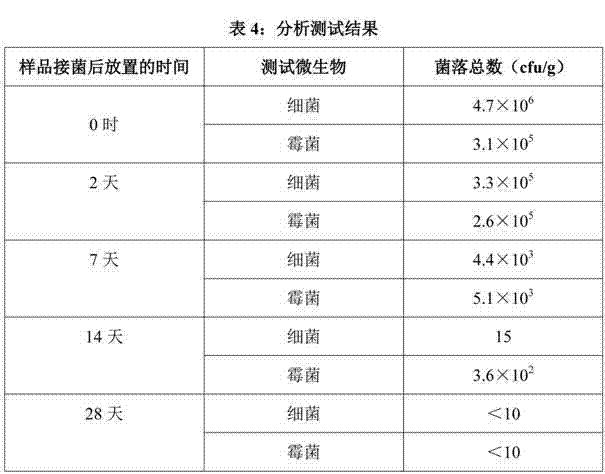
Acetic Acid Esters of Monoglyceride is a less oily liquid that has some emulsification activity. This product, also known as Acetylated Monoglyceride (AMG), is obtained from an acetic acid bound with monoglyceride. Acetic Acid Esters of Monoglycerides are used in pastry, cakes, breads, creams, candies, and sausages.
Aldehyde removal
Disclosed are filter elements constructed of a filter support material coated with an acetoacetate-functional polymeric composition that reacts with and removes aldehydes, especially formaldehyde, present in gases such as air. Also disclosed are methods for the removal of aldehydes utilizing the coated filter support materials.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Low-temperature scouring and bleaching agent and preparation method thereof and preprocessing technique
InactiveCN101037842AReduce the bleaching temperatureThe effect of the pretreatment process is obviousBleaching apparatusTextile treatment by spraying/projectingTextile printerBenzene
The present invention realtes to a low temperature scouring and bleaching agent belonging to the pretreatment process technology field of the textile printing and dyeing industry, a manufacturing method thereof and a pretreatment process. Said low temperature scouring and bleaching agent consists of promoter QR2010 consisting of carbon tetrachloride, acetic acid esters, alkyl benzenes, emulsifying agents and scouring agents; promoter QR2011 consisting of potassium hydroxide, carbonates and penetrating agents; and promoter QR2020 consisting of acyls and nitriles activating agents and builders. Said three promoters are prepared using routine methods and are deposited solely. When used, the three promoters, together with hydrogen peroxide, are mixed according to different proportions to prepare solutions. Said low temperature scouring and bleaching agent is capable of annealing, boiling and bleaching a variety of cotton as well as cotton blending textiles at any temperature ranging from 40 DEG C to 80 DEG C, and being processed at different scouring and bleaching equipments, with a whiteness of higher than 80% and a capillary effect of 10-20 cm. Compared with the process in existing, the amount used of hydrogen peroxide activating agent is 1 / 7 to 1 / 5 of that originally used, the total energy consumption is reduced, the tonnage of used water is decreased, and billet flaws such as holes bleached by oxygen and lycra folded crepes sourced and bleached are avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIRUI TEXTILE CHEM
Barrier film
InactiveUS7854994B2Improve the level ofImprove homogeneityFibre treatmentBottlesPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene oxide
A barrier composition which is injection mouldable and able to be made into a transparent film or incorporated (by co-extrusion and / or lamination) into multi-layer film products, the composition on dry basis: a) from 45 to 90% by weight of a starch and / or a modified starch selected from starches modified by reaction with a hydroxyl alkyl group, an acetate or a dicarboxylic acid anhydride or a grafting polymer; b) from 4 to 12% by weight of a water soluble polymer selected from polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylacetate, and copolymers of ethylene and vinylalcohol which have a melting point compatible with the molten state of the starch components c) from 5 to 45% by weight of a non-crystallising mixture of sorbitol and at least one other plasticizer selected from glycerol, maltitol, xylitol, mannitol, glycerol trioleate, epoxidised linseed or soybean oil, tributyl citrate, acetyl tri-ethyl citrate, glyceryl triacetate, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate; polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol; d) from 0.3 to 2.5% by weight of a C12-22 fatty acid or salt; e) from 0.25% to 3% of an emulsifier system having a hydrophilic lipophilic balance value between 2 and 10. The barrier film may be co-injection moulded with polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polylactic acid (PLA) for blow moulding into beverage bottles, with polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) or biodegradable polymers for high gas-barrier containers or closures, or may be co-extruded with polyethylene, polypropylene or polylactic acid for thin film packaging applications or for blow-moulded containers.
Owner:PLANTIC TECH
Liquid cleansing composition
A personal cleansing composition exhibiting enhanced skin feel (i.e., enhanced skin softness, reduced skin irritation, reduced residue, and reduced greasy, tacky, or tight skin feel), enhanced foaming and lather, and good cleansing, more specifically, a personal cleansing composition comprising a mixture of alpha sulfonated alkyl esters or sulfonated fatty acids, or salts thereof, with an alkyl sulfoacetate or ethoxylated alkyl sulfoacetate, or salts thereof, secondary surfactants, and optional additives.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
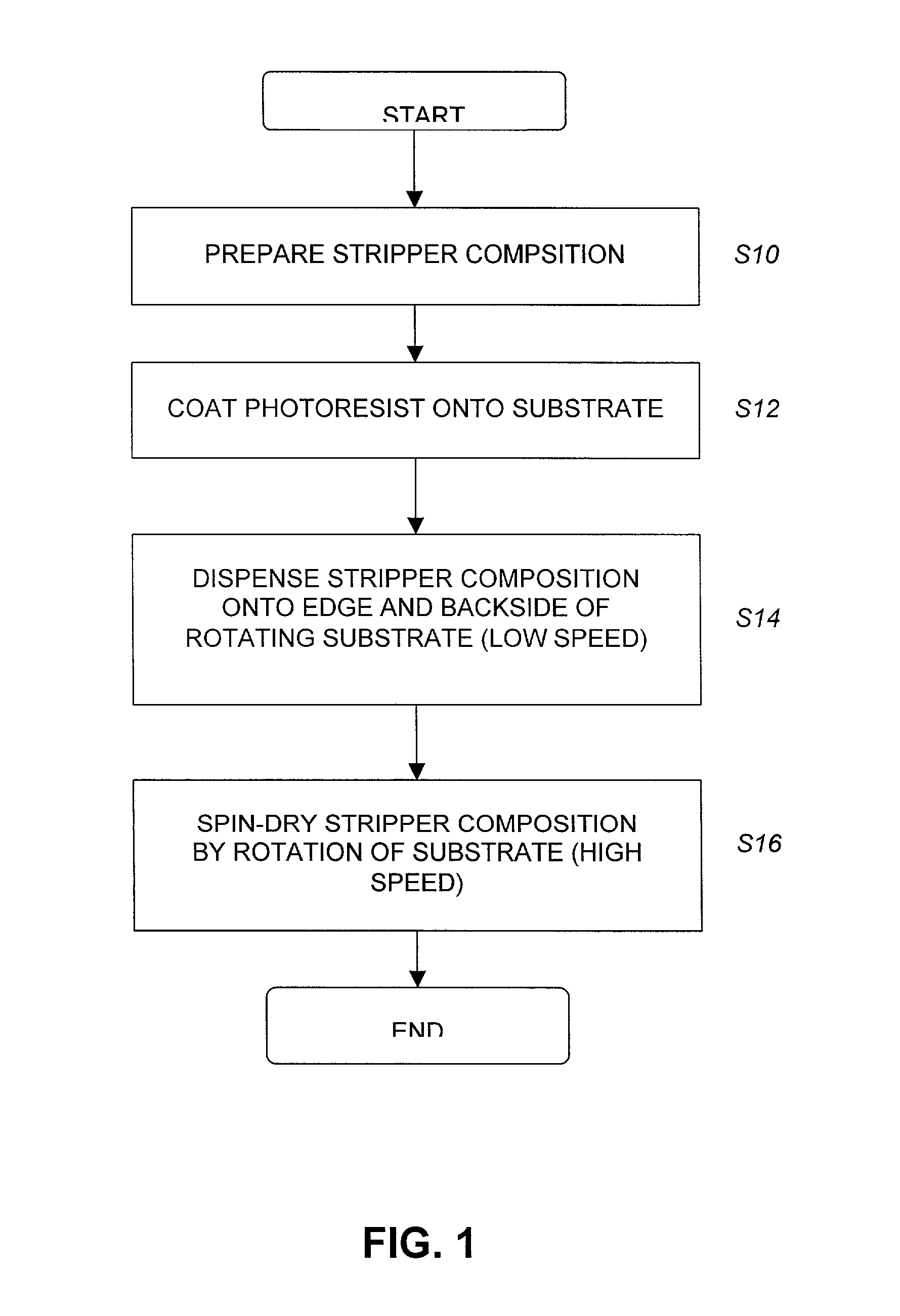
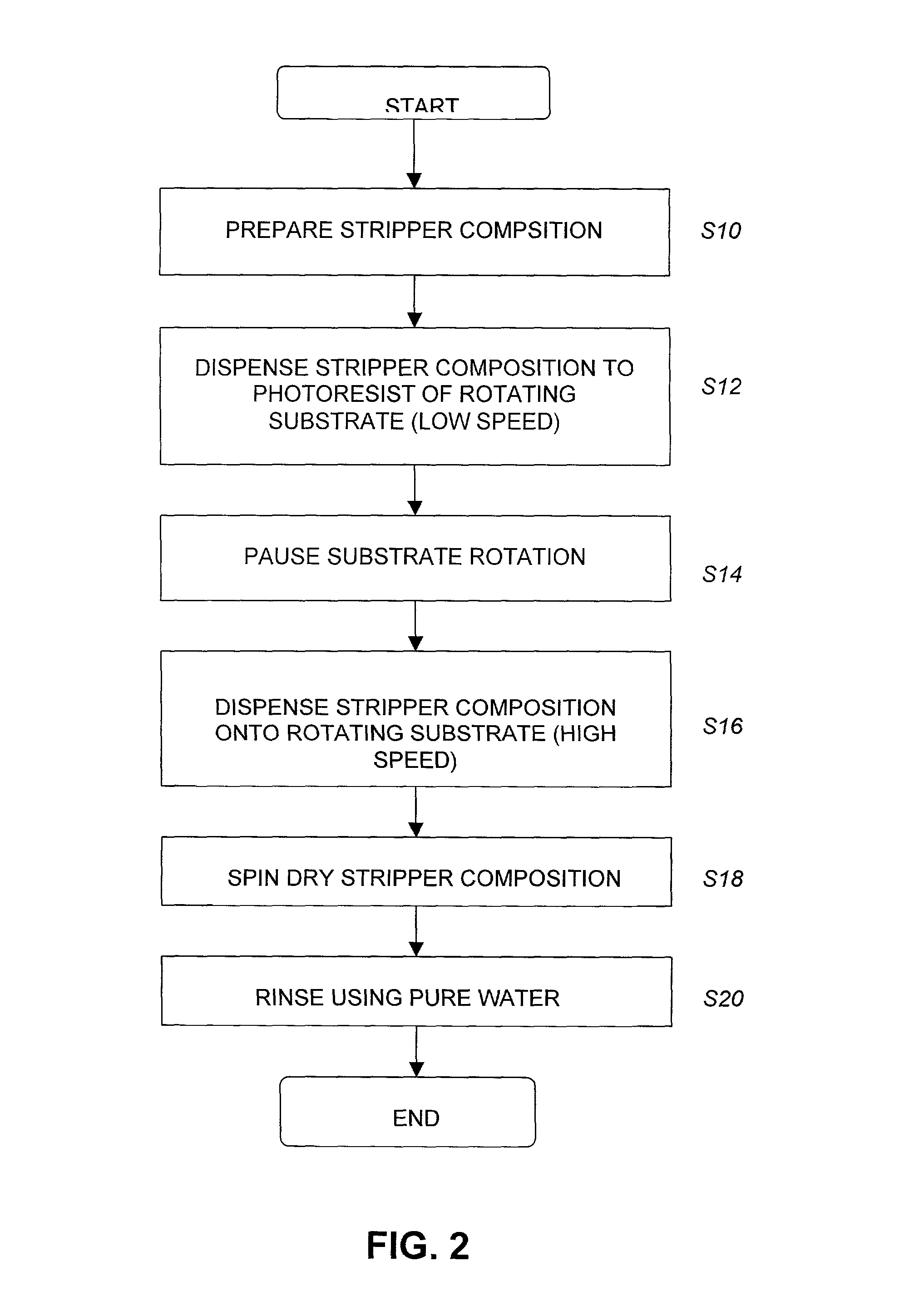
Photoresist stripper compositions
InactiveUS20030113673A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusAmyl acetateMethyl group
A photoresist stripper composition is made up of a mixture of an acetic acid ester, gamma-butyrolactone (GBL), and a non-acetate ester or a poly alkyl alcohol derivative. The acetic acid ester may be at least one of n-butyl acetate, amyl acetate, ethyl aceto-acetate, and isopropyl acetate. The non-acetate ester may be at least one of ethyl lactate (EL), ethyl-3-ethoxy propionate (EEP) and methyl-3-methoxy (MMP). The poly alkyl alcohol derivative may be at least one of propylene glycol monomethyl ester (PGME) and propylene glycol monomethyl ester acetate (PGMEA).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vinyl alcohol copolymers for use in aqueous dispersions and melt extruded articles
In a method of preparing an aqueous dispersion selected from drilling fluids, hydraulic cement compositions, mineral pigment containing coatings, and papermaking furnishes or in a method of preparing a melt extrudate, the improvement comprising: a) producing a copolymer of vinyl alcohol (VOH) and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid or a salt of such acid (AMPS) by steps including continuously feeding with agitation, vinyl acetate (VAM) and AMPS as comonomers, a free radical yielding polymerization initiator, and a solvent for said comonomers, initiator, and copolymer resulting from the copolymerization of said comonomers, maintaining the resulting reaction mass in said first reaction zone under polymerization conditions for a residence time sufficient for a major proportion of AMPS fed to said first reaction zone to polymerize, continuously feeding reaction mass from said first reaction zone with an additional supply of AMPS to a second reaction zone, maintaining the reaction mass in the second reaction zone for a residence time sufficient to polymerize a major proportion of the AMPS added to the second reaction zone, continuously withdrawing reaction mass from the second reaction zone, separating copolymer of VAM and AMPS from the latter reaction mass, and saponifying by hydrolysis and / or alcoholysis a major proportion of the acetate groups in said copolymer to form a copolymer of VOH and AMPS; and b) incorporating the saponified copolymer into the aqueous dispersion or melt extrudate.
Owner:SEKISUI SPECIALTY CHEM AMERICA
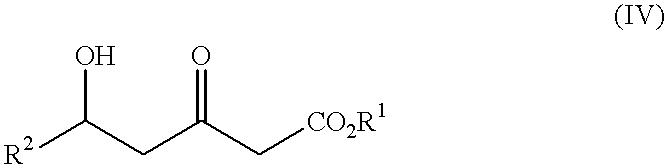
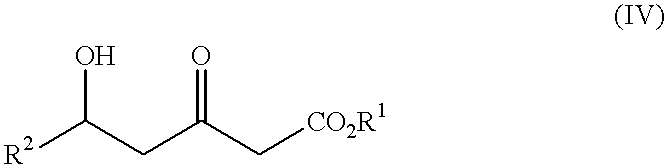
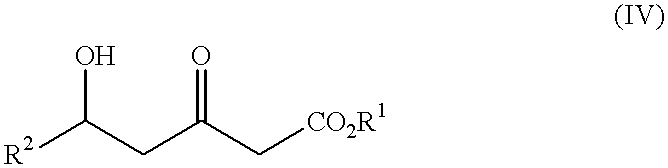
Processes for the preparation of 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acid derivatives
InactiveUS6340767B1Increase productionGreat advantageCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acid3-Hydroxypropionic acid
This invention provides a process for producing a 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acid, a useful pharmaceutical intermediate, easily from a readily available, inexpensive starting material without using any extraordinary production equipment such as a very-low-temperature reactor.Thus, this invention provides a process for producing a 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acidwhich comprises permitting a lithium amide to act upon a mixture of an acetic acid ester and a 3-hydroxypropionic acid derivative at not below -20° C.Further, this invention also provides a process for producing a 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acidwhich comprises treating a mixture of an acetic acid ester and a 3-hydroxypropionic acid derivative with a Grignard reagent to prepare a mixture of a compound and an acetic acid ester of the above formula (I),and permitting a lithium amide to act upon the mixture at a temperature not below -20° C.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
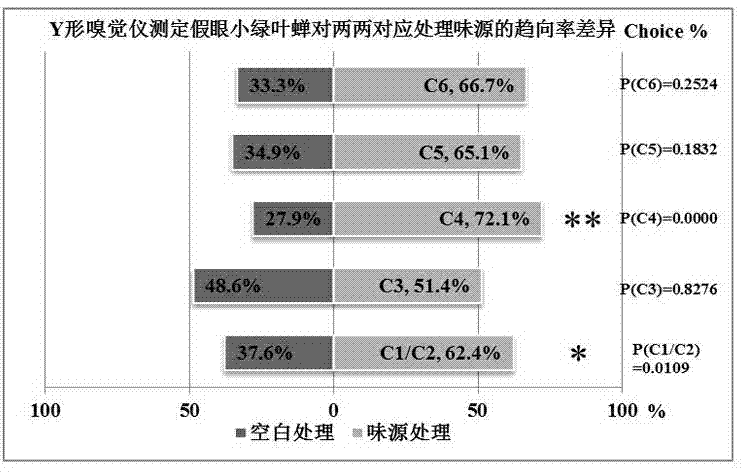
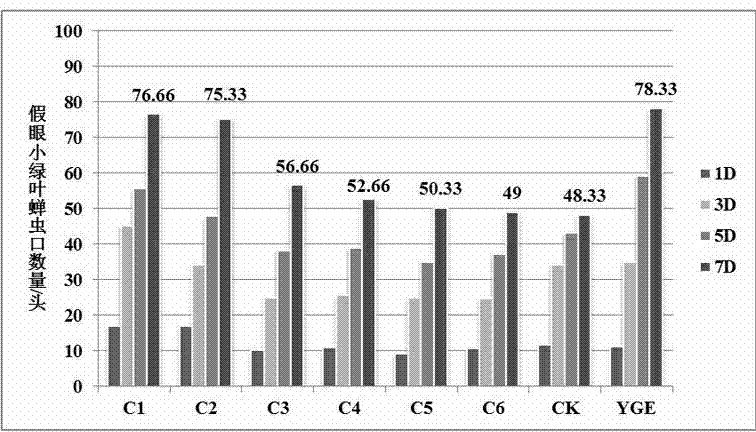
Empoasca vitis gothe attractant and application method thereof
InactiveCN103783041AStrong specificityGood lure effectBiocidePest attractantsButylated hydroxytolueneTert butyl
The invention provides a novel empoasca vitis gothe attractant formula and application of the novel empoasca vitis gothe attractant. The application method comprises the following steps: mainly preparing the attractant by the following components including tea tree volatile matters trans-2-hexenal, cis-3-hexene-1-ol and cis-3-hexenyl acetate, geraniol, linalool and trans-ocimene as components of the attractant and an additional antioxidant 2, 6-butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) in a weight ratio of (0.5-5.0):(10-20):(1.0-15):(5.0-15):(30-40):(1.0-15):(1.0-10); loading the attractant on a silicone rubber head to prepare a lure; and embedding the lure on a yellow sticky colored card to form a trap of empoasca vitis gothe. Imago of empoasca vitis gothe is trapped in a stable stage of trapping, preventing and treating the empoasca vitis gothe, so that the quantity of the empoasca vitis gothe can be effectively restricted. Researches show that the lure with the novel empoasca vitis gothe attractant can obviously enhance the trapping and killing effects of a single yellow sticky colored card, the lasting trapping capacity of the trap to the empoasca vitis gothe can be remarkably improved, the service period of the trap is remarkably prolonged, and use of chemical pesticides in the tea garden is remarkably reduced and cancelled. The attractant applied to the tea garden has the advantages of convenience in use, safety, greenness and no pollution and meets the national green prevention and control principle, thereby accelerating the industrial development of organic tea gardens.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
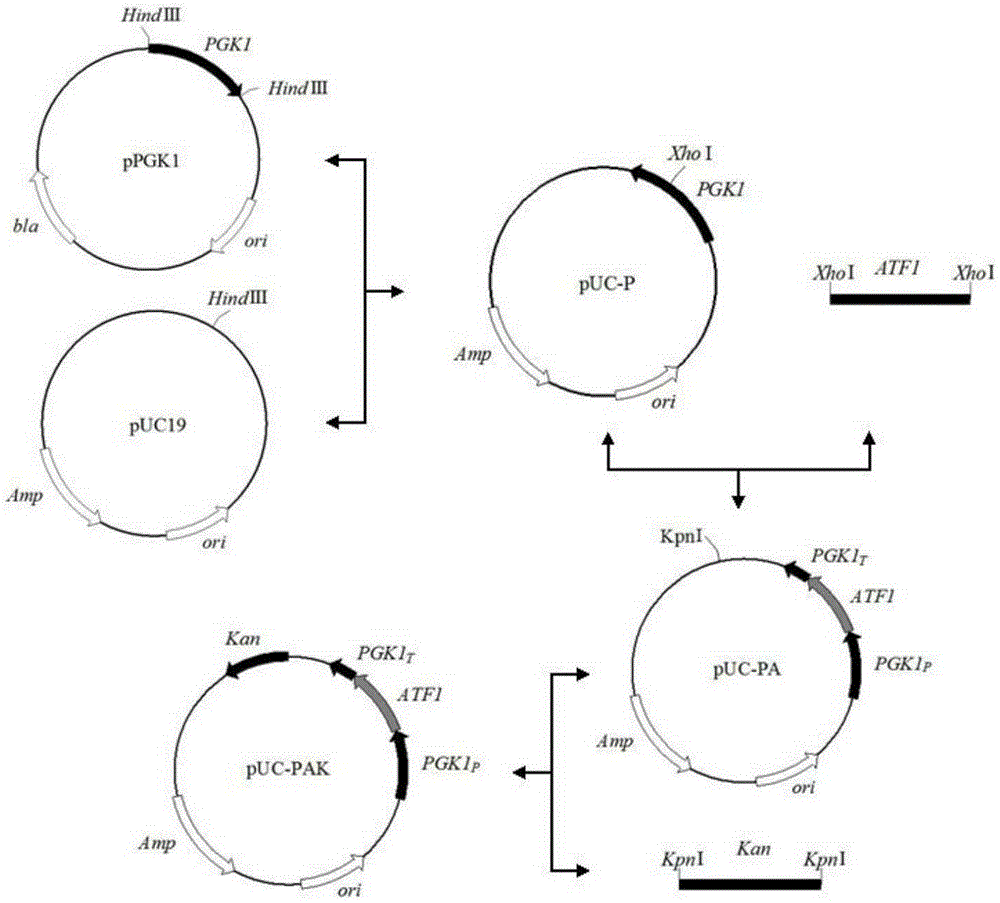
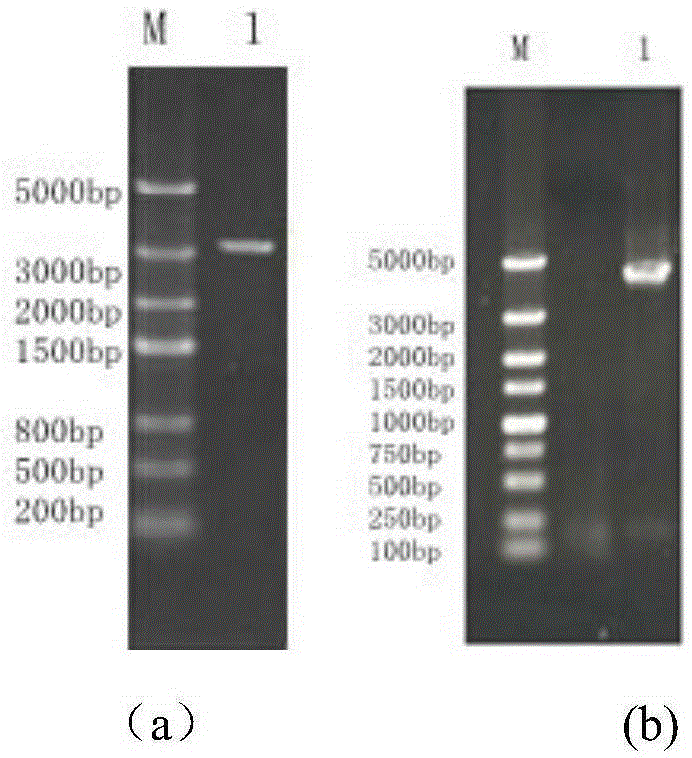
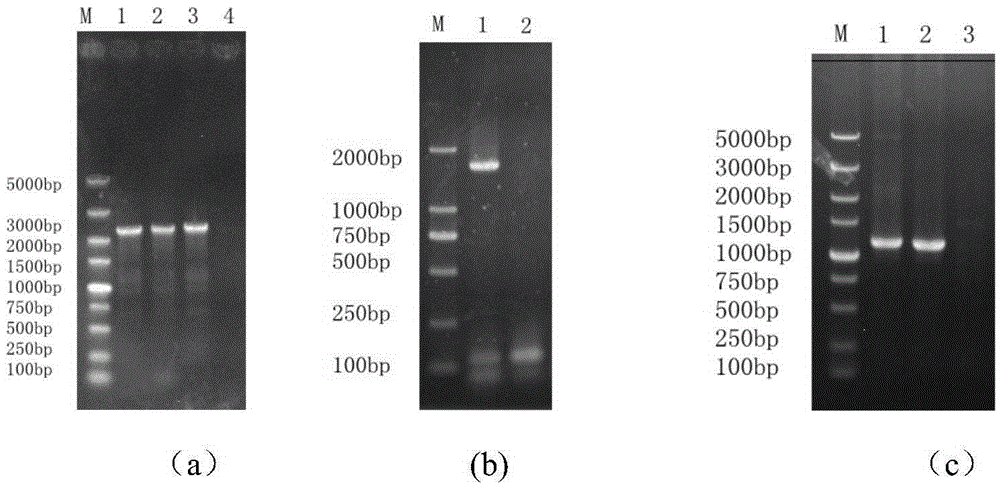
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as building and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
PendingCN105385615AReduce outputOvercome flavor incongruityFungiHydrolasesEster hydrolaseBio engineering
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as a building method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the building method provided by the invention, through completely knocking out an amino acid transaminase gene BAT2 and an ester hydrolase gene IAH1 in an original strain, and selecting a strong promoter PGK1 over-expression alcohol acetyltransferase I gene ATF1 at the same time, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol is obtained. Compared with a parent strain, other fermentation performances of built recombinant bacteria are not affected, the total quantity of acetic acid ester is obviously increased and reaches 1303.6mg / L, wherein the content of ethyl acetate is 52 times that of the original strain, isoamyl acetate is increased to 73.7mg / L, the content of main higher alcohol is 151.8mg / L and is reduced by 61.4 percent in comparison with that of the original strain. By using the saccharomyces cerevisiae, ester yield is significantly increased while the higher alcohol yield is reduced, the higher requirements of white spirit related fields on yeast are met and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Single-component polyurethane sealant capable of quickly curing moisture and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102690626AFast curingWon't foamNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesAcetoacetatesCyclodextrin
The invention relates to a single-component polyurethane sealant capable of quickly curing moisture and a preparation method thereof. The polyurethane sealant comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 10 to 20 percent of polyisocyanate monomer, 20 to 45 percent of polyether polyol, 1 to 10 percent of acetoacetic ester sealed end polyether prepolymer, 5 to 20 percent of plasticizer, 25 to 40 percent of modified mineral powder, 1 to 5 percent of latent curing agent, 0.1 to 2 percent of cyclodextrin wrapped environment-friendly catalyst, 0.1 to 1 percent of defoaming agent and 0.1 to 1 percent of water-removing agent, wherein the water-removing agent is one or more of mono-isocyanate compound or functionalized silane compound. The single-component polyurethane sealant avoids bubble fundamentally, can be quickly cured, is stable in storage, and can be applied to construction on damp interfaces.
Owner:苏州中材非金属矿工业设计研究院有限公司 +1
Preparation method of 2-(4-haloethyl) phenyl-2-methyl propionic ester and synthesis method of bilastine
InactiveCN102675101AAvoid expensive reagentsRaw materials are cheap and easy to getPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesPropanoic acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2-(4-haloethyl) phenyl-2-methyl propionic ester and a synthesis method of bilastine, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out acylation reaction on 2, 2-dimethyl phenylacetate and halogen acetyl halides under the action of catalyst, to generate 2-(4-halogen acetyl) phenyl-2-methyl propionic ester; carrying out kishner-wolff-huang reduction reaction on the 2-(4-halogen acetyl) phenyl-2-methyl propionic ester, to reduce the carbonyl so as to generate the 2-(4-haloethyl) phenyl-2-methyl propionic ester; having condensation reaction with 1-ethoxy ethyl-2-pyridine-4-group benzimidazole by taking the 2-(4-haloethyl) phenyl-2-methyl propionic ester as a midbody to obtain esterified bilastine; and hydrolyzing, to generate the bilastine. The novel synthesis method of the bilastine provided by the invention can easily obtain raw materials, and is simple to operate, lower in cost, environment-friendly, and completely suitable for the industrial production.
Owner:王蕾
Preparation method of alkyd resin
InactiveCN102408551AImprove adhesionFullnessCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolymer scienceNitrocellulose
The invention relates to a preparation method of alkyd resin. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: (1) adding neopentyl glycol, trihydroxymethyl propane, phthalic anhydride, hydrogenated phthalic anhydride and antioxidant to a reaction container, and heating to carry out melt esterification on the materials at the temperature of 200-240 DEG C; (2) when esterification is carried out to an acid value being 40-45 mgKOH / g, cooling to 120-160 DEG C, and adding short-chain synthetic fatty acid and an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent; (3) heating to carry out reflux esterification at the temperature of 180-200 DEG C, and diluting with acetic acid ester organic solvent when the acid value is smaller than or equal to 8 mgKOH / g; and (4) cooling to 100 DEG C and filtering to obtain alkyd resin. The paint prepared from the alkyd resin obtained in the invention and nitrocellulose has the characteristics of rapid drying, high hardness, good fullness, good adhesion force, and good water resistance.
Owner:JIANGSU SANMU GROUP CORPORATION
Functional skin care product containing purslane extractive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102764217AMild textureImprove securityCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticGlycerolPurslane extract
The invention is a functional skin care product containing purslane extractive. Raw materials of the functional skin care product include, by weight, 10 parts of purslane extractive, 1-2 parts of Prinsepia utilis rogle oil, 2-5 parts of glycerol, 0.3-0.5 parts of crylic acid (ester) / C10-30 alkanol acrylate cross-linked polymer, 2-3 parts of 1,2-pentanediol, 1-5 parts of synthesized squalane, 1-2 parts of tocopheryl acetate, 2-3 parts of cetostearyl alcohol, 0.1-0.2 part of allantoin, 0.3-0.8 part of sodium hyaluronate, 3-5 parts of Butyrospermum parkii butter, and 100 parts of deionized water. Or the Prinsepia utilis rogle oil and the Butyrospermum parkii butter are not added. By the aid of animal experiments, namely, mouse auricle swelling models due to dimethlbenzene, the functional skin care product containing purslane extractive is fine in anti-inflammation and anti-allergy effects, mild in nature and fine in safety, and is free of toxic reaction and anaphylaxis. The functional skin care product has an adjuvant therapy function to skin barrier recovery of common discosmetic dermatosis such as hormone dependent dermatitis and acne, and is fine in curative effect and safety.
Owner:YUNNAN BOTANEE BIO TECH GRP CO LTD
Method and test strips for the measurement of fat loss during weight loss programs
InactiveUS20040043376A1Great advantageEasy to manufactureMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
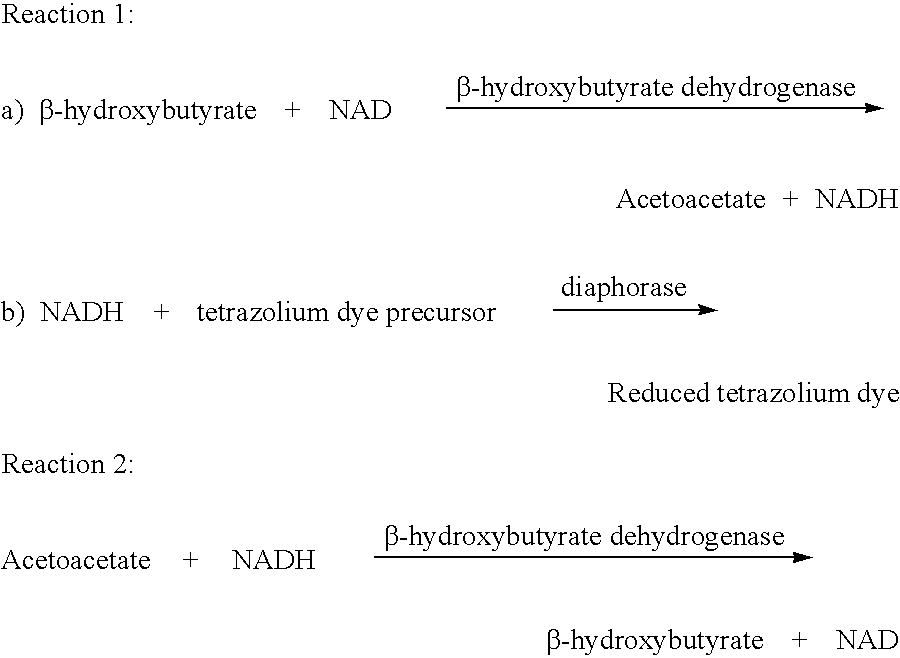
Disposable test strips and a wet chemistry method for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate or total ketone bodies (i.e., beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) in human bodily fluid samples, including but not limited to urine, saliva or sweat are described. The test strips need only be dipped in the sample and can be used by anyone in almost any milieu. Measurement can be made electrochemically, spectrophotometrically, fluorometrically or by comparision to a color standard. Combined acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate which account for 97-98% of total ketone bodies and may be measured in a cyclic reaction that occurs at pH about 7.0 to about 8.3 with beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, (beta-HBD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a tetrazolium dye precursor and an electron mediator. Using this reaction, false positive results obtained from urine samples taken from patients on sulfhydryl drugs are avoided. beta-HBD from some sources was found to cause false negative results in samples (e.g. urine) containing high chloride content due to chloride inhibition of beta-HBD. Using a simple test for chloride inhibition, it was found that beta-HBD from Alcaligenes is not so inhibited. Using either beta-HBD that is not inhibited by chloride or using 10-20 times the normal concentration of this enzyme eliminates false negatives in samples having substantial chloride content, such as urine, both in the reaction described above and in other reactions disclosed for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate and total ketone bodies, all of which reactions occur in the pH range of about 8.6 to about 9.5.
Owner:GUPTA SURENDRA
Non-additivated antisenescence cosmetic
ActiveCN103156786AImprove anti-aging effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycerolDimethyl siloxane
The invention discloses a non-additivated antisenescence cosmetic, which comprises the following components by weight: a component A composed of glycerin, propylene glycol, hydroxyethyl urea, allantoin, sodium hyaluronate and water; a component B composed of MONTANOV68, dipalmitoyl hydroxyproline, caprylic / capric triglyceride, shea butter, jojoba oil, tocopheryl acetate, polydimethylsiloxane, wheat germ oil and COSMOFERMMI XIII; a component C composed of hydroxyethyl acrylate / acryloyl dimethyltaurate crosspolymer; a component D composed of nicotinamide, panthenol, beta-glucan, mycose and water; a component E composed of acetyl Hexapeptide-8 and water; and a component F composed of SYMDIOL68T and SYMTRIOL. The antisenescence cosmetic has good antisenescence effect, simultaneously, no harmful antiseptic is added in the cosmetic.
Owner:广州市美驰化妆品有限公司
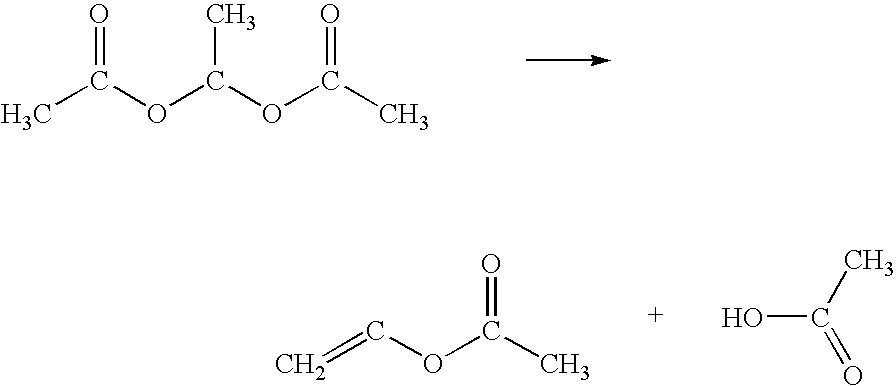
Integrated process for the production of vinyl acetate from acetic acid via acetaldehyde
InactiveUS20100168466A1High selectivity and yieldOrganic compound preparationPreparation from ketenes/polyketenesAcetic anhydridePalladium
This invention provides an integrated multistep economical process for the production of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) from acetic acid in the vapor phase. First, acetic acid is selectively hydrogenated over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde so formed can be converted to ethylidene diacetate via reaction with acetic anhydride. In a subsequent step so formed ethylidene diacetate is thermally decomposed to form VAM and acetic acid. Alternatively, acetaldehyde formed in the first step can selectively be reacted with ketene to form VAM. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over platinum and iron supported on silica selectively produces acetaldehyde in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 300° C., which is selectively hydrogenated over platinum supported catalyst to form ethanol and dehydrated over NAFION catalyst to form ethylene at a temperature of about 185° C., which is mixed with molecular oxygen, acetic acid and reacted over a palladium / gold / potassium catalyst supported on titania to form VAM at a temperature of about 150° C. to 170° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Fungicidal compositions
InactiveUS20160183526A1Emulsion stabilizationImprove performanceBiocideDead animal preservationActive agentOrganosolv
Described herein are fungicidal compositions in the form of emulsifiable concentrates that comprise a first fungicidal compound, optionally, at least one additional fungicidal compound, two or more surfactants and a water immiscible organic solvent comprised of a mixture of organic compounds including an acetate ester, an N,N-dialkylcarboxamide and at least one of a ketone and an alcohol. The compositions are homogeneous, stable upon storage, and upon dilution in water form stable emulsions that can be sprayed onto plants to control important fungal diseases.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Anti-wrinkle face cream and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105147591AAnti agingImprove youthCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEthylhexyl palmitateApple extract
The invention belongs to the technical field of cosmetics, and in particular relates to an anti-wrinkle face cream and a preparation method thereof. The anti-wrinkle face cream comprises butanediol, ethylhexyl palmitate, caprylic / capric triglyceride, glycerol, polyglycerol-10, ethylhexyl isononanoate, polymethyl methacrylate, polydimethylsiloxane, ceteareth-21, cetostearyl alcohol, ceteareth-2, acrylic acid (ester) type / acrylamide copolymer, betaine, avocado fruit butter, a lactic acid bacillus / balausta fermentation product extract, an arctic rock chlamydomonas essence, a starfish essence, a ginseng extract, a lucid ganoderma extract, an apple extract, tocopheryl acetate and the like. The anti-wrinkle face cream provided by the invention is good in penetrability and easy to absorb, can effectively replenish water and preserve moisture, and can repair skin wrinkles and inhibit generation of the winkles, thereby delaying skin aging.
Owner:广州科玛生物科技股份有限公司
Particulate filter media
InactiveUS20080134893A1Low costCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationAcetic acidAcetoacetates
Disclosed are particulate filter media comprising a particulate or powdery acetoacetate-functional compound or composition that is effective in removing gaseous aldehydes present in gases such as air. The particulate filter media are capable of reacting with and irreversibly removing airborne aldehydes, such as formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and acrolein. Also disclosed is a method or process for the removal of an aldehyde from a gas such as air or tobacco smoke by contacting the aldehyde-containing gas with the particulate filter media.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Diesel oil pour point depressant composition, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102517104AGood dispersionImprove low temperature fluidityLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesWaxOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a diesel oil pour point depressant composition and its preparation method. The diesel oil pour point depressant composition, i.e. a diesel oil pour point depressant composition formed by mixing acetic ester organic solvents with a pour point depressant, comprises the following raw materials by mass percent: 0-20% of methyl acetate, 0-20% of ethyl acetate, 0-10% of propyl acetate, 0-30% of butyl acetate, and 20-80% of the pour point depressant. The preparation method consists of: mixing all the raw materials and then conducting stirring in water bath at a constant temperature of 50DEG C for 20min, and controlling the rotation speed at 150r / min, thus obtaining the diesel oil pour point depressant composition. Adding of the obtained diesel oil pour point depressant composition into commercially available 0# diesel oil can make the cold filter plugging point of the diesel oil reduced by 5-11DEG C and the condensation point reduced by 6-10DEG C. The diesel oil pour point depressant composition provided in the invention enhances the dispersion effect of pour point depressants on wax crystals, and improves the low temperature fluidity of diesel oil.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Composite multi-functional two-component aqueous wood white top coat and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106243966AExcellent antibacterial and aldehyde removal functionReasonable materialsAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesCross-linkSlurry
The invention discloses a composite multi-functional two-component aqueous wood white top coat, which comprises a component A, a component B and water according to a mass part ratio of 100:20-25:10-20, wherein the component A is prepared from the following raw materials by mass: an aqueous hydroxy acrylic acid resin, a compound modified self-cross-linking acrylic acid polymer, an aqueous titanium white slurry, an aqueous matting agent, a defoamer, a wetting agent, a thickening agent, a dispersant, a leveling agent, an anti-mildew bactericidal agent, and the balance of water, and the component B is prepared from the following raw materials by mass: hydrophilic aliphatic polyisocyanate and propylene glycol methyl ether acetic acid ester. The composite multi-functional two-component aqueous wood white top coat of the present invention has advantages of good antibacterial effect, good aldehyde removing effect, good stain resistance, environmental protection, good hardness, high fullness, and moderate cost.
Owner:广东伊思曼新材料科技有限公司
Moisturizing and nourishing facial cream and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105434285AImprove skin qualityImprove skin toneCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSodium hyaluronateTocopheryl acetate
The invention provides a composition for moisturizing and nourishing facial cream. The composition comprises effective components in parts by weight as follows: jojoba seed oil, avocado tree fruit grease, a purslane herb extract, phytosterol isostearate, mycose, decarboxy carnosine HCL, tocopheryl acetate, a Chinese angelica root extract, a baical skullcap root extract, sodium hyaluronate, aloe barbadensis leaf juice, a ginseng root extract and a centella leaf extract. The composition is applied to the facial cream, can provide lasting moisturizing and water supplement functions for the face, and can whiten the skin and resist wrinkles obviously after being used for a long time.
Owner:TIANJIN DARENTANG JINGWANHONG PHARMA
Gum base
Owner:FONTERRA TECH LIMITED FORMERLY KIWITECH
Infant lip gloss and making method thereof
ActiveCN105853326AImprove securityAvoid bad consequencesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAllergyMeadowfoam seed oil
The invention relates to infant lip gloss and a making method thereof. The infant lip gloss is made from beeswax, Candelilla wax, shea butter, jojoba seed oil, Meadowfoam seed oil, Argania spinosa kernel oil, squalane, tocopheryl acetate, diisostearyl malate, honey, olive fruit oil and plant enzyme. The making method is simple and convenient, completely uses natural raw materials, solves the problems of allergy, anti-inflammation, sterilization, anticorrosion, anti-oxidation and ultraviolet resistance, and makes the infant lip gloss be pure natural, safe and reliable.
Owner:DANDONG KANGCHILING CLEANING PROD CO LTD
Trimethylcyclohexenylcyclopropyl ketones perfume composition
InactiveUS6051548ANeed can be quite largeCosmetic preparationsOrganic compound preparationPropionateAcetic acid
Described are trimethylcyclohexenylcyclopropyl ketones having the structure: wherein one of the dashed lines is a carbon-carbon double bond and the other of the dashed lines is a carbon-carbon single bond, uses thereof in augmenting, enhancing or imparting aromas in or to perfume compositions, colognes and perfumed articles, and mixtures of same with 3-methyl-1-phenylpentanol-5 and / or butanoylcyclohexane derivatives and / or acetic or propionic acid esters of o-methylphenyl isopropanol.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Flushable wipe and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20180140529A1Without losing its functional strength propertiesCosmetic preparationsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAlcoholWet wipe
A single or multi-ply flushable and dispersible wet wipe including a wet laid fibrous web imprinted using a structuring fabric, a binder composition comprising poly(vinyl) alcohol, poly(vinyl) acetate, poly (ethylene) (vinyl) alcohols, poly (ethylene) (vinyl) acetate, copolymers of vinyl acetate-ethylene, or combinations thereof, and one or more additives. In an exemplary embodiment, the fibrous web is wetted by a wetting solution comprising 0.1% to about 10% by weight of one of the following: (1) boric acid; and (2) boric acid and a mono or divalent salt.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY TISSUE
Highland barley wine with whisky flavor and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN104342339AHigh alcohol production capacityAdaptableAlcoholic beverage preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChaptalization
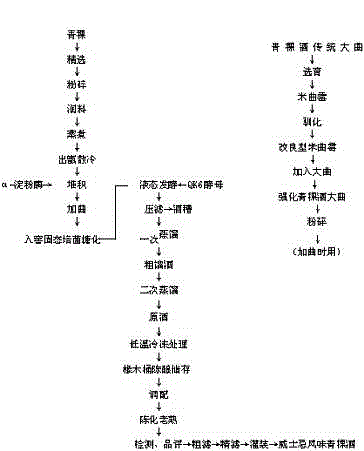
The invention relates to wine making techniques and in particular relates to highland barley wine with a whisky flavor and a preparation process thereof. The highland barley wine with a whisky flavor is characterized by being made from Plateau crops ('Black crow' and sky blue highland barley) in high-attitude areas in high Qinghai-Tibet Plateau by process steps of fermentation distillation, oak barrel aging and blending according to a wine making technique combining granite slab cellar solid-state saccharification with a liquid-state fermentation process, thus obtaining the highland barley wine with whisky flavor. Adopted QK6 yeast can generate good-flavor substances, the contents of all the generated total acid, total acetate and total ethyl ester are high, the flavor complexity of the raw highland barley wine is improved, and the highland barley wine has unique product characteristics in terms of fragrance, flavor and style. The highland barley wine with whisky flavor is clear and transparent, is pale yellow to golden yellow, is free of suspended solids and sediment, has harmonious and strong aromatic odor endowed by cereal and oak barrels and is elegant and fine; the body of the highland barley wine is plump, pure, mild and sweet and has aromatic odor endowed by cereal and oak barrels.
Owner:青海互助天佑德青稞酒股份有限公司
Sustained release eye drop formulations
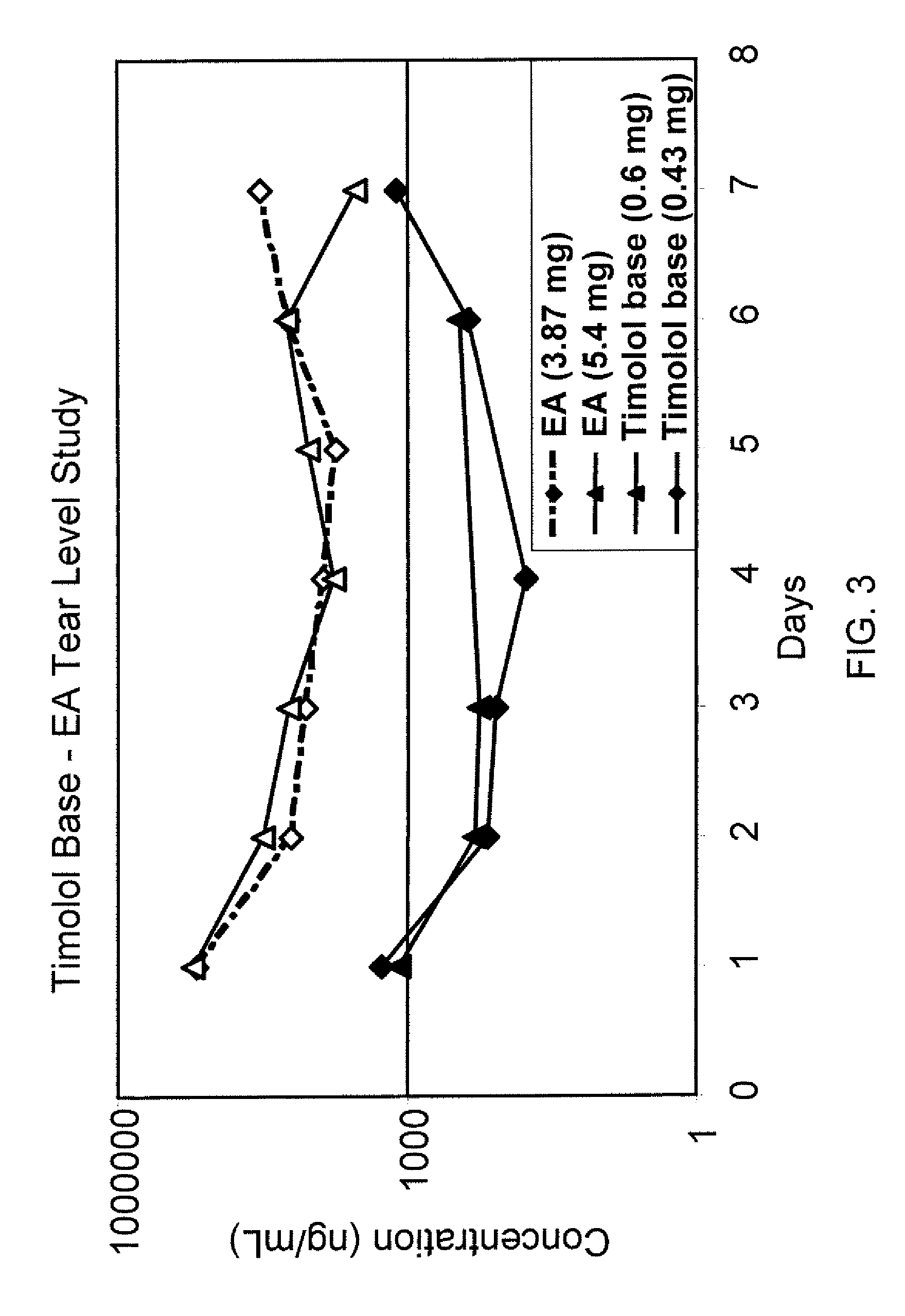
ActiveUS8541413B2Easy to useEfficient deliveryAntibacterial agentsBiocideActive agentAqueous solubility
This invention provides for biocompatible, biodegradable eye drop pharmaceutical formulations useful for the treatment of ocular indications. In particular, tocopherols and their esters of low water solubility, notably α-tocopheryl acetate, are exceptional vehicles for biocompatible, nonirritating topical eye drop formulations that provide sustained release of active agents.
Owner:RAMSCOR
Control method for preparing salvianolic acid A
InactiveCN101121658AIncrease contentReduce performanceCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationPlant ingredientsAcetic acidOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a control method for the preparation of salvianolic acid; in the method, the proper quantity of solvent is added into the salvia drinking piece or the smashed salvia to be used as the menstruum; after the extraction and the solid-liquid separation, the extracted liquid reacts at the high temperature and a high pressure; then the medical liquid is added into the chromatography column; after eluted by water, elute with the eluant; collect the high-purity salvianolic acid A solution; compress the eluant until the eluant has no organic solvent under the reduced pressure or the normal pressure; the alkali is used to adjust the pH value of the acquired solution; the solution is extracted with the chloroform or ether organic solvent; after the organic solvent are extracted, the acetic acid ester and similar organics solvents are added into the water for extraction; the medical liquid is compressed and dried with the acetic acid ester and similar organics solvents and then the salvianolic acid A product of 50 to 84 percent is gotten. Through controlling the content of the salvianolic acid A in the final extracted materials, the performance of the final extracted materials are more stable; and the invention is low in the requirements for the chemical medicine, more universal, and more suitable for the industrialization.
Owner:PHARMA RES INST OF BENCAO TIANYUAN OF BEIJING
Method for extracting phenolic compounds from biological oil
InactiveCN102603498ASimple processEther separation/purificationOrganic compound preparationWater bathsAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for extracting phenolic compounds from a biological oil, and relates to an extraction process of the biological oil. The method comprises the steps of preprocessing the biological oil, and extracting a distillate containing phenolic compounds; adding a soluble salt into the extracted distillate containing phenolic compounds to obtain a solution A; adjusting a pH value of the solution A to be more than 7 so as to obtain a solution B; placing the solution B in a water bath and heating to obtain a complexing precipitate; collecting the complexing precipitate, and performing vacuum filtration to prepare a filter cake; placing the filter cake into hydrochloric acid to perform replacement, extracting with an extractant, and performing vacuum drying on the extract liquor to extract the phenolic compounds. By use of a soluble metal salt as a precipitant and an acetic acid ester or dichloromethane solution as the extractant, the phenolic compounds can be extracted from a biomass pyrolysis oil. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, and the purities of the extracted phenolic compounds can be up to more than 96%.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com