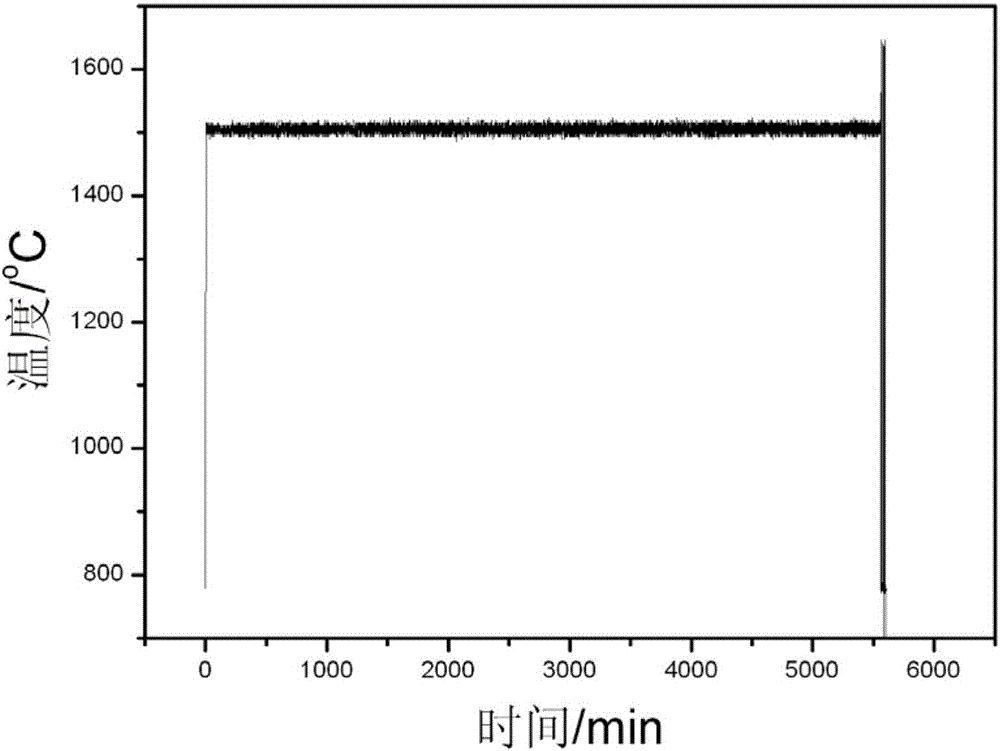
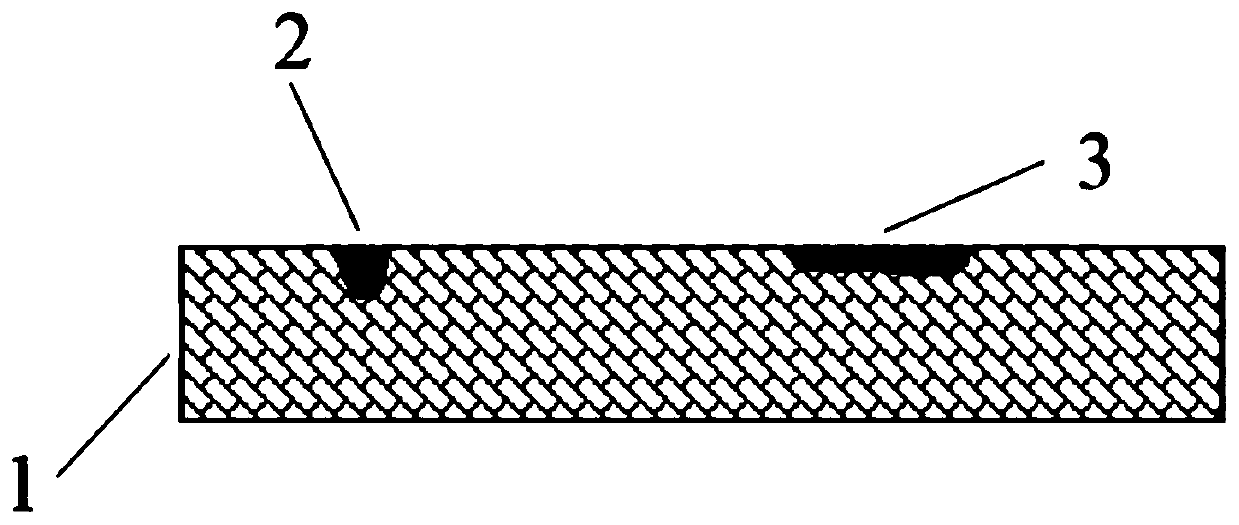
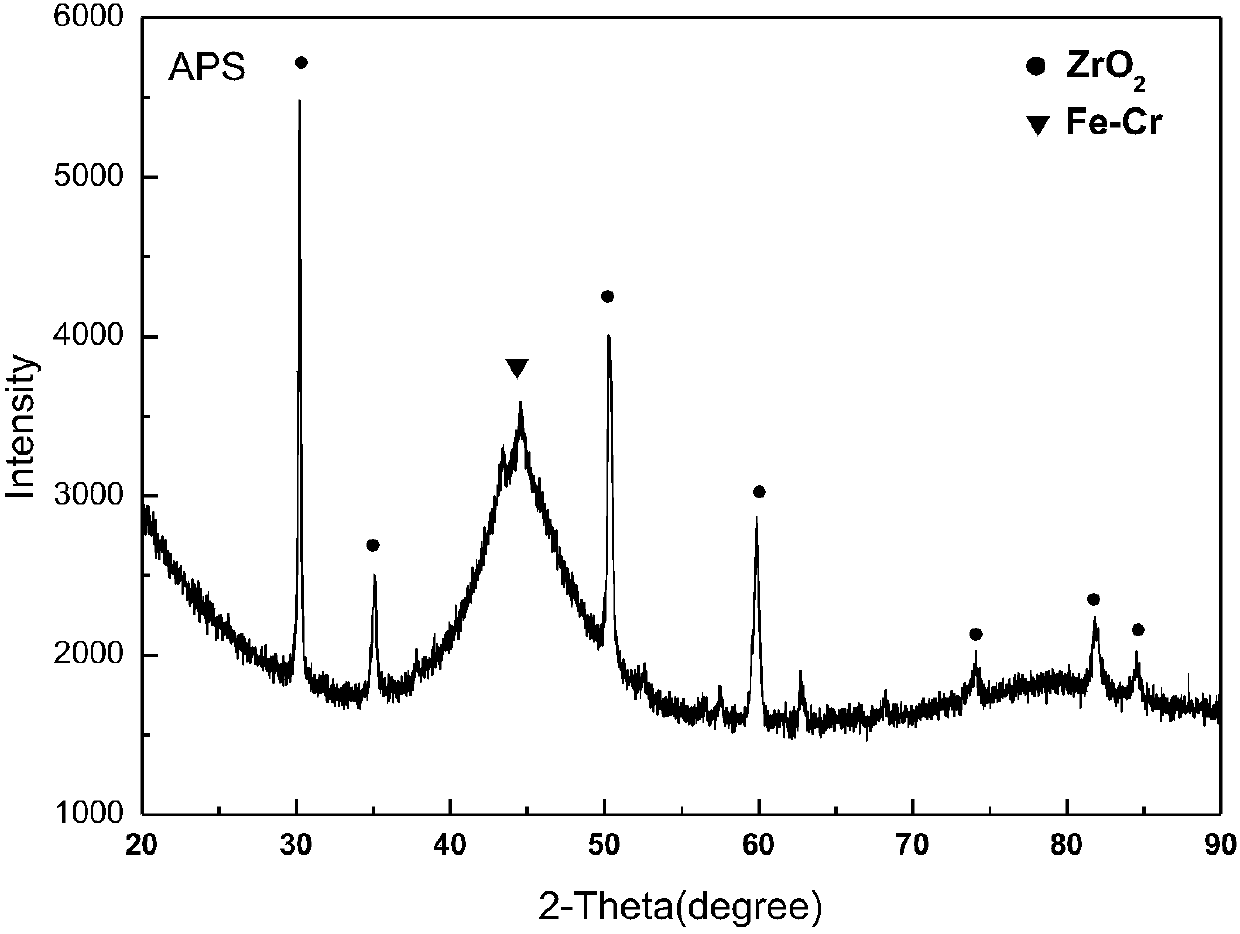
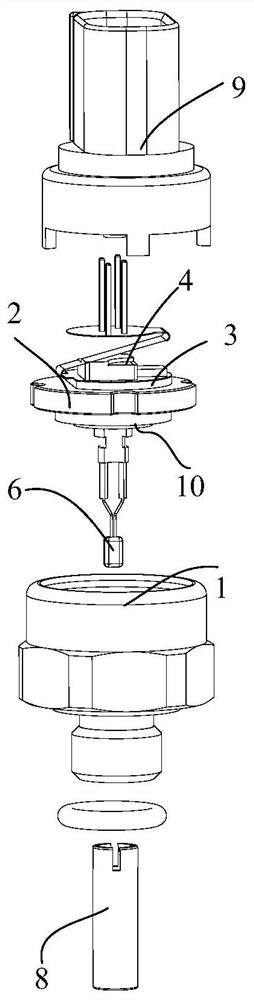
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67results about How to "Well matched thermal expansion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
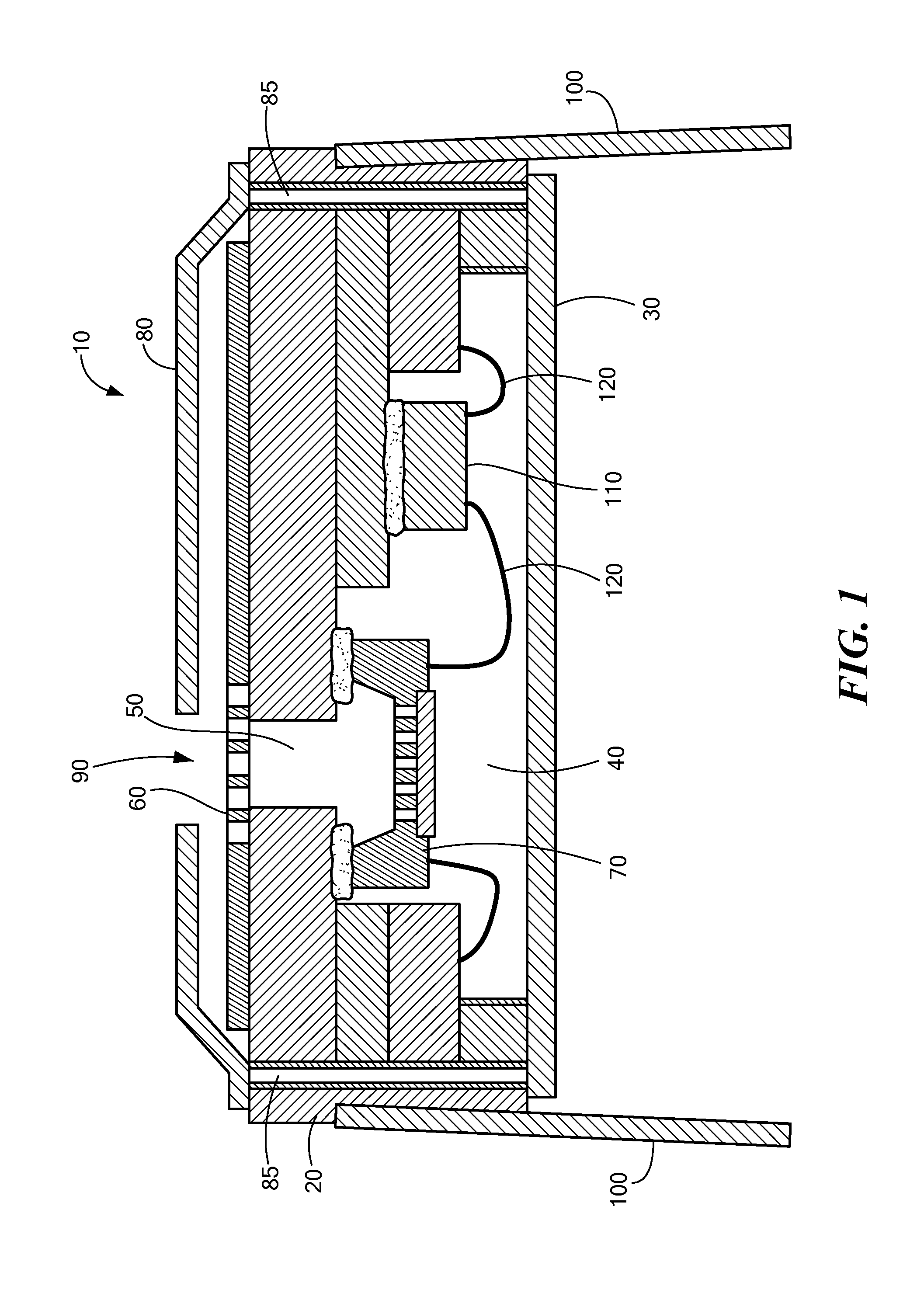
MEMS Microphone System for Harsh Environments
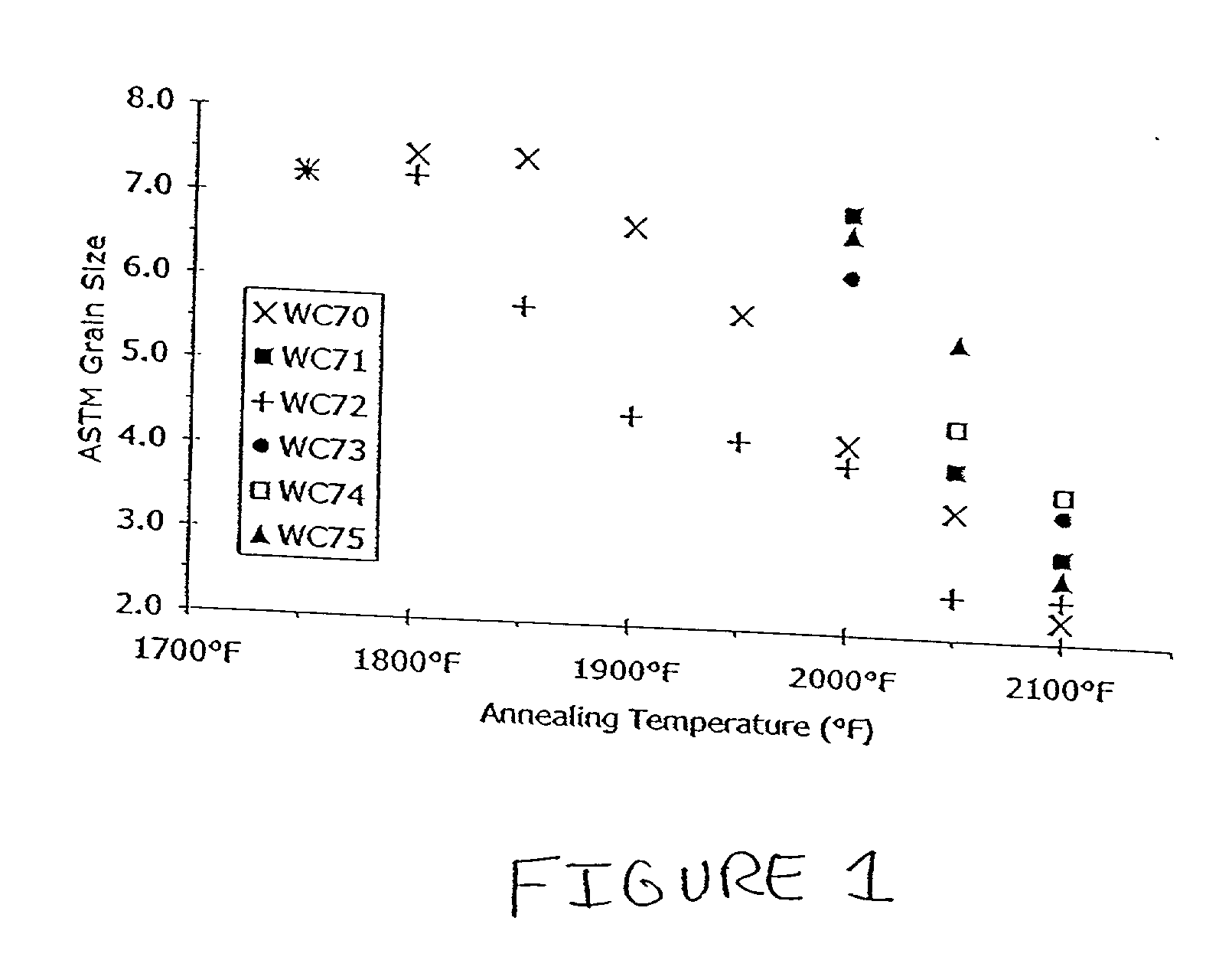
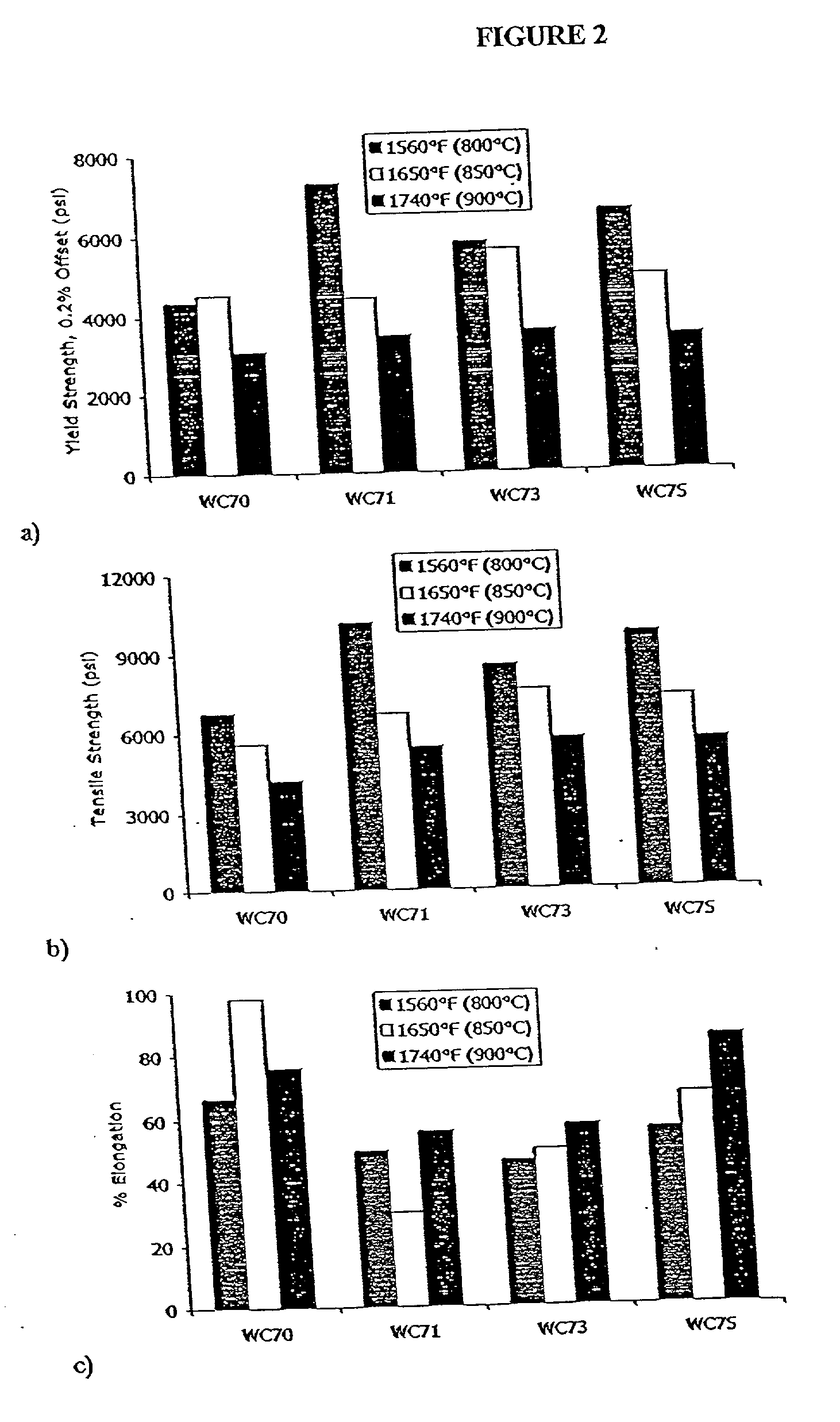
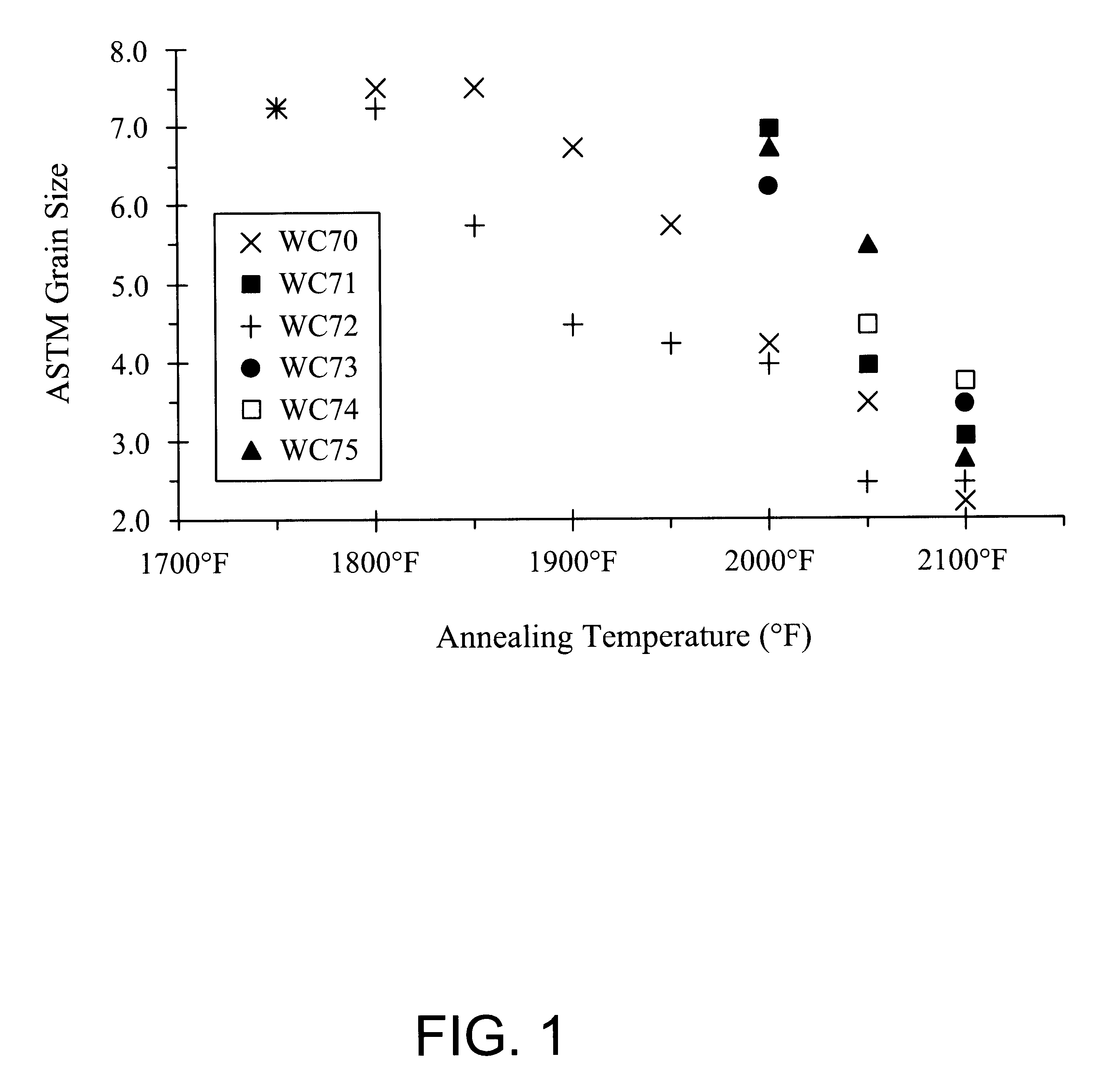
ActiveUS20140091406A1Avoid problemsWell matched thermal expansionTransducer detailsSemiconductor electrostatic transducersEngineeringMems microphone
A MEMS microphone system suited for harsh environments. The system uses an integrated circuit package. A first, solid metal lid covers one face of a ceramic package base that includes a cavity, forming an acoustic chamber. The base includes an aperture through the opposing face of the base for receiving audio signals into the chamber. A MEMS microphone is attached within the chamber about the aperture. A filter covers the aperture opening in the opposing face of the base to prevent contaminants from entering the acoustic chamber. A second metal lid encloses the opposing face of the base and may attach the filter to this face of the base. The lids are electrically connected with vias forming a radio frequency interference shield. The ceramic base material is thermally matched to the silicon microphone material to allow operation over an extended temperature range.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Solid oxide fuel cell with symmetrical electrodes, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103811789AGood thermal expansion matching performanceGood thermal shock resistanceCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsChemistryThermal shock
The invention discloses a solid oxide fuel cell with symmetrical electrodes and a preparation method and application thereof. The solid oxide fuel cell has the following symmetrical structure: an electrocatalysis membrane electrode deposited on the inner wall of the pore of a porous electrolyte, a compact electrolyte layer and another electrocatalysis membrane electrode deposited on the inner wall of the pore of the porous electrolyte. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a porous electrolyte / compact electrolyte / porous electrolyte skeleton structure and an electrocatalysis membrane electrode infiltration precursor solution; infiltrating the prepared porous electrolyte / compact electrolyte / porous electrolyte skeleton structure in the electrocatalysis membrane electrode infiltration precursor solution by using an impregnation method; and carrying out heat treatment. The cell provided by the invention has the advantages of good thermal expansion coupling performance, good thermal shock resistance, low cost, a short preparation period, etc.; and when hydrocarbon is used as a fuel, carbon deposition on the positive electrode of the cell can be effectively prevented, and the cell can be used as an electrolytic bath and has commercialization prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Functionalized graphene-based solar back aluminum slurry and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103500597AGood electrical conductivityImprove conversion efficiencyNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureCvd grapheneWeather resistance
The invention discloses functionalized graphene-based solar back aluminum slurry and a preparation method thereof. The solar back aluminum slurry is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 65-73 percent of aluminum powder, 1-3 percent of glass powder, functionalized graphene dispersion liquid containing 0.12-0.15 percent of functionalized pure graphene, 20-30 percent of organic carrier, 3-5 percent of auxiliary agent and the balance of diluent, wherein oxidized graphene is modified by using a coupling agent; the modified oxidized graphene is obtained through reaction of the coupling agent and the oxidized graphene and then is reduced to obtain the functionalized graphene; the functionalized graphene is dispersed into terpineol and butyl carbitol with a mass ratio of 5.5-6.5:1 after being subjected to ultrasonic treatment to form the functionalized graphene dispersion liquid. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing, grinding and vacuum deformation of the raw materials. The solar back aluminum slurry has the advantages of high printing rate and good adhesion, conductivity, bending resistance and weathering resistance.
Owner:广州市尤特新材料有限公司
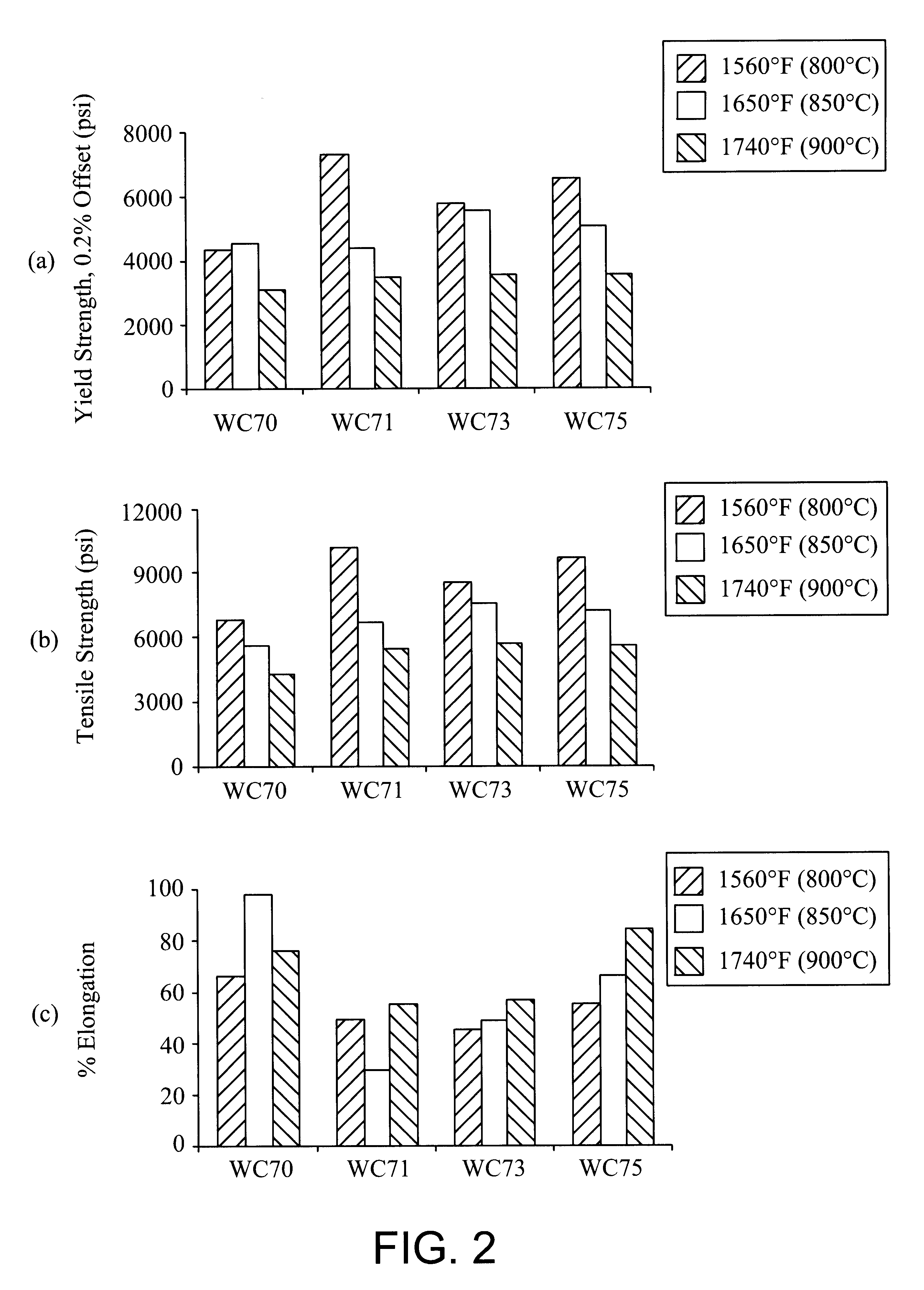
Ferritic stainless steel having high temperature creep resistance
InactiveUS20040050462A1Improve efficiencyEasy to operateFinal product manufactureFurnace typesNiobiumThermal expansion
A ferritic stainless steel having improved high temperature mechanical properties includes greater than 25 weight percent chromium, 0.75 up to 1.5 weight percent molybdenum, up to 0.05 weight percent carbon, and at least one of niobium, titanium, and tantalum, wherein the sum of the weight percentages of niobium, titanium, and tantalum satisfies the following equation: 0.4<=(% Nb+% Ti+½(% Ta))<=1. The coefficient of thermal expansion of the ferritic stainless steel is within 25 percent of the CTE of stabilized zirconia between 20° C. (68° F.) and 1000° C. (1832° F.), and the steel exhibits at least one creep property selected from creep rupture strength of at least 1000 psi at 900° C. (1652° F.), time to 1% creep strain of at least 100 hours at 900° C. (1652° F.) under load of 1000 psi, and time to 2% creep strain of at least 200 hours at 900° C. (1652° F.) under load of 1000 psi. The steel is particularly suited for high temperature applications including, but not limited to, current collecting interconnects in solid oxide fuel cells, furnace hardware, equipment for the chemical process, petrochemical, electrical power generation, and pollution control industries, and equipment for handling molten copper and other molten metals.
Owner:GRUBB JOHN F
Carbon-silicon carbide base composite material toughened by carbon fiber and its preparation method
InactiveCN1868971AWell matched thermal expansionLow temperature crack defect reductionCeramic layered productsFiberCarbon fibers
A carbon fiber toughened carbon-silicon carbide based composition with high thermal expansion match performance, low-temp antioxidizing performance, toughness and purity features that its reinforcing phase is carbon fiber, its basic body phase is the alternatively laminated 2-5 carbon-silicon carbide layers, and its external layer is silicon carbide for high antioxidizing performance. Its preparing process is sequential impregnation and thermodecomposing of boronphenolic aldehyde and polycarbonsilane.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Ferritic stainless steel having high temperature creep resistance
InactiveUS20030124019A1Improve efficiencyHigh efficiencyFinal product manufactureFurnace typesAustenitic stainless steelPetroleum
A ferritic stainless steel having improved high temperature mechanical properties includes greater than 25 weight percent chromium, 0.75 up to 1.5 weight percent molybdenum, up to 0.05 weight percent carbon, and at least one of niobium, titanium, and tantalum, wherein the sum of the weight percentages of niobium, titanium, and tantalum satisfies the following equation: 0.4<=(% Nb+% Ti+½(% Ta))<=1. The coefficient of thermal expansion of the ferritic stainless steel is within 25 percent of the CTE of stabilized zirconia between 20° C. (68° F.) and 1000° C. (1832° F.), and the steel exhibits at least one creep property selected from creep rupture strength of at least 1000 psi at 900° C. (1652° F.), time to 1% creep strain of at least 100 hours at 900° C. (1652° F.) under load of 1000 psi, and time to 2% creep strain of at least 200 hours at 900° C. (1652° F.) under load of 1000 psi. The steel is particularly suited for high temperature applications including, but not limited to, current collecting interconnects in solid oxide fuel cells, furnace hardware, equipment for the chemical process, petrochemical, electrical power generation, and pollution control industries, and equipment for handling molten copper and other molten metals.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES +1
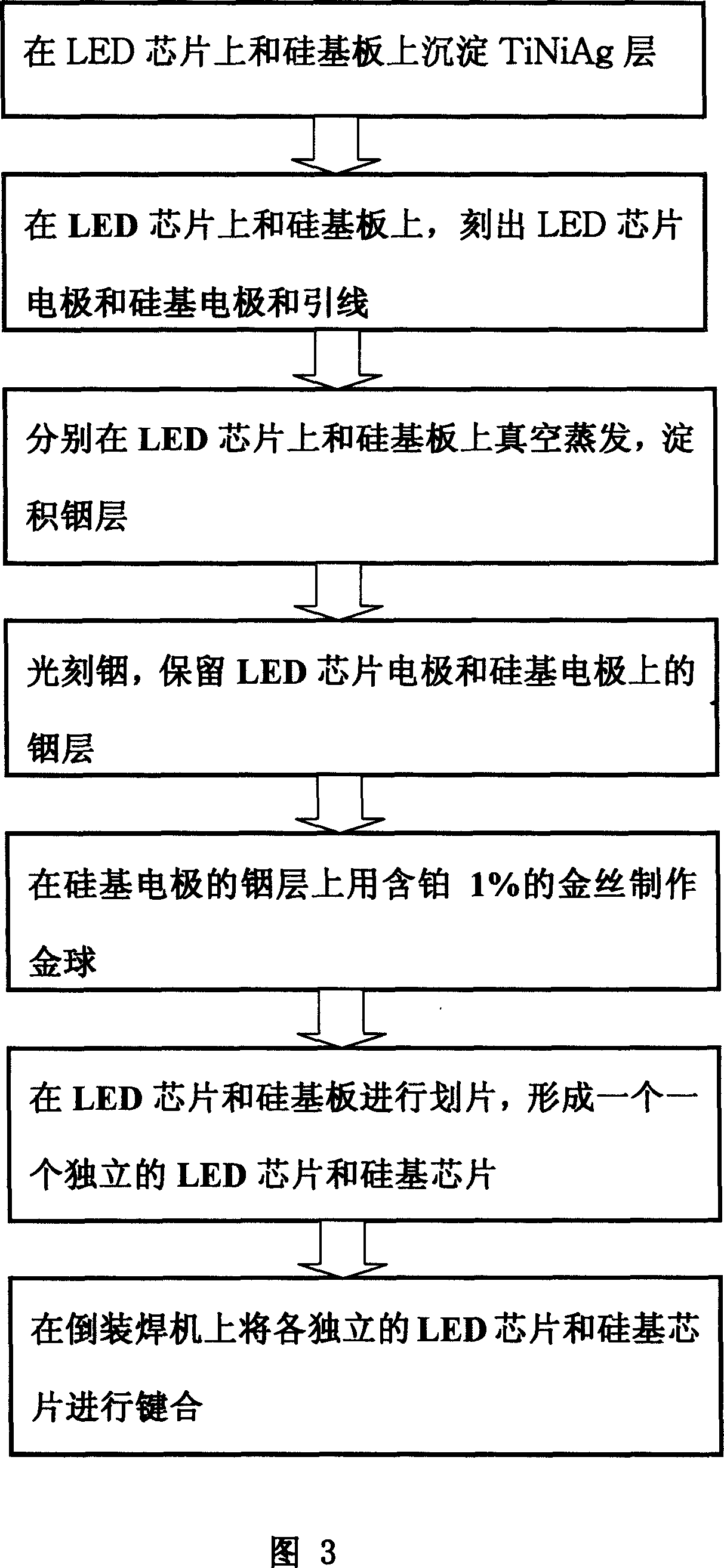
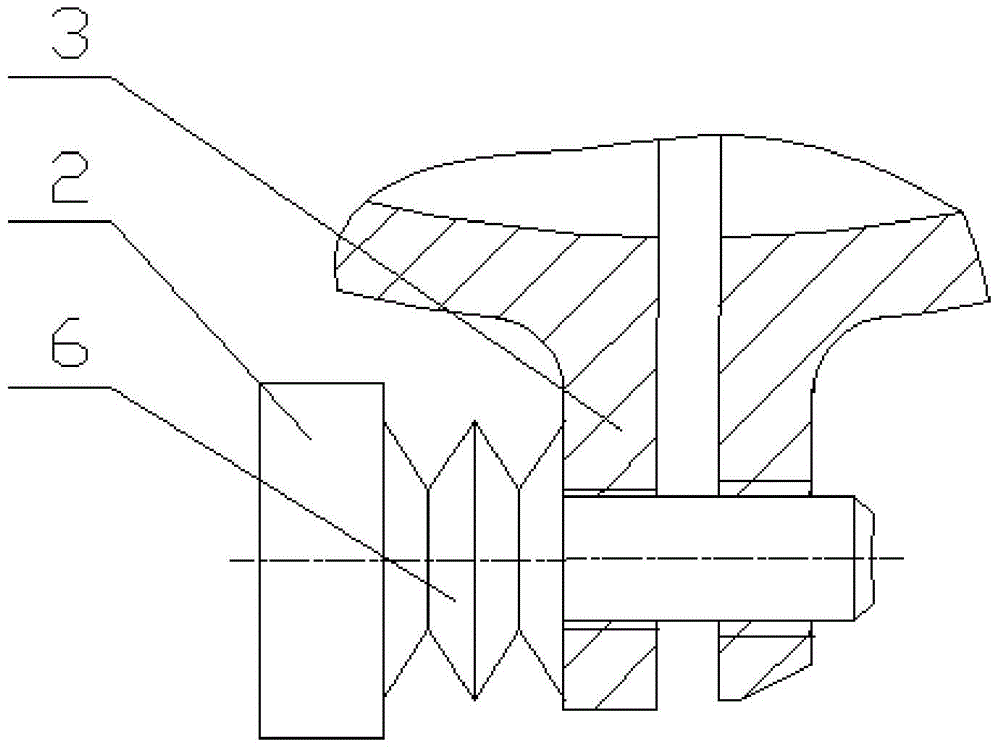
Converse welding method of high power LED chip
InactiveCN1971952AWell matched thermal expansionImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumGold ball
This invention relates to one large power LED chip inverse weld method in micro electron technique, which comprises the following steps: depositing Tania layer on LED chip and metal indium on LED chip electrode; depositing Tania layer on silicon baseboard and indium on silicon base circuit board on LED chip electrode position to process gold ball; then welding the LED chip and silicon baseboard together to form indium to gold to cadmium structure with cadmium as expansion buffer.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell and making method thereof
ActiveCN103219525ASimple processEasy industrial scale-upFinal product manufactureCell electrodesOxide ceramicFuel cells
The invention relates to a low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell and a making method thereof. The structure of the low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell comprises an anode film deposited on the inner wall of a porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta composite film, a cathode film deposited on the inner wall of the porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgXO3-delta composite film, and a compact perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta electrolyte film positioned between the anode film and the cathode film, wherein each of x, y and delta is equal to or more than 0 and equal to or lower than 0.2, and the perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta composite film is formed through a porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta substrate, the perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta and a porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta film. The invention also provides the making method of the low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
MEMS microphone system for harsh environments
ActiveUS8841738B2Well matched thermal expansionTransducer detailsSemiconductor electrostatic transducersEngineeringMems microphone
A MEMS microphone system suited for harsh environments. The system uses an integrated circuit package. A first, solid metal lid covers one face of a ceramic package base that includes a cavity, forming an acoustic chamber. The base includes an aperture through the opposing face of the base for receiving audio signals into the chamber. A MEMS microphone is attached within the chamber about the aperture. A filter covers the aperture opening in the opposing face of the base to prevent contaminants from entering the acoustic chamber. A second metal lid encloses the opposing face of the base and may attach the filter to this face of the base. The lids are electrically connected with vias forming a radio frequency interference shield. The ceramic base material is thermally matched to the silicon microphone material to allow operation over an extended temperature range.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Glass sealing material for thermal battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102070300AWell matched thermal expansionGood wettingInsulation resistanceMixed alkali effect
The invention discloses a glass sealing material for a thermal battery and a preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized in that the glass sealing material comprises the following components in percentage by mole : 60-80% of SiO2, 3-15% of BaO, 5-15% of Na2O, 4-15% of K2O, 0-6% of Al2O3, 0-6% of B2O3, 0-5% of Li2O, and 0-5% of La2O3. The glass sealing material disclosed by the invention basically comprises SiO2, Al2O3 and B2O3, is added with proper matching of alkali metal oxide (mixed alkali effect) so as to control a softening point and viscosity of glass, improve the flowability of the glass and improve the performance of glass powder by adding modified oxides such as La2O3 with certain content and auxiliary ingredients, so that the wetting property of the glass to a titanium battery cover is improved. In addition, the invention prepares the glass sealing material by reasonable manufacturing technologies such as smelting, clearing, pulverizing, granulating and the like, so that the leakage rate of a sealing cover of the thermal battery produced by the sealing material disclosed by the invention is less than 1.0 multiplied by 10-10Pa.m<3> / s, and the insulation resistance is improved by more than one times compared with that of the sealing cover produced by the prior art.
Owner:西安华泰有色金属实业有限责任公司
Ferritic stainless steel having high temperature creep resistance
InactiveUS6641780B2Improve efficiencyEasy to operateFinal product manufactureFurnace typesNiobiumThermal expansion
A ferritic stainless steel having improved high temperature mechanical properties includes greater than 25 weight percent chromium, 0.75 up to 1.5 weight percent molybdenum, up to 0.05 weight percent carbon, and at least one of niobium, titanium, and tantalum, wherein the sum of the weight percentages of niobium, titanium, and tantalum satisfies the following equation:The coefficient: of thermal expansion of the ferritic stainless steel is within 25 percent of the CTE of stabilized zirconia between 20° C. (68° F.) and 1000° C. (1832° F.), and the steel exhibits at least one creep property selected from creep rupture strength of at least 1000 psi at 900° C. (1,652° F.), time to 1% creep strain of at least 100 hours at 900° C. (1652° F.) under load of 1000 psi, and time to 2% creep strain of at least 200 hours at 900° C. (1652° F.) Under load of 1000 psi. The steel is particularly suited for high temperature applications including, but not limited to, current collecting interconnects in solid oxide fuel cells, furnace hardware, equipment for the chemical process, petrochemical, electrical power generation, and pollution control industries, and equipment for handling molten copper and other molten metals.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES +1
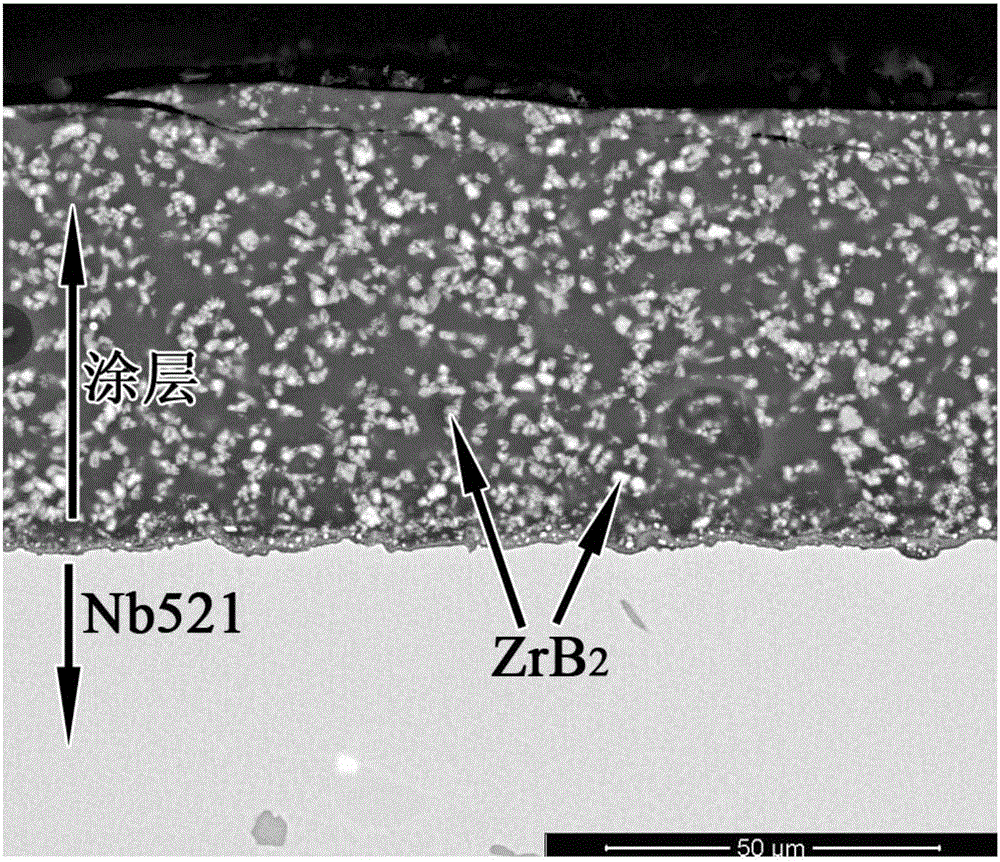
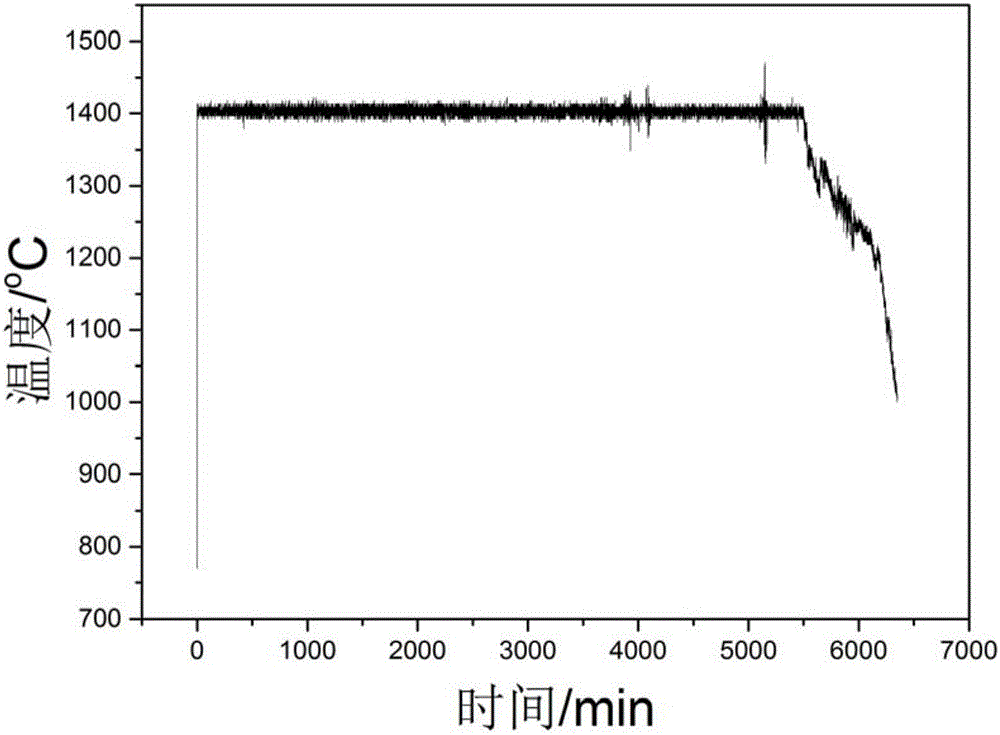
Boride modified glass ceramic based composite high-temperature oxidation resisting coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106587629AGood heat erosion resistanceWide protection temperature rangeOxidation resistantBoride
The invention discloses a boride modified glass ceramic based composite high-temperature oxidation resisting coating. The composite high-temperature oxidation resisting coating fired on the surface of a refractory metal matrix is prepared from boride and silicate glass, wherein the boride is at least one or two of HfB2, ZrB2 and TiB2; besides, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the coating. The method comprises steps as follows: 1, the surface of the refractory metal matrix is treated; 2, boride particle modified glass ceramic composite slurry is prepared; 3, a preset layer is obtained by presetting the slurry on the surface of the refractory metal matrix, and the boride modified glass ceramic based composite high-temperature oxidation resisting coating is obtained vacuum high-temperature firing. The composite high-temperature oxidation resisting coating is used for high-temperature protection of the refractory metal matrix and can continuously protect the refractory metal matrix at the protection temperature of 400-1,600 DEG C for 5 h or longer.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Preparation method of ceramic matrix composite surface priming coat
The invention relates to a preparation method of a ceramic matrix composite surface priming coat. A combined method of combining a slurry method with a silicon carbide in-situ reaction process is utilized to realize surface leveling of a composite material, and then a low-pressure chemical vapor deposition process is matched to prepare a silicon-rich silicon carbide priming coat of the environmental barrier coating for SiC / SiC and C / SiC composite materials. The method has the advantages that 1) the proportion of each component in a slurry precursor can be adjusted according to the characteristics of different surface defects to obtain proper viscosity, so that a better defect filling effect is achieved; 2) an integrated reaction of the repair slurry and the composite material through a high-temperature cracking process is realized; 3) a silicon-rich silicon carbide priming coat is obtained on the surface of a composite material by adopting a low-pressure chemical vapor deposition process, so that the quality of the environmental barrier coating is improved, and the service life of the environmental barrier coating is prolonged; and (4) the silicon-rich silicon carbide coating is deposited on the surface of the composite material, so that the temperature resistance and the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the composite material are improved, the bonding strength of the environmental barrier coating and the composite material matrix is enhanced, and the thermal expansion matching of the environmental barrier coating and the composite material matrix is improved.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Preparation method for fuel cell with ordered porous structured electrode
ActiveCN106876753AGood performanceGood thermal expansion matching performanceCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsOxideElectrolytic cell
The invention discloses a preparation method for a fuel cell with an ordered porous structured electrode. The preparation method is characterized in that the electrode has an ordered columnar porous structure; and the battery structure comprises a porous electrolyte layer impregnated with an electrode catalyst / compact electrolyte layer / porous electrolyte layer impregnated with the electrode catalyst. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) preparing ordered porous structured electrolyte layer paste, compact electrolyte layer paste and an electrode catalyst impregnation liquid; (2) preparing porous electrolyte layer / compact electrolyte layer / porous electrolyte layer framework; and (3) impregnating the porous electrolyte layer framework with the electrode catalyst. The fuel cell provided by the invention can provide high gas transmission channels and ionic and electronic conductive network, and has better performance compared with a conventional solid oxide fuel cell; and meanwhile, the fuel cell has the advantages of high thermal expansion matching performance, low preparation cost, simple preparation process and the like, can be used as the fuel cell and an electrolytic cell and has high development prospect.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Iron-based coating material for heat insulating protection and coating preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105603350ALow thermal conductivityImprove toughnessMolten spray coatingFerroniobiumGranularity
The invention discloses an iron-based coating material for heat insulating protection and a coating preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of surface coatings. Raw materials selected include alloy blocks and pure metal blocks, and specifically are ferroboron, ferroniobium, ferrosilicon, pure chromium and pure iron; a high-temperature nitrogen gas atomizing method is adopted to prepare alloy powder, and the alloy powder of 20-45 um in degree of sphericity and granularity; a hypersonic flame spraying method is adopted to prepare an iron-based noncrystalline or nanocrystalline coating. The coating prepared by the method has relatively low heat conductivity and can be used for heat insulating protection of heat-end parts of automobile engines.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Cermet composite material and coating preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107653430AGood matching of thermal expansionGood bonding strengthMolten spray coatingSurface engineeringNitrogen gas
The invention provides a cermet composite material and a coating preparation method thereof, belongs to the field of thermal spraying in composite materials and surface engineering, and particularly relates to a preparation method for metal-based composite powder with low thermal conductivity and a coating thereof by atmospheric plasma spraying. The method comprises the following steps that iron-based amorphous powder prepared by the high pressure nitrogen gas atomization method is mixed with zirconia powder prepared by the agglomeration sintering method according to a certain mass ratio, andfinally the composite powder with a better sphericity and a particle size of 25-75 [mu]m is obtained. The iron-based-ceramic composite coating is prepared by adopting the atmospheric plasma spraying mode, and the composite coating prepared has relatively low thermal conductivity, and can be used for insulation protection for hot end parts of a diesel engine.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Non-cobalt IT-SOFC (Intermediate-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell) stable anode material and application thereof
ActiveCN103682373AReduced responseSimple structureCell electrodesChemical compatibilityThermal expansion
The invention relates to a non-cobalt IT-SOFC (Intermediate-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell) stable anode material and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of fuel cells. The A site of SrFeO3-delta is doped with Nd, and the B site of the SrFeO3-delta is doped with Cu, so that the prepared (Nd1-xSrx)a (Fe1-yCuy)bO3-detal (NSCFu) anode material has high oxygen reduction catalytic activity, and the electrochemical performance is greatly improved. The anode material has long-term stability, and meanwhile has the advantages of high electronic conductivity, and high chemical compatibility and thermal expansion compatibility with cerium-oxide-based electrolytes. Thus, the SOFC anode material is potential.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Temperature and pressure sensor
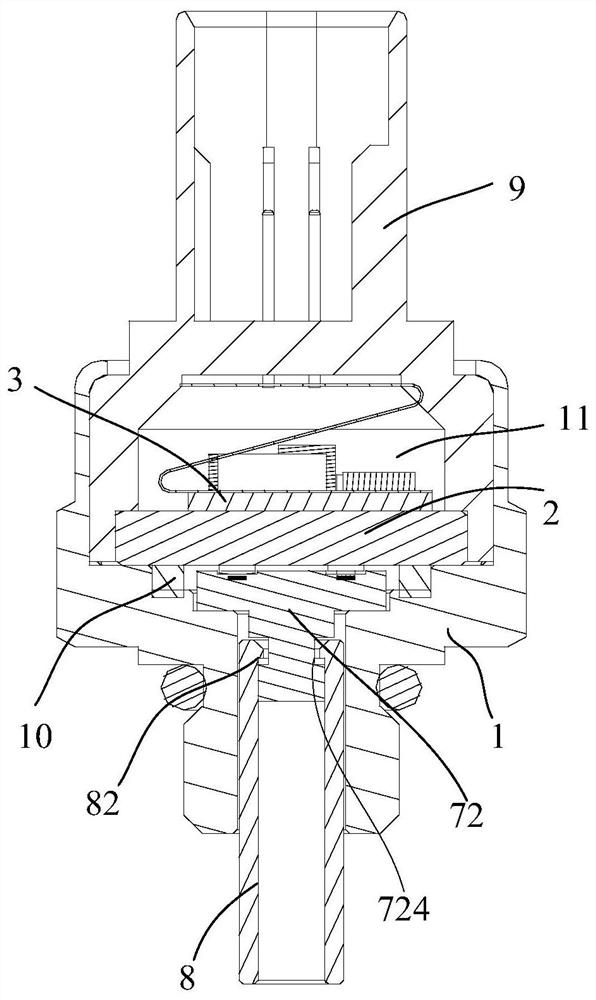
PendingCN112611504AWell matched thermal expansionImprove performanceThermometer detailsFluid pressure measurementSealantStress sensors
The invention provides a temperature and pressure sensor, which comprises a shell, a ceramic piece, a circuit board, a pressure sensitive element, a conductive element and a temperature sensitive element, and is characterized in that the shell is provided with a mounting cavity with an upper opening and a lower opening, the ceramic piece is arranged in the mounting cavity and is provided with a pressure hole in a penetrating manner, the ceramic piece is in sealed connection with the inner wall of the mounting cavity so as to divide the mounting cavity into an upper cavity and a medium channel, the circuit board is mounted at the upper end of the ceramic piece, the pressure sensitive element is mounted on the upper surface of the ceramic piece, covers the pressure hole and is electrically connected with the circuit board, one end of the conductive element is electrically connected with the circuit board, the other end of the conductive element penetrates through the ceramic piece and is hermetically connected with the ceramic piece through a sealant, and the temperature sensitive element is electrically connected with the conductive element.
Owner:WUHAN FINEMEMS
High-temperature resistant metal sealing material for mixed conductor oxygen permeable ceramic membrane and application method thereof
InactiveCN101928855AGood chemical inertnessReduce chemical reactionsElectrical conductorRoom temperature
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-temperature resistant metal sealing material for a compact mixed conductor oxygen permeable ceramic membrane and a sealing application method of the material, in particular to a preparation method of the sealing material between a compact mixed conductor oxygen permeable ceramic membrane piece and a supporting component thereof and an application method of the sealing material, belonging to the technical field of a special ceramic welding material. The high-temperature resistant metal sealing material comprises the following components in weight percentage: 92-95% of Cu, 4-7% of Sn, 0-0.005% of Al, 0.1-0.3% of Zn, 0-0.05% of Fe, 0.04-0.2% of Pb, 0.1-0.3% of Ni and 0.1-0.5% of P. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing raw materials according to the formula for blending; placing the mixed materials in a vacuum induction furnace the vacuum degree of which is less than 2Pam for smelting at the temperature of 1100-1150 DEG C for 3-5 minutes until the materials are molten; and cooling to room temperature, and then taking out molten blocks to finally obtain the high-temperature resistant sealing material. The sealing material obtained by the method of the invention has very high sealing tightness as well as good chemical stability on the oxygen permeable ceramic membrane.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Full-carbon fiber composite material reflecting mirror substrate and preparation method thereof
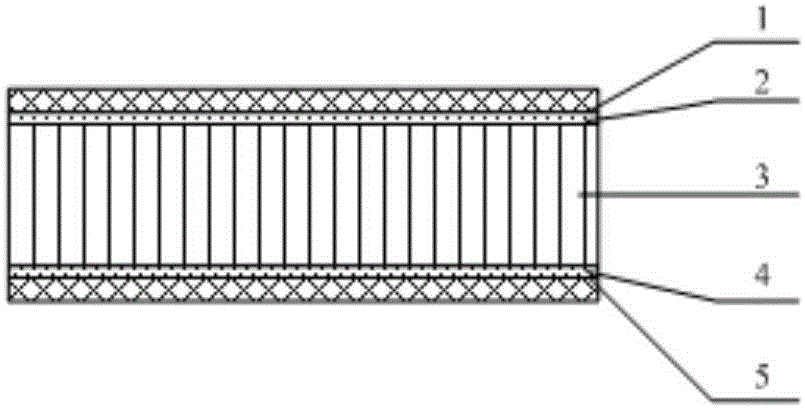
ActiveCN106739192AWell matched thermal expansionDesignableLaminationLamination apparatusHoneycombThermal expansion
The invention discloses a full-carbon fiber composite material reflecting mirror substrate and a preparation method thereof. The full-carbon fiber composite material reflecting mirror substrate comprises a first panel, a first adhesive film, a honeycomb core, a second adhesive film and a second panel, wherein the first panel is adhered to one side of the first adhesive film; the second panel is adhered to one side of the second adhesive film; and the other side of the first adhesive film and the other side of the second adhesive film are adhered to two sides of the honeycomb core. By designing the first panel, the honeycomb core and the second panel, properties of a carbon fiber composite material are effectively utilized and the problems of a traditional reflecting mirror that the weight is great, the coefficient of thermal expansion is high and the thermal performance is not matched are solved; and layering angles and sequences of the honeycomb core are designed so that the specific modulus of the reflecting mirror is improved and the defect that the honeycomb vertical performances of the traditional reflecting mirror are poor is overcome.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE HEZHONG TECH DEV +1
OLED display device and packaging technology thereof
InactiveCN105336878AMaximizeWell matched thermal expansionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolten stateGlass cover
The invention discloses an OLED display device and a packaging technology thereof. The technology concretely comprises the steps that a packaging glass cover plate and a substrate are cut, and glass material is heated to the molten state of glass water for standby application; the packaging glass cover plate is arranged on the substrate; and glass water is coated on the end surface, which is contacted with the substrate, of the packaging glass cover plate and then naturally cooled to room temperature so that the preparation process is completed. The size of the packaging glass cover plate is less than that of the substrate so that a circle of bare peripheral part of the substrate is formed outside the external edge of the packaging glass cover plate, and glass water is coated on the bare peripheral part of the substrate. According to the packaging technology of the OLED display device, packaging glass is processed in advance so that maximization of a display region can be realized and packaging speed can also be enhanced.
Owner:北京维信诺光电技术有限公司
Wide-temperature-range large-suction pushing-pulling electromagnet and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105761876ASmooth slidingSmall motion sensitivityMagnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufacturePush pullEngineering
The invention discloses a wide-temperature-range large-suction pushing-pulling electromagnet and a manufacturing method thereof. The electromagnet comprises a shell, a rear sealing cover, a movable iron core, a winding framework, a coil and an electric connector socket, the winding framework is positioned in a first groove in the shell and fixedly connected with the shell through the rear sealing cover for sealing, and the coil is wound in a winding groove of the winding framework and enables two poles of the coil to penetrate the shell to be electrically connected with the electric connector socket. One end of the movable iron core is positioned in a magnetic core hole of the winding framework and connected with the rear sealing cover through a resetting spring while the other end of the same penetrates a first through hole in the shell and extends to the outer side of the shell, the shell, the rear sealing cover and the movable iron core are made of electromagnetic pure iron, and the winding framework is made of aluminum bronze. The electromagnet has the advantages of simple structure, small size, large suction and flexibility, and the electromagnet can work stably in an environment with a wide temperature range and rain and other environments. The manufacturing method has the advantages of simple process, convenience in assembly and high working efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACE LAUNCH TECH +1
Vehicle body skirt plate structure for rail traffic vehicle and shaping method thereof
ActiveCN109263156AImprove fatigue resistanceReduce weightSynthetic resin layered productsPaper/cardboard layered productsHoneycombEngineering
The invention provides a vehicle body skirt plate structure for a rail traffic vehicle and a shaping method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of composite material structure shaping. The skirt plate structure comprises an outer panel, a force bearing framework, an inner panel and honeycomb cores, wherein the force bearing framework comprises an upper end frame, a lower end frame and reinforcing strips arranged between the upper end frame and the lower end frame; the force bearing framework is made of a material of a structure coating a foam inner core by a fiber enhanced resin-basedcomposite material; the outer panel and the inner panel are made of fiber enhanced resin-based composite materials; the outer panel, the force bearing framework and the inner panel are sequentially overlapped and are fixedly connected; the force bearing framework separates a sandwich layer between the outer panel and the inner panel into a plurality of regions; the honeycomb cores are filled in the plurality of regions. The skirt plate structure has the characteristics of good rigidity, impact resistance, fatigue resistance and the like; meanwhile, the weight of the whole skirt plate can be reduced by about 30 percent.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH +2
Solid oxide electrolysis cell cathode material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104313632AEfficient removalEliminate SrMoO
<sub>3</sub>
MiscellaneousElectrodesElectrolysisChemical composition
The invention provides a solid oxide electrolysis cell cathode material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) providing gel; (2) heating the gel to be combusted, thereby obtaining a combustion product; (3) grinding the combustion product, thereby obtaining combustion powder; (4) pre-sintering the combustion powder, thereby obtaining pre-sintered powder; and (5) calcining the pre-sintered powder, thereby obtaining the solid oxide electrolysis cell cathode material. According to the method, the solid oxide electrolysis cell cathode material with the chemical composition of Sr2Fe(1-x)MxO6-delta can be rapidly and effectively prepared, and due to the two-section calcining method, the Sr2MoO3 mixed phase can be effectively eliminated, a single perovskite phase product is obtained, and the obtained product is small in particle size and high in electrical conductivity. In addition, the thermal expansion coefficient of the obtained solid oxide electrolysis cell cathode material is close to LSGM and is well matched with thermal expansion of an electrolyte material with excellent performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Complex protective coating of sink roll used for hot dip coating and preparation method
ActiveCN107523780AWell matched thermal expansionEasy to operateHot-dipping/immersion processesMolten spray coatingThermal expansionOxygen
The invention discloses a complex protective coating of a sink roll used for hot dip coating and a preparation method. The complex protective coating comprises a bottom layer, a transition layer and a working layer; the bottom layer is a CoCrW coating, the transition layer is a coating of a mixture formed by CaO-SiO2 and CoCrW according to a proportion, and the working layer is a CaO-SiO2 coating; and a thermal expansivity relation among the coatings and a thermal expansivity relation among the coatings and a roll body are set. Coating is performed on the bottom layer by means of high velocity oxygen-fuel equipment, coating is performed on the transition layer and the working layer by means of plasma spraying equipment, corresponding technological parameters are set in the coating forming processes, and accordingly the complex protective coating on the surface of the sink roll is obtained. According to the complex protective coating provided by the invention, through design on the coating structure, good thermal expansion matching between the complex protective coating and base metal of the roll is achieved, and the purpose that the complex protective coating can be applied to practical production stably in a long term is achieved; and the preparation method is easy to operate, and the complex protective coating on the surface of the roll can be prepared and obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOSTEEL IND TECHNOLOGICAL SERVICE
Hard alloy surface treatment method and application
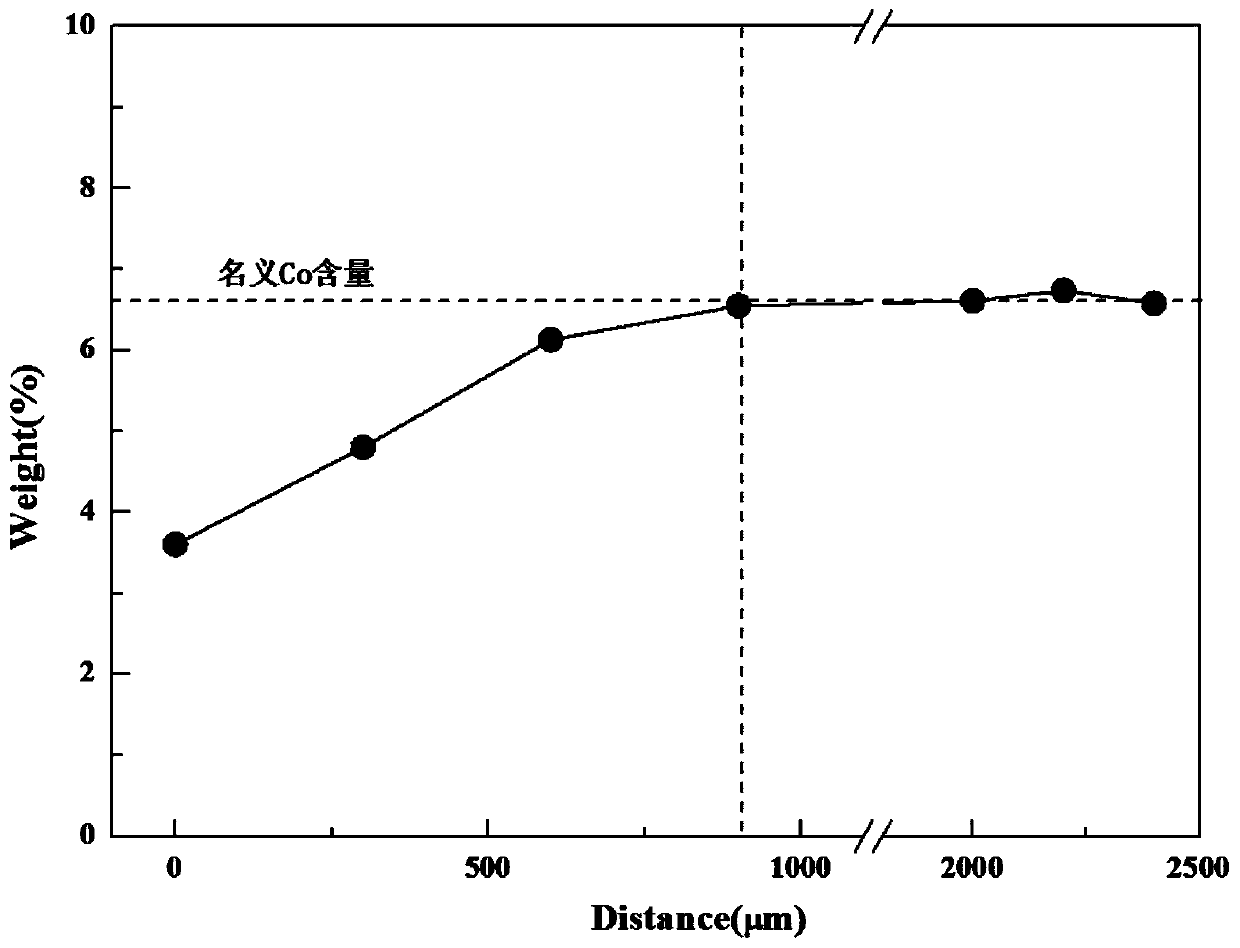
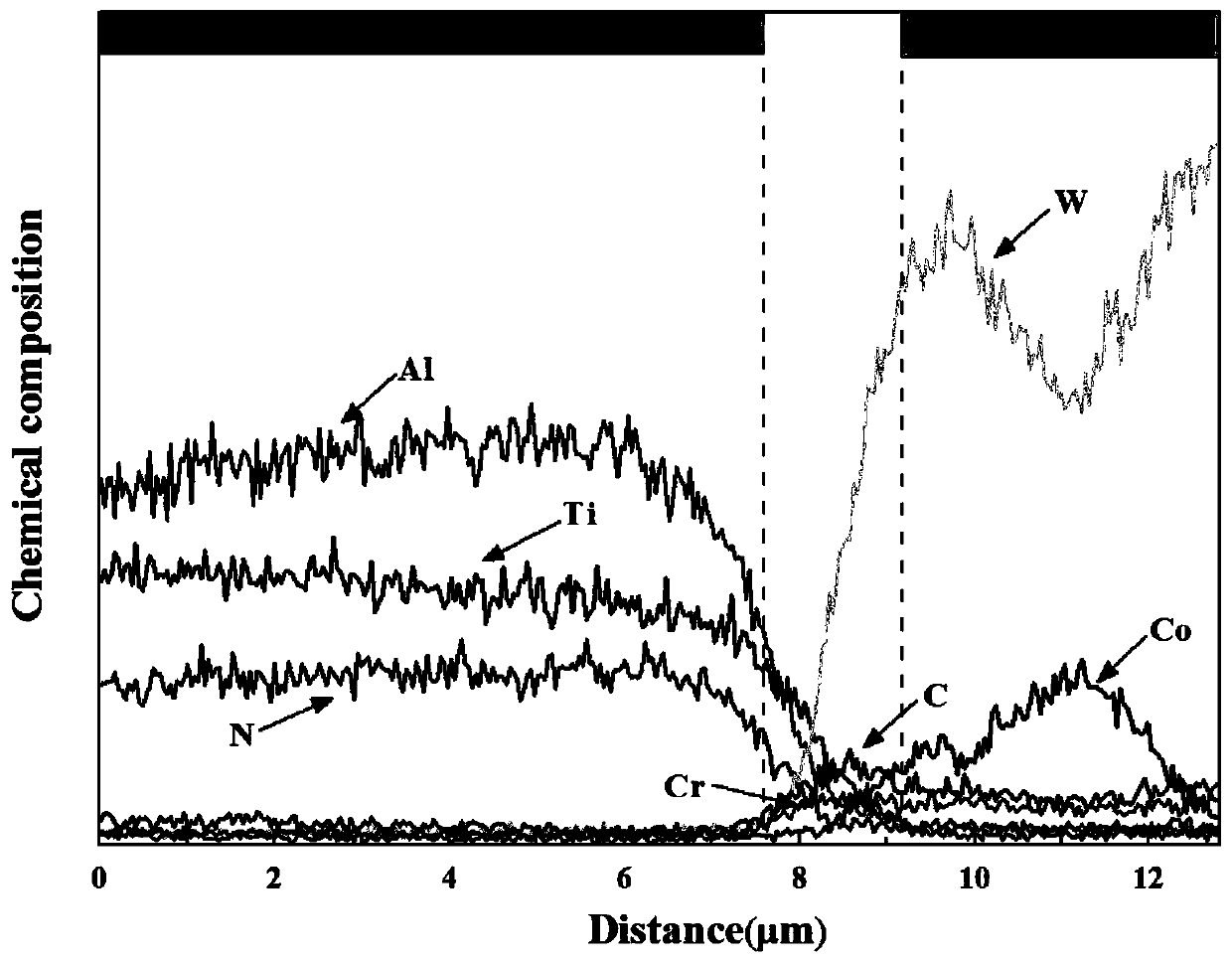
InactiveCN110343993AImproved thermal expansion matchingImprove mechanical propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAlloy surfaceCoating
The invention belongs to the technical field of hard alloy materials, and in particular relates to a hard alloy surface treatment method and an application. According to the hard alloy surface treatment method provided by the invention, as surface carburizing treatment or surface nitriding treatment is carried out on a hard alloy, the obtained hard alloy has a surface Co poor layer and can inhibitdiffusion of Co in the hard alloy to a coating effectively. The thermal expansion matching property of the coating and the hard alloy is improved, so that the mechanical property of the coating at ahigh temperature is improved. The service performance of the coating is improved obviously, and the service life of an AlTiN coating is prolonged. A product is high in mechanical property, good in wear resistance and excellent in cutting performance at a high temperature.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
RHU shell with thermal expansion matching performance
InactiveCN105792562AAvoid destructionSolve the problem of poor thermal matchingCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsThermal expansionEngineering
The invention relates to a RHU shell with a thermal expansion matching performance and belongs to the technical field of isotope heat sources for space. The RHU shell with the thermal expansion matching performance is characterized in that a gap is arranged at the side face of the RHU shell with the thermal expansion matching performance, and the RHU shell releases stress through the gap when the RHU shell is heated to expand; a convex lug is arranged at the position of the gap and is fastened by a screw; a butterfly spring is added between the screw and the convex lug; and retraction of the gap is realized through deformation of the butterfly spring. The RHU shell with the thermal expansion matching performance has the advantages of simple structure, operation convenience, good safety and good reliability, steady performances, a capability of releasing thermal stress efficiently, good RHU shell thermal expansion matching performance and the like.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Low temperature solid oxide fuel cell and its preparation method
ActiveCN103219525BSimple processEasy industrial scale-upCell electrodesFinal product manufactureOxide ceramicComposite film
The invention relates to a low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell and a making method thereof. The structure of the low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell comprises an anode film deposited on the inner wall of a porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta composite film, a cathode film deposited on the inner wall of the porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgXO3-delta composite film, and a compact perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta electrolyte film positioned between the anode film and the cathode film, wherein each of x, y and delta is equal to or more than 0 and equal to or lower than 0.2, and the perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta composite film is formed through a porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta substrate, the perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta and a porous perovskite structure oxide ceramic La1-xSrxGa1-yMgyO3-delta film. The invention also provides the making method of the low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fabrication process of carbon fiber concave mirror
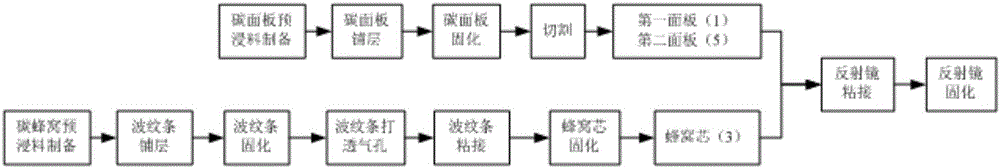
The invention relates to a preparation process of a carbon fiber concave reflector, which belongs to the technical field of optical element preparation. The invention solves the problems of high manufacturing process cost of the carbon fiber concave reflector, difficult mold processing and the like in the prior art. In the preparation process of the present invention, optical glass is firstly used as a material to prepare a concave reflector mold having the same structure as the carbon fiber concave reflector to be prepared, and then a release agent is applied on the concave reflector mold and multiple layers are spread on the release agent. layer of carbon fiber prepreg, solidify and mold the laid carbon fiber prepreg, and demould to obtain a convex carbon fiber mirror mold, and then apply a release agent on the convex carbon fiber mirror mold and lay multiple layers of carbon fiber prepreg on the release agent. Soak the cloth, solidify and mold the laid carbon fiber prepreg cloth, and demould to obtain a concave carbon fiber reflector blank; finally, carry out surface treatment on the concave carbon fiber reflector blank to obtain a carbon fiber concave reflector. The preparation process is simple and easy, the cost is low, and the prepared reflection mirror has high precision.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
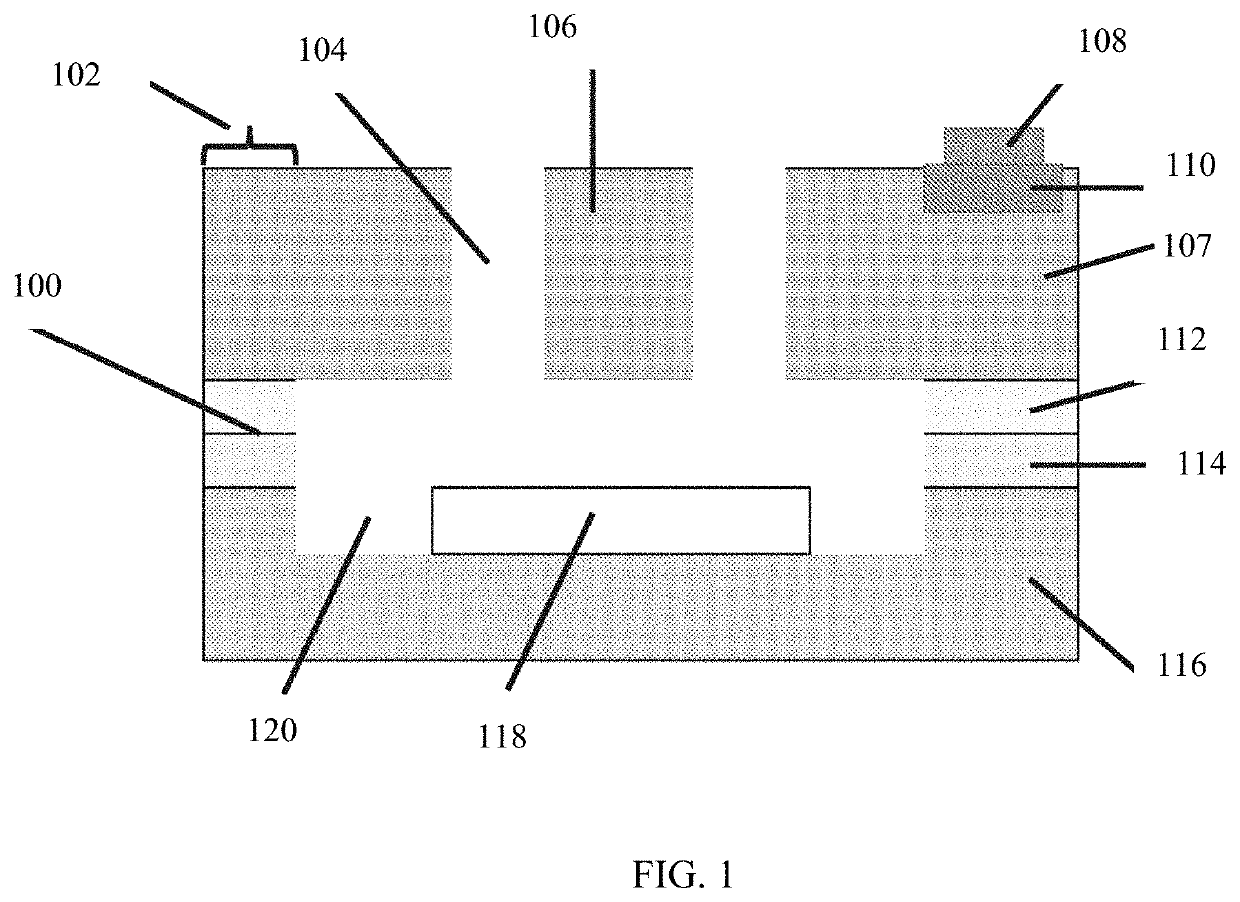
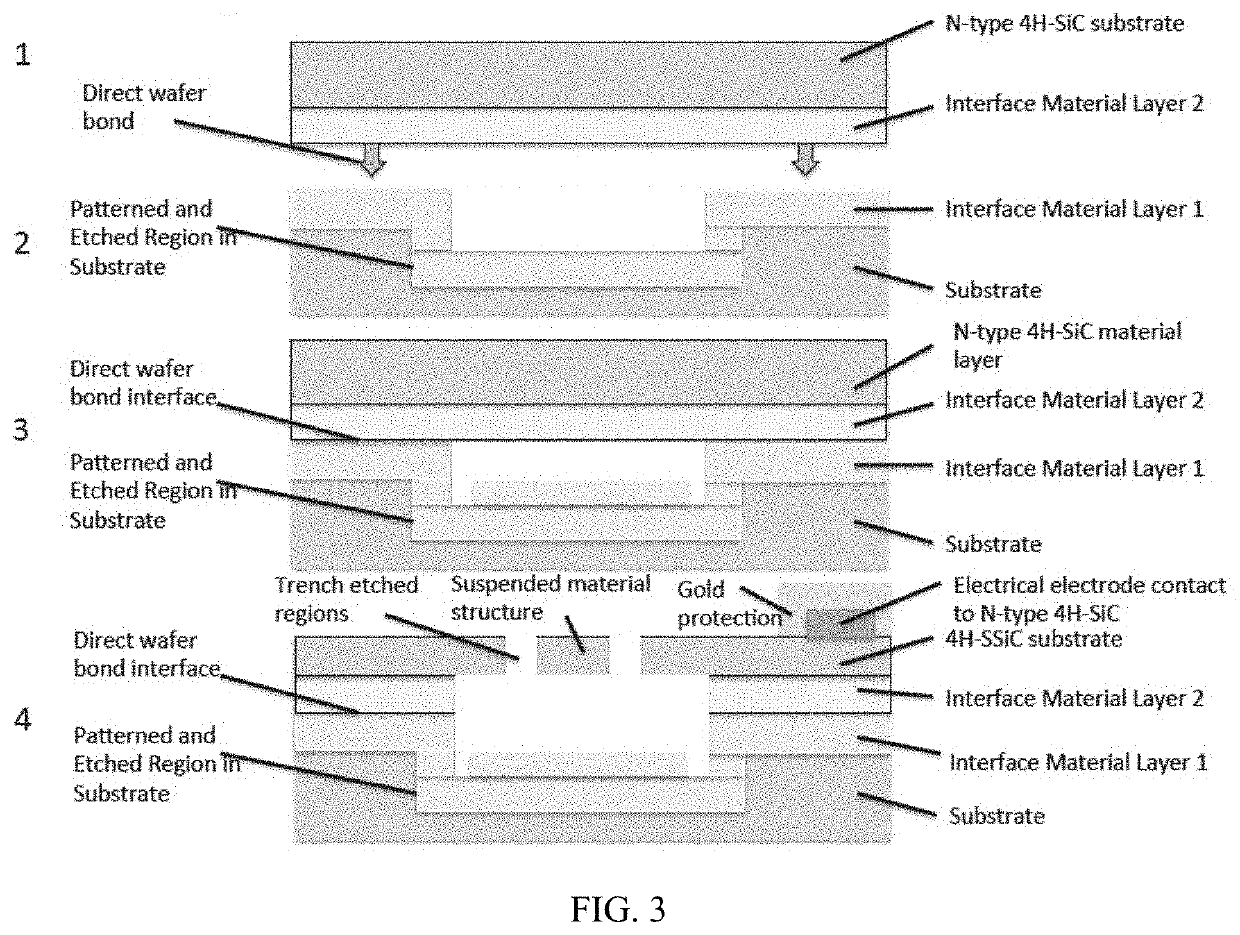
Silicon carbide structure, device, and method
ActiveUS20200407213A1Reduce capacitanceWell matched thermal expansionDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingCapacitanceThermal dilatation
A method of fabricating suspended beam silicon carbide microelectromechanical (MEMS) structure with low capacitance and good thermal expansion match. A suspended material structure is attached to an anchor material structure that is direct wafer bonded to a substrate. The anchor material structure and the suspended material structure are formed from either a hexagonal single-crystal SiC material, and the anchor material structure is bonded to the substrate while the suspended material structure does not have to be attached to the substrate. The substrate may be a semi-insulating or insulating SiC substrate. The substrate may have an etched recess region on the substrate first surface to facilitate the formation of the movable suspended material structures. The substrate may have patterned electrical electrodes on the substrate first surface, within recesses etched into the substrate.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com