Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "Achieve sintering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
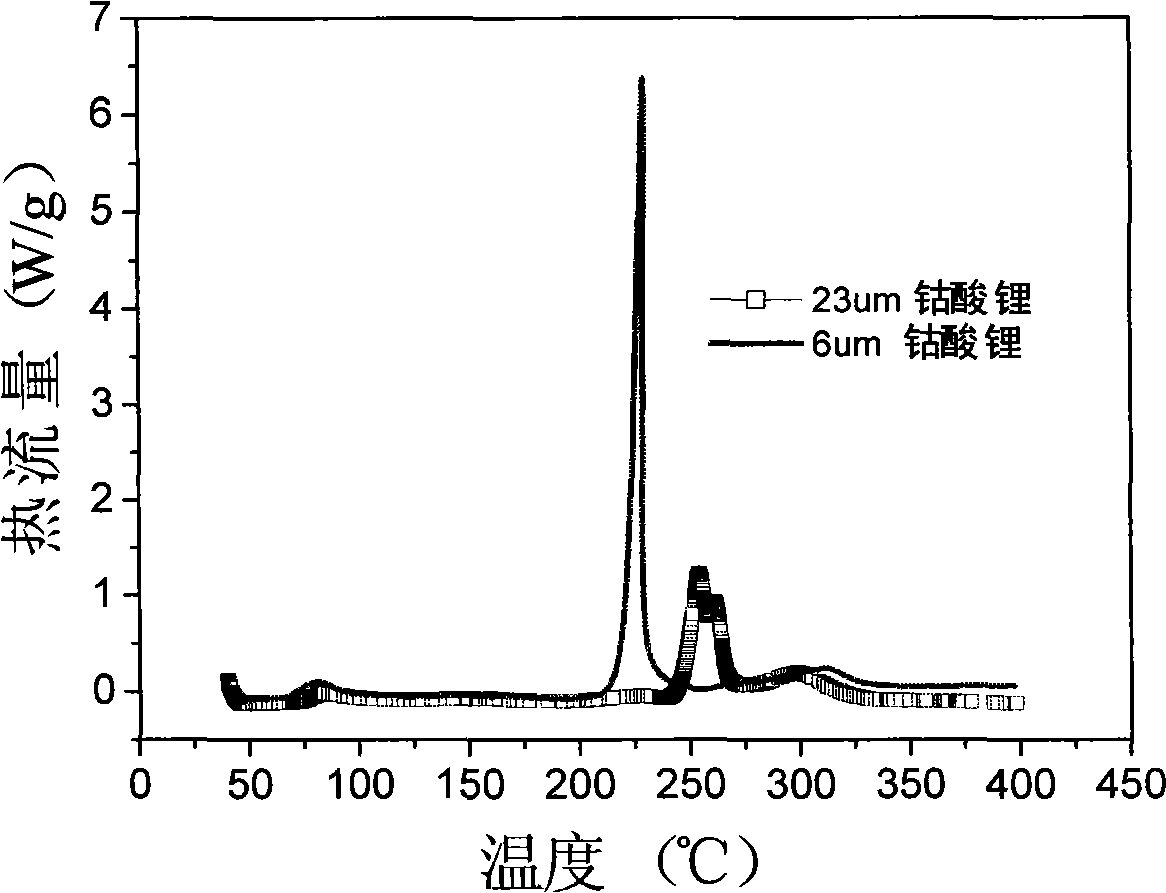
Super-size and high-density lithium cobalt oxide and method for preparing the same
ActiveCN101284681ALarge particle sizeHigh tap densityCell electrodesLithium compoundsHigh densityThermal impact
The invention relates to a high-density lithium cobalt oxide power material with a super-large grain diameter. The method comprises the steps of mixing a cobalt compound, a lithium compound or meanwhile a small amount of doping element compounds; sintering for 3 to 30 hours at the high temperature of 950 to 1,100 DEG C to form a block sintered product; crushing and grading the product to obtain the lithium cobalt oxide power material (molecular formula is LiaCo1-bMbO2), wherein, when b is not equal to 0, the middle diameter of the lithium cobalt oxide containing the doping elements is larger than or equal to 15 Mum, and the tap density is higher than or equal to 2.5g / cm<3>; when b is equal to 0, the middle diameter of the lithium cobalt oxide without the doping elements is larger than 20 Mum, and the tap density is higher than or equal to 2.6g / cm<3>. the 3.6V platform capacity rate of the material as the anode active substance for a lithium battery is higher than or equal to 75%; in the thermal impact test in a 150 DEG C thermotank, the lithium battery with the material is free from leakage and does not catch fire or explode for 60 minutes; the 1C5A specific capacity of the material in the battery is larger than or equal to 135mAh / g.
Owner:BEIJING EASPRING MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
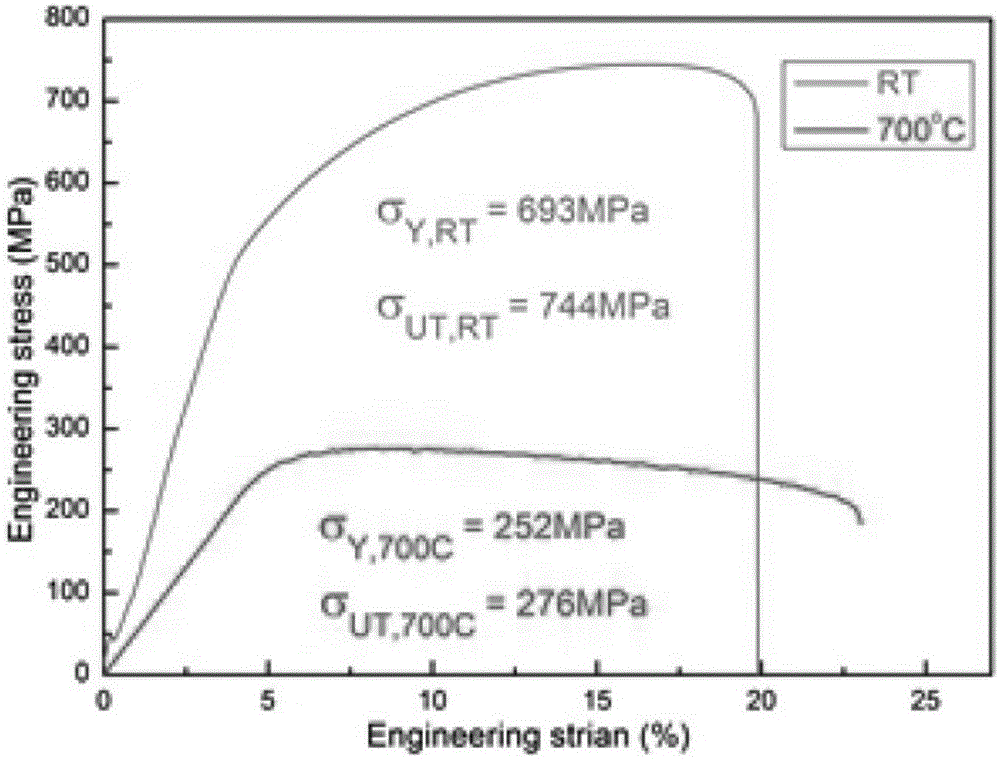
Oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite/martensitic steel and preparing method
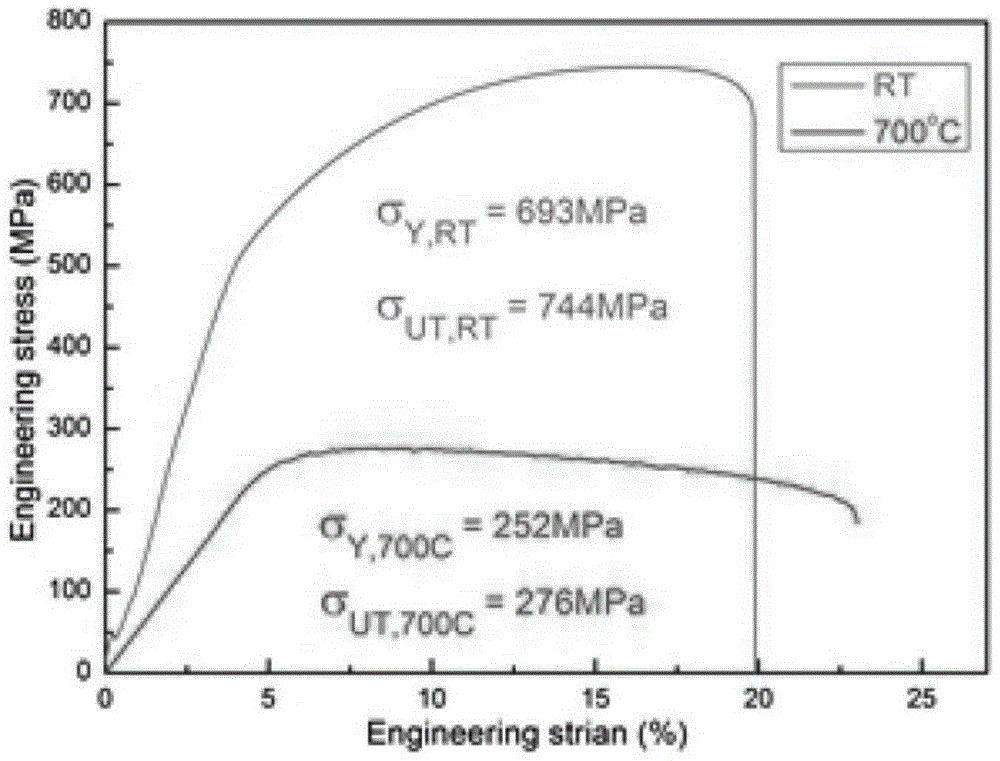
The invention relates to oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite / martensitic steel with the excellent high-temperature strength and the good oxidation resistance and a preparing method of the oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite / martensitic steel. The oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite / martensitic steel comprises 8% to 10% of Cr, 0.5% to 2% of W, 1.5% to 5.5% of Al, 0.1% to 0.4% of V, 0.1% to 0.5% of Mn, 0% to 1.0% of Zr, 0% to 1.0% of Hf and 0.25% to 0.5% of Y2O3. The content of C and the content of N are controlled to be lower than 0.1%, and at least one kind of the Hf and the Zr is contained; the oxygen content of atomized powder is controlled to be lower than 0.05 wt.%, the atomized powder with the particle size ranging from 50 meshes to 200 meshes is selected to be mechanically alloyed with Al powder, Zr powder, Hf powder and Y2O3 powder, and the size of obtained powder ranges from 90 micrometers to 200 micrometers; silicate glass is used for wrapping, compressing and molding, the pressure is started to be boosted to 120 MPa to 180 MPa at the temperature of 850 DEG C, a two-stage sintering manner in which the temperature ranging from 850 DEG C to 950 DEG C is kept for 1 hour and the temperature ranging from 1050 DEG C to 1150 DEG C is kept for 1 hour is adopted, the tensile strength of the finally-obtained ferrite / martensitic steel at the temperature of 700 DEG C ranges from 250 MPa to 320 MPa, and the ductility of the finally-obtained ferrite / martensitic steel at the temperature of 700 DEG C ranges from 18% to 32%; and the oxidation performance of the dispersion-strengthening steel is also greatly improved on the premise that the high-temperature strength and the high-temperature plasticity are guaranteed, and after 100-h oxidation is carried out at the temperature of 850 DEG C, the oxidation weight increase only ranges from 0.0327 mg / cm<3> to 0.098 mg / cm<3>.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
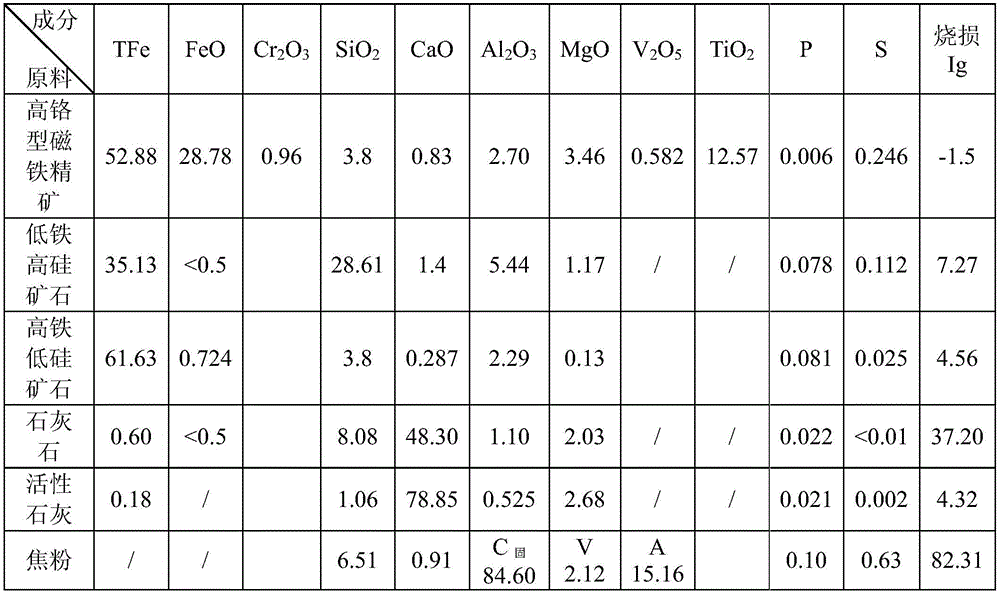
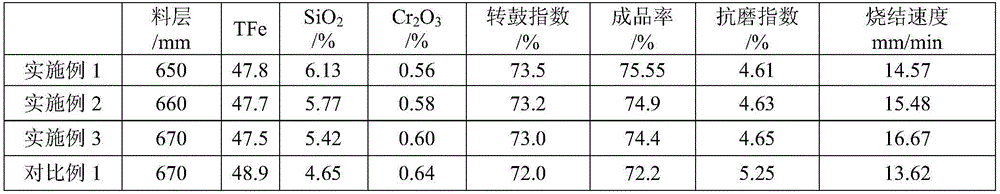
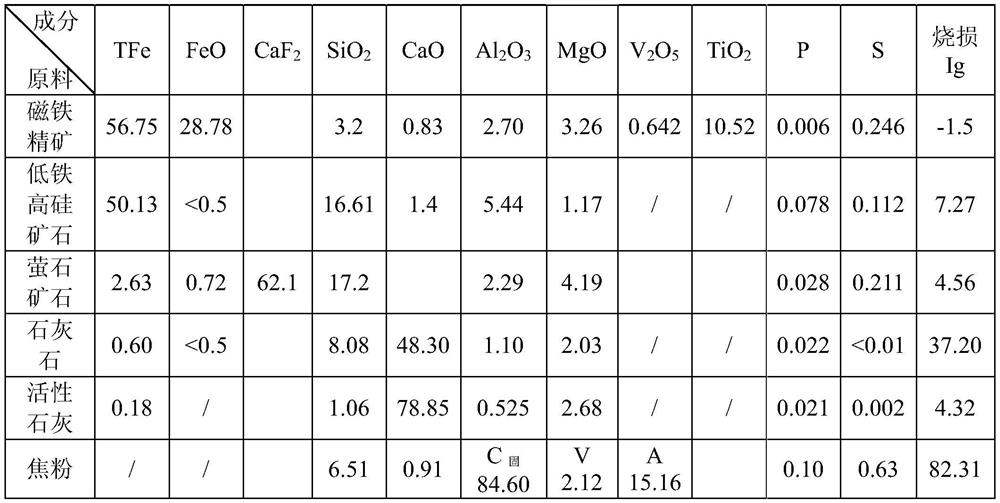
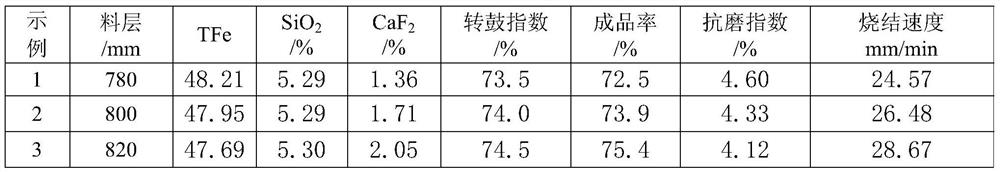
Sintering method of high-chromium type vanadium titano-magnetite
The invention discloses a sintering method of high-chromium type vanadium titano-magnetite. The sintering method comprises steps as follows: step one, components including, in parts by weight, 3-8 parts of low-iron high-silicon powder ore, 18-22 parts of high-iron low-silicon powder ore, 50-60 parts of high-chromium type vanadium titano-magnetite, 3-8 parts of limestone powder, 6-10 parts of active lime and 4.5-5 parts of coke powder are blended to form a mixture, and the alkalinity of the mixture is controlled to be 1.7-2.1; step two, water is added to the mixture, and the weight percentage of water in the mixture after the water is added is 7.2%-7.6%; step three, primary mixing and granulation as well as secondary mixing and granulation are performed, a material after secondary mixing and granulation is added to a sintering machine to be sintered, and the height of the material layer is controlled at 630-730 mm. Through reasonable control of the proportion of materials, the high-chromium type vanadium titano-magnetite can be sintered, a silicate binding phase of sintering ore can be increased, and the strength of the sintering ore is improved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste used for low-temperature sintering and interconnection and production method
ActiveCN112756841AEnsure replacementFully integratedWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMicro nanoOrganic solvent
The invention provides micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste used for low-temperature sintering and interconnection and a production method. The production method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing an organic solvent, a thickener, a dispersant, a coupling agent and a defoamer according to a certain ratio to produce an organic carrier of the micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste; and then evenly mixing silver-copper nano-alloy particles and silver microparticles which are produced through a chemical reduction method, and a certain amount of the organic carrier to obtain the micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste used for low-temperature sintering and interconnection. According to the micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste used for low-temperature sintering and interconnection and the production method, by adopting a solid solution alloy principle to dope a silver phase with copper atoms, the single-phase silver-copper alloy particles are obtained; the problem of oxidation of copper is solved, meanwhile, due to doping of the copper atoms, the atom diffusion rate is reduced, the problem of massive volume shrinkage of pure nanometer welding paste in sintering processes is solved, and meanwhile, cost reduction and yield raising are facilitated, so that the micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste used for low-temperature sintering and interconnection and the production method are suitable for mass production; and the micro-nano compound silver-copper alloy welding paste can be substituted for traditional Sn-based solder and pure nano-Ag paste in low-temperature connection of third-generation semiconductors, and has higher reliability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
LiZnTi gyromagnetic ferrite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a LiZnTi gyromagnetic ferrite material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of magnetic material preparation. The LiZnTi gyromagnetic ferrite material is composed of 98.8-99.9 wt% of main material and 0.1-1.2wt% of glass phase sintering aid. The main material is Li0.43Zn0.27Ti0.12Fe2.18O4; and the glass phase sintering aid is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 2 parts of BaO, 2 parts of Bi2O3, 2 parts of B2O3, 3 parts of Li2O and 1 part of SiO2. The method implements the sintering and preparation of the LiZnTi ferrite at low temperature (900-940 DEG C); and the obtained LiZnTi gyromagnetic ferrite material has the advantages of low sintering temperature, low ferromagnetic resonance line width and high saturation magnetization.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low melting point glass powder for barrier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102010131AMeet environmental protection requirementsAchieve sinteringMetallurgyAir tightness
The invention discloses a low melting point glass powder for a barrier and a preparation method thereof. The glass powder comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 30-50% of Bi2O3, 5-30% of B2O3, 5-30% of BaO, 5-30% of V2O5, 1-10% of P2O5, 1-10% of Na2O, 1-5% of MgO, 1-5% of SiO2 and 1-5% of Al2O3. The total percentage by weight of the Bi2O3, the V2O5 and the P2O5 is 45-75%. The total percentage by weight of the MgO, the SiO2 and the Al2O3 is 3-12%. The glass powder is prepared by the processes of weighing, mixing, founding, preforming, ball milling and sieving. The invention has the advantages of low softening temperature, no lead, excellent sealing air tightness and color diversification.
Owner:郑庆云
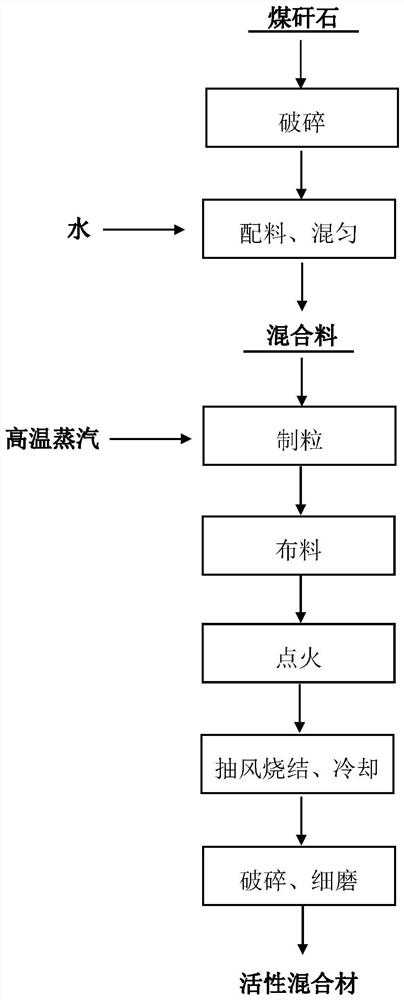
Coal gangue fuel-free self-heating type ultrahigh material bed decarburization process
ActiveCN113526883AIncrease temperaturePromote decarbonization reactionSolid waste managementCement productionCoal gangueDecarburization
The invention discloses a coal gangue fuel-free self-heating type ultrahigh material bed decarburization process, which utilizes the automatic heat storage effect in the sintering process of an ultrahigh material bed (1000-2000mm), the temperature of a sintering material bed is increased along with the increase of the height of the material bed, and the heat is increased, so that the temperature of a combustion zone is favorably increased, the decarburization reaction of coal gangue is promoted, the mineralization reaction of minerals such as silicon, aluminum and the like in the coal gangue is accelerated, a large amount of heat is converted into chemical energy to be stored in minerals, and the product activity is improved. By utilizing the automatic heat storage principle of an ultrahigh material bed and combining fixed carbon contained in the coal gangue, the sintering of the coal gangue can be realized under the condition of not additionally adding fuel, so that the energy is saved, the energy consumption is reduced, the environmental protection is facilitated, and the cost is reduced; and meanwhile, the decarburization reaction is facilitated due to low solid fuel ratio and higher oxygen level of the material bed, and a high-quality active mixed material product can be obtained.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Sintering method of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate
The invention relates to the field of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate preparation, and in particular to a sintering method of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate for effectively improvingthe quality of sintered ore products. The method comprises the following steps that by weight, 5-10 parts of medium-grade common fine ore, 1-5 parts of fluorite ore powder, 65-75 parts of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, 3-8 parts of limestone powder, 6-10 parts of active lime and 4-5 parts of coke powder are prepared to form a mixture, and the alkalinity of the mixture is controlled to be1.8-2.4; water is added into the mixture, and the weight percentage of water in the water-added mixture is controlled to be 7.2%-7.6%; and first-time mixing granulation and second-time mixing granulation is carried out, the materials subjected to the second-time mixing granulation are added into a sintering machine for sintering, and finally the finished product is obtained. According to the sintering method, the ratio of the materials is controlled, the sintering of the vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate is realized, the binding phase of sintered ore is increased, the liquid phase generation amount in the sintering process is improved, and the strength of vanadium-titanium sintered ore is improved. The method is particularly suitable for the sintering process of the vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Low-temperature normal-pressure sintering preparation method of mass-producible high-purity SiC ceramic coating
ActiveCN111517797AEffective control of purityLow purityNuclear energy generationCeramic coatingOxidation resistant
The invention relates to a low-temperature normal-pressure sintering preparation method of a mass-producible high-purity SiC ceramic coating, which is applied to the fields needing high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance and other protective properties in the form of coatings. The preparation method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps: preparing high-purity SiC slurry, carrying out brush-coating, and carrying out low-temperature pressureless sintering. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the purity and the sintering temperature of the SiC coating are controlled by regulating and controlling the formula of the high-purity SiC slurry, so that normal-pressure sintering and industrial preparation and productionof the high-purity SiC coating at the temperature of 1750-1800 DEG C are realized. The high-purity SiC slurry formula and the brush-coating and sintering processes are flexible and controllable, thecoating and the matrix are well combined, obvious peeling and cracks are avoided, the technological process is easy to operate and short in consumed time, and the cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
High-purity aluminum oxide ceramic substrate and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a high-purity aluminum oxide ceramic substrate and a preparation process thereof. The ceramic substrate adopts specially purified superfine alpha-aluminum oxide powder as a main phase material, magnesium aluminate spinel powder as a fluxing agent and lanthanum oxide and yttrium oxide as additives; the requirements of the alumina powder are as follows: the purity of Al2O3 is greater than or equal to 99.9%, the content of SiO2 is less than 0.05%, the content of Fe2O3 is less than 0.02%, and the content of Na2O is less than 0.02%; the conversion rate of alpha-Al2O3 is greater than or equal to 96%; and the conductivity is less than 100s / cm. and 2, the volume density of the ceramic substrate prepared by the preparation process of the high-purity aluminum oxide ceramic substrate is greater than or equal to 3.92 g / cm < 3 >, the volume resistivity is greater than or equal to 10145 omega.cm, the heat conductivity is greater than 2930W / (m.K), the dielectric constant is 9-10 (1MHz, 25 DEG C), and the bending strength is greater than or equal to 450MPa. The preparation process adopts a tape casting process and a normal-pressure sintering method.
Owner:SINOCERAM TECH (ZHENGZHOU) CO LTD
Method for preparing porous ceramic by coating beta-Si3N4 granule with oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous ceramic by coating beta-Si3N4 particles with a composite oxide CaO-SiO2-B2O3, which is a porous body preparation technology comprising the following steps: the beta-Si3N4 particles are put into a CaO-SiO2-B2O3 sol made from tetraethoxysilane, boric acid, calcium nitrate, citric acid, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water, and the vacuum filtration method is adopted to form the porous body by self porous structure of the columnar beta-Si3N4 crystalline particles. The surface of the sintered beta-Si3N4 particles is coated with a modification layer of CaO-SiO2-B2O3 oxide interface, and the modification layer effectively connects the beta-Si3N4 particles and prevents the beta-Si3N4 particles from oxidation at high temperature. The porous ceramic prepared by the method can be used as a radome and a catalyst carrier material.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Environmentally-friendly lead-free low-temperature glass powder used for barrier of PDP (plasma display panel), and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102190444AMeet environmental protection requirementsAchieve sinteringSofteningMaterials science
The invention discloses an environmentally-friendly lead-free glass powder used for a barrier of a PDP (plasma display panel), and a preparation method thereof. The glass powder is composed of the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 30-50% Bi2O3, 5-30% of B2O3, 5-30% of MgO, 5-30% of V2O5, 1-10% of P2O5, 1-10% of K2O, 1-5% CaO, 1-5% of SiO2 and 1-5% of Al2O3, wherein the total percentage of Bi2O3, V2O5 and P2O5 is 45-75% by weight and the total percentage of CaO, SiO2 and Al2O3 is 3-12% by weight. The preparation method comprises the following processes: weighing, mixing raw materials, melting, tabletting, ball-milling and screening. The glass powder has the advantages of low softening temperature, no lead, high sealing airtightness and diverse colors.
Owner:李胜春
Room temperature sintering method of nano copper conductive ink
The invention discloses a room temperature sintering method of the nano copper conductive ink and belongs to the technical field of the conductive ink. The method comprises steps that a. the ink is printed or coated on a flexible film substrate with a printing machine or a film coating machine; b. the film of the step a is dipped in alcohol solution of 0.1-100 v% organic acid for 0.1-30 min, and washed with solvent for 2-4 times and blown dry; c. the steps a and b are repeated for repeated printing or coating to achieve desired thickness of the printed layer; and d. the film in the step c is dipped in a certain concentration of reducing agent solution for 0.05-60 min, and then washed with the water for 2-4 times and blown dry. The method is advantaged in that the method is suitable for thecheap nano-copper ink, sintering in the air at the room temperature is achieved, the prepared copper film has low resistivity and can be utilized on a variety of heat-sensitive and flexible substrates, and the process is simple and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Premixing type pressure-adjusting secondary fuel gas nozzle and method
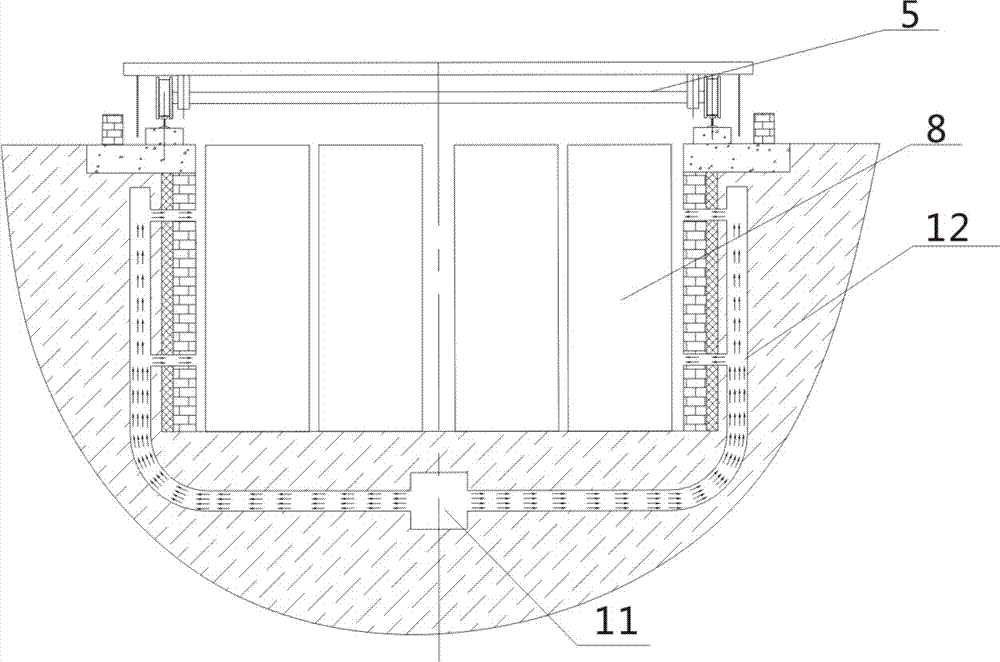
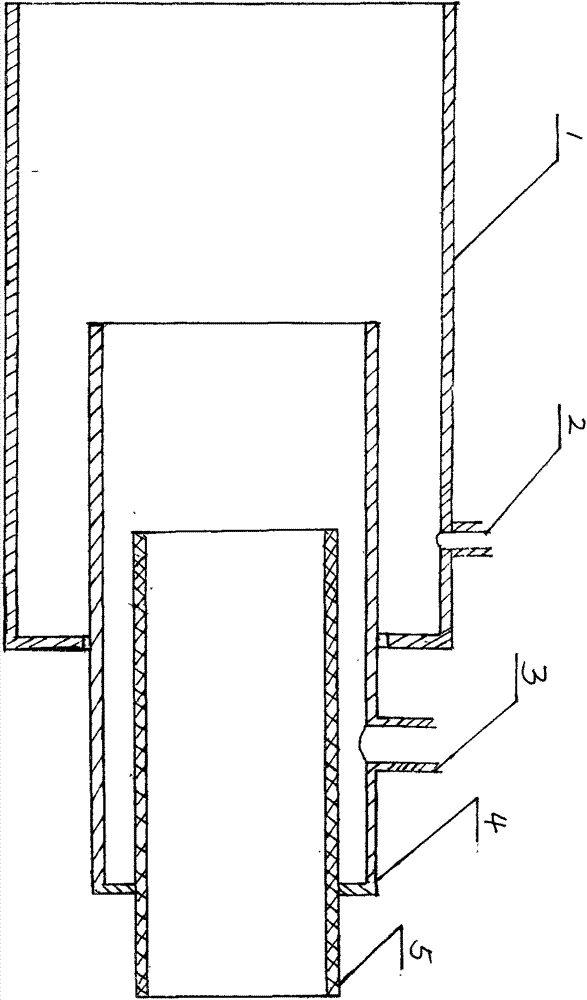
The invention relates to a premixing type pressure-adjusting secondary fuel gas nozzle and a method. The remixing type pressure-adjusting secondary fuel gas nozzle is provided with a fuel gas pipe (5) which is fixedly connected with a mixing pipe (6). The mixing pipe (6) sleeves the fuel gas pipe (5). A secondary air port (3) is formed in the mixing pipe (6). A pressure gauge interface (4) is disposed on the secondary air port (3). The mixing pipe (6) is fixedly connected with an air inlet pipe (1). The air inlet pipe (1) sleeves the air inlet pipe (1) and is provided with a main air port (2).
Owner:梁燕龙
Novel rotary kiln
InactiveCN104501589AReasonable structural designImprove utilization efficiencyFurnace typesWaste heat treatmentBrickEngineering
The invention discloses a novel rotary kiln which comprises a kiln body and a kiln car. The kiln body is of an annular structure integrally, the kiln car is provided with a drying section, a preheating section, a high-temperature calcining section and a cooling section, the kiln body integrally falls into the ground to form a trench-type structure, an air suction passage is formed on two side faces or at the bottom of the cooling section of the kiln body, a passage is formed below the bottom of the kiln body to form a main flue, an air feeding flue is formed on two side faces or at the bottom of each of the cooling section and the drying section, and the main flue is communicated with the air suction flue and the air feeding flues. Waste heat of finished brick products and hot air are extracted from the side faces of the cooling section of the trench-type rotary kiln to enter the main flue at the bottom, and are divided to enter the air feeding passages after reaching the drying section, and the air feeding flues feed hot air from the side face of the kiln body into the drying section in the kiln body to dry wet blank bricks.
Owner:宜宾恒旭窑炉科技开发有限公司
Oxide dispersion strengthened ferrite/martensitic steel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite / martensitic steel with the excellent high-temperature strength and the good oxidation resistance and a preparing method of the oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite / martensitic steel. The oxide-dispersion-strengthening ferrite / martensitic steel comprises 8% to 10% of Cr, 0.5% to 2% of W, 1.5% to 5.5% of Al, 0.1% to 0.4% of V, 0.1% to 0.5% of Mn, 0% to 1.0% of Zr, 0% to 1.0% of Hf and 0.25% to 0.5% of Y2O3. The content of C and the content of N are controlled to be lower than 0.1%, and at least one kind of the Hf and the Zr is contained; the oxygen content of atomized powder is controlled to be lower than 0.05 wt.%, the atomized powder with the particle size ranging from 50 meshes to 200 meshes is selected to be mechanically alloyed with Al powder, Zr powder, Hf powder and Y2O3 powder, and the size of obtained powder ranges from 90 micrometers to 200 micrometers; silicate glass is used for wrapping, compressing and molding, the pressure is started to be boosted to 120 MPa to 180 MPa at the temperature of 850 DEG C, a two-stage sintering manner in which the temperature ranging from 850 DEG C to 950 DEG C is kept for 1 hour and the temperature ranging from 1050 DEG C to 1150 DEG C is kept for 1 hour is adopted, the tensile strength of the finally-obtained ferrite / martensitic steel at the temperature of 700 DEG C ranges from 250 MPa to 320 MPa, and the ductility of the finally-obtained ferrite / martensitic steel at the temperature of 700 DEG C ranges from 18% to 32%; and the oxidation performance of the dispersion-strengthening steel is also greatly improved on the premise that the high-temperature strength and the high-temperature plasticity are guaranteed, and after 100-h oxidation is carried out at the temperature of 850 DEG C, the oxidation weight increase only ranges from 0.0327 mg / cm<3> to 0.098 mg / cm<3>.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Preparation method of indium tin oxide grinding balls
InactiveCN111807832AHigh densityImprove grinding efficiencyOther chemical processesPress rollersIndiumHigh density
The invention discloses a preparation method of indium tin oxide grinding balls. The preparation method comprises the steps that adding indium oxide powder and tin oxide powder into water to be mixed,ground and granulated to obtain a granulation powder, wherein the total weight of the indium oxide powder and the tin oxide powder is 90 to 97%; then putting the granulation powder into a mold, carrying out isostatic cool pressing treatment to obtain a green body, and crushing and screening the green body to obtain a seed crystal; taking the seed crystal as the core of the ball blank, and rollingand forming the granulation powder and the seed crystal to obtain the ball blank; carrying out wax sealing on the surface of the ball blank, and then carrying out isostatic cool pressing treatment onthe ball blank; and degreasing the ball blank subjected to isostatic cool pressing, and sintering the degreased ball blank to obtain the indium tin oxide grinding balls. The indium tin oxide grindingball with high density and small crystal grains is obtained by a method of matching roll forming, isostatic cool pressing and sintering, the ITO target material prepared by the grinding balls has thedensity of more than 7.12 g / cm < 3 > and the purity of more than 99.99%, and the grinding requirement of ITO target material preparation can be met.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Preparation method of high-strength silicon carbide porous ceramic
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-strength silicon carbide porous ceramic. Raw materials are composed of 98%-99% of mixture of alpha-silicon carbide powder and beta-silicon carbide powder, 0.1%-1.0% of aluminum diboride and 0.5%-1% of polycarbosilane, by weight percent. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding the raw materials into an organic dispersing solvent, ball-milling, mixing and drying; 2) dry-pressing and forming the obtained silicon carbide compound powder under the 45-55 MPa; and 3) placing a silicon carbide blank into a vacuum pressure-less sintering furnace, for sintering at two steps, thereby obtaining the high-strength silicon carbide porous ceramic. The preparation method is simple and the prepared silicon carbide porous ceramic is characterized by high mechanical strength, suitable porosity, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Aluminum-silicon alloy binding agent diamond abrasive disc and manufacture method thereof
The invention discloses an aluminum-silicon alloy binding agent diamond abrasive disc and a manufacture method thereof. An aluminum-silicon alloy binding agent comprises, by weight, 0%-30% of Si, 0.25%-6% of Ti, 0%-0.5% of Mg, 0%-5% of Cu, 0%-0.5% of Ga, 0%-0.5% of Ce, 0%-0.5% of Sr, 0%-0.5% of of Na and the balance Al and inevitable impurities. The aluminum-silicon alloy binding agent and diamondpowder are sufficiently mixed; after the mixture is subjected to cold press molding, vacuum hot pressing sintering is conducted under a certain sintering process, and aluminum-silicon alloy based diamond abrasive disc section blocks are obtained; and then the diamond abrasive disc section blocks obtained through sintering are installed on and connected to an abrasive disc base body, and the diamond abrasive disc is obtained. By means of the aluminum-silicon binding agent adopted for the aluminum-silicon alloy binding agent diamond abrasive disc, low-temperature sintering can be achieved, anddiamond thermal damage is reduced; and meanwhile by introducing the active Ti element, the holding capacity of diamond abrasive particles can be remarkably increased, the wear resistance of the abrasive disc is improved through the aluminum-silicon binding agent and the Ti element together, and the service life of the diamond abrasive disc is prolonged.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Low-loss LiZnTiMn gyromagnetic ferrite material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113845359AAchieve sinteringAchieve preparationInorganic material magnetismFerrite (magnet)Ceramic materials
The invention provides a low-loss LiZnTiMn gyromagnetic ferrite material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials. The gyromagnetic ferrite material comprises a main material and a composite sintering aid, the weight percentage of the main material is 99.0%-99.5%, and the weight percentage of the composite sintering aid is 0.5%-1.0%; the main material is Li < 0.42 > Zn < 0.27 > Ti < 0.11 > Mn < 0.1 > Fe < 2.1 > O < 4 >, the composite sintering aid is composed of Bi2O3 and Nb2O5, and the mass ratio of Bi2O3 to Nb2O5 is 5: (1-5). The low-temperature sintering of LiZnTiMn is realized by optimizing the sintering process and adding the composite sintering aid, the LiZnTiMn ferrite material with low loss is obtained, the coercive force of the material is reduced, and the performance of the material is optimized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Premixed adjustable gas burner and method
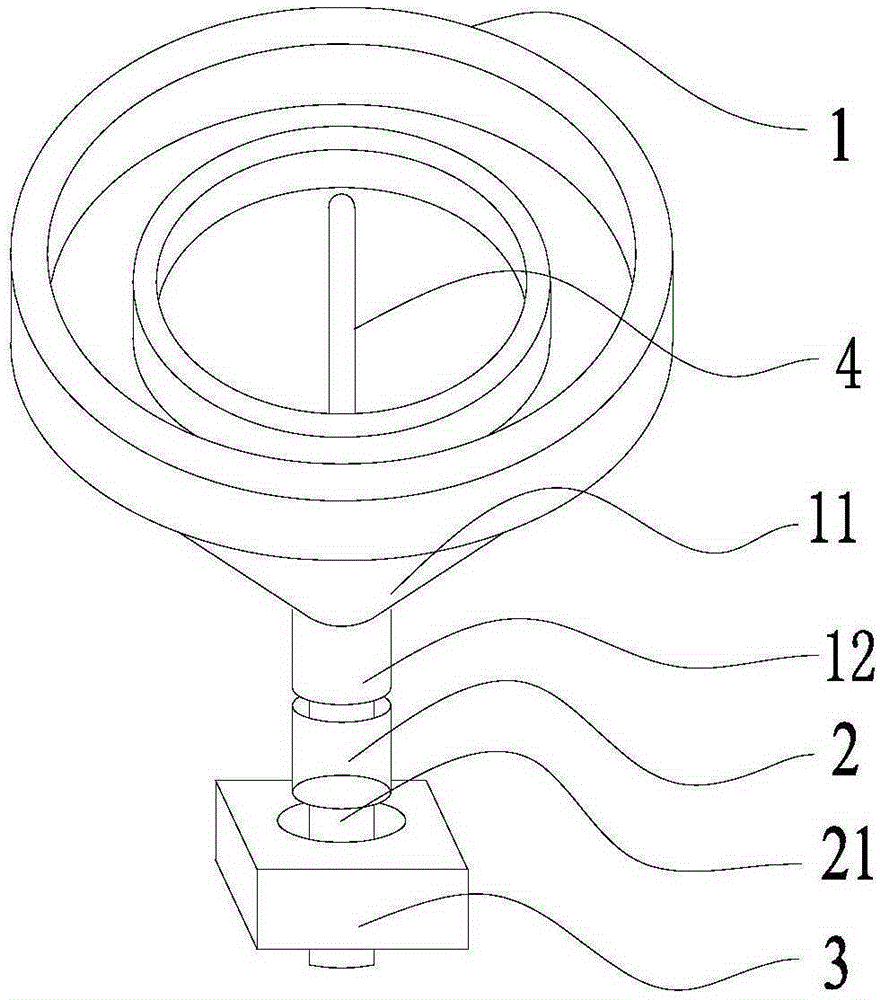
InactiveCN104515133ACorrect temperature constantReduce dosageFurnace typesGaseous fuel burnerProcess engineeringGas burner
The invention discloses a premixed adjustable gas burner and a method. The premixed adjustable gas burner comprises a gas pipe (5), wherein the gas pipe (5) is fixedly connected with a mixing pipe (4), the mixing pipe (4) sleeves the gas pipe (5), a secondary air inlet (3) is formed in the mixing pipe (4), a certain gap is reserved between the mixing pipe (4) and an air pipe (1), the air pipe (1) sleeves the mixing pipe (4), and a main air inlet (2) is formed in the air pipe (1).
Owner:梁燕龙
Low-cost batch preparation method and application of noble metal electrode array
InactiveCN111948263AIncrease profitThe preparation device is simpleMaterial electrochemical variablesInorganic saltsMetallic electrode
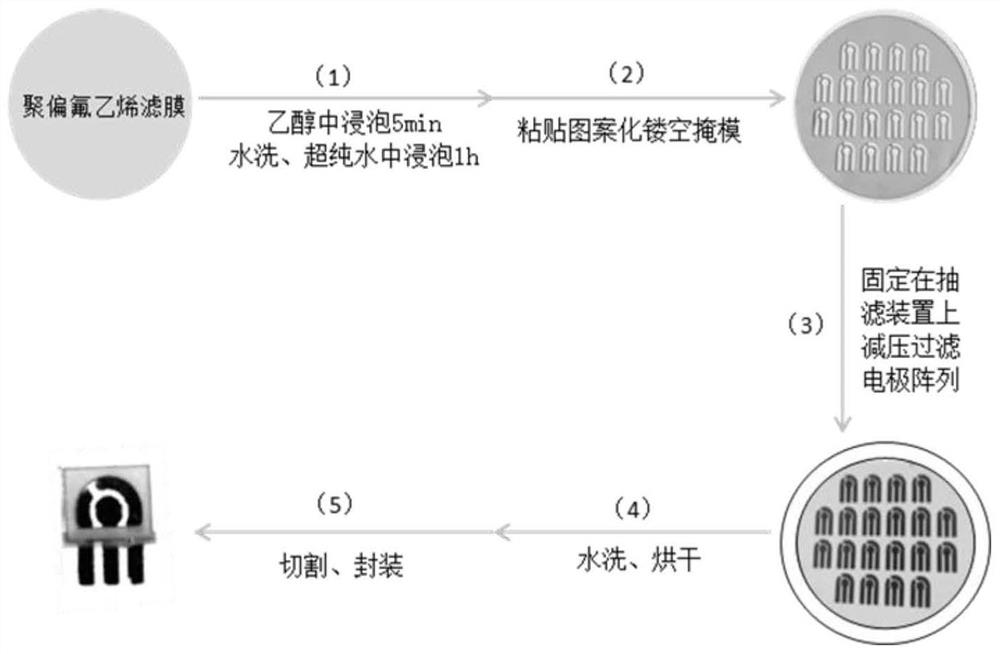
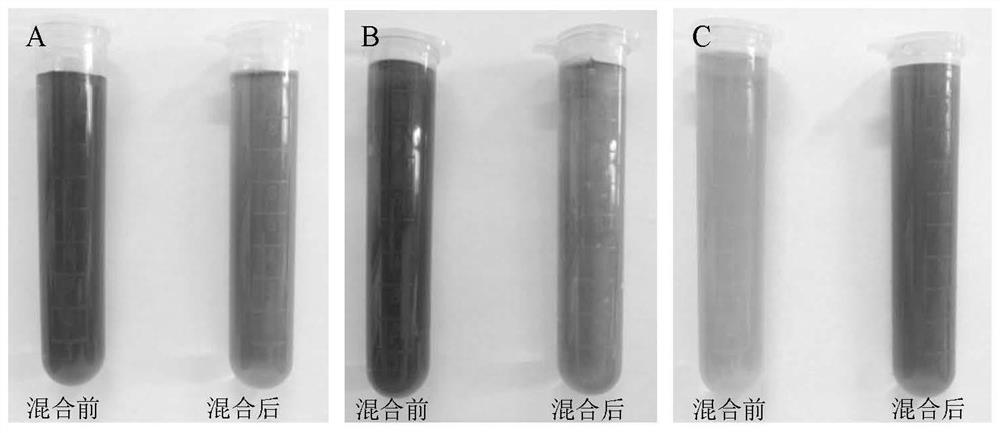
The invention provides a low-cost batch preparation method and application of a noble metal electrode array. The method comprises the following steps: mixing an aqueous solution of noble metal nanoparticles with an inorganic salt aqueous solution with a certain concentration in an isopyknic manner, and aggregating the noble metal nanoparticles to increase the particle size by utilizing a salting-out effect; pouring the mixed solution into a device fixed with a templated microporous filter membrane, and carrying out rapid deposition and room-temperature sintering on the aggregated noble metal nanoparticles in a blank area of the microporous filter membrane in a reduced-pressure filtration manner to form a patterned electrode array; and finally, carrying out washing and drying treatment, soas to produce the low-cost and high-conductivity noble metal electrode array in batches. The method utilizes a template filtering method and has the characteristics of simple preparation device and process, low preparation cost, high material utilization rate and the like. The prepared electrode array is easy to modify, controllable in thickness and good in uniformity and conductivity, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of electrochemical sensors, flexible electronic devices and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Machining device and process for heat-pipe capillary structure
The invention discloses a machining device and process for a heat-pipe capillary structure. The machining device for the heat-pipe capillary structure comprises a powder mixing mechanism, a shaping mechanism and a sintering mechanism. The powder mixing mechanism comprises at least two powder storage hoppers which are coaxially arranged in a nested mode. The sizes of the powder storage hoppers are gradually increased from inside to outside. The lower end of each powder storage hopper is correspondingly connected with a pipe body, and a spiral groove is formed in the inner wall of each pipe body. The shaping mechanism is connected to the lower ends of the pipe bodies. A through hole is formed in the shaping mechanism. A positioning shaft is arranged on the top of the sintering mechanism. The top of the positioning shaft penetrates through the through hole of the shaping mechanism. The machining device for the heat-pipe capillary structure is only provided with one central shaft, so that mixing, shaping and sintering of multiple layers of powder are achieved, and the multilayer heat-pipe capillary structure is obtained. In addition, the machining process for the heat-pipe capillary structure is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:昆山捷桥电子科技有限公司
A kind of soft magnetic composite powder and its application
ActiveCN107424713BOxygen deficiencyImprove magnetismTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMagnetizationCoprecipitation
Owner:湖南天盛新材料科技有限公司
Rotary kiln
InactiveCN104501589BReasonable structural designImprove utilization efficiencyFurnace typesWaste heat treatmentBrickEngineering
The invention discloses a novel rotary kiln which comprises a kiln body and a kiln car. The kiln body is of an annular structure integrally, the kiln car is provided with a drying section, a preheating section, a high-temperature calcining section and a cooling section, the kiln body integrally falls into the ground to form a trench-type structure, an air suction passage is formed on two side faces or at the bottom of the cooling section of the kiln body, a passage is formed below the bottom of the kiln body to form a main flue, an air feeding flue is formed on two side faces or at the bottom of each of the cooling section and the drying section, and the main flue is communicated with the air suction flue and the air feeding flues. Waste heat of finished brick products and hot air are extracted from the side faces of the cooling section of the trench-type rotary kiln to enter the main flue at the bottom, and are divided to enter the air feeding passages after reaching the drying section, and the air feeding flues feed hot air from the side face of the kiln body into the drying section in the kiln body to dry wet blank bricks.
Owner:宜宾恒旭窑炉科技开发有限公司
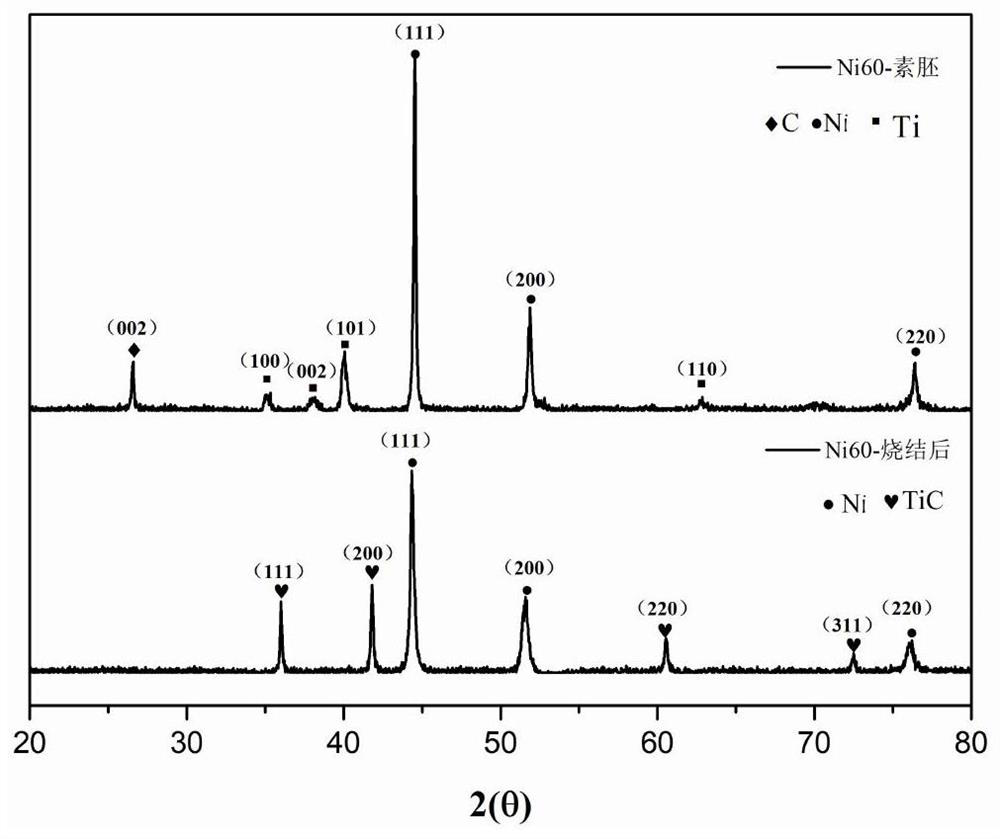
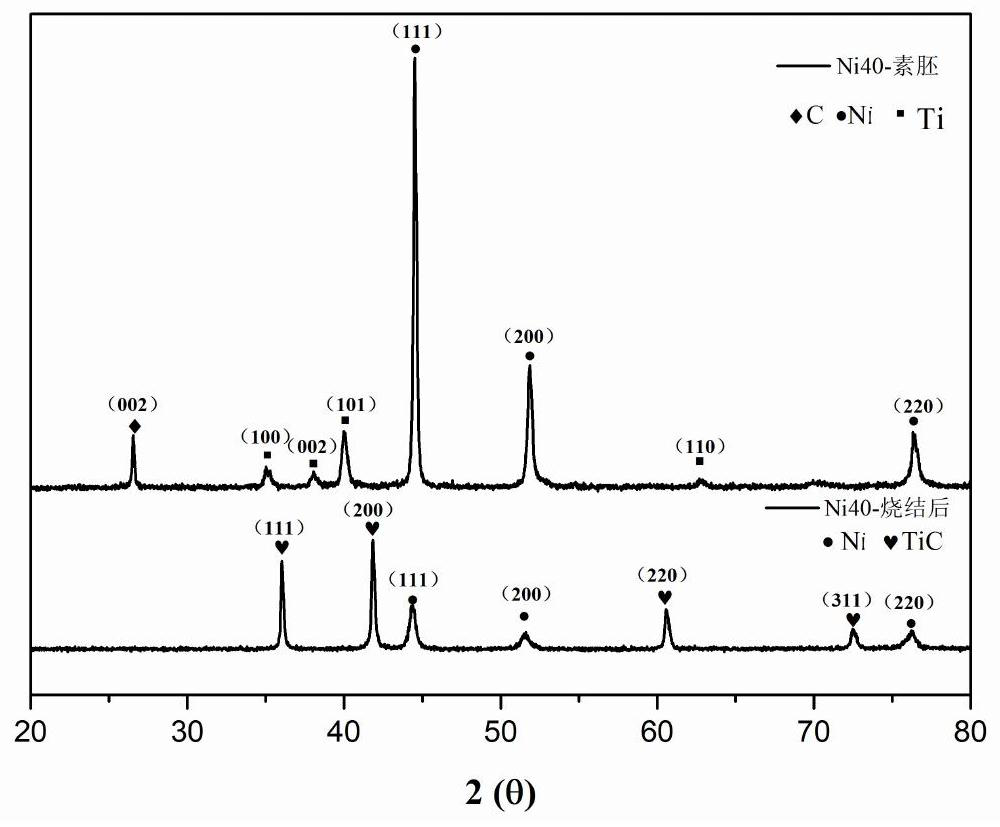
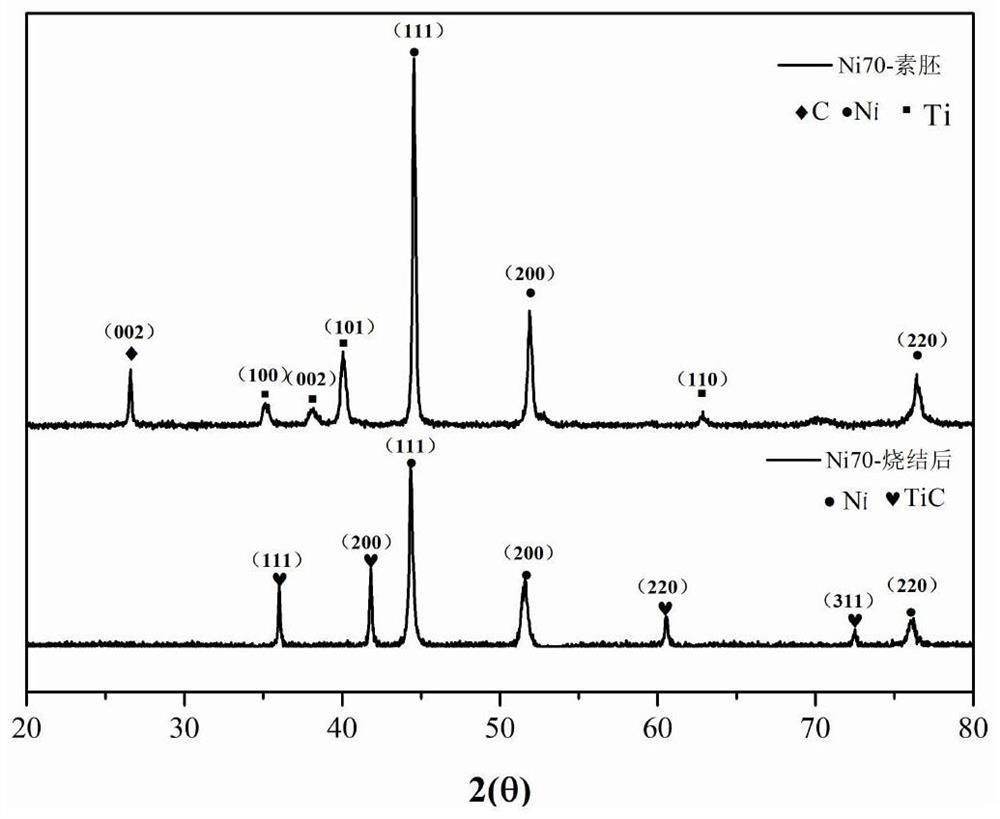
In-situ reaction synthesis method of TiC/Ni composite material
The invention relates to an in-situ reaction synthesis method of a TiC / Ni composite material. The method comprises the following steps that raw materials including Ni powder, Ti powder and graphite are uniformly mixed in proportion, a blank is prepared after cold press forming, then the heating rate is controlled to perform argon protection normal pressure sintering or vacuum sintering on the blank, exothermic chemical reaction occurs among the components at a certain temperature, and thus microscopic reinforcing particles in dispersed distribution are obtained. The material is mainly applied to the fields of aerospace, military, transportation tools, electronic components, fuel cell connectors, ceramic cutting tool materials and the like. In-situ reaction and densification of the TiC / Ni composite material are achieved in one step, complex processes such as high-energy ball milling and pressure sintering are not needed, thus the process is convenient and simple, is not limited by equipment and is low in cost, and the problem that an existing in-situ reaction synthesis technology of the high-density TiC / Ni composite material is limited by equipment, complex in process and high in cost can be effectively solved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aluminum silicon carbide tube shell electrical insulator and sintering method thereof
The invention discloses an aluminum silicon carbide tube shell electrical insulator and a sintering method thereof. The sintering method comprises the following steps: an aluminum silicon carbide tubeshell is placed on a sintering mold, a glass powder hollow tube sleeves a corresponding hole position in the aluminum silicon carbide tube shell, a lead wire is inserted into the middle, then two ends of the hole are separated and filled with carbon powder, the mold is placed into a microwave sintering furnace together with the tube shell, microwave output power and time are adjusted, sintering is performed, and therefore welding of the aluminum silicon carbide tube shell, the electrical insulator and the lead wire is completed. According to the method provided by the invention, different temperature fields are provided by means of microwave selective heating, sintering of the glass electrical insulator of the aluminum silicon carbide tube shell is realized, and the problem that aluminumsilicon carbide is not resistant to heat in a conventional sintering process is solved.
Owner:西安明科微电子材料有限公司
Natural gas burner and method
Provided are a natural gas burner and a method. The natural gas burner is provided with an air pipe (4). The pipe wall of the front end of a primary gas pipe (4) is provided with a natural gas port (5). The outside of the primary gas pipe (4) is sleeved with a mixed gas pipe (1). The pipe wall of the back wall of the mixed gas pipe (1) is provided with a natural gas inlet (3). The pipe wall of the front end of the mixed air pipe (1) is provided with a mixed gas outlet (7). One end, close to the natural gas port (5), of the mixed gas pipe (1) is provided with a choke plug (8). A secondary gas pipe (2) is sleeved with the outside of the mixed gas pipe (1). The pipe wall of the secondary gas pipe (2) is provided with a secondary gas inlet (6).
Owner:梁燕龙
Method for preparing membrane material by using activated aluminum oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a membrane material by using activated aluminum oxide, and relates to the field of membrane materials. The method comprises the following steps: adding water into pseudo-boehmite, titanium oxide micro powder, tourmaline powder, nano magnesium oxide and kaolin to prepare slurry, adding a rare earth material, uniformly conducting mixing, continuously adding an organic additive to prepare mixed slurry, coating a support body with the mixed slurry, and conducting sintering at a low temperature to prepare the inorganic membrane. The rare earth material is added, and oxide in the rare earth material is a good surface active substance, so that wettability among inorganic particles can be improved, a low-melting-point liquid phase is easy to form, the melting point of the material is reduced, and sintering at low temperature is realized.
Owner:江西嘉陶无机材料有限公司
Sintering method of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate
The invention relates to the field of vanadium-titanium-magnetite concentrate preparation, in particular to a sintering method for vanadium-titanium-magnetite concentrate which can effectively improve the quality of sintered ore products. Fluorite ore powder, 65-75 parts of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, 3-8 parts of limestone powder, 6-10 parts of active lime and 4.5-5 parts of coke powder are mixed to form a mixture, and the mixing is controlled The alkalinity of the material is 1.8 to 2.4; water is added to the mixture, and the weight percentage of water in the mixture after adding water is controlled to be 7.2% to 7.6%; the first mixing granulation and the second mixing The material after the second mixing and granulation is added to the sintering machine for sintering, and finally the finished product is obtained. The invention controls the proportion of each material, realizes the sintering of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, increases the binding phase of the sintered ore, increases the liquid phase generation amount in the sintering process, and improves the strength of the vanadium-titanium sintered ore. The invention is especially suitable for the sintering process of vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com