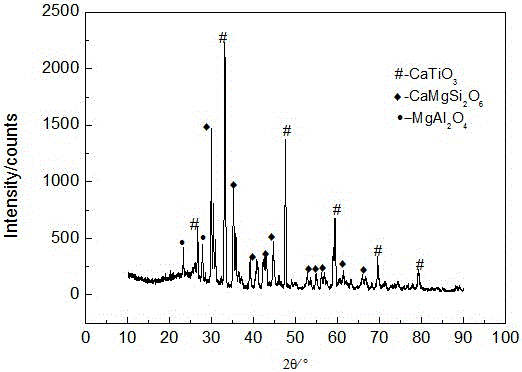
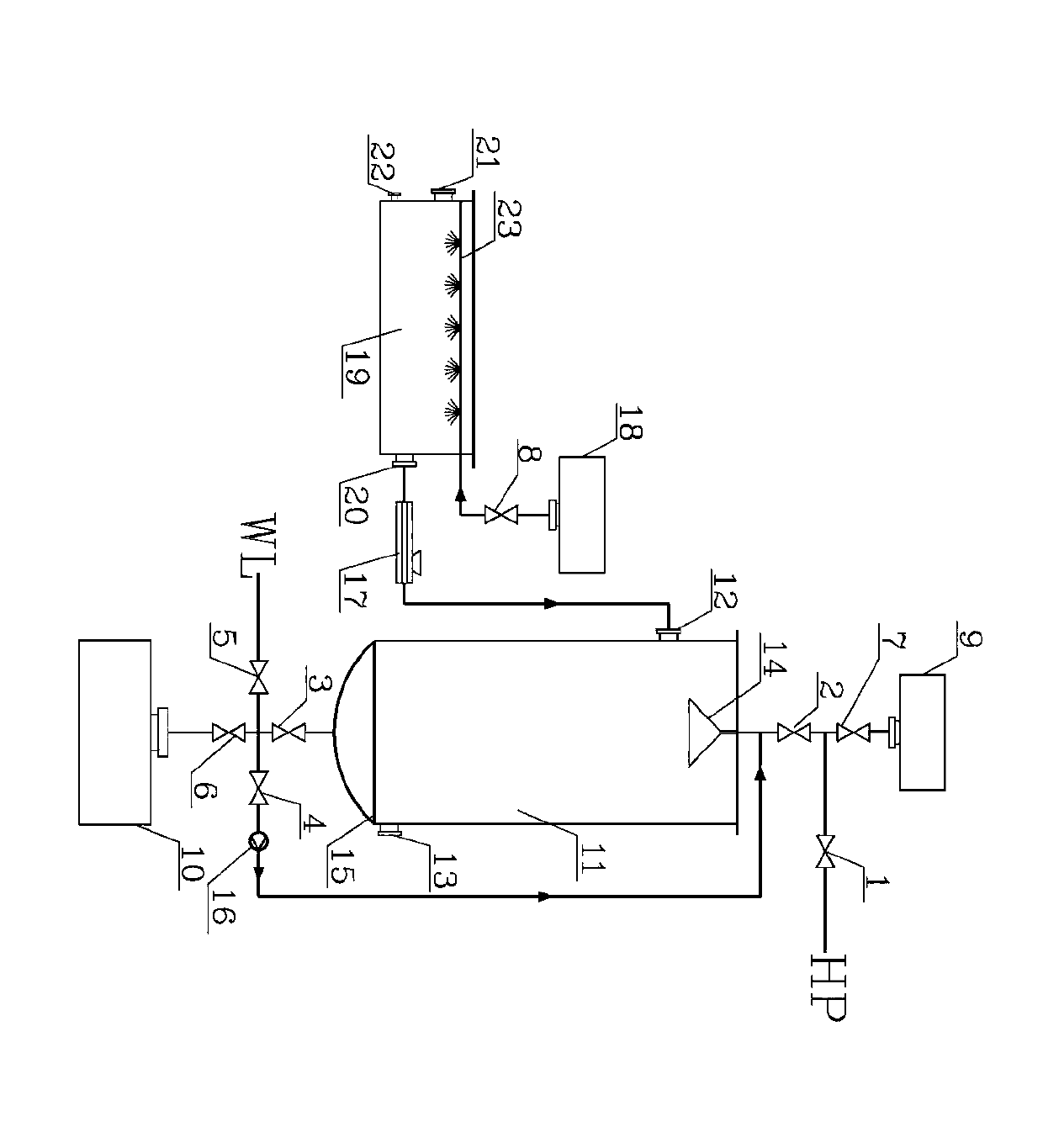
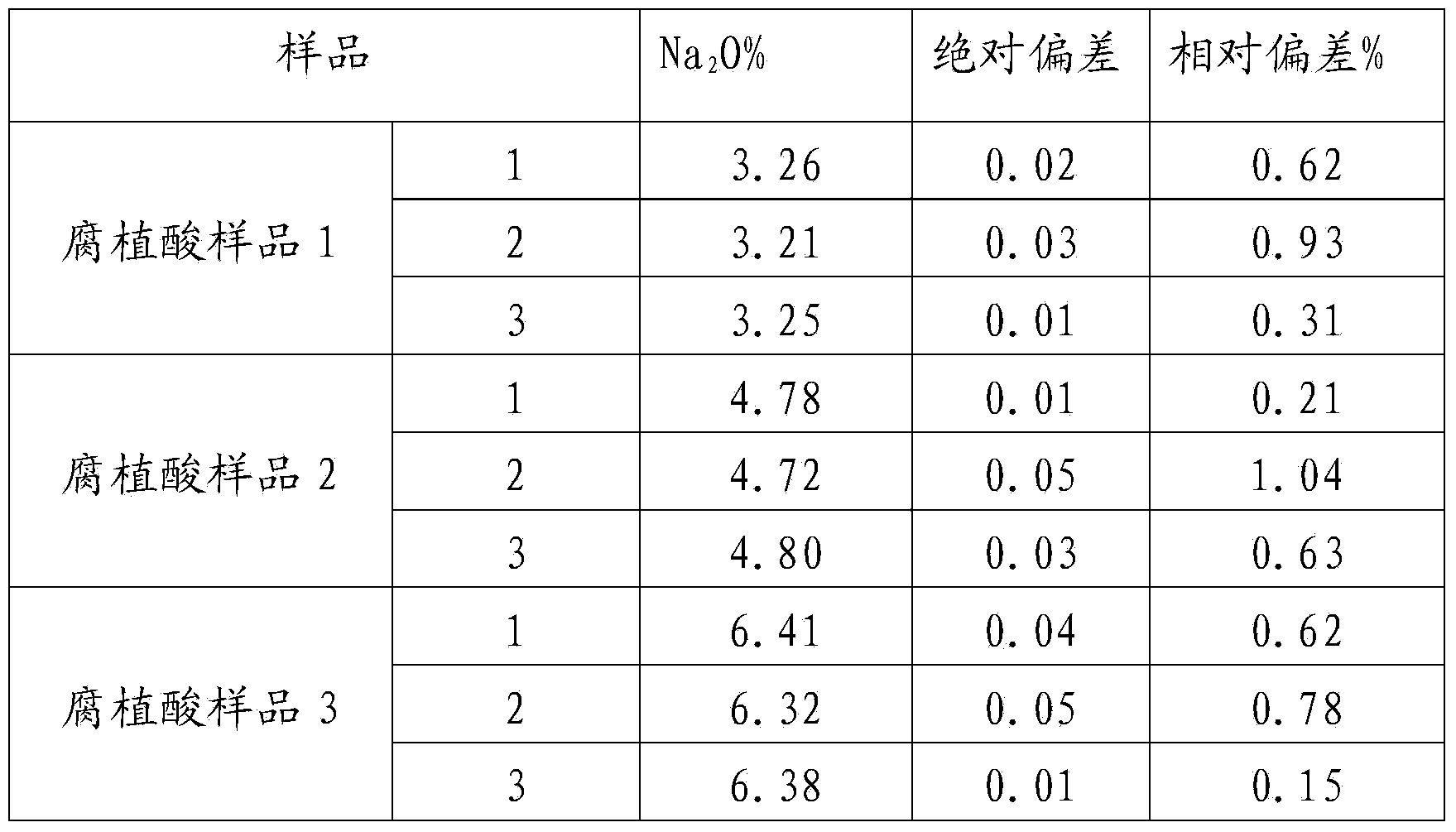
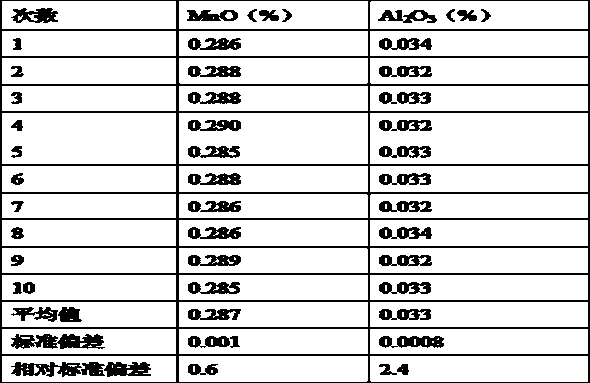
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55results about How to "Less acid consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
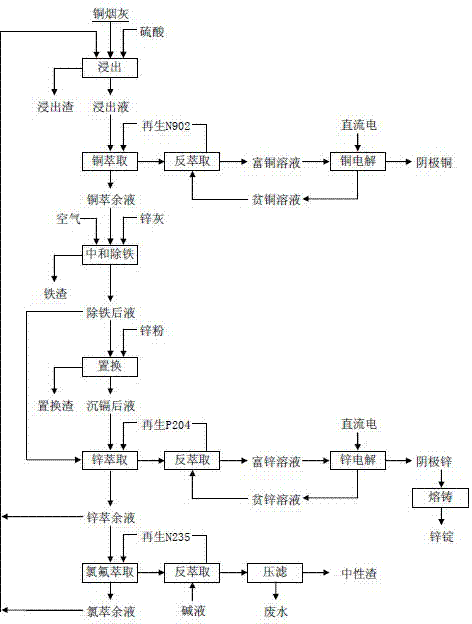
Technology for recovering production of electrolytic copper and zinc from smelting ash
ActiveCN102851693AWide adaptabilityFlexiblePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisCopper oxide
The invention discloses a technology for recovering production of electrolytic copper and zinc from smelting ash. The technology comprises a step of smelting ash leaching, a step of copper extraction and purification through copper electrodeposition, a step of iron removal through neutralization, a step of cadmium removal, and a step of zinc extraction and purification through zinc electrodeposition. The method is characterized in that chemical components in the smelting ash are analyzed, and the smelting ash is leached by a sulfuric acid solution leaching agent; the leachate obtained after the above leaching reaction undergoes a separation operation of copper extraction and purification through the copper electrodeposition; the resultant copper extraction liquor is neutralized by high-zinc dust which is a neutralizer to remove iron; cadmium is displaced and deposited by zinc powder having a mass same with cadmium after the iron removal through the neutralization; and the zinc extraction is carried out through the zinc electrodeposition by casting zinc ingot products. The technology has a wide adaptability, adopts two steps to complete the exchange reaction of zinc oxide and copper oxide in the raw material with an acid, and adopts the high-zinc dust as the neutralizer, so the massive zinc loss caused by entrainment of routine neutralizers comprising calcium oxide and sodium hydroxide is avoided. A zinc extraction liquor obtained in the above step is purified by N235, so economy and effectiveness are realized.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
Extraction seperation method of rare-earth element
ActiveCN102618736AHigh separation factorLow extraction acidityProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementRare earth ions
The invention discloses an extraction seperation method of a rare-earth element. According to extraction seperation method, positive ions and negative ions in a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid extracting agent, i.e. 2-ethylhexyl phosphonic acid mono 2-ethylhexyl ester trialkyl methyl ammonium and phosphonic acid binary (2-ethylhexyl) ester trialkyl methyl ammonium react with rare earth ions to form neutral complex molecules, and the positive ions and negative ions in the quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid extracting agent have inner synergistic effect and competitive effect in the process of extracting the rare-earth element, thereby the seperation factor of the rare-earth element is increased. Therefore, the extraction seperation method provided by the invention has the advantages that an interfacial phenomenon is good in the extraction process, no emulsification is generated, and an extracting solvent does not need to be saponified, the extraction seperation method has higher seperation factor of the rare-earth element and particularly high extraction seperation effect on heavy rare earth. In addition, the extraction seperation method of the rare-earth element, which is provided by the invention, has low extraction acidity and back extraction acidity and consumes little acid.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting scandium from modified red mud by using composite extractant
InactiveCN102061392ALess acid consumptionEasy extractionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionRed mud
The invention relates to a method for extracting scandium from modified red mud by using a composite extractant, belonging to the technical field of extraction and preparation methods of rare-earth metal scandium. The method for extracting the scandium from the modified red mud ensures good extracting effect, high recovery rate and product purity and is suitable for industrialized production. The method comprises the following steps of: a first step: preparing the modified red mud; a second step: leaching the modified red mud by using hydrochloric acids so as to obtain an acid leaching solution; a third step: preparing the composite extractant; a fourth step: mixing the acid leaching solution obtained from the second step with the composite extractant for extraction and separation; a fifth step: washing extracted upper organic phases by using the hydrochloric acids, then washing by using water, and then carrying out back extraction by using a NaOH solution to obtain an Sc(OH)3 solution; a sixth step: precipitating the Sc(OH)3 solution by using oxalic acids, and filtering, and drying; and a seventh step: roasting a solid obtained from the sixth step at high temperature to obtain white scandium oxide powder. The invention can be widely used for the technical field of extraction and preparation of the rare-earth metal scandium.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for extracting vanadic anhydride from stone coal vanadium ore
InactiveCN101182596AReduced drying processFew ingredientsVanadium oxidesProcess efficiency improvementCelsius DegreeDesorption
The invention relates to a method for extracting vanadic oxide from bone coal vanadium mine; the method comprises the following steps that the bone coal vanadium mine is selected to be delivered into a kiln for baking and the kiln temperature is controlled between 750 to 1100 Celsius degrees and the discharge temperature of the baked material is 750 to 1000 Celsius degrees; and then the materials are delivered into a heat-preservation warehouse to be kept still for 24 to 120 hours; and then the material is extracted and the pH value of the obtained extraction liquid is adjusted to be 2.5; the liquid is absorbed and desorbed to obtain the desorption liquid and then the desorption liquid is purified and the silicon and phosphor in the desorption liquid is removed; ammonium chloride is added to precipitate vanadium and obtain ammonium meta-vanadate; the ammonium meta-vanadate is implemented with the process of pyrolysis to obtain the vanadic oxide. The beneficial effect of the invention is that the bone coal vanadium mine is directly baked which reduces the working procedures of baking, proportioning, ball grinding and balling; the invention adopts the heat-preserving warehouse for preserving heat and the extraction rate can reach more than 90 percent if the temperature is kept between 750 to 1100 Celsius degrees for more than 72 hours; the extraction rate is higher if the heat-preserving time is longer; moreover, the mechanization degree is high and no dust pollution exists.
Owner:杨秋良
Method for extracting and separating rare earth elements in hydrochloric acid system
InactiveCN102876894AHigh separation factorLow extraction acidityProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementSeparation coefficient
The invention provides a method for extracting and separating rare earth elements in a hydrochloric acid system. The method includes the steps: taking mono (2-ethylhexyl) phosphonate 2-ethylhexyl methoxy cinnamate trialkyl methyl ammonium or phosphonate (2-ethylhexyl) diester trialkyl methyl ammonium as an extracting agent; taking normal heptane as diluent; and extracting the rare earth elements in rare earth chloride water solution into the normal heptane. The extracting agent used in the method does not need to be saponified, extraction and reverse extraction acidity is low, and separation coefficient for the rare earth elements is high.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chromium slag processing method for chemical-biological coupling reduction of hexavalent chrome
The invention relates to a chromium slag treatment when coupling and reducing hexavalent chromium from chromium slag, wherein said method comprises using wet method to break, and adding the solution with acid and reducer, controlling the pH value, reducing the density of hexavalent chromium; transferring the liquid-solid mixture to another reactor, adding acid and reducer, mixing to reduce the hexavalent chromium; adding anaerobe, emerging. The acid can be sulfuric acid, etc; the reducer can be sulfite, etc; the anaerobe can be the mixture of SRB, Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
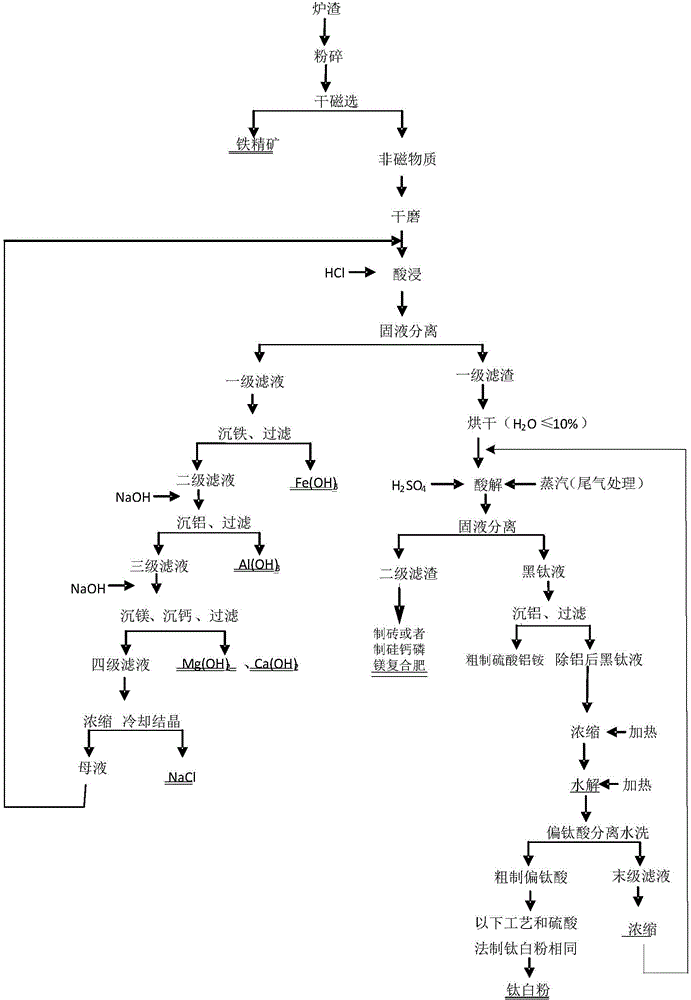
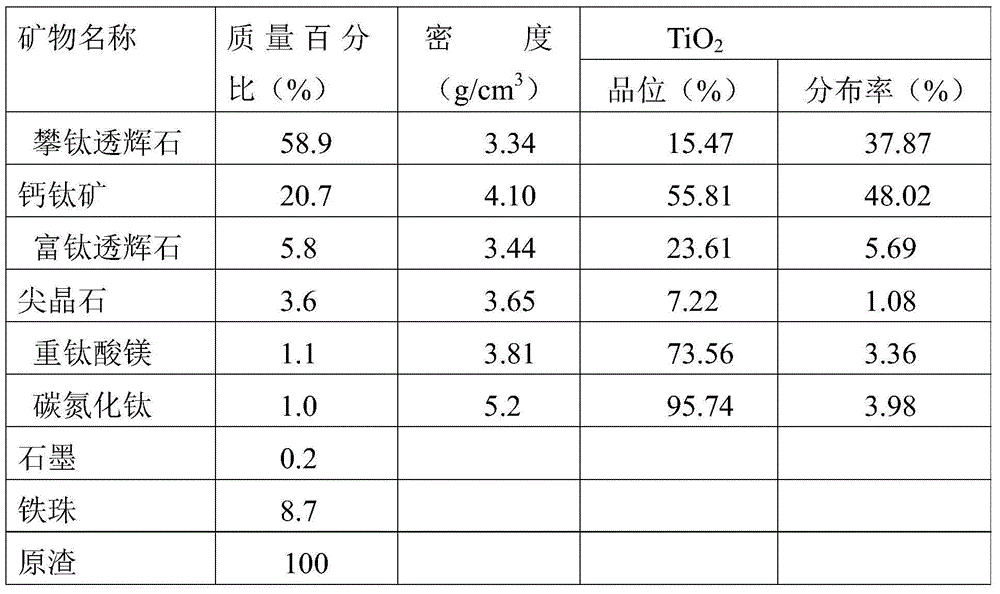
Comprehensive utilization method of high titanium slag
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization method of high titanium slag in the slag treatment technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out acid leaching by using diluted hydrochloric acid; then, carrying out acidolysis by using dilute sulphuric acid, wherein the leaching rate is improved; using a black titaniferous liquid after acidolysis to prepare titanium dioxide; settling Fe(OH)3, Al(OH)3, Mg(OH)2 and Ca(OH)2 from a primary filtrate obtained by acid leaching and recovering sodium chloride; and using Si, Mg and Ca in slag to prepare an Si-Ca-P-Mg composite fertilizer. The method disclosed by the invention is extremely low in acid consumption of acid which is recycled, various effective components of high titanium slag can be comprehensively utilized, and factors in many aspects such as environment friendliness, technology and economical benefit are taken into consideration. The slag is low in cost, and titanium, ferrum, aluminum, magnesium, calcium, silicon, sodium chloride and the like can be comprehensively recovered, so that the economic benefit is remarkable, the long-term pendent problem on utilization of high titanium slag is solved, the land for slag is saved, the environmental pollution is reduced, wastes are turned into wealth, and the high titanium slag has a good social benefit.
Owner:攀枝花市德信科技有限公司
Biological leaching process for separating out metal ions from waste battery directly
InactiveCN101020963ALess acid consumptionReduce processing costsProcess efficiency improvementIonStrong acids
The present invention is biological leaching process for separating out metal ions from waste battery directly, and the green process may be used in supplementing or replacing high temperature chemical leaching with strong acid. The present invention has direct waste battery leaching process with simultaneous acid generating and leaching, and is suitable for all kinds of waste battery. The process of the present invention has lower acid consumption, low cost, high metal leaching rate, mild operation and other advantages, and possesses excellent application foreground.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for extracting and separating rare earth elements in sulfuric acid system
InactiveCN102876893AHigh separation factorLow extraction acidityProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementSeparation coefficient
The invention provides a method for extracting and separating rare earth elements in a sulfuric acid system. The method includes the steps: taking mono (2-ethylhexyl) phosphonate 2-ethylhexyl methoxy cinnamate trialkyl methyl ammonium as an extracting agent; taking normal heptane as diluent; and extracting the rare earth elements in rare earth sulfate water solution into the normal heptane. The extracting agent used in the method does not need to be saponified, extraction and reverse extraction acidity is low, and separation coefficient for the rare earth elements is high.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of expandable graphite
InactiveCN103663443AHigh expansion volume at low temperatureLess acid consumptionCarbon compoundsWater contentPhosphoric acid
A preparation method of expandable graphite comprises the following steps: oxidizing natural flake graphite for 5-120 min at 0-90 DEG C in the presence of an oxidant by using a mixed solution of perchloric acid and phosphoric acid in a mass ratio of 1:(0.05-3); deacidifying by centrifuging; further impregnating and intercalating the oxidized natural flake graphite by using organic acid; after water washing, drying at low temperature till the moisture content is less than 1% to prepare the expandable graphite. The expandable graphite is high in cryogenic expansion volume, low in energy consumption and acid consumption, sulfur-free or low in sulfur and stable in quality; the environmental pollution is reduced; the preparation method is easy to master.
Owner:王伟
Preparation method for noble metal modified titanium anode materials
InactiveCN102505127AReduce consumptionImprove activation etching efficiencyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrodesOrganic solventExposed point
The invention relates to a preparation method for noble metal modified titanium anode materials, belonging to the technical field of high-performance electrode materials. The preparation method for noble metal modified titanium anode materials comprises the following steps of: taking noble metal organic complex as a precursor; atomizing the precursor into atomizing flow after being dissolved in organic solvent; depositing the precursor on the surface of a titanium sheet; thermally decomposing and cooling under the existence of inertia gas; repeating three continuous steps of depositing, thermally decomposing and cooling for at least once; and carrying out aftertreatment, so as to obtain the noble metal modified titanium anode materials. The titanium anode prepared by the method has high yield and less surface exposed point; the noble metal and pure titanium base material have high binding force; and the whole coating has better homogeneity and uniformity. Experiments show that the titanium anode prepared by the method has better electrochemical performance and long service life.
Owner:文广 +4
Pickling apparatus, pickling method, and quartz sand preparation method
The invention discloses a pickling apparatus, a pickling method, and a quartz sand preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of quartz sand preparation. The apparatus comprises a raw acid barrel, a complex acid barrel, a wastewater treatment structure, a selective conveying structure, an acid recovery structure, a pickling barrel and a visual device. The raw acid barrel, the complex acid barrel, the pickling barrel, the visual device and the selective conveying structure are sequentially connected, the output end of the selective conveying structure is only communicated with the input end of the acid recovery structure when the foaming time in the visual device is less than a predetermined value, and the output end of the selective conveying structure is only communicated with the wastewater treatment structure when the foaming time in the visual device is not less than a predetermined value; and the output end of the acid recovery structure is connected with the complex acid barrel, an acid in the complex acid barrel can be directly output to the pickling barrel when the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the complex acid barrel is greater than 16 Baume gravities, and the complex acid barrel is communicated with the raw acid barrel to make the concentration of hydrochloric acid in a range of 20-22 Baume gravities when the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the complex acid barrel is not greater than 16 Baume gravities. The pickling apparatus, the pickling method and the quartz sand preparation method allow 98% of hydrochloric acid to be recovered, the wastewater emission to be reduced and the wastewater treatment cost to be reduced.
Owner:周金堂
Method for enriching germanium from lignite flue dust
InactiveCN105907979ALess acid consumptionAvoid emissionsProcess efficiency improvementWastewaterReducing atmosphere
The invention discloses a method for enriching germanium from lignite flue dust. The method comprises the following steps: 1, mixing lignite flue dust with coal powder and lime, and granulating the obtained mixture to obtain material particles; and 2, putting the material particles in a heating furnace, carrying out reducing volatilization at 1200-1500DEG C in reducing atmosphere in the heating furnace for 2-18h, and collecting dusts to obtain a germanium-rich material. The method greatly reduces the acid consumption in the subsequent wet treatment process of germanium concentrate, avoids discharge and treatment of a large amount of wastewater and waste residues, reduces the device size, and reduces the investment cost.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Method for preparing vanadium liquid through vanadium oxide industrial waste water
ActiveCN105296762AEfficient use ofLess acid consumptionProcess efficiency improvementWater bathsIndustrial waste water
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgical chemistry engineering and discloses a method for preparing vanadium liquid through vanadium oxide industrial waste water. The method is mainly applied to the process of leaching for vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing clinker. The method aims at being used for acid leaching of calcium roasting clinker through two kinds of waste water including manganese extraction waste water and water bath materials which are produced through vanadium oxide, and used for recycling valuable elements in the calcium roasting clinker, and therefore waste water is effectively utilized. The method includes the following steps that firstly, the water bath materials are filtered, a filtrate is mixed with the manganese increasing water according to a certain proportion, and mixed liquid is obtained; secondly, the calcium roasting clinker is added to the mixed liquid according to a certain liquid-solid ratio, stirring is conducted, the temperature is raised to 40-55 DEG C, the pH of a system is adjusted to 2.6-3.0; and thirdly, solid-liquid separation is conducted, filter residues are washed through the mixed liquid in the first step, and the obtained filtrate is a vanadium-containing leaching agent.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Strip steel pickling circulating system
The invention discloses a strip steel pickling circulating system. The strip steel pickling circulating system is mainly characterized in that a strip steel inlet is formed in a first pickling tank, and the first pickling tank is connected with a second pickling tank; the second pickling tank is connected with a third pickling tank, and the first pickling tank, the second pickling tank and the third pickling tank are all connected with an acid mist pretreatment device; the acid mist pretreatment device is connected with an acid mist purification tower and a rinsing tank, and the right end of the acid mist purification tower is directly connected with atmosphere through a pipeline; the lower end of the acid mist pretreatment device and the left end of the rinsing tank are connected with the upper end of a third acid storage tank through pipelines; a water supplementing pipe is connected with the upper end of a condensate water tank, and the condensate water tank is connected with a first heater, a second heater and a third heater through pipelines; a strip steel outlet is formed in the right end of the rinsing tank, and a rinse water draining opening is formed in the bottom end of the rinsing tank; and the bottom end of the rinsing tank is connected with the right end of the condensate water tank through a water pump.
Owner:JIANGSU SERO ANTICORROSION EQUIP
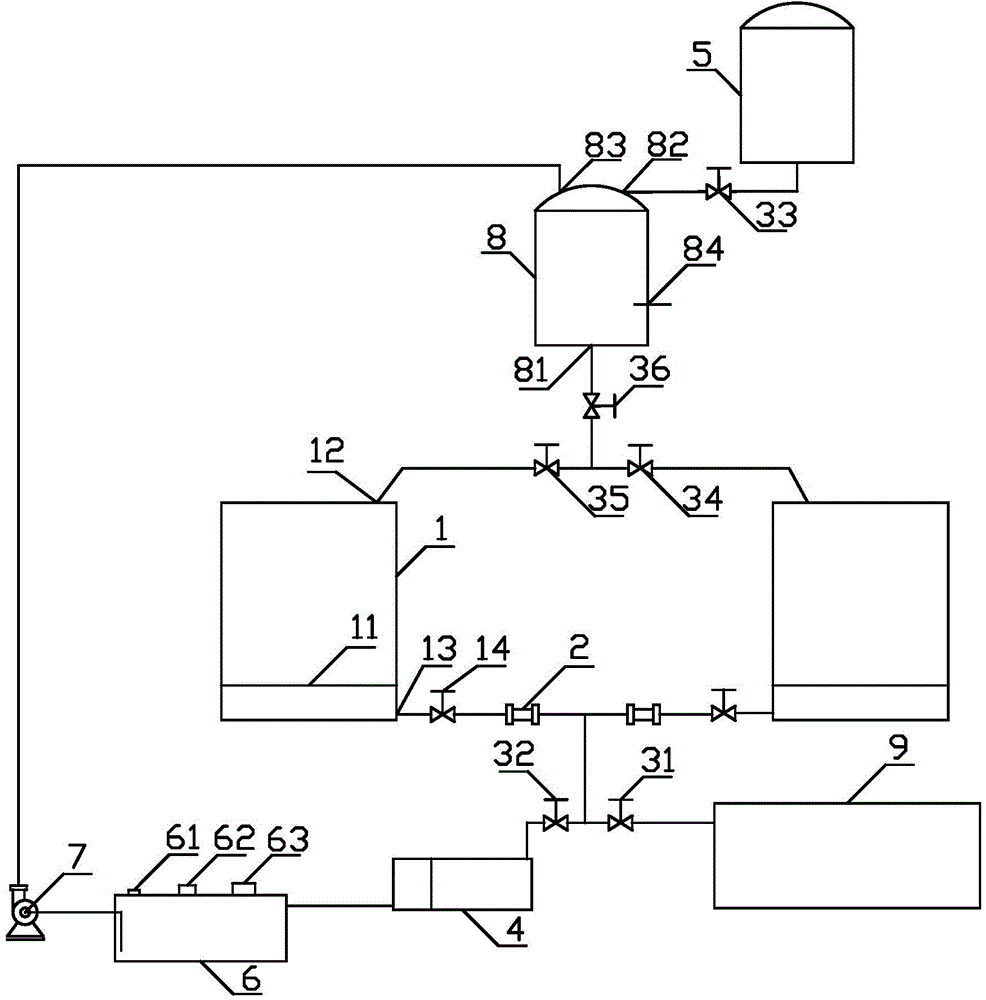
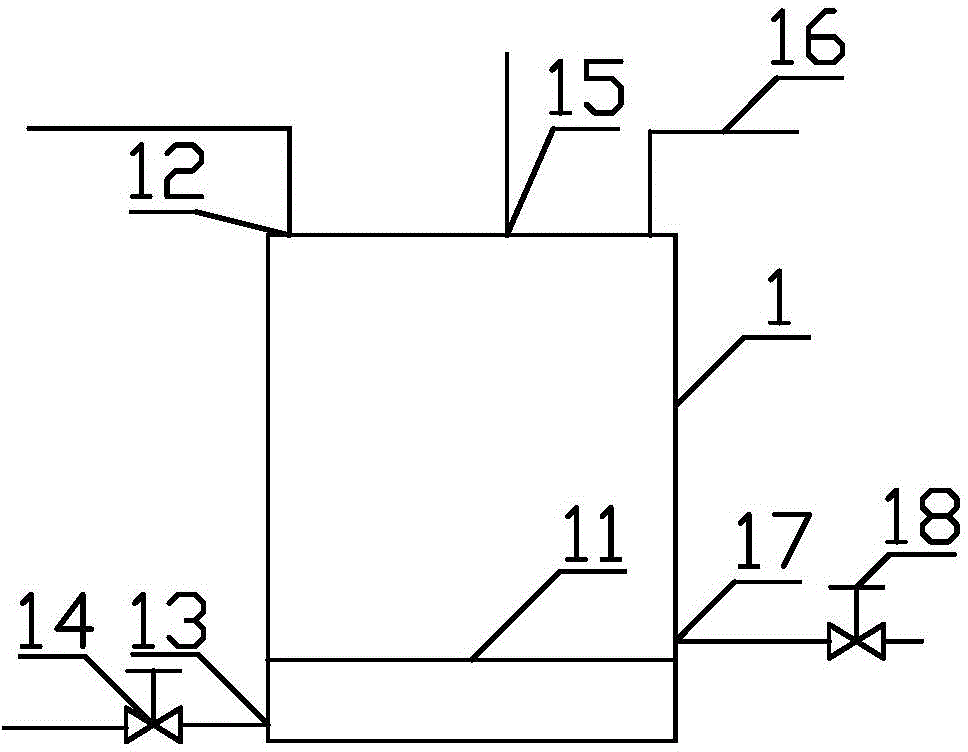
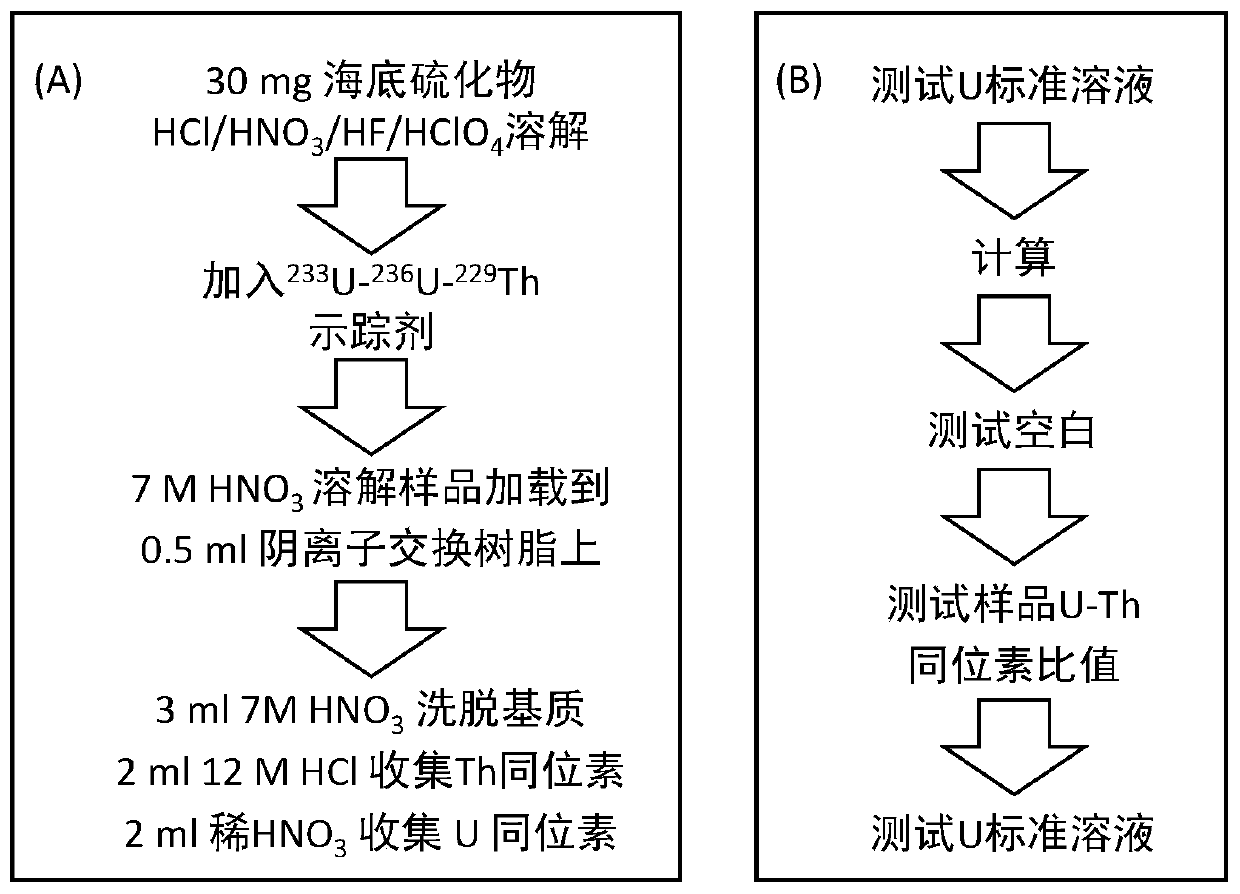
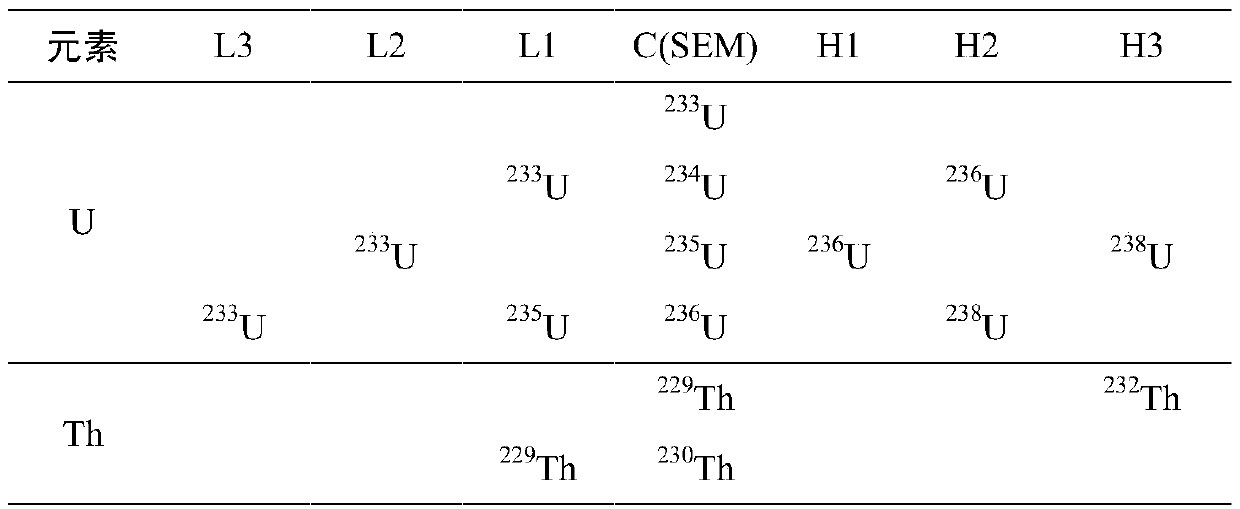
Method for testing fourth-stage submarine hydrothermal sulfide age
The invention provides a method for testing the fourth-stage submarine hydrothermal sulfide age. The method comprises the steps of testing the U / Th isotope ratio of the submarine hydrothermal sulfideby adopting MC-ICPMS; and calculating the age of the 230Th uranium system. The method is characterized in that modified strongly basic anion exchange resin containing quaternary ammonium salt groups is adopted in U-Th separation and purification, and the modified strongly basic anion exchange resin is obtained after chloromethyl styrene-divinyl benzene copolymer microspheres react with long-chaintertiary amine and spiro-cyclic tertiary amine. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, the seabed polymetallic sulfide dating sample is smaller in dosage and smaller in acid consumption; the operation is simple; sample dissolution is more complete; age test data are more accurate; and data reliability and repeatability are better. The technology is simple to operate. The uranium and thorium age of the fourth-stage seabed sulfide can be determined. The sample amount only needs tens of milligrams, and the precision of the determined isotope ratio of U to Th can be superior to 0.5%.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treatment method for titanium extraction from titanium-containing blast furnace slag based on vacuum carbothermal reduction
InactiveCN104498734BAchieve separationLess acid consumptionRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementSlagTitanium
The invention provides a treatment method for extracting titanium from titanium-containing blast furnace slag based on vacuum carbothermal reduction, which adopts a combined process of vacuum carbothermal reduction-acid leaching, and keeps the pressure in the vacuum carbon tube furnace at 101-100 Pa during the vacuum reduction process between, and maintain a high reduction temperature, so that the SiO2 that is difficult to reduce under normal pressure is reduced to SiO, and at the same time, the MgO in the titanium-containing blast furnace slag can be reduced to metal Mg, because both SiO and metal Mg have the characteristics of high vapor pressure , during the reduction process, they leave the reaction system with the vacuuming process, so that the silicon and titanium in the titanium-containing slag can be completely separated; after vacuum carbothermal reduction to obtain the reduced slag, other impurities in the slag are removed by acid leaching, and TiC products are obtained. And because the silicon and magnesium compounds in the slag have been removed in the vacuum carbothermal reduction process, the acid consumption in the acid leaching process can be greatly reduced, and the acid leaching time can also be shortened, so that the overall efficiency of titanium extraction is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Method for corroding germanium wafers
ActiveCN113174597AImprove the finishReduce roughnessFinal product manufactureReaction ratePhysical chemistry
The invention provides a method for corroding germanium wafers. The method comprises the following steps of that A) the germanium wafers with the thickness difference within + / -0.025 mm are fixed in the same clamping groove, and then the clamping groove containing the germanium wafers is placed into corrosive liquid to carry out corroding; wherein the corrosive liquid is a mixed liquid of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid in the volume ratio of (2-5): 1; B) when the corrosive liquid begins to emit red smoke, pure water is slowly added into the corrosive liquid until the red smoke turns yellow smoke, and corroding continues for 1-2 minutes; and C) the corrosive liquid is diluted with pure water, then the clamping groove is taken out, and the germanium wafers are cleaned and dried. According to the method, the pure water is slowly added when the corrosive liquid begins to emit red smoke, so that the germanium wafers can quickly react in the early reaction stage, and it can be avoided that the surfaces of the germanium wafers are blackened due to too high temperature and too intense reaction in the later reaction stage. The method ensures the corrosion efficiency and meanwhile solves the technical problems that the reaction rate is difficult to control and the surfaces of the germanium wafers are likely to blacken in the existing acid corrosion.
Owner:清远先导材料有限公司
Biological-chemical combined pretreatment method of lignocellulosic materials
ActiveCN102261004BReduced encapsulationImprove permeabilityPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsMicroorganismCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering and particularly relates to a method and system for carrying out combined pretreatment on lignocellulosic materials by combining microbiological treatment and dilute acid treatment. The method is characterized by grinding the lignocellulosic materials to 5-60 meshes, then putting the ground lignocellulosic materials in a microbiological treatment tank, and injecting microbiological bacteria liquid for biological treatment for 5-10 days; and putting the materials subjected to microbiological treatment in a dilute acid recycle reactor, injecting dilute acid, and starting a circulating pump to carry out circulating treatment at 80-100 DEG C for 1-4 hours, thus completing pretreatment. The method has the advantages of lowacid consumption, mild operation conditions, low requirements for compression resistance and corrosion resistance of the reactor, low treatment cost, less secondary pollution, environment friendliness and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method for measuring sodium in sodium humate
InactiveCN104165883ALess acid consumptionFast analysisAnalysis by thermal excitationTemperature controlDigestion
The invention discloses a method for measuring sodium in sodium humate. By carrying out pretreatment with H2SO4-H2O2 in a temperature control type infrared digestion furnace and optimizing ICP-AES measurement parameters, the method for measuring the content of sodium in sodium humate by ICP-AES is established. The method has the advantages of being small in acid consumption, high in analysis speed, simple to operate and being relatively high in precision and accuracy and being suitable for analytic detection on the content of sodium in daily sodium humate.
Owner:HUBEI FORBON TECH
Method for determining content of impurity elements in ferric oxide with X-ray fluorescence spectrum in filter paper sheets
InactiveCN109324073AFor long-term storageEasy to handleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescence spectrometryFilter paper
The invention discloses a method for determining content of impurity elements in the ferric oxide with an X-ray fluorescence spectrum in filter paper sheets. The determination comprises the followingsteps: (1) preparing a series of standard sample solution; (2) preparing a sample solution to be detected; (3) preparing a series of standard sample and the sample to be tested; (4) leveling a seriesof standard samples and the sample to be detected; (5) obtaining a calibration curve through a series of standard samples; and(6) obtaining the content of the impurity elements to be detected in the ferric oxide sample, according to the calibration curve. According to the method for determining content of impurity elements in the ferric oxide with the X-ray fluorescence spectrum in filter paper sheets, the method is simple to operate, high in determination speed, less in acid consumption, accurate in measurement, and easy to treat the waste liquid.
Owner:HUNAN AEROSPACE MAGNET & MAGNETO
Method for recycling metal in lithium ion battery through inorganic acid leaching-bioleaching collaboration
ActiveCN108285980AImprove leaching rateAdaptableProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansIron(II) oxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of waste battery metal recovery treatment, and relates to a method for recycling metal in a lithium ion battery through inorganic acid leaching-bioleachingcollaboration. The method includes the steps that (1) domestication of thiobacillus ferrooxidans is conducted; (2) battery disassembling is performed; (3) acid leaching is carried out, inorganic acidis thrown into mixed electrode material powder, a solution containing heavy metal and electrode powder is obtained, and the final pH of a reaction system is 1.8-2.5; and (4) bioleaching is performed,a culture solution is added into the solution, the domesticated thiobacillus ferrooxidans are further added, the mixed solution is precipitated and separated after reacting is completed, the mixed solution obtained through separation is centrifuged, and the centrifuged solution containing the heavy metal is subjected to heavy metal recovery. According to the method for recycling the metal in thelithium ion battery through inorganic acid leaching-bioleaching collaboration, inorganic acid leaching and bioleaching are combined, the using amount of acid is small, the metal leaching rate is high,the advantage of being moderate in bioleaching reaction condition is given into play, and environmental protection and safety are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Technology for recovering production of electrolytic copper and zinc from smelting ash
ActiveCN102851693BWide adaptabilityFlexiblePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisCopper oxide
The invention discloses a technology for recovering production of electrolytic copper and zinc from smelting ash. The technology comprises a step of smelting ash leaching, a step of copper extraction and purification through copper electrodeposition, a step of iron removal through neutralization, a step of cadmium removal, and a step of zinc extraction and purification through zinc electrodeposition. The method is characterized in that chemical components in the smelting ash are analyzed, and the smelting ash is leached by a sulfuric acid solution leaching agent; the leachate obtained after the above leaching reaction undergoes a separation operation of copper extraction and purification through the copper electrodeposition; the resultant copper extraction liquor is neutralized by high-zinc dust which is a neutralizer to remove iron; cadmium is displaced and deposited by zinc powder having a mass same with cadmium after the iron removal through the neutralization; and the zinc extraction is carried out through the zinc electrodeposition by casting zinc ingot products. The technology has a wide adaptability, adopts two steps to complete the exchange reaction of zinc oxide and copper oxide in the raw material with an acid, and adopts the high-zinc dust as the neutralizer, so the massive zinc loss caused by entrainment of routine neutralizers comprising calcium oxide and sodium hydroxide is avoided. A zinc extraction liquor obtained in the above step is purified by N235, so economy and effectiveness are realized.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
Method for separating and recycling metal silver and gallium
InactiveCN113355701AReduce hoardingHigh speedProcess efficiency improvementElectrolytic agentGallium
The invention provides a method for separating and recycling metal silver and gallium. The method comprises the steps that S1, waste containing silver and gallium and an alkali material are evenly mixed and then smelted; S2, dross obtained after smelting in S1 is soaked with alkali liquor and filtered, and then leach liquor is subjected to electro-deposition to obtain metal gallium; and S3, a silver ingot obtained after smelting in S1 serves as an anode, silver nitrate serves as electrolyte, and metal silver is purified through electrolysis. According to the method for separating and recycling metal silver and gallium, the pyrogenic process and the wet process are combined, then silver and gallium can be rapidly separated and recycled, the whole technological process is low in acid consumption and high in speed, accumulation of silver powder can be reduced, and the purity of the recycled product is good.
Owner:FIRST RARE MATERIALS CO LTD
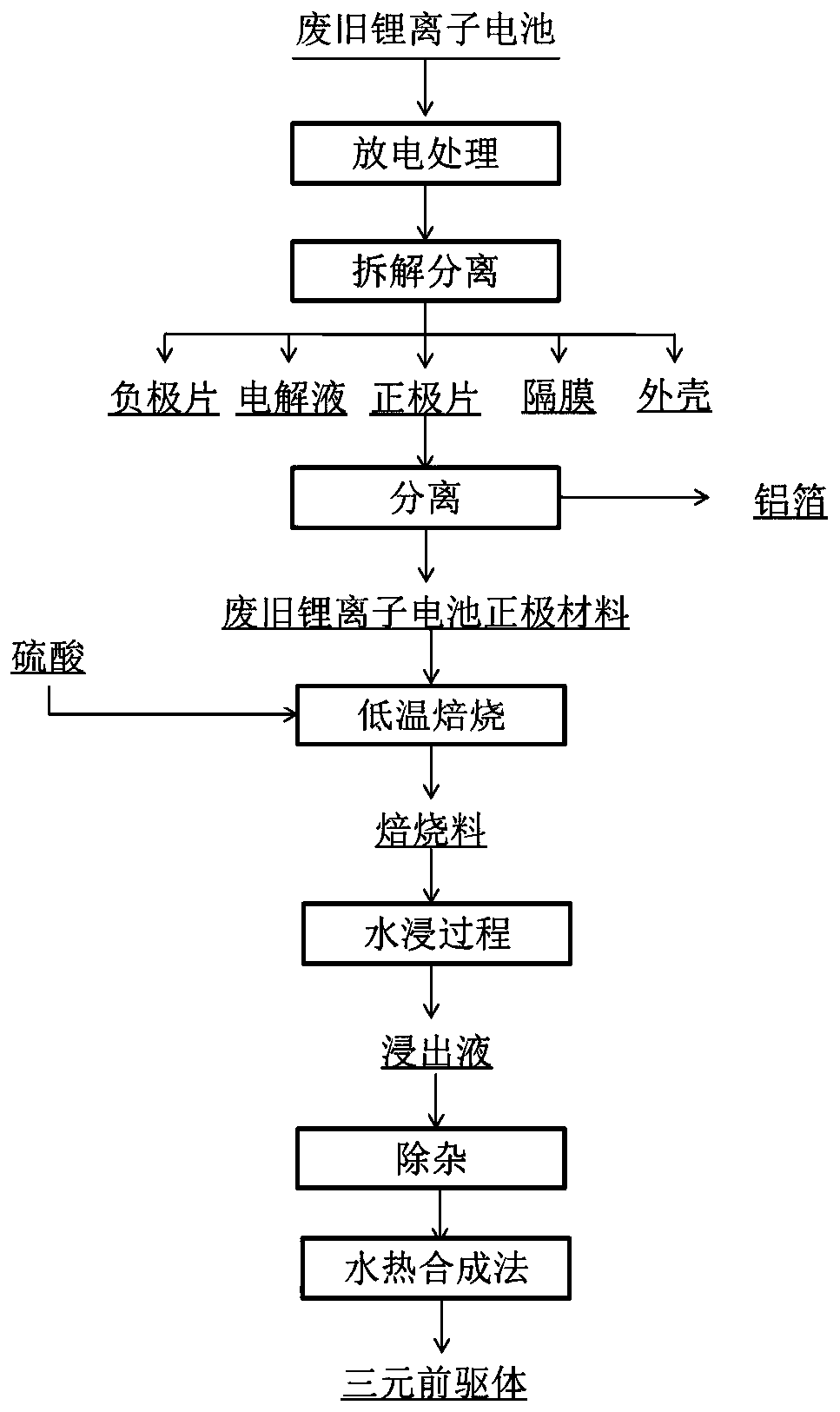
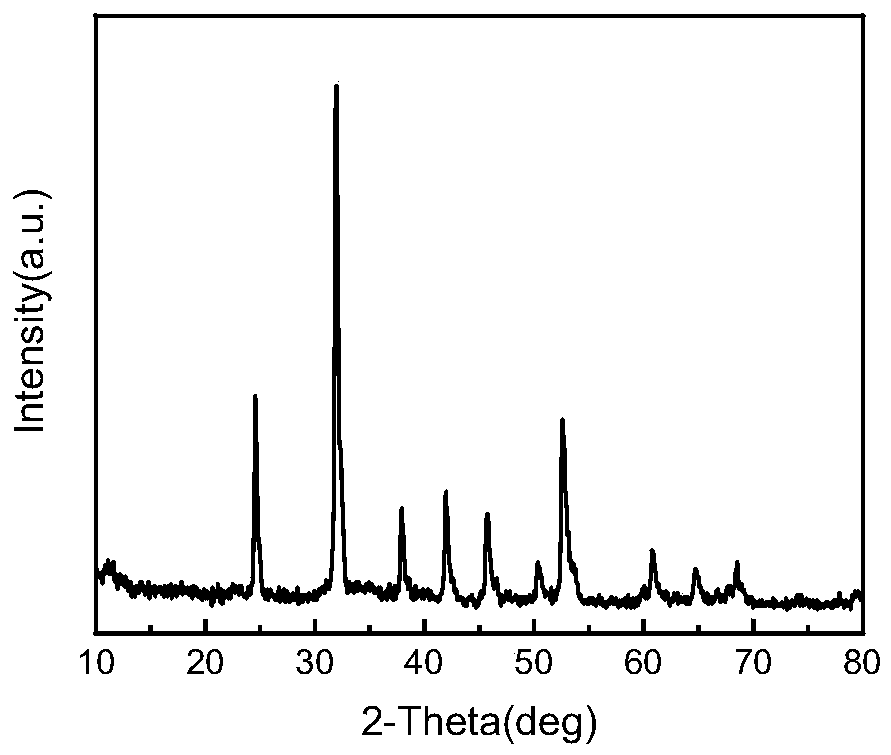
Methods for leaching valuable metals from waste lithium ion ternary positive electrode material and preparing ternary positive electrode material precursor
PendingCN111333123ALess acid consumptionEfficient leachingCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingElectrical batteryMetal leaching
The invention discloses a method for leaching valuable metals from a waste lithium ion ternary positive electrode material. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out ball milling on an active substance separated from the waste lithium ion battery positive electrode material to obtain powder; wetting the powder with water to obtain a wet material; mixing the wet material with concentrated sulfuric acid; roasting at low temperature to obtain a roasted material; and carrying out water leaching on the roasted material, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain carbon and a metal leachate. According to the method for leaching the valuable metal, efficient leaching of the metal is achieved under the condition that no reducing agent or additive exists, and energy consumptionis reduced. The invention further discloses a method for adjusting the molar ratio of nickel to cobalt to manganese in the leachate, then adding the urea, mixing with the ethylene glycol and carryingout a hydrothermal reaction to prepare a ternary positive electrode material precursor, so that separation of different metals is avoided, valuable metals are effectively recycled, the process flow is shortened, the operation is simple, industrial production is facilitated, and the prepared ternary positive electrode material precursor has excellent electrochemical performance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Novel pool-type process for removing alkali of alkaline uranium ore by using hydrochloric acid
The invention discloses a method for removing alkali of an alkaline uranium ore. The method is characterized by comprising the following step: removing alkali by adopting hydrochloric acid, wherein the step of removing alkali by adopting hydrochloric acid mainly performs calcium carbonate removal substantially; a measurement index of the process of removing calcium carbonate by hydrochloric acid is a boundary value of the calcium content of a leaching liquid without calcium sulfate precipitation; the process conditions of removing alkali by using hydrochloric acid are that in an initial stage, operating conditions that a pH value control value of a 10g / L hydrochloric acid leaching solution and leaching liquid exchange liquid is 4 are adopted. The calcium removal process condition is relatively high in working efficiency, and is relatively acid-saving; the average liquid calcium removal rate is 36.6%; the calcium carbonate removal rate can reach 65-90%; the calcium content in the leaching liquid is smaller than 50-550mg / L; the average acid consumption rate is 13.39%; the average calcium removal cycle is 51 days; and moreover, the threats of calcium sulfate precipitation can be eliminated.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Extraction separation method of rare-earth element
ActiveCN102618736BHigh separation factorLow extraction acidityProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementPhosphate
A method for extracting and separating a rare-earth element. Cations and anions in a quaternary ammonium ionic liquid extractant, that is, 2-ethylhexyl phosphate mono-2-ethylhexyl acrylate trialkyl-ammonium and phosphate di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate trialkyl-ammonium, are reacted with rare-earth ions to form neutral complex molecules, also, a collaborative effect and a competitive effect are present between the cations and the anions in the quaternary ammonium ionic liquid extractant in a rare-earth element extraction process, the separation factor for the rare-earth element is thus increased. The method for extracting and separating the rare-earth element provides great interfacial phenomena in the extraction process, generates no emulsification, obviates the need for extractant saponification, and provides increased separation factor for rare-earth elements, and particularly increased separation factor for heavy rare-earth elements. In addition, the rare-earth element extraction and separation method is of reduced extraction acidity, of reduced stripping acidity, and of reduced acid consumption.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for reducing contents of zinc and copper in smelting ash acid leaching residues
ActiveCN102851511AImprove leaching rateLess acid consumptionProcess efficiency improvementPre treatmentZinc
The invention discloses a method for reducing the contents of zinc and copper in smelting ash acid leaching residues. The method is characterized in that the method comprises a pretreatment technology and a leaching technology of the smelting ash acid leaching residues, wherein the pretreatment technology comprises the following steps: stacking the smelting ash acid leaching residues, carrying out hot air baking through utilizing the waste heat of a smelting smoke, overturning with a forklift once every 2-3 days, and airing for 10-30 days; and the leaching technology comprises a step that aired residues undergo oxidation leaching through filling with air under a low acid condition. The method which allows the aired acid leaching residues to be leached again enables the zinc leaching rate to be improved by 10% and the copper leaching rate to be improved by 20%; the method adopting stacking airing does not need special equipment, and basically does not consume energy; and no need of high acid condition and low acid consumption are realized in the leaching of the aired leaching residues.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
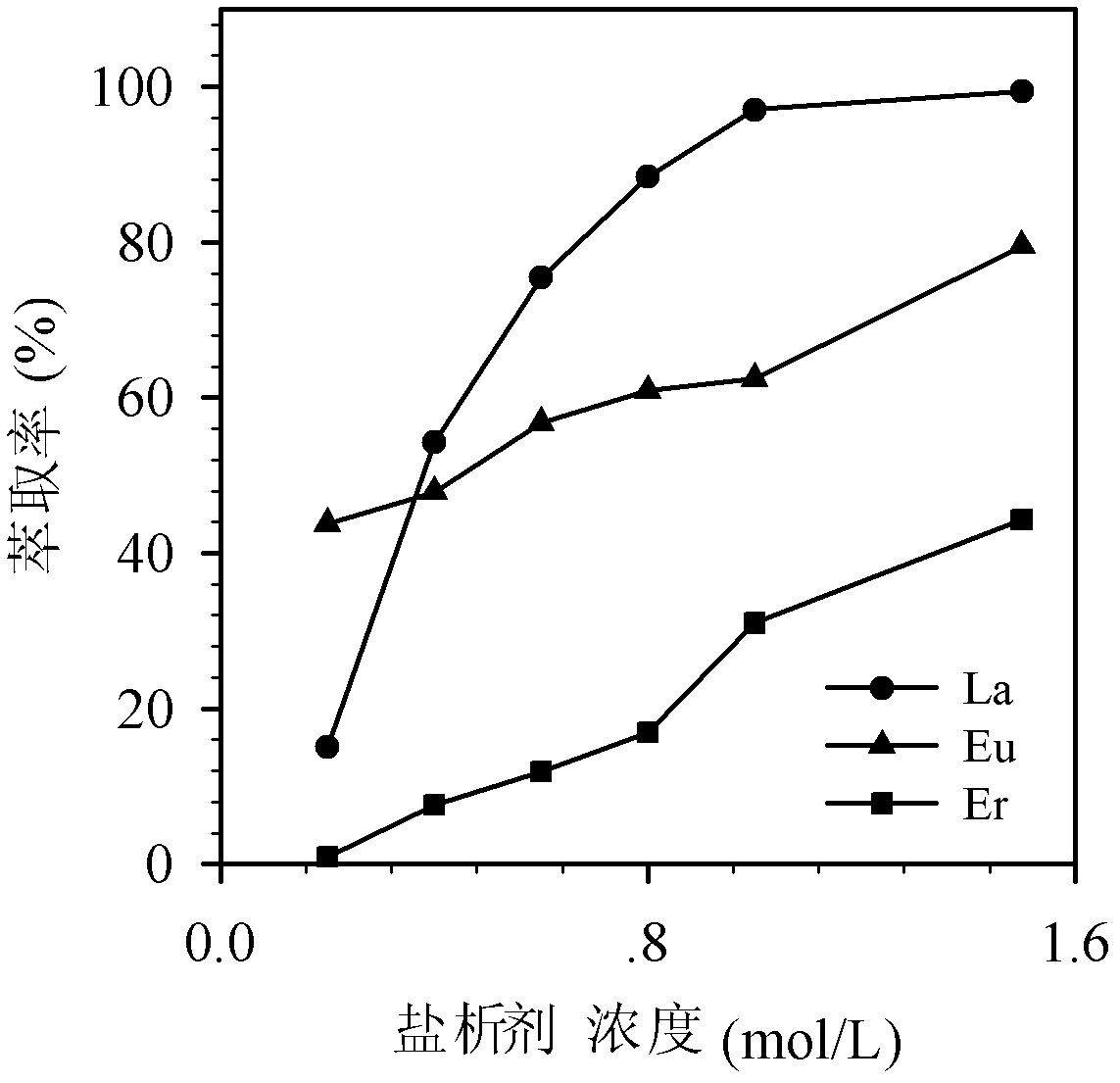
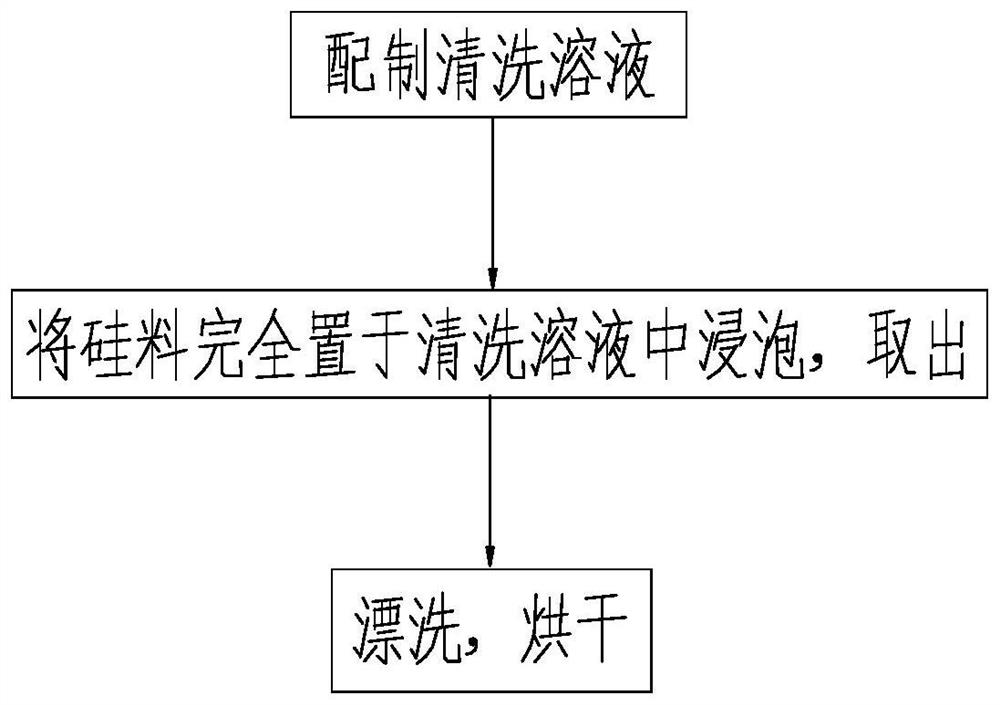
Cleaning method for removing oxide layer on surface of silicon material
PendingCN114653667ALess acid consumptionLower skill requirementsCleaning using liquidsSurface oxidationSilicon
The invention relates to a cleaning method for removing an oxide layer on the surface of a silicon material, and belongs to a silicon material cleaning technology. A cleaning solution is prepared and evenly stirred, and the silicon material is completely placed in the cleaning solution to be soaked, taken out, rinsed and dried. By optimizing the formula and proportion of the cleaning solution, the oxide layer on the surface of the silicon material can be removed only by soaking the silicon material, operation is convenient and fast, and cleaning efficiency is high. And the acid consumption is low, the skill requirement on operators is low, acid marks are avoided, and the cleaning effect is remarkable.
Owner:青岛晶易新材料科技股份有限公司
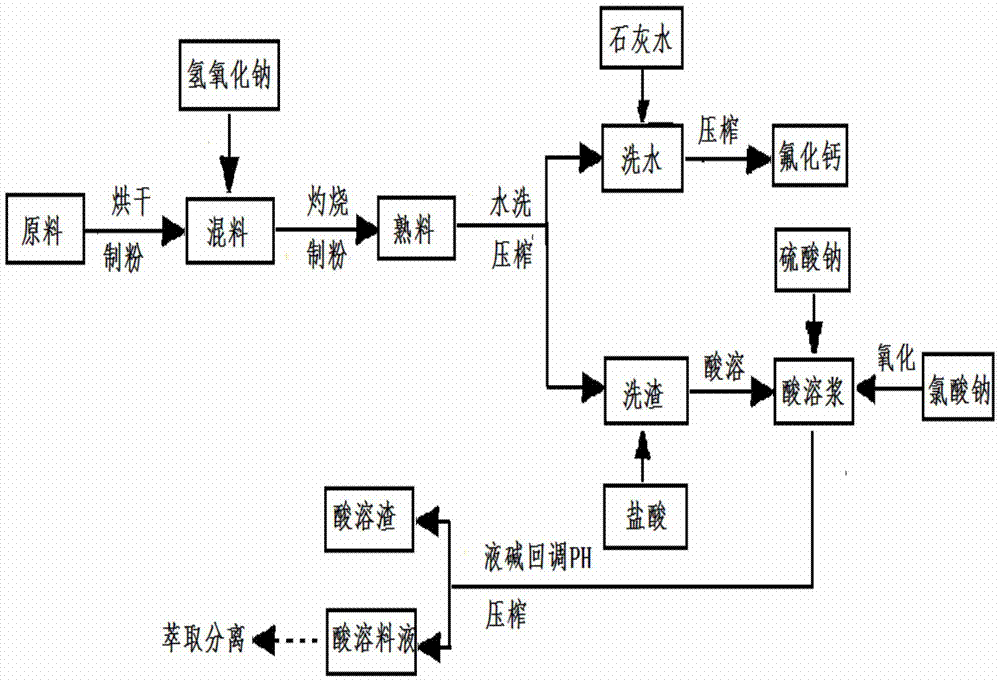
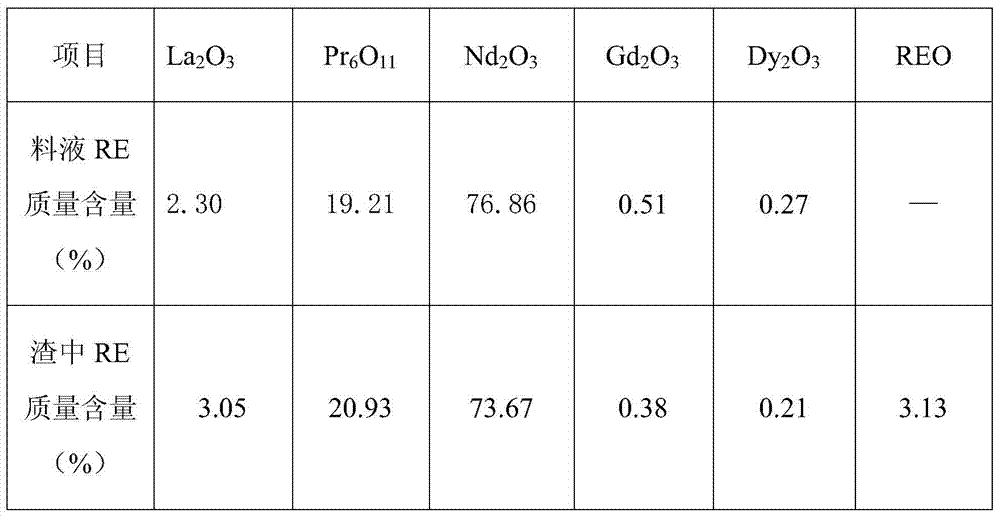
A process for decomposing fluorine-containing rare earth molten salt waste slag
ActiveCN105256156BImprove leaching efficiencyEfficient separationProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the field of resource recycling, and particularly relates to a method for recycling rare earth elements by processing fluorine-contained rare earth molten salt electrolytic waste residues through sodium hydroxide alkaline transfer and hydrochloric acid dissolving treatment. The method comprises the following steps that raw materials of the fluorine-contained rare earth molten salt electrolytic waste residues are dried and made into powder, roasting alkaline transfer and alkali fusant washing and fluoride removal are conducted to obtain calcium fluoride, hydrochloric acid dissolving is conducted, and the pH value of acid soluble material liquid is enabled to reach 12. Importantly, in the production process, low-temperature alkaline transfer, calcium fluoride recycle and caustic soda liquid recycle are conducted, so that compared with other processes, the method has the outstanding advantages that the procedure is simple, energy is saved, the environment is protected, and the primary recovery rate of rare earth is high so that the leaching rate of the rare earth elements can be 98% or above.
Owner:赣州集盛科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com